GENERAL FOOT PAIN. Contents The Foot Joint...3
|
|
|
- Cody Tyler
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Contents The Foot Joint What causes foot pain? YOUR GUIDE TO GENERAL FOOT PAIN Common foot injuries What treatment can I receive? What exercises can I do? Phase Phase Phase Helpful hint Contact us MUSCULOSKELETAL An IPRS Guide to provide you with exercises and advice to ease your condition Introduction Please take note of the following before starting any of the exercises in this guide: IPRS are committed to helping you recover in the shortest and safest possible time. The information contained in this guide is intended to assist in managing your recovery. This guide is based on the latest medical research in the field and contains, to the best of our knowledge, the best advice available. This guide is complimentary to other medical services and is not intended as a substitute for a health care provider s consultation. Never disregard medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you ve read in this guide. Should you doubt a particular exercise in your situation, please consult your health professional. When consulting your health professional, it is wise to take this guide with you to show them. If you have any uncertainties or queries regarding the information, please do not hesitate to contact us on our freephone number or us at info@iprsgroup.com 2
2 The Foot Joint The human foot combines mechanical complexity and structural strength. The ankle serves as a foundation, shock absorber, and propulsion mechanism in walking and standing. It can sustain enormous amounts of pressure (several tons over the course of a one-mile run) whilst providing flexibility and resiliency. One-quarter of the bones in the human body are in the feet, with more than 100 muscles, tendons, and ligaments found in the foot alone. These components work together to provide the body with support, balance, and mobility. A malfunction in one part of the foot can result in problems elsewhere in the body, such as the knees and the back. In the same manner, abnormalities in other parts of the body can lead to problems in the feet. The forefoot is composed of five toes (called phalanges) and their connecting long bones (metatarsals). Each toe (phalanx) is made up of several smaller bones. The big toe (also known as the hallux) has two phalanx bones. Underneath the first metatarsal head are two tiny, round bones called sesamoids. The main function of the forefoot is to bear the body's weight on the ball of the foot. The middle of the foot has five irregularly shaped tarsal bones and this forms the foot's arch, which serves as a shock absorber. The bones of the midfoot are connected to the forefoot and the hindfoot by muscles and the plantar fascia (arch ligament). The back of the foot is composed of three joints and links the midfoot to the ankle (talus). The top of the talus is connected to the two bones of the lower leg (the tibia and fibula), forming a hinge that allows the foot to move up and down. The heel bone (calcaneus) is the largest bone in the foot. The bottom of the heel bone is cushioned by a layer of fat. A network of muscles, tendons, and ligaments supports the bones and joints in the foot. There are 20 muscles in the foot that give the foot its shape and allowing movement. The main muscles of the foot are: the anterior tibialis, which enables the foot to move upward; the posterior tibialis, which supports the arch; the peroneal tibialis, which controls movement on the outside of the ankle; the extensors, which help the ankle raise the toes to initiate the act of stepping forward; and The flexors, which help stabilize the toes against the ground. Smaller muscles enable the toes to lift and curl. There are elastic tissues (tendons) in the foot that connect the muscles to the bones. The largest and strongest tendon of the foot is the Achilles tendon, which extends from the calf muscle to the heel. Its strength and joint function facilitate running, jumping, walking up stairs, and raising the body onto the toes. Ligaments (fibrous tissue that link bone to bone) hold the tendons in place and stabilize the joints. The plantar fascia, forms the arch on the sole of the foot from the heel to the toes. By stretching and contracting, it allows the arch to curve or flatten, providing balance and giving the foot strength to initiate the act of walking. Medial ligaments on the inside and lateral ligaments on outside of the foot provide stability and enable the foot to move up and down. Skin, blood vessels, and nerves give the foot its shape and durability, provide cell regeneration and essential muscular nourishment, and control its varied movements. 3 4
3 What causes foot pain? At one time or another, everyone has had a minor toe, foot, or ankle injury that has caused pain or swelling. Most of the time our body movements do not cause problems, but it's not surprising that symptoms develop from everyday wear and tear, overuse, or from an injury. Toe, foot, or ankle injuries most commonly occur from sports or recreational activities, workrelated tasks, activities around the home and accidents. There are 2 types of injuries, acute and chronic. An acute injury may occur from a direct blow, a penetrating injury, a fall, or from twisting, jerking, jamming, or bending ACHILLES TENDONITIS Achilles tendonitis is a painful condition of the tendon that connects the heel of the foot to the calf muscles. Achilles pain commonly occurs from shearing and stretching forces placed on the Achilles tendon. This micro tearing in the tendon, leads to swelling and pain. This can be caused by a variety of factors including extra strain on the tendon from a tight calf muscle, or misalignment of the foot (i.e. excessive pronation or outward tilt of the foot). Other causes can include sudden increase in training or sport activity, or excessive running. Symptoms include pain which may be a limb abnormally. Your pain may be sudden and severe. Bruising and swelling may develop soon after your injury. Acute injuries include bruises, injury or tears to the soft tissues, broken bones (fractures), muscle sprains and dislocations. Chronic injuries are usually overuse injuries which occur when too much stress is placed on your joint or other tissue, often by "overdoing" an activity or repeating the same activity over and over. Overuse injuries include bursitis, tendonopothies, stress fractures, plantar fasciitis, and metatarsalgia. Common foot problems 5 present at the Achilles tendon during activity and may also increase once activity has ceased. ANKLE SPRAINS An ankle sprain is a common walking and sporting injury. It occurs due to the ankle twisting and causing damage to the soft tissues and ligaments. An ankle sprain may result in a partial or complete tear of the ligament which stabilizes the ankle joint. Once the ligament is torn, it becomes weak which in turn affects ankle stability. An audible "pop" or "snap" may be heard, which sometimes signals ligamentous rupture. If you can walk on the injured ankle, the likelihood of a serious injury is less, but athletic activities should be discontinued. Symptoms include a swollen, painful ankle with possible bruising due to ruptured blood vessels. Apply the R.I.C.E (Rest, Ice Compression, and Elevation). principal to reduce the sprain symptoms. BUNIONS Bunions are one of the most common forefoot problems, and are commonly just described as a bump on the side of the foot. They are actually caused by changes in the alignment of the bones, as the big toe moves in towards the smaller toes. This shifting of the bones causes a bony prominence on the inside of the foot. A bunion is more common in women than men due to women wearing tighter fitting shoes. Although this is not the cause, it can bring the symptoms on earlier. Causes include family history, arthritis, abnormal foot function, weak ligaments and genetic foot composition. Symptoms include redness, swelling and pain which may be present on the prominent bump on the inside of the foot. The feet may become too wide to fit into their normal size shoe. FLAT FEET This is a condition in which the foot doesn't have a normal arch. It may affect one foot or both feet. Feet that have a low arch or no arch at all are referred to as flat feet or fallen arches. The symptoms vary depending on the severity of the condition. Individuals may experience corns and hard skin under the sole of the foot. The arch area may be tender and shoes will tend to wear out quickly. In severe cases the patient may experience calf, knee, hip and back pain. The causes may be hereditary, or from biomechanical abnormalities, or a ruptured tendon. HIGH ARCHED FOOT Feet that have a high arch are sometimes referred to as cavus type feet. Symptoms include corns, faster wear out of shoes, pain along the arch, stiffness and difficulty fitting shoes. Wear wide fitting shoes and make use of insoles or orthotics to decrease or improve symptoms. HAMMER TOES Patients often refer to all forms of toe abnormalities as a hammer toe. There are in fact four main forms of toe abnormalities, hammer toes, claw toes, mallet toes and trigger toes. A hammer toe can be best described as an abnormal contraction or "buckling" of a toe. This occurs due to a partial or complete dislocation of one of the joints that form the toe. As the toe continues to be deformed, it will press up against the shoe and may cause corns. Symptoms include pain that is aggravated by a shoe, cramps in the toes, foot and leg, and corns. The toe will also appear bent. Some of the causes may include inappropriate 6
4 shoes, flat feet, high arched feet, bunions and rheumatoid arthritis. Wear wide fitted, low heeled shoes and make sure that your stockings, tights or socks are not too tight. POSTERIOR TIBIAL TENDON DYSFUNCTION Tendonitis in the foot is a common problem amongst hard working people. This is usually a classic over use injury and affects a particular tendon in the foot, the posterior tibial tendon. This tendon helps to hold the arch of the foot and prevents your feet from rolling in too much. Symptoms include pain at the in step of the foot, especially along the course of the tendon in addition to a sudden acquired flat foot. There may be burning, tingling, shooting or stabbing pain present in the foot. This is due to the inflammation of the nerve that surrounds the tendon. You may also have a sudden change in your walking pattern and feel quite unstable due to the reduced support in the arch of your foot. Initial treatment may include making use of the R.I.C.E principal and antiinflammatory medication, however it is important to consult your allied health professional to prevent long term deformity. HEEL PAIN The most common cause of heel pain is plantar fasciitis which is commonly referred to as a heel spur. Plantar fascia is a broad band of fibrous tissue which runs along the bottom surface of the foot, from the heel to the toes. Long standing inflammation causes the deposition of calcium at the point where the plantar fascia inserts into the heel. The result is an appearance of a sharp thorn like heel spur on an x- ray. The heel spur is asymptomatic (not painful), the pain arises from the inflammation of the plantar fascia. Symptoms include a dull ache which is felt most of the time with episodes of a sharp pain in the centre of the heel or on the inside margin of the heel. Often the pain is worse on first rising in the morning and after rest and is aggravated by prolonged weight bearing & thin soled shoes. Causes may include excessive load on the foot due to obesity, a sudden increase in activity, tight plantar fascia, biomechanical problems and arthritis. Make use of hot and cold gel packs, stretching exercises and non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce symptoms. OSTEOARTHRITIS Osteoarthritis is commonly known as a wear and tear disease of the joints, commonly found in the older population. Symptoms usually develop slowly and gradually, and can affect the hips, knees, thumb joints, lower spine, shoulders, elbows, ankles, toes and wrists. In some cases of OA you will not experience any symptoms at all. Changes in the joint would appear on an X-ray. The symptoms may include pain, swelling, loss of movement, grating or crackling, weakness, and stiffness. What treatment can I receive? The treatment you will receive will depend upon the cause, nature and severity of your foot pain. Your GP or health professional will be able to diagnose your injury from the following information: A history of the injury: The type of injury and how it occurred gives vital information as to the site, and what structures may have been injured. If there has been no violent incident there may be some underlying cause for the injury and it is important that the underlying cause is determined on examination. Description of Symptoms: The type and site of the pain, swelling present and other sensations such as clicking, grinding, locking, giving way, all provide clues of what is going on within the joint. REST ICE COMPRESSION ELEVATION X-rays: If your GP or health professional suspects a broken bone, or structural damage to the bones or cartilage, an X-ray may be done to confirm this. MRI scan/ultra sound scan: MRI/US scans are done to confirm a diagnosis of a soft tissue injury (such as ligaments or mensci). In most cases foot pain can be treated with common conservative measures. The goal of treatment is to reduce pain by reducing the inflammation, and to return the knee to full function. If you have sustained a foot injury from a traumatic event, or if there is swelling present, the RICE principle should be followed initially following the accident or injury. Stop using the injured area. Allow your injured region to rest from weight bearing, or any activity that brings on symptoms, for approximately 24 hours after the injury. You can move the area, but make sure that it is pain free to prevent any further damage Ice the area every 2 hours for minutes to decrease pain and swelling for the first hours Apply pressure to the area in the form of a stocking, tight sock, brace, strapping or bandage to provide both support and pressure to decrease any swelling Keep the injured area raised. Elevate the area ideally higher than your heart, to reduce swelling and pain 7 8
5 PRECAUTIONS WHEN USING ICE THERAPY Ice treatment must be used carefully otherwise it may cause a skin burn. Never put an ice pack directly onto the skin, always use a damp towel or cloth to prevent an ice burn. Only apply an ice pack to areas of skin with normal sensation i.e. you must be able to feel hot and cold. Never put an ice pack over an open wound or graze. Do not apply an ice pack to an area with poor circulation. Never leave an ice pack on the skin longer than the time stated in this advice sheet. Adults should always supervise young children when using ice packs. Application may be reduced and extra care should be taken when checking the skin. Remember to check the skin underneath every 5 minutes for: Blotchy and painful skin Excessive numbness If you get any of these symptoms remove the ice pack immediately. ANTI-INFLAMMATORY MEDICATION This can be taken to control inflammation. It is important to get advice from your pharmacist before starting a course of anti-inflammatory medicine. PHYSIOTHERAPY This would include a full assessment and treatments such as soft tissue techniques, education and a full rehabilitation programme to ensure return to full function. They may also refer you to a podiatrist for a biomechanical assessment and advice regarding footwear. What exercises can I do? It is important that you are aware that the exercise programme in this pack is a general exercise programme to encourage the return of muscle strength and range of movement to the foot joint. If you are seeing a health professional regarding your injury, please take this guide with you. When starting an exercise programme it is important that you start slowly, and ensure that you are able to do all exercises in a controlled, pain free range of movement before moving on to the next exercise phase. If you are not used to doing exercise, always start gradually, feeling only a slight exertion, and slowly progress as you get stronger. You may feel some discomfort while doing the exercises or afterwards, and this is completely normal, especially if the exercises are not familiar to you. However, the exercises should never exacerbate your existing symptoms. Try to include aerobic exercises (exercise which gets your heart beating faster) such as cycling, swimming and walking, as long it is pain free, and has benefits for not only your injury, but your general health. If you experience an increase in your pain during any of the exercises, decrease the intensity of the exercises by: decreasing the number of sets decreasing the number of repetitions decreasing the range of movement decreasing the resistance Do all exercises slowly and breathe normally. Progress gradually according to your own level of comfort. Stiffness or fatigue may result following the exercises, but should not last longer than 24 hrs, and your symptoms should not in any way be aggravated by the exercises. 9 10
6 Exercises phase 1 STRETCHING You can start with Phase one exercises when the swelling and the pain starts to decrease. Pain is your guide as to when you can start, and how much activity is enough. The goal of this phase is to increase the range of motion and strength, which will aid in circulation and help eliminate swelling. Hold each stretch for 30 seconds and repeat 2-3 times on each leg Repeat each stretch 3x on each side, 2-3 times a day. Perform them in a slow and controlled manner, until you feel the stretch but not into the pain threshold If you do not have tubing you can make use of an old stocking SOLEUS STRETCH In the above position, now keep the back leg slightly bent, with the heel on the floor and toes pointing in a straight line to the wall. Lean into the wall until a stretch is felt in the lower calf. HAMSTRING STRETCH Lie on your back and support your thigh behind the knee. Slowly pull the leg towards your chest and then straighten the knee until a stretch is felt in the back of the thigh. PLANTAR FASCIITIS STRETCH Sit with your leg straight and place a towel or old stocking over the ball of your foot. Pull it towards you until a stretch is felt through the arch of your foot. (You may also feel the stretch in the back of the thigh and the calf) GASTROCNEMIUS STRETCH Stand about a meter away from a wall. Place both hands against the wall with one foot further back than the other. Now lean in towards the wall, bending the front knee and keeping the back knee straight and the heel on the floor. ANKLE ALPHABET Sitting/lying with your leg outstretched in front. Now raise the leg, keeping knee straight and leg still. Paint the alphabet in the air, with ankle using capital letters, slowly to get full range of movement in ankle. The movement should not be from your hip, only your ankle and range should be pain free. WEIGHT SHIFTING Stand up straight and shift your weight from one leg to another in a slow and controlled manner
7 Exercises phase 2 This phase of exercise can be started when you are able to complete phase 1 exercises pain free and with control. You should no longer have swelling or pain and if this is not the case it is important that you consult your health professional to ensure that there are no other problems and that you are completing the exercise programme correctly. Do not be afraid Repeat 2 sets of repetitions of each exercise to go back to phase 1 if you feel that you are unable to safely continue with the phase 2 exercise or you can overlap the phases if you are not completely confident to do all the exercises in phase 2 yet. Be aware of pain as your marker of doing too much or maybe even doing the exercise incorrectly. Continue with the stretches as in phase 1. MOBILITY & STRENGTHENING These exercises should be performed at least once a day, twice if possible Make sure that you work in a pain free range of movement and gradually increase your range as you go RESISTED DORSIFLEXION (TOES UP) With the tubing (or an old stocking) anchored to a fixed object (table leg), and attached around your foot, pull the foot towards you. Return slowly to your starting position. RESISTED PLANTARFLEXION (TOES DOWN) Whilst holding one end of the tubing and the other tied around your ankle, press the foot downwards towards the floor. Return slowly to starting position. RESISTED INVERSION (TOES IN) Tie ends of the band together, and anchor the band around a table. Sitting side on to the table, loop the band around the foot of your injured ankle which should be closest to the table. Move toes up and in toward opposite knee. Be sure to only use your ankle. RESISTED EVERSION (TOES OUT) Now turn around so your injured ankle is furthest from the table, with the band attached around the foot. Now move the toes of the foot up and out toward outer shin, pulling the band away from the table. CALF RAISES Standing on both legs, raise up onto your toes in the following manner: First onto your big toe, then onto your middle toes and lastly onto your little toe. Repeat this sequence 10 times. Ensure you have something to hold onto, should your balance not be good
8 Exercises phase 2 (continued) STANDING TOE RAISE Standing with your weight now on your heels, raise your toes off the ground in the same sequence as the calf raises, i.e. middle of your heel, outside and inside. STEP STRENGTHENING EXERCISES Stand on a step (facing down stairs) and tighten the quads (the thigh muscle) as you bend and straighten the knee. Don t let the leg being lowered become weight bearing. Exercises phase 3 STORK STANDING Balanced on one leg for 30 seconds and repeat with the other leg. Repeat with your eyes closed. Progress the above standing to an unsteady surface e.g. a cushion or a narrow piece of wood. STRENGTHENING & PROPRIOCEPTIVE This phase of exercise can be started when you are able to complete phase 2 exercises pain free and with control. You should no longer have swelling or pain and if this is not the case it is important that you consult your health professional to ensure that there are no other problems and that you are completing the exercise programme correctly. This phase of exercises is specifically designed if you are actively participating in sports and like to return back to competitive sports. Repeat two sets of repetitions of each exercise. Make sure that you work in a pain free range of movement and gradually increase your range as you go STATIC LUNGE Place one foot in front of the other. Bend both knees together until you have a 90º bend in both. Ensure that your front knee does not go over your front foot when bending to 90º. Return to the starting position. Complete all repetitions on one leg before changing to the other. SINGLE LEG CALF RAISE Supporting yourself against a wall or holding onto a table, stand on one leg and raise up onto your toes in the following manner; first onto your big toe, then onto the middle of your foot and lastly onto your little toe. This sequence equals one repetition
9 1 2 FUNCTIONAL EXERCISES Only start these exercises once you are able to do the above with no pain and good control, and if you want to return to sporting activities. It is also important that you consult with your allied health professional before starting any jumping activities to ensure that you are safe to do so. HOPPING Standing on two legs hop from one point to another in the following manner 1. Forwards and backwards 2. Side to side 3. In a square (clockwise and anticlockwise) 4. In a zigzag forwards and then backwards Repeat each sequence 10 times per leg. Progress to hopping on one leg. ACTIVITY SPECIFIC TRAINING Activity specific exercises may include simply walking or jogging, or may be more intense for athletes who participate in basketball, soccer, or other sports. The key, no matter what level of recreational or competitive athlete you may be, is to progress slowly. Begin at very low intensity, and very low duration of activity, and slowly work up never suddenly increase either the intensity or duration of your activity. Helpful hint For pain and swelling on the planter aspect (sole) of the foot. Use a plastic water bottle, fill it with water and put it in the fridge. When the water has frozen you can use this to ice the sole of your foot (instead of the normal ice pack) while applying a gentle stretch to the sole of the foot. Stand up and role your foot back and forth on the icy bottle while putting some weight on the foot being iced. This will allow you to ice the area while also stretching the facia and plantar muscles. 3 RUNNING DRILLS In order to get back to normal activity it is important to practice some of these movements during your rehabilitation programme to ensure that you are ready. Therefore perform various running drills i.e. short sprints, backward running, zig-zag running, stop/start and so on to prepare yourself for your specific sport
10 Contact us This guide is designed to assist you in the self-management of your injury/condition. We are here to assist your recovery in the shortest but safest possible time. If you have any uncertainties or queries regarding the information, please do not hesitate to contact us on: Tel: Phone / info@iprsgroup.com DM Ref.: MSkel072 21
ANKLE FRACTURES. Contents The Ankle Joint... 3
 Contents The Ankle Joint................................................. 3 What is a fractured ankle?........................................ 4 YOUR GUIDE TO ANKLE FRACTURES What treatment can I receive?.....................................
Contents The Ankle Joint................................................. 3 What is a fractured ankle?........................................ 4 YOUR GUIDE TO ANKLE FRACTURES What treatment can I receive?.....................................
Contents The Ankle Joint What is a sprained ankle? What treatment can I receive? Exercises Introduction Please take note of the following
 Contents The Ankle Joint................................ 3 What is a sprained ankle?.................... 4 MUSCULOSKELETAL YOUR GUIDE TO ANKLE SPRAINS An IPRS Guide to provide you with exercises and advice
Contents The Ankle Joint................................ 3 What is a sprained ankle?.................... 4 MUSCULOSKELETAL YOUR GUIDE TO ANKLE SPRAINS An IPRS Guide to provide you with exercises and advice
ACHILLES TENDON DISORDERS
 MUSCULOSKELETAL YOUR GUIDE TO ACHILLES TENDON DISORDERS An IPRS Guide to provide you with exercises and advice to ease your condition Contents What is the Achilles Tendon?.....................................
MUSCULOSKELETAL YOUR GUIDE TO ACHILLES TENDON DISORDERS An IPRS Guide to provide you with exercises and advice to ease your condition Contents What is the Achilles Tendon?.....................................
PLANTAR FASCIITIS. Contents What is Plantar Fasciitis?... 3
 Contents What is Plantar Fasciitis?........................................................ 3 What causes Plantar Fasciitis?.................................................. 4 YOUR GUIDE TO PLANTAR FASCIITIS
Contents What is Plantar Fasciitis?........................................................ 3 What causes Plantar Fasciitis?.................................................. 4 YOUR GUIDE TO PLANTAR FASCIITIS
LATERAL LIGAMENT SPRAIN OF THE ANKLE
 MUSCULOSKELETAL YOUR GUIDE TO LATERAL LIGAMENT SPRAIN OF THE ANKLE An IPRS Guide to provide you with exercises and advice to ease your condition Contents The ankle joint..................................................
MUSCULOSKELETAL YOUR GUIDE TO LATERAL LIGAMENT SPRAIN OF THE ANKLE An IPRS Guide to provide you with exercises and advice to ease your condition Contents The ankle joint..................................................
ACHILLES RUPTURE YOUR GUIDE TO. An IPRS Guide to provide you with exercises and advice to ease your condition
 YOUR GUIDE TO ACHILLES RUPTURE Contents What is an Achilles Rupture?..................................... 3 What treatment can I receive?................................... 4 What exercises should I do?......................................
YOUR GUIDE TO ACHILLES RUPTURE Contents What is an Achilles Rupture?..................................... 3 What treatment can I receive?................................... 4 What exercises should I do?......................................
PLICA SYNDROME. Contents What is Plica Syndrome?... 3
 Contents What is Plica Syndrome?........................................................... 3 What are Plicae?..................................................................... 3 YOUR GUIDE TO PLICA
Contents What is Plica Syndrome?........................................................... 3 What are Plicae?..................................................................... 3 YOUR GUIDE TO PLICA
LOWER LEG FRACTURES. Contents Anatomy of the lower leg...3
 Contents Anatomy of the lower leg.............................................................3 What is a fracture?....................................................................3 YOUR GUIDE TO LOWER
Contents Anatomy of the lower leg.............................................................3 What is a fracture?....................................................................3 YOUR GUIDE TO LOWER
Lateral Collateral Ligament Sprain
 What is lateral collateral ligament sprain? Lateral Collateral Ligament Sprain A sprain is a joint injury that causes a stretch or tear in a ligament, a strong band of tissue connecting one bone to another.
What is lateral collateral ligament sprain? Lateral Collateral Ligament Sprain A sprain is a joint injury that causes a stretch or tear in a ligament, a strong band of tissue connecting one bone to another.
GENERAL KNEE PAIN. Contents The Knee Joint...3
 Contents The Knee Joint.........................................................................3 Understanding pain...................................................................3 YOUR GUIDE TO GENERAL
Contents The Knee Joint.........................................................................3 Understanding pain...................................................................3 YOUR GUIDE TO GENERAL
ANKLE SPRAINS. Explanation. Causes. Symptoms
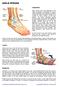 ANKLE SPRAINS Explanation Ankle sprains occur when ligaments in the ankle are partially or completely torn due to sudden stretching, either laterally or medially, or when the ankle is suddenly twisted
ANKLE SPRAINS Explanation Ankle sprains occur when ligaments in the ankle are partially or completely torn due to sudden stretching, either laterally or medially, or when the ankle is suddenly twisted
Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
 43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome The foot is subjected to forces hundreds of times the bodyweight, thousands of times
43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome The foot is subjected to forces hundreds of times the bodyweight, thousands of times
LOW BACK PAIN. Contents What causes Low Back Pain?... 3
 YOUR GUIDE TO LOW BACK PAIN An IPRS Guide to provide you with exercises and advice to ease your condition Contents What causes Low Back Pain?....... 3 What treatment can I receive?..... 4 What about exercise?...............
YOUR GUIDE TO LOW BACK PAIN An IPRS Guide to provide you with exercises and advice to ease your condition Contents What causes Low Back Pain?....... 3 What treatment can I receive?..... 4 What about exercise?...............
MENISCAL TEARS. Contents What is a Meniscus?...3
 Contents What is a Meniscus?..............................................3 What causes a Meniscal tear of the knee?............................4 YOUR GUIDE TO MENISCAL TEARS What treatment can I receive?.....................................5
Contents What is a Meniscus?..............................................3 What causes a Meniscal tear of the knee?............................4 YOUR GUIDE TO MENISCAL TEARS What treatment can I receive?.....................................5
ACROMIO- CLAVICULAR (A/C) JOINT SPRAIN An IPRS Guide to provide you with exercises and advice to ease your condition
 Contents What causes an A/C joint sprain?..................................3 What treatment can I receive?.....................................4 YOUR GUIDE TO ACROMIO- CLAVICULAR (A/C) JOINT SPRAIN An
Contents What causes an A/C joint sprain?..................................3 What treatment can I receive?.....................................4 YOUR GUIDE TO ACROMIO- CLAVICULAR (A/C) JOINT SPRAIN An
A patient s guide to. Inferior Heel Pain
 A patient s guide to Inferior Heel Pain The Foot & Ankle Unit at the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital is made up of a multi-disciplinary team. The team consists of four specialist orthopaedic foot and
A patient s guide to Inferior Heel Pain The Foot & Ankle Unit at the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital is made up of a multi-disciplinary team. The team consists of four specialist orthopaedic foot and
Everything. You Should Know. About Your Ankles
 Everything You Should Know About Your Ankles How Your Ankle Works The ankle joint is a hinge type joint that participates in movement and is involved in lower limb stability. There are 2 types of motions
Everything You Should Know About Your Ankles How Your Ankle Works The ankle joint is a hinge type joint that participates in movement and is involved in lower limb stability. There are 2 types of motions
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome
 What is patellofemoral pain syndrome? Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome Patellofemoral pain syndrome is pain behind the kneecap. It has been given many names, including patellofemoral disorder, patellar malalignment,
What is patellofemoral pain syndrome? Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome Patellofemoral pain syndrome is pain behind the kneecap. It has been given many names, including patellofemoral disorder, patellar malalignment,
Advice and exercises for managing knee and hip osteoarthritis October 2018 V1.2 April 2018 April 2021
 Advice and exercises for managing knee and hip osteoarthritis 0496 October 2018 V1.2 April 2018 April 2021 This advice and exercise booklet has been produced by senior physiotherapists working for DynamicHealth.
Advice and exercises for managing knee and hip osteoarthritis 0496 October 2018 V1.2 April 2018 April 2021 This advice and exercise booklet has been produced by senior physiotherapists working for DynamicHealth.
ORTHOTIC ARCH SUPPORTS
 ORTHOTIC ARCH SUPPORTS COMMON FOOT PROBLEMS & ORTHOTIC THERAPY The foot and ankle are the foundation for the overall posture of the skeletal body. Many problems with the feet, legs, knees, hips and lower
ORTHOTIC ARCH SUPPORTS COMMON FOOT PROBLEMS & ORTHOTIC THERAPY The foot and ankle are the foundation for the overall posture of the skeletal body. Many problems with the feet, legs, knees, hips and lower
DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS
 YOUR GUIDE TO DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS Contents What is tendonitis and tenosynovitis?.............................. 3 What is de Quervain s tenosynovitis?.............................. 3 What treatment
YOUR GUIDE TO DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS Contents What is tendonitis and tenosynovitis?.............................. 3 What is de Quervain s tenosynovitis?.............................. 3 What treatment
Plantar Fasciitis and Heel Pain
 PATIENT INFORMATION Plantar Fasciitis and Heel Pain What is plantar fasciitis? Heel pain and plantar fasciitis Plantar fasciitis causes pain under your heel. It usually goes in time. Treatment may speed
PATIENT INFORMATION Plantar Fasciitis and Heel Pain What is plantar fasciitis? Heel pain and plantar fasciitis Plantar fasciitis causes pain under your heel. It usually goes in time. Treatment may speed
ACHILLES TENDON RUPTURE
 ACHILLES TENDON RUPTURE Description Expected Outcome Achilles tendon rupture is a complete tear of the Achilles tendon. This tendon, sometimes called the heel cord, is the tendon attachment of the calf
ACHILLES TENDON RUPTURE Description Expected Outcome Achilles tendon rupture is a complete tear of the Achilles tendon. This tendon, sometimes called the heel cord, is the tendon attachment of the calf
POSTERIOR TIBIAL TENDON RUPTURE
 POSTERIOR TIBIAL TENDON RUPTURE Description Expected Outcome Posterior tibial tendon rupture is a complete tear of the posterior tibial tendon. This structure is the tendon attachment of leg muscles (posterior
POSTERIOR TIBIAL TENDON RUPTURE Description Expected Outcome Posterior tibial tendon rupture is a complete tear of the posterior tibial tendon. This structure is the tendon attachment of leg muscles (posterior
Key Points for Success:
 ANKLE & FOOT 1 2 All of the stretches described in this chapter are detailed to stretch the right side. Key Points for Success: Keep your movements slow and precise. Breathe in before you move and breathe
ANKLE & FOOT 1 2 All of the stretches described in this chapter are detailed to stretch the right side. Key Points for Success: Keep your movements slow and precise. Breathe in before you move and breathe
What are the symptoms of plantar fasciitis? The main symptoms of plantar fasciitis include: What causes plantar fasciitis?
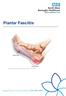 Plantar Fasciitis Plantar fasciitis is a condition which can cause heel pain. It happens when the strong band of tissue on the sole of your foot (fascia) becomes irritated, after repetitive use or due
Plantar Fasciitis Plantar fasciitis is a condition which can cause heel pain. It happens when the strong band of tissue on the sole of your foot (fascia) becomes irritated, after repetitive use or due
MEDIAL HEAD GASTROCNEMIUS TEAR (Tennis Leg)
 MEDIAL HEAD GASTROCNEMIUS TEAR (Tennis Leg) Description Expected Outcome Medial head gastrocnemius tear is a strain of the inner part (medial head) of the major calf muscle (gastrocnemius muscle). Muscle
MEDIAL HEAD GASTROCNEMIUS TEAR (Tennis Leg) Description Expected Outcome Medial head gastrocnemius tear is a strain of the inner part (medial head) of the major calf muscle (gastrocnemius muscle). Muscle
SCIATICA. Contents YOUR GUIDE TO. An IPRS Guide to provide you with exercises and advice to ease your condition. What is sciatica?...
 Contents What is sciatica?................................................3 What causes sciatica?............................................3 YOUR GUIDE TO SCIATICA An IPRS Guide to provide you with exercises
Contents What is sciatica?................................................3 What causes sciatica?............................................3 YOUR GUIDE TO SCIATICA An IPRS Guide to provide you with exercises
CHONDROMALACIA PATELLA
 Contents What is Chondromalacia Patella?.................................. 3 YOUR GUIDE TO CHONDROMALACIA PATELLA What Causes Chondromalacia Patella?............................. 4 What Treatment can I
Contents What is Chondromalacia Patella?.................................. 3 YOUR GUIDE TO CHONDROMALACIA PATELLA What Causes Chondromalacia Patella?............................. 4 What Treatment can I
PHASE ONE: THE FIRST SIX WEEKS AFTER INJURY
 Exercises After Injury to the Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) of the Knee Dr. Abigail R. Hamilton, M.D. PHASE ONE: THE FIRST SIX WEEKS AFTER INJURY Initially, the knee needs to be protected-use the knee
Exercises After Injury to the Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) of the Knee Dr. Abigail R. Hamilton, M.D. PHASE ONE: THE FIRST SIX WEEKS AFTER INJURY Initially, the knee needs to be protected-use the knee
WHAT IS PLANTAR FASCIITIS?
 WHAT IS PLANTAR FASCIITIS? If you're finding when you climb out of bed each morning that your first couple steps cause your foot and heel to hurt, this might be a sign of plantar fasciitis. A common condition
WHAT IS PLANTAR FASCIITIS? If you're finding when you climb out of bed each morning that your first couple steps cause your foot and heel to hurt, this might be a sign of plantar fasciitis. A common condition
ANKLE SPRAIN, ACUTE. Description
 Description ANKLE SPRAIN, ACUTE An acute ankle sprain involves the stretching and tearing of one or more ligaments in the ankle. A two-ligament sprain causes more disability than a single-ligament sprain.
Description ANKLE SPRAIN, ACUTE An acute ankle sprain involves the stretching and tearing of one or more ligaments in the ankle. A two-ligament sprain causes more disability than a single-ligament sprain.
METATARSAL FRACTURE (Including Jones and Dancer s Fractures)
 METATARSAL FRACTURE (Including Jones and Dancer s Fractures) Description Possible Complications Metatarsal fracture is a broken bone (fracture) in the middle Nonunion (fracture does not heal, particularly
METATARSAL FRACTURE (Including Jones and Dancer s Fractures) Description Possible Complications Metatarsal fracture is a broken bone (fracture) in the middle Nonunion (fracture does not heal, particularly
Plantar fasciitis occurs when the strong band of tissue that supports the arch of your foot becomes irritated and inflamed.
 Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition every year.
Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition every year.
STERNO- CLAVICULAR (S/C) JOINT SPRAIN
 Contents What is a sprain?................................................3 What causes an S/C joint injury?...................................5 YOUR GUIDE TO STERNO- CLAVICULAR (S/C) JOINT SPRAIN An IPRS
Contents What is a sprain?................................................3 What causes an S/C joint injury?...................................5 YOUR GUIDE TO STERNO- CLAVICULAR (S/C) JOINT SPRAIN An IPRS
(Also known as a, Lateral Cartilage Tear,, Bucket Handle Tear of the Lateral Meniscus, Torn Cartilage)
 Lateral Meniscus Tear (Also known as a, Lateral Cartilage Tear,, Bucket Handle Tear of the Lateral Meniscus, Torn Cartilage) What is a lateral meniscus tear? The knee joint comprises of the union of two
Lateral Meniscus Tear (Also known as a, Lateral Cartilage Tear,, Bucket Handle Tear of the Lateral Meniscus, Torn Cartilage) What is a lateral meniscus tear? The knee joint comprises of the union of two
Common Foot and Ankle Conditions: How Can You Find Relief?
 Common Foot and Ankle Conditions: How Can You Find Relief? Your Feet and Ankles are Workhorses They bear a lot of weight They perform various movements Common Conditions That Cause Foot/Ankle Pain Plantar
Common Foot and Ankle Conditions: How Can You Find Relief? Your Feet and Ankles are Workhorses They bear a lot of weight They perform various movements Common Conditions That Cause Foot/Ankle Pain Plantar
A Patient s Guide to Adult-Acquired Flatfoot Deformity
 A Patient s Guide to Adult-Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Glendale Adventist Medical Center 1509 Wilson Terrace Glendale, CA 91206 Phone: (818) 409-8000 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Adult-Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Glendale Adventist Medical Center 1509 Wilson Terrace Glendale, CA 91206 Phone: (818) 409-8000 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL)
 Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the 4 major ligament stabilizers of the knee. ACL tears are among the most common major knee injuries in active people of
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the 4 major ligament stabilizers of the knee. ACL tears are among the most common major knee injuries in active people of
Static Flexibility/Stretching
 Static Flexibility/Stretching Points of Emphasis Always stretch before and after workouts. Stretching post-exercise will prevent soreness and accelerate recovery. Always perform a general warm-up prior
Static Flexibility/Stretching Points of Emphasis Always stretch before and after workouts. Stretching post-exercise will prevent soreness and accelerate recovery. Always perform a general warm-up prior
Ankle Rehabilitation with Wakefield Sports Clinic
 Ankle Rehabilitation with Wakefield Sports Clinic With Michael Woodcock Adelaide 36ERS & Wakefield Sports Clinic Physiotherapist The ankle joint is one of the major weight bearing structures in the body.
Ankle Rehabilitation with Wakefield Sports Clinic With Michael Woodcock Adelaide 36ERS & Wakefield Sports Clinic Physiotherapist The ankle joint is one of the major weight bearing structures in the body.
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME
 Dr. S. Matthew Hollenbeck, MD Kansas Orthopaedic Center, PA 7550 West Village Circle, Wichita, KS 67205 2450 N Woodlawn, Wichita, KS 67220 Phone: (316) 838-2020 Fax: (316) 838-7574 Description ILIOTIBIAL
Dr. S. Matthew Hollenbeck, MD Kansas Orthopaedic Center, PA 7550 West Village Circle, Wichita, KS 67205 2450 N Woodlawn, Wichita, KS 67220 Phone: (316) 838-2020 Fax: (316) 838-7574 Description ILIOTIBIAL
MENISCUS TEAR. Description
 MENISCUS TEAR Description Expected Outcome The meniscus is a C-shaped cartilage structure in the knee that sits on top of the leg bone (tibia). Each knee has two menisci, an inner and outer meniscus. The
MENISCUS TEAR Description Expected Outcome The meniscus is a C-shaped cartilage structure in the knee that sits on top of the leg bone (tibia). Each knee has two menisci, an inner and outer meniscus. The
Foot and Ankle Conditioning Program
 Foot and Ankle Conditioning Program Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle.
Foot and Ankle Conditioning Program Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle.
Make sure you have properly fitting running shoes and break these in gradually. Never wear new running shoes for a race or a long run.
 Common Running Injuries We are delighted that you have decided to run in the next Bath Half Marathon and very much hope that you have good running shoes, undertake a regular training programme and don
Common Running Injuries We are delighted that you have decided to run in the next Bath Half Marathon and very much hope that you have good running shoes, undertake a regular training programme and don
Foot and Ankle Conditioning Program
 Foot and Ankle Conditioning Program Studies show, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle. A program of this nature, focused
Foot and Ankle Conditioning Program Studies show, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle. A program of this nature, focused
Dr. Abigail R. Hamilton, MD
 ACHILLES TENDINITIS Dr. Abigail R. Hamilton, MD ANATOMY The Achilles tendon is a strong tendon that connects the calf muscles to the heel. When the calf muscles contract, they pull on the Achilles tendon
ACHILLES TENDINITIS Dr. Abigail R. Hamilton, MD ANATOMY The Achilles tendon is a strong tendon that connects the calf muscles to the heel. When the calf muscles contract, they pull on the Achilles tendon
Achilles Tendonitis and Tears
 Achilles Tendonitis and Tears The Achilles tendon is an important structure for normal ankle motion and normal function, even for daily activities such as walking. Achilles tendonitis can occur in patients
Achilles Tendonitis and Tears The Achilles tendon is an important structure for normal ankle motion and normal function, even for daily activities such as walking. Achilles tendonitis can occur in patients
MEDIAL TIBIAL STRESS SYNDROME (Shin Splints)
 MEDIAL TIBIAL STRESS SYNDROME (Shin Splints) Description Expected Outcome Shin splints is a term broadly used to describe pain in the lower extremity brought on by exercise or athletic activity. Most commonly
MEDIAL TIBIAL STRESS SYNDROME (Shin Splints) Description Expected Outcome Shin splints is a term broadly used to describe pain in the lower extremity brought on by exercise or athletic activity. Most commonly
Sky Ridge Medical Center, Aspen Building Ridgegate Pkwy., Suite 309 Lone Tree, Colorado Office: Fax:
 ANKLE SPRAIN What is the ATFL? The ankle joint is made up of the tibia, fibula (bones in the lower leg) and the talus (bone below the tibia and fibula). Ligaments in the ankle connect bone to bone and
ANKLE SPRAIN What is the ATFL? The ankle joint is made up of the tibia, fibula (bones in the lower leg) and the talus (bone below the tibia and fibula). Ligaments in the ankle connect bone to bone and
ANTERIOR KNEE PAIN. Explanation. Causes. Symptoms
 ANTERIOR KNEE PAIN Explanation Anterior knee pain is most commonly caused by irritation and inflammation of the patellofemoral joint of the knee (where the patella/kneecap connects to the femur/thigh bone).
ANTERIOR KNEE PAIN Explanation Anterior knee pain is most commonly caused by irritation and inflammation of the patellofemoral joint of the knee (where the patella/kneecap connects to the femur/thigh bone).
ANTERIOR ANKLE IMPINGEMENT
 ANTERIOR ANKLE IMPINGEMENT Description Possible Complications Pinching of bone or soft tissue, including scar tissue, at the Frequent recurrence of symptoms, resulting in chronically front of the ankle
ANTERIOR ANKLE IMPINGEMENT Description Possible Complications Pinching of bone or soft tissue, including scar tissue, at the Frequent recurrence of symptoms, resulting in chronically front of the ankle
Injury Recovery and Prevention. ~Joshua Bowen
 Injury Recovery and Prevention ~Joshua Bowen Injury and Warming up Playing sports as an athlete competitively or just for fun can often lend itself to injuries, sometimes minor and sometimes serious. Like
Injury Recovery and Prevention ~Joshua Bowen Injury and Warming up Playing sports as an athlete competitively or just for fun can often lend itself to injuries, sometimes minor and sometimes serious. Like
PREGNANCY AND BACK PAIN
 Contents The Pelvis.............................................................3 What happens during pregnancy........................................ 3 MUSCULOSKELETAL YOUR GUIDE TO PREGNANCY AND BACK
Contents The Pelvis.............................................................3 What happens during pregnancy........................................ 3 MUSCULOSKELETAL YOUR GUIDE TO PREGNANCY AND BACK
ACL Reconstruction Physiotherapy advice for patients
 ACL Reconstruction Physiotherapy advice for patients Introduction This booklet is designed to provide you with advice and guidance on your rehabilitation after reconstruction of your anterior cruciate
ACL Reconstruction Physiotherapy advice for patients Introduction This booklet is designed to provide you with advice and guidance on your rehabilitation after reconstruction of your anterior cruciate
Foot and Ankle Conditioning Program
 Prepared for: Prepared by: Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle. Following
Prepared for: Prepared by: Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle. Following
Plantar Fasciitis. Equipment: Anti-inflammatory drugs: Night splints keep the plantar fascia from getting will relieve pain and reduce swelling.
 Plantar fasciitis is the most common cause of heel pain for which professional care is sought. This is caused by irritation of the plantar fascia a thickened fibrous band that runs from the heel to the
Plantar fasciitis is the most common cause of heel pain for which professional care is sought. This is caused by irritation of the plantar fascia a thickened fibrous band that runs from the heel to the
Advice for patients with Plantar Fasciitis
 For Huntingdon and Cambridge City and South areas If you are unsure about any of the advice in this leaflet or if you require further advice from a Chartered Physiotherapist, please contact your local
For Huntingdon and Cambridge City and South areas If you are unsure about any of the advice in this leaflet or if you require further advice from a Chartered Physiotherapist, please contact your local
LEG EXERCISES. Remember to always stretch out the legs after each workout you do to avoid muscle soreness from setting in.
 No other training will burn fat faster than lower body training. Since the legs are the largest muscles in the body, they ll use up a high amount of energy each and every time they contract, giving you
No other training will burn fat faster than lower body training. Since the legs are the largest muscles in the body, they ll use up a high amount of energy each and every time they contract, giving you
WRIST SPRAIN. Description
 WRIST SPRAIN Description Other sports, such as skiing, bowling, pole vaulting Wrist sprain is a violent overstretching and tearing of one Poor physical conditioning (strength and flexibility) or more ligaments
WRIST SPRAIN Description Other sports, such as skiing, bowling, pole vaulting Wrist sprain is a violent overstretching and tearing of one Poor physical conditioning (strength and flexibility) or more ligaments
Prevention and Treatment of Injuries. Anatomy. Anatomy. Tibia: the second longest bone in the body
 Prevention and Treatment of Injuries The Ankle and Lower Leg Westfield High School Houston, Texas Anatomy Tibia: the second longest bone in the body Serves as the principle weight-bearing bone of the leg.
Prevention and Treatment of Injuries The Ankle and Lower Leg Westfield High School Houston, Texas Anatomy Tibia: the second longest bone in the body Serves as the principle weight-bearing bone of the leg.
BUCKS MSK: FOOT AND ANKLE PATHWAY GP MANAGEMENT. Hallux Valgus. Assessment: Early Management. (must be attempted prior to any referral to imsk):
 Hallux Valgus Common condition: affecting around 28% of the adult population. Prevalence increases with age and in females. Observation: Lateral deviation of the great toe. May cause secondary irritation
Hallux Valgus Common condition: affecting around 28% of the adult population. Prevalence increases with age and in females. Observation: Lateral deviation of the great toe. May cause secondary irritation
KNEE AND LEG EXERCISE PROGRAM
 KNEE AND LEG EXERCISE PROGRAM These exercises are specifically designed to rehabilitate the muscles of the hip and knee by increasing the strength and flexibility of the involved leg. This exercise program
KNEE AND LEG EXERCISE PROGRAM These exercises are specifically designed to rehabilitate the muscles of the hip and knee by increasing the strength and flexibility of the involved leg. This exercise program
WHAT SHOULD I DO IF I SPRAIN MY ANKLE? HOW SHOULD I REHABILITATE MY ANKLE?
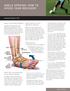 ANKLE SPRAINS: HOW TO SPEED YOUR RECOVERY AOSSM SPORTS TIPS WHAT IS AN ANKLE SPRAIN? A sprain is a stretch injury of the ligaments that support the ankle. About 25,000 ankle sprains occur in the United
ANKLE SPRAINS: HOW TO SPEED YOUR RECOVERY AOSSM SPORTS TIPS WHAT IS AN ANKLE SPRAIN? A sprain is a stretch injury of the ligaments that support the ankle. About 25,000 ankle sprains occur in the United
A Patient s Guide to Flatfoot Deformity (Pes Planus) in Children
 A Patient s Guide to Flatfoot Deformity (Pes Planus) in Children 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Flatfoot Deformity (Pes Planus) in Children 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
.org. Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction. Anatomy. Cause. Symptoms
 Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
This article is also available in Spanish: Fascitis plantar y protuberancias óseas (topic.cfm?topic=a00702).
 1 of 5 17 Oct 2015 11:04 AM This article is also available in Spanish: Fascitis plantar y protuberancias óseas (topic.cfm?topic=a00702). Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of
1 of 5 17 Oct 2015 11:04 AM This article is also available in Spanish: Fascitis plantar y protuberancias óseas (topic.cfm?topic=a00702). Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of
HOW TO USE NOW ROLLER MASSAGER & LACROSSE BALL - EXERCISES AND TIPS -
 HOW TO USE ROLLER MASSAGER & LACROSSE BALL - EXERCISES AND TIPS - BOOST YOUR RECOVERY NOW Thank you! Hi, it s Jeff again, Co-Founder of Maogani. Our team would like to thank you for giving us the opportunity
HOW TO USE ROLLER MASSAGER & LACROSSE BALL - EXERCISES AND TIPS - BOOST YOUR RECOVERY NOW Thank you! Hi, it s Jeff again, Co-Founder of Maogani. Our team would like to thank you for giving us the opportunity
right Initial examination established that you have 'flat feet'. Additional information left Left foot is more supinated possibly due to LLD
 Motion analysis report for Feet In Focus at 25/01/2013 Personal data: Mathew Vaughan DEMO REPORT, 20 Churchill Way CF10 2DY Cardiff - United Kingdom Birthday: 03/01/1979 Telephone: 02920 644900 Email:
Motion analysis report for Feet In Focus at 25/01/2013 Personal data: Mathew Vaughan DEMO REPORT, 20 Churchill Way CF10 2DY Cardiff - United Kingdom Birthday: 03/01/1979 Telephone: 02920 644900 Email:
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME
 ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description Maintain appropriate conditioning: The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description Maintain appropriate conditioning: The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the
Caring For Your Lateral Ankle Middlebury College
 Caring For Your Lateral Ankle Sprain @ Middlebury College ** severe sprains or medial (inner side of ankle) sprains may require a different program Anatomy, Pathology, and Classification of Ankle Sprains
Caring For Your Lateral Ankle Sprain @ Middlebury College ** severe sprains or medial (inner side of ankle) sprains may require a different program Anatomy, Pathology, and Classification of Ankle Sprains
Mr. Siva Chandrasekaran Orthopaedic Surgeon MBBS MSpMed MPhil (surg) FRACS
 Sprained Ankle An ankle sprain occurs when the strong ligaments that support the ankle stretch beyond their limits and tear. Ankle sprains are common injuries that occur among people of all ages. They
Sprained Ankle An ankle sprain occurs when the strong ligaments that support the ankle stretch beyond their limits and tear. Ankle sprains are common injuries that occur among people of all ages. They
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises. Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises
 Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Introduction Weight-bearing and resistance exercises have
Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Introduction Weight-bearing and resistance exercises have
Assessment of the Feet Handbook
 Assessment of the Feet Handbook The content of this handbook has been adapted from the assessment methods designed by Simon J. Wikler, Doctor of Surgical Chiropody Step Forward to Better Health Reflexology
Assessment of the Feet Handbook The content of this handbook has been adapted from the assessment methods designed by Simon J. Wikler, Doctor of Surgical Chiropody Step Forward to Better Health Reflexology
SEMIMEMBRANOSUS TENDINITIS
 SEMIMEMBRANOSUS TENDINITIS Description Maintain appropriate conditioning: Semimembranosus tendinitis is characterized by inflammation and pain at the knee joint on the back part of the inner side of the
SEMIMEMBRANOSUS TENDINITIS Description Maintain appropriate conditioning: Semimembranosus tendinitis is characterized by inflammation and pain at the knee joint on the back part of the inner side of the
Acute Lower Back Pain. Physiotherapy department
 Acute Lower Back Pain Physiotherapy department Back pain is a common condition and in the UK it affects 7 out of 10 people at some point in their lives. Back pain can be very uncomfortable but it is not
Acute Lower Back Pain Physiotherapy department Back pain is a common condition and in the UK it affects 7 out of 10 people at some point in their lives. Back pain can be very uncomfortable but it is not
PLANTAR FASCIITIS - Advice & Rehabilitation Leaflet
 Dr Patrick Wheeler Consultant in Sport and Exercise Medicine Leicester General Hospital Gwendolen Road, Leicester, LE5 4PW Telephone: 0116 258 4365 Patient information and rehabilitation leaflet Plantar
Dr Patrick Wheeler Consultant in Sport and Exercise Medicine Leicester General Hospital Gwendolen Road, Leicester, LE5 4PW Telephone: 0116 258 4365 Patient information and rehabilitation leaflet Plantar
TIBIAL PLATEAU FRACTURE
 TIBIAL PLATEAU FRACTURE Description Preventive Measures A tibial plateau fracture is a complete or incomplete break Appropriately warm up and stretch before practice or in the larger of the two leg bones
TIBIAL PLATEAU FRACTURE Description Preventive Measures A tibial plateau fracture is a complete or incomplete break Appropriately warm up and stretch before practice or in the larger of the two leg bones
Rehabilitation for Patellar Tendinitis (jumpers knee) and Patellofemoral Syndrome (chondromalacia patella)
 Rehabilitation for Patellar Tendinitis (jumpers knee) and Patellofemoral Syndrome (chondromalacia patella) Patellar Tendinitis The most common tendinitis about the knee is irritation of the patellar tendon.
Rehabilitation for Patellar Tendinitis (jumpers knee) and Patellofemoral Syndrome (chondromalacia patella) Patellar Tendinitis The most common tendinitis about the knee is irritation of the patellar tendon.
DISCOID MENISCUS. Description
 DISCOID MENISCUS Description For participation in jumping (basketball, volleyball) or The meniscus is a cartilage structure in the knee that sits on contact sports, protect the knee joint with supportive
DISCOID MENISCUS Description For participation in jumping (basketball, volleyball) or The meniscus is a cartilage structure in the knee that sits on contact sports, protect the knee joint with supportive
This information leaflet has been produced by Senior Physiotherapists working at Queen Victoria Hospital NHS Foundation Trust.
 Hip Osteoarthritis This information leaflet has been produced by Senior Physiotherapists working at Queen Victoria Hospital NHS Foundation Trust. Osteoarthritis (OA) is a painful inflammatory condition
Hip Osteoarthritis This information leaflet has been produced by Senior Physiotherapists working at Queen Victoria Hospital NHS Foundation Trust. Osteoarthritis (OA) is a painful inflammatory condition
Physiotherapy Information following Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction
 Physiotherapy Information following Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction Name:... Surgery Date:... Graft:... Orthopaedic Outpatient Appointment Date: Time: Location: Contact Number: Contacting
Physiotherapy Information following Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction Name:... Surgery Date:... Graft:... Orthopaedic Outpatient Appointment Date: Time: Location: Contact Number: Contacting
Servers Disease (Calcaneal Apophysitis ) 101
 Servers Disease (Calcaneal Apophysitis ) 101 Servers Disease Causes a disturbance to the growing area at the back of the heel bone (calcaneus) where the strong Achilles tendon attaches to it. It is most
Servers Disease (Calcaneal Apophysitis ) 101 Servers Disease Causes a disturbance to the growing area at the back of the heel bone (calcaneus) where the strong Achilles tendon attaches to it. It is most
Knee Pain Solutions. Assess Your Pain. Make a Plan. Take Action
 Knee Pain Solutions Assess Your Pain Make a Plan Take Action By Jared Evans Certified Strength and Conditioning Specialist Giammalva Fitness Director There are many different causes of knee pain and understanding
Knee Pain Solutions Assess Your Pain Make a Plan Take Action By Jared Evans Certified Strength and Conditioning Specialist Giammalva Fitness Director There are many different causes of knee pain and understanding
Knee Conditioning Program
 Knee Conditioning Program Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle. Following
Knee Conditioning Program Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle. Following
AMERICAN RED CROSS FIRST AID RESPONDING TO EMERGENCIES FOURTH EDITION Copyright 2006 by The American National Red Cross All rights reserved.
 Musculoskeletal injuries are most commonly caused by Mechanical forms of energy. Chemicals. Electrical energy. Heat Mechanical energy produces direct, indirect, twisting and contracting forces. Can be
Musculoskeletal injuries are most commonly caused by Mechanical forms of energy. Chemicals. Electrical energy. Heat Mechanical energy produces direct, indirect, twisting and contracting forces. Can be
Recognizing common injuries to the lower extremity
 Recognizing common injuries to the lower extremity Bones Femur Patella Tibia Tibial Tuberosity Medial Malleolus Fibula Lateral Malleolus Bones Tarsals Talus Calcaneus Metatarsals Phalanges Joints - Knee
Recognizing common injuries to the lower extremity Bones Femur Patella Tibia Tibial Tuberosity Medial Malleolus Fibula Lateral Malleolus Bones Tarsals Talus Calcaneus Metatarsals Phalanges Joints - Knee
Flexibility and Stretching
 Flexibility and Stretching Stretching before exercise prepares the joints for motion, helps avoid injury and increases the range of motion of the area being stretched. After exercise stretching reduces
Flexibility and Stretching Stretching before exercise prepares the joints for motion, helps avoid injury and increases the range of motion of the area being stretched. After exercise stretching reduces
What is arthroscopy? Normal knee anatomy
 What is arthroscopy? Arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure for examining and repairing the inside of your knee. It is a minimally invasive surgical procedure which uses an Arthroscope and other specialized
What is arthroscopy? Arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure for examining and repairing the inside of your knee. It is a minimally invasive surgical procedure which uses an Arthroscope and other specialized
Ankle Rehabilitation Program
 Ankle Rehabilitation Program Ankle stretches: Ankle Plantarflexion: With your foot relaxed, use your hands to gently move your ankle into a position where your toes are pointed down. Continuing moving
Ankle Rehabilitation Program Ankle stretches: Ankle Plantarflexion: With your foot relaxed, use your hands to gently move your ankle into a position where your toes are pointed down. Continuing moving
STRETCHES.
 STRETCHES I have put this document together for you to learn and understand the important stretches that you should be doing regularly as part of your fitness programme so I hope it helps you. Hold each
STRETCHES I have put this document together for you to learn and understand the important stretches that you should be doing regularly as part of your fitness programme so I hope it helps you. Hold each
Bunions / Hallux Valgus deviation of the big toe
 Bunions / Hallux Valgus deviation of the big toe A bunion (hallux valgus) is a deformity of the base joint of the big toe. The cause is not clear in many cases. The deformity may cause the foot to rub
Bunions / Hallux Valgus deviation of the big toe A bunion (hallux valgus) is a deformity of the base joint of the big toe. The cause is not clear in many cases. The deformity may cause the foot to rub
1 of 5 1/8/2017 8:06 PM
 Four s: Recognizing Plantar Fasciitis Symptoms Understanding the Causes of Plantar Fasciitis Getting a Diagnosis Treating Plantar Fasciitis Plantar fasciitis is a common heel inflammatory disorder that
Four s: Recognizing Plantar Fasciitis Symptoms Understanding the Causes of Plantar Fasciitis Getting a Diagnosis Treating Plantar Fasciitis Plantar fasciitis is a common heel inflammatory disorder that
FEEL GOOD GLOW Low intensity workout
 Welcome to the low intensity workout, Feel good glow. If this is your first time doing one of our workouts, we recommend you check out the introductory video at www.healthier.qld.gov.au to get more information
Welcome to the low intensity workout, Feel good glow. If this is your first time doing one of our workouts, we recommend you check out the introductory video at www.healthier.qld.gov.au to get more information
Knee Replacement PROGRAM. Nightingale. Home Healthcare
 Knee Replacement PROGRAM TM Nightingale Home Healthcare With the help of Nightingale s experienced and professional rehabilitation team, you will be guided through a more complete and successful recovery
Knee Replacement PROGRAM TM Nightingale Home Healthcare With the help of Nightingale s experienced and professional rehabilitation team, you will be guided through a more complete and successful recovery
Unit 1 The Human Body in Motion AREA OF STUDY 1 - HOW DOES THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM WORK TO PRODUCE MOVEMENT?
 Unit 1 The Human Body in Motion AREA OF STUDY 1 - HOW DOES THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM WORK TO PRODUCE MOVEMENT? Acute and Chronic Injuries of the Musculoskeletal System AREA OF STUDY 1 - HOW DOES THE MUSCULOSKELETAL
Unit 1 The Human Body in Motion AREA OF STUDY 1 - HOW DOES THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM WORK TO PRODUCE MOVEMENT? Acute and Chronic Injuries of the Musculoskeletal System AREA OF STUDY 1 - HOW DOES THE MUSCULOSKELETAL
Extra-corporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) for plantar fasciitis / heel pain
 Extra-corporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) for plantar fasciitis / heel pain Source: Trauma & Orthopaedics Reference No: 6460-1 Issue date: 1/2/19 Review date: 1/2/22 Page 1 of 6 Plantar fasciitis / heel
Extra-corporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) for plantar fasciitis / heel pain Source: Trauma & Orthopaedics Reference No: 6460-1 Issue date: 1/2/19 Review date: 1/2/22 Page 1 of 6 Plantar fasciitis / heel
