Effect of Helicobacter pylori infection and its eradication on nutrition
|
|
|
- Daisy Greer
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2002; 16: Effect of Helicobacter pylori infection and its eradication on nutrition T. FURUTA*, N. SHIRAI*, F. XIAO*, M. TAKASHIMA* & H. HANAI *First Department of Medicine and Department of Endoscopic and Photodynamic Medicine, Hamamatsu University School of Medicine, Hamamatsu, Japan Accepted for publication 6 December 2001 SUMMARY Aims: To investigate the effects of Helicobacter pylori infection and eradication on nutrition. Methods: The body weight, height, blood pressure, gastric juice ph and fasting serum levels of glucose, total protein, albumin, total cholesterol and triglyceride were measured in H. pylori-positive and H. pylorinegative subjects, and the effect of eradication of H. pylori on these parameters was determined. The development of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease after treatment was also examined. Eight patients underwent a pancreatic function test before and after H. pylori eradication therapy. Results: The incidence of hypoproteinaemia in H. pylori-positive subjects was significantly higher than that in H. pylori-negative subjects. After eradication of H. pylori, the gastric juice ph values were significantly decreased, and the body weight and serum levels of total cholesterol, total protein and albumin were significantly increased. The incidence of hyperlipidaemia significantly increased and that of hypoproteinaemia significantly decreased in the group with eradication. Pancreatic function improved significantly after eradication of H. pylori. No significant changes in these parameters were observed in the group without eradication. Obese patients had a higher risk of the development of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease after eradication of H. pylori infection. Conclusions: The eradication of H. pylori appears to improve some nutritional parameters. INTRODUCTION A close relationship between Helicobacter pylori infection and upper gastrointestinal disorders has been demonstrated. The eradication of H. pylori infection improves histological gastritis, 1, 2 decreases the rate of recurrence of peptic ulcer disease, 3 5 cures some cases of gastric mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma 6 and prevents the recurrence of gastric cancer after resection of early disease. 7 Therefore, the eradication of H. pylori Correspondence to: Dr T. Furuta, First Department of Medicine, Hamamatsu University School of Medicine, , Handa-Yama, Hamamatsu, , Japan. furuta@hama-med.ac.jp in patients with gastroduodenal disorders has been widely performed throughout the world. The eradication of H. pylori infection has been reported to improve gastric acid secretion. 8, 9 Moreover, the occurrence of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GERD) after the eradication of H. pylori infection has recently 10, 11 been reported. The mechanism by which GERD occurs after the eradication of H. pylori infection is assumed to be related to the improvement of gastric acid secretion. 10, 11 Obesity is a well-known risk factor for the development of GERD Recently, hypoproteinaemia observed in Menetrier s disease has been reported to improve after the eradication of H. pylori infection However, few studies have been performed on the effect of H. pylori infection on nutrition. Ó 2002 Blackwell Science Ltd 799
2 800 T. FURUTA et al. On the basis of the background discussed above, we investigated nutritional parameters, such as body weight and serum levels of lipids and proteins, in H. pylori-positive and H. pylori-negative subjects and determined the changes in these parameters in patients who received H. pylori eradication therapy. We also performed a pancreatic function diagnostic test as a marker of digestive ability in some patients before and after H. pylori eradication therapy. The development of GERD after the eradication of H. pylori infection was also examined. Endoscopy and collection of samples During gastroduodenoscopy, 10 ml of gastric juice was aspirated through the suction channel of the endoscope and collected in a trap placed in the suction line. Routine inspection of the upper gastrointestinal tract was performed, and several biopsy specimens from both the antrum and the corpus of the greater curvature were obtained for rapid urease test, bacteriological culture and histology. The ph of the gastric juice was measured with a glass-electrode ph meter just after collection. 8 METHODS Subjects A total of 609 H. pylori-positive patients, with gastric ulcer (n ¼ 246), duodenal ulcer (n ¼ 232) or gastritis (n ¼ 131), were enrolled in the study. Their disorders were diagnosed on the basis of results of gastroduodenoscopy and histology. A total of 152 H. pylorinegative subjects, with no endoscopically proven lesions in the stomach, were also enrolled as controls. H. pylori infection was diagnosed on the basis of rapid urease test, culture and histology, as described below. The demographic and clinical characteristics of the subjects enrolled in the study are summarized in Table 1. The protocol was approved in advance by the Human Institutional Review Board of Hamamatsu University School of Medicine. Written informed consent for participation in the study was obtained from all subjects. Eradication of H. pylori Patients were treated with dual therapy with omeprazole, 20 mg b.d., and amoxicillin, 500 mg q.d.s., for 2 weeks (n ¼ 192), or triple therapy with omeprazole, 20 mg b.d., or lansoprazole, 30 mg b.d., clarithromycin, 200 mg t.d.s., and amoxicillin, 500 mg t.d.s., for 1 week (n ¼ 417). Success or failure of the eradication of H. pylori infection was determined on the basis of culture test, rapid urease test, histology, polymerase chain reaction and 13 C-urea breath test performed 1 month after treatment. 8 If any one of these tests yielded a positive result, failure to eliminate H. pylori infection was diagnosed. At the second endoscopy, the gastric juice ph was measured again. Nutritional parameters The body weight, height, blood pressure and fasting serum levels of glucose, total protein, albumin, total Table 1. Demographic and clinical characteristics and nutritional parameters in Helicobacter pylori-positive and H. pylori-negative subjects enrolled in this study Parameter H. pylori-positive (n ¼ 609) H. pylori-negative (n ¼ 152) P value Age (years) (mean ± s.e.) 48.0 ± ± 0.9 > 0.2 Male/female (n/n) 456/ /41 > 0.2 Height (cm) (mean ± s.e.) ± ± 0.6 > 0.2 Body weight (kg) (mean ± s.e.) 64.6 ± ± 1.0 > 0.2 BMI (kg/m 2 ) (mean ± s.e.) 22.8 ± ± Upper blood pressure (mmhg) (mean ± s.e.) ± ± 1.8 > 0.2 Lower blood pressure (mmhg) (mean ± s.e.) 75.6 ± ± 1.2 > 0.2 Total protein (g/dl) (mean ± s.e.) 7.02 ± ± Albumin (g/dl) (mean ± s.e.) 4.02 ± ± Total cholesterol (mg/dl) (mean ± s.e.) ± ± 2.3 > 0.2 Triglyceride (mg/dl) (mean ± s.e.) ± ± 10.5 > 0.2 FBS (mg/dl) (mean ± s.e.) 95.4 ± ± 1.9 > 0.2 Gastric juice ph (median with interquartile ranges) 3.00 ( ) 1.70 ( ) < BMI, body mass index; FBS, fasting blood sugar.
3 H. PYLORI ERADICATION AND NUTRITION 801 cholesterol and triglyceride were determined before and 1 year after treatment. The body mass index was calculated as BMI ¼ body weight (kg)/[height (m)] 2. Development of GERD We examined whether GERD developed after eradication therapy. When any oesophageal mucosal break was observed during second endoscopy or when patients complained of GERD symptoms, such as heartburn, within 1 year after treatment, the development of GERD was diagnosed. Pancreatic function test Eight patients with gastric adenoma and H. pylori infection, who underwent endoscopic mucosal resection of gastric adenoma, participated in another study. Before endoscopic mucosal resection, the pancreatic function test was performed in the standard manner. In brief, 500 mg of N-benzoyl-L-tyrosyl-p-aminobenzoic acid (corresponding to mg of p-aminobenzoic acid) was orally administered to the patients and urine was collected for 6 h after administration. p-aminobenzoic acid excreted in the urine during the 6-h period was measured. The result of the pancreatic function test was expressed as the ratio (%) of p-aminobenzoic acid excreted (mg) in the urine to the total administered (169.5 mg). After endoscopic mucosal resection, the patients were treated with lansoprazole, 30 mg b.d., clarithromycin, 200 mg t.d.s., and amoxicillin, 500 mg t.d.s., for 1 week to eradicate H. pylori infection. After treatment, the pancreatic function test was performed again in the same manner. Success or failure to eradicate H. pylori infection was determined on the basis of several tests performed 1 month after treatment as described above. Statistics All numerical values were expressed as the mean ± standard error (s.e.) or medians with interquartile ranges. To determine whether the male/female ratio, gastric juice ph, body weight, height, body mass index, blood pressure and fasting serum levels of glucose, total protein, albumin, total cholesterol and triglyceride differed between H. pylori-positive and H. pylori-negative subjects, Student s t-test, the Mann Whitney U-test and the chi-squared test were used. To determine whether these parameters and the pancreatic function test values were different before and after eradication therapy, as a function of eradication status, the paired t-test and Wilcoxon s signed rank test were used. Differences in the frequency of hyperlipidaemia and hypoproteinaemia between H. pylori-positive and H. pylori-negative groups or between groups with and without eradication after treatment were assessed by Fisher s exact test. All P values were two-sided: findings of P < 0.05 were considered to be significant. RESULTS Effect of H. pylori infection on nutritional parameters There were no statistically significant differences in body mass index and fasting serum levels of glucose, total protein and total cholesterol between H. pylori-positive and H. pylori-negative subjects (Figure 1). However, the frequency of hypoproteinaemia (total protein < 6.5 g/ ml) in H. pylori-positive subjects (7.2%, 44/609) was significantly higher than that in H. pylori-negative subjects (2.6%, 4/152). The median gastric juice ph in patients with hypoproteinaemia and H. pylori infection was 4.80 ( ), which was significantly higher Figure 1. The frequency of hypoproteinaemia in Helicobacter pylori-positive and H. pylori-negative subjects. The frequency of hypoproteinaemia (total protein (Tp) < 6.5 g/dl) in the H. pylori-positive group was significantly higher than that in the H. pylori-negative subjects.
4 802 T. FURUTA et al. than that in patients without hypoproteinaemia and with H. pylori infection (3.00; ) (P < ). Differences in gastric juice ph and nutritional parameters before and after eradication of H. pylori infection A total of 579 of 609 patients underwent second endoscopy to determine the success or failure of eradication of H. pylori infection 1 month after treatment, and a medical check 1 year later. We present the results for these 579 patients in order to analyse the effects of H. pylori eradication. The eradication of H. pylori infection was observed in 421 of the 579 patients. Before treatment, there were no significant differences in the gastric ulcer/duodenal ulcer/gastritis ratio, body weight, height, body mass index, blood pressure, gastric juice ph or serum levels of total protein, total cholesterol or triglyceride between the groups with and without eradication of H. pylori. In the group with eradication of H. pylori, gastric juice ph values were significantly decreased and the body weight and body mass index were significantly increased (Figures 2a c). However, no significant changes in these parameters were observed in the group without eradication. No significant changes in blood pressure were observed during the study period (1 year) in the groups with and without eradication of H. pylori (Figure 2d). Figure 2. Gastric juice ph (a), body weight (b), body mass index (c), blood pressure (d) and serum levels of fasting blood sugar (e), triglyceride (f), total cholesterol (g), total protein (h) and albumin (i) before and after Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy as a function of eradication status. The median gastric juice ph (a) was significantly decreased and the means of the body weight (b), body mass index (c) and serum levels of total cholesterol (g), total protein (h) and albumin (i) were significantly increased in the group with eradication of H. pylori. In the group without eradication of H. pylori, no significant changes in the parameters noted above were observed.
5 H. PYLORI ERADICATION AND NUTRITION 803 Fasting blood glucose levels were unchanged before and 1 year after treatment in the groups with and without eradication (Figure 2e). Serum triglyceride levels in the group with eradication tended to increase (Figure 2f), but not to a significant extent. On the other hand, serum total cholesterol levels significantly increased in the group with eradication of H. pylori (Figure 2g). No significant changes were observed in the group without eradication. Serum levels of total protein and albumin were also increased in the group with eradication of H. pylori, but not in the group without eradication. One year after treatment, total protein and albumin levels in the group with eradication were significantly higher than those in the group without eradication (Figure 2h,i). One year after treatment, the incidence of hypoproteinaemia (total protein < 6.5 g/dl) in the group with eradication was significantly lower than that in the group without eradication (Figure 3a), although no differences were observed before treatment. The serum cholesterol levels of 477 of 579 patients were less than 220 mg/dl before treatment. They were considered as non-hyperlipidaemic. Of the 477 non-hyperlipidaemic patients, 359 showed eradication of H. pylori. In47of these 359 patients, serum total cholesterol levels had increased to more than 220 mg/dl 1 year after the eradication of H. pylori. One hundred and eighteen of the 477 patients failed to show clearance of H. pylori infection. A serum cholesterol level higher than 220 mg/dl was observed in only two patients in this group 1 year after treatment (Figure 3b). Changes in pancreatic function test values Eradication of H. pylori was observed in seven of the eight patients who underwent pancreatic function tests before and after endoscopic mucosal resection and H. pylori eradication therapy. The results of the pancreatic function test significantly increased after treatment in the group with eradication of H. pylori (Figure 4). Development of GERD after eradication of H. pylori infection To determine whether GERD developed after treatment for H. pylori infection, 419 patients were assessed. Of the 366 patients with eradication of H. pylori, development of GERD was seen in 41. Of Figure 3. Incidence of hypoproteinaemia (a) and hyperlipidaemia (b) after treatment as a function of eradication status. The incidence of hypoproteinaemia (total protein (Tp) < 6.5 g/dl) in the group with eradication (0.95%) was significantly lower than that in the group without eradication (10.1%) (a). Before treatment, 477 patients were non-hyperlipidaemic (total cholesterol (T-cho) ¼ 220 mg/dl). Of these 477 patients, 359 had successful eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Of the 359 patients with eradication, 47 patients (13.1%) had become hyperlipidaemic, whereas only two patients had become hyperlipidaemic in the group without eradication of H. pylori (b).
6 804 T. FURUTA et al. H. pylori was lower than that of patients with GERD and H. pylori infection (Figure 5). DISCUSSION Figure 4. Results of the pancreatic function diagnostic test before and after Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy. The results of the pancreatic function test were significantly increased in patients with clearance of H. pylori infection. PABA, p-aminobenzoic acid. the 53 patients without eradication of H. pylori, four developed GERD. The median values of the gastric juice ph in patients with and without the development of GERD after eradication of H. pylori infection were 1.44 ( ) and 1.42 ( ), respectively (P > 0.2). The effect of obesity on the development of GERD after the eradication of H. pylori infection was also studied. The body mass index increased after eradication therapy in the groups with and without GERD development. However, the mean body mass index before and after treatment in the group with GERD development was significantly higher than that in the group without GERD development. Moreover, the body mass index of patients with the development of GERD after the eradication of We determined the effects of H. pylori infection and eradication on nutritional parameters, such as the body mass index and serum levels of proteins and lipids, and found that some of the parameters were affected by H. pylori infection and increased or improved after eradication. Moreover, results of pancreatic function testing revealed that the digestive ability improved after the eradication of H. pylori in some patients. Because most peptic ulcer diseases do not recur and the symptoms of some patients with non-ulcer dyspepsia 3 5, 18 are relieved after the eradication of H. pylori, appetite may be restored and improved after the eradication of H. pylori infection and this might contribute to the improvement of nutritional parameters. However, the results of the pancreatic function test in this study suggest another factor: improvement of digestive ability after eradication of H. pylori. Therefore, we assume that nutritional parameters, such as serum levels of total cholesterol and proteins, will improve even if the amount of food intake or appetite remains unchanged after the eradication of H. pylori infection because of improved digestion and absorption. In this study, the incidence of hypoproteinaemia was significantly higher in H. pylori-positive subjects than in H. pylori-negative subjects and was significantly decreased after the eradication of H. pylori. Recently, the hypoproteinaemia observed in Menetrier s disease, which is characterized by enlarged fold gastritis, has Figure 5. Changes in body mass index (BMI) in the groups with and without gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GERD) development as a function of eradication status. BMI values were significantly increased in the group with eradication of H. pylori irrespective of GERD development. The mean BMI value of the group with GERD development after the eradication of H. pylori infection was significantly higher than that of the group without GERD development after the eradication of H. pylori infection. The BMI value of the group with GERD development and H. pylori infection was higher than that of any of the other groups before and after treatment. GERD (+), development of GERD after treatment; GERD ( ), no development of GERD after treatment.
7 H. PYLORI ERADICATION AND NUTRITION 805 been reported to improve after the eradication of H. pylori infection As the enlarged folds of Menetrier s disease improve after the eradication of H. pylori, leakage of proteins from the gastric wall decreases, resulting in an improvement of serum protein levels. However, the hypoproteinaemia observed in Menetrier s disease cannot be explained by the leakage of proteins from the gastric wall alone, because the leaked proteins should be digested and re-absorbed in the small intestine. This suggests that the digestion and absorption of proteins are disturbed in patients with Menetrier s disease. Consequently, leaked proteins cannot be digested or re-absorbed sufficiently in the small intestine, which might contribute to the pathogenesis of hypoproteinaemia in Menetrier s disease. After the eradication of H. pylori infection, this impaired digestive and absorptive ability is improved, resulting in the restoration of serum protein levels. In this study, the frequency of hypoproteinaemia was significantly higher in H. pylori-positive subjects and decreased to the levels found in H. pylori-negative subjects on eradication of H. pylori. Similarly, serum levels of cholesterol and the frequency of hyperlipidaemia were increased after the eradication of H. pylori. Therefore, the eradication of H. pylori appears to contribute to an improvement or increase in certain nutritional parameters. As shown by the results of the PFD test in this study, the eradication of H. pylori restores digestive and absorptive ability, which may contribute to the improvement or increase in nutritional parameters. Although we cannot offer an appropriate explanation for the decreased digestive or absorptive ability observed in some H. pylori-positive subjects, we assume that impaired acid secretion by H. pylori infection might be involved, because the median gastric juice ph of patients with hypoproteinaemia was much higher (4.80) than that of the group with normal protein levels. The occurrence of GERD after the eradication of H. pylori infection has been reported. 10, 11 One of the main causes of the development of GERD after the eradication of H. pylori infection has been reported to be the restoration of acid secretion. 10, 19 In this study, the gastric juice ph was decreased after the eradication of H. pylori infection. Therefore, an increase in gastric acidity after the eradication of H. pylori infection must have contributed to the development of GERD. In other words, the increase in the acidity of the gastric juice refluxed from the stomach to the oesophagus must be one of the important factors for GERD development after the eradication of H. pylori infection, as previously reported. However, an increase in gastric 10, 19 juice acidity (i.e. decrease in gastric juice ph) after the eradication of H. pylori infection was observed in patients with and without the development of GERD. Therefore, other determinants must exist. In this study, the pre- and post-treatment body mass indices of the group with GERD development were significantly higher than those of the group without GERD development. Therefore, obesity may be one of the cofactors associated with the development of GERD after the eradication of H. pylori infection, and obese patients may have a higher risk of the development of GERD after the eradication of H. pylori infection. Moreover, the mean pre- and post-treatment body mass indices of patients who developed GERD after the eradication of H. pylori infection were lower than those of H. pylori-positive patients with GERD, which suggests that the eradication of H. pylori infection seems to lower the threshold level of obesity for the development of GERD. The findings of this study suggest the possibility that the eradication of H. pylori increases the incidence of hyperlipidaemia and obesity and decreases the incidence of hypoproteinaemia. Increases in body weight, serum cholesterol and protein levels are associated with increased risk of the development of arteriosclerosis, hypertension, thrombosis and other related disorders, as well as GERD, although it was unclear during the short study period whether the eradication of H. pylori leads to an increased incidence of such disorders other than GERD. Therefore, long-term follow-up is recommended for patients after the eradication of H. pylori. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This study was supported by grants-in-aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Science and Sports of Japan ( ). The abstract of this manuscript was presented at the annual meeting of the American Gastroenterological Association held in Atlanta in May, We thank Dr Yves Pommier (Chief of the Laboratory of Molecular Pharmacology, National Cancer Institute, NIH) for his critical review of the manuscript and useful suggestions. The assistance of Drs Munetaka Sano, Makoto Kodaira, Hajime Arai and Yoshihiko Sato was greatly appreciated.
8 806 T. FURUTA et al. REFERENCES 1 Blaser MJ. Hypothesis on the pathogenesis and natural history of Helicobacter pylori-induced inflammation. Gastroenterology 1992; 102: Goodwin CS, Mendall MM, Northfield TC. Helicobacter pylori infection. Lancet 1997; 349: Graham DY, Lew GM, Klein PD, et al. Effect of treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection on the long-term recurrence of gastric or duodenal ulcer. A randomized, controlled study. Ann Intern Med 1992; 116: Soll AH. Consensus conference. Medical treatment of peptic ulcer disease. Practice guidelines. Practice Parameters Committee of the American College of Gastroenterology. J Am Med Assoc 1996; 275: Marshall BJ, Goodwin CS, Warren JR, et al. Prospective double-blind trial of duodenal ulcer relapse after eradication of Campylobacter pylori. Lancet 1988; 2: Wotherspoon AC, Doglioni C, Diss TC, et al. Regression of primary low-grade B-cell gastric lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue type after eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Lancet 1993; 342: Uemura N, Mukai T, Okamoto S, et al. Effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on subsequent development of cancer after endoscopic resection of early gastric cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 1997; 6: Furuta T, Baba S, Takashima M, et al. Effect of Helicobacter pylori infection on gastric juice ph. Scand J Gastroenterol 1998; 33: El-Omar EM, Oien K, El-Nujumi A, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection and chronic gastric acid hyposecretion. Gastroenterology 1997; 113: Labenz J, Blum AL, Bayerdorffer E, Meining A, Stolte M, Borsch G. Curing Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with duodenal ulcer may provoke reflux esophagitis. Gastroenterology 1997; 112: Hamada H, Haruma K, Mihara M, et al. High incidence of reflux esophagitis after eradication therapy for Helicobacter pylori: impact of hiatal hernia and corpus gastritis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2000; 14: Locke GR, Talley NJ, Fett SL, et al. Risk factors associated with symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux. Am J Med 1999; 106: Fisher BL, Pennathur A, Mutnick JL, Little AG. Obesity correlates with gastroesophageal reflux. Dig Dis Sci 1999; 44: Wilson LJ, Ma W, Hirschowitz BI. Association of obesity with hiatal hernia and esophagitis. Am J Gastroenterol 1999; 94(10): Badov D, Lambert JR, Finlay M, Balazs ND. Helicobacter pylori as a pathogenic factor in Menetrier s disease. Am J Gastroenterol 1998; 93: Shimoyama T, Fukuda S, Tanaka M, et al. Healing of cimetidineresistant Menetrier s disease by eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection. J Clin Gastroenterol 1998; 27: Kawasaki M, Hizawa K, Aoyagi K, Nakamura S, Fujishima M. Menetrier s disease associated with Helicobacter pylori infection: resolution of enlarged gastric folds and hypoproteinemia after antibacterial treatment. Am J Gastroenterol 1997; 92: McColl K, Murray L, El-Omar E, et al. Symptomatic benefit from eradicating Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with nonulcer dyspepsia. N Engl J Med 1998; 339: Koike T, Ohara S, Sekine H, et al. Increased gastric acid secretion after Helicobacter pylori eradication may be a factor for developing reflux oesophagitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2001; 15:
Esophageal Adenocarcinoma Developing after Eradication of Helicobacter pylori
 355 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 License (www.karger.com/oa-license), applicable to the online version of the
355 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 License (www.karger.com/oa-license), applicable to the online version of the
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen
 PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a publisher's version. For additional information about this publication click this link. http://hdl.handle.net/2066/48400
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a publisher's version. For additional information about this publication click this link. http://hdl.handle.net/2066/48400
Assessment of symptomatic response as predictor of Helicobacter pylori status following eradication therapy in patients with ulcer
 618 University Department of Medicine and Therapeutics, Western Infirmary, Glasgow G11 6NT, UK K E L McColl A El-Nujumi L S Murray E M El-Omar A Dickson A W Kelman T E Hilditch Correspondence to: Professor
618 University Department of Medicine and Therapeutics, Western Infirmary, Glasgow G11 6NT, UK K E L McColl A El-Nujumi L S Murray E M El-Omar A Dickson A W Kelman T E Hilditch Correspondence to: Professor
Increased gastric acid secretion after Helicobacter pylori eradication may be a factor for developing re ux oesophagitis
 Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2001; 15: 813±820. Increased gastric acid secretion after Helicobacter pylori eradication may be a factor for developing re ux oesophagitis T. KOIKE, S. OHARA, H. SEKINE, K. IIJIMA,
Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2001; 15: 813±820. Increased gastric acid secretion after Helicobacter pylori eradication may be a factor for developing re ux oesophagitis T. KOIKE, S. OHARA, H. SEKINE, K. IIJIMA,
COMPARISON OF ONCE-A-DAY VERSUS TWICE-A-DAY CLARITHROMYCIN IN TRIPLE THERAPY FOR HELICOBACTER PYLORI ERADICATION
 Phil J Gastroenterol 2006; 2: 25-29 COMPARISON OF ONCE-A-DAY VERSUS TWICE-A-DAY CLARITHROMYCIN IN TRIPLE THERAPY FOR HELICOBACTER PYLORI ERADICATION Marianne P Collado, Ma Fatima P Calida, Peter P Sy,
Phil J Gastroenterol 2006; 2: 25-29 COMPARISON OF ONCE-A-DAY VERSUS TWICE-A-DAY CLARITHROMYCIN IN TRIPLE THERAPY FOR HELICOBACTER PYLORI ERADICATION Marianne P Collado, Ma Fatima P Calida, Peter P Sy,
Empirical prescribing for dyspepsia: randomised controlled trial of test and treat versus omeprazole treatment Abstract Objective Design Setting
 Empirical prescribing for dyspepsia: randomised controlled trial of test and treat versus omeprazole treatment Gianpiero Manes, Antonella Menchise, Claudio de Nucci, Antonio Balzano Abstract Objective
Empirical prescribing for dyspepsia: randomised controlled trial of test and treat versus omeprazole treatment Gianpiero Manes, Antonella Menchise, Claudio de Nucci, Antonio Balzano Abstract Objective
Risk Factors for Helicobacter pylori Infection and Endoscopic Reflux Esophagitis in Healthy Young Japanese Volunteers
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.8669-16 Intern Med 56: 2979-2983, 2017 http://internmed.jp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Risk Factors for Helicobacter pylori Infection and Endoscopic Reflux in Healthy Young Japanese
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.8669-16 Intern Med 56: 2979-2983, 2017 http://internmed.jp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Risk Factors for Helicobacter pylori Infection and Endoscopic Reflux in Healthy Young Japanese
High use of maintenance therapy after triple therapy regimes in Ireland
 High use of maintenance therapy after triple therapy regimes in Ireland K Bennett, H O Connor, M Barry, C O Morain, J Feely Department of Pharmacology & Therapeutics Department of Gastroenterology Trinity
High use of maintenance therapy after triple therapy regimes in Ireland K Bennett, H O Connor, M Barry, C O Morain, J Feely Department of Pharmacology & Therapeutics Department of Gastroenterology Trinity
Helicobacter 2008;13:1-6. Am J Gastroent 2007;102: Am J of Med 2004;117:31-35.
 An Update on Helicobacter pylori and Its Treatment Trenika Mitchell, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Assistant Professor University of Kentucky College of Pharmacy October 18, 2008 Objectives Review the epidemiology
An Update on Helicobacter pylori and Its Treatment Trenika Mitchell, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Assistant Professor University of Kentucky College of Pharmacy October 18, 2008 Objectives Review the epidemiology
Helicobacter pylori: Diagnosis, treatment and risks of untreated infection
 Helicobacter pylori: Diagnosis, treatment and risks of untreated infection Klaus Mönkemüller Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology und Infectius Diseases Otto-von-Guericke University, Magdeburg bb
Helicobacter pylori: Diagnosis, treatment and risks of untreated infection Klaus Mönkemüller Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology und Infectius Diseases Otto-von-Guericke University, Magdeburg bb
Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection
 Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection Epidemiology of H. pylori infection (North America) Which are the high risk groups? Epidemiology of H. pylori infection (North America) Which are the high risk
Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection Epidemiology of H. pylori infection (North America) Which are the high risk groups? Epidemiology of H. pylori infection (North America) Which are the high risk
The Risk Factors and Quality of Life in Patients with Overlapping Functional Dyspepsia or Peptic Ulcer Disease with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
 Gut and Liver, Vol. 8, No. 2, March 2014, pp. 160-164 ORiginal Article The Risk Factors and Quality of Life in Patients with Overlapping Functional Dyspepsia or Peptic Ulcer Disease with Gastroesophageal
Gut and Liver, Vol. 8, No. 2, March 2014, pp. 160-164 ORiginal Article The Risk Factors and Quality of Life in Patients with Overlapping Functional Dyspepsia or Peptic Ulcer Disease with Gastroesophageal
KEYWORDS Dyspepsia, Acid Peptic Disease, Helicobacter Pylori, Urease, Giemsa, Peptic Ulcer, Non-Ulcer Dyspepsia.
 INCIDENCE OF HELICOBACTER PYLORI WITH ACID PEPTIC DISEASE AND MALIGNANT CONDITIONS OF UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT IN A TERTIARY CENTRE - A PROSPECTIVE STUDY Karunamoorthy Rajachidambaram 1, Dinkaran Kaarthesan
INCIDENCE OF HELICOBACTER PYLORI WITH ACID PEPTIC DISEASE AND MALIGNANT CONDITIONS OF UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT IN A TERTIARY CENTRE - A PROSPECTIVE STUDY Karunamoorthy Rajachidambaram 1, Dinkaran Kaarthesan
Management of dyspepsia and of Helicobacter pylori infection
 Management of dyspepsia and of Helicobacter pylori infection The University of Nottingham John Atherton Wolfson Digestive Diseases Centre University of Nottingham, UK Community management of dyspepsia
Management of dyspepsia and of Helicobacter pylori infection The University of Nottingham John Atherton Wolfson Digestive Diseases Centre University of Nottingham, UK Community management of dyspepsia
What is the status of Sequential Therapy Versus Standard Triple- Drug Therapy in peptic ulcer disease in eradicating H pylori?
 What is the status of Sequential Therapy Versus Standard Triple- Drug Therapy in peptic ulcer disease in eradicating H pylori? Sequential Therapy Versus Standard Triple- Drug Therapy for Helicobacter pylori
What is the status of Sequential Therapy Versus Standard Triple- Drug Therapy in peptic ulcer disease in eradicating H pylori? Sequential Therapy Versus Standard Triple- Drug Therapy for Helicobacter pylori
Corpus gastritis is protective against reflux oesophagitis
 Gut 1999;45:181 185 181 Corpus is protective against reflux H B El-Serag, A Sonnenberg, M M Jamal, J M Inadomi, L A Crooks, R M Feddersen Department of Veterans AVairs Medical Centre, University of New
Gut 1999;45:181 185 181 Corpus is protective against reflux H B El-Serag, A Sonnenberg, M M Jamal, J M Inadomi, L A Crooks, R M Feddersen Department of Veterans AVairs Medical Centre, University of New
Helicobacter Pylori Testing HELICOBACTER PYLORI TESTING HS-131. Policy Number: HS-131. Original Effective Date: 9/17/2009
 Easy Choice Health Plan, Inc. Harmony Health Plan of Illinois, Inc. Missouri Care, Inc. Ohana Health Plan, a plan offered by WellCare Health Insurance of Arizona, Inc. WellCare Health Insurance of Illinois,
Easy Choice Health Plan, Inc. Harmony Health Plan of Illinois, Inc. Missouri Care, Inc. Ohana Health Plan, a plan offered by WellCare Health Insurance of Arizona, Inc. WellCare Health Insurance of Illinois,
Eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection induces an increase in body mass index
 Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2002; 16 (Suppl. 2): 240 244. Eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection induces an increase in body mass index T. AZUMA, H. SUTO*, Y. ITO*, A. MURAMATSU*, M. OHTANI*, M. DOJO*,
Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2002; 16 (Suppl. 2): 240 244. Eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection induces an increase in body mass index T. AZUMA, H. SUTO*, Y. ITO*, A. MURAMATSU*, M. OHTANI*, M. DOJO*,
Helicobacter pylori infection: several studies on epidemiology, eradication and gastric epithelial cell turnover Liu, W.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Helicobacter pylori infection: several studies on epidemiology, eradication and gastric epithelial cell turnover Liu, W. Link to publication Citation for published
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Helicobacter pylori infection: several studies on epidemiology, eradication and gastric epithelial cell turnover Liu, W. Link to publication Citation for published
The usual dose is 40 mg daily with amoxycillin 1.5 g (750 mg b.d.) for 2 weeks. Up to 2 g/day of amoxycillin has been used in clinical trials.
 Name Gasec - 2 Gastrocaps Composition Gasec-20 Gastrocaps Each Gastrocaps contains: Omeprazole 20 mg (in the form of enteric-coated pellets) Properties, effects Proton Pump Inhibitor Omeprazole belongs
Name Gasec - 2 Gastrocaps Composition Gasec-20 Gastrocaps Each Gastrocaps contains: Omeprazole 20 mg (in the form of enteric-coated pellets) Properties, effects Proton Pump Inhibitor Omeprazole belongs
The Association and Clinical Implications of Gastroesophgeal Reflux Disease and H. pylori
 The Association and Clinical Implications of Gastroesophgeal Reflux Disease and H. pylori Maxwell M. Chait The relationship between GERD and H. pylori is complex and negatively associated with important
The Association and Clinical Implications of Gastroesophgeal Reflux Disease and H. pylori Maxwell M. Chait The relationship between GERD and H. pylori is complex and negatively associated with important
Endoscopic atrophic classification before and after H. pylori eradication is closely associated with histological atrophy and intestinal metaplasia
 E311 before and after H. pylori eradication is closely associated with histological atrophy and intestinal metaplasia Authors Institution Masaaki Kodama, Tadayoshi Okimoto, Ryo Ogawa, Kazuhiro Mizukami,
E311 before and after H. pylori eradication is closely associated with histological atrophy and intestinal metaplasia Authors Institution Masaaki Kodama, Tadayoshi Okimoto, Ryo Ogawa, Kazuhiro Mizukami,
Characteristics of patients with erosive and nonerosive GERD in high-helicobacter-pylori prevalence region
 Diseases of the Esophagus (2004) 17, 223 227 2004 ISDE Blackwell Publishing, Ltd. Original article Characteristics of patients with erosive and nonerosive GERD in high-helicobacter-pylori prevalence region
Diseases of the Esophagus (2004) 17, 223 227 2004 ISDE Blackwell Publishing, Ltd. Original article Characteristics of patients with erosive and nonerosive GERD in high-helicobacter-pylori prevalence region
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Time Covering Eradication for All Patients Infected with Helicobacter pylori in Japan
 Review Published online: January 14, 216 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Time Covering Eradication for All Patients Infected with Helicobacter pylori in Mitsushige Sugimoto a, c Takahiro Uotani c, e
Review Published online: January 14, 216 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Time Covering Eradication for All Patients Infected with Helicobacter pylori in Mitsushige Sugimoto a, c Takahiro Uotani c, e
Proton Pump Inhibitors Drug Class Prior Authorization Protocol
 Proton Pump Inhibitors Drug Class Prior Authorization Protocol Line of Business: Medi-Cal P&T Approval Date: November 15, 2017 Effective Date: January 1, 2018 This policy has been developed through review
Proton Pump Inhibitors Drug Class Prior Authorization Protocol Line of Business: Medi-Cal P&T Approval Date: November 15, 2017 Effective Date: January 1, 2018 This policy has been developed through review
Module 2 Heartburn Glossary
 Absorption Antacids Antibiotic Module 2 Heartburn Glossary Barrett s oesophagus Bloating Body mass index Burping Chief cells Colon Digestion Endoscopy Enteroendocrine cells Epiglottis Epithelium Absorption
Absorption Antacids Antibiotic Module 2 Heartburn Glossary Barrett s oesophagus Bloating Body mass index Burping Chief cells Colon Digestion Endoscopy Enteroendocrine cells Epiglottis Epithelium Absorption
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for 2005
 The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for 2005 jointly to Barry J. Marshall and J. Robin Warren for their discovery of "the bacterium Helicobacter pylori and its role in gastritis and peptic ulcer
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for 2005 jointly to Barry J. Marshall and J. Robin Warren for their discovery of "the bacterium Helicobacter pylori and its role in gastritis and peptic ulcer
Gastric mucosal status in patients with reflux esophagitis
 Gastric mucosal status in patients with reflux esophagitis Riyadh Mohamad Hasan 1, Batool Mutar Mahdi 2 1. Department of Surgery, Al-Kindy College of Medicine, University of Baghdad, Iraq 2. Department
Gastric mucosal status in patients with reflux esophagitis Riyadh Mohamad Hasan 1, Batool Mutar Mahdi 2 1. Department of Surgery, Al-Kindy College of Medicine, University of Baghdad, Iraq 2. Department
GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS. Submitted by: Shaema M. Ali
 GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS Submitted by: Shaema M. Ali GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS by: Shaema M. Ali There are four common medical conditions involving the GI system 1) peptic ulcers
GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS Submitted by: Shaema M. Ali GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS by: Shaema M. Ali There are four common medical conditions involving the GI system 1) peptic ulcers
Comparative study of invasive methods for diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori in humans
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 2 Number 7 (2013) pp. 63-68 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Comparative study of invasive methods for diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori in humans V.Subbukesavaraja
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 2 Number 7 (2013) pp. 63-68 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Comparative study of invasive methods for diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori in humans V.Subbukesavaraja
Rpts. GENERAL General Schedule (Code GE) Program Prescriber type: Dental Medical Practitioners Nurse practitioners Optometrists Midwives
 Esomeprazole 20mg Name, Restriction, Manner of esomeprazole 20 mg enteric tablet, 30 (8886Q) (029W) Gastric ulcer Peptic ulcer Treatment Phase: Initial treatment The therapy must be for initial treatment
Esomeprazole 20mg Name, Restriction, Manner of esomeprazole 20 mg enteric tablet, 30 (8886Q) (029W) Gastric ulcer Peptic ulcer Treatment Phase: Initial treatment The therapy must be for initial treatment
헬리코박터파일로리감염에서고용량및다빈도덱스란소프라졸과아모시실린이중치료 : 단일군전향연구
 Korean J Gastroenterol Vol. 70 No. 4, 176-180 https://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2017.70.4.176 pissn 1598-9992 eissn 2233-6869 ORIGINAL ARTICLE 헬리코박터파일로리감염에서고용량및다빈도덱스란소프라졸과아모시실린이중치료 : 단일군전향연구 박혜윤, 강은정, 김동근, 김기주,
Korean J Gastroenterol Vol. 70 No. 4, 176-180 https://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2017.70.4.176 pissn 1598-9992 eissn 2233-6869 ORIGINAL ARTICLE 헬리코박터파일로리감염에서고용량및다빈도덱스란소프라졸과아모시실린이중치료 : 단일군전향연구 박혜윤, 강은정, 김동근, 김기주,
Epidemiology of Peptic Ulcer Disease
 Epidemiology of Peptic Ulcer Disease Introduction Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD) is disruption of the mucosal integrity of the stomach and/or duodenum leading to a local defect or excavation due to active
Epidemiology of Peptic Ulcer Disease Introduction Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD) is disruption of the mucosal integrity of the stomach and/or duodenum leading to a local defect or excavation due to active
Helicobacter Connections. Barry Marshall
 Helicobacter Connections Barry Marshall The greatest obstacle to knowledge is not ignorance, it is the illusion of knowledge. Daniel Boorstein - Historian Peptic Ulcers Duodenal Ulcer (DU) Gastric Ulcer
Helicobacter Connections Barry Marshall The greatest obstacle to knowledge is not ignorance, it is the illusion of knowledge. Daniel Boorstein - Historian Peptic Ulcers Duodenal Ulcer (DU) Gastric Ulcer
ACG Clinical Guideline: Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection
 ACG Clinical Guideline: Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection William D. Chey, MD, FACG 1, Grigorios I. Leontiadis, MD, PhD 2, Colin W. Howden, MD, FACG 3 and Steven F. Moss, MD, FACG 4 1 Division
ACG Clinical Guideline: Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection William D. Chey, MD, FACG 1, Grigorios I. Leontiadis, MD, PhD 2, Colin W. Howden, MD, FACG 3 and Steven F. Moss, MD, FACG 4 1 Division
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: helicobacter_pylori_testing 01/01/2019 N/A 01/01/2020 01/01/2019 Policy Effective April 1, 2019 Description
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: helicobacter_pylori_testing 01/01/2019 N/A 01/01/2020 01/01/2019 Policy Effective April 1, 2019 Description
Eradication of H. pylori Infection in Patients Allergic to Penicillin Using Triple Therapy with a PPI, Metronidazole and Sitafloxacin
 CASE REPORT Eradication of H. pylori Infection in Patients Allergic to Penicillin Using Triple Therapy with a PPI, Metronidazole and Sitafloxacin Takahisa Furuta 1, Mitsushige Sugimoto 2, Mihoko Yamade
CASE REPORT Eradication of H. pylori Infection in Patients Allergic to Penicillin Using Triple Therapy with a PPI, Metronidazole and Sitafloxacin Takahisa Furuta 1, Mitsushige Sugimoto 2, Mihoko Yamade
Duodenal Ulcer And Other Gastro-intestinal Conditions By Sir Adolphe Abrahams
 Duodenal Ulcer And Other Gastro-intestinal Conditions By Sir Adolphe Abrahams If searching for a ebook by Sir Adolphe Abrahams Duodenal Ulcer and Other Gastro-intestinal Conditions in pdf format, then
Duodenal Ulcer And Other Gastro-intestinal Conditions By Sir Adolphe Abrahams If searching for a ebook by Sir Adolphe Abrahams Duodenal Ulcer and Other Gastro-intestinal Conditions in pdf format, then
Acid-Peptic Diseases of the Stomach and Duodenum Including Helicobacter pylori and NSAIDs Prof. Sheila Crowe
 Acid-Peptic Diseases of the Stomach and Duodenum Including Helicobacter pylori and NSAIDs 1 Division of Gastroenterology UC San Diego School of Medicine Clinical presentations of Helicobacter pylori infection
Acid-Peptic Diseases of the Stomach and Duodenum Including Helicobacter pylori and NSAIDs 1 Division of Gastroenterology UC San Diego School of Medicine Clinical presentations of Helicobacter pylori infection
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adherence, to bismuth quadruple therapy, 543 546 Adjuvant therapy, probiotics as, 567 569 Age factors, in gastric cancer, 611 612, 616 AID protein,
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adherence, to bismuth quadruple therapy, 543 546 Adjuvant therapy, probiotics as, 567 569 Age factors, in gastric cancer, 611 612, 616 AID protein,
Review article: gastric acidity ) comparison of esomeprazole with other proton pump inhibitors
 Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2003; 17 (Suppl. 1): 10 15. Review article: gastric acidity ) comparison of esomeprazole with other proton pump inhibitors J. G. HATLEBAKK Department of Medicine, Haukeland Sykehus,
Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2003; 17 (Suppl. 1): 10 15. Review article: gastric acidity ) comparison of esomeprazole with other proton pump inhibitors J. G. HATLEBAKK Department of Medicine, Haukeland Sykehus,
Study population The study population comprised hypothetical patients with gastric and duodenal ulcer.
 Evaluation of the cost-effectiveness of Helicobacter pylori eradication triple therapy vs. conventional therapy for ulcers in Japan Ikeda S, Tamamuro T, Hamashima C, Asaka M Record Status This is a critical
Evaluation of the cost-effectiveness of Helicobacter pylori eradication triple therapy vs. conventional therapy for ulcers in Japan Ikeda S, Tamamuro T, Hamashima C, Asaka M Record Status This is a critical
Title. Author(s)Kato, Mototsugu. Issue Date Doc URL. Type. Note. File Information.
 Title Effects of lansoprazole plus amoxycillin on the cure Author(s)Kato, Mototsugu Issue Date 1996-12-25 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/32629 Type theses (doctoral) Note 共著者あり 共著者名 :Asaka Masahiro,
Title Effects of lansoprazole plus amoxycillin on the cure Author(s)Kato, Mototsugu Issue Date 1996-12-25 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/32629 Type theses (doctoral) Note 共著者あり 共著者名 :Asaka Masahiro,
Patients with established gastro-esophageal reflux disease might benefit from Helicobacter pylori eradication
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Gastroenterology (2014) 27, 352-356 Patients with established gastro-esophageal reflux disease might benefit from Helicobacter pylori eradication John M. Moschos a, George Kouklakis
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Gastroenterology (2014) 27, 352-356 Patients with established gastro-esophageal reflux disease might benefit from Helicobacter pylori eradication John M. Moschos a, George Kouklakis
H elicobacter pylori is a human pathogen that causes
 1543 STOMACH Effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on development of dyspeptic and reflux disease in healthy asymptomatic subjects D Vaira, N Vakil, M Rugge, L Gatta, C Ricci, M Menegatti, G Leandro,
1543 STOMACH Effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on development of dyspeptic and reflux disease in healthy asymptomatic subjects D Vaira, N Vakil, M Rugge, L Gatta, C Ricci, M Menegatti, G Leandro,
Correlation Between Endoscopic and Histological Findings in Different Gastroduodenal Lesion and its Association with Helicobacter Pylori
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correlation Between Endoscopic and Histological Findings in Different Gastroduodenal Lesion and its Association with Helicobacter Pylori *A. Sultana 1, SM Badruddoza 2, F Rahman 3 1 Dr.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correlation Between Endoscopic and Histological Findings in Different Gastroduodenal Lesion and its Association with Helicobacter Pylori *A. Sultana 1, SM Badruddoza 2, F Rahman 3 1 Dr.
MANAGEMENT OF DYSPEPSIA AND GASTRO-OESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GORD)
 DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) MANAGEMENT OF DYSPEPSIA AND GASTRO-OESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GORD) Routine endoscopic investigation of patients of any age, presenting with dyspepsia
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) MANAGEMENT OF DYSPEPSIA AND GASTRO-OESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GORD) Routine endoscopic investigation of patients of any age, presenting with dyspepsia
Disclosures. Co-founder and Chief Science Officer, TechLab
 H. pylori testing Disclosures Co-founder and Chief Science Officer, TechLab Learning Objectives Evaluate the appropriate testing methodology by balancing performance, economics, and workflow. Discuss the
H. pylori testing Disclosures Co-founder and Chief Science Officer, TechLab Learning Objectives Evaluate the appropriate testing methodology by balancing performance, economics, and workflow. Discuss the
Omeprazole 10mg. Name, Restriction, Manner of administration and form OMEPRAZOLE omeprazole 10 mg enteric tablet, 30 (8332M) Max. Qty.
 Omeprazole 10mg Name, Restriction, Manner of administration and form omeprazole 10 mg enteric tablet, 30 (8332M) Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease Name, Restriction, Manner of administration and form omeprazole
Omeprazole 10mg Name, Restriction, Manner of administration and form omeprazole 10 mg enteric tablet, 30 (8332M) Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease Name, Restriction, Manner of administration and form omeprazole
Disclosures. GI Motility Disorders. Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders & Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders & Irritable Bowel Syndrome None Disclosures Jasmine Zia, MD Acting Assistant Professor Division of Gastroenterology, University of Washington 6 th Asian Health Symposium
Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders & Irritable Bowel Syndrome None Disclosures Jasmine Zia, MD Acting Assistant Professor Division of Gastroenterology, University of Washington 6 th Asian Health Symposium
The New England Journal of Medicine. Patients
 HELICOBACTER PYLORI INFECTION AND THE DEVELOPMENT OF GASTRIC CANCER NAOMI UEMURA, M.D., SHIRO OKAMOTO, M.D., SOICHIRO YAMAMOTO, M.D., NOBUTOSHI MATSUMURA, M.D., SHUJI YAMAGUCHI, M.D., MICHIO YAMAKIDO,
HELICOBACTER PYLORI INFECTION AND THE DEVELOPMENT OF GASTRIC CANCER NAOMI UEMURA, M.D., SHIRO OKAMOTO, M.D., SOICHIRO YAMAMOTO, M.D., NOBUTOSHI MATSUMURA, M.D., SHUJI YAMAGUCHI, M.D., MICHIO YAMAKIDO,
Rpts. GENERAL General Schedule (Code GE)
 Pantoprazole 20mg Name, Restriction, Manner of administration and form Pantoprazole 20mg enteric tablet, 30 (8399C) Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease Name, Restriction, Manner of administration and form
Pantoprazole 20mg Name, Restriction, Manner of administration and form Pantoprazole 20mg enteric tablet, 30 (8399C) Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease Name, Restriction, Manner of administration and form
Urea Breath Test for Diagnosis of Helicobactor pylori. Original Policy Date 12:2013
 MP 2.04.04 Urea Breath Test for Diagnosis of Helicobactor pylori Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date 12:2013 Return to Medical Policy Index
MP 2.04.04 Urea Breath Test for Diagnosis of Helicobactor pylori Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date 12:2013 Return to Medical Policy Index
ÐÑÏÓÊÅÊËÇÌÅÍÅÓ ÎÅÍÏÃËÙÓÓÅÓ ÁÍÁÊÏÉÍÙÓÅÉÓ ÅËËÇÍÙÍ ÅÑÅÕÍÇÔÙÍ
 ÐÑÏÓÊÅÊËÇÌÅÍÅÓ ÎÅÍÏÃËÙÓÓÅÓ ÁÍÁÊÏÉÍÙÓÅÉÓ ÅËËÇÍÙÍ ÅÑÅÕÍÇÔÙÍ 205 206 ÐÑÏÓÊÅÊËÇÌÅÍÅÓ ÎÅÍÏÃËÙÓÓÅÓ ÁÍÁÊÏÉÍÙÓÅÉÓ ÅËËÇÍÙÍ ÅÑÅÕÍÇÔÙÍ EPITHELIAL CELL TURNOVER IN NON-DYSPLASTIC GASTRIC MUCOSA ADJACENT TO EARLY AND
ÐÑÏÓÊÅÊËÇÌÅÍÅÓ ÎÅÍÏÃËÙÓÓÅÓ ÁÍÁÊÏÉÍÙÓÅÉÓ ÅËËÇÍÙÍ ÅÑÅÕÍÇÔÙÍ 205 206 ÐÑÏÓÊÅÊËÇÌÅÍÅÓ ÎÅÍÏÃËÙÓÓÅÓ ÁÍÁÊÏÉÍÙÓÅÉÓ ÅËËÇÍÙÍ ÅÑÅÕÍÇÔÙÍ EPITHELIAL CELL TURNOVER IN NON-DYSPLASTIC GASTRIC MUCOSA ADJACENT TO EARLY AND
Clinical Trial of Efcid (Himcocid) in Patients of Acid Peptic Disease
 [The Antiseptic (2001): (98), 2, 50] Clinical Trial of Efcid (Himcocid) in Patients of Acid Peptic Disease Rangamani, K., Professor of Medicine, Bowring and Lady Curzon Hospitals, Shivajinagar, Bangalore,
[The Antiseptic (2001): (98), 2, 50] Clinical Trial of Efcid (Himcocid) in Patients of Acid Peptic Disease Rangamani, K., Professor of Medicine, Bowring and Lady Curzon Hospitals, Shivajinagar, Bangalore,
Barrett s Esophagus. Abdul Sami Khan, M.D. Gastroenterologist Aurora Healthcare Burlington, Elkhorn, Lake Geneva, WI
 Barrett s Esophagus Abdul Sami Khan, M.D. Gastroenterologist Aurora Healthcare Burlington, Elkhorn, Lake Geneva, WI A 58 year-old, obese white man has had heartburn for more than 20 years. He read a magazine
Barrett s Esophagus Abdul Sami Khan, M.D. Gastroenterologist Aurora Healthcare Burlington, Elkhorn, Lake Geneva, WI A 58 year-old, obese white man has had heartburn for more than 20 years. He read a magazine
Update on the pathological classification of gastritis. Hala El-Zimaity, M.D. M.S. Epidemiology McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario Canada
 Update on the pathological classification of gastritis Hala El-Zimaity, M.D. M.S. Epidemiology McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario Canada CLASSIFICATION GASTRITIS GASTROPATHY 1. Acute 2. Chronic 3. Uncommon
Update on the pathological classification of gastritis Hala El-Zimaity, M.D. M.S. Epidemiology McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario Canada CLASSIFICATION GASTRITIS GASTROPATHY 1. Acute 2. Chronic 3. Uncommon
Proton Pump Inhibitor Treatment Decreases the Incidence of Upper Gastrointestinal Disorders in Elderly Japanese Patients Treated with NSAIDs
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Proton Pump Inhibitor Treatment Decreases the Incidence of Upper Gastrointestinal Disorders in Elderly Japanese Patients Treated with NSAIDs Yuki Sakamoto, Tadashi Shimoyama, Satoru Nakagawa,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Proton Pump Inhibitor Treatment Decreases the Incidence of Upper Gastrointestinal Disorders in Elderly Japanese Patients Treated with NSAIDs Yuki Sakamoto, Tadashi Shimoyama, Satoru Nakagawa,
Chapter 4. Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy analyses
 Chapter 4 Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy analyses Chapter 4.1 Medley of Helicobacter pylori eradication regimens Combinations using lansoprazole Angela A.M.C. Claessens MD 1,2, Eibert R. Heerdink
Chapter 4 Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy analyses Chapter 4.1 Medley of Helicobacter pylori eradication regimens Combinations using lansoprazole Angela A.M.C. Claessens MD 1,2, Eibert R. Heerdink
National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Gastritis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is gastritis? Gastritis is a condition in which the stomach
Gastritis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is gastritis? Gastritis is a condition in which the stomach
Barrett s Esophagus: Old Dog, New Tricks
 Barrett s Esophagus: Old Dog, New Tricks Stuart Jon Spechler, M.D. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology, VA North Texas Healthcare System; Co-Director, Esophageal Diseases Center, Professor of Medicine,
Barrett s Esophagus: Old Dog, New Tricks Stuart Jon Spechler, M.D. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology, VA North Texas Healthcare System; Co-Director, Esophageal Diseases Center, Professor of Medicine,
KK College of Nursing Peptic Ulcer Badil D ass Dass, Lecturer 25th July, 2011
 KK College of Nursing Peptic Ulcer Badil Dass, Lecturer 25 th July, 2011 Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the students t will be able to: Define peptic pp ulcer Describe the etiology and pathology
KK College of Nursing Peptic Ulcer Badil Dass, Lecturer 25 th July, 2011 Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the students t will be able to: Define peptic pp ulcer Describe the etiology and pathology
Key words : low-grade MALT lymphoma, epithelial change, empty lamina propria, B-cell clonality, H. pylori, eradication, long-term follow-up
 Department of Pathology, The University of Tokushima School of Medicine, Tokushima, Japan ; Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, The University of Tokushima School of Dentistry, Tokushima, Japan
Department of Pathology, The University of Tokushima School of Medicine, Tokushima, Japan ; Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, The University of Tokushima School of Dentistry, Tokushima, Japan
Helicobacter pylori Improved Detection of Helicobacter pylori
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2016.17.4.2099 RESEARCH ARTICLE Improved Detection of Helicobacter pylori Infection and Premalignant Gastric Mucosa Using Conventional White Light Source Gastroscopy
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2016.17.4.2099 RESEARCH ARTICLE Improved Detection of Helicobacter pylori Infection and Premalignant Gastric Mucosa Using Conventional White Light Source Gastroscopy
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION. Effectiveness of Helicobacter pylori Therapies in a Clinical Practice Setting
 ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Effectiveness of Helicobacter pylori Therapies in a Clinical Practice Setting M. Brian Fennerty, MD; David A. Lieberman, MD; Nimish Vakil, MD; Nathan Magaret; Douglas O. Faigel,
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Effectiveness of Helicobacter pylori Therapies in a Clinical Practice Setting M. Brian Fennerty, MD; David A. Lieberman, MD; Nimish Vakil, MD; Nathan Magaret; Douglas O. Faigel,
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease and peptic ulcer disease. By: Dr. Singanamala Suman Assistant Professor Department of Pharm.D
 Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease and peptic ulcer disease By: Dr. Singanamala Suman Assistant Professor Department of Pharm.D Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease and peptic ulcer disease Learning objectives:
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease and peptic ulcer disease By: Dr. Singanamala Suman Assistant Professor Department of Pharm.D Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease and peptic ulcer disease Learning objectives:
Effect of Helicobacter pylori Eradication on Reflux Esophagitis Therapy: A Multi center Randomized Control Study
 Original Article Effect of Helicobacter pylori Eradication on Reflux Esophagitis Therapy: A Multi center Randomized Control Study Yan Xue 1, Li Ya Zhou 1, San Ren Lin 1, Xiao Hua Hou 2, Zhao Shen Li 3,
Original Article Effect of Helicobacter pylori Eradication on Reflux Esophagitis Therapy: A Multi center Randomized Control Study Yan Xue 1, Li Ya Zhou 1, San Ren Lin 1, Xiao Hua Hou 2, Zhao Shen Li 3,
Committee Approval Date: October 14, 2014 Next Review Date: October 2015
 Medication Policy Manual Topic: esomeprazole-containing medications: - Nexium - Vimovo - esomeprazole strontium Policy No: dru039 Date of Origin: May 2001 Committee Approval Date: October 14, 2014 Next
Medication Policy Manual Topic: esomeprazole-containing medications: - Nexium - Vimovo - esomeprazole strontium Policy No: dru039 Date of Origin: May 2001 Committee Approval Date: October 14, 2014 Next
Helicobacter and gastritis
 1 Helicobacter and gastritis Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Helicobacter pylori is a spiral-shaped gram-negative rod. H. pylori is associated with antral gastritis, duodenal (peptic) ulcer disease, gastric ulcers,
1 Helicobacter and gastritis Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Helicobacter pylori is a spiral-shaped gram-negative rod. H. pylori is associated with antral gastritis, duodenal (peptic) ulcer disease, gastric ulcers,
The Impact of Gender on the Symptom Presentation and Life Quality of Patients with Erosive Esophagitis and Non-Erosive Reflux Disease
 ARC Journal of Hepatology and Gastroenterology Volume 1, Issue 1, 2016, PP 3-8 www.arcjournals.org The Impact of Gender on the Symptom Presentation and Life Quality of Patients with Erosive Esophagitis
ARC Journal of Hepatology and Gastroenterology Volume 1, Issue 1, 2016, PP 3-8 www.arcjournals.org The Impact of Gender on the Symptom Presentation and Life Quality of Patients with Erosive Esophagitis
TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 13 December 2006
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 13 December 2006 HELIKIT 75 mg, powder for oral solution CIP : 343 132-1 Applicant : MAYOLY SPINDLER 13 Curea anhydrous
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 13 December 2006 HELIKIT 75 mg, powder for oral solution CIP : 343 132-1 Applicant : MAYOLY SPINDLER 13 Curea anhydrous
Comparison of the Accuracy of Two Commercial Rapid Urase Tests, CLOtest and Pronto Dry, in Detecting Helicobacter pylori Infection ABSTRACT
 Original Article Rojborwonwitaya J, Vijitjunyakul N THAI J GASTROENTEROL 2005 Vol. 6 No. 2 May - Aug. 2005 55 Comparison of the Accuracy of Two Commercial Rapid Urase Tests, CLOtest and Pronto Dry, in
Original Article Rojborwonwitaya J, Vijitjunyakul N THAI J GASTROENTEROL 2005 Vol. 6 No. 2 May - Aug. 2005 55 Comparison of the Accuracy of Two Commercial Rapid Urase Tests, CLOtest and Pronto Dry, in
Helicobacter pylori Eradication Therapy Success Regarding Different Treatment Period Based on Clarithromycin or Metronidazole Triple-Therapy Regimens
 Helicobacter ISSN 1523-5378 Filipec Blackwell Oxford, HEL 1083-4389 1523-5378 Journal XXX Original H. 2008 pylori Kanizaj compilation The UK Eradication Publishing Article Authors et al. Ltd 2008 Therapy
Helicobacter ISSN 1523-5378 Filipec Blackwell Oxford, HEL 1083-4389 1523-5378 Journal XXX Original H. 2008 pylori Kanizaj compilation The UK Eradication Publishing Article Authors et al. Ltd 2008 Therapy
58 year old male complaining of 3-week history of increasing epigastric pain
 Peptic Ulcer Disease 58 year old male complaining of 3-week history of increasing epigastric pain Has had dyspepsia in the past for which he took Tums, but this is much worse and only partially relieved
Peptic Ulcer Disease 58 year old male complaining of 3-week history of increasing epigastric pain Has had dyspepsia in the past for which he took Tums, but this is much worse and only partially relieved
Peptic Ulcer Disease Update
 Peptic Ulcer Disease Update Col Pat Storms RAM 2005 Disclosure Information 84th Annual AsMA Scientific Meeting Col Patrick Storms I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will discuss the following
Peptic Ulcer Disease Update Col Pat Storms RAM 2005 Disclosure Information 84th Annual AsMA Scientific Meeting Col Patrick Storms I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will discuss the following
Zantac for stomach ulcers
 P ford residence southampton, ny Zantac for stomach ulcers Information on the drug ranitidine (Zantac) used in and duodenal ulcers, heartburn, esophagitis, and Zollinger Ellison Syndrome. Side. But with
P ford residence southampton, ny Zantac for stomach ulcers Information on the drug ranitidine (Zantac) used in and duodenal ulcers, heartburn, esophagitis, and Zollinger Ellison Syndrome. Side. But with
QUICK QUERIES. Topical Questions, Sound Answers
 QUICK QUERIES Topical Questions, Sound Answers Dyspepsia: An Evidence-Based Approach Alan B. R. Thomson, MD, PhD, FRCPC, FACP, FACG Presented at the University of Alberta s Medical Grand Rounds, University
QUICK QUERIES Topical Questions, Sound Answers Dyspepsia: An Evidence-Based Approach Alan B. R. Thomson, MD, PhD, FRCPC, FACP, FACG Presented at the University of Alberta s Medical Grand Rounds, University
THE PREVALENCE OF HELICBACTER PYLORI AMONG PATIENTS COMPLAINING FROM ABDOMINAL PAIN
 THE PREVALENCE OF HELICBACTER PYLORI AMONG PATIENTS COMPLAINING FROM ABDOMINAL PAIN Ahed J. Al-Khatib Jordan University of Science and Technology, Jordan Ahmed Saber Abu-zaiton Al-albayt University Abstract
THE PREVALENCE OF HELICBACTER PYLORI AMONG PATIENTS COMPLAINING FROM ABDOMINAL PAIN Ahed J. Al-Khatib Jordan University of Science and Technology, Jordan Ahmed Saber Abu-zaiton Al-albayt University Abstract
Efficacy of the Kyoto Classification of Gastritis in Identifying Patients at High Risk for Gastric Cancer
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Efficacy of the Kyoto Classification of Gastritis in Identifying Patients at High Risk for Gastric Cancer Mitsushige Sugimoto 1,2, Hiromitsu Ban 1, Hitomi Ichikawa 2, Shu Sahara 2, Taketo
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Efficacy of the Kyoto Classification of Gastritis in Identifying Patients at High Risk for Gastric Cancer Mitsushige Sugimoto 1,2, Hiromitsu Ban 1, Hitomi Ichikawa 2, Shu Sahara 2, Taketo
Nutritional assessments and diagnosis of digestive disorders
 Nutritional assessments and diagnosis of digestive disorders AASER ABDELAZIM Assistant professor of Medical Biochemistry Zagazig University, Egypt University of Bisha, KSA aaserabdelazim@yahoo.com 7 Mal
Nutritional assessments and diagnosis of digestive disorders AASER ABDELAZIM Assistant professor of Medical Biochemistry Zagazig University, Egypt University of Bisha, KSA aaserabdelazim@yahoo.com 7 Mal
Helicobacter pylori:an Emerging Pathogen
 Bacteriology at UW-Madison Bacteriology 330 Home Page Helicobacter pylori:an Emerging Pathogen by Karrie Holston, Department of Bacteriology University of Wisconsin-Madison Description of Helicobacter
Bacteriology at UW-Madison Bacteriology 330 Home Page Helicobacter pylori:an Emerging Pathogen by Karrie Holston, Department of Bacteriology University of Wisconsin-Madison Description of Helicobacter
Helicobacter pylori still matters clinically
 REVIEW M. BRIAN FENNERTY, MD Division of Gastroenterology Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, OR Helicobacter pylori: Why it still matters in 2005 Helicobacter pylori still matters clinically
REVIEW M. BRIAN FENNERTY, MD Division of Gastroenterology Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, OR Helicobacter pylori: Why it still matters in 2005 Helicobacter pylori still matters clinically
Clinical Evaluation of Himcocid Suspension in Patients with Non-ulcer Dyspepsia
 [The Antiseptic (21): (98), 11, 49-411] Clinical Evaluation of Himcocid Suspension in Patients with Non-ulcer Dyspepsia Upadhyaya, B.N., Reader and Head, and Khagen Basumathy, Junior Resident Department
[The Antiseptic (21): (98), 11, 49-411] Clinical Evaluation of Himcocid Suspension in Patients with Non-ulcer Dyspepsia Upadhyaya, B.N., Reader and Head, and Khagen Basumathy, Junior Resident Department
Prevalence of Multiple White and Flat Elevated Lesions in Individuals Undergoing a Medical Checkup
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.9808-17 http://internmed.jp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prevalence of Multiple White and Flat Elevated Lesions in Individuals Undergoing a Medical Checkup Kyoichi Adachi 1, Tomoko Mishiro
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.9808-17 http://internmed.jp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prevalence of Multiple White and Flat Elevated Lesions in Individuals Undergoing a Medical Checkup Kyoichi Adachi 1, Tomoko Mishiro
Helicobacter pylori infection: several studies on epidemiology, eradication and gastric epithelial cell turnover Liu, W.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Helicobacter pylori infection: several studies on epidemiology, eradication and gastric epithelial cell turnover Liu, W. Link to publication Citation for published
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Helicobacter pylori infection: several studies on epidemiology, eradication and gastric epithelial cell turnover Liu, W. Link to publication Citation for published
Association between Helicobacter Pylori Eradication and Weight Gain
 ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: Helicobacter Pylori is a common infection highly prevalent globally causing chronic gastritis, duodenal ulcer and gastric carcinoma. It is observed clinically that patients who underwent
ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: Helicobacter Pylori is a common infection highly prevalent globally causing chronic gastritis, duodenal ulcer and gastric carcinoma. It is observed clinically that patients who underwent
Endoscopic Corner CASE 1. Sirimontaporn N Klaikaew N Imraporn B Rerknimitr R
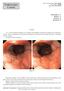 Endoscopic Corner Sirimontaporn N, et al. THAI J GASTROENTEROL 2010 Vol. 11 No. 3 Sept. - Dec. 2010 171 Sirimontaporn N Klaikaew N Imraporn B Rerknimitr R CASE 1 A 47- year-old female presented to the
Endoscopic Corner Sirimontaporn N, et al. THAI J GASTROENTEROL 2010 Vol. 11 No. 3 Sept. - Dec. 2010 171 Sirimontaporn N Klaikaew N Imraporn B Rerknimitr R CASE 1 A 47- year-old female presented to the
Table 2.9. Case control studies of helicobacter pylori infection and oesophageal adenocarcinoma
 Characteristics of Characteristics of controls Detection Chow et al (1998) 1993-1995 129 of newly diagnosed oesophageal/gastric cardia (OGC) adenocarcinoma. 224 population controls selected by random digit
Characteristics of Characteristics of controls Detection Chow et al (1998) 1993-1995 129 of newly diagnosed oesophageal/gastric cardia (OGC) adenocarcinoma. 224 population controls selected by random digit
American College of Gastroenterology Guideline on the Management of Helicobacter pylori Infection
 American Journal of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270 C 2007 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2007.01393.x Published by Blackwell Publishing American College of Gastroenterology
American Journal of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270 C 2007 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2007.01393.x Published by Blackwell Publishing American College of Gastroenterology
H. pylori Antigen ELISA Kit
 H. pylori Antigen ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA3142 96 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of
H. pylori Antigen ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA3142 96 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Abstract. Introduction. Masaki Miyamoto 1, Noriaki Manabe 2 and Ken Haruma 2
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Efficacy of the Addition of Prokinetics for Proton Pump Inhibitor (PPI) Resistant Non-erosive Reflux Disease (NERD) Patients: Significance of Frequency Scale for the Symptom of GERD (FSSG)
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Efficacy of the Addition of Prokinetics for Proton Pump Inhibitor (PPI) Resistant Non-erosive Reflux Disease (NERD) Patients: Significance of Frequency Scale for the Symptom of GERD (FSSG)
Peptic ulcer disease Disorders of the esophagus
 Peptic ulcer disease Disorders of the esophagus Peptic ulcer disease Burning epigastric pain Exacerbated by fasting Improved with meals Ulcer: disruption of mucosal integrity >5 mm in size, with depth
Peptic ulcer disease Disorders of the esophagus Peptic ulcer disease Burning epigastric pain Exacerbated by fasting Improved with meals Ulcer: disruption of mucosal integrity >5 mm in size, with depth
Regression of Advanced Gastric MALT Lymphoma after the Eradication of Helicobacter pylori
 Gut and Liver, Vol. 6, No. 2, April 2012, pp. 270-274 CASE REPORT Regression of Advanced Gastric MALT Lymphoma after the Eradication of Helicobacter pylori Soo-Kyung Park, Hwoon-Yong Jung, Do Hoon Kim,
Gut and Liver, Vol. 6, No. 2, April 2012, pp. 270-274 CASE REPORT Regression of Advanced Gastric MALT Lymphoma after the Eradication of Helicobacter pylori Soo-Kyung Park, Hwoon-Yong Jung, Do Hoon Kim,
Duodenal gastric metaplasia and Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with diffuse nodular duodenitis
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2007) Online Ahead of Print Duodenal gastric metaplasia and Helicobacter pylori infection ISSN 0100-879X 1 Duodenal gastric metaplasia and Helicobacter
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2007) Online Ahead of Print Duodenal gastric metaplasia and Helicobacter pylori infection ISSN 0100-879X 1 Duodenal gastric metaplasia and Helicobacter
A Heaney, J S A Collins, RGPWatson, R J McFarland, K B Bamford, T C K Tham
 186 Royal Victoria Hospital, Belfast, A Heaney J S A Collins Department of Medicine, Queen s University, Belfast, RGPWatson Ulster Hospital, Dundonald, R J McFarland T C K Tham Department of Microbiology
186 Royal Victoria Hospital, Belfast, A Heaney J S A Collins Department of Medicine, Queen s University, Belfast, RGPWatson Ulster Hospital, Dundonald, R J McFarland T C K Tham Department of Microbiology
The role of antisecretory drugs in the treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection
 Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1997; 11 (Suppl. 1): 21 25. The role of antisecretory drugs in the treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection W. L. PETERSON Department of Internal Medicine, University of Texas
Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1997; 11 (Suppl. 1): 21 25. The role of antisecretory drugs in the treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection W. L. PETERSON Department of Internal Medicine, University of Texas
Cholecystectomy and duodenogastric reflux: interacting effects over the gastric mucosa
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-3641-z RESEARCH Open Access Cholecystectomy and duodenogastric reflux: interacting effects over the gastric mucosa Erdinc Mercan 1, Ugur Duman 1, Deniz Tihan 1, Evren Dilektasli
DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-3641-z RESEARCH Open Access Cholecystectomy and duodenogastric reflux: interacting effects over the gastric mucosa Erdinc Mercan 1, Ugur Duman 1, Deniz Tihan 1, Evren Dilektasli
Functional dyspepsia: relationship between clinical subgroups and Helicobacter pylori status in Western Turkey
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2003) 36: 747-751 Dyspepsia and Helicobacter pylori ISSN 0100-879X 747 Functional dyspepsia: relationship between clinical subgroups and Helicobacter
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2003) 36: 747-751 Dyspepsia and Helicobacter pylori ISSN 0100-879X 747 Functional dyspepsia: relationship between clinical subgroups and Helicobacter
