Clinical & Experimental Allergy
|
|
|
- Ashlee Charles
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 doi: /j x Clinical & Experimental Allergy, 1 8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Asthma and Rhinitis 2011 Blackwell Publishing Ltd Inflammation and remodelling patterns in early stage chronic rhinosinusitis N. Van Bruaene, C. P. Novo, K. Van Crombruggen, N. Deruyck, G. Holtappels, P. Van Cauwenberge, P. Gevaert and C. Bachert Upper Airway Research Laboratory (URL), Department of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology, Ghent University Hospital, Ghent, Belgium Clinical & Experimental Allergy Correspondence Nicholas Van Bruaene, Upper Airway Research Laboratory (URL), Department of Oto-Rhino- Laryngology, Ghent University Hospital, B-9000 Ghent, Belgium. Nicholas.Vanbruaene@ Ugent.be Summary Background A distinct set of inflammatory and remodelling factors have been found elevated in chronic rhinosinusitis. Objective The investigation of their expression in early stage disease may reveal early events in this common disease. Methods Sinonasal mucosal samples from nine patients with early stage CRSsNP were taken from the inferior and middle turbinates, the uncinate process, maxillary sinus, anterior ethmoid, bulla ethmoidalis and the posterior ethmoid and measured for TGF-beta 1 and it s receptors, MPO protein as well as pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-alpha and IL- 1beta) and the Th1 cell signature (IFN-gamma and T-bet). As outcome parameter for TGFbeta signalling collagen deposition was analysed. Inferior turbinates from patients undergoing (rhino-) septoplasty were collected as controls. Results TGF-beta 1 protein concentrations were significantly increased in the maxillary sinuses (P = 0.006), the uncinate process (P = 0.01), the anterior ethmoid including the bulla ethmoidalis (P = 0.005) and the posterior ethmoid (P = 0.037) when compared to the inferior and middle turbinates. Collagen deposition was significantly increased in the maxillary sinus when compared to the inferior turbinates (P = 0.008). In contrast, mrna for TGF-beta receptors, Th1 related markers (IFN-gamma and T-bet), pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1 beta and TNF-alpha), and MPO protein as neutrophil marker were expressed at all locations but showed no significant differences between the various locations. TGF-beta 1 mrna expression in inferior turbinates of CRSsNP was significantly higher when compared to inferior turbinates of controls (P = 0.017). The pro-inflammatory cytokines and Th1-related cytokines did not show an upregulation in inferior turbinates of CRSsNP when compared to controls. Conclusions In early stage chronic sinus disease, TGF-beta protein is expressed in significantly higher concentrations within the paranasal sinuses when compared to turbinates, whereas pro-inflammatory, neutrophilic and Th1 markers did not show any difference. These findings suggest that TGF-beta plays a central role in the initiation of CRSsNP, and represents a major target for further research and future intervention. Keywords chronic rhinosinusitis, inflammation, remodelling, TGF-beta Abbreviations CRSsNP, chronic rhinosinusitis without nasal polyps; IFN-c, interferon gamma; MPO, myeloperoxidase; T-bet, T-box transcription factor; TGF-beta 1, transforming growth factor beta 1; Th, T helper (cell); PCR, polymerase chain reaction. Submitted 22 March 2011; revised 24 September 2011; accepted 28 September 2011 Introduction Chronic rhinosinusitis represents a common and often debilitating form of sinusitis with important impact on the quality of life of the patients. The prevalence is high and still increasing [2], estimated to affect up to 14% of the global population in the United States. Its aetiology is probably multifactorial, including anatomical factors, allergic inflammation, immune deficiency, microbial factors, and immune-microbial interactions [3].
2 2 N. Van Bruaene et al Chronic rhinosinusitis clinically represents a spectrum of disorders that share chronic inflammation of the nose and paranasal sinuses; however, it is today considered a heterogenous group of diseases. Based on the differential expression of inflammatory cytokines and remodelling patterns, chronic rhinosinusitis with polyp formation (CRSwNP) can be distinguished from chronic rhinosinusitis without polyp formation (CRSsNP) [4]. Clinically late stage CRSwNP in Caucasians is characterized by a reduced expression of members of the TGF-beta family and its receptors, a preferentially Th2 driven eosinophilic inflammation and a deficit in T regulatory cells, whereas CRSsNP shows an increased expression of Th1 cytokines with a consequently neutrophilic inflammation, and an upregulation of TGF-beta and its receptors vs. inferior turbinate mucosa. The focus of this study was restricted to early stage CRSsNP disease and aimed to define and localize early events in the development of CRSsNP, using inferior turbinate mucosa as comparator [4 6]. The aim of the present study was to analyse the inflammation and remodelling parameters in the different paranasal sinuses in early stage CRSsNP patients, who were selected on the basis of their history and CT scan, and to define the mediators and location of early changes in this frequent disease. Material and methods Patients Nasal tissue was obtained from nine patients with chronic rhinosinusitis without polyp formation (CRSsNP) during routine endoscopic sinus surgery at the department of Otorhinolaryngology at the Ghent University Hospital, Belgium. Biopsies of the mucosa were taken at the following anatomical locations: inferior turbinate, middle turbinate, uncinate process, maxillary sinus, anterior ethmoid including bulla ethmoidalis, and posterior ethmoid. Inferior turbinate samples from patients without sinus disease undergoing septoplasty or rhinoseptoplasty were collected as controls (n = 10, median age 27 years, range 18 45, 4F/ 6M). None of the control patients had a history of allergic rhinitis and/or asthma and all controls were skin prick test negative. The diagnosis of chronic rhinosinusitis without polyps (CRSsNP) was based on history, clinical examination, and nasal endoscopy and computed tomography according to the current EP³OS guidelines [3]. Sinus CT scans were scored according to the Lund-Mackay system [1]. Herein we included only patients with early stage bilateral disease, with a Lund-Mackay Score of not higher than 12/24 after adequate treatment following the EPOS guidelines (Fig. 3). Solitary unilateral maxillary or sphenoidal sinus disease was excluded from this study, as these manifestations may not necessarily lead to bilateral CRSsNP. The ostiomeatal complex and the anterior ethmoid were the most frequent sinuses demonstrating mucosal thickening. All patients had been treated with a combination of topical corticosteroids and clarithromycine 250 mg per day for at least 2 months, but still suffered from or again developed symptoms justifying functional endoscopic sinus surgery. A washout period of 4 weeks before surgery was maintained for oral and topical corticosteroids and antibiotics. Patients underwent a skin prick test for common inhalant allergens, and were asked about asthma symptoms and smoking habits. Rhinosinusitis symptoms were pre-operatively scored by a physician on a scale from 0 to 3 (no symptoms, mild, moderate, severe). General exclusion criteria were based on the EP³OS definition for research (cystic fibrosis, gross immunodeficiency, congenital mucociliary problems, non-invasive fungal balls and invasive fungal disease, systemic vasculitis and granulomatous diseases). Patients who underwent prior nasal or sinus surgery were excluded. The study was approved by the local Ethical committee of the University Hospital Ghent, Belgium. An informed consent was obtained from each patient and control subject before collecting samples. PCR Gene expression analysis by means of quantitative realtime PCR The cdna was synthesized from 2 lg of RNA with the iscript cdna synthesis kit (Bio-Rad Laboratories, CA, USA) following the manufacturer s instructions. Levels of the transcription factor T-bet, the cytokines IFNgamma, TNF-alpha, IL1beta and TGF-beta receptor 1 and 2 were determined by real-time PCR. Amplification reactions were performed on an icycler iq Real-Time PCR Detection System (Bio-Rad laboratories) using specific primer sequences (see online repository, Table 1). PCR reactions contained 30 ng cdna (total RNA equivalent), 250 nm of primer pairs, 1X SYBR Green I Master mix (Bio-Rad laboratories) or 1X TaqMan mix with 100 nm of the TaqMan probe in a final volume of 20 ll. PCR protocol consisted of 1 cycle at 95 C for 10 min followed by 40 cycles at 95 C for 30 s and at 60 C for 1 min and for reactions using TaqMan probes of 1.5 min at 95 C followed by 50 cycles: 15 s at 95 C and 1 min at 60 C. The expression of the housekeeping genes Beta actin (ACTB) and Hydroxymethyl-bilane synthase (HMBS) was used to normalize for transcription and amplification variations among samples after a validation using the
3 Inflammation and remodelling patterns 3 Table 1. Patient characteristics and symptom scores N 9 Gender:Female/male 5/4 Median age 46 ( ) Duration of the disease (months) 24 ( ) SPT positive 3/9 Asthma in history 1/9 Aspirin hypersensitivity in history 0/9 Smoking 1/9 COPD 0/9 Previous FESS 0/9 Median CT score (Lund/Mackay) 6/24 Nasal obstruction 2 (1.75 3) Rhinorrhea 0 (0 2) Sneezing 0(0 0.25) Anosmia 1 ( ) Post-nasal drip 2 (1 2.25) Headache 1 (0 2.25) Dyspnoea 0 (0 1) Cough 1 (0 1.5) N, number of included patients. Data are reported as median and interquartile ranges. genorm software [7, 8]. The relative expression units of each gene per 30 ng of cdna sample, was determined by using the qbase program (version 1.3.5; UGent, Belgium) and results are expressed as the logarithm of normalized relative expression units/30 ng cdna. Protein concentrations of TGF-beta 1 and MPO Surgical samples were snap frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at 80 C until homogenization. The tissue was thawed, weighed and 1 ml of 0.9% NaCl with protease inhibitor Complete (Roche, Mannheim, Germany) was added per every 0.1 g of tissue. The tissue was then homogenized using a B. Braun homogenizer for 5 min. The homogenates were centrifuged at 3000 g, 4 C for 10 min. After centrifugation 250 ll aliquots were made and stored at 80 C until needed for ELISA. To release latent TGF-beta from the extracellular matrix, samples were treated with acid prior to the ELISA. TGF-beta 1 and MPO levels were determined using commercially available ELISA kits from R&D Systems (Minneapolis, MN, USA). All data were expressed as ng/ml. Collagen deposition by means of picrosirius red stainings Collagen was measured by means of picrosirius red staining [9]. Tissue was fixed in formalin (Fluka, Belgium) and embedded in paraffin. Paraffin sections were prepared (thickness 4 5 lm) and air dried for 24 h at 37 C. Sections were deparaffinized, hydrated and stained with picrosirius red (direct red 80; Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) for 60 min. The sections were then washed in two changes of acidified water, dehydrated in three changes of 100% ethanol, and mounted in Tissue-Tek (Miles Inc, Elkhart, IN, USA). The sections were analysed using an Olympus microscope (CX-40) equipped with filters to provide circularly polarized illumination. The lower filter was placed above the microscope s field iris diaphragm ring, while the upper filter was placed below the linear polarizer aligned such that its transmission axis was at 45. Tissue images viewed under bright-field and polarized light were obtained with a 40X objective lens (final magnification 400X) and recorded on a digital camera (Olympus C-5050). Image analysis Collagen content was quantified under polarized light microscopy. Image analysis was carried out with Image J software (Rasband, W.S., ImageJ, U. S. National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, USA, info.nih.gov/ij/, ). Briefly, the entire section of a slide was captured by consecutive fields under bright-field at a final magnification of 400X, with no overlapping zones. The total collagen amount was calculated for each image after subtraction of background and conversion to 8-bit images. The total collagen content was calculated for each section expressed as percentage of the total area. Statistical analysis Statistical analysis was performed with MEDCALC software version (F. Schoonjans, Belgium). Data are expressed as median and interquartile ranges. When comparisons were made between groups, significant between-group variability was first assessed using Kruskall Wallis test. The Mann Whitney U-test two tailed was then used for between-group comparison. Exact P-values are reported. The significance level was set at a = Results Patient characteristics (Table 1) Nine patients with early stage CRSsNP were included, with median disease duration of 24 months. Symptom scores showed that nasal obstruction and post-nasal drip were predominant. The median age of our study group was 46 years. Three of the nine patients had a positive skin prick test to common aeroallergens, one patient was asthmatic and one patient was a smoker. None of the patients had previous sinus surgery. The median Lund and Mackay CT score was 6/24.
4 4 N. Van Bruaene et al TGF-beta 1 protein expression, mrna expression of TGF-beta receptors I and II (Fig. 1) The TGF-beta 1 protein concentrations were significantly higher in this order in the maxillary sinuses (14281 pg/ml; IQR and P = 0.006), the uncinate process (14048 pg/ml; IQR and P = 0.01), the anterior ethmoid including the bulla ethmoidalis (10645 pg/ml; IQR and P = 0.005) and the posterior ethmoid (10130 pg/ml; IQR and P = 0.038) when compared to the inferior and middle turbinates (5027 pg/ml; IQR ). No significant differences were noted in TGFbeta1, RI and II mrna expression between the different locations. Th1 and pro-inflammatory cytokines, MPO protein (Fig. 2) Transcription factors T-bet and IFN-gamma, markers of a Th1driven inflammation, and TNF-alpha and IL-1 beta, representing pro-inflammatory cytokines, were expressed in all nasal and sinus locations, with no significant differences between the sites. The same was true for MPO protein, a marker of neutrophil inflammation, which could be detected in all anatomical locations without significant differences between the sites. Comparison of TGF-beta 1 protein concentrations in inferior turbinates of CRSsNP vs. control patients showed no significant difference. The pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1 and TNF-alpha and Th1-related cytokines did neither show an upregulation in inferior turbinates of CRSsNP when compared to control patients. Picrosirius red staining for collagen (Fig. 4) Picrosirius red staining was performed to assess collagen content in the extracellular matrix. Sections were examined through crossed polars (see Fig. 4a). Larger collagen fibres light up in bright orange and thinner fibres show green. This birefringence, also called double refraction is highly specific for collagen. Orange collagen fibres were present in significantly higher amount present in the maxillary sinuses (median percentage of area 41.17%) when compared to inferior turbinates (33.49%, P = 0.008), as presented in Fig. 4b. Fig. 1. Expression of TGF-beta 1 protein, and TGF-beta receptors I and II mrna in sinunasal mucosal tissue. Inferior and middle turbinates served as control. IT, inferior turbinate; MT, middle turbinate; PU, processus uncinatus; MS, maxillary sinus; BE, bulla ethmoidalis; AE, anterior ethmoid; PE, posterior ethmoid. Discussion Inflammatory mucosal disease in the sinuses shows specific remodelling and inflammatory patterns. CRSsNP has previously been described as being a predominant Th1-mediated neutrophilic disease, characterized by increased levels of IFN-gamma and MPO [4, 6]. Moreover, it was recently shown that TGF-beta 1 and its receptors TGF-beta RI and RIII are strongly upregulated in CRSsNP, resulting in a high number of phospho-smad 2-positive cells that indicate pro-fibrotic signalling [4 6]. This is reflected by a typical remodelling process characterized by a higher collagen deposition in CRSsNP together with the presence of thick collagen fibres when compared to healthy controls [5].
5 Inflammation and remodelling patterns 5 Fig. 2. Expression of mrna for Th1 (IFN-gamma and T-bet) and pro-inflammatory (IL-1 beta and TNF-alpha) markers and protein of the neutrophil marker MPO in turbinates and sinus mucosa. No significant differences were noted between all groups. IT, inferior turbinate; MT, middle turbinate; PU, processus uncinatus; MS, maxillary sinus; BE, bulla ethmoidalis; AE, anterior ethmoid; PE, posterior ethmoid. Herein we show that in early stage CRSsNP disease, surprisingly little mucosal inflammation in the sinuses can be shown, whereas there is a manifest upregulation of TGF-beta protein expression. TGF-beta 1 was significantly overexpressed in the paranasal sinuses when compared to turbinates, with the highest expression in the maxillary sinuses; concentrations of TGF-beta 1 were threefold higher compared to nasal turbinates. Although we were not able to demonstrate a significant upregulation of the TGF-beta RI, we noted the presence and a marginal, but insignificant increase in the expression of this receptor. We could not find significant differences for TGF-ß at mrna level between the various locations. However, it is well known that regulation of TGF-b1 mainly occurs at the post-transcriptional level. TGF-b1 is secreted from cells as small latent complexes, preventing binding of TGF-b1 to ubiquitously expressed receptors, assuring an extracellular reservoir of TGF-b that can be activated on demand. Therefore we performed additional protein quantification by means of ELISA, measuring both active and latent forms of TGF-b1. Latent forms were released from extracellular matrix by adding acid prior to the ELISA measurements. Subsequently, we could demonstrate that the upregulation of TGF-beta 1 in the presence of the receptor was accompanied by an increased deposition of collagen within the maxillary sinuses. As TGF-beta 1 protein shows a higher expression within the paranasal sinuses, whereas the inflammatory and Th1 cytokines appear not to be upregulated, we suggest that TGF-beta plays a crucial role in the regulation of remodelling and fibrosis formation, which only secondarily may be associated with inflammation of the mucosa. The selection of markers for inflammation was based on previous studies [4, 6]. As markers for a Th1 biased
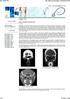
6 6 N. Van Bruaene et al Fig. 3. CT scan: A typical CT scan of a patient with early stage CRSsNP, showing some opacification of the OMC-area and the maxillary sinuses. Fig. 4. (a) Picrosirius red staining for collagen in inferior turbinates (IT) and maxillary sinus (MS) viewed under polarized light. (b) Quantification by means of image analysis of total collagen content in inferior turbinates and maxillary sinuses demonstrating significantly higher collagen deposition in maxillary sinuses when compared to inferior turbinates inflammation, T-bet and IFN-gamma were analysed. T- bet is a Th1 specific T box transcription factor that controls the expression of the hallmark Th1-cytokine IFN-c [10]. T-bet and IFN-gamma were found to be upregulated in CRSsNP in previous studies in patients who suffered more severe disease with a median disease duration of 4.2 years [4 6]. Strikingly, in this study involving patients with a median duration of 24 months, these markers are ubiquitously expressed in the turbinates and sinuses, but did not show any significant topological differences. The TNF-alpha and IL-1beta mrna expression were measured as major pro-inflammatory cytokines [4], reflecting pro-inflammatory responses against e.g. bacterial infection. We here detect these cytokines in both paranasal sinuses and turbinates, but were unable to find upregulation in the sinuses. Finally, MPO (myeloperoxidase) was used as a marker for neutrophilic granulocyte activation, which also demonstrated no difference between turbinates and sinuses. Thus, to our surprise, we could not find any sign of inflammation in early stage CRSsNP in the sinuses. Th1-related and proinflammatory cytokines did not show an upregulation in inferior turbinates of chronic rhinosinusitis vs. control patients. As TGF-beta 1 protein showed a higher expression within the paranasal sinuses, whereas the inflammatory and Th1 cytokines appear not to be upregulated, we suggest that chronic rhinosinusitis is a TGF-beta plays a crucial role in remodelling and fibrosis formation, which only secondarily may be associated with chronic inflammation of the mucosa. The increased expression of TGF-beta 1 is in line with previous findings where we detected an upregulation of TGF-beta 1 in advanced CRSsNP when compared to CRSwNP [6], coinciding with adequate expression of the T regulatory cell marker FOXP3 [6]. We have already demonstrated that inflammation and remodelling may be separate processes in upper airway disease, specifically in nasal polyps, which are likely to develop independently from each other. Whereas remodelling patterns in Chinese and Caucasian CRSwNP disease appear similar [11], inflammatory patterns in those polyps are clearly different between the ethnic groups [12], showing a Th2- vs. a Th17-biased inflammation. These observations suggest that different inflammatory patterns exist despite comparable remodelling patterns, questioning the association between inflammation and remodelling. In comparison to lower airway disease, there was so far a clear lack of knowledge regarding the natural history of the upper airway inflammatory response. In early stage asthma mucosal inflammation seems consistently present, and remodelling may develop in parallel [13, 14]. The central role of TGF-beta in airway fibrosis has been described extensively [13, 15]. It is often assumed that there is a linear progression between an initiating stimulus leading to inflammation, which in
7 Inflammation and remodelling patterns 7 turn leads to remodelling. However, this paradigm has recently been challenged also in lower airway disease [16, 17]. Based on studies on airway biopsies in children, it has been suggested that remodelling may occur very early in asthma and may in some cases even precede clinical symptoms [18]. Similarly, we found an initial upregulation of TGF-beta with subsequent collagen deposition in early stage chronic rhinosinusitis, however, further investigation is needed. We wish to mention that this study is limited to cross-sectional data on inflammation and remodelling patterns in a small group of nine patients with limited chronic sinus disease existing for approximately 24 months. Indication for surgery in early stage chronic rhinosinusitis is an exception, and therefore it is difficult to obtain larger numbers of patients. However, despite small the number of cases, we could find significant differences in TGF-beta production and collagen deposition between different sites. Frontal sinus tissue and sphenoidal tissue was not obtained on a regular basis in these patients, who had no involvement of those sinuses and thus no indication for surgery. We therefore limited the investigation to the mentioned locations. Furthermore, biopsies had to be limited in size, as the preservation of sinus mucosa showing no relevant alterations is mandatory in functional sinus surgery; this restricted the number of possible investigations. The use of control tissue was restricted to inferior turbinates from patients undergoing septoplasty or rhinoseptoplasty with inferior turbinotomy, as it is considered unethical to surgically open healthy sinuses and resect sinusal mucosa in control subjects. In line with previous work of co-author Van Crombruggen et al. [19], no significant difference was noted at TGF-beta protein level between inferior turbinates of controls vs. chronic rhinosinusitis inferior turbinates. We wish to mention that the term early chronic rhinosinusitis has been defined rather arbitrarily, as there is no current definition for early chronic rhinosinusitis. We here intended to include patients with bilateral, but limited disease showing persistent changes on CT scan after recommended medical therapy. These findings provide a new view on the natural course of CRSsNP, and suggest further research on the regulation of TGF-beta in the initiation and maintenance of the disease. The role of inflammation in the persistence of disease and its role in tissue remodelling need to be investigated in depth. Furthermore, these findings underline the importance of TGF-beta as target for therapeutic intervention, may it be early or late stage disease. Conclusion In early chronic sinus disease, TGF-beta is upregulated within the paranasal sinuses, initiating the production of collagen and initiating a remodelling processes, whereas signs of inflammation are lacking. We suggest that TGF-beta plays a central role in the initiation of CRSsNP, and represents a major target for further research and future intervention. Acknowledgements This work was supported by grants to Claus Bachert from the Flemish Scientific Research Board, FWO, Nr. A12/5-HB-KH3 and G , the Global Allergy and Asthma European Network (GA²LEN), and the Interuniversity Attraction Poles Programme Belgian State Belgian Science Policy, Nr. IAP P6/35. Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest. References 1 Lund VJ, Kennedy DW. Quantification for staging sinusitis. The Staging and Therapy Group. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl 1995; 167Suppl: Benninger MS, Ferguson BJ, Hadley JA, Hamilos DL, Jacobs M, Kennedy DW et al. Adult chronic rhinosinusitis: definitions, diagnosis, epidemiology, and pathophysiology. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2003; 129Suppl. 3:S Fokkens W, Lund V, Mullol J. European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps Rhinol Suppl 2007; 20: van Zele T, Claeys S, Gevaert P, Van Maele G, Holtappels G, Van Cauwenberge P et al. Differentiation of chronic sinus diseases by measurement of inflammatory mediators. Allergy 2006; 61: Van Bruaene N, Derycke L, Perez-Novo CA, Gevaert P, Holtappels G, De Ruyck N et al. TGF-beta signalling and collagen deposition in chronic rhinosinusitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2009; 124: Van Bruaene N, Perez-Novo CA, Basinski TM, van Zele T, Holtappels G, De Ruyck N et al. T-cell regulation in chronic paranasal sinus disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2008; 121: Perez-Novo CA, Claeys C, Speleman F, Van Cauwenberge P, Bachert C, Vandesompele J. Impact of RNA quality on reference gene expression stability. BioTechniques 2005; 39: Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A et al. Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 2002; 3: RESEARCH Whittaker P, Kloner RA, Boughner DR, Pickering JG. Quantitative assessment of myocardial collagen with picrosirius red staining and circularly polarized light. Basic Res Cardiol 1994; 89: Hohler T, Reuss E, Adams P, Bartsch B, Weigmann B, Worns M et al. A genetic basis for IFN-gamma production and
8 8 N. Van Bruaene et al T-bet expression in humans. J Immunol 2005; 175: Li X, Meng J, Qiao X, Liu Y, Liu F, Zhang N et al. Expression of TGF, matrix metalloproteinases, and tissue inhibitors in Chinese chronic rhinosinusitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2010; 125: Zhang N, van Zele T, Perez-Novo C, Van Bruaene N, Holtappels G, DeRuyck N et al. Different types of T-effector cells orchestrate mucosal inflammation in chronic sinus disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2008; 122: Redington AE. Airway fibrosis in asthma: mechanisms, consequences, and potential for therapeutic intervention. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis 2000; 55: Redington AE. Fibrosis and airway remodelling. Clin Exp Allergy 2000; 30Suppl. 1: Redington AE, Howarth PH. Airway wall remodelling in asthma. Thorax 1997; 52: Murphy DM, O Byrne PM. Recent advances in the pathophysiology of asthma. Chest 2010; 137: Bergeron C, Al Ramli W, Hamid Q. Remodelling in asthma. Proc Am Thorac Soc 2009; 6: Barbato A, Turato G, Baraldo S, Bazzan E, Calabrese F, Panizzolo C et al. Epithelial damage and angiogenesis in the airways of children with asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2006; 174: Van Crombruggen K, Van Bruaene N, Holtappels G, Bachert C. Chronic sinusitis and rhinitis: Clinical terminology Chronic Rhinosinusitis further supported. Rhinology 2010; 48:54 8.
Middleton Chapter 43 (pages ) Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps Prepared by: Malika Gupta, MD
 FIT Board Review Corner December 2017 Welcome to the FIT Board Review Corner, prepared by Amar Dixit, MD, and Christin L. Deal, MD, senior and junior representatives of ACAAI's Fellows-In- Training (FITs)
FIT Board Review Corner December 2017 Welcome to the FIT Board Review Corner, prepared by Amar Dixit, MD, and Christin L. Deal, MD, senior and junior representatives of ACAAI's Fellows-In- Training (FITs)
Presence of IL-5 protein and IgE antibodies to staphylococcal enterotoxins in nasal polyps is associated with comorbid asthma
 Original articles Presence of IL-5 protein and IgE antibodies to staphylococcal enterotoxins in nasal polyps is associated with comorbid asthma Claus Bachert, MD, PhD, a Nan Zhang, MD, PhD, a,b Gabriele
Original articles Presence of IL-5 protein and IgE antibodies to staphylococcal enterotoxins in nasal polyps is associated with comorbid asthma Claus Bachert, MD, PhD, a Nan Zhang, MD, PhD, a,b Gabriele
Cytokine Profiles in Japanese Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis
 Allergology International. 212;61:115-122 DOI: 1.2332 allergolint.1-oa-29 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cytokine Profiles in Japanese Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis Takayuki Sejima 1,2, Gabriele Holtappels 1,
Allergology International. 212;61:115-122 DOI: 1.2332 allergolint.1-oa-29 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cytokine Profiles in Japanese Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis Takayuki Sejima 1,2, Gabriele Holtappels 1,
Rhinosinusitis. John Ramey, MD Joseph Russell, MD
 Rhinosinusitis John Ramey, MD Joseph Russell, MD Disclosure Statement RSFH as a continuing medical education provider, accredited by the South Carolina Medical Association, it is the policy of RSFH to
Rhinosinusitis John Ramey, MD Joseph Russell, MD Disclosure Statement RSFH as a continuing medical education provider, accredited by the South Carolina Medical Association, it is the policy of RSFH to
Retrospective Analysis of Patients with Allergy Sinusitis
 Original article: Retrospective Analysis of Patients with Allergy Sinusitis G.S. Thalor Senior Specialist (MS) (department of Oto Rhino Laryngology), Govt. S.K. Hospital, Sikar, Rajasthan, India. Corresponding
Original article: Retrospective Analysis of Patients with Allergy Sinusitis G.S. Thalor Senior Specialist (MS) (department of Oto Rhino Laryngology), Govt. S.K. Hospital, Sikar, Rajasthan, India. Corresponding
thus, the correct terminology is now rhinosinusitis.
 By: Ibrahim Alarifi Introduction Rhinitis and sinusitis usually coexist and are concurrent in most individuals; thus, the correct terminology is now rhinosinusitis. Mucosa of the nose is a continuation
By: Ibrahim Alarifi Introduction Rhinitis and sinusitis usually coexist and are concurrent in most individuals; thus, the correct terminology is now rhinosinusitis. Mucosa of the nose is a continuation
OSTEITIS IN CRS. Rhinology Chair Meeting presented by Amal Binhazza a
 OSTEITIS IN CRS Rhinology Chair Meeting presented by Amal Binhazza a ROAD MAP Definition. pathophysiology. Diagnosis. Grading systems. Clinical implications. Management. OSTEITIS Presence of new bone formation,
OSTEITIS IN CRS Rhinology Chair Meeting presented by Amal Binhazza a ROAD MAP Definition. pathophysiology. Diagnosis. Grading systems. Clinical implications. Management. OSTEITIS Presence of new bone formation,
Original Article. The Role of Transforming Growth Factor Beta 1 (TGFβ1) in Nasal and Paranasal Sinuses Polyposis
 Iran 72 J Pathol (21)5 (2), 72-76 Original Article The Role of Transforming Growth Factor Beta 1 (TGFβ1) in Nasal and Paranasal Sinuses Polyposis Mohammad Ebrahim Yarmohammadi 1, Horieh Saderi 2, Pupak
Iran 72 J Pathol (21)5 (2), 72-76 Original Article The Role of Transforming Growth Factor Beta 1 (TGFβ1) in Nasal and Paranasal Sinuses Polyposis Mohammad Ebrahim Yarmohammadi 1, Horieh Saderi 2, Pupak
Different types of T-effector cells orchestrate mucosal inflammation in chronic sinus disease
 Different types of T-effector cells orchestrate mucosal inflammation in chronic sinus disease Nan Zhang, MD, PhD, a,b * Thibaut Van Zele, MD, PhD, a * Claudina Perez-Novo, PhD, a Nicholas Van Bruaene,
Different types of T-effector cells orchestrate mucosal inflammation in chronic sinus disease Nan Zhang, MD, PhD, a,b * Thibaut Van Zele, MD, PhD, a * Claudina Perez-Novo, PhD, a Nicholas Van Bruaene,
European position paper on Rhinosinusitis & Nnasal Polyps 2012 (summary)
 Rhinology Chair Weekly Activity European position paper on Rhinosinusitis & Nnasal Polyps 2012 (summary) Mohammed s. Al-Ahmari 12/02/2012 www.rhinologychair.org conference@rhinologychair.org Rhinology
Rhinology Chair Weekly Activity European position paper on Rhinosinusitis & Nnasal Polyps 2012 (summary) Mohammed s. Al-Ahmari 12/02/2012 www.rhinologychair.org conference@rhinologychair.org Rhinology
Role of staphylococcal superantigens in upper airway disease Claus Bachert, Nan Zhang, Joke Patou, Thibaut van Zele and Philippe Gevaert
 Role of staphylococcal superantigens in upper airway disease Claus Bachert, Nan Zhang, Joke Patou, Thibaut van Zele and Philippe Gevaert Upper Airway Research Laboratory, Ear Nose and Throat Department,
Role of staphylococcal superantigens in upper airway disease Claus Bachert, Nan Zhang, Joke Patou, Thibaut van Zele and Philippe Gevaert Upper Airway Research Laboratory, Ear Nose and Throat Department,
Rhinosinusitis: A Prospective Study
 االله الرحمن الرحيم بسم Pathological l & Radiological i l Evidences in the Pathogenesis es s of Chronic Rhinosinusitis: A Prospective Study Prof. Dr. H. ABDEL FATAH, MD A. Prof. Dr. K. NOWEAM, MD Dr. Z.
االله الرحمن الرحيم بسم Pathological l & Radiological i l Evidences in the Pathogenesis es s of Chronic Rhinosinusitis: A Prospective Study Prof. Dr. H. ABDEL FATAH, MD A. Prof. Dr. K. NOWEAM, MD Dr. Z.
Incidence of accessory ostia in patients with chronic maxillary sinusitis
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Ghosh P et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Mar;4(2):443-447 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937 Original
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Ghosh P et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Mar;4(2):443-447 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937 Original
Dr.Adel A. Al Ibraheem
 Rhinology Chair Weekly Activity Dr.Adel A. Al Ibraheem www.rhinologychair.org conference@rhinologychair.org Rhinology Chair Introduction: It is important to classify and stage nasal polyposis. ( decide
Rhinology Chair Weekly Activity Dr.Adel A. Al Ibraheem www.rhinologychair.org conference@rhinologychair.org Rhinology Chair Introduction: It is important to classify and stage nasal polyposis. ( decide
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Computed Tomographic Staging and the Fate of the Dependent Sinuses in Revision Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
 Computed Tomographic Staging and the Fate of the Dependent es in Revision Endoscopic Surgery Neil Bhattacharyya, MD ORIGINAL ARTICLE Objectives: To determine the patterns of disease recurrence in chronic
Computed Tomographic Staging and the Fate of the Dependent es in Revision Endoscopic Surgery Neil Bhattacharyya, MD ORIGINAL ARTICLE Objectives: To determine the patterns of disease recurrence in chronic
Chronic Rhinosinusitis-Treatment
 Chronic Rhinosinusitis-Treatment INFECTION INFLAMMATION Predisposing Factors Anatomical variations Allergic rhinitis Acute sinusitis Immune deficiency Rhinosinusitis Non-allergic rhinitis Chronic sinusitis
Chronic Rhinosinusitis-Treatment INFECTION INFLAMMATION Predisposing Factors Anatomical variations Allergic rhinitis Acute sinusitis Immune deficiency Rhinosinusitis Non-allergic rhinitis Chronic sinusitis
Nasal Polyposis. DEPARTMENT OF ENT K.S.Hegde Medical Academy Deralakatte, Mangalore
 Nasal Polyposis DEPARTMENT OF ENT K.S.Hegde Medical Academy Deralakatte, Mangalore Def: INTRODUCTION Chronic inflammatory disease of the mucous membrane in the nose & PNS, presenting as pedunculated smooth
Nasal Polyposis DEPARTMENT OF ENT K.S.Hegde Medical Academy Deralakatte, Mangalore Def: INTRODUCTION Chronic inflammatory disease of the mucous membrane in the nose & PNS, presenting as pedunculated smooth
Concepts in Rhinosinusitis. Nick Jones University of Nottingham
 Concepts in Rhinosinusitis Nick Jones University of Nottingham Definition of rhinosinusitis Very broad and is based on clinical symptoms, CT and endoscopy NOT on pathology Definition of rhinosinusitis
Concepts in Rhinosinusitis Nick Jones University of Nottingham Definition of rhinosinusitis Very broad and is based on clinical symptoms, CT and endoscopy NOT on pathology Definition of rhinosinusitis
DIFFICULT-TO-TREAT CHRONIC
 MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES FOR DIFFICULT-TO-TREAT CHRONIC RHINOSINUSITIS DR ZULKEFLI HUSSEIN CONSULTANT EAR NOSE & THROAT SURGEON PANTAI HOSPITAL PENANG DISCLAIMER Nothing to disclose PENANG ISLAND, MALAYSIA
MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES FOR DIFFICULT-TO-TREAT CHRONIC RHINOSINUSITIS DR ZULKEFLI HUSSEIN CONSULTANT EAR NOSE & THROAT SURGEON PANTAI HOSPITAL PENANG DISCLAIMER Nothing to disclose PENANG ISLAND, MALAYSIA
Conventional Sinus Surgery Vs Fess
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. III (July. 2017), PP 44-51 www.iosrjournals.org Conventional Sinus Surgery Vs Fess *
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. III (July. 2017), PP 44-51 www.iosrjournals.org Conventional Sinus Surgery Vs Fess *
Evaluation of the Change in Recent Diagnostic Criteria of Chronic Rhinosinusitis: A Cross-sectional Study
 Abhishek Ramadhin REVIEW ARTICLE 10.5005/jp-journals-10013-1246 Evaluation of the Change in Recent Diagnostic Criteria of Chronic Rhinosinusitis: A Cross-sectional Study Abhishek Ramadhin ABSTRACT There
Abhishek Ramadhin REVIEW ARTICLE 10.5005/jp-journals-10013-1246 Evaluation of the Change in Recent Diagnostic Criteria of Chronic Rhinosinusitis: A Cross-sectional Study Abhishek Ramadhin ABSTRACT There
Tibet is a plateau region in China, northeast of the
 Immunopathology features of chronic rhinosinusitis in high-altitude dwelling Tibetans Ba Luo, M.D., 1,2 Liu Feng, M.D., 1 Du Jintao, Ph.D., 1 Liu Yafeng, M.D., 1 Liu Shixi, M.D., Ph.D., 1 Zhang Nan, Ph.D.,
Immunopathology features of chronic rhinosinusitis in high-altitude dwelling Tibetans Ba Luo, M.D., 1,2 Liu Feng, M.D., 1 Du Jintao, Ph.D., 1 Liu Yafeng, M.D., 1 Liu Shixi, M.D., Ph.D., 1 Zhang Nan, Ph.D.,
Chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS), characterized by chronic
 Chronic rhinosinusitis management beyond intranasal steroids and saline solution irrigations Newton Li, M.D., and Anju T. Peters, M.D. ABSTRACT Background: Chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) is a heterogeneous
Chronic rhinosinusitis management beyond intranasal steroids and saline solution irrigations Newton Li, M.D., and Anju T. Peters, M.D. ABSTRACT Background: Chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) is a heterogeneous
MANAGEMENT OF RHINOSINUSITIS IN ADULTS IN PRIMARY CARE
 PROFESSOR DR SALINA HUSAIN DEPUTY HEAD DEPARTMENT OF OTORHINOLARYNGOLOGY-HEAD NECK SURGERY UKM MEDICAL CENTRE MANAGEMENT OF RHINOSINUSITIS IN ADULTS IN PRIMARY CARE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES ON MANAGEMENT
PROFESSOR DR SALINA HUSAIN DEPUTY HEAD DEPARTMENT OF OTORHINOLARYNGOLOGY-HEAD NECK SURGERY UKM MEDICAL CENTRE MANAGEMENT OF RHINOSINUSITIS IN ADULTS IN PRIMARY CARE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES ON MANAGEMENT
ORIGINAL ARTICLE INTRODUCTION
 Allergology International. 14;63:27-35 DOI: 1.2332 allergolint.13-oa-579 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Lung Functions of Japanese Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis Who Underwent Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Shota Tanaka
Allergology International. 14;63:27-35 DOI: 1.2332 allergolint.13-oa-579 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Lung Functions of Japanese Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis Who Underwent Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Shota Tanaka
EPIGENETICS OF CHRONIC RHINOSINUSITIS
 Rhinology Chair Weekly Activity EPIGENETICS OF CHRONIC RHINOSINUSITIS AND THE ROLE OF THE EOSINOPHIL: ARTICLE REVIEW www.rhinologychair.org conference@rhinologychair.org Dr.Dana Aljomah March, 2012 Rhinology
Rhinology Chair Weekly Activity EPIGENETICS OF CHRONIC RHINOSINUSITIS AND THE ROLE OF THE EOSINOPHIL: ARTICLE REVIEW www.rhinologychair.org conference@rhinologychair.org Dr.Dana Aljomah March, 2012 Rhinology
Reliability of computed tomography scans in the diagnosis of chronic rhinosinusitis
 Original papers Reliability of computed tomography scans in the diagnosis of chronic rhinosinusitis Marcin Frączek 1, A D, F, Marcin Masalski 1, B, B, E, Maciej Guziński 1 Department of Otolaryngology,
Original papers Reliability of computed tomography scans in the diagnosis of chronic rhinosinusitis Marcin Frączek 1, A D, F, Marcin Masalski 1, B, B, E, Maciej Guziński 1 Department of Otolaryngology,
Epidemiology of nasal polyps in hilly areas and its risk factors
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Nanda MS et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017 Jan;3(1):77-81 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937 Original
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Nanda MS et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017 Jan;3(1):77-81 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937 Original
Expressions of Eosinophil in Chronic Rhinosinusitis Patients with Nasal Polyp
 ISSN: 2250-0359 Expressions of Eosinophil in Chronic Rhinosinusitis Patients with Nasal Polyp Indrawati LPL* Department of Otolaryngology, Gajah Mada University, Sardjito General Hospital, Jl. Kesehatan
ISSN: 2250-0359 Expressions of Eosinophil in Chronic Rhinosinusitis Patients with Nasal Polyp Indrawati LPL* Department of Otolaryngology, Gajah Mada University, Sardjito General Hospital, Jl. Kesehatan
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 10 Page October 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-45 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/1.18535/jmscr/v5i1.116 Nasal Polyps- Causes and Associated Symptoms-
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-45 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/1.18535/jmscr/v5i1.116 Nasal Polyps- Causes and Associated Symptoms-
Eosinophilic Rhinosinusitis is Not a Disease of Ostiomeatal Occlusion
 The Laryngoscope VC 2013 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Eosinophilic Rhinosinusitis is Not a Disease of Ostiomeatal Occlusion Kornkiat Snidvongs, MD; David Chin,
The Laryngoscope VC 2013 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Eosinophilic Rhinosinusitis is Not a Disease of Ostiomeatal Occlusion Kornkiat Snidvongs, MD; David Chin,
Does osteopathic treatments improve the symptoms of headache and/or head-pressure in patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis (CRS)?
 Does osteopathic treatments improve the symptoms of headache and/or head-pressure in patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis (CRS)? A randomized controlled trial Roos S 1, Steinbauer U 1, Amann P 1, Schwerla
Does osteopathic treatments improve the symptoms of headache and/or head-pressure in patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis (CRS)? A randomized controlled trial Roos S 1, Steinbauer U 1, Amann P 1, Schwerla
Raising awareness of upper airway diseases: Overview of management and prevention strategies WANG De-yun *
 Med J Chin PLA, Vol. 42, No. 10, October 1, 2017 843 ( ) 2017 10 11 (ARIA2001 2008) (GA2LEN) - (EP3OS 2007 2012) (2016) Allergy Therapeutics and Clinical Risk Management Military Medical Research 20-230
Med J Chin PLA, Vol. 42, No. 10, October 1, 2017 843 ( ) 2017 10 11 (ARIA2001 2008) (GA2LEN) - (EP3OS 2007 2012) (2016) Allergy Therapeutics and Clinical Risk Management Military Medical Research 20-230
Tomographical Findings in Adult Patients Undergoing Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Revision
 THIEME Original Research 73 Tomographical Findings in Adult Patients Undergoing Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Revision Jan Alessandro Socher 1 Jonas Mello 2 Barbara Batista Baltha 2 1 Department of Otorhinolaryngology,
THIEME Original Research 73 Tomographical Findings in Adult Patients Undergoing Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Revision Jan Alessandro Socher 1 Jonas Mello 2 Barbara Batista Baltha 2 1 Department of Otorhinolaryngology,
Recalcitrant chronic rhinosinusitis. Difficulties in diagnosis and treatment Videler, W.J.M.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Recalcitrant chronic rhinosinusitis. Difficulties in diagnosis and treatment Videler, W.J.M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Videler, W.
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Recalcitrant chronic rhinosinusitis. Difficulties in diagnosis and treatment Videler, W.J.M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Videler, W.
RoleofAllergyinNasalPolyposis. Role of Allergy in Nasal Polyposis
 Global Journal of Medical Research: J Dentistry & Otolaryngology Volume 17 Issue 1 Version 1.0 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online
Global Journal of Medical Research: J Dentistry & Otolaryngology Volume 17 Issue 1 Version 1.0 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online
The role of plain radiographs in the diagnosis of chronic maxillary rhinosinusitis in adults
 The role of plain radiographs in the diagnosis of chronic maxillary rhinosinusitis in adults *Kolo ES Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Bayero University Kano/Aminu Kano Teaching Hospital, Kano, Nigeria
The role of plain radiographs in the diagnosis of chronic maxillary rhinosinusitis in adults *Kolo ES Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Bayero University Kano/Aminu Kano Teaching Hospital, Kano, Nigeria
Spheno-Ethmoidectomy
 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy, Vol. 5, pp. 1-8 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1998 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) N.V. Published
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy, Vol. 5, pp. 1-8 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1998 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) N.V. Published
INSTRUCTIONS ON THE ANNOTATION OF PDF FILES
 P-annotatePDF-v11 INSTRUCTIONS ON THE ANNOTATION OF PDF FILES To view, print and annotate your article you will need Adobe Reader version 9 (or higher). This program is freely available for a whole series
P-annotatePDF-v11 INSTRUCTIONS ON THE ANNOTATION OF PDF FILES To view, print and annotate your article you will need Adobe Reader version 9 (or higher). This program is freely available for a whole series
Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis in Japan
 Allergology International. 2010;59:239-245 DOI: 10.2332 allergolint.10-rai-0231 REVIEW ARTICLE Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis in Japan Junichi Ishitoya 1, Yasunori Sakuma 1 and Mamoru Tsukuda 2 ABSTRACT
Allergology International. 2010;59:239-245 DOI: 10.2332 allergolint.10-rai-0231 REVIEW ARTICLE Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis in Japan Junichi Ishitoya 1, Yasunori Sakuma 1 and Mamoru Tsukuda 2 ABSTRACT
JMSCR Vol 04 Issue 05 Page May 2016
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 5.88 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i5.25 Radiologic Variations of Nose and Paranasal
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 5.88 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i5.25 Radiologic Variations of Nose and Paranasal
Risk Factors of Chronic Rhinosinusitis After Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
 e-issn 1643-3750 DOI: 10.12659/MSM.900421 Received: 2016.07.05 Accepted: 2016.07.22 Published: 2017.02.28 Risk Factors of Chronic Rhinosinusitis After Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Authors Contribution:
e-issn 1643-3750 DOI: 10.12659/MSM.900421 Received: 2016.07.05 Accepted: 2016.07.22 Published: 2017.02.28 Risk Factors of Chronic Rhinosinusitis After Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Authors Contribution:
IL-5 and IL-6 are increased in the frontal recess of eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis patients
 Kubota et al. Journal of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery (2017) 46:36 DOI 10.1186/s40463-017-0214-2 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access IL-5 and IL-6 are increased in the frontal recess of eosinophilic
Kubota et al. Journal of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery (2017) 46:36 DOI 10.1186/s40463-017-0214-2 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access IL-5 and IL-6 are increased in the frontal recess of eosinophilic
Chronic Sinusitis. Acute Sinusitis. Sinusitis. Anatomy of the Paranasal Sinuses. Sinusitis. Medical Topics - Sinusitis
 1 Acute Chronic is the inflammation of the inner lining of the parnasal sinuses due to infection or non-infectious causes such as allergies or environmental pullutants. If the inflammation lasts more than
1 Acute Chronic is the inflammation of the inner lining of the parnasal sinuses due to infection or non-infectious causes such as allergies or environmental pullutants. If the inflammation lasts more than
Role of Tyk-2 in Th9 and Th17 cells in allergic asthma
 Supplementary File Role of Tyk-2 in Th9 and Th17 cells in allergic asthma Caroline Übel 1*, Anna Graser 1*, Sonja Koch 1, Ralf J. Rieker 2, Hans A. Lehr 3, Mathias Müller 4 and Susetta Finotto 1** 1 Laboratory
Supplementary File Role of Tyk-2 in Th9 and Th17 cells in allergic asthma Caroline Übel 1*, Anna Graser 1*, Sonja Koch 1, Ralf J. Rieker 2, Hans A. Lehr 3, Mathias Müller 4 and Susetta Finotto 1** 1 Laboratory
Recalcitrant chronic rhinosinusitis. Difficulties in diagnosis and treatment Videler, W.J.M.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Recalcitrant chronic rhinosinusitis. Difficulties in diagnosis and treatment Videler, W.J.M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Videler, W.
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Recalcitrant chronic rhinosinusitis. Difficulties in diagnosis and treatment Videler, W.J.M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Videler, W.
FRONTAL SINUPLASTY P R E P A R E D A N D P R E S E N T E D B Y : D R. Y A H Y A F A G E E H R 4 16/ 12/ 2013
 FRONTAL SINUPLASTY P R E P A R E D A N D P R E S E N T E D B Y : D R. Y A H Y A F A G E E H R 4 16/ 12/ 2013 ANATOMY: FRONTAL SINUS Not present at birth Starts developing at 4 years Radiographically visualized
FRONTAL SINUPLASTY P R E P A R E D A N D P R E S E N T E D B Y : D R. Y A H Y A F A G E E H R 4 16/ 12/ 2013 ANATOMY: FRONTAL SINUS Not present at birth Starts developing at 4 years Radiographically visualized
Treatment Options for Chronic Sinusitis
 Treatment Options for Chronic Sinusitis Jesse Ryan, M.D. Assistant Professor Head and Neck Surgery & Reconstruction Department of Otolaryngology January 17, 2019 Disclosures I have no financial relationship
Treatment Options for Chronic Sinusitis Jesse Ryan, M.D. Assistant Professor Head and Neck Surgery & Reconstruction Department of Otolaryngology January 17, 2019 Disclosures I have no financial relationship
The Relationship between Staphylococcus aureus Infection and Some Asthma Markers As (IL 4, IL 10, IFN γ, IgE and FOXP3) in Asthmatic Patients
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 12 (2016) pp. 897-902 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.512.097
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 12 (2016) pp. 897-902 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.512.097
White Paper: Balloon Sinuplasty for Chronic Sinusitis, The Latest Recommendations
 White Paper: Balloon Sinuplasty for Chronic Sinusitis, The Latest Recommendations For Health Plans, Medical Management Organizations and TPAs Executive Summary Despite recent advances in instrumentation
White Paper: Balloon Sinuplasty for Chronic Sinusitis, The Latest Recommendations For Health Plans, Medical Management Organizations and TPAs Executive Summary Despite recent advances in instrumentation
Original Article Inflammatory infiltration and tissue remodeling in nasal polyps and adjacent mucosa of unaffected sinus
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2018;11(5):2707-2713 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0071698 Original Article Inflammatory infiltration and tissue remodeling in nasal polyps and adjacent mucosa of unaffected
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2018;11(5):2707-2713 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0071698 Original Article Inflammatory infiltration and tissue remodeling in nasal polyps and adjacent mucosa of unaffected
ISSN X (Print) Research Article. *Corresponding author Dr.V. Krishna Chaitanya
 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2015; 3(1G):508-513 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2015; 3(1G):508-513 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2017) Vol.68 (3), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2017) Vol.68 (3), Page 1390-1394 Anatomical Variations of Nasal Structures in Chronic Rhinosinusitis as Detected by Computed Tomography Scan Omar Adnan Hasan,
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2017) Vol.68 (3), Page 1390-1394 Anatomical Variations of Nasal Structures in Chronic Rhinosinusitis as Detected by Computed Tomography Scan Omar Adnan Hasan,
Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Padjadjaran, Dr. Hasan Sadikin General Hospital
 Original Article Chronic Rhinosinusitis Patient with Nasal Polyp Characteristics at Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Outpatient Clinic, Dr. Hasan Sadikin General Hospital, Bandung Dina Riana,
Original Article Chronic Rhinosinusitis Patient with Nasal Polyp Characteristics at Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Outpatient Clinic, Dr. Hasan Sadikin General Hospital, Bandung Dina Riana,
ENDOSCOPIC SURGERY OF THE PARANASAL SINUSES & SKULL BASE
 30 th International Course on ENDOSCOPIC SURGERY OF THE PARANASAL SINUSES & SKULL BASE Ghent (Belgium) 29 August-1 September 2018 INTERNATIONAL FACULTY Claus Bachert (Ghent, Belgium) Philippe Gevaert (Ghent,
30 th International Course on ENDOSCOPIC SURGERY OF THE PARANASAL SINUSES & SKULL BASE Ghent (Belgium) 29 August-1 September 2018 INTERNATIONAL FACULTY Claus Bachert (Ghent, Belgium) Philippe Gevaert (Ghent,
Dose-dependent effects of tobramycin in an animal model of Pseudomonas sinusitis Am J Rhino Jul-Aug; 21(4):423-7
 AMINOGLYCOSIDES Dose-dependent effects of tobramycin in an animal model of Pseudomonas sinusitis Am J Rhino. 2007 Jul-Aug; 21(4):423-7 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17882910 Evaluation of the in-vivo
AMINOGLYCOSIDES Dose-dependent effects of tobramycin in an animal model of Pseudomonas sinusitis Am J Rhino. 2007 Jul-Aug; 21(4):423-7 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17882910 Evaluation of the in-vivo
A CONTRIBUTION TO THE ETIOPATHOGENESIS, DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF SINONASAL INVERTED PAPILLOMAS
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF TÂRGU MUREȘ ROMANIA A CONTRIBUTION TO THE ETIOPATHOGENESIS, DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF SINONASAL INVERTED PAPILLOMAS PhD THESIS ABSTRACT PhD Student Viorel Emanoil
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF TÂRGU MUREȘ ROMANIA A CONTRIBUTION TO THE ETIOPATHOGENESIS, DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF SINONASAL INVERTED PAPILLOMAS PhD THESIS ABSTRACT PhD Student Viorel Emanoil
Real-life study showing uncontrolled rhinosinusitis after sinus surgery in a tertiary referral centre
 Allergy ORIGINAL ARTICLE AIRWAY DISEASES Real-life study showing uncontrolled rhinosinusitis after sinus surgery in a tertiary referral centre J. van der Veen 1, S. F. Seys 2, M. Timmermans 1, P. Levie
Allergy ORIGINAL ARTICLE AIRWAY DISEASES Real-life study showing uncontrolled rhinosinusitis after sinus surgery in a tertiary referral centre J. van der Veen 1, S. F. Seys 2, M. Timmermans 1, P. Levie
ROLE OF ANATOMICAL OBSTRUCTION IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF CHRONIC SINUSITIS
 From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan July 1, 2012 ROLE OF ANATOMICAL OBSTRUCTION IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF CHRONIC SINUSITIS Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/51/
From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan July 1, 2012 ROLE OF ANATOMICAL OBSTRUCTION IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF CHRONIC SINUSITIS Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/51/
A Study of Anatomical Variations in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis.
 DOI: 10.2127/aimdr.201..2.EN1 Original Article ISSN (O):239-222; ISSN (P):239-21 A Study of Anatomical Variations in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Smruti Swain 1 1 Associate Professor, Department
DOI: 10.2127/aimdr.201..2.EN1 Original Article ISSN (O):239-222; ISSN (P):239-21 A Study of Anatomical Variations in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Smruti Swain 1 1 Associate Professor, Department
Congestion, headache, recurrent infection, post-nasal drip, smell problems? We can find the source and offer solutions for relief.
 Sinus Sinus Congestion, headache, recurrent infection, post-nasal drip, smell problems? We can find the source and offer solutions for relief. So what is sinusitis? Although many individuals interpret
Sinus Sinus Congestion, headache, recurrent infection, post-nasal drip, smell problems? We can find the source and offer solutions for relief. So what is sinusitis? Although many individuals interpret
Department of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology, Upper Airway Research Laboratory (URL), Ghent University Hospital, De Pintelaan 185, 9000 Ghent, Belgium 2
 Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Volume 212, Article ID 673145, 9 pages doi:1.1155/212/673145 Research Article A Herbal Composition of Scutellaria baicalensis and Eleutherococcussenticosus
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Volume 212, Article ID 673145, 9 pages doi:1.1155/212/673145 Research Article A Herbal Composition of Scutellaria baicalensis and Eleutherococcussenticosus
Causes of higher symptomatic airway load in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis
 Eskeland et al. BMC Ear, Nose and Throat Disorders (2017) 17:15 DOI 10.1186/s12901-017-0048-6 RESEARCH ARTICLE Causes of higher symptomatic airway load in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis Øystein Eskeland
Eskeland et al. BMC Ear, Nose and Throat Disorders (2017) 17:15 DOI 10.1186/s12901-017-0048-6 RESEARCH ARTICLE Causes of higher symptomatic airway load in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis Øystein Eskeland
Staphylococcus aureus superantigens and their role in eosinophilic nasal polyp disease
 Review article Staphylococcus aureus superantigens and their role in eosinophilic nasal polyp disease Pongsakorn Tantilipikorn, 1 Chaweewan Bunnag, 1 Zhang Nan, 2 and Claus Bachert 2 Summary Nasal polyposis
Review article Staphylococcus aureus superantigens and their role in eosinophilic nasal polyp disease Pongsakorn Tantilipikorn, 1 Chaweewan Bunnag, 1 Zhang Nan, 2 and Claus Bachert 2 Summary Nasal polyposis
OLFACTION IN ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY. Mohammed Alsukayt R2 18/05/2016
 OLFACTION IN ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY Mohammed Alsukayt R2 18/05/2016 Introduction Chronic Rhinosinusitis (CRS) accounts for 14-30% of olfactory dysfunction cases In patients with CRS, 28% to 84% complain
OLFACTION IN ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY Mohammed Alsukayt R2 18/05/2016 Introduction Chronic Rhinosinusitis (CRS) accounts for 14-30% of olfactory dysfunction cases In patients with CRS, 28% to 84% complain
Volume 2 issue 4 ISSN A STUDY ON CHRONIC OTITIS MEDIA ACTIVE MUCOSAL TYPE WITH SINUSITIS AS FOCAL SEPSIS
 Volume 2 issue 4 ISSN 2250-0359 A STUDY ON CHRONIC OTITIS MEDIA ACTIVE MUCOSAL TYPE WITH SINUSITIS AS FOCAL SEPSIS * Sankaranaryanan Gopalakrishnan, * Satheesh kumar * Kilpaulk Medical College, Royepettah
Volume 2 issue 4 ISSN 2250-0359 A STUDY ON CHRONIC OTITIS MEDIA ACTIVE MUCOSAL TYPE WITH SINUSITIS AS FOCAL SEPSIS * Sankaranaryanan Gopalakrishnan, * Satheesh kumar * Kilpaulk Medical College, Royepettah
Reasons for Failure and Surgical Revisions. Stil Kountakis, MD, PhD Professor and Chief, Division of Rhinology
 Reasons for Failure and Surgical Revisions Stil Kountakis, MD, PhD Professor and Chief, Division of Rhinology Medical College of Georgia of Georgia Regents University Department of Otolaryngology / Head
Reasons for Failure and Surgical Revisions Stil Kountakis, MD, PhD Professor and Chief, Division of Rhinology Medical College of Georgia of Georgia Regents University Department of Otolaryngology / Head
Original Article Comparison of different surgical approaches of functional endoscopic sinus surgery on patients with chronic rhinosinusitis
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(6):1585-1591 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0000315 Original Article Comparison of different surgical approaches of functional endoscopic sinus surgery on patients with chronic
Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(6):1585-1591 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0000315 Original Article Comparison of different surgical approaches of functional endoscopic sinus surgery on patients with chronic
Mepolizumab, a humanized anti IL-5 mab, as a treatment option for severe nasal polyposis
 Rhinitis, sinusitis, and upper airway disease Mepolizumab, a humanized anti IL-5 mab, as a treatment option for severe nasal polyposis Philippe Gevaert, MD, PhD, a * Nicholas Van Bruaene, MD, a * Tom Cattaert,
Rhinitis, sinusitis, and upper airway disease Mepolizumab, a humanized anti IL-5 mab, as a treatment option for severe nasal polyposis Philippe Gevaert, MD, PhD, a * Nicholas Van Bruaene, MD, a * Tom Cattaert,
Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
 WHAT IS FUNCTIONAL ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY (FESS)? The nasal telescope has greatly changes the evaluation and treatment of rhino-sinusitis. This instrument, which provides a view of the structures in
WHAT IS FUNCTIONAL ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY (FESS)? The nasal telescope has greatly changes the evaluation and treatment of rhino-sinusitis. This instrument, which provides a view of the structures in
Pediatric Endoscopic Sinus Surgery in a Tertiary Government Hospital: Patient Profile and Surgical Indications
 Philippine Journal Of Otolaryngology-Head And Neck Surgery Vol. 4 No. January June ichael Joseph C. David, D Gil. Vicente, D, Antonio H. Chua, D, Jose R. Reyes emorial edical Center St. Luke s edical Center
Philippine Journal Of Otolaryngology-Head And Neck Surgery Vol. 4 No. January June ichael Joseph C. David, D Gil. Vicente, D, Antonio H. Chua, D, Jose R. Reyes emorial edical Center St. Luke s edical Center
A study of causes of nasal obstruction in Garhwal region of Uttarakhand
 Original Research Article Amit Arya 1, R S Bisht 2,*, Venkatashivareddy B 3, Richa Mina 4 1,4 Senior Resident, 2 Professor, Dept. of ENT, 3 Assistant Professor, Dept. of Community Medicine, VCSGGMS & RI
Original Research Article Amit Arya 1, R S Bisht 2,*, Venkatashivareddy B 3, Richa Mina 4 1,4 Senior Resident, 2 Professor, Dept. of ENT, 3 Assistant Professor, Dept. of Community Medicine, VCSGGMS & RI
9/18/2018. Disclosures. Objectives
 Is It Really Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis? Assessment, Differential Diagnosis and Management of Common Sinonasal Symptoms Kristina Haralambides, MS, RN, FNP-C Disclosures The content of this presentation
Is It Really Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis? Assessment, Differential Diagnosis and Management of Common Sinonasal Symptoms Kristina Haralambides, MS, RN, FNP-C Disclosures The content of this presentation
EVALUATION OF PATIENT'S OUTCOME AFTER ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY
 Basrah Journal Of Surgery Bas J Surg, September, 16, 2010 EVALUATION OF PATIENT'S OUTCOME AFTER ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY Hiwa A Abdulkareem MB.ChB, FICMS, CABS(ENT); Teaching Hospital; University of Sulaimania.
Basrah Journal Of Surgery Bas J Surg, September, 16, 2010 EVALUATION OF PATIENT'S OUTCOME AFTER ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY Hiwa A Abdulkareem MB.ChB, FICMS, CABS(ENT); Teaching Hospital; University of Sulaimania.
ENDOSCOPIC LASER SURGERY OF THE MIDDLE MEATUS FOR CHRONIC PARANASAL SINUSITIS
 ENDOSCOPIC LASER SURGERY OF THE MIDDLE MEATUS FOR CHRONIC PARANASAL SINUSITIS Yosaku Shiomi, Nobuya Fujiki*, Kyosuke Kurata* Department of Otolaryngology, Matsue Municipal Hospital, Shimane *Department
ENDOSCOPIC LASER SURGERY OF THE MIDDLE MEATUS FOR CHRONIC PARANASAL SINUSITIS Yosaku Shiomi, Nobuya Fujiki*, Kyosuke Kurata* Department of Otolaryngology, Matsue Municipal Hospital, Shimane *Department
Distinct Inflammatory Profiles in Atopic and Nonatopic Patients With Chronic Rhinosinustis Accompanied by Nasal Polyps in Western China
 Original Article Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 215 July;7(4):346-358. http://dx.doi.org/1.4168/aair.215.7.4.346 pissn 292-7355 eissn 292-7363 Distinct Inflammatory Profiles in Atopic and Nonatopic Patients
Original Article Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 215 July;7(4):346-358. http://dx.doi.org/1.4168/aair.215.7.4.346 pissn 292-7355 eissn 292-7363 Distinct Inflammatory Profiles in Atopic and Nonatopic Patients
Controlled Trial for Long-Term Low-Dose Erythromycin After Sinus Surgery for Chronic Rhinosinusitis
 The Laryngoscope VC 2014 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Controlled Trial for Long-Term Low-Dose Erythromycin After Sinus Surgery for Chronic Rhinosinusitis Boris
The Laryngoscope VC 2014 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Controlled Trial for Long-Term Low-Dose Erythromycin After Sinus Surgery for Chronic Rhinosinusitis Boris
Impact of Asthma in the U.S. per Year. Asthma Epidemiology and Pathophysiology. Risk Factors for Asthma. Childhood Asthma Costs of Asthma
 American Association for Respiratory Care Asthma Educator Certification Prep Course Asthma Epidemiology and Pathophysiology Robert C. Cohn, MD, FAARC MetroHealth Medical Center Cleveland, OH Impact of
American Association for Respiratory Care Asthma Educator Certification Prep Course Asthma Epidemiology and Pathophysiology Robert C. Cohn, MD, FAARC MetroHealth Medical Center Cleveland, OH Impact of
Maximum Medical Therapy of Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Riyadh Alhedaithy R5 ENT Resident, Combined KSUF and SB. 30/12/2015
 Maximum Medical Therapy of Chronic Rhinosinusitis Riyadh Alhedaithy R5 ENT Resident, Combined KSUF and SB. 30/12/2015 ARTICLE REVIEW INTRODUCTION Chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) is a common, debilitating,
Maximum Medical Therapy of Chronic Rhinosinusitis Riyadh Alhedaithy R5 ENT Resident, Combined KSUF and SB. 30/12/2015 ARTICLE REVIEW INTRODUCTION Chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) is a common, debilitating,
Sinusitis what it is and what is SNOT: Updates on therapies and other assorted snacks. Shane Gailushas, MD Mercy Ear, Nose, and Throat Clinic
 Sinusitis what it is and what is SNOT: Updates on therapies and other assorted snacks Shane Gailushas, MD Mercy Ear, Nose, and Throat Clinic ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Factors that predispose patients to Rhinosinusitis:
Sinusitis what it is and what is SNOT: Updates on therapies and other assorted snacks Shane Gailushas, MD Mercy Ear, Nose, and Throat Clinic ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Factors that predispose patients to Rhinosinusitis:
Nasal nitric oxide in relation to quality-of-life improvements after endoscopic sinus surgery DO NOT COPY. American Journal of Rhinology & Allergy
 Nasal nitric oxide in relation to quality-of-life improvements after endoscopic sinus surgery Chia-Hsiang Fu, M.D., 1,2 Chi-Che Huang, M.D., 1,2 Yi-Wei Chen, M.D., 1 Po-Hung Chang, M.D., 1,2 and Ta-Jen
Nasal nitric oxide in relation to quality-of-life improvements after endoscopic sinus surgery Chia-Hsiang Fu, M.D., 1,2 Chi-Che Huang, M.D., 1,2 Yi-Wei Chen, M.D., 1 Po-Hung Chang, M.D., 1,2 and Ta-Jen
MANAGEMENT OF RHINOSINUSITIS IN ADOLESCENTS AND ADULTS
 MANAGEMENT OF RHINOSINUSITIS IN ADOLESCENTS AND ADULTS Ministry of Health Malaysia Malaysian Society of Otorhinolaryngologist - Head & Neck Surgeons (MS)-HNS) Academy of Medicine Malaysia KEY MESSAGES
MANAGEMENT OF RHINOSINUSITIS IN ADOLESCENTS AND ADULTS Ministry of Health Malaysia Malaysian Society of Otorhinolaryngologist - Head & Neck Surgeons (MS)-HNS) Academy of Medicine Malaysia KEY MESSAGES
An Insight into Allergy and Allergen Immunotherapy Co-morbidities of allergic disease
 An Insight into Allergy and Allergen Immunotherapy Co-morbidities of allergic disease Carmen Vidal Athens, September 11, 2014 Pucci S & Incorvaia C, 2008; 153:1-2 1. The major player in driving the immune
An Insight into Allergy and Allergen Immunotherapy Co-morbidities of allergic disease Carmen Vidal Athens, September 11, 2014 Pucci S & Incorvaia C, 2008; 153:1-2 1. The major player in driving the immune
STUDY OF CORRELATION BETWEEN NASAL ENDOSCOPY AND RHINOGENIC HEADACHE Santhosha Kumar B 1, Manjunath Rao S. V 2
 STUDY OF CORRELATION BETWEEN NASAL ENDOSCOPY AND RHINOGENIC HEADACHE Santhosha Kumar B 1, Manjunath Rao S. V 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Santhosha Kumar B, Manjunath Rao S. V. Study of Correlation between
STUDY OF CORRELATION BETWEEN NASAL ENDOSCOPY AND RHINOGENIC HEADACHE Santhosha Kumar B 1, Manjunath Rao S. V 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Santhosha Kumar B, Manjunath Rao S. V. Study of Correlation between
Chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) is a common inflammatory
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Unsupervised cluster analysis of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyp using routinely available clinical markers and its implication in treatment outcomes Jeong-Whun Kim, MD, PhD 1,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Unsupervised cluster analysis of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyp using routinely available clinical markers and its implication in treatment outcomes Jeong-Whun Kim, MD, PhD 1,
Quality of life after functional endoscopic sinus surgery in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis
 Quality of life after functional endoscopic sinus surgery in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis Received: 26/6/2016 Accepted: 13/3/2017 Arsalan Awlla Mustafa Shem* Introduction Chronic Rhinosinusitis
Quality of life after functional endoscopic sinus surgery in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis Received: 26/6/2016 Accepted: 13/3/2017 Arsalan Awlla Mustafa Shem* Introduction Chronic Rhinosinusitis
The advent of high-resolution computerized tomography
 An anatomic classification of the ethmoidal bulla REUBEN C. SETLIFF, III, MD, PETER J. CATALANO, MD, FACS, LISA A. CATALANO, MPH, and CHAD FRANCIS, BA, Sioux Falls, South Dakota, and Burlington, Massachusetts
An anatomic classification of the ethmoidal bulla REUBEN C. SETLIFF, III, MD, PETER J. CATALANO, MD, FACS, LISA A. CATALANO, MPH, and CHAD FRANCIS, BA, Sioux Falls, South Dakota, and Burlington, Massachusetts
An epidemiologic study of factors associated with nasal septum deviation by computed tomography scan: a cross sectional study
 Mohebbi et al. BMC Ear, Nose and Throat Disorders 2012, 12:15 RESEARCH ARTICLE An epidemiologic study of factors associated with nasal septum deviation by computed tomography scan: a cross sectional study
Mohebbi et al. BMC Ear, Nose and Throat Disorders 2012, 12:15 RESEARCH ARTICLE An epidemiologic study of factors associated with nasal septum deviation by computed tomography scan: a cross sectional study
Grafting to denuded nasal cavity for prevention of recurrent nasal polyposis by endoscopic sinus surgery
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Amin H et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Sep;4(5):1135-1141 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Amin H et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Sep;4(5):1135-1141 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937
Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS)
 Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS) Last Review Date: December 12, 2017 Number: MG.MM.SU.56C2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or
Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS) Last Review Date: December 12, 2017 Number: MG.MM.SU.56C2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or
Endoscopic Management Of A Giant Ethmoid Mucocele
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 6 Number 1 S Ceylan, F Bora Citation S Ceylan, F Bora.. The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology. 2006 Volume 6 Number 1. Abstract We present
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 6 Number 1 S Ceylan, F Bora Citation S Ceylan, F Bora.. The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology. 2006 Volume 6 Number 1. Abstract We present
Provider Led Entity. CDI Quality Institute PLE Rhinosinusitis AUC 12/04/2018
 Provider Led Entity CDI Quality Institute PLE Rhinosinusitis AUC 12/04/2018 Appropriateness of advanced imaging procedures* in patients with rhinosinusitis and the following clinical presentations or diagnoses:
Provider Led Entity CDI Quality Institute PLE Rhinosinusitis AUC 12/04/2018 Appropriateness of advanced imaging procedures* in patients with rhinosinusitis and the following clinical presentations or diagnoses:
Total IgE serum levels correlate with sinus mucosal thickness on computerized tomography scans
 Rapid communications Total IgE serum levels correlate with sinus mucosal thickness on computerized tomography scans Fuad M. Baroody, MD, Se-Hoon Suh, MD, and Robert M. Naclerio, MD Chicago, Ill. Background:
Rapid communications Total IgE serum levels correlate with sinus mucosal thickness on computerized tomography scans Fuad M. Baroody, MD, Se-Hoon Suh, MD, and Robert M. Naclerio, MD Chicago, Ill. Background:
Suppression of Cytokine Release by Fluticasone Furoate vs. Mometasone Furoate in Human Nasal Tissue Ex-Vivo
 Suppression of Cytokine Release by Fluticasone Furoate vs. Mometasone Furoate in Human Nasal Tissue Ex-Vivo Nan Zhang 1 *, Koen Van Crombruggen 1, Gabriele Holtappels 1, Feng Lan 1, Michail Katotomichelakis
Suppression of Cytokine Release by Fluticasone Furoate vs. Mometasone Furoate in Human Nasal Tissue Ex-Vivo Nan Zhang 1 *, Koen Van Crombruggen 1, Gabriele Holtappels 1, Feng Lan 1, Michail Katotomichelakis
Chronic rhinosinusitis with polyps and without polyps is associated with increased expression of suppressors of cytokine signaling 1 and 3
 Rhinitis, sinusitis, and upper airway disease Chronic rhinosinusitis with polyps and without polyps is associated with increased expression of suppressors of cytokine signaling 1 and 3 Se Jin Park, MD,
Rhinitis, sinusitis, and upper airway disease Chronic rhinosinusitis with polyps and without polyps is associated with increased expression of suppressors of cytokine signaling 1 and 3 Se Jin Park, MD,
Anatomical Variations in Osteomeatal Complex among Patients undergoing Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
 V Narendrakumar, V Subramanian Original article 10.5005/jp-journals-10013-1259 Anatomical Variations in Osteomeatal Complex among Patients undergoing Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery 1 V Narendrakumar,
V Narendrakumar, V Subramanian Original article 10.5005/jp-journals-10013-1259 Anatomical Variations in Osteomeatal Complex among Patients undergoing Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery 1 V Narendrakumar,
Sinus computed tomography predicts clinical response to corticosteroids in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps
 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13601-018-0211-1 Clinical and Translational Allergy RESEARCH Open Access Sinus computed tomography predicts clinical response to corticosteroids in chronic rhinosinusitis with
https://doi.org/10.1186/s13601-018-0211-1 Clinical and Translational Allergy RESEARCH Open Access Sinus computed tomography predicts clinical response to corticosteroids in chronic rhinosinusitis with
SIGNIFICANCE OF INTERLEUKIN-17A AND INTERLEUKIN-23 IN CHRONIC RHINOSINUSITIS WITH NASAL POLYPS
 Acta Medica Mediterranea, 2017, 33: 211 SIGNIFICANCE OF INTERLEUKIN-17A AND INTERLEUKIN-23 IN CHRONIC RHINOSINUSITIS WITH NASAL POLYPS RAHIME KOCA 1, METE EYIGOR 2, USTUN OSMA 1, HULYA EYIGOR 2, MUSTAFA
Acta Medica Mediterranea, 2017, 33: 211 SIGNIFICANCE OF INTERLEUKIN-17A AND INTERLEUKIN-23 IN CHRONIC RHINOSINUSITIS WITH NASAL POLYPS RAHIME KOCA 1, METE EYIGOR 2, USTUN OSMA 1, HULYA EYIGOR 2, MUSTAFA
Chapter Five. 1 of 8 11/3/2008 2:52 PM.
 1 of 8 11/3/2008 2:52 PM Email : myousefmian@hotmail.com Chapter Five FRONT COVER Introduction Acknowledgement CHAPTERS Chapter One Chapter Two Chapter Three Chapter Four Chapter Five Chapter Six Chapter
1 of 8 11/3/2008 2:52 PM Email : myousefmian@hotmail.com Chapter Five FRONT COVER Introduction Acknowledgement CHAPTERS Chapter One Chapter Two Chapter Three Chapter Four Chapter Five Chapter Six Chapter
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Gene Expression Analysis: Immunoblot analysis: Immunohistochemistry:
 General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
