Paper Reference (complete below) Monday 24 May 2004 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes
|
|
|
- Brian Chapman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Centre No. Paper Reference (complete below) Surname Initial(s) Candidate No. Signature Paper Reference(s) 1827/01 Edexcel GCSE Physical Education Paper 1 Monday 24 May 2004 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Materials required for examination Nil Items included with question papers Nil Instructions to Candidates In the boxes above, write your centre number, candidate number, your surname and initials, the paper reference and your signature. The paper reference is shown above. Answer ALL questions in the spaces provided in this book. For Section 1: Do not use pencil. Use blue or black ink. For each question, choose an answer, A, B, C or D and put a cross in the box ( ). Mark only one answer for each question. If you change your mind about an answer, put a line through the box ( ) and then mark your new answer with a cross ( ). Write your answers to Sections 2 and 3 in the spaces provided. Information for Candidates The total mark for this paper is 150. The marks for the various questions are shown in round brackets: e.g. (2). There are 28 pages in this question paper. All pages are indicated. Calculators may be used. Advice to Candidates You are reminded of the importance of clear and orderly presentation in your answers. Examiner s use only Team Leader s use only Question Number Blank This publication may only be reproduced in accordance with London Qualifications Limited copyright policy London Qualifications Limited. Printer s Log. No. W850/S1827/ /6/6/6/6/6/6/6/6/6/6/6/6/ ** Total Turn over
2 SECTION ONE Answer ALL questions. For each question, choose an answer A, B, C or D and put a cross in the box. Mark only one answer for each question. If you change your mind about an answer, put a line through the box and then mark your new answer with a cross. eg: Mark the box like this: If you change your mind, mark the boxes like this: A A This shows your final answer B B C This shows your answer C First answer D D 1. (a) Which of the following training methods is most likely to result in improved cardiovascular fitness for a long distance runner? A Continuous B Weight C Interval D Circuit (b) Which of the following activities would be most suitable to include in a training programme designed to improve strength for a shot putter? A Throwing a tennis ball to correct technique. B Weight training, using heavy weights, with few repetitions. C Swimming training. D Weight training, using light weights, with many repetitions. (c) Health is: A A capability of the heart, blood vessels, lungs and muscles to function at optimal efficiency. B The ability to meet the demands of the environment. C A state of complete mental, physical and social well-being, and not merely the absence of disease and infirmity. D Training regularly. 2
3 (d) Obese is: A Having an excess of muscle which restricts mobility. B The percentage of body weight which is fat, muscle and bone. C Muscles in a state of slight tension. D Being very overfat. (e) Athlete s foot is caused by: A An increase in foot size due to training. B A virus. C A fungus. D An injury associated with 100 m runners. (f) Which of the following activities would present an unsupervised beginner with the greatest risk? A Skiing B Table Tennis C Badminton D Aerobics (g) Which of the following is a TRUE statement about tennis or golfer s elbow? A You can only get tennis or golfer s elbow if you play tennis or golf. B Tennis and golfer s elbow is a joint injury. C Tennis and golfer s elbow is a soft tissue injury. D Tennis or golfer s elbow can be caused by under-use of the muscles in the lower arm. (h) Which of the following statements describes the double pump action of the heart? A The amount of blood pumped from the heart per minute. B Blood is pumped out of the atria to the ventricles and then from the ventricles to the lungs and to the body. C Blood is pumped from the ventricles to the lungs and to the body. D The pumping of the right and left ventricles. 3 Turn over
4 (i) Ossification is: A The formation of bone from cartilage. B The area of growth within a bone. C The formation of cartilage from bone. D The outer skin surrounding the bone. (j) What type of joint is formed by the atlas and axis at the neck? A Hinge B Ball and socket C Ball D Pivot (Total 10 marks) TOTAL FOR SECTION ONE: 10 MARKS Q1 4
5 SECTION TWO Answer all questions 2. Hugh is 16 years old. Although he has always enjoyed PE, he is very shy and overweight. Complete the table below stating THREE possible benefits of Hugh joining a sports club. Explain how joining a club may achieve these benefits. Benefit How Achieved Q2 (Total 6 marks) 5 Turn over
6 3. Figure 1 shows a badminton player about to play a shot. Figure 1 (a) The flexibility of the player helps him to reach the shuttlecock. Define the term flexibility. (b) Complete the table below by naming TWO other components of Health Related Exercise that will be important to the badminton player s success. Explain how these components will help him improve his performance. Component of health related exercise How component helps performance 1 2 (4) Q3 (Total 5 marks) 6
7 4. Figure 2 shows performers participating in physical activity. A B C Figure 2 Complete the table below naming ONE component of Skill Related Fitness that will be important to each performer. Explain how these components will help each performer in his/her activity. You must choose a different component for each performer. Performer Component of skill related fitness How component of skill related fitness helps performance A: GYMNAST B: SPRINTER C: SHOT PUTTER Q4 (Total 6 marks) 7 Turn over
8 5. The F.I.T.T. principle is an important principle of training. Susanne is a hockey player and she has been applying the F.I.T.T. principle to her Personal Exercise Programme. (a) Complete the following statements about the F.I.T.T. principle by filling in the missing words. (i) F stands for... and means how often you train. (ii) Intensity refers to how... you work when training. (iii) T refers to... and means how long each training session lasts. (iv) Type means that you should make sure that your training programme... the activity you are training for. (b) The following statements explain how Susanne has applied the F.I.T.T. principle to her training. Complete each statement. (i) Instead of training once a week, she now trains... times per week. (ii) Instead of working at 50% of her maximum she now works at.... (iii) Instead of working for 30 minutes per session, she now works for... minutes. Q5 (Total 7 marks) 8
9 6. (a) Complete the table below by ticking the training methods that you think would be most likely to increase the aerobic and anaerobic fitness of an athlete. You may tick more than one training method for each aspect of fitness. Interval Circuit Weight Example: Strength Aerobic fitness Anaerobic fitness (b) What extreme body type (somatotype) is associated with elite athletes who carry out a lot of (i) strength training... (4) (ii) continuous training... Q6 (Total 6 marks) 9 Turn over
10 7. Referees and umpires help prevent injury to players by enforcing the rules of an activity. (a) The chances of becoming injured are also reduced by balancing competition. Explain the term balancing competition. (b) State FOUR ways that competition in activities could be balanced (c) Name an activity of your choice, giving specific examples of TWO ways in which competition within that activity is balanced. ACTIVITY (d) State THREE other ways (apart from obeying the rules and balancing competition), that performers can reduce the risk of injury Q7 (Total 10 marks) 10
11 8. (a) Figure 3 shows a swimmer placed in the recovery position at the side of a swimming pool. Figure 3 (i) When would someone be placed in the recovery position? (ii) What might have happened to the swimmer to require her to be placed in the recovery position? (iii) Why would the swimmer be placed in the recovery position rather than laid on her back or front on the poolside? (iv) Once the swimmer has been placed in the recovery position, what should the First Aider do whilst waiting for expert help to arrive? 11 Turn over
12 (b) Figure 4 shows the position of the head of a casualty during mouth-to-mouth ventilation. Figure 4 (i) Why is it important that the head is tilted back in this way? (ii) What should the First Aider do to the casualty s nose as he breathes into the casualty s mouth? (iii) Why should the First Aider do this to the casualty s nose? (iv) How long should the First Aider continue to perform mouth-to-mouth ventilation? (v) What should the First Aider do if the casualty begins to breathe? (c) During resuscitation the First Aider may be required to carry out cardiac massage. What is the purpose of cardiac massage? Q8 (Total 10 marks) 12
13 9. Figure 5 is a diagram of the human heart. (a) Name the parts labelled A, B and C. Figure 5 (i) A... (ii) B... (iii) C... (b) What effect would long-term training have on the part of the heart labelled B? (c) Why do the walls of the vessel labelled A need to be thicker than those labelled C? Q9 (Total 5 marks) 13 Turn over
14 10. During breathing, gases are inhaled and exhaled. (a) Complete the table below to show the percentage of each gas in inhaled and exhaled air. Use some of the percentages shown in the box. 79% 21% 3% 17% 0.03% 9% Gas Inspiration (%) Expiration (%) Oxygen Carbon Dioxide (4) (b) Explain why the percentage of oxygen varies from inspiration to expiration. (c) Explain why the percentage of carbon dioxide varies from inspiration to expiration. Q10 (Total 6 marks) 14
15 11. Figure 6 shows a high jumper clearing the bar. Fosbury Flop Figure 6 (a) State TWO regions of the vertebral column and explain how the function of these regions helps the high jumper clear the bar. You must use a different function for each of the regions of the vertebral column. Region of vertebral column Function How this helps high jumpers 1 2 (6) (b) The bones of the vertebral column are separated by discs. (i) What are these discs made of? (ii) What is their function? 15 Turn over
16 (c) Bones in other areas of the skeleton meet to form important joints, for example, the knee. (i) What type of synovial joint is the knee? (ii) There can be very slight rotation or sideways movement at the knee joint. What stabilises the knee joint to prevent unwanted movement? (iii) As well as slight rotation, what are the TWO types of movement possible at the knee? (2) Q11 (Total 12 marks) 12. Figure 7 shows the legs of a runner. A B C Figure 7 (a) Label the muscles A, B and C. (i) A... (ii) B... (iii) C... (3) 16
17 (b) Which muscle, A, B or C, allows the runner to drive forwards off the toes during his running action? (c) Which muscle, A, B or C, allows the runner to extend the leg at the hip? (d) Two of the muscles named in the box below work as an antagonistic pair. Name the two muscles. Bicep Deltoid Gluteals Hamstrings Quadriceps and (e) Explain the term antagonistic pair. Q12 (Total 7 marks) TOTAL FOR SECTION TWO: 80 MARKS 17 Turn over
18 SECTION THREE Answer all questions 13. Ashan is 16 years old. He is studying GCSE PE and has decided to measure his heart rate during training to help him monitor his fitness. Figure 8 shows a record of Ashan s heart rate before, during and after a training session. (a) Define the term heart rate. Figure 8 (b) (i) What happens to Ashan s heart rate at the start of the training session? (ii) What effect will this have on his cardiac output? (c) Explain why it is important to Ashan that his heart rate alters in this way. 18
19 (d) The graph shows that Ashan s heart rate varies during the training session. Give a possible reason for this variation. (e) Name a type of training method that would cause this variation in heart rate. (f) What happens to Ashan s heart rate during the 10 minute period after training has finished? (g) Give TWO reasons why the heart needs to continue to work harder than normal, even after the training session has finished (h) At times Ashan is working well within his target heart rate training zone. What does this mean? (i) Ashan is 16. Use this information to show how he would calculate his training zone by completing the following statements. (i) Maximum heart rate is... minus his age. (ii) Therefore Ashan s maximum heart rate will be...(bpm). (iii) The upper limit of his target heart rate training zone should be... % of his maximum heart rate. (iv) The lower limit of his target heart rate training zone should be... % of his maximum heart rate. (4) 19 Turn over
20 (j) (i) Complete the statement below about the type of muscle found in the heart. The heart wall is... muscle. (ii) How does this type of muscle differ from voluntary muscle? (k) In addition to keeping fit, Ashan also knows that it is important to consider what and how much he eats. Why would Ashan include the following in his diet? (i) Carbohydrates... (ii) Water... (l) Why is it important that Ashan does not under eat? (m) It is important that Ashan does not over eat. Explain the term over eat. Q13 (Total 20 marks) 20
21 14. Fara is a 100m hurdler. She trains regularly and thinks carefully about her Personal Exercise Programme (PEP) as she has seen many of her team mates injured through over training. To help her understand the requirements of her sport, she analyses her performance regularly. Fara s coach told her that her training was proving effective as her performance was improving. (a) Define the term performance. (b) The following are statements taken from Fara s PEP. A B C D E (i) I need to make sure my training matches the requirement of my sport, therefore I shall be using interval training. I found the workload far too easy last week so I shall be training harder this week. I think it is important to gradually increase the amount of work that I do. I need to structure my PEP to my needs, no one else s. Unfortunately I had to have a minor operation on my knee. I was unable to train for 6 weeks, which means that I have already started to lose my fitness. Complete the table below by naming THREE principles of training (other than the F.I.T.T principle) that Fara has referred to in the statements from her PEP. Explain the meaning of each of the principles. Principle of training Explanation (6) 21 Turn over
22 (ii) Complete the table below to match each of the statements from Fara s PEP to the correct principle of training. Statement from PEP Principle of Training A C E (c) During a recent competition one of the hurdlers fell and sprained her ankle. (3) (i) State ONE visible symptom of a sprained ankle. (ii) What type of injury is a sprained ankle? (iii) What treatment should she be given for this type of injury? 22
23 (d) Figure 9 shows a diagram of the skeleton of the lower leg and foot. A B C D Figure 9 (i) Name the bones labelled A, B, C and D. A... B... C... D... (ii) The bones labelled D are short bones. How does the function of a short bone help the hurdler? (e) The 100m hurdles is a sprint event. (i) What type of muscle fibres would be most useful to a 100m hurdler? Fibre Type... (ii) Why would this type of muscle fibre be useful to a 100m hurdler? Q14 (Total 20 marks) 23 Turn over
24 15. As part of their GCSE PE programme John, Tony and Ben each devised a Personal Exercise Programme (PEP). (a) What is the purpose of exercise? (b) Figure 10 shows the activities that the boys completed as part of their training. Figure 10 (i) What type of training method is represented in Figure 10? (ii) Complete the table below by filling in the gaps to give the names of the exercises the main muscles being worked in each of the exercises the action being produced. Exercise Main Muscle Action Triceps Pull ups Flexion of arm at the elbow Sit ups Flexion of trunk Squat thrusts Hamstring (5) 24
25 (c) Exercises can be isotonic or isometric. Explain these terms. (i) Isotonic... (ii) Isometric... (d) Which type of exercise (isotonic or isometric) is being carried out in the training session shown in Figure 10? (e) Before undertaking any physical activity the boys make sure they warm up. State, in order, the three phases of a warm up? (f) The boys are hoping to improve the efficiency of their cardiovascular and respiratory systems through their training. (i) State ONE way in which the cardiovascular system could improve as a result of training. (ii) State ONE way in which the respiratory system could improve as a result of training. 25 Turn over
26 (g) John, Tony and Ben rely on hard work to improve their fitness but some athletes resort to taking drugs to improve their performance. Complete the following statements about performance enhancing drugs. (i) Diuretics aid water loss from the body. This drug could be taken by athletes who need to lose weight quickly to allow them to meet weight requirements of their activity, for example,.... (ii) A possible side-effect of taking a diuretic is.... (iii) Anabolic agents, such as steroids, are taken to allow athletes to train.... (iv) Narcotic analgesics are used to.... (v) If narcotic analgesics are used and the athlete continues to train this is dangerous because they... Q15 (Total 20 marks) TOTAL FOR SECTION THREE: 60 MARKS TOTAL FOR PAPER: 150 MARKS END Edexcel gratefully acknowledges the following sources used in the preparation of this paper: PE Essentials by Doug Neate, Feltham Press PE Essentials Teaching Support Pack by Doug Neate, Feltham Press PE for you by Honeybourne, Hill & Wyse, Stanley Thornes Publishers
27 BLANK PAGE 27
28 BLANK PAGE 28
Paper Reference. 1827/01 Edexcel GCSE Physical Education Paper 1. Wednesday 25 May 2005 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 45 minutes
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 1827/01 Edexcel GCSE Physical Education Paper 1 Wednesday 25 May 2005 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Materials required for examination Nil Paper Reference
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 1827/01 Edexcel GCSE Physical Education Paper 1 Wednesday 25 May 2005 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Materials required for examination Nil Paper Reference
Paper Reference. 1827/01 Edexcel GCSE Physical Education Paper 1. Wednesday 24 May 2006 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 45 minutes
 entre No. andidate No. Paper Reference(s) 1827/01 Edexcel GSE Physical Education Paper 1 Wednesday 24 May 2006 fternoon Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Materials required for examination Nil Paper Reference 1
entre No. andidate No. Paper Reference(s) 1827/01 Edexcel GSE Physical Education Paper 1 Wednesday 24 May 2006 fternoon Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Materials required for examination Nil Paper Reference 1
Paper Reference. Paper Reference(s) 1827/01 Edexcel GCSE Physical Education Paper 1. Friday 18 May 2007 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 1827/01 Edexcel GCSE Physical Education Paper 1 Friday 18 May 2007 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Materials required for examination Nil Paper Reference 1 8
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 1827/01 Edexcel GCSE Physical Education Paper 1 Friday 18 May 2007 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Materials required for examination Nil Paper Reference 1 8
Physical Education. Unit 1: The Theory of Physical Education
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Physical Education Unit 1: The Theory of Physical Education Candidate Number Tuesday 14 May 2013 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30 minutes You
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Physical Education Unit 1: The Theory of Physical Education Candidate Number Tuesday 14 May 2013 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30 minutes You
Physical Education. Unit 1: The Theory of Physical Education
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Physical Education Unit 1: The Theory of Physical Education Candidate Number Tuesday 24 May 2011 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30 minutes You
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Physical Education Unit 1: The Theory of Physical Education Candidate Number Tuesday 24 May 2011 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30 minutes You
Paper Reference. Paper Reference(s) 1827/01 Edexcel GCSE Physical Education Paper 1. Thursday 14 May 2009 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 1827/01 Edexcel GCSE Physical Education Paper 1 Thursday 14 May 2009 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Materials required for examination Nil Paper Reference 1
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 1827/01 Edexcel GCSE Physical Education Paper 1 Thursday 14 May 2009 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Materials required for examination Nil Paper Reference 1
1. Describe the main functions of the skeletal system that keep the body healthy and active. [4]
![1. Describe the main functions of the skeletal system that keep the body healthy and active. [4] 1. Describe the main functions of the skeletal system that keep the body healthy and active. [4]](/thumbs/79/80173575.jpg) GCSE PE Structured questions 1a Applied anatomy and physiology Understand the structure and functions of the skeleton 1. Describe the main functions of the skeletal system that keep the body healthy and
GCSE PE Structured questions 1a Applied anatomy and physiology Understand the structure and functions of the skeleton 1. Describe the main functions of the skeletal system that keep the body healthy and
Paper 1 (1827/01 Full Course) - Factors Affecting Participation and Performance
 June 2005 GCSE Physical Education Examiners Report Paper 1 (1827/01 Full Course) - Factors Affecting Participation and Performance General Comments As with last year, the vast majority of candidates confined
June 2005 GCSE Physical Education Examiners Report Paper 1 (1827/01 Full Course) - Factors Affecting Participation and Performance General Comments As with last year, the vast majority of candidates confined
Edexcel GCSE Physical Education Revision and Examination Tips
 Edexcel GCSE Physical Education Revision and Examination Tips Benefits of a Healthy, Active lifestyle Unit 1 (Full and Short Course) Healthy Active Lifestyle = complete state of mental, physical and social
Edexcel GCSE Physical Education Revision and Examination Tips Benefits of a Healthy, Active lifestyle Unit 1 (Full and Short Course) Healthy Active Lifestyle = complete state of mental, physical and social
Year 7 End of Year Exam Revision
 Year 7 End of Year Exam Revision Physical Education https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=el1_enlemka Starter Video The Exam The exam you will sit is out of 40 marks. 25 of these are multiple choice, 7 are short
Year 7 End of Year Exam Revision Physical Education https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=el1_enlemka Starter Video The Exam The exam you will sit is out of 40 marks. 25 of these are multiple choice, 7 are short
Water. 1. Which of the following are macro-nutrients? A: Fibre, Fat, Protein B: Protein, Fat and. C: Vitamins, Minerals, and Fibre
 10 Questions 1. Which of the following are macro-nutrients? A: Fibre, Fat, Protein B: Protein, Fat and Water C: Vitamins, Minerals, and Fibre D: Carbohydrate, Fat and Protein 2. What is the correct equation
10 Questions 1. Which of the following are macro-nutrients? A: Fibre, Fat, Protein B: Protein, Fat and Water C: Vitamins, Minerals, and Fibre D: Carbohydrate, Fat and Protein 2. What is the correct equation
Y12 Transition Pack Sports Leadership
 Y12 Transition Pack Sports Leadership Name: Base School: Section 1: The Muscular System Read through the following information on the Muscular System Cardiac muscle is unique to the heart. It never tires.
Y12 Transition Pack Sports Leadership Name: Base School: Section 1: The Muscular System Read through the following information on the Muscular System Cardiac muscle is unique to the heart. It never tires.
KULLEĠĠ SAN BENEDITTU Boys Secondary, Kirkop
 KULLEĠĠ SAN BENEDITTU Boys Secondary, Kirkop Mark HALF-YEARLY EXAMINATION 2012/2013 Track 3 FORM 3 PHYSICAL EDUCATION TIME: 1h 30min Instructions to students: Answer ALL questions. Read carefully each
KULLEĠĠ SAN BENEDITTU Boys Secondary, Kirkop Mark HALF-YEARLY EXAMINATION 2012/2013 Track 3 FORM 3 PHYSICAL EDUCATION TIME: 1h 30min Instructions to students: Answer ALL questions. Read carefully each
Friday 16 May 2014 Afternoon
 Friday 16 May 2014 Afternoon GCSE PHYSICAL EDUCATION B453/01 Developing Knowledge in Physical Education *1116837436* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials
Friday 16 May 2014 Afternoon GCSE PHYSICAL EDUCATION B453/01 Developing Knowledge in Physical Education *1116837436* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials
. Area Area of study Learning Objectives Knowledge/concepts/task examples
 . Area Area of study Learning Objectives Knowledge/concepts/task examples 1.1.1 Healthy active lifestyles To understand the Physical, mental and social benefits of exercise. To be able to categorise reasons
. Area Area of study Learning Objectives Knowledge/concepts/task examples 1.1.1 Healthy active lifestyles To understand the Physical, mental and social benefits of exercise. To be able to categorise reasons
Year 10 GCSE Revision - Physical Education Paper 1 Fitness and Body Systems Topic Areas for Revision Key questions
 Year 10 GCSE Revision - Physical Education Paper 1 Fitness and Body Systems Topic Areas for Revision Key questions 1.1 The structure and functions of the musculoskeletal s Functions of the Skeleton for
Year 10 GCSE Revision - Physical Education Paper 1 Fitness and Body Systems Topic Areas for Revision Key questions 1.1 The structure and functions of the musculoskeletal s Functions of the Skeleton for
CHAPTER 2: Muscular skeletal system - Biomechanics. Exam style questions - pages QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS. Answers
 CHAPTER 2: Muscular skeletal system - Biomechanics Exam style questions - pages 32-35 1) A Level. Warm up is considered to be an essential element of a training programme. Explain how the muscular and
CHAPTER 2: Muscular skeletal system - Biomechanics Exam style questions - pages 32-35 1) A Level. Warm up is considered to be an essential element of a training programme. Explain how the muscular and
HEALTH: A complete state of mental, physical and social wellbeing and not merely the absence of disease and infirmity.
 FITNESS BENEFITS Increase CVE Increased Muscular Endurance Increased Flexibility Increased Strength Reduced chance of Stroke Stronger Boner Reduced chance of Obesity Reduced risk of CHD HEALTH BENEFITS
FITNESS BENEFITS Increase CVE Increased Muscular Endurance Increased Flexibility Increased Strength Reduced chance of Stroke Stronger Boner Reduced chance of Obesity Reduced risk of CHD HEALTH BENEFITS
GCSE PHYSICAL EDUCATION (Double Award)
 Please write clearly in block capitals. Centre number Candidate number Surname Forename(s) Candidate signature _ GCSE PHYSICAL EDUCATION (Double Award) Unit 5 Knowledge and Understanding for the Involved
Please write clearly in block capitals. Centre number Candidate number Surname Forename(s) Candidate signature _ GCSE PHYSICAL EDUCATION (Double Award) Unit 5 Knowledge and Understanding for the Involved
B453. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Developing Knowledge in Physical Education GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION. Tuesday 25 January 2011 Afternoon
 GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION PHYSICAL EDUCATION Developing Knowledge in Physical Education B453 *OCE/39061* Candidates answer on the question paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials
GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION PHYSICAL EDUCATION Developing Knowledge in Physical Education B453 *OCE/39061* Candidates answer on the question paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials
PE Improvement Targets
 PE Improvement Targets VCERT - Year 10 11 6. Ensure key words and terminology is used Try to use a variety sports related vocabulary in your answers. Below are vocabulary lists and brief teaching points
PE Improvement Targets VCERT - Year 10 11 6. Ensure key words and terminology is used Try to use a variety sports related vocabulary in your answers. Below are vocabulary lists and brief teaching points
PiXL Independence: PE Answer Booklet KS4. Applied Anatomy and Physiology. Contents: Answers
 PiXL Independence: PE Answer Booklet KS4 Applied Anatomy and Physiology Contents: Answers 1 I. Quizzes Multiple Choice Quiz 1. Which one of the following statements is false? a. The scapula, cranium and
PiXL Independence: PE Answer Booklet KS4 Applied Anatomy and Physiology Contents: Answers 1 I. Quizzes Multiple Choice Quiz 1. Which one of the following statements is false? a. The scapula, cranium and
Tuesday 14 May 2013 Afternoon
 Tuesday 14 May 2013 Afternoon GCSE PHYSICAL EDUCATION B453/01 Developing Knowledge in Physical Education *B426740613* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials
Tuesday 14 May 2013 Afternoon GCSE PHYSICAL EDUCATION B453/01 Developing Knowledge in Physical Education *B426740613* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials
TeachPE.com progress charts
 Exercise Physiology topic 2: Preparation and training methods in relation to maintaining physical activity and performance Topic 2A: Physiological effects and benefits of a warm up and cool down Term Identify
Exercise Physiology topic 2: Preparation and training methods in relation to maintaining physical activity and performance Topic 2A: Physiological effects and benefits of a warm up and cool down Term Identify
EARLSTON HIGH SCHOOL N4/5 PHYSICAL EDUCATION PREPARATION COURSE
 EARLSTON HIGH SCHOOL N4/5 PHYSICAL EDUCATION PREPARATION COURSE REVISION BOOKLET 2013 Contents Page Section 1: Information Topic Page Aspects of Fitness Feedback Personal and Physical Qualities Principles
EARLSTON HIGH SCHOOL N4/5 PHYSICAL EDUCATION PREPARATION COURSE REVISION BOOKLET 2013 Contents Page Section 1: Information Topic Page Aspects of Fitness Feedback Personal and Physical Qualities Principles
Year 11 GCSE Revision - Physical Education Topics for revision Re-visit work Suggested activities
 Week beginning 30 th Jan Year 11 GCSE Revision - Physical Education Topics for revision Re-visit work Suggested activities 1.1.2 Influences on your healthy, active lifestyle; people: family, peers, role
Week beginning 30 th Jan Year 11 GCSE Revision - Physical Education Topics for revision Re-visit work Suggested activities 1.1.2 Influences on your healthy, active lifestyle; people: family, peers, role
How can sportspeople train the body systems to ensure there are long term benefits? Excercise Physiology. Chapter 2. GCSE Physical Education
 How can sportspeople train the body systems to ensure there are long term benefits? Excercise Physiology GCSE Physical Education To answer the big question you will need to be able to complete the following
How can sportspeople train the body systems to ensure there are long term benefits? Excercise Physiology GCSE Physical Education To answer the big question you will need to be able to complete the following
SPORT AND COACHING PRINCIPLES
 VOCATIONAL WJEC Level 1/2 Vocational Award in SPORT AND COACHING PRINCIPLES REGULATED BY OFQUAL DESIGNATED BY QUALIFICATIONS WALES SAMPLE ASSESSMENT MATERIALS - EXTERNAL Teaching from 2018 For award from
VOCATIONAL WJEC Level 1/2 Vocational Award in SPORT AND COACHING PRINCIPLES REGULATED BY OFQUAL DESIGNATED BY QUALIFICATIONS WALES SAMPLE ASSESSMENT MATERIALS - EXTERNAL Teaching from 2018 For award from
PE Assessment Point 2 Revision booklet
 PE Assessment Point 2 Revision booklet Assessment point 2 PE assessment Theory Practical Theory Topics Locations of major bones Functions of the skeletal system Aerobic and anaerobic Warm ups and cool
PE Assessment Point 2 Revision booklet Assessment point 2 PE assessment Theory Practical Theory Topics Locations of major bones Functions of the skeletal system Aerobic and anaerobic Warm ups and cool
1.1 The structure and functions of the musculo-skeletal system Learning objectives
 1.1 The structure and functions of the musculo-skeletal system Learning objectives To be able to describe the functions of the skeleton. To understand different bone classifications and functioning. To
1.1 The structure and functions of the musculo-skeletal system Learning objectives To be able to describe the functions of the skeleton. To understand different bone classifications and functioning. To
Pearson Edexcel GCSE Physical Education: Short Course Unit 1: The Theory of Physical Education
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GSE entre Number Physical Education: Short ourse Unit 1: The Theory of Physical Education Friday 20th May 2016 fternoon Time: 1 hour andidate Number
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GSE entre Number Physical Education: Short ourse Unit 1: The Theory of Physical Education Friday 20th May 2016 fternoon Time: 1 hour andidate Number
Cardiovascular Learners MUST KNOW R A G. Know the double- circulatory system (systemic and pulmonary)
 Please do the following 1. Read the Learners must know section (see below) 2. Watch the GCSE POD video 3. Attempt Exam Questions 4. Mark your answers 5. Reflect and repeat until you are successful and
Please do the following 1. Read the Learners must know section (see below) 2. Watch the GCSE POD video 3. Attempt Exam Questions 4. Mark your answers 5. Reflect and repeat until you are successful and
GCSE 4421/01 PHYSICAL EDUCATION UNIT 1
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4421/01 PHYSICAL EDUCATION UNIT 1 S16-4421-01 P.M. FRIDAY, 20 May 2016 1 hour 30 minutes For s use ADDITIONAL MATERIALS DVD. Question Maximum Mark
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE 4421/01 PHYSICAL EDUCATION UNIT 1 S16-4421-01 P.M. FRIDAY, 20 May 2016 1 hour 30 minutes For s use ADDITIONAL MATERIALS DVD. Question Maximum Mark
A Healthy, Active. Lifestyle and Your. Muscular System
 A Healthy, Active Lifestyle and Your Muscular System 1. Muscular System 2. Types of Muscle muscle - Smooth Muscle that works without consciousness. a. Arteries - The walls of the arteries contract and
A Healthy, Active Lifestyle and Your Muscular System 1. Muscular System 2. Types of Muscle muscle - Smooth Muscle that works without consciousness. a. Arteries - The walls of the arteries contract and
Physical Education. Paper 1 [G9741] FRIDAY 20 MAY, AFTERNOON. TIME 1 hour 30 minutes, plus your additional time allowance.
![Physical Education. Paper 1 [G9741] FRIDAY 20 MAY, AFTERNOON. TIME 1 hour 30 minutes, plus your additional time allowance. Physical Education. Paper 1 [G9741] FRIDAY 20 MAY, AFTERNOON. TIME 1 hour 30 minutes, plus your additional time allowance.](/thumbs/85/92854166.jpg) Centre Number Candidate Number General Certificate of Secondary Education 2016 Physical Education Paper 1 ML [G9741] FRIDAY 20 MAY, AFTERNOON TIME 1 hour 30 minutes, plus your additional time allowance.
Centre Number Candidate Number General Certificate of Secondary Education 2016 Physical Education Paper 1 ML [G9741] FRIDAY 20 MAY, AFTERNOON TIME 1 hour 30 minutes, plus your additional time allowance.
Please do the following
 Please do the following 1. Read the Learners must know section (see below) 2. Watch the GCSE POD video 3. Attempt Exam Questions 4. Mark your answers 5. Reflect and repeat until you are successful and
Please do the following 1. Read the Learners must know section (see below) 2. Watch the GCSE POD video 3. Attempt Exam Questions 4. Mark your answers 5. Reflect and repeat until you are successful and
Physical Education: Short Course Unit 1: The Theory of Physical Education
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GSE entre Number andidate Number Physical Education: Short ourse Unit 1: The Theory of Physical Education Tuesday 24 May 2011 fternoon Time: 1 hour You
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GSE entre Number andidate Number Physical Education: Short ourse Unit 1: The Theory of Physical Education Tuesday 24 May 2011 fternoon Time: 1 hour You
Which one of the following performers relies most heavily on a high level of cardiovascular fitness for success?
 Questions Q1. Which one of the following performers relies most heavily on a high level of cardiovascular fitness for success? A 200m runner B 400m runner C 800m runner D 1500m runner Q2. Which component
Questions Q1. Which one of the following performers relies most heavily on a high level of cardiovascular fitness for success? A 200m runner B 400m runner C 800m runner D 1500m runner Q2. Which component
Name: Form: Teacher:
 Name: Form: Teacher: Topic 1: pplied anatomy and physiology 1.1 The structure and functions of the skeletal system- Part 1 1. List three major types of bones, found in the human skeleton. (3) (i) Irregular
Name: Form: Teacher: Topic 1: pplied anatomy and physiology 1.1 The structure and functions of the skeletal system- Part 1 1. List three major types of bones, found in the human skeleton. (3) (i) Irregular
GCSE Physical Education
 GCSE Physical Education Extension Work Booklet Name Tutor Group 2 Introduction and Contents Welcome to GCSE Physical Education! This work booklet will be like your bible! Please ensure you have this with
GCSE Physical Education Extension Work Booklet Name Tutor Group 2 Introduction and Contents Welcome to GCSE Physical Education! This work booklet will be like your bible! Please ensure you have this with
Topic Guide 1: Applied Anatomy and Physiology. GCSE (9-1) Physical Education
 Topic Guide 1: Applied Anatomy and Physiology GCSE (9-1) Physical Education Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) in Physical Education (1PE0) Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) in Physical
Topic Guide 1: Applied Anatomy and Physiology GCSE (9-1) Physical Education Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) in Physical Education (1PE0) Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) in Physical
Thursday 21 May 2015 Afternoon
 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Thursday 21 May 2015 Afternoon GCSE PHYSICAL EDUCATION B453/01 Developing Knowledge in Physical Education *2691490725* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials:
Oxford Cambridge and RSA Thursday 21 May 2015 Afternoon GCSE PHYSICAL EDUCATION B453/01 Developing Knowledge in Physical Education *2691490725* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials:
Friday 20 May 2016 Afternoon
 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Friday 20 May 2016 Afternoon GCSE PHYSICAL EDUCATION B451/01 An Introduction to Physical Education *5056088471* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials:
Oxford Cambridge and RSA Friday 20 May 2016 Afternoon GCSE PHYSICAL EDUCATION B451/01 An Introduction to Physical Education *5056088471* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials:
REVISION BOOKLET. The Body Systems
 REVISION BOOKLET The Body Systems GCSE PE 2016 Skeletal System Functions of the skeleton Joints for movement Muscle attachment Protection of vital organs Red and white blood cell production platelets Storage
REVISION BOOKLET The Body Systems GCSE PE 2016 Skeletal System Functions of the skeleton Joints for movement Muscle attachment Protection of vital organs Red and white blood cell production platelets Storage
Level 1/2 Technical Award in Health and Fitness (603/2650/5) Unit 01 Introduction to body systems and principles of training in health and fitness
 Level /2 Technical Award in Health and Fitness (603/2650/5) Sample 207 Unit 0 Introduction to body systems and principles of training in health and fitness Mark Scheme v0. All the material in this publication
Level /2 Technical Award in Health and Fitness (603/2650/5) Sample 207 Unit 0 Introduction to body systems and principles of training in health and fitness Mark Scheme v0. All the material in this publication
CHAPTER 4: The musculo-skeletal system. Practice questions - text book pages QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS. Answers
 CHAPTER 4: The musculo-skeletal system Practice questions - text book pages 64-66 1) A prime mover of hip flexion is the: a. rectus femoris. b. Iliopsoas. c. vastus muscles. d. gluteus maximus. b. Key
CHAPTER 4: The musculo-skeletal system Practice questions - text book pages 64-66 1) A prime mover of hip flexion is the: a. rectus femoris. b. Iliopsoas. c. vastus muscles. d. gluteus maximus. b. Key
Muscular System Learners MUST KNOW R A G Locations of the major muscle groups
 Please do the following 1. Read the Learners must know section (see below) 2. Watch the GCSE POD video 3. Attempt Exam Questions 4. Mark your answers 5. Reflect and repeat until you are successful and
Please do the following 1. Read the Learners must know section (see below) 2. Watch the GCSE POD video 3. Attempt Exam Questions 4. Mark your answers 5. Reflect and repeat until you are successful and
G.C.S.E REVISION QUESTION SHEET 1
 G.C.S.E REVISION QUESTION SHEET 1 1. Heart Rate (bmp) 205 D 185 C Aerobic training zone 120 B HR training zones for a 15-year-old a) Which letter represents the person s Maximum Heart Rate A, B, C or D?
G.C.S.E REVISION QUESTION SHEET 1 1. Heart Rate (bmp) 205 D 185 C Aerobic training zone 120 B HR training zones for a 15-year-old a) Which letter represents the person s Maximum Heart Rate A, B, C or D?
Applied anatomy and physiology: definitions of key terms
 Applied anatomy and physiology: definitions of key terms See pages 5 46 These are the key terms from Chapter 1. Try cutting them out and then matching the key terms with their definitions, or asking friends
Applied anatomy and physiology: definitions of key terms See pages 5 46 These are the key terms from Chapter 1. Try cutting them out and then matching the key terms with their definitions, or asking friends
B451. PHYSICAL EDUCATION An Introduction to Physical Education GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION. Tuesday 25 January 2011 Afternoon
 GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION PHYSICAL EDUCATION An Introduction to Physical Education B451 *OCE/26742* Candidates answer on the question paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials
GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION PHYSICAL EDUCATION An Introduction to Physical Education B451 *OCE/26742* Candidates answer on the question paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials
Physical Education: Short Course
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GSE entre Number Physical Education: Short ourse Unit 1: The Theory of Physical Education Friday 15 May 2015 fternoon Time: 1 hour andidate Number
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GSE entre Number Physical Education: Short ourse Unit 1: The Theory of Physical Education Friday 15 May 2015 fternoon Time: 1 hour andidate Number
Year 9 Options PE. Knowledge Book
 Year 9 Options PE Knowledge Book Topic 3 - Physical Training - Definitions and relationships between terms Grade 1-3 Grade 4-5 Grade 6-9 Curriculum Content Students will be expected to know and understand:
Year 9 Options PE Knowledge Book Topic 3 - Physical Training - Definitions and relationships between terms Grade 1-3 Grade 4-5 Grade 6-9 Curriculum Content Students will be expected to know and understand:
KULLEĠĠ SAN BENEDITTU Boys Secondary, Kirkop
 KULLEĠĠ SAN BENEDITTU Boys Secondary, Kirkop Mark HALF-YEARLY EXAMINATION 0/04 Track FORM 4 PHYSICAL EDUCATION TIME: h 0min Instructions to students: Answer ALL questions. Read carefully each question
KULLEĠĠ SAN BENEDITTU Boys Secondary, Kirkop Mark HALF-YEARLY EXAMINATION 0/04 Track FORM 4 PHYSICAL EDUCATION TIME: h 0min Instructions to students: Answer ALL questions. Read carefully each question
KS3 - PE THEORY REVISION GUIDE Y9
 KS3 - PE THEORY REVISION GUIDE Y9 Theory Knowledge Checklist Topic Tick off I can explain why physical activity is essential to a healthy lifestyle I can identify different types of movement using the
KS3 - PE THEORY REVISION GUIDE Y9 Theory Knowledge Checklist Topic Tick off I can explain why physical activity is essential to a healthy lifestyle I can identify different types of movement using the
Dep. Educación Física PHYSICAL CONDITION
 1. PHYSICAL FITNESS PHYSICAL CONDITION There are a set of elements that allow us to know the level of physical fitness of a person. One or more of these elements are necessary to perform any activity.
1. PHYSICAL FITNESS PHYSICAL CONDITION There are a set of elements that allow us to know the level of physical fitness of a person. One or more of these elements are necessary to perform any activity.
Strength, any two: curl-ups/crunches, push-ups, step-ups; heart and lung endurance, any two:
 Chapter 3 Study Guide Study Tips Read the chapter objectives. Look up any unfamiliar words. Read the questions below before you read the chapter. As you read the chapter, answer the following questions.
Chapter 3 Study Guide Study Tips Read the chapter objectives. Look up any unfamiliar words. Read the questions below before you read the chapter. As you read the chapter, answer the following questions.
Physical Education: Short Course Unit 1: The Theory of Physical Education
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GSE entre Number andidate Number Physical Education: Short ourse Unit 1: The Theory of Physical Education Tuesday 14 May 2013 fternoon Time: 1 hour You
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GSE entre Number andidate Number Physical Education: Short ourse Unit 1: The Theory of Physical Education Tuesday 14 May 2013 fternoon Time: 1 hour You
GCSE Physical Education. You Should Know Guide
 GCSE Physical Education You Should Know Guide 1.1 Healthy Active Lifestyle and How it Could Benefit You What is a healthy active lifestyle? A lifestyle that contributes positively to physical, mental,
GCSE Physical Education You Should Know Guide 1.1 Healthy Active Lifestyle and How it Could Benefit You What is a healthy active lifestyle? A lifestyle that contributes positively to physical, mental,
3 Movement analysis. Muscle contractions: isotonic and isometric. Exam practice. Now test yourself
 3 Movement analysis Muscle contractions: isotonic and isometric There are two types of muscle contraction: isotonic isometric. An isotonic contraction occurs when the muscle changes length as it contracts
3 Movement analysis Muscle contractions: isotonic and isometric There are two types of muscle contraction: isotonic isometric. An isotonic contraction occurs when the muscle changes length as it contracts
THe Skeletal System 1
 THe Skeletal System 1 What the Skeletal System DOes! Skeleton: works as the framework of your body and is made up of all of the bones in your body The number of bones in your skeleton depends on your age.
THe Skeletal System 1 What the Skeletal System DOes! Skeleton: works as the framework of your body and is made up of all of the bones in your body The number of bones in your skeleton depends on your age.
CHAPTER 1: 1.1 Muscular skeletal system. Question - text book page 16. Question - text book page 20 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS. Answers
 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS CHAPTER 1: 1.1 Muscular skeletal system Question - text book page 16 Using the information on pages 12 to 14 above, complete the table below. joint joint type articulating bones associated
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS CHAPTER 1: 1.1 Muscular skeletal system Question - text book page 16 Using the information on pages 12 to 14 above, complete the table below. joint joint type articulating bones associated
SIR MICHELANGELO REFALO
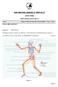 SIR MICHELANGELO REFALO SIXTH FORM Half Yearly Exam 2014 Name: Subject: Physical Education Intermediate Time: 2 Hours Answer ALL questions Question 1: (The Skeleton) The human skeleton is made up of 206
SIR MICHELANGELO REFALO SIXTH FORM Half Yearly Exam 2014 Name: Subject: Physical Education Intermediate Time: 2 Hours Answer ALL questions Question 1: (The Skeleton) The human skeleton is made up of 206
Btec Exam Guide Practice Questions - Unit 1.1 Components of Fitness
 Btec Exam Guide Practice Questions - Unit 1.1 Components of Fitness 1) What is the main difference between aerobic endurance and muscular endurance? (2 marks) 2) Explain the following components of physical
Btec Exam Guide Practice Questions - Unit 1.1 Components of Fitness 1) What is the main difference between aerobic endurance and muscular endurance? (2 marks) 2) Explain the following components of physical
Great Balls of Fire Revision Game
 Great Balls of Fire Revision Game Task: - The class needs to be divided in to teams (4/5 per team) - The students are positioned at the back of the class, each team with a bean bag (the colour denoting
Great Balls of Fire Revision Game Task: - The class needs to be divided in to teams (4/5 per team) - The students are positioned at the back of the class, each team with a bean bag (the colour denoting
SAMPLE ASSESSMENT MATERIALS GCSE. WJEC GCSE in PHYSICAL EDUCATION (SHORT COURSE) Teaching from 2017 APPROVED BY QUALIFICATIONS WALES
 GCSE WJEC GCSE in PHYSICAL EDUCATION (SHORT COURSE) APPROVED BY QUALIFICATIONS WALES SAMPLE ASSESSMENT MATERIALS Teaching from 2017 This Qualifications Wales regulated qualification is not available to
GCSE WJEC GCSE in PHYSICAL EDUCATION (SHORT COURSE) APPROVED BY QUALIFICATIONS WALES SAMPLE ASSESSMENT MATERIALS Teaching from 2017 This Qualifications Wales regulated qualification is not available to
Friday 16 May 2014 Afternoon
 Friday 16 May 2014 Afternoon GCSE PHYSICAL EDUCATION B451/01 An Introduction to Physical Education *1116336093* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials required:
Friday 16 May 2014 Afternoon GCSE PHYSICAL EDUCATION B451/01 An Introduction to Physical Education *1116336093* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials required:
THEORY OF FIRST TERM. PHYSICAL EDUCATION: 2nd E.S.O.
 THEORY OF FIRST TERM. PHYSICAL EDUCATION: 2nd E.S.O. 1.- WHAT IS THE WARM-UP? It is a set of exercises for muscles and joints which prepare the body for the physical activity, reducing the risk of suffering
THEORY OF FIRST TERM. PHYSICAL EDUCATION: 2nd E.S.O. 1.- WHAT IS THE WARM-UP? It is a set of exercises for muscles and joints which prepare the body for the physical activity, reducing the risk of suffering
Copyright Cardiff University
 This exercise programme has been developed by physiotherapists specifically for people with movement disorders. Exercise is not without its risks and this or any other exercise programme has potential
This exercise programme has been developed by physiotherapists specifically for people with movement disorders. Exercise is not without its risks and this or any other exercise programme has potential
KS4 Physical Education
 KS4 Physical Education The Effects of Exercise These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities
KS4 Physical Education The Effects of Exercise These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities
Five for Life Student Portfolio
 Five for Life Student Series 1, Student Edition Table of Contents Student Essential Question: How do my current behaviors and fitness affect my health now and in the future? Over the course of this portfolio,
Five for Life Student Series 1, Student Edition Table of Contents Student Essential Question: How do my current behaviors and fitness affect my health now and in the future? Over the course of this portfolio,
4. Which one of the following correctly identifies the part of the skeleton that produces red blood cells?
 GSE P.E. questions and mark schemes 1 a pplied natomy and Physiology 1. Which of one of the following is NOT a function of the skeleton? 2. Which one of the following is NOT a function of the skeleton?
GSE P.E. questions and mark schemes 1 a pplied natomy and Physiology 1. Which of one of the following is NOT a function of the skeleton? 2. Which one of the following is NOT a function of the skeleton?
PED1. General Certificate of Education January 2009 Advanced Subsidiary Examination. SPORT AND PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1
 General Certificate of Education January 2009 Advanced Subsidiary Examination SPORT AND PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 PED1 Friday 16 January 2009 1.30 pm to 3.00 pm For this paper you must have: a 12-page
General Certificate of Education January 2009 Advanced Subsidiary Examination SPORT AND PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 PED1 Friday 16 January 2009 1.30 pm to 3.00 pm For this paper you must have: a 12-page
2016 PHYSICAL EDUCATION
 1 2016 PHYSICAL EDUCATION External Examination 2016 FOR OFFICE USE ONLY SUPERVISOR CHECK ATTACH SACE REGISTRATION NUMBER LABEL TO THIS BOX QUESTION BOOKLET 1 16 pages, 6 questions RE-MARKED Thursday 17
1 2016 PHYSICAL EDUCATION External Examination 2016 FOR OFFICE USE ONLY SUPERVISOR CHECK ATTACH SACE REGISTRATION NUMBER LABEL TO THIS BOX QUESTION BOOKLET 1 16 pages, 6 questions RE-MARKED Thursday 17
Revision Booklet Paper 1
 OCR GCSE Physical Education Paper 1 Revision Booklet Revision Booklet Paper 1 Name.. Tutor. Teacher.. 1 OCR GCSE Physical Education Paper 1 Revision Booklet Paper 1 Anatomy & Physiology About the Paper:
OCR GCSE Physical Education Paper 1 Revision Booklet Revision Booklet Paper 1 Name.. Tutor. Teacher.. 1 OCR GCSE Physical Education Paper 1 Revision Booklet Paper 1 Anatomy & Physiology About the Paper:
Physical Education PHED1 PHED1 (JUN10PHED101) General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination June 2010
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Physical Education Unit 1 General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Physical Education Unit 1 General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination
General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination June 2013
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Physical Education General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination June 2013
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Physical Education General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination June 2013
Separate information into components and identify their characteristics. Finish a task by adding to given information.
 Exam technique GCSE PE Command Words Analyse Apply Calculate Compare Complete Consider Define Describe Discuss Evaluate Explain Identify Illustrate Interpret Justify Outline Suggest State Separate information
Exam technique GCSE PE Command Words Analyse Apply Calculate Compare Complete Consider Define Describe Discuss Evaluate Explain Identify Illustrate Interpret Justify Outline Suggest State Separate information
1.1 Healthy, active lifestyles
 1.1 Healthy, active lifestyles 1.1.4b Physical activity as part of your healthy, active lifestyle: assessing fi tness and developing an exercise programme Contents Worksheets Worksheet 1: Interval training,
1.1 Healthy, active lifestyles 1.1.4b Physical activity as part of your healthy, active lifestyle: assessing fi tness and developing an exercise programme Contents Worksheets Worksheet 1: Interval training,
Which of the following best describes the intensity element of the FITT principle of training?
 Developing skills, techniques and motivation. Developing physical and mental capacity. Which of the following best describes the intensity element of the FITT principle of training? (a) The type of exercise
Developing skills, techniques and motivation. Developing physical and mental capacity. Which of the following best describes the intensity element of the FITT principle of training? (a) The type of exercise
Grade 10 Intro to Resistance Training
 Grade 10 Intro to Resistance Training Benefits to Training with Weights Hypertrophy - Increase in existing muscle fibers Strengthening of tendons and ligament tissues Improve posture Decrease the size
Grade 10 Intro to Resistance Training Benefits to Training with Weights Hypertrophy - Increase in existing muscle fibers Strengthening of tendons and ligament tissues Improve posture Decrease the size
Warm-Up and Stretching Exercises
 Warm-Up and Stretching Exercises Most athletes (swimmers included) use a combination of controlled movement exercises and specific joint/muscle stretching to improve performance potential. The proposed
Warm-Up and Stretching Exercises Most athletes (swimmers included) use a combination of controlled movement exercises and specific joint/muscle stretching to improve performance potential. The proposed
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *0481812698* PHYSICAL EDUCATION 0413/13 Paper 1 October/November 2013 1 hour 45 minutes Candidates
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *0481812698* PHYSICAL EDUCATION 0413/13 Paper 1 October/November 2013 1 hour 45 minutes Candidates
Physical Education Unit 1: The Theory of Physical Education
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Physical Education Unit 1: The Theory of Physical Education Candidate Sample Assessment Material Time: 1 hour 30 minutes You do not need any
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Physical Education Unit 1: The Theory of Physical Education Candidate Sample Assessment Material Time: 1 hour 30 minutes You do not need any
KS4 Physical Education
 KS4 Physical Education Principles of Training These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities created
KS4 Physical Education Principles of Training These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities created
Physical Education: Short Course Unit 1: The Theory of Physical Education
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GSE entre andidate Physical Education: Short ourse Unit 1: The Theory of Physical Education Sample ssessment Material Time: 1 hour You do not need any other
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GSE entre andidate Physical Education: Short ourse Unit 1: The Theory of Physical Education Sample ssessment Material Time: 1 hour You do not need any other
1.1.4 Mock Examination Questions
 1.1.4 Mock Examination Questions Questions Q1 GCSE PE students were determined to help their parents, Janet and John, become involved in sport so that Janet and John could benefit from a healthy, active
1.1.4 Mock Examination Questions Questions Q1 GCSE PE students were determined to help their parents, Janet and John, become involved in sport so that Janet and John could benefit from a healthy, active
Training 1. Training c Training. For AQA
 Training 1 Training Training 2 What you will learn about in this topic: 1. Methods of training 2. What each training method develops 3. How each method works Training 3 Learning objectives By the end of
Training 1 Training Training 2 What you will learn about in this topic: 1. Methods of training 2. What each training method develops 3. How each method works Training 3 Learning objectives By the end of
THE STRUCTURE OF OUR BODY
 THE STRUCTURE OF OUR BODY 1. INTRODUCTION This chapter will describe the basic anatomy of the human body, explaining the most important elements of the muscular and skeletal system. 2. THE MUSCULOSKELETAL
THE STRUCTURE OF OUR BODY 1. INTRODUCTION This chapter will describe the basic anatomy of the human body, explaining the most important elements of the muscular and skeletal system. 2. THE MUSCULOSKELETAL
1.2 Your healthy, active body
 1.2 Your healthy, active body 1.2.4 A healthy, active lifestyle and your muscular system Contents Worksheets Worksheet 1: Types of muscle, Level A 152 Worksheet 1: Types of muscle, Level B 153 Worksheet
1.2 Your healthy, active body 1.2.4 A healthy, active lifestyle and your muscular system Contents Worksheets Worksheet 1: Types of muscle, Level A 152 Worksheet 1: Types of muscle, Level B 153 Worksheet
GCSE PE Component 1 Fitness & Body Systems - Revision Booklet Name:
 WWW.THEPECLASSROOM.COM GCSE PE Component 1 Fitness & Body Systems - Revision Booklet Name: WWW.THEPECLASSROOM.COM For all questions that are worth more than one mark you need to make sure that you give
WWW.THEPECLASSROOM.COM GCSE PE Component 1 Fitness & Body Systems - Revision Booklet Name: WWW.THEPECLASSROOM.COM For all questions that are worth more than one mark you need to make sure that you give
GCSE PERSONAL LEARNING CHECKLIST PHYSICAL EDUCATION
 GCSE PERSONAL LEARNING CHECKLIST PHYSICAL EDUCATION PLC KEY: COMPONENT 1: FITNESS AND BODY SYSTEMS 1.1-4.1 You have covered the concept in lesson by the teacher. You have extended the concept in your file
GCSE PERSONAL LEARNING CHECKLIST PHYSICAL EDUCATION PLC KEY: COMPONENT 1: FITNESS AND BODY SYSTEMS 1.1-4.1 You have covered the concept in lesson by the teacher. You have extended the concept in your file
1.1 The Structure and Functions of the Musculo- Skeletal System Teacher Answer Booklet
 GCSE EDEXCEL 1.1 1.1 The Structure and Functions of the Musculo- Skeletal System Teacher Answer Booklet GCSE EDEXCEL 1.1 WWW.THEPECLASSROOM.COM Topic Description from Specification Pupil comments How confident
GCSE EDEXCEL 1.1 1.1 The Structure and Functions of the Musculo- Skeletal System Teacher Answer Booklet GCSE EDEXCEL 1.1 WWW.THEPECLASSROOM.COM Topic Description from Specification Pupil comments How confident
Physical Education GCSE 1PE0/01. Component 1: Fitness and Body Systems. Time: 1 hour and 45 minutes. You will need a calculator.
 Write your name here Surname Other names GCSE Physical Education Component 1: Fitness and Body Systems Time: 1 hour and 45 minutes Paper Reference 1PE0/01 You will need a calculator. Total Marks Instructions
Write your name here Surname Other names GCSE Physical Education Component 1: Fitness and Body Systems Time: 1 hour and 45 minutes Paper Reference 1PE0/01 You will need a calculator. Total Marks Instructions
The F.I.T.T. Principle
 The F.I.T.T. Principle The F.I.T.T. principle is a basic philosophy of what is necessary to gain a training effect from an exercise program. F.I.T.T. stands for Frequency, Intensity, Type and Time. We
The F.I.T.T. Principle The F.I.T.T. principle is a basic philosophy of what is necessary to gain a training effect from an exercise program. F.I.T.T. stands for Frequency, Intensity, Type and Time. We
Dumbarton Academy. Physical Education Department. Fitness booklet. Standard Grade
 Dumbarton Academy Physical Education Department Fitness booklet Standard Grade What happens when I take part in an activity? 1. Blood is circulated more quickly and more of it goes to the hardest working
Dumbarton Academy Physical Education Department Fitness booklet Standard Grade What happens when I take part in an activity? 1. Blood is circulated more quickly and more of it goes to the hardest working
Tuesday 14 May 2013 Afternoon
 Tuesday 14 May 2013 Afternoon GCSE PHYSICAL EDUCATION B451/01 An Introduction to Physical Education *B426720613* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials required:
Tuesday 14 May 2013 Afternoon GCSE PHYSICAL EDUCATION B451/01 An Introduction to Physical Education *B426720613* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials required:
Monday 28 January 2013 Afternoon
 Monday 28 January 2013 Afternoon GCSE PHYSICAL EDUCATION B453/01 Developing Knowledge in Physical Education *B426730113* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials
Monday 28 January 2013 Afternoon GCSE PHYSICAL EDUCATION B453/01 Developing Knowledge in Physical Education *B426730113* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials
Health and Fitness You have no colds, flu, aches or pains, and you can run 1500m in six minutes. But does that mean you are healthy and fit?
 PHYSICAL FITNESS Health and Fitness You have no colds, flu, aches or pains, and you can run 1500m in six minutes. But does that mean you are healthy and fit? What is health? Health does not mean the absence
PHYSICAL FITNESS Health and Fitness You have no colds, flu, aches or pains, and you can run 1500m in six minutes. But does that mean you are healthy and fit? What is health? Health does not mean the absence
What are the three categories of a healthy active lifestyle? There are seven benefits for a healthy active lifestyle. Name three.
 What are the three categories of a healthy active lifestyle? (Physical, Social, Mental) There are seven benefits for a healthy active lifestyle. Name three. (Wellbeing, feel good, stress relief, self-esteem,
What are the three categories of a healthy active lifestyle? (Physical, Social, Mental) There are seven benefits for a healthy active lifestyle. Name three. (Wellbeing, feel good, stress relief, self-esteem,
GCSE PHYSICAL EDUCATION - Course Summary
 Subject Overview Curriculum pathway GCSE PHYSICAL EDUCATION - Course Summary Unit / Module Course: GCSE Edexcel Physical Education Overall Summary Exam / Controlled % of course UMS allocation Marks available
Subject Overview Curriculum pathway GCSE PHYSICAL EDUCATION - Course Summary Unit / Module Course: GCSE Edexcel Physical Education Overall Summary Exam / Controlled % of course UMS allocation Marks available
