8 - Muscular System. Introduction Taft College Human Physiology
|
|
|
- Brandon Berry
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 8 - Muscular System Introduction Taft College Human Physiology
2 Muscular System - Introduction The bones provide the levers and structure of the skeleton but it is the muscles that cause movement. Motion results from the contraction and relaxation of muscles. Muscles account for 40-50% of total body weight. 40% of body weight is due to skeletal muscle. 10% due to cardiac & smooth muscle combined. The muscles change chemical energy (ATP) into mechanical energy to generate force and perform work. We will discuss this process over the next few weeks. The scientific study of muscles is known as myology.
3 Functions of Muscle Tissue Muscle tissues have a specialized property- contractility, the capability of shortening. Through the contraction and relaxation of muscles, 4 functions can be described: 1. Motion such as walking, running, grasping. These movements rely on the integrated function of bones, joints, and skeletal muscles. The muscles are connected to the skeleton and pull to cause movement. 2. Propulsion of materials through the body (blood, ingested food). Examples: Cardiac muscle contracts to pump blood to all body tissues. Smooth muscle contractions aid in the movement of food through the GI tract, urine through urinary system. Skeletal muscle helps return venous blood to the heart. 3. Maintain body posture and sphincter control. Examples: Skeletal muscle contractions maintain the body in stable positions as a when standing. Sustained contraction of smooth muscles (sphincters) prevent outflow of contents of a hollow organ, as in the urinary bladder, colon, or stomach. 4. Thermogenesis (generating heat). Heat is a byproduct of muscle contraction. Muscle generates about 85% of body heat. When more heat is needed to maintain body temperature, involuntary muscle contraction (shivering), can increase thermogenesis by several 100%.
4 Contractile Proteins Movement in living cells involves special protein molecules, contractile proteins. Ex. Actin and Myosin Contractile proteins can convert chemical energy like ATP, into the mechanical energy of motion. Surprisingly, contractile proteins have been found in many types of cells other than muscle cells. They account for things like: 1. Movement of chromosomes in cell division. 2. Movement of WBCs. Movement of cilia and flagella (as in sperm). **Therefore, muscle tissue is not unique in its possession of contractile proteins but muscle tissue is distinguished by its high concentration of contractile proteins.
5 3 Types of Muscle Tissue Very Large micron Diameter Small 3-8 micron Diameter Large micron Diameter 1. Skeletal muscle. 2. Smooth (visceral) muscle. 3. Cardiac muscle.
6 1. Skeletal Muscle 1. Skeletal Muscle- is the muscle that is typically attached to the skeleton and is responsible for the movement: a: of the skeleton. b: of the diaphragm in breathing. c. Sphincters- circles of skeletal muscle important in voluntary release of urine and feces. Contraction of skeletal muscle occurs by way of nerve impulses. You have voluntary control of the contraction of skeletal muscle. Therefore sometimes called, voluntary muscle. Skeletal muscle is the largest tissue of the body, approximately 40% of body weight.
7 2. Smooth (visceral) muscle 2. Smooth (visceral) muscle- viscera refers to internal organs of chest and abdomen. Smooth muscle surrounds the hollow tubes and chambers of the body. Found in organs of digestive system, reproductive, urinary, and blood vessels. a. Smooth muscle functions to propel things through tubes peristalsis = wave like contractions of smooth muscle b. May change size (diameter) of an organ, important in maintaining blood flow and pressure. Do you have voluntary control over contraction of smooth muscle? No, therefore it is also called Involuntary muscle. Contraction of smooth muscle is inherent (automatic or involuntary). Contraction of smooth muscle may be altered by: 1. Physical pressure (stretching). 2. Nerves (via neurotransmitters) 3. body chemicals (several hormones, chemical changes (ph, O 2, CO 2 )).
8 3. Cardiac muscle 3. Cardiac muscle- cardiac muscle is the muscle of the heart. It serves to pump (propel) the blood. Cardiac muscle contractions are inherent, but may be altered by nerves and chemicals (hormones). Cardiac and smooth muscle together makeup about 10% of body weight. In this exam, we will discuss skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. We will not discuss heart muscle until we get to the cardiovascular system.
9 Microscopic Functional Anatomy of Skeletal Muscle Over 600 skeletal muscles have been identified on the human body. They are attached to bone by bundles of C.T. called tendons. If we examine a skeletal muscle we see that it is composed of elongated cells or fibers. Muscle cell = muscle fiber. Let's examine the structural organization of a skeletal muscle:
10 Functional Anatomy of Skeletal Dense Irregular C.T. Muscle Muscle Fibers = Muscle Cells = Myofibers 100 s or 1000 s per muscle Tendon To Next Drawing Skeletal Muscle Why stretch prior to exercise? To stretch C.T., not muscle tissue! Tendon
11 Functional Anatomy of Skeletal Muscle notes- a skeletal muscle is surrounded by dense, irregular C.T. that strengthens and protects the muscle. The C.T. extends beyond the muscle at each end to form a tendon that attaches to periosteum of a bone. Individual muscle fibers run longitudinally (parallel to each other) though the muscle. They number from 100s to 1000s in a muscle. Muscle Fiber = Muscle Cell = Myofiber Muscle
12 Skeletal Muscle Fiber = Muscle Cell = Myofiber Multiple Nuclei Sarcolemma= Muscle cell Membrane Myofibrils Myofibrils Striations in To Next Fig. Myofibrils Muscle Fiber = Muscle Cell = Myofiber Sarcoplasm = Muscle cell X-section Cytoplasm
13 Muscle Fiber = Muscle Cell = Myofiber Muscle fiber notes- Skeletal muscle cells are the largest cells (but formed from many myoblasts during development) in the body. Each cell has numerous nuclei. Notice the nuclei are at the periphery out of the way of the contractile elements. Does the nucleus have a difficult time controlling such a large cell? No. They cheat, they are multinucleated! The plasma membrane is called the sarcolemma. The cytoplasm is called sarcoplasm. The muscle fiber is stuffed with tiny threads called myofibrils. They extend lengthwise within the muscle fiber. They stain with alternating light and dark bands giving a striated appearance. These bands are called cross-striations, which give rise the reference to striated muscle.
14 Myofibril Dark Bands = A Bands Light Bands = I Bands Z Discs Sarcomere Sarcomere Etc. To next Fig
15
16 Myofibril Notes Each myofibril is made up of a series of repeated units called sarcomeres. Z discs serve as the border for adjacent sarcomeres. Sarcomeres are the smallest unit of muscle contraction. Light = I bands (isotropic) and Dark = A bands (anisotropic) are more evident at this magnification.
17 Myofibril Notes A myofibril in turn is made up of myofilaments = contractile proteins. There are 2 major contractile proteins: 1. Myosin- thick filament, MW = 500, Actin- thin filament, MW = 60,000. A band (dark) consists mostly of myosin and portions of actin that overlap thick filaments. I band (light) consists of actin only. The Z disc passes through the center of each I band, and anchors the thin filaments. = Border for sarcomere The narrow H zone in the center of each A band contains myosin only.
18 Sarcomere Sarcomere Relaxed Myosin Actin Myosin Actin Z Disc Z H Zone Z H Zone Z I = Light Band Contracted A = Dark Band Myosin I = Light Band A =Dark Band Actin I = Light Band A = Dark Band I Band A= Dark Band
19
20 Components A Band (Dark) = Actin and Myosin I Band (Light) = Actin only H Zone = Myosin only Elastic filaments Elastic filament notes- The 3rd most common muscle protein is a non contractile filament, the elastic filament. The elastic filament is composed of the stretchy protein called titan (huge MW). Titan is especially important in returning contracted muscle back to it s original position to begin contraction again
21 Summary of Changes During Contraction The A band (dark) is unchanged in width. The I band (light) is reduced or absent. The H zone is absent.
22
23
24 Physiology Quiz 2.1 Name Due Draw and label the microscopic anatomy of skeletal muscle as per lecture. 1. Label the following in 2 adjacent sarcomeres for both a relaxed and a contracted muscle if present: Sarcomere A band (dark) I Band (light) H zone Actin Myosin Z disc titan 2. State the components of the A band, I band, and H zone. 3. State what happens to the A band, I band, and H zone during contraction.
Muscle Tissue. General concepts. Classification of muscle. I. Functional classification is based on the type of neural control.
 Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
Muscular System. Human A & P
 Muscular System Human A & P There are 3 types of muscle tissue: A. Skeletal B. Smooth C. Cardiac The essential function of a muscle is contraction, or shortening, and are responsible for essentially all
Muscular System Human A & P There are 3 types of muscle tissue: A. Skeletal B. Smooth C. Cardiac The essential function of a muscle is contraction, or shortening, and are responsible for essentially all
Muscle tissues. Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD
 Muscle tissues Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD Muscle tissue is a soft tissue that composes muscles in animal bodies, and gives rise to muscles' ability to contract. Muscle tissue
Muscle tissues Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD Muscle tissue is a soft tissue that composes muscles in animal bodies, and gives rise to muscles' ability to contract. Muscle tissue
Ch.10 Muscle Tissue. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Ch.10 Muscle Tissue Preview Chapter 10 In groups we will define the following terms 1. Skeletal muscle 2. Smooth muscle 3. Cardiac muscle 4. Sarcomere 5. Myofibril 6. Myofilament 7. Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Ch.10 Muscle Tissue Preview Chapter 10 In groups we will define the following terms 1. Skeletal muscle 2. Smooth muscle 3. Cardiac muscle 4. Sarcomere 5. Myofibril 6. Myofilament 7. Sarcoplasmic reticulum
The Muscular System PART A
 6 The Muscular System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Muscular System
6 The Muscular System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Muscular System
Lecture 9A. Muscle structure. Outline
 Lecture 9A Muscle structure Outline Smooth, skeletal, and cardiac muscle tissues Structure and function of skeletal muscle cells. Sarcomeres structure and contraction Actin-myosin interaction and sliding
Lecture 9A Muscle structure Outline Smooth, skeletal, and cardiac muscle tissues Structure and function of skeletal muscle cells. Sarcomeres structure and contraction Actin-myosin interaction and sliding
How many skeletal muscles are present in our body? Muscles are excitable & contractile, extensible and elastic to some extent.
 Muscles How many skeletal muscles are present in our body? -646 muscles The functions of the muscles are: Movement Maintenance of posture Generation of heat Stabilization of joints : amount of muscle surrounding
Muscles How many skeletal muscles are present in our body? -646 muscles The functions of the muscles are: Movement Maintenance of posture Generation of heat Stabilization of joints : amount of muscle surrounding
Skeletal muscle. General features :
 Muscular tissues In the first embryonic life the muscular tissues arise from mesoderm, The function of movement in multicellular organisms is usually assumed by specialized cells called muscle fibers which
Muscular tissues In the first embryonic life the muscular tissues arise from mesoderm, The function of movement in multicellular organisms is usually assumed by specialized cells called muscle fibers which
Muscle Tissue. Alternating contraction and relaxation of cells. Chemical energy changed into mechanical energy
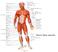 Know these muscles Muscle Tissue Alternating contraction and relaxation of cells Chemical energy changed into mechanical energy 3 Types of Muscle Tissue Skeletal muscle attaches to bone, skin or fascia
Know these muscles Muscle Tissue Alternating contraction and relaxation of cells Chemical energy changed into mechanical energy 3 Types of Muscle Tissue Skeletal muscle attaches to bone, skin or fascia
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
Chapter 7 The Muscular System. Mosby items and derived items 2012 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1
 Chapter 7 The Muscular System Mosby items and derived items 2012 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1 INTRODUCTION A. Muscular tissue enables the body and its parts to move 1. Three types of
Chapter 7 The Muscular System Mosby items and derived items 2012 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1 INTRODUCTION A. Muscular tissue enables the body and its parts to move 1. Three types of
Integrated Muscle. Red: important. Black: in male female slides. Gray: notes extra. Editing File
 Integrated Muscle Red: important. Black: in male female slides. Gray: notes extra. Editing File OBJECTIVES Identify and describe the histological structure of the three types of muscle cells and list the
Integrated Muscle Red: important. Black: in male female slides. Gray: notes extra. Editing File OBJECTIVES Identify and describe the histological structure of the three types of muscle cells and list the
Muscular System- Part 1. Unit 5 Miss Wheeler
 Muscular System- Part 1 Unit 5 Miss Wheeler Fun Facts! The tongue is the strongest muscle in your body The smallest muscles in the body are in the middle ear The largest muscle in the body is the gluteus
Muscular System- Part 1 Unit 5 Miss Wheeler Fun Facts! The tongue is the strongest muscle in your body The smallest muscles in the body are in the middle ear The largest muscle in the body is the gluteus
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 09: The Muscular System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 09: The Muscular System Question No. 1 of 10 The muscular system of the human body fulfills many different roles. Which of the following statements about the
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 09: The Muscular System Question No. 1 of 10 The muscular system of the human body fulfills many different roles. Which of the following statements about the
Chapter 9 - Muscle and Muscle Tissue
 Chapter 9 - Muscle and Muscle Tissue I. Overview of muscle tissue A. Three muscle types in the body: B. Special characteristics 1. Excitability: able to receive and respond to a stimulus 2. Contractility:
Chapter 9 - Muscle and Muscle Tissue I. Overview of muscle tissue A. Three muscle types in the body: B. Special characteristics 1. Excitability: able to receive and respond to a stimulus 2. Contractility:
Medical Biology. Dr. Khalida Ibrahim
 Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Medical Biology MUSCLE TISSUE 1. Muscle tissue is characterized by its well-developed properties of contraction. 2. Muscle is responsible for the movements of the body and the various
Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Medical Biology MUSCLE TISSUE 1. Muscle tissue is characterized by its well-developed properties of contraction. 2. Muscle is responsible for the movements of the body and the various
Muscular System. Honors Anatomy & Physiology. Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School
 Muscular System Honors Anatomy & Physiology Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Skeletal, Smooth, or Cardiac SKELETAL Striated Voluntary Multinucleated Bound to bones Moves skeleton SMOOTH Not striated
Muscular System Honors Anatomy & Physiology Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Skeletal, Smooth, or Cardiac SKELETAL Striated Voluntary Multinucleated Bound to bones Moves skeleton SMOOTH Not striated
Muscle Physiology. Dr. Ebneshahidi Ebneshahidi
 Muscle Physiology Dr. Ebneshahidi Skeletal Muscle Figure 9.2 (a) Functions of the muscular system 1. Locomotion body movements are due to skeletal muscle contraction. 2. Vasoconstriction and vasodilatation
Muscle Physiology Dr. Ebneshahidi Skeletal Muscle Figure 9.2 (a) Functions of the muscular system 1. Locomotion body movements are due to skeletal muscle contraction. 2. Vasoconstriction and vasodilatation
Muscle Tissue- 3 Types
 AN INTRODUCTION TO MUSCLE TISSUE Muscle Tissue- 3 Types Skeletal muscle (focus on these) Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle FUNCTIONS OF SKELETAL MUSCLES Produce movement of the skeleton Maintain posture and
AN INTRODUCTION TO MUSCLE TISSUE Muscle Tissue- 3 Types Skeletal muscle (focus on these) Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle FUNCTIONS OF SKELETAL MUSCLES Produce movement of the skeleton Maintain posture and
The Muscular System. Muscle tissue is one of the 4 tissue types in vertebrates Muscle
 The Muscular System The Muscular System Muscle tissue is one of the 4 tissue types in vertebrates Muscle The Muscular System Muscle tissue is one of the 4 tissue types in vertebrates Muscle Nervous The
The Muscular System The Muscular System Muscle tissue is one of the 4 tissue types in vertebrates Muscle The Muscular System Muscle tissue is one of the 4 tissue types in vertebrates Muscle Nervous The
Page 1. Introduction Skeletal muscle cells have unique characteristics which allow for body movement.
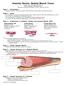 Anatomy Review: Skeletal Muscle Tissue Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) Page 1. Introduction Skeletal muscle
Anatomy Review: Skeletal Muscle Tissue Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) Page 1. Introduction Skeletal muscle
#1 20. physiology. Muscle tissue 30/9/2015. Ahmad Adel Sallal. Mohammad Qudah
 # 20 physiology Muscle tissue Ahmad Adel Sallal 30/9/205 Mohammad Qudah MUSCLES PHYSIOLOGY Awn, welcome to the first physiology lecture in the MSS, I wish you a perfect exams with high grades, and never
# 20 physiology Muscle tissue Ahmad Adel Sallal 30/9/205 Mohammad Qudah MUSCLES PHYSIOLOGY Awn, welcome to the first physiology lecture in the MSS, I wish you a perfect exams with high grades, and never
Lecture Overview. Muscular System. Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Chapter 9 Muscles and Muscle Tissue Lecture 16
 Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 9 Muscles and Muscle Tissue Lecture 16 1 Lecture Overview Types, characteristics, functions of muscle Structure of skeletal muscle Mechanism of
Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 9 Muscles and Muscle Tissue Lecture 16 1 Lecture Overview Types, characteristics, functions of muscle Structure of skeletal muscle Mechanism of
Microanatomy of Muscles. Anatomy & Physiology Class
 Microanatomy of Muscles Anatomy & Physiology Class Three Main Muscle Types Objectives: By the end of this presentation you will have the information to: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Describe the 3 main types of muscles.
Microanatomy of Muscles Anatomy & Physiology Class Three Main Muscle Types Objectives: By the end of this presentation you will have the information to: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Describe the 3 main types of muscles.
Chapter Skeletal Muscle Structure and Function
 Chapter 10.2 Skeletal Muscle Structure and Function Introduction to Muscle Physiology Movement is a fundamental characteristic of all living things All muscle cells (skeletal, cardiac, and smooth) are
Chapter 10.2 Skeletal Muscle Structure and Function Introduction to Muscle Physiology Movement is a fundamental characteristic of all living things All muscle cells (skeletal, cardiac, and smooth) are
Outline. Bio 105: Muscular System. Muscular System. Types of Muscles. Smooth Muscle. Cardiac Muscle 4/6/2016
 Outline Bio 105: Muscular System Lecture 11 Chapter 6 Characteristics of muscles 3 types of muscles Functions of muscles Structure of skeletal muscles Mechanics of muscle contraction Energy sources for
Outline Bio 105: Muscular System Lecture 11 Chapter 6 Characteristics of muscles 3 types of muscles Functions of muscles Structure of skeletal muscles Mechanics of muscle contraction Energy sources for
1. General characteristics of muscle tissues: 2. A. Skeletal muscle tissue ("striated muscle tissue")
 1. General characteristics of muscle tissues: Muscle fibers, AKA, muscle cells Vascularized. Other tissues dense and loose C.T. nerves and nerve fibers Muscle fibers (muscle cells) close together. From
1. General characteristics of muscle tissues: Muscle fibers, AKA, muscle cells Vascularized. Other tissues dense and loose C.T. nerves and nerve fibers Muscle fibers (muscle cells) close together. From
Ch 10: Skeletal Muscle Tissue (Myology)
 Ch 10: Skeletal Muscle Tissue (Myology) main objectives: Describe the distinguishing characteristics of the different muscle tissues Discuss the organization of skeletal muscle Explain the micro-anatomy
Ch 10: Skeletal Muscle Tissue (Myology) main objectives: Describe the distinguishing characteristics of the different muscle tissues Discuss the organization of skeletal muscle Explain the micro-anatomy
MUSCULAR TISSUE. Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 MUSCULAR TISSUE Dr. Gary Mumaugh MUSCLE OVERVIEW The three types of muscle tissue are skeletal, cardiac, and smooth These types differ in structure, location, function, and means of activation FUNCTIONAL
MUSCULAR TISSUE Dr. Gary Mumaugh MUSCLE OVERVIEW The three types of muscle tissue are skeletal, cardiac, and smooth These types differ in structure, location, function, and means of activation FUNCTIONAL
MODULE 6 MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY
 MODULE 6 MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY III SEMESTER BOTANY Syllabi: Striated, Non striated and Cardiac muscle, Ultra structure of striated muscle fibre, Mechanism of muscle contraction, Threshold and spike potential,
MODULE 6 MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY III SEMESTER BOTANY Syllabi: Striated, Non striated and Cardiac muscle, Ultra structure of striated muscle fibre, Mechanism of muscle contraction, Threshold and spike potential,
33.2. Muscular System. Humans have three types of muscle.
 33.2 Muscular System VOCABULARY muscular system muscle fiber skeletal muscle tendon smooth muscle cardiac muscle myofibril sarcomere 10A, 10C, 11A Key Concept Muscles are tissues that can contract, enabling
33.2 Muscular System VOCABULARY muscular system muscle fiber skeletal muscle tendon smooth muscle cardiac muscle myofibril sarcomere 10A, 10C, 11A Key Concept Muscles are tissues that can contract, enabling
Muscle Tissue. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Muscle Tissue Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Functions of muscle tissue Movement Maintenance of posture Joint stabilization Heat generation Tendon Belly Tendon Types of
Muscle Tissue Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Functions of muscle tissue Movement Maintenance of posture Joint stabilization Heat generation Tendon Belly Tendon Types of
Human Anatomy. Muscle Tissue and Organization. DR.SADIQ ALI (K.E Medalist) 10-1
 Human Anatomy Muscle Tissue and Organization DR.SADIQ ALI (K.E Medalist) 10-1 Tissue and Organization Over 700 skeletal muscles have been named. Form the muscular system. Muscle tissue is distributed almost
Human Anatomy Muscle Tissue and Organization DR.SADIQ ALI (K.E Medalist) 10-1 Tissue and Organization Over 700 skeletal muscles have been named. Form the muscular system. Muscle tissue is distributed almost
Muscle Histology. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Muscle Histology Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Functions of muscle tissue Movement Maintenance of posture Joint stabilization Heat generation Types of Muscle Tissue Skeletal
Muscle Histology Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Functions of muscle tissue Movement Maintenance of posture Joint stabilization Heat generation Types of Muscle Tissue Skeletal
Skeletal Muscle : Structure
 1 Skeletal Muscle : Structure Dr.Viral I. Champaneri, MD Assistant Professor Department of Physiology 2 Learning objectives 1. Gross anatomy of the skeletal muscle 2. Myofilaments & their molecular structure
1 Skeletal Muscle : Structure Dr.Viral I. Champaneri, MD Assistant Professor Department of Physiology 2 Learning objectives 1. Gross anatomy of the skeletal muscle 2. Myofilaments & their molecular structure
Muscle Tissue and Motion
 Muscle Tissue and Motion Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Muscle tissue is characterized by properties that allow movement. Muscle cells are excitable; they respond to a stimulus. They are contractile, meaning they
Muscle Tissue and Motion Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Muscle tissue is characterized by properties that allow movement. Muscle cells are excitable; they respond to a stimulus. They are contractile, meaning they
MUSCLE TISSUE (MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY) PART I: MUSCLE STRUCTURE
 PART I: MUSCLE STRUCTURE Muscle Tissue A primary tissue type, divided into: skeletal muscle cardiac muscle smooth muscle Functions of Skeletal Muscles Produce skeletal movement Maintain body position Support
PART I: MUSCLE STRUCTURE Muscle Tissue A primary tissue type, divided into: skeletal muscle cardiac muscle smooth muscle Functions of Skeletal Muscles Produce skeletal movement Maintain body position Support
Smooth Cardiac Skeletal Location Around tubes Heart tissue attached to skeleton Moves stuff thru Heart beat pumps Moves body parts
 Biology 067 - Muscular system A. Type of muscles: Smooth Cardiac Skeletal Location Around tubes Heart tissue attached to skeleton Function Moves stuff thru Heart beat pumps Moves body parts tubes blood
Biology 067 - Muscular system A. Type of muscles: Smooth Cardiac Skeletal Location Around tubes Heart tissue attached to skeleton Function Moves stuff thru Heart beat pumps Moves body parts tubes blood
Since we ll be studying muscular and nervous tissue extensively later on in the year, this is just a brief overview of these two tissue types.
 1 Since we ll be studying muscular and nervous tissue extensively later on in the year, this is just a brief overview of these two tissue types. Muscular tissue is unique because it is the only tissue
1 Since we ll be studying muscular and nervous tissue extensively later on in the year, this is just a brief overview of these two tissue types. Muscular tissue is unique because it is the only tissue
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. The Muscular System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology The Muscular System The Muscular System Muscles are responsible for all types of body movement they contract or shorten and are the machine of the body Three basic
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology The Muscular System The Muscular System Muscles are responsible for all types of body movement they contract or shorten and are the machine of the body Three basic
Muscle Tissue. Xie Fenfen. Department of Histology and Embryology School of Basic Medicine Anhui Medical University
 Muscle Tissue Xie Fenfen Email:xff2005024@126.com Department of Histology and Embryology School of Basic Medicine Key points The structural differences (LM) of 3 types of muscle fibers Molecular structure
Muscle Tissue Xie Fenfen Email:xff2005024@126.com Department of Histology and Embryology School of Basic Medicine Key points The structural differences (LM) of 3 types of muscle fibers Molecular structure
Muscle Cells & Muscle Fiber Contractions. Packet #8
 Muscle Cells & Muscle Fiber Contractions Packet #8 Skeletal muscle is attached to bones and is responsible for movement. Introduction Introduction II Skeletal muscle is composed of bundles of muscle fibers
Muscle Cells & Muscle Fiber Contractions Packet #8 Skeletal muscle is attached to bones and is responsible for movement. Introduction Introduction II Skeletal muscle is composed of bundles of muscle fibers
1/4/2017. Introduction. Connective Tissue Coverings. 9.1: Structure of a Skeletal Muscle. Skeletal Muscle Fibers. Connective Tissue Coverings
 Introduction Chapter 09 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Introduction Chapter 09 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Functions of Muscle Tissue
 The Muscular System Functions of Muscle Tissue Movement Facilitation Thermogenesis Postural Support Regulation of Organ Volume Protects Internal Organs Pumps Blood (HEART) Characteristics of Muscle Tissue
The Muscular System Functions of Muscle Tissue Movement Facilitation Thermogenesis Postural Support Regulation of Organ Volume Protects Internal Organs Pumps Blood (HEART) Characteristics of Muscle Tissue
The Nervous and Muscular Systems and the role of ATP
 The Nervous and Muscular Systems and the role of ATP Overview of the Nervous System General parts: The brain The spinal cord The nerves and sense organs General functions: controls and coordinates body
The Nervous and Muscular Systems and the role of ATP Overview of the Nervous System General parts: The brain The spinal cord The nerves and sense organs General functions: controls and coordinates body
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Microscopic Anatomy and Organization of Skeletal Muscle This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Microscopic Anatomy and Organization of Skeletal Muscle,
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Microscopic Anatomy and Organization of Skeletal Muscle This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Microscopic Anatomy and Organization of Skeletal Muscle,
CHAPTER 6 2/9/2016. Learning Objectives List the four traits that all muscle types have in common.
 Learning Objectives List the four traits that all muscle types have in common. CHAPTER 6 The Muscular System Demonstrate and explain the use of antagonistic muscle pairs. Describe the attachment of muscle
Learning Objectives List the four traits that all muscle types have in common. CHAPTER 6 The Muscular System Demonstrate and explain the use of antagonistic muscle pairs. Describe the attachment of muscle
******************************************************************************************************* MUSCLE CYTOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY
 BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ******************************************************************************************************* MUSCLE CYTOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY *******************************************************************************************************
BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ******************************************************************************************************* MUSCLE CYTOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY *******************************************************************************************************
Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Lecture Outline
 Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Lecture Outline Muscle tissue types 1. Skeletal muscle = voluntary striated 2. Cardiac muscle = involuntary striated 3. Smooth muscle = involuntary nonstriated Characteristics
Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Lecture Outline Muscle tissue types 1. Skeletal muscle = voluntary striated 2. Cardiac muscle = involuntary striated 3. Smooth muscle = involuntary nonstriated Characteristics
Muscle and Muscle Tissue
 Muscle and Muscle Tissue Make up about half of total body mass Exerts force by converting chemical energy, ATP, to mechanical energy Muscle tissue is classified based on Shape Number and position of nuclei
Muscle and Muscle Tissue Make up about half of total body mass Exerts force by converting chemical energy, ATP, to mechanical energy Muscle tissue is classified based on Shape Number and position of nuclei
GENERAL HISTOLOGY 4. Muscular Tissue
 Biology-232 GENERAL HISTOLOGY 4. Muscular Tissue Dr. Manal Othman Anatomy Department CMMS, AGU Responsible for MOST types of BODY MOVEMENT Made up of groups of elongated MUSCLE cells with contractile filaments
Biology-232 GENERAL HISTOLOGY 4. Muscular Tissue Dr. Manal Othman Anatomy Department CMMS, AGU Responsible for MOST types of BODY MOVEMENT Made up of groups of elongated MUSCLE cells with contractile filaments
Muscles Muscles are effectors which enable movement to be carried out
 Muscles 13.8 Muscles are effectors which enable movement to be carried out Muscle Is responsible for almost all the movements in animals 3 types Cardiac muscle Smo oth muscle Skeletal mus cle (aka striped
Muscles 13.8 Muscles are effectors which enable movement to be carried out Muscle Is responsible for almost all the movements in animals 3 types Cardiac muscle Smo oth muscle Skeletal mus cle (aka striped
SKELETAL MUSCLE CHARACTERISTICS
 THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM SKELETAL MUSCLE CHARACTERISTICS Most are attached by tendons to bones Cells are multinucleate Striated have visible banding Voluntary subject to conscious control Cells are surrounded
THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM SKELETAL MUSCLE CHARACTERISTICS Most are attached by tendons to bones Cells are multinucleate Striated have visible banding Voluntary subject to conscious control Cells are surrounded
Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction. Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology
 Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology Types and structure of muscle cells Structural basis of contraction Triggering muscle contraction Skeletal muscle consists of
Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology Types and structure of muscle cells Structural basis of contraction Triggering muscle contraction Skeletal muscle consists of
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Mrs. Hummer. Chapter 9 Muscular System
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 9 Muscular System 1 Chapter 9 Muscular System Skeletal Muscle usually attached to bones under conscious control striated Three Types
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 9 Muscular System 1 Chapter 9 Muscular System Skeletal Muscle usually attached to bones under conscious control striated Three Types
Lecture Overview. CT Framework of the Body. Chapter 4 Muscle & Nervous Tissues Lecture 11. Connective tissue framework of the body
 Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 4 Muscle & Nervous Tissues Lecture 11 Lecture Overview Connective tissue framework of the body Introduction to muscle tissue Classification/characteristics
Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 4 Muscle & Nervous Tissues Lecture 11 Lecture Overview Connective tissue framework of the body Introduction to muscle tissue Classification/characteristics
Chapter 10: Muscles. Vocabulary: aponeurosis, fatigue
 Chapter 10: Muscles 37. Describe the structural components of skeletal muscle tissue from the molecular to the organ level. 38. Describe the structure, function, and importance of sarcomeres. 39. Identify
Chapter 10: Muscles 37. Describe the structural components of skeletal muscle tissue from the molecular to the organ level. 38. Describe the structure, function, and importance of sarcomeres. 39. Identify
Chapter 8: Skeletal Muscle: Structure and Function
 Chapter 8: Skeletal Muscle: Structure and Function Objectives Draw & label the microstructure of skeletal muscle Outline the steps leading to muscle shortening Define the concentric and isometric Discuss:
Chapter 8: Skeletal Muscle: Structure and Function Objectives Draw & label the microstructure of skeletal muscle Outline the steps leading to muscle shortening Define the concentric and isometric Discuss:
Muscle Tissue.
 Muscle Tissue Email:lizhongjie@zju.edu.cn General description 1) components: ---cell: muscle cell - myofiber ---extracellular ground substance: CT with BV, LV and nerve Nomenclature in muscular cell Muscular
Muscle Tissue Email:lizhongjie@zju.edu.cn General description 1) components: ---cell: muscle cell - myofiber ---extracellular ground substance: CT with BV, LV and nerve Nomenclature in muscular cell Muscular
The All-or-None Principle Motor units also comply to a rule known as the all-ornone principle (or law).
 The All-or-None Principle Motor units also comply to a rule known as the all-ornone principle (or law). This principle stipulates that, when a motor unit is stimulated to contract, it will do so to its
The All-or-None Principle Motor units also comply to a rule known as the all-ornone principle (or law). This principle stipulates that, when a motor unit is stimulated to contract, it will do so to its
Muscle tissue. 1) Striated skeletal muscle tissue. 2) Striated cardiac muscle tissue. 3) Smooth muscle tissue.
 Muscle tissue 1) Striated skeletal muscle tissue. 2) Striated cardiac muscle tissue. 3) Smooth muscle tissue. General characteristic of muscle tissue Origin: mesoderm and mesenchyme Excitability Contraction
Muscle tissue 1) Striated skeletal muscle tissue. 2) Striated cardiac muscle tissue. 3) Smooth muscle tissue. General characteristic of muscle tissue Origin: mesoderm and mesenchyme Excitability Contraction
Assignment 4: Muscle Structure and Function
 Assignment 4: Muscle Structure and Function Unit 2: Chapter 5 Part A Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following statements about skeletal muscle is true: A) Skeletal muscles are usually linked
Assignment 4: Muscle Structure and Function Unit 2: Chapter 5 Part A Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following statements about skeletal muscle is true: A) Skeletal muscles are usually linked
Chapter 10 -Muscle Tissue
 Chapter 10 -Muscle Tissue Muscles: 1. Overview of Muscle Tissue A. Review 5 functions of muscle tissue. B. Review the 5 properties of muscle tissue. WHICH do they share with nervous tissue? (2, plus the
Chapter 10 -Muscle Tissue Muscles: 1. Overview of Muscle Tissue A. Review 5 functions of muscle tissue. B. Review the 5 properties of muscle tissue. WHICH do they share with nervous tissue? (2, plus the
Muscles and Muscle Tissue
 1 Muscles and Muscle Tissue Chapter 9 2 Overview of Muscle Tissues Compare and Contrast the three basic types of muscle tissue List four important functions of muscle tissue 3 Muscle Terminology Muscle
1 Muscles and Muscle Tissue Chapter 9 2 Overview of Muscle Tissues Compare and Contrast the three basic types of muscle tissue List four important functions of muscle tissue 3 Muscle Terminology Muscle
The Muscular System. Myology the study of muscles
 The Muscular System Myology the study of muscles Functions of muscles: 1. Movement 2. Stability /support posture 3. Heat production 85% of our body heat 4. Communication 5. Constriction of organs and vessels
The Muscular System Myology the study of muscles Functions of muscles: 1. Movement 2. Stability /support posture 3. Heat production 85% of our body heat 4. Communication 5. Constriction of organs and vessels
5. What component of the sarcomere is not attached to the Z line?
 Model 2: Anatomy of a Sarcomere 1. Label the thick filament and the thin filament in Model 2. 2. How many sarcomeres are shown in Model 2? 3. Using Model 2, based on the locations of thick and thin filaments,
Model 2: Anatomy of a Sarcomere 1. Label the thick filament and the thin filament in Model 2. 2. How many sarcomeres are shown in Model 2? 3. Using Model 2, based on the locations of thick and thin filaments,
Muscular System. This chapter will focus on muscle cells and tissues. Muscle tissue has several functions:
 Muscular System Slide 2 This chapter will focus on muscle cells and tissues. Muscle tissue has several functions: Movement: Muscles work as pulleys on bones to help create changes in body position. Muscles
Muscular System Slide 2 This chapter will focus on muscle cells and tissues. Muscle tissue has several functions: Movement: Muscles work as pulleys on bones to help create changes in body position. Muscles
Class XI Chapter 20 Locomotion and Movement Biology
 Question 1: Draw the diagram of a sarcomere of skeletal muscle showing different regions. The diagrammatic representation of a sarcomere is as follows: Question 2: Define sliding filament theory of muscle
Question 1: Draw the diagram of a sarcomere of skeletal muscle showing different regions. The diagrammatic representation of a sarcomere is as follows: Question 2: Define sliding filament theory of muscle
Cardiac Muscle Tissue. Cardiac Muscle Tissue
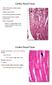 Walls of the heart (cardia: heart); myocardium. Cardiac muscle fibers not as densely packed as skeletal cardiac muscle tissue is highly vascularized Other components; dense C.T. septa, larger blood vessels,
Walls of the heart (cardia: heart); myocardium. Cardiac muscle fibers not as densely packed as skeletal cardiac muscle tissue is highly vascularized Other components; dense C.T. septa, larger blood vessels,
Muscular System. IB Sports, exercise and health science 1.2
 Muscular System IB Sports, exercise and health science 1.2 Characteristics Common to Contractility-ability to shorten the muscles length Extensibility-ability to lengthen the muscles length Elasticity-muscle
Muscular System IB Sports, exercise and health science 1.2 Characteristics Common to Contractility-ability to shorten the muscles length Extensibility-ability to lengthen the muscles length Elasticity-muscle
Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue and Physiology Chapter Outline
 Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue and Physiology Chapter Outline Module 10.1 Overview of muscle tissue (Figures 10.1 10.2) A. Types of Muscle Tissue (Figure 10.1) 1. The three types of cells in muscle tissue are,,
Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue and Physiology Chapter Outline Module 10.1 Overview of muscle tissue (Figures 10.1 10.2) A. Types of Muscle Tissue (Figure 10.1) 1. The three types of cells in muscle tissue are,,
Muscle Physiology. Introduction. Four Characteristics of Muscle tissue. Skeletal Muscle
 Muscle Physiology Introduction Muscle = tissue capable of forceful shortening or contraction Converts chemical energy (ATP) into mechanical energy Important in: Respiration Urine collection & flow Gastrointestinal
Muscle Physiology Introduction Muscle = tissue capable of forceful shortening or contraction Converts chemical energy (ATP) into mechanical energy Important in: Respiration Urine collection & flow Gastrointestinal
Muscular Tissue. Functions of Muscular Tissue. Types of Muscular Tissue. Skeletal Muscular Tissue. Properties of Muscular Tissue
 Muscular Tissue Functions of Muscular Tissue Muscle makes up a large percentage of the body s weight (40-50%) Their main functions are to: Create motion muscles work with nerves, bones, and joints to produce
Muscular Tissue Functions of Muscular Tissue Muscle makes up a large percentage of the body s weight (40-50%) Their main functions are to: Create motion muscles work with nerves, bones, and joints to produce
Ch. 6: Contraction of Skeletal Muscle Physiological Anatomy of Skeletal Muscle
 Ch. 6: Contraction of Skeletal Muscle 40% skeletal muscle + 10% smooth and cardiac muscle Ch. 7: Excitation of Skeletal Muscle Ch. 9: Contraction and Excitation of Smooth Muscle Physiological Anatomy of
Ch. 6: Contraction of Skeletal Muscle 40% skeletal muscle + 10% smooth and cardiac muscle Ch. 7: Excitation of Skeletal Muscle Ch. 9: Contraction and Excitation of Smooth Muscle Physiological Anatomy of
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.49 - MUSCLE SYSTEMS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com BIOLOGY - CLUTCH Muscle system organ system that includes skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle Muscle tissue capable of contracting through the interaction of actin and myosin proteins
!! www.clutchprep.com BIOLOGY - CLUTCH Muscle system organ system that includes skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle Muscle tissue capable of contracting through the interaction of actin and myosin proteins
Anatomy & Physiology Muscular System Worksheet
 Anatomy & Physiology Muscular System Worksheet 1. What are the three categories of muscle tissue? a) b) c) 2. The smallest functional unit of a muscle fiber is called a. 3. What are the four characteristics
Anatomy & Physiology Muscular System Worksheet 1. What are the three categories of muscle tissue? a) b) c) 2. The smallest functional unit of a muscle fiber is called a. 3. What are the four characteristics
Muscular system MOVE ME!
 Muscular system MOVE ME! MUSCLES Day 1 Nov 13 and 16 TYPES OF MUSCLES, STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS. FUNCTIONS of MUSCLE Movement Maintains posture Stabilize joints Generates heat Byproduct of muscular contraction
Muscular system MOVE ME! MUSCLES Day 1 Nov 13 and 16 TYPES OF MUSCLES, STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS. FUNCTIONS of MUSCLE Movement Maintains posture Stabilize joints Generates heat Byproduct of muscular contraction
Chapter 8 Notes. Muscles
 Chapter 8 Notes Muscles 8.1 Intro Three muscle types Skeletal Smooth cardiac 8.2 Structure of Skeletal Muscle Composition Skeletal muscle tissue Nervous tissue Blood Connective tissue Connective tissue
Chapter 8 Notes Muscles 8.1 Intro Three muscle types Skeletal Smooth cardiac 8.2 Structure of Skeletal Muscle Composition Skeletal muscle tissue Nervous tissue Blood Connective tissue Connective tissue
CLASS SET Unit 4: The Muscular System STUDY GUIDE
 NPHS Anatomy & Physiology Questions to answer: 1) List three functions of the muscular system. 1) movement 2) thermogenesis (generates heat) 3) posture & body/joint support CLASS SET Unit 4: The Muscular
NPHS Anatomy & Physiology Questions to answer: 1) List three functions of the muscular system. 1) movement 2) thermogenesis (generates heat) 3) posture & body/joint support CLASS SET Unit 4: The Muscular
1. Locomotion. 2. Repositioning. 3. Internal movement
 MUSCLE and MOVEMENT Chapters 20, 8, 21 1. Locomotion A. Movement B. 2. Repositioning A. 3. Internal movement A. 1 Muscle Cells 1. Contractile 2. Myocytes 3. Striated A. Skeletal B. Cardiac 4. Smooth 5.
MUSCLE and MOVEMENT Chapters 20, 8, 21 1. Locomotion A. Movement B. 2. Repositioning A. 3. Internal movement A. 1 Muscle Cells 1. Contractile 2. Myocytes 3. Striated A. Skeletal B. Cardiac 4. Smooth 5.
1. Locomotion. 2. Repositioning. 3. Internal movement
 MUSCLE and MOVEMENT Chapters 20, 8, 21 1. Locomotion A. Movement B. 2. Repositioning A. 3. Internal movement A. Muscle Cells 1. Contractile 2. Myocytes 3. Striated A. Skeletal B. Cardiac 4. Smooth 5. Striated
MUSCLE and MOVEMENT Chapters 20, 8, 21 1. Locomotion A. Movement B. 2. Repositioning A. 3. Internal movement A. Muscle Cells 1. Contractile 2. Myocytes 3. Striated A. Skeletal B. Cardiac 4. Smooth 5. Striated
Skeletal muscle in the light of its structure
 Mechanism of contraction of Skeletal muscle in the light of its structure By Dr. Mudassar Ali Roomi (MBBS, M. Phil) Muscle Tissue Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle Skeletal Muscle Long cylindrical
Mechanism of contraction of Skeletal muscle in the light of its structure By Dr. Mudassar Ali Roomi (MBBS, M. Phil) Muscle Tissue Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle Skeletal Muscle Long cylindrical
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 10 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD.
 Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 10 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) Which of the following is a recognized function of skeletal muscle? A) produce movement B) maintain posture C) maintain body temperature
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 10 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) Which of the following is a recognized function of skeletal muscle? A) produce movement B) maintain posture C) maintain body temperature
Connective tissue MUSCLE TISSUE
 Connective tissue MUSCLE TISSUE Part 1 General features of MT Develop from mesoderm Many cells, less intercellular matrix Function contraction (shortening) Skeletal (striated, voluntary) Types of MT Cardiac
Connective tissue MUSCLE TISSUE Part 1 General features of MT Develop from mesoderm Many cells, less intercellular matrix Function contraction (shortening) Skeletal (striated, voluntary) Types of MT Cardiac
Muscles & Muscle Tissue
 Muscles & Muscle Tissue Chapter 6 I. Overview of Muscle 1 A. MUSCLE TYPES SKELETAL: striated, voluntary CARDIAC: only in heart involuntary striated SMOOTH: walls of organs involuntary nonstriated All Muscle
Muscles & Muscle Tissue Chapter 6 I. Overview of Muscle 1 A. MUSCLE TYPES SKELETAL: striated, voluntary CARDIAC: only in heart involuntary striated SMOOTH: walls of organs involuntary nonstriated All Muscle
The Muscular System. - composed of mostly skeletal muscle tissue, nervous tissue, blood and connective tissue
 The Muscular System Every action the body takes utilizes a muscular activity. Some of the muscles of the body are under voluntary control (skeletal muscles), and by using these muscle, you are able to
The Muscular System Every action the body takes utilizes a muscular activity. Some of the muscles of the body are under voluntary control (skeletal muscles), and by using these muscle, you are able to
(C) Muscles provide structural support, are involved in thermoregulation, but have no effect on organ function.
 OAT Biology - Problem Drill 13: The Muscular System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which statement about muscles is correct? Question #01 (A) Muscles have an origin that is usually attached to a movable bone,
OAT Biology - Problem Drill 13: The Muscular System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which statement about muscles is correct? Question #01 (A) Muscles have an origin that is usually attached to a movable bone,
Skeletal Muscle. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The best-known feature of skeletal muscle is its ability to contract and cause movement. Skeletal muscles act not only to produce movement but also to stop movement, such as resisting
Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The best-known feature of skeletal muscle is its ability to contract and cause movement. Skeletal muscles act not only to produce movement but also to stop movement, such as resisting
Smooth Muscle. OpenStax College
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46478 1 Smooth Muscle OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be
OpenStax-CNX module: m46478 1 Smooth Muscle OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues. V. Muscle Tissues
 BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues V. Muscle Tissues Nomenclature Sarcolemma = plasma membrane Sarcoplasmic reticulum = endoplasmic reticulum Muscle fiber = cell Myofibril = subcellular fibers
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues V. Muscle Tissues Nomenclature Sarcolemma = plasma membrane Sarcoplasmic reticulum = endoplasmic reticulum Muscle fiber = cell Myofibril = subcellular fibers
Overview of Muscle Tissues *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46473 1 Overview of Muscle Tissues * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you
OpenStax-CNX module: m46473 1 Overview of Muscle Tissues * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you
Skeletal Muscle. Skeletal Muscle
 Skeletal Muscle Skeletal Muscle Types of muscle Skeletal muscle-moves the skeleton by pulling on the tendons that are connected to the bones Cardiac muscle-pumps blood through the heart and blood vessels
Skeletal Muscle Skeletal Muscle Types of muscle Skeletal muscle-moves the skeleton by pulling on the tendons that are connected to the bones Cardiac muscle-pumps blood through the heart and blood vessels
Muscular System. 3 types of muscle tissue. How skeletal muscles arrange CARDIAC SMOOTH SKELETAL
 Muscular System Functions Support the body by allowing us to stay upright Allow for movement by attaching to the skeleton Help maintain a constant body temperature Assist in movement in the cardiovascular
Muscular System Functions Support the body by allowing us to stay upright Allow for movement by attaching to the skeleton Help maintain a constant body temperature Assist in movement in the cardiovascular
or Everything you ever wanted to know about Muscles, but were afraid to ask!!!
 The Muscular System or Everything you ever wanted to know about Muscles, but were afraid to ask!!! Did you know that? - more than 50% of body weight is muscle! - And muscle is made up of proteins and water
The Muscular System or Everything you ever wanted to know about Muscles, but were afraid to ask!!! Did you know that? - more than 50% of body weight is muscle! - And muscle is made up of proteins and water
Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue
 Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. Differ in their microscopic anatomy, location and how they are controlled by the endocrine and nervous system. 3 Types of Muscle
Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. Differ in their microscopic anatomy, location and how they are controlled by the endocrine and nervous system. 3 Types of Muscle
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 10 Muscular Tissue Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Learn about the structure and function of the 3 types of muscular tissue
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 10 Muscular Tissue Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Learn about the structure and function of the 3 types of muscular tissue
Skeletal Muscle Contraction and ATP Demand
 Skeletal Muscle Contraction and ATP Demand Anatomy & Structure Contraction Cycling Calcium Regulation Types of Contractions Force, Power, and Contraction Velocity Epimysium - separates fascia and muscle
Skeletal Muscle Contraction and ATP Demand Anatomy & Structure Contraction Cycling Calcium Regulation Types of Contractions Force, Power, and Contraction Velocity Epimysium - separates fascia and muscle
Muscle tissue- part 2
 Muscle tissue- part 2 Motor unit: The muscle cells that are supplied by a single neuron/axon, its size is variable according to the muscle action. EX: quadriceps muscle is a large muscle and its contraction
Muscle tissue- part 2 Motor unit: The muscle cells that are supplied by a single neuron/axon, its size is variable according to the muscle action. EX: quadriceps muscle is a large muscle and its contraction
The Musculoskeletal System. Chapter 46
 The Musculoskeletal System Chapter 46 Types of Skeletal Systems Changes in movement occur because muscles pull against a support structure Zoologists recognize three types: 1. Hydrostatic skeletons a fluid
The Musculoskeletal System Chapter 46 Types of Skeletal Systems Changes in movement occur because muscles pull against a support structure Zoologists recognize three types: 1. Hydrostatic skeletons a fluid
A. Structure - Your skeletal system is your basic framework in your body.
 II. Skeletal System A. Structure - Your skeletal system is your basic framework in your body. 1. 206 bones - Comprise the adult human body. 2. "os-", "osteo-" Both of these roots mean bone. What is an
II. Skeletal System A. Structure - Your skeletal system is your basic framework in your body. 1. 206 bones - Comprise the adult human body. 2. "os-", "osteo-" Both of these roots mean bone. What is an
