Transverse-Sigmoid Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Malformations
|
|
|
- Virgil Craig
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Transverse-Sigmoid Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Malformations Kenan I. Amautovic, M.D., and Ali F. Krisht, M.D. ' Learning Objectives: After reading this article, the participant should: 1. Have an in-depth knowledge ofthe etiologic factors and clinical symptoms oftransverse-sigmoid sinus dural arteriovenous malformations. 2. Have an in-depth knowledge ofthe radiologic features oftransverse-sigmoid sinus dural arteriovenous malformations. 3. Have in-depth knowledge ofindications for treatment and treatment options oftransverse-sigmoid sinus dural arteriovenous malformations. Dural arteriovenous malformations (AVM), also commonly described in the literature as dural arteriovenous fistulae, consist of a lesion, or nidus, containing arteriovenous shunting and confined within the dural leaflets. The essential radiologic defining features are the nidus of the malformation and the early appearance of venous structures during the arterial phase of cerebral angiography. The intracranial arteriovenous malformations are classified on the basis of their arterial supply into pure pial, mixed pial and dural, and pure dural AVMs. Dural AVMs account for 10% to 15% of all arteriovenous intracranial malformations; they account for 6% of supratentorial and 35% of infratentorial arteriovenous malformations. Dural AVMs most commonly involve the transverse sinus (63% of cases), with the nidus invariably located at the transverse-sigmoid sinus junction. There is a female preponderance (61% to 66%) and a slight left-sided preference (60%). Patients usually are in the fifth or sixth decade of life. Pathogenesis Dural AVMs are a nosologically heterogeneous group of lesions linked by similar architecture. Theories vary regarding the etiology and pathogenesis of these lesions. Some researchers believe that congenital factors, namely the persistence and enlargement of primitive dural arteriovenous Department of Neurosurgery; University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, 4301 West Markham, Slot 507, Little Rock, AR communications that normally involute during fetal development, are causal. Dural AVMs rarely are seen during childhood, however. When they do occur in children, these lesions tend to be complex and bilateral. They are more common in boys, and usually are seen with cardiac failure at presentation and have a high mortality rate (38%). Most dural AVMs occur in middle-aged patients. However, this fact does not exclude a certain degree of embryological contribution to their pathogenesis. For example, in some patients "spontaneous" transverse-sigmoid sinus dural AVMs have developed without evidence of compromise to flow in the sinus. Nonetheless, acquired factors are believed to play the major role in the etiology of transversesigmoid sinus dural AVMs. Few reports have suggested that sinus thrombosis is secondary or subsequent to occurrence of transverse-sigmoid sinus dural AVMs. However, most of the evidence suggests that thrombosis of the dural venous sinus precedes their appearance. A rate as high as 72% has been reported for sinus thrombosis concomitant with transverse-sigmoid sinus dural AVMs. A sequence of three stages in the natural history of transverse-sigmoid sinus dural AVMs has been suggested as a possibility: (1) occurrence of sinus thrombosis with engorged Category: Vascular Key Words: Dural arteriovenous malformations, Transverse sinus, Treatment, Diagnosis, Sigmoid sinus
2 dural venous collaterals and the opening of embryonic arteriovenous communications; (2) development of arteriovenous shunting, which favors the recruitment of arterial feeders into the nidus, which can lead to secondary venous hypertension; and (3) development of leptomeningeal retrograde venous drainage in the later phase, predisposing to varicose and aneurysmal dilation of the pial veins and a higher possibility of intracranial hemorrhage. The role of venous hypertension in the development of transversesigmoid sinus dural AVMs has been experimentally studied in rats and successfully reproduced. Other factors reported to compromise transverse-sigmoid sinus flow and precede the development of a dural AVM are previous surgery in the area, trauma, sinus thrombosis, infection, tumors, conditions of increased coagulability, rupture of an aneurysm, arterial dysplasia, pregnancy, hormonal factors, and vascular diseases. Transverse-sigmoid sinus dural AVMs appear to be more commonly associated with compromise of the dominant transverse-sigmoid venous sinus. Clinical Signs and Symptoms Clinical signs and symptoms are related to the location of the lesion or, more commonly, to the pattern of venous drainage. Pulsatile tinnitus, the most common symptom, often is very disturbing, and may lead to insomnia and significant discomfort and distress. It is one of the most common indications for surgery. More than 40% of all patients presenting with pulsatile tinnitus have an objective bruit. Other symptoms include headache; altered mental status; memory problems; ataxia and neurological deficits related to cranial nerve involvement; hemorrhage (subdural, subarachnoidal, and intracerebral); increased intracranial pressure (marked by headache, nausea, vomiting, papilledema, optic atrophy, and decreased visual acuity); venous outflow obstruction; seizures; vertigo; and hydrocephalus due to the hemorrhage or mechanical CSF obstruction. Table 1 presents the incidence of the different clinical signs and symptoms. Diagnostic Studies The primary diagnostic study for transverse-sigmoid sinus dural AVMs is selective cerebral angiography (Figs. la, lb, and 2). The goals are the proper analysis of arterial feeders, localization of the nidus, and verification of the venous TABLE 1. Clinical Signs and Symptoms Associated With Transverse-Sigmoid Sinus Dural AVMs Signs and Symptoms Pulsatile tinnitus Headaches and intracranial pain Increased intracranial pressure Seizures Hemorrhage (subdural, subarachnoidal, intracerebral) Focal neurological signs Altered mental status and memory Ataxia Cranial nerve involvement Vertigo Incidence (%) drainage pattern. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is helpful in evaluating the cortical venous drainage and associated sinus thrombosis (Fig. 3). Spin-echo and gradient echo MRI images can help differentiate the slow flow in the sinus from sinus thrombosis, or the dilated cortical veins from hemorrhage. Distinguishing between partial and complete occlusion of the transverse-sigmoid sinus may be difficult because of the anterograde flow from the transverse-sigmoid sinus dural AVMs to the sigmoid sinus, and the retrograde flow from the involved transverse sinus toward the torcula Herophill. Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) and magnetic resonance venography (MRV) are being used with increasing frequency, and can provide most ofthe information that previously could be obtained only by cerebral angiography. Arterial Feeders Cerebral angiography is the best diagnostic study of arterial feeders of transverse-sigmoid dural AVMs. Feeders of transverse-sigmoid sinus duralavms come from the external carotid, internal carotid, and vertebral arteries. The most common primary feeder is the occipital artery. Other involved arteries are the posterior auricular artery, the ascending pharyngeal artery, branches of the internal carotid artery (meningohypophyseal trunk, inferolateral trunk), the 2
3 Figure 1. (A) Transverse-sigmoid sinus dural AVM located at the transverse-sigmoid junction and draining into the sigmoid sinus and further into the jugular vein (arrow). It is seen in the early arterial phase of external carotid artery injection (lateral view). Feeders to the malformation arise from the branches of the occipital artery (arrowheads), dural feeders (open arrows), and feeders from the superficial temporal artery. (8) Anteroposterior projection of the early arterial phase of the external carotid artery injection of the same patient. Note the contralateral contribution of the occipital artery branches and the posterior branches of the middle meningeal artery (arrowheads). '--- middle meningeal artery, the superficial temporal artery, and branches of the vertebral artery (the posterior meningeal artery, the muscular branch, and its anastomosis) (Figs. la, lb, and 2). Bilateral feeders are common in more complex dural AVMs (Figs. la and lb), especially mixed pial and dural AVMs. Table 2 lists the vessels that feed transverse-sigmoid sinus dural AVMs. Venous Drainage The venous drainage flow pattern of transverse-sigmoid sinus dural AVMs may be normal on angiography (that is, toward the sigmoid sinus and the internal jugular vein), but Table 2. Arterial Feeders of Transverse-Sigmoid Sinus Dural AVMs Arterial Feeder (artery) Frequency (%) General External carotid 89 Internal carotid 51 Vertebral 31 Principal Occipital Middle meningeal Ascending pharyngeal 26 Vertebral artery branches (posterior meningeal, muscular) Internal carotid branches (meningohypophyseal, inferolateral trunk) Posterior auricular Superficial temporal 4 3 Figure 2. Anteroposterior view of the early arterial phase of external carotid artery injection. Note the branches of occipital artery (arrowheads) supplying the transverse-sigmoid sinus dural AVM and the venous drainage into the ipsilateral sigmoid sinus (arrow).
4 Figure 3. Coronal gadolinium-enhanced MRI of the brain showing a partially thrombosed transverse sinus. The dural AVM enhancement is indicated by the arrows, and the lumen is marked with an X. more often there is partial compromise of sinus drainage or complete sinus thrombosis. In the latter case, the flow is abnormal, with venous reflux seen in several directions, including the contralateral transverse sinus, the superior and inferior petrosal sinuses, the cavernous sinus, and the vein of Labbe. Insuch cases, subsequent rise of sinus venous pressure may lead to intracranial hypertension. The increased pressure within the superior sagittal sinus (and its occasional thrombosis) leads to cerebrospinal fluid malabsorption, a hydrostatic type of hydrocephalus that results in a rise in the intracranial pressure and generalized central nervous system dysfunction. The most dangerous phase during the course of a transverse-sigmoid AVM is the development of leptomeningeal retrograde venous drainage, which results in varicose and aneurysmal venous formations. This phase commonly presents with an aggressive clinical course, with increased risk of subdural, subarachnoid, intraventricular, or intracerebral hemorrhage and focal neurologic symptoms. Fortunately, transverse-sigmoid sinus dural AVMs progress to this dangerous phase less often (in only 8% to 10% of cases) than do dural AVMs at other locations. Treatment The course of most transverse-sigmoid sinus dural AVMs is benign. Treatment ranges from expectant observation to 4 more involved multimodality treatment interventions. There are reports of spontaneous regression and closure of dural AVMs with presumed thrombosis within the lesion, but this possibility does not necessarily imply a cure. It could be a phase in the dynamic processes that these lesions undergo, because they may later recanalize and recruit new feeders with further enlargement of the fistula. For this reason, spontaneous obliteration of a previously diagnosed transverse-sigmoid sinus dural AVM should not be considered a cure, and the AVM should continue to be observed as a chronic disease process. When these lesions progress and become more symptomatic, a treatment plan should be initiated. Incapacitating tinnitus is one such reason to initiate a treatment plan. Venous hypertension and evidence of cortical venous reflux are strong indications for initiating a treatment plan even in the absence of significant clinical symptoms, because lesions with such changes have a high potential for causing intracranial hemorrhage. The goal of treatment should be complete obliteration of the arteriovenous shunting. Endovascular transarterial therapeutic embolization with various thrombogenic materials, including polyvinyl alcohol particles and cyanoacrylate, initially was used as an adjunct to surgery. It embolizes the nidus only incompletely and does not lead to a cure. Later recruitment of nonembolized feeders and enlargement of the fistula are likely. Provocative testing, such as administration of amobarbital, to predict any functional loss from embolizing the vessel before occluding the leptomeningeal feeders may be beneficial. However, transarterial embolization is reserved for very specific situations because of its low potential to lead to a cure. One such situation is that in which the transvenous route is not possible because the patient is considered to be at high surgical risk, and cortical venous drainage and increased intracranial pressure are present. In such a case, transarterial embolization may decrease arterial input across the fistula and also may decrease venous reflux into the pial vessels, thus decreasing the chance of hemorrhage from cortical veins. There are complications related to transarterial embolization, however, including ischemic stroke, which has been reported as a result of embolic material embolizing into the posterior cerebral artery. Venous infarction has been reported to have been caused by embolic material passing retrogradely into the fistula and lodging in the cortical veins. The transvenous route uses the draining sinus as an access route for obliteration or thrombosis of the nidus of the dural AVM. It leads to a higher rate of cure in most patients when compared with transarterial embolization. There are risks associated with the transvenous approach, however. Pulmonary embolization of the embolic material is one possibility. Incomplete obliteration of the fistula is in itself a potential cause of morbidity due to compromise of the cortical venous drainage, leading to venous hypertension and the increased possibility of hemorrhage. The goal of treatment should not stop short of complete obliteration of the fistula. In most patients this is achieved by complete obliteration of the sinus itself. When the decision to obliterate the sinus is made, it is important to confirm that the
5 other sinus is patent; if it is not patent, open surgical treatment is a better choice. The surgical approach currently is used as part of a multimodality treatment plan that includes both transarterial and transvenous embolization. It is used more commonly for complex lesions with multiple arterial feeders. All of the tentorial and dural feeders to the fistula are coagulated and cut, and the transverse sinus is resected. Surgery also is indicated when sacrifice of the sinus could compromise the cortical venous drainage, as in the absence of the contralateral sinus. In this case, resection of the fistula involving the dura of the tentorium and skeletonizing the sinus without sacrificing it becomes an option. Preoperative embolization of the fistula is helpful in reducing blood loss during surgery, especially during the exposure steps of the craniotomy. Use of the high-speed diamond drill can be very helpful in cutting down on blood loss arising from the arterialized venous drainage that has developed through the bone diploe. Even though surgery is curative, in the majority of patients it is most commonly considered when the endovascular option is not possible or is considered very risky. Stereotactic radiosurgery has recently been used in the treatment of tentorial dural AVMs. However, although it is not frequently considered in the treatment plan of dural AVMs, it can potentially be used for treating transverse dural AVMs in select patients. Readings Awad I, Barrow D, eds: Dural Arteriovenous Malformations. Park Ridge, IL: American Association of Neurological Surgeons, 1993 Awad IA, Little JR, Akrawi Wp, Ahl J: Intracranial dural arteriovenous malformations: factors predisposing to an aggressive neurological course.jneurosurg 72:839, 1990 Djindjian R, Merland JJ: Meningeal arteriovenous fistulae, in Super-selective Arteriography ofthe External Carotid Artery. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1978, pp Fermand M, Reizine D, Melki JP, et al: Long-term follow-up of 43 pure dural arteriovenous fistulae (AVF) of the lateral sinus. Neuroradiology 29:348,1987 Houser OW, Campbell JK, Campbell RJ, Sundt TM: Arteriovenous malformation affecting the transverse dural venous sinus-an acquired lesion. Mayo Clin Proc 54:651, 1979 Lasjaunias P, Chiu M, TerBrugge K, et al: Neurological manifestations of intracranial dural arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 64:724,1986 Mullan S, Mohtajedi S, Johnson DL, Macdonald RL: Embryological basis ofsome aspects of cerebral vascular fistulas and malformations. JNeurosurg 85:1, 1996 Newton TH, Cronquist S: Involvement of dural arteries in intracranial arteriovenous malformations. Radiology 93:1071,1969 Nishijima M, Takaku A, Endo S, et al: Etiological evaluation of dural arteriovenous malformations of the lateral and sigmoid sinuses based on histopathological examinations.jneurosurg 76:600, 1992 Obrador S, Soto M, Silvela J: Clinical syndromes of arteriovenous malformations of the transverse-sigmoid sinus. JNeurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 38:436,1975 Sundt TM, Piepgras DC: The surgical approach to arteriovenous malformationsof the lateraland sigmoid duralsinuses. JNeurosurg 59:32,
6 To earn CME credit, you must read the CME article and complete the quiz, answering at least 70% of the questions correctly. Select the best answer, and darken the corresponding space on the response card. Use #2 pencil only. To earn credit for this article, response card must be mailed on or before October 1, This CME activity was planned and produced in accordance with the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education Essentials and Standards. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to sponsor continuing medical education for physicians. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins designates this educational activity for a maximum of 1.5 hours in category 1 credit for each of the issues 1-26 and 1 hour in category 1 credit for bonus issue 27 towards the AMA Physician's Recognition Award (for a maximum of 40 credit hours per subscription year). Each physician should claim only those hours of credit that he/she actually spent in the educational activity. The Committee on Education of the American Association of Neurological Surgeons and the Congress of Neurological Surgeons designates this continuing medical education activity for 40 neurosurgical credit hours towards the Continuing Education Award in Neurosurgery. 1. The persistence and enlargement of embryonic dural arteri- 6. Generalized intracranial hypertension usually does not occur ovenous communications is one of the suggested factors in with transverse-sigmoid sinus dural AVMs. the etiology of transverse sinus dural AVMs. 7. A transverse sinus dural AVM with evidence of retrograde lep- 2. Transverse sinus dural AVMs are the most common type of tomeningeal venous drainage is a predictor of a more aggresdural AVM. sive clinical course. 8. The presence of cortical venous reflux in transverse-sigmoid 3. Thrombosis of the dural venous sinus is seen in more than sinus dural AVMs is not an indication to initiate treatment in two thirds of patients with transverse sinus dural AVMs. the absence of progressive clinical symptoms. 4. Pulsatile tinnitus is one of the most common symptoms in patients with dural AVMs. 9. Endovascular transarterial embolization is the treatment of choice in transverse-sigmoid sinus dural AVMs because of its high rate in achieving cure. 5. The posterior auricular artery usually is the primary feeder of 10. The direct surgical approach no longer has a role in the treattransverse-sigmoid sinus dural AVMs. ment of transverse-sigmoid sinus dural AVMs. 6
Dural Arteriovenous Malformations and Fistulae (DAVM S DAVF S)
 Jorge Guedes Campos NEUROIMAGING DEPARTMENT HOSPITAL SANTA MARIA UNIVERSITY OF LISBON PORTUGAL DEFINITION region of arteriovenous shunting confined to a leaflet of packymeninges often adjacent to a major
Jorge Guedes Campos NEUROIMAGING DEPARTMENT HOSPITAL SANTA MARIA UNIVERSITY OF LISBON PORTUGAL DEFINITION region of arteriovenous shunting confined to a leaflet of packymeninges often adjacent to a major
Complex dural arteriovenous fistulas. Results of combined endovascular and neurosurgical treatment in 16 patients
 J Neurosurg 71:352-358,1989 Complex dural arteriovenous fistulas Results of combined endovascular and neurosurgical treatment in 16 patients STANLEY L. BARNWELL, M.D., PH.D., VAN V. HALBACH, M.D., RANDALL
J Neurosurg 71:352-358,1989 Complex dural arteriovenous fistulas Results of combined endovascular and neurosurgical treatment in 16 patients STANLEY L. BARNWELL, M.D., PH.D., VAN V. HALBACH, M.D., RANDALL
A.J. Hauer Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae
 A.J. Hauer 27-06-2018 Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae Dural arteriovenous fistulae (davfs) epidemiology Pathological anastomoses (within the dural leaflets) between meningeal arteries and dural
A.J. Hauer 27-06-2018 Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae Dural arteriovenous fistulae (davfs) epidemiology Pathological anastomoses (within the dural leaflets) between meningeal arteries and dural
Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Therapeutic Embolization of the Dural Arteriovenous Malformation Involving the Jugular Bulb
 J Korean Med Sci 2001; 16: 527-31 ISSN 1011-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Therapeutic Embolization of the Dural Arteriovenous Malformation Involving the Jugular Bulb Pulsatile tinnitus
J Korean Med Sci 2001; 16: 527-31 ISSN 1011-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Therapeutic Embolization of the Dural Arteriovenous Malformation Involving the Jugular Bulb Pulsatile tinnitus
Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) with retrograde
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH W.J. van Rooij M. Sluzewski G.N. Beute Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Cortical Venous Drainage: Incidence, Clinical Presentation, and Treatment BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Our purpose
ORIGINAL RESEARCH W.J. van Rooij M. Sluzewski G.N. Beute Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Cortical Venous Drainage: Incidence, Clinical Presentation, and Treatment BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Our purpose
Selective disconnection of cortical venous reflux as treatment for cranial dural arteriovenous fistulas
 J Neurosurg 101:31 35, 2004 Selective disconnection of cortical venous reflux as treatment for cranial dural arteriovenous fistulas J. MARC C. VAN DIJK, M.D., PH.D., KAREL G. TERBRUGGE, M.D., ROBERT A.
J Neurosurg 101:31 35, 2004 Selective disconnection of cortical venous reflux as treatment for cranial dural arteriovenous fistulas J. MARC C. VAN DIJK, M.D., PH.D., KAREL G. TERBRUGGE, M.D., ROBERT A.
A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula
 A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula By : Mohamed Elkhawaga 2 nd Year Resident of Ophthalmology Alexandria University A 19 year old male patient came to our outpatient clinic, complaining of : -Severe conjunctival
A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula By : Mohamed Elkhawaga 2 nd Year Resident of Ophthalmology Alexandria University A 19 year old male patient came to our outpatient clinic, complaining of : -Severe conjunctival
Vascular Malformations
 Vascular Malformations LTC Robert Shih Chief of Neuroradiology Walter Reed Medical Center Special thanks to LTC Alice Smith (retired) Disclosures: None. This presentation reflects the personal views of
Vascular Malformations LTC Robert Shih Chief of Neuroradiology Walter Reed Medical Center Special thanks to LTC Alice Smith (retired) Disclosures: None. This presentation reflects the personal views of
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3
 PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
Cerebrovascular Malformations in the Elderly Indications for Treatment
 Cerebrovascular Malformations in the Elderly Indications for Treatment Johanna T. Fifi, MD, FAHA, FSVIN Director of Endovascular Ischemic Stroke Assistant Professor of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Radiology
Cerebrovascular Malformations in the Elderly Indications for Treatment Johanna T. Fifi, MD, FAHA, FSVIN Director of Endovascular Ischemic Stroke Assistant Professor of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Radiology
Three Cases of Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Anterior Condylar Vein within the Hypoglossal Canal
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:2016 2020, November/December 1999 Case Report Three Cases of Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Anterior Condylar Vein within the Hypoglossal Canal Robert Ernst, Robert Bulas,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:2016 2020, November/December 1999 Case Report Three Cases of Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Anterior Condylar Vein within the Hypoglossal Canal Robert Ernst, Robert Bulas,
Transvenous Embolization of Dural Fistulas Involving the Transverse and Sigmoid Sinuses
 385 Transvenous Embolization of Dural Fistulas Involving the Transverse and Sigmoid Sinuses Van V. Halbach 1 Randall T. Higashida 1 Grant B. Hieshima 1 C. Mark Mehringer 2 Carl W. Hardin 1 Received February
385 Transvenous Embolization of Dural Fistulas Involving the Transverse and Sigmoid Sinuses Van V. Halbach 1 Randall T. Higashida 1 Grant B. Hieshima 1 C. Mark Mehringer 2 Carl W. Hardin 1 Received February
Spontaneous Closure of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: Report of Three Cases and Review of the Literature
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:992 996, May 2001 Case Report Spontaneous Closure of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: Report of Three Cases and Review of the Literature Alain Luciani, Emmanuel Houdart, Charbel Mounayer,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:992 996, May 2001 Case Report Spontaneous Closure of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: Report of Three Cases and Review of the Literature Alain Luciani, Emmanuel Houdart, Charbel Mounayer,
Pediatric Neurointervention: Vein of Galen Malformations
 Pediatric Neurointervention: Vein of Galen Malformations Johanna T. Fifi, M.D. Assistant Professor of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Radiology Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai November 9 th, 2014
Pediatric Neurointervention: Vein of Galen Malformations Johanna T. Fifi, M.D. Assistant Professor of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Radiology Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai November 9 th, 2014
Transvenous Embolization of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Shunts Involving the Laterocavernous Sinus
 Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2017; 11: 1 7 Online November 9, 2016 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.oa.2016-0062 Transvenous Embolization of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Shunts Involving
Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2017; 11: 1 7 Online November 9, 2016 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.oa.2016-0062 Transvenous Embolization of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Shunts Involving
Untangling Cerebral Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas
 Untangling Cerebral Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Bradley A. Gross, MD Assistant Professor, Dept of Neurosurgery, University of Pittsburgh September 2017 davfs Definition Clinical Presentation Natural History
Untangling Cerebral Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Bradley A. Gross, MD Assistant Professor, Dept of Neurosurgery, University of Pittsburgh September 2017 davfs Definition Clinical Presentation Natural History
Dural arteriovenous fistulas of the cavernous sinus - clinical case and treatment
 166 Chiriac et al Dural arteriovenous fistulas of the cavernous sinus Dural arteriovenous fistulas of the cavernous sinus - clinical case and treatment A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin*, St.M. Iencean, I. Poeata
166 Chiriac et al Dural arteriovenous fistulas of the cavernous sinus Dural arteriovenous fistulas of the cavernous sinus - clinical case and treatment A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin*, St.M. Iencean, I. Poeata
CASE OF THE WEEK PROFESSOR YASSER METWALLY
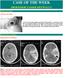 CLINICAL PICTURE CLINICAL PICTURE: CASE OF THE WEEK PROFESSOR YASSER METWALLY A 29 years old male patients presented with proptosis, ecchymoses of the left eye with both subjective and objective bruit
CLINICAL PICTURE CLINICAL PICTURE: CASE OF THE WEEK PROFESSOR YASSER METWALLY A 29 years old male patients presented with proptosis, ecchymoses of the left eye with both subjective and objective bruit
Fatal progression of posttraumatic dural arteriovenous fistulas refractory to multimodal therapy
 See the Letter to the Editor and the Response in this issue in Neurosurgical Forum, pp 858 861. J Neurosurg 94:831 835, 2001 Fatal progression of posttraumatic dural arteriovenous fistulas refractory to
See the Letter to the Editor and the Response in this issue in Neurosurgical Forum, pp 858 861. J Neurosurg 94:831 835, 2001 Fatal progression of posttraumatic dural arteriovenous fistulas refractory to
Treatment of Dural Arteriovenous Malformations Involving the Superior Sagittal Sinus
 337 Treatment of Dural Arteriovenous Malformations Involving the Superior Sagittal Sinus Van V. Halbach1 Randall T. Higashida 1 Grant B. Hieshima 1 Mark Rosenblum 2 Les Cahan 3 We report the diagnosis
337 Treatment of Dural Arteriovenous Malformations Involving the Superior Sagittal Sinus Van V. Halbach1 Randall T. Higashida 1 Grant B. Hieshima 1 Mark Rosenblum 2 Les Cahan 3 We report the diagnosis
EMBOLIZATION OF ARTERIOVENOUS FISTULA AFTER RADIOSURGERY FOR MULTIPLE CEREBRAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS
 Arteriovenous fistula after radiosurgery for multiple CAVM EMBOLIZATION OF ARTERIOVENOUS FISTULA AFTER RADIOSURGERY FOR MULTIPLE CEREBRAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS Chao-Bao Luo, Wan-Yuo Guo, Michael
Arteriovenous fistula after radiosurgery for multiple CAVM EMBOLIZATION OF ARTERIOVENOUS FISTULA AFTER RADIOSURGERY FOR MULTIPLE CEREBRAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS Chao-Bao Luo, Wan-Yuo Guo, Michael
Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Following Translabyrinthine Resection of Cerebellopontine Angle Tumors: Report of Two Cases
 Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Following Translabyrinthine Resection of Cerebellopontine Angle Tumors: Report of Two Cases Peter M.M.C. Li, M.D., 1 Nancy J. Fischbein, M.D., 1,2 Huy M. Do, M.D., 2,3 and Nikolas
Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Following Translabyrinthine Resection of Cerebellopontine Angle Tumors: Report of Two Cases Peter M.M.C. Li, M.D., 1 Nancy J. Fischbein, M.D., 1,2 Huy M. Do, M.D., 2,3 and Nikolas
Dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) are abnormal. Long-term angiographic results of endovascularly cured intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas
 clinical article J Neurosurg 124:1123 1127, 2016 Long-term angiographic results of endovascularly cured intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas Sudheer Ambekar, MD, Brandon G. Gaynor, MD, Eric C. Peterson,
clinical article J Neurosurg 124:1123 1127, 2016 Long-term angiographic results of endovascularly cured intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas Sudheer Ambekar, MD, Brandon G. Gaynor, MD, Eric C. Peterson,
Endovascular Treatment of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations. Bs. Nguyễn Ngọc Pi Doanh- Bs Đặng Ngọc Dũng Khoa Ngoại Thần Kinh
 Endovascular Treatment of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations Bs. Nguyễn Ngọc Pi Doanh- Bs Đặng Ngọc Dũng Khoa Ngoại Thần Kinh Stroke Vascular Malformations of the Brain Epidemiology: - Incidence: 0.1%,
Endovascular Treatment of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations Bs. Nguyễn Ngọc Pi Doanh- Bs Đặng Ngọc Dũng Khoa Ngoại Thần Kinh Stroke Vascular Malformations of the Brain Epidemiology: - Incidence: 0.1%,
Advanced Vascular Imaging: Pulsatile Tinnitus. Disclosures. Pulsatile Tinnitus: Differential Diagnosis. Pulsatile Tinnitus
 Advanced Vascular Imaging: Pulsatile Tinnitus Patrick Turski MD, Zach Clark MD, Tabby Kennedy MD The Objectives of this presentation are to: Review the differential diagnosis of pulsatile tinnitus Discuss
Advanced Vascular Imaging: Pulsatile Tinnitus Patrick Turski MD, Zach Clark MD, Tabby Kennedy MD The Objectives of this presentation are to: Review the differential diagnosis of pulsatile tinnitus Discuss
MR Imaging of Spinal Cord Arteriovenous Malformations at 0.5 T: Study of 34 Cases
 833 MR Imaging of Spinal Cord Arteriovenous Malformations at 0.5 T: Study of 34 Cases D. Dormont 1 F. Gelbert 2 E. Assouline 2 D. Reizine 2 A. Helias 2 M. C. Riche 2 J. Chiras 1 J. Sories 1 J. J. Merland
833 MR Imaging of Spinal Cord Arteriovenous Malformations at 0.5 T: Study of 34 Cases D. Dormont 1 F. Gelbert 2 E. Assouline 2 D. Reizine 2 A. Helias 2 M. C. Riche 2 J. Chiras 1 J. Sories 1 J. J. Merland
The surgical approach to arteriovenous malformations of the lateral and sigmoid dural sinuses
 J Neurosurg 59:32-39, 1983 The surgical approach to arteriovenous malformations of the lateral and sigmoid dural sinuses THORALF M. SUNDT, JR., M.D., AND DAVID G. I~EPGRAS, M.D. Cerebral Vascular Research,
J Neurosurg 59:32-39, 1983 The surgical approach to arteriovenous malformations of the lateral and sigmoid dural sinuses THORALF M. SUNDT, JR., M.D., AND DAVID G. I~EPGRAS, M.D. Cerebral Vascular Research,
Differences between CS-DAVF and TCCF to reveal and redefine CS-DAVF
 Pan et al. Chinese Neurosurgical Journal (2018) 4:26 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41016-018-0121-z CHINESE MEDICAL ASSOCIATION COMMENTARY Differences between CS-DAVF and TCCF to reveal and redefine CS-DAVF
Pan et al. Chinese Neurosurgical Journal (2018) 4:26 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41016-018-0121-z CHINESE MEDICAL ASSOCIATION COMMENTARY Differences between CS-DAVF and TCCF to reveal and redefine CS-DAVF
Fluoroscopy-guided Combined (Surgical/Endovascular) Treatment of Dural Arteriovenous Fistula
 Journal of Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery pissn 2234-8565, eissn 2287-3139, http://dx.doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2017.19.2.106 Case Report Fluoroscopy-guided Combined (Surgical/Endovascular) Treatment
Journal of Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery pissn 2234-8565, eissn 2287-3139, http://dx.doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2017.19.2.106 Case Report Fluoroscopy-guided Combined (Surgical/Endovascular) Treatment
Dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) constitute 10% to
 Color Doppler Flow Imaging of the Superior Ophthalmic Vein in Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Shoichiro Kawaguchi, MD; Toshisuke Sakaki, MD; Ryunosuke Uranishi, MD Background and Purpose This article evaluates
Color Doppler Flow Imaging of the Superior Ophthalmic Vein in Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Shoichiro Kawaguchi, MD; Toshisuke Sakaki, MD; Ryunosuke Uranishi, MD Background and Purpose This article evaluates
41 year old female with headache. Elena G. Violari MD and Leo Wolansky MD
 41 year old female with headache Elena G. Violari MD and Leo Wolansky MD ? Dural Venous Sinus Thrombosis with Hemorrhagic Venous Infarct Acute intraparenchymal hematoma measuring ~3 cm in diameter centered
41 year old female with headache Elena G. Violari MD and Leo Wolansky MD ? Dural Venous Sinus Thrombosis with Hemorrhagic Venous Infarct Acute intraparenchymal hematoma measuring ~3 cm in diameter centered
Dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) are
 TOPIC DURAL FISTULAS DURAL FISTULAS Advances in Surgical Approaches to Dural Fistulas Patrick P. Youssef, MD Albert Jess Schuette, MD C. Michael Cawley, MD Daniel L. Barrow, MD Department of Neurosurgery,
TOPIC DURAL FISTULAS DURAL FISTULAS Advances in Surgical Approaches to Dural Fistulas Patrick P. Youssef, MD Albert Jess Schuette, MD C. Michael Cawley, MD Daniel L. Barrow, MD Department of Neurosurgery,
Neurosurgical decision making in structural lesions causing stroke. Dr Rakesh Ranjan MS, MCh, Dip NB (Neurosurgery)
 Neurosurgical decision making in structural lesions causing stroke Dr Rakesh Ranjan MS, MCh, Dip NB (Neurosurgery) Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Every year, an estimated 30,000 people in the United States experience
Neurosurgical decision making in structural lesions causing stroke Dr Rakesh Ranjan MS, MCh, Dip NB (Neurosurgery) Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Every year, an estimated 30,000 people in the United States experience
MASSIVE EPISTAXIS IN A NEONATE: A SYMPTOM OF VEIN OF GALEN MALFORMATION!
 CASE REPORT MASSIVE EPISTAXIS IN A NEONATE: A SYMPTOM OF VEIN OF GALEN MALFORMATION! Shagufta Wahab 1, Rizwan Ahmad Khan 2, Manjari Thapa Manger 3 1. Radiodiagnosis, Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh,
CASE REPORT MASSIVE EPISTAXIS IN A NEONATE: A SYMPTOM OF VEIN OF GALEN MALFORMATION! Shagufta Wahab 1, Rizwan Ahmad Khan 2, Manjari Thapa Manger 3 1. Radiodiagnosis, Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh,
What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)?
 American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
Brain Arteriovenous Malformations Endovascular Therapy and Associated Therapeutic Protocols Jorge Guedes Cabral de Campos
 Endovascular Therapy and Associated Therapeutic Protocols Jorge Guedes Cabral de Campos Neuroradiology Department Hospital de Santa Maria University of Lisbon CEREBRAL AVM CLINICAL / EPIDEMIOLOGY Brain
Endovascular Therapy and Associated Therapeutic Protocols Jorge Guedes Cabral de Campos Neuroradiology Department Hospital de Santa Maria University of Lisbon CEREBRAL AVM CLINICAL / EPIDEMIOLOGY Brain
An Onyx tunnel: reconstructive transvenous balloon-assisted Onyx embolization for dural arteriovenous fistula of the transverse-sigmoid sinus
 TECHNICAL NOTE J Neurosurg 129:922 927, 2018 An Onyx tunnel: reconstructive transvenous balloon-assisted Onyx embolization for dural arteriovenous fistula of the transverse-sigmoid sinus *Mena G. Kerolus,
TECHNICAL NOTE J Neurosurg 129:922 927, 2018 An Onyx tunnel: reconstructive transvenous balloon-assisted Onyx embolization for dural arteriovenous fistula of the transverse-sigmoid sinus *Mena G. Kerolus,
The superior ophthalmic vein approach for the treatment of carotid-cavernous fistulas: our first experience
 230 Chiriac et al - Superior ophthalmic vein approach The superior ophthalmic vein approach for the treatment of carotid-cavernous fistulas: our first experience A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin 1, Georgiana Ion
230 Chiriac et al - Superior ophthalmic vein approach The superior ophthalmic vein approach for the treatment of carotid-cavernous fistulas: our first experience A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin 1, Georgiana Ion
Tentorial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: A Single-Center Cohort of 12 Patients
 Journal of Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery pissn 2234-8565, eissn 2287-3139, http://dx.doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2017.19.4.284 Original Article Tentorial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: A Single-Center
Journal of Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery pissn 2234-8565, eissn 2287-3139, http://dx.doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2017.19.4.284 Original Article Tentorial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: A Single-Center
General Data. Gender: Female Birthday and age: 1932/11/03, 73 y/o Occupation: house keeper Date of Admission: 2005/03/30
 General Data Gender: Female Birthday and age: 1932/11/03, 73 y/o Occupation: house keeper Date of Admission: 2005/03/30 Chief Complain Dizziness and light headache for recent 1 year. Present illness Hypertension
General Data Gender: Female Birthday and age: 1932/11/03, 73 y/o Occupation: house keeper Date of Admission: 2005/03/30 Chief Complain Dizziness and light headache for recent 1 year. Present illness Hypertension
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF
 Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks
 Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks Comprehensive Neuroradiology: Best Practices October 27-30, 2016 Sudhakar R. Satti, MD Associate Director Neurointerventional
Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks Comprehensive Neuroradiology: Best Practices October 27-30, 2016 Sudhakar R. Satti, MD Associate Director Neurointerventional
Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation after subtotal endovascular embolisation
 206 Chiriac et al Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation after subtotal endovascular embolisation A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin*,
206 Chiriac et al Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation after subtotal endovascular embolisation A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin*,
PEER-REVIEW REPORTS. various signs and symptoms such as headaches, tinnitus, bruit, neurologic deficits, venous hypertensive encephalopathy with
 Multimodality Treatment of Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas in the Onyx Era: a Single Center Experience Sabareesh K. Natarajan 1, Basavaraj Ghodke 1,2, Louis J. Kim 1,2, Danial K. Hallam 1,2,
Multimodality Treatment of Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas in the Onyx Era: a Single Center Experience Sabareesh K. Natarajan 1, Basavaraj Ghodke 1,2, Louis J. Kim 1,2, Danial K. Hallam 1,2,
Meninges and Ventricles
 Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Dural arteriovenous shunts (DAVSs), also called dural
 Natural History of Dural Arteriovenous Shunts Michael Söderman, MD, PhD; Ladislav Pavic, MD, PhD; Göran Edner, MD; Staffan Holmin, MD, PhD; Tommy Andersson, MD, PhD Background and Purpose Dural arteriovenous
Natural History of Dural Arteriovenous Shunts Michael Söderman, MD, PhD; Ladislav Pavic, MD, PhD; Göran Edner, MD; Staffan Holmin, MD, PhD; Tommy Andersson, MD, PhD Background and Purpose Dural arteriovenous
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1715 1722, August 2005 Dural Sinus Compartment in Dural Arteriovenous Shunts: A New Angioarchitectural Feature Allowing Superselective Transvenous Dural Sinus Occlusion Treatment
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1715 1722, August 2005 Dural Sinus Compartment in Dural Arteriovenous Shunts: A New Angioarchitectural Feature Allowing Superselective Transvenous Dural Sinus Occlusion Treatment
Dural arteriovenous fistula discovered in patient presenting with recent head trauma
 ISSN 1507-6164 DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.889610 Received: 2013.07.25 Accepted: 2013.08.08 Published: 2013.10.28 Dural arteriovenous fistula discovered in patient presenting with recent head trauma Authors Contribution:
ISSN 1507-6164 DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.889610 Received: 2013.07.25 Accepted: 2013.08.08 Published: 2013.10.28 Dural arteriovenous fistula discovered in patient presenting with recent head trauma Authors Contribution:
Carotid Cavernous Fistula
 Chief Complaint: Double vision. Carotid Cavernous Fistula Alex W. Cohen, MD, PhD; Richard Allen, MD, PhD May 14, 2010 History of Present Illness: A 46 year old female patient presented to the Oculoplastics
Chief Complaint: Double vision. Carotid Cavernous Fistula Alex W. Cohen, MD, PhD; Richard Allen, MD, PhD May 14, 2010 History of Present Illness: A 46 year old female patient presented to the Oculoplastics
Vascular Malformations of the Brain. William A. Cox, M.D. Forensic Pathologist/Neuropathologist. September 8, 2014
 Vascular Malformations of the Brain William A. Cox, M.D. Forensic Pathologist/Neuropathologist September 8, 2014 Vascular malformations of the brain are classified into four principal groups: arteriovenous
Vascular Malformations of the Brain William A. Cox, M.D. Forensic Pathologist/Neuropathologist September 8, 2014 Vascular malformations of the brain are classified into four principal groups: arteriovenous
Borden type3 superior sagittal sinus dural arteriovenous fistula, angiographic features and endovascular treatment.
 Borden type3 superior sagittal sinus dural arteriovenous fistula, angiographic features and endovascular treatment. Poster No.: C-1939 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: T. Dotsu 1, H.
Borden type3 superior sagittal sinus dural arteriovenous fistula, angiographic features and endovascular treatment. Poster No.: C-1939 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: T. Dotsu 1, H.
Dementia Resulting from Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: The Pathologic Findings of Venous Hypertensive Encephalopathy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:1267 1273, August 1998 Dementia Resulting from Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: The Pathologic Findings of Venous Hypertensive Encephalopathy Robert W. Hurst, Linda J. Bagley, Steven
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:1267 1273, August 1998 Dementia Resulting from Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: The Pathologic Findings of Venous Hypertensive Encephalopathy Robert W. Hurst, Linda J. Bagley, Steven
Posterior fossa veins: Embryology, anatomy, variations and pathology
 Posterior fossa veins: Embryology, anatomy, variations and pathology Poster No.: C-2668 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: S. Nair, D. B. Sarkar, J. J. Bhattacharya, M.
Posterior fossa veins: Embryology, anatomy, variations and pathology Poster No.: C-2668 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: S. Nair, D. B. Sarkar, J. J. Bhattacharya, M.
Sinus Venous Thrombosis
 Sinus Venous Thrombosis Joseph J Gemmete, MD FACR, FSIR, FAHA Professor Departments of Radiology and Neurosurgery University of Michigan Hospitals Ann Arbor, MI Outline Introduction Medical Treatment Options
Sinus Venous Thrombosis Joseph J Gemmete, MD FACR, FSIR, FAHA Professor Departments of Radiology and Neurosurgery University of Michigan Hospitals Ann Arbor, MI Outline Introduction Medical Treatment Options
Supratentorial cerebral arteriovenous malformations : a clinical analysis
 Original article: Supratentorial cerebral arteriovenous malformations : a clinical analysis Dr. Rajneesh Gour 1, Dr. S. N. Ghosh 2, Dr. Sumit Deb 3 1Dept.Of Surgery,Chirayu Medical College & Research Centre,
Original article: Supratentorial cerebral arteriovenous malformations : a clinical analysis Dr. Rajneesh Gour 1, Dr. S. N. Ghosh 2, Dr. Sumit Deb 3 1Dept.Of Surgery,Chirayu Medical College & Research Centre,
Historical perspective
 SPINAL AVM Introduction Vascular malformations of spinal cord are a rare clinical entity, representing 5% of all primary spinal cord lesions, with arteriovenous malformations(avm) & cavernous malformations
SPINAL AVM Introduction Vascular malformations of spinal cord are a rare clinical entity, representing 5% of all primary spinal cord lesions, with arteriovenous malformations(avm) & cavernous malformations
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD
 Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
HEAD/NECK VESSELS. Objectives
 Objectives Arterial Supply to Head and Neck Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain Common carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External
Objectives Arterial Supply to Head and Neck Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain Common carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External
Cranial dural arteriovenous fistula: transarterial Onyx embolization experience and technical nuances
 Division of Neurological Surgery, Barrow Neurological Institute, St. Joseph s Hospital and Medical Center, Phoenix, Arizona, USA Correspondence to Dr C G McDougall, Division of Neurological Surgery, Barrow
Division of Neurological Surgery, Barrow Neurological Institute, St. Joseph s Hospital and Medical Center, Phoenix, Arizona, USA Correspondence to Dr C G McDougall, Division of Neurological Surgery, Barrow
Venous Stroke with Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistula
 Case Reports 24 Venous Stroke with Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Tzung-Wen Chiang 1,2, Shung-Lon Lai 1, Leang-Kai Chang 2, Yung-Yee Chang 1, Min-Yu Lan 1, Yeh-Lin Kuo 3, Chen-Chung Lu 3, and
Case Reports 24 Venous Stroke with Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Tzung-Wen Chiang 1,2, Shung-Lon Lai 1, Leang-Kai Chang 2, Yung-Yee Chang 1, Min-Yu Lan 1, Yeh-Lin Kuo 3, Chen-Chung Lu 3, and
Multiple Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas
 Multiple Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Satoshi USHIKOSHI, Yoichi KIKUCHI*, Kiyohiro HOUKIN**, Hisatoshi SAITO, and Hiroshi ABE** Sapporo Azabu Neurosurgical Hospital, Sapporo; Departments of *Radiology
Multiple Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Satoshi USHIKOSHI, Yoichi KIKUCHI*, Kiyohiro HOUKIN**, Hisatoshi SAITO, and Hiroshi ABE** Sapporo Azabu Neurosurgical Hospital, Sapporo; Departments of *Radiology
Combining endovascular and neurosurgical treatments of high-risk dural arteriovenous fistulas in the lateral sinus and the confluence of the sinuses
 J Neurosurg 90:289 299, 1999 Combining endovascular and neurosurgical treatments of high-risk dural arteriovenous fistulas in the lateral sinus and the confluence of the sinuses KATSUYA GOTO, M.D., PH.D.,
J Neurosurg 90:289 299, 1999 Combining endovascular and neurosurgical treatments of high-risk dural arteriovenous fistulas in the lateral sinus and the confluence of the sinuses KATSUYA GOTO, M.D., PH.D.,
Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: A Brief Review on Classification and General Features
 Review rticle Intracranial ural rteriovenous istulas: rief Review on lassification and General eatures ltay SNR Talat KIRIfi epartment of Neurosurgery, School of Medicine, Istanbul University, stanbul,
Review rticle Intracranial ural rteriovenous istulas: rief Review on lassification and General eatures ltay SNR Talat KIRIfi epartment of Neurosurgery, School of Medicine, Istanbul University, stanbul,
A Case of Curable Dementia Treated by Effective Endovascular Embolization for Dural Arteriovenous Fistula
 Published online: April 16, 2014 1662 680X/14/0061 0116$39.50/0 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 Unported license (CC BY-NC)
Published online: April 16, 2014 1662 680X/14/0061 0116$39.50/0 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 Unported license (CC BY-NC)
Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVF) have long
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Noguchi M. Kubo N. Kuwayama Y. Kamisaki G. Tomizawa K. Kameda H. Kawabe S. Ogawa N. Watanabe S. Endo H. Seto Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Retrograde Cortical Venous
ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Noguchi M. Kubo N. Kuwayama Y. Kamisaki G. Tomizawa K. Kameda H. Kawabe S. Ogawa N. Watanabe S. Endo H. Seto Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Retrograde Cortical Venous
Peripheral Spinal Cord Hypointensity on T2-weighted MR Images: A Reliable Imaging Sign of Venous Hypertensive Myelopathy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:781 786, April 2000 Peripheral Spinal Cord Hypointensity on T2-weighted MR Images: A Reliable Imaging Sign of Venous Hypertensive Myelopathy Robert W. Hurst and Robert I. Grossman
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:781 786, April 2000 Peripheral Spinal Cord Hypointensity on T2-weighted MR Images: A Reliable Imaging Sign of Venous Hypertensive Myelopathy Robert W. Hurst and Robert I. Grossman
Dural arteriovenous fistulas (dural AVFs) constitute 10%
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH N. Horie M. Morikawa N. Kitigawa K. Tsutsumi M. Kaminogo I. Nagata 2D Thick-Section MR Digital Subtraction Angiography for the Assessment of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas BACKGROUND AND
ORIGINAL RESEARCH N. Horie M. Morikawa N. Kitigawa K. Tsutsumi M. Kaminogo I. Nagata 2D Thick-Section MR Digital Subtraction Angiography for the Assessment of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas BACKGROUND AND
Dural arteriovenous malformations
 Dural Arteriovenous Malformations 383 Dural Arteriovenous Malformations of the Transverse/Sigmoid Sinus Acquired from Dominant Sinus Occlusion by a Tumor: Report of Two Cases Kenan I. Arnautovic, M.D.,
Dural Arteriovenous Malformations 383 Dural Arteriovenous Malformations of the Transverse/Sigmoid Sinus Acquired from Dominant Sinus Occlusion by a Tumor: Report of Two Cases Kenan I. Arnautovic, M.D.,
Dural Arteriovenous Malformations: A Review of the Literature and a Presentation of the JHN Series
 JHN Journal Volume 5 Issue 2 Article 2 12-2010 Dural Arteriovenous Malformations: A Review of the Literature and a Presentation of the JHN Series Ed Marchan edward.marchan@jefferson.edu Stavropoula Tjoumakaris
JHN Journal Volume 5 Issue 2 Article 2 12-2010 Dural Arteriovenous Malformations: A Review of the Literature and a Presentation of the JHN Series Ed Marchan edward.marchan@jefferson.edu Stavropoula Tjoumakaris
Occlusive hyperemia: a theory for the hemodynamic complications following resection of intracerebral arteriovenous malformations
 J Neurosurg 78: 167-175, 1993 Occlusive hyperemia: a theory for the hemodynamic complications following resection of intracerebral arteriovenous malformations NAYEF R. F. AL-RODHAN, M.D., PH.D., THORALF
J Neurosurg 78: 167-175, 1993 Occlusive hyperemia: a theory for the hemodynamic complications following resection of intracerebral arteriovenous malformations NAYEF R. F. AL-RODHAN, M.D., PH.D., THORALF
OBJECTIVES. At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: List the cerebral arteries.
 DR JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: List the cerebral arteries. Describe the cerebral arterial supply regarding the origin, distribution and branches.
DR JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: List the cerebral arteries. Describe the cerebral arterial supply regarding the origin, distribution and branches.
Dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) are acquired abnormal
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH R.G. Nogueira G. Dabus J.D. Rabinov C.J. Eskey C.S. Ogilvy J.A. Hirsch J.C. Pryor Preliminary Experience with Onyx Embolization for the Treatment of Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas
ORIGINAL RESEARCH R.G. Nogueira G. Dabus J.D. Rabinov C.J. Eskey C.S. Ogilvy J.A. Hirsch J.C. Pryor Preliminary Experience with Onyx Embolization for the Treatment of Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas
Combining endovascular and neurosurgical treatments of high-risk dural arteriovenous fistulas in the lateral sinus and the confluence of the sinuses
 Neurosurg Focus 5 (4):Article 10, 1998 Combining endovascular and neurosurgical treatments of high-risk dural arteriovenous fistulas in the lateral sinus and the confluence of the sinuses Katsuya Goto,
Neurosurg Focus 5 (4):Article 10, 1998 Combining endovascular and neurosurgical treatments of high-risk dural arteriovenous fistulas in the lateral sinus and the confluence of the sinuses Katsuya Goto,
Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas of the Posterior Fossa Draining into Subarachnoid Veins
 Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas of the Posterior Fossa Draining into Subarachnoid Veins Laurent Pierot, 1 Jacques Chiras, 1 Jean-Frans:ois Meder, 2 Michele Rose, 1 Maurice Rivierez, 3 and Claude Marsault
Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas of the Posterior Fossa Draining into Subarachnoid Veins Laurent Pierot, 1 Jacques Chiras, 1 Jean-Frans:ois Meder, 2 Michele Rose, 1 Maurice Rivierez, 3 and Claude Marsault
Adult Choroidal Vein of Galen Malformation
 Adult Choroidal Vein of Galen Malformation Thomas A. Tomsick, Robert J. Ernst, John M. Tew, Thomas G. Brott, and John C. Breneman Summary: We report staged embolization and stereotactic radiation in a
Adult Choroidal Vein of Galen Malformation Thomas A. Tomsick, Robert J. Ernst, John M. Tew, Thomas G. Brott, and John C. Breneman Summary: We report staged embolization and stereotactic radiation in a
Methods. Yahya Paksoy, Bülent Oğuz Genç, and Emine Genç. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24: , August 2003
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1364 1368, August 2003 Retrograde Flow in the Left Inferior Petrosal Sinus and Blood Steal of the Cavernous Sinus Associated with Central Vein Stenosis: MR Angiographic Findings
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1364 1368, August 2003 Retrograde Flow in the Left Inferior Petrosal Sinus and Blood Steal of the Cavernous Sinus Associated with Central Vein Stenosis: MR Angiographic Findings
Dural Arteriovenous Fistula in Children: Endovascular Treatment and Outcomes in Seven Cases
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1217 1225, June/July 2001 Dural Arteriovenous Fistula in Children: Endovascular Treatment and Outcomes in Seven Cases Patricia K. Kincaid, Gary R. Duckwiler, Y. Pierre Gobin, and
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1217 1225, June/July 2001 Dural Arteriovenous Fistula in Children: Endovascular Treatment and Outcomes in Seven Cases Patricia K. Kincaid, Gary R. Duckwiler, Y. Pierre Gobin, and
Prevalence of venous sinus stenosis in Pseudotumor cerebri(ptc) using digital subtraction angiography (DSA)
 Prevalence of venous sinus stenosis in Pseudotumor cerebri(ptc) using digital subtraction angiography (DSA) Dr.Mohamed hamdy ibrahim MBBC,MSc,MD, PhD Neurology Degree Kings lake university (USA). Fellow
Prevalence of venous sinus stenosis in Pseudotumor cerebri(ptc) using digital subtraction angiography (DSA) Dr.Mohamed hamdy ibrahim MBBC,MSc,MD, PhD Neurology Degree Kings lake university (USA). Fellow
Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 18 Number 1 Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins K Kragha Citation K Kragha. Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 18 Number 1 Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins K Kragha Citation K Kragha. Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic
Vascular and Parameningeal Infections of the Head and Neck
 Vascular and Parameningeal Infections of the Head and Neck Kevin B. Laupland, MD, MSc, FRCPC Associate Professor Departments of Medicine, Critical Care Medicine, Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, and
Vascular and Parameningeal Infections of the Head and Neck Kevin B. Laupland, MD, MSc, FRCPC Associate Professor Departments of Medicine, Critical Care Medicine, Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, and
Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Cavernous Sinus Presenting with Progressive Venous Congestion of the Pons and Cerebrum: Report of one case
 Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Cavernous Sinus Presenting with Progressive Venous Congestion of the Pons and Cerebrum: Report of one case Soo-Bin Yim, M.D., Jong-Sung Kim, M.D., Yang Kwon,M.D.*, Choong-Gon
Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Cavernous Sinus Presenting with Progressive Venous Congestion of the Pons and Cerebrum: Report of one case Soo-Bin Yim, M.D., Jong-Sung Kim, M.D., Yang Kwon,M.D.*, Choong-Gon
North Oaks Trauma Symposium Friday, November 3, 2017
 Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage Aaron C. Sigler, DO, MS Neurosurgery Tulane Neurosciences None Disclosures Overview Anatomy Epidural hematoma Subdural hematoma Cerebral contusions Outline Traumatic ICH
Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage Aaron C. Sigler, DO, MS Neurosurgery Tulane Neurosciences None Disclosures Overview Anatomy Epidural hematoma Subdural hematoma Cerebral contusions Outline Traumatic ICH
Spontaneous Obliteration of Pial Arteriovenous Malformations: A Review of 27 Cases
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :, March 00 Spontaneous Obliteration of Pial Arteriovenous Malformations: A Review of ases Maneesh. Patel, Timothy J. Hodgson, Andras A. Kemeny, and David M. Forster BAKGROUND AND
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :, March 00 Spontaneous Obliteration of Pial Arteriovenous Malformations: A Review of ases Maneesh. Patel, Timothy J. Hodgson, Andras A. Kemeny, and David M. Forster BAKGROUND AND
Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography
 Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography Medical Guideline Number: MRG2001-05 Effective Date: 2/13/01 Revised Date: 2/14/2006 OHCA Reference OAC 317:30-5-24. Radiology. (f) Magnetic Resonance
Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography Medical Guideline Number: MRG2001-05 Effective Date: 2/13/01 Revised Date: 2/14/2006 OHCA Reference OAC 317:30-5-24. Radiology. (f) Magnetic Resonance
Identifying Cerebrovascular Disorders. Wengui Yu, MD, PhD Department of Neurology, University of California, Irvine
 Identifying Cerebrovascular Disorders Wengui Yu, MD, PhD Department of Neurology, University of California, Irvine Objectives Review different types of cerebrovascular disorders. Briefly discuss etiology,
Identifying Cerebrovascular Disorders Wengui Yu, MD, PhD Department of Neurology, University of California, Irvine Objectives Review different types of cerebrovascular disorders. Briefly discuss etiology,
Microsurgery for ruptured cerebellar arteriovenous malformations
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Microsurgery for ruptured cerebellar arteriovenous malformations S.-F. GONG 1,2, X.-B. WANG 1,3, Y.-Q. LIAO 1,2, T.-P. JIANG 1,2, J.-B. HE 1,2,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Microsurgery for ruptured cerebellar arteriovenous malformations S.-F. GONG 1,2, X.-B. WANG 1,3, Y.-Q. LIAO 1,2, T.-P. JIANG 1,2, J.-B. HE 1,2,
Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: the value of Carotid Ultrasonography.
 Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: the value of Carotid Ultrasonography. Poster No.: C-2199 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. P. Filipe, T. Parreira, C. Andrade, R. Santos, E. Azevedo;
Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: the value of Carotid Ultrasonography. Poster No.: C-2199 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. P. Filipe, T. Parreira, C. Andrade, R. Santos, E. Azevedo;
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14
 Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Marc Norman, Ph.D. - Do Not Use without Permission 1. Cerebrovascular Accidents. Marc Norman, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry
 Cerebrovascular Accidents Marc Norman, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry Neuropsychiatry and Behavioral Medicine Neuropsychology Clinical Training Seminar 1 5 http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/images/ency/fullsize/18009.jpg
Cerebrovascular Accidents Marc Norman, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry Neuropsychiatry and Behavioral Medicine Neuropsychology Clinical Training Seminar 1 5 http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/images/ency/fullsize/18009.jpg
Vein of Galen Aneurysms
 Interventional Neuroradiology 7 (Suppll): 99103, 2001 Vein of Galen Aneurysms Experience with Eleven Cases. KOIYAA, H. NAKAJIA,. NISHIKAWA, K. YAANAKA, Y. IWAI, T. YASUI, T. ORIKAWA*, S. KITANO*, H. SAKAOTO*,A.
Interventional Neuroradiology 7 (Suppll): 99103, 2001 Vein of Galen Aneurysms Experience with Eleven Cases. KOIYAA, H. NAKAJIA,. NISHIKAWA, K. YAANAKA, Y. IWAI, T. YASUI, T. ORIKAWA*, S. KITANO*, H. SAKAOTO*,A.
Overview of Cerebrovascular Malformations
 Overview of Cerebrovascular Malformations Pursuit of Neurovascular Excellence 8 th annual Barbara Albani, MD Chief, Neurointerventional Surgery Christiana Care Health Systems Newark, DE Financial Disclosures
Overview of Cerebrovascular Malformations Pursuit of Neurovascular Excellence 8 th annual Barbara Albani, MD Chief, Neurointerventional Surgery Christiana Care Health Systems Newark, DE Financial Disclosures
7/5/2016. Neonatal high-output cardiac failure. Case 1 POSTNATAL STRATEGIES FOR CEREBRAL ATERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS
 John Deveikis, M.D. POSTNATAL STRATEGIES FOR CEREBRAL ATERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS JULY, 2016 Neonatal high-output cardiac failure Tachypnea, tachycardia, hypotension, failure to thrive When congenital heart
John Deveikis, M.D. POSTNATAL STRATEGIES FOR CEREBRAL ATERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS JULY, 2016 Neonatal high-output cardiac failure Tachypnea, tachycardia, hypotension, failure to thrive When congenital heart
Cerebellar Hemorrhage due to a Direct Carotid Cavernous Fistula after Surgery for Maxillary Cancer
 Case Report J Korean Neurosurg Soc 60 (1) : 89-93, 2017 https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.1206.001 pissn 2005-3711 eissn 1598-7876 Cerebellar Hemorrhage due to a Direct Carotid Cavernous Fistula after
Case Report J Korean Neurosurg Soc 60 (1) : 89-93, 2017 https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.1206.001 pissn 2005-3711 eissn 1598-7876 Cerebellar Hemorrhage due to a Direct Carotid Cavernous Fistula after
Cerebral Vascular Diseases. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD
 Cerebral Vascular Diseases Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD Outline I. Stroke statistics II. Cerebral circulation III. Clinical symptoms of stroke IV. Pathogenesis of cerebral infarcts (Stroke) 1. Ischemic - Thrombotic
Cerebral Vascular Diseases Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD Outline I. Stroke statistics II. Cerebral circulation III. Clinical symptoms of stroke IV. Pathogenesis of cerebral infarcts (Stroke) 1. Ischemic - Thrombotic
High-Flow, Small-Hole Arteriovenous Fistulas: Treatment with Electrodetachable Coils
 High-Flow, Small-Hole Arteriovenous Fistulas: Treatment with Electrodetachable Coils Guido Guglielmi, Fernando Viñuela, Gary Duckwiler, Jacques Dion, and Alfredo Stocker Summary: We present one case of
High-Flow, Small-Hole Arteriovenous Fistulas: Treatment with Electrodetachable Coils Guido Guglielmi, Fernando Viñuela, Gary Duckwiler, Jacques Dion, and Alfredo Stocker Summary: We present one case of
DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY
 Neuroradiology (2008) 50:1013 1023 DOI 10.1007/s00234-008-0433-3 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY The anterior medullary anterior pontomesencephalic venous system and its bridging veins communicating to the dural
Neuroradiology (2008) 50:1013 1023 DOI 10.1007/s00234-008-0433-3 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY The anterior medullary anterior pontomesencephalic venous system and its bridging veins communicating to the dural
SURGICAL TREATMENT OF SPINAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS: VASCULAR ANATOMY AND SURGICAL OUTCOME
 Spinal Arteriovenous Malformations SURGICAL TREATMENT OF SPINAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS: VASCULAR ANATOMY AND SURGICAL OUTCOME Po-An Tai, Yong-Kwang Tu, and Hon-Man Liu 1 Background and purpose: Spinal
Spinal Arteriovenous Malformations SURGICAL TREATMENT OF SPINAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS: VASCULAR ANATOMY AND SURGICAL OUTCOME Po-An Tai, Yong-Kwang Tu, and Hon-Man Liu 1 Background and purpose: Spinal
Spinal Vascular Lesions
 Spinal Vascular Lesions Spinal Vascular Lesions Spinal cord infarction Hemangioblastoma Cavernous malformation Vascular malformations (Type 1-4) Spinal artery aneurysm Troy Hutchins, MD Assistant Professor
Spinal Vascular Lesions Spinal Vascular Lesions Spinal cord infarction Hemangioblastoma Cavernous malformation Vascular malformations (Type 1-4) Spinal artery aneurysm Troy Hutchins, MD Assistant Professor
Course of apparent diffusion coefficient values in cerebral edema of dural arteriovenous
 Title Page Title: Course of apparent diffusion coefficient values in cerebral edema of dural arteriovenous fistula before and after treatment Authors: Shigeyuki Sakamoto, Shinji Ohba, Masaaki Shibukawa,
Title Page Title: Course of apparent diffusion coefficient values in cerebral edema of dural arteriovenous fistula before and after treatment Authors: Shigeyuki Sakamoto, Shinji Ohba, Masaaki Shibukawa,
