Original Article MicroRNA-34a negatively regulates anesthesia-induced hippocampal apoptosis and memory impairment through FGFR1
|
|
|
- Giles Washington
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(10): /ISSN: /IJCEP Original Article MicroRNA-34a negatively regulates anesthesia-induced hippocampal apoptosis and memory impairment through FGFR1 Xiu-Li Jiang 1, Bo-Xiang Du 1, Jie Chen 2, Lin Liu 1, Wei-Bin Shao 2, Jie Song 1 Departments of 1 Anesthesiology, 2 Hepatobiliary Surgery, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Nantong University, Nantong , Jiangsu Province, China Received July 30, 2014; Accepted August 23, 2014; Epub September 15, 2014; Published October 1, 2014 Abstract: Background: Mounting evidence has shown the toxic effects of anesthesia to neonatal hippocampus. We used an in vivo mouse model to explore the role of microrna 34a (mir-34a) in regulating anesthesia-induced hippocampal neurotoxicity. Methods: One-month old C57/BL6 mice received daily intraperitoneal injection of anesthesia (ketamine, 50 mg/kg) for 7 days. One day after, apoptosis was evaluated by TUNEL staining in hippocampal CA1 region, and expression level of mir-34a assessed by real-time quantitative PCR (qpcr). Hippocampal mir-34a was then down-regulated through lentivirus mediated cortical injection prior to anesthesia. The effects of inhibiting hippocampal mir-34a on anesthesia-induced hippocampal apoptosis and memory impairment were further investigated by TUNEL staining and Morris water maze (MWM) test. The predicted molecular target of mir-34a, fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1) was down-regulated in hippocampus through sirna-mediated cortical injection and its effect on hippocampal apoptosis was also examined. Results: Anesthesia caused severe apoptosis among hippocampal CA1 neurons and upregulated hippocampal mir-34a. On the other hand, lentivirual inhibition of mir-34a protected anesthesia-induced hippocampal apoptosis and memory impairment. Luciferase essay demonstrated FGFR1 was directly regulated by mir-34a in hippocampus. sirna-induced FGFR1 downregulation further exaggerated anesthesia-induced apoptosis in hippocampus. Conclusions: Overall, we showed that mir-34a negatively modulated anesthesia-induced hippocampal neurotoxicity. Keywords: Anesthesia, mir-34a, FGFR1, neurotoxicity, hippocampus Introduction Clinical and laboratory studies have revealed that commonly used anesthetics would unavoidably induce neurodegeneration in neonatal brains, both in animals and humans [1-3]. Among them, ketamine is an excitatory glutamate N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors antagonist [4, 5], and generally used in neonatal anesthesia. Emerging evidence has brought the attention among both physicians and researchers that prolonged or high dosages of ketamine administration would cause severe neurotoxicity in the neonatal hippocampus and induce long-term memory impairment [6-10]. Unfortunately, the exact mechanisms of anesthesia-induced hippocampal neurodegeneration or memory loss are largely unknown. MicroRNAs (mirnas) are groups of shortsequenced noncoding ribonucleic acids (RNAs) that abundantly expressed in brain and play essential roles in various aspects of brain development, including neurogenesis and maturation [11, 12], regeneration [13], cortical neuropathy and neurodegenerative diseases [14-16]. Among many of the cortically expressed mirnas, microrna 34a (mir-34a) belongs to the family of mir-34 (mir-34 a/b/c) and played critical roles in many aspects of cortical development and tumorigenesis [17-19]. In the present study, we set to examine whether mir-34a was involved in the process of anesthesia-induced neurodegeneration in hippocampus. We introduced prolonged administration of ketamine to induce hippocampal neural
2 apoptosis and memory impairment in young animals (one-month old mice). We then examined the corresponding expressional change of mir-34a in mouse hippocampus. Subsequently, we applied lentivirus-mediated mir-34a inhibition and small interfering RNA (sirna) mediated gene knocking-down to explore the molecular role of mir-34a in ketamine-induced hippocampal apoptosis and memory dysfunction. The purpose of this study is to identify the molecular target to clinically intervene or protect anesthesia-induced neurodegeneration in neonatal cortex. Experimental procedures Animals C57/BL6 mice were purchased from Shanghai Laboratory Animal Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences (Shanghai, China). All animals were maintained in animal facility of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Nantong University. The animal procedures were reviewed and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at the Second Affiliated Hospital of Nantong University in Nantong, Jiangsu Province, China. In vivo anesthesia At one-month age, mice received an intraperitoneal injection of 50 mg/kg of body weight of ketamine hydrochloride (Shanghai Sino-west Pharmaceutical Company, Shanghai, China), once a day for seven days. The control group of mice received intraperitoneal injection of normal saline (N.S.). Hippocampal terminal transferase dutp nick end labeling (TUNEL) staining Twenty-four hours after the completion of ketamine administration, mice were sacrificed and hippocampal slices (300 μm) were prepared by a vibratone (Leica, Germany). Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated biotinylated UTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) staining was then performed by an In-situ cell death kit (Roche, USA) to examine the apoptosis in hippocampal CA1 region. An antibody against neuronal marker microtubule-associated protein MAP2 (1:100, Santa Cruz, USA) was also applied to identify neurons in hippocampal CA1 region. The percentages (mean ± SEM) of neurons with apoptotic nuclei (both MAP2+ and TUNEL+) were then quantified. RNA isolation and real-time quantitative PCR (qpcr) After mice were sacrificed, hippocampus was quickly extracted, frozen on dry ice and homogenized with a Trizol Reagent (Invitrogen, USA). 200 μl chloroform was added. Tissue samples were centrifuged for 20 min and the aqueous tissue was isolated with RNase-free tubes (Solarbio, China). Total RNA was then washed by 75% ethanol and collected in 50 μl pure water. The RNA concentration was assessed by a nanodrop spectrophotometer (260/280 nm, Ocean Optics, USA) followed by 2% agarose gel electrophoresis. Hippocampal messenger RN- As, mir-34a and internal control U6, FGFR1 and internal control GAPDH, were analyzed with a mirnas qpcr Quantitation Kit (GenePharma, Shanghai, China) with a DNA Engine Opticon 2 Two-color real-time PCR Detection System (Bio- Rad, USA) according to manufacturer s manuals. Lentivirus production The inhibition of hippocampal mir-34a was performed with lentivirual conduction. The coding oligonucleotides of mouse antisense mir- 34a inhibitor, mir-34a mimics and non-specific control were purchased from RiboBio (Shanghai, China). The sequences were then cloned into feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV) based lentivirus expression vector, Pcdh-CMV-MCS-EF1- copgfp (SBI, USA) and co-expressed with ppack packaging system in 293 TN cells to produce viral particles of mir-34a antisense inhibitor (mir34a-i), mir-34a mimics (mir34a-mimics) and non-specific control vector (mir-nc). SiRNA production Short interfering RNA (sirna), including FGFR1 sirna (FGFR1_siRNA) and control sirna (Ctrl_ sirna) were purchased from Stanta Cruz (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, USA). The concentration of in vivo application was 50 um. In vivo hippocampal injection Twenty-four hours prior to anesthesia, lentiviruses (mir34a-i and mir-nc) or sirnas (FGFR1_siRNA and Ctrl_siRNA) were delivered to mouse hippocampus through an injection on on the right side of the brain. Under a surgical microscope, a tiny hole (0.05 mm in diameter) 6761 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(10):
3 Figure 1. In vivo anesthesia lead to hippocampal apoptosis and upregulation of mir-34a C57/BL6 mice were conducted with I.P. injection of 50 mg/kg ketamine once a day for seven consecutive days. Control mice were injected with normal saline (N.S.). A. One day after treatment, hippocampal slices under both ketamine and N.S. conditions were prepared. In CA1 area, a neuronal marker of MAP2 (Blue, 1:100, Sigma-Aldrich, USA) was used to visualize CA1 neurons and TUNEL staining (Red) to visualize apoptotic nuclei. Cells positive to both TUNEL and MAP2 signals are identified as apoptotic CA1 neurons (arrows); B. One day after treatment, hippocampal tissues under both ketamine and N.S. conditions were examined by qpcr to compare the expression levels of mir-34a. (*: P < 0.05, as compared to N.S.). was drilled on the right cortex just above hippocampus. A Hamilton syringe was applied to inject total volume of 2 μl lentiviruses or sir- NAs into dorsal hippocampus (from bregma: dorso-ventral, -2.0 mm, medio-lateral, +2.4 mm; anterio-posterior, -1.8 mm). Luciferase reporter assays Hippocampal cdna was produced by regular PCR. The wild-type 3 -UTR and mutant 3 -UTR of FGFR1 were then amplified and cloned into a pmir-report luciferase reporter vector (Ambion, USA) to produce Luc- FGFR1 and Luc- FGFR1-mu constructs. The pmir-report control vector, and Luc- FGFR1 and Luc- FGFR1-mu were then co-transfected with β-galactosidase and lentivirus mir34a-mimics into HEK293 cells with Lipofectamine 2000 reagent according to manufacturer s manual (Invitrogen, USA). The MWM test was conducted according to previous study with minor modification [20]. The MWM was built as a circular pool (200 cm diameter), filled with warm water at 21 C. Mice, at 2-month age, were trained to swim in water to a submerged platform (1.5 cm 1.5 cm. 1.5 cm beneath water surface) guided by distal cues attached to the walls. A computerized tracking/analyzing video system was used to record all animal movements. The acquisition phase included four training sessions per day for four consecutive days. Mice were and allowed to swim freely until they reached the platform in 2 minutes and rested on it for 30 seconds. If mice did not locate the platform then, they were manually placed on the platform for 30 seconds. On 5 th day, animals was conducted an examining session, in which the path length and path time to reach the platform were recorded. Statistical analysis All data were presented as mean ± standarddeviations (SEM). All experiments were repeated at least three times. Statistic analysis was conducted with a MS-Windows-based SPSS software (version 13.0). The statistic differences were evaluated by student s t-test, and the significance was defined while P < Results The luciferase reporter assay (Promega, USA) was then conducted 24 hours after transfection. The fluorescent intensities were measured in triplicates and normalized to the intensity of β-galactosidase of control vector. Morris water maze (MWM) test Anesthesia caused apoptosis in hippocampal CA1 neurons and upregulated mir-34a It was shown previously in an in vivo rat experiment that consecutive treatment of high concentrations of ketamine caused neuronal dam Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(10):
4 Figure 2. Knocking down mir-34a reduced hippocampal apoptosis and memory impairment One day before ketamine administration, C57/BL6 mice received cortical injection of lentivirus vector of mir-34a inhibitor (mi- R34a-I) to specifically knock down mir-34a in hippocampus. Control mice were injected with non-specific lentivirus (mir-nc). After ketamine administration, hippocampal slices were examined and apoptotic CA1 neurons were identified as both positive to TUNEL and MAP2 immuno-stainings (arrows) (A). Three groups of mice received different combination of lentivirual and ketamine administration, including those received mir-nc hippocampal injection and normal saline treatment (N.S.+miR-NC), those received mir- NC hippocampal injection and ketamine administration (Ketamine+miR- NC) and those received mir34a-i hippocampal injection and ketamine administration (Ketamine+miR34a-I). One day after ketamine administration, quantification of apoptotic CA1 neurons was performed (B) (*: P < 0.05; : P < 0.05). One month after ketamine administration, cognitive memory test of Morris Water Maze (MWM) test was performed to measure the path length (C) and path time (D) for mice to swim to the hidden platform (*: P < 0.05; : P < 0.05). rificed and the hippocampal slices were prepared to examine the status of apoptosis among neurons. In control group, mice were injected with normal saline (N.S.) and prepared as the same way as ketamine-treated mice. The TUNEL staining, along with immuno-staining of neuronal marker MAP2 were conducted in CA1 regions of the prepared hippocampal slices (Figure 1A). Under N.S. condition, there seemed to be little or no apoptotic CA1 neurons, based on double-positive staining of TUNEL and MAP2. However, in hippocampi treated with ketamine, considerable amount of apoptotic CA1 neurons were identified with double-staining of TUNEL and MAP2 (arrows), suggesting significant apoptosis induced by anesthesia. The qpcr was also conducted one day after the last administration of ketamine to compare the expression levels of mir-34a between ketaminetreated and control (N.S.) hippocampi. It demonstrated that mir- 34a was markedly upregulated due to ketamine administration (Figure 1B, *: P < 0.05, as compared to N.S.). Inhibition of hippocampal mir- 34a reduced neuronal apoptosis and memory impairment As we discovered that mir-34a upregulation was associated with anesthesia-induced hippocampal apoptosis, we wondered whether mir-34a had a functional role in it. For that purpose, we constructed lentivirual vector age in hippocampus in young brain [6]. In the present study, we used similar approach and successfully induced hippocampal apoptosis in the developing mouse brain. Yong C57/BL6 mice (one-month old) were conducted with intraperitoneal (I.P.) injection of ketamine (50 mg/kg per day) for 7 days. One day after the last administration of ketamine, mice were sac- containing antisense oligonucle- otides to specifically knock know mir-34a (mir34-i) and injected it into mouse hippocampus. The control mice received hippocampal injection of non-specific lentivirual vector (mir- NC). One day following hippocampal injection, two groups of mice were conducted with ketamine administration for 7 days, followed by immuno-staining of TUNEL essay in 24 hours Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(10):
5 Figure 3. mir-34a targeted FGFR1. A. The predicted binding site between mir-34a and FGFR1 3 -UTR. Also listed is the mutated sequence of 3 -UTR of FGFR1 (FGFR1-mu); B. Luciferase essay transfected HEK293 cells with β-galactosidase, mir34a-mimics and one of the reporter, the control construct (Luc-control), mutant 3 -UTR FGFR1 (Luc-FGFR1-mu) or wild-type 3 -UTR FGFR1 (Luc-FGFR1). The measurments were normalized to β-galactosidase activity of Luc-control. (*: P < 0.05). Mouse hippocampus was injected with FGFR1-specific sirna (FGFR1_siRNA, 50 um) or negative control sirna (Ctrl_siRNA, 50 um); C. The hippocampal expressions of FGFR1were measured by qpcr 24 hours after cortical injection of Ctrl_siRNA or FGFR1_siRNA (*: P < 0.05); D. Mice received cortical sirna injections and then 7-day ketamine administration. One day after ketamine administration, TUNEL staining was performed on hippocampal slices and apoptosis of CA1 neurons were compared between mice received Ctrl_siRNA and FGFR_siRNA (*: P < 0.05). As expected, with non-specific mir-nc treatment, ketamine induced severe apoptosis in hippocampal CA1 regions (Figure 2A, upper panel, arrows). However, while mice were pretreated with mir34a-i to down-regulate mir- 34a in hippocampus, significantly less CA1 neurons were dying after ketamine administration (Figure 2A, lower panel, arrows). This result suggested that inhibition of mir-34a had a protective effect on neuronal death in anesthesiainduced hippocampal apoptosis. We then gave mice combined treatment of lentivirus and ketamine, and conducted both in vitro quantitative apoptosis essay and in vivo memory function essay, to further verify this hypothesis. In one group, mice received mir- NC hippocampal injection followed with normal saline administration (N.S.+miR-NC). In second group, mice received mir-nc hippocampal injection followed by ketamine administration (Ketamine+miR-NC). In third and final group, mice received mir34a-i hippocampal injection followed by ketamine administration (Ketamine+miR34a-I). One day after ketamine administration, hippocampus of three groups of mice were prepared in slices and examined with TUNEL staining. Quantitative measurement demonstrated that between two groups of mice received pre- hippocampal injection of control sirna (mir-nc), ketamine induced larger number of apoptotic CA1 neurons (Figure 2B, *: P < 0.05). It also showed that, between two groups of mice receiving ketamine administration, lentivirual inhibitor of mir-34a (mir34a-i) significantly reduced the number of apoptotic CA1 neurons (Figure 2B, : P < 0.05). One month after ketamine administration, three groups of mice 6764 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(10):
6 were examined with Morris Water Maze (MWM) test. The results demonstrated that between two groups of mice received pre-hippocampal injection of control sirna (mir-nc), ketamine caused significant memory impairment with increased path length and path time for mice to reach the center platform (Figure 2C, 2D, *: P < 0.05). It also showed that, between two groups of mice receiving ketamine administration, lentivirual inhibitor of mir-34a (mir34a- I) significantly rescued the memory impairment with improved path length and path time for mice to reach the center platform (Figure 2C, 2D, : P < 0.05). FGFR1 was likely the target of mir-34a in protecting hippocampus from anesthesia-induced damage We then investigated the possible molecular pathway involved in the inhibition of mir-34a on protecting anesthesia-induced hippocampal damage. Based on some of the internet-based mirna target predicting services, such as TargetScan ( and miranda ( home.do ), we identified that a member of the fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) family, FGFR1, was a potential target of mir-34a (Figure 3A). We thus used a luciferase assay, including the construct containing mouse hippocampal FGFR1 (luc-fgfr1) and its 3 -UTR mutated construct (Luc-FGFR1-mu) to verify that it was indeed the case for FGFR1 to be targeted with mir-34a in mouse hippocampus (Figure 3B). Based on that result, we then conducted in vivo hippocampal injection of FGFR1 specific sirna (FGFR1_siRNA, 50 um) in one-month old mice to further examine whether FGFR1 would directly play a role in anesthesia associated hippocampal apoptosis. The negative control sirna (Ctrl_siRNA, 50 um) was also injected to examine the efficiency of sirna modulation. It demonstrated by qpcr that the expression level of FGFR1 was significantly down-regulated by FGFR1_siRNA, but not by Ctrl_siRNA (Figure 3C, *: P < 0.05). Finally, one day after hippocampal injection of sirna to genetically knock down FGFR1 in hippocampus, mice were administrated with 7 days of ketamine followed by TUNEL staining and quantitative measurement of hippocampal apoptosis. The result revealed that the more apoptotic CA1 neurons were found in mice received FGFR1_siRNA, as compared to mice just received control sirna (Figure 3D). Thus, our results strongly supported the hypothesis that FGFR1 was directly targeted by mir-34a to regulate anesthesia-induced hippocampal apoptosis. Discussion General anesthetics are extensively used in modern days and generally considered to be effectively safe. However, more and more clinical or experimental studies have brought caution among the anesthetic society that, prolonged or high dosage application of anesthetics would induce neurotoxicity or neurodegeneration in developing brains. In the present study, we used an in vivo animal model to introduce prolonged and continuous administration of ketamine (50 mg/kg per day, seven days) in young mice. The induced toxic effects, including severe apoptosis among hippocampal CA1 neurons and long-term memory impairment are in line with previous studies showing similar neurodegenerative effects of ketamine on neonatal brains [6, 7], further solidify the notation that caution shall be taken while putting infants under general anesthetics. We found that, under the condition of anesthesia-induced hippocampal neurodegeneration, mir-34a was significantly upregulated. We then used lentivirual tools to genetically down-regulate the expression of mir-34a in hippocampus, and discovered that inhibition of mir-34a was protective against ketamine-induced hippocampal apoptosis and memory impairment. Previous reports showed that mir-34a was acting as tumor-suppressor that commonly downreuglated and induced apoptosis in tumor cells [17, 19]. In hippocampus, mir-34 family (mir- 34a/b/c) is the targets of p53 and they are essential for cortical development as deficit of mir-34a lead to under-development of neuronal differentiation and synaptogenesis [21]. Furthermore, hippocampal mir-34a was upregulated under pathological conditions, such as epilepsy or neurodegenerative disease [22, 23]. Thus, the results of our experiment showing mir-34a inhibition protected hippocampal apoptosis are in line with previous ones demonstrating mir-34a downregulating reduced caspase-3 and protected apoptosis in Alzheimer s disease [23], suggesting a protective role of mir-34a in cortical development against apoptosis or neurodegeneration Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(10):
7 Also in the present study, we showed that FGFR1 was very likely to be the direct modulatory target of mir-34a in hippocampus and downregulation of FGFR1 exaggerated the hippocampal apoptosis induced by anesthesia. The fibroblast growth factor family, including fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1), is essential for the development of hippocampus. Previous reports have demonstrated that under the condition of social defeat, FGFs were significantly downregulated in hippocampus [24], and long-term activation of FGFR1 reduced apoptosis in retinal pigmented epithelial cells [25]. Although we did not present direct evidence of FGFR1 activation or upregulation reduced/protected anesthesia-induced apoptosis, the results of our study showing knocking down FGFR1 facilitated apoptosis in hippocampal CA1 neurons would support this hypothesis and future experiment exploring the correlation between mir-34a and FGFR1, as well as the direct effect of FGFR1 against hippocampal neurodegeneration would certainly further our understanding on their regulation on neurodegeneration in neonatal cortex. Overall, our study demonstrated a new mechanism of mir-34a negatively regulating anesthesia-induced hippocampal apoptosis and its regulation was very likely through FGFR1 in hippocampus. Disclosure of conflict of interest None. Address correspondence to: Dr. Jie Song, Department of Anesthesiology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Nantong University, 6 North Hai er Lane Road, Nangtong City , Jiangsu Province, China. Tel: ; songjie18@ aol.com References [1] Flick RP, Nemergut ME, Christensen K and Hansen TG. Anesthetic-related neurotoxicity in the young and outcome measures: the devil is in the details. Anesthesiology 2014; 120: [2] Olsen EA and Brambrink AM. Anesthetic neurotoxicity in the newborn and infant. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol 2013; [Epub ahead of print]. [3] Loepke AW and Soriano SG. An assessment of the effects of general anesthetics on developing brain structure and neurocognitive function. Anesth Analg 2008; 106: [4] Kohrs R and Durieux ME. Ketamine: teaching an old drug new tricks. Anesth Analg 1998; 87: [5] Olney JW, Labruyere J, Wang G, Wozniak DF, Price MT and Sesma MA. NMDA antagonist neurotoxicity: mechanism and prevention. Science 1991; 254: [6] Huang L, Liu Y, Jin W, Ji X and Dong Z. Ketamine potentiates hippocampal neurodegeneration and persistent learning and memory impairment through the PKCgamma-ERK signaling pathway in the developing brain. Brain Res 2012; 1476: [7] Huang L, Liu Y, Zhang P, Kang R, Li X, Bo L and Dong Z. In vitro dose-dependent inhibition of the intracellular spontaneous calcium oscillations in developing hippocampal neurons by ketamine. PLoS One 2013; 8: e [8] Peng S, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Wang H and Ren B. Effect of ketamine on ERK expression in hippocampal neural cell and the ability of learning behavior in minor rats. Mol Biol Rep 2010; 37: [9] Wang C, Liu F, Patterson TA, Paule MG and Slikker W Jr. Preclinical assessment of ketamine. CNS Neurosci Ther 2013; 19: [10] Zou X, Patterson TA, Divine RL, Sadovova N, Zhang X, Hanig JP, Paule MG, Slikker W, Jr. and Wang C. Prolonged exposure to ketamine increases neurodegeneration in the developing monkey brain. Int J Dev Neurosci 2009; 27: [11] Volvert ML, Rogister F, Moonen G, Malgrange B and Nguyen L. MicroRNAs tune cerebral cortical neurogenesis. Cell Death Differ 2012; 19: [12] Miranda RC. MicroRNAs and Fetal Brain Development: Implications for Ethanol Teratology during the Second Trimester Period of Neurogenesis. Front Genet 2012; 3: 77. [13] Wu D and Murashov AK. MicroRNA-431 regulates axon regeneration in mature sensory neurons by targeting the Wnt antagonist Kremen1. Front Mol Neurosci 2013; 6: 35. [14] Singh P, Soon PS, Feige JJ, Chabre O, Zhao JT, Cherradi N, Lalli E and Sidhu SB. Dysregulation of micrornas in adrenocortical tumors. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2012; 351: [15] Bithell A, Johnson R and Buckley NJ. Transcriptional dysregulation of coding and noncoding genes in cellular models of Huntington s disease. Biochem Soc Trans 2009; 37: [16] Goedeke L and Fernandez-Hernando C. micrornas: A connection between cholesterol metabolism and neurodegeneration. Neurobiol Dis 2014; [Epub ahead of print] Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(10):
8 [17] Rathod SS, Rani SB, Khan M, Muzumdar D and Shiras A. Tumor suppressive mirna-34a suppresses cell proliferation and tumor growth of glioma stem cells by targeting Akt and Wnt signaling pathways. FEBS Open Bio 2014; 4: [18] Silber J, Jacobsen A, Ozawa T, Harinath G, Pedraza A, Sander C, Holland EC and Huse JT. mir-34a repression in proneural malignant gliomas upregulates expression of its target PDGFRA and promotes tumorigenesis. PLoS One 2012; 7: e [19] Rokavec M, Li H, Jiang L and Hermeking H. The p53/mir-34 axis in development and disease. J Mol Cell Biol 2014; 6: [20] Patil SS, Sunyer B, Hoger H and Lubec G. Evaluation of spatial memory of C57BL/6J and CD1 mice in the Barnes maze, the Multiple T-maze and in the Morris water maze. Behav Brain Res 2009; 198: [21] Agostini M, Tucci P, Steinert JR, Shalom- Feuerstein R, Rouleau M, Aberdam D, Forsythe ID, Young KW, Ventura A, Concepcion CP, Han YC, Candi E, Knight RA, Mak TW and Melino G. microrna-34a regulates neurite outgrowth, spinal morphology, and function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2011; 108: [22] Hu K, Xie YY, Zhang C, Ouyang DS, Long HY, Sun DN, Long LL, Feng L, Li Y and Xiao B. MicroRNA expression profile of the hippocampus in a rat model of temporal lobe epilepsy and mir-34a-targeted neuroprotection against hippocampal neurone cell apoptosis post-status epilepticus. BMC Neurosci 2012; 13: 115. [23] Wang X, Liu P, Zhu H, Xu Y, Ma C, Dai X, Huang L, Liu Y, Zhang L and Qin C. mir-34a, a micror- NA up-regulated in a double transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer s disease, inhibits bcl2 translation. Brain Res Bull 2009; 80: [24] Turner CA, Calvo N, Frost DO, Akil H and Watson SJ. The fibroblast growth factor system is downregulated following social defeat. Neurosci Lett 2008; 430: [25] Bryckaert M, Guillonneau X, Hecquet C, Courtois Y and Mascarelli F. Both FGF1 and bcl-x synthesis are necessary for the reduction of apoptosis in retinal pigmented epithelial cells by FGF2: role of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2. Oncogene 1999; 18: Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(10):
Supplemental Information. Menin Deficiency Leads to Depressive-like. Behaviors in Mice by Modulating. Astrocyte-Mediated Neuroinflammation
 Neuron, Volume 100 Supplemental Information Menin Deficiency Leads to Depressive-like Behaviors in Mice by Modulating Astrocyte-Mediated Neuroinflammation Lige Leng, Kai Zhuang, Zeyue Liu, Changquan Huang,
Neuron, Volume 100 Supplemental Information Menin Deficiency Leads to Depressive-like Behaviors in Mice by Modulating Astrocyte-Mediated Neuroinflammation Lige Leng, Kai Zhuang, Zeyue Liu, Changquan Huang,
Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases
 Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
mir-7a regulation of Pax6 in neural stem cells controls the spatial origin of forebrain dopaminergic neurons
 Supplemental Material mir-7a regulation of Pax6 in neural stem cells controls the spatial origin of forebrain dopaminergic neurons Antoine de Chevigny, Nathalie Coré, Philipp Follert, Marion Gaudin, Pascal
Supplemental Material mir-7a regulation of Pax6 in neural stem cells controls the spatial origin of forebrain dopaminergic neurons Antoine de Chevigny, Nathalie Coré, Philipp Follert, Marion Gaudin, Pascal
Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained
 Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained with MitoTracker (red), then were immunostained with
Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained with MitoTracker (red), then were immunostained with
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioural effects of ketamine in non-stressed and stressed mice. Naive C57BL/6 adult male mice (n=10/group) were given a single dose of saline vehicle or ketamine (3.0 mg/kg,
Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioural effects of ketamine in non-stressed and stressed mice. Naive C57BL/6 adult male mice (n=10/group) were given a single dose of saline vehicle or ketamine (3.0 mg/kg,
Functional Development of Neuronal Networks in Culture -An in vitro Assay System of Developing Brain for Endocrine Disruptors
 Functional Development of Neuronal Networks in Culture -An in vitro Assay System of Developing Brain for Endocrine Disruptors Masahiro Kawahara and Yoichiro Kuroda Tokyo Metropolitan Institute for Neuroscience
Functional Development of Neuronal Networks in Culture -An in vitro Assay System of Developing Brain for Endocrine Disruptors Masahiro Kawahara and Yoichiro Kuroda Tokyo Metropolitan Institute for Neuroscience
Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v)
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
Sevoflurane induces neurotoxicity in young mice through FAS/FASL signaling
 Sevoflurane induces neurotoxicity in young mice through FAS/FASL signaling Q. Song 1 *, Y.L. Ma 1 *, J.Q. Song 1, Q. Chen 1, G.S. Xia 1, J.Y. Ma 1, F. Feng 1, X.J. Fei 2,3 and Q.M. Wang 1 1 Department
Sevoflurane induces neurotoxicity in young mice through FAS/FASL signaling Q. Song 1 *, Y.L. Ma 1 *, J.Q. Song 1, Q. Chen 1, G.S. Xia 1, J.Y. Ma 1, F. Feng 1, X.J. Fei 2,3 and Q.M. Wang 1 1 Department
Selective filtering defect at the axon initial segment in Alzheimer s disease mouse models. Yu Wu
 Selective filtering defect at the axon initial segment in Alzheimer s disease mouse models Yu Wu Alzheimer s Disease (AD) Mouse models: APP/PS1, PS1δE9, APPswe, hps1 Wirths, O. et al, Acta neuropathologica
Selective filtering defect at the axon initial segment in Alzheimer s disease mouse models Yu Wu Alzheimer s Disease (AD) Mouse models: APP/PS1, PS1δE9, APPswe, hps1 Wirths, O. et al, Acta neuropathologica
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
Effect of chronic treatment of ketamine on hippocampus cell count of adult rats
 Quarterly of the Horizon of Medical Sciences Vol. 19, No. 1, Spr 2013 Pages: 35-39 Effect of chronic treatment of ketamine on hippocampus cell count of adult rats Downloaded from hms.gmu.ac.ir at 12:09
Quarterly of the Horizon of Medical Sciences Vol. 19, No. 1, Spr 2013 Pages: 35-39 Effect of chronic treatment of ketamine on hippocampus cell count of adult rats Downloaded from hms.gmu.ac.ir at 12:09
Ketamine also decreases serum BDNF levels and spatial learning while causes apoptosis in neonatal rats
 Ketamine also decreases serum BDNF levels and spatial learning while causes apoptosis in neonatal rats A. B. Ozer 1, S. Ceribasi 2, A. O. Ceribasi 2, I. Demirel 1, M. K. Bayar 3, B. Ustundag 4, A. Yildiz
Ketamine also decreases serum BDNF levels and spatial learning while causes apoptosis in neonatal rats A. B. Ozer 1, S. Ceribasi 2, A. O. Ceribasi 2, I. Demirel 1, M. K. Bayar 3, B. Ustundag 4, A. Yildiz
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature05772 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental figure 1. Enrichment facilitates learning. a. Images showing a home cage and a cage used for environmental enrichment (EE). For EE up to
doi: 10.1038/nature05772 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental figure 1. Enrichment facilitates learning. a. Images showing a home cage and a cage used for environmental enrichment (EE). For EE up to
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figures S1-S9. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
Epigenetic Principles and Mechanisms Underlying Nervous System Function in Health and Disease Mark F. Mehler MD, FAAN
 Epigenetic Principles and Mechanisms Underlying Nervous System Function in Health and Disease Mark F. Mehler MD, FAAN Institute for Brain Disorders and Neural Regeneration F.M. Kirby Program in Neural
Epigenetic Principles and Mechanisms Underlying Nervous System Function in Health and Disease Mark F. Mehler MD, FAAN Institute for Brain Disorders and Neural Regeneration F.M. Kirby Program in Neural
Berberine Sensitizes Human Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin Through mir-93/ PTEN/Akt Signaling Pathway
 Chen Accepted: et al.: February Berberine 24, Sensitizes 2015 Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin www.karger.com/cpb 956 1421-9778/15/0363-0956$39.50/0 Original Paper This is an Open Access article licensed
Chen Accepted: et al.: February Berberine 24, Sensitizes 2015 Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin www.karger.com/cpb 956 1421-9778/15/0363-0956$39.50/0 Original Paper This is an Open Access article licensed
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date:
 microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
Supplemental Data. TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim.
 Supplemental Data TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim. Molly A. Taylor 1, Khalid Sossey-Alaoui 2, Cheryl L. Thompson 3, David Danielpour 4, and William
Supplemental Data TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim. Molly A. Taylor 1, Khalid Sossey-Alaoui 2, Cheryl L. Thompson 3, David Danielpour 4, and William
Supplemental Information. A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit. for Place Navigation
 Neuron, Volume 99 Supplemental Information A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit for Place Navigation Han Qin, Ling Fu, Bo Hu, Xiang Liao, Jian Lu, Wenjing He, Shanshan Liang, Kuan Zhang, Ruijie Li, Jiwei
Neuron, Volume 99 Supplemental Information A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit for Place Navigation Han Qin, Ling Fu, Bo Hu, Xiang Liao, Jian Lu, Wenjing He, Shanshan Liang, Kuan Zhang, Ruijie Li, Jiwei
RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice Paul N Valdmanis, Shuo Gu, Kirk Chu, Lan Jin, Feijie Zhang,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice Paul N Valdmanis, Shuo Gu, Kirk Chu, Lan Jin, Feijie Zhang,
Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein
 Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein Lei Wang 1, Tian-Peng Zhang 1, Yuan Zhang 2, Hai-Lian
Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein Lei Wang 1, Tian-Peng Zhang 1, Yuan Zhang 2, Hai-Lian
PUMA gene transfection can enhance the sensitivity of epirubicin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells
 PUMA gene transfection can enhance the sensitivity of epirubicin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells C.-G. Sun 1 *, J. Zhuang 1 *, W.-J. Teng 1, Z. Wang 2 and S.-S. Du 3 1 Department of Oncology,
PUMA gene transfection can enhance the sensitivity of epirubicin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells C.-G. Sun 1 *, J. Zhuang 1 *, W.-J. Teng 1, Z. Wang 2 and S.-S. Du 3 1 Department of Oncology,
Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2)
 Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
mir 375 inhibits the proliferation of gastric cancer cells by repressing ERBB2 expression
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 7: 1757-1761, 2014 mir 375 inhibits the proliferation of gastric cancer cells by repressing ERBB2 expression ZHI YONG SHEN *, ZI ZHEN ZHANG *, HUA LIU, EN HAO ZHAO
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 7: 1757-1761, 2014 mir 375 inhibits the proliferation of gastric cancer cells by repressing ERBB2 expression ZHI YONG SHEN *, ZI ZHEN ZHANG *, HUA LIU, EN HAO ZHAO
Supplementary Figure S I: Effects of D4F on body weight and serum lipids in apoe -/- mice.
 Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure S I: Effects of D4F on body weight and serum lipids in apoe -/- mice. Male apoe -/- mice were fed a high-fat diet for 8 weeks, and given PBS (model group) or
Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure S I: Effects of D4F on body weight and serum lipids in apoe -/- mice. Male apoe -/- mice were fed a high-fat diet for 8 weeks, and given PBS (model group) or
Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4278-4282 Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer Q.-H. ZHOU 1, Y.-M. ZHAO 2, L.-L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4278-4282 Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer Q.-H. ZHOU 1, Y.-M. ZHAO 2, L.-L.
Original Article High serum mir-203 predicts the poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):4688-4693 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0047128 Original Article High serum mir-203 predicts the poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer Jun Ma, Xiaokun
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):4688-4693 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0047128 Original Article High serum mir-203 predicts the poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer Jun Ma, Xiaokun
Biomed Environ Sci, 2015; 28(9):
 Biomed Environ Sci, 2015; 28(9): 691-695 691 Letter to the Editor Protective Effects of Tetramethylpyrazine on Cerebrovascular Regulations in Rats with Chronic Alcoholic Encephalopathy LI Hui 1,, YANG
Biomed Environ Sci, 2015; 28(9): 691-695 691 Letter to the Editor Protective Effects of Tetramethylpyrazine on Cerebrovascular Regulations in Rats with Chronic Alcoholic Encephalopathy LI Hui 1,, YANG
Analysis of small RNAs from Drosophila Schneider cells using the Small RNA assay on the Agilent 2100 bioanalyzer. Application Note
 Analysis of small RNAs from Drosophila Schneider cells using the Small RNA assay on the Agilent 2100 bioanalyzer Application Note Odile Sismeiro, Jean-Yves Coppée, Christophe Antoniewski, and Hélène Thomassin
Analysis of small RNAs from Drosophila Schneider cells using the Small RNA assay on the Agilent 2100 bioanalyzer Application Note Odile Sismeiro, Jean-Yves Coppée, Christophe Antoniewski, and Hélène Thomassin
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer. MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola
 Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at
 Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at E10.5 were double-stained for TUNEL (red) and PECAM-1 (green).
Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at E10.5 were double-stained for TUNEL (red) and PECAM-1 (green).
Supplementary Figure 1 (Related with Figure 4). Molecular consequences of Eed deletion. (a) ChIP analysis identifies 3925 genes that are associated
 Supplementary Figure 1 (Related with Figure 4). Molecular consequences of Eed deletion. (a) ChIP analysis identifies 3925 genes that are associated with the H3K27me3 mark in chondrocytes (see Table S1,
Supplementary Figure 1 (Related with Figure 4). Molecular consequences of Eed deletion. (a) ChIP analysis identifies 3925 genes that are associated with the H3K27me3 mark in chondrocytes (see Table S1,
An Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microrna targets PUMA to promote host cell survival
 An Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microrna targets to promote host cell survival The Journal of Experimental Medicine 205(11): 2551-2560, 2008. 1 Elizabeth Yee-Wai Choy, Kam-Leung Siu, Kin-Hang Kok, Raymond
An Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microrna targets to promote host cell survival The Journal of Experimental Medicine 205(11): 2551-2560, 2008. 1 Elizabeth Yee-Wai Choy, Kam-Leung Siu, Kin-Hang Kok, Raymond
RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
 Xu et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:8 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0932-8 LETTER TO THE EDITOR RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
Xu et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:8 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0932-8 LETTER TO THE EDITOR RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Bromodeoxyuridine
 Kateřina Náměstková, Zuzana Šimonová, Eva Syková Behavioural Brain Research Bromodeoxyuridine : Doublecortin : DCX Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein : GFAP Trace eye blink conditioning 1 Volume 163 : pp.
Kateřina Náměstková, Zuzana Šimonová, Eva Syková Behavioural Brain Research Bromodeoxyuridine : Doublecortin : DCX Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein : GFAP Trace eye blink conditioning 1 Volume 163 : pp.
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells
 MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
Electron micrograph of phosphotungstanic acid-stained exosomes derived from murine
 1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. Physical properties of murine DC-derived exosomes. a, Electron micrograph of phosphotungstanic acid-stained exosomes derived from
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. Physical properties of murine DC-derived exosomes. a, Electron micrograph of phosphotungstanic acid-stained exosomes derived from
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine
 Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation
 Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation J. Du 1, Z.H. Tao 2, J. Li 2, Y.K. Liu 3 and L. Gan 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation J. Du 1, Z.H. Tao 2, J. Li 2, Y.K. Liu 3 and L. Gan 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis
 Review Article MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis * Abstract MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small non-coding single stranded RNA molecules that are physiologically produced in eukaryotic
Review Article MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis * Abstract MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small non-coding single stranded RNA molecules that are physiologically produced in eukaryotic
http / /cjbmb. bjmu. edu. cn Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology A431 . Western aza-dC FUT4-siRNA
 ISSN 1007-7626 CN 11-3870 / Q http / /cjbmb bjmu edu cn Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2015 8 31 8 836 ~ 842 DOI 10 13865 /j cnki cjbmb 2015 08 09 FUT4-siRNA 5-aza-dC 1 3 * 1 1 3
ISSN 1007-7626 CN 11-3870 / Q http / /cjbmb bjmu edu cn Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2015 8 31 8 836 ~ 842 DOI 10 13865 /j cnki cjbmb 2015 08 09 FUT4-siRNA 5-aza-dC 1 3 * 1 1 3
Supplemental Information. Otic Mesenchyme Cells Regulate. Spiral Ganglion Axon Fasciculation. through a Pou3f4/EphA4 Signaling Pathway
 Neuron, Volume 73 Supplemental Information Otic Mesenchyme Cells Regulate Spiral Ganglion Axon Fasciculation through a Pou3f4/EphA4 Signaling Pathway Thomas M. Coate, Steven Raft, Xiumei Zhao, Aimee K.
Neuron, Volume 73 Supplemental Information Otic Mesenchyme Cells Regulate Spiral Ganglion Axon Fasciculation through a Pou3f4/EphA4 Signaling Pathway Thomas M. Coate, Steven Raft, Xiumei Zhao, Aimee K.
Microglia, Inflammation, and FTD
 FTD Minicourse April, 2009 Microglia, Inflammation, and FTD Li Gan, Ph.D Gladstone Institute of Neurological Disease University of California, San Francisco Outline Why study inflammation in neurodegeneration?
FTD Minicourse April, 2009 Microglia, Inflammation, and FTD Li Gan, Ph.D Gladstone Institute of Neurological Disease University of California, San Francisco Outline Why study inflammation in neurodegeneration?
Canqiu Yu 1, Jinwei Chen 2, Li Huang 3*
 A STUDY ON THE ANTITUMOUR EFFECT OF TOTAL FLAVONOIDS FROM PTERIS MULTIFIDA POIR IN H22 TUMOUR-BEARING MICE 459 Canqiu Yu 1, Jinwei Chen 2, Li Huang 3* 1 Department of General Surgery, The Second Xiangya
A STUDY ON THE ANTITUMOUR EFFECT OF TOTAL FLAVONOIDS FROM PTERIS MULTIFIDA POIR IN H22 TUMOUR-BEARING MICE 459 Canqiu Yu 1, Jinwei Chen 2, Li Huang 3* 1 Department of General Surgery, The Second Xiangya
High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases
 https://helda.helsinki.fi High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases Gupta, Richa 2010-09-20 Gupta, R, Soni, N, Patnaik, P, Sood, I, Singh, R, Rawal, K & Rani, V 2010, ' High
https://helda.helsinki.fi High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases Gupta, Richa 2010-09-20 Gupta, R, Soni, N, Patnaik, P, Sood, I, Singh, R, Rawal, K & Rani, V 2010, ' High
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
marker. DAPI labels nuclei. Flies were 20 days old. Scale bar is 5 µm. Ctrl is
 Supplementary Figure 1. (a) Nos is detected in glial cells in both control and GFAP R79H transgenic flies (arrows), but not in deletion mutant Nos Δ15 animals. Repo is a glial cell marker. DAPI labels
Supplementary Figure 1. (a) Nos is detected in glial cells in both control and GFAP R79H transgenic flies (arrows), but not in deletion mutant Nos Δ15 animals. Repo is a glial cell marker. DAPI labels
Micro RNA Research. Ken Kosik. Harriman Professor, Department of Molecular, Cellular & Developmental Biology and Biomolecular Sciences & Engr.
 Ken Kosik Harriman Professor, Department of Molecular, Cellular & Developmental Biology and Biomolecular Sciences & Engr. Program Co-Director, Neurosciences Research Institute Micro RNA Research Neuroscience
Ken Kosik Harriman Professor, Department of Molecular, Cellular & Developmental Biology and Biomolecular Sciences & Engr. Program Co-Director, Neurosciences Research Institute Micro RNA Research Neuroscience
Zhu et al, page 1. Supplementary Figures
 Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Doctoral Degree Program in Marine Biotechnology, College of Marine Sciences, Doctoral Degree Program in Marine Biotechnology, Academia Sinica, Taipei,
 Cyclooxygenase 2 facilitates dengue virus replication and serves as a potential target for developing antiviral agents Chun-Kuang Lin 1,2, Chin-Kai Tseng 3,4, Yu-Hsuan Wu 3,4, Chih-Chuang Liaw 1,5, Chun-
Cyclooxygenase 2 facilitates dengue virus replication and serves as a potential target for developing antiviral agents Chun-Kuang Lin 1,2, Chin-Kai Tseng 3,4, Yu-Hsuan Wu 3,4, Chih-Chuang Liaw 1,5, Chun-
MicroRNA 98 suppresses cell growth and invasion of retinoblastoma via targeting the IGF1R/k Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ONCOLOGY 54: 807-820, 2019 MicroRNA 98 suppresses cell growth and invasion of retinoblastoma via targeting the IGF1R/k Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway LONG GUO 1, YU BAI 2, SHUZHE
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ONCOLOGY 54: 807-820, 2019 MicroRNA 98 suppresses cell growth and invasion of retinoblastoma via targeting the IGF1R/k Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway LONG GUO 1, YU BAI 2, SHUZHE
Supplementary Figure 1: Hsp60 / IEC mice are embryonically lethal (A) Light microscopic pictures show mouse embryos at developmental stage E12.
 Supplementary Figure 1: Hsp60 / IEC mice are embryonically lethal (A) Light microscopic pictures show mouse embryos at developmental stage E12.5 and E13.5 prepared from uteri of dams and subsequently genotyped.
Supplementary Figure 1: Hsp60 / IEC mice are embryonically lethal (A) Light microscopic pictures show mouse embryos at developmental stage E12.5 and E13.5 prepared from uteri of dams and subsequently genotyped.
MicroRNA mir-326 regulates T H -17 differentiation and is associated with the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis
 correction notice Nat. Immunol. 10, 1252 1259 (2009) MicroRNA mir-326 regulates T H -17 differentiation and is associated with the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis Changsheng Du, Chang Liu, Jiuhong Kang,
correction notice Nat. Immunol. 10, 1252 1259 (2009) MicroRNA mir-326 regulates T H -17 differentiation and is associated with the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis Changsheng Du, Chang Liu, Jiuhong Kang,
Original Article mir-338-3p inhibits the proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells by targeting ADAM17
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(9):10922-10928 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0011715 Original Article mir-338-3p inhibits the proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells by targeting ADAM17 Jiang-Tao
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(9):10922-10928 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0011715 Original Article mir-338-3p inhibits the proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells by targeting ADAM17 Jiang-Tao
Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy
 Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy Jianhua Chen, Pei Gao, Sujing Yuan, Rongxin Li, Aimin Ni, Liang Chu, Li Ding, Ying Sun, Xin-Yuan Liu, Yourong
Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy Jianhua Chen, Pei Gao, Sujing Yuan, Rongxin Li, Aimin Ni, Liang Chu, Li Ding, Ying Sun, Xin-Yuan Liu, Yourong
Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis of individual mice during maze learning. a,
 Goal-oriented searching mediated by ventral hippocampus early in trial-and-error learning Ruediger, S, Spirig, D., Donato, F., Caroni, P. Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis
Goal-oriented searching mediated by ventral hippocampus early in trial-and-error learning Ruediger, S, Spirig, D., Donato, F., Caroni, P. Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis
Jumpstart your research with ViraPower Lentiviral Expression Systems
 ViraPower Lentiviral Expression Systems Jumpstart your research with ViraPower Lentiviral Expression Systems With ViraPower Lentiviral Systems you can: Efficiently transduce both dividing and non-dividing
ViraPower Lentiviral Expression Systems Jumpstart your research with ViraPower Lentiviral Expression Systems With ViraPower Lentiviral Systems you can: Efficiently transduce both dividing and non-dividing
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures
 Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
Supplementary Figure 1. The mir-182 binding site of SMAD7 3 UTR and the. mutated sequence.
 Supplementary Figure 1. The mir-182 binding site of SMAD7 3 UTR and the mutated sequence. 1 Supplementary Figure 2. Expression of mir-182 and SMAD7 in various cell lines. (A) Basal levels of mir-182 expression
Supplementary Figure 1. The mir-182 binding site of SMAD7 3 UTR and the mutated sequence. 1 Supplementary Figure 2. Expression of mir-182 and SMAD7 in various cell lines. (A) Basal levels of mir-182 expression
Supplementary Information. Staged decline of neuronal function in vivo in an animal model of Alzheimer s Disease. Supplementary Figures S1-10
 Supplementary Information Staged decline of neuronal function in vivo in an animal model of Alzheimer s Disease Christine Grienberger 1 *, Nathalie L. Rochefort 1 *, Helmuth Adelsberger 1, Horst A. Henning
Supplementary Information Staged decline of neuronal function in vivo in an animal model of Alzheimer s Disease Christine Grienberger 1 *, Nathalie L. Rochefort 1 *, Helmuth Adelsberger 1, Horst A. Henning
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
Original Article MicroRNA-27a acts as a novel biomarker in the diagnosis of patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(2):2049-2053 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0014841 Original Article MicroRNA-27a acts as a novel biomarker in the diagnosis of patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(2):2049-2053 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0014841 Original Article MicroRNA-27a acts as a novel biomarker in the diagnosis of patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
mir-542-3p targets sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 and regulates cell proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 108-114 mir-542-3p targets sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 and regulates cell proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells H.-X.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 108-114 mir-542-3p targets sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 and regulates cell proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells H.-X.
well for 2 h at rt. Each dot represents an individual mouse and bar is the mean ±
 Supplementary data: Control DC Blimp-1 ko DC 8 6 4 2-2 IL-1β p=.5 medium 8 6 4 2 IL-2 Medium p=.16 8 6 4 2 IL-6 medium p=.3 5 4 3 2 1-1 medium IL-1 n.s. 25 2 15 1 5 IL-12(p7) p=.15 5 IFNγ p=.65 4 3 2 1
Supplementary data: Control DC Blimp-1 ko DC 8 6 4 2-2 IL-1β p=.5 medium 8 6 4 2 IL-2 Medium p=.16 8 6 4 2 IL-6 medium p=.3 5 4 3 2 1-1 medium IL-1 n.s. 25 2 15 1 5 IL-12(p7) p=.15 5 IFNγ p=.65 4 3 2 1
Tumor-secreted mir-214 induces regulatory T cells: a major link between immune evasion and tumor growth
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cell Research (2014) 24:1164-1180. 2014 IBCB, SIBS, CAS All rights reserved 1001-0602/14 www.nature.com/cr npg Tumor-secreted mir-214 induces regulatory T cells: a major link between immune
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cell Research (2014) 24:1164-1180. 2014 IBCB, SIBS, CAS All rights reserved 1001-0602/14 www.nature.com/cr npg Tumor-secreted mir-214 induces regulatory T cells: a major link between immune
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl
 mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
Supplementary Figure S1. Effect of stress during withdrawal on expression of sensitization to repeated cocaine exposure in WT and D2R / mice.
 Supplementary Figure S1. Effect of stress during withdrawal on expression of sensitization to repeated cocaine exposure in WT and D2R / mice. The time course of locomotor activity for WT (a, b) or D2R
Supplementary Figure S1. Effect of stress during withdrawal on expression of sensitization to repeated cocaine exposure in WT and D2R / mice. The time course of locomotor activity for WT (a, b) or D2R
microrna 181 promotes prostate cancer cell proliferation by regulating DAX 1 expression
 1296 microrna 181 promotes prostate cancer cell proliferation by regulating DAX 1 expression SHI JUN TONG *, JUN LIU *, XIANG WANG and LIAN XI QU Department of Urologic Surgery, Huashan Hospital Affiliated
1296 microrna 181 promotes prostate cancer cell proliferation by regulating DAX 1 expression SHI JUN TONG *, JUN LIU *, XIANG WANG and LIAN XI QU Department of Urologic Surgery, Huashan Hospital Affiliated
Original Article microrna-137 modulates pancreatic cancer cells tumor growth, invasion and sensitivity to chemotherapy
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(11):7442-7450 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0000933 Original Article microrna-137 modulates pancreatic cancer cells tumor growth, invasion and sensitivity to chemotherapy
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(11):7442-7450 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0000933 Original Article microrna-137 modulates pancreatic cancer cells tumor growth, invasion and sensitivity to chemotherapy
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
Supplemental Figure 1. Intracranial transduction of a modified ptomo lentiviral vector in the mouse
 Supplemental figure legends Supplemental Figure 1. Intracranial transduction of a modified ptomo lentiviral vector in the mouse hippocampus targets GFAP-positive but not NeuN-positive cells. (A) Stereotaxic
Supplemental figure legends Supplemental Figure 1. Intracranial transduction of a modified ptomo lentiviral vector in the mouse hippocampus targets GFAP-positive but not NeuN-positive cells. (A) Stereotaxic
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
Supplemental information
 Carcinoemryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) promotes EGF receptor signaling of oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via the complex N-glycosylation y Chiang et al. Supplemental
Carcinoemryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) promotes EGF receptor signaling of oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via the complex N-glycosylation y Chiang et al. Supplemental
Chapter 2. Investigation into mir-346 Regulation of the nachr α5 Subunit
 15 Chapter 2 Investigation into mir-346 Regulation of the nachr α5 Subunit MicroRNA s (mirnas) are small (< 25 base pairs), single stranded, non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression at the post transcriptional
15 Chapter 2 Investigation into mir-346 Regulation of the nachr α5 Subunit MicroRNA s (mirnas) are small (< 25 base pairs), single stranded, non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression at the post transcriptional
The lncrna MIR4435-2HG is upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes cancer cell proliferation by upregulating mirna-487a
 Kong et al. Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters (2019) 24:26 https://doi.org/10.1186/s11658-019-0148-y Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters RESEARCH LETTER Open Access The lncrna MIR4435-2HG is upregulated
Kong et al. Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters (2019) 24:26 https://doi.org/10.1186/s11658-019-0148-y Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters RESEARCH LETTER Open Access The lncrna MIR4435-2HG is upregulated
Supplementary Fig. 1. Delivery of mirnas via Red Fluorescent Protein.
 prfp-vector RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 prfp-mir-124 mir-93/124 RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 Untransfected prfp-vector prfp-mir-93 prfp-mir-124 Supplementary Fig. 1. Delivery of mirnas via Red Fluorescent
prfp-vector RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 prfp-mir-124 mir-93/124 RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 Untransfected prfp-vector prfp-mir-93 prfp-mir-124 Supplementary Fig. 1. Delivery of mirnas via Red Fluorescent
A263 A352 A204. Pan CK. pstat STAT3 pstat3 STAT3 pstat3. Columns Columns 1-6 Positive control. Omentum. Rectosigmoid A195.
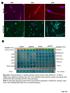 pstat3 75 Pan CK A A263 A352 A24 B Columns 1-6 Positive control A195 A22 A24 A183 Rectal Nodule STAT3 pstat3 STAT3 pstat3 Columns 7-12 Omentum Rectosigmoid Left Ovary Right Ovary Omentum Uterus Uterus
pstat3 75 Pan CK A A263 A352 A24 B Columns 1-6 Positive control A195 A22 A24 A183 Rectal Nodule STAT3 pstat3 STAT3 pstat3 Columns 7-12 Omentum Rectosigmoid Left Ovary Right Ovary Omentum Uterus Uterus
Chinese Pharmacological Bulletin 2012 Sep ~ 6. http / /www. cnki. net /kcms /detail / R html
 1262 1262 ~ 6 2012-8 - 14 17 19 http / /www. cnki. net /kcms /detail /34. 1086. R. 20120814. 1719. 018. html MG - 63 1 1 2 2 1. 453003 2. 361005 doi 10. 3969 /j. issn. 1001-1978. 2012. 09. 018 A 1001-1978
1262 1262 ~ 6 2012-8 - 14 17 19 http / /www. cnki. net /kcms /detail /34. 1086. R. 20120814. 1719. 018. html MG - 63 1 1 2 2 1. 453003 2. 361005 doi 10. 3969 /j. issn. 1001-1978. 2012. 09. 018 A 1001-1978
Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry
 Original Paper 2015 The Author(s). 2015 Published The Author(s) by S. Karger AG, Basel Published online: November 27, 2015 www.karger.com/cpb Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 2194 1421-9778/15/0376-2194$39.50/0
Original Paper 2015 The Author(s). 2015 Published The Author(s) by S. Karger AG, Basel Published online: November 27, 2015 www.karger.com/cpb Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 2194 1421-9778/15/0376-2194$39.50/0
MicroRNA-338-3p inhibits glucocorticoidinduced osteoclast formation through RANKL targeting
 MicroRNA-338-3p inhibits glucocorticoidinduced osteoclast formation through RANKL targeting X.H. Zhang 1 *, G.L. Geng 2 *, B. Su 1, C.P. Liang 1, F. Wang 1 and J.C. Bao 3 1 Department of Physical Therapy,
MicroRNA-338-3p inhibits glucocorticoidinduced osteoclast formation through RANKL targeting X.H. Zhang 1 *, G.L. Geng 2 *, B. Su 1, C.P. Liang 1, F. Wang 1 and J.C. Bao 3 1 Department of Physical Therapy,
p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO
 Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
MicroRNAs: Regulatory Function and Potential for Gene Therapy
 Lidia Park Genomics and Medicine November 23, 2008 MicroRNAs: Regulatory Function and Potential for Gene Therapy When Victor Ambros, Rosalind Lee, and Rhonda Feinbaum published the first finding of a microrna,
Lidia Park Genomics and Medicine November 23, 2008 MicroRNAs: Regulatory Function and Potential for Gene Therapy When Victor Ambros, Rosalind Lee, and Rhonda Feinbaum published the first finding of a microrna,
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
Annals of Oncology Advance Access published January 10, 2005
 Annals of Oncology Advance Access published January 10, 2005 Original article Annals of Oncology doi:10.1093/annonc/mdi077 Expression of survivin and bax/bcl-2 in peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-g
Annals of Oncology Advance Access published January 10, 2005 Original article Annals of Oncology doi:10.1093/annonc/mdi077 Expression of survivin and bax/bcl-2 in peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-g
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Figure S1 Treatment with both Sema6D and Plexin-A1 sirnas induces the phenotype essentially identical to that induced by treatment with Sema6D sirna alone or Plexin-A1 sirna alone. (a,b) The cardiac tube
Figure S1 Treatment with both Sema6D and Plexin-A1 sirnas induces the phenotype essentially identical to that induced by treatment with Sema6D sirna alone or Plexin-A1 sirna alone. (a,b) The cardiac tube
SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S2. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of dnscs.
 Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of anpcs. A panel of lineage-specific markers were used
Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of anpcs. A panel of lineage-specific markers were used
Original Article Artemin promotes proliferation and metastasis in human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(10):10413-10418 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0058793 Original Article Artemin promotes proliferation and metastasis in human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma Chao-Bing
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(10):10413-10418 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0058793 Original Article Artemin promotes proliferation and metastasis in human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma Chao-Bing
Knockdown of Long Noncoding RNA LUCAT1 Inhibits Cell Viability and Invasion by Regulating mir-375 in Glioma
 Oncology Research, Vol. 26, pp. 307 313 0965-0407/18 $90.00 +.00 Printed in the USA. All rights reserved. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3727/096504017x15088061795756 Copyright Ó 2018 Cognizant, LLC. E-ISSN 1555-3906
Oncology Research, Vol. 26, pp. 307 313 0965-0407/18 $90.00 +.00 Printed in the USA. All rights reserved. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3727/096504017x15088061795756 Copyright Ó 2018 Cognizant, LLC. E-ISSN 1555-3906
NNZ-2566 in Rett Syndrome and Autism Spectrum Disorders Role and Update
 NNZ-2566 in Rett Syndrome and Autism Spectrum Disorders Role and Update 1 Overview The natural growth factor IGF-1 is broken down in the body to IGF-1[1-3] NNZ-2566 is an analogue of IGF-1[1-3] developed
NNZ-2566 in Rett Syndrome and Autism Spectrum Disorders Role and Update 1 Overview The natural growth factor IGF-1 is broken down in the body to IGF-1[1-3] NNZ-2566 is an analogue of IGF-1[1-3] developed
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/2/1/ra81/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Delivery of MicroRNA-126 by Apoptotic Bodies Induces CXCL12- Dependent Vascular Protection Alma Zernecke,* Kiril Bidzhekov,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/2/1/ra81/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Delivery of MicroRNA-126 by Apoptotic Bodies Induces CXCL12- Dependent Vascular Protection Alma Zernecke,* Kiril Bidzhekov,
Original Article B7-H3 repression by mir-539 suppresses cell proliferation in human gliomas
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):4363-4369 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0043994 Original Article B7-H3 repression by mir-539 suppresses cell proliferation in human gliomas Rong-Gang Li 1, Zhuo Gao
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):4363-4369 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0043994 Original Article B7-H3 repression by mir-539 suppresses cell proliferation in human gliomas Rong-Gang Li 1, Zhuo Gao
9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Declarative memory conscious,
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Declarative memory conscious,
m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation and tumorigenicity of endometrial cancer
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer
 Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer J. Li 1, Z.J. Song 2, Y.Y. Wang 1, Y. Yin 1, Y. Liu 1 and X. Nan 1 1 Tumor Research Department, Shaanxi Provincial Tumor Hospital,
Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer J. Li 1, Z.J. Song 2, Y.Y. Wang 1, Y. Yin 1, Y. Liu 1 and X. Nan 1 1 Tumor Research Department, Shaanxi Provincial Tumor Hospital,
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 EGFR inhibition activates signaling pathways (a-b) EGFR inhibition activates signaling pathways (a) U251EGFR cells were treated with erlotinib (1µM) for the indicated times followed
Supplementary Figure 1 EGFR inhibition activates signaling pathways (a-b) EGFR inhibition activates signaling pathways (a) U251EGFR cells were treated with erlotinib (1µM) for the indicated times followed
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2607 Figure S1 Elf5 loss promotes EMT in mammary epithelium while Elf5 overexpression inhibits TGFβ induced EMT. (a, c) Different confocal slices through the Z stack image. (b, d) 3D rendering
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2607 Figure S1 Elf5 loss promotes EMT in mammary epithelium while Elf5 overexpression inhibits TGFβ induced EMT. (a, c) Different confocal slices through the Z stack image. (b, d) 3D rendering
