Strength ratios are affected by years of experience in American collegiate rugby athletes: A preliminary study AUTHOR COPY
|
|
|
- Emmeline Weaver
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Isokinetics and Exercise Science 24 (2016) DOI /IES IOS Press Strength ratios are affected by years of experience in American collegiate rugby athletes: A preliminary study Kyle S. Beyer a, David H. Fukuda a,,ameliam.miramonti a, David D. Church a,satorutanigawa a,b, Jeffrey R. Stout a and Jay R. Hoffman a a Institute of Exercise Physiology and Wellness, University of Central Florida, Orlando, FL, USA b Faculty of Health and Sport Sciences, University of Tsukuba, Ibaraki, Japan Received 4 January 2016 Accepted 29 March 2016 Abstract. BACKGROUND: Hamstring:quadriceps ratios (HQRs) have been studied as potential markers for an athlete s risk of injury, but little is known about how sport-specific experience affects HQRs. OBJECTIVE: This study compared isokinetic and isotonic strength measures, including determining HQRs, between American collegiate male rugby athletes with at least two years of experience (XP; n = 10) and those with less than two years of experience (IN; n = 14). METHODS: Isokinetic concentric (ConH) and eccentric (EccH) hamstring and concentric only quadriceps (ConQ) strength was measured at 60 and 180 /s. The strength ratio: Hcon/Qcon (HQR), was calculated for both velocities, HQR 60, HQR 180, while the strength ratio: ConH/ConQ, the dynamic control ratio (DCR), was likewise calculated, DCR 60 and DCR 180. The isotonic strength was assessed via squat 1-repetition maximum. Analysis of covariance was used to examine differences between IN and XP while body weight and age served as the covariates. RESULTS: No significant differences were noted between groups in isokinetic or isotonic strength. However, a significant difference was observed in DCR 60 (p = 0.047) between the two groups, with XP (0.94 ± 0.11) being greater than IN (0.81 ± 0.16). CONCLUSIONS: In view of the preliminary nature of this study, the implication of this finding is yet obscure. However, given the role of the DCR in an underlying proneness to injury, we suggest that a more comprehensive study with a substantial followup period is undertaken for uncovering the potential importance of this ratio vis-à-vis other major functional parameters as well as injury prediction and assessment of rehabilitation. Keywords: Muscle imbalance, injury risk, rugby union, isokinetic strength, agonist-antagonist ratio 1. Introduction Rugby union is a physically demanding sport played all over the world. Like most field-based team sports, Corresponding author: David H. Fukuda, Institute of Exercise Physiology and Wellness, University of Central Florida, Orlando, FL 32817, USA. Tel.: ; Fax: ; david.fukuda@ucf.edu. it requires numerous bouts of high intensity running, tackling and rapid changes of direction, interspersed by periods of lower intensity activity such as walking or jogging [1]. Rugby is a full contact sport with high physical demands, and, consequently, a high injury rate [2]. The lower limb is the most common site for an injury, and regardless of the affected site, the ligaments, muscles, and tendons are the most commonly injured tissues [3]. Therefore, it can be inferred that the ISSN /16/$35.00 c 2016 IOS Press and the authors. All rights reserved
2 258 K.S. Beyer et al. / Strength ratios are affected by years of experience in American collegiate rugby athletes largest potential areas of injury are to the musculature and connective tissue of the knee and ankle. Regardless of playing position, hamstring injuries are the first and second most common injuries in training and match play, respectively [4,5]. Additionally, anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries resulted in the most missed time amongst rugby union players in the English Premiership [4,5]. There are many factors associated with an athlete s risk for sustaining a lower body injury, such as a hamstring strain or an ACL sprain [6,7]. A proposed risk factor is strength imbalances between the hamstring and quadriceps muscle groups [8 10]. Typically, strength imbalances are assessed via isokinetic dynamometry in the form of a hamstring:quadriceps ratio (HQR). This ratio has two variants: the conventional ratio (HQR), which is widely described in the isokinetic muscle performance literature, and the dynamic control ratio (DCR [11,12]). While the clinical significance of the HQR has never been validated, the DCR has been shown to vary significantly both in individuals with compromised ACL [13] as well as individuals with strain of the hamstring [9]. Previous research has shown that as athletes age, there is a greater incidence of hamstring injury, but this may be due to a greater exposure (minutes played) to injury or to the development of a recurring injury earlier in their career rather than a muscle imbalance at the knee joint [14]. The effects of aging on HQRs are unclear [15,16]. However, the age-related difference in these ratios may be a product of increased sportspecific experience. It is expected, that the years of sport-specific experience increases with age, but the physiological changes associated with normal growth and development may mask any experience-related differences [15]; therefore, it is important to control for age when trying to compare novice and experienced athletes. Previous research has shown that highly trained female runners have greater HQRs than their recreational counterparts, but age was not controlled in this study [17]. The relationship between HQRs and sport-specific experience has not been investigated in rugby union, which may be of particular relevance due to the nature of the sport, including the use of rapid accelerations, decelerations, and changes of direction [1]. The repeated loading of the knee joint with each practice and game may result in sport-specific adaptations, such as variable increases in lower body strength, which could lead to muscle imbalances [18]. The purpose of the current study is to compare the strength and strength ratios between rugby athletes with at least two years of playing experience and those with less than two years of playing experience. Only 31 US high schools offer rugby as a scholastic sport [19], while over 300 universities field club teams [20]. Therefore, many individuals in the USA are not exposed to rugby until they enroll in college/ university. The selected two-year cutoff point likely demarcates athletes being introduced to rugby union and those who have been engaged in the sport. We hypothesize that individuals with at least two years of playing experience will have greater isotonic and isokinetic strength and better HQRs than those with less than two years of playing experience. 2. Methods 2.1. Subjects Twenty-five members of the university men s rugby team provided verbal consent and volunteered to participate in the current research study. One participant was excluded from data analysis due to pre-existing injury. The age, height, weight and years of competitive rugby experience were recorded for all participants. The participants were then grouped based on years of experience, with two years of experience selected as the cutoff, to create XP (n = 10; ± 1.95y; 1.79 ± 0.08 m; ± kg; 4.00 ± 1.56 years of experience) and IN (n = 14; ± 1.31y; 1.77 ± 0.05 m; ± kg; 0.29 ± 0.47 years of experience) groups. This study was approved by the university Institutional Review Board and was in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki Procedures Isokinetic strength procedures Prior to beginning the isokinetic testing, participants completed a general warm-up, which consisted of: five minutes of sub-maximal cycling at a selfselected resistance, ten body-weight squats, ten alternating lunges, ten walking knee hugs, and ten walking butt kicks. Following the general warm-up, participants were seated in an isokinetic dynamometer (S4, Biodex Medical System, Inc., New York, NY, USA) with a hip angle of 110 and strapped to the chair at the waist, shoulders and across the thigh to complete a series of isokinetic strength assessments. Chair and dynamometer settings were adjusted for each participant to properly align the axis of rotation with the lat-
3 K.S. Beyer et al. / Strength ratios are affected by years of experience in American collegiate rugby athletes 259 eral condyle of the femur. All participants were tested on their dominant leg (kicking preference) which was secured to the dynamometer arm just above the medial and lateral malleoli. Range of motion was assessed for each participant. All participants were able to achieve a range of motion of without discomfort. The gravity effect of moment was measured at 30 of knee flexion (0 representing full extension) and subsequently corrected for during testing using a previously published equation by Nelson and Duncan [21]. For each muscle action, participants completed 3 warm-up repetitions (50% of perceived maximum) and 3 maximal repetitions separated by a 10- s rest period. Quadriceps peak moment (PM) was assessed concentrically at 60 /s (Q 60 ) and 180 /s (Q 180 ). Hamstring PM was measured both concentrically and eccentrically at 60 /s (ConH 60 and EccH 60, respectively) and 180 /s (ConH 180 and EccH 180, respectively). The muscle action/speed sets were completed in a random order and participants were given two minutes of rest between sets in order to limit the effects of testing. Peak moment was recorded for all repetitions and the greatest value was used for subsequent analysis, including the calculation of HQR and DCR. Previous unpublished reliability measures within our laboratory have shown intraclass correlations (ICC; model 3,1) [22] of greater than 0.90 for all peak moment data and greater than 0.89 for HQR and DCR Isotonic strength procedures On a separate testing day, participants reported to the Strength and Conditioning Laboratory to complete a 1- repetition maximum (1RM) squat. Prior to beginning the 1RM test, each participant completed a general and specific warm up. The general warm up consisted of riding a cycle ergometer for 5 minutes at the participant s preferred resistance. The specific warm up consisted of 10 body weight squats, 10 alternating lunges, 10 walking knee hugs and 10 walking butt kicks. Each participant performed 2 warm-up trials using a resistance that was approximately 40 60% and 60 80% of their perceived maximum, respectively. The third trial served as the first attempt at the participant s 1RM. If the trial was successfully completed, then weight was added and another trial was attempted. If the trial was not successfully completed, then the weight was reduced and another trial was attempted. The amount of weight that was added or removed was at the discretion of the Certified Strength and Conditioning Specialist supervising the testing session. A 3 5 minute rest period was provided between each trial. This process of adding and removing weight continued until a 1RM was reached. Attempts not meeting the range of motion criterion for each exercise, as determined by the trainer following previously established guidelines [23], were discarded Statistical analysis All peak moment data were assessed for normality using Shapiro-Wilk tests of normality. All descriptive data (age, height, and weight) were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). All isotonic and isokinetic PM and ratio data were analyzed using a one-way analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) with age and body weight serving as the covariates. Homogeneity of variance was assessed for each ANOVA and AN- COVA via Levene s test for equality of variance. For effect size, the partial eta squared (η 2 ) statistic was calculated, and according to Green and Salkind [24], 0.01, 0.06, and 0.14 were interpreted as small, medium, and large effect sizes, respectively. Statistical software (SPSS; V. 20.0; SPSS, Inc, Chicago, IL, USA) was used for all analyses. Results were considered significantatanalphalevelofp All data are reported as mean ± SD. 3. Results 3.1. Descriptives Age, height, weight, and years of experience data can be seen in Table 1. Statistical analysis revealed no significant differences between XP and IN groups for age (F = 1.900, p = 0.182, η 2 = 0.08), height (F = 0.655, p = 0.427, η 2 = 0.029), and weight (F = 2.403, p = 0.135, η 2 = 0.098). The medium effect sizes noted for age and weight were used as partial justification for their use as covariates. As expected, there was a significant difference in years of experience between XP and IN groups (F = , p<0.000, η 2 = 0.764) Isokinetic and isotonic strength Isokinetic and isotonic strength data are outlined in Table 2. The assumptions of normality and equality of variance were met for all data. When controlling for age and body weight, ANCOVA revealed no significant difference between XP and IN groups in terms of Q 60 (F = 1.226, p = 0.281, η 2 = 0.058) or Q 180 (F = 1.693, p = 0.208, η 2 = 0.078). When control-
4 260 K.S. Beyer et al. / Strength ratios are affected by years of experience in American collegiate rugby athletes Table 1 Age, height, body weight and years of experience (mean ± SD) for the inexperienced and experienced groups Inexperienced (n = 14) Experienced (n = 10) Effect size interpretation Age (y) ± ± 1.95 Medium Height (m) 1.77 ± ± 0.08 Small Weight (kg) ± ± Medium Years of Experience (y) 0.29 ± ± 1.56 Large Denotes significant difference between inexperienced and experienced (p <0.05). Table 2 Isokinetic and isotonic strength (PM, mean ± SEM) for the inexperienced and experienced groups adjusted for age and body weight (covariate: age = y; body weight = kg) Inexperienced (n = 14) Experienced (n = 10) Effect size interpretation Q 60 (Nm) ± ± Small Q 180 (Nm) ± ± 6.94 Medium ConH 60 (Nm) ± ± 5.82 Small ConH 180 (Nm) ± ± 4.73 None EccH 60 (Nm) ± ± 9.89 Medium EccH 180 (Nm) ± ± Small Squat 1RM (kg) ± ± Small Denotes different sample sizes for inexperienced (n = 12) and experienced (n = 8). ling for age and body weight, ANCOVA revealed no significant difference between XP and IN groups in terms of ConH 60 (F = 0.419, p = 0.525, η 2 = 0.021) or ConH 180 (F = 0.023, p = 0.881, η 2 = 0.001). Furthermore, there were no significant differences between XP and IN groups for EccH 60 (F = 1.941, p = 0.179, η 2 = 0.088) or EccH 180 (F = 0.563, p = 0.462, η 2 = 0.027). In congruence with isokinetic strength data, there was no significant different between XP and IN in squat 1RM when controlling for age and body weight (F = 0.523, p = 0.480, η 2 = 0.032) Hamstring:quadriceps ratios HQR ratio data can be seen in Table 3. When controlling for age and body weight, ANCOVA revealed no significant difference between XP and IN groups in terms of HQR 60 (F = 3.607, p = 0.072, η 2 = 0.153), HQR 180 (F = 0.873, p = 0.361, η 2 = 0.042), or DCR 180 (F = 1.279, p = 0.271, η 2 = 0.060). However, the XP group had a significantly higher DCR 60 when compared to the inexperienced group (F = 4.502, p = 0.047, η 2 = 0.184). 4. Discussion The main findings of this study were no significant differences between XP and IN in quadriceps and hamstring strength, or isotonic squat 1RM when controlling for age and body weight but a significantly higher DCR 60 in the former compared to the latter group. In addition, there were large effect sizes for both ratios at 60 /s and a medium effect for the DCR 180.Theeffect sizes for Q 60 and Q 180 revealed small to medium effects favoring IN after controlling for age and body weight. Conversely, hamstring isokinetic strength data revealed small to medium effects favoring XP after controlling for age and body weight. Despite the significant difference in DCR 60 between XP and IN, there was no significant difference in DCR 180. This discrepancy in results may be due to speed-specific adaptations to rugby union or larger degrees of variance at faster testing speeds. However, considering rugby union is a fast-paced sport with repeated sprints [1], it is expected that adaptations would have occurred at high velocities. Therefore, the lack of significance may be due to the larger standard deviations observed at 180 /s which in turn may be due to a lack of familiarization with the test velocity. Previous research in basketball [16] and soccer [25] athletes have observed higher standard deviations in DCR at 180 /s than at 60 /s regardless of age. Despite the lack of significant differences in DCR 180 between groups, the current preliminary study did observe a medium effect, which should be further investigated in a future study. Rugby union experience may be causing adaptations specifically to the hamstring muscle group during eccentric muscle action. Indeed, rugby union athletes have been shown to have stronger hamstring muscles than soccer [26] and rugby league athletes [18], which may indicate the high stresses being placed on the hamstring muscle of these players. Previous research
5 K.S. Beyer et al. / Strength ratios are affected by years of experience in American collegiate rugby athletes 261 Table 3 Hamstring: quadriceps ratios (mean ± SEM) for the inexperienced and experienced groups adjusted for age and body weight (covariate: age = y; body weight = kg) Inexperienced (n = 14) Experienced (n = 10) Effect size interpretation HQR ± ± 0.02 Large HQR ± ± 0.03 Small DCR ± ± 0.05 Large DCR ± ± 0.06 Medium Denotes significant difference between inexperienced and experienced (p <0.05). has examined isokinetic leg extensor and leg flexor strength testing at the same speeds in different populations. When compared to a study conducted in professional Australian Rules footballers [27], the current study observed lower conventional HQRs but higher DCRs which may be due to the differences in the physical demands of the sport. Similarly, Cometti and colleagues [28] observed greater conventional HQRs in professional French soccer players, but the DCR 60 was similar to the findings of the current study. Furthermore, in comparison to a similar population of English Premiership Rugby Union Club athletes [29], our study yielded similar conventional HQRs, but higher DCRs. The proposed effect of sport-specific experience on HQRs is that by participating in practices and games over numerous years, an athlete may adapt to the rapid accelerations, decelerations, changes of directions and landings [1]. Previous research on experience-related differences in HQRs is limited; however, lower DCRs have been reported in youth soccer players when compared to age-matched controls [30]. Conversely, Evangelidis and colleagues [31] observed no differences in HQRs between soccer athletes and recreational males. However, with additional sport experience, there may be differences in level of play or playing time. With regard to level of play, Cometti and colleagues [28] found that elite and subelite athletes, with similar playing experience over the last 5 years, had greater HQRs than amateur athletes. Conversely, a study in NCAA women s soccer athletes showed that there was no difference in DCRs between starters and nonstarters, despite a greater eccentric hamstring strength in starters [32]. Althoughplayingtimedatawas notincluded in the current study, we can conclude that all athletes were competing at the same level of play as they were all on the same team. While the current study is reporting years of rugbyspecific experience to have an effect on DCR 60,it is important to consider that different sports [33 35] and genders [36,37] display varying HQRs. Future research should examine experience-related differences in muscle imbalances in athletes of differing playing time/talent levels, varied sporting contexts, and amongst genders. Limitations to this study include a very small sample in each group, an arbitrarily set divider (2y) between the groups, and the lack of injury data and longitudinal tracking of HQRs with increased rugby experience. Future studies should investigate how these ratios adapt to increased sporting experience, and if those adaptations affect risk of injury. 5. Conclusion In conclusion, this preliminary study observed a significantly greater DCR 60 in American collegiate rugby athletes with at least two years from sport-specific experience when compared to athletes of the same team with less than two years of experience. Furthermore, by statistically controlling for age and body weight, we have inferred that the difference is likely due to the years of experience playing the sport of rugby. Interestingly, there were no statistically significant differences between groups in terms of absolute measures of isokinetic strength or squat 1RM. Thus, absolute measures of strength may not be able to differentiate inexperienced and experienced US collegiate rugby athletes. While this study was preliminary in nature, future research should further investigate the role of sport-specific experience on HQR and DCR. Findings from this and future studies may assist professionals working with athletes to identify injury risk and prevent subsequent injury. Conflict of interest The authors declare no conflict of interest. References [1] Roberts SP, Trewartha G, Higgitt RJ, El-Abd J, Stokes KA. The physical demands of elite English rugby union. J Sports Sci. 2008; 26(8):
6 262 K.S. Beyer et al. / Strength ratios are affected by years of experience in American collegiate rugby athletes [2] Nicholl JP, Coleman P, Williams BT. The epidemiology of sports and exercise related injury in the United Kingdom. Br J Sports Med. 1995; 29(4): [3] Williams S, Trewartha G, Kemp S, Stokes K. A meta-analysis of injuries in senior men s professional rugby union. Sports Med. 2013; 43(10): [4] Brooks JH, Fuller CW, Kemp SP, Reddin DB. Epidemiology of injuries in English professional rugby union: part 1 match injuries. Br J Sports Med. 2005; 39(10): [5] Brooks JH, Fuller CW, Kemp SP, Reddin DB. Epidemiology of injuries in English professional rugby union: part 2 training Injuries. Br J Sports Med. 2005; 39(10): [6] Brooks JH, Fuller CW, Kemp SP, Reddin DB. Incidence, risk, and prevention of hamstring muscle injuries in professional rugby union. Am J Sports Med. 2006; 34(8): [7] Lee AJ, Garraway WM, Arneil DW. Influence of preseason training, fitness, and existing injury on subsequent rugby injury. Br J Sports Med. 2001; 35(6): [8] Croisier JL, Forthomme B, Namurois MH, Vanderthommen M, Crielaard JM. Hamstring muscle strain recurrence and strength performance disorders. Am J Sports Med. 2002; 30(2): [9] Croisier JL, Ganteaume S, Binet J, Genty M, Ferret JM. Strength imbalances and prevention of hamstring injury in professional soccer players: A prospective study. Am J Sports Med. 2008; 36(8): [10] Petersen J, Holmich P. Evidence based prevention of hamstring injuries in sport. Br J Sports Med. 2005; 39(6): [11] Dvir Z. Isokinetics: Muscle Testing, Interpretation and Clinical Applications. 2nd ed. Edinburgh; New York: Elsevier- Churchill Livingstone, [12] Aagaard P, Simonsen EB, Magnusson SP, Larsson B, Dyhre- Poulsen P. A new concept for isokinetic hamstring: Quadriceps muscle strength ratio. Am J Sports Med. 1998; 26(2): [13] Dvir Z, Eger G, Halperin N, Shklar A. Thigh muscle activity and anterior cruciate ligament insufficiency. Clin Biomech Bristol Avon. 1989; 4(2): [14] Verrall GM, Slavotinek JP, Barnes PG, Fon GT, Spriggins AJ. Clinical risk factors for hamstring muscle strain injury: A prospective study with correlation of injury by magnetic resonance imaging. Br J Sports Med. 2001; 35(6): [15] Gür H, Akova B, Pündük Z, Küçükoglu S. Effects of age on the reciprocal peak torque ratios during knee muscle contractions in elite soccer players. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 1999; 9(2): [16] Gerodimos V, Mandou V, Zafeiridis A, Ioakimidis P. Isokinetic peak torque and hamstring/quadriceps ratios in young basketball players: Effects of age, velocity, and contraction mode. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2003; 43(4): [17] Sundby ØH, Gorelick ML. Relationship between functional hamstring: quadriceps ratios and running economy in highly trained and recreational female runners. J Strength Cond Res. 2014; 28(8): [18] Brown SR, Brughelli M, Griffiths PC, Cronin JB. Lowerextremity isokinetic strength profiling in professional rugby league and rugby union. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2014; 9(2): [19] National Federation of State High School Associations High School Athletics Participation Survey Results [Internet] [cited 2016 Mar 10]. Available from: \ulhttp:// [20] USA Rugby. USA Rugby [Internet] [cited 2016 Mar 10]. Available from: \ulhttp://usarugby.org/. [21] Nelson SG, Duncan PW. Correction of isokinetic and isometric torque recordings for the effects of gravity. A Clinical Report. Phys Ther. 1983; 63(5): [22] Weir JP. Quantifying test-retest reliability using the intraclass correlation coefficient and the SEM. J Strength Cond Res. 2005; 19(1): [23] Hoffman J. Norms for fitness, performance, and health. Human Kinetics, [24] Green SB, Salkind NJ. Using SPSS for Windows and Macintosh: Analyzing and understanding data. 5th ed. Prentice Hall Press, [25] Hoshikawa Y, Iida T, Muramatsu M, Nakajima Y, Fukunaga T, Kanehisa H. Differences in thigh muscularity and dynamic torque between junior and senior soccer players. J Sports Sci. 2009; 27(2): [26] Kuhn WA. Comparative analysis of selected motor performance variables in American football, rugby union and soccer players. Sci Footb II. 1993; [27] Bennell K, Wajswelner H, Lew P, Schall-Riaucour A, Leslie S, Plant D, et al. Isokinetic strength testing does not predict hamstring injury in Australian Rules footballers. Br J Sports Med. 1998; 32(4): [28] Cometti G, Maffiuletti NA, Pousson M, Chatard JC, Maffulli N. Isokinetic strength and anaerobic power of elite, subelite and amateur French soccer players. Int J Sports Med. 2001; 22(1): [29] Deighan MA, Serpell BG, Bitcon MJ, Croix MDS. Knee joint strength ratios and effects of hip position in rugby players. J Strength Cond Res. 2012; 26(7): [30] Iga J, George K, Lees A, Reilly T. Cross-sectional investigation of indices of isokinetic leg strength in youth soccer players and untrained individuals. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2009; 19(5): [31] Evangelidis PE, Pain MTG, Folland J. Angle-specific hamstring-to-quadriceps ratio: A comparison of football players and recreationally active males. J Sports Sci. 2015; 33(3): [32] Jenkins ND, Hawkey MJ, Costa PB, Fiddler RE, Thompson BJ, Ryan ED, et al. Functional hamstrings: Quadriceps ratios in elite women s soccer players. J Sports Sci. 2013; 31(6): [33] Rosene JM, Fogarty TD, Mahaffey BL. Isokinetic hamstrings: Quadriceps ratios in intercollegiate athletes. J Athl Train. 2001; 36(4): [34] Read MT, Bellamy MJ. Comparison of hamstring/quadriceps isokinetic strength ratios and power in tennis, squash and track athletes. Br J Sports Med. 1990; 24(3): [35] Cheung R, Smith A, Wong D. H:Q ratios and bilateral leg strength in college field and court sports players. J Hum Kinet. 2012; 33: [36] Ahmad CS, Clark AM, Heilmann N, Schoeb JS, Gardner TR, Levine WN. Effect of gender and maturity on quadriceps-tohamstring strength ratio and anterior cruciate ligament laxity. Am J Sports Med. 2006; 34(3): [37] Hewett TE, Myer GD, Zazulak BT. Hamstrings to quadriceps peak torque ratios diverge between sexes with increasing isokinetic angular velocity. J Sci Med Sport. 2008; 11(5):
Muscle strength imbalances and injuries
 Muscle strength imbalances and injuries Joaquim Chaler PM&R department. Egarsat-SUMA.Terrassa, Barcelona Lecturer. Psicology, Education and Sports Science School Blanquerna. Universitat Ramon Llull. Barcelona
Muscle strength imbalances and injuries Joaquim Chaler PM&R department. Egarsat-SUMA.Terrassa, Barcelona Lecturer. Psicology, Education and Sports Science School Blanquerna. Universitat Ramon Llull. Barcelona
Isokinetic strength effects of FIFA s The 11+ injury prevention training programme
 Isokinetics and Exercise Science 18 (2010) 211 215 211 DOI 10.3233/IES-2010-0386 IOS Press Isokinetic strength effects of FIFA s The 11+ injury prevention training programme João Brito a,, Pedro Figueiredo
Isokinetics and Exercise Science 18 (2010) 211 215 211 DOI 10.3233/IES-2010-0386 IOS Press Isokinetic strength effects of FIFA s The 11+ injury prevention training programme João Brito a,, Pedro Figueiredo
The Reliability of Four Different Methods. of Calculating Quadriceps Peak Torque Angle- Specific Torques at 30, 60, and 75
 The Reliability of Four Different Methods. of Calculating Quadriceps Peak Torque Angle- Specific Torques at 30, 60, and 75 By: Brent L. Arnold and David H. Perrin * Arnold, B.A., & Perrin, D.H. (1993).
The Reliability of Four Different Methods. of Calculating Quadriceps Peak Torque Angle- Specific Torques at 30, 60, and 75 By: Brent L. Arnold and David H. Perrin * Arnold, B.A., & Perrin, D.H. (1993).
Validity of Data Extraction Techniques on the Kinetic Communicator (KinCom) Isokinetic Device
 Validity of Data Extraction Techniques on the Kinetic Communicator (KinCom) Isokinetic Device By: Laurie L. Tis, PhD, AT,C * and David H. Perrin, PhD, AT,C Tis, L.L., & Perrin, D.H. (1993). Validity of
Validity of Data Extraction Techniques on the Kinetic Communicator (KinCom) Isokinetic Device By: Laurie L. Tis, PhD, AT,C * and David H. Perrin, PhD, AT,C Tis, L.L., & Perrin, D.H. (1993). Validity of
Maximal isokinetic and isometric muscle strength of major muscle groups related to age, body weight, height, and sex in 178 healthy subjects
 Maximal isokinetic and isometric muscle strength of major muscle groups related to age, body weight, height, and sex in 178 healthy subjects Test protocol Muscle test procedures. Prior to each test participants
Maximal isokinetic and isometric muscle strength of major muscle groups related to age, body weight, height, and sex in 178 healthy subjects Test protocol Muscle test procedures. Prior to each test participants
Hamstring to quadriceps strength ratio and noncontact leg injuries: A prospective study during one season
 Isokinetics and Exercise Science 19 (2011) 1 6 1 DOI 10.3233/IES-2011-0406 IOS Press Hamstring to quadriceps strength ratio and noncontact leg injuries: A prospective study during one season Daehan Kim
Isokinetics and Exercise Science 19 (2011) 1 6 1 DOI 10.3233/IES-2011-0406 IOS Press Hamstring to quadriceps strength ratio and noncontact leg injuries: A prospective study during one season Daehan Kim
Effect of Preload and Range of Motion on Isokinetic Torque in Women
 Effect of Preload and Range of Motion on Isokinetic Torque in Women By: Laurie L. Tis, David H. Perrin, Arthur Weltman, Donald W. Ball, and Joe H. Gieck * Tis, L.L., Perrin, D.H., Weltman, A., Ball, D.W.,
Effect of Preload and Range of Motion on Isokinetic Torque in Women By: Laurie L. Tis, David H. Perrin, Arthur Weltman, Donald W. Ball, and Joe H. Gieck * Tis, L.L., Perrin, D.H., Weltman, A., Ball, D.W.,
 p< e-mail: m.abbaszadeh@mubabol.ac.ir strain gauge (repeatability) (accuracy) SG110 EMG SENIAM ASIS Biodex Medical System, Inc., Shirley, New York, Drouin Biometrics (EMG) DataLog RMS Band pass filter:
p< e-mail: m.abbaszadeh@mubabol.ac.ir strain gauge (repeatability) (accuracy) SG110 EMG SENIAM ASIS Biodex Medical System, Inc., Shirley, New York, Drouin Biometrics (EMG) DataLog RMS Band pass filter:
Effect of cold treatment on the concentric and eccentric torque-velocity relationship of the quadriceps femoris
 Effect of cold treatment on the concentric and eccentric torque-velocity relationship of the quadriceps femoris By: Kerriann Catlaw *, Brent L. Arnold, and David H. Perrin Catlaw, K., Arnold, B.L., & Perrin,
Effect of cold treatment on the concentric and eccentric torque-velocity relationship of the quadriceps femoris By: Kerriann Catlaw *, Brent L. Arnold, and David H. Perrin Catlaw, K., Arnold, B.L., & Perrin,
EFFECTS OF TWO WARM-UP PROGRAMS ON BALANCE AND ISOKINETIC STRENGTH IN MALE HIGH SCHOOL SOCCER PLAYERS ACCEPTED
 Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research Publish Ahead of Print DOI: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000001509 By EFFECTS OF TWO WARM-UP PROGRAMS ON BALANCE AND ISOKINETIC STRENGTH IN MALE HIGH SCHOOL SOCCER PLAYERS
Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research Publish Ahead of Print DOI: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000001509 By EFFECTS OF TWO WARM-UP PROGRAMS ON BALANCE AND ISOKINETIC STRENGTH IN MALE HIGH SCHOOL SOCCER PLAYERS
strength ratios and power in tennis, squash and track athletes
 Br. J. Sp. Med; Vol 24, No. 3 Comparison of hamstring/quadriceps isokinetic strength ratios and power in tennis, squash and track M.T.F. Read, MA, MRCGP and M.J. Bellamy, BSc Sport and Fitness, London
Br. J. Sp. Med; Vol 24, No. 3 Comparison of hamstring/quadriceps isokinetic strength ratios and power in tennis, squash and track M.T.F. Read, MA, MRCGP and M.J. Bellamy, BSc Sport and Fitness, London
Rapid hamstrings/quadriceps strength capacity in professional soccer players with different conventional isokinetic muscle strength ratios
 Journal of Sports Science and Medicine (2012) 11, 418-422 http://www.jssm.org Research article Rapid hamstrings/quadriceps strength capacity in professional soccer players with different conventional isokinetic
Journal of Sports Science and Medicine (2012) 11, 418-422 http://www.jssm.org Research article Rapid hamstrings/quadriceps strength capacity in professional soccer players with different conventional isokinetic
Intramachine and intermachine reproducibility of concentric performance: A study of the Con-Trex MJ and the Cybex Norm dynamometers
 Isokinetics and Exercise Science 12 (4) 91 97 91 IOS Press Intramachine and intermachine reproducibility of concentric performance: A study of the Con-Trex MJ and the Cybex Norm dynamometers C. Bardis
Isokinetics and Exercise Science 12 (4) 91 97 91 IOS Press Intramachine and intermachine reproducibility of concentric performance: A study of the Con-Trex MJ and the Cybex Norm dynamometers C. Bardis
Hellenic Journal of Physical Education & Sport Science, 2009, 29 (2):
 FREE FULL TEXT This is a summary plus of a paper published in Hellenic Journal of Physical Education and Sport Science. You can cite this article as follows: P.D. Tsimeas, A. Poulios, K. Valasotiris and
FREE FULL TEXT This is a summary plus of a paper published in Hellenic Journal of Physical Education and Sport Science. You can cite this article as follows: P.D. Tsimeas, A. Poulios, K. Valasotiris and
A descriptive profile of age-specific knee extension flexion strength in elite junior tennis players
 728 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A descriptive profile of age-specific knee extension flexion strength in elite junior tennis players Todd S Ellenbecker, E Paul Roetert, Tetsuro Sueyoshi, Scott Riewald... Br J Sports
728 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A descriptive profile of age-specific knee extension flexion strength in elite junior tennis players Todd S Ellenbecker, E Paul Roetert, Tetsuro Sueyoshi, Scott Riewald... Br J Sports
Ratios of torques of antagonist muscle groups in female soccer players
 Acta of Bioengineering and Biomechanics Vol. 20, No. 1, 2018 Original paper DOI: 10.5277/ABB-00942-2017-02 Ratios of torques of antagonist muscle groups in female soccer players ARTUR STRUZIK 1, ADAM SIEMIEŃSKI
Acta of Bioengineering and Biomechanics Vol. 20, No. 1, 2018 Original paper DOI: 10.5277/ABB-00942-2017-02 Ratios of torques of antagonist muscle groups in female soccer players ARTUR STRUZIK 1, ADAM SIEMIEŃSKI
The Star Excursion Balance Test (SEBT) is a unilateral, UNILATERAL BALANCE PERFORMANCE IN FEMALE COLLEGIATE SOCCER ATHLETES
 UNILATERAL BALANCE PERFORMANCE IN FEMALE COLLEGIATE SOCCER ATHLETES JENNIFER L. THORPE AND KYLE T. EBERSOLE University of Illinois, Department of Kinesiology and Community Health, Urbana, Illinois ABSTRACT
UNILATERAL BALANCE PERFORMANCE IN FEMALE COLLEGIATE SOCCER ATHLETES JENNIFER L. THORPE AND KYLE T. EBERSOLE University of Illinois, Department of Kinesiology and Community Health, Urbana, Illinois ABSTRACT
Effects of motorized vs non-motorized treadmill training on hamstring/quadriceps strength ratios
 Journal of Sports Science and Medicine (2012) 11, 71-76 http://www.jssm.org Research article Effects of motorized vs non-motorized treadmill training on hamstring/quadriceps strength ratios Kelly A. Franks
Journal of Sports Science and Medicine (2012) 11, 71-76 http://www.jssm.org Research article Effects of motorized vs non-motorized treadmill training on hamstring/quadriceps strength ratios Kelly A. Franks
H:Q Ratios and Bilateral Leg Strength in College Field and Court Sports Players
 Journal of Human Kinetics volume 33/2012, 63-71 DOI: 10.2478/v10078-012-0045-1 63 Section I Kinesiology H:Q Ratios and Bilateral Leg Strength in College Field and Court Sports Players by Roy T.H. Cheung
Journal of Human Kinetics volume 33/2012, 63-71 DOI: 10.2478/v10078-012-0045-1 63 Section I Kinesiology H:Q Ratios and Bilateral Leg Strength in College Field and Court Sports Players by Roy T.H. Cheung
performance in young jumpers
 BIOLOGY OF EXERCISE VOLUME 5.2, 2009 Isokinetic muscle strength and running long jump performance in young jumpers D.O.I: http:doi.org/10.4127/jbe.2009.0030 YIANNIS KOUTSIORAS, ATHANASIOS TSIOKANOS, DIMITRIOS
BIOLOGY OF EXERCISE VOLUME 5.2, 2009 Isokinetic muscle strength and running long jump performance in young jumpers D.O.I: http:doi.org/10.4127/jbe.2009.0030 YIANNIS KOUTSIORAS, ATHANASIOS TSIOKANOS, DIMITRIOS
The Relationship between Previous Lower Extremity Injury, Body Weight and Bilateral Eccentric Hamstring Strength Imbalance in Young Soccer Players
 ORIGINAL SCIENTIFIC PAPER The Relationship between Previous Lower Extremity Injury, Body Weight and Bilateral Eccentric Hamstring Strength Imbalance in Young Soccer Players Anil Isık 1, Gurcan Unlu 2,
ORIGINAL SCIENTIFIC PAPER The Relationship between Previous Lower Extremity Injury, Body Weight and Bilateral Eccentric Hamstring Strength Imbalance in Young Soccer Players Anil Isık 1, Gurcan Unlu 2,
Title: Is there a potential relationship between prior hamstring strain injury and increased risk for
 1 TITLE 2 Running head: Impact of hamstring injury on ACL risk. 3 4 Title: Is there a potential relationship between prior hamstring strain injury and increased risk for future anterior cruciate ligament
1 TITLE 2 Running head: Impact of hamstring injury on ACL risk. 3 4 Title: Is there a potential relationship between prior hamstring strain injury and increased risk for future anterior cruciate ligament
Comparison of N-K Table Offset Angles with the Human Knee Flexor Torque Curve
 Comparison of N-K Table Offset Angles with the Human Knee Flexor Torque Curve By: Daniel J. LaPlaca *, Douglas R. Keskula, Kristinn I. Heinrichs, and David H. Perrin LaPlaca, D.J., Keskula, D., Heinrichs,
Comparison of N-K Table Offset Angles with the Human Knee Flexor Torque Curve By: Daniel J. LaPlaca *, Douglas R. Keskula, Kristinn I. Heinrichs, and David H. Perrin LaPlaca, D.J., Keskula, D., Heinrichs,
The adaptations to resistance training are largely
 INFLUENCE OF SUPERVISION RATIO ON MUSCLE ADAPTATIONS TO RESISTANCE TRAINING IN NONTRAINED SUBJECTS PAULO GENTIL AND MARTIM BOTTARO College of Physical Education, University of Brasilia, Brasilia, Brazil
INFLUENCE OF SUPERVISION RATIO ON MUSCLE ADAPTATIONS TO RESISTANCE TRAINING IN NONTRAINED SUBJECTS PAULO GENTIL AND MARTIM BOTTARO College of Physical Education, University of Brasilia, Brasilia, Brazil
A cute hamstring strains are common injuries in sport.1
 4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Type of acute hamstring strain affects flexibility, strength, and time to return to pre-injury level C Askling, T Saartok, A Thorstensson... See end of article for authors affiliations...
4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Type of acute hamstring strain affects flexibility, strength, and time to return to pre-injury level C Askling, T Saartok, A Thorstensson... See end of article for authors affiliations...
Peak Torque Comparison between isam 9000 and Biodex Isokinetic Devices
 International Journal of Health Sciences September 2016, Vol. 4, No. 3, pp. 7-13 ISSN: 2372-5060 (Print), 2372-5079 (Online) Copyright The Author(s). All Rights Reserved. Published by American Research
International Journal of Health Sciences September 2016, Vol. 4, No. 3, pp. 7-13 ISSN: 2372-5060 (Print), 2372-5079 (Online) Copyright The Author(s). All Rights Reserved. Published by American Research
The Effectiveness of Injury-Prevention Programs in Reducing the Incidence of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Sprains in Adolescent Athletes
 Critically Appraised Topics Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 2012, 21, 371-377 2012 Human Kinetics, Inc. The Effectiveness of Injury-Prevention Programs in Reducing the Incidence of Anterior Cruciate Ligament
Critically Appraised Topics Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 2012, 21, 371-377 2012 Human Kinetics, Inc. The Effectiveness of Injury-Prevention Programs in Reducing the Incidence of Anterior Cruciate Ligament
Resistive Eccentric Exercise: Effects of Visual
 Resistive Eccentric Exercise: Effects of Visual Feed back on Maximum Moment of Knee Extensors and Flexors Eleftherios Kellis, BScl Vasilios Baltzopoulos, Ph D, M Phil, BSc2 Copyright 1996. All rights reserved.
Resistive Eccentric Exercise: Effects of Visual Feed back on Maximum Moment of Knee Extensors and Flexors Eleftherios Kellis, BScl Vasilios Baltzopoulos, Ph D, M Phil, BSc2 Copyright 1996. All rights reserved.
Quadriceps and Hamstrings Strength in Athletes
 Quadriceps and Hamstrings Strength in Athletes Nienke W. Willigenburg, Michael P. McNally, and Timothy E. Hewett Introduction N.W. Willigenburg, PhD OSU Sports Health and Performance Institute, The Ohio
Quadriceps and Hamstrings Strength in Athletes Nienke W. Willigenburg, Michael P. McNally, and Timothy E. Hewett Introduction N.W. Willigenburg, PhD OSU Sports Health and Performance Institute, The Ohio
Isokinetic Strength Responses to Season-long Training and Competition in Turkish Elite Soccer Players
 Journal of Human Kinetics volume 31/2012, 159-168 DOI: 10.2478/v10078-012-0017-5 159 Section III Sports Training Isokinetic Strength Responses to Season-long Training and Competition in Turkish Elite Soccer
Journal of Human Kinetics volume 31/2012, 159-168 DOI: 10.2478/v10078-012-0017-5 159 Section III Sports Training Isokinetic Strength Responses to Season-long Training and Competition in Turkish Elite Soccer
EXAMINATION OF HAMSTRING TO QUADRICEP MUSCLE RATIOS IN NCAA DIVISION I WOMEN VOLLEYBALL ATHLETES
 Southern Illinois University Carbondale OpenSIUC Research Papers Graduate School Summer 8-2015 EXAMINATION OF HAMSTRING TO QUADRICEP MUSCLE RATIOS IN NCAA DIVISION I WOMEN VOLLEYBALL ATHLETES Laura S.
Southern Illinois University Carbondale OpenSIUC Research Papers Graduate School Summer 8-2015 EXAMINATION OF HAMSTRING TO QUADRICEP MUSCLE RATIOS IN NCAA DIVISION I WOMEN VOLLEYBALL ATHLETES Laura S.
Rehabilitation Guidelines Following Proximal Hamstring Primary Repair
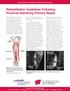 UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines Following Proximal Hamstring Primary Repair The hamstring muscle group consists of three muscles: the biceps femoris, semitendinosus and semimembranosus.
UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines Following Proximal Hamstring Primary Repair The hamstring muscle group consists of three muscles: the biceps femoris, semitendinosus and semimembranosus.
Isokinetic strength testing does not predict hamstring injury in Australian Rules footballers
 Br J Sports Med 1998;32:309 314 309 School of Physiotherapy, University of Melbourne, Australia K Bennell H Wajswelner P Lew A Schall-Riaucour S Leslie J Cirone Department of Physiology D Plant Correspondence
Br J Sports Med 1998;32:309 314 309 School of Physiotherapy, University of Melbourne, Australia K Bennell H Wajswelner P Lew A Schall-Riaucour S Leslie J Cirone Department of Physiology D Plant Correspondence
Change in knee flexor torque after fatiguing exercise identifies previous hamstring injury in football players
 Edith Cowan University Research Online ECU Publications Post 2013 2018 Change in knee flexor torque after fatiguing exercise identifies previous hamstring injury in football players Cameron Lord Edith
Edith Cowan University Research Online ECU Publications Post 2013 2018 Change in knee flexor torque after fatiguing exercise identifies previous hamstring injury in football players Cameron Lord Edith
Neither Stretching nor Postactivation Potentiation Affect Maximal Force and Rate of Force Production during Seven One-Minute Trials
 Neither Stretching nor Postactivation Potentiation Affect Maximal Force and Rate of Force Production during Seven One-Minute Trials David M. Bazett-Jones Faculty Sponsors: Jeffery M. McBride & M. R. McGuigan
Neither Stretching nor Postactivation Potentiation Affect Maximal Force and Rate of Force Production during Seven One-Minute Trials David M. Bazett-Jones Faculty Sponsors: Jeffery M. McBride & M. R. McGuigan
Comparative study of two isokinetics dynamometers: CYBEX NORM vs CON-TREX MJ
 Isokinetics and Exercise Science 11 (2003) 37 43 37 IOS Press Comparative study of two isokinetics dynamometers: CYBEX NORM vs CON-TREX MJ T. Cotte and J.-M. Ferret Centre de Médecine du Sport de Lyon
Isokinetics and Exercise Science 11 (2003) 37 43 37 IOS Press Comparative study of two isokinetics dynamometers: CYBEX NORM vs CON-TREX MJ T. Cotte and J.-M. Ferret Centre de Médecine du Sport de Lyon
In the lower extremity, it is very important to maintain
 PREDICTING ASYMMETRICAL LOWER EXTREMITY STRENGTH DEFICITS IN COLLEGE-AGED MEN AND WOMEN USING COMMON HORIZONTAL AND VERTICAL POWER FIELD TESTS: A POSSIBLE SCREENING MECHANISM DAVID W. KEELEY, HILLARY A.
PREDICTING ASYMMETRICAL LOWER EXTREMITY STRENGTH DEFICITS IN COLLEGE-AGED MEN AND WOMEN USING COMMON HORIZONTAL AND VERTICAL POWER FIELD TESTS: A POSSIBLE SCREENING MECHANISM DAVID W. KEELEY, HILLARY A.
DATA INTERPRETATION AND ANALYSIS
 DATA INTERPRETATION AND ANALYSIS Numerical and Curve Analysis Ref: Compendium of Isokinetics George Davies Report Parameters Peak Torque Highest muscular force output at any moment during a repetition.
DATA INTERPRETATION AND ANALYSIS Numerical and Curve Analysis Ref: Compendium of Isokinetics George Davies Report Parameters Peak Torque Highest muscular force output at any moment during a repetition.
A Study on the Norm-Referenced Criteria for Isokinetic Functional Strength of the Wrist for Junior Baseball Players
 Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 8(18), DOI: 10.17485/ijst/2015/v8i18/76239, August 2015 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 A Study on the Norm-Referenced Criteria for Isokinetic
Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 8(18), DOI: 10.17485/ijst/2015/v8i18/76239, August 2015 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 A Study on the Norm-Referenced Criteria for Isokinetic
ACL Injury Prevention: Considerations for Children and Adolescents
 ACL Injury Prevention: Considerations for Children and Adolescents Susan Sigward PhD, PT, ATC Human Performance Laboratory University of Southern California 1 ACL Injury Season ending/ Career ending 82%
ACL Injury Prevention: Considerations for Children and Adolescents Susan Sigward PhD, PT, ATC Human Performance Laboratory University of Southern California 1 ACL Injury Season ending/ Career ending 82%
Managing life s multi-tasking with kids; and the need for self care.
 Lessons on Staying in Shape After the Olympics While Working and being a Mom Deborah Saint-Phard, M.D. Director, CU Women's Sports Medicine Program at University of Colorado Hospital Associate Professor
Lessons on Staying in Shape After the Olympics While Working and being a Mom Deborah Saint-Phard, M.D. Director, CU Women's Sports Medicine Program at University of Colorado Hospital Associate Professor
Strength-Based Physiological profiles of NCAA Division I Womens Basketball and Gymnastics Athletes: Implications for Injury Risk Assessment
 Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU All Graduate Plan B and other Reports Graduate Studies 8-2017 Strength-Based Physiological profiles of NCAA Division I Womens Basketball and Gymnastics Athletes:
Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU All Graduate Plan B and other Reports Graduate Studies 8-2017 Strength-Based Physiological profiles of NCAA Division I Womens Basketball and Gymnastics Athletes:
To return-to-play or not to return-to-play: Assessing quadriceps strain in a professional soccer player
 To return-to-play or not to return-to-play: Assessing quadriceps strain in a professional soccer player Hembre, A. 1 and Eriksrud, O. 2 1 Apex klinikken, Oslo, Norway 2 1080 Motion AB, Stockholm, Sweden
To return-to-play or not to return-to-play: Assessing quadriceps strain in a professional soccer player Hembre, A. 1 and Eriksrud, O. 2 1 Apex klinikken, Oslo, Norway 2 1080 Motion AB, Stockholm, Sweden
5/13/2016. ACL I Risk Factors AAP Position Statement. Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injuries: Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention.
 ACL I Risk Factors AAP Position Statement Timothy E. Hewett, PhD 2016 Chicago Sports Medicine Symposium Chicago, Illinois August 5-7, 2016 2015 MFMER slide-1 Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injuries: Diagnosis,
ACL I Risk Factors AAP Position Statement Timothy E. Hewett, PhD 2016 Chicago Sports Medicine Symposium Chicago, Illinois August 5-7, 2016 2015 MFMER slide-1 Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injuries: Diagnosis,
Eccentric Knee-flexor Strength and Risk of Hamstring Injuries in Rugby Union: A
 1 TITLE 2 3 Eccentric Knee-flexor Strength and Risk of Hamstring Injuries in Rugby Union: A Prospective Study 4 5 6 Authors 7 Matthew N. Bourne 1, David A. Opar 2, Morgan D. Williams 3, Anthony J. Shield
1 TITLE 2 3 Eccentric Knee-flexor Strength and Risk of Hamstring Injuries in Rugby Union: A Prospective Study 4 5 6 Authors 7 Matthew N. Bourne 1, David A. Opar 2, Morgan D. Williams 3, Anthony J. Shield
V ORCID: (2017) ISSN
 This is a peer-reviewed, post-print (final draft post-refereeing) version of the following published document and is licensed under Creative Commons: Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 4.0 license:
This is a peer-reviewed, post-print (final draft post-refereeing) version of the following published document and is licensed under Creative Commons: Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 4.0 license:
Hamstring strains and prevention
 Research Center of Movement Science Department of Physiotherapy University of Iceland UIVERSITY OF ICELAD DEPARTMET OF PHYSIOTHERAPY Hamstring strains and prevention Árni Árnason PT, PhD University of
Research Center of Movement Science Department of Physiotherapy University of Iceland UIVERSITY OF ICELAD DEPARTMET OF PHYSIOTHERAPY Hamstring strains and prevention Árni Árnason PT, PhD University of
By: TEDDY W. WORRELL, MEd, PT, ATC, CRAID R. DENEGAR, PhD, ATC, SUSAN L. ARMSTRONG, MEd, ATC, and DAVID H. PERRIN, PhD, ATC
 Effect of Body Position on Hamstring Muscle Group Average Torque By: TEDDY W. WORRELL, MEd, PT, ATC, CRAID R. DENEGAR, PhD, ATC, SUSAN L. ARMSTRONG, MEd, ATC, and DAVID H. PERRIN, PhD, ATC Worrell, T.W.,
Effect of Body Position on Hamstring Muscle Group Average Torque By: TEDDY W. WORRELL, MEd, PT, ATC, CRAID R. DENEGAR, PhD, ATC, SUSAN L. ARMSTRONG, MEd, ATC, and DAVID H. PERRIN, PhD, ATC Worrell, T.W.,
Electrostimulation for Sport Training
 Electrostimulation for Sport Training abstracts collected by Globus Sport and Health Technologies The effects of electromyostimulation training and basketball practice on muscle strength and jumping ability;...
Electrostimulation for Sport Training abstracts collected by Globus Sport and Health Technologies The effects of electromyostimulation training and basketball practice on muscle strength and jumping ability;...
IJPHY. Effect of isometric quadriceps strengthening exercise at multiple angles in knee joint among normal adults. ABSTRACT ORIGINAL RESEARCH
 IJPHY ORIGINAL RESEARCH Effect of isometric quadriceps strengthening exercise at multiple angles in knee joint among normal adults. Jibi Paul 1 Pradeep Balakrishnan 2 ABSTRACT Introduction: Strengthening
IJPHY ORIGINAL RESEARCH Effect of isometric quadriceps strengthening exercise at multiple angles in knee joint among normal adults. Jibi Paul 1 Pradeep Balakrishnan 2 ABSTRACT Introduction: Strengthening
Comparison of Isokinetic Knee Flexion and Extension Strength between Trained Dancers and Traditional Sport Female Collegiate Athletes
 Original Research Comparison of Isokinetic Knee Flexion and Extension Strength between Trained Dancers and Traditional Sport Female Collegiate Athletes RACHELE E. VOGELPOHL 1, LYNN WOLZ* 1, TYLER NELTNER*
Original Research Comparison of Isokinetic Knee Flexion and Extension Strength between Trained Dancers and Traditional Sport Female Collegiate Athletes RACHELE E. VOGELPOHL 1, LYNN WOLZ* 1, TYLER NELTNER*
ACL and Knee Injury Prevention. Presented by: Zach Kirkpatrick, PT, MPT, SCS
 ACL and Knee Injury Prevention Presented by: Zach Kirkpatrick, PT, MPT, SCS ACL Anatomy ACL Mechanism of Injury Contact ACL Tear Noncontact ACL Tear ACL MOI and Pathology Common in young individual who
ACL and Knee Injury Prevention Presented by: Zach Kirkpatrick, PT, MPT, SCS ACL Anatomy ACL Mechanism of Injury Contact ACL Tear Noncontact ACL Tear ACL MOI and Pathology Common in young individual who
POST-ACTIVATION POTENTIATION AND VERTICAL JUMP PERFORMANCE. Cody Hardwick
 POST-ACTIVATION POTENTIATION AND VERTICAL JUMP PERFORMANCE Cody Hardwick Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements For the degree Master of Science in Kinesiology In the School of Public Health
POST-ACTIVATION POTENTIATION AND VERTICAL JUMP PERFORMANCE Cody Hardwick Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements For the degree Master of Science in Kinesiology In the School of Public Health
MEASURING BILATERAL ASYMMETRY IN A LONG TERM ATHLETE MONITORING
 MEASURING BILATERAL ASYMMETRY IN A LONG TERM ATHLETE MONITORING Kimitake Sato Department of Exercise and Sport Science, Center of Excellence for Sport Science and Coach Education, East Tennessee State
MEASURING BILATERAL ASYMMETRY IN A LONG TERM ATHLETE MONITORING Kimitake Sato Department of Exercise and Sport Science, Center of Excellence for Sport Science and Coach Education, East Tennessee State
Can Muscle Power Be Estimated From Thigh Bulk Measurements? A Preliminary Study
 Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 1999, 8.50-59 O 1999 Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. Can Muscle Power Be Estimated From Thigh Bulk Measurements? A Preliminary Study Eric Maylia, John A. Fairclough, Leonard
Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 1999, 8.50-59 O 1999 Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. Can Muscle Power Be Estimated From Thigh Bulk Measurements? A Preliminary Study Eric Maylia, John A. Fairclough, Leonard
CHANGES IN LOWER-LIMB MUSCLE FORCES WITH PROPHYLACTIC KNEE BRACING DURING LANDING AND STOP-JUMP TASKS
 CHANGES IN LOWER-LIMB MUSCLE FORCES WITH PROPHYLACTIC KNEE BRACING DURING LANDING AND STOP-JUMP TASKS Katie Ewing 1, Rezaul Begg 2, Peter Lee 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Melbourne,
CHANGES IN LOWER-LIMB MUSCLE FORCES WITH PROPHYLACTIC KNEE BRACING DURING LANDING AND STOP-JUMP TASKS Katie Ewing 1, Rezaul Begg 2, Peter Lee 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Melbourne,
Chapter 14 Training Muscles to Become Stronger
 Chapter 14 Training Muscles to Become Stronger Slide Show developed by: Richard C. Krejci, Ph.D. Professor of Public Health Columbia College 11.22.11 Objectives 1. Describe the following four methods to
Chapter 14 Training Muscles to Become Stronger Slide Show developed by: Richard C. Krejci, Ph.D. Professor of Public Health Columbia College 11.22.11 Objectives 1. Describe the following four methods to
Test-Retest Reliability of Isokinetic Knee Extension and Flexion
 626 ORIGINAL ARTICLE TestRetest Reliability of Isokinetic Knee Extension and Flexion Gisela Sole, BSc(Physio), MSc(Med), Jonas Hamrén, BSc(Physio), Stephan Milosavljevic, BAppSc(Physio), PhD, Helen Nicholson,
626 ORIGINAL ARTICLE TestRetest Reliability of Isokinetic Knee Extension and Flexion Gisela Sole, BSc(Physio), MSc(Med), Jonas Hamrén, BSc(Physio), Stephan Milosavljevic, BAppSc(Physio), PhD, Helen Nicholson,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE
 A STUDY TO ANALYSE THE ISOMETRIC STRENGTH AND ISOKINETIC PEAK TORQUES OF HAMSTRING AND QUADRICEPS AT DIFFERENT ANGLES AND ANGULAR VELOCITY OF KNEE USING ISOKINETIC DEVICE IN NORMAL INDIVIDUALS SHANTHI
A STUDY TO ANALYSE THE ISOMETRIC STRENGTH AND ISOKINETIC PEAK TORQUES OF HAMSTRING AND QUADRICEPS AT DIFFERENT ANGLES AND ANGULAR VELOCITY OF KNEE USING ISOKINETIC DEVICE IN NORMAL INDIVIDUALS SHANTHI
ISOKINETIC TESTING AND DATA INTERPRETATION
 ISOKINETIC TESTING AND DATA INTERPRETATION PRINCIPLES OF ISOKINETIC The principle behind Isokinetic exercise and testing is that the lever arm moves at a preset fixed speed allowing for accommodating resistance
ISOKINETIC TESTING AND DATA INTERPRETATION PRINCIPLES OF ISOKINETIC The principle behind Isokinetic exercise and testing is that the lever arm moves at a preset fixed speed allowing for accommodating resistance
The relationship between peak isokinetic torques of hip, knee and ankle joints with single and double leg jump performance in young men
 International Journal of Sport Studies. ISSN (online) 2251-7502 Vol., 6 (4), 227-232, 2016 www.ijssjournal.com The relationship between peak isokinetic torques of hip, knee and ankle joints with single
International Journal of Sport Studies. ISSN (online) 2251-7502 Vol., 6 (4), 227-232, 2016 www.ijssjournal.com The relationship between peak isokinetic torques of hip, knee and ankle joints with single
BARBELL HIP THRUST. Eckert, RM 1 and Snarr, RL 1,2
 Eckert, RM and Snarr, RL. Barbell hip thrust. J Sport Human Perf 2014;2(2):1-9. DOI: 10.12922/jshp.0037.2014 1 SHORT REPORT BARBELL HIP THRUST OPEN ACCESS Eckert, RM 1 and Snarr, RL 1,2 1 School of Nutrition
Eckert, RM and Snarr, RL. Barbell hip thrust. J Sport Human Perf 2014;2(2):1-9. DOI: 10.12922/jshp.0037.2014 1 SHORT REPORT BARBELL HIP THRUST OPEN ACCESS Eckert, RM 1 and Snarr, RL 1,2 1 School of Nutrition
EVALUATION OF KNEE FLEXORS AND EXTENSORS MUSCLE STRENGTH AFTER LIGAMENTOPLASTY FOR ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT AFTER 6 MONTHS OF SURGERY
 EVALUATION OF KNEE FLEXORS AND EXTENSORS MUSCLE STRENGTH AFTER LIGAMENTOPLASTY FOR ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT AFTER 6 MONTHS OF SURGERY Racha Hamad PT, MPT Student Department of Physical Therapy, Faculty
EVALUATION OF KNEE FLEXORS AND EXTENSORS MUSCLE STRENGTH AFTER LIGAMENTOPLASTY FOR ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT AFTER 6 MONTHS OF SURGERY Racha Hamad PT, MPT Student Department of Physical Therapy, Faculty
EMG Analysis of Lower Extremity Muscles in Three Different Squat Exercises
 REPORT EMG Analysis of Lower Extremity Muscles in Three Different Squat Exercises Gaston Ariel NISHIWAKI 1, Yukio URABE 1 and Kosuke TANAKA 1 1 Department of Sport Rehabilitation, Graduate School of Health
REPORT EMG Analysis of Lower Extremity Muscles in Three Different Squat Exercises Gaston Ariel NISHIWAKI 1, Yukio URABE 1 and Kosuke TANAKA 1 1 Department of Sport Rehabilitation, Graduate School of Health
Girls and Sports. Title IX. You Go Girl! : Female Athlete Hot Topics. Women in Sports
 You Go Girl! : Female Athlete Hot Topics Rebecca A. Demorest, MD Associate Director, Pediatric and Young Adult Sports Medicine Children s Hospital & Research Center Oakland rdemorest@mail.cho.org Girls
You Go Girl! : Female Athlete Hot Topics Rebecca A. Demorest, MD Associate Director, Pediatric and Young Adult Sports Medicine Children s Hospital & Research Center Oakland rdemorest@mail.cho.org Girls
Tennis places high biomechanical demands upon
 EFFECTS OF A SHOULDER INJURY PREVENTION STRENGTH TRAINING PROGRAM ON ECCENTRIC EXTERNAL ROTATOR MUSCLE STRENGTH AND GLENOHUMERAL JOINT IMBALANCE IN FEMALE OVERHEAD ACTIVITY ATHLETES YVONNE NIEDERBRACHT,
EFFECTS OF A SHOULDER INJURY PREVENTION STRENGTH TRAINING PROGRAM ON ECCENTRIC EXTERNAL ROTATOR MUSCLE STRENGTH AND GLENOHUMERAL JOINT IMBALANCE IN FEMALE OVERHEAD ACTIVITY ATHLETES YVONNE NIEDERBRACHT,
ELECTRICAL MUSCLE STIMULATION (EMS) IMPLEMENTATION IN EXPLOSIVE STRENGTH DEVELOPMENT
 Zoran Đokić, Bojan Međedović Fakultet za sport i turizam, Novi Sad UDK:796.012.11:615.84 ELECTRICAL MUSCLE STIMULATION (EMS) IMPLEMENTATION IN EXPLOSIVE STRENGTH DEVELOPMENT 1. INTRODUCTION Research on
Zoran Đokić, Bojan Međedović Fakultet za sport i turizam, Novi Sad UDK:796.012.11:615.84 ELECTRICAL MUSCLE STIMULATION (EMS) IMPLEMENTATION IN EXPLOSIVE STRENGTH DEVELOPMENT 1. INTRODUCTION Research on
Anthropometric and Physical Qualities of Elite Male Youth Rugby League Players
 Sports Med (2017) 47:2171 2186 DOI 10.1007/s40279-017-0745-8 REVIEW ARTICLE Anthropometric and Physical Qualities of Elite Male Youth Rugby League Players Kevin Till 1,2 Sean Scantlebury 1 Ben Jones 1,2,3
Sports Med (2017) 47:2171 2186 DOI 10.1007/s40279-017-0745-8 REVIEW ARTICLE Anthropometric and Physical Qualities of Elite Male Youth Rugby League Players Kevin Till 1,2 Sean Scantlebury 1 Ben Jones 1,2,3
Eccentric Hamstring Strength and Hamstring Injury Risk in Australian Footballers
 Eccentric Hamstring Strength and Hamstring Injury Risk in Australian Footballers DAVID A. OPAR 1, MORGAN D. WILLIAMS 2, RYAN G. TIMMINS 1, JACK HICKEY 3, STEVEN J. DUHIG 4, and ANTHONY J. SHIELD 4,5 1
Eccentric Hamstring Strength and Hamstring Injury Risk in Australian Footballers DAVID A. OPAR 1, MORGAN D. WILLIAMS 2, RYAN G. TIMMINS 1, JACK HICKEY 3, STEVEN J. DUHIG 4, and ANTHONY J. SHIELD 4,5 1
Relative Isometric Force of the Hip Abductor and Adductor Muscles
 Relative Isometric Force of the Hip Abductor and Adductor Muscles WARREN W. MAY, Captain, AMSC A-LTHOUGH THE CONCEPT of the muscular force curve is not new, its clinical application has been generally
Relative Isometric Force of the Hip Abductor and Adductor Muscles WARREN W. MAY, Captain, AMSC A-LTHOUGH THE CONCEPT of the muscular force curve is not new, its clinical application has been generally
Comparing Dominant and Non-Dominant Torque and Work using Biodex 3 Isokinetic Protocol for Knee Flexors and Extensors INTRODUCTION PURPOSE METHODS
 Comparing Dominant and Non-Dominant Torque and Work using Biodex 3 Isokinetic Protocol for Knee Flexors and Extensors Joshua R. Sparks B.S., ACSM HFS, BACCHUS PHE KINE 533C, Louisiana Tech University INTRODUCTION
Comparing Dominant and Non-Dominant Torque and Work using Biodex 3 Isokinetic Protocol for Knee Flexors and Extensors Joshua R. Sparks B.S., ACSM HFS, BACCHUS PHE KINE 533C, Louisiana Tech University INTRODUCTION
DIFFERENCES IN THE MECHANICS BETWEEN THE DOMINANT AND NON-DOMINANT PLANT LIMB DURING INSTEP SOCCER KICKING. Cassidy M. Berlin.
 DIFFERENCES IN THE MECHANICS BETWEEN THE DOMINANT AND NON-DOMINANT PLANT LIMB DURING INSTEP SOCCER KICKING by Cassidy M. Berlin A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree
DIFFERENCES IN THE MECHANICS BETWEEN THE DOMINANT AND NON-DOMINANT PLANT LIMB DURING INSTEP SOCCER KICKING by Cassidy M. Berlin A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree
Prediction of Hamstring injury in professional soccer players by isokinetic measurements
 Prediction of Hamstring injury in professional soccer players by isokinetic measurements Original article Marc Dauty Pierre Menu Alban Fouasson-Chaillou Sophie Ferréol Charles Dubois Department of Pôle
Prediction of Hamstring injury in professional soccer players by isokinetic measurements Original article Marc Dauty Pierre Menu Alban Fouasson-Chaillou Sophie Ferréol Charles Dubois Department of Pôle
The influence of soccer-specific fatigue on hip range of motion and peak isokinetic hip flexor torque in male soccer players
 Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate College 2011 The influence of soccer-specific fatigue on hip range of motion and peak isokinetic hip flexor torque in male soccer players Timothy William Robinson
Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate College 2011 The influence of soccer-specific fatigue on hip range of motion and peak isokinetic hip flexor torque in male soccer players Timothy William Robinson
Diane Vives, MS, CSCS, *D Owner, Fit4Austin, Austin, TX Member of the Board of Directors, NSCA
 Diane Vives, MS, CSCS, *D Owner, Fit4Austin, Austin, TX Member of the Board of Directors, NSCA 1. Introduction a. Through my experience as a strength coach over the last 11 years, I have often been faced
Diane Vives, MS, CSCS, *D Owner, Fit4Austin, Austin, TX Member of the Board of Directors, NSCA 1. Introduction a. Through my experience as a strength coach over the last 11 years, I have often been faced
Chapter 20: Test Administration and Interpretation
 Chapter 20: Test Administration and Interpretation Thought Questions Why should a needs analysis consider both the individual and the demands of the sport? Should test scores be shared with a team, or
Chapter 20: Test Administration and Interpretation Thought Questions Why should a needs analysis consider both the individual and the demands of the sport? Should test scores be shared with a team, or
PROFESSIONAL TENNIS PLAYERS
 INFLUENCE OF PHYSICAL TRAINING ON CORE MUSCLES IN PROFESSIONAL TENNIS PLAYERS Mara Estevez, PT, Cert. MDT 1 Alejandro R. Greco, PT 2 Santiago Gómez Argüello, PT, Cert. MDT 3 ABSTRACT Objective: To evaluate
INFLUENCE OF PHYSICAL TRAINING ON CORE MUSCLES IN PROFESSIONAL TENNIS PLAYERS Mara Estevez, PT, Cert. MDT 1 Alejandro R. Greco, PT 2 Santiago Gómez Argüello, PT, Cert. MDT 3 ABSTRACT Objective: To evaluate
STRENGTH MEASUREMENTS IN ATHLETES WITH GROIN PAIN
 STRENGTH MEASUREMENTS IN ATHLETES WITH GROIN PAIN Written by Kristian Thorborg, Denmark INTRODUCTION Hip and groin pain is a common problem often related to physical functioning and sports activities.
STRENGTH MEASUREMENTS IN ATHLETES WITH GROIN PAIN Written by Kristian Thorborg, Denmark INTRODUCTION Hip and groin pain is a common problem often related to physical functioning and sports activities.
Tittle: Velocity based training of lower limb to improve absolute and relative power
 Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research Publish Ahead of Print DOI: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000000407 Tittle: Velocity based training of lower limb to improve absolute and relative power outputs in concentric
Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research Publish Ahead of Print DOI: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000000407 Tittle: Velocity based training of lower limb to improve absolute and relative power outputs in concentric
Preventing Rehab with Prehab:
 Where Regional Athletes Succeed Western Region Academy of Sport Regional Athlete Coach Education 2015 Preventing Rehab with Prehab: Injury prevention with the FIFA+11 Rehab or Prehab? What s the difference
Where Regional Athletes Succeed Western Region Academy of Sport Regional Athlete Coach Education 2015 Preventing Rehab with Prehab: Injury prevention with the FIFA+11 Rehab or Prehab? What s the difference
MSc in Athletic Therapy
 NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES MSc in Athletic Therapy Research Paper: Sports Strength and Conditioning in conjunction with Therapy Arun Kumar 6/22/2015 Student Number: S140212 Topic: Sports Strength
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES MSc in Athletic Therapy Research Paper: Sports Strength and Conditioning in conjunction with Therapy Arun Kumar 6/22/2015 Student Number: S140212 Topic: Sports Strength
LOWER-EXTREMITY SIDE-TO-SIDE STRENGTH ASYMMETRY OF PROFESSIONAL SOCCER PLAYERS ACCORDING TO PLAYING POSITION
 LOWER-EXTREMITY SIDE-TO-SIDE STRENGTH ASYMMETRY OF PROFESSIONAL SOCCER PLAYERS ACCORDING TO PLAYING POSITION Cassio V. Ruas 1, Lee E. Brown 2, and Ronei S. Pinto 1 1 Federal University of Rio Grande do
LOWER-EXTREMITY SIDE-TO-SIDE STRENGTH ASYMMETRY OF PROFESSIONAL SOCCER PLAYERS ACCORDING TO PLAYING POSITION Cassio V. Ruas 1, Lee E. Brown 2, and Ronei S. Pinto 1 1 Federal University of Rio Grande do
***Note: Figures may be missing for this format of the document ***Note: Footnotes and endnotes indicated with brackets
 Isokinetic Strength of the Trunk and Hip in Female Runners By: Laurie L. Tis, MEd, ATC *, David H. Perrin, PhD, ATC, David B. Snead, PhD, Arthur Weltman University of Virginia and Washington University
Isokinetic Strength of the Trunk and Hip in Female Runners By: Laurie L. Tis, MEd, ATC *, David H. Perrin, PhD, ATC, David B. Snead, PhD, Arthur Weltman University of Virginia and Washington University
The effectiveness of different exercises protocols to prevent the incidence of hamstring injury in athletes
 Page 1 of 6 Training, Performance & Rehabilitation The effectiveness of different exercises protocols to prevent the incidence of hamstring injury in athletes F Naclerio*, M Goss-Sampson Abstract Introduction
Page 1 of 6 Training, Performance & Rehabilitation The effectiveness of different exercises protocols to prevent the incidence of hamstring injury in athletes F Naclerio*, M Goss-Sampson Abstract Introduction
Anterior Cruciate Ligament Rehabilitation. Rehab Summit Omni Orlando Resort at ChampionsGate Speaker: Terry Trundle, PTA, ATC, LAT
 Anterior Cruciate Ligament Rehabilitation Rehab Summit Omni Orlando Resort at ChampionsGate Speaker: Terry Trundle, PTA, ATC, LAT ACL Graft Selection 1. Autograft Bone-Patella Tendon Bone Hamstrings: Semitendinosus
Anterior Cruciate Ligament Rehabilitation Rehab Summit Omni Orlando Resort at ChampionsGate Speaker: Terry Trundle, PTA, ATC, LAT ACL Graft Selection 1. Autograft Bone-Patella Tendon Bone Hamstrings: Semitendinosus
ISOKINETIC ASSESSMENT OF THE FOREARM AND WRIST MUSCLES
 ISOKINETIC ASSESSMENT OF THE FOREARM AND WRIST MUSCLES B. FORTHOMME, J.L. CROISIER, M. FOIDART-DESSALLE, J.M. CRIELAARD Department of Physical Medicine, CHU Sart Tilman, Liege, Belgium 1 1. Introduction
ISOKINETIC ASSESSMENT OF THE FOREARM AND WRIST MUSCLES B. FORTHOMME, J.L. CROISIER, M. FOIDART-DESSALLE, J.M. CRIELAARD Department of Physical Medicine, CHU Sart Tilman, Liege, Belgium 1 1. Introduction
The isokinetic strength profile of quadriceps and hamstrings in elite volleyball players
 Isokinetics and Exercise Science 18 (2010) 31 37 31 DOI 10.3233/IES-2010-0365 IOS Press The isokinetic strength profile of quadriceps and hamstrings in elite volleyball players Vedran Hadzic a,, Tine Sattler
Isokinetics and Exercise Science 18 (2010) 31 37 31 DOI 10.3233/IES-2010-0365 IOS Press The isokinetic strength profile of quadriceps and hamstrings in elite volleyball players Vedran Hadzic a,, Tine Sattler
Comparative Effect of Three Modes of Plyometric Training on Leg Muscle Strength of University Male Students
 European Journal of Scientific Research ISSN 1450-216X Vol.31 No.4 (2009), pp.577-582 EuroJournals Publishing, Inc. 2009 http://www.eurojournals.com/ejsr.htm Comparative Effect of Three Modes of Plyometric
European Journal of Scientific Research ISSN 1450-216X Vol.31 No.4 (2009), pp.577-582 EuroJournals Publishing, Inc. 2009 http://www.eurojournals.com/ejsr.htm Comparative Effect of Three Modes of Plyometric
A Comparison of Plyometric Training Techniques for Improving Vertical Jump Ability and Energy Production
 Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 1998, 12(2), 85-89 1998 National Strength & Conditioning Association A Comparison of Plyometric Training Techniques for Improving Vertical Jump Ability and
Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 1998, 12(2), 85-89 1998 National Strength & Conditioning Association A Comparison of Plyometric Training Techniques for Improving Vertical Jump Ability and
KNEE AND LEG EXERCISE PROGRAM
 KNEE AND LEG EXERCISE PROGRAM These exercises are specifically designed to rehabilitate the muscles of the hip and knee by increasing the strength and flexibility of the involved leg. This exercise program
KNEE AND LEG EXERCISE PROGRAM These exercises are specifically designed to rehabilitate the muscles of the hip and knee by increasing the strength and flexibility of the involved leg. This exercise program
Analyses of Isokinetic and Closed Chain Movements for Hamstring Reciprocal Coactivation
 Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 2007, 16, 319-325 2007 Human Kinetics, Inc. Analyses of Isokinetic and Closed Chain Movements for Hamstring Reciprocal Coactivation John P. Miller and Ronald V. Croce Context:
Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 2007, 16, 319-325 2007 Human Kinetics, Inc. Analyses of Isokinetic and Closed Chain Movements for Hamstring Reciprocal Coactivation John P. Miller and Ronald V. Croce Context:
Reliability of two dimensional video assessment of frontal plane dynamic knee valgus during common athletic screening tasks
 Reliability of two dimensional video assessment of frontal plane dynamic knee valgus during common athletic screening tasks Munro, AG, Herrington, LC and Carolan, M Title Authors Type URL Reliability of
Reliability of two dimensional video assessment of frontal plane dynamic knee valgus during common athletic screening tasks Munro, AG, Herrington, LC and Carolan, M Title Authors Type URL Reliability of
The Risk Factors of Hamstring Strain Injury Induced by High-Speed Running
 Journal of Sports Science and Medicine (2018) 17, 650-655 http://www.jssm.org ` Research article The Risk Factors of Hamstring Strain Injury Induced by High-Speed Running Gaku Tokutake 1, Rieko Kuramochi
Journal of Sports Science and Medicine (2018) 17, 650-655 http://www.jssm.org ` Research article The Risk Factors of Hamstring Strain Injury Induced by High-Speed Running Gaku Tokutake 1, Rieko Kuramochi
Dynamic Stretching Program augmented by self-myofascial Release on Knee Flexion
 Dynamic Stretching Program augmented by self-myofascial Release on Knee Flexion Passive Motion and Sprint Speed Context: Stretching techniques as well as self-myofascial release (self-mfr) have recently
Dynamic Stretching Program augmented by self-myofascial Release on Knee Flexion Passive Motion and Sprint Speed Context: Stretching techniques as well as self-myofascial release (self-mfr) have recently
Muscular power is a basic constituent of neuromuscular SHORT-TERM EFFECTS OF SELECTED EXERCISE
 Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 2005, 19(1), 135 139 2005 National Strength & Conditioning Association SHORT-TERM EFFECTS OF SELECTED EXERCISE AND LOAD IN CONTRAST TRAINING ON VERTICAL JUMP
Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 2005, 19(1), 135 139 2005 National Strength & Conditioning Association SHORT-TERM EFFECTS OF SELECTED EXERCISE AND LOAD IN CONTRAST TRAINING ON VERTICAL JUMP
Journal of Sport Rehabilitation. The reliability of strength tests performed in elevated shoulder positions using a hand-held dynamometer
 The reliability of strength tests performed in elevated shoulder positions using a hand-held dynamometer Journal: Manuscript ID: JSR.2015-0034.R2 Manuscript Type: Technical Report Keywords: dynamometry,
The reliability of strength tests performed in elevated shoulder positions using a hand-held dynamometer Journal: Manuscript ID: JSR.2015-0034.R2 Manuscript Type: Technical Report Keywords: dynamometry,
Effect of Gravity Correction on Shoulder Average Force and Reciprocal Muscle Group Ratios
 Effect of Gravity Correction on Shoulder Average Force and Reciprocal Muscle Group Ratios By: David H. Perrin, PhD, ATC *, Evan V. Hellwig, PT, ATC, Laurie L. Tis, MeD, ATC, Byron S. Shenk, EdD Perrin,
Effect of Gravity Correction on Shoulder Average Force and Reciprocal Muscle Group Ratios By: David H. Perrin, PhD, ATC *, Evan V. Hellwig, PT, ATC, Laurie L. Tis, MeD, ATC, Byron S. Shenk, EdD Perrin,
Identify and describe each sub-component within the three primary components of plyometrics
 PLYOMETRICS THEORY AND APPLICATION LEARNING OBJECTIVES Define plyometrics and list the three primary components Identify and describe each sub-component within the three primary components of plyometrics
PLYOMETRICS THEORY AND APPLICATION LEARNING OBJECTIVES Define plyometrics and list the three primary components Identify and describe each sub-component within the three primary components of plyometrics
ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT RECONSTRUCTION REHABILITATION GUIDELINES
 ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT RECONSTRUCTION REHABILITATION GUIDELINES While there is no consensus on the best accelerated rehabilitation program or which specific surgical techniques result in the most favorable
ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT RECONSTRUCTION REHABILITATION GUIDELINES While there is no consensus on the best accelerated rehabilitation program or which specific surgical techniques result in the most favorable
Movement, Health & Exercise, 1(1), 39-48, 2012
 Movement, Health & Exercise, 1(1), 39-48, 2012 Introduction Although strength training is a widespread activity and forms an important part of training for many sports, little is known about optimum training
Movement, Health & Exercise, 1(1), 39-48, 2012 Introduction Although strength training is a widespread activity and forms an important part of training for many sports, little is known about optimum training
