Chapter 8. Bellringer. Identify areas of your body where joints allow movement of your skeleton. Lesson 2 The Skeletal System
|
|
|
- Eustace Hampton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lesson 2 The Skeletal System Bellringer Identify areas of your body where joints allow movement of your skeleton.
2 Lesson 2 The Skeletal System Objectives Describe the functions of the skeletal system. Explain how the skeletal system changes with age.
3 Lesson 2 The Skeletal System Start Off Write How do bones help your body?
4 Lesson 2 The Skeletal System Bones and Joints Bones A bone is an organ of the skeletal system. Bones are hard because they store minerals. Bone Marrow Inside a bone is soft tissue called bone marrow. Bone marrow makes blood cells for the body. Joints A joint is a place where two or more bones meet.
5 Lesson 2 The Skeletal System
6 Lesson 2 The Skeletal System Bone and Joint Development Cartilage Before birth, most of the bones in a baby s body are made of cartilage. Cartilage is a soft, flexible tissue. Bone Formation Cartilage starts changing to bone before a baby is born. The soft tissue hardens and becomes bone tissue as minerals, such as calcium, build up in the bone. This change is not finished until a person is around 18 years old.
7 Lesson 3 The Muscular System Bellringer Make a list of places in your body where muscles are constantly at work.
8 Lesson 3 The Muscular System Objectives Describe the three different types of muscle. Explain the three different types of muscle.
9 Lesson 3 The Muscular System Start Off Write Why do muscles work in pairs?
10 Lesson 3 The Muscular System Many Kinds of Muscles Skeletal Muscle Skeletal muscle is muscle that is attached to bones. Smooth Muscle Smooth muscle is muscle that forms some internal organs. Cardiac Muscle Cardiac muscle is muscle that forms the heart.
11 Lesson 3 The Muscular System
12 Lesson 3 The Muscular System Muscles and Movement How Muscles Move Bones When skeletal muscles contract, they pull on bones. When a muscle contracts, its two ends are pulled towards its center. If the two ends are attached to different bones, the bones are pulled towards each other.
13 Lesson 3 The Muscular System Muscles work in pairs. Here, the biceps and triceps move the bones of the arm by pulling them in opposite directions.
14 Lesson 4 The Digestive System Bellringer List the organs that make up your digestive system.
15 Lesson 4 The Digestive System Objectives Explain how the body uses food. Explain four ways that the body releases waste products.
16 Lesson 4 The Digestive System Start Off Write Why do people need food?
17 Lesson 4 The Digestive System Food and Nutrients What Is Digestion? Digestion is the process of breaking down food into a form your body can use. What Are Nutrients? Nutrients are substances in food that the body needs to work properly.
18 Lesson 4 The Digestive System
19 Lesson 4 The Digestive System Solid Waste The Large Intestine and Food Material The large intestine absorbs water and salts from the remaining food material. The parts of food that the body cannot use become solid waste.
20 Lesson 4 The Digestive System Nondigestive Waste Removal The Kidneys The kidneys mix wastes with water to form urine. Urine is released from the body by the urinary system. The Lungs Carbon dioxide is released from the body when you breathe. The Skin Sweat glands in the skin remove salt and water by sweating.
21 Quote of the Day The human body is a machine which winds its own springs. Julien Offroy de la Mettrie, L Homme Machine
Nervous System. Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body
 Human Body Systems Nervous System Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body Nervous System Main Parts Brain Nerves Spinal cord What it
Human Body Systems Nervous System Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body Nervous System Main Parts Brain Nerves Spinal cord What it
The Human Body. Mrs. Green
 The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
By Helen and Mark Warner
 By Helen and Mark Warner www.teachingpacks.co.uk Teaching Packs - The Human Body - Page 1 Image ThinkStock In this section, you will learn about... 1. The major systems and organs in the human body. 2.
By Helen and Mark Warner www.teachingpacks.co.uk Teaching Packs - The Human Body - Page 1 Image ThinkStock In this section, you will learn about... 1. The major systems and organs in the human body. 2.
THe Skeletal System 1
 THe Skeletal System 1 What the Skeletal System DOes! Skeleton: works as the framework of your body and is made up of all of the bones in your body The number of bones in your skeleton depends on your age.
THe Skeletal System 1 What the Skeletal System DOes! Skeleton: works as the framework of your body and is made up of all of the bones in your body The number of bones in your skeleton depends on your age.
S7L Which part of the body receives messages transmitted by nerve cells located throughout the body?
 S7L2-3 1. Which of the following is the heart's function? A. pumping blood B. breaking down food C. removing wastes from the blood D. taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide 2. The body takes in
S7L2-3 1. Which of the following is the heart's function? A. pumping blood B. breaking down food C. removing wastes from the blood D. taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide 2. The body takes in
Unit 3 Lesson 5 How Do Our Bodies Digest Food, Remove Wastes, and Send Messages? Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Unit 3 Lesson 5 How Do Our Bodies Digest Food, Remove Wastes, and Send Messages? How do our bodies digest food, remove wastes and send messages? Let s think together? Why do we need food? How could food
Unit 3 Lesson 5 How Do Our Bodies Digest Food, Remove Wastes, and Send Messages? How do our bodies digest food, remove wastes and send messages? Let s think together? Why do we need food? How could food
 The human body is amazing! Like a machine, the human body is made of smaller parts that all work together. The human body is always working. Think about this: while you read this, your heart is pumping
The human body is amazing! Like a machine, the human body is made of smaller parts that all work together. The human body is always working. Think about this: while you read this, your heart is pumping
Challenge Question: Prediction: (Wait for directions) Evidence: (Draw, color and label how your Clay model looked when it was complete)
 Activity #12 What s happening inside? Challenge Question: Prediction: (Wait for directions) Evidence: (Draw, color and label how your Clay model looked when it was complete) Act #12 pg 1 of 3 Analysis
Activity #12 What s happening inside? Challenge Question: Prediction: (Wait for directions) Evidence: (Draw, color and label how your Clay model looked when it was complete) Act #12 pg 1 of 3 Analysis
Warm Up Get homework out to turn in!
 Warm Up Get homework out to turn in! Feb 23-8:52 AM Feb 4-8:14 PM 1.) What is the function of your digestive system? After checking, put the number of problems missed at the top of the sheet. 2.) Which
Warm Up Get homework out to turn in! Feb 23-8:52 AM Feb 4-8:14 PM 1.) What is the function of your digestive system? After checking, put the number of problems missed at the top of the sheet. 2.) Which
Skin: The Body s Protection
 Ch 34: Protection, Support and Locomotion 34.1 - Skin: The Body s Protection Inside This Section... The Structure of Skin The Function of Skin Response to Injury Structure and Function of the skin 4 tissue
Ch 34: Protection, Support and Locomotion 34.1 - Skin: The Body s Protection Inside This Section... The Structure of Skin The Function of Skin Response to Injury Structure and Function of the skin 4 tissue
Bodies and Systems. What is your body made of?
 What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
Chapter 16. Human Anatomy
 Chapter 16 Human Anatomy Each System we will examine: Structures types Problems or health concerns How to care for that system Skeletal System Made up of bones, joints, connective tissue Is the frame for
Chapter 16 Human Anatomy Each System we will examine: Structures types Problems or health concerns How to care for that system Skeletal System Made up of bones, joints, connective tissue Is the frame for
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin. KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body.
 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Name Date Class Structure and Movement 33 Chapter 17 Structure and
 Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Name Date Class Structure and Movement 33 Chapter 17 Structure and Movement Section 1 The Skeletal System A. All the in your
Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Name Date Class Structure and Movement 33 Chapter 17 Structure and Movement Section 1 The Skeletal System A. All the in your
In Activity 12, What s Happening Inside? you learned about the functions
 16 Support System: Bones, Joints and Muscles l a b o r at o ry In Activity 12, What s Happening Inside? you learned about the functions of the skeletal and muscular systems in supporting and moving your
16 Support System: Bones, Joints and Muscles l a b o r at o ry In Activity 12, What s Happening Inside? you learned about the functions of the skeletal and muscular systems in supporting and moving your
Structure, Movement, and Control
 Human Body Systems Structure, Movement, and Control What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
Human Body Systems Structure, Movement, and Control What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism. A collection of the same type of cells working together to perform a function.
 Name the 5 Basic Levels of Organization in Living Things Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism What is HOMEOSTASIS? The process by which your body maintains a stable internal environment. What is
Name the 5 Basic Levels of Organization in Living Things Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism What is HOMEOSTASIS? The process by which your body maintains a stable internal environment. What is
Name: Period: Review for Animal Systems Test II - KEY
 Name: Period: Review for Animal Systems Test II - KEY Questions 1-9: Write the main functions of the following body s in the spaces below. Then, write the levels of organization for each body. Give specific
Name: Period: Review for Animal Systems Test II - KEY Questions 1-9: Write the main functions of the following body s in the spaces below. Then, write the levels of organization for each body. Give specific
Structure, Movement, and Control
 Lesson 2 Structure, Movement, and Control Scan Lesson 2. Read the lesson titles and bold words. Look at the pictures. Identify three facts you discovered about the structure, movement, and control of the
Lesson 2 Structure, Movement, and Control Scan Lesson 2. Read the lesson titles and bold words. Look at the pictures. Identify three facts you discovered about the structure, movement, and control of the
Warm Up Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells?
 Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
The Skeletal System. Functions of the Skeletal System
 Skeletal System The Skeletal System Functions of the Skeletal System Provide support Protect internal organs Allows your body to move Stores and produced materials that your body needs You have 206 bones
Skeletal System The Skeletal System Functions of the Skeletal System Provide support Protect internal organs Allows your body to move Stores and produced materials that your body needs You have 206 bones
System Name: INTEGUMENTARY (cell wall) (Lysosomes) Main Organs: Main Organs: SKIN HAIR NAILS KIDNEYS URETERS BLADDER URETHRA
 URINARY System Name: (Lysosomes) KIDNEYS URETERS BLADDER URETHRA LUNGS SKIN EXCRETORY System Name: INTEGUMENTARY (cell wall) SKIN HAIR NAILS Skin is the largest Organ. The excretory system collects and
URINARY System Name: (Lysosomes) KIDNEYS URETERS BLADDER URETHRA LUNGS SKIN EXCRETORY System Name: INTEGUMENTARY (cell wall) SKIN HAIR NAILS Skin is the largest Organ. The excretory system collects and
Human Body. The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structure and functions that are related.
 Human Body The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structure and functions that are related. Cells Cells are the smallest living structures. All living things are made up of one or
Human Body The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structure and functions that are related. Cells Cells are the smallest living structures. All living things are made up of one or
THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM AND THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
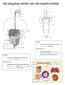 THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM AND THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Location: The location of the Excretory System Is the body. Major Function: Location: The Excretory System the toxic build up of wastes, such as ammonia or
THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM AND THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Location: The location of the Excretory System Is the body. Major Function: Location: The Excretory System the toxic build up of wastes, such as ammonia or
Karen Storey. Multiple Choice: Draw a Complete Circle around the ONE BEST answer.
 Human Body Systems Test Review Karen Storey 7th Grade Science Multiple Choice: Draw a Complete Circle around the ONE BEST answer. 1. Which organ system makes blood cells? a. nervous system b. circulatory
Human Body Systems Test Review Karen Storey 7th Grade Science Multiple Choice: Draw a Complete Circle around the ONE BEST answer. 1. Which organ system makes blood cells? a. nervous system b. circulatory
Contents. Section 1: Life s Building Blocks. Section 2: The Human Framework. Section 3: The Senses and the Respiratory System
 Contents Section 1: Life s Building Blocks 1. Cell Structure.... 2 2. Cell Functions.... 5 3. Cell Teamwork... 8 4. Quiz 1.... 12 Section 2: The Human Framework 5. Skeletal System.... 13 6. Muscular System....
Contents Section 1: Life s Building Blocks 1. Cell Structure.... 2 2. Cell Functions.... 5 3. Cell Teamwork... 8 4. Quiz 1.... 12 Section 2: The Human Framework 5. Skeletal System.... 13 6. Muscular System....
Diagnostic Assessment for The Inside Story
 Diagnostic Assessment for The Inside Story Cells, Organs, and Systems of the Human Body Table of Contents Item Page Number Diagnostic Assessment, The Inside Story, Instructions page 2 Diagnostic Assessment,
Diagnostic Assessment for The Inside Story Cells, Organs, and Systems of the Human Body Table of Contents Item Page Number Diagnostic Assessment, The Inside Story, Instructions page 2 Diagnostic Assessment,
Heal a th t y h y B o B dy d Systems
 Chapter 16 Healthy Body Systems The Cell The smallest unit of structure in a living organism Robert Hooke Identified & coined the term Cell when he saw cork under the microscope He used a compound microscope
Chapter 16 Healthy Body Systems The Cell The smallest unit of structure in a living organism Robert Hooke Identified & coined the term Cell when he saw cork under the microscope He used a compound microscope
December 3, Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow?
 December 3, 2013 Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow? Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Chapter 36: Biology II The Skeleton
December 3, 2013 Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow? Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Chapter 36: Biology II The Skeleton
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism. Cells: the smallest unit of life.
 Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
THE SKELETAL, MUSCULAR AND INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEMS. Chapter 22 Sections
 THE SKELETAL, MUSCULAR AND INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEMS Chapter 22 Sections THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM Ch. 22 Section 3 (588-591) Muscles of the Body WHAT ARE THE THREE TYPES OF MUSCLES? 1.Skeletal muscle - move us
THE SKELETAL, MUSCULAR AND INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEMS Chapter 22 Sections THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM Ch. 22 Section 3 (588-591) Muscles of the Body WHAT ARE THE THREE TYPES OF MUSCLES? 1.Skeletal muscle - move us
SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS WHAT MOVES YOU!
 SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS WHAT MOVES YOU! WHAT ARE THE MAIN FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM? THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeletal system is the organ system that supports and protects the body and allows
SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS WHAT MOVES YOU! WHAT ARE THE MAIN FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM? THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeletal system is the organ system that supports and protects the body and allows
Body Organization and Structure
 CHAPTER 19 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET Body Organization and Structure As you read Chapter 19, which begins on page 462 of your textbook, answer the following questions. This Really Happened... (p. 462)
CHAPTER 19 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET Body Organization and Structure As you read Chapter 19, which begins on page 462 of your textbook, answer the following questions. This Really Happened... (p. 462)
The Human Body: An Orientation
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Human Body: An Orientation 1 PART A The Human Body An Orientation Anatomy Study of the structure
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Human Body: An Orientation 1 PART A The Human Body An Orientation Anatomy Study of the structure
The Digestive System: to convert food particles into simpler micro molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body
 Body Systems The Digestive System: to convert food particles into simpler micro molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body Major Organs and their Functions: Mouth to chew
Body Systems The Digestive System: to convert food particles into simpler micro molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body Major Organs and their Functions: Mouth to chew
Chapter 1 Introduction to Physiology and Homeostasis
 Chapter 1 Introduction to Physiology and Homeostasis MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Select the incorrect association. a. anatomy/function b. human body/multicellular. c. carbon dioxide/cell waste product. d. physiology/body
Chapter 1 Introduction to Physiology and Homeostasis MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Select the incorrect association. a. anatomy/function b. human body/multicellular. c. carbon dioxide/cell waste product. d. physiology/body
Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation
 Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation 1 Anatomy Study of the body Structure what something looks like where something is located how big or small it is Ex- what the heart looks like Gross Anatomy structures
Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation 1 Anatomy Study of the body Structure what something looks like where something is located how big or small it is Ex- what the heart looks like Gross Anatomy structures
Human Body Systems. Human Body Project Notes
 Human Body Systems Human Body Project Notes Human Body Organ Systems for the Project Big Idea: Organ systems are composed of organs that are made of more than one type of tissue. Tissues are made of one
Human Body Systems Human Body Project Notes Human Body Organ Systems for the Project Big Idea: Organ systems are composed of organs that are made of more than one type of tissue. Tissues are made of one
Overview of Physiology. Homeostasis
 Overview of Physiology Homeostasis Life s Challenges Nutrients Oxygen Water Temperature regulation Atmospheric pressure Life s Challenges Homeostasis Responding to life s challenges (Maintaining a stable
Overview of Physiology Homeostasis Life s Challenges Nutrients Oxygen Water Temperature regulation Atmospheric pressure Life s Challenges Homeostasis Responding to life s challenges (Maintaining a stable
Name: BLK. Anatomy Test.. Good Luck :)
 Name: BLK Anatomy Test.. Good Luck :) 1) A boy jumps into a cold swimming pool and his body temperature goes down. His muscles, blood vessels, and nervous system work together to restore his body temperature.which
Name: BLK Anatomy Test.. Good Luck :) 1) A boy jumps into a cold swimming pool and his body temperature goes down. His muscles, blood vessels, and nervous system work together to restore his body temperature.which
What is homeostasis? How is the human body organized? What are the 11 different human organ systems?
 CHAPTER 22 1 Body Organization SECTION Body Organization and Structure BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is homeostasis? How is the human body
CHAPTER 22 1 Body Organization SECTION Body Organization and Structure BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is homeostasis? How is the human body
**Take your homework out to be stamped**
 Warm Up: 3/5-3/6 **Take your homework out to be stamped** 1. What is the difference between osteocytes and osteoblasts? 2. What body systems work with the muscular system? Give specific examples. 3. Your
Warm Up: 3/5-3/6 **Take your homework out to be stamped** 1. What is the difference between osteocytes and osteoblasts? 2. What body systems work with the muscular system? Give specific examples. 3. Your
Introduction to the Human Body
 Introduction to the Human Body Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. Your brain is a structure composed of different kinds of tissue. What is
Introduction to the Human Body Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. Your brain is a structure composed of different kinds of tissue. What is
Lecture 5. Skeletal and Muscular Systems. Skeletal and Muscular Systems. 1. Skeletal System Bones Cartilage Ligaments & Tendons Joints 2.
 Lecture 5 Skeletal and Muscular Systems 1 Skeletal and Muscular Systems 1. Skeletal System Bones Cartilage Ligaments & Tendons Joints 2. Muscles 2 1 Skeletal System 3 Functions of Skeleton Support of the
Lecture 5 Skeletal and Muscular Systems 1 Skeletal and Muscular Systems 1. Skeletal System Bones Cartilage Ligaments & Tendons Joints 2. Muscles 2 1 Skeletal System 3 Functions of Skeleton Support of the
Bodies and Systems. What is your body made of?
 What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
The Human Body: An Orientation
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Human Body: An Orientation 1 PART A The Human Body An Orientation Anatomy Study of the structure
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Human Body: An Orientation 1 PART A The Human Body An Orientation Anatomy Study of the structure
Test Review: Animal Systems
 Name: Date: Period: Test Review: Animal Systems This review is due on the day of your Animal Systems test. 1. Overview of Animals a. What is Homeostasis? b. Complete the levels of organization: Cells Organism
Name: Date: Period: Test Review: Animal Systems This review is due on the day of your Animal Systems test. 1. Overview of Animals a. What is Homeostasis? b. Complete the levels of organization: Cells Organism
Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view
 Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
**************CLASS COPY DO NOT WRITE ON************** Body Packet 5. Muscular System
 **************CLASS COPY ------ DO NOT WRITE ON************** Body Packet 5 Muscular System INSTRUCTIONS: Complete a Quick Notes for paragraphs 1-10 on the next few pages. Answer all other questions on
**************CLASS COPY ------ DO NOT WRITE ON************** Body Packet 5 Muscular System INSTRUCTIONS: Complete a Quick Notes for paragraphs 1-10 on the next few pages. Answer all other questions on
Department of Science Second Term: Revision Worksheet - 1 L-1.6, 1.7 & 1.8 Muscles and bones
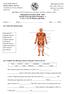 Department of Science 2018-2019 Second Term: Revision Worksheet - 1 L-1.6, 1.7 & 1.8 Muscles and bones Grade 4... Name:... Date:.../.../2019 Q.1 Label each muscle group. neck muscles shoulder muscles thigh
Department of Science 2018-2019 Second Term: Revision Worksheet - 1 L-1.6, 1.7 & 1.8 Muscles and bones Grade 4... Name:... Date:.../.../2019 Q.1 Label each muscle group. neck muscles shoulder muscles thigh
Levels of Organization
 Levels of Organization What do you think the 5 Levels of Organization are in the body?? Brainstorm with your group and write down what you think are the 5 Levels Pick a recorder. Levels of Organization:
Levels of Organization What do you think the 5 Levels of Organization are in the body?? Brainstorm with your group and write down what you think are the 5 Levels Pick a recorder. Levels of Organization:
Major Functions of the Skeletal System
 Skeletal System Major Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Provide shape and support. 2. Enables you to move 3. Protects your organs 4. Produces blood cells 5. stores minerals and other materials until
Skeletal System Major Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Provide shape and support. 2. Enables you to move 3. Protects your organs 4. Produces blood cells 5. stores minerals and other materials until
Nervous System. Skeletal System. Muscular System. Reproductive System. Circulatory System. Endocrine System. Respiratory System. Integumentary System
 The Human Body Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Nervous System Reproductive System Endocrine System Integumentary System Excretory System Lymphatic/Immune
The Human Body Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Nervous System Reproductive System Endocrine System Integumentary System Excretory System Lymphatic/Immune
Body Systems Overview
 Body Systems Overview Body Systems work together: If you damage one system, you may damage several for example, smoking irritates the lungs and destroys the cells of the immune system Levels of Organization
Body Systems Overview Body Systems work together: If you damage one system, you may damage several for example, smoking irritates the lungs and destroys the cells of the immune system Levels of Organization
The Muscular System. The Muscular System: Moving your Body
 The Muscular System: Moving your Body The Muscular System So, which systems have Which systems will we learned about sowe far? learn about next? Can you sit totally still without moving a muscle? Ø Try
The Muscular System: Moving your Body The Muscular System So, which systems have Which systems will we learned about sowe far? learn about next? Can you sit totally still without moving a muscle? Ø Try
Department of Science Second Term: Revision Worksheet - 1 L-1.6, 1.7 & 1.8 Muscles and bones
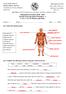 Department of Science 2018-2019 Second Term: Revision Worksheet - 1 L-1.6, 1.7 & 1.8 Muscles and bones Grade 4... Name:... Date:.../.../2019 Q.1 Label each muscle group. neck muscles shoulder muscles thigh
Department of Science 2018-2019 Second Term: Revision Worksheet - 1 L-1.6, 1.7 & 1.8 Muscles and bones Grade 4... Name:... Date:.../.../2019 Q.1 Label each muscle group. neck muscles shoulder muscles thigh
SECTION 45-1 REVIEW. VOCABULARY REVIEW Describe the functions of the tissues listed below.
 SECTION 45-1 REVIEW THE HUMAN BODY PLAN VOCABULARY REVIEW Describe the functions of the tissues listed below. 1. nervous tissue 2. muscular tissue 3. skeletal muscle 4. epithelial tissue 5. connective
SECTION 45-1 REVIEW THE HUMAN BODY PLAN VOCABULARY REVIEW Describe the functions of the tissues listed below. 1. nervous tissue 2. muscular tissue 3. skeletal muscle 4. epithelial tissue 5. connective
Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view
 Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
BIO 2 GO! 3213b Movement in Animals-Skeletal Muscular System
 BIO 2 GO! 3213b Movement in Animals-Skeletal Muscular System All multicellular animals that can move to escape harm or to capture food have an advantage over those animals that cannot move. After the successful
BIO 2 GO! 3213b Movement in Animals-Skeletal Muscular System All multicellular animals that can move to escape harm or to capture food have an advantage over those animals that cannot move. After the successful
Multicellular living things are able to divide up the labor required to perform life functions between the different levels of organization ( organs
 Multicellular living things are able to divide up the labor required to perform life functions between the different levels of organization ( organs and organ systems). A multicellular living thing will
Multicellular living things are able to divide up the labor required to perform life functions between the different levels of organization ( organs and organ systems). A multicellular living thing will
The Circulatory System. Lesson 4. Quick Check. Trace the path of blood after it is pumped from the heart. 22. First
 Lesson 4 The Circulatory System How does blood transport materials? Your circulatory system is a delivery system. Red blood cells travel in the blood, bringing things to and from your body cells. The main
Lesson 4 The Circulatory System How does blood transport materials? Your circulatory system is a delivery system. Red blood cells travel in the blood, bringing things to and from your body cells. The main
A. Incorrect! Axons covey messages from the cell body of the neuron. D. Correct! Dendrites convey messages to the cell body of the neuron.
 CLEP Biology - Problem Drill 14: Animal Form No. 1 of 10 1. The branches of a neuron receiving information from another cell and which transmit the message to the cell body are called? (A) (B) (C) (D)
CLEP Biology - Problem Drill 14: Animal Form No. 1 of 10 1. The branches of a neuron receiving information from another cell and which transmit the message to the cell body are called? (A) (B) (C) (D)
Chapter 7: Human body system
 Grade: 8 END OF SEMESTER EXAMINATION FIRST SEMESTER REVISION BOOKLET AY 2018-2019 Subject: Science Teacher: Mr. Hafiz Muhammad Ahsan Ali Chapter 7: Human body system 1. Directions: On the line before each
Grade: 8 END OF SEMESTER EXAMINATION FIRST SEMESTER REVISION BOOKLET AY 2018-2019 Subject: Science Teacher: Mr. Hafiz Muhammad Ahsan Ali Chapter 7: Human body system 1. Directions: On the line before each
Created by 6 th grade students THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM AND THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
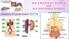 Created by 6 th grade students 2017-18 THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM AND THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM LOCATION: MAJOR FUNCTIONS, AND LOCATION: THE LOCATION OF THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM IS THROUGHOUT THE BODY THE MAJOR FUNCTION:
Created by 6 th grade students 2017-18 THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM AND THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM LOCATION: MAJOR FUNCTIONS, AND LOCATION: THE LOCATION OF THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM IS THROUGHOUT THE BODY THE MAJOR FUNCTION:
Table of Contents. Introduction to the Teacher...1. Body Organization...2 Cells, tissues, organs, and systems
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Introduction to the Teacher...1 Body Organization...2 Cells, tissues, organs, and systems...3 Purpose and parts of the skeletal system, bones, joints, cartilage, etc....8
Table of Contents Table of Contents Introduction to the Teacher...1 Body Organization...2 Cells, tissues, organs, and systems...3 Purpose and parts of the skeletal system, bones, joints, cartilage, etc....8
Function Alimentary Canal
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Function: to help convert food into simpler molecules that can be absorbed and used by the cells of the body. Alimentary Canala one way tube that passes through the body. (found in
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Function: to help convert food into simpler molecules that can be absorbed and used by the cells of the body. Alimentary Canala one way tube that passes through the body. (found in
Unit 7: Skeletal and muscular systems
 Unit 7: Skeletal and muscular systems 1. The locomotor system 2. The skeletal system 2.1. The human skeleton 2.2. Bones 2.3. Joints 2.4. Tendons and ligaments 3. The muscular system 3.1. Muscles of the
Unit 7: Skeletal and muscular systems 1. The locomotor system 2. The skeletal system 2.1. The human skeleton 2.2. Bones 2.3. Joints 2.4. Tendons and ligaments 3. The muscular system 3.1. Muscles of the
Organ Systems and Homeostasis
 Bones and Muscles Review and Reinforce Organ Systems and Homeostasis Understanding Main Ideas The illustration below shows the units of organization in a reptile. The units are numbered 1 4. Label the
Bones and Muscles Review and Reinforce Organ Systems and Homeostasis Understanding Main Ideas The illustration below shows the units of organization in a reptile. The units are numbered 1 4. Label the
3. A process that occurs in the human body is represented in the diagram below.
 1. Molecules in a certain medication attach to receptors on nerve cells. This prevents the normal chemical signal from binding to the receptor. One immediate result of taking this medication might be a
1. Molecules in a certain medication attach to receptors on nerve cells. This prevents the normal chemical signal from binding to the receptor. One immediate result of taking this medication might be a
Day 1 Essential Questions:
 Day 1 Essential Questions: ~What are the different body systems? ~What are the parts of the systems? ~How is this system connected to other body systems? ~How do you keep this system working properly?
Day 1 Essential Questions: ~What are the different body systems? ~What are the parts of the systems? ~How is this system connected to other body systems? ~How do you keep this system working properly?
Laughter and the Body Systems
 Laughter and the Body Systems Laughter causes the lungs to pump out carbon dioxide, the eyes to cleanse themselves with tears, the muscles to relax, the flow of adrenaline to increase, and the cardiovascular
Laughter and the Body Systems Laughter causes the lungs to pump out carbon dioxide, the eyes to cleanse themselves with tears, the muscles to relax, the flow of adrenaline to increase, and the cardiovascular
BODY SYSTEMS UNIT ANCHOR CHARTS:
 BODY SYSTEMS UNIT ANCHOR CHARTS: LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION smallest unit Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems largest unit Body TISSUES IN THE HUMAN BODY Tissue Function Example Muscle makes parts of the body
BODY SYSTEMS UNIT ANCHOR CHARTS: LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION smallest unit Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems largest unit Body TISSUES IN THE HUMAN BODY Tissue Function Example Muscle makes parts of the body
3. There are three pairs of salivary glands that have three important functions. These are: a)
 Reference: 1. Use the human systems in your textbook.. 2. Pig instruction packet. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1. What is the process of digestion? 2. List three major glands involved in this process? 3. There are
Reference: 1. Use the human systems in your textbook.. 2. Pig instruction packet. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1. What is the process of digestion? 2. List three major glands involved in this process? 3. There are
Body Systems. Before You Read. What parts make up each system of the human body? What is tissue? What is an organ?
 BC Science 8 CH02 11/5/06 11:39 AM Page 20 Body Systems Textbook pages 52 63 Before You Read In this section, you will find out about the s of the human body. A is made of two or more parts that work together
BC Science 8 CH02 11/5/06 11:39 AM Page 20 Body Systems Textbook pages 52 63 Before You Read In this section, you will find out about the s of the human body. A is made of two or more parts that work together
The Skeletal System. Chapter 8
 The Skeletal System Chapter 8 1 Introduction Movement is essential for animals. This is done by moving muscles with the skeleton. 2 Functions of the skeleton 1. Gives shape and support to the body. The
The Skeletal System Chapter 8 1 Introduction Movement is essential for animals. This is done by moving muscles with the skeleton. 2 Functions of the skeleton 1. Gives shape and support to the body. The
Body Systems Notes. Nervous, Integumentary, Immune/Lymphatic, Circulatory, Skeletal, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, Endocrine, Reproductive
 Body Systems Notes Nervous, Integumentary, Immune/Lymphatic, Circulatory, Skeletal, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, Endocrine, Reproductive Homeostasis: maintaining a balance. Examples: temperature,
Body Systems Notes Nervous, Integumentary, Immune/Lymphatic, Circulatory, Skeletal, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, Endocrine, Reproductive Homeostasis: maintaining a balance. Examples: temperature,
Human Anatomy and Body Systems
 Human Anatomy and Body Systems Levels of Organization The human body is organized in several levels, from the simplest to the most complex... Cells the basic unit of life Tissues clusters of cells performing
Human Anatomy and Body Systems Levels of Organization The human body is organized in several levels, from the simplest to the most complex... Cells the basic unit of life Tissues clusters of cells performing
SUPPORT, MOVEMENT AND LOCOMOTION
 SUPPORT, MOVEMENT AND LOCOMOTION Overview Bones Joints Antagonistic Muscles Forelimbs Bones Functions of the skeleton Locomotion The ability to move from place to place Support Holds the body off the ground
SUPPORT, MOVEMENT AND LOCOMOTION Overview Bones Joints Antagonistic Muscles Forelimbs Bones Functions of the skeleton Locomotion The ability to move from place to place Support Holds the body off the ground
STUDY GUIDE SECTION 45-1 The Human Body Plan
 STUDY GUIDE SECTION 45-1 The Human Body Plan Name Period Date Multiple Choice-Write the correct letter in the blank 1. Nervous tissue contains specialized cells called a. Transmitters. b. neurons c. messenger
STUDY GUIDE SECTION 45-1 The Human Body Plan Name Period Date Multiple Choice-Write the correct letter in the blank 1. Nervous tissue contains specialized cells called a. Transmitters. b. neurons c. messenger
Big Idea. The human body is made up of systems that have different functions, an these systems work together to maintain the body.
 Big Idea The human body is made up of systems that have different functions, an these systems work together to maintain the body. Body Organization CELLS TISSUES ORGANS Organ Systems Unit 1 Lesson 1 Introduction
Big Idea The human body is made up of systems that have different functions, an these systems work together to maintain the body. Body Organization CELLS TISSUES ORGANS Organ Systems Unit 1 Lesson 1 Introduction
Chapter 20 UNIFYING CONCEPTS OF ANIMAL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 Chapter 20 UNIFYING CONCEPTS OF ANIMAL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION I. Life is based on many structural levels Levels of animal structure: Atoms and molecules Cells Tissues Organs Organ systems Organism: May
Chapter 20 UNIFYING CONCEPTS OF ANIMAL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION I. Life is based on many structural levels Levels of animal structure: Atoms and molecules Cells Tissues Organs Organ systems Organism: May
Book Second Term Test Model Answers. Page 84 to 87
 1. Write the scientific term: a. Red blood cells b. Aorta c. Ball bearings d. Air resistance e. silt soil f. sand soil 2. Write a brief account: Book Second Term Test Model Answers Page 84 to 87 a. friction:
1. Write the scientific term: a. Red blood cells b. Aorta c. Ball bearings d. Air resistance e. silt soil f. sand soil 2. Write a brief account: Book Second Term Test Model Answers Page 84 to 87 a. friction:
Body Science: Cell Theory (3 rd -5 th Grades) Pre-Visit Activities
 Body Science: Cell Theory (3 rd -5 th Grades) Pre-Visit Activities Vocabulary List and Student Definitions (elementary level): Cell: basic unit of life, too small to see with the naked eye Tissue: group
Body Science: Cell Theory (3 rd -5 th Grades) Pre-Visit Activities Vocabulary List and Student Definitions (elementary level): Cell: basic unit of life, too small to see with the naked eye Tissue: group
5 th Primary. Science
 Final revision sheet A-Complete the following: 1. two lungs. 2. Kidney 3. Soil 4. friction. 5. cancelled 6. silt soil, clay soil,sand soil. 7. avoid mixing of the blood. 8. Silt - yellow. 9. Clay - sand.
Final revision sheet A-Complete the following: 1. two lungs. 2. Kidney 3. Soil 4. friction. 5. cancelled 6. silt soil, clay soil,sand soil. 7. avoid mixing of the blood. 8. Silt - yellow. 9. Clay - sand.
Review of 10 major human body systems using a puzzle technique. Systems Shuffle. By: Heidi Hisrich of The Dork Side
 Review of 10 major human body systems using a puzzle technique Systems Shuffle By: Heidi Hisrich of The Dork Side Teaching students about the different human body systems is one of my favorite things to
Review of 10 major human body systems using a puzzle technique Systems Shuffle By: Heidi Hisrich of The Dork Side Teaching students about the different human body systems is one of my favorite things to
Overview of Anatomy & Physiology
 Overview of Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic Developmental Physiology the study of the function
Overview of Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic Developmental Physiology the study of the function
Chapter 22. Body Organization & Structure
 Chapter 22 Body Organization & Structure Start-Up Activity Too Cold for Comfort Hold a few pieces of ice in one hand. Hold the ice until the cold is uncomfortable. Then release the ice into the dish. Compare
Chapter 22 Body Organization & Structure Start-Up Activity Too Cold for Comfort Hold a few pieces of ice in one hand. Hold the ice until the cold is uncomfortable. Then release the ice into the dish. Compare
Human Body Systems Study Guide
 Human Body Systems Study Guide Nervous System 1. Brain stem part of nervous system and controls the heartbeat and breathing by controlling the cardiac muscle and diaphragm. Also receives information from
Human Body Systems Study Guide Nervous System 1. Brain stem part of nervous system and controls the heartbeat and breathing by controlling the cardiac muscle and diaphragm. Also receives information from
*Hierarchical Organization of Multicellular Organisms
 *Hierarchical Organization of Multicellular Organisms 7.L.1.3 - Summarize the hierarchical organization of multicellular organisms from cells to tissues to organs to systems to organisms. Table of Contents
*Hierarchical Organization of Multicellular Organisms 7.L.1.3 - Summarize the hierarchical organization of multicellular organisms from cells to tissues to organs to systems to organisms. Table of Contents
DeltaScience. Content Readers. Summary. Science Background. Objectives. Reading Comprehension Skills. Supporting English Learners
 DeltaScience Content Readers TM Red Edition Grade 3 4 reading level Purple Edition Grade 4 5 reading level Objectives Describe cells, the basic units of all living things. List the four main kinds of tissue
DeltaScience Content Readers TM Red Edition Grade 3 4 reading level Purple Edition Grade 4 5 reading level Objectives Describe cells, the basic units of all living things. List the four main kinds of tissue
PAP Animal Body Systems Test Review. 1. List the levels of organization from largest to smallest. (Organ-Organism-Cell-Organ System-Tissue),,,,
 Name Period PAP Animal Body Systems Test Review 1. List the levels of organization from largest to smallest. (Organ-Organism-Cell-Organ System-Tissue),,,, 2. Put the following pictures below in the correct
Name Period PAP Animal Body Systems Test Review 1. List the levels of organization from largest to smallest. (Organ-Organism-Cell-Organ System-Tissue),,,, 2. Put the following pictures below in the correct
Introduction to Human Anatomy (Chapter 1)
 Name Date Period Introduction to Human Anatomy (Chapter 1) 1. Anatomy is the study of structures making up an organism. 2. Physiology is the study of how an organism functions. 3. The major organ systems
Name Date Period Introduction to Human Anatomy (Chapter 1) 1. Anatomy is the study of structures making up an organism. 2. Physiology is the study of how an organism functions. 3. The major organ systems
Introduction to Body Systems
 Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do the body systems interact to maintain homeostasis? By the end of this lesson, you should be able to describe the functions of the human body
Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do the body systems interact to maintain homeostasis? By the end of this lesson, you should be able to describe the functions of the human body
Growing bones. Baby s s bones are made from cartilage Babies have 300 bones Adults have 206. bones
 Body Systems Objectives Students should be able to list the different body systems Students should be able to give a general function of each of the body systems Students should be able to tell the differences
Body Systems Objectives Students should be able to list the different body systems Students should be able to give a general function of each of the body systems Students should be able to tell the differences
BENCHMARK REVIEW (THIS WILL BE GRADED)
 BENCHMARK REVIEW (THIS WILL BE GRADED) NAME D E F C B J A I H G QL QN QN QL QL 4 5 1 2 3 USE THE WORDBANK AND WRITE THE WORD THAT BEST FITS THE DEFINITION TESTABLE VARIABLE INDEPENDENT VARIABLE Sample
BENCHMARK REVIEW (THIS WILL BE GRADED) NAME D E F C B J A I H G QL QN QN QL QL 4 5 1 2 3 USE THE WORDBANK AND WRITE THE WORD THAT BEST FITS THE DEFINITION TESTABLE VARIABLE INDEPENDENT VARIABLE Sample
CHAPTER 1: THE HUMAN BODY A & P 8/20/13
 CHAPTER 1: THE HUMAN BODY A & P 8/20/13 ANATOMY The study of the Structure and Shapes of the body and their relationships to one another. Gross Anatomy: The study of large easily observable structures
CHAPTER 1: THE HUMAN BODY A & P 8/20/13 ANATOMY The study of the Structure and Shapes of the body and their relationships to one another. Gross Anatomy: The study of large easily observable structures
CHAPTER 14 Bones, Muscles, Skin
 CHAPTER 14 Bones, Muscles, Skin SECTION 1 Body Organization and Homeostasis Levels of Organization Basic to Complex Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems CELLS Basic unit in living thing Main Parts: Cell
CHAPTER 14 Bones, Muscles, Skin SECTION 1 Body Organization and Homeostasis Levels of Organization Basic to Complex Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems CELLS Basic unit in living thing Main Parts: Cell
STRUCTURES ORGANIZATION
 HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS STRUCTURES ORGANIZATION CELL - the smallest unit of living things TISSUE - cells, joined together for a similar functions. ORGAN - grouping of tissues that perform a specific function
HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS STRUCTURES ORGANIZATION CELL - the smallest unit of living things TISSUE - cells, joined together for a similar functions. ORGAN - grouping of tissues that perform a specific function
