Body Organization and Structure
|
|
|
- Chastity Eaton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHAPTER 19 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET Body Organization and Structure As you read Chapter 19, which begins on page 462 of your textbook, answer the following questions. This Really Happened... (p. 462) 1. The people who were wearing life jackets didn t drown after the Titanic struck an iceberg. Why did they die? They died because the cold water lowered their body temperature so that their body systems couldn t function. 2. In this chapter, you ll learn how our bodies maintain a constant internal temperature. What Do You Think? (p. 463) Answer these questions in your ScienceLog now. Then later, you ll have a chance to revise your answers based on what you ve learned. Investigate! (p. 463) 3. You experience pain when someone steps on your toe. What is your body trying to tell you? Your body is trying to tell you to move your toe to safety. Section 1: Body Organization (p. 464) 4. How did Jack Thayer survive in the icy water during the Titanic disaster? His body s internal conditions did not change enough to stop his cells from working properly. 5. Homeostasis is the maintenance of a stable internal environment. 6. Cells can die if homeostasis is disrupted. True or False? (Circle one.) CHAPTER 19 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEETS 133
2 Four Types of Tissue (p. 464) 7. How is your body like a soccer team? My body is like a soccer team because every cell has a specific job in maintaining homeostasis, just like every member of a soccer team has a special role in the game. Look at Figure 1 on pages Then match each tissue type in Column B with its correct function in Column A, and write the corresponding letter in the space provided. d c a b Column A 8. joins, supports, and insulates organs 9. covers and protects underlying tissue 10. sends electrical signals through the body 11. produces movement Column B a. nervous tissue b. muscle tissue c. epithelial tissue d. connective tissue Tissues Form Organs (p. 465) 12. Several types of tissue working together can do jobs that one type of tissue could not do by itself. True or False? (Circle one.) Use Figure 2 to answer questions How does your brain know when your stomach is full? My brain knows when my stomach is full because nervous tissue in my stomach sends a signal to my brain. 14. Muscle tissue helps your stomach digest food by a. protecting the stomach during digestion. b. supplying the stomach with oxygen. c. crushing and grinding stomach contents. d. producing the acids that are used during digestion. 15. The stomach is supplied with oxygen by the blood. 16. The inside of your stomach is lined with epithelial tissue. 134 HOLT SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
3 Organs Form Systems (p. 465) 17. Your stomach does all the work of digesting your food. True or False? (Circle one.) Use the diagrams of human organ systems on pages to answer the following questions. Each of the following statements is false. Change the underlined word to make the statement true. Write the new word in the space provided. 18. The digestive system provides a frame to protect and support body parts. skeletal 19. Your cardiovascular system consists of your heart and blood vessels, which break down blood throughout your body. pump 20. The nervous system releases chemical messengers from certain glands that regulate body functions. endocrine 21. In your respiratory system, your lungs absorb nutrients and release carbon dioxide. oxygen 22. Your integumentary system returns leaked fluids to your blood vessels and helps you get rid of harmful germs. lymphatic 23. Your skeletal system allows you to move your bones. muscular 24. The male reproductive system produces and delivers eggs. sperm 25. The urinary system removes wastes from the blood and regulates the body s temperature. fluids CHAPTER 19 Review (p. 467) Now that you ve finished Section 1, review what you learned by answering the Review questions in your ScienceLog. DIRECTED READING WORKSHEETS 135
4 Section 2: The Skeletal System (p. 468) 1. Your skeleton is alive. True or False? (Circle one.) The Burden of Being a Bone (p. 468) 2. Look at Figure 3. Which of the following statements are true about human bones? (Circle all that apply.) a. Some bones contain a material that makes white blood cells. b. Arm bones have hollow cavities that store fat. c. Bones protect your brain, heart, lungs, and spinal cord. d. Without bones, you could still sit. e. Adult humans have 260 bones. f. Bones store minerals. What s in a Bone? (p. 469) 3. Bones contain two different kinds of bone tissue. True or False? (Circle one.) Determine whether each of the following statements is true of compact bone or spongy bone. In the space provided, write a C if it is true of compact bone and an S if it is true of spongy bone. 4. S It has many open spaces. 5. S It is where red blood cells are made. 6. C It contains small blood vessels. 7. C It contains tiny canals. 8. S It contains marrow. 9. C It provides most of the strength for the bone. Growing Bones (p. 470) 10. Most of your skeleton was soft and rubbery when you were born. True or False? (Circle one.) 11. How do bones continue to grow during childhood? Growth plates made of cartilage remain in most bones, allowing bones to grow. 12. In Figure 5, the cartilage does not show up on the X ray because cartilage does not have the mineral density of bone. 136 HOLT SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
5 What s the Point of a Joint? (p. 470) Use the text and Figure 6 to match the term in Column B with the correct phrase in Column A, and write the corresponding letter in the space provided. c f e g d b a Column A 13. immovable joint found in the skull 14. allows motion in all directions 15. allows you to only flex and extend 16. cushion found where two bones meet 17. the place where two or more bones connect 18. elastic bands of tissue that hold joints together 19. allows bones to glide over one another Column B a. sliding joint b. ligament c. fixed joint d. joint e. hinge joint f. ball-and-socket joint g. cartilage Can Levers Lessen Your Load? (p. 471) 20. Your limbs are examples of simple machines. True or False? (Circle one.) 21. The measure of how many times a simple machine multiplies an effort applied to a load is known as the mechanical advantage. 22. Which of the pictures in Figure 7 shows a lever that cannot increase force? The arm bending is an example of a third class lever. Third class levers cannot increase force. Review (p. 471) Now that you ve finished Section 2, review what you learned by answering the Review questions in your ScienceLog. CHAPTER 19 Section 3: The Muscular System (p. 472) 1. Why can t you stay perfectly still no matter how hard you try? I can t stay perfectly still because some of my muscles are always working. DIRECTED READING WORKSHEETS 137
6 2. The muscular system is made up of muscles and connective tissue. Types of Muscle (p. 472) Mark each of the following statements True or False. 3. True Cardiac muscle is found only in the heart. 4. False When smooth muscle moves blood through your blood vessels, the action is voluntary. 5. False The actions of skeletal muscles are always voluntary. 6. True Cardiac-muscle action is always involuntary. 7. True Skeletal muscles help protect your inner organs. 8. False There are three types of muscle: cardiac, voluntary and skeletal. Making Your Move (p. 473) 9. To make a funny face, what has to happen in your body? To make a funny face, electrical signals have to travel from my brain to the skeletal muscle cells, and those cells have to respond by getting shorter. 10. Look at Figure 9. It takes more muscles to smile than to frown. True or False? (Circle one.) 11. Tendons are strands of connective tissue that connect skeletal muscles to bones. 12. Most skeletal muscles a. work independently. b. are connected to each other by bones. c. are strands of tough connective tissue. d. work in pairs. 13. When your arm is extended, the triceps muscle a. is bending. c. is the flexor. b. acts involuntarily. d. is the extensor. 138 HOLT SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
7 Use It or Lose It (p. 474) 14. How does having strong muscles benefit the rest of the body? Having strong muscles benefits the rest of the body because when the muscles contract, the blood vessels in the muscles get squeezed. This action increases blood flow without making the heart work harder. 15. A resistance exercise requires the to overcome the weight of another object. muscles 16. Aerobic exercises, such as swimming, are best for strengthening your heart endurance skeletal and for increasing the of your muscles. Muscle Injury (p. 475) 17. List two things that can cause a muscle to overstretch or tear. Answers should include two of the following: improper muscle conditioning, an exercise being done improperly, and inadequately warming up a muscle. 18. When tendons are overused, they can become inflamed. (immobile or inflamed) 19. Which of the following characteristics of anabolic steroids is NOT true? a. They resemble a male sex hormone. b. They threaten the heart. c. They cause immature bones to stop growing. d. They make muscles bigger and stronger. e. They make you lose weight. CHAPTER 19 Review (p. 475) Now that you ve finished Section 3, review what you learned by answering the Review questions in your ScienceLog. DIRECTED READING WORKSHEETS 139
8 Section 4: The Integumentary System (p. 476) 1. What organ comes in a variety of colors, is partly dead, and protects people from the outside world? The skin comes in a variety of colors, is partly dead, and protects people from the outside world. 2. The integumentary system is made up of skin, hair, and nails. The Skin: More than Just a Coat (p. 476) 3. Which of the following are true of skin? (Circle all that apply.) a. It contains nerve endings. b. It uses sweat to keep you warm. c. It keeps moisture inside the body. d. It releases sweat that removes wastes from the bloodstream. 4. Darker skin has more melanin than lighter skin. True or False? (Circle one.) 5. How does the melanin in your skin help prevent cancer? The melanin in my skin helps prevent cancer by absorbing much of the harmful radiation from the sun that can cause DNA damage that can lead to cancer. A Tale of Two Layers (p. 477) Mark each of the following statements True or False. 6. False The epidermis is thicker than the dermis. 7. False Epidermal cells have no known function because they are dead. 8. True The dermis is strong yet flexible. 9. True Skin is a complex organ that contains many smaller structures. 140 HOLT SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
9 10. Look at Figure 16. The oil glands in your skin a. make oil that causes the hair to stand up straight. b. make oil that helps keep the epidermis waterproof. c. help the sweat glands make extra sweat. d. make oil that keeps the hair hard and brittle. Hair and Nails (p. 478) 11. All the living cells in your hair are in the hair follicle. 12. Hairs do not block ultraviolet light. True or False? (Circle one.) 13. Hair and skin use different pigments for color. True or False? (Circle one.) 14. What causes a goose bump to form? A goose bump forms when the tiny muscle attached to the hair follicle contracts. When the muscle contracts, the hair follicle bends, pushing up the epidermis to form a goose bump. 15. A furry animal might get goose bumps on a cold day because a. the muscles attached to the hair follicles contract. b. the lifted hairs block the wind. c. the animal looks bigger. d. making goose bumps uses a lot of energy and takes extra heat. 16. Your nails decrease the sensitivity of your fingertips. True or False? (Circle one.) Living in Harm s Way (p. 479) 17. Look at Figure 19. How does your skin heal itself when you get a cut? When I get a cut, a blood clot forms that keeps bacteria from entering the wound. Bacteria-fighting cells come to kill the bacteria, and the damaged CHAPTER 19 cells are replaced through cell division. DIRECTED READING WORKSHEETS 141
10 18. Look at Figure 20. What is the difference between an ordinary mole and a mole that may become cancerous? a. Cancerous moles are darker than ordinary moles. b. Cancerous moles are more symmetrical than ordinary moles. c. Cancerous moles are smaller than ordinary moles. d. Cancerous moles are more asymmetrical than ordinary moles. Answer the following questions after you finish reading page 479. Match each term in Column B with the correct phrase in Column A, and write the corresponding letter in the space provided. e f b a c d Column A 19. caused by hair follicles clogged with oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria 20. a mass of skin cells caused by uncontrolled cell division 21. darkened area of the skin 22. the most exposed part of the body 23. a tumor that invades other tissues 24. chemicals that cause oil glands to produce too much oil Column B a. skin b. mole c. cancer d. sex hormones e. infections f. tumor Review (p. 479) Now that you ve finished Section 4, review what you learned by answering the Review questions in your Science Log. 142 HOLT SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
THE SKELETAL, MUSCULAR AND INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEMS. Chapter 22 Sections
 THE SKELETAL, MUSCULAR AND INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEMS Chapter 22 Sections THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM Ch. 22 Section 3 (588-591) Muscles of the Body WHAT ARE THE THREE TYPES OF MUSCLES? 1.Skeletal muscle - move us
THE SKELETAL, MUSCULAR AND INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEMS Chapter 22 Sections THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM Ch. 22 Section 3 (588-591) Muscles of the Body WHAT ARE THE THREE TYPES OF MUSCLES? 1.Skeletal muscle - move us
SECTION 45-1 REVIEW. VOCABULARY REVIEW Describe the functions of the tissues listed below.
 SECTION 45-1 REVIEW THE HUMAN BODY PLAN VOCABULARY REVIEW Describe the functions of the tissues listed below. 1. nervous tissue 2. muscular tissue 3. skeletal muscle 4. epithelial tissue 5. connective
SECTION 45-1 REVIEW THE HUMAN BODY PLAN VOCABULARY REVIEW Describe the functions of the tissues listed below. 1. nervous tissue 2. muscular tissue 3. skeletal muscle 4. epithelial tissue 5. connective
What is homeostasis? How is the human body organized? What are the 11 different human organ systems?
 CHAPTER 22 1 Body Organization SECTION Body Organization and Structure BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is homeostasis? How is the human body
CHAPTER 22 1 Body Organization SECTION Body Organization and Structure BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is homeostasis? How is the human body
The Human Body. Mrs. Green
 The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
Introduction to Body Systems
 Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do the body systems interact to maintain homeostasis? By the end of this lesson, you should be able to describe the functions of the human body
Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do the body systems interact to maintain homeostasis? By the end of this lesson, you should be able to describe the functions of the human body
STUDY GUIDE SECTION 45-1 The Human Body Plan
 STUDY GUIDE SECTION 45-1 The Human Body Plan Name Period Date Multiple Choice-Write the correct letter in the blank 1. Nervous tissue contains specialized cells called a. Transmitters. b. neurons c. messenger
STUDY GUIDE SECTION 45-1 The Human Body Plan Name Period Date Multiple Choice-Write the correct letter in the blank 1. Nervous tissue contains specialized cells called a. Transmitters. b. neurons c. messenger
CHAPTER 14 Bones, Muscles, Skin
 CHAPTER 14 Bones, Muscles, Skin SECTION 1 Body Organization and Homeostasis Levels of Organization Basic to Complex Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems CELLS Basic unit in living thing Main Parts: Cell
CHAPTER 14 Bones, Muscles, Skin SECTION 1 Body Organization and Homeostasis Levels of Organization Basic to Complex Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems CELLS Basic unit in living thing Main Parts: Cell
Structure and Movement
 Name Structure and Movement How do bones, muscles, and skin help maintain the body s homeostasis? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about the topic Record three things
Name Structure and Movement How do bones, muscles, and skin help maintain the body s homeostasis? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about the topic Record three things
Chapter 22. Body Organization & Structure
 Chapter 22 Body Organization & Structure Start-Up Activity Too Cold for Comfort Hold a few pieces of ice in one hand. Hold the ice until the cold is uncomfortable. Then release the ice into the dish. Compare
Chapter 22 Body Organization & Structure Start-Up Activity Too Cold for Comfort Hold a few pieces of ice in one hand. Hold the ice until the cold is uncomfortable. Then release the ice into the dish. Compare
THe Skeletal System 1
 THe Skeletal System 1 What the Skeletal System DOes! Skeleton: works as the framework of your body and is made up of all of the bones in your body The number of bones in your skeleton depends on your age.
THe Skeletal System 1 What the Skeletal System DOes! Skeleton: works as the framework of your body and is made up of all of the bones in your body The number of bones in your skeleton depends on your age.
December 3, Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow?
 December 3, 2013 Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow? Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Chapter 36: Biology II The Skeleton
December 3, 2013 Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow? Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Chapter 36: Biology II The Skeleton
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin. KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body.
 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
Nervous System. Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body
 Human Body Systems Nervous System Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body Nervous System Main Parts Brain Nerves Spinal cord What it
Human Body Systems Nervous System Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body Nervous System Main Parts Brain Nerves Spinal cord What it
Nervous System. Skeletal System. Muscular System. Reproductive System. Circulatory System. Endocrine System. Respiratory System. Integumentary System
 The Human Body Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Nervous System Reproductive System Endocrine System Integumentary System Excretory System Lymphatic/Immune
The Human Body Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Nervous System Reproductive System Endocrine System Integumentary System Excretory System Lymphatic/Immune
Structure, Movement, and Control
 Human Body Systems Structure, Movement, and Control What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
Human Body Systems Structure, Movement, and Control What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
Introduction to the Human Body
 Introduction to the Human Body Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. Your brain is a structure composed of different kinds of tissue. What is
Introduction to the Human Body Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. Your brain is a structure composed of different kinds of tissue. What is
Structure, Movement, and Control
 Lesson 2 Structure, Movement, and Control Scan Lesson 2. Read the lesson titles and bold words. Look at the pictures. Identify three facts you discovered about the structure, movement, and control of the
Lesson 2 Structure, Movement, and Control Scan Lesson 2. Read the lesson titles and bold words. Look at the pictures. Identify three facts you discovered about the structure, movement, and control of the
Circulation and Respiration
 CHAPTER 20 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET Circulation and Respiration As you read Chapter 20, which begins on page 486 of your textbook, answer the following questions. This Really Happened... (p. 486) 1.
CHAPTER 20 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET Circulation and Respiration As you read Chapter 20, which begins on page 486 of your textbook, answer the following questions. This Really Happened... (p. 486) 1.
Laughter and the Body Systems
 Laughter and the Body Systems Laughter causes the lungs to pump out carbon dioxide, the eyes to cleanse themselves with tears, the muscles to relax, the flow of adrenaline to increase, and the cardiovascular
Laughter and the Body Systems Laughter causes the lungs to pump out carbon dioxide, the eyes to cleanse themselves with tears, the muscles to relax, the flow of adrenaline to increase, and the cardiovascular
*Hierarchical Organization of Multicellular Organisms
 *Hierarchical Organization of Multicellular Organisms 7.L.1.3 - Summarize the hierarchical organization of multicellular organisms from cells to tissues to organs to systems to organisms. Table of Contents
*Hierarchical Organization of Multicellular Organisms 7.L.1.3 - Summarize the hierarchical organization of multicellular organisms from cells to tissues to organs to systems to organisms. Table of Contents
Human Body Systems Study Guide
 Human Body Systems Study Guide Nervous System 1. Brain stem part of nervous system and controls the heartbeat and breathing by controlling the cardiac muscle and diaphragm. Also receives information from
Human Body Systems Study Guide Nervous System 1. Brain stem part of nervous system and controls the heartbeat and breathing by controlling the cardiac muscle and diaphragm. Also receives information from
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism. Cells: the smallest unit of life.
 Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
A Single Neuron from the Brain
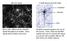 Nervous Tissue A Single Neuron from the Brain Dendrites Cell Body Axon Nerve cells, called neurons, transmit signals throughout our bodies. These signals tell our bodies what to do. Dendrites transmit
Nervous Tissue A Single Neuron from the Brain Dendrites Cell Body Axon Nerve cells, called neurons, transmit signals throughout our bodies. These signals tell our bodies what to do. Dendrites transmit
Body Systems Notes. Nervous, Integumentary, Immune/Lymphatic, Circulatory, Skeletal, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, Endocrine, Reproductive
 Body Systems Notes Nervous, Integumentary, Immune/Lymphatic, Circulatory, Skeletal, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, Endocrine, Reproductive Homeostasis: maintaining a balance. Examples: temperature,
Body Systems Notes Nervous, Integumentary, Immune/Lymphatic, Circulatory, Skeletal, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, Endocrine, Reproductive Homeostasis: maintaining a balance. Examples: temperature,
Table of Contents. Introduction to the Teacher...1. Body Organization...2 Cells, tissues, organs, and systems
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Introduction to the Teacher...1 Body Organization...2 Cells, tissues, organs, and systems...3 Purpose and parts of the skeletal system, bones, joints, cartilage, etc....8
Table of Contents Table of Contents Introduction to the Teacher...1 Body Organization...2 Cells, tissues, organs, and systems...3 Purpose and parts of the skeletal system, bones, joints, cartilage, etc....8
Challenge Question: Prediction: (Wait for directions) Evidence: (Draw, color and label how your Clay model looked when it was complete)
 Activity #12 What s happening inside? Challenge Question: Prediction: (Wait for directions) Evidence: (Draw, color and label how your Clay model looked when it was complete) Act #12 pg 1 of 3 Analysis
Activity #12 What s happening inside? Challenge Question: Prediction: (Wait for directions) Evidence: (Draw, color and label how your Clay model looked when it was complete) Act #12 pg 1 of 3 Analysis
Skin. the largest organ of the body 1 mm to 2 mm thick almost 2 square meters 6% of a person s body weight
 Skin the largest organ of the body 1 mm to 2 mm thick almost 2 square meters 6% of a person s body weight Functions of the Skin protection disease-causing organisms dangerous chemicals blood loss fluid
Skin the largest organ of the body 1 mm to 2 mm thick almost 2 square meters 6% of a person s body weight Functions of the Skin protection disease-causing organisms dangerous chemicals blood loss fluid
Lab Report Sheet. Title: Hypothesis (What I Think Will Happen) Materials (What We Used) Procedure (What We Did)
 Appendix 107 108 Lab Report Sheet Title: Hypothesis (What I Think Will Happen) Materials (What We Used) Procedure (What We Did) Observations and Results (What I Saw and Measured) Worksheet prepared by
Appendix 107 108 Lab Report Sheet Title: Hypothesis (What I Think Will Happen) Materials (What We Used) Procedure (What We Did) Observations and Results (What I Saw and Measured) Worksheet prepared by
April 20, Living Organisms: The Skeletal System
 Living Organisms: The Skeletal System Day 1 April 20, 2018 The skeleton is a structural framework that supports and protects the human body.. April 20, 2018 Estimate- How many bones you have in your body?
Living Organisms: The Skeletal System Day 1 April 20, 2018 The skeleton is a structural framework that supports and protects the human body.. April 20, 2018 Estimate- How many bones you have in your body?
The Skeletal System. Functions of the Skeletal System
 Skeletal System The Skeletal System Functions of the Skeletal System Provide support Protect internal organs Allows your body to move Stores and produced materials that your body needs You have 206 bones
Skeletal System The Skeletal System Functions of the Skeletal System Provide support Protect internal organs Allows your body to move Stores and produced materials that your body needs You have 206 bones
Warm Up Get homework out to turn in!
 Warm Up Get homework out to turn in! Feb 23-8:52 AM Feb 4-8:14 PM 1.) What is the function of your digestive system? After checking, put the number of problems missed at the top of the sheet. 2.) Which
Warm Up Get homework out to turn in! Feb 23-8:52 AM Feb 4-8:14 PM 1.) What is the function of your digestive system? After checking, put the number of problems missed at the top of the sheet. 2.) Which
Warm Up Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells?
 Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
Skin is a multilayered organ that covers and protects the body.
 Section 1: Skin is a multilayered organ that covers and protects the body. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the four tissue types that are found in
Section 1: Skin is a multilayered organ that covers and protects the body. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the four tissue types that are found in
Skin: The Body s Protection
 Ch 34: Protection, Support and Locomotion 34.1 - Skin: The Body s Protection Inside This Section... The Structure of Skin The Function of Skin Response to Injury Structure and Function of the skin 4 tissue
Ch 34: Protection, Support and Locomotion 34.1 - Skin: The Body s Protection Inside This Section... The Structure of Skin The Function of Skin Response to Injury Structure and Function of the skin 4 tissue
Structure and Movement
 Structure and Movement The Skin Key Concepts What does the skin do? How do the three layers of skin differ? How does the skin interact with other body systems? What do you think? Read the two statements
Structure and Movement The Skin Key Concepts What does the skin do? How do the three layers of skin differ? How does the skin interact with other body systems? What do you think? Read the two statements
Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Name Date Class Structure and Movement 33 Chapter 17 Structure and
 Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Name Date Class Structure and Movement 33 Chapter 17 Structure and Movement Section 1 The Skeletal System A. All the in your
Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Name Date Class Structure and Movement 33 Chapter 17 Structure and Movement Section 1 The Skeletal System A. All the in your
Chapter 8. Bellringer. Identify areas of your body where joints allow movement of your skeleton. Lesson 2 The Skeletal System
 Lesson 2 The Skeletal System Bellringer Identify areas of your body where joints allow movement of your skeleton. Lesson 2 The Skeletal System Objectives Describe the functions of the skeletal system.
Lesson 2 The Skeletal System Bellringer Identify areas of your body where joints allow movement of your skeleton. Lesson 2 The Skeletal System Objectives Describe the functions of the skeletal system.
Major Functions of the Skeletal System
 Skeletal System Major Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Provide shape and support. 2. Enables you to move 3. Protects your organs 4. Produces blood cells 5. stores minerals and other materials until
Skeletal System Major Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Provide shape and support. 2. Enables you to move 3. Protects your organs 4. Produces blood cells 5. stores minerals and other materials until
Name: Period: Review for Animal Systems Test II - KEY
 Name: Period: Review for Animal Systems Test II - KEY Questions 1-9: Write the main functions of the following body s in the spaces below. Then, write the levels of organization for each body. Give specific
Name: Period: Review for Animal Systems Test II - KEY Questions 1-9: Write the main functions of the following body s in the spaces below. Then, write the levels of organization for each body. Give specific
By Helen and Mark Warner
 By Helen and Mark Warner www.teachingpacks.co.uk Teaching Packs - The Human Body - Page 1 Image ThinkStock In this section, you will learn about... 1. The major systems and organs in the human body. 2.
By Helen and Mark Warner www.teachingpacks.co.uk Teaching Packs - The Human Body - Page 1 Image ThinkStock In this section, you will learn about... 1. The major systems and organs in the human body. 2.
Organs and Systems Organ: System:
 3.2 Organ Systems Organs and Systems Organ: a combination of several types of tissues working together to perform a specific function System: a group of tissues and organs that perform specific functions
3.2 Organ Systems Organs and Systems Organ: a combination of several types of tissues working together to perform a specific function System: a group of tissues and organs that perform specific functions
CHAPTER 14. Bones Muscles Skin
 CHAPTER 14 Bones Muscles Skin Chapter 14 Objectives Section 1 Body Organization and Homeostasis 1. Define homeostasis and a give a specific example. 2. Explain why energy is important to the human body.
CHAPTER 14 Bones Muscles Skin Chapter 14 Objectives Section 1 Body Organization and Homeostasis 1. Define homeostasis and a give a specific example. 2. Explain why energy is important to the human body.
Function Alimentary Canal
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Function: to help convert food into simpler molecules that can be absorbed and used by the cells of the body. Alimentary Canala one way tube that passes through the body. (found in
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Function: to help convert food into simpler molecules that can be absorbed and used by the cells of the body. Alimentary Canala one way tube that passes through the body. (found in
In Activity 12, What s Happening Inside? you learned about the functions
 16 Support System: Bones, Joints and Muscles l a b o r at o ry In Activity 12, What s Happening Inside? you learned about the functions of the skeletal and muscular systems in supporting and moving your
16 Support System: Bones, Joints and Muscles l a b o r at o ry In Activity 12, What s Happening Inside? you learned about the functions of the skeletal and muscular systems in supporting and moving your
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism. A collection of the same type of cells working together to perform a function.
 Name the 5 Basic Levels of Organization in Living Things Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism What is HOMEOSTASIS? The process by which your body maintains a stable internal environment. What is
Name the 5 Basic Levels of Organization in Living Things Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism What is HOMEOSTASIS? The process by which your body maintains a stable internal environment. What is
What type of tissue is this
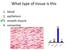 What type of tissue is this 1. blood 2. epithelium 3. smooth muscle 4. connective 83% 1 7% blood epithelium smooth muscle connective What type of tissue is this 1. connective 2. nervous 3. smooth muscle
What type of tissue is this 1. blood 2. epithelium 3. smooth muscle 4. connective 83% 1 7% blood epithelium smooth muscle connective What type of tissue is this 1. connective 2. nervous 3. smooth muscle
Chapter 4 :Organization & Regulation of Body Systems
 Chapter 4 :Organization & Regulation of Body Systems 4.1 Types of tissues What is a tissue? A collection of cells of the same type that perform a common function There are 4 major tissue types in the body:
Chapter 4 :Organization & Regulation of Body Systems 4.1 Types of tissues What is a tissue? A collection of cells of the same type that perform a common function There are 4 major tissue types in the body:
Epithelial Tissues. Types of Epithelial Tissues: Lining of Kidney
 Epithelial Tissues Covers the entire body surface and most of the body s inner cavities Outer epidermis (skin) protects from injury and drying out Inner epidermal tissue (on internal surfaces) often serves
Epithelial Tissues Covers the entire body surface and most of the body s inner cavities Outer epidermis (skin) protects from injury and drying out Inner epidermal tissue (on internal surfaces) often serves
BODY SYSTEMS UNIT ANCHOR CHARTS:
 BODY SYSTEMS UNIT ANCHOR CHARTS: LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION smallest unit Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems largest unit Body TISSUES IN THE HUMAN BODY Tissue Function Example Muscle makes parts of the body
BODY SYSTEMS UNIT ANCHOR CHARTS: LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION smallest unit Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems largest unit Body TISSUES IN THE HUMAN BODY Tissue Function Example Muscle makes parts of the body
Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin
 Name Class Date Station # Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 415-421 in your textbook for a general discussion
Name Class Date Station # Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 415-421 in your textbook for a general discussion
Levels of Organization
 Levels of Organization What do you think the 5 Levels of Organization are in the body?? Brainstorm with your group and write down what you think are the 5 Levels Pick a recorder. Levels of Organization:
Levels of Organization What do you think the 5 Levels of Organization are in the body?? Brainstorm with your group and write down what you think are the 5 Levels Pick a recorder. Levels of Organization:
**Take your homework out to be stamped**
 Warm Up: 3/5-3/6 **Take your homework out to be stamped** 1. What is the difference between osteocytes and osteoblasts? 2. What body systems work with the muscular system? Give specific examples. 3. Your
Warm Up: 3/5-3/6 **Take your homework out to be stamped** 1. What is the difference between osteocytes and osteoblasts? 2. What body systems work with the muscular system? Give specific examples. 3. Your
Heal a th t y h y B o B dy d Systems
 Chapter 16 Healthy Body Systems The Cell The smallest unit of structure in a living organism Robert Hooke Identified & coined the term Cell when he saw cork under the microscope He used a compound microscope
Chapter 16 Healthy Body Systems The Cell The smallest unit of structure in a living organism Robert Hooke Identified & coined the term Cell when he saw cork under the microscope He used a compound microscope
Chapter 16. Human Anatomy
 Chapter 16 Human Anatomy Each System we will examine: Structures types Problems or health concerns How to care for that system Skeletal System Made up of bones, joints, connective tissue Is the frame for
Chapter 16 Human Anatomy Each System we will examine: Structures types Problems or health concerns How to care for that system Skeletal System Made up of bones, joints, connective tissue Is the frame for
Chapter: Structure and Movement
 Table of Contents Chapter: Structure and Movement Section 1: The Skeletal System Section 2: The Muscular System Section 3: The Skin 1 Living Bones The Skeletal System The bones in your body are very much
Table of Contents Chapter: Structure and Movement Section 1: The Skeletal System Section 2: The Muscular System Section 3: The Skin 1 Living Bones The Skeletal System The bones in your body are very much
Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System
 Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System Introduction: A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more different tissues. B. The skin and its accessory organs make up the integumentary system. Types of
Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System Introduction: A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more different tissues. B. The skin and its accessory organs make up the integumentary system. Types of
THE HUMAN BODY. Chapter 24 SUPPORT AND MOVEMENT OF THE BODY 24A - HUMAN SKIN THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
 THE HUMAN BODY Chapter 24 SUPPORT AND MOVEMENT OF THE BODY 24A - HUMAN SKIN THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Approx. 1.9 square meters (about 18 sq. feet) of skin cover the body. Although the thickness varies,
THE HUMAN BODY Chapter 24 SUPPORT AND MOVEMENT OF THE BODY 24A - HUMAN SKIN THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Approx. 1.9 square meters (about 18 sq. feet) of skin cover the body. Although the thickness varies,
Bodies and Systems. What is your body made of?
 What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS EXAM (S7L2)
 HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS EXAM (S7L2) Multiple Choice Directions: Select the best answer for each of the following questions. 1. Teeth are part of the skeletal system, but they are also part of the digestive
HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS EXAM (S7L2) Multiple Choice Directions: Select the best answer for each of the following questions. 1. Teeth are part of the skeletal system, but they are also part of the digestive
Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view
 Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
High School Biology - Problem Drill 20: Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems
 High School Biology - Problem Drill 20: Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following about the skeletal system is true? Question #01 A. There are two types
High School Biology - Problem Drill 20: Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following about the skeletal system is true? Question #01 A. There are two types
04/10/2013. Pick up a Human Body Book and PUT YOUR NAME ON IT!
 04/10/2013 Pick up a Human Body Book and PUT YOUR NAME ON IT! Did you know?? 1. The adult body is made up of: 100 trillion cells, 206 bones, 600 muscles, and 22 internal organs. 2. Every square inch of
04/10/2013 Pick up a Human Body Book and PUT YOUR NAME ON IT! Did you know?? 1. The adult body is made up of: 100 trillion cells, 206 bones, 600 muscles, and 22 internal organs. 2. Every square inch of
Body Science: Cell Theory (3 rd -5 th Grades) Pre-Visit Activities
 Body Science: Cell Theory (3 rd -5 th Grades) Pre-Visit Activities Vocabulary List and Student Definitions (elementary level): Cell: basic unit of life, too small to see with the naked eye Tissue: group
Body Science: Cell Theory (3 rd -5 th Grades) Pre-Visit Activities Vocabulary List and Student Definitions (elementary level): Cell: basic unit of life, too small to see with the naked eye Tissue: group
CHAPTER 3. The Human Body National Safety Council
 CHAPTER 3 The Human Body The Human Body Composed of many different organs and tissues All parts work together: To sustain life Allow activity Injury or illness impairs functions 3-3 Cranial located in
CHAPTER 3 The Human Body The Human Body Composed of many different organs and tissues All parts work together: To sustain life Allow activity Injury or illness impairs functions 3-3 Cranial located in
Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view
 Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
Big Idea. The human body is made up of systems that have different functions, an these systems work together to maintain the body.
 Big Idea The human body is made up of systems that have different functions, an these systems work together to maintain the body. Body Organization CELLS TISSUES ORGANS Organ Systems Unit 1 Lesson 1 Introduction
Big Idea The human body is made up of systems that have different functions, an these systems work together to maintain the body. Body Organization CELLS TISSUES ORGANS Organ Systems Unit 1 Lesson 1 Introduction
Introduction to Body Structure
 Chapter 37 Introduction to Body Structure Section 1: Body Organization Section 2: Skeletal System Section 3: Muscular System Section 4: Skin, Hair, and Nails Section 1 Body Organization Objectives: Identify
Chapter 37 Introduction to Body Structure Section 1: Body Organization Section 2: Skeletal System Section 3: Muscular System Section 4: Skin, Hair, and Nails Section 1 Body Organization Objectives: Identify
Unsaved Test, Version: 1 1
 Name: Choose the letter of the best answer. 1. Functions of the skeletal system include A. forcing blood to circulate through the body B. sending electrical signals to the brain C. providing support and
Name: Choose the letter of the best answer. 1. Functions of the skeletal system include A. forcing blood to circulate through the body B. sending electrical signals to the brain C. providing support and
Anatomy Review-INTRODUCTION. The study of the function of the body parts is called. Examples include:
 Anatomy Review-INTRODUCTION The study of the organs and parts of the body is called Examples include: The study of the function of the body parts is called. Examples include: Use the numbers from the diagram
Anatomy Review-INTRODUCTION The study of the organs and parts of the body is called Examples include: The study of the function of the body parts is called. Examples include: Use the numbers from the diagram
Muscular System. Muscular System Video 1. Does a muscular person have more muscles than a smaller person?
 Muscular System Muscular System Video 1. Does a muscular person have more muscles than a smaller person? 2. What are the three types of muscles? 1. 2. 3. 3. Smooth muscles make up what? _ 4. What do you
Muscular System Muscular System Video 1. Does a muscular person have more muscles than a smaller person? 2. What are the three types of muscles? 1. 2. 3. 3. Smooth muscles make up what? _ 4. What do you
Warm Up. You have 10 minutes to complete your poster and prepare what you would like to share with the class.
 Warm Up You have 10 minutes to complete your poster and prepare what you would like to share with the class. Reflection 1. What were 2 similarities between your classification scheme and others in the
Warm Up You have 10 minutes to complete your poster and prepare what you would like to share with the class. Reflection 1. What were 2 similarities between your classification scheme and others in the
Answer the bell work questions. Write the underline portion of the state standard for your class. Follow the directions given for the graphic
 Answer the bell work questions. Write the underline portion of the state standard for your class. Follow the directions given for the graphic organizer and take notes for each of the body systems. Copy
Answer the bell work questions. Write the underline portion of the state standard for your class. Follow the directions given for the graphic organizer and take notes for each of the body systems. Copy
SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS WHAT MOVES YOU!
 SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS WHAT MOVES YOU! WHAT ARE THE MAIN FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM? THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeletal system is the organ system that supports and protects the body and allows
SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS WHAT MOVES YOU! WHAT ARE THE MAIN FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM? THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeletal system is the organ system that supports and protects the body and allows
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Chapter 6
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Chapter 6
Body Organization and Structure
 22 Body Organization and Structure The human body is composed of major systems that have differing functions, but all of the systems work together to maintain homeostasis. SECTION 1 Body Organization..........
22 Body Organization and Structure The human body is composed of major systems that have differing functions, but all of the systems work together to maintain homeostasis. SECTION 1 Body Organization..........
Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems
 34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems section 1 Circulatory System Before You Read Press the tips of two fingers to the inside of your wrist, at a point just below your thumb. Can you feel
34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems section 1 Circulatory System Before You Read Press the tips of two fingers to the inside of your wrist, at a point just below your thumb. Can you feel
ANIMAL ORGANIZATION, HOMEOSTASIS, AND THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM. Chapter 31
 ANIMAL ORGANIZATION, HOMEOSTASIS, AND THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Chapter 31 Tissue Tissues are groups of similar cells performing similar functions Organs are groups of tissues performing a specialized function
ANIMAL ORGANIZATION, HOMEOSTASIS, AND THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Chapter 31 Tissue Tissues are groups of similar cells performing similar functions Organs are groups of tissues performing a specialized function
CELLS/TISSUE/ORGANS/ORGAN SYSTEM
 CELLS/TISSUE/ORGANS/ORGAN SYSTEM CELLS ARE THE BASIC BUILDING BLOCKS OF LIFE TISSUES ARE MADE OF CELLS ORGANS ARE MADE OF TISSUES ORGAN SYSTEMS ARE MADE OF ORGANS THESE WORK TOGETHER TO HELP TO PROVIDE
CELLS/TISSUE/ORGANS/ORGAN SYSTEM CELLS ARE THE BASIC BUILDING BLOCKS OF LIFE TISSUES ARE MADE OF CELLS ORGANS ARE MADE OF TISSUES ORGAN SYSTEMS ARE MADE OF ORGANS THESE WORK TOGETHER TO HELP TO PROVIDE
Lecture 5. Skeletal and Muscular Systems. Skeletal and Muscular Systems. 1. Skeletal System Bones Cartilage Ligaments & Tendons Joints 2.
 Lecture 5 Skeletal and Muscular Systems 1 Skeletal and Muscular Systems 1. Skeletal System Bones Cartilage Ligaments & Tendons Joints 2. Muscles 2 1 Skeletal System 3 Functions of Skeleton Support of the
Lecture 5 Skeletal and Muscular Systems 1 Skeletal and Muscular Systems 1. Skeletal System Bones Cartilage Ligaments & Tendons Joints 2. Muscles 2 1 Skeletal System 3 Functions of Skeleton Support of the
Body Systems Overview
 Body Systems Overview Body Systems work together: If you damage one system, you may damage several for example, smoking irritates the lungs and destroys the cells of the immune system Levels of Organization
Body Systems Overview Body Systems work together: If you damage one system, you may damage several for example, smoking irritates the lungs and destroys the cells of the immune system Levels of Organization
 The human body is amazing! Like a machine, the human body is made of smaller parts that all work together. The human body is always working. Think about this: while you read this, your heart is pumping
The human body is amazing! Like a machine, the human body is made of smaller parts that all work together. The human body is always working. Think about this: while you read this, your heart is pumping
1. INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM: skin is the largest system.
 Chapter 7 Body Structure and Function Cell: Tissue: Examples: lining of the nose, mouth, stomach, muscle tissue Organs: Example: heart, brain, liver, lungs, kidneys Systems: organs that work together to
Chapter 7 Body Structure and Function Cell: Tissue: Examples: lining of the nose, mouth, stomach, muscle tissue Organs: Example: heart, brain, liver, lungs, kidneys Systems: organs that work together to
Digestive and Excretory Systems
 Digestive and Excretory Systems Homeostasis Q: How are the materials that enter and leave your body related to the processes that maintain homeostasis? 30.1 How is the human body organized and regulated?
Digestive and Excretory Systems Homeostasis Q: How are the materials that enter and leave your body related to the processes that maintain homeostasis? 30.1 How is the human body organized and regulated?
REVISION BOOKLET. The Body Systems
 REVISION BOOKLET The Body Systems GCSE PE 2016 Skeletal System Functions of the skeleton Joints for movement Muscle attachment Protection of vital organs Red and white blood cell production platelets Storage
REVISION BOOKLET The Body Systems GCSE PE 2016 Skeletal System Functions of the skeleton Joints for movement Muscle attachment Protection of vital organs Red and white blood cell production platelets Storage
Strength, any two: curl-ups/crunches, push-ups, step-ups; heart and lung endurance, any two:
 Chapter 3 Study Guide Study Tips Read the chapter objectives. Look up any unfamiliar words. Read the questions below before you read the chapter. As you read the chapter, answer the following questions.
Chapter 3 Study Guide Study Tips Read the chapter objectives. Look up any unfamiliar words. Read the questions below before you read the chapter. As you read the chapter, answer the following questions.
Name Score. The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone
 Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
CHAPTER 3. The Human Body National Safety Council
 CHAPTER 3 The Human Body Lesson Objectives 1. Describe the primary areas of the body. 2. List the 10 body systems and explain a key function of each. 3. For each body system, describe at least 1 injury
CHAPTER 3 The Human Body Lesson Objectives 1. Describe the primary areas of the body. 2. List the 10 body systems and explain a key function of each. 3. For each body system, describe at least 1 injury
Chicken Wing Dissection Lab
 Name Period Assignment # Chicken Wing Dissection Lab Prelab (Questions 1-12) A tissue is composed of a layer or group of cells of similar size, shape, and function. Within the human body, there are four
Name Period Assignment # Chicken Wing Dissection Lab Prelab (Questions 1-12) A tissue is composed of a layer or group of cells of similar size, shape, and function. Within the human body, there are four
Karen Storey. Multiple Choice: Draw a Complete Circle around the ONE BEST answer.
 Human Body Systems Test Review Karen Storey 7th Grade Science Multiple Choice: Draw a Complete Circle around the ONE BEST answer. 1. Which organ system makes blood cells? a. nervous system b. circulatory
Human Body Systems Test Review Karen Storey 7th Grade Science Multiple Choice: Draw a Complete Circle around the ONE BEST answer. 1. Which organ system makes blood cells? a. nervous system b. circulatory
Outline. Bio 105: Tissues Laboratory. Organization of the Human Body. Tissue - Epithelium. Tissues 3/2/ Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc
 Outline Bio 105: Tissues Laboratory Laboratory 5 Reading: Chapter 4 I. Cell to cell contact II. Body Cavities III. Membranes IV. Homeostasis V. Integumentary System I. Includes skin, hair and nails 1 2
Outline Bio 105: Tissues Laboratory Laboratory 5 Reading: Chapter 4 I. Cell to cell contact II. Body Cavities III. Membranes IV. Homeostasis V. Integumentary System I. Includes skin, hair and nails 1 2
Section B: Epithelial Tissue 1. Where are epithelial tissues found within the body? 2. What are the functions of the epithelial tissues?
 Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Unit 6.1 Test Review - Teacher THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
 Name: Period: Due Date: Unit 6.1 Test Review - Teacher THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS The Nervous System: 1. What are the 3 parts of a neuron and what do they do? Dendrites:
Name: Period: Due Date: Unit 6.1 Test Review - Teacher THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS The Nervous System: 1. What are the 3 parts of a neuron and what do they do? Dendrites:
Homework Packet. The branch of biological science that studies and describes how body parts. The study of the shape and structure of body parts
 Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
11/8/2012. Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Skin = Integument = Cutaneous Membrane. The Structure of Skin. Epidermis
 Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Define organ, and associate the skin as an organ of the integumentary system. List the general functions of the skin. Describe the structure of the layers of the skin. Summarize
Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Define organ, and associate the skin as an organ of the integumentary system. List the general functions of the skin. Describe the structure of the layers of the skin. Summarize
The Human Body: An Orientation
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Human Body: An Orientation 1 PART A The Human Body An Orientation Anatomy Study of the structure
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Human Body: An Orientation 1 PART A The Human Body An Orientation Anatomy Study of the structure
CHAPTER 2 Tissue Types and Functions
 CHAPTER 2 Tissue Types and Functions Answers to Review Questions 1. Define any 10 of the following terms: tissue a collection of cells organized for a particular function organs collections of tissue displaced
CHAPTER 2 Tissue Types and Functions Answers to Review Questions 1. Define any 10 of the following terms: tissue a collection of cells organized for a particular function organs collections of tissue displaced
Skin The Integumentary System
 Skin The Integumentary System THINK about IT What s the largest organ in your body? No, it is not your ears or stomach, or even your lungs or heart. By far the largest human organ is the skin. If that
Skin The Integumentary System THINK about IT What s the largest organ in your body? No, it is not your ears or stomach, or even your lungs or heart. By far the largest human organ is the skin. If that
Overview of Anatomy and Physiology
 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic Developmental
1 The Human Body: An Orientation Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic Developmental
Science 8 Chapter 12 Section 1
 Science 8 Chapter 12 Section 1 How Body Systems are Connected (pp. 436-445) System Coordination Cellular Respiration There are 4 different body systems that all play a part in the process of cellular respiration:
Science 8 Chapter 12 Section 1 How Body Systems are Connected (pp. 436-445) System Coordination Cellular Respiration There are 4 different body systems that all play a part in the process of cellular respiration:
