Vision Health: Conditions, Disorders & Treatments GLAUCOMA
|
|
|
- Camron Vincent Short
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Vision Health: Conditions, Disorders & Treatments GLAUCOMA Glaucoma is a disease of the optic nerve, which transmits the images you see from the eye to the brain. The optic nerve is made up of many nerve fibers (like an electric cable with its numerous wires). Glaucoma damages nerve fibers, which can cause blind spots and vision loss. Glaucoma is related to the pressure inside the eye, known as the intraocular pressure (IOP). When the aqueous humor (a clear liquid that normally flows in and out of the eye) cannot drain properly, pressure builds up in the eye. The resulting increase in IOP can damage the optic nerve and lead to vision loss. Open-Angle Glaucoma The most common form of glaucoma is primary open-angle glaucoma, in which the aqueous fluid is blocked from flowing back out of the eye at a normal rate through a tiny drainage system. Most people who develop primary open-angle glaucoma notice no symptoms until their vision is impaired. Ocular hypertension is often a forerunner to actual open-angle glaucoma. When ocular pressure is above normal, the risk of developing glaucoma increases. Several risk factors will affect whether you will develop glaucoma, including the level of IOP (intraocular pressure), family history, and corneal thickness. If your risk is high, your eye surgeon may recommend treatment to lower your IOP to prevent future damage. Angle Closure Glaucoma In angle-closure glaucoma, the iris (the colored part of the eye) may drop over and completely close off the drainage angle, abruptly blocking the flow of aqueous fluid and leading to increased IOP or optic nerve damage. In acute angle-closure glaucoma there is a sudden increase in IOP (intraocular pressure) due to the buildup of aqueous fluid. This condition is considered an emergency because optic nerve damage and vision loss can occur within hours of the problem. Symptoms can include nausea, vomiting, seeing halos around lights, and eye pain. Even some people with normal IOP can experience vision loss from glaucoma. This condition is called normal-tension glaucoma.
2 In this type of glaucoma, the optic nerve is damaged even though the IOP is considered normal. Normaltension glaucoma is not well understood, but lowering IOP has been shown to slow progression of this form of glaucoma. Childhood glaucoma, which starts in infancy, childhood, or adolescence, is rare. Like primary open-angle glaucoma, there are few, if any, symptoms in the early stage. Blindness can result if it is left untreated. Like most types of glaucoma, childhood glaucoma may run in families. Your eye surgeon may tell you that you are at risk for glaucoma if you have one or more risk factors, including having an elevated IOP, a family history of glaucoma, certain optic nerve conditions, are of a particular ethnic background, or are of advanced age. Regular examinations with your eye MD are important if you are at risk for this condition. The goal of glaucoma treatment is to lower your eye pressure to prevent or slow further vision loss. Your eye surgeon will recommend treatment if the risk of vision loss is high enough to justify intervention. Treatment often consists of eyedrops but can include laser treatment or surgery to create a new drain in the eye. Glaucoma is a chronic disease that can be controlled but not cured. Ongoing monitoring (up to every three to six months, but more often annually) is needed to watch for changes. Ask your eye surgeon if you have any questions about glaucoma or your treatment. Glaucoma Testing Because it has no noticeable symptoms, glaucoma is a difficult disease to detect without regular, complete eye exams. During a glaucoma evaluation, your surgeon will perform the following tests: Tonometry Your Surgeon measures the pressure in your eyes (intraocular pressure, or IOP) using a technique called tonometry. Tonometry measures your IOP by determining how your cornea responds when an instrument (or sometimes a puff of air) presses on the surface of your eye. Eyedrops are usually used to numb the surface of your eye for this test. Gonioscopy For this test, Your Surgeon inspects your eye s drainage angle the area where fluid drains out of your eye. During gonioscopy, you sit in a chair facing the microscope used to look inside your eye. You will place your chin on a chin rest and your forehead against a support bar while looking straight ahead.
3 The goniolens is placed lightly on the front of your eye, and a narrow beam of light is directed into your eye while your doctor looks through the slit lamp at the drainage angle. Drops will be used to numb the eye before the test. Ophthalmoscopy With this test, your surgeon can evaluate whether or not there is any optic nerve damage by looking at the back of the eye (called the fundus). With ophthalmoscopy, your surgeon uses a powerfully magnified light that magnifies up to about 15 times. This type of ophthalmoscopy is most commonly done during a routine physical examination. Ophthalmoscopy allows a better view of the fundus, even if your natural lens is clouded by cataracts. Visual Field Test A visual field test (perimetry test), measures all areas of your eyesight, including your side, or peripheral, vision. A visual field test can help find certain patterns of vision loss and is a key way to check for glaucoma. It is very useful in finding early changes in vision caused by nerve damage from glaucoma. To take this painless test, you sit at a bowl-shaped instrument called a perimeter. While you stare at the center of the bowl, lights flash. Each time you see a flash you press a button. A computer records the location of each flash and whether you pressed the button when the light flashed in that location. At the end of the test, a printout shows if there are areas of your field of vision where you did not see the flashes of light. This test shows if you have any areas of vision loss. Loss of peripheral vision is often an early sign of glaucoma. Visual field testing is used together with the clinical exam and HRT testing to determine if you have glaucoma or if your glaucoma is worsening. Photography Sometimes photographs or other computerized images are taken of the optic nerve to inspect the nerve more closely for damage from elevated pressure in the eye. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a special scan used to study the anatomy of the retina and optic nerve in fine detail.
4 OCT testing requires dilation of the pupils but does not require a needle in the arm and does not involve touching the eye. A healthy retina is only ¼ of a millimeter thick, but it contains multiple layers of specialized cells. One layer converts light into nerve signals, another processes the nerve impulses, while another transmits these processed impulses to the brain where they are interpreted. OCT testing is like having an optical biopsy of the retina and optic nerve; it provides excellent visualization of these structures, and aids greatly in the diagnosis and treatment of glaucoma. Not every patient needs an OCT test. In Ontario, OCT testing is now covered by OHIP. Each of these evaluation tools is an important way to monitor your vision to help ensure that glaucoma does not rob you of your sight. Some of these tests will not be necessary for everyone. Your surgeon will discuss which tests are best for you. Some tests may need to be repeated on a regular basis to monitor any changes in your vision caused by glaucoma. Glaucoma Treatment While there is no cure for glaucoma, it can be controlled with proper management. Elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) can damage the optic nerve, which may lead to vision loss. Treatment for glaucoma focuses on lowering the IOP to a level that is less likely to cause further optic nerve damage. This is known as the target pressure. The target pressure differs from individual to individual. Your target pressure may change during your course of treatment. If you have glaucoma, your surgeon may prescribe a medication to lower your eye pressure. For glaucoma medications to work, you must take them regularly and as prescribed by your doctor. Medication Tips With each new medication that your ophthalmologist prescribes, make sure you understand the following: the name of the medication; how to take it; how often to take it; how to store it; if you can take it with your other medications (make sure all of your doctors know about all the different medications you take, including nonprescription medications); what the possible side effects may be; what you should do if you experience side effects; and what you should do if you miss a dose.
5 There are several different medications available for the treatment of glaucoma including: 1) beta-blockers 2) prostaglandin analogues 3) alpha-agonists 4) carbonic anhydrase inhibitors 5) combined agents Beta-Blockers in the Treatment of Glaucoma How do beta blockers work? Beta-blocker (beta adrenergic antagonist) medications are reliable for lowering intraocular pressure. They work by decreasing the amount of fluid that the eye continually produces, called the aqueous humor. For many years, beta blockers were the mainstay of treatment. Thus, we have a lot of experience with this medication for the treatment of glaucoma. Types of beta-blocker medications There are two general classes of beta blockers: nonselective and selective. Nonselective beta blockers have more effects on the body s beta receptors system-wide and are associated with more side effects. The nonselective beta blockers are also more effective at lowering IOP. The nonselective beta blockers include: levobunolol (Betagan, AKBeta) timolol (Timoptic) timolol gel (Timoptic XE) Generic versions of timolol and timolol gel are now available. Consult with your ophthalmologist to be sure that a generic product is an acceptable alternative for you. The only available selective beta-blocker medication is betaxolol (Betoptic, Betoptic S) Betaxolol is the generic form of Betoptic While a selective beta-blocker eyedrop has a better safety profile, especially in terms of respiratory symptoms, it still must be used with caution in patients with asthma or emphysema. The eye pressure-lowering effect is slightly less with selective beta blockers. There is only a minimal additive effect in terms of lowering eye pressure in patients already taking oral beta blockers, and there is the risk of further additive side effects. If you are already taking a beta-blocker medication by mouth or if your primary care doctor newly prescribes a beta blocker, please notify your ophthalmologist. Possible side effects of beta blockers
6 All medications, including eyedrops, can have side effects. Some people taking beta-blocker eyedrops may experience: wheezing or difficulty breathing; slow or irregular heart beat or decreased response of heart rate to exercise; increased risk for heart failure; depression; impotence; headache, dizziness or weakness; in diabetics, difficulty sensing blood glucose changes; and eye irritation or allergy. Prostaglandin Analogs & Prostamides in the Treatment of Glaucoma How do prostaglandin analogs or prostamides work? Prostaglandin analogs and prostamides lower IOP by increasing the outflow of the aqueous humor, the fluid made continuously by the eye. All of these medications are taken once a day, except for Rescula, which is taken twice per day. What are the prostaglandin analog and prostamide medications? latanoprost (Xalatan) bimatoprost (Lumigan) travoprost (Travatan) Possible side effects of prostaglandin analogs or prostamides All medications, including eyedrops, can have side effects. Some people taking these eyedrops may experience: redness of the eye darkening of the iris (the colored part of the eye); this color change occurs slowly and may not be noticeable for months or even years; increased growth, thickness, and pigmentation of the eyelashes; eye irritation or itching; blurred vision; darkening of the eyelid skin; muscle aches (rare); and headaches (rare). Patients with a history of uveitis (inflammation in the eye), ocular herpes infection, or swelling in the retina (called cystoid macular edema) should use this medication with caution. If you have a history of any of these conditions, please discuss it with your doctor. Alpha-Agonists in the Treatment of Glaucoma How do alpha-agonists work? Alpha agonist medications are reliable for lowering the intraocular pressure. They work by decreasing the production of the fluid that the eye continually makes, called the aqueous humor. What are the alpha-agonists?
7 There are three alpha agonist drugs: apraclonidine (Iopidine); brimonidine (Alphagan, Alphagan P); and dipivefrin (Propine). A generic version of Alphagan called brimonidine is available. Possible side effects of alpha-agonists All medications, including eyedrops, can have side effects. Some people taking alpha-agonist eyedrops may experience: dry mouth; ocular allergy with a red eye or red eyelids (30% of patients); tiredness or fatigue; low or high blood pressure and possible slowing of heart rate (less than with beta blockers); blurred vision; sensitivity of the eyes to bright light; and headache. Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors (CAIs) in the Treatment of Glaucoma How do CAIs work? CAI medications are very reliable at lowering the intraocular pressure. They work by decreasing the production of the fluid that the eye continually makes, called the aqueous humor. What are CAI medications? Topical drugs: dorzolamide (Trusopt); and brinzolamide (Azopt). Oral medications: acetazolamide (Diamox, AK-Zol); acetazolamide sustained-release (Diamox Sequels); and methazolamide (Neptazane, GlaucTabs). Generic versions of the eyedrop formulations are not yet available. Possible side effects of CAIs All medications, including eyedrops, can have side effects. Some people taking topical carbonic anhydrase medications (eyedrops) experience: blurred vision bitter taste in the mouth dry eyes eye irritation or allergy with a red eye or red eyelids headache or dizziness upset stomach. The oral (pill) form of these medications has more side effects, including:
8 increased need to urinate; tingling sensation in fingers and toes; rarely, severe allergic reactions or blood disorders can occur; change in taste (especially with carbonated beverages); and unusual tiredness or weakness. WARNING These medications are sulfonamides. If you are allergic to sulfa antibiotics, the same types of adverse reactions can occur with carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Also, rare adverse drug interactions have occurred in patients taking high doses of aspirin and carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Combined Agents in the Treatment of Glaucoma Several eyedrops are available that combine the actions of two drugs from different categories. The reasoning behind the use of combined agents is that it is easier for patients to put just one drop in their eyes instead of two; it may also be healthier for the eye as less preservative is being applied. What are the combined medications? Combigan (Combines a beta-blocker and an alpha-agonist) Cosopt (Combines a beta-blocker and a CAI) DuoTrav (Combines a prostaglandin analog and a beta-blocker) Xalacom (Combines a prostaglandin analog and a beta-blocker) For glaucoma medications to work, you must take them regularly and continuously as prescribed by your doctor. Selective Laser Trabeculoplasty (SLT) in the Treatment of Glaucoma What is selective laser trabeculoplasty? Selective laser trabeculoplasty is a common laser procedure used to treat glaucoma. Glaucoma is an eye disease in which the optic nerve is damaged, usually by high pressure inside the eye. Eye pressure can become too high if you have a problem with the drainage of fluid from your eye. Damage to the optic nerve can cause a loss of vision. In this procedure, your surgeon uses a laser to create microscopic bursts of energy in the drainage pathways (the trabecular meshwork) in your eye. The burns open the drainage holes in the meshwork and allows fluid to drain better through them. The procedure can lower the pressure in your eye and help prevent more damage to the optic nerve and loss of vision. Your Surgeon may recommend this procedure after you have tried treating high pressure in your eye with eye drops or pills. These medicines may not be reducing your eye pressure enough, or they may be causing side effects.
9 As the laser is very selective in its application of energy, sometimes Your Surgeon may even recommend it before starting glaucoma drops. What happens during the procedure? This procedure is performed in your surgeon s office. Your surgeon uses eye drops to numb your eye and other drops are used to make the pupil small. A special contact lens is put on your eye to help direct the laser's high-energy beam of light at the trabecular meshwork in your eye. The laser makes about 50 evenly spaced burns over 180 degrees of the eye. You will see a few brief flashes of light and feel little, if any, discomfort. The procedure usually takes less than 10 minutes. You will be able to go home soon after it is done. Your surgeon will ask you to return to the office two hours after your laser treatment to check the eye pressure. You will also have a further appointment in approximately two weeks to have the other 180 degrees lasered. What happens after the procedure? Your vision will probably be blurred for a few hours, but then it should clear. You will not need to wear an eye patch. Your surgeon will ask you to use Voltaren eye drops four times a day for five days. If your vision does not clear within a day or if you feel any pain or discomfort, call your surgeon. If it is the evening or the weekend and you are having problems, you should go to emergency to be assessed. This procedure is usually successful. Several days or weeks after the procedure, the flow of fluid from your eye should improve. Improved flow usually reduces the pressure inside the eye. It can take 2 to 4 weeks, and sometimes longer, to learn the results. Most people do still need to take glaucoma drops after the procedure. The effects of this treatment may not last. In 50% of people it stops working in about 5 years. It can be repeated at that point. What are the risks? Although there are some risks with the laser treatment such as inflammation, bleeding inside the eye, and raised pressure in the eye, the risks are fewer risks than with other types of surgery. Problems may occur that could threaten your vision, but they are rare. If you have any questions about the risks of selective laser trabeculoplasty, ask your surgeon. Laser Peripheral Iridotomy in the Treatment of Glaucoma What is laser peripheral iridotomy? Laser peripheral iridotomy is a surgical procedure in which a laser is used to create an opening in the iris (the coloured part of the eye) so that fluid can leave the angle of the eye more easily.
10 It is performed for patients with narrow angles, or angles that look like they might be prone to closure. Narrow angles may predispose one to an episode of angle closure glaucoma, in which raised pressure in the eye can rapidly threaten vision and even cause blindness. What happens during the procedure? This procedure is performed in the out-patient department of your hospital or your doctor's office. Your surgeon uses eye drops to numb your eye and to make the pupil small. A special contact lens is put on your eye to help direct the laser's high-energy beam of light at the iris in your eye. The laser makes one or two holes in the iris. You will see a few brief flashes of light and feel little, if any, discomfort. The procedure usually takes less than 5 minutes. You will be able to go home soon after it is done. What are the risks? Although there are some risks with the laser treatment such as inflammation, bleeding inside the eye, and raised pressure in the eye, the risks are fewer risks than with other types of surgery. Problems may occur that could threaten your vision, but they are rare. If you have any questions about the risks of this laser treatment, ask your surgeon. What happens after the procedure? You will receive a prescription for a steroid drop from your surgeon after your surgery is completed. Take your usual glaucoma drops as well as the steroid drops four times a day for 5 days to the operated eye(s). Your surgeon will want to check you that afternoon to make sure that the laser iridotomies are still open and working properly. You will have an appointment at 12:45 pm the same day of your surgery to check the eye pressure. Your vision will probably be blurred for a short period, but then it should clear in an hour or two. You will not need to wear an eye patch. If your vision does not clear within a day or if you feel any pain or discomfort, call your surgeon. If it is the evening or the weekend and you are having problems, you should go to emergency to be assessed. Fortunately, this procedure is almost always successful. Glaucoma Surgery If you have glaucoma and medications and laser surgeries do not lower your eye pressure adequately, your eye surgeon may recommend you be evaluated by a glaucoma specialist to evaluate your suitability for a procedure called a trabeculectomy.
11 In this procedure, a tiny drainage hole is made in the sclera (the white part of the eye). The new drainage hole allows fluid to flow out of the eye into a filtering area called a bleb. The bleb is mostly hidden under the eyelid. When successful, the procedure will lower your intraocular pressure (IOP), minimizing the risk of vision loss from glaucoma. The surgery is performed in an operating room on an outpatient basis. Some of the risks and complications from trabeculectomy surgery include the following: failure to control intraocular pressure, with the need for another operation; infection; bleeding in the eye; swelling in the eye; irritation or discomfort in the eye; eye pressure that is too low; cataract (in cases where cataract has not already been removed); and decreased or lost vision. Using Antimetabolite Medicines with Glaucoma Surgery Certain medications, called antimetabolites, were originally developed to help treat some kinds of cancer. These same medications have also been found to be helpful when used with some types of glaucoma surgery. These medicines may be applied to the eye during or after the surgery to reduce the growth of scar tissue, a common cause of failure in glaucoma surgery. Mitomycin-C and 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) are the most commonly used antimetabolites for glaucoma surgery. When these antimetabolites are used with other medications that reduce inflammation, the success rate of surgery is greatly improved, especially for patients who are at high risk for excessive scarring. Your glaucoma specialist may consider using antimetabolite medicines with your glaucoma surgery if: you are having surgery on an eye that has been operated on before; you have inflammation in your eye (called uveitis); you have glaucoma due to new blood vessel formation within the eye; you are having glaucoma and cataract surgery at the same time; you are relatively young; you have more deeply pigmented skin; or your eyes are at risk for postoperative scarring. In addition to the usual complications of glaucoma surgery, other risks associated with using antimetabolites include: eye pressure that is too low; leaking incisions; slower healing of the cornea; blurred vision;
12 fluid in or behind the retina; thinning of the eye tissues; and infection. If your glaucoma specialist has decided to use antimetabolite medications, he or she will explain why they are recommended for you. While some people may experience side effects from medications or surgery, the risks associated with these side effects should be balanced against the greater risk of leaving glaucoma untreated and losing your vision. Information about eye conditions, disorders and treatments is presented courtesy of the Eye Physicians & Surgeons of Ontario.
Treatments for Open-Angle Glaucoma. A Review of the Research for Adults
 Treatments for Open-Angle Glaucoma A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, this information is for you if: Your eye doctor has said that you have open-angle glaucoma,
Treatments for Open-Angle Glaucoma A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, this information is for you if: Your eye doctor has said that you have open-angle glaucoma,
BrightFocus Foundation is the new name for American Health Assistance Foundation.
 In this section, you will find the following: Glaucoma Medications Laser Therapies Conventional Surgical Procedures In the second section, you will find information on how to search for potential treatments
In this section, you will find the following: Glaucoma Medications Laser Therapies Conventional Surgical Procedures In the second section, you will find information on how to search for potential treatments
Glaucoma. What is glaucoma? Eye Words to Know. What causes glaucoma?
 2014 2015 Glaucoma What is glaucoma? Glaucoma is a disease that damages your eye s optic nerve. It usually happens when fluid builds up in the front part of your eye. That extra fluid increases the pressure
2014 2015 Glaucoma What is glaucoma? Glaucoma is a disease that damages your eye s optic nerve. It usually happens when fluid builds up in the front part of your eye. That extra fluid increases the pressure
glaucoma a closer look
 0AMERICAN ACADEMY OF OPHTHALMOLOGY The Eye M.D. Association 2012-2013 glaucoma a closer look WHAT IS GLAUCOMA? < Glaucoma is a disease of the optic nerve the part of the eye that carries the images we
0AMERICAN ACADEMY OF OPHTHALMOLOGY The Eye M.D. Association 2012-2013 glaucoma a closer look WHAT IS GLAUCOMA? < Glaucoma is a disease of the optic nerve the part of the eye that carries the images we
Written by Administrator Wednesday, 13 January :27 - Last Updated Thursday, 21 January :34
 angle closure glaucoma A type of glaucoma caused by a sudden and severe rise in eye pressure. Occurs when the pupil enlarges too much or too quickly, and the outer edge of the iris blocks the eye s drainage
angle closure glaucoma A type of glaucoma caused by a sudden and severe rise in eye pressure. Occurs when the pupil enlarges too much or too quickly, and the outer edge of the iris blocks the eye s drainage
Glaucoma. How is Glaucoma Diagnosed? Glaucoma Testing
 Glaucoma How is Glaucoma Diagnosed? Glaucoma Testing There is no single test for glaucoma. The diagnosis is made by evaluating the patient from a number of perspectives, using specialized instruments.
Glaucoma How is Glaucoma Diagnosed? Glaucoma Testing There is no single test for glaucoma. The diagnosis is made by evaluating the patient from a number of perspectives, using specialized instruments.
WORLD GLAUCOMA WEEK What is Glaucoma? Can I develop glaucoma if I have increased eye pressure?
 WORLD GLAUCOMA WEEK What is Glaucoma? Glaucoma is a group of diseases that damage the optic nerve and can result in gradual vision loss and blindness. However, with early detection and treatment, you can
WORLD GLAUCOMA WEEK What is Glaucoma? Glaucoma is a group of diseases that damage the optic nerve and can result in gradual vision loss and blindness. However, with early detection and treatment, you can
East and North Hertfordshire treatment pathway for primary open angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension in adults
 East and North Hertfordshire treatment pathway for primary open angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension in adults Introduction Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases causing optic nerve damage. In most cases
East and North Hertfordshire treatment pathway for primary open angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension in adults Introduction Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases causing optic nerve damage. In most cases
Glaucoma What You Should Know
 Glaucoma What You Should Know U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health National Eye Institute The National Eye Institute (NEI) conducts and supports research that leads
Glaucoma What You Should Know U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health National Eye Institute The National Eye Institute (NEI) conducts and supports research that leads
Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma
 www.eyesurgeonlondon.co.uk Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma What is Glaucoma? Glaucoma is a condition in which there is damage to the optic nerve. This nerve carries visual signals from the eye to the brain.
www.eyesurgeonlondon.co.uk Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma What is Glaucoma? Glaucoma is a condition in which there is damage to the optic nerve. This nerve carries visual signals from the eye to the brain.
Glaucoma. Cornea. Iris
 Glaucoma Introduction Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that can lead to blindness if not treated. Openangle glaucoma, the most common form of glaucoma, affects about 3 million Americans. Half of those
Glaucoma Introduction Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that can lead to blindness if not treated. Openangle glaucoma, the most common form of glaucoma, affects about 3 million Americans. Half of those
GENERAL INFORMATION GLAUCOMA GLAUCOMA
 GENERAL INFORMATION GLAUCOMA GLAUCOMA WHAT IS GLAUCOMA? Glaucoma is commonly known as the sneak thief of sight because it can cause irreversible vision loss without any obvious symptoms. The term glaucoma
GENERAL INFORMATION GLAUCOMA GLAUCOMA WHAT IS GLAUCOMA? Glaucoma is commonly known as the sneak thief of sight because it can cause irreversible vision loss without any obvious symptoms. The term glaucoma
ANSWERS TO YOUR MOST COMMON GLAUCOMA QUESTIONS
 For Your Eyes Only: ANSWERS TO YOUR MOST COMMON GLAUCOMA QUESTIONS www.kremereyecenter.com / 800-694-3937 1 Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Glaucoma Defined... 4 Symptoms of Glaucoma... 6 Treatment
For Your Eyes Only: ANSWERS TO YOUR MOST COMMON GLAUCOMA QUESTIONS www.kremereyecenter.com / 800-694-3937 1 Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Glaucoma Defined... 4 Symptoms of Glaucoma... 6 Treatment
VI.2.2 Summary of treatment benefits
 EU-Risk Management Plan for Bimatoprost V01 aetiology), both OAG and ACG can be secondary conditions. Secondary glaucoma refers to any case in which another disorder (e.g. injury, inflammation, vascular
EU-Risk Management Plan for Bimatoprost V01 aetiology), both OAG and ACG can be secondary conditions. Secondary glaucoma refers to any case in which another disorder (e.g. injury, inflammation, vascular
Ophthalmology. Glaucoma
 Ophthalmology Glaucoma The Ophthalmology service offers the latest and most comprehensive eye care for patients. With a dedicated team of eye surgeons and consultants, we treat vision problems ranging
Ophthalmology Glaucoma The Ophthalmology service offers the latest and most comprehensive eye care for patients. With a dedicated team of eye surgeons and consultants, we treat vision problems ranging
Get a grip on your glaucoma Booklet 1
 Information for Patients Glaucoma services Welcome! Get a grip on your glaucoma Booklet 1 Group-based Glaucoma information Course Session 1 What happens in session 1? Finding out what questions you have
Information for Patients Glaucoma services Welcome! Get a grip on your glaucoma Booklet 1 Group-based Glaucoma information Course Session 1 What happens in session 1? Finding out what questions you have
Elements for a Public Summary. Overview of disease epidemiology
 VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology Epidemiology of the disease Incidence and prevalence Increased pressure in the eye occurs in more than 100 million people, and
VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology Epidemiology of the disease Incidence and prevalence Increased pressure in the eye occurs in more than 100 million people, and
Diabetes & Your Eyes
 Diabetes & Your Eyes Diabetes is a disease that occurs when the pancreas does not secrete enough insulin or the body is unable to process it properly. Insulin is the hormone that regulates the level of
Diabetes & Your Eyes Diabetes is a disease that occurs when the pancreas does not secrete enough insulin or the body is unable to process it properly. Insulin is the hormone that regulates the level of
Save time at your check-in and register online before your appointment! It s as easy as 1-2-3
 Save time at your check-in and register online before your appointment! It s as easy as 1-2-3 1. Go online to www.blackhillseyes.com 2. Click this logo on our home page for the link to register: 3. Set-up
Save time at your check-in and register online before your appointment! It s as easy as 1-2-3 1. Go online to www.blackhillseyes.com 2. Click this logo on our home page for the link to register: 3. Set-up
Patient & Family Guide. Glaucoma Management.
 Patient & Family Guide Glaucoma Management 2018 www.nshealth.ca Glaucoma Management What is glaucoma? Your eyes are filled with a fluid made by the ciliary body (1). This fluid flows through the pupil
Patient & Family Guide Glaucoma Management 2018 www.nshealth.ca Glaucoma Management What is glaucoma? Your eyes are filled with a fluid made by the ciliary body (1). This fluid flows through the pupil
THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS
 THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS WHAT IS GLAUCOMA? People with glaucoma have lost some of their field of all round vision. It is often the edge or periphery that is lost. That is why the condition can be missed until
THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS WHAT IS GLAUCOMA? People with glaucoma have lost some of their field of all round vision. It is often the edge or periphery that is lost. That is why the condition can be missed until
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 28 May 2008
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 28 May 2008 COSOPT 20 mg/5 mg/ml, eye drops, solution in single dose container Box of 60 0.2 ml single dose containers
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 28 May 2008 COSOPT 20 mg/5 mg/ml, eye drops, solution in single dose container Box of 60 0.2 ml single dose containers
5/12/2014. Lynn E. Lawrence, CPOT, ABOC, COA
 Lynn E. Lawrence, CPOT, ABOC, COA Glaucoma is an optic neuropathy characterized by a loss of ganglion cells and their axons, in the RNFL. The loss of retinal ganglion cells in glaucoma is irreversible
Lynn E. Lawrence, CPOT, ABOC, COA Glaucoma is an optic neuropathy characterized by a loss of ganglion cells and their axons, in the RNFL. The loss of retinal ganglion cells in glaucoma is irreversible
South East London Area Prescribing Committee Chronic Open Angle Glaucoma and Ocular Hypertension Treatment Pathway
 Proceed to 2 nd line treatment if further reduction in IOP required and there is good response to PGAs or (& no South East London Area Prescribing Committee Chronic Open Angle Glaucoma and Ocular Hypertension
Proceed to 2 nd line treatment if further reduction in IOP required and there is good response to PGAs or (& no South East London Area Prescribing Committee Chronic Open Angle Glaucoma and Ocular Hypertension
Closed Angle Glaucoma Or Narrow Angle Glaucoma. What s is a closed angle type of glaucoma,
 Closed Angle Glaucoma Or Narrow Angle Glaucoma What s is a closed angle type of glaucoma, This is where the iris is found to be blocking the drainage of the eye through the trabecular meshwork. The eye
Closed Angle Glaucoma Or Narrow Angle Glaucoma What s is a closed angle type of glaucoma, This is where the iris is found to be blocking the drainage of the eye through the trabecular meshwork. The eye
THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS
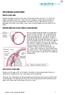 THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS WHAT IS GLAUCOMA People with glaucoma have lost some of their field of all round vision. It is often the edge or periphery that is lost. That is why the condition can be missed until
THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS WHAT IS GLAUCOMA People with glaucoma have lost some of their field of all round vision. It is often the edge or periphery that is lost. That is why the condition can be missed until
Brampton Hurontario Street Brampton, ON L6Y 0P6
 Diabetic Retinopathy What is Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetic retinopathy is one of the leading causes of blindness world-wide. Diabetes damages blood vessels in many organs of the body including the eyes.
Diabetic Retinopathy What is Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetic retinopathy is one of the leading causes of blindness world-wide. Diabetes damages blood vessels in many organs of the body including the eyes.
Financial Disclosure. Prostaglandin Analogs (PGs) The Glaucoma Grab Bag: Practical Guidelines for Effective Glaucoma Therapy
 The Glaucoma Grab Bag: Practical Guidelines for Effective Glaucoma Therapy Danica J. Marrelli, OD, FAAO University of Houston College of Optometry Financial Disclosure I have received I have received speaking
The Glaucoma Grab Bag: Practical Guidelines for Effective Glaucoma Therapy Danica J. Marrelli, OD, FAAO University of Houston College of Optometry Financial Disclosure I have received I have received speaking
A. Incorrect! Acetazolamide is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor given orally or by intravenous injection.
 Pharmacology - Problem Drill 20: Drugs that Treat Glaucoma Question No. 1 of 10 1. is a topical carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. Question #01 (A) Acetazolamide (B) Clonidine (C) Dorzolamide (D) Apraclonidine
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 20: Drugs that Treat Glaucoma Question No. 1 of 10 1. is a topical carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. Question #01 (A) Acetazolamide (B) Clonidine (C) Dorzolamide (D) Apraclonidine
Managing the Patient with POAG
 Managing the Patient with POAG Vision Institute Annual Fall Conference Mitchell W. Dul, OD, MS, FAAO mdul@sunyopt.edu Richard J. Madonna, MA, OD, FAAO rmadonna@sunyopt.edu Ocular Hypertension (OHT) Most
Managing the Patient with POAG Vision Institute Annual Fall Conference Mitchell W. Dul, OD, MS, FAAO mdul@sunyopt.edu Richard J. Madonna, MA, OD, FAAO rmadonna@sunyopt.edu Ocular Hypertension (OHT) Most
GLAUCOMA. An Overview
 GLAUCOMA An Overview Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2004) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com --()-- IMPORTANT The health information contained herein is not meant as a substitute for advice from your
GLAUCOMA An Overview Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2004) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com --()-- IMPORTANT The health information contained herein is not meant as a substitute for advice from your
 measure of your overall performance. An isolated glucose test is helpful to let you know what your sugar level is at one moment, but it doesn t tell you whether or not your diabetes is under adequate control
measure of your overall performance. An isolated glucose test is helpful to let you know what your sugar level is at one moment, but it doesn t tell you whether or not your diabetes is under adequate control
Glaucoma Intraocular Pressure What Will I Notice?
 Glaucoma Glaucoma is the name given to a group of eye conditions in which the optic nerve at the back of the eye is slowly damaged. The diagnosis of glaucoma is made when your optometrist or ophthalmologist
Glaucoma Glaucoma is the name given to a group of eye conditions in which the optic nerve at the back of the eye is slowly damaged. The diagnosis of glaucoma is made when your optometrist or ophthalmologist
PATIENT GUIDE TO LUMIGAN 0.01%
 Treatment Tracker enclosed PATIENT GUIDE TO LUMIGAN 0.01% LUMIGAN (bimatoprost ophthalmic solution) 0.01% is used for the treatment of high eye pressure, also called intraocular pressure (IOP), in people
Treatment Tracker enclosed PATIENT GUIDE TO LUMIGAN 0.01% LUMIGAN (bimatoprost ophthalmic solution) 0.01% is used for the treatment of high eye pressure, also called intraocular pressure (IOP), in people
Diabetic retinopathy damage to the blood vessels in the retina. Cataract clouding of the eye s lens. Cataracts develop at an earlier age in people
 Diabetic Retinopathy What is diabetic eye disease? Diabetic eye disease refers to a group of eye problems that people with diabetes may face as a complication of diabetes. All can cause severe vision loss
Diabetic Retinopathy What is diabetic eye disease? Diabetic eye disease refers to a group of eye problems that people with diabetes may face as a complication of diabetes. All can cause severe vision loss
Goals. Glaucoma PARA PEARL TO DO. Vision Loss with Glaucoma
 Glaucoma Janet R. Fett, OD Drs. Kincaid, Fett and Tharp So Sioux City, NE eyewear21@hotmail.com Goals Understand Glaucoma Disease process Understand how your data (objective and subjective) assists in
Glaucoma Janet R. Fett, OD Drs. Kincaid, Fett and Tharp So Sioux City, NE eyewear21@hotmail.com Goals Understand Glaucoma Disease process Understand how your data (objective and subjective) assists in
Frequently Asked Questions about General Ophthalmology:
 1. Normal Eye Structure The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The parts of the eye include: Cornea (a clear dome over the iris), Iris (the pigmented part); Pupil (the black
1. Normal Eye Structure The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The parts of the eye include: Cornea (a clear dome over the iris), Iris (the pigmented part); Pupil (the black
YOUR VYZULTA TREATMENT GUIDE. Please see Important Safety Information on pages 1, 9, 10, 17 and 18. Please see accompanying Prescribing Information.
 YOUR VYZULTA TREATMENT GUIDE Please see Important Safety Information on pages 1, 9, 10, 17 and 18. Please see accompanying Prescribing Information. INDICATION VYZULTA TM (latanoprostene bunod ophthalmic
YOUR VYZULTA TREATMENT GUIDE Please see Important Safety Information on pages 1, 9, 10, 17 and 18. Please see accompanying Prescribing Information. INDICATION VYZULTA TM (latanoprostene bunod ophthalmic
Diabetic Retinopathy Information
 http://www.midwestretina.com Phone: (614)-339-8500 Toll Free: (866)-373-8462 Sugat S. Patel, M.D. Louis J. Chorich III, M.D. Dino D. Klisovic, M.D. Lisa M. Borkowski, M.D. Dominic M. Buzzacco, M.D. Johnstone
http://www.midwestretina.com Phone: (614)-339-8500 Toll Free: (866)-373-8462 Sugat S. Patel, M.D. Louis J. Chorich III, M.D. Dino D. Klisovic, M.D. Lisa M. Borkowski, M.D. Dominic M. Buzzacco, M.D. Johnstone
GENERAL INFORMATION DIABETIC EYE DISEASE
 GENERAL INFORMATION DIABETIC EYE DISEASE WHAT IS DIABETIC EYE DISEASE? Diabetic eye disease is a term used to describe the common eye complications seen in people with diabetes. It includes: Diabetic retinopathy
GENERAL INFORMATION DIABETIC EYE DISEASE WHAT IS DIABETIC EYE DISEASE? Diabetic eye disease is a term used to describe the common eye complications seen in people with diabetes. It includes: Diabetic retinopathy
Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
 Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD) What is the Macula? What is Dry AMD (Age-related Macular Degeneration)? Dry AMD is an aging process that causes accumulation of waste product under the macula leading
Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD) What is the Macula? What is Dry AMD (Age-related Macular Degeneration)? Dry AMD is an aging process that causes accumulation of waste product under the macula leading
OCULAR PHARMACOLOGY GLAUCOMA. increased intraocular pressure. normally mm Hg. when to Tx no fixed level.
 OCULAR PHARMACOLOGY GLAUCOMA increased intraocular pressure normally 12 20 mm Hg. when to Tx no fixed level. literature sets ~21 mm Hg as upper limit of normal. some safe at 30 mm Hg some may have damage
OCULAR PHARMACOLOGY GLAUCOMA increased intraocular pressure normally 12 20 mm Hg. when to Tx no fixed level. literature sets ~21 mm Hg as upper limit of normal. some safe at 30 mm Hg some may have damage
Divakar Gupta Glaucoma Fellow, Duke Eye Center 5/14/16
 Divakar Gupta Glaucoma Fellow, Duke Eye Center 5/14/16 Pathophysiology of glaucoma Consider risk factors of glaucoma Understand the side effects of glaucoma medications Diagnostic testing Leading cause
Divakar Gupta Glaucoma Fellow, Duke Eye Center 5/14/16 Pathophysiology of glaucoma Consider risk factors of glaucoma Understand the side effects of glaucoma medications Diagnostic testing Leading cause
Collaboration in the care of glaucoma patients and glaucoma suspects. Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Nico Ristorante November 29, 2012
 Collaboration in the care of glaucoma patients and glaucoma suspects Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Nico Ristorante November 29, 2012 Goals of Collaboration Patient-centred and evidence based approach Timely access
Collaboration in the care of glaucoma patients and glaucoma suspects Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Nico Ristorante November 29, 2012 Goals of Collaboration Patient-centred and evidence based approach Timely access
PRACTICAL APPROACH TO MEDICAL MANAGEMENT OF GLAUCOMA
 PRACTICAL APPROACH TO MEDICAL MANAGEMENT OF GLAUCOMA DR. RAVI THOMAS, DR. RAJUL PARIKH, DR. SHEFALI PARIKH IJO MAY 2008 PRESENTER AT JDOS : DR. RAHUL SHUKLA T.N. SHUKLA EYE HOSPITAL TERMINOLOGY POAG: PRIMARY
PRACTICAL APPROACH TO MEDICAL MANAGEMENT OF GLAUCOMA DR. RAVI THOMAS, DR. RAJUL PARIKH, DR. SHEFALI PARIKH IJO MAY 2008 PRESENTER AT JDOS : DR. RAHUL SHUKLA T.N. SHUKLA EYE HOSPITAL TERMINOLOGY POAG: PRIMARY
Glaucoma: Diagnostic Modalities
 Glaucoma: Diagnostic Modalities - Dr. Barun Kumar Nayak, Dr. Sarika Ramugade Glaucoma is a leading cause of blindness in the world, especially in older people. Early detection and treatment by ophthalmologist
Glaucoma: Diagnostic Modalities - Dr. Barun Kumar Nayak, Dr. Sarika Ramugade Glaucoma is a leading cause of blindness in the world, especially in older people. Early detection and treatment by ophthalmologist
ILUVIEN 190 micrograms intravitreal implant in applicator (fluocinolone acetonide)
 ILUVIEN 190 micrograms intravitreal implant in applicator (fluocinolone acetonide) Read all of this information carefully before you are given this medicine because it contains important information for
ILUVIEN 190 micrograms intravitreal implant in applicator (fluocinolone acetonide) Read all of this information carefully before you are given this medicine because it contains important information for
Retinal Tears and Detachments
 Retinal Tears and Detachments Understanding Retinal Problems When your eyes are working well, it s easy to take them for granted. But a tear or detachment of your eye s retina (the light-sensing lining
Retinal Tears and Detachments Understanding Retinal Problems When your eyes are working well, it s easy to take them for granted. But a tear or detachment of your eye s retina (the light-sensing lining
Glaucoma Clinical Update. Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Giovanni Caboto Club October 3, 2012
 Glaucoma Clinical Update Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Giovanni Caboto Club October 3, 2012 Objectives Understand the different categories of glaucoma Recognize the symptoms and signs of open angle and angle-closure
Glaucoma Clinical Update Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Giovanni Caboto Club October 3, 2012 Objectives Understand the different categories of glaucoma Recognize the symptoms and signs of open angle and angle-closure
Selective Laser Trabeculoplasty (SLT) for Glaucoma
 Patient & Family Guide 2018 Selective Laser Trabeculoplasty (SLT) for Glaucoma Aussi disponible en français : Trabéculoplastie sélective au laser (TSL) pour le glaucome (FF85-1912) www.nshealth.ca Selective
Patient & Family Guide 2018 Selective Laser Trabeculoplasty (SLT) for Glaucoma Aussi disponible en français : Trabéculoplastie sélective au laser (TSL) pour le glaucome (FF85-1912) www.nshealth.ca Selective
Patient Information Leaflet Glaucoma Procedures. Trabeculectomy
 Dr. Andrew J. Tatham MBChB (Hon), FRCOphth, FEBO, FRCS(Ed) Consultant Glaucoma and Cataract Surgeon Patient Information Leaflet Glaucoma Procedures Trabeculectomy What is glaucoma? Glaucoma is a term used
Dr. Andrew J. Tatham MBChB (Hon), FRCOphth, FEBO, FRCS(Ed) Consultant Glaucoma and Cataract Surgeon Patient Information Leaflet Glaucoma Procedures Trabeculectomy What is glaucoma? Glaucoma is a term used
Trabeculectomy. Draining the aqueous humour reduces the pressure on the optic nerve that causes loss of vision in glaucoma.
 Trabeculectomy Other formats If you need this information in another format such as audio tape or computer disk, Braille, large print, high contrast, British Sign Language or translated into another language,
Trabeculectomy Other formats If you need this information in another format such as audio tape or computer disk, Braille, large print, high contrast, British Sign Language or translated into another language,
Volume 9; Number 6 May 2015 PRESCRIBING FOR CHRONIC OPEN ANGLE GLAUCOMA (COAG) AND OCULAR HYPERTENSION (OHT)
 Greater East Midlands Commissioning Support Unit in association with Lincolnshire Clinical Commissioning Groups, Lincolnshire Community Health Services, United Lincolnshire Hospitals Trust and Lincolnshire
Greater East Midlands Commissioning Support Unit in association with Lincolnshire Clinical Commissioning Groups, Lincolnshire Community Health Services, United Lincolnshire Hospitals Trust and Lincolnshire
Understanding and Living with Glaucoma
 Understanding and Living with Glaucoma Amanda hopes future generations won t have to live with glaucoma. Dr. Dubra s breakthrough research could mean they won t have to. I genuinely believe that a cure
Understanding and Living with Glaucoma Amanda hopes future generations won t have to live with glaucoma. Dr. Dubra s breakthrough research could mean they won t have to. I genuinely believe that a cure
Factsheet. Glaucoma. Are there different types of glaucoma? Yes. There are four main types.
 What is glaucoma? Glaucoma is the name for a group of eye conditions in which the optic nerve is damaged at the point where it leaves the eye. This nerve carries information from the light sensitive layer
What is glaucoma? Glaucoma is the name for a group of eye conditions in which the optic nerve is damaged at the point where it leaves the eye. This nerve carries information from the light sensitive layer
Understanding Diabetic Retinopathy
 Understanding Diabetic Retinopathy What Is Diabetic Retinopathy? Diabetes damages blood vessels in the rear of the eye. This condition is called diabetic retinopathy. It can lead to vision loss or blindness.
Understanding Diabetic Retinopathy What Is Diabetic Retinopathy? Diabetes damages blood vessels in the rear of the eye. This condition is called diabetic retinopathy. It can lead to vision loss or blindness.
A Patient s Guide to Diabetic Retinopathy
 Diabetic Retinopathy A Patient s Guide to Diabetic Retinopathy 840 Walnut Street, Philadelphia PA 19107 www.willseye.org Diabetic Retinopathy 1. Definition Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes
Diabetic Retinopathy A Patient s Guide to Diabetic Retinopathy 840 Walnut Street, Philadelphia PA 19107 www.willseye.org Diabetic Retinopathy 1. Definition Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes
Cataract Surgery. This reference summary will help you understand what cataracts are and how they can be treated surgically.
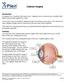 Cataract Surgery Introduction A cataract is a clouding of the eye s lens. Cataracts are a common eye condition that affect many people aged 65 or older. Your doctor may recommend cataract surgery to enhance
Cataract Surgery Introduction A cataract is a clouding of the eye s lens. Cataracts are a common eye condition that affect many people aged 65 or older. Your doctor may recommend cataract surgery to enhance
Glaucoma. Glaucoma. Glaucoma. Trevor Arnold, MS, DVM, DACVO
 Glaucoma Trevor Arnold, MS, DVM, DACVO Glaucoma Physiology of Aqueous Humor Produced in the ciliary body Flows out the iridocorneal angle and ciliary cleft High intraocular pressures are caused by a decreased
Glaucoma Trevor Arnold, MS, DVM, DACVO Glaucoma Physiology of Aqueous Humor Produced in the ciliary body Flows out the iridocorneal angle and ciliary cleft High intraocular pressures are caused by a decreased
Understanding And Living With Glaucoma
 Understanding And Living With Glaucoma Samantha hopes future generations won t have to live with glaucoma. Dr. Horner s breakthrough research could mean they won t have to. Supported by an educational
Understanding And Living With Glaucoma Samantha hopes future generations won t have to live with glaucoma. Dr. Horner s breakthrough research could mean they won t have to. Supported by an educational
Introduction How the eye works
 1 Introduction Diabetic retinopathy is a condition that can cause permanent loss of eyesight and even blindness. It is a major cause of loss of vision. But if a person with diabetes receives proper eye
1 Introduction Diabetic retinopathy is a condition that can cause permanent loss of eyesight and even blindness. It is a major cause of loss of vision. But if a person with diabetes receives proper eye
Information for patients considering cataract surgery Castleton Day Surgery Unit, Yeatman Hospital, Sherborne
 Information for patients considering cataract surgery Castleton Day Surgery Unit, Yeatman Hospital, Sherborne 01935 384 309 yeovilhospital.nhs.uk This leaflet gives you information that will help you decide
Information for patients considering cataract surgery Castleton Day Surgery Unit, Yeatman Hospital, Sherborne 01935 384 309 yeovilhospital.nhs.uk This leaflet gives you information that will help you decide
GLAUCOMA (2006) PHILIPPINE GLAUCOMA SOCIETY
 GLAUCOMA (2006) PHILIPPINE GLAUCOMA SOCIETY CPM 9 TH EDITION Philippine Glaucoma Society (PGS) Correspondence to: Eye Referral Center, T. M. Kalaw Street, Ermita, Manila Telephone: 524-7119/525-9360 Mobile:
GLAUCOMA (2006) PHILIPPINE GLAUCOMA SOCIETY CPM 9 TH EDITION Philippine Glaucoma Society (PGS) Correspondence to: Eye Referral Center, T. M. Kalaw Street, Ermita, Manila Telephone: 524-7119/525-9360 Mobile:
Visit Type (Check one)
 Page 1 of 14 OHFV21.01 MULE: Page 1 Visit Type (Check one) Visit prior to 078 month visit enter visit window 0 Semi-Annual: Annual: 078 mo. 090 mo. 102 mo. 114 mo. 126 mo. 138 mo. 150 mo. 162 mo. 084 mo.
Page 1 of 14 OHFV21.01 MULE: Page 1 Visit Type (Check one) Visit prior to 078 month visit enter visit window 0 Semi-Annual: Annual: 078 mo. 090 mo. 102 mo. 114 mo. 126 mo. 138 mo. 150 mo. 162 mo. 084 mo.
Hydrus. What is a Hydrus Microstent? By Nathan Kerr and Keith Barton. Eye words to know. MIGS.org
 MIGS.org Hydrus By Nathan Kerr and Keith Barton What is a Hydrus Microstent? The Hydrus Microstent is a small flexible scaffold inserted into the natural drainage channel of the eye to lower eye pressure
MIGS.org Hydrus By Nathan Kerr and Keith Barton What is a Hydrus Microstent? The Hydrus Microstent is a small flexible scaffold inserted into the natural drainage channel of the eye to lower eye pressure
relative s privacy, do not identify your relative by full name in any assignment.
 Overview Do you or a family member have glaucoma? Do you wonder what this diagnosis means? Glaucoma affects tens of millions of people worldwide. Despite its prevalence, many people lack accurate information
Overview Do you or a family member have glaucoma? Do you wonder what this diagnosis means? Glaucoma affects tens of millions of people worldwide. Despite its prevalence, many people lack accurate information
Glaucoma. Glaucoma. Optic Disc Cupping
 Glaucoma What is Glaucoma? Bruce James A group of diseases in which damage to the optic nerve occurs as a result of intraocualar pressure being above the physiological norm for that eye Stoke Mandeville
Glaucoma What is Glaucoma? Bruce James A group of diseases in which damage to the optic nerve occurs as a result of intraocualar pressure being above the physiological norm for that eye Stoke Mandeville
Glaucoma Surgery Trabeculectomy
 What is Glaucoma? The optic nerve carries images from the retina (light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye) to the brain, allowing you to see (see figure 1). Glaucoma is the name given to a group of
What is Glaucoma? The optic nerve carries images from the retina (light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye) to the brain, allowing you to see (see figure 1). Glaucoma is the name given to a group of
Pre-Operative Health Questionnaire. 3. Are you currently taking any of the following medications for. glaucoma: TRAVATAN LUMIGAN XALATAN
 Pre-Operative Health Questionnaire 1. Are you Diabetic? YES / NO 2. Are you currently on dialysis? YES / NO 3. Are you currently taking any of the following medications for glaucoma: TRAVATAN LUMIGAN XALATAN
Pre-Operative Health Questionnaire 1. Are you Diabetic? YES / NO 2. Are you currently on dialysis? YES / NO 3. Are you currently taking any of the following medications for glaucoma: TRAVATAN LUMIGAN XALATAN
CORNEAL CONDITIONS CORNEAL TRANSPLANTATION
 GENERAL INFORMATION CORNEAL CONDITIONS CORNEAL TRANSPLANTATION WHAT ARE CORNEAL CONDITIONS? The cornea is the clear outer layer of the eye. Shaped like a dome, it helps to protect the eye from foreign
GENERAL INFORMATION CORNEAL CONDITIONS CORNEAL TRANSPLANTATION WHAT ARE CORNEAL CONDITIONS? The cornea is the clear outer layer of the eye. Shaped like a dome, it helps to protect the eye from foreign
Trabectome. What is a Trabectome? Who is suitable for a Trabectome? By Nathan Kerr and Keith Barton. Eye words to know. MIGS.org
 MIGS.org Trabectome By Nathan Kerr and Keith Barton What is a Trabectome? The Trabectome is a minimally invasive glaucoma procedure that increases the natural drainage of fluid from the eye by removing
MIGS.org Trabectome By Nathan Kerr and Keith Barton What is a Trabectome? The Trabectome is a minimally invasive glaucoma procedure that increases the natural drainage of fluid from the eye by removing
Trabeculectomy (Glaucoma Drainage) Surgery
 Information for Patients Manchester Royal Eye Hospital Glaucoma services Trabeculectomy (Glaucoma Drainage) Surgery You may have been told by your doctor that you require an operation to control the pressure
Information for Patients Manchester Royal Eye Hospital Glaucoma services Trabeculectomy (Glaucoma Drainage) Surgery You may have been told by your doctor that you require an operation to control the pressure
RETINAL CONDITIONS RETINAL CONDITIONS
 GENERAL INFORMATION RETINAL CONDITIONS RETINAL CONDITIONS WHAT ARE RETINAL CONDITIONS? Retinal conditions affect the light-sensitive tissue at the back of eye known as the retina. They include diseases
GENERAL INFORMATION RETINAL CONDITIONS RETINAL CONDITIONS WHAT ARE RETINAL CONDITIONS? Retinal conditions affect the light-sensitive tissue at the back of eye known as the retina. They include diseases
NEPTUNE RED BANK BRICK
 NEPTUNE RED BANK BRICK Diabetes & The Eye Diabetics are more likely to develop Cataracts at a younger age. Diabetics are twice as likely to develop Glaucoma when compared to non-diabetics. The primary
NEPTUNE RED BANK BRICK Diabetes & The Eye Diabetics are more likely to develop Cataracts at a younger age. Diabetics are twice as likely to develop Glaucoma when compared to non-diabetics. The primary
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC)
 Guidelines for the medical treatment of chronic open angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension Summary: DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) Diagnosis and management of ocular hypertension (OHT)
Guidelines for the medical treatment of chronic open angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension Summary: DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) Diagnosis and management of ocular hypertension (OHT)
MicroPulse Cyclodiode
 MIGS.org MicroPulse Cyclodiode By Nathan Kerr and Keith Barton What is MicroPulse cyclodiode laser? The MicroPulse cyclodiode laser is a non-invasive laser treatment of the part of the eye that produces
MIGS.org MicroPulse Cyclodiode By Nathan Kerr and Keith Barton What is MicroPulse cyclodiode laser? The MicroPulse cyclodiode laser is a non-invasive laser treatment of the part of the eye that produces
1/31/2018. Course Objectives. Diagnostic Testing. Optic Nerve Damage ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF A GLAUCOMA WORK-UP/TONOMETRY TECHNICIAN: -SDP
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF A GLAUCOMA WORK-UP/TONOMETRY KNOW THE DISEASE PROCESS TECHNICIAN: EXPLAIN PROCESS OF EXAMINATION Presenters: Dana McMahan, COA Nicole Smith, COA Engage with patient s, help alleviate
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF A GLAUCOMA WORK-UP/TONOMETRY KNOW THE DISEASE PROCESS TECHNICIAN: EXPLAIN PROCESS OF EXAMINATION Presenters: Dana McMahan, COA Nicole Smith, COA Engage with patient s, help alleviate
Glaucoma Basics OVERVIEW GENETICS SIGNALMENT/DESCRIPTION OF PET
 Glaucoma Basics OVERVIEW Glaucoma is a disease of the eye, in which the pressure within the eye is increased (pressure within the eye is known as intraocular pressure or IOP) High intraocular pressure
Glaucoma Basics OVERVIEW Glaucoma is a disease of the eye, in which the pressure within the eye is increased (pressure within the eye is known as intraocular pressure or IOP) High intraocular pressure
Understanding. Glaucoma
 Understanding Glaucoma Contact us We re here to answer any questions you have about your eye condition or treatment. If you need further information about glaucoma or on coping with changes in your vision,
Understanding Glaucoma Contact us We re here to answer any questions you have about your eye condition or treatment. If you need further information about glaucoma or on coping with changes in your vision,
PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET. PROPRIETARY NAME, STRENGTH AND PHARMACEUTICAL FORM OZURDEX, dexamethasone 700 μg intravitreal implant
 Page 1 of 6 SCHEDULING STATUS Schedule 4 PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET PROPRIETARY NAME, STRENGTH AND PHARMACEUTICAL FORM, dexamethasone 700 μg intravitreal implant Read all of this leaflet carefully before
Page 1 of 6 SCHEDULING STATUS Schedule 4 PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET PROPRIETARY NAME, STRENGTH AND PHARMACEUTICAL FORM, dexamethasone 700 μg intravitreal implant Read all of this leaflet carefully before
Understanding Glaucoma
 Understanding Glaucoma What is glaucoma? Glaucoma is the name for a group of eye conditions in which the optic nerve is damaged at the point at which it leaves the eye. As the diagram below shows, this
Understanding Glaucoma What is glaucoma? Glaucoma is the name for a group of eye conditions in which the optic nerve is damaged at the point at which it leaves the eye. As the diagram below shows, this
Long Term Care Formulary RS 14. RESTRICTED STATUS Topical Medical Treatment of Glaucoma 1 of 5
 RESTRICTED STATUS Topical Medical Treatment of Glaucoma 1 of 5 PREAMBLE Significance: Glaucoma occurs in 1-2% of white people aged over 40 years, rising to 5% at 70 years and exponentially with advancing
RESTRICTED STATUS Topical Medical Treatment of Glaucoma 1 of 5 PREAMBLE Significance: Glaucoma occurs in 1-2% of white people aged over 40 years, rising to 5% at 70 years and exponentially with advancing
GLAUCOMA. phone (64) fax (64) web
 GLAUCOMA phone (64) 09 529 2480 fax (64) 09 529 2481 email admin@aucklandeye.co.nz web www.aucklandeye.co.nz www.aucklandeye.co.nz GLAUCOMA ABOUT GLAUCOMA Glaucoma is an eye disease that affects 2-3% of
GLAUCOMA phone (64) 09 529 2480 fax (64) 09 529 2481 email admin@aucklandeye.co.nz web www.aucklandeye.co.nz www.aucklandeye.co.nz GLAUCOMA ABOUT GLAUCOMA Glaucoma is an eye disease that affects 2-3% of
Technicians & Nurses Program
 ASCRS ASOA Symposium & Congress Technicians & Nurses Program May 6-10, 2016 New Orleans I have none Sunday, May 8, 2016, 10:30-11:30am Amy Jost, BS, COMT, CCRC Cincinnati Eye Institute Identify the tech
ASCRS ASOA Symposium & Congress Technicians & Nurses Program May 6-10, 2016 New Orleans I have none Sunday, May 8, 2016, 10:30-11:30am Amy Jost, BS, COMT, CCRC Cincinnati Eye Institute Identify the tech
Information for patients
 Information for patients Intravitreal Anti-VEGF Treatment (vascular endothelial growth factor) This leaflet gives you information that will help you decide whether to have intravitreal treatment. It also
Information for patients Intravitreal Anti-VEGF Treatment (vascular endothelial growth factor) This leaflet gives you information that will help you decide whether to have intravitreal treatment. It also
Uveitis. Pt Info Brochure. Q: What is Uvea?
 Pt Info Brochure Uveitis Q: What is Uvea? A: Uvea is the middle layer of the eye. It is the most vascular structure of the eye. It provides nutrition to the other parts of the eye. The uvea is made up
Pt Info Brochure Uveitis Q: What is Uvea? A: Uvea is the middle layer of the eye. It is the most vascular structure of the eye. It provides nutrition to the other parts of the eye. The uvea is made up
Patient Information Cataract Surgery
 Patient Information Cataract Surgery Introduction This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about surgery for a cataract. It explains what the operation involves, the benefits and risks
Patient Information Cataract Surgery Introduction This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about surgery for a cataract. It explains what the operation involves, the benefits and risks
N W KNOW. What You Need to Know. What You Know About Glaucoma Could Save Your Sight
 What You Need to Know is the second leading cause of blindness around the world, so it is important to understand its significance and treatment options. While glaucoma is not curable, there are several
What You Need to Know is the second leading cause of blindness around the world, so it is important to understand its significance and treatment options. While glaucoma is not curable, there are several
Diabetic Retinopathy
 Diabetic Retinopathy Introduction People with diabetes are more likely to have eye problems that can lead to blindness. Diabetic retinopathy is a disease of the eye s retina that is caused by diabetes.
Diabetic Retinopathy Introduction People with diabetes are more likely to have eye problems that can lead to blindness. Diabetic retinopathy is a disease of the eye s retina that is caused by diabetes.
Age-Related. macular degeneration.
 Age-Related Macular Degeneration This pamphlet is designed to help people with age-related macular degeneration and their families better understand the disease. It describes the causes, symptoms, diagnosis,
Age-Related Macular Degeneration This pamphlet is designed to help people with age-related macular degeneration and their families better understand the disease. It describes the causes, symptoms, diagnosis,
Package leaflet: information for the user. OZURDEX 700 micrograms intravitreal implant in applicator dexamethasone
 Package leaflet: information for the user OZURDEX 700 micrograms intravitreal implant in applicator dexamethasone Read all of this leaflet carefully before you are given this medicine because it contains
Package leaflet: information for the user OZURDEX 700 micrograms intravitreal implant in applicator dexamethasone Read all of this leaflet carefully before you are given this medicine because it contains
Package Leaflet: Information for the user. LUMIGAN 0.3 mg/ml, eye drops, solution, in single-dose container Bimatoprost
 Package Leaflet: Information for the user LUMIGAN 0.3 mg/ml, eye drops, solution, in single-dose container Bimatoprost Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it
Package Leaflet: Information for the user LUMIGAN 0.3 mg/ml, eye drops, solution, in single-dose container Bimatoprost Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it
Information for Patients. Deep sclerectomy for the treatment of Glaucoma
 Manchester Royal Eye Hospital Glaucoma Services Information for Patients Deep sclerectomy for the treatment of Glaucoma Introduction This leaflet provides information for patients being offered deep sclerectomy
Manchester Royal Eye Hospital Glaucoma Services Information for Patients Deep sclerectomy for the treatment of Glaucoma Introduction This leaflet provides information for patients being offered deep sclerectomy
Glaucoma surgery (trabeculectomy)
 Glaucoma surgery (trabeculectomy) Information for patients This leaflet tells you about glaucoma surgery. Please read it carefully, since it contains important and useful information for you. If, after
Glaucoma surgery (trabeculectomy) Information for patients This leaflet tells you about glaucoma surgery. Please read it carefully, since it contains important and useful information for you. If, after
Scrub In. What is the function of vitreous humor? What does the pupil do when exposed to bright light? a. Maintain eye shape and provide color vision
 Scrub In What is the function of vitreous humor? a. Maintain eye shape and provide color vision b. Maintain eye shape and refract light rays c. Provide night vision and color vision d. Provide night vision
Scrub In What is the function of vitreous humor? a. Maintain eye shape and provide color vision b. Maintain eye shape and refract light rays c. Provide night vision and color vision d. Provide night vision
Elements for a public summary. VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology
 VI.2 Elements for a public summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology The term ocular hypertension usually refers to any situation in which the pressure inside the eye, called intraocular pressure,
VI.2 Elements for a public summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology The term ocular hypertension usually refers to any situation in which the pressure inside the eye, called intraocular pressure,
X-Plain Diabetic Retinopathy Reference Summary
 X-Plain Diabetic Retinopathy Reference Summary Introduction Patients with diabetes are more likely to have eye problems that can lead to blindness. Diabetic retinopathy is a disease of the eye s retina
X-Plain Diabetic Retinopathy Reference Summary Introduction Patients with diabetes are more likely to have eye problems that can lead to blindness. Diabetic retinopathy is a disease of the eye s retina
VISIONCARE S IMPLANTABLE MINIATURE TELESCOPE (by Dr. Isaac Lipshitz)
 PATIENT INFORMATION BOOKLET PAGE 1 OF 32 VISIONCARE S IMPLANTABLE MINIATURE TELESCOPE (by Dr. Isaac Lipshitz) AN INTRAOCULAR TELESCOPE FOR TREATING SEVERE TO PROFOUND VISION IMPAIRMENT DUE TO BILATERAL
PATIENT INFORMATION BOOKLET PAGE 1 OF 32 VISIONCARE S IMPLANTABLE MINIATURE TELESCOPE (by Dr. Isaac Lipshitz) AN INTRAOCULAR TELESCOPE FOR TREATING SEVERE TO PROFOUND VISION IMPAIRMENT DUE TO BILATERAL
UNDERSTANDING COMMON EYE DISEASES INTRODUCTION. Diseases of the eye are very common and if a Certified Nursing Assistant
 UNDERSTANDING COMMON EYE DISEASES INTRODUCTION Diseases of the eye are very common and if a Certified Nursing Assistant (CNA) is working with an elderly population it is very likely that some of these
UNDERSTANDING COMMON EYE DISEASES INTRODUCTION Diseases of the eye are very common and if a Certified Nursing Assistant (CNA) is working with an elderly population it is very likely that some of these
PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET. PROPRIETARY NAME, STRENGTH AND PHARMACEUTICAL FORM LUMIGAN 0,01 %, bimatoprost 0,1 mg/ml eye drops
 Page 1 of 6 SCHEDULING STATUS Schedule 4 PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET PROPRIETARY NAME, STRENGTH AND PHARMACEUTICAL FORM LUMIGAN 0,01 %, bimatoprost 0,1 mg/ml eye drops Read all of this leaflet carefully
Page 1 of 6 SCHEDULING STATUS Schedule 4 PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET PROPRIETARY NAME, STRENGTH AND PHARMACEUTICAL FORM LUMIGAN 0,01 %, bimatoprost 0,1 mg/ml eye drops Read all of this leaflet carefully
