A Guide to the Radiologic Evaluation of Extra-Axial Hemorrhage
|
|
|
- Alisha Bridges
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 July 2013 A Guide to the Radiologic Evaluation of Extra-Axial Hemorrhage John Dickson, Harvard Medical School Year III
2 Agenda 1. Define extra-axial hemorrhage and introduce its subtypes 2. Review coup and contrecoup head injuries 3. Review relevant brain, ventricular system, and meningeal anatomy 4. Present the menu of tests available for neuroimaging in the setting of head trauma 5. View several subtypes of extra-axial hemorrhages in our patient, AB 6. Describe the characteristic radiologic findings of each extraaxial hemorrhage subtype 7. Provide an update on our patient, AB 8. Summarize key points 2
3 Agenda 1. Define extra-axial hemorrhage and introduce its subtypes 2. Review coup and contrecoup head injuries 3. Review relevant brain, ventricular system, and meningeal anatomy 4. Present the menu of tests available for neuroimaging in the setting of head trauma 5. View several subtypes of extra-axial hemorrhages in our patient, AB 6. Describe the characteristic radiologic findings of each extraaxial hemorrhage subtype 7. Provide an update on our patient, AB 8. Summarize key points 3
4 Extra-Axial Hemorrhage: The Basics Bleeding inside the skull but outside the brain parenchyma 4 Subtypes Epidural hematoma Subdural hematoma Subarachnoid hemorrhage Intraventricular hemorrhage Head trauma is most common cause Other causes include Arteriovenous malformation Infection Coagulopathy Complication of neurosurgery Hemorrhagic tumors SLE John Dickson, MSIII 4 (Kubal, 2012; McBride, accessed 2013)
5 Agenda 1. Define extra-axial hemorrhage and introduce its subtypes 2. Review coup and contrecoup head injuries 3. Review relevant brain, ventricular system, and meningeal anatomy 4. Present the menu of tests available for neuroimaging in the setting of head trauma 5. View several subtypes of extra-axial hemorrhages in our patient, AB 6. Describe the characteristic radiologic findings of each extraaxial hemorrhage subtype 7. Provide an update on our patient, AB 8. Summarize key points 5
6 Coup and Contrecoup Injuries Coup injury: Injury at the point on impact Contrecoup injury: Injury opposite the point of impact Coup and contrecoup injuries. From Patrick Lynch. 6 (Kubal, 2012)
7 Agenda 1. Define extra-axial hemorrhage and introduce its subtypes 2. Review coup and contrecoup head injuries 3. Review relevant brain, ventricular system, and meningeal anatomy 4. Present the menu of tests available for neuroimaging in the setting of head trauma 5. View several subtypes of extra-axial hemorrhages in our patient, AB 6. Describe the characteristic radiologic findings of each extraaxial hemorrhage subtype 7. Provide an update on our patient, AB 8. Summarize key points 7
8 Neuroanatomy: Brain and Ventricular System 4 th Ventricle Gyrus Sulcus Lateral Ventricles 3 rd Ventricle 4 th Ventricle 3 rd Ventricle Lateral Ventricle Midsagittal view of the human brain. From John Beal. The ventricular system. From Life Science Databases. 8
9 Neuroanatomy: The Meninges The meninges. From Korribot. _diagram.jpg The meninges and surrounding structures. From Mysid. 9
10 Agenda 1. Define extra-axial hemorrhage and introduce its subtypes 2. Review coup and contrecoup head injuries 3. Review relevant brain, ventricular system, and meningeal anatomy 4. Present the menu of tests available for neuroimaging in the setting of head trauma 5. View several subtypes of extra-axial hemorrhages in our patient, AB 6. Describe the characteristic radiologic findings of each extraaxial hemorrhage subtype 7. Provide an update on our patient, AB 8. Summarize key points 10
11 Menu of Tests: Neuroimaging in Head Trauma Skull Radiography: Penetrating trauma, foreign bodies Computed Tomography (CT) of the Head CT without IV contrast: Hemorrhage, herniation, fractures CT Perfusion (CTP): Prediction of enlarging contusion CT Angiography (CTA): Pseudoaneurysm, dissection, extravasation Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) of the Head FLAIR: Contusions, traumatic axonal injury, subarachnoid hemorrhage GRE T2* Weighted Imaging: Traumatic axonal injury SWI: Traumatic axonal injury TWI: Traumatic axonal injury, contusions Diffusion Tensor Imaging: White matter tract integrity Magnetization Transfer Imaging: Traumatic axonal injury Angiography: Traumatic fistula, dissection, pseudoaneurysm (Aiken and Gean, 2010; Kubal, 2012) 11
12 Menu of Tests: CT vs MRI Comparison of CT and MRI for evaluation of head trauma Noncontrast head CT is the modality of choose for neuroimaging in the setting of acute head trauma CT MRI Availability Widespread More limited Speed Fast Slow Compatibility with trauma devices Compatible Incompatible with some devices Best for acute trauma Yes No Best for subacute trauma No Yes Best for chronic trauma No Yes Detects axonal injury well No Yes Ionizing radiation Yes No 12 (Aiken and Gean, 2010; Kubal, 2012)
13 Agenda 1. Define extra-axial hemorrhage and introduce its subtypes 2. Review coup and contrecoup head injuries 3. Review relevant brain, ventricular system, and meningeal anatomy 4. Present the menu of tests available for neuroimaging in the setting of head trauma 5. View several subtypes of extra-axial hemorrhages in our patient, AB 6. Describe the characteristic radiologic findings of each extraaxial hemorrhage subtype 7. Provide an update on our patient, AB 8. Summarize key points 13
14 History John Dickson, MSIII Our Patient AB: History and Physical AB is a 54 year-old man who fell from a height of >20 feet. He lost consciousness following the fall, temporarily regained consciousness with confusion, and lost consciousness again. He had a GCS score of 5-6 prior to being intubated in the field. He was brought to BIDMC by Boston MedFlight and was evaluated in the ED. Pertinent Physical Exam Findings HEENT: Intubated, cervical collar in place Neuro: Sedated 14
15 A noncontrast head CT was used to evaluate our patient. 15
16 Our Patient AB: Skull Fracture on Head CT (PACS, BIDMC) NONCONTRAST HEAD CT, AXIAL VIEW Skull fracture (PACS, BIDMC) NONCONTRAST HEAD CT, AXIAL VIEW 16
17 Our Patient AB: Epidural Hematoma on Head CT (PACS, BIDMC) NONCONTRAST HEAD CT, AXIAL VIEW Epidural hematoma containing air 17
18 Our Patient AB: Subdural Hematoma and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage on Head CT (PACS, BIDMC) NONCONTRAST HEAD CT, AXIAL VIEW Subdural hematoma Subarachnoid hemorrhage (PACS, BIDMC) NONCONTRAST HEAD CT, SAGITTAL VIEW 18
19 Our Patient AB: Parafalcine Subdural Hematoma on Head CT (PACS, BIDMC) NONCONTRAST HEAD CT, AXIAL VIEW Parafalcine subdural hematoma: Subdural hematoma extending into the longitudinal fissure along the falx cerebri 19
20 Agenda 1. Define extra-axial hemorrhage and introduce its subtypes 2. Review coup and contrecoup head injuries 3. Review relevant brain, ventricular system, and meningeal anatomy 4. Present the menu of tests available for neuroimaging in the setting of head trauma 5. View several subtypes of extra-axial hemorrhages in our patient, AB 6. Describe the characteristic radiologic findings of each extraaxial hemorrhage subtype 7. Provide an update on our patient, AB 8. Summarize key points 20
21 Companion Patient #1: Epidural Hematoma Blood in the potential space between the periosteum of inner table of the skull and the dura mater Arterial bleeding in 85% of cases Most often at the coup site Characteristic appearance on CT Biconcave Hyperdense Does not cross sutures May cross dural reflections Differential Diagnosis Subdural hematoma (Aiken and Gean, 2010; Dähnert, 1991; Hijaz, Cento, and Walker, 2011 ) From Jpogi. acute_epidual_hematoma.jpg NONCONTRAST HEAD CT, AXIAL VIEW Epidural hematoma 21
22 Companion Patient #2: Subdural Hematoma Blood between the dura mater and arachnoid mater Bleeding from bridging veins in more than 50% of cases More commonly found at contrecoup sites Characteristic appearance on CT Crescentic Hyperdense May cross sutures (holohemispheric) Does not cross dural reflections May pool adjacent to dural reflections Differential diagnosis Epidural hematoma Arachnoid cyst Subarachnoid hemorrhage From James Heilman. org/wiki/file:subduralandherniation.png NONCONTRAST HEAD CT, AXIAL VIEW Subdural hematoma 22 (Aiken and Gean, 2010; Dähnert, 1991; Hijaz, Cento, and Walker, 2011 )
23 Companion Patient #3: Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Blood in the subarachnoid space (between arachnoid and pia mater) Bleeding from small pial or arachnoidal cortical vessels or extension of intracerebral bleeding More commonly found at contrecoup sites Characteristic appearance on CT Hyperdensity in sulci Differential diagnosis Pseudo-subarachnoid hemorrhage From Hellerhoff. wiki/file:traumatische_sab_003.png NONCONTRAST HEAD CT, AXIAL VIEW Subarachnoid hemorrhage (Aiken and Gean, 2010; Dähnert, 1991; Hijaz, Cento, and Walker, 2011 ) 23
24 Companion Patient #4: Intraventricular Hemorrhage Blood within the ventricles Primary intraventricular hemorrhage is rare Secondary intraventricular hemorrhage is usually due to extension of a subarachnoid or intracerebral hemorrhage into the ventricles Characteristic appearance on CT Hyperintensity within the ventricles Hyperintensity in dependent position From Yadav et al. Intracerebral_hemorrhage.jpg NONCONTRAST HEAD CT, AXIAL VIEW Intraventricular hemorrhage 24 (Aiken and Gean, 2010; Cuccharia, accessed 2013)
25 Agenda 1. Define extra-axial hemorrhage and introduce its subtypes 2. Review coup and contrecoup head injuries 3. Review relevant brain, ventricular system, and meningeal anatomy 4. Present the menu of tests available for neuroimaging in the setting of head trauma 5. View several subtypes of extra-axial hemorrhages in our patient, AB 6. Describe the characteristic radiologic findings of each extraaxial hemorrhage subtype 7. Provide an update on our patient, AB 8. Summarize key points 25
26 Our Patient AB: Update Admitted to the trauma surgical intensive care unit (TSICU) following evaluation in the ED Gradually improved Extubated on hospital day 9 Transferred to the floor on hospital day 10 Discharged to a rehabilitation center on hospital day 16 At the time of discharge, AB was alert and interactive. However, he has some receptive language delay and sometimes becomes confused. 26
27 Agenda 1. Define extra-axial hemorrhage and introduce its subtypes 2. Review coup and contrecoup head injuries 3. Review relevant brain, ventricular system, and meningeal anatomy 4. Present the menu of tests available for neuroimaging in the setting of head trauma 5. View several subtypes of extra-axial hemorrhages in our patient, AB 6. Describe the characteristic radiologic findings of each extraaxial hemorrhage subtype 7. Provide an update on our patient, AB 8. Summarize key points 27
28 Summary of Key Points 1. Extra-axial hemorrhage is bleeding inside the skull but outside the brain parenchyma 2. Coup injury occurs at the site of impact and contrecoup injury occurs opposite the site of impact 3. Knowing brain, ventricular system, and meningeal anatomy is essential in understanding the appearance of extra-axial hemorrhage on CT images 4. Several tests are available for neuroimaging in the setting of head trauma, but noncontrast head CT is the study of choice for the initial evaluation of acute head trauma 5. Our patient, AB, developed three subtypes of extra-axial hemorrhage following trauma to the head 6. Each extra-axial hemorrhage subtype has characteristic radiologic features on CT: Epidural hematoma: biconcave hyperdensity that does not cross sutures Subdural hematoma: crescent hyperdensity that may cross sutures Subarachnoid hemorrhage: hyperdensity in sulci Intraventricular hemorrhage: hyperdensity in the ventricles in dependent position 7. Our patient, AB, is improving at a rehabilitation facility 28
29 References Aiken AH, Gean AD. Imaging of head trauma. Semin Roentgenol 2010;45: Cucchiara, Brett. Intraventricular hemorrhage. age&selectedtitle=1%7e141&provider=noprovider. Accessed 7/19/2013. Dähnert, Wolfgang. Radiology Review Manual. Baltimore, MD: Williams & Wilkins: Hijaz TA, Cento EA, Walker MT. Imaging of head trauma. Radiol Clin N Am 2011;49: Kubal, WS. Updated Imaging of Traumatic Brain Injury. Radiol Clin N Am 2012;50: McBride, William. Intracranial epidural hematoma in adults. le=1%7e62&provider=noprovider. Accessed 7/19/2013 Yadav YR, Mukerji G, Shenoy R, Basoor A, Jain G, Nelson A. Endoscopic management of hypertensive intraventricular hemorrhage with obstructive hydrocephalus. BMC Neurol 2007;7:1 29
30 Acknowledgements We would like to thank the following people for their assistance in preparing this case: Dr. David Khatami Claire Odom 30
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 3
 NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 3 Bleeds and hemorrhages K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 3 Bleeds and hemorrhages K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD
 Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
THE ESSENTIAL BRAIN INJURY GUIDE
 THE ESSENTIAL BRAIN INJURY GUIDE Neuroanatomy & Neuroplasticity Section 2 Contributors Erin D. Bigler, PhD Michael R. Hoane, PhD Stephanie Kolakowsky-Hayner, PhD, CBIST, FACRM Dorothy A. Kozlowski, PhD
THE ESSENTIAL BRAIN INJURY GUIDE Neuroanatomy & Neuroplasticity Section 2 Contributors Erin D. Bigler, PhD Michael R. Hoane, PhD Stephanie Kolakowsky-Hayner, PhD, CBIST, FACRM Dorothy A. Kozlowski, PhD
NEURO IMAGING 2. Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity
 NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA
 V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA I. Concussion - Is a clinical syndrome of altered consiousness secondary to head injury - Brought by a change in the momentum of the head when a moving head suddenly arrested
V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA I. Concussion - Is a clinical syndrome of altered consiousness secondary to head injury - Brought by a change in the momentum of the head when a moving head suddenly arrested
Imaging of Acute Cerebral Trauma
 July, 2005 Imaging of Acute Cerebral Trauma Louis Rivera, Harvard Medical School, Year III 46 y/o Female s/p Trauma - Unrestrained? MVC requiring Med Flight - Facial bruising/swelling - DEEP COMA - SEIZURES
July, 2005 Imaging of Acute Cerebral Trauma Louis Rivera, Harvard Medical School, Year III 46 y/o Female s/p Trauma - Unrestrained? MVC requiring Med Flight - Facial bruising/swelling - DEEP COMA - SEIZURES
Meninges and Ventricles
 Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Classical CNS Disease Patterns
 Classical CNS Disease Patterns Inflammatory Traumatic In response to the trauma of having his head bashed in GM would have experienced some of these features. NOT TWO LITTLE PEENY WEENY I CM LACERATIONS.
Classical CNS Disease Patterns Inflammatory Traumatic In response to the trauma of having his head bashed in GM would have experienced some of these features. NOT TWO LITTLE PEENY WEENY I CM LACERATIONS.
Cerebro-vascular stroke
 Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Benign brain lesions
 Benign brain lesions Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology Hung-Wen Kao Department of Radiology, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center Computed tomography Hounsfield unit (HU)
Benign brain lesions Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology Hung-Wen Kao Department of Radiology, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center Computed tomography Hounsfield unit (HU)
North Oaks Trauma Symposium Friday, November 3, 2017
 Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage Aaron C. Sigler, DO, MS Neurosurgery Tulane Neurosciences None Disclosures Overview Anatomy Epidural hematoma Subdural hematoma Cerebral contusions Outline Traumatic ICH
Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage Aaron C. Sigler, DO, MS Neurosurgery Tulane Neurosciences None Disclosures Overview Anatomy Epidural hematoma Subdural hematoma Cerebral contusions Outline Traumatic ICH
2. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
 Causes: 2. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage A. Saccular (berry) aneurysm - Is the most frequent cause of clinically significant subarachnoid hemorrhage is rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm. B. Vascular malformation
Causes: 2. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage A. Saccular (berry) aneurysm - Is the most frequent cause of clinically significant subarachnoid hemorrhage is rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm. B. Vascular malformation
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING. James Chen (MS IV)
 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
Paul Gigante HMS IV Gillian Lieberman, MD. Sept Mr. T s T s Headache. Paul Gigante,, Harvard Medical School Year IV Gillian Lieberman, MD
 Sept 2005 Mr. T s T s Headache Paul Gigante,, Harvard Medical School Year IV Mr. T s T s Presentation 45 year-old welder complains of sudden severe headache and witnessed seizure with loss of consciousness
Sept 2005 Mr. T s T s Headache Paul Gigante,, Harvard Medical School Year IV Mr. T s T s Presentation 45 year-old welder complains of sudden severe headache and witnessed seizure with loss of consciousness
NEURORADIOLOGY Part I
 NEURORADIOLOGY Part I Vörös Erika University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED BRAIN IMAGING METHODS Plain film radiography Ultrasonography (US) Computer tomography (CT) Magnetic resonance imaging
NEURORADIOLOGY Part I Vörös Erika University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED BRAIN IMAGING METHODS Plain film radiography Ultrasonography (US) Computer tomography (CT) Magnetic resonance imaging
THE ROLE OF IMAGING IN DIAGNOSIS OF SUBDURAL HEMATOMA: REVIEW ARTICLE
 THE ROLE OF IMAGING IN DIAGNOSIS OF SUBDURAL HEMATOMA: REVIEW ARTICLE * Dr. Sumendra Raj Pandey, Prof. Dr. Liu Pei WU, Dr. Sohan Kumar Sah, Dr. Lalu Yadav, Md. Sadam Husen Haque and Rajan KR. Chaurasiya
THE ROLE OF IMAGING IN DIAGNOSIS OF SUBDURAL HEMATOMA: REVIEW ARTICLE * Dr. Sumendra Raj Pandey, Prof. Dr. Liu Pei WU, Dr. Sohan Kumar Sah, Dr. Lalu Yadav, Md. Sadam Husen Haque and Rajan KR. Chaurasiya
Marc Norman, Ph.D. - Do Not Use without Permission 1. Cerebrovascular Accidents. Marc Norman, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry
 Cerebrovascular Accidents Marc Norman, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry Neuropsychiatry and Behavioral Medicine Neuropsychology Clinical Training Seminar 1 5 http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/images/ency/fullsize/18009.jpg
Cerebrovascular Accidents Marc Norman, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry Neuropsychiatry and Behavioral Medicine Neuropsychology Clinical Training Seminar 1 5 http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/images/ency/fullsize/18009.jpg
Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Index. aneurysm, 92 carotid occlusion, 94 ICA stenosis, 95 intracranial, 92 MCA, 94
 A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
For Emergency Doctors. Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011
 For Emergency Doctors Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011 A: Orbit B: Sphenoid Sinus C: Temporal Lobe D: EAC E: Mastoid air cells F: Cerebellar hemisphere A: Frontal lobe B: Frontal bone C: Dorsum sellae
For Emergency Doctors Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011 A: Orbit B: Sphenoid Sinus C: Temporal Lobe D: EAC E: Mastoid air cells F: Cerebellar hemisphere A: Frontal lobe B: Frontal bone C: Dorsum sellae
Brain Injuries. Presented By Dr. Said Said Elshama
 Brain Injuries Presented By Dr. Said Said Elshama Types of head injuries 1- Scalp injuries 2- Skull injuries 3- Intra Cranial injuries ( Brain ) Anatomical structure of meninges Intra- Cranial Injuries
Brain Injuries Presented By Dr. Said Said Elshama Types of head injuries 1- Scalp injuries 2- Skull injuries 3- Intra Cranial injuries ( Brain ) Anatomical structure of meninges Intra- Cranial Injuries
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. By: Shifaa AlQa qa
 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage By: Shifaa AlQa qa Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Causes: Rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm Vascular malformation Trauma Hematologic disturbances
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage By: Shifaa AlQa qa Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Causes: Rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm Vascular malformation Trauma Hematologic disturbances
Intracranial spontaneous hemorrhage mechanisms, imaging and management
 Intracranial spontaneous hemorrhage mechanisms, imaging and management Dora Zlatareva Department of Diagnostic Imaging Medical University, Sofia, Bulgaria Intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) ICH 15% of strokes
Intracranial spontaneous hemorrhage mechanisms, imaging and management Dora Zlatareva Department of Diagnostic Imaging Medical University, Sofia, Bulgaria Intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) ICH 15% of strokes
ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATION OR CONTUSION : A DIAGNOSTIC DILEMMA. Yong Pei Yee, Ibrahim Lutfi Shuaib, Jafri Malin Abdullah*
 Malaysian Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol. 8, No. 2, July 2001 (47-51) CASE REPORT ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATION OR CONTUSION : A DIAGNOSTIC DILEMMA Yong Pei Yee, Ibrahim Lutfi Shuaib, Jafri Malin Abdullah*
Malaysian Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol. 8, No. 2, July 2001 (47-51) CASE REPORT ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATION OR CONTUSION : A DIAGNOSTIC DILEMMA Yong Pei Yee, Ibrahim Lutfi Shuaib, Jafri Malin Abdullah*
Mild Traumatic Brain Injury
 Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Concussions This presentation is for information purposes only, not for any commercial purpose, and may not be sold or redistributed. David Wesley, M.D. Outline Epidemiology
Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Concussions This presentation is for information purposes only, not for any commercial purpose, and may not be sold or redistributed. David Wesley, M.D. Outline Epidemiology
8/29/2011. Brain Injury Incidence: 200/100,000. Prehospital Brain Injury Mortality Incidence: 20/100,000
 Traumatic Brain Injury Almario G. Jabson MD Section Of Neurosurgery Asian Hospital And Medical Center Brain Injury Incidence: 200/100,000 Prehospital Brain Injury Mortality Incidence: 20/100,000 Hospital
Traumatic Brain Injury Almario G. Jabson MD Section Of Neurosurgery Asian Hospital And Medical Center Brain Injury Incidence: 200/100,000 Prehospital Brain Injury Mortality Incidence: 20/100,000 Hospital
8th Annual NKY TBI Conference 3/28/2014
 Closed Head Injury: Headache to Herniation A N T H O N Y T. K R A M E R U N I V E R S I T Y O F C I N C I N N A T I B L U E A S H E M S T E C H N O L O G Y P R O G R A M Objectives Describe the pathological
Closed Head Injury: Headache to Herniation A N T H O N Y T. K R A M E R U N I V E R S I T Y O F C I N C I N N A T I B L U E A S H E M S T E C H N O L O G Y P R O G R A M Objectives Describe the pathological
Concomitant Traumatic Spinal Subdural Hematoma and Hemorrhage from Intracranial Arachnoid Cyst Following Minor Injury
 Chin J Radiol 2005; 30: 173-177 173 Concomitant Traumatic Spinal Subdural Hematoma and Hemorrhage from Intracranial Arachnoid Cyst Following Minor Injury HUI-YI CHEN 1 YING-SHYUAN LI 1 CHUNG-HO CHEN 1
Chin J Radiol 2005; 30: 173-177 173 Concomitant Traumatic Spinal Subdural Hematoma and Hemorrhage from Intracranial Arachnoid Cyst Following Minor Injury HUI-YI CHEN 1 YING-SHYUAN LI 1 CHUNG-HO CHEN 1
An Introduction to Imaging the Brain. Dr Amy Davis
 An Introduction to Imaging the Brain Dr Amy Davis Common reasons for imaging: Clinical scenarios: - Trauma (NICE guidelines) - Stroke - Tumours - Seizure - Neurological degeneration memory, motor dysfunction,
An Introduction to Imaging the Brain Dr Amy Davis Common reasons for imaging: Clinical scenarios: - Trauma (NICE guidelines) - Stroke - Tumours - Seizure - Neurological degeneration memory, motor dysfunction,
Pre-hospital Response to Trauma and Brain Injury. Hans Notenboom, M.D. Asst. Medical Director Sacred Heart Medical Center
 Pre-hospital Response to Trauma and Brain Injury Hans Notenboom, M.D. Asst. Medical Director Sacred Heart Medical Center Traumatic Brain Injury is Common 235,000 Americans hospitalized for non-fatal TBI
Pre-hospital Response to Trauma and Brain Injury Hans Notenboom, M.D. Asst. Medical Director Sacred Heart Medical Center Traumatic Brain Injury is Common 235,000 Americans hospitalized for non-fatal TBI
How to interpret an unenhanced CT brain scan. Part 2: Clinical cases
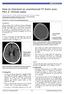 How to interpret an unenhanced CT brain scan. Part 2: Clinical cases Thomas Osborne a, Christine Tang a, Kivraj Sabarwal b and Vineet Prakash c a Radiology Registrar; b Radiology Foundation Year 1 Doctor;
How to interpret an unenhanced CT brain scan. Part 2: Clinical cases Thomas Osborne a, Christine Tang a, Kivraj Sabarwal b and Vineet Prakash c a Radiology Registrar; b Radiology Foundation Year 1 Doctor;
NEURORADIOLOGY Part I
 NEURORADIOLOGY Part I Vörös Erika University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED DISEASES OF CNS BRAIN Developmental anomalies Cerebrovascular disorders Tumours Inflammatory diseases Trauma DISEASES
NEURORADIOLOGY Part I Vörös Erika University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED DISEASES OF CNS BRAIN Developmental anomalies Cerebrovascular disorders Tumours Inflammatory diseases Trauma DISEASES
MISSED FINDINGS IN EMERGENCY RADIOLOGY: CASE BASE SESSION 5 th Nordic Trauma Radiology Course Oslo, Norway
 MISSED FINDINGS IN EMERGENCY RADIOLOGY: CASE BASE SESSION 5 th Nordic Trauma Radiology Course Oslo, Norway K.SHANMUGANATHAN M.D. EASILY MISSED FINDINGS IN EMERGENCY RADIOLOGY OBJECTIVES Commonly missed
MISSED FINDINGS IN EMERGENCY RADIOLOGY: CASE BASE SESSION 5 th Nordic Trauma Radiology Course Oslo, Norway K.SHANMUGANATHAN M.D. EASILY MISSED FINDINGS IN EMERGENCY RADIOLOGY OBJECTIVES Commonly missed
Traumatic brain injuries are caused by external mechanical forces such as: - Falls - Transport-related accidents - Assault
 PP2231 Brain injury Cerebrum consists of frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal lobes Diencephalon consists of thalamus, hypothalamus Cerbellum Brain stem consists of midbrain, pons, medulla Central
PP2231 Brain injury Cerebrum consists of frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal lobes Diencephalon consists of thalamus, hypothalamus Cerbellum Brain stem consists of midbrain, pons, medulla Central
Introduction to Neuroimaging Aaron S. Field, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Radiology Neuroradiology Section University of Wisconsin Madison
 Introduction to Neuroimaging Aaron S. Field, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Radiology Neuroradiology Section University of Wisconsin Madison Updated 7/17/07 Neuroimaging Modalities Radiography (X-Ray)
Introduction to Neuroimaging Aaron S. Field, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Radiology Neuroradiology Section University of Wisconsin Madison Updated 7/17/07 Neuroimaging Modalities Radiography (X-Ray)
Cranial computed tomography in trauma
 Hong Kong Journal of Emergency Medicine Cranial computed tomography in trauma TH Tan, KL Ong Introduction Head trauma accounts for a substantial proportion of morbidity and mortality in all age groups
Hong Kong Journal of Emergency Medicine Cranial computed tomography in trauma TH Tan, KL Ong Introduction Head trauma accounts for a substantial proportion of morbidity and mortality in all age groups
Introduction to Neurosurgical Subspecialties:
 Introduction to Neurosurgical Subspecialties: Trauma and Critical Care Neurosurgery Brian L. Hoh, MD 1, Gregory J. Zipfel, MD 2 and Stacey Q. Wolfe, MD 3 1 University of Florida, 2 Washington University,
Introduction to Neurosurgical Subspecialties: Trauma and Critical Care Neurosurgery Brian L. Hoh, MD 1, Gregory J. Zipfel, MD 2 and Stacey Q. Wolfe, MD 3 1 University of Florida, 2 Washington University,
LOSS OF CONSCIOUSNESS & ASSESSMENT. Sheba Medical Center Acute Medicine Department MATTHEW WRIGHT
 LOSS OF CONSCIOUSNESS & ASSESSMENT Sheba Medical Center Acute Medicine Department MATTHEW WRIGHT OUTLINE Causes Head Injury Clinical Features Complications Rapid Assessment Glasgow Coma Scale Classification
LOSS OF CONSCIOUSNESS & ASSESSMENT Sheba Medical Center Acute Medicine Department MATTHEW WRIGHT OUTLINE Causes Head Injury Clinical Features Complications Rapid Assessment Glasgow Coma Scale Classification
Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center
 Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Department of Neurosurgery Student Clerkship Guide 2017 2018 Introduction Welcome to LSUHSC New Orleans neurosurgery rotation. Our department is dedicated
Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Department of Neurosurgery Student Clerkship Guide 2017 2018 Introduction Welcome to LSUHSC New Orleans neurosurgery rotation. Our department is dedicated
Neuroimaging 101. Amy Shatila, LSSP/NCSP Kelsey Theis, LSSP/NCSP. TASP Convention November 4, 2017
 Neuroimaging 101 Amy Shatila, LSSP/NCSP Kelsey Theis, LSSP/NCSP TASP Convention November 4, 2017 A bit-o-trivia: Gray matter in a live brain is actually more of a pink color But Gray matter is the cell
Neuroimaging 101 Amy Shatila, LSSP/NCSP Kelsey Theis, LSSP/NCSP TASP Convention November 4, 2017 A bit-o-trivia: Gray matter in a live brain is actually more of a pink color But Gray matter is the cell
PRACTICE GUIDELINE. DEFINITIONS: Mild head injury: Glasgow Coma Scale* (GCS) score Moderate head injury: GCS 9-12 Severe head injury: GCS 3-8
 PRACTICE GUIDELINE Effective Date: 9-1-2012 Manual Reference: Deaconess Trauma Services TITLE: TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY GUIDELINE OBJECTIVE: To provide practice management guidelines for traumatic brain
PRACTICE GUIDELINE Effective Date: 9-1-2012 Manual Reference: Deaconess Trauma Services TITLE: TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY GUIDELINE OBJECTIVE: To provide practice management guidelines for traumatic brain
The dura is sensitive to stretching, which produces the sensation of headache.
 Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
Head injuries. Severity of head injuries
 Head injuries ED Teaching day 23 rd October Severity of head injuries Minor GCS 14-15 Must not have any of the following: Amnesia 10min Neurological sign or symptom Skull fracture (clinically or radiologically)
Head injuries ED Teaching day 23 rd October Severity of head injuries Minor GCS 14-15 Must not have any of the following: Amnesia 10min Neurological sign or symptom Skull fracture (clinically or radiologically)
Traumatic brain Injury- An open eye approach
 Traumatic brain Injury- An open eye approach Dr. Sunit Dr Sunit, Apollo children's hospital Blah blah Lots of head injury Lot of ill children Various methods of injury Various mechanisms of brain damage
Traumatic brain Injury- An open eye approach Dr. Sunit Dr Sunit, Apollo children's hospital Blah blah Lots of head injury Lot of ill children Various methods of injury Various mechanisms of brain damage
M555 Medical Neuroscience Blood Flow in CNS Meninges Blood Brain Barrier CSF
 M555 Medical Neuroscience Blood Flow in CNS Meninges Blood Brain Barrier CSF Arterial Blood Flow to CNS approximately % of what goes wrong within the skull that produces neurological deficits is vascular
M555 Medical Neuroscience Blood Flow in CNS Meninges Blood Brain Barrier CSF Arterial Blood Flow to CNS approximately % of what goes wrong within the skull that produces neurological deficits is vascular
Applicable Neuroradiology
 For the Clinical Neurology Clerkship LSU Medical School New Orleans Amy W Voigt, MD Clerkship Director Introduction The field of Radiology first developed following the discovery of X-Rays by Wilhelm Roentgen
For the Clinical Neurology Clerkship LSU Medical School New Orleans Amy W Voigt, MD Clerkship Director Introduction The field of Radiology first developed following the discovery of X-Rays by Wilhelm Roentgen
Internal Carotid Artery Dissection
 May 2011 Internal Carotid Artery Dissection Carolyn April, HMS IV Agenda Presentation of a clinical case Discussion of the clinical features of ICA dissection Discussion of the imaging modalities used
May 2011 Internal Carotid Artery Dissection Carolyn April, HMS IV Agenda Presentation of a clinical case Discussion of the clinical features of ICA dissection Discussion of the imaging modalities used
Ventricles, CSF & Meninges. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Ventricles, CSF & Meninges Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Coffee Hour Thursday (Sept 14) 8:30-9:30am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium Stop by for a minute or an
Ventricles, CSF & Meninges Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Coffee Hour Thursday (Sept 14) 8:30-9:30am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium Stop by for a minute or an
10/6/2017. Notice. Traumatic Brain Injury & Head Trauma
 Notice All EMS Live@Nite presentations will be recorded (both audio and video) and available for public viewing online. By participating in EMS Live@Nite, you consent to audio and video recording and its/their
Notice All EMS Live@Nite presentations will be recorded (both audio and video) and available for public viewing online. By participating in EMS Live@Nite, you consent to audio and video recording and its/their
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF
 Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
Neuroimaging of TBI: Current Clinical Guidelines and Future Direction Brain Injury Alliance of Colorado 2017
 Neuroimaging of TBI: Current Clinical Guidelines and Future Direction Brain Injury Alliance of Colorado 2017 Peter E. Ricci, M.D. Staff Neuroradiologist Radiology Imaging Associates OBJECTIVES 1. Understand
Neuroimaging of TBI: Current Clinical Guidelines and Future Direction Brain Injury Alliance of Colorado 2017 Peter E. Ricci, M.D. Staff Neuroradiologist Radiology Imaging Associates OBJECTIVES 1. Understand
Case Report Isolated Central Sulcus Hemorrhage: A Rare Presentation Most Frequently Associated with Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy
 Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2012, Article ID 574849, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/574849 Case Report Isolated Central Sulcus Hemorrhage: A Rare Presentation Most Frequently Associated with Cerebral Amyloid
Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2012, Article ID 574849, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/574849 Case Report Isolated Central Sulcus Hemorrhage: A Rare Presentation Most Frequently Associated with Cerebral Amyloid
THE ESSENTIAL BRAIN INJURY GUIDE
 THE ESSENTIAL BRAIN INJURY GUIDE Carolyn Scott PhD, CBIST Rainbow Rehab Centers Neuroanatomy & Neuroplasticity Section 2 Neuroanatomy and Neuroimaging Chapter 2 2 Learning Objectives Understand the anatomy
THE ESSENTIAL BRAIN INJURY GUIDE Carolyn Scott PhD, CBIST Rainbow Rehab Centers Neuroanatomy & Neuroplasticity Section 2 Neuroanatomy and Neuroimaging Chapter 2 2 Learning Objectives Understand the anatomy
Neuropathology Of Head Trauma. Mary E. Case, M.D. Professor of Pathology St. Louis University Health Sciences Center
 Neuropathology Of Head Trauma Mary E. Case, M.D. Professor of Pathology St. Louis University Health Sciences Center Nothing to disclose Disclosure Introduction 500,000 cases/year of serious head injury
Neuropathology Of Head Trauma Mary E. Case, M.D. Professor of Pathology St. Louis University Health Sciences Center Nothing to disclose Disclosure Introduction 500,000 cases/year of serious head injury
Central Nervous System: Part 2
 Central Nervous System: Part 2 1. Meninges 2. CSF 3. Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Explain spinal cord anatomy, including gray and white matter and meninges (give the general functions of this organ).
Central Nervous System: Part 2 1. Meninges 2. CSF 3. Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Explain spinal cord anatomy, including gray and white matter and meninges (give the general functions of this organ).
Diagnostic modalities of the Central Nervous System
 NEURORADIOLOGY Kinga Karlinger, MD, PhD Associate Professor Semmelweis University, Budapest Diagnostic modalities of the Central Nervous System X-ray: screening is not used any more, x-ray images instead
NEURORADIOLOGY Kinga Karlinger, MD, PhD Associate Professor Semmelweis University, Budapest Diagnostic modalities of the Central Nervous System X-ray: screening is not used any more, x-ray images instead
TBI are twice as common in males High potential for poor outcome Deaths occur at three points in time after injury
 Head Injury Any trauma to (closed vs. open) Skull Scalp Brain Traumatic brain injury (TBI) High incidence Most common causes Falls Motor vehicle accidents Other causes Firearm- related injuries Assaults
Head Injury Any trauma to (closed vs. open) Skull Scalp Brain Traumatic brain injury (TBI) High incidence Most common causes Falls Motor vehicle accidents Other causes Firearm- related injuries Assaults
New Frontiers in Intracerebral Hemorrhage
 New Frontiers in Intracerebral Hemorrhage Ryan Hakimi, DO, MS Director, Neuro ICU Director, Inpatient Neurology Services Greenville Health System Clinical Associate Professor Department of Medicine (Neurology)
New Frontiers in Intracerebral Hemorrhage Ryan Hakimi, DO, MS Director, Neuro ICU Director, Inpatient Neurology Services Greenville Health System Clinical Associate Professor Department of Medicine (Neurology)
Pediatric Subdural Hematoma and Traumatic Brain Injury J. Charles Mace MD FACS Springfield Neurological Institute CoxHealth. Objectives 11/7/2017
 Pediatric Subdural Hematoma and Traumatic Brain Injury J. Charles Mace MD FACS Springfield Neurological Institute CoxHealth Objectives 1. Be able to discuss brain anatomy and physiology as it applies to
Pediatric Subdural Hematoma and Traumatic Brain Injury J. Charles Mace MD FACS Springfield Neurological Institute CoxHealth Objectives 1. Be able to discuss brain anatomy and physiology as it applies to
The CNS Part II pg
 The CNS Part II pg. 455-474 Protection of the Brain Objectives Describe how the meninges, cerebrospinal fluid, and the blood brain barrier protect the CNS. Explain how Cerebrospinal fluid is formed, and
The CNS Part II pg. 455-474 Protection of the Brain Objectives Describe how the meninges, cerebrospinal fluid, and the blood brain barrier protect the CNS. Explain how Cerebrospinal fluid is formed, and
Imaging in a confused patient: Infections and Inflammation
 American Society of Neuroimaging Imaging in a confused patient: Infections and Inflammation January 21, 2017 Los Angeles, California Joshua P. Klein, MD, PhD, FANA, FAAN, FASN Chief, Division of Hospital
American Society of Neuroimaging Imaging in a confused patient: Infections and Inflammation January 21, 2017 Los Angeles, California Joshua P. Klein, MD, PhD, FANA, FAAN, FASN Chief, Division of Hospital
Functional Neuroanatomy and Traumatic Brain Injury The Frontal Lobes
 Functional Neuroanatomy and Traumatic Brain Injury The Frontal Lobes Jessica Matthes, Ph.D., ABN Barrow TBI Symposium March 23, 2019 jessica.matthes@dignityhealth.org Outline TBI Mechanisms of Injury Types
Functional Neuroanatomy and Traumatic Brain Injury The Frontal Lobes Jessica Matthes, Ph.D., ABN Barrow TBI Symposium March 23, 2019 jessica.matthes@dignityhealth.org Outline TBI Mechanisms of Injury Types
NEURO IMAGING OF ACUTE STROKE
 1 1 NEURO IMAGING OF ACUTE STROKE ALICIA RICHARDSON, MSN, RN, ACCNS-AG, ANVP-BC WENDY SMITH, MA, RN, MBA, SCRN, FAHA LYNN HUNDLEY, APRN, CNRN, CCNS, ANVP-BC 2 2 1 DISCLOSURES Alicia Richardson: Stryker
1 1 NEURO IMAGING OF ACUTE STROKE ALICIA RICHARDSON, MSN, RN, ACCNS-AG, ANVP-BC WENDY SMITH, MA, RN, MBA, SCRN, FAHA LYNN HUNDLEY, APRN, CNRN, CCNS, ANVP-BC 2 2 1 DISCLOSURES Alicia Richardson: Stryker
Head Trauma Inservice (October)
 John Tramell - Head Trauma Inservice, October 2005.doc Page 1 Head Trauma Inservice (October) Head trauma is the leading cause of death in trauma patients. Having a basic understanding of the anatomy and
John Tramell - Head Trauma Inservice, October 2005.doc Page 1 Head Trauma Inservice (October) Head trauma is the leading cause of death in trauma patients. Having a basic understanding of the anatomy and
General Imaging. Imaging modalities. Incremental CT. Multislice CT Multislice CT [ MDCT ]
![General Imaging. Imaging modalities. Incremental CT. Multislice CT Multislice CT [ MDCT ] General Imaging. Imaging modalities. Incremental CT. Multislice CT Multislice CT [ MDCT ]](/thumbs/76/74079340.jpg) General Imaging Imaging modalities Conventional X-rays Ultrasonography [ US ] Computed tomography [ CT ] Radionuclide imaging Magnetic resonance imaging [ MRI ] Angiography conventional, CT,MRI Interventional
General Imaging Imaging modalities Conventional X-rays Ultrasonography [ US ] Computed tomography [ CT ] Radionuclide imaging Magnetic resonance imaging [ MRI ] Angiography conventional, CT,MRI Interventional
CLEAR III TRIAL : UPDATE ON SURGICAL MATTERS THAT MATTER
 CLEAR III TRIAL : UPDATE ON SURGICAL MATTERS THAT MATTER CLEAR Surgical Center Team July 2011 Trial Enrollment Status Updates Insert latest enrollment update chart from most recent CLEAR newsletter Imaging
CLEAR III TRIAL : UPDATE ON SURGICAL MATTERS THAT MATTER CLEAR Surgical Center Team July 2011 Trial Enrollment Status Updates Insert latest enrollment update chart from most recent CLEAR newsletter Imaging
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a leading cause of mortality
 Imaging of Head Trauma Tuong H. Le, MD, PhD, and Alisa D. Gean, MD Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a leading cause of mortality and morbidity in the world s population, especially those under age 44. 1
Imaging of Head Trauma Tuong H. Le, MD, PhD, and Alisa D. Gean, MD Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a leading cause of mortality and morbidity in the world s population, especially those under age 44. 1
Intracranial hemorrhage: ultrasound, CT and MRI findings
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2005 Intracranial hemorrhage: ultrasound, CT and MRI findings Huisman, Thierry
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2005 Intracranial hemorrhage: ultrasound, CT and MRI findings Huisman, Thierry
Overview of imaging modalities for cerebral aneurysms
 Overview of imaging modalities for cerebral aneurysms Soroush Zaghi BIDMC PCE: Radiology August 2008 (Images from BIDMC, PACS.) Our Patient: Presentation Our patient is a 57 y/o woman who reports blowing
Overview of imaging modalities for cerebral aneurysms Soroush Zaghi BIDMC PCE: Radiology August 2008 (Images from BIDMC, PACS.) Our Patient: Presentation Our patient is a 57 y/o woman who reports blowing
Concussion. Concussion is a disturbance of brain function caused by a direct or indirect force to the head.
 Concussion Concussion is a disturbance of brain function caused by a direct or indirect force to the head. Disturbances of brain tissue is largely related to neurometabolic dysfunction rather then structural
Concussion Concussion is a disturbance of brain function caused by a direct or indirect force to the head. Disturbances of brain tissue is largely related to neurometabolic dysfunction rather then structural
NEURORADIOLOGY Angela Lignelli, MD
 Neuroradiology NEURORADIOLOGY Angela Lignelli, MD Plain radiographs CT MRI Cerebral Angiogram Myelograms Neuroradiology Computerized Axial Tomography (CT) CT without and with contrast CTA CT angiogram
Neuroradiology NEURORADIOLOGY Angela Lignelli, MD Plain radiographs CT MRI Cerebral Angiogram Myelograms Neuroradiology Computerized Axial Tomography (CT) CT without and with contrast CTA CT angiogram
NEURORADIOLOGY Angela Lignelli, MD
 NEURORADIOLOGY Angela Lignelli, MD Neuroradiology Plain radiographs CT MRI Cerebral Angiogram Myelograms 1 Neuroradiology Computerized Axial Tomography (CT) CT without and with contrast CTA CT angiogram
NEURORADIOLOGY Angela Lignelli, MD Neuroradiology Plain radiographs CT MRI Cerebral Angiogram Myelograms 1 Neuroradiology Computerized Axial Tomography (CT) CT without and with contrast CTA CT angiogram
with susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine
 Emerg Radiol (2012) 19:565 569 DOI 10.1007/s10140-012-1051-2 CASE REPORT Susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine Christopher Miller
Emerg Radiol (2012) 19:565 569 DOI 10.1007/s10140-012-1051-2 CASE REPORT Susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine Christopher Miller
Non-Traumatic Neuro Emergencies
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Non-Traumatic Neuro Emergencies John R. Hesselink, M.D. Nontraumatic Neuroemergencies 1. Acute focal neurological deficit 2. Worst headache of
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Non-Traumatic Neuro Emergencies John R. Hesselink, M.D. Nontraumatic Neuroemergencies 1. Acute focal neurological deficit 2. Worst headache of
Pediatric Head Trauma August 2016
 PEDIATRIC HEAD TRAUMA AUGUST 2016 Pediatric Head Trauma August 2016 EDUCATION COMMITTEE PEER EDUCATION Quick Review of Pathophysiology of TBI Nuggets of knowledge to keep in mind with TBI Intracranial
PEDIATRIC HEAD TRAUMA AUGUST 2016 Pediatric Head Trauma August 2016 EDUCATION COMMITTEE PEER EDUCATION Quick Review of Pathophysiology of TBI Nuggets of knowledge to keep in mind with TBI Intracranial
Acute stroke imaging
 Acute stroke imaging Aims Imaging modalities and differences Why image acute stroke Clinical correlation to imaging appearance What is stroke Classic definition: acute focal injury to the central nervous
Acute stroke imaging Aims Imaging modalities and differences Why image acute stroke Clinical correlation to imaging appearance What is stroke Classic definition: acute focal injury to the central nervous
secondary effects and sequelae of head trauma.
 Neuroimaging of vascular/secondary secondary effects and sequelae of head trauma. Andrès Server Alonso Department of Neuroradiology Division of Radiology Ullevål University Hospital Oslo, Norway. Guidelines
Neuroimaging of vascular/secondary secondary effects and sequelae of head trauma. Andrès Server Alonso Department of Neuroradiology Division of Radiology Ullevål University Hospital Oslo, Norway. Guidelines
Overview of Abusive Head Trauma: What Everyone Needs to Know. 11 th Annual Keeping Children Safe Conference Boise, ID October 17, 2012
 Overview of Abusive Head Trauma: What Everyone Needs to Know 11 th Annual Keeping Children Safe Conference Boise, ID October 17, 2012 Deborah Lowen, MD Associate Professor Pediatrics Director, Child Abuse
Overview of Abusive Head Trauma: What Everyone Needs to Know 11 th Annual Keeping Children Safe Conference Boise, ID October 17, 2012 Deborah Lowen, MD Associate Professor Pediatrics Director, Child Abuse
Neuroradiological Findings in Non- Accidental Trauma Educational Pictorial Review
 Neuroradiological Findings in Non- Accidental Trauma Educational Pictorial Review M B Moss, MD; L Lanier, MD; R Slater; C L Sistrom, MD; R G Quisling, MD; I M Schmalfuss, MD; and D Rajderkar, MD Contact:
Neuroradiological Findings in Non- Accidental Trauma Educational Pictorial Review M B Moss, MD; L Lanier, MD; R Slater; C L Sistrom, MD; R G Quisling, MD; I M Schmalfuss, MD; and D Rajderkar, MD Contact:
Shenandoah Co. Fire & Rescue. Injuries to. and Spine. December EMS Training Bill Streett Training Section Chief
 Shenandoah Co. Fire & Rescue Injuries to the Head and Spine December EMS Training Bill Streett Training Section Chief C.E. Card Information BLS Providers 2 Cards / Provider Category 1 Course # Blank Topic#
Shenandoah Co. Fire & Rescue Injuries to the Head and Spine December EMS Training Bill Streett Training Section Chief C.E. Card Information BLS Providers 2 Cards / Provider Category 1 Course # Blank Topic#
Traumatic Brain Injuries
 Traumatic Brain Injuries Scott P. Sherry, MS, PA-C, FCCM Assistant Professor Department of Surgery Division of Trauma, Critical Care and Acute Care Surgery DISCLOSURES Nothing to disclose Discussion of
Traumatic Brain Injuries Scott P. Sherry, MS, PA-C, FCCM Assistant Professor Department of Surgery Division of Trauma, Critical Care and Acute Care Surgery DISCLOSURES Nothing to disclose Discussion of
The Role of Neuroimaging in Acute Stroke. Bradley Molyneaux, HMS IV
 The Role of Neuroimaging in Acute Stroke Bradley Molyneaux, HMS IV Patient CR 62 yo F w/ 2 wk h/o altered mental status Presents to ED w/ confusion following a fall 1 day prior New onset left facial droop
The Role of Neuroimaging in Acute Stroke Bradley Molyneaux, HMS IV Patient CR 62 yo F w/ 2 wk h/o altered mental status Presents to ED w/ confusion following a fall 1 day prior New onset left facial droop
Cerebral aneurysms A case study
 August 2001 Cerebral aneurysms A case study Heather L. Hinds, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient 57yr old woman History of migraines Presents with persistent headache several months duration different
August 2001 Cerebral aneurysms A case study Heather L. Hinds, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient 57yr old woman History of migraines Presents with persistent headache several months duration different
Unit #3: Dry Lab A. David A. Morton, Ph.D.
 Unit #3: Dry Lab A David A. Morton, Ph.D. Skull Intracranial Hemorrhage Pg. 26 Epidural Hematoma Pg. 26 Skull Pg. 26 Subdural Hematoma Pg. 26 Subdural Hematoma Pg. 26 Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Pg. 26 Subarachnoid
Unit #3: Dry Lab A David A. Morton, Ph.D. Skull Intracranial Hemorrhage Pg. 26 Epidural Hematoma Pg. 26 Skull Pg. 26 Subdural Hematoma Pg. 26 Subdural Hematoma Pg. 26 Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Pg. 26 Subarachnoid
Brief Clinical Report: Recognizing Subdural Hemorrhage in Older Adults
 Research Brief Clinical Report: Recognizing Subdural Hemorrhage in Older Adults Mark T. Pfefer, RN, MS, DC *1 ; Richard Strunk MS, DC 2 Address: 1 Professor and Director of Research, Cleveland Chiropractic
Research Brief Clinical Report: Recognizing Subdural Hemorrhage in Older Adults Mark T. Pfefer, RN, MS, DC *1 ; Richard Strunk MS, DC 2 Address: 1 Professor and Director of Research, Cleveland Chiropractic
ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING
 ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING ผศ.พญ พญ.จ ร ร ตน ธรรมโรจน ภาคว ชาร งส ว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยขอนแก น A case of acute hemiplegia Which side is the abnormality, right or left? Early Right MCA infarction
ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING ผศ.พญ พญ.จ ร ร ตน ธรรมโรจน ภาคว ชาร งส ว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยขอนแก น A case of acute hemiplegia Which side is the abnormality, right or left? Early Right MCA infarction
Perioperative Management Of Extra-Ventricular Drains (EVD)
 Perioperative Management Of Extra-Ventricular Drains (EVD) Dr. Vijay Tarnal MBBS, FRCA Clinical Assistant Professor Division of Neuroanesthesiology Division of Head & Neck Anesthesiology Michigan Medicine
Perioperative Management Of Extra-Ventricular Drains (EVD) Dr. Vijay Tarnal MBBS, FRCA Clinical Assistant Professor Division of Neuroanesthesiology Division of Head & Neck Anesthesiology Michigan Medicine
Case Conference: Neuroradiology. Case 1: Tumor Case 1: 22yo F w/ HA and prior Seizures
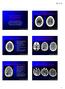 Case Conference: Neuroradiology Case 1: 22yo F w/ HA and prior Seizures David E. Rex, MD, PhD Stanford University Hospital Department of Radiology Case 1: Tumor Most likely gangiloglioma, oligodendroglioma,
Case Conference: Neuroradiology Case 1: 22yo F w/ HA and prior Seizures David E. Rex, MD, PhD Stanford University Hospital Department of Radiology Case 1: Tumor Most likely gangiloglioma, oligodendroglioma,
Traumatic Head Injury
 Traumatic Head Injury Liu Yi, MD. PhD, associate professor Dept. Neurosurgery Conception Any injury to the skull, or brain, caused by external physical forces, in stead of degenerative or congenital nature
Traumatic Head Injury Liu Yi, MD. PhD, associate professor Dept. Neurosurgery Conception Any injury to the skull, or brain, caused by external physical forces, in stead of degenerative or congenital nature
Neuroradiology. Peter Bogner Dept. of Radiology, chairman
 Neuroradiology Peter Bogner Dept. of Radiology, chairman Imaging methods radiography - limited ultrasonography - neonatal, vascular imaging CT neurotrauma, stroke, spine imaging, CTA MRI almost anything
Neuroradiology Peter Bogner Dept. of Radiology, chairman Imaging methods radiography - limited ultrasonography - neonatal, vascular imaging CT neurotrauma, stroke, spine imaging, CTA MRI almost anything
The central nervous system
 Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Neurotrauma. Béla Faludi Dept.. of Neurology University of PécsP
 Neurotrauma Béla Faludi Dept.. of Neurology University of PécsP Emergency!!! Why here? Opened cranial injury visible: neurosurgery Closed injuries sometimes diagnosed by neurologist Masking situation:
Neurotrauma Béla Faludi Dept.. of Neurology University of PécsP Emergency!!! Why here? Opened cranial injury visible: neurosurgery Closed injuries sometimes diagnosed by neurologist Masking situation:
PA SYLLABUS. Syllabus for students of the FACULTY OF MEDICINE No.2
 Approved At the meeting of the Faculty Council Medicine No. of Approved At the meeting of the chair of Neurosurgery No. of Dean of the Faculty Medicine No.2 PhD, associate professor M. Betiu Head of the
Approved At the meeting of the Faculty Council Medicine No. of Approved At the meeting of the chair of Neurosurgery No. of Dean of the Faculty Medicine No.2 PhD, associate professor M. Betiu Head of the
Chapter 14. The Brain Meninges and Cerebral Spinal Fluid
 Chapter 14 The Brain Meninges and Cerebral Spinal Fluid Meninges of the Brain Skull Brain: Blood vessel Pia mater Gray matter White matter Dura mater: Periosteal layer Meningeal layer Arachnoid villus
Chapter 14 The Brain Meninges and Cerebral Spinal Fluid Meninges of the Brain Skull Brain: Blood vessel Pia mater Gray matter White matter Dura mater: Periosteal layer Meningeal layer Arachnoid villus
MRI imaging in meningeal diseases
 Original article MRI imaging in meningeal diseases 1Dr. Narendrakumar M Shah, 2 Dr Vaishali D M 1Associate professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis, SDM Medical college, Dharwad 2Consultant radiologist,
Original article MRI imaging in meningeal diseases 1Dr. Narendrakumar M Shah, 2 Dr Vaishali D M 1Associate professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis, SDM Medical college, Dharwad 2Consultant radiologist,
How to Read a Head CT. Andrew D. Perron, MD, FACEP. Head CT. Head CT. Head CT. Head CT. EM Residency Program Director
 Blood Can Be Very Bad How to Read a Head CT EM Residency Program Director (or How I learned to stop worrying and love computed tomography ) Department of Emergency Medicine Maine Medical Center Portland,
Blood Can Be Very Bad How to Read a Head CT EM Residency Program Director (or How I learned to stop worrying and love computed tomography ) Department of Emergency Medicine Maine Medical Center Portland,
Cross sectional imaging of Intracranial cystic lesions Abdel Razek A
 Cross sectional imaging of Intracranial cystic lesions Abdel Razek A Department of Radiology. Mansoura Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura. Egypt. arazek@mans.edu.eg Introduction Intracranial cystic lesions
Cross sectional imaging of Intracranial cystic lesions Abdel Razek A Department of Radiology. Mansoura Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura. Egypt. arazek@mans.edu.eg Introduction Intracranial cystic lesions
Imaging for the Diagnosis and Management of Traumatic Brain Injury
 Neurotherapeutics: The Journal of the American Society for Experimental NeuroTherapeutics Imaging for the Diagnosis and Management of Traumatic Brain Injury Jane J. Kim and Alisa D. Gean Department of
Neurotherapeutics: The Journal of the American Society for Experimental NeuroTherapeutics Imaging for the Diagnosis and Management of Traumatic Brain Injury Jane J. Kim and Alisa D. Gean Department of
Dating Neurological Injury
 Dating Neurological Injury wwwwwwwww Jeff L. Creasy Dating Neurological Injury A Forensic Guide for Radiologists, Other Expert Medical Witnesses, and Attorneys Jeff L. Creasy Associate Professor of Neuroradiology
Dating Neurological Injury wwwwwwwww Jeff L. Creasy Dating Neurological Injury A Forensic Guide for Radiologists, Other Expert Medical Witnesses, and Attorneys Jeff L. Creasy Associate Professor of Neuroradiology
