Intranasal drug administration for procedural sedation in children admitted to pediatric Emergency Room
|
|
|
- Oswin Benson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: Intranasal drug administration for procedural sedation in children admitted to pediatric Emergency Room C. FANTACCI 1, G. C. FABRIZIO 1, P. FERRARA 1, F. FRANCESCHI 2, A. CHIARETTI 1 1 Department of Pediatrics, Catholic University of the Sacred Heart, School of Medicine, Gemelli Hospital Foundation, Rome, Italy 2 Institute of Internal Medicine, Catholic University of the Sacred Heart, School of Medicine, Gemelli Hospital Foundation, Rome, Italy Abstract. OBJECTIVE: Pain relief is a very important aspect in Pediatrician s clinical practice. It is often thought that young children, particularly infants, do not perceive as much pain as adults because of their immature nervous system and that untreated pain would not have adverse long-term consequences. Instead, it has been demonstrated that infants and children experience pain in a similar manner to adults. Many factors, particularly emotional factors, can increase the child s pain perception. Children live with anxiety even minor procedures. This suggests the need for an adequate sedation and the way of sedation should be free of pain itself. We believe the route to be followed may be the intranasal (IN) administration of sedative drugs. MATERIALS AND METHODS: We have conducted a brief review of the literature by Pubmed about the most commonly used sedative drugs: sufentanyl, fentanyl, midazolam, ketamine, nitrous oxide and dexmedetomidine. We have investigated in the literature the type of administration of IN drugs: drop instillation or by a mucosal atomizer device (MAD). RESULTS: In our study, it was noted that IN drugs administration is an effective and safe method to reduce anxiety and to deliver analgesia because it is practical and non-invasive. Moreover, therapeutic levels of sedatives are low due to the presence of a rich vascular plexus in the nasal cavity, which communicates with the subarachnoid space via the olfactory nerve and reduce the time of medication delivery, that is, the onset of action. The use of MAD even gives as better bioavailability of drugs. CONCLUSIONS: IN sedation via MAD is effective and safe and should be one of the first choices for procedural sedation in children. Key Words: Intranasal sedation, Procedures, Pain, Children. Introduction Pain relief is a very important aspect in Pediatrician s clinical practice, although it may sometimes be overlooked because pain is often underestimated in childhood. This is due to the common belief that young children, particularly infants, do not perceive as much pain as adults because of their immature nervous system and that untreated pain would not have adverse long-term consequences 1,2. On the contrary, it has been shown that infants and children experience pain in a similar manner to adults 3. Furthermore, high levels of pain in children may have significant neurophysiological and physiological effects 4,5. Inadequately managed pain in children can also have detrimental psychological consequences, which can in turn lead to higher levels of pain during medical treatments. For example, emotional factors such as elevated anxiety, distress, anger and low mood can increase the child s pain perception and make subsequent medical procedures and pain management more difficult 6,7. In addition, a large-scale early researche found that as many as one third of children who experienced medical procedures for diagnosis or treatment showed some evidence of subsequent psychological adjustment problems 8. Moreover, reports of fear and pain experienced during medical procedures in childhood are predictive of fear and pain during medical procedures in young adulthood 9. Children often live with many anxiety and anguish even minor procedures, most notably the placement of a venous access, and even more seizure control, laceration repair, dental and ophthalmologic procedures. Usually, children s fear and anticipatory anxiety increase the likelihood of experiencing more pain and distress during the actual procedures; in addition, children typically report having overly negative expectations prior to medical procedures, regardless of whether a pharmacologic or behavioral pain management intervention will be employed 10. Corresponding Author: Claudia Fantacci, MD; claudiafantacci@yahoo.it 217
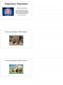
2 C. Fantacci, G.C. Fabrizio, P. Ferrara, F. Franceschi, A. Chiaretti This entails the need to propose not only adequate sedation but also a way of sedation free of pain itself as much as possible 11. The benefits of providing adequate procedural sedation for children include decreasing patient anxiety and emotional trauma, decreasing parental emotional discomfort, and facilitating ease and/or completion of the procedure. A desirable sedating agent has a rapid onset with short duration of action; it is effective and safe 12. In recent years, the use of intranasal (IN) administration of sedative drugs before performing the procedures has taken hold, because it is a practical and non-invasive route of administration. Therapeutic levels of sedatives can be reached via IN administration due to the rich vascular plexus cavity which communicates with the subarachnoid space via the olfactory nerve 13,14. In the recent past many authors preferred IN midazolam administer by drop instillation; nowadays many studies investigate new methods such as the use of spray devices. A mucosal atomizer device (MAD, Figure 1) delivers drug via a fine spray over a broad surface area in the nasal cavity (Figure 2). It also reduces sneezing and coughing compared to other devices Different drugs have been used for IN sedation for procedural sedation in children; this review aims to re-evaluate this method of sedation and the drugs most commonly used for its usage. Figure 1. MAD (Mucosal Atomizer Device). Figure 2. With the use of MAD, the drug is delivered via a fine spray over a broad surface area in the nasal cavity, favoring its absorption. Materials and Methods Relevant studies were identified from two sources: a key word search including intranasal, drugs, sedation, children, medication, sufentanil, fentanyl, midazolam, ketamine, nitrous oxide, dexmedetomidine; a review of the references from each identified article. We included in this review only pediatric articles. Results Ketamine Ketamine is usually administered intravenously (IV) or intramuscularly (IM), but it may also be administered nasally 18. The dose required to achieve a state of dissociative sedation in children is typically 1.0 to 1.5 mg/kg IV or 3 to 4 mg/kg IM 19. When used nasally, the recommended administration dose is 9 mg/kg 18. In 2001, Acworth et al 20 compared IN midazolam vs. ketamine IV plus midazolam IV in children requiring minor procedures, such as laceration repair or foreign body removal, in the ambulatory setting, and concluded that the combination is higher to IN midazolam alone in terms of speed of onset and consistency of effect. In 2013, Nielsen et al 21 studied the association of ketamine with sufentanil administered IN. They did not report any serious adverse events; oxygen saturation and heart rate remained stable. The reported adverse effects were mild and 218
3 IN drug administration for procedural sedation in children admitted to Pediatric Emergency Room mostly related to an unpleasant bitter taste immediately after the administration of the nasal spray, which disappeared after drinking. Midazolam The bioavailability of IN route ranges from 50-83% 22. It can be administered orally, nasally, rectally, IV or IM. In a randomized, double-blind, placebo control study, Shapiro et al 11 showed that midazolam spray offers relief to children anxious about minor medical procedures, such as insertion of a needle in a subcutaneously implanted intravenous port, venous blood sampling and venous cannulation. A double-blind, randomized, controlled trial conducted by Rakaf et al 22 in 2011 reported a success rate of 91% to 100% for completing dental procedures following IN midazolam administration. The dose of intranasal midazolam used in the different studies range between 0.2 mg/ kg and 0.4 mg/kg or 0.5 mg/kg The most common adverse effects reported following IN midazolam are burning or irritation in the nose and a bitter taste in the mouth. It can determine respiratory and circulatory depression, but these side effects are unlikely when midazolam is used as a single drug, while they increase when it is used with opioids or other sedatives. In their work, Lane et al 12 had 1/205 children who received IN administration of midazolam with an adverse event. This was a minor desaturation episode following ketamine administration requiring brief blow by oxygen. They did not find any adverse events in patients who received midazolam alone. Sufentanil Sufentanil has been administered IV, epidural, intrathecal transdermal and nasally. Hronova et al 24 examined children in a randomized study to receive sufentanil vs. placebo. Sufentanil was given as drops and patients that received the drug had less anxiety in 10 min compared to those who were given placebo. Bayrak et al 25 demonstrated that children who received midazolam administration cried more compared with sufentanil administration. Concerning sufentanil, in the past the administration route was by drops, actually many authors prefer MAD for its simplicity and accuracy of dosing. The onset of sufentanil aerosol is about 5-10 min with a maximum sedative and analgesic effect at about min. Doses used for procedural pain was usually µg/ kg. It was demonstrated that the children who received sufentanil had a marked decreased ventilatory compliance during the induction of anesthesia and had a higher incidence of vomiting during the first postoperative day 24. Nitrous Oxide and Fentanyl Seith et al 26 administered a continuous flow of nitrous oxide of 50 to 70% via a full-face mask in association with a pre-calculated dose of 1.5 µg/ kg of IN fentanyl that was administered through MAD A nitrous oxide alone agent has been associated with higher levels of emesis; instead, according to Seith et al 26, the association with IN fentanyl reduces the incidence of vomiting. Fentanyl is an opiate analgesic with the most evidence to support IN route. It is most used for acute pain management like orthopedic fractures or burns because it controls at relatively high doses the pain. Its usage in pediatric patients has shown comparable effectiveness with the IV administration 31. Dexmedetomidine Recently, some Emergency Pediatric Departments have gained a useful experience of this IN medication for short procedures in pediatric outpatient. Intranasal route is more rapidly absorbed in blood stems compared to oral form and it preserves the airway reflexes and respiratory drive 32. Generally, this drug is administered at dose of 2-4 µg/kg. Patel et al 33 described an 11-year-old girl sedated with 2.4 µg/kg of IN dexmedetomidine who reported symptomatic bradycardia precipitating vasovagal syncope. Discussion IN drugs were studied to light procedural sedation and anxiety and their use include laceration repair, MRI, computed tomography scan, burn-dressing changes, dental extractions, endoscopies and accessing central venous port Procedural sedation is now being used in a variety of conditions, both for diagnostic purposes, such as urine sampling and lumbar punctures, and therapeutic purposes, such as intravenous insertion, wound care and orthopedic trauma 37. Each of these medical situations deserves focused research and clinical attention, and each could serve as a referral source for assistance in reducing children s pain and suffering. Health care professionals strive to provide medical treatment while avoiding any undue pain and 219
4 C. Fantacci, G.C. Fabrizio, P. Ferrara, F. Franceschi, A. Chiaretti suffering by the patient. Children almost always have fear even of minor procedures and their pain relief is important both for their comfort and for the success of the procedure. Furthermore, we have to consider that children who have experienced procedural pain are more likely to have increased pain during future painful procedures 10. It can be often difficult even the use of an intravenous sedation as it involves the use of needles. For that reason, in recent years the use of the IN route is becoming more widespread as it is essentially painless and effective. In fact, without the need of finding a venous access, it allows a rapid absorption through nasal mucosa directly into the systemic circulation, avoiding fist-pass metabolism 18. Successful IN medication delivery requires a basic understanding of delivery techniques that include minimizing drug volume and maximizing drug concentration with adequate dose of drug, with the usage of both nostrils to double the absorptive mucosal surface, with the use of MAD to enhance medication absorption 35. Talon et al 32 and Pandey et al 38 compare the use of MAD with droplets in the nasal cavity. It was noted that drops into the nose are primarily deposited on the ciliary surface with excess runoff down the throat. In comparison, atomized particles cover more surface area and they are better distributed into the nasal mucosa, resulting in better bioavailability 39. The advantages of atomized delivery include less drug being lost to the oropharynx, higher cerebrospinal fluid drug levels, better patient acceptability and improved sedative effects 38,40. IN midazolam is the most commonly studied although there are many data also about fentanyl, ketamine, and sufentanil. Atomized IN midazolam and ketamine are useful also to make gastric aspirates more acceptable and easy to perform in children 41. Midazolam at dose route of mg/kg was demonstrated to have advantageous properties like amnesia and anxiety 12,15. Sufentanil and nitrous oxide have a similar action of midazolam; in fact, these drugs do not control the pain but they have a sedation effect 24. On the contrary, ketamine and fentanyl are used for their pain controlling action at the administration dose of respectively 5-9 mg/kg and µg/kg (Table I) 18. In literature, many authors recommend the usage of IN drugs in children to low adverse effects; in fact at recommended doses these drugs are effective and safe 33. Recently, there is growing interest in the use of IN dexmedetomidine and several studies are showing its valuable utility for pediatric sedation in the Emergency Room Conclusions IN drug administration is an effective method for delivering analgesia; in fact, it can reduce the time of medication delivery, the onset of action, the pain due to the injection, and patients and parents anxiety. This review has shown that the use of these drugs is effective and safe if they are administered by personnel with expertise and equipment necessary to monitor patients during and after administration (Table II). Therefore, we believe these drugs may be inserted in standard protocols to an adequate use in pediatric Emergency Department. Conflict of Interest The Authors declare that they have no conflict of interests. Table I. Drug characteristics for intranasal administration or inhalation. Drug Dose Characteristics Ketamine 5-9 mg/kg Pain control like laceration repair. No serious side effects Midazolam mg/kg Sedation. Adverse event is burning o irritation of mucosa Sufentanil µg/kg Sedation. Decreased ventilatory compliance and increased vomiting Nitrous oxide Continous flow of 0-70% with Sedation. Increased vomiting mask Fentanyl µg/kg Pain control like orthopedic fractures. No serious side effects Dexmedetomidine µg/kg Sedation. Symptomatic bradycardia 220
5 IN drug administration for procedural sedation in children admitted to Pediatric Emergency Room Table II. Comparison of the main literature. References Drug Conclusions Acworth et al 20 Intranasal midazolam The combination is higher vs. intravenous ketamine with intravenous midazolam Nielsen et al 21 Ketamine with sufentanil Good level of sedation without serious administered intranasally adverse effects Shapiro et al 11 Intranasal midazolam Good effectiveness in minor procedures Rakaf et al 22 Intranasal midazolam Good effectiveness in dental procedures Lane et al 12 Intranasal midazolam spray Good effectiveness in minor procedures in Pediatric Emergency Department Hronova et al 24 Sufentanil intranasal drops Reduced anxiety compared to placebo Bayrak et al 25 Midazolam vs. sufentanil Sufentanil was more effective than midazolam in reducing babies crying Borland et al 31 Intranasal fentanyl Intranasal fentanyl is an effective vs. intravenous morphine analgesic in children with an acute fracture References 1) Birnie KA, Chambers CT, Fernandez CV, Forgeron PA, Latimer MA, McGrath PJ, Cummings EA, Finley GA. Hospitalized children continue to report undertreated and preventable pain. Pain Res Manag 2014; 19: ) Young VB. Effective management of pain and anxiety for the pediatric patient in the Emergency Department. Crit Care Nurs Clin North Am 2017; 29: ) Manocha S, Taneja N. Assessment of paediatric pain: a critical review. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 2016; 27: ) Weingarten L, Kircher J, Drendel AL, Newton AS, Ali S. A Survey of children s perspectives on pain management in the Emergency Department. J Emerg Med 2014; 47: ) Chiaretti A, Pierri F, Valentini P, Russo I, Gargiullo L, Riccardi R. Current practice and recent advances in pediatric pain management. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2013; 17: ) Oliveira NC, Santos JL, Linhares MB. Audiovisual distraction for pain relief in paediatric inpatients: a crossover study. Eur J Pain 2017; 21: ) Dufresne A, Dugas MA, Samson Y, Barré P, Turcot L, Marc I. Do children undergoing cancer procedures under pharmacological sedation still report pain and anxiety? A preliminary study. Pain Med 2010; 11: ) Davies R, Butler N, Goldstein H. From birth to seven: the second report of the National Child Development Study (1958 Cohort). London: National Children s Bureau ) Valeri BO, Ranger M, Chau CM, Cepeda IL, Synnes A, Linhares MB, Grunau RE. Neonatal invasive procedures predict pain intensity at school age in children born very preterm. Clin J Pain 2016; 32: ) Duchicela SI, Meltzer JA, Cunningham SJ. A randomized controlled study in reducing procedural pain and anxiety using high concentration nitrous oxide. Am J Emerg Med 2017 May 1. pii: S (17) doi: /j. ajem [Epub ahead of print] 11) Shapiro F, Athiraman U, Clendenin DJ, Hoagland M, Sethna NF. Anesthetic management of 877 pediatric patients undergoing muscle biopsy for neuromuscular disorders: a 20-year review. Pediatr Anaesth 2016; 26: ) Lane RD, Achunk JE. Atomized intranasal midazolam use for minor procedures in the pediatric emergency department. Pediatr Emerg Care 2008; 24: ) Conway A, Rolley J, Sutherland JR. Midazolam for sedation before procedures. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2016;(5):CD ) Luwagen P, Johansson BB, Nordborg C. The nasal route of cerebrospinal fluid drainage in man. A light-microscope study. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 1994; 20: ) Chiaretti A, Barone G, Rigante D, Ruggiero A, Pierri F, Barbi E, Barone G, Riccardi R. Intranasal lidocaine and midazolam for procedural sedation in children. Arch Dis Child 2011; 96: ) Inthavong K, Fung MC, Yang W, Tu J. Measurements of droplet size distribution and analysis of nasal spray atomization from different actuation pressure. J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv 2015; 28: ) Xue FS, Yang QY, Liao X, Liu JH, Tong SY. Topical anesthesia of the airway using fibreoptic bronchoscope and the MADgic atomizer in patients with predicted difficult intubation. Can J Anesth 2007; 54: ) Poonai N, Canton K, Ali S, Hendrikx S, Shah A, Miller M, Joubert G, Rieder M, Hartling L. Intranasal ketamine for procedural sedation and analgesia in children: a systematic review. PLoS One 2017; 12: e
6 C. Fantacci, G.C. Fabrizio, P. Ferrara, F. Franceschi, A. Chiaretti 19) Green SM, Roback MG, Kennedy RM, Krauss B. Clinical practice guideline for emergency department ketamine dissociative sedation: 2011 update. Ann Emerg Med 2011; 57: ) Acworth JP, Purdie D, Clark RC. Intravenous ketamine plus midazolam is superior to intranasal midazolam for emergency pediatric procedural sedation. Emerg Med J 2001; 18: ) Nielsen B, Friis S, Romsing J, Schmiegelow K, Anderson BJ, Ferreirós N, Labocha S, Henneberg SW. Intranasal sufentanil/ketamine analgesia in children. Paediatr Anaesth 2013; 24: ) Rakaf AL, Bello LL, Turkustani A, Adenubi JO. Intranasal midazolam in conscious sedation of young paediatric dental patients. Int J Paediatr Dent 2001; 11: ) Lundeberg S, Roelofse JA. Aspects of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of sufentanil in pediatric practice. Paediatr Anaesth 2011; 21: ) Hronova K, Pokorna P, Posch L, Stanar O. Sufentanil and Midazolam dosing and pharmacogenetic factors in pediatric analgosedation and withdrawal syndrome. Physiol Res 2016; 65: S463-S ) Bayrak F, Gunday I, Memis D, Turan A. A comparison of oral midazolam, oral tramadol, and intranasal sufentanil premedication in pediatric patients. J Opioid Manag 2007; 3: ) Seith RW, Theophilos T, Babl FE. Intranasal fentanyl and high-concentration inhaled nitrous oxide for procedural sedation: a prospective observational pilot study of adverse events and depth of sedation. Acad Emerg Med 2012; 19: ) Babl FE, Oakley E, Seaman C, Barnett P, Sharwood LN. High-concentration nitrous oxide for procedural sedation in children: adverse events and depth of sedation. Pediatrics 2008; 121: ) Herd D, Borland M. Intranasal fentanyl pediatric clinical practice guidelines. Emerg Med Australas 2009; 21: ) Crellin D, Ling RX, Babl FE. Does the standard intravenous solution of fentanyl (50 mcg/ml) administered intranasally have analgesic efficacy? Emerg Med Australas 2010; 22: ) Finn M, Harris D. Intranasal fentanyl for analgesia in the pediatric emergency department. Emerg Med J 2010; 27: ) Borland M, Jacobs I, King B, O Brien D. A randomized controlled trial comparing intranasal fentanyl to intravenous morphine for managing acute pain in children in the emergency department. Ann Emerg Med 2007; 49: ) Talon MD, Woodson LC, Sherwood ER, Aarsland A, McRae L, Benham T. Intranasal dexmedetomidine premedication is comparable with midazolam in burn children undergoing reconstructive surgery. J Burn Care Res 2009; 30: ) Patel VJ, Ahmed SS, Nitu ME, Rigby MR. Vasovagal syncope and severe bradycardia following intranasal dexmedetomidine for pediatric procedural sedation. Paediatr Anaesth 2014; 24: ) Tan JA, Ho KM. Use of dexmedetomidine as a sedative and analgesic agent in critically ill adult patients: a meta-analysis. Intensive Care Med 2010; 36: ) Wolfe TR, Braude DA. Intranasal mediaction delivery for children: a brief review and update. Pediatrics 2010; 126: ) Merkitarian Filho E, Robinson F, de Carvalho WB, Gilio AE, Mason KP. Intranasal dexmedetomidine for sedation for pediatric computed tomography imaging. J Pedaitr 2015; 165: ) Borland M, Esson A, Babl F, Krieser D. Procedural sedation in children in the emergency department: a predict study. Emerg Med Australas 2009; 21: ) Pandey RK, Bahetwar SK, Saksena AK, Chandra G. A comparative evaluation of drop vs. atomized administration of intranasal ketamine for procedural sedation of young uncooperative pediatric dental patients: a prosepective crossover. J Clin Pediatr Dent 2011; 36: ) Waarington SE, Kunn RJ. Use of intranasal medications in pediatric patients. Orthopedics 2011; 34: ) Primosch RE, Guelmann M. Comparison of drops vs. spray administration of intranasal midazolam in two and three year-old children for dental sedation. Pediatr Dent 2005; 27: ) Buonsenso D, Barone G, Valentini P, Pierri F, Riccardi R, Chiaretti A. Utility of intranasal ketamine and midazolam to perform gastric aspirates in children: a double-blind, placebo controlled, randomized study. BMC Pediatr 2014; 14: ) Ghai B, Jain K, Saxena AK, Bhatia N, Sodhi KS. Comparison of oral midazolam with intransal dexmedetomidine premedication for children undergoing CT imaging: a randomized, double-blind, and controlled study. Paedaitr Anaesth 2017; 27: ) Yuen VM, Hui TW, Irwin MG, Yuen MK. A comparison of intranasal dexmedetomidine and oral midazolam for premedication in pediatric anesthesia: a double-blinded randomized controlled trial. Anesth Analg 2008; 106:
Intranasal (IN) Medication Administration MBED Clinical Practice Guideline
 Intranasal (IN) Medication Administration MBED Clinical Practice Guideline Purpose and Indications: Intranasal administration of medications can be used to achieve rapid sedation/anxiolysis, pain control,
Intranasal (IN) Medication Administration MBED Clinical Practice Guideline Purpose and Indications: Intranasal administration of medications can be used to achieve rapid sedation/anxiolysis, pain control,
Subspecialty Rotation: Anesthesia
 Subspecialty Rotation: Anesthesia Faculty: John Heaton, M.D. GOAL: Maintenance of Airway Patency and Oxygenation. Recognize and manage upper airway obstruction and desaturation. Recognize and manage upper
Subspecialty Rotation: Anesthesia Faculty: John Heaton, M.D. GOAL: Maintenance of Airway Patency and Oxygenation. Recognize and manage upper airway obstruction and desaturation. Recognize and manage upper
Preoperative Anxiety
 Alyssa Brzenski Case You are called by a parent of a child who you took care of a week and a half ago. The child, a 4 year old boy, came to IR for the first of many sclerotherapy of a Venous Malformation
Alyssa Brzenski Case You are called by a parent of a child who you took care of a week and a half ago. The child, a 4 year old boy, came to IR for the first of many sclerotherapy of a Venous Malformation
CLINICAL POLICY FOR THE USE OF INTRANASAL DIAMORPHINE FOR ANALGESIA IN CHILDREN ATTENDING THE PAEDIATRIC EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT, SASH
 CLINICAL POLICY FOR THE USE OF INTRANASAL DIAMORPHINE FOR ANALGESIA IN CHILDREN ATTENDING THE PAEDIATRIC EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT, SASH Background Adequate analgesia is a vital aspect of early management of
CLINICAL POLICY FOR THE USE OF INTRANASAL DIAMORPHINE FOR ANALGESIA IN CHILDREN ATTENDING THE PAEDIATRIC EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT, SASH Background Adequate analgesia is a vital aspect of early management of
Administrating Medications with the MAD Device
 Disclosures Administrating Medications with the MAD Device Nothing to disclose 2015 VSHP Spring Seminar April 18, 2015 Megan Davis Hoesly, PharmD, BCPS Sentara Virginia Beach General Hospital Clinical
Disclosures Administrating Medications with the MAD Device Nothing to disclose 2015 VSHP Spring Seminar April 18, 2015 Megan Davis Hoesly, PharmD, BCPS Sentara Virginia Beach General Hospital Clinical
Results of a one-year, retrospective medication use evaluation. Joseph Ladd, PharmD PGY-1 Pharmacy Resident BHSF Homestead Hospital
 Results of a one-year, retrospective medication use evaluation Joseph Ladd, PharmD PGY-1 Pharmacy Resident BHSF Homestead Hospital Briefly review ketamine s history, mechanism of action, and unique properties
Results of a one-year, retrospective medication use evaluation Joseph Ladd, PharmD PGY-1 Pharmacy Resident BHSF Homestead Hospital Briefly review ketamine s history, mechanism of action, and unique properties
SEDATION FOR SMALL PROCEDURES
 SEDATION FOR SMALL PROCEDURES Sinno Simons Erasmus MC Sophia Children s Hospital Rotterdam, the Netherlands s.simons@erasmusmc.nl SEDATION in newborns How and when How to evaluate How to dose Why to use
SEDATION FOR SMALL PROCEDURES Sinno Simons Erasmus MC Sophia Children s Hospital Rotterdam, the Netherlands s.simons@erasmusmc.nl SEDATION in newborns How and when How to evaluate How to dose Why to use
CHILDREN S SERVICES. Trust Medicines Policy and Procedures Paediatric Pain Assessment Chart
 CHILDREN S SERVICES POLICY AND PROCEDURE FOR THE ADMINISTRATION OF INTRANASAL DIAMORPHINE VIA SYRINGE OR ATOMIZER FOR PAEDIATRIC ANALGESIA IN PAEDIATRIC A&E See also: Trust Medicines Policy and Procedures
CHILDREN S SERVICES POLICY AND PROCEDURE FOR THE ADMINISTRATION OF INTRANASAL DIAMORPHINE VIA SYRINGE OR ATOMIZER FOR PAEDIATRIC ANALGESIA IN PAEDIATRIC A&E See also: Trust Medicines Policy and Procedures
Pharmacological methods of behaviour management
 Pharmacological methods of behaviour management Pharmacological methods CONCIOUS SEDATION?? Sedation is the use of a mild sedative (calming drug) to manage special needs or anxiety while a child receives
Pharmacological methods of behaviour management Pharmacological methods CONCIOUS SEDATION?? Sedation is the use of a mild sedative (calming drug) to manage special needs or anxiety while a child receives
MEDICAL ADVISORY COUNCIL Position Statement PREHOSPITAL PAIN MANAGEMENT
 MEDICAL ADVISORY COUNCIL Position Statement PREHOSPITAL PAIN MANAGEMENT MAC PS 2013-002 Appropriate treatment of acute pain in the prehospital arena offers an opportunity to positively impact many patients.
MEDICAL ADVISORY COUNCIL Position Statement PREHOSPITAL PAIN MANAGEMENT MAC PS 2013-002 Appropriate treatment of acute pain in the prehospital arena offers an opportunity to positively impact many patients.
Analgesic-Sedatives Drug Dose Onset
 Table 4. Commonly used medications in procedural sedation and analgesia Analgesic-Sedatives Fentanyl Morphine IV: 1-2 mcg/kg Titrate 1 mcg/kg q3-5 minutes prn IN: 2 mcg/kg Nebulized: 3 mcg/kg IV: 0.05-0.15
Table 4. Commonly used medications in procedural sedation and analgesia Analgesic-Sedatives Fentanyl Morphine IV: 1-2 mcg/kg Titrate 1 mcg/kg q3-5 minutes prn IN: 2 mcg/kg Nebulized: 3 mcg/kg IV: 0.05-0.15
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF ORAL MIDAZOLAM, ORAL KETAMINE AND THEIR COMBINATION AS PREMEDICATION IN PEDIATRIC CARDIAC SURGERY
 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF ORAL MIDAZOLAM, ORAL KETAMINE AND THEIR COMBINATION AS PREMEDICATION IN PEDIATRIC CARDIAC SURGERY Shah R.B 1, Patel R.D 1, Patel J.J 2, Mishra A.A 3, Thosani R.M 1. U N Mehta Institute
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF ORAL MIDAZOLAM, ORAL KETAMINE AND THEIR COMBINATION AS PREMEDICATION IN PEDIATRIC CARDIAC SURGERY Shah R.B 1, Patel R.D 1, Patel J.J 2, Mishra A.A 3, Thosani R.M 1. U N Mehta Institute
Series 2 dexmedetomidine, tramadol, fentanyl, intellectually disabled patients:
 Series 2 dexmedetomidine, tramadol, fentanyl, intellectually disabled patients: Read the following published scientific articles and answer the questions at the end: Abstract We get a substantial number
Series 2 dexmedetomidine, tramadol, fentanyl, intellectually disabled patients: Read the following published scientific articles and answer the questions at the end: Abstract We get a substantial number
Awake regional versus general anesthesia in preterms and ex-preterm infants for herniotomy
 Awake regional versus general anesthesia in preterms and ex-preterm infants for herniotomy Department of Anaesthesia University Children s Hospital Zurich Switzerland Epidemiology Herniotomy needed in
Awake regional versus general anesthesia in preterms and ex-preterm infants for herniotomy Department of Anaesthesia University Children s Hospital Zurich Switzerland Epidemiology Herniotomy needed in
Top 5 things you need to know about pediatric procedural sedation
 Top 5 things you need to know about pediatric procedural sedation Dr. Marc N. Francis MD, FRCPC ACH/FMC Emergency Physician Clinical Lecturer University of Calgary Assistant Program Director FRCPC-EM STARS
Top 5 things you need to know about pediatric procedural sedation Dr. Marc N. Francis MD, FRCPC ACH/FMC Emergency Physician Clinical Lecturer University of Calgary Assistant Program Director FRCPC-EM STARS
New Methods for Analgesia Delivery
 New Methods for Analgesia Delivery Guy Ludbrook MBBS PhD FANZCA Royal Adelaide Hospital and University of Adelaide South Australia Anesthesiology is on the verge of a major evolution that will involve
New Methods for Analgesia Delivery Guy Ludbrook MBBS PhD FANZCA Royal Adelaide Hospital and University of Adelaide South Australia Anesthesiology is on the verge of a major evolution that will involve
Optimal sedation and management of anxiety in patients undergoing endobronchial ultrasound (EBUS)
 Optimal sedation and management of anxiety in patients undergoing endobronchial ultrasound (EBUS) Georgios Dadoudis Anesthesiologist ICU DIRECTOR INTERBALKAN MEDICAL CENTER Optimal performance requires:
Optimal sedation and management of anxiety in patients undergoing endobronchial ultrasound (EBUS) Georgios Dadoudis Anesthesiologist ICU DIRECTOR INTERBALKAN MEDICAL CENTER Optimal performance requires:
Conscious sedation in children
 Michael Sury FRCA PhD Matrix reference 2D06, 3A07, 3D00 Key points Effective sedation techniques are specific to the procedure. Conscious sedation in children can be time-consuming but may save anaesthesia
Michael Sury FRCA PhD Matrix reference 2D06, 3A07, 3D00 Key points Effective sedation techniques are specific to the procedure. Conscious sedation in children can be time-consuming but may save anaesthesia
Title: Nasal Midazolam for Sedation in Pediatric Patients Prior to Invasive Procedures: Clinical Safety and Effectiveness
 Title: Nasal Midazolam for Sedation in Pediatric Patients Prior to Invasive Procedures: Clinical Safety and Effectiveness Date: 19 March 2008 Context and policy issues: Midazolam is a benzodiazepine 1
Title: Nasal Midazolam for Sedation in Pediatric Patients Prior to Invasive Procedures: Clinical Safety and Effectiveness Date: 19 March 2008 Context and policy issues: Midazolam is a benzodiazepine 1
Intranasal Medications
 Intranasal Medications Mike Harlos MD, CCFP, FCFP Professor and Section Head, Palliative Medicine, University of Manitoba Medical Director, WRHA Adult and Pediatric Palliative Care The presenter has no
Intranasal Medications Mike Harlos MD, CCFP, FCFP Professor and Section Head, Palliative Medicine, University of Manitoba Medical Director, WRHA Adult and Pediatric Palliative Care The presenter has no
2008 EAGLES PRESENTATION. Intranasal Versed Usage in an Urban Fire Based EMS System: PARAMEDIC PERCEPTION OF UTILITY
 2008 EAGLES PRESENTATION Intranasal Versed Usage in an Urban Fire Based EMS System: PARAMEDIC PERCEPTION OF UTILITY CFD EMS OVERVIEW CFD EMS OVERVIEW CFD EMS OVERVIEW All ALS EMS System Two EMT-Ps on each
2008 EAGLES PRESENTATION Intranasal Versed Usage in an Urban Fire Based EMS System: PARAMEDIC PERCEPTION OF UTILITY CFD EMS OVERVIEW CFD EMS OVERVIEW CFD EMS OVERVIEW All ALS EMS System Two EMT-Ps on each
Aspects of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of sufentanil in pediatric practice
 Pediatric Anesthesia ISSN 1155-5645 REVIEW ARTICLE Aspects of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of sufentanil in pediatric practice Stefan Lundeberg 1 & James A. Roelofse 2,3 1 Department of Pediatric
Pediatric Anesthesia ISSN 1155-5645 REVIEW ARTICLE Aspects of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of sufentanil in pediatric practice Stefan Lundeberg 1 & James A. Roelofse 2,3 1 Department of Pediatric
May 2013 Anesthetics SLOs Page 1 of 5
 May 2013 Anesthetics SLOs Page 1 of 5 1. A client is having a scalp laceration sutured and is to be given Lidocaine that contains Epinephrine. The nurse knows that this combination is desgined to: A. Cause
May 2013 Anesthetics SLOs Page 1 of 5 1. A client is having a scalp laceration sutured and is to be given Lidocaine that contains Epinephrine. The nurse knows that this combination is desgined to: A. Cause
Pediatric Procedural Sedation
 Pediatric Procedural Sedation Case 1: 2 year old complex facial laceration Judith R. Klein, MD, FACEP Assistant Professor of Emergency Medicine UCSF-SFGH Department of Emergency Medicine Objectives: The
Pediatric Procedural Sedation Case 1: 2 year old complex facial laceration Judith R. Klein, MD, FACEP Assistant Professor of Emergency Medicine UCSF-SFGH Department of Emergency Medicine Objectives: The
Sedation in Children
 CHILDREN S SERVICES Sedation in Children See text for full explanation and drug doses Patient for Sedation Appropriate staffing Resuscitation equipment available Monitoring equipment Patient suitability
CHILDREN S SERVICES Sedation in Children See text for full explanation and drug doses Patient for Sedation Appropriate staffing Resuscitation equipment available Monitoring equipment Patient suitability
BRITISH ASSOCIATION FOR EMERGENCY MEDICINE Registered Charity No
 BRITISH ASSOCIATION FOR EMERGENCY MEDICINE Registered Charity No 273876 AT THE ROYAL COLLEGE OF SURGEONS OF ENGLAND 35-43 LINCOLN'S INN FIELDS, LONDON, WC2A 3PE, UNITED KINGDOM Telephone: +44 (0)20 7831
BRITISH ASSOCIATION FOR EMERGENCY MEDICINE Registered Charity No 273876 AT THE ROYAL COLLEGE OF SURGEONS OF ENGLAND 35-43 LINCOLN'S INN FIELDS, LONDON, WC2A 3PE, UNITED KINGDOM Telephone: +44 (0)20 7831
Paediatric Premedication: A Comparison of Sublingual Buprenorphine and Midazolam in Children (4-10 Years) Scheduled for Adenotonsillectomy
 0000-0000/02/11-12-16 IRANIAN JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY & THERAPEUTICS Copyright 2002 by Razi Institute for Drug Research (RIDR) IJPT 1:12-16, 2002 Paediatric Premedication: A Comparison of Sublingual Buprenorphine
0000-0000/02/11-12-16 IRANIAN JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY & THERAPEUTICS Copyright 2002 by Razi Institute for Drug Research (RIDR) IJPT 1:12-16, 2002 Paediatric Premedication: A Comparison of Sublingual Buprenorphine
revision Nov 2011 Andrew Triebwasser Department of Anesthesiology Hasbro Children s Hospital
 revision Nov 2011 Andrew Triebwasser Department of Anesthesiology Hasbro Children s Hospital safety efficiency acceptance outcome evaluation and preparation decision to use premedication involvement of
revision Nov 2011 Andrew Triebwasser Department of Anesthesiology Hasbro Children s Hospital safety efficiency acceptance outcome evaluation and preparation decision to use premedication involvement of
Chapter 7, Medication Administration Part 1 Principles and Routes of Medication Administration Caution: Administering medications is business Always
 1 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Chapter 7, Medication Administration Part 1 Principles and Routes of Medication Administration Caution: Administering medications is business Always take appropriate Standard measures
1 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Chapter 7, Medication Administration Part 1 Principles and Routes of Medication Administration Caution: Administering medications is business Always take appropriate Standard measures
Oral Midazolam for Premedication in Children Undergoing Various Elective Surgical procedures
 Oral Midazolam for Premedication in Children Undergoing Various Elective Surgical procedures E-mail gauripanjabi@yahoo.co.in 1 st Author:. Dr Panjabi Gauri M., M.D., D.A., Senior Assistant professor. 2
Oral Midazolam for Premedication in Children Undergoing Various Elective Surgical procedures E-mail gauripanjabi@yahoo.co.in 1 st Author:. Dr Panjabi Gauri M., M.D., D.A., Senior Assistant professor. 2
Ketofol: risky or revolutionary: CPD article IV
 Ketofol: risky or revolutionary: CPD article IV Abstract Ketofol, a sedative/analgesic combination of ketamine and propofol, which can be administered as a mixture in the same syringe or independently,
Ketofol: risky or revolutionary: CPD article IV Abstract Ketofol, a sedative/analgesic combination of ketamine and propofol, which can be administered as a mixture in the same syringe or independently,
Procedural Sedation. Conscious Sedation AAP Sedation Guidelines: Disclosures. What does it mean for my practice? We have no disclosures
 2016 AAP Sedation Guidelines: What does it mean for my practice? Amber P. Rogers MD FAAP Assistant Professor of Section of Hospital Medicine and Anesthesiology Corrie E. Chumpitazi MD FAAP FACEP Assistant
2016 AAP Sedation Guidelines: What does it mean for my practice? Amber P. Rogers MD FAAP Assistant Professor of Section of Hospital Medicine and Anesthesiology Corrie E. Chumpitazi MD FAAP FACEP Assistant
Sedation in children and young people. Appendix J. Sedation for diagnostic and therapeutic procedures in children and young people
 SEDATION IN CHILDREN AND YOUNG PEOPLE 1 Sedation in children and young people Sedation for diagnostic and therapeutic procedures in children and young people Appendix J 2 SEDATION IN CHILDREN AND YOUNG
SEDATION IN CHILDREN AND YOUNG PEOPLE 1 Sedation in children and young people Sedation for diagnostic and therapeutic procedures in children and young people Appendix J 2 SEDATION IN CHILDREN AND YOUNG
DEEP SEDATION TEST QUESTIONS
 Mailing Address: Phone: Fax: The Study Guide is provided for those physicians eligible to apply for Deep Sedation privileges. The Study Guide is approximately 41 pages, so you may consider printing only
Mailing Address: Phone: Fax: The Study Guide is provided for those physicians eligible to apply for Deep Sedation privileges. The Study Guide is approximately 41 pages, so you may consider printing only
Acute Pain Management in Children an update
 Acute Pain Management in Children an update Frances W. Craig, MD FAAP East Tennessee Children s Hospital Overview Some pain basics Why we don t treat pain and why we should Non pharmacologic approaches
Acute Pain Management in Children an update Frances W. Craig, MD FAAP East Tennessee Children s Hospital Overview Some pain basics Why we don t treat pain and why we should Non pharmacologic approaches
Pain & Sedation Management in PICU. Marut Chantra, M.D.
 Pain & Sedation Management in PICU Marut Chantra, M.D. Pain Diseases Trauma Procedures Rogers Textbook of Pediatric Intensive Care, 5 th ed, 2015 Emotional Distress Separation from parents Unfamiliar
Pain & Sedation Management in PICU Marut Chantra, M.D. Pain Diseases Trauma Procedures Rogers Textbook of Pediatric Intensive Care, 5 th ed, 2015 Emotional Distress Separation from parents Unfamiliar
PREANAESTHETIC MEDICATION WITH DIFFERENT DOSES OF INTRANASAL MIDAZOLAM: A RANDOMIZED CLINICAL STUDY IN CHILDREN
 RESEARCH ARTICLE PREANAESTHETIC MEDICATION WITH DIFFERENT DOSES OF INTRANASAL MIDAZOLAM: A RANDOMIZED CLINICAL STUDY IN CHILDREN Mukesh Somvanshi 1, *, Archana Tripathi 2, Anil Rajoriya 3 1 Associate Professor,
RESEARCH ARTICLE PREANAESTHETIC MEDICATION WITH DIFFERENT DOSES OF INTRANASAL MIDAZOLAM: A RANDOMIZED CLINICAL STUDY IN CHILDREN Mukesh Somvanshi 1, *, Archana Tripathi 2, Anil Rajoriya 3 1 Associate Professor,
MD (Anaesthesiology) Title (Plan of Thesis) (Session )
 S.No. 1. To study the occurrence of postoperative hyponatremia in paediatric patients under 2 years of age 2. Influence of timing of intravenous fluid therapy on maternal hemodynamics in patients undergoing
S.No. 1. To study the occurrence of postoperative hyponatremia in paediatric patients under 2 years of age 2. Influence of timing of intravenous fluid therapy on maternal hemodynamics in patients undergoing
Mythbusters: No Pain, No Gain Managing Painful Pediatric Procedures. Vicki L. Sakata, MD
 Mythbusters: No Pain, No Gain Managing Painful Pediatric Procedures Vicki L. Sakata, MD Objectives Identify myths regarding pediatric pain perception. Identify proper use and dosages of intranasal fentanyl
Mythbusters: No Pain, No Gain Managing Painful Pediatric Procedures Vicki L. Sakata, MD Objectives Identify myths regarding pediatric pain perception. Identify proper use and dosages of intranasal fentanyl
DISCLOSURES. Learning goals 19/09/2013 PEDIATRIC ACUTE PAIN MANAGEMENT. No financial investment in the material or medications presented
 PEDIATRIC ACUTE PAIN MANAGEMENT Dr. Samina Ali, MDCM, FRCPC(PEM) Associate Professor Departments of Pediatrics & Emergency Medicine University of Alberta September 2013 DISCLOSURES No financial investment
PEDIATRIC ACUTE PAIN MANAGEMENT Dr. Samina Ali, MDCM, FRCPC(PEM) Associate Professor Departments of Pediatrics & Emergency Medicine University of Alberta September 2013 DISCLOSURES No financial investment
PEDIATRIC ANALGESIA AND SEDATION DRUG MANUAL
 PEDIATRIC ANALGESIA AND SEDATION DRUG MANUAL HARBOR-UCLA MEDICAL CENTER PEDIATRIC ANALGESIA AND SEDATION DRUG MANUAL SECTION Preface Disclaimer Nonpharmacologic Methods Table of Contents PAGE i ii iii
PEDIATRIC ANALGESIA AND SEDATION DRUG MANUAL HARBOR-UCLA MEDICAL CENTER PEDIATRIC ANALGESIA AND SEDATION DRUG MANUAL SECTION Preface Disclaimer Nonpharmacologic Methods Table of Contents PAGE i ii iii
James J. Mooney * and Ashley McDonell ** Introduction
 Opioid Administration as Predictor of Pediatric Epidural Failure James J. Mooney * and Ashley McDonell ** Background: Increasing use of regional analgesia in pediatric populations requires a better understanding
Opioid Administration as Predictor of Pediatric Epidural Failure James J. Mooney * and Ashley McDonell ** Background: Increasing use of regional analgesia in pediatric populations requires a better understanding
Ali Mohammadshahi 1, Ali Omraninava 1 *, Amir Masoud Hashemian 2 and Mohammad Mehdi Forouzanfar 3
 BIOSCIENCES BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH ASIA, August 2014. Vol. 11(2), 993-997 Comparission Between Midazolam and Midazolam Plus Diphenhydramine Efficacy of Sedation in Children Undergoing CT-scan admitted
BIOSCIENCES BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH ASIA, August 2014. Vol. 11(2), 993-997 Comparission Between Midazolam and Midazolam Plus Diphenhydramine Efficacy of Sedation in Children Undergoing CT-scan admitted
Comparison of Ease of Insertion and Hemodynamic Response to Lma with Propofol and Thiopentone.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 12 Ver. IV (Dec. 2015), PP 22-30 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison of Ease of Insertion and Hemodynamic
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 12 Ver. IV (Dec. 2015), PP 22-30 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison of Ease of Insertion and Hemodynamic
SEEING KETAMINE IN A NEW LIGHT
 SEEING KETAMINE IN A NEW LIGHT BobbieJean Sweitzer, M.D., FACP Professor of Anesthesiology Director of Perioperative Medicine Northwestern University Bobbie.Sweitzer@northwestern.edu LEARNING OBJECTIVES
SEEING KETAMINE IN A NEW LIGHT BobbieJean Sweitzer, M.D., FACP Professor of Anesthesiology Director of Perioperative Medicine Northwestern University Bobbie.Sweitzer@northwestern.edu LEARNING OBJECTIVES
MD (Anaesthesiology) Title (Plan of Thesis) (Session )
 S.No. 1. COMPARATIVE STUDY OF CENTRAL VENOUS CANNULATION USING ULTRASOUND GUIDANCE VERSUS LANDMARK TECHNIQUE IN PAEDIATRIC CARDIAC PATIENT. 2. TO EVALUATE THE ABILITY OF SVV OBTAINED BY VIGILEO-FLO TRAC
S.No. 1. COMPARATIVE STUDY OF CENTRAL VENOUS CANNULATION USING ULTRASOUND GUIDANCE VERSUS LANDMARK TECHNIQUE IN PAEDIATRIC CARDIAC PATIENT. 2. TO EVALUATE THE ABILITY OF SVV OBTAINED BY VIGILEO-FLO TRAC
Date 8/95; Rev.12/97; 7/98; 2/99; 5/01, 3/03, 9/03; 5/04; 8/05; 3/07; 10/08; 10/09; 10/10 Manual of Administrative Policy Source Sedation Committee
 Code No. 711 Section Subject Moderate Sedation (formerly termed Conscious Sedation ) Date 8/95; Rev.12/97; 7/98; 2/99; 5/01, 3/03, 9/03; 5/04; 8/05; 3/07; 10/08; Manual of Administrative Policy Source
Code No. 711 Section Subject Moderate Sedation (formerly termed Conscious Sedation ) Date 8/95; Rev.12/97; 7/98; 2/99; 5/01, 3/03, 9/03; 5/04; 8/05; 3/07; 10/08; Manual of Administrative Policy Source
General anesthetics. Dr. Shamil AL-Noaimy Lecturer of Pharmacology Dept. of Pharmacology College of Medicine
 General anesthetics Dr. Shamil AL-Noaimy Lecturer of Pharmacology Dept. of Pharmacology College of Medicine Rationale General anesthesia is essential to surgical practice, because it renders patients analgesic,
General anesthetics Dr. Shamil AL-Noaimy Lecturer of Pharmacology Dept. of Pharmacology College of Medicine Rationale General anesthesia is essential to surgical practice, because it renders patients analgesic,
Oral Preanesthetic Medication In Children: A Comparison of Midazolam Syrup Versus Midazolam Syrup Plus Fentanyl Lozenge.
 13 Oral Preanesthetic Medication In Children: A Comparison of Midazolam Syrup Versus Midazolam Syrup Plus Fentanyl Lozenge. Tarek Atef Tawfic MD Lecturer of anesthesia, faculty of medicine, Alexandria
13 Oral Preanesthetic Medication In Children: A Comparison of Midazolam Syrup Versus Midazolam Syrup Plus Fentanyl Lozenge. Tarek Atef Tawfic MD Lecturer of anesthesia, faculty of medicine, Alexandria
The Use of Midazolam to Modify Children s Behavior in the Dental Setting. by Fred S. Margolis, D.D.S.
 The Use of Midazolam to Modify Children s Behavior in the Dental Setting by Fred S. Margolis, D.D.S. I. Introduction: One of the most common challenges that the dentist who treats children faces is the
The Use of Midazolam to Modify Children s Behavior in the Dental Setting by Fred S. Margolis, D.D.S. I. Introduction: One of the most common challenges that the dentist who treats children faces is the
Chapter 7. Principles of Pharmacology
 Chapter 7 Principles of Pharmacology Introduction Administering medications is a serious business. Medications may alleviate pain and improve patient s well-being. Used inappropriately, may cause harm
Chapter 7 Principles of Pharmacology Introduction Administering medications is a serious business. Medications may alleviate pain and improve patient s well-being. Used inappropriately, may cause harm
Isaac Wiebe Medical Student C W Wiebe Medical Centre June & July 2015
 Isaac Wiebe Medical Student C W Wiebe Medical Centre June & July 2015 Needlestick procedures Many interventions rely on needlestick procedures Venipuncture, intravenous cannulation, vaccination, lumbar
Isaac Wiebe Medical Student C W Wiebe Medical Centre June & July 2015 Needlestick procedures Many interventions rely on needlestick procedures Venipuncture, intravenous cannulation, vaccination, lumbar
Pediatric Sedation and Analgesia. Disclosure
 Pediatric Sedation and Analgesia Michael Young IWK Health Centre 1 Disclosure No financial or other conflict of interest Lots of borrowed slides and content: Erin Killorn Chris McCrossin Michelle McTimoney
Pediatric Sedation and Analgesia Michael Young IWK Health Centre 1 Disclosure No financial or other conflict of interest Lots of borrowed slides and content: Erin Killorn Chris McCrossin Michelle McTimoney
MORPHINE ADMINISTRATION
 Introduction Individualised Administration Drug of Choice Route of Administration & Doses Monitoring of Neonates & high risk patients Team Management Responsibility Morphine Protocol Flow Chart Introduction
Introduction Individualised Administration Drug of Choice Route of Administration & Doses Monitoring of Neonates & high risk patients Team Management Responsibility Morphine Protocol Flow Chart Introduction
Perioperative Pain Management
 Perioperative Pain Management Overview and Update As defined by the Anesthesiologist's Task Force on Acute Pain Management are from the practice guidelines from the American Society of Anesthesiologists
Perioperative Pain Management Overview and Update As defined by the Anesthesiologist's Task Force on Acute Pain Management are from the practice guidelines from the American Society of Anesthesiologists
POST-INTUBATION ANALGESIA AND SEDATION. August 2012 J Pelletier
 POST-INTUBATION ANALGESIA AND SEDATION August 2012 J Pelletier Intubated patients experience pain and anxiety Mechanical ventilation, endotracheal tube Blood draws, positioning, suctioning Surgical procedures,
POST-INTUBATION ANALGESIA AND SEDATION August 2012 J Pelletier Intubated patients experience pain and anxiety Mechanical ventilation, endotracheal tube Blood draws, positioning, suctioning Surgical procedures,
Indications. Physical Properties of Nitrous Oxide. Nitrous Oxide/Oxygen Conscious Sedation in the Pediatric Patient. Steven Chussid, D.D.S.
 Nitrous Oxide/Oxygen Conscious Sedation in the Pediatric Patient Steven Chussid, D.D.S. Columbia University School of Dental and Oral Surgery Indications Reduce anxiety Increase pain threshold Suppress
Nitrous Oxide/Oxygen Conscious Sedation in the Pediatric Patient Steven Chussid, D.D.S. Columbia University School of Dental and Oral Surgery Indications Reduce anxiety Increase pain threshold Suppress
Chapter 004 Procedural Sedation and Analgesia
 Chapter 004 Procedural Sedation and Analgesia NOTE: CONTENT CONTAINED IN THIS DOCUMENT IS TAKEN FROM ROSEN S EMERGENCY MEDICINE 9th Ed. Italicized text is quoted directly from Rosen s. Key Concepts: 1.
Chapter 004 Procedural Sedation and Analgesia NOTE: CONTENT CONTAINED IN THIS DOCUMENT IS TAKEN FROM ROSEN S EMERGENCY MEDICINE 9th Ed. Italicized text is quoted directly from Rosen s. Key Concepts: 1.
Preprocedural Fasting and Adverse Events in Procedural Sedation and Analgesia in a Pediatric Emergency Department: Are They Related?
 PEDIATRICS/ORIGINAL RESEARCH Preprocedural Fasting and Adverse Events in Procedural Sedation and Analgesia in a Pediatric Emergency Department: Are They Related? Mark G. Roback, MD Lalit Bajaj, MD, MPH
PEDIATRICS/ORIGINAL RESEARCH Preprocedural Fasting and Adverse Events in Procedural Sedation and Analgesia in a Pediatric Emergency Department: Are They Related? Mark G. Roback, MD Lalit Bajaj, MD, MPH
Comparison of Bier's Block and Systemic Analgesia for Upper Extremity Procedures: A Randomized Clinical Trial
 J Arch Mil Med. 1 August; (3): e1977. Published online 1 August 3. DOI: 1.81/jamm.1977 Research Article Comparison of Bier's Block and Systemic Analgesia for Upper Extremity Procedures: A Randomized Clinical
J Arch Mil Med. 1 August; (3): e1977. Published online 1 August 3. DOI: 1.81/jamm.1977 Research Article Comparison of Bier's Block and Systemic Analgesia for Upper Extremity Procedures: A Randomized Clinical
What Works and What s Safe in Pediatric Emergency Procedural Sedation: An Overview of Reviews
 PROGRESSIVE CLINICAL PRACTICE What Works and What s Safe in Pediatric Emergency Procedural Sedation: An Overview of Reviews Lisa Hartling, PhD, Andrea Milne, MLIS, Michelle Foisy, MA, Eddy S. Lang, MD,
PROGRESSIVE CLINICAL PRACTICE What Works and What s Safe in Pediatric Emergency Procedural Sedation: An Overview of Reviews Lisa Hartling, PhD, Andrea Milne, MLIS, Michelle Foisy, MA, Eddy S. Lang, MD,
Using methadone alongside other opioids. Dr. Jo Murrell BVSc. (hons), PhD, DiplECVAA, MRCVS
 Using methadone alongside other opioids Dr. Jo Murrell BVSc. (hons), PhD, DiplECVAA, MRCVS Why might we want to use methadone alongside other opioids? 1. Multi-modal analgesia strategies e.g. using methadone
Using methadone alongside other opioids Dr. Jo Murrell BVSc. (hons), PhD, DiplECVAA, MRCVS Why might we want to use methadone alongside other opioids? 1. Multi-modal analgesia strategies e.g. using methadone
Guideline for the management of pain in children
 The College of Emergency Medicine Patron: HRH The Princess Royal Churchill House Tel +44 (0)207 404 1999 35 Red Lion Square Fax +44 (0)207 067 1267 London WC1R 4SG www.collemergencymed.ac.uk CLINICAL EFFECTIVENESS
The College of Emergency Medicine Patron: HRH The Princess Royal Churchill House Tel +44 (0)207 404 1999 35 Red Lion Square Fax +44 (0)207 067 1267 London WC1R 4SG www.collemergencymed.ac.uk CLINICAL EFFECTIVENESS
Current evidence in acute pain management. Jeremy Cashman
 Current evidence in acute pain management Jeremy Cashman Optimal analgesia Best possible pain relief Lowest incidence of side effects Optimal analgesia Best possible pain relief Lowest incidence of side
Current evidence in acute pain management Jeremy Cashman Optimal analgesia Best possible pain relief Lowest incidence of side effects Optimal analgesia Best possible pain relief Lowest incidence of side
One-Drug Oral Sedation
 One-Drug Oral Sedation Triazolam (Halcion) Oral Sedation 0.25 mg. taken one hour before procedure. Dental patient so scared, she begins clonic activity immediately upon placing an IV needle and goes into
One-Drug Oral Sedation Triazolam (Halcion) Oral Sedation 0.25 mg. taken one hour before procedure. Dental patient so scared, she begins clonic activity immediately upon placing an IV needle and goes into
Appendix A: Pharmacologic approaches to pain management during MVA
 Pain medication Though the medications shown below are commonly used for pain management during uterine evacuation, many other options exist. This table does not cover general anesthetic agents. Both anxiolytics
Pain medication Though the medications shown below are commonly used for pain management during uterine evacuation, many other options exist. This table does not cover general anesthetic agents. Both anxiolytics
Sedation For Cardiac Procedures A Review of
 Sedation For Cardiac Procedures A Review of Sedative Agents Dr Simon Chan Consultant Anaesthesiologist Department of Anaesthesia and Intensive Care Prince of Wales Hospital Hong Kong 21 February 2009 Aims
Sedation For Cardiac Procedures A Review of Sedative Agents Dr Simon Chan Consultant Anaesthesiologist Department of Anaesthesia and Intensive Care Prince of Wales Hospital Hong Kong 21 February 2009 Aims
Sierra Sacramento Valley EMS Agency
 Sierra Sacramento Valley EMS Agency BLS IN NALOXONE ADMINISTRATION OPTIONAL SKILL (UPDATED 06/2017) Acknowledgement: Siskiyou County SO - source of some slide content In order for PSFA, EMR or EMT personnel
Sierra Sacramento Valley EMS Agency BLS IN NALOXONE ADMINISTRATION OPTIONAL SKILL (UPDATED 06/2017) Acknowledgement: Siskiyou County SO - source of some slide content In order for PSFA, EMR or EMT personnel
Procedural Sedation in the Rural ER
 Procedural Sedation in the Rural ER Hal Irvine MD FCFP Rural FP Anesthetist Sundre, Alberta June 17, 2011 Disclosure I do not have any affiliations (financial or otherwise) with a commercial organization
Procedural Sedation in the Rural ER Hal Irvine MD FCFP Rural FP Anesthetist Sundre, Alberta June 17, 2011 Disclosure I do not have any affiliations (financial or otherwise) with a commercial organization
Goals for sedation during mechanical ventilation
 New Uses of Old Medications Gina Riggi, PharmD, BCCCP, BCPS Clinical Pharmacist Trauma ICU Jackson Memorial Hospital Disclosure I do not have anything to disclose Objectives Describe the use of ketamine
New Uses of Old Medications Gina Riggi, PharmD, BCCCP, BCPS Clinical Pharmacist Trauma ICU Jackson Memorial Hospital Disclosure I do not have anything to disclose Objectives Describe the use of ketamine
Pain Management in the NICU. Tamorah Lewis MD, PhD
 Pain Management in the NICU & Iatrogenic Opiate Withdrawal Tamorah Lewis MD, PhD Assistant Professor Divisions of Neonatology & Clinical Pharmacology, Toxicology and Therapeutic Innovation The Children's
Pain Management in the NICU & Iatrogenic Opiate Withdrawal Tamorah Lewis MD, PhD Assistant Professor Divisions of Neonatology & Clinical Pharmacology, Toxicology and Therapeutic Innovation The Children's
Paediatric sedation Michael R. J. Sury FRCA
 Michael R. J. Sury FRCA Key points Sedation in children needs special consideration. Conscious sedation requires cooperation: unlikely for many procedures especially if painful. Deep sedation by nonanaesthetists
Michael R. J. Sury FRCA Key points Sedation in children needs special consideration. Conscious sedation requires cooperation: unlikely for many procedures especially if painful. Deep sedation by nonanaesthetists
Evaluation of methoxyflurane (Penthrox ) efficacity for acute traumatic pain relief: a pilot study
 A R T Y K U Ł O R Y G I N A L N Y / O R I G I N A L PA P E R Otrzymano/Submitted: 11.12.09 Poprawiono/Corrected 17.05.10 Zaakceptowano/Accepted: 25.05.10 Akademia Medycyny Evaluation of methoxyflurane
A R T Y K U Ł O R Y G I N A L N Y / O R I G I N A L PA P E R Otrzymano/Submitted: 11.12.09 Poprawiono/Corrected 17.05.10 Zaakceptowano/Accepted: 25.05.10 Akademia Medycyny Evaluation of methoxyflurane
Continuous Nitrous Oxide Sedation in Paediatrics
 Guideline: Page 1 of 6 Continuous Nitrous Oxide Sedation in Paediatrics Purpose This guideline applies to all nitrous oxide sedation of all children under 15 years of age The aim of this guideline is to
Guideline: Page 1 of 6 Continuous Nitrous Oxide Sedation in Paediatrics Purpose This guideline applies to all nitrous oxide sedation of all children under 15 years of age The aim of this guideline is to
Efficacy and Safety of Sublingual Sufentanil 30 mcg for the Management of Acute Pain Following Ambulatory Surgery. Pamela P.
 Efficacy and Safety of Sublingual Sufentanil 30 mcg for the Management of Acute Pain Following Ambulatory Surgery Pamela P. Palmer, MD, PhD Disclosures for Dr. Pamela Palmer AcelRx employee Currently own
Efficacy and Safety of Sublingual Sufentanil 30 mcg for the Management of Acute Pain Following Ambulatory Surgery Pamela P. Palmer, MD, PhD Disclosures for Dr. Pamela Palmer AcelRx employee Currently own
The use of Pudendal Nerve Block in Hemorrhoidectomy Operations: A Prospective Double Blind Placebo Control Study
 Kasr El Aini Journal of Surgery VOL., 10, NO 3 September 2009 97 The use of Pudendal Nerve Block in Hemorrhoidectomy Operations: A Prospective Double Blind Placebo Control Study Sherif Adly and Mohamed
Kasr El Aini Journal of Surgery VOL., 10, NO 3 September 2009 97 The use of Pudendal Nerve Block in Hemorrhoidectomy Operations: A Prospective Double Blind Placebo Control Study Sherif Adly and Mohamed
Management of Pain in Children. The Royal College of Emergency Medicine. Best Practice Guideline
 The Royal College of Emergency Medicine Best Practice Guideline Management of Pain in Children Revised Management of pain in children (REV July 2017) 1 July 2017 Summary of recommendations 1. Recognition
The Royal College of Emergency Medicine Best Practice Guideline Management of Pain in Children Revised Management of pain in children (REV July 2017) 1 July 2017 Summary of recommendations 1. Recognition
Anesthesia: Analgesia: Loss of bodily SENSATION with or without loss of consciousness. Absence of the sense of PAIN without loss of consciousness
 1 2 Anesthesia: Loss of bodily SENSATION with or without loss of consciousness Analgesia: Absence of the sense of PAIN without loss of consciousness 3 1772: Joseph Priestly discovered Nitrous Oxide NO
1 2 Anesthesia: Loss of bodily SENSATION with or without loss of consciousness Analgesia: Absence of the sense of PAIN without loss of consciousness 3 1772: Joseph Priestly discovered Nitrous Oxide NO
IEHP UM Subcommittee Approved Authorization Guideline Guideline Intravenous Sedation and General Guideline # UM_DEN 01. Date
 IEHP UM Subcommittee Approved Authorization Guideline Guideline Intravenous Sedation and General Guideline # UM_DEN 01 Anesthesia for Dental Services Original Effective Date 01/26/06 Section Dental Revision
IEHP UM Subcommittee Approved Authorization Guideline Guideline Intravenous Sedation and General Guideline # UM_DEN 01 Anesthesia for Dental Services Original Effective Date 01/26/06 Section Dental Revision
A survey of dental treatment under general anesthesia in a Korean university hospital pediatric dental clinic
 Original Article pissn 2383-9309 eissn 2383-9317 J Dent Anesth Pain Med 2016;16(3):203-208 http://dx.doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2016.16.3.203 A survey of dental treatment under general anesthesia in a Korean
Original Article pissn 2383-9309 eissn 2383-9317 J Dent Anesth Pain Med 2016;16(3):203-208 http://dx.doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2016.16.3.203 A survey of dental treatment under general anesthesia in a Korean
RI ACEP Clinical Policies Committee. Position Paper on the Use of Propofol in the ED 12/15/2014
 RI ACEP Clinical Policies Committee Position Paper on the Use of Propofol in the ED 12/15/2014 The modern day practice of emergency medicine requires a practitioner to be skilled in procedural sedation
RI ACEP Clinical Policies Committee Position Paper on the Use of Propofol in the ED 12/15/2014 The modern day practice of emergency medicine requires a practitioner to be skilled in procedural sedation
Oral midazolam for conscious sedation of children during minor procedures
 244 Arrowe Park Hospital, Upton, Wirral L49 5PE F C Davies Countess of Chester Hospital, Chester M Waters Correspondence to: Dr Davies (e-mail: ffiond(compuserve.com). Accepted for publication 16 March
244 Arrowe Park Hospital, Upton, Wirral L49 5PE F C Davies Countess of Chester Hospital, Chester M Waters Correspondence to: Dr Davies (e-mail: ffiond(compuserve.com). Accepted for publication 16 March
Routes of drug administration
 Routes of drug administration Definition:- A route of administration in pharmacy is the path by which a drug is taken into the body. Classification:- The various routes of administrations are classified
Routes of drug administration Definition:- A route of administration in pharmacy is the path by which a drug is taken into the body. Classification:- The various routes of administrations are classified
Anesthetic Neurotoxicity Will this anesthetic make my kid stupid:
 Vexing issues in pediatric anesthesia 1 -Will this anesthetic make my kid stupid: Anesthetic Neurotoxicity 2- Parental Presence, Premedication and Induction Techniques Peter J. Davis MD Professor of Anesthesia
Vexing issues in pediatric anesthesia 1 -Will this anesthetic make my kid stupid: Anesthetic Neurotoxicity 2- Parental Presence, Premedication and Induction Techniques Peter J. Davis MD Professor of Anesthesia
Kids in pain. Chris Lipp PGY 3 - Vic.
 Kids in pain Chris Lipp PGY 3 - Vic. No disclosures Outline Objectives Case based learning Assessment of pain Management do s and don ts Topical Oral Intranasal IV Special circumstances Audience feedback
Kids in pain Chris Lipp PGY 3 - Vic. No disclosures Outline Objectives Case based learning Assessment of pain Management do s and don ts Topical Oral Intranasal IV Special circumstances Audience feedback
Comparison of Drug Clonidine and Midazolam as Premedication s in Children: An Institutional Based Study
 Original article: Comparison of Drug Clonidine and Midazolam as Premedication s in Children: An Institutional Based Study Dr. Gurdeep Singh Jheetay Associate Professor, Department of Anaesthesia, Shri
Original article: Comparison of Drug Clonidine and Midazolam as Premedication s in Children: An Institutional Based Study Dr. Gurdeep Singh Jheetay Associate Professor, Department of Anaesthesia, Shri
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 3/ Issue 74/Dec 29, 2014 Page 15535
 RANDOMISED CLINICAL TRIAL TO COMPARE THE EFFECT OF PRETREATMENT OF KETAMINE AND LIGNOCAINE ON PROPOFOL INJECTION PAIN Hanumanthappa V. Airani 1, Bhagyashree Amingad 2, Chandra Kumar B. M 3 HOW TO CITE
RANDOMISED CLINICAL TRIAL TO COMPARE THE EFFECT OF PRETREATMENT OF KETAMINE AND LIGNOCAINE ON PROPOFOL INJECTION PAIN Hanumanthappa V. Airani 1, Bhagyashree Amingad 2, Chandra Kumar B. M 3 HOW TO CITE
SAN JOAQUIN COUNTY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY. Administration of Naloxone for Opiate Overdose
 SAN JOAQUIN COUNTY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY Administration of Naloxone for Opiate Overdose Disclaimer: Authorization - EMT Optional Skills Only authorized Emergency Medical Technicians (EMT) who
SAN JOAQUIN COUNTY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY Administration of Naloxone for Opiate Overdose Disclaimer: Authorization - EMT Optional Skills Only authorized Emergency Medical Technicians (EMT) who
UMC HEALTH SYSTEM Lubbock, Texas :
 Consent for Commonly Performed Procedures in the Adult Critical Care Units I, the undersigned, understand that the adult intensive and intermediate care units ( critical care units ) are places where seriously
Consent for Commonly Performed Procedures in the Adult Critical Care Units I, the undersigned, understand that the adult intensive and intermediate care units ( critical care units ) are places where seriously
Single- and Repeat-Dose Pharmacokinetics of Sublingual Sufentanil NanoTab in Healthy Volunteers
 Single- and Repeat-Dose Pharmacokinetics of Sublingual Sufentanil NanoTab in Healthy Volunteers Pamela P. Palmer, MD, PhD AcelRx Pharmaceuticals, Inc. October 20, 2009 1 Sufentanil: A Superior Opioid Approved
Single- and Repeat-Dose Pharmacokinetics of Sublingual Sufentanil NanoTab in Healthy Volunteers Pamela P. Palmer, MD, PhD AcelRx Pharmaceuticals, Inc. October 20, 2009 1 Sufentanil: A Superior Opioid Approved
Sedation is a dynamic process.
 19th Annual Mud Season Nursing Symposium Timothy R. Lyons, M.D. 26 March 2011 To allow patients to tolerate unpleasant procedures by relieving anxiety, discomfort or pain To expedite the conduct of a procedure
19th Annual Mud Season Nursing Symposium Timothy R. Lyons, M.D. 26 March 2011 To allow patients to tolerate unpleasant procedures by relieving anxiety, discomfort or pain To expedite the conduct of a procedure
Drugs Used In Management Of Pain. Dr. Aliah Alshanwani
 Drugs Used In Management Of Pain Dr. Aliah Alshanwani 1 Drugs Used In Management Of Pain A CASE OF OVERDOSE Sigmund Freud, the father of psychoanalysis His cancer of the jaw was causing him increasingly
Drugs Used In Management Of Pain Dr. Aliah Alshanwani 1 Drugs Used In Management Of Pain A CASE OF OVERDOSE Sigmund Freud, the father of psychoanalysis His cancer of the jaw was causing him increasingly
Intranasal Premedication Effect of Dexmedetomidine Versus Midazolam on the Behavior of 2-6-Year-Old Uncooperative Children in Dental Clinic
 Original Article Intranasal Premedication Effect of Dexmedetomidine Versus Midazolam on the Behavior of 2-6-Year-Old Uncooperative Children in Dental Clinic Alireza Mahdavi 1, Masoud Fallahinejad Ghajari
Original Article Intranasal Premedication Effect of Dexmedetomidine Versus Midazolam on the Behavior of 2-6-Year-Old Uncooperative Children in Dental Clinic Alireza Mahdavi 1, Masoud Fallahinejad Ghajari
Anesthesia Safety. What is anesthesia and how does it work? Local anesthesia
 Scan for mobile link. Anesthesia Safety What is anesthesia and how does it work? Anesthesia is a state of consciousness or sedation achieved by using medications and/or non-pharmacologic adjuncts (therapy
Scan for mobile link. Anesthesia Safety What is anesthesia and how does it work? Anesthesia is a state of consciousness or sedation achieved by using medications and/or non-pharmacologic adjuncts (therapy
Postoperative Analgesia for Circumcision in Children: A Comparative Study of Caudal Block versus High Dose Rectal Acetaminophen or EMLA Cream
 Postoperative Analgesia for Circumcision in Children: A Comparative Study of Caudal Block versus High Dose Rectal Acetaminophen or EMLA Cream Jehan Ahmed Sayed 1 and Mohamed Amir Fathy 2 1 Department of
Postoperative Analgesia for Circumcision in Children: A Comparative Study of Caudal Block versus High Dose Rectal Acetaminophen or EMLA Cream Jehan Ahmed Sayed 1 and Mohamed Amir Fathy 2 1 Department of
What else is new (symptoms)? DR ANDREW DAVIES
 What else is new (symptoms)? DR ANDREW DAVIES Introduction Outline Rapid onset opioids for episodic breathlessness Alcohol for anorexia (white wine) Rapid onset opioids for episodic breathlessness Episodic
What else is new (symptoms)? DR ANDREW DAVIES Introduction Outline Rapid onset opioids for episodic breathlessness Alcohol for anorexia (white wine) Rapid onset opioids for episodic breathlessness Episodic
Chapter 25. General Anesthetics
 Chapter 25 1. Introduction General anesthetics: 1. Analgesia 2. Amnesia 3. Loss of consciousness 4. Inhibition of sensory and autonomic reflexes 5. Skeletal muscle relaxation An ideal anesthetic: 1. A
Chapter 25 1. Introduction General anesthetics: 1. Analgesia 2. Amnesia 3. Loss of consciousness 4. Inhibition of sensory and autonomic reflexes 5. Skeletal muscle relaxation An ideal anesthetic: 1. A
Emergency nurses are frequently asked to assist in
 PEDIATRIC INTRAVENOUS MEDICATION ADMINISTRATION IN THE EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT, PART 3: RIP VAN WINKLE S APPROACH TO PEDIATRIC PROCEDURAL SEDATION Authors: Patricia A. Normandin, DNP, RN, CEN, CPN, CPEN,
PEDIATRIC INTRAVENOUS MEDICATION ADMINISTRATION IN THE EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT, PART 3: RIP VAN WINKLE S APPROACH TO PEDIATRIC PROCEDURAL SEDATION Authors: Patricia A. Normandin, DNP, RN, CEN, CPN, CPEN,
Respiratory Depression
 Respiratory Depression H. William Gottschalk, D.D.S. Fellow, Academy of General Dentistry Fellow, American Dental Society of Anesthesiology Diplomate, American Board of Dental Anesthesiology Diplomate,
Respiratory Depression H. William Gottschalk, D.D.S. Fellow, Academy of General Dentistry Fellow, American Dental Society of Anesthesiology Diplomate, American Board of Dental Anesthesiology Diplomate,
The Game Plan. Should I Be Doing This? The Perfect Drug. Procedural Sedation
 Procedural Sedation Sanjay Arora MD Associate Professor of Emergency Medicine Keck School of Medicine at USC Los Angeles County + USC Medical Center May 23, 2012 The Game Plan Who shouldn t get sedation
Procedural Sedation Sanjay Arora MD Associate Professor of Emergency Medicine Keck School of Medicine at USC Los Angeles County + USC Medical Center May 23, 2012 The Game Plan Who shouldn t get sedation
