FROM MOVEMENT to meat production, the muscular
|
|
|
- Elinor Maxwell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Structures and Functions of the Muscular System FROM MOVEMENT to meat production, the muscular system provides benefits to animals and producers. Like other body systems, the muscular system is a fantastic example of small units working together to produce major results. An effective use of the muscular system is critical for an animal to live and grow. Objective: Describe the muscular system and the way in which muscles contract to create movement. Key Terms: actin cardiac muscle muscular system myosin sarcomere skeletal muscle smooth muscle tendons The Muscular System When we see a big, juicy steak on a plate, most of us do not immediately think of which muscle of the steer this steak came from. In fact, many people may not realize that meat is muscle tissue. Similarly, most of us know that cats can jump well and dogs can run fast, but we do not understand the types of muscles working in their bodies to give them these abilities. Page 1
2 Knowledge of the muscular system will improve our production in meat livestock and make us better pet owners in general. The muscular system can be defined as all forms of tissue in the body that can contract to perform movement or similar functions. Some types of muscle create movements that are easily seen, such as moving legs or blinking eyes. Other types of muscle are somewhat more difficult to observe, but these muscles are still important. Gizzards in poultry and heart muscle in all animals are two examples of critical muscle movement that we normally do not see, but we know the muscles are moving. The muscular system is a vast network that covers almost the entire body of the animal. This system, however, is composed of three types of muscle tissue. Each type of muscle tissue has a distinct structure and function within the body. SKELETAL MUSCLE FIGURE 1. Draft Horses exhibit excellent muscling. Skeletal muscle, or striated voluntary muscle, is attached to the skeleton and contracts to produce body movement. Skeletal muscle is voluntary muscle, so it can be moved whenever the animal desires and will not contract without effort. Most of the edible meat portions of livestock are composed of skeletal muscle, which is sometimes prepared still attached to the bone, as in the case of chicken drumsticks. FURTHER EXPLORATION ONLINE CONNECTION: Muscle Animations Muscles may seem to be a confusing mixture of proteins and filaments, and it may be difficult to visualize muscles working together. Use the following Web site to explore a number of anatomy- and physiology-related animations that can help explain the action of muscle contraction and the structure of muscle tissues. Using these animations, find your favorite that explains some part of the muscular system. Share it with the class. Page 2
3 Skeletal muscle is attached to bones directly or by the use of tendons. Tendons are connective tissue that anchor muscle to bone. Tendons are tough to chew and are not very appetizing. As a result, tendons are not normally consumed. Sometimes with extreme use or extension of a bone, tendons can be torn, producing a painful and slow-healing injury. Muscles do not extend to produce movement. They can only contract. Movement in opposite directions, such as a leg moving forward and then backward, is caused by two sets of muscle, each contracting in an order to produce the desired movement. The entire muscular system can be thought of as a series of rubber bands that contract to produce movement and then relax while another muscle contracts to produce a different movement. Trapezius Thoracalis Trapezius Cervicalis Latissimus Dorsi External Intercoastal Obliquus Abdominis Externus Tensor Fasciae Latae Brachiocephalicus Semitendinosis Sterno-Cephalicus Deltoid Long Head of Triceps Serratus Thoracis Posterior Deep Pectoral Lateral Head of Triceps FIGURE 2. The muscular system of a hog. Movement of a muscle is possible because the muscle contracts (shortens). This shortening of a muscle is due to the shortening of the cells that compose the muscle tissue. The basic unit of contraction within the muscle is known as a sarcomere. When all the sarcomeres in a muscle tissue contract, the net result is a total shortening of the muscle. Sarcomeres are found within myofibers, which resemble tiny strands like the wires in a wound cable. These myofibers are made of myofibrils, or even smaller strands, which are composed of two types of protein filaments: actin and myosin. Myosin, a thick filament, and actin, a thin filament, work together to produce the contractive force that causes muscles to shorten. During a contraction, the myosin actually pulls itself along the actin filament. Page 3
4 SMOOTH MUSCLE Smooth muscle is commonly found in the reproductive, digestive, and urinary organs of the body. Smooth muscle is an involuntary muscle, which means the animal has no control over the action of this muscle. The contraction of the intestines and the movement of wastes in the ureters are examples of smooth muscle in action. The oviducts, iris of the eye, and most blood vessels are also examples of smooth muscle. Smooth muscle is composed of the same actin and myosin protein filaments as skeletal muscle, but in different proportions, and will contract differently than voluntary skeletal muscles. Esophagus Rumen Small intestine Reticulum Omasum Abomasum FIGURE 3. The digestive system of a cow. CARDIAC MUSCLE Cardiac muscle is found only in the hearts of animals and is an involuntary muscle. Cardiac muscle is specialized to perform under continuous operation without fatigue, which is what keeps animals and humans alive. In humans, the heart begins to beat at 21 days after conception and must continue to beat regularly for possibly one hundred years. In an average lifespan, the human heart will beat nearly 2.5 billion times. The main purpose of cardiac muscle is Page 4
5 to pump blood throughout the body as part of the circulatory system. Without this blood flow to the lungs and throughout the body, the tissues and brain would quickly begin to die. Cardiac muscle differs from the other two types of muscle tissue in that it does not require outside stimuli for contraction. Special cells in the heart are able to contract at a regular interval on their own, which causes the rest of the heart tissue cells to contract. The autonomic nervous system regulates this rhythmic contracting of cardiac tissue. Cardiac tissue can go into fibrillation, or an uncontrolled contraction, when the timing of the contractions is somehow disrupted. Pericardium Fibrous pericardium Serous pericardium Myocardium Endocardium Pericardial cavity Epicardium FIGURE 4. Major parts of a heart (longitudinal section). Summary: Skeletal muscle, or striated voluntary muscle, is attached to the skeleton and contracts to produce body movement. Muscles do not extend to produce movement; they can only contract. The basic unit of contraction within the muscle is known as a sarcomere. Myosin (a thick filament) and actin (a thin filament) work together to produce the contractive force that causes muscles to shorten. Smooth muscle is commonly found in the reproductive, digestive, and urinary organs of the body. Cardiac muscle is found only in the hearts of animals and is an involuntary muscle. The main purpose of cardiac muscle is to pump blood throughout the body as part of the circulatory system. The autonomic nervous system regulates this rhythmic contracting of cardiac tissue. Without the use of all three types of muscle tissue, our movement, internal functions, and even blood circulation would not be possible. Page 5
6 Checking Your Knowledge: 1. List the three types of muscle fiber found in the body. 2. Using the terms sarcomere, actin, and myosin, explain how a muscle contracts. 3. List three organs that use smooth muscle for operation. 4. How does cardiac muscle differ from smooth or skeletal muscle? 5. What is the purpose of tendons? Expanding Your Knowledge: Visit a local meat locker to view the three different types of muscle tissue in a recently butchered livestock animal. If a visit is not possible, ask your instructor to obtain samples of the tissue. Web Links: Interactive Feline Dissection Images Interactive Muscular System of the Human Body Muscle Tissues, Common Muscles, and Microscopic Muscle Images Agricultural Career Profiles Page 6
The Muscular System. Muscle tissue is one of the 4 tissue types in vertebrates Muscle
 The Muscular System The Muscular System Muscle tissue is one of the 4 tissue types in vertebrates Muscle The Muscular System Muscle tissue is one of the 4 tissue types in vertebrates Muscle Nervous The
The Muscular System The Muscular System Muscle tissue is one of the 4 tissue types in vertebrates Muscle The Muscular System Muscle tissue is one of the 4 tissue types in vertebrates Muscle Nervous The
8 - Muscular System. Introduction Taft College Human Physiology
 8 - Muscular System Introduction Taft College Human Physiology Muscular System - Introduction The bones provide the levers and structure of the skeleton but it is the muscles that cause movement. Motion
8 - Muscular System Introduction Taft College Human Physiology Muscular System - Introduction The bones provide the levers and structure of the skeleton but it is the muscles that cause movement. Motion
Outline. Bio 105: Muscular System. Muscular System. Types of Muscles. Smooth Muscle. Cardiac Muscle 4/6/2016
 Outline Bio 105: Muscular System Lecture 11 Chapter 6 Characteristics of muscles 3 types of muscles Functions of muscles Structure of skeletal muscles Mechanics of muscle contraction Energy sources for
Outline Bio 105: Muscular System Lecture 11 Chapter 6 Characteristics of muscles 3 types of muscles Functions of muscles Structure of skeletal muscles Mechanics of muscle contraction Energy sources for
How many skeletal muscles are present in our body? Muscles are excitable & contractile, extensible and elastic to some extent.
 Muscles How many skeletal muscles are present in our body? -646 muscles The functions of the muscles are: Movement Maintenance of posture Generation of heat Stabilization of joints : amount of muscle surrounding
Muscles How many skeletal muscles are present in our body? -646 muscles The functions of the muscles are: Movement Maintenance of posture Generation of heat Stabilization of joints : amount of muscle surrounding
Muscle Tissue. General concepts. Classification of muscle. I. Functional classification is based on the type of neural control.
 Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
2º ESO - PE Workbook - IES Joan Miró Physical Education Department THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM
 THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM The muscular system is one of 10 organ systems in the human body. The human body has more than 650 muscles, which make up half of a person's body weight. Without muscles, we would not
THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM The muscular system is one of 10 organ systems in the human body. The human body has more than 650 muscles, which make up half of a person's body weight. Without muscles, we would not
Muscle Tissue- 3 Types
 AN INTRODUCTION TO MUSCLE TISSUE Muscle Tissue- 3 Types Skeletal muscle (focus on these) Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle FUNCTIONS OF SKELETAL MUSCLES Produce movement of the skeleton Maintain posture and
AN INTRODUCTION TO MUSCLE TISSUE Muscle Tissue- 3 Types Skeletal muscle (focus on these) Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle FUNCTIONS OF SKELETAL MUSCLES Produce movement of the skeleton Maintain posture and
Types of Muscle: Skeletal- muscle involved in movement of the skeleton. Striated, has alternating bands of light and dark due to overlapping
 Types of Muscle: Skeletal- muscle involved in movement of the skeleton. Striated, has alternating bands of light and dark due to overlapping filaments within the muscle cell. Skeletal muscle can be consciously
Types of Muscle: Skeletal- muscle involved in movement of the skeleton. Striated, has alternating bands of light and dark due to overlapping filaments within the muscle cell. Skeletal muscle can be consciously
Muscular System. Human A & P
 Muscular System Human A & P There are 3 types of muscle tissue: A. Skeletal B. Smooth C. Cardiac The essential function of a muscle is contraction, or shortening, and are responsible for essentially all
Muscular System Human A & P There are 3 types of muscle tissue: A. Skeletal B. Smooth C. Cardiac The essential function of a muscle is contraction, or shortening, and are responsible for essentially all
Microanatomy of Muscles. Anatomy & Physiology Class
 Microanatomy of Muscles Anatomy & Physiology Class Three Main Muscle Types Objectives: By the end of this presentation you will have the information to: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Describe the 3 main types of muscles.
Microanatomy of Muscles Anatomy & Physiology Class Three Main Muscle Types Objectives: By the end of this presentation you will have the information to: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Describe the 3 main types of muscles.
Muscle Cells & Muscle Fiber Contractions. Packet #8
 Muscle Cells & Muscle Fiber Contractions Packet #8 Skeletal muscle is attached to bones and is responsible for movement. Introduction Introduction II Skeletal muscle is composed of bundles of muscle fibers
Muscle Cells & Muscle Fiber Contractions Packet #8 Skeletal muscle is attached to bones and is responsible for movement. Introduction Introduction II Skeletal muscle is composed of bundles of muscle fibers
Chapter 7 The Muscular System. Mosby items and derived items 2012 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1
 Chapter 7 The Muscular System Mosby items and derived items 2012 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1 INTRODUCTION A. Muscular tissue enables the body and its parts to move 1. Three types of
Chapter 7 The Muscular System Mosby items and derived items 2012 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1 INTRODUCTION A. Muscular tissue enables the body and its parts to move 1. Three types of
33.2. Muscular System. Humans have three types of muscle.
 33.2 Muscular System VOCABULARY muscular system muscle fiber skeletal muscle tendon smooth muscle cardiac muscle myofibril sarcomere 10A, 10C, 11A Key Concept Muscles are tissues that can contract, enabling
33.2 Muscular System VOCABULARY muscular system muscle fiber skeletal muscle tendon smooth muscle cardiac muscle myofibril sarcomere 10A, 10C, 11A Key Concept Muscles are tissues that can contract, enabling
Functions of Muscle Tissue
 The Muscular System Functions of Muscle Tissue Movement Facilitation Thermogenesis Postural Support Regulation of Organ Volume Protects Internal Organs Pumps Blood (HEART) Characteristics of Muscle Tissue
The Muscular System Functions of Muscle Tissue Movement Facilitation Thermogenesis Postural Support Regulation of Organ Volume Protects Internal Organs Pumps Blood (HEART) Characteristics of Muscle Tissue
The Muscular System. - composed of mostly skeletal muscle tissue, nervous tissue, blood and connective tissue
 The Muscular System Every action the body takes utilizes a muscular activity. Some of the muscles of the body are under voluntary control (skeletal muscles), and by using these muscle, you are able to
The Muscular System Every action the body takes utilizes a muscular activity. Some of the muscles of the body are under voluntary control (skeletal muscles), and by using these muscle, you are able to
Skeletal Muscle. Move your bones. Voluntary ( ) Over. Long. Cardiac Muscle. The muscle of the heart. Involuntary ( ) Works. Strongest. Only.
 Muscular System Tour Name Hour Skeletal Muscle Move your bones. Muscular System There are more than muscles in the Human Body!!! Muscles are: Voluntary ( ) Over Needed for Needed for Needed for Needed
Muscular System Tour Name Hour Skeletal Muscle Move your bones. Muscular System There are more than muscles in the Human Body!!! Muscles are: Voluntary ( ) Over Needed for Needed for Needed for Needed
SECTION 45-1 REVIEW. VOCABULARY REVIEW Describe the functions of the tissues listed below.
 SECTION 45-1 REVIEW THE HUMAN BODY PLAN VOCABULARY REVIEW Describe the functions of the tissues listed below. 1. nervous tissue 2. muscular tissue 3. skeletal muscle 4. epithelial tissue 5. connective
SECTION 45-1 REVIEW THE HUMAN BODY PLAN VOCABULARY REVIEW Describe the functions of the tissues listed below. 1. nervous tissue 2. muscular tissue 3. skeletal muscle 4. epithelial tissue 5. connective
Muscular System. IB Sports, exercise and health science 1.2
 Muscular System IB Sports, exercise and health science 1.2 Characteristics Common to Contractility-ability to shorten the muscles length Extensibility-ability to lengthen the muscles length Elasticity-muscle
Muscular System IB Sports, exercise and health science 1.2 Characteristics Common to Contractility-ability to shorten the muscles length Extensibility-ability to lengthen the muscles length Elasticity-muscle
MUSCULAR TISSUE. Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 MUSCULAR TISSUE Dr. Gary Mumaugh MUSCLE OVERVIEW The three types of muscle tissue are skeletal, cardiac, and smooth These types differ in structure, location, function, and means of activation FUNCTIONAL
MUSCULAR TISSUE Dr. Gary Mumaugh MUSCLE OVERVIEW The three types of muscle tissue are skeletal, cardiac, and smooth These types differ in structure, location, function, and means of activation FUNCTIONAL
Muscular System- Part 1. Unit 5 Miss Wheeler
 Muscular System- Part 1 Unit 5 Miss Wheeler Fun Facts! The tongue is the strongest muscle in your body The smallest muscles in the body are in the middle ear The largest muscle in the body is the gluteus
Muscular System- Part 1 Unit 5 Miss Wheeler Fun Facts! The tongue is the strongest muscle in your body The smallest muscles in the body are in the middle ear The largest muscle in the body is the gluteus
MUSCLE TISSUE (MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY) PART I: MUSCLE STRUCTURE
 PART I: MUSCLE STRUCTURE Muscle Tissue A primary tissue type, divided into: skeletal muscle cardiac muscle smooth muscle Functions of Skeletal Muscles Produce skeletal movement Maintain body position Support
PART I: MUSCLE STRUCTURE Muscle Tissue A primary tissue type, divided into: skeletal muscle cardiac muscle smooth muscle Functions of Skeletal Muscles Produce skeletal movement Maintain body position Support
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. The Muscular System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology The Muscular System The Muscular System Muscles are responsible for all types of body movement they contract or shorten and are the machine of the body Three basic
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology The Muscular System The Muscular System Muscles are responsible for all types of body movement they contract or shorten and are the machine of the body Three basic
CHAPTER 6 2/9/2016. Learning Objectives List the four traits that all muscle types have in common.
 Learning Objectives List the four traits that all muscle types have in common. CHAPTER 6 The Muscular System Demonstrate and explain the use of antagonistic muscle pairs. Describe the attachment of muscle
Learning Objectives List the four traits that all muscle types have in common. CHAPTER 6 The Muscular System Demonstrate and explain the use of antagonistic muscle pairs. Describe the attachment of muscle
The muscles in the body each fall into one of three groups:
 MUSCLES The muscles in the body each fall into one of three groups: 1. VOLUNTARY or SKELETAL MUSCLESthese muscles are under the control of our will. All these muscles are attached to the skeleton. These
MUSCLES The muscles in the body each fall into one of three groups: 1. VOLUNTARY or SKELETAL MUSCLESthese muscles are under the control of our will. All these muscles are attached to the skeleton. These
THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. 1
 THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM 2015 Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. 1 The Musculoskeletal System The musculoskeletal system consists of bones, joints, and muscles that provide support, and stability
THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM 2015 Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. 1 The Musculoskeletal System The musculoskeletal system consists of bones, joints, and muscles that provide support, and stability
The Nervous and Muscular Systems and the role of ATP
 The Nervous and Muscular Systems and the role of ATP Overview of the Nervous System General parts: The brain The spinal cord The nerves and sense organs General functions: controls and coordinates body
The Nervous and Muscular Systems and the role of ATP Overview of the Nervous System General parts: The brain The spinal cord The nerves and sense organs General functions: controls and coordinates body
Muscle Histology. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Muscle Histology Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Functions of muscle tissue Movement Maintenance of posture Joint stabilization Heat generation Types of Muscle Tissue Skeletal
Muscle Histology Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Functions of muscle tissue Movement Maintenance of posture Joint stabilization Heat generation Types of Muscle Tissue Skeletal
Muscle. Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College
 Muscle Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions Movements of bones and soft body parts Movements of fluids through a tube (blood, digestive) Functions Maintain posture Support soft
Muscle Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions Movements of bones and soft body parts Movements of fluids through a tube (blood, digestive) Functions Maintain posture Support soft
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.49 - MUSCLE SYSTEMS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com BIOLOGY - CLUTCH Muscle system organ system that includes skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle Muscle tissue capable of contracting through the interaction of actin and myosin proteins
!! www.clutchprep.com BIOLOGY - CLUTCH Muscle system organ system that includes skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle Muscle tissue capable of contracting through the interaction of actin and myosin proteins
SKELETAL MUSCLE CHARACTERISTICS
 THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM SKELETAL MUSCLE CHARACTERISTICS Most are attached by tendons to bones Cells are multinucleate Striated have visible banding Voluntary subject to conscious control Cells are surrounded
THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM SKELETAL MUSCLE CHARACTERISTICS Most are attached by tendons to bones Cells are multinucleate Striated have visible banding Voluntary subject to conscious control Cells are surrounded
Class XI Chapter 20 Locomotion and Movement Biology
 Question 1: Draw the diagram of a sarcomere of skeletal muscle showing different regions. The diagrammatic representation of a sarcomere is as follows: Question 2: Define sliding filament theory of muscle
Question 1: Draw the diagram of a sarcomere of skeletal muscle showing different regions. The diagrammatic representation of a sarcomere is as follows: Question 2: Define sliding filament theory of muscle
Muscle Tissue. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Muscle Tissue Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Functions of muscle tissue Movement Maintenance of posture Joint stabilization Heat generation Tendon Belly Tendon Types of
Muscle Tissue Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Functions of muscle tissue Movement Maintenance of posture Joint stabilization Heat generation Tendon Belly Tendon Types of
******************************************************************************************************* MUSCLE CYTOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY
 BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ******************************************************************************************************* MUSCLE CYTOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY *******************************************************************************************************
BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ******************************************************************************************************* MUSCLE CYTOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY *******************************************************************************************************
Chapter 10 -Muscle Tissue
 Chapter 10 -Muscle Tissue Muscles: 1. Overview of Muscle Tissue A. Review 5 functions of muscle tissue. B. Review the 5 properties of muscle tissue. WHICH do they share with nervous tissue? (2, plus the
Chapter 10 -Muscle Tissue Muscles: 1. Overview of Muscle Tissue A. Review 5 functions of muscle tissue. B. Review the 5 properties of muscle tissue. WHICH do they share with nervous tissue? (2, plus the
The Muscular System PART A
 6 The Muscular System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Muscular System
6 The Muscular System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Muscular System
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 09: The Muscular System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 09: The Muscular System Question No. 1 of 10 The muscular system of the human body fulfills many different roles. Which of the following statements about the
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 09: The Muscular System Question No. 1 of 10 The muscular system of the human body fulfills many different roles. Which of the following statements about the
Ch.10 Muscle Tissue. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Ch.10 Muscle Tissue Preview Chapter 10 In groups we will define the following terms 1. Skeletal muscle 2. Smooth muscle 3. Cardiac muscle 4. Sarcomere 5. Myofibril 6. Myofilament 7. Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Ch.10 Muscle Tissue Preview Chapter 10 In groups we will define the following terms 1. Skeletal muscle 2. Smooth muscle 3. Cardiac muscle 4. Sarcomere 5. Myofibril 6. Myofilament 7. Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Muscles Muscles are effectors which enable movement to be carried out
 Muscles 13.8 Muscles are effectors which enable movement to be carried out Muscle Is responsible for almost all the movements in animals 3 types Cardiac muscle Smo oth muscle Skeletal mus cle (aka striped
Muscles 13.8 Muscles are effectors which enable movement to be carried out Muscle Is responsible for almost all the movements in animals 3 types Cardiac muscle Smo oth muscle Skeletal mus cle (aka striped
Muscle tissues. Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD
 Muscle tissues Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD Muscle tissue is a soft tissue that composes muscles in animal bodies, and gives rise to muscles' ability to contract. Muscle tissue
Muscle tissues Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD Muscle tissue is a soft tissue that composes muscles in animal bodies, and gives rise to muscles' ability to contract. Muscle tissue
Ch 10: Skeletal Muscle Tissue (Myology)
 Ch 10: Skeletal Muscle Tissue (Myology) main objectives: Describe the distinguishing characteristics of the different muscle tissues Discuss the organization of skeletal muscle Explain the micro-anatomy
Ch 10: Skeletal Muscle Tissue (Myology) main objectives: Describe the distinguishing characteristics of the different muscle tissues Discuss the organization of skeletal muscle Explain the micro-anatomy
Concept 50.5: The physical interaction of protein filaments is required for muscle function
 Concept 50.5: The physical interaction of protein filaments is required for muscle function Muscle activity is a response to input from the nervous system The action of a muscle is always to contract Vertebrate
Concept 50.5: The physical interaction of protein filaments is required for muscle function Muscle activity is a response to input from the nervous system The action of a muscle is always to contract Vertebrate
The Muscular System. Muscles are. There are more than 600 muscles in the Human Body!!! Needed for all types of movement. Needed to pump blood
 The Muscular System There are more than 600 muscles in the Human Body!!! Muscles are Needed for all types of movement. Needed to pump blood Needed to breathe (diaphragm muscle). Needed to produce body
The Muscular System There are more than 600 muscles in the Human Body!!! Muscles are Needed for all types of movement. Needed to pump blood Needed to breathe (diaphragm muscle). Needed to produce body
Smooth Cardiac Skeletal Location Around tubes Heart tissue attached to skeleton Moves stuff thru Heart beat pumps Moves body parts
 Biology 067 - Muscular system A. Type of muscles: Smooth Cardiac Skeletal Location Around tubes Heart tissue attached to skeleton Function Moves stuff thru Heart beat pumps Moves body parts tubes blood
Biology 067 - Muscular system A. Type of muscles: Smooth Cardiac Skeletal Location Around tubes Heart tissue attached to skeleton Function Moves stuff thru Heart beat pumps Moves body parts tubes blood
or Everything you ever wanted to know about Muscles, but were afraid to ask!!!
 The Muscular System or Everything you ever wanted to know about Muscles, but were afraid to ask!!! Did you know that? - more than 50% of body weight is muscle! - And muscle is made up of proteins and water
The Muscular System or Everything you ever wanted to know about Muscles, but were afraid to ask!!! Did you know that? - more than 50% of body weight is muscle! - And muscle is made up of proteins and water
The Muscular System. Myology the study of muscles
 The Muscular System Myology the study of muscles Functions of muscles: 1. Movement 2. Stability /support posture 3. Heat production 85% of our body heat 4. Communication 5. Constriction of organs and vessels
The Muscular System Myology the study of muscles Functions of muscles: 1. Movement 2. Stability /support posture 3. Heat production 85% of our body heat 4. Communication 5. Constriction of organs and vessels
Chapter 9. The Muscular System
 1 Chapter 9 The Muscular System 2 Introduction Skeletal muscles: movement in environment Smooth muscles: intestines, ureters, veins and arteries Cardiac muscle: pumps blood through heart and blood vessels
1 Chapter 9 The Muscular System 2 Introduction Skeletal muscles: movement in environment Smooth muscles: intestines, ureters, veins and arteries Cardiac muscle: pumps blood through heart and blood vessels
Chapter 9 Muscle. Types of muscle Skeletal muscle Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle. Striated muscle
 Chapter 9 Muscle Types of muscle Skeletal muscle Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle Striated muscle Chapter 9 Muscle (cont.) The sliding filament mechanism, in which myosin filaments bind to and move actin
Chapter 9 Muscle Types of muscle Skeletal muscle Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle Striated muscle Chapter 9 Muscle (cont.) The sliding filament mechanism, in which myosin filaments bind to and move actin
The Muscular System and Homeostasis
 Chapter 10 Chapter 10 The Muscular System and Homeostasis The Muscular System and Homeostasis 10.1 Movement and Muscle Tissue 10.2 Muscles, Health, and Homeostasis 10.1 Movement and Muscle Tissue Muscles
Chapter 10 Chapter 10 The Muscular System and Homeostasis The Muscular System and Homeostasis 10.1 Movement and Muscle Tissue 10.2 Muscles, Health, and Homeostasis 10.1 Movement and Muscle Tissue Muscles
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Mrs. Hummer. Chapter 9 Muscular System
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 9 Muscular System 1 Chapter 9 Muscular System Skeletal Muscle usually attached to bones under conscious control striated Three Types
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 9 Muscular System 1 Chapter 9 Muscular System Skeletal Muscle usually attached to bones under conscious control striated Three Types
1. Locomotion. 2. Repositioning. 3. Internal movement
 MUSCLE and MOVEMENT Chapters 20, 8, 21 1. Locomotion A. Movement B. 2. Repositioning A. 3. Internal movement A. 1 Muscle Cells 1. Contractile 2. Myocytes 3. Striated A. Skeletal B. Cardiac 4. Smooth 5.
MUSCLE and MOVEMENT Chapters 20, 8, 21 1. Locomotion A. Movement B. 2. Repositioning A. 3. Internal movement A. 1 Muscle Cells 1. Contractile 2. Myocytes 3. Striated A. Skeletal B. Cardiac 4. Smooth 5.
1. Locomotion. 2. Repositioning. 3. Internal movement
 MUSCLE and MOVEMENT Chapters 20, 8, 21 1. Locomotion A. Movement B. 2. Repositioning A. 3. Internal movement A. Muscle Cells 1. Contractile 2. Myocytes 3. Striated A. Skeletal B. Cardiac 4. Smooth 5. Striated
MUSCLE and MOVEMENT Chapters 20, 8, 21 1. Locomotion A. Movement B. 2. Repositioning A. 3. Internal movement A. Muscle Cells 1. Contractile 2. Myocytes 3. Striated A. Skeletal B. Cardiac 4. Smooth 5. Striated
A. Structure - Your skeletal system is your basic framework in your body.
 II. Skeletal System A. Structure - Your skeletal system is your basic framework in your body. 1. 206 bones - Comprise the adult human body. 2. "os-", "osteo-" Both of these roots mean bone. What is an
II. Skeletal System A. Structure - Your skeletal system is your basic framework in your body. 1. 206 bones - Comprise the adult human body. 2. "os-", "osteo-" Both of these roots mean bone. What is an
KS4 Physical Education
 KS4 Physical Education Muscles and Muscle Action These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities
KS4 Physical Education Muscles and Muscle Action These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities
The Muscular System. The Muscular System: Moving your Body
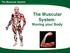 The Muscular System: Moving your Body The Muscular System So, which systems have Which systems will we learned about sowe far? learn about next? Can you sit totally still without moving a muscle? Ø Try
The Muscular System: Moving your Body The Muscular System So, which systems have Which systems will we learned about sowe far? learn about next? Can you sit totally still without moving a muscle? Ø Try
(C) Muscles provide structural support, are involved in thermoregulation, but have no effect on organ function.
 OAT Biology - Problem Drill 13: The Muscular System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which statement about muscles is correct? Question #01 (A) Muscles have an origin that is usually attached to a movable bone,
OAT Biology - Problem Drill 13: The Muscular System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which statement about muscles is correct? Question #01 (A) Muscles have an origin that is usually attached to a movable bone,
Human Anatomy. Muscle Tissue and Organization. DR.SADIQ ALI (K.E Medalist) 10-1
 Human Anatomy Muscle Tissue and Organization DR.SADIQ ALI (K.E Medalist) 10-1 Tissue and Organization Over 700 skeletal muscles have been named. Form the muscular system. Muscle tissue is distributed almost
Human Anatomy Muscle Tissue and Organization DR.SADIQ ALI (K.E Medalist) 10-1 Tissue and Organization Over 700 skeletal muscles have been named. Form the muscular system. Muscle tissue is distributed almost
MODULE 6 MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY
 MODULE 6 MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY III SEMESTER BOTANY Syllabi: Striated, Non striated and Cardiac muscle, Ultra structure of striated muscle fibre, Mechanism of muscle contraction, Threshold and spike potential,
MODULE 6 MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY III SEMESTER BOTANY Syllabi: Striated, Non striated and Cardiac muscle, Ultra structure of striated muscle fibre, Mechanism of muscle contraction, Threshold and spike potential,
Skeletal and Muscular Systems. Bone myths
 Skeletal and Muscular Systems Bone myths Myth No. 1: A fracture is a milder form of bone injury than a broken bone. Myth No. 2: Once bones are fully developed, they stop changing. Myth No. 3: Osteoporosis
Skeletal and Muscular Systems Bone myths Myth No. 1: A fracture is a milder form of bone injury than a broken bone. Myth No. 2: Once bones are fully developed, they stop changing. Myth No. 3: Osteoporosis
Improving Muscular Strength and Endurance
 Improving Muscular Strength and Endurance Introduction Outline Structure of Skeletal Muscle How Skeletal Muscle Contracts Motor Neurons Actin and Myosin Types of Contractions Muscle Fiber Types Determinants
Improving Muscular Strength and Endurance Introduction Outline Structure of Skeletal Muscle How Skeletal Muscle Contracts Motor Neurons Actin and Myosin Types of Contractions Muscle Fiber Types Determinants
Unit 7: Skeletal and muscular systems
 Unit 7: Skeletal and muscular systems 1. The locomotor system 2. The skeletal system 2.1. The human skeleton 2.2. Bones 2.3. Joints 2.4. Tendons and ligaments 3. The muscular system 3.1. Muscles of the
Unit 7: Skeletal and muscular systems 1. The locomotor system 2. The skeletal system 2.1. The human skeleton 2.2. Bones 2.3. Joints 2.4. Tendons and ligaments 3. The muscular system 3.1. Muscles of the
How Muscles are Classified Muscles The three main types of muscles are,, and
 7.5 Muscles: Designed for Motion How Muscles are Classified Muscles The three main types of muscles are,, and o Muscles Muscles that are generally under control (usually ) o Muscles Muscles that not under
7.5 Muscles: Designed for Motion How Muscles are Classified Muscles The three main types of muscles are,, and o Muscles Muscles that are generally under control (usually ) o Muscles Muscles that not under
MicroAnatomy Muscle Fiber Model
 MicroAnatomy Muscle Fiber Model Muscle fiber whole model (but model is only a fraction of a fiber) Sarcolemma 14 Myofibril 1 Nucleus 8 Mitochondria 2 Triad 16 Sarcoplasmic reticulum 17 T tubule 15 Thin
MicroAnatomy Muscle Fiber Model Muscle fiber whole model (but model is only a fraction of a fiber) Sarcolemma 14 Myofibril 1 Nucleus 8 Mitochondria 2 Triad 16 Sarcoplasmic reticulum 17 T tubule 15 Thin
Connective tissue MUSCLE TISSUE
 Connective tissue MUSCLE TISSUE Part 1 General features of MT Develop from mesoderm Many cells, less intercellular matrix Function contraction (shortening) Skeletal (striated, voluntary) Types of MT Cardiac
Connective tissue MUSCLE TISSUE Part 1 General features of MT Develop from mesoderm Many cells, less intercellular matrix Function contraction (shortening) Skeletal (striated, voluntary) Types of MT Cardiac
Muscles Unit TEST and Final Exam Study Guide May 2017
 Muscles Unit TEST and Final Exam Study Guide May 2017 Part 1 of final exam is pictures, see bottom of the study guide Part 2 of the final exam is only going to cover muscles unit. If you do this study
Muscles Unit TEST and Final Exam Study Guide May 2017 Part 1 of final exam is pictures, see bottom of the study guide Part 2 of the final exam is only going to cover muscles unit. If you do this study
OBJECTIVES. Unit 7:5 PROPERTIES OR CHARACTERISTICS OF MUSCLES. Introduction. 3 Kinds of Muscles. 3 Kinds of Muscles 4/17/2018 MUSCULAR SYSTEM
 OBJECTIVES Unit 7:5 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Compare the three main kinds of muscles by describing the action of each Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles List at least three functions of muscles
OBJECTIVES Unit 7:5 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Compare the three main kinds of muscles by describing the action of each Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles List at least three functions of muscles
1/4/2017. Introduction. Connective Tissue Coverings. 9.1: Structure of a Skeletal Muscle. Skeletal Muscle Fibers. Connective Tissue Coverings
 Introduction Chapter 09 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Introduction Chapter 09 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Lecture 9A. Muscle structure. Outline
 Lecture 9A Muscle structure Outline Smooth, skeletal, and cardiac muscle tissues Structure and function of skeletal muscle cells. Sarcomeres structure and contraction Actin-myosin interaction and sliding
Lecture 9A Muscle structure Outline Smooth, skeletal, and cardiac muscle tissues Structure and function of skeletal muscle cells. Sarcomeres structure and contraction Actin-myosin interaction and sliding
Skeletal Muscle Qiang XIA (
 Skeletal Muscle Qiang XIA ( 夏强 ), PhD Department of Physiology Rm C518, Block C, Research Building, School of Medicine Tel: 88208252 Email: xiaqiang@zju.edu.cn Course website: http://10.71.121.151/physiology
Skeletal Muscle Qiang XIA ( 夏强 ), PhD Department of Physiology Rm C518, Block C, Research Building, School of Medicine Tel: 88208252 Email: xiaqiang@zju.edu.cn Course website: http://10.71.121.151/physiology
The Muscular System. Specialized tissue that enable the body and its parts to move.
 The Muscular System Specialized tissue that enable the body and its parts to move. Anterior View Posterior View TRIVIA! How many muscles are there in the human body? Answer: 640 Muscles The muscles make
The Muscular System Specialized tissue that enable the body and its parts to move. Anterior View Posterior View TRIVIA! How many muscles are there in the human body? Answer: 640 Muscles The muscles make
Muscles. Grade Level: 4-6
 Muscles Grade Level: 4-6 Teacher Guidelines pages 1 2 Instructional Pages pages 3 6 Activity Page pages 7 Practice Page page 8-9 Homework Page page 10 Answer Key page 11-13 Classroom Procedure: 1. Ask
Muscles Grade Level: 4-6 Teacher Guidelines pages 1 2 Instructional Pages pages 3 6 Activity Page pages 7 Practice Page page 8-9 Homework Page page 10 Answer Key page 11-13 Classroom Procedure: 1. Ask
Muscular System. Honors Anatomy & Physiology. Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School
 Muscular System Honors Anatomy & Physiology Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Skeletal, Smooth, or Cardiac SKELETAL Striated Voluntary Multinucleated Bound to bones Moves skeleton SMOOTH Not striated
Muscular System Honors Anatomy & Physiology Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Skeletal, Smooth, or Cardiac SKELETAL Striated Voluntary Multinucleated Bound to bones Moves skeleton SMOOTH Not striated
Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems 929
 The Muscular System Key Questions What are the principal types of muscle tissue? How do muscles contract? How do muscle contractions produce movement? Vocabulary muscle fiber myofibril myosin actin sarcomere
The Muscular System Key Questions What are the principal types of muscle tissue? How do muscles contract? How do muscle contractions produce movement? Vocabulary muscle fiber myofibril myosin actin sarcomere
BIPN 100 F15 (Kristan) Human Physiology Lecture 10. Smooth muscle p. 1
 BIPN 100 F15 (Kristan) Human Physiology Lecture 10. Smooth muscle p. 1 Terms you should understand: smooth muscle, L-type Ca ++ channels, actin, myosin, sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR), myosine phosphatase,
BIPN 100 F15 (Kristan) Human Physiology Lecture 10. Smooth muscle p. 1 Terms you should understand: smooth muscle, L-type Ca ++ channels, actin, myosin, sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR), myosine phosphatase,
THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM FUNCTION OF MUSCLES
 FUNCTION OF MUSCLES THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM The 600 muscles in your body that function to move the skeleton are called skeletal muscles. The skeletal muscles make up the voluntary muscle system. They are called
FUNCTION OF MUSCLES THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM The 600 muscles in your body that function to move the skeleton are called skeletal muscles. The skeletal muscles make up the voluntary muscle system. They are called
Table of Contents # Date Title Page # /27/14 Ch 7: Skeletal System 01/29/14 Ch 8: Muscular System
 Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 1 2. 3. 4. 5. 01/27/14 Ch 7: Skeletal System 01/29/14 Ch 8: Muscular System 12 i 1 01/30/14 Ch 8: Muscular System 12 Objective: Students will be able to describe
Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 1 2. 3. 4. 5. 01/27/14 Ch 7: Skeletal System 01/29/14 Ch 8: Muscular System 12 i 1 01/30/14 Ch 8: Muscular System 12 Objective: Students will be able to describe
Cardiovascular System. I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart
 Cardiovascular System I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart 1. : Pericardial Cavity serous fluid filled space between the heart and the pericardium B. Heart Wall 1.
Cardiovascular System I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart 1. : Pericardial Cavity serous fluid filled space between the heart and the pericardium B. Heart Wall 1.
Skeletal Muscle and the Molecular Basis of Contraction. Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry
 Skeletal Muscle and the Molecular Basis of Contraction Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry Like neurons, all muscle cells can be excited chemically, electrically, and
Skeletal Muscle and the Molecular Basis of Contraction Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry Like neurons, all muscle cells can be excited chemically, electrically, and
Skeletal muscle. General features :
 Muscular tissues In the first embryonic life the muscular tissues arise from mesoderm, The function of movement in multicellular organisms is usually assumed by specialized cells called muscle fibers which
Muscular tissues In the first embryonic life the muscular tissues arise from mesoderm, The function of movement in multicellular organisms is usually assumed by specialized cells called muscle fibers which
THE STRUCTURE OF OUR BODY
 THE STRUCTURE OF OUR BODY 1. INTRODUCTION This chapter will describe the basic anatomy of the human body, explaining the most important elements of the muscular and skeletal system. 2. THE MUSCULOSKELETAL
THE STRUCTURE OF OUR BODY 1. INTRODUCTION This chapter will describe the basic anatomy of the human body, explaining the most important elements of the muscular and skeletal system. 2. THE MUSCULOSKELETAL
Skeletal muscle in the light of its structure
 Mechanism of contraction of Skeletal muscle in the light of its structure By Dr. Mudassar Ali Roomi (MBBS, M. Phil) Muscle Tissue Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle Skeletal Muscle Long cylindrical
Mechanism of contraction of Skeletal muscle in the light of its structure By Dr. Mudassar Ali Roomi (MBBS, M. Phil) Muscle Tissue Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle Skeletal Muscle Long cylindrical
AP Biology. Animal Locomotion. Muscles & Motor Locomotion. Why Do We Need All That ATP? Lots of ways to get around. Muscle
 Muscles & Motor Locomotion Animal Locomotion What are the advantages of locomotion? sessile motile Why Do We Need All That? 2006-2007 Lots of ways to get around Lots of ways to get around mollusk mammal
Muscles & Motor Locomotion Animal Locomotion What are the advantages of locomotion? sessile motile Why Do We Need All That? 2006-2007 Lots of ways to get around Lots of ways to get around mollusk mammal
AP Biology
 Chapter 49. Animal Locomotion What are the advantages of locomotion? sessile motile Muscles & Motor Locomotion Muscle voluntary, striated involuntary, striated auto-rhythmic involuntary, non-striated 1
Chapter 49. Animal Locomotion What are the advantages of locomotion? sessile motile Muscles & Motor Locomotion Muscle voluntary, striated involuntary, striated auto-rhythmic involuntary, non-striated 1
Chapter 49. Muscles & Motor Locomotion. AP Biology
 Chapter 49. Muscles & Motor Locomotion Animal Locomotion What are the advantages of locomotion? sessile motile Muscle voluntary, striated involuntary, striated auto-rhythmic involuntary, non-striated
Chapter 49. Muscles & Motor Locomotion Animal Locomotion What are the advantages of locomotion? sessile motile Muscle voluntary, striated involuntary, striated auto-rhythmic involuntary, non-striated
**Take your homework out to be stamped**
 Warm Up: 3/5-3/6 **Take your homework out to be stamped** 1. What is the difference between osteocytes and osteoblasts? 2. What body systems work with the muscular system? Give specific examples. 3. Your
Warm Up: 3/5-3/6 **Take your homework out to be stamped** 1. What is the difference between osteocytes and osteoblasts? 2. What body systems work with the muscular system? Give specific examples. 3. Your
Action and Support: The Muscles and Skeleton
 Lesson 15 Action and Support: The Muscles and Skeleton Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Muscle Contraction Muscles: tissues that produce movement by contracting Vertebrates have three types of
Lesson 15 Action and Support: The Muscles and Skeleton Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Muscle Contraction Muscles: tissues that produce movement by contracting Vertebrates have three types of
MCAT Biology Problem Drill 18: The Muscular System
 MCAT Biology Problem Drill 18: The Muscular System Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which statement about muscles is correct? Question #01 A. Muscles have an origin that is usually attached to a movable
MCAT Biology Problem Drill 18: The Muscular System Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which statement about muscles is correct? Question #01 A. Muscles have an origin that is usually attached to a movable
Muscles & Motor Locomotion Why Do We Need All That ATP?
 Muscles & Motor Locomotion Why Do We Need All That ATP? 2006-2007 Animal Locomotion What are the advantages of locomotion? sessile motile Lots of ways to get around Lots of ways to get around mollusk mammal
Muscles & Motor Locomotion Why Do We Need All That ATP? 2006-2007 Animal Locomotion What are the advantages of locomotion? sessile motile Lots of ways to get around Lots of ways to get around mollusk mammal
Skeletal Muscle Contraction 5/11/2017 Dr. Hiwa Shafiq
 Skeletal Muscle Contraction 5/11/2017 Dr. Hiwa Shafiq Skeletal Muscle Fiber About 40 per cent of the body is skeletal muscle, and 10 per cent is smooth and cardiac muscle. Skeletal muscles are composed
Skeletal Muscle Contraction 5/11/2017 Dr. Hiwa Shafiq Skeletal Muscle Fiber About 40 per cent of the body is skeletal muscle, and 10 per cent is smooth and cardiac muscle. Skeletal muscles are composed
Muscle and Muscle Tissue
 Muscle and Muscle Tissue Make up about half of total body mass Exerts force by converting chemical energy, ATP, to mechanical energy Muscle tissue is classified based on Shape Number and position of nuclei
Muscle and Muscle Tissue Make up about half of total body mass Exerts force by converting chemical energy, ATP, to mechanical energy Muscle tissue is classified based on Shape Number and position of nuclei
Lecture Overview. CT Framework of the Body. Chapter 4 Muscle & Nervous Tissues Lecture 11. Connective tissue framework of the body
 Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 4 Muscle & Nervous Tissues Lecture 11 Lecture Overview Connective tissue framework of the body Introduction to muscle tissue Classification/characteristics
Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 4 Muscle & Nervous Tissues Lecture 11 Lecture Overview Connective tissue framework of the body Introduction to muscle tissue Classification/characteristics
Shapes and Sizes of Muscles By Jennifer Kenny
 Shapes and Sizes of Muscles By Jennifer Kenny 1 Do you remember playing when you were a young child? Did you like to group things like rocks by their shapes or colors? Did you put your toys away based
Shapes and Sizes of Muscles By Jennifer Kenny 1 Do you remember playing when you were a young child? Did you like to group things like rocks by their shapes or colors? Did you put your toys away based
Chapter 9. The Muscular System
 Chapter 9 The Muscular System Introduction Skeletal muscles - movement in environment Smooth muscles - intestines, ureters, veins and arteries Cardiac muscle - pumps blood through heart and blood vessels
Chapter 9 The Muscular System Introduction Skeletal muscles - movement in environment Smooth muscles - intestines, ureters, veins and arteries Cardiac muscle - pumps blood through heart and blood vessels
Department of Science Second Term: Revision Worksheet - 1 L-1.6, 1.7 & 1.8 Muscles and bones
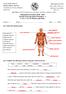 Department of Science 2018-2019 Second Term: Revision Worksheet - 1 L-1.6, 1.7 & 1.8 Muscles and bones Grade 4... Name:... Date:.../.../2019 Q.1 Label each muscle group. neck muscles shoulder muscles thigh
Department of Science 2018-2019 Second Term: Revision Worksheet - 1 L-1.6, 1.7 & 1.8 Muscles and bones Grade 4... Name:... Date:.../.../2019 Q.1 Label each muscle group. neck muscles shoulder muscles thigh
Chapter 8 Notes. Muscles
 Chapter 8 Notes Muscles 8.1 Intro Three muscle types Skeletal Smooth cardiac 8.2 Structure of Skeletal Muscle Composition Skeletal muscle tissue Nervous tissue Blood Connective tissue Connective tissue
Chapter 8 Notes Muscles 8.1 Intro Three muscle types Skeletal Smooth cardiac 8.2 Structure of Skeletal Muscle Composition Skeletal muscle tissue Nervous tissue Blood Connective tissue Connective tissue
Animal Locomotion. Lots of ways to get around. What are the advantages of locomotion? Why Do We Need All That ATP?
 Animal Locomotion What are the advantages of locomotion? Motor Mechanisms sessile (Muscles & Motor Locomotion) motile Why Do We Need All That ATP? 2006-2007 mollusk mammal bird reptile We saw how some
Animal Locomotion What are the advantages of locomotion? Motor Mechanisms sessile (Muscles & Motor Locomotion) motile Why Do We Need All That ATP? 2006-2007 mollusk mammal bird reptile We saw how some
1) A motor neuron and all the muscle cells that it stimulates are referred to as a motor end plate. 1)
 Chapter 6: Muscular System Test Study Guide CP Anatomy Mrs. Puzon Name TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. Please mark "A" for True and "B" for false on your
Chapter 6: Muscular System Test Study Guide CP Anatomy Mrs. Puzon Name TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. Please mark "A" for True and "B" for false on your
CLASS SET Unit 4: The Muscular System STUDY GUIDE
 NPHS Anatomy & Physiology Questions to answer: 1) List three functions of the muscular system. 1) movement 2) thermogenesis (generates heat) 3) posture & body/joint support CLASS SET Unit 4: The Muscular
NPHS Anatomy & Physiology Questions to answer: 1) List three functions of the muscular system. 1) movement 2) thermogenesis (generates heat) 3) posture & body/joint support CLASS SET Unit 4: The Muscular
STUDY GUIDE SECTION 45-1 The Human Body Plan
 STUDY GUIDE SECTION 45-1 The Human Body Plan Name Period Date Multiple Choice-Write the correct letter in the blank 1. Nervous tissue contains specialized cells called a. Transmitters. b. neurons c. messenger
STUDY GUIDE SECTION 45-1 The Human Body Plan Name Period Date Multiple Choice-Write the correct letter in the blank 1. Nervous tissue contains specialized cells called a. Transmitters. b. neurons c. messenger
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
Assignment 4: Muscle Structure and Function
 Assignment 4: Muscle Structure and Function Unit 2: Chapter 5 Part A Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following statements about skeletal muscle is true: A) Skeletal muscles are usually linked
Assignment 4: Muscle Structure and Function Unit 2: Chapter 5 Part A Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following statements about skeletal muscle is true: A) Skeletal muscles are usually linked
