Nosebleeds are divided into two types, depending on whether the bleeding is coming from the front or back of the nose.
|
|
|
- Gervase Moore
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Nosebleeds Anatomy and Physiology The nose is an area of the body that contains many tiny blood vessels or arterioles that can break easily. One of every seven people will develop a nosebleed some time in their lifetime. Nosebleeds can occur at any age but are most common in children aged 2-10 years and adults aged years. Nosebleeds may arise from arteries or from veins. The blood pressure in veins is lower than the blood pressure in arteries. Compressing the nose or packing the nostril with a ribbon of gauze or a balloon in order to exert pressure on the bleeding point is more likely to fail to stop a nosebleed if it comes from an artery. In this situation it is normally possible to stop the bleeding by tying off or blocking the artery which supplies the bleeding point. The arterial blood supply to the nose comes from two main sources. The top of the nasal cavity and the partition between the nostrils (nasal septum) is supplied by fine branches of the internal carotid artery, one of the main arteries supplying the brain. These reach the nose after they pass through the eye socket, supplying blood to its contents en route. This artery is called the ophthalmic artery and the branches which reach the nose are called the ethmoidal arteries. Most of the lower part of the nasal cavity is supplied by a large branch of the external carotid artery, the artery which supplies blood to most of the face and underlying structures. This artery reaches the nose by passing behind the sinus of the cheek and entering the nose through its sidewall near the back of the nose. Before it reaches the nose it is known as the maxillary artery, but as it enters the known its name changes to the sphenopalatine artery. Nosebleeds are divided into two types, depending on whether the bleeding is coming from the front or back of the nose. What is an anterior nosebleed? Most nosebleeds or epistaxes begin in the lower part of the septum, the semi-rigid wall that separates the two nostrils of the nose. The septum contains blood vessels that can be broken by a blow to the nose or the edge of a sharp fingernail. Nosebleed coming from the front of the nose or anterior nosebleeds often begin with a flow of blood out one nostril when the patient is sitting or standing. Anterior nosebleeds are common in dry climates or during the winter months when dry, heated indoor air dehydrates the nasal membranes. Dryness may result in crusting, cracking, and bleeding. This can be prevented by placing a light coating of petroleum jelly or an antibiotic ointment on the end of a fingertip and then rub it inside the nose, especially on the middle portion of the nose (the septum).
2 How to stop an anterior nosebleed Stay calm, or help a young child stay calm. A person who is agitated may bleed more profusely than someone who s been reassured and supported. Keep head higher than the level of the heart. Sit up. Lean slightly forward so the blood won t drain in the back of the throat. Using the thumb and index finger, pinch all the soft parts of the nose. The area where pressure should be applied is located between the end of the nose and the hard, bony ridge that forms the bridge of the nose. Do not pack the inside of the nose with gauze or cotton. Apply ice crushed in a plastic bag or washcloth to nose and cheeks. Hold the position for five minutes. If it s still bleeding, hold it again for an additional 10 minutes. What is a posterior nosebleed? More rarely, a nosebleed can begin high and deep within the nose and flow down the back of the mouth and throat even if the patient is sitting or standing. Obviously, when lying down, even anterior (front of nasal cavity) nosebleeds may seem to flow toward the back of the throat especially if coughing or blowing the nose. It is important to try to make the distinction between the anterior and posterior nosebleed, since posterior nosebleeds are often more severe and almost always require a physician s care. Posterior nosebleeds are more likely to occur in older people, persons with high blood pressure, and in cases of injury to the nose or face. What are the causes of recurring nosebleeds? Allergies, infections, or dryness that cause itching and lead to picking of the nose. Vigorous nose blowing that ruptures superficial blood vessels. Clotting disorders that run in families or are due to medications. Drugs (such as anticoagulants or anti-inflammatories). Fractures of the nose or the base of the skull. Head injuries that cause nosebleeds should be regarded seriously. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia, a disorder involving a blood vessel growth similar to a birthmark in the back of the nose. Tumors, both malignant and nonmalignant, have to be considered, particularly in the older patient or in smokers. Primary Treatment:
3 1. Stay calm. 2. Sit down and lean the head slightly forward (so that the blood doesn t drip down the back of the throat and cause an upset stomach). 3. Use your thumb and index finger to firmly squeeze the entire SOFT part of the nose for AT LEAST 5 minutes. Time yourself to make sure that the nose is squeezed constantly for the full 5 minutes. If it is still bleeding, squeeze for another 5 minutes. 4. Optional: Place an ice pack across the nose. If the nose continues to bleed: 1. Blow the nose to remove the blood clots. 2. Spray each nostril 2 times with an over-the-counter decongestant spray, like Afrin or Neo-Synephrine. 3. Squeeze the nose an additional 5-10 minutes. 4. If you can t get the bleeding to stop, call your doctor or go to the emergency room. Prevention: To prevent nosebleeds: Gently apply a thin layer of petroleum jelly (Vaseline) to each nostril 1-2 times a day as directed. You can also use saline nasal spray 2-4 times a day. Don t pick your nose. Don t blow your nose too hard. Surgical Indications Most nosebleeds can be controlled by cauterising the bleeding point or by packing the nose. This may be made easier by straightening the nasal septum. Those that cannot be controlled by simpler measures will need surgery to tie off (ligate) the blood supply to the bleeding point or blocking off (embolization) of the blood supply to the affected area. Anesthetic
4 Operations to tie off the arteries are usually performed under a general anesthetic, with local anesthetic being applied to the nose to constrict the blood vessels and slow the bleeding. Embolization is usually carried out under heavy sedation or a general anesthetic. Surgical Technique Tying off arteries involves an operation to expose the artery and then tying a tight thread around the vessel to stop blood flowing through it. The ethmoidal arteries are exposed by making a small cut in the skin of the side of the nose, adjacent to the inner corner of the eye, and then pulling the contents of the eye socket sideways to expose the arteries as they come out of the contents of the socket, which lie in a fibrous covering. They are then tied or cauterized at the point where they enter holes in the bony side wall of the nose and pass into the nose. The skin incision is then stitched. The maxillary artery is exposed by making a cut under the upper lip and removing bone from the front wall of the sinus of the cheek (the Maxillary Sinus). Bone is then removed from the back wall of the sinus too to expose the artery which runs in a pad of fat behind the sinus. The artery is blocked off with metal clips and the cut in the gum is closed with dissolving sutures. Some surgeons will tie off the external carotid artery in the neck after making a cut in the skin over the artery and retracting muscles to reveal the artery. It is tied above the level of the branch to the tongue to avoid depriving it of blood flow. An increasingly popular technique is the tie off the sphenopalatine artery as it enters the mucous membrane of the wall of the nose. A telescope is passed up the nose and used to visualise the outer wall of the nose near the back. Instruments are passed beside the telescope and used to raise a flap of mucous membrane where the artery enters the nose, exposing the artery. The artery can then be cauterised or clipped to stop blood flow. Embolisation of arteries is usually carried out by the Interventional Radiologist in the X-ray Department. After numbing the skin with local anaesthetic, a thin tube is passed through a needle into the main artery of the leg and up through the arterial system to the nose. Dye, which shows up under an X-ray camera, is squirted through the tube to outline the vessels. This allows the Radiologist to know where he is pushing the tube. The tube is wriggled through the system until it lies in the artery supplying bleeding point. Small particles or blobs of glue are then squirted into the vessel from the tube to block the vessel and stop it bleeding, upstream and downstream of the leaking point. The tube is then removed and pressure is exerted on the artery in the leg to prevent a bruise forming. This technique is not generally available and requires great expertise on the part of the Radiologist. Length of Operation
5 Tying off the ethmoidal arteries takes 15 to 30 minutes. Tying off the external carotid artery takes 20 to 40 minutes. Tying off the maxillary artery takes up to an hour. Tying off the sphenopalatine artery takes 10 to 20 minutes. It may take longer if bleeding is profuse and may be impossible if the surgeon is unable to see clearly. It may be necessary to tie off more than one vessel. This may extend the operating time. Embolisation of an artery may take 30 to 90 minutes. Again multiple embolisations may be necessary which may prolong the procedure. Time in Hospital In general most patients are discharged within 48 hours of bleeding stopping unless they have other problems such as anaemia and require a blood transfusion. Time off Work/Limitations Any patient who has had a severe nosebleed should be discouraged from forceful nose blowing for 2 to 3 weeks after it has stopped as this may promote further bleeding. They should also be encouraged to sneeze with their mouth open for at least 2 weeks. Nasal obstruction may be reduced by the judicious use of blood vessel constricting nasal sprays, saline nasal douches and gentle sniffing. Strenuous exercise and heavy lifting are to be discouraged for 4 weeks. Nose picking may also promote further bleeding and is to be discouraged. A dry environment may promote crusting and wasting (atrophy) of the nasal lining, which may in turn promote further bleeding. Risks and Complications The operation to tie off the ethmoidal arteries may cause a temporary black eye. Theoretically the eye sight can be affected by retracting the contents of the eye socket but in practise this very rarely happens. Tying off the external carotid rarely causes any complications other than a scar, although there are a variety of delicate nerves which need to be carefully identified and preserved during the procedure if one is to avoid a numb or weak tongue. The cross flow of blood from other arteries to the other structures supplied by the artery tends to prevent a lack of blood flow to the face. Blindness may very
6 occasionally occur if the artery to the eye aberrantly arises from the external carotid artery rather than the internal carotid artery. Tying off the maxillary artery may cause problems with numbness to the face and upper teeth, a persistent hole between the mouth and the sinus through the gum incision (oro-antral fistula). It may also fail to stop bleeding as the artery may be tricky to identify in the fat behind the back wall of the sinus. Tying off the sphenopalatine artery is usually effective unless a tortuous nasal passageway or excessive bleeding makes it difficult to see the vessel as it enters the nose. This may result in misplacing the clip or inadvertent division of the artery rather than tying it off. This tends to cause more bleeding. Embolisation of nasal vessels is not risk free. As with any procedure which involves the passing of a tube into the arteries supplying the brain there is a 1% risk of causing a stroke either by dislodging particles which fly off into the artery and block one or several of the branches. Occasional severe allergic reactions occur to the dyes which are used. Outcome and Prognosis In general tying off vessels and embolisation are very successful in controlling nosebleeds. Where there is a disorder of blood clotting this has to be treated as well or surgery/embolisation is not likely to succeed. Alternative Treatments Less invasive measures such as compression of the nose, packing, warm water irrigation and blood vessel constricting sprays have usually been tried and failed before ligation or embolisation are required. Once this point has been reached there are no other alternative treatments. When should an otolaryngologist be consulted? If frequent nosebleeds are a problem, it is important to consult an otolaryngologist. An ear, nose, and throat specialist will carefully examine the nose using an endoscope, a tube with a light for seeing inside the nose, prior to making a treatment recommendation. Two of the most common treatments are cautery and packing the nose. Cautery is a technique in which the blood vessel is burned with an electric current, silver nitrate, or a laser. Sometimes, a doctor may just pack the nose with a special gauze or an inflatable latex balloon to put pressure on the blood vessel.
7 Tips to prevent a nosebleed Keep the lining of the nose moist by gently applying a light coating of petroleum jelly or an antibiotic ointment with a cotton swab three times daily, including at bedtime. Commonly used products include Bacitracin, A and D Ointment, Eucerin, Polysporin, and Vaseline. Keep children s fingernails short to discourage nose picking. Counteract the effects of dry air by using a humidifier. Use a saline nasal spray to moisten dry nasal membranes. Quit smoking. Smoking dries out the nose and irritates it. Tips to prevent rebleeding after initial bleeding has stopped Do not pick or blow nose. Do not strain or bend down to lift anything heavy. Keep head higher than the heart. If rebleeding occurs: Attempt to clear nose of all blood clots. Spray nose four times in the bleeding nostril(s) with a decongestant spray such as Afrin or Neo- Synephrine. Repeat the steps to stop an anterior nosebleed. Call a doctor if bleeding persists after 30 minutes or if nosebleed occurs after an injury to the head. Nosebleeds: Treatment and Prevention Treatment: 1. Stay calm. 2. Sit down and lean the head slightly forward (so that the blood doesn t drip down the back of the throat and cause an upset stomach).
8 3. Use your thumb and index finger to firmly squeeze the entire SOFT part of the nose for AT LEAST 5 minutes. Time yourself to make sure that the nose is squeezed constantly for the full 5 minutes. If it is still bleeding, squeeze for another 5 minutes. 4. Optional: Place an ice pack across the nose. If the nose continues to bleed: 1. Blow the nose to remove the blood clots. 2. Spray each nostril 2 times with an over-the-counter decongestant spray. 3. Squeeze the nose an additional 5-10 minutes. 4. If you can t get the bleeding to stop, call your doctor or go to the emergency room. Alternatives: There is an over the counter product named Nosebleed QR that may be of benefit to patients with frequent nosebleeds who need help stopping an active nosebleed. This should not be considered an endorsement of any particular product, but it may be helpful to you. Prevention: To prevent nosebleeds: 1. Gently apply a thin layer of petroleum jelly (Vaseline) to each nostril 1-2 times a day as directed. You can also use saline nasal spray 2-4 times a day. 2. Don t pick your nose. 3. Don t blow your nose too hard. If you go to your health care provider with a nosebleed, he or she will have you sit up and lean forward to determine the rate and site of the bleeding. Your provider may check your pulse and blood pressure and take a blood sample to check for anemia and your blood type in case you need a transfusion. How is it treated? First aid for a nosebleed includes these steps: When your nose starts bleeding, sit up and lean forward to prevent blood from passing into your throat, which may cause choking. Pinch the nose firmly together between the thumb and index finger, just below the nasal bones,
9 and hold it for 10 minutes. Moisten a cotton ball or pad with a saline nasal spray and press it against the bleeding part of the nose if possible. Continue to sit quietly and press on your nose. After the bleeding stops, apply zinc oxide to the septum to prevent drying and abrasions. Also, use a saline nasal spray to keep the nose moist. If a nosebleed lasts more than 20 minutes or doesn't respond to first aid, call your health care provider. If you go to your health care provider with a nosebleed, he or she will likely apply a cotton ball soaked in epinephrine, or a nose drop to the site of the bleeding for 5 to 10 minutes. If the bleeding starts again, your provider may apply a cotton ball soaked in stronger medication for 5 minutes in order to numb and temporarily reduce the blood supply to the mucous membrane. Most anterior nosebleeds respond to direct pressure. If this doesn't work, your health care provider may numb the site of the bleeding again, then pack your nose. Packing for anterior nosebleeds is less complicated and more comfortable than the packing required for posterior nosebleeds. Your health care provider may use a procedure called cauterization to force the blood to clot (coagulate) at the bleeding site. Your provider must remove any packing. Severe bleeding and improperly handled packing can be fatal. Treatment, especially for posterior nosebleeds, may sometimes include hospitalization. How long do the effects last? Most nosebleeds stop by themselves within 10 minutes. How can I take care of myself? Follow the treatment prescribed by your health care provider. In addition you can: Use a cool-mist humidifier. Keep a nasal spray on hand. Put bacitracin ointment, Vaseline, or a saline nasal spray inside your nostrils to control dryness. Check with your health care provider about any other medications you may be using. Nosebleeds may be more severe or frequent if you are taking aspirin. Don't use cocaine. Don't smoke. Limit your intake of spicy and hot foods and hot liquids. Don't take hot showers. Avoid bending over, straining, and lifting heavy objects. Don't exercise vigorously for a few days. Use a laxative to avoid straining during bowel movements. If you have another posterior nosebleed, contact your health care provider. How can I help prevent a nosebleed? Some causes of nosebleeds can be prevented or managed as follows:
10 When you have a nasal infection, keep your nasal septum well coated with a petrolatum-based ointment or an antibiotic ointment until your nose heals (usually 3 to 5 days). Then apply the ointment regularly to the nasal septum to prevent drying and breakdown of the membranes. Avoid injuring the nasal mucosa with nose-picking, rubbing, or forceful blowing. Keep your home humidified. Control minor recurrent nosebleeds by applying cotton balls or pads soaked in Xylometazoline nasal drops. Special Instructions: 1.Apply Saline Nasal Spray into both nostrils 3 to 6 times a day to keep the membranes moist and promote healing. 2.Applybactroban on a Qtip GENTLY inside each nostril twice a day for at least a month. 3. When bleeding actively, roll a cotton ball into a "cigarette shaped cylinder" and gently put it inside each nostril, and then soak the cotton with AFRIN. 4. Leave the packs in for 10 minutes and then gently pull them out. 5. Avoid blowing your nose until the nasal lining tissue is fully healed.
Nosebleed (Epistaxis)
 2015 WebMD, LLC. All rights reserved. Nosebleed (Epistaxis) Nosebleed Overview Nosebleed Causes Nosebleeds in Children Nosebleed Symptoms When to Seek Medical Care Nosebleed Diagnosis Nosebleed Self-Care
2015 WebMD, LLC. All rights reserved. Nosebleed (Epistaxis) Nosebleed Overview Nosebleed Causes Nosebleeds in Children Nosebleed Symptoms When to Seek Medical Care Nosebleed Diagnosis Nosebleed Self-Care
NASHVILLE EAR, NOSE &THROAT CLINIC STEPHEN A. MITCHELL, M.D., F.A.C.S MITCHELL K. SCHWABER, M.D. STEVEN ENRICH, M.D. MATTHEW SPEYER. M.D., P.C.
 N A S H V I L L E ENT C L I N I C NASHVILLE EAR, NOSE &THROAT CLINIC STEPHEN A. MITCHELL, M.D., F.A.C.S MITCHELL K. SCHWABER, M.D. STEVEN ENRICH, M.D. MATTHEW SPEYER. M.D., P.C. WHAT TO EXPECT AFTER SEPTOPLASTY
N A S H V I L L E ENT C L I N I C NASHVILLE EAR, NOSE &THROAT CLINIC STEPHEN A. MITCHELL, M.D., F.A.C.S MITCHELL K. SCHWABER, M.D. STEVEN ENRICH, M.D. MATTHEW SPEYER. M.D., P.C. WHAT TO EXPECT AFTER SEPTOPLASTY
Ears. Mouth. Jowls 6 Major Bones of the Face Nasal bone Two
 1 2 3 4 5 Chapter 25 Injuries to the Face, Neck, and Eyes Injuries to the Face and Neck Face and neck are to injury Relatively unprotected positions on body Some injuries are life-threatening. trauma to
1 2 3 4 5 Chapter 25 Injuries to the Face, Neck, and Eyes Injuries to the Face and Neck Face and neck are to injury Relatively unprotected positions on body Some injuries are life-threatening. trauma to
Nasal Surgery. Types of Surgery. This handout explains different types of nasal surgery and what to expect.
 Nasal Surgery This handout explains different types of nasal surgery and what to expect. Types of Surgery Septoplasty is a surgery done to straighten the septum. The septum is made of bone and cartilage.
Nasal Surgery This handout explains different types of nasal surgery and what to expect. Types of Surgery Septoplasty is a surgery done to straighten the septum. The septum is made of bone and cartilage.
Sinus Surgery. Middle Meatus
 Sinus Surgery Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus surgery is also yours. This
Sinus Surgery Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus surgery is also yours. This
Post Operative Instructions: Wisdom Teeth
 The removal of impacted teeth is a serious surgical procedure. Post-operative care is very important. Unnecessary pain and the complications of infection and swelling can be minimized if the instructions
The removal of impacted teeth is a serious surgical procedure. Post-operative care is very important. Unnecessary pain and the complications of infection and swelling can be minimized if the instructions
What is Otolaryngology? (pronounced oh/toe/lair/in/goll/oh/jee) is the oldest medical specialty in the United States.
 What is Otolaryngology? (pronounced oh/toe/lair/in/goll/oh/jee) is the oldest medical specialty in the United States. Otolaryngologists are physicians trained in the medical and surgical management and
What is Otolaryngology? (pronounced oh/toe/lair/in/goll/oh/jee) is the oldest medical specialty in the United States. Otolaryngologists are physicians trained in the medical and surgical management and
Potential Complications
 Potential Complications The risk of complications associated with wisdom teeth removal is less than 0.5 percent when performed by an experienced oral surgeons who uses contemporary techniques and surgical
Potential Complications The risk of complications associated with wisdom teeth removal is less than 0.5 percent when performed by an experienced oral surgeons who uses contemporary techniques and surgical
NO SMOKING UNDER ANY CIRCUMSTANCES.
 Aftercare Instructions: Wisdom Tooth Romoval The removal of impacted teeth is a serious surgical procedure. Post-operative care is very important. Unnecessary pain and the complications of infection and
Aftercare Instructions: Wisdom Tooth Romoval The removal of impacted teeth is a serious surgical procedure. Post-operative care is very important. Unnecessary pain and the complications of infection and
Caring for your Dentures
 DENTURES SERIES Caring for your Dentures It s important that your dentures, like natural teeth, be kept free from plaque and tartar. This prevents permanent staining and bad breath. Use a denture brush
DENTURES SERIES Caring for your Dentures It s important that your dentures, like natural teeth, be kept free from plaque and tartar. This prevents permanent staining and bad breath. Use a denture brush
Septal surgery / turbinate reduction surgery
 Septal surgery / turbinate reduction surgery What is septal surgery? The septum is a thin piece of cartilage and bone inside the nose between the right and left nostrils. It is about seven centimetres
Septal surgery / turbinate reduction surgery What is septal surgery? The septum is a thin piece of cartilage and bone inside the nose between the right and left nostrils. It is about seven centimetres
Mr Glenn Watson M.B., B.S., B.Sc. (Hons), F.R.A.C.S. Ear, Nose and Throat Head and Neck Surgeon
 Mr Glenn Watson M.B., B.S., B.Sc. (Hons), F.R.A.C.S. Ear, Nose and Throat Head and Neck Surgeon FUNCTIONAL ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY A guide for Mr Watson s patients During your consultation with Mr Watson,
Mr Glenn Watson M.B., B.S., B.Sc. (Hons), F.R.A.C.S. Ear, Nose and Throat Head and Neck Surgeon FUNCTIONAL ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY A guide for Mr Watson s patients During your consultation with Mr Watson,
INFORMATION REGARDING YOUR NASAL SURGERY
 INFORMATION REGARDING YOUR NASAL SURGERY This document contains information about the following aspects of nasal surgery: Pre-op information: How to prepare for surgery. Procedure: Wat is done during surgery.
INFORMATION REGARDING YOUR NASAL SURGERY This document contains information about the following aspects of nasal surgery: Pre-op information: How to prepare for surgery. Procedure: Wat is done during surgery.
Surgical Instructions. Wisdom Tooth TREASURE VALLEY ORAL & FACIAL SURGERY
 TREASURE VALLEY ORAL & FACIAL SURGERY Surgical Instructions Wisdom Tooth 1000 North Curtis Road, Suite 103 Boise, ID 83706 Phone: 208-343-0909 Fax: 208-343-6282 TREASURE VALLEY ORAL & FACIAL SURGERY AFTER
TREASURE VALLEY ORAL & FACIAL SURGERY Surgical Instructions Wisdom Tooth 1000 North Curtis Road, Suite 103 Boise, ID 83706 Phone: 208-343-0909 Fax: 208-343-6282 TREASURE VALLEY ORAL & FACIAL SURGERY AFTER
Post-Op Instructions
 Post-Op Instructions The Day of Surgery 1. There will be some degree of discomfort, and pain arises as the numbness subsides. At the first sign of pain or discomfort, take (3-4) tablets of 200mg Motrin/Ibuprofen/Advil.
Post-Op Instructions The Day of Surgery 1. There will be some degree of discomfort, and pain arises as the numbness subsides. At the first sign of pain or discomfort, take (3-4) tablets of 200mg Motrin/Ibuprofen/Advil.
After Wisdom Teeth Removal
 After Wisdom Teeth Removal It is our desire that your recovery be as smooth and pleasant as possible. Following these instructions will assist you, but if you have questions about your progress, please
After Wisdom Teeth Removal It is our desire that your recovery be as smooth and pleasant as possible. Following these instructions will assist you, but if you have questions about your progress, please
SINUS SURGERY. Dr Zenia Chow MBBS(hons), FRACS
 SINUS SURGERY Dr Zenia Chow MBBS(hons), FRACS Facial Plastic & Reconstructive Surgeon Otolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgeon ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY/FESS What are sinuses The sinuses are a connected system
SINUS SURGERY Dr Zenia Chow MBBS(hons), FRACS Facial Plastic & Reconstructive Surgeon Otolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgeon ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY/FESS What are sinuses The sinuses are a connected system
Endoscopic Sinus Surgery. Definition
 Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Definition An operation carried out through the nose to re-establish the normal ventilation and mucus drainage mechanisms in the chronically infected nose and sinuses by removing
Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Definition An operation carried out through the nose to re-establish the normal ventilation and mucus drainage mechanisms in the chronically infected nose and sinuses by removing
Facial Sports Injuries
 Facial Sports Injuries Playing catch, shooting hoops, bicycling on a scenic path or just kicking around a soccer ball have more in common than you may think. On the up side, these activities are good exercise
Facial Sports Injuries Playing catch, shooting hoops, bicycling on a scenic path or just kicking around a soccer ball have more in common than you may think. On the up side, these activities are good exercise
After Dental Extractions or Wisdom Teeth Removal
 Patient & Family Guide After Dental Extractions or Wisdom Teeth Removal 2017 Aussi disponible en français : Après l extraction des dents ou l enlèvement des dents de sagesse (FF85-1786) www.nshealth.ca
Patient & Family Guide After Dental Extractions or Wisdom Teeth Removal 2017 Aussi disponible en français : Après l extraction des dents ou l enlèvement des dents de sagesse (FF85-1786) www.nshealth.ca
Care After Your Dental Treatment For Hospital Dentistry patients
 Patient Education Care After Your Dental Treatment For Hospital Dentistry patients Your surgeon today was Dr.. Please carefully follow the instructions in this handout. General Do not disturb the wound
Patient Education Care After Your Dental Treatment For Hospital Dentistry patients Your surgeon today was Dr.. Please carefully follow the instructions in this handout. General Do not disturb the wound
Information for patients preparing for a tracheostomy at Toronto General Hospital
 Tracheostomy Information for patients preparing for a tracheostomy at Toronto General Hospital This booklet will answer the following questions: What is a tracheostomy or trach? Why do I need a tracheostomy?
Tracheostomy Information for patients preparing for a tracheostomy at Toronto General Hospital This booklet will answer the following questions: What is a tracheostomy or trach? Why do I need a tracheostomy?
For the Patient: Trastuzumab emtansine Other names: KADCYLA
 For the Patient: Trastuzumab emtansine Other names: KADCYLA Trastuzumab emtansine (tras tooz' ue mab em tan' seen) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. Trastuzumab emtansine is a clear
For the Patient: Trastuzumab emtansine Other names: KADCYLA Trastuzumab emtansine (tras tooz' ue mab em tan' seen) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. Trastuzumab emtansine is a clear
Preventing Bleeding When You Have a Low Platelet Count
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Preventing Bleeding When You Have a Low Platelet Count What is a low platelet count? A platelet count measures the number of platelets you have in your blood.
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Preventing Bleeding When You Have a Low Platelet Count What is a low platelet count? A platelet count measures the number of platelets you have in your blood.
POST-OPERATIVE CARE. nyimplantdentistry.com/postop
 POST-OPERATIVE CARE nyimplantdentistry.com/postop The Diamond Schlesinger Group 30 East 60 th Street, Suite 703 New York, NY 10022 Welcome! Please read through the information carefully and use good judgment.
POST-OPERATIVE CARE nyimplantdentistry.com/postop The Diamond Schlesinger Group 30 East 60 th Street, Suite 703 New York, NY 10022 Welcome! Please read through the information carefully and use good judgment.
Mr Glenn Watson M.B., B.S., B.Sc. (Hons), F.R.A.C.S. Ear, Nose and Throat Head and Neck Surgeon
 Mr Glenn Watson M.B., B.S., B.Sc. (Hons), F.R.A.C.S. Ear, Nose and Throat Head and Neck Surgeon SURGICAL REMOVAL OF TONSILS AND ADENOIDS A guide for Mr Watson s patients During your consultation with Mr
Mr Glenn Watson M.B., B.S., B.Sc. (Hons), F.R.A.C.S. Ear, Nose and Throat Head and Neck Surgeon SURGICAL REMOVAL OF TONSILS AND ADENOIDS A guide for Mr Watson s patients During your consultation with Mr
Pituitary Tumour Surgery. Remember to bring this handout to the hospital with you.
 Pituitary Tumour Surgery Remember to bring this handout to the hospital with you. 1 Pituitary Tumour Surgery Table of contents Page What is the pituitary gland?... 2 What is a pituitary tumour?... 3 Why
Pituitary Tumour Surgery Remember to bring this handout to the hospital with you. 1 Pituitary Tumour Surgery Table of contents Page What is the pituitary gland?... 2 What is a pituitary tumour?... 3 Why
CAST CARE. Helping Broken Bones Heal
 CAST CARE Helping Broken Bones Heal When You Need a Cast Are you injured and in need of a cast? Don t worry, you ll get through it. Wearing a cast will help your injured body part heal. Healing takes time,
CAST CARE Helping Broken Bones Heal When You Need a Cast Are you injured and in need of a cast? Don t worry, you ll get through it. Wearing a cast will help your injured body part heal. Healing takes time,
Head and neck cancer - patient information guide
 Head and neck cancer - patient information guide The development of reconstructive surgical techniques in the last 20 years has led to major advances in the treatment of patients with head and neck cancer.
Head and neck cancer - patient information guide The development of reconstructive surgical techniques in the last 20 years has led to major advances in the treatment of patients with head and neck cancer.
Instructions for MACS LIFT Post- Operative
 Instructions for MACS LIFT Post- Operative INTRODUCTION The following instructions are based on experience with many MACS- Lift operations. They will answer practically every question that may arise regarding
Instructions for MACS LIFT Post- Operative INTRODUCTION The following instructions are based on experience with many MACS- Lift operations. They will answer practically every question that may arise regarding
CM01 Facelift. Copyright 2007 Page 1 of 6
 CM01 Facelift What is a facelift? A facelift is an operation to tighten and lift the soft tissues of your face and neck. Your surgeon will assess you and let you know if a facelift is suitable for you.
CM01 Facelift What is a facelift? A facelift is an operation to tighten and lift the soft tissues of your face and neck. Your surgeon will assess you and let you know if a facelift is suitable for you.
Table of Contents. Dialysis Port Care Chemotherapy Port Care G-Tube Care Colostomy Bags Wound Dressings
 Table of Contents Dialysis Port Care Chemotherapy Port Care G-Tube Care Colostomy Bags Wound Dressings Dialysis Port Care Know What Type of Vascular Access You Have. Fistula: An artery in your forearm
Table of Contents Dialysis Port Care Chemotherapy Port Care G-Tube Care Colostomy Bags Wound Dressings Dialysis Port Care Know What Type of Vascular Access You Have. Fistula: An artery in your forearm
Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
 WHAT IS FUNCTIONAL ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY (FESS)? The nasal telescope has greatly changes the evaluation and treatment of rhino-sinusitis. This instrument, which provides a view of the structures in
WHAT IS FUNCTIONAL ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY (FESS)? The nasal telescope has greatly changes the evaluation and treatment of rhino-sinusitis. This instrument, which provides a view of the structures in
MEDICAL NOSEBLEED MANAGEMENT: HEREDITARY HEMORRHAGIC TELANGIECTASIA ASSOCIATED EPISTAXIS COPYRIGHT NOTICE
 MEDICAL NOSEBLEED MANAGEMENT: HEREDITARY HEMORRHAGIC TELANGIECTASIA ASSOCIATED EPISTAXIS COPYRIGHT NOTICE Washington University grants permission to use and reproduce the Medical Nosebleed Management:
MEDICAL NOSEBLEED MANAGEMENT: HEREDITARY HEMORRHAGIC TELANGIECTASIA ASSOCIATED EPISTAXIS COPYRIGHT NOTICE Washington University grants permission to use and reproduce the Medical Nosebleed Management:
Patient & Family Guide. Nose Surgery.
 Patient & Family Guide Nose Surgery 2017 www.nshealth.ca Nose Surgery Types of nose surgery Nasal polypectomy Removes polyps (pale, grey swellings that may interfere with breathing). Septoplasty Repairs
Patient & Family Guide Nose Surgery 2017 www.nshealth.ca Nose Surgery Types of nose surgery Nasal polypectomy Removes polyps (pale, grey swellings that may interfere with breathing). Septoplasty Repairs
EduCare Knowledge & Skill Assessment Medication I Routes
 EduCare Knowledge & Skill Assessment Medication I Routes Employee Name Date Demonstration/Skill Assessment Oral (O) Pass Fail 1. Wash your hands; apply gloves. 2. Perform the 3 safety checks on the Simple
EduCare Knowledge & Skill Assessment Medication I Routes Employee Name Date Demonstration/Skill Assessment Oral (O) Pass Fail 1. Wash your hands; apply gloves. 2. Perform the 3 safety checks on the Simple
Minimally Invasive Endoscopic Resection of the Pituitary (MIERP) Patient Information
 Minimally Invasive Endoscopic Resection of the Pituitary (MIERP) Patient Information Introduction The pituitary gland is located at the base of the brain behind the sphenoid sinus and between the eyes.
Minimally Invasive Endoscopic Resection of the Pituitary (MIERP) Patient Information Introduction The pituitary gland is located at the base of the brain behind the sphenoid sinus and between the eyes.
OV United Soccer Club
 Preventing disease transmission Place an effective barrier between you and the victim s blood when you give first aid. Examples of such barriers are: the victim s hand, a piece of plastic, clean folded
Preventing disease transmission Place an effective barrier between you and the victim s blood when you give first aid. Examples of such barriers are: the victim s hand, a piece of plastic, clean folded
Medications. Managing and Administering Medication
 Medications Managing and Administering Medication The Medication Administration Checklist Administering medications is an important and vital responsibility. It is important to make sure that no errors
Medications Managing and Administering Medication The Medication Administration Checklist Administering medications is an important and vital responsibility. It is important to make sure that no errors
First Aid Policy. One member of every coaching staff (competitive) is "required" to be first aid certified.
 First Aid Policy When you accept the role of coach with LSSC, regardless of what level, you accept a major responsibility for the care and safety of your players. Although the athletes share in the responsibility
First Aid Policy When you accept the role of coach with LSSC, regardless of what level, you accept a major responsibility for the care and safety of your players. Although the athletes share in the responsibility
Medical & Safety. Stay safe at Kamp Dovetail 2011
 Medical & Safety Stay safe at Kamp Dovetail 2011 Seizures Seizures are very misunderstood and may be caused by many different types of conditions, such as: Insulin shock High fevers Viral infections of
Medical & Safety Stay safe at Kamp Dovetail 2011 Seizures Seizures are very misunderstood and may be caused by many different types of conditions, such as: Insulin shock High fevers Viral infections of
Instructions After Getting Tooth Pulled Can You Smoke
 Instructions After Getting Tooth Pulled Can You Smoke After the tooth is removed, you may need stitches. The removed tooth can be replaced with an implant, a denture, or a bridge. Avoid smoking. Having
Instructions After Getting Tooth Pulled Can You Smoke After the tooth is removed, you may need stitches. The removed tooth can be replaced with an implant, a denture, or a bridge. Avoid smoking. Having
The pillars defining our quality care. We Care!
 The pillars defining our quality care We Care! 1 An umbilical hernia occurs when a tissue bulges out through an opening in time muscles on the abdomen near the navel or belly button (umbilicus). About
The pillars defining our quality care We Care! 1 An umbilical hernia occurs when a tissue bulges out through an opening in time muscles on the abdomen near the navel or belly button (umbilicus). About
13: Condoms. Words of Wisdom. How to Use a Male Condom. Condom Line-Up Cards. Shopping Information Form. Condoms Dos & Don ts
 13: Condoms Words of Wisdom How to Use a Male Condom Condom Line-Up Cards Shopping Information Form Condoms Dos & Don ts Wishing cannot bring autumn glory nor cause winter to cease. Kiowa How to Use a
13: Condoms Words of Wisdom How to Use a Male Condom Condom Line-Up Cards Shopping Information Form Condoms Dos & Don ts Wishing cannot bring autumn glory nor cause winter to cease. Kiowa How to Use a
Post Op Instructions For Composite Fillings
 Post Op Instructions For Composite Fillings Do not eat or chew anything until the numbness has completely worn off. It is very easy to injure your lip or tongue while you are numb. It is normal to experience
Post Op Instructions For Composite Fillings Do not eat or chew anything until the numbness has completely worn off. It is very easy to injure your lip or tongue while you are numb. It is normal to experience
ATI Skills Modules Checklist for Medication Administration 2
 For faculty use only Educator s name Score Date ATI Skills Modules Checklist for Medication Administration 2 Student s name Date Verify order Patient record Assess for procedure need Identify, gather,
For faculty use only Educator s name Score Date ATI Skills Modules Checklist for Medication Administration 2 Student s name Date Verify order Patient record Assess for procedure need Identify, gather,
The Surgical Treatment of Migraine Headaches
 The Surgical Treatment of Migraine Headaches Being migraine-free for 11 years has been a dream come true. I live my life now with a freedom that I hadn t known for more than 23 years. Kathy Where is the
The Surgical Treatment of Migraine Headaches Being migraine-free for 11 years has been a dream come true. I live my life now with a freedom that I hadn t known for more than 23 years. Kathy Where is the
What causes swimmer s ear?
 Swimmer s Ear Affecting the outer ear, swimmer s ear is a painful condition resulting from inflammation, irritation, or infection. These symptoms often occur after water gets trapped in your ear, with
Swimmer s Ear Affecting the outer ear, swimmer s ear is a painful condition resulting from inflammation, irritation, or infection. These symptoms often occur after water gets trapped in your ear, with
This information was created and reviewed through a partnership with the UAMS Patient and Family Advisory Councils.
 Tracheostomy Care You have a: Cuffed Tracheostomy Cuffless Tracheostomy What is a tracheostomy? A tracheostomy (sometimes called a trach rhymes with cake ) is a small opening, or stoma, in your throat.
Tracheostomy Care You have a: Cuffed Tracheostomy Cuffless Tracheostomy What is a tracheostomy? A tracheostomy (sometimes called a trach rhymes with cake ) is a small opening, or stoma, in your throat.
For the Patient: Everolimus tablets Other names: AFINITOR
 For the Patient: Everolimus tablets Other names: AFINITOR Everolimus (e'' ver oh' li mus) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if
For the Patient: Everolimus tablets Other names: AFINITOR Everolimus (e'' ver oh' li mus) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if
Advice to patients having an angioplasty
 What is an angioplasty? Advice to patients having an angioplasty An angioplasty is an x ray procedure to open a narrowed or blocked artery in order to improve blood flow. It involves inserting a long tube
What is an angioplasty? Advice to patients having an angioplasty An angioplasty is an x ray procedure to open a narrowed or blocked artery in order to improve blood flow. It involves inserting a long tube
X-Plain Tympanoplasty Reference Summary
 X-Plain Tympanoplasty Reference Summary Introduction Tympanoplasty is a surgical procedure to repair a perforated eardrum. The eardrum is a thin membrane inside the ear at the end of the ear canal. Eardrum
X-Plain Tympanoplasty Reference Summary Introduction Tympanoplasty is a surgical procedure to repair a perforated eardrum. The eardrum is a thin membrane inside the ear at the end of the ear canal. Eardrum
Ortho Hygiene. #2078, Tuscany Blvd. NW, Calgary, AB T3L 2V7 Phone: Fax:
 Ortho Hygiene You already know that maintaining good oral hygiene is important for everyone but when you re having orthodontic treatment, it s even more critical. Why? Because, while the appliances (such
Ortho Hygiene You already know that maintaining good oral hygiene is important for everyone but when you re having orthodontic treatment, it s even more critical. Why? Because, while the appliances (such
For the Patient: Fludarabine injection Other names: FLUDARA
 For the Patient: Fludarabine injection Other names: FLUDARA Fludarabine (floo-dare-a-been) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell
For the Patient: Fludarabine injection Other names: FLUDARA Fludarabine (floo-dare-a-been) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell
About your Hernia Operation
 Patient Information About your Hernia Operation Introduction We expect you to make a rapid recovery after your operation and to experience no serious problems. However, it is important that you should
Patient Information About your Hernia Operation Introduction We expect you to make a rapid recovery after your operation and to experience no serious problems. However, it is important that you should
EPISTAXIS. Rory Attwood MBChB,FRCS Department of Otorhinolaryngology Faculty of Health Sciences Tygerberg Campus, University of Stellenbosch
 EPISTAXIS Rory Attwood MBChB,FRCS Department of Otorhinolaryngology Faculty of Health Sciences Tygerberg Campus, University of Stellenbosch EPISTAXIS Bleeding from the nose Age Incidence Children Elderly
EPISTAXIS Rory Attwood MBChB,FRCS Department of Otorhinolaryngology Faculty of Health Sciences Tygerberg Campus, University of Stellenbosch EPISTAXIS Bleeding from the nose Age Incidence Children Elderly
Having a radiologically inserted gastrostomy. An information guide
 TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Having a radiologically inserted gastrostomy An information guide Having a radiologically inserted gastrostomy Introduction This leaflet
TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Having a radiologically inserted gastrostomy An information guide Having a radiologically inserted gastrostomy Introduction This leaflet
Rhinoplasty. Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England.
 Rhinoplasty Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained the information in this
Rhinoplasty Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained the information in this
Chapter 6 Epistaxis. What You Need. Página 1 de 6.
 Página 1 de 6 Chapter 6 Epistaxis Epistaxis is a common problem; although the vast majority of cases are trivial, some may present as life-threatening problems because of hypotension or aspiration of blood.
Página 1 de 6 Chapter 6 Epistaxis Epistaxis is a common problem; although the vast majority of cases are trivial, some may present as life-threatening problems because of hypotension or aspiration of blood.
PRE-SEDATION RECORD PHYSICIAN S ASSESSMENT
 PRE-SEDATION RECORD PHYSICIAN S ASSESSMENT Dear Doctor, Your patient is scheduled for dental treatment under intravenous sedation. Please complete this history and physical examination form and return
PRE-SEDATION RECORD PHYSICIAN S ASSESSMENT Dear Doctor, Your patient is scheduled for dental treatment under intravenous sedation. Please complete this history and physical examination form and return
What causes abnormal secretions?
 Post-Nasal Drip Glands in your nose and throat continually produce mucus (one to two quarts a day). Mucus moistens and cleans the nasal membranes, humidifies air, traps and clears inhaled foreign matter,
Post-Nasal Drip Glands in your nose and throat continually produce mucus (one to two quarts a day). Mucus moistens and cleans the nasal membranes, humidifies air, traps and clears inhaled foreign matter,
THE PLASTIC SURGERY CLINIC
 FACELIFT SURGERY INSTRUCTIONS FOLLOWING SURGERY WHAT TO EXPECT IMMEDIATELY AFTER SURGERY You will wake up with a helmet dressing on your head (i.e. bandages) and you may have some drains/tubes inserted
FACELIFT SURGERY INSTRUCTIONS FOLLOWING SURGERY WHAT TO EXPECT IMMEDIATELY AFTER SURGERY You will wake up with a helmet dressing on your head (i.e. bandages) and you may have some drains/tubes inserted
For the Patient: Lenvatinib Other names: LENVIMA
 For the Patient: Lenvatinib Other names: LENVIMA Lenvatinib (len va' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a capsule that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if you have ever
For the Patient: Lenvatinib Other names: LENVIMA Lenvatinib (len va' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a capsule that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if you have ever
How is 1st MTP joint fusion carried out? Patient Information: Big Toe Fusion Metatarsophalangeal (MTP)
 Patient Information: Big Toe Fusion Metatarsophalangeal (MTP) How is 1st MTP joint fusion carried out? You will be asked to wash your feet thoroughly on the day of operation and keep them clean, as this
Patient Information: Big Toe Fusion Metatarsophalangeal (MTP) How is 1st MTP joint fusion carried out? You will be asked to wash your feet thoroughly on the day of operation and keep them clean, as this
Dental or Oral Surgery
 Patient Education Dental Clinic Dental or Oral Surgery Post-operative care instructions This handout provides care instructions for you to follow after your dental or oral surgery. It also provides the
Patient Education Dental Clinic Dental or Oral Surgery Post-operative care instructions This handout provides care instructions for you to follow after your dental or oral surgery. It also provides the
Heart Valve Replacement
 Heart Valve Replacement Introduction Sometimes people have serious problems with the valves in their hearts. A heart valve repair or replacement surgery restores or replaces a defective heart valve. If
Heart Valve Replacement Introduction Sometimes people have serious problems with the valves in their hearts. A heart valve repair or replacement surgery restores or replaces a defective heart valve. If
MASTOID EXPLORATION (MASTOID SURGERY) AND MASTOIDECTOMY
 MASTOID EXPLORATION (MASTOID SURGERY) AND MASTOIDECTOMY This information leaflet is to support your decision with your Specialist. This leaflet will explain about the ear are and what surgery can be offered
MASTOID EXPLORATION (MASTOID SURGERY) AND MASTOIDECTOMY This information leaflet is to support your decision with your Specialist. This leaflet will explain about the ear are and what surgery can be offered
Gynaecology Department Patient Information Leaflet
 Vaginal repair Gynaecology Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet gives information about vaginal repair surgery used to treat a vaginal prolapse. The leaflet explains what a
Vaginal repair Gynaecology Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet gives information about vaginal repair surgery used to treat a vaginal prolapse. The leaflet explains what a
E09 PEG. Expires end of March 2018 VITALITY.CO.UK
 VITALITY.CO.UK E09 PEG Expires end of March 2018 You can get more information and share your experiences at www.aboutmyhealth.org Tell us how useful you found this document at www.patientfeedback.org eidohealthcare.com
VITALITY.CO.UK E09 PEG Expires end of March 2018 You can get more information and share your experiences at www.aboutmyhealth.org Tell us how useful you found this document at www.patientfeedback.org eidohealthcare.com
Commen Nose Diseases
 Commen Nose Diseases Symptoms List: Nasal obstruction. Nasal discharge: Anterior (Rhinorrhea). Posterior (Postnasal discharge). Epistaxis. Hyposmia and Anosmia. Headache. Snoring. Nasal Obstruction Definition:
Commen Nose Diseases Symptoms List: Nasal obstruction. Nasal discharge: Anterior (Rhinorrhea). Posterior (Postnasal discharge). Epistaxis. Hyposmia and Anosmia. Headache. Snoring. Nasal Obstruction Definition:
YOUR COMPREHENSIVE GUIDE TO. Wisdom Teeth. (03) omfs.com.au
 YOUR COMPREHENSIVE GUIDE TO Wisdom Teeth (03) 9347 3788 omfs.com.au Wisdom teeth 3 Symptoms caused by impacted wisdom teeth 4 Treatment options 5 The removal procedure 6 Important facts to consider with
YOUR COMPREHENSIVE GUIDE TO Wisdom Teeth (03) 9347 3788 omfs.com.au Wisdom teeth 3 Symptoms caused by impacted wisdom teeth 4 Treatment options 5 The removal procedure 6 Important facts to consider with
Your Anaesthetic Explained
 Your Anaesthetic Explained Patient Information Sheet Pre Admission Assessment Clinic Tel: 4920307 What is anaesthesia? The word anaesthesia means loss of sensation. If you have ever had a dental injection
Your Anaesthetic Explained Patient Information Sheet Pre Admission Assessment Clinic Tel: 4920307 What is anaesthesia? The word anaesthesia means loss of sensation. If you have ever had a dental injection
Open Radical Prostatectomy Surgery
 To learn about radical prostatectomy surgery, you will need to know these words: The prostate is the sexual gland that makes fluid to help sperm move around. The prostate surrounds the urethra at the neck
To learn about radical prostatectomy surgery, you will need to know these words: The prostate is the sexual gland that makes fluid to help sperm move around. The prostate surrounds the urethra at the neck
Flexible Fiberoptic Exam
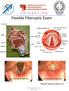 Flexible Fiberoptic Exam True Vocal Cords abducted True Vocal Cords adducted *Fiberoptic endoscopy, image is true. Cerumen Removal Position Patient -Explain Procedure Visualize Canal/Landmarks Determine
Flexible Fiberoptic Exam True Vocal Cords abducted True Vocal Cords adducted *Fiberoptic endoscopy, image is true. Cerumen Removal Position Patient -Explain Procedure Visualize Canal/Landmarks Determine
MIDDLE EAR SURGERY. For Better Health and Hearing
 MIDDLE EAR SURGERY For Better Health and Hearing Help for Ongoing Ear Problems Your doctor has found a problem with your middle ear. This is a part of the ear that you can t see. You may have taken medication,
MIDDLE EAR SURGERY For Better Health and Hearing Help for Ongoing Ear Problems Your doctor has found a problem with your middle ear. This is a part of the ear that you can t see. You may have taken medication,
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE HUMIRA 40 MG/0.8 ML, 20 MG/0.4 ML AND 10 MG/0.2 ML SINGLE-USE PREFILLED SYRINGE
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE HUMIRA (Hu-MARE-ah) (adalimumab) 40 MG/0.8 ML, 20 MG/0.4 ML AND 10 MG/0.2 ML SINGLE-USE PREFILLED SYRINGE Do not try to inject HUMIRA yourself until you have been shown the right way
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE HUMIRA (Hu-MARE-ah) (adalimumab) 40 MG/0.8 ML, 20 MG/0.4 ML AND 10 MG/0.2 ML SINGLE-USE PREFILLED SYRINGE Do not try to inject HUMIRA yourself until you have been shown the right way
RHINOPLASTY (NOSE RE-SHAPING)
 PROCEDURE FACT SHEET PLASTIC SURGERY RHINOPLASTY (NOSE RE-SHAPING) This is a guide for people who are considering having a nose re-shaping (Rhinoplasty) operation. We advise that you talk to a plastic
PROCEDURE FACT SHEET PLASTIC SURGERY RHINOPLASTY (NOSE RE-SHAPING) This is a guide for people who are considering having a nose re-shaping (Rhinoplasty) operation. We advise that you talk to a plastic
Nasal Polyps. Multimedia Health Education. Disclaimer
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. All decisions about the management of Nasal Polyps must be made in conjunction with your Physician or
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. All decisions about the management of Nasal Polyps must be made in conjunction with your Physician or
Patient information leaflet about Lower Wisdom Teeth (3 rd Molars)
 Patient information leaflet about Lower Wisdom Teeth (3 rd Molars) This leaflet is designed to give you more information about what the issues are with wisdom teeth, what treatment options may be given,
Patient information leaflet about Lower Wisdom Teeth (3 rd Molars) This leaflet is designed to give you more information about what the issues are with wisdom teeth, what treatment options may be given,
Surgery to the middle ear to improve hearing (stapedectomy)
 Surgery to the middle ear to improve hearing (stapedectomy) Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to
Surgery to the middle ear to improve hearing (stapedectomy) Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to
Instructions for Use. Welcome!
 Instructions for Use Welcome! The AMJEVITA SureClick autoinjector is a single-use prefilled autoinjector. Consult your doctor if you have any questions about your dose. Your doctor has prescribed AMJEVITA
Instructions for Use Welcome! The AMJEVITA SureClick autoinjector is a single-use prefilled autoinjector. Consult your doctor if you have any questions about your dose. Your doctor has prescribed AMJEVITA
For the Patient: GOOVDDCAT
 For the Patient: GOOVDDCAT Other Names: Primary Treatment of Advanced Epithelial Ovarian, Fallopian Tube and Primary Peritoneal Cancer Using Carboplatin and Paclitaxel GO = Gynecologic Oncology (tumor
For the Patient: GOOVDDCAT Other Names: Primary Treatment of Advanced Epithelial Ovarian, Fallopian Tube and Primary Peritoneal Cancer Using Carboplatin and Paclitaxel GO = Gynecologic Oncology (tumor
For the Patient: GOOVCATM
 For the Patient: GOOVCATM Other Names: Treatment of No Visible Residual (Moderate- High Risk) Invasive Epithelial Ovarian, Fallopian Tube and Primary Peritoneal Cancer Using Carboplatin and Paclitaxel
For the Patient: GOOVCATM Other Names: Treatment of No Visible Residual (Moderate- High Risk) Invasive Epithelial Ovarian, Fallopian Tube and Primary Peritoneal Cancer Using Carboplatin and Paclitaxel
 Introduction Posterior cervical fusion is done through the back posterior of the neck. The surgery joins two or more neck vertebrae into one solid section of bone. The medical term for fusion is arthrodesis.
Introduction Posterior cervical fusion is done through the back posterior of the neck. The surgery joins two or more neck vertebrae into one solid section of bone. The medical term for fusion is arthrodesis.
Functional rehab after breast reconstruction surgery
 Functional rehab after breast reconstruction surgery A guide for women who had DIEP, latissimus dorsi with a tissue expander or implant, or two-stage implant based breast reconstruction surgery Read this
Functional rehab after breast reconstruction surgery A guide for women who had DIEP, latissimus dorsi with a tissue expander or implant, or two-stage implant based breast reconstruction surgery Read this
PAUL E. SAVOCA, MD, FACS, FASCRS Consent Form for Hemorrhoidectomy
 PAUL E. SAVOCA, MD, FACS, FASCRS Consent Form for Hemorrhoidectomy The doctor has explained that I have the following condition: Hemorrhoids- abnormally enlarged anal veins. The following procedure will
PAUL E. SAVOCA, MD, FACS, FASCRS Consent Form for Hemorrhoidectomy The doctor has explained that I have the following condition: Hemorrhoids- abnormally enlarged anal veins. The following procedure will
EPISTAXIS. Nasal Trauma, and other emergencies. Marc A. Tewfik MDCM, MSc, FRCSC
 EPISTAXIS Nasal Trauma, and other emergencies Marc A. Tewfik MDCM, MSc, FRCSC Assistant Professor, McGill University Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery DISCLOSURES Speaker/Consultant Merck Novartis MEDA
EPISTAXIS Nasal Trauma, and other emergencies Marc A. Tewfik MDCM, MSc, FRCSC Assistant Professor, McGill University Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery DISCLOSURES Speaker/Consultant Merck Novartis MEDA
Physiotherapy following cardiac surgery. Information for patients Cardiac Surgery
 Physiotherapy following cardiac surgery Information for patients Cardiac Surgery Physiotherapy is an essential part of your recovery from your operation. The physiotherapist will see you before you have
Physiotherapy following cardiac surgery Information for patients Cardiac Surgery Physiotherapy is an essential part of your recovery from your operation. The physiotherapist will see you before you have
FOREHEAD LIFT/ENDOSCOPIC BROWLIFT INSTRUCTIONS FOLLOWING SURGERY
 FOREHEAD LIFT/ENDOSCOPIC BROWLIFT INSTRUCTIONS FOLLOWING SURGERY WHAT TO EXPECT IMMEDIATELY AFTER SURGERY You will wake up with a helmet dressing on your head (i.e. bandages) and you may have some drains/tubes
FOREHEAD LIFT/ENDOSCOPIC BROWLIFT INSTRUCTIONS FOLLOWING SURGERY WHAT TO EXPECT IMMEDIATELY AFTER SURGERY You will wake up with a helmet dressing on your head (i.e. bandages) and you may have some drains/tubes
What to expect after Dupuytren's surgery and what to do to get the best possible results.
 What to expect after Dupuytren's surgery and what to do to get the best possible results. Directly after surgery: You can expect a bulky bandage covering the palm and the fingers that were operated on.
What to expect after Dupuytren's surgery and what to do to get the best possible results. Directly after surgery: You can expect a bulky bandage covering the palm and the fingers that were operated on.
Going home after an AV Fistula or AV Graft
 Going home after an AV Fistula or AV Graft TGH Information for patients and families During your hospital stay, your surgeon created an: AV Fistula AV Graft Read this booklet to learn: how to care for
Going home after an AV Fistula or AV Graft TGH Information for patients and families During your hospital stay, your surgeon created an: AV Fistula AV Graft Read this booklet to learn: how to care for
Patient consent form for liposuction Part 2 of 3
 Patient consent form for liposuction Part 2 of 3 This is an informed consent document. It explains the risks of and alternatives to liposuction. It is important that you read this information carefully
Patient consent form for liposuction Part 2 of 3 This is an informed consent document. It explains the risks of and alternatives to liposuction. It is important that you read this information carefully
Head and Chest. Back and Stomach. Muscles and Joints. Skin. General Symptoms. Women s Health
 Head and Chest Back and Stomach Muscles and Joints Skin General Symptoms Women s Health How to Use the Symptom Evaluation Charts The symptom evaluation charts are part of the Self-care Program. If you
Head and Chest Back and Stomach Muscles and Joints Skin General Symptoms Women s Health How to Use the Symptom Evaluation Charts The symptom evaluation charts are part of the Self-care Program. If you
Dynamic hip screw (sliding hip screw)
 Dynamic hip screw (sliding hip screw) Trauma and Orthopaedics Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is about an operation called a dynamic hip screw, sometimes also known as a sliding hip
Dynamic hip screw (sliding hip screw) Trauma and Orthopaedics Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is about an operation called a dynamic hip screw, sometimes also known as a sliding hip
Before and After Your Surgery
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Before and After Your Surgery Artificial urinary sphincter or male urethral sling surgery This handout explains how to prepare for and what to expect after artificial urinary
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Before and After Your Surgery Artificial urinary sphincter or male urethral sling surgery This handout explains how to prepare for and what to expect after artificial urinary
Review date: February Lumbar Discectomy
 Review date: February 2019 Lumbar Discectomy Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon, you have been diagnosed as having a lumbar disc protrusion, resulting in nerve root
Review date: February 2019 Lumbar Discectomy Following your recent MRI scan and consultation with your spinal surgeon, you have been diagnosed as having a lumbar disc protrusion, resulting in nerve root
For the Patient: Paclitaxel Other names: TAXOL
 For the Patient: Paclitaxel Other names: TAXOL Paclitaxel (pak'' li tax' el) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell your doctor if
For the Patient: Paclitaxel Other names: TAXOL Paclitaxel (pak'' li tax' el) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell your doctor if
1160 Park Avenue 31 River Road New York, NY Greenwich, CT Tel Tel
 New York Office Connecticut Office 1160 Park Avenue 31 River Road New York, NY 10128 Greenwich, CT 06807 Tel. 212.876.5200 Tel. 203.863.2003 POST OPERATIVE INSTRUCTIONS FOR KNEE ARTHROSCOPY Elevation and
New York Office Connecticut Office 1160 Park Avenue 31 River Road New York, NY 10128 Greenwich, CT 06807 Tel. 212.876.5200 Tel. 203.863.2003 POST OPERATIVE INSTRUCTIONS FOR KNEE ARTHROSCOPY Elevation and
Varicose Vein Surgery. Varicose Vein Surgery
 What Are Varicose Veins? Varicose veins are veins under the skin of the legs which have become widened, bulging and twisted. They are very common and do not cause medical problems in most people. Normally
What Are Varicose Veins? Varicose veins are veins under the skin of the legs which have become widened, bulging and twisted. They are very common and do not cause medical problems in most people. Normally
