Neurologic Disorders: Headache in Children
|
|
|
- Tyler Ball
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 of 12 17/06/2014 7:57 PM Print Close Neurologic Disorders: Headache in Children Sharon Whiting, MBBS, FRCPC Date of revision: February 2014 Headaches occur commonly in children and adolescents. They may occur as a primary disorder such as migraine, or accompany systemic disorders or infectious diseases. In Canada, more than 25% of 12- to 13-year-olds experience headache at least weekly. 1 The prevalence of migraine shows an increase with age, i.e., 2.4% in 12- to 14-year-olds and 5% in 15- to 19-year-olds. 2 Migraine in children is usually associated with at least one of the following: vomiting, photophobia, family history of migraine. Goals of Therapy Make an accurate diagnosis of headache 3 Relieve or abort pain and associated symptoms Prevent further headaches Investigations (Figure 1 - Investigations Based on Headache Profile ) The history is the key to the diagnosis of headache and should be obtained from both parent and child with attention to: specific questions such as where pain began, progress, duration, frequency, relieving and aggravating factors (especially sleep loss, excitement, certain foods, relief with activity) and associated symptoms such as vomiting and photophobia specific neurologic symptoms such as seizures, visual disturbances, difficulty with balance, personality change, weakness symptoms suggestive of renal, cardiac, dental or infectious disease degree of interference with school and social life, e.g., pedmidas questionnaire 4 analgesic use child's growth and development, behaviour, academic function Note: During the interview, observe interaction between parent and child. Physical examination: blood pressure, vital signs, palpation of sinuses, examination of teeth, neck stiffness, examination of optic fundi height, weight, head circumference thorough neurologic examination including cranial nerves, muscle tone, power and reflexes and coordination tests Investigations: sinus x-rays if sinusitis suspected CT followed by lumbar puncture with measurement of opening pressure if pseudotumor cerebri suspected based on history of raised intracranial pressure with a negative CT lumbar puncture if infectious process suspected CT and/or MRI if abnormal neurologic examination, decreased visual acuity, recent behaviour change, increasing severity and frequency of headaches, or if headache does not fit a known pattern The routine use of any diagnostic study is not indicated when the clinical history has no associated risk factors and the child's examination is normal 5 Tension-type Headache Therapeutic Choices Nonpharmacologic Choices Pharmacologic Choices
2 2 of 12 17/06/2014 7:57 PM Therapeutic Choices Nonpharmacologic Choices Psychological evaluation Relaxation therapy Biofeedback Pharmacologic Choices Simple analgesics (acetaminophen, ASA) and NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, are effective for the treatment of acute tension-type headache (Table 1). Because of the possible association with Reye's syndrome, avoid ASA in children and adolescents for headache or fever associated with viral illness such as influenza or chickenpox. 6 Amitriptyline (Table 2) is effective in reducing headache frequency and severity. 7, 8 Preventive therapy may be appropriate when headaches are frequent and significantly disabling and disruptive. Medication-overuse Headache The occurrence of headache induced by chronic use of analgesics, such as acetaminophen and NSAIDs, is now recognized in pediatric patients. Treatment involves education and gradual withdrawal of analgesic drugs. Consider use of a prophylactic agent (Table 2). 9 Migraine Therapeutic Choices Nonpharmacologic Choices Pharmacologic Choices Therapeutic Choices Nonpharmacologic Choices After exclusion of mass lesion or other causes: Provide reassurance and information about the headache condition. Discuss triggers of migraine, e.g., lack of sleep, too much sleep, excitement, foods, stress, menstruation. Encourage sleep at the time of headache and medication early in the course of the Biofeedback and relaxation therapy are effective. Pharmacologic Choices These can be divided into medication given at the time of the headache (symptomatic) and medication to prevent headache (prophylactic). 10 Symptomatic Treatments (Table 1) Analgesics Intermittent oral analgesics, given as early in the course of the headache as feasible, are the mainstay of pharmacologic management of childhood migraine. Acetaminophen, ibuprofen and ASA are effective at appropriate doses. 11 As for tension-type headache, avoid ASA in children and adolescents for fever or headache associated with viral illness such as
3 3 of 12 17/06/2014 7:57 PM varicella or influenza. Two evaluations of the evidence for treatment of migraine in children concluded that ibuprofen and 10, 12, 13 acetaminophen are effective. Combination products containing ASA, caffeine and butalbital ± codeine (e.g., Fiorinal) should generally be avoided, but may be appropriate in exceptional circumstances when initial agents fail. These sedating drugs have abuse potential and should be reserved for adolescents (12 18 years) for brief periods only. Take care to avoid unnecessary opioids. Antiemetics Nausea and vomiting occur in up to 90% of young migraine sufferers and besides being disabling, inhibit oral administration of analgesics. Antiemetics alone (e.g., chlorpromazine, 14 prochlorperazine, metoclopramide) are surprisingly effective in relieving all symptoms including the 15 Ergot Derivatives Ergotamine compounds have very limited use in pediatrics for the following reasons: Auras are uncommon and inconsistent; therefore, warning indicators that trigger the time to treat with ergot are often unreliable. Ergots can exacerbate gastrointestinal upset. Ergots are complicated migraine syndromes because of the risk of increasing vasospasm. Oral dihydroergotamine showed no significant difference in headache improvement in a study comparing it with placebo. 16 In severe intractable headache, dihydroergotamine can be used iv in combination with an antiemetic in the emergency department. 17 Of the 7 agents available in Canada (almotriptan, eletriptan, frovatriptan,naratriptan, rizatriptan, sumatriptan and zolmitriptan), only almotriptan is specifically approved for use in children aged years, though several triptans have been shown to be safe in this age group. 13,18,19 The best evidence exists for nasal sumatriptan, shown to be safe and effective for acute migraine pain in adolescents 12 years and older. 20,21,22 Consider triptans for use in adolescents with moderate to severe migraine that is unresponsive analgesics [Evidence: SORT B]. 13,18,19 Unpleasant taste is a common side effect. Prophylactic Agents (Table 2) A practice parameter on the pharmacologic treatment of childhood migraine examined the evidence for efficacy of several medications. 10 Although many are in current use and may be effective, only flunarizine was deemed probably effective based 23, 24 on evidence. Flunarizine has been shown to significantly reduce headache frequency and severity in children. Although evidence of its efficacy is lacking, pizotifen (pizotyline) may be helpful. Evidence for propranolol is conflicting, although it is commonly used and is effective in some cases. 25 Propranolol is reactive airway disease, diabetes mellitus and bradyarrhythmias. Symptoms of depression are an underreported but common side effect in adolescents. Despite a lack of evidence of efficacy, cyproheptadine, an antihistamine with antiserotonergic and calcium channel blocking properties, is widely used as a prophylactic agent. Its use in older children and adolescents is limited by sedation and increased appetite/weight gain. Amitriptyline has shown efficacy in adults; studies in children are limited. 8, 26 NSAIDs reduce headache frequency and severity in adults, presumably through prostaglandin inhibition. Although evidence of efficacy in children is lacking, naproxen sodium can be tried in adolescents as prophylaxis (see Therapeutic Tips). Valproic acid has been studied in children; 27, 28 however, there is insufficient evidence to recommend its use. 10 Phenobarbital and phenytoin are no longer used. Topiramate is approved for migraine prophylaxis in adults. While not specifically approved for use in children it is used in 8, 29, 30 adolescents.
4 4 of 12 17/06/2014 7:57 PM Riboflavin 200 mg/day may be effective in reducing migraine frequency and intensity of migraine. 31 Therapeutic Tips There are very few controlled trials of pharmacologic management of childhood migraine; hence, anecdotal experience prevails. Most young patients with migraine do not require daily medication but need access to reliable analgesia at home and at school. Children are debilitated by nausea and vomiting and benefit greatly from antiemetics. Rest and sleep are usually very helpful. Consider prophylactic agents for children who cycle through periods of time when they experience such frequency of headache that their lifestyle is disrupted, or when isolated or infrequent events are severe and complex. For prophylaxis, consider medications with the fewest side effects first. Cyproheptadine is usually used in younger children. For adolescents, consider using propranolol, amitriptyline, naproxen sodium or flunarizine. A period of 6 12 months is a reasonable trial of prophylactic medication, followed by very gradual tapering and discontinuation to assess ongoing need. Calendars/diaries are helpful in identifying triggers, headache patterns, frequency and severity and are invaluable for management and evaluation of response to therapy. The prognosis for children with migraine is favourable with 50% of patients reporting improvement within 6 months after medical intervention, regardless of treatment methods used. Most children respond to reassurance, general advice and simple remedies for attacks when they occur. Algorithm Figure 1 - Investigations Based on Headache Profile Drug Tables Table 1: Drug Treatment of Headache in Children Class Drug Dose a Effects Adverse Drug Interactions Comments Analgesics acetaminophen Atasol Preparations, Tempra, Tylenol, mg/kg/dose Q4H prn GI upset; liver toxicity in overdose. May enhance anticoagulant effect of warfarin, particularly with doses of >1.3 g/day for >1 wk Analgesics are the most commonly used abortive medications for Limit use to <15 days per mo to avoid medicationoveruse
5 5 of 12 17/06/2014 7:57 PM Class Drug Dose a Adverse Effects Drug Interactions Comments Analgesics ASA Aspirin, Coated Aspirin, Age 12 y: single dose of mg per headache GI upset (usually the only more common adverse effect when single doses are used to treat acute headache). For a detailed description of adverse effects associated with continuous or frequent NSAID use, see, Table 2. Warfarin: increased anticoagulant effect. Because of the concern of Reye's syndrome, ASA should not be used in the context of headache or fever associated with a viral illness; do not use more frequently than Q4 6H. Analgesics ibuprofen Advil, Motrin, Motrin Children's, 5 10 mg/kg/dose, up to 4 times daily GI upset (usually the only more common adverse effect when single doses are used to treat acute headache). For a detailed description of adverse effects associated with continuous or frequent NSAID use, see, Table 2. Warfarin: increased anticoagulant effect. Analgesics naproxen sodium Aleve, Anaprox, Maxidol, Age >2 y: 5 7 mg/kg/dose Q8 12H prn GI upset (usually the only more common adverse effect when single doses are used to treat acute headache). For a detailed description of adverse effects associated with continuous or frequent NSAID use, see, Table 2. Warfarin: increased anticoagulant effect. Analgesics, combination butalbital + ASA + caffeine ± codeine Fiorinal, Fiorinal C1/4, C1/2, Adolescents: mg (1 2 tablets) up to 4 times daily GI upset; dependence and tolerance to barbiturates Possible additive sedation with other CNS Should generally be avoided. May be appropriate in exceptional circumstances. Limit use
6 6 of 12 17/06/2014 7:57 PM Class Drug Dose a Adverse Effects Drug Interactions Comments and opioids. depressants, e.g., alcohol. to adolescents, no more than 2 days/wk, 7 days/month. Risk of tolerance, addiction and misuse. Antiemetics chlorpromazine Oral/IM: 1 mg/kg to a maximum of 25 mg Q8H IV: 0.1 mg/kg Q10 15 min prn to a maximum of 30 mg Hypotension. Possible additive sedation with other CNS depressants, e.g., alcohol. Can cause hypotension when given iv; used in the emergency department. Antiemetics metoclopramide PMS-Metoclopramide, other IV: Adolescents: mg/kg ( 10 mg) single dose May repeat once if necessary; maximum 20 mg Extrapyramidal dysfunction. Possible enhanced sedative effect of alcohol. Use iv in adolescents in the emergency department. See also dihydroergotamine. Antiemetics prochlorperazine Oral: mg BID prn IV: Adolescents: 10 mg Extrapyramidal dysfunction. Possible additive sedation with other CNS depressants, e.g., alcohol. Used iv in adolescents in the emergency department. Ergot Derivatives dihydroergotamine injection >6 years: mg/dose iv May repeat Q20 min 3 Give metoclopramide 0.2 mg/kg/dose (maximum 20 mg) 30 min prior to iv dihydroergotamine Flushed feeling, tingling in extremities, nausea and vomiting. Do potent inhibitors of CYP3A4 such as cimetidine, clarithromycin, efavirenz, erythromycin, itraconazole, ketoconazole and ritonavir. Useful in patients with severe and prolonged migraine headache; protocol to take place in hospital; contraindicated in complicated migraine, coronary heart disease, abnormal blood pressure, abnormal ECG. Ergot Derivatives dihydroergotamine nasal spray Migranal >6 years: 1 spray into each nostril May repeat in 15 min if required Nausea, taste disturbance, rhinitis. Do potent inhibitors of CYP3A4 such as cimetidine, clarithromycin, efavirenz, erythromycin, itraconazole, ketoconazole and ritonavir. Contraindicated in complicated migraine, coronary heart disease, abnormal blood pressure, abnormal ECG. almotriptan Axert, 12 y: Oral: 6.25 mg at start of headache; if headache returns, dose may be repeated after 2 h;
7 7 of 12 17/06/2014 7:57 PM Class Drug Dose a Adverse Effects Drug Interactions Comments no more than 2 doses in a 24-h period Almotriptan: Do MAOIs. Inhibitors of CYP3A4 (e.g., cimetidine, clarithromycin, efavirenz, erythromycin, grapefruit juice, itraconazole, ketoconazole and ritonavir) may increase bioavailability of almo eletriptan Relpax, 12 y: Oral: mg as soon after headache onset as possible; if initial dose is 20 mg and headache returns after 2 h, may repeat 20 mg dose; maximum 40 mg in a 24-h period Eletriptan: Contraindicated within 72 h of the following inhibitors of CYP3A4: clarithromycin, itraconazole, ketoconazole, nelfinavir and ritonavir, or any potent inhibitor of CYP3A4. frovatriptan Frova 12 y: Oral: 2.5 mg; if headache recurs after initial relief, may repeat in 4 24 h; maximum 5 mg/24 h Frovatriptan: Oral contraceptives and propranolol may increase frovatriptan
8 Class Drug Dose a Adverse Effects Drug Interactions Comments serum concentrations by 30 60%. naratriptan Amerge, 12 y: Oral: 1 mg at start of headache; if partial response or headache returns, dose may be repeated once after 4 h; maximum dose of 5 mg in a 24-h period Naratriptan may be associated with fewer side effects than the other triptans. rizatriptan Maxalt, Maxalt RPD, 12 y: Oral: 5 10 mg (tablet or wafer) at start of headache Do not repeat if no relief from first dose; if headache returns 2 h or more after partial or complete relief from an initial 5 mg dose, may repeat 5 mg dose (daily maximum 10 mg) Rizatriptan: Do MAOIs. Use with caution in patients taking propranolol (increased bioavailability of rizatriptan). Fastmelt wafers can be taken without water. sumatriptan Imitrex Nasal Spray, Imitrex DF, 12 y: 25 mg tablet or 20 mg nasal spray at start of headache Do not repeat if no relief from first dose; if headache returns 2 h or more after first dose, may repeat dose (daily maximum 2 doses) Nasal spray may cause taste disturbance. Sumatriptan: Do MAOIs. Faster onset with nasal spray than with oral formulations. zolmitriptan Zomig, Zomig Rapimelt, Zomig Nasal Spray, 12 y: mg (tablet, orally dispersible tablet or nasal spray) at start of headache 8 of 12 17/06/2014 7:57 PM
9 9 of 12 17/06/2014 7:57 PM Class Drug Dose a Adverse Effects Drug Interactions Comments Do not repeat if no relief from first dose; if headache returns 2 h or more after first dose, may repeat dose (daily maximum 2 doses) Nasal spray may cause taste disturbance. Zolmitriptan: Do MAOIs. Maximum dose of 5 mg/24 h if also taking fluvoxamine or cimetidine. Zolmitriptan orally dispersible tablets can be taken without water. a. Not to exceed maximum adult dose. b. Cost per dose, based on 20 kg body weight; includes drug cost only. Dosage adjustment may be required in renal impairment; see Appendices: Dosage Adjustment in Renal Impairment. Legend: < Table 2: Drugs Used for Prophylaxis of Headache in Children Class Drug a Dose Adverse Effects Drug Interactions Comments Antiepileptic Drugs topiramate Topamax, Adolescents: Start at 25 mg daily, increase by 25 mg daily at weekly intervals to 100 mg/day in 1 or 2 divided doses Most common: somnolence, anorexia, weight loss, paresthesias. Less common: psychomotor slowing, metabolic acidosis. Avoid use with alcohol or other CNS depressants. Used in adolescents. Antihistamines cyproheptadine Age 2 6 y: 2 mg Q8 12H (maximum 12 mg/day) Age 7 14 y: 4 mg Q8 12H (maximum 16 mg/day) Drowsiness, weight gain. Possible additive sedation with other CNS depressants, e.g., alcohol. More useful in younger children; use in older children and adolescents limited by sedation and increased appetite/weight gain. Beta 1 - adrenergic Antagonists propranolol Oral: mg/kg/day in 2 3 divided doses Fatigue, bradycardia, hypotension, depression. Antacids may decrease absorption. Contraindicated in asthma, diabetes, heart block, bradyarrhythmias, pregnancy; avoid abrupt withdrawal. Calcium Channel Blockers flunarizine Oral: 5 mg/day Bradycardia, hypotension, depression, Additive sedation with other CNS depressants. May take several weeks to be effective; do not
10 10 of 12 17/06/2014 7:57 PM Class Drug a Dose Adverse Effects Drug Interactions Comments drowsiness. use in depressed patients or those with extrapyramidal disorders. NSAIDs naproxen sodium Aleve, Anaprox, Maxidol Adolescents: mg twice daily For a detailed description of adverse effects associated with continuous NSAID use, see, Table 2. Warfarin: increased anticoagulant effect. Antihypertensives (diuretics, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, alphablockers): possible reduction in antihypertensive effect; may require additional antihypertensive therapy. Used in adolescents. Aleve NonRx: Rx: Lithium may interfere with sodium/water balance. Monitor lithium levels when NSAID added. Tricyclic Analgesics (TCAs) amitriptyline Elavil mg/day Weight gain, drowsiness; anticholinergic symptoms such as dry mouth and constipation. Possible additive sedation with other CNS depressants, e.g., alcohol; metabolized by cytochrome P450 enzyme system clearance may be affected by inhibitors (e.g., erythromycin, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, isoniazid, itraconazole, ketoconazole, paroxetine, valproic acid), inducers (e.g., phenobarbital, carbamazepine, phenytoin, rifampin) or other substrates of these enzymes. Contraindicated in significant cardiac disease or hypotension. Serotonin Antagonists pizotifen Sandomigran/ Sandomigran DS Oral: mg/day in divided doses Sedation and weight gain. Possible additive sedation with other CNS depressants including alcohol. Start medication slowly and increase over 1 3 wk. - a. Not to exceed maximum adult dose. b. Cost of 30-day supply based on 20 kg body weight; includes drug cost only. Dosage adjustment may be required in renal impairment; see Appendices: Dosage Adjustment in Renal Impairment. Abbreviations: NonRx=nonprescription; Rx=prescription product Legend: < Suggested Readings Brna PM, Dooley JM. Headaches in the pediatric population. Semin Pediatr Neurol 2006;13(4):
11 Friedman G. Advances in paediatric migraine. Paediatr Child Health 2002;7(4): Hershey AD. Recent developments in pediatric Curr Opin Neurol 2010;23(3): Lewis DW. Headaches in children and adolescents. Am Fam Physician 2002;65(4): Lewis DW. Toward the definition of childhood migraine. Curr Opin Pediatr 2004;16(6): Winner P. Pediatric Curr Opin Neurol 2008;21(3): References Dooley JM, Gordon KE, Wood EP. Frequent headaches in Canadian adolescents: prevalence and associated features. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 2003;7: Gordon KE, Dooley JM, Wood EP. Prevalence of reported migraine headaches in Canadian adolescents. Can J Neurol Sci 2004;31(3): Overview of diagnosis and management of paediatric Part I: diagnosis. J Headache Pain 2011(1): Hershey AD, Powers SW, Vockell AL et al. PedMIDAS: development of a questionnaire to assess disability of migraines in children. Neurology 2001;57(11): Lewis DW, Ashwal S, Dahl G et al. Practice parameter: evaluation of children and adolescents with recurrent headaches: report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the Practice Committee of the Child Neurology Society. Neurology 2002;59(4): Steiner TJ, Lange R, Voelker M. Aspirin in episodic tension-type headache: placebo-controlled dose-ranging comparison with paracetamol. Cephalalgia 2003;23(1): Hershey AD, Powers SW, Bentti AL et al. Effectiveness of amitriptyline in the prophylactic management of childhood headaches. Headache 2000;40(7): Sezer T, Kandemir H, Alehan F. A randomized trial comparing amitriptyline versus topiramate for the prophylaxis of chronic daily headache in pediatric patients. Int J Neurosci 2013;123(8): Mathew NT, Kurman R, Perez F. Drug induced refractory headache--clinical features and management. Headache 1990;30(10): Lewis D, Ashwal S, Hershey A et al. Practice parameter: pharmacological treatment of migraine headache in children and adolescents: report of the American Academy of Neurology Quality Standards Subcommittee and the Practice Committee of the Child Neurology Society. Neurology 2004;63(12): Hamalainen ML, Hoppu K, Valkeila E et al. Ibuprofen or acetaminophen for the acute treatment of migraine in children: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover study. Neurology 1997;48(1): Damen L, Bruijn JK, Verhagen AP et al. Symptomatic treatment of migraine in children: a systematic review of medication trials. Pediatrics 2005;116(2):e Termine C, Ozge A, Antonaci F et al. Overview of the diagnosis and management of pediatric Part II: therapeutic management. J Headache Pain 2011;12(1): Logan P, Lewis D. Towards evidence based emergency medicine: best BETs from the Manchester Royal Infirmary. Chlorpromazine in migraine. Emerg Med J 2007;24(4): Iserson KV. Parenteral chlorpromazine treatment of migraine. Ann Emerg Med 1983;12(12): Hamalainen ML, Hoppu K, Santavuori PR. Oral dihydroergotamine for therapy-resistant migraine attacks in children. Pediatr Neurol 1997;16(2): Linder SL. Treatment of childhood headache with dihydroergotamine mesylate. Headache 1994;34(10): Eiland LS, Hunt MO. The use of triptans for pediatric migraines. Paediatr Drugs 2010;12(6): Wöber-Bingöl Ç. Pharmacological treatment of acute migraine in adolescents and children. Paediatr Drugs 2013;15(3): Winner P, Rothner AD, Wooten JD et al. Sumatriptan nasal spray in adolescent migraineurs: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, acute study. Headache 2006;46(2): Winner P, Rothner AD, Saper J et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of sumatriptan nasal spray in the treatment of acute migraine in adolescents. Pediatrics 2000;106(5): Ahonen K, Hamalainen ML, Rantala H et al. Nasal sumatriptan is effective in treatment of migraine attacks in children: a randomized trial. Neurology 2004;62(6): Sorge F, De Simone R, Marano E et al. Flunarizine in prophylaxis of childhood migraine. A double-blind, placebocontrolled, crossover study. Cephalalgia 1988;8(1):1-6. Martinez-Lage JM. Flunarizine (Sibelium) in the prophylaxis of migraine. An open, long-term, multicenter trial. Cephalalgia 1988;8(Suppl 8): Ludvigsson J. Propranolol used in prophylaxis of migraine in children. Acta Neurol Scand 1974;50(1): of 12 17/06/2014 7:57 PM
12 Hershey AD, Powers SW, Bentti AL et al. Effectiveness of amitriptyline in the prophylactic management of childhood headaches. Headache 2000;40(7): Caruso JM, Brown WD, Exil G et al. The efficacy of divalproex sodium in the prophylactic treatment of children with migraine. Headache 2000;40(8): Serdaroglu G, Erhan E, Tekgul H et al. Sodium valproate prophylaxis in childhood migraine. Headache 2001;42(8): Winner P, Gendolla A, Stayer C et al. Topiramate for prevention of migraine in adolescents: a pooled analysis of efficacy and safety. Headache 2006;46(10): Lakshmi CV, Singhi P, Malhi P et al. Topiramate in the prophylaxis of pediatric migraine: a double-blind placebocontrolled trial. J Child Neurol 2007;22(7): Condo M, Posar A, Arbizzani A et al. Riboflavin prophylaxis in pediatric and adolescent migraine. J Headache Pain 2009;10(5): Therapeutic Choices. Canadian Pharmacists Association, All rights reserved. 12 of 12 17/06/2014 7:57 PM
Çiçek Wöber-Bingöl HEADACHE UNIT FOR CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENCE
 Headache in children and adolescents Çiçek Wöber-Bingöl HEADACHE UNIT FOR CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENCE Dept. of Psychiatry of Childhood and Adolescence Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria Impact
Headache in children and adolescents Çiçek Wöber-Bingöl HEADACHE UNIT FOR CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENCE Dept. of Psychiatry of Childhood and Adolescence Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria Impact
Management of headache
 Management of headache TJ Steiner Imperial College London Based on European principles of management of common headache disorders TJ Steiner, K Paemeleire, R Jensen, D Valade, L Savi, MJA Lainez, H-C Diener,
Management of headache TJ Steiner Imperial College London Based on European principles of management of common headache disorders TJ Steiner, K Paemeleire, R Jensen, D Valade, L Savi, MJA Lainez, H-C Diener,
How do we treat migraine? New SIGN Guidelines
 How do we treat migraine? New SIGN Guidelines Managing your migraine Migraine Trust, Edinburgh 2018 Callum Duncan Consultant Neurologist Aberdeen Royal Infirmary Chair SIGN Guideline 155 Premonitory Mood
How do we treat migraine? New SIGN Guidelines Managing your migraine Migraine Trust, Edinburgh 2018 Callum Duncan Consultant Neurologist Aberdeen Royal Infirmary Chair SIGN Guideline 155 Premonitory Mood
ADVANCES IN MIGRAINE MANAGEMENT
 ADVANCES IN MIGRAINE MANAGEMENT Joanna Girard Katzman, M.D.MSPH Assistant Professor, Dept. of Neurology Project ECHO, Chronic Pain Program University of New Mexico Outline Migraine throughout the decades
ADVANCES IN MIGRAINE MANAGEMENT Joanna Girard Katzman, M.D.MSPH Assistant Professor, Dept. of Neurology Project ECHO, Chronic Pain Program University of New Mexico Outline Migraine throughout the decades
HMFP Comprehensive Headache Center Department of Anesthesia, Critical Care and Pain Medicine Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Instructor in
 HMFP Comprehensive Headache Center Department of Anesthesia, Critical Care and Pain Medicine Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Instructor in Anesthesia and Neurology Harvard Medical School Limited time
HMFP Comprehensive Headache Center Department of Anesthesia, Critical Care and Pain Medicine Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Instructor in Anesthesia and Neurology Harvard Medical School Limited time
Disclosures. Triptans for Kids 5/16/13
 5/16/13 Disclosures Triptans for Kids Amy A. Gelfand, MD GelfandA@neuropeds.ucsf.edu Departments of Neurology and Pediatrics UCSF Child Neurology and Headache Center I receive grant funding from: NIH/NINDS
5/16/13 Disclosures Triptans for Kids Amy A. Gelfand, MD GelfandA@neuropeds.ucsf.edu Departments of Neurology and Pediatrics UCSF Child Neurology and Headache Center I receive grant funding from: NIH/NINDS
I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss investigational use of medication in my presentation.
 I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss investigational use of medication in my presentation. In 1962, Bille published landmark epidemiologic survey of headache among 9,000 school
I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss investigational use of medication in my presentation. In 1962, Bille published landmark epidemiologic survey of headache among 9,000 school
Adult & Pediatric Patients. Stanford Health Care, Division Pain Medicine
 Acute Treatment Strategies in Adult & Pediatric Patients Theresa Mallick Searle, MS, RN BC, ANP BC Disclosures Speakers Bureau: Allergan, Depomed Acute Treatment Strategies in Adult & Pediatric Patients
Acute Treatment Strategies in Adult & Pediatric Patients Theresa Mallick Searle, MS, RN BC, ANP BC Disclosures Speakers Bureau: Allergan, Depomed Acute Treatment Strategies in Adult & Pediatric Patients
Short Clinical Guidelines: Headache, Key Points for Diagnosis and Treatment
 Clinical Highlights 1. Headache is diagnosed by history and physical examination with limited need for imaging or laboratory tests. 2. Warning signs of possible disorder other than primary headache are:
Clinical Highlights 1. Headache is diagnosed by history and physical examination with limited need for imaging or laboratory tests. 2. Warning signs of possible disorder other than primary headache are:
Medication For Migraine Chart: Table 1: Acute Treatment when the attack begins
 Medication For Migraine Chart: Table 1: Acute Treatment when the attack begins Page a Analgesics (painkillers) Non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) Prescription required Brand Name Formulation
Medication For Migraine Chart: Table 1: Acute Treatment when the attack begins Page a Analgesics (painkillers) Non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) Prescription required Brand Name Formulation
Treatments for migraine
 Treatments for migraine Information for patients and carers Department of Neurology Aberdeen Royal Infirmary Contents Page About this leaflet Abortive medication for migraine Painkillers Antisickness medication
Treatments for migraine Information for patients and carers Department of Neurology Aberdeen Royal Infirmary Contents Page About this leaflet Abortive medication for migraine Painkillers Antisickness medication
Pharmacological treatment of attacks in juvenile migraine
 J Headache Pain (2004) 5:S62 S66 DOI 10.1007/s10194-004-0110-9 Beatrice Gallai Giovanni Mazzotta Paola Sarchielli Pharmacological treatment of attacks in juvenile migraine Received: Accepted in revised
J Headache Pain (2004) 5:S62 S66 DOI 10.1007/s10194-004-0110-9 Beatrice Gallai Giovanni Mazzotta Paola Sarchielli Pharmacological treatment of attacks in juvenile migraine Received: Accepted in revised
Acute Migraine Treatment in Adults
 PL Detail-Document #301104 This PL Detail-Document gives subscribers additional insight related the Recommendations published in PHARMACIST S LETTER / PRESCRIBER S LETTER November 2014 Acute Migraine Treatment
PL Detail-Document #301104 This PL Detail-Document gives subscribers additional insight related the Recommendations published in PHARMACIST S LETTER / PRESCRIBER S LETTER November 2014 Acute Migraine Treatment
Goals. Primary Headache Syndromes. One-Year Prevalence of Common Headache Disorders
 Goals One-Year Prevalence of Common Headache Disorders Impact of primary headache syndromes Non pharmacologic Rx of migraine individualized to patient triggers Complementary and alternative Rx of migraine
Goals One-Year Prevalence of Common Headache Disorders Impact of primary headache syndromes Non pharmacologic Rx of migraine individualized to patient triggers Complementary and alternative Rx of migraine
Abortive Agents. Available Strengths. Formulary Limits. Tablet: 5mg, 10mg ODT: 5mg, 10 mg 25mg, 50mg, 100mg. 5mg/act, 20mg/act
 MEDICATION COVERAGE POLICY PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS ADVISORY COMMITTEE POLICY: Migraine Therapy P&T DATE: 9/12/2017 CLASS: Neurological Disorders REVIEW HISTORY 12/16, 9/15, 2/15, 2/10, 5/07 LOB: MCL
MEDICATION COVERAGE POLICY PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS ADVISORY COMMITTEE POLICY: Migraine Therapy P&T DATE: 9/12/2017 CLASS: Neurological Disorders REVIEW HISTORY 12/16, 9/15, 2/15, 2/10, 5/07 LOB: MCL
Management options for Migraine. Prof. Dr. Khwaja Nazimuddin Head Dept. of Internal Medicine BIRDEM
 Management options for Migraine Prof. Dr. Khwaja Nazimuddin Head Dept. of Internal Medicine BIRDEM Assessment The Migraine Disability Assessment Score MIDAS Complete loss of work Partial loss of work Off
Management options for Migraine Prof. Dr. Khwaja Nazimuddin Head Dept. of Internal Medicine BIRDEM Assessment The Migraine Disability Assessment Score MIDAS Complete loss of work Partial loss of work Off
Headaches in the Pediatric Emergency Dept
 Headaches in Children February 23, 2011 Jinny Tavee, MD Associate Professor Neuromuscular Center Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland, OH 1 Headaches in the Pediatric Emergency Dept Burton Gutierrez Kan
Headaches in Children February 23, 2011 Jinny Tavee, MD Associate Professor Neuromuscular Center Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland, OH 1 Headaches in the Pediatric Emergency Dept Burton Gutierrez Kan
COMBINATION THERAPIES PREVENTATIVE THERAPIES BETA BLOCKERS
 ACUTE THEAPIES TIPTANS TICYCLIC ANTIDEPESSANTS When starting acute treatment, healthcare professionals should warn patients about the risk of developing medication-overuse headache. ASPIIN Aspirin (900
ACUTE THEAPIES TIPTANS TICYCLIC ANTIDEPESSANTS When starting acute treatment, healthcare professionals should warn patients about the risk of developing medication-overuse headache. ASPIIN Aspirin (900
A case of a patient with chronic headache. Focus on Migraine. None related to the presentation Grants to conduct clinical trials from: Speaker bureau:
 Chronic Daily Headache Bassel F. Shneker, MD, MBA Associate Professor Vice Chair, OSU Neurology The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Financial Disclosures None related to the presentation Grants
Chronic Daily Headache Bassel F. Shneker, MD, MBA Associate Professor Vice Chair, OSU Neurology The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Financial Disclosures None related to the presentation Grants
MIGRAINE UPDATE. Objectives & Disclosures. Learn techniques used to diagnose headaches. Become familiar with medications used for headache treatment.
 MIGRAINE UPDATE Karen L. Bremer, MD November 16, 2018 Objectives & Disclosures Learn techniques used to diagnose headaches. Become familiar with medications used for headache treatment. Disclosure: I am
MIGRAINE UPDATE Karen L. Bremer, MD November 16, 2018 Objectives & Disclosures Learn techniques used to diagnose headaches. Become familiar with medications used for headache treatment. Disclosure: I am
Prevention and Treatment of Migraines CAITLIN BARNES, PHARM.D. CANDIDATE AMBULATORY CARE JOE CAMMILLERI, PHARM.D. NATOHYA MALLORY, PHARM.D.
 Prevention and Treatment of Migraines CAITLIN BARNES, PHARM.D. CANDIDATE AMBULATORY CARE JOE CAMMILLERI, PHARM.D. NATOHYA MALLORY, PHARM.D. Objectives Present patient case Review epidemiology/pathophysiology
Prevention and Treatment of Migraines CAITLIN BARNES, PHARM.D. CANDIDATE AMBULATORY CARE JOE CAMMILLERI, PHARM.D. NATOHYA MALLORY, PHARM.D. Objectives Present patient case Review epidemiology/pathophysiology
Migraine in Children. Germano Falcao, MD Pediatric Neurology 03/07/2014
 Migraine in Children Germano Falcao, MD Pediatric Neurology 03/07/2014 Headaches in Children One of the most common concerns reported by children 3% for children age 3-7 years 4-11% for children age 7-11
Migraine in Children Germano Falcao, MD Pediatric Neurology 03/07/2014 Headaches in Children One of the most common concerns reported by children 3% for children age 3-7 years 4-11% for children age 7-11
Update on Diagnosis and Management of Migraines
 Update on Diagnosis and Management of Migraines Joel J. Heidelbaugh, MD, FAAFP, FACG Clinical Professor Departments of Family Medicine and Urology University of Michigan Learning Objectives To distinguish
Update on Diagnosis and Management of Migraines Joel J. Heidelbaugh, MD, FAAFP, FACG Clinical Professor Departments of Family Medicine and Urology University of Michigan Learning Objectives To distinguish
Regulatory Status FDA approved indication: Migranal Nasal Spray is indicated for the acute treatment of migraine headaches with or without aura (1).
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.60 Subject: Migranal Nasal Spray Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Migranal Nasal Spray
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.60 Subject: Migranal Nasal Spray Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Migranal Nasal Spray
Page: 1 of 6. Aimovig (erenumab-aooe) injection, Ajovy (fremanezumab-vfrm) injection, Emgality (galcanezumab-gnim)
 Page: 1 of 6 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Description Aimovig (erenumab-aooe) injection, Ajovy (fremanezumab-vfrm)
Page: 1 of 6 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Description Aimovig (erenumab-aooe) injection, Ajovy (fremanezumab-vfrm)
Index. Prim Care Clin Office Pract 31 (2004) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Prim Care Clin Office Pract 31 (2004) 441 447 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess, brain, headache in, 388 Acetaminophen for migraine, 406 407 headache from, 369
Prim Care Clin Office Pract 31 (2004) 441 447 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess, brain, headache in, 388 Acetaminophen for migraine, 406 407 headache from, 369
MEASURE #1: MEDICATION PRESCRIBED FOR ACUTE MIGRAINE ATTACK Headache
 MEASURE #1: MEDICATION PRESCRIBED FOR ACUTE MIGRAINE ATTACK Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 12 years and older with a diagnosis of migraine who were prescribed a guideline recommended
MEASURE #1: MEDICATION PRESCRIBED FOR ACUTE MIGRAINE ATTACK Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 12 years and older with a diagnosis of migraine who were prescribed a guideline recommended
Chronic Migraine in Primary Care. December 11 th, 2017 Werner J. Becker University of Calgary
 Chronic Migraine in Primary Care December 11 th, 2017 Werner J. Becker University of Calgary Disclosures Faculty: Werner J. Becker Relationships with commercial interests: Grants/Research Support: Clinical
Chronic Migraine in Primary Care December 11 th, 2017 Werner J. Becker University of Calgary Disclosures Faculty: Werner J. Becker Relationships with commercial interests: Grants/Research Support: Clinical
Migranal Nasal Spray. Migranal Nasal Spray (dihydroergotamine) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.60 Subject: Migranal Nasal Spray Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: June 22, 2017 Migranal Nasal Spray
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.60 Subject: Migranal Nasal Spray Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: June 22, 2017 Migranal Nasal Spray
ปวดศ รษะมา 5 ป ก นยาแก ปวดก ย งไม ข น นพ.พาว ฒ เมฆว ช ย โรงพยาบาลนครราชส มา
 ปวดศ รษะมา 5 ป ก นยาแก ปวดก ย งไม ข น นพ.พาว ฒ เมฆว ช ย โรงพยาบาลนครราชส มา 1 CONTENT 1 2 3 Chronic Daily Headache Medical Overused Headache Management Headaches are one of the most common symptoms List
ปวดศ รษะมา 5 ป ก นยาแก ปวดก ย งไม ข น นพ.พาว ฒ เมฆว ช ย โรงพยาบาลนครราชส มา 1 CONTENT 1 2 3 Chronic Daily Headache Medical Overused Headache Management Headaches are one of the most common symptoms List
Faculty Disclosures. Learning Objectives. Acute Treatment Strategies
 WWW.AMERICANHEADACHESOCIETY.ORG Acute Treatment Strategies Content developed by: Lawrence C. Newman, MD, FAHS Donna Gutterman, PharmD Faculty Disclosures LAWRENCE C. NEWMAN, MD, FAHS Dr. Newman has received
WWW.AMERICANHEADACHESOCIETY.ORG Acute Treatment Strategies Content developed by: Lawrence C. Newman, MD, FAHS Donna Gutterman, PharmD Faculty Disclosures LAWRENCE C. NEWMAN, MD, FAHS Dr. Newman has received
How could I be having migraine when I don't have a headache?
 Migraine Your doctor thinks you may have migraine. Classic migraine attacks start with visual symptoms (often zig-zag colored lights or flashes of light expanding to one side over 10-30 minutes) followed
Migraine Your doctor thinks you may have migraine. Classic migraine attacks start with visual symptoms (often zig-zag colored lights or flashes of light expanding to one side over 10-30 minutes) followed
SIGN on the pharmacological management of migraine
 GUIDELINES SIGN on the pharmacological management of migraine STEVE CHAPLIN In February 2018, the Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN) published a new guideline on the pharmacological management
GUIDELINES SIGN on the pharmacological management of migraine STEVE CHAPLIN In February 2018, the Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN) published a new guideline on the pharmacological management
Vestibular Migraine. Information for patients and carers. Department of Neurology and Otolaryngology Aberdeen Royal Infirmary
 Vestibular Migraine Information for patients and carers Department of Neurology and Otolaryngology Aberdeen Royal Infirmary What is vestibular migraine? Migraine is a disabling headache disorder that affects
Vestibular Migraine Information for patients and carers Department of Neurology and Otolaryngology Aberdeen Royal Infirmary What is vestibular migraine? Migraine is a disabling headache disorder that affects
MIGRAINE A MYSTERY HEADACHE
 MIGRAINE A MYSTERY HEADACHE The migraine is a chronic neurological disease that is characterized by moderate to severe episodes of headache that is mostly associated with other central nervous system (CNS)
MIGRAINE A MYSTERY HEADACHE The migraine is a chronic neurological disease that is characterized by moderate to severe episodes of headache that is mostly associated with other central nervous system (CNS)
Faculty Disclosure. Karen L. Bremer, MD. Dr. Bremer has listed no financial interest/arrangement that would be considered a conflict of interest.
 Faculty Disclosure Karen L. Bremer, MD Dr. Bremer has listed no financial interest/arrangement that would be considered a conflict of interest. HEADACHE UPDATE Karen L. Bremer, MD November 10, 2017 karen.bremer@creighton.edu
Faculty Disclosure Karen L. Bremer, MD Dr. Bremer has listed no financial interest/arrangement that would be considered a conflict of interest. HEADACHE UPDATE Karen L. Bremer, MD November 10, 2017 karen.bremer@creighton.edu
Clinical Policy: Triptans Reference Number: CP.CPA.217 Effective Date: Last Review Date: Line of Business: Commercial
 Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.CPA.217 Effective Date: 11.16.16 Last Review Date: 11.17 Line of Business: Commercial Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory
Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.CPA.217 Effective Date: 11.16.16 Last Review Date: 11.17 Line of Business: Commercial Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory
Sumatriptan Tablets, Nasal Spray (Imitrex), Nasal Powder (Onzetra Xsail), sumatriptan and naproxen sodium (Treximet tablets)
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 0 Subject: Sumatriptan Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Sumatriptan Description Sumatriptan
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 0 Subject: Sumatriptan Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Sumatriptan Description Sumatriptan
Case Presentation. Case Presentation. Case Presentation. Truths about Headaches (2017) Most headaches were muscle-tension headaches
 Agenda Case presentation Migraine Morphology Primary and Premonitory Phase Secondary Headache Aura Headache Primer on Pain Medication Overuse Headache Case Presentation RT is a 25 year old woman with daily
Agenda Case presentation Migraine Morphology Primary and Premonitory Phase Secondary Headache Aura Headache Primer on Pain Medication Overuse Headache Case Presentation RT is a 25 year old woman with daily
Sumatriptan Tablets, Nasal Spray (Imitrex), Nasal Powder (Onzetra Xsail), sumatriptan and naproxen sodium (Treximet tablets)
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 05.70.10 Subject: Sumatriptan Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: March 16, 2018 Sumatriptan Description Sumatriptan
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 05.70.10 Subject: Sumatriptan Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: March 16, 2018 Sumatriptan Description Sumatriptan
UTILIZATION MANAGEMENT CRITERIA
 SUMATRIPTAN (ALSUMA, IMITREX, SUMAVEL DOSEPRO, ZECUITY ) UTILIZATION MANAGEMENT CRITERIA DRUG CLASS: BRAND (generic) NAME: Serotonin 5-HT1 receptor agonists Imitrex (sumatriptan), Alsuma (sumatriptan),
SUMATRIPTAN (ALSUMA, IMITREX, SUMAVEL DOSEPRO, ZECUITY ) UTILIZATION MANAGEMENT CRITERIA DRUG CLASS: BRAND (generic) NAME: Serotonin 5-HT1 receptor agonists Imitrex (sumatriptan), Alsuma (sumatriptan),
Acute Migraine Treatment: What you and your family should know to help you make the best choices with your doctor
 Acute Migraine Treatment: What you and your family should know to help you make the best choices with your doctor TAKE CONTROL OF YOUR MIGRAINES! ABOUT THIS PATIENT GUIDE: Migraine attacks are often debilitating
Acute Migraine Treatment: What you and your family should know to help you make the best choices with your doctor TAKE CONTROL OF YOUR MIGRAINES! ABOUT THIS PATIENT GUIDE: Migraine attacks are often debilitating
Migraine treatment in developmental age: guidelines update
 J Headache Pain (2010) 11:267 276 DOI 10.1007/s10194-010-0205-4 TUTORIAL Migraine treatment in developmental age: guidelines update Laura Papetti Alberto Spalice Francesco Nicita Maria Chiara Paolino Rosa
J Headache Pain (2010) 11:267 276 DOI 10.1007/s10194-010-0205-4 TUTORIAL Migraine treatment in developmental age: guidelines update Laura Papetti Alberto Spalice Francesco Nicita Maria Chiara Paolino Rosa
11. HEADACHE 1. Pablo Lapuerta, MD, Steven Asch, MD, MPH, and Kenneth Clark, MD, MPH
 11. HEADACHE 1 Pablo Lapuerta, MD, Steven Asch, MD, MPH, and Kenneth Clark, MD, MPH We identified articles on the evaluation and management of headache by conducting a MEDLINE search of English language
11. HEADACHE 1 Pablo Lapuerta, MD, Steven Asch, MD, MPH, and Kenneth Clark, MD, MPH We identified articles on the evaluation and management of headache by conducting a MEDLINE search of English language
Clinical Policy: Triptans Reference Number: CP.HNMC.217 Effective Date: Last Review Date: Line of Business: Medicaid Medi-Cal
 Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.HNMC.217 Effective Date: 11.16.16 Last Review Date: 11.17 Line of Business: Medicaid Medi-Cal Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important
Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.HNMC.217 Effective Date: 11.16.16 Last Review Date: 11.17 Line of Business: Medicaid Medi-Cal Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important
OH, MY ACHING HEAD! I HAVE NO DISCLOSURES OR CONFLICTS OF INTERESTS TO DECLARE MANAGING HEADACHE IN THE OUTPATIENT SETTING SECONDARY HEADACHES
 1 JUSTIN A. OSSMAN, MD CHATTANOOGA FAMILY MEDICINE UPDATE OH, MY ACHING HEAD! MANAGING HEADACHE IN THE OUTPATIENT SETTING 2 I HAVE NO DISCLOSURES OR CONFLICTS OF INTERESTS TO DECLARE OBJECTIVES International
1 JUSTIN A. OSSMAN, MD CHATTANOOGA FAMILY MEDICINE UPDATE OH, MY ACHING HEAD! MANAGING HEADACHE IN THE OUTPATIENT SETTING 2 I HAVE NO DISCLOSURES OR CONFLICTS OF INTERESTS TO DECLARE OBJECTIVES International
TABLE 1. Current Diagnostic Criteria for Migraine Without Aura 2 A. At least 5 attacks fulfilling criteria B-D B. Headache attacks lasting 4-72 hours
 ANSWERS CONCISE TO FREQUENTLY REVIEW ASKED QUESTIONS FOR CLINICIANS ABOUT MIGRAINE Answers to Frequently Asked Questions About Migraine IVAN GARZA, MD, AND JERRY W. SWANSON, MD Migraine is a common primary
ANSWERS CONCISE TO FREQUENTLY REVIEW ASKED QUESTIONS FOR CLINICIANS ABOUT MIGRAINE Answers to Frequently Asked Questions About Migraine IVAN GARZA, MD, AND JERRY W. SWANSON, MD Migraine is a common primary
M0BCore Safety Profile. Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: ordispersible tablet SE/H/PSUR/0022/002 Date of FAR:
 M0BCore Safety Profile Active substance: Zolmitriptan Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: ordispersible tablet P-RMS: SE/H/PSUR/0022/002 Date of FAR: 15.03.2014 4.3 Contraindications Zolmitriptan is contraindicated
M0BCore Safety Profile Active substance: Zolmitriptan Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: ordispersible tablet P-RMS: SE/H/PSUR/0022/002 Date of FAR: 15.03.2014 4.3 Contraindications Zolmitriptan is contraindicated
Headache A Practical Approach
 Headache A Practical Approach Integrated Pain Symposium December 1, 2017 Alyssa Lettich. MD Neurosciences Institute/Neurosciences Clinical Program Medical Director Headache and Pain Development Teams Disclosures:
Headache A Practical Approach Integrated Pain Symposium December 1, 2017 Alyssa Lettich. MD Neurosciences Institute/Neurosciences Clinical Program Medical Director Headache and Pain Development Teams Disclosures:
COLUMBIA UNIVERSITY HEADACHE CENTER: NEW PATIENT QUESTIONNAIRE
 COLUMBIA UNIVERSITY HEADACHE CENTER: NEW PATIENT QUESTIONNAIRE HEADACHE CHARACTERISTICS Frequency and Severity 1. At what AGE did you get your first headache, of ANY kind? 2. At what AGE did your headaches
COLUMBIA UNIVERSITY HEADACHE CENTER: NEW PATIENT QUESTIONNAIRE HEADACHE CHARACTERISTICS Frequency and Severity 1. At what AGE did you get your first headache, of ANY kind? 2. At what AGE did your headaches
Strategies in Migraine Care
 Strategies in Migraine Care Julie L. Roth, MD Rhode Island Hospital Assistant Professor, Neurology The Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University March 28, 2015 Financial Disclosures None. Objectives
Strategies in Migraine Care Julie L. Roth, MD Rhode Island Hospital Assistant Professor, Neurology The Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University March 28, 2015 Financial Disclosures None. Objectives
TREXIMET UTILIZATION MANAGEMENT CRITERIA
 TREXIMET UTILIZATION MANAGEMENT CRITERIA DRUG CLASS: BRAND (generic) NAME: 5HT1 agonists Treximet (sumatriptan/naproxen sodium) 85 mg / 500 mg tablet FDA INDICATIONS: Sumatriptan/naproxen is indicated
TREXIMET UTILIZATION MANAGEMENT CRITERIA DRUG CLASS: BRAND (generic) NAME: 5HT1 agonists Treximet (sumatriptan/naproxen sodium) 85 mg / 500 mg tablet FDA INDICATIONS: Sumatriptan/naproxen is indicated
10/13/17. Christy M. Jackson, MD Director, Dalessio Headache Center Scripps Clinic, La Jolla Clinical Professor, Neurosciences UCSD
 Christy M. Jackson, MD Director, Dalessio Headache Center Scripps Clinic, La Jolla Clinical Professor, Neurosciences UCSD } Depomed Consultant 2014 to present } Avanir Consultant 2014 to present } Amgen
Christy M. Jackson, MD Director, Dalessio Headache Center Scripps Clinic, La Jolla Clinical Professor, Neurosciences UCSD } Depomed Consultant 2014 to present } Avanir Consultant 2014 to present } Amgen
Anti-Migraine Agents
 DRUG POLICY BENEFIT APPLICATION Anti-Migraine Agents Benefit determinations are based on the applicable contract language in effect at the time the services were rendered. Exclusions, limitations or exceptions
DRUG POLICY BENEFIT APPLICATION Anti-Migraine Agents Benefit determinations are based on the applicable contract language in effect at the time the services were rendered. Exclusions, limitations or exceptions
Ishaq Abu Arafeh Consultant Paediatrician Royal Hospital for Children, Glasgow Forth Valley Royal Hospital, Larbert
 Ishaq Abu Arafeh Consultant Paediatrician Royal Hospital for Children, Glasgow Forth Valley Royal Hospital, Larbert Childhood headache: Is it really difficult to manage? It shouldn t be... But it can be...
Ishaq Abu Arafeh Consultant Paediatrician Royal Hospital for Children, Glasgow Forth Valley Royal Hospital, Larbert Childhood headache: Is it really difficult to manage? It shouldn t be... But it can be...
Outpatient Headache Care Guideline
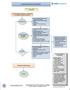 1 Outpatient Care Guideline Inclusion criteria: children > 3 yrs with headaches Is urgent emergency department, neuroimaging, or Neurology consultation indicated? Referral to ED if: New severe headache
1 Outpatient Care Guideline Inclusion criteria: children > 3 yrs with headaches Is urgent emergency department, neuroimaging, or Neurology consultation indicated? Referral to ED if: New severe headache
Paediatric headaches. Dr Jaycen Cruickshank Director of Clinical Training Ballarat Health Services. Brevity, levity, repetition
 Paediatric headaches Dr Jaycen Cruickshank Director of Clinical Training Ballarat Health Services Brevity, levity, repetition Paediatric)headache?)! Headache!in!children!is!not!that!common.!The!question!is!which!headaches!do!I!
Paediatric headaches Dr Jaycen Cruickshank Director of Clinical Training Ballarat Health Services Brevity, levity, repetition Paediatric)headache?)! Headache!in!children!is!not!that!common.!The!question!is!which!headaches!do!I!
Long-Term Care Updates
 Long-Term Care Updates September 2017 By Lindsay Slowiczek, PharmD Migraines are often considered to be a condition affecting younger or middle-aged patients, during which patients experience episodic,
Long-Term Care Updates September 2017 By Lindsay Slowiczek, PharmD Migraines are often considered to be a condition affecting younger or middle-aged patients, during which patients experience episodic,
What You Should Know About Your HEADACHE. Learn more about headache types, triggers, and treatments, when to get help, and how to help yourself
 What You Should Know About Your HEADACHE Learn more about headache types, triggers, and treatments, when to get help, and how to help yourself Introduction The purpose of this brochure is to give you a
What You Should Know About Your HEADACHE Learn more about headache types, triggers, and treatments, when to get help, and how to help yourself Introduction The purpose of this brochure is to give you a
MEASURE #3: PREVENTIVE MIGRAINE MEDICATION PRESCRIBED Headache
 MEASURE #3: PREVENTIVE MIGRAINE MEDICATION PRESCRIBED Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 18 years old and older diagnosed with migraine headache whose migraine frequency is 4 migraine
MEASURE #3: PREVENTIVE MIGRAINE MEDICATION PRESCRIBED Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 18 years old and older diagnosed with migraine headache whose migraine frequency is 4 migraine
Zomig. Zomig / Zomig-ZMT (zolmitriptan) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.22 Subject: Zomig Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: March 16, 2018 Zomig Description Zomig / Zomig-ZMT
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.22 Subject: Zomig Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: March 16, 2018 Zomig Description Zomig / Zomig-ZMT
Migraine Management. Jane Melling Headache nurse Mater Misericordiae Hospital
 Migraine Management Jane Melling Headache nurse Mater Misericordiae Hospital Migraine facts Among the most common disorders of the nervous system 3 rd most prevalent medical disorder on the planet (lancet
Migraine Management Jane Melling Headache nurse Mater Misericordiae Hospital Migraine facts Among the most common disorders of the nervous system 3 rd most prevalent medical disorder on the planet (lancet
Headaches in Children and Adolescents. Paul Shillito
 Headaches in Children and Adolescents Paul Shillito Topics For Discussion What s different about childhood migraine Chronic daily headache (CDH) Tumours and other things to worry about Management of childhood
Headaches in Children and Adolescents Paul Shillito Topics For Discussion What s different about childhood migraine Chronic daily headache (CDH) Tumours and other things to worry about Management of childhood
Adult with headache. Problem-specific video guides to diagnosing patients and helping them with management and prevention
 Adult with headache Problem-specific video guides to diagnosing patients and helping them with management and prevention London Strategic Clinical Networks London Neuroscience Strategic Clinical Network
Adult with headache Problem-specific video guides to diagnosing patients and helping them with management and prevention London Strategic Clinical Networks London Neuroscience Strategic Clinical Network
ZONISAMIDE THERAPEUTICS. Brands * Zonegran. Generic? Not in US. If It Doesn t Work * Class Antiepileptic drug (AED), structurally a sulfonamide
 Z:/3-PAGINATION/SBT/2-PROOFS/NWMS/9780521136723C111//9780521136723C111.3D 376 [376 380] ZONISAMIDE Brands Zonegran Generic? Not in US THERAPEUTICS Class Antiepileptic drug (AED), structurally a sulfonamide
Z:/3-PAGINATION/SBT/2-PROOFS/NWMS/9780521136723C111//9780521136723C111.3D 376 [376 380] ZONISAMIDE Brands Zonegran Generic? Not in US THERAPEUTICS Class Antiepileptic drug (AED), structurally a sulfonamide
PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE. Headache. This document should be read in conjunction with this DISCLAIMER
 Princess Margaret Hospital for Children PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE Scope (Staff): Scope (Area): All Emergency Department Clinicians Emergency Department This document should be read in conjunction
Princess Margaret Hospital for Children PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE Scope (Staff): Scope (Area): All Emergency Department Clinicians Emergency Department This document should be read in conjunction
Zomig. Zomig / Zomig-ZMT (zolmitriptan) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.22 Subject: Zomig Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Zomig Description Zomig / Zomig-ZMT
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.22 Subject: Zomig Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Zomig Description Zomig / Zomig-ZMT
Clinical Learning Days November 10, 2017
 Migraine Clinical Learning Days November 10, 2017 Alyssa Lettich. MD Neurosciences Institute/Neurosciences Clinical Program Medical Director Headache Disclosures: none Learning Objectives: At the conclusion
Migraine Clinical Learning Days November 10, 2017 Alyssa Lettich. MD Neurosciences Institute/Neurosciences Clinical Program Medical Director Headache Disclosures: none Learning Objectives: At the conclusion
Treatment of Primary Headache Syndromes
 Presenter Disclosure Information 2:45 3:45pm Treatment of Primary Headache Syndromes SPEAKER Gerald W. Smetana, MD The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Gerald W.Smetana, MD,
Presenter Disclosure Information 2:45 3:45pm Treatment of Primary Headache Syndromes SPEAKER Gerald W. Smetana, MD The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Gerald W.Smetana, MD,
ONZETRA XSAIL (sumatriptan) nasal powder
 ONZETRA XSAIL (sumatriptan) nasal powder Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Pharmacy
ONZETRA XSAIL (sumatriptan) nasal powder Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Pharmacy
Headache. Section 1. Migraine headache. Clinical presentation
 Section 1 Headache Migraine headache 1 Clinical presentation It is important to recognize just how significant a problem migraine headache is. It has been estimated that migraine affects 11% of the United
Section 1 Headache Migraine headache 1 Clinical presentation It is important to recognize just how significant a problem migraine headache is. It has been estimated that migraine affects 11% of the United
Headache Master School Japan-Osaka 2016 (HMSJ-Osaka2016) October 23, II. Management of Refractory Headaches
 Headache Master School Japan-Osaka 2016 (HMSJ-Osaka2016) October 23, 2016 II. Management of Refractory Headaches Case presentation 1: A case of intractable daily-persistent headache Keio University School
Headache Master School Japan-Osaka 2016 (HMSJ-Osaka2016) October 23, 2016 II. Management of Refractory Headaches Case presentation 1: A case of intractable daily-persistent headache Keio University School
Dsuvia (sufentanil) NEW PRODUCT SLIDESHOW
 Dsuvia (sufentanil) NEW PRODUCT SLIDESHOW Introduction Brand name: Dsuvia Generic name: Sufentanil Pharmacological class: Opioid agonist Strength and Formulation: 30mcg; sublingual tabs (housed in a disposable,
Dsuvia (sufentanil) NEW PRODUCT SLIDESHOW Introduction Brand name: Dsuvia Generic name: Sufentanil Pharmacological class: Opioid agonist Strength and Formulation: 30mcg; sublingual tabs (housed in a disposable,
Inpatient Treatment of Status Migraine With Dihydroergotamine in Children and Adolescents
 Headache 2008 the Authors Journal compilation 2008 American Headache Society ISSN 0017-8748 doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.2008.01293.x Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Brief Communication Inpatient Treatment
Headache 2008 the Authors Journal compilation 2008 American Headache Society ISSN 0017-8748 doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.2008.01293.x Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Brief Communication Inpatient Treatment
Triptans Quantity Limit Program Summary
 Triptans Quantity Limit Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS AND DOSAGE 1-13,14,23,24 Agents Amerge (naratriptan) 1, 2.5 tablets Axert (almotriptan) 6.25, 12.5 tablets migraine attacks with/without
Triptans Quantity Limit Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS AND DOSAGE 1-13,14,23,24 Agents Amerge (naratriptan) 1, 2.5 tablets Axert (almotriptan) 6.25, 12.5 tablets migraine attacks with/without
Dubai Standards of Care (Migraine)
 Dubai Standards of Care 2018 (Migraine) Preface Migraine is one of the most common problem dealt with in daily practice. In Dubai, the management of migraine is done through various different strategies.
Dubai Standards of Care 2018 (Migraine) Preface Migraine is one of the most common problem dealt with in daily practice. In Dubai, the management of migraine is done through various different strategies.
Migraleve, Migraleve Pink and Migraleve Yellow Product Information
 Migraleve, Migraleve Pink and Migraleve Yellow Product Information Adverse events should be reported. Reporting forms and information can be found at www.mhra.gov.uk/yellowcard Adverse events should also
Migraleve, Migraleve Pink and Migraleve Yellow Product Information Adverse events should be reported. Reporting forms and information can be found at www.mhra.gov.uk/yellowcard Adverse events should also
10/31/2017 PRIMARY CARE AND HEADACHE DISCLOSURES WHERE DO THOSE WITH HEADACHE SEEK MEDICAL CARE? Primary Care 67%
 PRIMARY CARE AND HEADACHE Sonja Potrebic MD PhD Regional Headache Specialist Kaiser LAMC 1 WHERE DO THOSE WITH HEADACHE SEEK MEDICAL CARE? Column1 Primary Care 67% Primary Care Headache Specialty Other
PRIMARY CARE AND HEADACHE Sonja Potrebic MD PhD Regional Headache Specialist Kaiser LAMC 1 WHERE DO THOSE WITH HEADACHE SEEK MEDICAL CARE? Column1 Primary Care 67% Primary Care Headache Specialty Other
Clinical Policy: Triptans Reference Number: CP.CPA.217 Effective Date: Last Review Date: Line of Business: Commercial
 Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.CPA.217 Effective Date: 11.16.16 Last Review Date: 11.18 Line of Business: Commercial Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory
Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.CPA.217 Effective Date: 11.16.16 Last Review Date: 11.18 Line of Business: Commercial Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory
ABORTIVE AGENTS. Average cost per 30 days. Form Limits SEROTONIN AGONISTS $ $ Reserved for treatment failure to either Sumatriptan PA; QL
 MEDICATION COVERAGE POLICY PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS ADVISORY COMMITTEE POLICY: Migraine Therapy P&T DATE: 12/11/2018 CLASS: Neurological Disorders REVIEW HISTORY 9/17, 12/16, 9/15, 2/15, 2/10, LOB: MCL
MEDICATION COVERAGE POLICY PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS ADVISORY COMMITTEE POLICY: Migraine Therapy P&T DATE: 12/11/2018 CLASS: Neurological Disorders REVIEW HISTORY 9/17, 12/16, 9/15, 2/15, 2/10, LOB: MCL
Understanding. Migraine. Amy, diagnosed in 1989, with her family.
 Understanding Migraine Amy, diagnosed in 1989, with her family. What Is a Migraine? A migraine is a recurring moderate to severe headache. The pain usually occurs on one side of the head. It is typically
Understanding Migraine Amy, diagnosed in 1989, with her family. What Is a Migraine? A migraine is a recurring moderate to severe headache. The pain usually occurs on one side of the head. It is typically
Triptan Quantity Limit
 *- Florida Healthy Kids Triptan Quantity Limit Override(s) Quantity Limit Approval Duration 1 year Oral Tablets Axert (almotriptan) tablets Relpax (eletriptan) tablets 6 tablets (6.25 mg) 12 tablets (12.5
*- Florida Healthy Kids Triptan Quantity Limit Override(s) Quantity Limit Approval Duration 1 year Oral Tablets Axert (almotriptan) tablets Relpax (eletriptan) tablets 6 tablets (6.25 mg) 12 tablets (12.5
Sumatriptan Tablets, Nasal Spray (Imitrex), Nasal Powder (Onzetra Xsail), sumatriptan and naproxen sodium (Treximet tablets)
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 05.70.10 Subject: Sumatriptan Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: December 2, 2016 Sumatriptan Description Sumatriptan
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 05.70.10 Subject: Sumatriptan Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: December 2, 2016 Sumatriptan Description Sumatriptan
Reflections on NICE Headache Guideline. Dr Kay Kennis GPwSI in Headache, Bradford
 Reflections on NICE Headache Guideline Dr Kay Kennis GPwSI in Headache, Bradford Overview The process of guideline development illustrated with the headache guideline Reflections on the process Key recommendations
Reflections on NICE Headache Guideline Dr Kay Kennis GPwSI in Headache, Bradford Overview The process of guideline development illustrated with the headache guideline Reflections on the process Key recommendations
Treatment Of Medication. Overuse Headache
 7 November 2012 BASH GPwSI Meeting Lecture title... Treatment Of Medication Dr... Overuse Headache Dr Marcus Lewis Dr... The National Migraine Centre International Headache Society Diagnostic criteria
7 November 2012 BASH GPwSI Meeting Lecture title... Treatment Of Medication Dr... Overuse Headache Dr Marcus Lewis Dr... The National Migraine Centre International Headache Society Diagnostic criteria
...SELECTED ABSTRACTS...
 The following abstracts, from medical journals containing literature on migraine management, were selected for their relevance to this Special Report supplement. Two Sumatriptan Studies Two double-blind
The following abstracts, from medical journals containing literature on migraine management, were selected for their relevance to this Special Report supplement. Two Sumatriptan Studies Two double-blind
ISSN doi: /head VC 2015 American Headache Society Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
 ISSN 0017-8748 Headache doi: 10.1111/head.12746 VC 2015 American Headache Society Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Review Article Acute Treatment Therapies for Pediatric Migraine: A Qualitative Systematic
ISSN 0017-8748 Headache doi: 10.1111/head.12746 VC 2015 American Headache Society Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Review Article Acute Treatment Therapies for Pediatric Migraine: A Qualitative Systematic
Headache Questionnaire
 Date: All Headache Patients We would appreciate your cooperation in filling out this form. In our evaluation of headache, your history is typically our most valuable tool for diagnosis and subsequent treatment.
Date: All Headache Patients We would appreciate your cooperation in filling out this form. In our evaluation of headache, your history is typically our most valuable tool for diagnosis and subsequent treatment.
The Pediatric Headache Handbook
 The Pediatric Headache Handbook For the Primary Care Physician Brought to you by the Division of Pediatric Neurology cardinalglennon.com Classification of headache patterns in children Acute onset of worst
The Pediatric Headache Handbook For the Primary Care Physician Brought to you by the Division of Pediatric Neurology cardinalglennon.com Classification of headache patterns in children Acute onset of worst
Maternity. Migraine in pregnancy Information for women
 Maternity Migraine in pregnancy Information for women You have been given this leaflet as you have a diagnosis of migraines. It contains advice to help you manage your migraines safely during your pregnancy.
Maternity Migraine in pregnancy Information for women You have been given this leaflet as you have a diagnosis of migraines. It contains advice to help you manage your migraines safely during your pregnancy.
disease or in clients who consume alcohol on a regular basis. bilirubin
 NON-OPIOID Acetaminophen(Tylenol) Therapeutic class: Analgesic, antipyretic Aspirin (ASA, Acetylsalicylic Acid) Analgesic, NSAID, antipyretic Non-Opioid Analgesics COMMON USES WHAT I NEED TO KNOW AS A
NON-OPIOID Acetaminophen(Tylenol) Therapeutic class: Analgesic, antipyretic Aspirin (ASA, Acetylsalicylic Acid) Analgesic, NSAID, antipyretic Non-Opioid Analgesics COMMON USES WHAT I NEED TO KNOW AS A
Page: 1 of 5. Sumatriptan Tablets and Nasal Spray (Imitrex) / sumatriptan and naproxen sodium (Treximet tablets)
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 0 Subject: Sumatriptan (Imitrex / Treximet) Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: September 12, 2014 Sumatriptan
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 0 Subject: Sumatriptan (Imitrex / Treximet) Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: September 12, 2014 Sumatriptan
Headache. Headache Case. Migraine Headache. Eric Kraus, MD. Types» Without aura (common)» With aura (classic)
 Headache Eric Kraus, MD Headache Case This 23 year-old female has headaches behind the right eye that cause her to lay down in a quiet room. They have a throbbing quality and she may vomit. Migraine Headache
Headache Eric Kraus, MD Headache Case This 23 year-old female has headaches behind the right eye that cause her to lay down in a quiet room. They have a throbbing quality and she may vomit. Migraine Headache
Pharmacy Medical Necessity Guidelines: Migraine Medications
 Pharmacy Medical Necessity Guidelines: Effective: September 18, 2017 Prior Authorization Required Type of Review Care Management Not Covered Type of Review Clinical Review Pharmacy (RX) or Medical (MED)
Pharmacy Medical Necessity Guidelines: Effective: September 18, 2017 Prior Authorization Required Type of Review Care Management Not Covered Type of Review Clinical Review Pharmacy (RX) or Medical (MED)
Maxalt. Maxalt / Maxalt-MLT (rizatriptan) Description. Section: Prescription Drugs Effective Date: April 1, 2016
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 Subject: Maxalt Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: March 18, 2016 Maxalt Description Maxalt / Maxalt-MLT (rizatriptan)
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 Subject: Maxalt Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: March 18, 2016 Maxalt Description Maxalt / Maxalt-MLT (rizatriptan)
HEADACHE: Benign or Severe Dr Gobinda Chandra Roy
 HEADACHE: Benign or Severe Dr Gobinda Chandra Roy Associate Professor, Department of Medicine, Shaheed Suhrawardy Medical College and Hospital Outlines 1. Introduction 2. Classification of headache 3.
HEADACHE: Benign or Severe Dr Gobinda Chandra Roy Associate Professor, Department of Medicine, Shaheed Suhrawardy Medical College and Hospital Outlines 1. Introduction 2. Classification of headache 3.
Prednisone vs. placebo in withdrawal therapy following medication overuse headache
 doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2007.01488.x Prednisone vs. placebo in withdrawal therapy following medication overuse headache L Pageler 1,2, Z Katsarava 2, HC Diener 2 & V Limmroth 1,2 1 Department of Neurology,
doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2007.01488.x Prednisone vs. placebo in withdrawal therapy following medication overuse headache L Pageler 1,2, Z Katsarava 2, HC Diener 2 & V Limmroth 1,2 1 Department of Neurology,
IMITREX UTILIZATION MANAGEMENT CRITERIA
 IMITREX UTILIZATION MANAGEMENT CRITERIA DRUG CLASS: 5HT1 agonists BRAND NAME: Imitrex 4 mg injection kit or refill (Generic) (sumatriptan) 6 mg injection kit or refill Injection vial (1 dose) 5 mg nasal
IMITREX UTILIZATION MANAGEMENT CRITERIA DRUG CLASS: 5HT1 agonists BRAND NAME: Imitrex 4 mg injection kit or refill (Generic) (sumatriptan) 6 mg injection kit or refill Injection vial (1 dose) 5 mg nasal
Allzital (butalbital-acetaminophen), butalbital-aspirin-caffeine, butalbitalaspirin-caffeine-codeine,
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 Subject: Butalbital Analgesics Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: March 16, 2018 Butalbital Analgesics Description
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 Subject: Butalbital Analgesics Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: March 16, 2018 Butalbital Analgesics Description
Study No.: Title: Rationale: Phase: Study Period: Study Design: Centres: Indication: Treatment: Objectives: Primary Outcome/Efficacy Variable:
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
