Structure and Movement
|
|
|
- Pearl Mason
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name Structure and Movement How do bones, muscles, and skin help maintain the body s homeostasis? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about the topic Record three things you already know about bones, muscles, and skin in the first column Then describe three things that you would like to learn about bones, muscles, and skin in the second column When you have completed the chapter, think about what you have learned and complete the What I Learned column Date K What I Know W What I Want to Learn L What I Learned Chapter Vocabulary Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 NEW skeletal system cartilage periosteum joint ligament arthritis osteoporosis REVIEW homeostasis NEW muscle skeletal muscle voluntary muscle smooth muscle involuntary muscle cardiac muscle ACADEMIC convert NEW integumentary system epidermis melanin dermis bruise A Lesson Content Vocabulary page for each lesson is provided in the Chapter Resources Files Structure and Movement 133
2 Lesson 1 The Skeletal System Skim Lesson 1 in your book Read the headings, and look at the photos and illustrations Identify three things you want to learn more about as you read the lesson Write your ideas in your Science Journal Functions of the Skeletal System 488 Identify the functions of the skeletal system Protection of tissues by hard bones Production red of blood cells Functions of the Skeletal System Storage of fat and calcium Support of the body Movement enabled by bones attached t o muscles Structure of Bones 489 Describe 2 types of bone tissue and bone marrow Compact the hard, outer part of bones; a dense web of fibers Red where red blood cells are made; found in the spongy ends of long bones and in some flat bones, such as the ribs Bone Tissue Bone Marrow Spongy has small holes that make it look like a sponge and make the bone less dense Yellow found inside the longest bones; stores fat 134 Structure and Movement
3 Lesson 1 Structure and Movement (continued) 490 Describe the location and function of cartilage and periosteum, two types of bone coverings cartilage: found at the end of bones; prevents rubbing Bone coverings periosteum: surrounds bone not covered by cartilage; produces n ew bone; nourishes bone 490 Sequence the steps in bone formation Include the purpose of the growth plate Before birth: The skeleton is made mostly of cartilage Infant: The cartilage begins to be replaced by bone Joints 491 Children and Young Teens: Long bones have growth plates, which produce cartilage that is then replaced by bone tissue Classify the types of joints Immovable Types of JointsMovable Example: skull ball and socket Example: hips hinge Example: knee pivot Example: neck Structure and Movement 135
4 Lesson 1 Structure and Movement (continued) Bone Injuries and Diseases 492 Sequence how bone fractures are treated A bone breaks A cast or a metal plate and screws are applied These materials hold the bone together while it heals 492 Define arthritis, and then draw an outline of a hand and color the location of the joints red arthritis: a disease in which joints become irritated and inflamed, such as when cartilage in joints is damaged or wears away Drawings should show a hand with the major joints colored red 492 Draw how the backbon e of a person with osteoporosis changes over time 55 years 65 years 75 years Drawings should show a backbone with normal curve Drawings should show a backbone with more curvature Drawings should show a backbone with severe curvature 136 Structure and Movement
5 Lesson 1 Structure and Movement (continued) Healthy Bones 493 Complete the cause-and-effect chart to detail the effect of behaviors on bone health Cause Eating a balanced diet Participating in weight bearing exercises Not getting enough calcium Getting enough vitamin D Effect provides calcium and vitamin D, which keeps bones strong strengthens bones and builds new bone tissue causes bones to become weak as the body uses calcium stored in them helps the body use calcium The Skeletal System and Homeostasis 493 Identify how bones contribute to the body s homeostasis Healthy bones supply calcium to nerves, muscles, and heart Healthy bones help a person respond to unpleasant stimuli with the ability A healthy skeletal system is important in maintaining homeostasis Describe what your body would be like without bones to move quickly Accept all reasonable responses Sample answer: Without bones, your body would not have the structural support to remain upright Overall health would suffer because bones supply calcium to the nerves, muscles, and heart Injuries could be more common because bones are hard and rigid and protect the soft tissues of the body Structure and Movement 137
6 Lesson 2 The Muscular System Scan Lesson 2 in your book Write three questions you have about your muscles in your Science Journal Try to answer your questions as you read Functions of the Muscular System 497 Organize information about the important functions of the muscular system movement protection Muscular System stability maintaining body temperature 497 Draw a relaxed muscle and a contracted muscle Have students flex their wrists so that they can feel muscle as it contracts and relaxes 498 Drawings should show an extended muscle fiber Relaxed Describe the role of tendons Drawings should show a shorter muscle fiber attach muscles to bones Contracted Tendons stabilize joints to hold the body in shape 138 Structure and Movement
7 Lesson 2 The Muscular System (continued) 498 Identify how muscle contractions affect the body s temperature regulation Muscles contract Chemical energy is changed to thermal energy, which warms the body Types of Muscles Summarize the 3 types of muscle tissue Describe and give an example of each type Type of Muscle Description Example 499 Skeletal, or voluntary muscles that you can consciously control; attach to bones; work in pairs; can become stronger with exercise bicep and tricep Students can squeeze gelatin or water in long balloons to simulate the movement of smooth muscles Cardiac, or heart Smooth, or involuntary type of involuntary muscle found only in the heart; have discs that enable these muscles to contract in unison named for smooth appearance; shorter and smoother than skeletal muscles heart lining of stomach, intestines, and blood vessels Structure and Movement 139
8 Lesson 2 The Muscular System (continued) Healthy Muscles 501 Detail the effects of behaviors on muscle healt h Cause Effect Eating a healthy diet Not getting enough exercise Muscle loss provides energy to muscles and helps keep them strong causes muscles to lose size and strength; increases risk of heart disease and injuries causes increased risk of heart disease and bone injuries; joints become unstable The Muscular System and Homeostasis 501 Sequence how the muscular system helps maintain homeostasis You are playing in a soccer game The temperature is 10 C You feel cold The game begins You start to exercise (or move) As you move, your muscles change chemical energy to thermal energy Your body gets warmer Your muscle cells also need more oxygen and need to get rid of wastes Cardiac muscles of the heart contract more often and pump more blood More oxygen is carried to the cells Supp ose that you were on a school bus t hat broke down on a cold winter day What could you suggest to help keep everyone warm? Accept all reasonable responses Sample answer: I know that exercise moves muscles Muscles convert chemical energy into thermal energy and will help to warm the body I would try to get everyone to move jumping, wiggling, or hopping in place 140 Structure and Movement
9 Lesson 3 The Skin Predict three things that will be discussed in Lesson 3 after reading the headings Write your predictions in your Science Journal Functions of the Skin 505 Summarize the parts of the integumentary system Integumentary System all the external coverings of the body including skin nails sweat glands hair Explain the 5 functions of the skin Functions of the Skin Protection covers bones and muscles; keeps the body from drying out; protects cells and tissues; protects against dirt, bacteria, viruses, and other substances Sensory response 3 Temperature regulation 4 Production of vitamin D 5 Elimination detects texture, temperature, and pain sweat from pores in skin evaporates, cooling the body; releases heat energy from dilated blood vessels near the skin s surface skin exposed to sunlight makes vitamin D, which the body uses to help it absorb calcium and phosphorous and to promote bone growth water, salts, and other waste products removed through pores, especially while sweating Structure and Movement 141
10 Lesson 3 The Skin (continued) Structures of the Skin 507 Organize information about the structures of the skin Include at least three facts about each layer Layer Description of function and structure Epidermis outmost layer of skin; only layer in direct contact with the outside environment; produces melanin, which absorbs some ultraviolet rays Dermis located below the epidermis; a thick layer that gives skin strength, nourishment, and flexibility; contains sweat glands, nerves, hair follicles, and muscles 507 Fatty layer innermost layer of skin; insulates the body, provides a protective padding, and stores energy; can be thin or thick, depending on location on the body Assess information about structures of the skin Read the statements below If the statement is true, write true on the line If the statement is false, rewrite the sentence so the underlined portion is true The epidermis is tough and thick False: The epidermis is tough and thin The fatty layer insulates the body True Melanin is a layer of skin that absorbs some of the Sun s damaging ultraviolet rays False: Melanin is a pigment that absorbs some of the Sun s damaging ultraviolet rays 142 Structure and Movement
11 Lesson 3 The Skin (continued) Skin Injuries and Repair 508 Summarize three kinds of skin injuries Write a short description of each kind of injury Skin Injuries bruise: cut: burn: area in which a break in one damage to skin blood vessels or more layers from chemicals, in skin are of skin radiation, broken, but the electricity, or skin is not cut friction; extreme or opened hot or cold temperatures Healthy Skin 510 Identify how behaviors affect skin health Cause Exposure to sunlight Effect can cause permanent damage to the skin, including wrinkles, dry skin, and skin cancer The Skin and Homeostasis 510 Lotion and gentle soap Describe how the skin helps maintain homeostasis skin + circulatory syste m = body temperature regulated skin + nerves + muscles = reaction to stimuli lotion keeps skin moist; gentle soap cleanses the skin Homeostasis Suppose you hit your thumb with a hammer What would you expect your thumb to look like the next day? What would it look like the next week? Sample answer: The next day, the skin around the injured area would be black and blue as the red blood cells break down In a week, the bruise would probably be greenish-yellow, indicating that the bruise is slowly fading away Structure and Movement 143
12 Review Chapter Wrap-Up Structure and Movement Now that you have read the chapter, think about what you have learned Complete the What I Learned column on the first page of the chapter Use this checklist to help you study Complete your Foldables Chapter Project Study your Science Notebook on this chapter Study the definitions of vocabulary words Reread the chapter, and review the charts, graphs, and illustrations Review the Understanding Key Concepts at the end of each lesson Look over the Chapter Review at the end of the chapter Reread the chapter Big Idea and the lesson Key Concepts Draw a picture of a person playing your favorite sport or doing some other physical activity, such as dancing or gymnastics Use captions and labels to explain how the person s bones, muscles, and skin are working together to help maintain homeostasis Accept all reasonable responses Drawings should include labels for bones, muscles, and skin Challenge Suppose that your science fair project this year is to show how bones and muscles work together What materials could you use to model the interactions of bones and muscles? 144 Structure and Movement
Structure and Movement
 Structure and Movement The Skin Key Concepts What does the skin do? How do the three layers of skin differ? How does the skin interact with other body systems? What do you think? Read the two statements
Structure and Movement The Skin Key Concepts What does the skin do? How do the three layers of skin differ? How does the skin interact with other body systems? What do you think? Read the two statements
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin. KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body.
 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
CHAPTER 14 Bones, Muscles, Skin
 CHAPTER 14 Bones, Muscles, Skin SECTION 1 Body Organization and Homeostasis Levels of Organization Basic to Complex Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems CELLS Basic unit in living thing Main Parts: Cell
CHAPTER 14 Bones, Muscles, Skin SECTION 1 Body Organization and Homeostasis Levels of Organization Basic to Complex Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems CELLS Basic unit in living thing Main Parts: Cell
December 3, Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow?
 December 3, 2013 Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow? Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Chapter 36: Biology II The Skeleton
December 3, 2013 Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow? Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Chapter 36: Biology II The Skeleton
THe Skeletal System 1
 THe Skeletal System 1 What the Skeletal System DOes! Skeleton: works as the framework of your body and is made up of all of the bones in your body The number of bones in your skeleton depends on your age.
THe Skeletal System 1 What the Skeletal System DOes! Skeleton: works as the framework of your body and is made up of all of the bones in your body The number of bones in your skeleton depends on your age.
Major Functions of the Skeletal System
 Skeletal System Major Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Provide shape and support. 2. Enables you to move 3. Protects your organs 4. Produces blood cells 5. stores minerals and other materials until
Skeletal System Major Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Provide shape and support. 2. Enables you to move 3. Protects your organs 4. Produces blood cells 5. stores minerals and other materials until
THE SKELETAL, MUSCULAR AND INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEMS. Chapter 22 Sections
 THE SKELETAL, MUSCULAR AND INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEMS Chapter 22 Sections THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM Ch. 22 Section 3 (588-591) Muscles of the Body WHAT ARE THE THREE TYPES OF MUSCLES? 1.Skeletal muscle - move us
THE SKELETAL, MUSCULAR AND INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEMS Chapter 22 Sections THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM Ch. 22 Section 3 (588-591) Muscles of the Body WHAT ARE THE THREE TYPES OF MUSCLES? 1.Skeletal muscle - move us
Skin: The Body s Protection
 Ch 34: Protection, Support and Locomotion 34.1 - Skin: The Body s Protection Inside This Section... The Structure of Skin The Function of Skin Response to Injury Structure and Function of the skin 4 tissue
Ch 34: Protection, Support and Locomotion 34.1 - Skin: The Body s Protection Inside This Section... The Structure of Skin The Function of Skin Response to Injury Structure and Function of the skin 4 tissue
What type of tissue is this
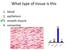 What type of tissue is this 1. blood 2. epithelium 3. smooth muscle 4. connective 83% 1 7% blood epithelium smooth muscle connective What type of tissue is this 1. connective 2. nervous 3. smooth muscle
What type of tissue is this 1. blood 2. epithelium 3. smooth muscle 4. connective 83% 1 7% blood epithelium smooth muscle connective What type of tissue is this 1. connective 2. nervous 3. smooth muscle
Chapter: Structure and Movement
 Table of Contents Chapter: Structure and Movement Section 1: The Skeletal System Section 2: The Muscular System Section 3: The Skin 1 Living Bones The Skeletal System The bones in your body are very much
Table of Contents Chapter: Structure and Movement Section 1: The Skeletal System Section 2: The Muscular System Section 3: The Skin 1 Living Bones The Skeletal System The bones in your body are very much
Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Name Date Class Structure and Movement 33 Chapter 17 Structure and
 Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Name Date Class Structure and Movement 33 Chapter 17 Structure and Movement Section 1 The Skeletal System A. All the in your
Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Name Date Class Structure and Movement 33 Chapter 17 Structure and Movement Section 1 The Skeletal System A. All the in your
Body Organization and Structure
 CHAPTER 19 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET Body Organization and Structure As you read Chapter 19, which begins on page 462 of your textbook, answer the following questions. This Really Happened... (p. 462)
CHAPTER 19 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET Body Organization and Structure As you read Chapter 19, which begins on page 462 of your textbook, answer the following questions. This Really Happened... (p. 462)
SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS WHAT MOVES YOU!
 SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS WHAT MOVES YOU! WHAT ARE THE MAIN FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM? THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeletal system is the organ system that supports and protects the body and allows
SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS WHAT MOVES YOU! WHAT ARE THE MAIN FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM? THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeletal system is the organ system that supports and protects the body and allows
SECTION 45-1 REVIEW. VOCABULARY REVIEW Describe the functions of the tissues listed below.
 SECTION 45-1 REVIEW THE HUMAN BODY PLAN VOCABULARY REVIEW Describe the functions of the tissues listed below. 1. nervous tissue 2. muscular tissue 3. skeletal muscle 4. epithelial tissue 5. connective
SECTION 45-1 REVIEW THE HUMAN BODY PLAN VOCABULARY REVIEW Describe the functions of the tissues listed below. 1. nervous tissue 2. muscular tissue 3. skeletal muscle 4. epithelial tissue 5. connective
Skin. the largest organ of the body 1 mm to 2 mm thick almost 2 square meters 6% of a person s body weight
 Skin the largest organ of the body 1 mm to 2 mm thick almost 2 square meters 6% of a person s body weight Functions of the Skin protection disease-causing organisms dangerous chemicals blood loss fluid
Skin the largest organ of the body 1 mm to 2 mm thick almost 2 square meters 6% of a person s body weight Functions of the Skin protection disease-causing organisms dangerous chemicals blood loss fluid
STUDY GUIDE SECTION 45-1 The Human Body Plan
 STUDY GUIDE SECTION 45-1 The Human Body Plan Name Period Date Multiple Choice-Write the correct letter in the blank 1. Nervous tissue contains specialized cells called a. Transmitters. b. neurons c. messenger
STUDY GUIDE SECTION 45-1 The Human Body Plan Name Period Date Multiple Choice-Write the correct letter in the blank 1. Nervous tissue contains specialized cells called a. Transmitters. b. neurons c. messenger
The Human Body. Mrs. Green
 The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
**Take your homework out to be stamped**
 Warm Up: 3/5-3/6 **Take your homework out to be stamped** 1. What is the difference between osteocytes and osteoblasts? 2. What body systems work with the muscular system? Give specific examples. 3. Your
Warm Up: 3/5-3/6 **Take your homework out to be stamped** 1. What is the difference between osteocytes and osteoblasts? 2. What body systems work with the muscular system? Give specific examples. 3. Your
Locomotion: The act or power of moving from place to place
 Locomotion Locomotion: The act or power of moving from place to place Vocabulary 1. Motile = The ability to move from place to place 2. Sessile = 3. Muscle contraction = 4. Exoskeleton = 5. Endoskeleton
Locomotion Locomotion: The act or power of moving from place to place Vocabulary 1. Motile = The ability to move from place to place 2. Sessile = 3. Muscle contraction = 4. Exoskeleton = 5. Endoskeleton
Section 11.1 Your Skeletal System
 Objectives Identify the five main roles of the skeletal system. Describe the functions of bones and joints. Explain how you can keep your skeletal system healthy. Slide 1 of 24 Quick Quiz Complete each
Objectives Identify the five main roles of the skeletal system. Describe the functions of bones and joints. Explain how you can keep your skeletal system healthy. Slide 1 of 24 Quick Quiz Complete each
The Skeletal System. Functions of the Skeletal System
 Skeletal System The Skeletal System Functions of the Skeletal System Provide support Protect internal organs Allows your body to move Stores and produced materials that your body needs You have 206 bones
Skeletal System The Skeletal System Functions of the Skeletal System Provide support Protect internal organs Allows your body to move Stores and produced materials that your body needs You have 206 bones
Structure, Movement, and Control
 Lesson 2 Structure, Movement, and Control Scan Lesson 2. Read the lesson titles and bold words. Look at the pictures. Identify three facts you discovered about the structure, movement, and control of the
Lesson 2 Structure, Movement, and Control Scan Lesson 2. Read the lesson titles and bold words. Look at the pictures. Identify three facts you discovered about the structure, movement, and control of the
In Activity 12, What s Happening Inside? you learned about the functions
 16 Support System: Bones, Joints and Muscles l a b o r at o ry In Activity 12, What s Happening Inside? you learned about the functions of the skeletal and muscular systems in supporting and moving your
16 Support System: Bones, Joints and Muscles l a b o r at o ry In Activity 12, What s Happening Inside? you learned about the functions of the skeletal and muscular systems in supporting and moving your
Structure, Movement, and Control
 Human Body Systems Structure, Movement, and Control What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
Human Body Systems Structure, Movement, and Control What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
April 20, Living Organisms: The Skeletal System
 Living Organisms: The Skeletal System Day 1 April 20, 2018 The skeleton is a structural framework that supports and protects the human body.. April 20, 2018 Estimate- How many bones you have in your body?
Living Organisms: The Skeletal System Day 1 April 20, 2018 The skeleton is a structural framework that supports and protects the human body.. April 20, 2018 Estimate- How many bones you have in your body?
The Skeletal System. Chapter 8
 The Skeletal System Chapter 8 1 Introduction Movement is essential for animals. This is done by moving muscles with the skeleton. 2 Functions of the skeleton 1. Gives shape and support to the body. The
The Skeletal System Chapter 8 1 Introduction Movement is essential for animals. This is done by moving muscles with the skeleton. 2 Functions of the skeleton 1. Gives shape and support to the body. The
Section Chapter 36. The Skeletal, Muscular and Integumentary Systems. Go to Section:
 Section 35-1 Chapter 36 The Skeletal, Muscular and Integumentary Systems Section Outline Section 36-1 36 1 The Skeletal System A. The Skeleton B. Structure of Bones C. Development of Bones D. Types of
Section 35-1 Chapter 36 The Skeletal, Muscular and Integumentary Systems Section Outline Section 36-1 36 1 The Skeletal System A. The Skeleton B. Structure of Bones C. Development of Bones D. Types of
High School Biology - Problem Drill 20: Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems
 High School Biology - Problem Drill 20: Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following about the skeletal system is true? Question #01 A. There are two types
High School Biology - Problem Drill 20: Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following about the skeletal system is true? Question #01 A. There are two types
CHAPTER 14. Bones Muscles Skin
 CHAPTER 14 Bones Muscles Skin Chapter 14 Objectives Section 1 Body Organization and Homeostasis 1. Define homeostasis and a give a specific example. 2. Explain why energy is important to the human body.
CHAPTER 14 Bones Muscles Skin Chapter 14 Objectives Section 1 Body Organization and Homeostasis 1. Define homeostasis and a give a specific example. 2. Explain why energy is important to the human body.
Challenge Question: Prediction: (Wait for directions) Evidence: (Draw, color and label how your Clay model looked when it was complete)
 Activity #12 What s happening inside? Challenge Question: Prediction: (Wait for directions) Evidence: (Draw, color and label how your Clay model looked when it was complete) Act #12 pg 1 of 3 Analysis
Activity #12 What s happening inside? Challenge Question: Prediction: (Wait for directions) Evidence: (Draw, color and label how your Clay model looked when it was complete) Act #12 pg 1 of 3 Analysis
04/10/2013. Pick up a Human Body Book and PUT YOUR NAME ON IT!
 04/10/2013 Pick up a Human Body Book and PUT YOUR NAME ON IT! Did you know?? 1. The adult body is made up of: 100 trillion cells, 206 bones, 600 muscles, and 22 internal organs. 2. Every square inch of
04/10/2013 Pick up a Human Body Book and PUT YOUR NAME ON IT! Did you know?? 1. The adult body is made up of: 100 trillion cells, 206 bones, 600 muscles, and 22 internal organs. 2. Every square inch of
36 1 The Skeletal System Slide 1 of 40
 1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
Epithelial Tissues. Types of Epithelial Tissues: Lining of Kidney
 Epithelial Tissues Covers the entire body surface and most of the body s inner cavities Outer epidermis (skin) protects from injury and drying out Inner epidermal tissue (on internal surfaces) often serves
Epithelial Tissues Covers the entire body surface and most of the body s inner cavities Outer epidermis (skin) protects from injury and drying out Inner epidermal tissue (on internal surfaces) often serves
THE HUMAN BODY. Chapter 24 SUPPORT AND MOVEMENT OF THE BODY 24A - HUMAN SKIN THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
 THE HUMAN BODY Chapter 24 SUPPORT AND MOVEMENT OF THE BODY 24A - HUMAN SKIN THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Approx. 1.9 square meters (about 18 sq. feet) of skin cover the body. Although the thickness varies,
THE HUMAN BODY Chapter 24 SUPPORT AND MOVEMENT OF THE BODY 24A - HUMAN SKIN THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Approx. 1.9 square meters (about 18 sq. feet) of skin cover the body. Although the thickness varies,
Introduction to Body Systems
 Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do the body systems interact to maintain homeostasis? By the end of this lesson, you should be able to describe the functions of the human body
Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do the body systems interact to maintain homeostasis? By the end of this lesson, you should be able to describe the functions of the human body
What is homeostasis? How is the human body organized? What are the 11 different human organ systems?
 CHAPTER 22 1 Body Organization SECTION Body Organization and Structure BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is homeostasis? How is the human body
CHAPTER 22 1 Body Organization SECTION Body Organization and Structure BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is homeostasis? How is the human body
Unit 7: Skeletal and muscular systems
 Unit 7: Skeletal and muscular systems 1. The locomotor system 2. The skeletal system 2.1. The human skeleton 2.2. Bones 2.3. Joints 2.4. Tendons and ligaments 3. The muscular system 3.1. Muscles of the
Unit 7: Skeletal and muscular systems 1. The locomotor system 2. The skeletal system 2.1. The human skeleton 2.2. Bones 2.3. Joints 2.4. Tendons and ligaments 3. The muscular system 3.1. Muscles of the
A Single Neuron from the Brain
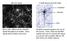 Nervous Tissue A Single Neuron from the Brain Dendrites Cell Body Axon Nerve cells, called neurons, transmit signals throughout our bodies. These signals tell our bodies what to do. Dendrites transmit
Nervous Tissue A Single Neuron from the Brain Dendrites Cell Body Axon Nerve cells, called neurons, transmit signals throughout our bodies. These signals tell our bodies what to do. Dendrites transmit
Function Alimentary Canal
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Function: to help convert food into simpler molecules that can be absorbed and used by the cells of the body. Alimentary Canala one way tube that passes through the body. (found in
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Function: to help convert food into simpler molecules that can be absorbed and used by the cells of the body. Alimentary Canala one way tube that passes through the body. (found in
Nervous System. Skeletal System. Muscular System. Reproductive System. Circulatory System. Endocrine System. Respiratory System. Integumentary System
 The Human Body Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Nervous System Reproductive System Endocrine System Integumentary System Excretory System Lymphatic/Immune
The Human Body Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Nervous System Reproductive System Endocrine System Integumentary System Excretory System Lymphatic/Immune
Skeletal System Tour Lab. Station Label the bones on your answer sheet.
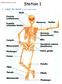 Station 1 1. Label the bones on your answer sheet. Station 2 2. Label the joints on your answer sheet. Fixed Pivot Hinge Hinge Gliding Ball and Socket Hinge Swivel Gliding Gliding Ball and Socket Types
Station 1 1. Label the bones on your answer sheet. Station 2 2. Label the joints on your answer sheet. Fixed Pivot Hinge Hinge Gliding Ball and Socket Hinge Swivel Gliding Gliding Ball and Socket Types
Table of Contents. Introduction to the Teacher...1. Body Organization...2 Cells, tissues, organs, and systems
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Introduction to the Teacher...1 Body Organization...2 Cells, tissues, organs, and systems...3 Purpose and parts of the skeletal system, bones, joints, cartilage, etc....8
Table of Contents Table of Contents Introduction to the Teacher...1 Body Organization...2 Cells, tissues, organs, and systems...3 Purpose and parts of the skeletal system, bones, joints, cartilage, etc....8
AP I f2014 E3 c_5 & 6
 AP I f2014 E3 c_5 & 6 Student: Multiple choice questions choose the best answer. True/false answer A for true and B for false 1. The layer within the epidermis that acts as the foundation providing new
AP I f2014 E3 c_5 & 6 Student: Multiple choice questions choose the best answer. True/false answer A for true and B for false 1. The layer within the epidermis that acts as the foundation providing new
Copyright 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2. Bone Structure. Copyright 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
 Chapter 7 The Skeleton: Bones and Joints The Skeleton Skeletal system is made up of bones and joints and supporting connective tissue. 1. Bone Functions 1. To store calcium salts 2. To protect delicate
Chapter 7 The Skeleton: Bones and Joints The Skeleton Skeletal system is made up of bones and joints and supporting connective tissue. 1. Bone Functions 1. To store calcium salts 2. To protect delicate
I. Structure A. Bones are living organs made of other tissue: Ex:,,
 Lesson 14.3 NOTES: The Skeletal System (Unlock) Essential Question: -What are the structures and functions of the skeletal system? Learning Target(s): -I can identify structures and explain functions of
Lesson 14.3 NOTES: The Skeletal System (Unlock) Essential Question: -What are the structures and functions of the skeletal system? Learning Target(s): -I can identify structures and explain functions of
BODY SYSTEMS UNIT ANCHOR CHARTS:
 BODY SYSTEMS UNIT ANCHOR CHARTS: LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION smallest unit Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems largest unit Body TISSUES IN THE HUMAN BODY Tissue Function Example Muscle makes parts of the body
BODY SYSTEMS UNIT ANCHOR CHARTS: LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION smallest unit Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems largest unit Body TISSUES IN THE HUMAN BODY Tissue Function Example Muscle makes parts of the body
Skin The Integumentary System
 Skin The Integumentary System THINK about IT What s the largest organ in your body? No, it is not your ears or stomach, or even your lungs or heart. By far the largest human organ is the skin. If that
Skin The Integumentary System THINK about IT What s the largest organ in your body? No, it is not your ears or stomach, or even your lungs or heart. By far the largest human organ is the skin. If that
Cell Structure and Function
 Name Cell Structure and Function Date How do the structures and processes of a cell enable it to survive? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about the topic Record your
Name Cell Structure and Function Date How do the structures and processes of a cell enable it to survive? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about the topic Record your
Biology v2 Describe the functioning of human digestive & skeletomuscular systems. Skeletomuscular system cards
 Biology 90166 v2 Describe the functioning of human digestive & skeletomuscular systems Skeletomuscular system cards Test yourself / test me cards Cover answer bottom 1/3; Read question / notes / diagram
Biology 90166 v2 Describe the functioning of human digestive & skeletomuscular systems Skeletomuscular system cards Test yourself / test me cards Cover answer bottom 1/3; Read question / notes / diagram
Nervous System. Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body
 Human Body Systems Nervous System Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body Nervous System Main Parts Brain Nerves Spinal cord What it
Human Body Systems Nervous System Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body Nervous System Main Parts Brain Nerves Spinal cord What it
Lecture 5. Skeletal and Muscular Systems. Skeletal and Muscular Systems. 1. Skeletal System Bones Cartilage Ligaments & Tendons Joints 2.
 Lecture 5 Skeletal and Muscular Systems 1 Skeletal and Muscular Systems 1. Skeletal System Bones Cartilage Ligaments & Tendons Joints 2. Muscles 2 1 Skeletal System 3 Functions of Skeleton Support of the
Lecture 5 Skeletal and Muscular Systems 1 Skeletal and Muscular Systems 1. Skeletal System Bones Cartilage Ligaments & Tendons Joints 2. Muscles 2 1 Skeletal System 3 Functions of Skeleton Support of the
Skin is a multilayered organ that covers and protects the body.
 Section 1: Skin is a multilayered organ that covers and protects the body. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the four tissue types that are found in
Section 1: Skin is a multilayered organ that covers and protects the body. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the four tissue types that are found in
Chapter 4 :Organization & Regulation of Body Systems
 Chapter 4 :Organization & Regulation of Body Systems 4.1 Types of tissues What is a tissue? A collection of cells of the same type that perform a common function There are 4 major tissue types in the body:
Chapter 4 :Organization & Regulation of Body Systems 4.1 Types of tissues What is a tissue? A collection of cells of the same type that perform a common function There are 4 major tissue types in the body:
Chapter 05. Lecture Outline. See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes.
 Chapter 05 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 05 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Skeletal and Muscular Systems. Bone myths
 Skeletal and Muscular Systems Bone myths Myth No. 1: A fracture is a milder form of bone injury than a broken bone. Myth No. 2: Once bones are fully developed, they stop changing. Myth No. 3: Osteoporosis
Skeletal and Muscular Systems Bone myths Myth No. 1: A fracture is a milder form of bone injury than a broken bone. Myth No. 2: Once bones are fully developed, they stop changing. Myth No. 3: Osteoporosis
Skeletal System. Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
*Hierarchical Organization of Multicellular Organisms
 *Hierarchical Organization of Multicellular Organisms 7.L.1.3 - Summarize the hierarchical organization of multicellular organisms from cells to tissues to organs to systems to organisms. Table of Contents
*Hierarchical Organization of Multicellular Organisms 7.L.1.3 - Summarize the hierarchical organization of multicellular organisms from cells to tissues to organs to systems to organisms. Table of Contents
33.1. Skeletal System. Your skeletal system is made up of the appendicular and axial skeletons.
 33.1 Skeletal System VOCABULARY skeletal system appendicular skeleton axial skeleton vertebrae cartilage joint ligament calcification Key Concept The skeletal system includes bones and tissues that are
33.1 Skeletal System VOCABULARY skeletal system appendicular skeleton axial skeleton vertebrae cartilage joint ligament calcification Key Concept The skeletal system includes bones and tissues that are
Introduction to Body Structure
 Chapter 37 Introduction to Body Structure Section 1: Body Organization Section 2: Skeletal System Section 3: Muscular System Section 4: Skin, Hair, and Nails Section 1 Body Organization Objectives: Identify
Chapter 37 Introduction to Body Structure Section 1: Body Organization Section 2: Skeletal System Section 3: Muscular System Section 4: Skin, Hair, and Nails Section 1 Body Organization Objectives: Identify
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism. Cells: the smallest unit of life.
 Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
Chapter 8. Bellringer. Identify areas of your body where joints allow movement of your skeleton. Lesson 2 The Skeletal System
 Lesson 2 The Skeletal System Bellringer Identify areas of your body where joints allow movement of your skeleton. Lesson 2 The Skeletal System Objectives Describe the functions of the skeletal system.
Lesson 2 The Skeletal System Bellringer Identify areas of your body where joints allow movement of your skeleton. Lesson 2 The Skeletal System Objectives Describe the functions of the skeletal system.
Human Body Systems Study Guide
 Human Body Systems Study Guide Nervous System 1. Brain stem part of nervous system and controls the heartbeat and breathing by controlling the cardiac muscle and diaphragm. Also receives information from
Human Body Systems Study Guide Nervous System 1. Brain stem part of nervous system and controls the heartbeat and breathing by controlling the cardiac muscle and diaphragm. Also receives information from
Anatomy Review-INTRODUCTION. The study of the function of the body parts is called. Examples include:
 Anatomy Review-INTRODUCTION The study of the organs and parts of the body is called Examples include: The study of the function of the body parts is called. Examples include: Use the numbers from the diagram
Anatomy Review-INTRODUCTION The study of the organs and parts of the body is called Examples include: The study of the function of the body parts is called. Examples include: Use the numbers from the diagram
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Mrs. Hummer. Chapter 6
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 6 1 Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 6 1 Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water
Bodies and Systems. What is your body made of?
 What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism. A collection of the same type of cells working together to perform a function.
 Name the 5 Basic Levels of Organization in Living Things Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism What is HOMEOSTASIS? The process by which your body maintains a stable internal environment. What is
Name the 5 Basic Levels of Organization in Living Things Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism What is HOMEOSTASIS? The process by which your body maintains a stable internal environment. What is
Growing bones. Baby s s bones are made from cartilage Babies have 300 bones Adults have 206. bones
 Body Systems Objectives Students should be able to list the different body systems Students should be able to give a general function of each of the body systems Students should be able to tell the differences
Body Systems Objectives Students should be able to list the different body systems Students should be able to give a general function of each of the body systems Students should be able to tell the differences
Body Systems Notes. Nervous, Integumentary, Immune/Lymphatic, Circulatory, Skeletal, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, Endocrine, Reproductive
 Body Systems Notes Nervous, Integumentary, Immune/Lymphatic, Circulatory, Skeletal, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, Endocrine, Reproductive Homeostasis: maintaining a balance. Examples: temperature,
Body Systems Notes Nervous, Integumentary, Immune/Lymphatic, Circulatory, Skeletal, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, Endocrine, Reproductive Homeostasis: maintaining a balance. Examples: temperature,
Chapter 9 The body and its movement
 Chapter 9 The body and its movement 1) All living things are made up of cells. 2) Cells make up tissues, tissues make up organs, organs make up organ system and organ systems make up the human body. 3)
Chapter 9 The body and its movement 1) All living things are made up of cells. 2) Cells make up tissues, tissues make up organs, organs make up organ system and organ systems make up the human body. 3)
Integumentary System
 Integumentary System The integumentary system is commonly known as the Skin Largest organ of human body 10% total body weight and would cover over 20 square feet Functions of Skin 1. Protection Barrier
Integumentary System The integumentary system is commonly known as the Skin Largest organ of human body 10% total body weight and would cover over 20 square feet Functions of Skin 1. Protection Barrier
Bones are made up of bone cells and tissues Hard, dense and smooth outer materials, which are made of calcium, give bones there shape and strength.
 1. 2. 3. 4. To protect your body and give it shape. To protect your internal organs. To provide a scaffolding for your muscles, allowing you to move. To store minerals and make blood cells. Bones are made
1. 2. 3. 4. To protect your body and give it shape. To protect your internal organs. To provide a scaffolding for your muscles, allowing you to move. To store minerals and make blood cells. Bones are made
The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action!
 Skeletal System The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action! 5 Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Movement: Skeletal system provides points of attachment for muscles. Your legs and arms
Skeletal System The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action! 5 Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Movement: Skeletal system provides points of attachment for muscles. Your legs and arms
11/8/2012. Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Skin = Integument = Cutaneous Membrane. The Structure of Skin. Epidermis
 Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Define organ, and associate the skin as an organ of the integumentary system. List the general functions of the skin. Describe the structure of the layers of the skin. Summarize
Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Define organ, and associate the skin as an organ of the integumentary system. List the general functions of the skin. Describe the structure of the layers of the skin. Summarize
Chapter 22. Body Organization & Structure
 Chapter 22 Body Organization & Structure Start-Up Activity Too Cold for Comfort Hold a few pieces of ice in one hand. Hold the ice until the cold is uncomfortable. Then release the ice into the dish. Compare
Chapter 22 Body Organization & Structure Start-Up Activity Too Cold for Comfort Hold a few pieces of ice in one hand. Hold the ice until the cold is uncomfortable. Then release the ice into the dish. Compare
The Skeletal System (Lexile 930L)
 7.12: Systems of the Human ody The Skeletal System (Lexile 930L) 1 id you know that babies are born with a total of 350 bones, compared to an adult with about 206 of them? The infant bones fuse as the
7.12: Systems of the Human ody The Skeletal System (Lexile 930L) 1 id you know that babies are born with a total of 350 bones, compared to an adult with about 206 of them? The infant bones fuse as the
Bendable Bones. Jill Crowder and Canzater Gillespie Milwaukee Area Technical College Milwaukee, WI
 Bendable Bones Jill Crowder and Canzater Gillespie Milwaukee Area Technical College Milwaukee, WI Research Hosts: Jeffrey L. Osborn, Ph.D. and Andrew S. Greene, Ph.D. Medical College of Wisconsin 1998
Bendable Bones Jill Crowder and Canzater Gillespie Milwaukee Area Technical College Milwaukee, WI Research Hosts: Jeffrey L. Osborn, Ph.D. and Andrew S. Greene, Ph.D. Medical College of Wisconsin 1998
Contents. Section 1: Life s Building Blocks. Section 2: The Human Framework. Section 3: The Senses and the Respiratory System
 Contents Section 1: Life s Building Blocks 1. Cell Structure.... 2 2. Cell Functions.... 5 3. Cell Teamwork... 8 4. Quiz 1.... 12 Section 2: The Human Framework 5. Skeletal System.... 13 6. Muscular System....
Contents Section 1: Life s Building Blocks 1. Cell Structure.... 2 2. Cell Functions.... 5 3. Cell Teamwork... 8 4. Quiz 1.... 12 Section 2: The Human Framework 5. Skeletal System.... 13 6. Muscular System....
Ch 4. Skin and Body Membranes
 Ch 4 Skin and Body Membranes TITLE HISTOLOGY SLIDES & NOTES ESSENTIAL QUESTION What tissues compose the integumentary system? Stratified Squamous Epithelium Stratified = several layers; Squamous = shape
Ch 4 Skin and Body Membranes TITLE HISTOLOGY SLIDES & NOTES ESSENTIAL QUESTION What tissues compose the integumentary system? Stratified Squamous Epithelium Stratified = several layers; Squamous = shape
The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move.
 Skeletal System The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move. BONE: A rigid connective tissue Helps to move & support the body Protect the organs (skull, ribs)
Skeletal System The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move. BONE: A rigid connective tissue Helps to move & support the body Protect the organs (skull, ribs)
By Helen and Mark Warner
 By Helen and Mark Warner www.teachingpacks.co.uk Teaching Packs - The Human Body - Page 1 Image ThinkStock In this section, you will learn about... 1. The major systems and organs in the human body. 2.
By Helen and Mark Warner www.teachingpacks.co.uk Teaching Packs - The Human Body - Page 1 Image ThinkStock In this section, you will learn about... 1. The major systems and organs in the human body. 2.
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Name: Period: Review for Animal Systems Test II - KEY
 Name: Period: Review for Animal Systems Test II - KEY Questions 1-9: Write the main functions of the following body s in the spaces below. Then, write the levels of organization for each body. Give specific
Name: Period: Review for Animal Systems Test II - KEY Questions 1-9: Write the main functions of the following body s in the spaces below. Then, write the levels of organization for each body. Give specific
Warm Up Get homework out to turn in!
 Warm Up Get homework out to turn in! Feb 23-8:52 AM Feb 4-8:14 PM 1.) What is the function of your digestive system? After checking, put the number of problems missed at the top of the sheet. 2.) Which
Warm Up Get homework out to turn in! Feb 23-8:52 AM Feb 4-8:14 PM 1.) What is the function of your digestive system? After checking, put the number of problems missed at the top of the sheet. 2.) Which
Human Body. Bones, Joints and Muscles
 Human Body Bones, Joints and Muscles 1 Bone cranium mandible clavicle sternum humerus ribs pelvis ulna femur patella phalanges phalanges vertebrae Also known as skull lower jaw collarbone breastplate upper
Human Body Bones, Joints and Muscles 1 Bone cranium mandible clavicle sternum humerus ribs pelvis ulna femur patella phalanges phalanges vertebrae Also known as skull lower jaw collarbone breastplate upper
Describe the functions of the vertebrate integumentary system. Discuss the structure of the skin and how it relates to function.
 Chapter 5 Describe the functions of the vertebrate integumentary system. Discuss the structure of the skin and how it relates to function. Explain the basis for different skin colors. Describe the structure
Chapter 5 Describe the functions of the vertebrate integumentary system. Discuss the structure of the skin and how it relates to function. Explain the basis for different skin colors. Describe the structure
STD.6 (2015) MOVEMENT IN THE BODY. When an organism moves from one place to another, it is termed as locomotion. locomotion.
 STD.6 (2015) MOVEMENT IN THE BODY Q.1 Define Locomotion. When an organism moves from one place to another, it is termed as locomotion. Ex.A jump, hop, walk and swim. Q.2 Differentiate between movement
STD.6 (2015) MOVEMENT IN THE BODY Q.1 Define Locomotion. When an organism moves from one place to another, it is termed as locomotion. Ex.A jump, hop, walk and swim. Q.2 Differentiate between movement
Introduction to the Human Body
 Introduction to the Human Body Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. Your brain is a structure composed of different kinds of tissue. What is
Introduction to the Human Body Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. Your brain is a structure composed of different kinds of tissue. What is
Laughter and the Body Systems
 Laughter and the Body Systems Laughter causes the lungs to pump out carbon dioxide, the eyes to cleanse themselves with tears, the muscles to relax, the flow of adrenaline to increase, and the cardiovascular
Laughter and the Body Systems Laughter causes the lungs to pump out carbon dioxide, the eyes to cleanse themselves with tears, the muscles to relax, the flow of adrenaline to increase, and the cardiovascular
Write It! Station Directions
 Write It! Station Directions It is recommended that you have completed at least two of the following stations before working at this station. -Read It! -Explore It! -Watch It! -Research It! Answer each
Write It! Station Directions It is recommended that you have completed at least two of the following stations before working at this station. -Read It! -Explore It! -Watch It! -Research It! Answer each
Organs and Systems Organ: System:
 3.2 Organ Systems Organs and Systems Organ: a combination of several types of tissues working together to perform a specific function System: a group of tissues and organs that perform specific functions
3.2 Organ Systems Organs and Systems Organ: a combination of several types of tissues working together to perform a specific function System: a group of tissues and organs that perform specific functions
Outline. Bio 105: Tissues Laboratory. Organization of the Human Body. Tissue - Epithelium. Tissues 3/2/ Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc
 Outline Bio 105: Tissues Laboratory Laboratory 5 Reading: Chapter 4 I. Cell to cell contact II. Body Cavities III. Membranes IV. Homeostasis V. Integumentary System I. Includes skin, hair and nails 1 2
Outline Bio 105: Tissues Laboratory Laboratory 5 Reading: Chapter 4 I. Cell to cell contact II. Body Cavities III. Membranes IV. Homeostasis V. Integumentary System I. Includes skin, hair and nails 1 2
CHAPTER 14. Bones Muscles Skin
 CHAPTER 14 Bones Muscles Skin Chapter 14 Objectives Section 1 Body Organization and Homeostasis 1. Define homeostasis and a give a specific example. 2. Explain why energy is important to the human body.
CHAPTER 14 Bones Muscles Skin Chapter 14 Objectives Section 1 Body Organization and Homeostasis 1. Define homeostasis and a give a specific example. 2. Explain why energy is important to the human body.
Your Skin. Section 14.2 Your Skin, Hair, and Nails
 Your Skin The skin covers and protects the body from injury, infection, and water loss. The skin also helps to regulate body temperature and gathers information from the environment. Protection The skin
Your Skin The skin covers and protects the body from injury, infection, and water loss. The skin also helps to regulate body temperature and gathers information from the environment. Protection The skin
Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System
 I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. the body Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System B. of vital organs C. Provide for movement D. storage (calcium & phosphate) E. cell formation II. Bone Structure A.
I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. the body Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System B. of vital organs C. Provide for movement D. storage (calcium & phosphate) E. cell formation II. Bone Structure A.
the Bone Teacher Pages Classroom Activities Grade Level 4-6
 Grade Level 4-6 Building Big Bones Students will work in pairs to investigate how the light, spongy layer around the bone s marrow makes the bones lighter for easier movement, by comparing cardboard tubes
Grade Level 4-6 Building Big Bones Students will work in pairs to investigate how the light, spongy layer around the bone s marrow makes the bones lighter for easier movement, by comparing cardboard tubes
Heal a th t y h y B o B dy d Systems
 Chapter 16 Healthy Body Systems The Cell The smallest unit of structure in a living organism Robert Hooke Identified & coined the term Cell when he saw cork under the microscope He used a compound microscope
Chapter 16 Healthy Body Systems The Cell The smallest unit of structure in a living organism Robert Hooke Identified & coined the term Cell when he saw cork under the microscope He used a compound microscope
What is a tissue? Points to ponder. Tissues Connective Tissue. 1. Connective tissue 2/23/2019. Organization and Regulation of Body Systems
 Organization and Regulation of Body Systems Chapter 04 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education.
Organization and Regulation of Body Systems Chapter 04 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education.
Action and Support: The Muscles and Skeleton
 Lesson 15 Action and Support: The Muscles and Skeleton Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Muscle Contraction Muscles: tissues that produce movement by contracting Vertebrates have three types of
Lesson 15 Action and Support: The Muscles and Skeleton Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Muscle Contraction Muscles: tissues that produce movement by contracting Vertebrates have three types of
SKELETAL STRUCTURES Objectives for Exam #1: Objective for Portfolio #1: Part I: Skeletal Stations Station A: Bones of the Body
 SKELETAL STRUCTURES Objectives for Exam #1: 1. Provide information on the various structures and functions of the skeletal system. 2. Describe various skeletal system disorders, including imaging techniques
SKELETAL STRUCTURES Objectives for Exam #1: 1. Provide information on the various structures and functions of the skeletal system. 2. Describe various skeletal system disorders, including imaging techniques
Functions of the Skeletal System. Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure. Classification of Bones. Bone Shapes
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
