Authors: K. L. Arendt, M. Royo, M. Fernández-Monreal, S. Knafo, C. N. Petrok, J.
|
|
|
- Josephine Carroll
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Title: PIP 3 controls synaptic function by maintaining AMPA receptor clustering at the postsynaptic membrane Authors: K. L. Arendt, M. Royo, M. Fernández-Monreal, S. Knafo, C. N. Petrok, J. R. Martens and J. A. Esteban A. PH-GRP1 Holding Current (pa) n=31 n=29 Uninf Inf. PH-GRP1-R284C Input Resistance (MΩ) Cell Capacitance (pf) n=31 n=29 n=31 n=29 Uninf Inf Uninf Inf Holding Current (pa) Holding Current (pa) C. Myr-p Input Resistance (MΩ) 1 1 n=24 n=22 n=24 n=22 n=24 n=22 Uninf Inf Uninf Inf Uninf Inf Input Resistance (MΩ) n= n=4 n=39 n=4 n=39 n=4 n=39 Uninf Inf Uninf Inf Uninf Inf Cell Capacitance (pf) Cell Capacitance (pf) Supplementary Figure 1. Alteration of PIP 3 does not alter passive membrane properties of CA1 pyramidal neurons. Expression of PH-GRP1 (A), PH-GRP1- R284C () or Myr-p11 (C) does not alter input resistance, holding current or cell Nature Neuroscience: doi:1.138/nn.2462
2 capacitance of infected CA1 pyramidal neurons (black columns) compared to uninfected cells (white columns). Average values ± s.e.m. are represented. A A 1 μm 2 μm LY2942 GFP GFP Myr-p11 P-Thr38 Akt Akt Supplementary Figure 2. Expression of Myr-p11-EGFP and alterations in Akt phosphorylation. A. Expression of Myr-p11-EGFP in a CA1 pyramidal neuron. Myrp11-EGFP is widely distributed throughout dendrites and spines (inset).. Expression of Myr-p11-EGFP in CA1 neurons increases the phosphorylation of Akt at Thr38 site compared to GFP infection. Slices infected with GFP then treated with 1 μm LY2942 for 1 hour show decreased phosphorylation of Akt compared to GFP control. Nature Neuroscience: doi:1.138/nn
3 A. GluA2-GFP. GFP GFP Cy5 GFP Cy5 surface (-Triton) surface (-Triton) total (+Triton) total (+Triton) Supplementary Figure 3. Surface immunostaining of AMPA receptors under nonpermeabilized conditions. Hippocampal slices were infected with GluA2-GFP (A) or cytosolic EGFP () and processed for immunostaining under permeabilizing ( +Triton, lower panels) or non-permeabilizing ( -Triton, upper panels) conditions. Total expression of the recombinant protein is detected from its green fluorescence ( GFP panels). Cy5 panels reflect immunostaining with an anti-gfp antibody and a secondary antibody coupled to Cy5. Under non-permeabilizing conditions, GluA2-GFP is only detected in the periphery of the cell (possibly the cell surface). Cytosolic GFP is not detectable under these conditions. Nature Neuroscience: doi:1.138/nn
4 A GluA2-GFP + RFP GluA2-GFP + RFP-PH-GRP1 Normalized GluA2-GFP fluorescence RFP (n=1) RFP-PH-GRP1 (n=8) Distance from cell soma (μm) Supplementary Figure 4. Depletion of PIP 3 does not alter long-range dendritic trafficking of AMPA receptors in CA1 neurons. A. Representative examples of CA1 hippocampal neurons expressing GluA2-GFP (green images) together with RFP or RFP-PH-GRP1 (red images), as indicated.. Fluorescence intensity of GluA2-GFP along the primary apical dendrite was quantified from neurons as those shown in A (GluA2-GFP + RFP: black; GluA2-GFP + RFP-PH-GRP1: red). Values are normalized to the GFP fluorescence at the cell soma. Averages are plotted with thick lines and Nature Neuroscience: doi:1.138/nn
5 s.e.m. with thin lines above and below the corresponding average. n represents number of cells analyzed. A. GFP. GFP-PH-PLC LY RFP + RFP-PH-GRP1 GFP (spine / dendrite) p=.3 n=12 n=122 LY2942 GFP-PH-PLC (spine / dendrite) p=.5 n=429 n=541 RFP RFP-PH-GRP1 Supplementary Figure 5. PIP 3 depletion does not alter spine size nor the distribution of PH-PLC (PIP 2 reporter). A. Quantification of spine size from - or LY2942-treated CA1 hippocampal neurons expressing cytosolic EGFP as a volumefilling indicator. Spine size is estimated as the ratio of EGFP fluorescence at the spine versus the dendrite. Two representative spines for each condition are shown above the quantification. n represents number of spines from 24 () or 26 (LY2942) different neurons.. Quantification of PIP 2 distribution from spine/dendrite ratios of GFP-PH-PLC in the presence of RFP or RFP-PH-GRP1. Representative images of Nature Neuroscience: doi:1.138/nn
6 dendritic spines expressing PH-PLC-GFP (green images) together with RFP (left) or RFP-PH-GRP1 (right) (red images) are shown above the quantification. n represents number of spines from 18 (RFP) or 19 (PH-GRP1) different neurons. In all cases, error bars represent s.e.m. A aseline leach +5 s +15 s +3 s 1 μm 3 μm LY μm C Normalized fluorescence (spine / dendrite) LY2942 (n=24) (n=25) Time, seconds Supplementary Figure 6. The mobility of membrane-anchored GFP is not altered by LY2942. A. Representative images of cell bodies (left panel) and dendritic branches (right panel) from neurons expressing farnesylated GFP (GFP-CAAX; see Methods).. Examples of spines expressing GFP-CAAX, treated with either (vehicle) or 1 µm LY2942 for 1 hour prior to undergoing a FRAP experiment ( or LY2942 are also present in the perfusion solution during imaging). Representative images are shown before photobleaching ( aseline ), immediatly after photobleaching Nature Neuroscience: doi:1.138/nn
7 ( leach ) and at different times during fluorescence recovery, as indicated. C. Quantification of the amount of GFP fluorescence at the spine normalized to the baseline value before photobleaching. Fluorescence intensity at the spine is normalized to the adjacent dendrite (spine/dendrite ratio) to compensate for ongoing photobleaching during image acquisition. n represents number of spines. Error bars represent s.e.m. A aseline leach 3 min 2 min LY Normalized Fluorescence Time, min (n=7) LY2942 (n=9) Supplementary Figure 7. The mobility of dendritic AMPARs is not altered by LY2942. A. Representative examples of dendritic branches expressing GFP-GluA2, treated with either (vehicle) or 1 µm LY2942 for 2 hours prior to undergoing a FRAP experiment ( or LY2942 are also present in the perfusion solution during Nature Neuroscience: doi:1.138/nn
8 imaging). Representative images are shown before photobleaching ( aseline ), immediately after photobleaching ( leach ) and at different times during fluorescence recovery, as indicated. The section of the dendrite undergoing bleaching is indicated with a dashed white rectangle.. Quantification of the amount of fluorescence recovery from images similar to those in A. GFP fluorescence intensity at the bleached area is normalized to the baseline value before photobleaching. Fluorescence intensity at the bleached area is also is normalized to an adjacent non-bleached region of the dendrite to compensate for ongoing photobleaching during image acquisition. n represents number of dendritic branches from different neurons. Error bars represent s.e.m. Grey and black lines correspond to the exponential best fits to the experimental data from - and LY2942-treated slices, respectively. A IP Input n.i. γ-8 γ-2 LY LY LY PSD-95 IgG γ-8 IgG C γ-2 IgG Supplementary Figure 8. Inhibition of PIP 3 synthesis does not impair PSD- 95/TARP interaction. Hippocampal slices were treated with 1 µm LY-2942 for 2 hours ( LY ) or left untreated ( ). Total protein extracts were then immunoprecipitated Nature Neuroscience: doi:1.138/nn
9 with anti-γ8, anti-γ2 (stargazin) or a non-immune antibody (n.i.), as indicated. Immunoprecipitated proteins were visualized with anti-psd-95 (A), γ8 () or γ2 (C). 1% of the input extracts are shown in the left panels. ands from the immunoprecipitating antibodies are indicated with arrows (IgG). A LY nm 1 nm Enrichment per synapse **p=.8 (n=57) LY2942 (n=52) C Cumulative probability PSD (n=245) Extra LY2942 (n=28) *p=.2 LY LY PSD Extra Lateral distance, nm Supplementary Figure 9. GluA3 distributes to the perisynaptic membrane after treatment with LY2942. A. Examples of electron micrographs from CA1 excitatory synapses labeled with anti-glua3 immunogold (arrows). The presynaptic terminal is indicated with an asterisk. Slices were treated with either (vehicle) or 1 µm LY2942 for 1 hour before fixation. Scale bars represent 1 nm.. Quantification of GluA3 immunogold abundance at the PSD or the extrasynaptic membrane ( Extra ) of the spine from slices treated with (grey columns) or LY2942 (black columns). Nature Neuroscience: doi:1.138/nn
10 The number of gold particles at each compartment for a given synapse was divided by the total number of gold particles in that synapse. Average values ± s.e.m. are plotted for each compartment. n represents number of synapses analyzed. Statistical significance is calculated according to the Mann-Whitney test. C. Cumulative frequency distribution of the lateral distribution of GluA3 immunogold particles contained within the PSD or the extrasynaptic membrane. Lateral distances are calculated for individual gold particles with respect to the closest PSD edge, with negative distances for particles within the PSD and positive distances for particles within the extrasynaptic membrane. Values are plotted for - (grey) and LY2942-treated slices (black). n represents number of gold particles. Statistical significance is calculated according to the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. Nature Neuroscience: doi:1.138/nn
Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity
 Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity Jerry L. Chen, Walter C. Lin, Jae Won Cha, Peter T. So, Yoshiyuki Kubota & Elly Nedivi SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1-6 a b M
Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity Jerry L. Chen, Walter C. Lin, Jae Won Cha, Peter T. So, Yoshiyuki Kubota & Elly Nedivi SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1-6 a b M
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal AMPAR-mediated fepsp input-output curve in CA3-Psen cdko mice. Input-output curves, which are plotted initial slopes of the evoked fepsp as function of the amplitude of the
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal AMPAR-mediated fepsp input-output curve in CA3-Psen cdko mice. Input-output curves, which are plotted initial slopes of the evoked fepsp as function of the amplitude of the
Supplementary Figure 1. mir124 does not change neuron morphology and synaptic
 Supplementary Figure 1. mir124 does not change neuron morphology and synaptic density. Hippocampal neurons were transfected with mir124 (containing DsRed) or DsRed as a control. 2 d after transfection,
Supplementary Figure 1. mir124 does not change neuron morphology and synaptic density. Hippocampal neurons were transfected with mir124 (containing DsRed) or DsRed as a control. 2 d after transfection,
Palmitoylation regulates glutamate receptor distributions in postsynaptic densities through control of PSD95 conformation and orientation
 Palmitoylation regulates glutamate receptor distributions in postsynaptic densities through control of PSD95 conformation and orientation Okunola Jeyifous a,b,1, Eric I. Lin a,b,1, Xiaobing Chen b,c, Sarah
Palmitoylation regulates glutamate receptor distributions in postsynaptic densities through control of PSD95 conformation and orientation Okunola Jeyifous a,b,1, Eric I. Lin a,b,1, Xiaobing Chen b,c, Sarah
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nature6416 Supplementary Notes Spine Ca 2+ signals produced by glutamate uncaging We imaged uncaging-evoked [Ca 2+ ] transients in neurons loaded with a green Ca 2+ - sensitive indicator (G;
doi: 1.138/nature6416 Supplementary Notes Spine Ca 2+ signals produced by glutamate uncaging We imaged uncaging-evoked [Ca 2+ ] transients in neurons loaded with a green Ca 2+ - sensitive indicator (G;
Supplementary Figure 1. Microglia do not show signs of classical immune activation following MD a-b. Images showing immunoreactivity for MHCII (a)
 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Microglia do not show signs of classical immune activation following MD a-b. Images showing immunoreactivity for MHCII (a) and CD45 (b) in fixed sections of binocular visual cortex
1 Supplementary Figure 1. Microglia do not show signs of classical immune activation following MD a-b. Images showing immunoreactivity for MHCII (a) and CD45 (b) in fixed sections of binocular visual cortex
Supplemental Materials Molecular Biology of the Cell
 Supplemental Materials Molecular Biology of the Cell Garcia-Alvarez et al. Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1.Expression and RNAi-mediated silencing of STIM1 in hippocampal neurons (DIV, days in vitro).
Supplemental Materials Molecular Biology of the Cell Garcia-Alvarez et al. Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1.Expression and RNAi-mediated silencing of STIM1 in hippocampal neurons (DIV, days in vitro).
Schwarz et al. Activity-Dependent Ubiquitination of GluA1 Mediates a Distinct AMPAR Endocytosis
 Schwarz et al Activity-Dependent Ubiquitination of GluA1 Mediates a Distinct AMPAR Endocytosis and Sorting Pathway Supplemental Data Supplemental Fie 1: AMPARs undergo activity-mediated ubiquitination
Schwarz et al Activity-Dependent Ubiquitination of GluA1 Mediates a Distinct AMPAR Endocytosis and Sorting Pathway Supplemental Data Supplemental Fie 1: AMPARs undergo activity-mediated ubiquitination
Endocytic Trafficking and Recycling Maintain apoolofmobilesurfaceampareceptors Required for Synaptic Potentiation
 Article Endocytic Trafficking and Recycling Maintain apoolofmobilesurfaceampareceptors Required for Synaptic Potentiation Enrica Maria Petrini, 1,2 Jiuyi Lu, 3 Laurent Cognet, 4 Brahim Lounis, 4 Michael
Article Endocytic Trafficking and Recycling Maintain apoolofmobilesurfaceampareceptors Required for Synaptic Potentiation Enrica Maria Petrini, 1,2 Jiuyi Lu, 3 Laurent Cognet, 4 Brahim Lounis, 4 Michael
Ionotropic glutamate receptors (iglurs)
 Ionotropic glutamate receptors (iglurs) GluA1 GluA2 GluA3 GluA4 GluN1 GluN2A GluN2B GluN2C GluN2D GluN3A GluN3B GluK1 GluK2 GluK3 GluK4 GluK5 The general architecture of receptor subunits Unique properties
Ionotropic glutamate receptors (iglurs) GluA1 GluA2 GluA3 GluA4 GluN1 GluN2A GluN2B GluN2C GluN2D GluN3A GluN3B GluK1 GluK2 GluK3 GluK4 GluK5 The general architecture of receptor subunits Unique properties
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References
 File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References File name: Supplementary Data 1 Description: Summary datasheets showing the spatial
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References File name: Supplementary Data 1 Description: Summary datasheets showing the spatial
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figure 1
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 The supralinear events evoked in CA3 pyramidal cells fulfill the criteria for NMDA spikes, exhibiting a threshold, sensitivity to NMDAR blockade, and all-or-none
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 The supralinear events evoked in CA3 pyramidal cells fulfill the criteria for NMDA spikes, exhibiting a threshold, sensitivity to NMDAR blockade, and all-or-none
Part 11: Mechanisms of Learning
 Neurophysiology and Information: Theory of Brain Function Christopher Fiorillo BiS 527, Spring 2012 042 350 4326, fiorillo@kaist.ac.kr Part 11: Mechanisms of Learning Reading: Bear, Connors, and Paradiso,
Neurophysiology and Information: Theory of Brain Function Christopher Fiorillo BiS 527, Spring 2012 042 350 4326, fiorillo@kaist.ac.kr Part 11: Mechanisms of Learning Reading: Bear, Connors, and Paradiso,
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental FIG. 1. Localization of myosin Vb in cultured neurons varies with maturation stage. A and B, localization of myosin Vb in cultured hippocampal neurons. A, in DIV
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental FIG. 1. Localization of myosin Vb in cultured neurons varies with maturation stage. A and B, localization of myosin Vb in cultured hippocampal neurons. A, in DIV
BIPN140 Lecture 12: Synaptic Plasticity (II)
 BIPN140 Lecture 12: Synaptic Plasticity (II) 1. Early v.s. Late LTP 2. Long-Term Depression 3. Molecular Mechanisms of Long-Term Depression: NMDA-R dependent 4. Molecular Mechanisms of Long-Term Depression:
BIPN140 Lecture 12: Synaptic Plasticity (II) 1. Early v.s. Late LTP 2. Long-Term Depression 3. Molecular Mechanisms of Long-Term Depression: NMDA-R dependent 4. Molecular Mechanisms of Long-Term Depression:
Supplementary Figure 1. SDS-FRL localization of CB 1 in the distal CA3 area of the rat hippocampus. (a-d) Axon terminals (t) in stratum pyramidale
 Supplementary Figure 1. SDS-FRL localization of CB 1 in the distal CA3 area of the rat hippocampus. (a-d) Axon terminals (t) in stratum pyramidale (b) show stronger immunolabeling for CB 1 than those in
Supplementary Figure 1. SDS-FRL localization of CB 1 in the distal CA3 area of the rat hippocampus. (a-d) Axon terminals (t) in stratum pyramidale (b) show stronger immunolabeling for CB 1 than those in
Disrupting GluA2-GAPDH Interaction Affects Axon and Dendrite Development
 Disrupting GluA2-GAPDH Interaction Affects Axon and Dendrite Development 1 Frankie Hang Fung Lee, 1 Ping Su, 1 Yu Feng Xie, 1 Kyle Ethan Wang, 2 Qi Wan and 1,3 Fang Liu 1 Campbell Research Institute, Centre
Disrupting GluA2-GAPDH Interaction Affects Axon and Dendrite Development 1 Frankie Hang Fung Lee, 1 Ping Su, 1 Yu Feng Xie, 1 Kyle Ethan Wang, 2 Qi Wan and 1,3 Fang Liu 1 Campbell Research Institute, Centre
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/283/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for JNK3 Couples the Neuronal Stress Response to Inhibition of Secretory Trafficking Guang Yang,* Xun Zhou, Jingyan Zhu,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/283/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for JNK3 Couples the Neuronal Stress Response to Inhibition of Secretory Trafficking Guang Yang,* Xun Zhou, Jingyan Zhu,
Supplementary Figure S1 (a) (b)
 Supplementary Figure S1: IC87114 does not affect basal Ca 2+ level nor nicotineinduced Ca 2+ influx. (a) Bovine chromaffin cells were loaded with Fluo-4AM (1 μm) in buffer A containing 0.02% of pluronic
Supplementary Figure S1: IC87114 does not affect basal Ca 2+ level nor nicotineinduced Ca 2+ influx. (a) Bovine chromaffin cells were loaded with Fluo-4AM (1 μm) in buffer A containing 0.02% of pluronic
Supporting Information
 ATP from synaptic terminals and astrocytes regulates NMDA receptors and synaptic plasticity through PSD- 95 multi- protein complex U.Lalo, O.Palygin, A.Verkhratsky, S.G.N. Grant and Y. Pankratov Supporting
ATP from synaptic terminals and astrocytes regulates NMDA receptors and synaptic plasticity through PSD- 95 multi- protein complex U.Lalo, O.Palygin, A.Verkhratsky, S.G.N. Grant and Y. Pankratov Supporting
Psychiatric Risk Factor ANK3/Ankyrin-G Nanodomains Regulate the Structure and Function of Glutamatergic Synapses
 Neuron Article Psychiatric Risk Factor ANK3/Ankyrin-G Nanodomains Regulate the Structure and Function of Glutamatergic Synapses Katharine R. Smith, 1 Katherine J. Kopeikina, 1 Jessica M. Fawcett-Patel,
Neuron Article Psychiatric Risk Factor ANK3/Ankyrin-G Nanodomains Regulate the Structure and Function of Glutamatergic Synapses Katharine R. Smith, 1 Katherine J. Kopeikina, 1 Jessica M. Fawcett-Patel,
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/317/5841/183/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Astrocytes Potentiate Transmitter Release at Single Hippocampal Synapses Gertrudis Perea and Alfonso Araque* *To whom
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/317/5841/183/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Astrocytes Potentiate Transmitter Release at Single Hippocampal Synapses Gertrudis Perea and Alfonso Araque* *To whom
Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC
 1 2 1 3 Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC 4 5 6 7 (a) Reconstructions of LII/III GIN-cells with somato-dendritic compartments in orange and axonal arborizations
1 2 1 3 Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC 4 5 6 7 (a) Reconstructions of LII/III GIN-cells with somato-dendritic compartments in orange and axonal arborizations
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. ACx plasticity is required for fear conditioning.
 Supplementary Figure 1 ACx plasticity is required for fear conditioning. (a) Freezing time of conditioned and control mice before CS presentation and during CS presentation in a new context. Student s
Supplementary Figure 1 ACx plasticity is required for fear conditioning. (a) Freezing time of conditioned and control mice before CS presentation and during CS presentation in a new context. Student s
a b c Supplementary Figure 1 R Shrm4 0 -/- -/- GABA B1b Wild type GABA B1a GABA B1a -GABA B1b mean intensity (a.u) Ponceau GABA B
 a b c 200 - H S1 P1 S2 P2 SYN TIF PSD Shrm4 95 - PSD95 34 - Synaptophysin 120-100 - Wil type GABA B1a -/- GABA B1b -/- -GABA B1a -GABA B1b e f 5 μm 10 μm 20 μm 100 - GABA B1a 600 400 200 Ponceau GABA B
a b c 200 - H S1 P1 S2 P2 SYN TIF PSD Shrm4 95 - PSD95 34 - Synaptophysin 120-100 - Wil type GABA B1a -/- GABA B1b -/- -GABA B1a -GABA B1b e f 5 μm 10 μm 20 μm 100 - GABA B1a 600 400 200 Ponceau GABA B
Supplementary Materials for VAMP4 directs synaptic vesicles to a pool that selectively maintains asynchronous neurotransmission
 Supplementary Materials for VAMP4 directs synaptic vesicles to a pool that selectively maintains asynchronous neurotransmission Jesica Raingo, Mikhail Khvotchev, Pei Liu, Frederic Darios, Ying C. Li, Denise
Supplementary Materials for VAMP4 directs synaptic vesicles to a pool that selectively maintains asynchronous neurotransmission Jesica Raingo, Mikhail Khvotchev, Pei Liu, Frederic Darios, Ying C. Li, Denise
Dep. Control Time (min)
 aa Control Dep. RP 1s 1 mv 2s 1 mv b % potentiation of IPSP 2 15 1 5 Dep. * 1 2 3 4 Time (min) Supplementary Figure 1. Rebound potentiation of IPSPs in PCs. a, IPSPs recorded with a K + gluconate pipette
aa Control Dep. RP 1s 1 mv 2s 1 mv b % potentiation of IPSP 2 15 1 5 Dep. * 1 2 3 4 Time (min) Supplementary Figure 1. Rebound potentiation of IPSPs in PCs. a, IPSPs recorded with a K + gluconate pipette
Supplementary Information
 1 Supplementary Information A role for primary cilia in glutamatergic synaptic integration of adult-orn neurons Natsuko Kumamoto 1,4,5, Yan Gu 1,4, Jia Wang 1,4, Stephen Janoschka 1,2, Ken-Ichi Takemaru
1 Supplementary Information A role for primary cilia in glutamatergic synaptic integration of adult-orn neurons Natsuko Kumamoto 1,4,5, Yan Gu 1,4, Jia Wang 1,4, Stephen Janoschka 1,2, Ken-Ichi Takemaru
Mechanisms for acute stress-induced enhancement of glutamatergic transmission and working memory
 (2011) 16, 156 170 & 2011 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved 1359-4184/11 www.nature.com/mp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Mechanisms for acute stress-induced enhancement of glutamatergic transmission
(2011) 16, 156 170 & 2011 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved 1359-4184/11 www.nature.com/mp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Mechanisms for acute stress-induced enhancement of glutamatergic transmission
BIPN 140 Problem Set 6
 BIPN 140 Problem Set 6 1) The hippocampus is a cortical structure in the medial portion of the temporal lobe (medial temporal lobe in primates. a) What is the main function of the hippocampus? The hippocampus
BIPN 140 Problem Set 6 1) The hippocampus is a cortical structure in the medial portion of the temporal lobe (medial temporal lobe in primates. a) What is the main function of the hippocampus? The hippocampus
MAP1B-dependent Rac activation is required for AMPA receptor endocytosis during long-term depression
 The EMBO Journal (3) 3, 87 99 www.embojournal.org MAPB-dependent Rac activation is required for AMPA receptor endocytosis during long-term depression THE EMBO JOURNAL Marion Benoist, Rocío Palenzuela,
The EMBO Journal (3) 3, 87 99 www.embojournal.org MAPB-dependent Rac activation is required for AMPA receptor endocytosis during long-term depression THE EMBO JOURNAL Marion Benoist, Rocío Palenzuela,
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Subcellular segregation of VGluT2-IR and TH-IR within the same VGluT2-TH axon (wild type rats). (a-e) Serial sections of a dual VGluT2-TH labeled axon. This axon (blue outline) has
Supplementary Figure 1 Subcellular segregation of VGluT2-IR and TH-IR within the same VGluT2-TH axon (wild type rats). (a-e) Serial sections of a dual VGluT2-TH labeled axon. This axon (blue outline) has
pt305-camkii stabilizes a learning-induced increase in AMPA receptors for ongoing memory consolidation after classical conditioning
 Received 6 Nov 213 Accepted 25 Apr 214 Published 3 May 214 pt35- stabilizes a learning-induced increase in AMPA receptors for ongoing memory consolidation after classical conditioning Souvik Naskar 1,,
Received 6 Nov 213 Accepted 25 Apr 214 Published 3 May 214 pt35- stabilizes a learning-induced increase in AMPA receptors for ongoing memory consolidation after classical conditioning Souvik Naskar 1,,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 SNARE Probes for FRET/2pFLIM Analysis Used in the Present Study. mturquoise (mtq) and Venus (Ven) are in blue and yellow, respectively. The soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 SNARE Probes for FRET/2pFLIM Analysis Used in the Present Study. mturquoise (mtq) and Venus (Ven) are in blue and yellow, respectively. The soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive
BIPN 140 Problem Set 6
 BIPN 140 Problem Set 6 1) Hippocampus is a cortical structure in the medial portion of the temporal lobe (medial temporal lobe in primates. a) What is the main function of the hippocampus? The hippocampus
BIPN 140 Problem Set 6 1) Hippocampus is a cortical structure in the medial portion of the temporal lobe (medial temporal lobe in primates. a) What is the main function of the hippocampus? The hippocampus
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature06994 A phosphatase cascade by which rewarding stimuli control nucleosomal response A. Stipanovich*, E. Valjent*, M. Matamales*, A. Nishi, J.H. Ahn, M. Maroteaux, J. Bertran-Gonzalez,
doi: 10.1038/nature06994 A phosphatase cascade by which rewarding stimuli control nucleosomal response A. Stipanovich*, E. Valjent*, M. Matamales*, A. Nishi, J.H. Ahn, M. Maroteaux, J. Bertran-Gonzalez,
Wenqin Hu, Cuiping Tian, Tun Li, Mingpo Yang, Han Hou & Yousheng Shu
 Distinct contributions of Na v 1.6 and Na v 1.2 in action potential initiation and backpropagation Wenqin Hu, Cuiping Tian, Tun Li, Mingpo Yang, Han Hou & Yousheng Shu Supplementary figure and legend Supplementary
Distinct contributions of Na v 1.6 and Na v 1.2 in action potential initiation and backpropagation Wenqin Hu, Cuiping Tian, Tun Li, Mingpo Yang, Han Hou & Yousheng Shu Supplementary figure and legend Supplementary
Supplementary Table I Blood pressure and heart rate measurements pre- and post-stroke
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09511 Supplementary Table I Blood pressure and heart rate measurements pre- and post-stroke Pre Post 7-days Systolic Diastolic BPM Systolic Diastolic BPM Systolic
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09511 Supplementary Table I Blood pressure and heart rate measurements pre- and post-stroke Pre Post 7-days Systolic Diastolic BPM Systolic Diastolic BPM Systolic
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Neuron class-specific arrangements of Khc::nod::lacZ label in dendrites.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Neuron class-specific arrangements of Khc::nod::lacZ label in dendrites. Staining with fluorescence antibodies to detect GFP (Green), β-galactosidase (magenta/white). (a, b) Class
Supplementary Figure 1 Neuron class-specific arrangements of Khc::nod::lacZ label in dendrites. Staining with fluorescence antibodies to detect GFP (Green), β-galactosidase (magenta/white). (a, b) Class
Supplementary Figure 1. SybII and Ceb are sorted to distinct vesicle populations in astrocytes. Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.
 Supplementary Figure 1 SybII and Ceb are sorted to distinct vesicle populations in astrocytes. (a) Exemplary images for cultured astrocytes co-immunolabeled with SybII and Ceb antibodies. SybII accumulates
Supplementary Figure 1 SybII and Ceb are sorted to distinct vesicle populations in astrocytes. (a) Exemplary images for cultured astrocytes co-immunolabeled with SybII and Ceb antibodies. SybII accumulates
Supplementary Figure 1: Validation of labeling specificity of immature OSNs and presynaptic terminals. (A) (B) (C) (D) (E)
 Supplementary Figure 1: Validation of labeling specificity of immature OSNs and presynaptic terminals. (A) Confocal images of septal olfactory epithelium of an adult Gγ8-sypGFP-tdTom mouse showing colocalization
Supplementary Figure 1: Validation of labeling specificity of immature OSNs and presynaptic terminals. (A) Confocal images of septal olfactory epithelium of an adult Gγ8-sypGFP-tdTom mouse showing colocalization
Supplemental Information. Differential Regulation. of Evoked and Spontaneous Release. by Presynaptic NMDA Receptors
 Neuron, Volume 96 Supplemental Information Differential Regulation of Evoked and Spontaneous Release by Presynaptic NMDA Receptors Therése Abrahamsson, hristina You hien hou, Si Ying Li, Adamo Mancino,
Neuron, Volume 96 Supplemental Information Differential Regulation of Evoked and Spontaneous Release by Presynaptic NMDA Receptors Therése Abrahamsson, hristina You hien hou, Si Ying Li, Adamo Mancino,
Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses
 Supplementary Information Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses Rogier Min and Thomas Nevian Department of Physiology, University of Berne, Bern, Switzerland
Supplementary Information Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses Rogier Min and Thomas Nevian Department of Physiology, University of Berne, Bern, Switzerland
Supplemental Figures:
 Supplemental Figures: Figure 1: Intracellular distribution of VWF by electron microscopy in human endothelial cells. a) Immunogold labeling of LC3 demonstrating an LC3-positive autophagosome (white arrow)
Supplemental Figures: Figure 1: Intracellular distribution of VWF by electron microscopy in human endothelial cells. a) Immunogold labeling of LC3 demonstrating an LC3-positive autophagosome (white arrow)
Zhu et al, page 1. Supplementary Figures
 Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 AAV-GFP injection in the MEC of the mouse brain C57Bl/6 mice at 4 months of age were injected with AAV-GFP into the MEC and sacrificed at 7 days post injection (dpi). (a) Brains
Supplementary Figure 1 AAV-GFP injection in the MEC of the mouse brain C57Bl/6 mice at 4 months of age were injected with AAV-GFP into the MEC and sacrificed at 7 days post injection (dpi). (a) Brains
Ultrastructural Contributions to Desensitization at the Cerebellar Mossy Fiber to Granule Cell Synapse
 Ultrastructural Contributions to Desensitization at the Cerebellar Mossy Fiber to Granule Cell Synapse Matthew A.Xu-Friedman and Wade G. Regehr Department of Neurobiology, Harvard Medical School, Boston,
Ultrastructural Contributions to Desensitization at the Cerebellar Mossy Fiber to Granule Cell Synapse Matthew A.Xu-Friedman and Wade G. Regehr Department of Neurobiology, Harvard Medical School, Boston,
How Synapses Integrate Information and Change
 How Synapses Integrate Information and Change Rachel Stewart class of 2016 http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s1/chapter06.html http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s1/chapter07.html Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of
How Synapses Integrate Information and Change Rachel Stewart class of 2016 http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s1/chapter06.html http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s1/chapter07.html Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of
Axon initial segment position changes CA1 pyramidal neuron excitability
 Axon initial segment position changes CA1 pyramidal neuron excitability Cristina Nigro and Jason Pipkin UCSD Neurosciences Graduate Program Abstract The axon initial segment (AIS) is the portion of the
Axon initial segment position changes CA1 pyramidal neuron excitability Cristina Nigro and Jason Pipkin UCSD Neurosciences Graduate Program Abstract The axon initial segment (AIS) is the portion of the
Theta sequences are essential for internally generated hippocampal firing fields.
 Theta sequences are essential for internally generated hippocampal firing fields. Yingxue Wang, Sandro Romani, Brian Lustig, Anthony Leonardo, Eva Pastalkova Supplementary Materials Supplementary Modeling
Theta sequences are essential for internally generated hippocampal firing fields. Yingxue Wang, Sandro Romani, Brian Lustig, Anthony Leonardo, Eva Pastalkova Supplementary Materials Supplementary Modeling
PKCλ Is Critical in AMPA Receptor Phosphorylation and Synaptic Incorporation during LTP
 Manuscript EMBO-2012-82900 PKCλ Is Critical in AMPA Receptor Phosphorylation and Synaptic Incorporation during LTP Si-Qiang Ren, Jing-Zhi Yan, Xiao-Yan Zhang, Yun-Fei Bu, Wei-Wei Pan, Wen Yao, Tian Tian
Manuscript EMBO-2012-82900 PKCλ Is Critical in AMPA Receptor Phosphorylation and Synaptic Incorporation during LTP Si-Qiang Ren, Jing-Zhi Yan, Xiao-Yan Zhang, Yun-Fei Bu, Wei-Wei Pan, Wen Yao, Tian Tian
Supplementary Information
 Hyperpolarization-activated cation channels inhibit EPSPs by interactions with M-type K + channels Meena S. George, L.F. Abbott, Steven A. Siegelbaum Supplementary Information Part 1: Supplementary Figures
Hyperpolarization-activated cation channels inhibit EPSPs by interactions with M-type K + channels Meena S. George, L.F. Abbott, Steven A. Siegelbaum Supplementary Information Part 1: Supplementary Figures
What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord
 What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord Jennifer LaVail, Ph.D. (http://anatomy.ucsf.edu/pages/lavaillab/index.html) What kinds of cells are these?" Neuron?" Epithelial cell?" Glial cell?" What makes
What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord Jennifer LaVail, Ph.D. (http://anatomy.ucsf.edu/pages/lavaillab/index.html) What kinds of cells are these?" Neuron?" Epithelial cell?" Glial cell?" What makes
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11775 Supplementary Discussion Based on our data, we propose that LTP requires a large extrasynaptic pool of surface receptors regardless of their subunit composition.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11775 Supplementary Discussion Based on our data, we propose that LTP requires a large extrasynaptic pool of surface receptors regardless of their subunit composition.
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt.3828
 Supplementary Figure 1 Development of a FRET-based MCS. (a) Linker and MA2 modification are indicated by single letter amino acid code. indicates deletion of amino acids and N or C indicate the terminus
Supplementary Figure 1 Development of a FRET-based MCS. (a) Linker and MA2 modification are indicated by single letter amino acid code. indicates deletion of amino acids and N or C indicate the terminus
293T cells were transfected with indicated expression vectors and the whole-cell extracts were subjected
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Formation of a complex between Slo1 and CRL4A CRBN E3 ligase. (a) HEK 293T cells were transfected with indicated expression vectors and the whole-cell
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Formation of a complex between Slo1 and CRL4A CRBN E3 ligase. (a) HEK 293T cells were transfected with indicated expression vectors and the whole-cell
Ube3a is required for experience-dependent maturation of the neocortex
 Ube3a is required for experience-dependent maturation of the neocortex Koji Yashiro, Thorfinn T. Riday, Kathryn H. Condon, Adam C. Roberts, Danilo R. Bernardo, Rohit Prakash, Richard J. Weinberg, Michael
Ube3a is required for experience-dependent maturation of the neocortex Koji Yashiro, Thorfinn T. Riday, Kathryn H. Condon, Adam C. Roberts, Danilo R. Bernardo, Rohit Prakash, Richard J. Weinberg, Michael
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Bidirectional optogenetic modulation of the tonic activity of CEA PKCδ + neurons in vitro. a, Top, Cell-attached voltage recording illustrating the blue light-induced increase in
Supplementary Figure 1 Bidirectional optogenetic modulation of the tonic activity of CEA PKCδ + neurons in vitro. a, Top, Cell-attached voltage recording illustrating the blue light-induced increase in
Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex
 Supplementary Information Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex Luc Gentet, Yves Kremer, Hiroki Taniguchi, Josh Huang, Jochen Staiger and Carl
Supplementary Information Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex Luc Gentet, Yves Kremer, Hiroki Taniguchi, Josh Huang, Jochen Staiger and Carl
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Distribution of starter cells for RV-mediated retrograde tracing.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Distribution of starter cells for RV-mediated retrograde tracing. Parcellation of cortical areas is based on Allen Mouse Brain Atlas and drawn to scale. Thick white curves, outlines
Supplementary Figure 1 Distribution of starter cells for RV-mediated retrograde tracing. Parcellation of cortical areas is based on Allen Mouse Brain Atlas and drawn to scale. Thick white curves, outlines
Supplementary Figure 1. Properties of various IZUMO1 monoclonal antibodies and behavior of SPACA6. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) .
 Supplementary Figure 1. Properties of various IZUMO1 monoclonal antibodies and behavior of SPACA6. (a) The inhibitory effects of new antibodies (Mab17 and Mab18). They were investigated in in vitro fertilization
Supplementary Figure 1. Properties of various IZUMO1 monoclonal antibodies and behavior of SPACA6. (a) The inhibitory effects of new antibodies (Mab17 and Mab18). They were investigated in in vitro fertilization
Chapter 9: Biochemical Mechanisms for Information Storage at the Cellular Level. From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D.
 Chapter 9: Biochemical Mechanisms for Information Storage at the Cellular Level From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Chapter 9: Dendritic Spine Figure 1 Summary: Three Primary
Chapter 9: Biochemical Mechanisms for Information Storage at the Cellular Level From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Chapter 9: Dendritic Spine Figure 1 Summary: Three Primary
Supplementary Figure 1. Basic properties of compound EPSPs at
 Supplementary Figure 1. Basic properties of compound EPSPs at hippocampal CA3 CA3 cell synapses. (a) EPSPs were evoked by extracellular stimulation of the recurrent collaterals and pharmacologically isolated
Supplementary Figure 1. Basic properties of compound EPSPs at hippocampal CA3 CA3 cell synapses. (a) EPSPs were evoked by extracellular stimulation of the recurrent collaterals and pharmacologically isolated
Basics of Computational Neuroscience: Neurons and Synapses to Networks
 Basics of Computational Neuroscience: Neurons and Synapses to Networks Bruce Graham Mathematics School of Natural Sciences University of Stirling Scotland, U.K. Useful Book Authors: David Sterratt, Bruce
Basics of Computational Neuroscience: Neurons and Synapses to Networks Bruce Graham Mathematics School of Natural Sciences University of Stirling Scotland, U.K. Useful Book Authors: David Sterratt, Bruce
How Synapses Integrate Information and Change
 How Synapses Integrate Information and Change Rachel Stewart class of 2016 https://nba.uth.tmc.edu/neuroscience/s1/chapter06.html https://nba.uth.tmc.edu/neuroscience/s1/chapter07.html Chris Cohan, Ph.D.
How Synapses Integrate Information and Change Rachel Stewart class of 2016 https://nba.uth.tmc.edu/neuroscience/s1/chapter06.html https://nba.uth.tmc.edu/neuroscience/s1/chapter07.html Chris Cohan, Ph.D.
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information D-Serine regulates cerebellar LTD and motor coordination through the 2 glutamate receptor Wataru Kakegawa, Yurika Miyoshi, Kenji Hamase, Shinji Matsuda, Keiko Matsuda, Kazuhisa
Supplementary Information D-Serine regulates cerebellar LTD and motor coordination through the 2 glutamate receptor Wataru Kakegawa, Yurika Miyoshi, Kenji Hamase, Shinji Matsuda, Keiko Matsuda, Kazuhisa
CRY2 binding to CIB1N w/ MTHF
 Supplemental Figures: CRY2 binding to CIB1N w/ MTHF.36 Polarization.34.32.3.28 Blue.26 5 1 15 [Cry2] in nm Figure S1: Addition of MTHF does not significantly change CRY2- CIB1N binding. Direct fluorescence
Supplemental Figures: CRY2 binding to CIB1N w/ MTHF.36 Polarization.34.32.3.28 Blue.26 5 1 15 [Cry2] in nm Figure S1: Addition of MTHF does not significantly change CRY2- CIB1N binding. Direct fluorescence
Supplementary Figure 1. GABA depolarizes the majority of immature neurons in the
 Supplementary Figure 1. GABA depolarizes the majority of immature neurons in the upper cortical layers at P3 4 in vivo. (a b) Cell-attached current-clamp recordings illustrate responses to puff-applied
Supplementary Figure 1. GABA depolarizes the majority of immature neurons in the upper cortical layers at P3 4 in vivo. (a b) Cell-attached current-clamp recordings illustrate responses to puff-applied
Supplemental information Acid-sensing ion channel 1a contributes to hippocampal LTP inducibility through multiple mechanisms
 Supplemental information Acid-sensing ion channel 1a contributes to hippocampal LTP inducibility through multiple mechanisms Ming-Gang Liu, Hu-Song Li, Wei-Guang Li, Yan-Jiao Wu, Shi-Ning Deng, Chen Huang,
Supplemental information Acid-sensing ion channel 1a contributes to hippocampal LTP inducibility through multiple mechanisms Ming-Gang Liu, Hu-Song Li, Wei-Guang Li, Yan-Jiao Wu, Shi-Ning Deng, Chen Huang,
mm Distance (mm)
 b a Magnet Illumination Coverslips MPs Objective 2575 µm 1875 µm 1575 µm 1075 µm 875 µm 545 µm 20µm 2 3 0.5 0.3mm 1 1000 100 10 1 0.1 1000 100 10 1 0.1 Field Induction (Gauss) 1.5 0 5 10 15 20 Distance
b a Magnet Illumination Coverslips MPs Objective 2575 µm 1875 µm 1575 µm 1075 µm 875 µm 545 µm 20µm 2 3 0.5 0.3mm 1 1000 100 10 1 0.1 1000 100 10 1 0.1 Field Induction (Gauss) 1.5 0 5 10 15 20 Distance
Activity level controls postsynaptic composition and signaling via the ubiquitin-proteasome system
 Activity level controls postsynaptic composition and signaling via the ubiquitin-proteasome system Michael D. Ehlers 1 1 Department of Neurobiology, Box 3209, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, North
Activity level controls postsynaptic composition and signaling via the ubiquitin-proteasome system Michael D. Ehlers 1 1 Department of Neurobiology, Box 3209, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, North
A genetically targeted optical sensor to monitor calcium signals in astrocyte processes
 A genetically targeted optical sensor to monitor calcium signals in astrocyte processes 1 Eiji Shigetomi, 1 Sebastian Kracun, 2 Michael V. Sofroniew & 1,2 *Baljit S. Khakh Ψ 1 Departments of Physiology
A genetically targeted optical sensor to monitor calcium signals in astrocyte processes 1 Eiji Shigetomi, 1 Sebastian Kracun, 2 Michael V. Sofroniew & 1,2 *Baljit S. Khakh Ψ 1 Departments of Physiology
Is action potential threshold lowest in the axon?
 Supplementary information to: Is action potential threshold lowest in the axon? Maarten H. P. Kole & Greg J. Stuart Supplementary Fig. 1 Analysis of action potential (AP) threshold criteria. (a) Example
Supplementary information to: Is action potential threshold lowest in the axon? Maarten H. P. Kole & Greg J. Stuart Supplementary Fig. 1 Analysis of action potential (AP) threshold criteria. (a) Example
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
Synaptic plasticityhippocampus. Neur 8790 Topics in Neuroscience: Neuroplasticity. Outline. Synaptic plasticity hypothesis
 Synaptic plasticityhippocampus Neur 8790 Topics in Neuroscience: Neuroplasticity Outline Synaptic plasticity hypothesis Long term potentiation in the hippocampus How it s measured What it looks like Mechanisms
Synaptic plasticityhippocampus Neur 8790 Topics in Neuroscience: Neuroplasticity Outline Synaptic plasticity hypothesis Long term potentiation in the hippocampus How it s measured What it looks like Mechanisms
hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGEND Fig. S1. Generation and characterization of. (A) Coomassie staining of soluble hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This protein was expressed
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGEND Fig. S1. Generation and characterization of. (A) Coomassie staining of soluble hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This protein was expressed
Synaptic Transmission: Ionic and Metabotropic
 Synaptic Transmission: Ionic and Metabotropic D. Purves et al. Neuroscience (Sinauer Assoc.) Chapters 5, 6, 7. C. Koch. Biophysics of Computation (Oxford) Chapter 4. J.G. Nicholls et al. From Neuron to
Synaptic Transmission: Ionic and Metabotropic D. Purves et al. Neuroscience (Sinauer Assoc.) Chapters 5, 6, 7. C. Koch. Biophysics of Computation (Oxford) Chapter 4. J.G. Nicholls et al. From Neuron to
mtorc2 controls actin polymerization required for consolidation of long-term memory
 CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Neurosci.; doi:1.138/nn.3351 mtorc2 controls actin polymerization required for consolidation of long-term memory Wei Huang, Ping Jun Zhu, Shixing Zhang, Hongyi Zhou, Loredana Stoica,
CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Neurosci.; doi:1.138/nn.3351 mtorc2 controls actin polymerization required for consolidation of long-term memory Wei Huang, Ping Jun Zhu, Shixing Zhang, Hongyi Zhou, Loredana Stoica,
N-methyl-D-aspartate Receptor Mediates X-irradiation-induced Drebrin Decrease in Hippocampus
 2018;68:111~115 Original N-methyl-D-aspartate Receptor Mediates X-irradiation-induced Drebrin Decrease in Hippocampus Shuchuan Miao 1, Noriko Koganezawa 1, Kenji Hanamura 1, Anggraeini Puspitasari 1,2
2018;68:111~115 Original N-methyl-D-aspartate Receptor Mediates X-irradiation-induced Drebrin Decrease in Hippocampus Shuchuan Miao 1, Noriko Koganezawa 1, Kenji Hanamura 1, Anggraeini Puspitasari 1,2
Developmental regulation of Medium Spiny Neuron dendritic arborization. Lorene M. Lanier Department of Neuroscience
 Developmental regulation of Medium Spiny Neuron dendritic arborization Lorene M. Lanier Department of Neuroscience Diversity in dendritic arbors Pyramidal Purkinje Medium Spiny http://youtu.be/_tqpca6wx84
Developmental regulation of Medium Spiny Neuron dendritic arborization Lorene M. Lanier Department of Neuroscience Diversity in dendritic arbors Pyramidal Purkinje Medium Spiny http://youtu.be/_tqpca6wx84
Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) 108 (b-c) (d) (e) (f) (g)
 Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) In four mice, cre-dependent expression of the hyperpolarizing opsin Arch in pyramidal cells
Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) In four mice, cre-dependent expression of the hyperpolarizing opsin Arch in pyramidal cells
Excitatory Post Synaptic Potentials in Dendritic Spines on Basal Dendrites of L5 Pyramidal Neurons
 University of Connecticut DigitalCommons@UConn Doctoral Dissertations University of Connecticut Graduate School 8-8-2014 Excitatory Post Synaptic Potentials in Dendritic Spines on Basal Dendrites of L5
University of Connecticut DigitalCommons@UConn Doctoral Dissertations University of Connecticut Graduate School 8-8-2014 Excitatory Post Synaptic Potentials in Dendritic Spines on Basal Dendrites of L5
Tyrodes solution in a custom-built imaging chamber as described previously. Images were acquired
 Supplemental Material Supplemental Methods Electrical stimulation of CX-G3-labeled hippocampal neurons Following 5 min incubation in 0.5 µm CX-G3 and washes, 18-20 DIV neurons were imaged in normal Tyrodes
Supplemental Material Supplemental Methods Electrical stimulation of CX-G3-labeled hippocampal neurons Following 5 min incubation in 0.5 µm CX-G3 and washes, 18-20 DIV neurons were imaged in normal Tyrodes
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Title Degeneration and impaired regeneration of gray matter oligodendrocytes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Authors Shin H. Kang, Ying Li, Masahiro Fukaya, Ileana Lorenzini,
Supplementary Information Title Degeneration and impaired regeneration of gray matter oligodendrocytes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Authors Shin H. Kang, Ying Li, Masahiro Fukaya, Ileana Lorenzini,
Local Presynaptic Activity Gates Homeostatic Changes in Presynaptic Function Driven by Dendritic BDNF Synthesis
 Article Local Presynaptic Activity Gates Homeostatic Changes in Presynaptic Function Driven by Dendritic Synthesis Sonya K. Jakawich, 1,2 Hassan B. Nasser, 2 Michael J. Strong, 2 Amber J. McCartney, 1,2
Article Local Presynaptic Activity Gates Homeostatic Changes in Presynaptic Function Driven by Dendritic Synthesis Sonya K. Jakawich, 1,2 Hassan B. Nasser, 2 Michael J. Strong, 2 Amber J. McCartney, 1,2
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Nat Neurosci. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2009 August 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Nat Neurosci. 2009 February ; 12(2): 172 181. doi:10.1038/nn.2249. A critical role for PSD-95/AKAP interactions in endocytosis of
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Nat Neurosci. 2009 February ; 12(2): 172 181. doi:10.1038/nn.2249. A critical role for PSD-95/AKAP interactions in endocytosis of
Dynamic mechanisms of neuroligin-dependent presynaptic terminal assembly in living cortical neurons
 Bury and Sabo Neural Development 2014, 9:13 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Dynamic mechanisms of neuroligin-dependent presynaptic terminal assembly in living cortical neurons Luke AD Bury 1 and Shasta L
Bury and Sabo Neural Development 2014, 9:13 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Dynamic mechanisms of neuroligin-dependent presynaptic terminal assembly in living cortical neurons Luke AD Bury 1 and Shasta L
Title: Smooth muscle cell-specific Tgfbr1 deficiency promotes aortic aneurysm formation by stimulating multiple signaling events
 Title: Smooth muscle cell-specific Tgfbr1 deficiency promotes aortic aneurysm formation by stimulating multiple signaling events Pu Yang 1, 3, radley M. Schmit 1, Chunhua Fu 1, Kenneth DeSart 1, S. Paul
Title: Smooth muscle cell-specific Tgfbr1 deficiency promotes aortic aneurysm formation by stimulating multiple signaling events Pu Yang 1, 3, radley M. Schmit 1, Chunhua Fu 1, Kenneth DeSart 1, S. Paul
S100B+ Cell Density day Spine Formation (%)
 b * CP * HC CP Th DAPI S100B ** 50 40 30 * 20 10 0-10 -20 * * ** 9 6 3 0 0-50 50-100 100-150 150-200 Distance from Prism Face (um) 1-day Spine Formation (%) 1-day Spine Elimination (%) 12 Distance from
b * CP * HC CP Th DAPI S100B ** 50 40 30 * 20 10 0-10 -20 * * ** 9 6 3 0 0-50 50-100 100-150 150-200 Distance from Prism Face (um) 1-day Spine Formation (%) 1-day Spine Elimination (%) 12 Distance from
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2294 Figure S1 Localization and function of cell wall polysaccharides in root hair cells. (a) Spinning-disk confocal sections of seven day-old A. thaliana seedlings stained with 0.1% S4B
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2294 Figure S1 Localization and function of cell wall polysaccharides in root hair cells. (a) Spinning-disk confocal sections of seven day-old A. thaliana seedlings stained with 0.1% S4B
Synaptic Plasticity and the NMDA Receptor
 Synaptic Plasticity and the NMDA Receptor Lecture 4.2 David S. Touretzky November, 2015 Long Term Synaptic Plasticity Long Term Potentiation (LTP) Reversal of LTP Long Term Depression (LTD) Reversal of
Synaptic Plasticity and the NMDA Receptor Lecture 4.2 David S. Touretzky November, 2015 Long Term Synaptic Plasticity Long Term Potentiation (LTP) Reversal of LTP Long Term Depression (LTD) Reversal of
Supplementary Figure 1
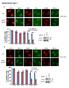 Supplementary Figure 1 a γ-h2ax MDC1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1 U2OS Cells sgrna-1 ** 60 sgrna 40 20 0 % positive Cells (>5 foci per cell) b ** 80 sgrna sgrna γ-h2ax MDC1 γ-h2ax RNF8 FK2 MDC1 BRCA1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1
Supplementary Figure 1 a γ-h2ax MDC1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1 U2OS Cells sgrna-1 ** 60 sgrna 40 20 0 % positive Cells (>5 foci per cell) b ** 80 sgrna sgrna γ-h2ax MDC1 γ-h2ax RNF8 FK2 MDC1 BRCA1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1
BME NEUROSCIENCE PRINCIPLES OF NEURAL SCIENCE 1 ST SEMESTER GRADUATE COURSE HYOUNG F. KIM
 BME NEUROSCIENCE PRINCIPLES OF NEURAL SCIENCE 1 ST SEMESTER GRADUATE COURSE HYOUNG F. KIM BASIC CONCEPT OF CELL BIOLOGY CELL & NEURON What are the differences? BASIC CONCEPT OF CELL 1. What are the cells
BME NEUROSCIENCE PRINCIPLES OF NEURAL SCIENCE 1 ST SEMESTER GRADUATE COURSE HYOUNG F. KIM BASIC CONCEPT OF CELL BIOLOGY CELL & NEURON What are the differences? BASIC CONCEPT OF CELL 1. What are the cells
How Nicotinic Signaling Shapes Neural Networks
 How Nicotinic Signaling Shapes Neural Networks Darwin K. Berg Division of Biological Sciences University of California, San Diego Nicotinic Cholinergic Signaling Uses the transmitter ACh to activate cation-selective
How Nicotinic Signaling Shapes Neural Networks Darwin K. Berg Division of Biological Sciences University of California, San Diego Nicotinic Cholinergic Signaling Uses the transmitter ACh to activate cation-selective
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse. a. Probability distribution of firing rates across the population (notice log scale) in our data. The range of firing rates is wide but
Supplementary Figure 1 Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse. a. Probability distribution of firing rates across the population (notice log scale) in our data. The range of firing rates is wide but
NMDA Receptor-Dependent Activation of the Small GTPase Rab5 Drives the Removal of Synaptic AMPA Receptors during Hippocampal LTD
 Neuron, Vol. 45, 81 94, January 6, 2005, Copyright 2005 by Elsevier Inc. DOI 10.1016/j.neuron.2004.12.023 NMDA Receptor-Dependent Activation of the Small GTPase Rab5 Drives the Removal of Synaptic AMPA
Neuron, Vol. 45, 81 94, January 6, 2005, Copyright 2005 by Elsevier Inc. DOI 10.1016/j.neuron.2004.12.023 NMDA Receptor-Dependent Activation of the Small GTPase Rab5 Drives the Removal of Synaptic AMPA
High-performance and site-directed in utero electroporation with a triple-electrode probe
 High-performance and site-directed in utero electroporation with a triple-electrode probe Marco dal Maschio 1 *, Diego Ghezzi 1 *, Guillaume Bony 1 *, Alessandro Alabastri 2, Gabriele Deidda 1, Marco Brondi
High-performance and site-directed in utero electroporation with a triple-electrode probe Marco dal Maschio 1 *, Diego Ghezzi 1 *, Guillaume Bony 1 *, Alessandro Alabastri 2, Gabriele Deidda 1, Marco Brondi
