Case Study. Andrew L. Dunn, MD, 1 Tameika Reed, MT (ASCP), 2 Charlotte Stewart, MT (ASCP), 2 Rebecca A. Levy, MD 1,2 * ABSTRACT
|
|
|
- Adela Deirdre Blake
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Naegleria fowleri That Induces Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis: Rapid Diagnosis and Rare Case of Survival in a 12-Year-Old Caucasian Girl Andrew L. Dunn, MD, 1 Tameika Reed, MT (ASCP), 2 Charlotte Stewart, MT (ASCP), 2 Rebecca A. Levy, MD 1,2 * Laboratory Medicine 47:2: DOI: /labmed/lmw008 ABSTRACT Primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM) is a rare and almost always fatal disease that is caused by Naegleria fowleri, a freshwater thermophilic amoeba. Our case involves an adolescent female who presented with fever of unknown origin. A lumbar puncture was performed, and the Wright-Giemsa and Gram stained cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) cytospin slides showed numerous organisms. Experienced medical technologists in the microbiology and hematology laboratories identified the organisms as morphologically consistent with Naegleria species. The laboratory made a rapid diagnosis and alerted emergency department care providers within 75 minutes. The patient was treated for PAM with amphotericin, rifampin, azithromycin, fluconazole and aggressive supportive therapy including dexamethasone. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) was contacted, and miltefosine, an investigational medication, was started. Additional treatment included an intraventricular shunt and controlled hypothermia in order to mitigate potential cerebral edema. Our patient is a rare success story, as she was diagnosed swiftly, successfully treated, and survived PAM. Keywords: primary amoebic meningocephalitis, Naegleria fowleri, thermophilic amoeba, microbiology, body fluid morphology, and body fluid interpretation Primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM) is a rare disease of the central nervous system (CNS) that is almost always fatal. 1,2 This disease is caused by Naegleria fowleri, a freshwater thermophilic amoeba. Infection is associated with swimming and diving in freshwater lakes, hot springs, ponds, and inadequately chlorinated pools and/or spas. 3 The amoeba enters the body through the nares, travels through the nasal mucosa along the olfactory nerves, across the cribriform plate, and enters the brain. 4 Patients commonly Abbreviations PAM, primary amoebic meningoencephalitis; CNS, central nervous system; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; ED, emergency department; CT, computed tomography; WBCs, white blood cells; RBCs, red blood cells; CDC, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging 1 Department of Pathology, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, 2 Department of Pathology, Clinical Laboratory Arkansas Children s Hospital, Little Rock *To whom correspondence should be addressed. RALevy@uams.edu experience fever, headache, nausea, vomiting, stiff neck, and, occasionally seizures. N. fowleri and its associated inflammatory reaction, including the release of cytotoxic molecules, cause extensive tissue damage and necrosis. 5,6 The sequelae include acute necrotizing meningoencephalitis and usually result in death in 7 to 10 days. Other flagellates found in the environment include several species of Acanthamoeba and Balamuthia mandrillaris, both of which can cause granulomatous amoebic encephalitis. It is important to consider these entities when evaluating PAM. Eight different types of the Naegleria fowleri pathogen show an uneven distribution throughout the world; 3 of those types have been identified within the United States. 1,2 Two patients in North America have been reported to have welldocumented treatments and survival despite contracting PAM. 7,8 The case of our patient, a 12-year-old proband girl from Arkansas, represents the third case of reported survival. The unique and experimental treatment plan for this individual is well described in an article by Matthew Linam, MD, an infectious disease specialist at Arkansas Children s VC American Society for Clinical Pathology, All rights reserved. For permissions, please journals.permissions@oup.com 149
2 Image 1 Naegleria fowleri on Wright-Giemsa stained cerebrospinal fluid cytospin slides (original magnification, 1000; oil immersion). Arrows indicate Naegleria organisms. Specimen was donated by our patient, a 12-year-old Caucasian girl. Hospital in Little Rock. 9 However, the speed of the diagnosis and the impact of this speed on the treatment algorithm have not yet been described in the literature, to our knowledge. PAM is a rare occurrence and is not often considered as a likely diagnosis; therefore, the laboratory s identification of the microorganism may be the first time an amoebic etiology is considered. This rapid identification can help avoid delays in diagnosis and therapy. Cytologic analysis of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in patients with PAM typically shows an increase in neutrophils; trophozoites of Naegleria can be identified in the CSF via Wright-Giemsa stain. 10,11 Earlier studies 12,13 have shown that CSF should be evaluated immediately after a lumbar puncture procedure for best leukocyte survival. CSF is a hypotonic solution, and leukocytes will lyse if left in the medium; specifically, neutrophils lyse more rapidly than lymphocytes and monocytes. 12 Manual microscopy is the criterion standard for bodily-fluid evaluation; 14 assessment of Wright-Giemsa and Gram stains also can be helpful, in combination with patient history, in initiating a treatment course for infectious disease while waiting for the results of confirmatory cultures or polymerase chain reaction (PCR) studies. 150 Lab Medicine 2016;47:2; DOI: /labmed/lmw008
3 Image 2 Naegleria fowleri on Gram-stained cerebrospinal fluid cytospin slides (original magnification, 500; oil immersion). Arrows indicate Naegleria organisms. Specimen was donated by our patient, a 12-year-old Caucasian girl. Case Presentation A previously healthy 12-year-old Caucasian female girl arrived at the emergency department (ED) with a 3-day history of headache, lethargy, and fever (temperature of 103 F). In the 12 hours before her arrival, she had developed nausea and vomiting. A computed tomography (CT) scan of her head yielded normal findings. A complete blood count identified mild neutrophilic leukocytosis and normocytic anemia. A lumbar puncture was performed; the results revealed leukocytosis with a predominance of neutrophils (Image 1). Wright-Giemsa and Gram stains, performed on slides and processed via a Cytospin instrument (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc), yielded positive results for numerous organisms. Medical technologists in the hematology and microbiology laboratories identified the organisms as morphologically consistent with Naegleria species (Image 1 and Image 2) and informed the ED staff of their test result interpretation 75 minutes after receiving the CSF specimen. The preanalytic and analytic stages of CSF evaluation can greatly affect diagnosis. At our institution, protocol dictates that all fluids be sent to the laboratory for analysis immediately and handled on a STAT (immediate) basis because lysis of cells takes place soon after removal from the body, generally within 1 hour of collection. 12 The specimen is evaluated grossly for color, turbidity, and the appearance of the supernatant. Next, slides are prepared via Cytospin centrifugation, and a cell count is performed on a hemacytometer for white blood cells (WBCs) and red blood cells (RBCs). The 2 Wright-Giemsa stained slides that had been prepared via Cytospin are reviewed, and a medical technologist performs a WBC differential count. In the case of this patient, her CSF was described as milky in color, with increased turbidity and a colorless supernatant. The WBC count was 3675 per ml and the RBC count was 53 per ml; a manual differential of 100 cells identified 86% neutrophils, 1% bands, 2% lymphocytes, 9% monocytes, and 2% other cells. Usually, a single Gram-stained slide is prepared. However, due to the turbid nature of the fluid, the elevated WBC count, and the increased neutrophil count, the microbiology technologist (T.R.), concerned about the possibility of meningitis, prepared 2 Gram-stained slides from CSF specimens, processed them via Cytospin, and examined them immediately. Lab Medicine 2016;47:2; DOI: /labmed/lmw008
4 Senior medical technologists in the hematology and mircobiology laboratories identified the organisims as morphologically consistent with Naegleria species Medical technologists informed in ED staff approximately 1 hour after receiving the CSF specimen Infectious Disease was consulted immediately and the patient was treated for PAM with amphotericin, rifampin, azithromycin, fluconazole, and dexamethasone (to control for cerebral edema) CDC was contacted and Miltefosine, an investigational medication, was started on day 2 of hospitalization Amoeba culture on CSF identified amoebae, consistent with Naegleria species Real time PCR was performed at the CDC: Positive for Naegleria fowleri Real time PCR was performed at the CDC: Negative for Acanthamoeba and Balamuthia mandrillaris Figure 1 Laboratory and clinical follow-up in treating the patient, a 12-year-old Caucasian girl. ED refers to emergency department; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; PAM, primary amoebic meningoencephalitis; CDC, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; PCR, polymerase chain reaction. In this case, the suspicious organisms were first identified in the Gram-stained smear by a microbiology technologist. She subsequently, the microbiology technologist evaluated the Wright-Giemsa stained slides processed via Cytospin in the Hematology division with 2 hematology technologists, including the shift supervisor, and came to the conclusion of suspicious organisms resembling amoebae: likely, Naegleria species. The Naegleria trophozoites are large, round to pear-shaped cells with a prominent, dark nucleus and scattered vacuoles. On Gram staining, the cells can appear similar to macrophages; however, the cytoplasm of the amoebae has a well-defined border. The diagnosis is noteworthy because the clinical findings at the time of diagnosis included fever, headache, and lethargy, all of these symptoms are nonspecific and offer a diverse differential diagnosis. At the time of the laboratory findings, no evidence existed in the clinical record that PAM was a considered or suspected diagnosis at that time. On the discovery of amoeba in the CSF, additional history indicated the patient had been swimming at a freshwater park 1 week before her arrival at the ER. Clinical Follow-Up Immediately after the ED physicians received the CSF results, they consulted the Division of Infectious Disease and began to treat the patient for PAM with amphotericin, rifampin, azithromycin, and fluconazole. She also received 152 Lab Medicine 2016;47:2; DOI: /labmed/lmw008
5 aggressive supportive therapy, including dexamethasone, to control for cerebral edema. The ED physicians contacted the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and on day 2 of hospitalization, they started the patient on miltefosine, an investigational medication, at 50 mg enterally every 8 hours. Amoeba culture of CSF was performed by a reference laboratory; the results identified the presence of amoebae, consistent with Naegleria species. Culture results were reported to the clinical team within 48 hours of the initial arrival of the patient at the ED. Laboratory professionals at the CDC performed real-time PCR on specimens from the patient; the results were positive for N. fowleri (Figure 1). The patient received 27 days of treatment with antifungals and antibiotics, in addition to placement of an external ventricular drain, hyperosmolar treatment with mannitol, and induced hypothermia to lower intracranial pressure. 9 The results of repeat CSF studies during hospital days 10 through 16 all had negative results for microorganisms. Further brain imaging showed significant improvement, with resolution of parenchymal edema. The patient made a full recovery after 52 days of hospitalization. At her 1-year follow-up visit, the patient was functioning at baseline. Follow-up magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain, performed 1 year after the patient was fully cured of PAM, identified subtle gliosis of both cerebral hemispheres involving the cortex and white matter. Gliosis is a nonspecific finding of reactive changes to the brain tissue. A subsequent MRI at the 18-month follow-up visit revealed some encephalomalacia of the left frontal lobe and cerebellum, with optic nerves having unremarkable characteristics. Encephalomalacia is a softening or degeneration of brain tissue; it is secondary to the inflammatory immune response to the amoeba infection. We observed no acute abnormalities via MRI. Discussion N. fowleri is a free-living, thermophilic amoeba commonly found in soil and stagnant freshwater locations, especially in the southern United States. 15 A fatal case of PAM was reported as far north as Minnesota, 16 which highlights the importance of clinical suspicion and history regardless of geography. N. fowleri infection begins by the amoebae entering the nasal cavity, usually through introduction of water via submersion, diving, or splashing. After rapidly tracking along the olfactory nerves and through the cribriform plate, the amoebae are able to bind to extracellular matrix glycoproteins on human host cells. Several pathogenic mechanisms enable the amoeba to harm its host, including secretion of pore-forming proteins, proteases, and phospholipases, all of which likely contribute to demyelination. This destruction leads to the lysis of erythrocytes and surrounding nerve cells. The amoeba also has immune-evasion mechanisms such as removal of the membrane attack complex and resistance to cytokines. 4 PAM has a variable incubation time, ranging from 1 day to as long as 7 days. 17 The clinical signs have similarities with those of bacterial and viral meningitis, including fever, neck stiffness, and severe headaches. 18 Symptoms can progress to prolonged nausea, vomiting, and even seizures. The disease can progress to acute hemorrhagic necrotizing meningoencephalitis, which can lead to death in as soon as 7 to 10 days. 4 CSF analysis reveals increased intracranial pressure, an increase in neutrophils, and the presence of amebic trophozoites consistent with N. fowleri. A variable delay in treatment can be secondary to time intervals in multiple stages of care, including exposure to exhibition of symptoms; arrival for treatment at a health care facility; workup of the diagnosis (initial diagnosis of likely bacterial meningitis); 16 and finally, from diagnosis to initiation of recommended therapy. Published data have shown that as many as 40% of WBCs in CSF may lyse after 2 hours at room temperature. 19 Results of another study 12 verified that CSF has a decrease in neutrophil counts at 1 hour by 32% and at 2 hours by 50%. Other bodily fluids may show a similar decrease in cell counts at room temperature. Therefore, our institutional policy is that cell counts should be performed for all fluid specimens within 2 hours of collection. If a delay is anticipated, the specimen should be refrigerated. At our institution, our goal is to interpret bodily fluid results generally within 1 hour on all shifts. In the case we have described herein, our hematology and microbiology technologists identified an unusual organism, diagnosed it as an amoeba (N. fowleri), and reported the result within 1 hour and 15 minutes of the specimen being received in the laboratory. The speed of the microscopic evaluation and diagnosis played a major role in the ability of the clinical teams to provide aggressive treatment and novel therapies to the patient. Lab Medicine 2016;47:2; DOI: /labmed/lmw008
6 Pediatric practitioners, especially those who practice in the southern United States during the summer months, should be careful to include this differential in the setting of meningitis-like symptoms. 15 Further, this diagnosis should be considered by medical technologists when evaluating a CSF specimen that has indicators of meningitis, including turbid fluid, elevated WBC count, and increased neutrophil count. Successful treatment of PAM is a rare occurrence and can only be attempted after correct diagnosis, which relies on rapid recognition of the microorganism by medical technologists and pathologists. In our patient, prompt diagnosis, followed by rapid communication with the treating physicians in the ED and consultation with Infectious Disease specialists, led to the patient being fully cured of PAM. Therefore, it is critical that medical technologists consistently provide timely CSF evaluation, explore the diagnosis of PAM, and look for amoebae in the setting of meningitis, especially in the summertime. LM References 1. De Jonckheere JF.What do we know by now about the genus Naegleria? Exp Parasitol. 2014;145(Suppl):S2 S9. 2. De Jonckheere JF.Origin and evolution of the worldwide distributed pathogenic amoebaflagellate Naegleria fowleri. Infect Genet Evol. 2011;11(7): Heggie TW. Swimming with death: Naegleria fowleri infections in recreational waters. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2010;8(4): Marciano-Cabral F, Cabral GA. The immune response to Naegleria fowleri amebae and pathogenesis of infection. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2007;51: Grace E, Asbill S, Virga K. Naegleria fowleri: pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment options. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59(11): Rojas-Hernandez S, Jarillo-Luna A, Rodriguez-Monroy M, Moreno- Fierros L, Campos-Rodriguez R. Immunohistochemical characterization of the initial stages of Naegleria fowleri meningoencephalitis in mice. Parasitol Res. 2004;94(1): Seidel JS, Harmatz P, Visvesvara GS, Cohen A, Edwards J, Turner J. Successful treatment of primary amebic meningocephalitis. N Engl J Med. 1982;306(6): Vargas-Zepeda J, Gomez-Alcala AV, Vasquez-Morales JA, Licea-Amaya L, De Jonckheere JF, Lares-Villa F. Successful treatment of Naegleria fowleri meningoencephalitis by using intravenous amphotericin B, fluoconazole and rifampicin. Arch Med Res. 2005;36(1): Linam WM, Ahmed M, Cope JR, et al. Successful treatment of an adolescent with Naegleria fowleri primary amebic meningoencephalitis. Pediatrics. 2015;135(3):e744 e Visvesvara GS, Moura H, Schuster FL. Pathogenic and opportunistic free-living amoebae: Acanthamoeba spp., Balamuthia mandrillaris, Naegleria fowleri, and Sappinia diploidea. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2007;50: Martınez AJ. Free-living amebas: natural history, prevention, diagnosis, pathology, and treatment of disease. CRC Press. 1985; Steele RW, Marmer DJ, O Brien MD, Tyson ST, Steele CR. Leukocyte survival in cerebrospinal fluid. J Clin Microbiol.1986;23(5): Deisenhammer A, Baros A, Egg R, Gilhus NE, Giovannoni G, Rauer S, Sellebjerg F. Guidelines on routine cerebrospinal fluid analysis. Report from an EFNS task force. Eur J Neurol. 2006;13: Fleming C, Russcher H, Lindemans J, de Jonge R. Clinical relevance and contemporary methods for counting blood cells in body fluid suspected of inflammatory disease. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2015;53: Lopez C, Budge P, Chen J, et al. Primary amebic meningoencephalitis: a case report and literature review. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2012;28(3): Kemble SK, Lynfield R, DeVries AS, et al. Fatal Naegleria fowleri infection acquired in Minnesota: possible expanded range of a deadly thermophilic organism. Clin Infect Dis. 2012;54(6): Yoder JS, Eddy BA, Visvesvara GS, Capewell L, Beach MJ. The epidemiology of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis in the USA, Epidemiol Infect. 2010;138(7): Abrahams-Sandı E, Retana-Moreira L, Castro-Castillo A, Reyes-Batlle M, Lorenzo-Morales J. Fatal meningoencephalitis in child and isolation of Naegleria fowleri from hot springs in Costa Rica. Emerg Infect Dis. 2015;21(2): Dux R, Kindler-R ohrborn A, Annas M, Faustmann P, Lennartz K, Zimmerman CW. A standardized protocol for flow cytometric analysis of cells isolated from cerebrospinal fluid. J Neurol Sci. 1994;121: Lab Medicine 2016;47:2; DOI: /labmed/lmw008
Downloaded from:
 Phu, NH; Hoang Mai, NT; Nghia, HD; Chau, TT; Loc, PP; Thai, leh; Phuong, TM; Thai, CQ; Man, DN; Van Vinh Chau, N; Nga, TV; Campbell, J; Baker, S; Whitehorn, J (2013) Fatal consequences of freshwater pearl
Phu, NH; Hoang Mai, NT; Nghia, HD; Chau, TT; Loc, PP; Thai, leh; Phuong, TM; Thai, CQ; Man, DN; Van Vinh Chau, N; Nga, TV; Campbell, J; Baker, S; Whitehorn, J (2013) Fatal consequences of freshwater pearl
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 8 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia)
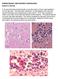 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 8 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 12 year-old male presented with a one-day history of fever and headache on the right side. Two days after admission, he developed a stiff neck
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 8 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 12 year-old male presented with a one-day history of fever and headache on the right side. Two days after admission, he developed a stiff neck
LASOP Case Presentation. Andrea D Auria, D.O. University of Southern California Department of Pathology
 LASOP Case Presentation Andrea D Auria, D.O. University of Southern California Department of Pathology Clinical Presentation 62 year old male With a history of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis 2 months status
LASOP Case Presentation Andrea D Auria, D.O. University of Southern California Department of Pathology Clinical Presentation 62 year old male With a history of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis 2 months status
Critical Masses. MIDG October 2015 Myra Hardy, Jeremy Carr, Tony He, Nigel Curtis
 Critical Masses MIDG October 2015 Myra Hardy, Jeremy Carr, Tony He, Nigel Curtis Case 2 16yo F 2 weeks focal seizures Intermittent left hemiparesis and sensory symptoms Headache PMHX: Asthma on Seretide
Critical Masses MIDG October 2015 Myra Hardy, Jeremy Carr, Tony He, Nigel Curtis Case 2 16yo F 2 weeks focal seizures Intermittent left hemiparesis and sensory symptoms Headache PMHX: Asthma on Seretide
Unusual Presentation of Multiple Nerve Palsies with Granulomatous encephalitis Due to Acanthamoeba Species
 Human Parasitic Diseases Case report Open Access Full open access to this and thousands of other papers at http://www.la-press.com. Unusual Presentation of Multiple Nerve Palsies with Granulomatous encephalitis
Human Parasitic Diseases Case report Open Access Full open access to this and thousands of other papers at http://www.la-press.com. Unusual Presentation of Multiple Nerve Palsies with Granulomatous encephalitis
After Reading discuss the following: 1. Based on the article, will you change any of your swimming habits? Why or Why not?
 As you read: Demonstrate evidence of a close reading by marking segments that are important, segments that are confusing, issues that your group should discuss. Common Core Reading Practice Article of
As you read: Demonstrate evidence of a close reading by marking segments that are important, segments that are confusing, issues that your group should discuss. Common Core Reading Practice Article of
Section 9: Amebic Meningitis/Encephalitis
 Section 9: Amebic Meningitis/Encephalitis BASIC EPIDEMIOLOGY Infectious Agent Naegleria fowleri, Acanthamoeba spp. and Balamuthia are microscopic, free-living amebae (single-celled living organisms). Naegleria
Section 9: Amebic Meningitis/Encephalitis BASIC EPIDEMIOLOGY Infectious Agent Naegleria fowleri, Acanthamoeba spp. and Balamuthia are microscopic, free-living amebae (single-celled living organisms). Naegleria
Case Report Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis in an Iranian Infant
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 782854, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/782854 Case Report Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis in an Iranian Infant Zahra Movahedi, 1 Mohammad Reza Shokrollahi,
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 782854, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/782854 Case Report Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis in an Iranian Infant Zahra Movahedi, 1 Mohammad Reza Shokrollahi,
Naegleria fowleri: A Review of the Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
 AAC Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 10 August 2015 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.01293-15 Copyright 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Naegleria fowleri:
AAC Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 10 August 2015 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.01293-15 Copyright 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Naegleria fowleri:
Clinical Information on West Nile Virus (WNV) Infection
 Clinical Information on West Nile Virus (WNV) Infection Introduction In 1999, West Nile Virus (WNV), an Old World flavivirus, producing a spectrum of disease including severe meningoencephalitis, appeared
Clinical Information on West Nile Virus (WNV) Infection Introduction In 1999, West Nile Virus (WNV), an Old World flavivirus, producing a spectrum of disease including severe meningoencephalitis, appeared
LAB DETECTION OF NAEGLERIA FOWLERI: CONTINUING EDUCATION VIDEO
 LAB DETECTION OF NAEGLERIA FOWLERI: CONTINUING EDUCATION VIDEO An educational video for all clinical laboratory personnel. Produced by The Jordan Smelski Foundation for Amoeba Awareness http://www.jordansmelskifoundation.org/
LAB DETECTION OF NAEGLERIA FOWLERI: CONTINUING EDUCATION VIDEO An educational video for all clinical laboratory personnel. Produced by The Jordan Smelski Foundation for Amoeba Awareness http://www.jordansmelskifoundation.org/
Pathogenic Free-Living Amebae
 Pathogenic Free-Living Amebae Naegleria fowleri primary amebic meningoencephalitis (PAM) Acanthamoeba spp. granulomatous amebic encephalitis (GAE) granulomatous skin and lung lesions (primarily immunocompromised)
Pathogenic Free-Living Amebae Naegleria fowleri primary amebic meningoencephalitis (PAM) Acanthamoeba spp. granulomatous amebic encephalitis (GAE) granulomatous skin and lung lesions (primarily immunocompromised)
SHASTA COUNTY Health and Human Services Agency
 FROM: 530 229 8447 TO: 15302293984 08/06/14 12:30 Pg 1 of 5 especially SHASTA COUNTY Health and Human Services Agency Public Health 2650RreslauerWay Redding, CA 96001-4297 (530) 229-8484 FAX (530) 225-3743
FROM: 530 229 8447 TO: 15302293984 08/06/14 12:30 Pg 1 of 5 especially SHASTA COUNTY Health and Human Services Agency Public Health 2650RreslauerWay Redding, CA 96001-4297 (530) 229-8484 FAX (530) 225-3743
Successful Treatment of Granulomatous Amoebic Encephalitis with Combination Antimicrobial Therapy
 CASE REPORT Successful Treatment of Granulomatous Amoebic Encephalitis with Combination Antimicrobial Therapy Hideki Kato 1, Shigehisa Mitake 1, Hiroyuki Yuasa 1, Shigemasa Hayashi 2, Tatsuru Hara 3 and
CASE REPORT Successful Treatment of Granulomatous Amoebic Encephalitis with Combination Antimicrobial Therapy Hideki Kato 1, Shigehisa Mitake 1, Hiroyuki Yuasa 1, Shigemasa Hayashi 2, Tatsuru Hara 3 and
FREE-LIVING PROTOZOA. PAM GAE; skin or lung lesions amebic keratitis; GAE; skin or lung lesions
 FREE-LIVING PROTOZOA Ameba Naegleria fowleri Acanthamoeba sp. Balamuthia mandrillaris Diseases PAM GAE; skin or lung lesions amebic keratitis; GAE; skin or lung lesions Naegleria fowleri ubiquitous in
FREE-LIVING PROTOZOA Ameba Naegleria fowleri Acanthamoeba sp. Balamuthia mandrillaris Diseases PAM GAE; skin or lung lesions amebic keratitis; GAE; skin or lung lesions Naegleria fowleri ubiquitous in
Pathogenic amoebae and ciliate. Dr. Narissara Jariyapan Department of Parasitology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University
 Pathogenic amoebae and ciliate Dr. Narissara Jariyapan Department of Parasitology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University Objectives After the lecture, students must know 1. General morphology of pathogenic
Pathogenic amoebae and ciliate Dr. Narissara Jariyapan Department of Parasitology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University Objectives After the lecture, students must know 1. General morphology of pathogenic
Brain abscess rupturing into the lateral ventricle causing meningitis: a case report
 Brain abscess rupturing into the lateral ventricle causing meningitis: a case report Endry Martinez, and Judith Berger SBH Health System, 4422 Third Ave, Bronx, NY 10457 Key words: brain abscess, rupture
Brain abscess rupturing into the lateral ventricle causing meningitis: a case report Endry Martinez, and Judith Berger SBH Health System, 4422 Third Ave, Bronx, NY 10457 Key words: brain abscess, rupture
CNS parasitic infections. Jarmila Klieščiková, MD 1.LF UK
 CNS parasitic infections Jarmila Klieščiková, MD 1.LF UK Cosmopolite distribution Low prevalence Interference with underlying diseases (immunocompromised state) Treatment not always available Main pathogens
CNS parasitic infections Jarmila Klieščiková, MD 1.LF UK Cosmopolite distribution Low prevalence Interference with underlying diseases (immunocompromised state) Treatment not always available Main pathogens
SCREENING OF ANTI-AMOEBIC ACTIVITY ON NAEGLERIA FOWLERI IN EXTRACTS OF THAI MEDICINAL PLANTS
 SCREENING OF ANTI-AMOEBIC ACTIVITY ON NAEGLERIA FOWLERI IN EXTRACTS OF THAI MEDICINAL PLANTS Tarmphong Luangboribun 1,2, Supathra Tiewcharoen 1, Jundee Rabablert 3, Prasert Auewarakul 2, Natchagorn Lumlerdkij
SCREENING OF ANTI-AMOEBIC ACTIVITY ON NAEGLERIA FOWLERI IN EXTRACTS OF THAI MEDICINAL PLANTS Tarmphong Luangboribun 1,2, Supathra Tiewcharoen 1, Jundee Rabablert 3, Prasert Auewarakul 2, Natchagorn Lumlerdkij
ENCEPHALITIS. Diana Montoya Melo
 ENCEPHALITIS Diana Montoya Melo 4 yo female patient, brought to the ED after having a GTC seizure 30 mins ago, which lasted up to a min. Mom reports that he has a ho 3 days of fever and runny nose, associated
ENCEPHALITIS Diana Montoya Melo 4 yo female patient, brought to the ED after having a GTC seizure 30 mins ago, which lasted up to a min. Mom reports that he has a ho 3 days of fever and runny nose, associated
Detail PRINCIPLE: Body fluids other than blood and urine will be analyzed according to their site of origin, and the providers specific orders.
 Subject Body Fluid Analysis - Affiliate Index Number Lab-8760 Section Laboratory Subsection Regional/Affiliates Category Departmental Contact Munson, Karen Last Revised 6/28/2017 References Required document
Subject Body Fluid Analysis - Affiliate Index Number Lab-8760 Section Laboratory Subsection Regional/Affiliates Category Departmental Contact Munson, Karen Last Revised 6/28/2017 References Required document
Case Report Three Cases of Neoplastic Meningitis Initially Diagnosed with Infectious Meningitis in Emergency Department
 Case Reports in Emergency Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 561475, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/561475 Case Report Three Cases of Neoplastic Meningitis Initially Diagnosed with Infectious Meningitis
Case Reports in Emergency Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 561475, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/561475 Case Report Three Cases of Neoplastic Meningitis Initially Diagnosed with Infectious Meningitis
Helpful Information for evaluation of new neurological symptoms in patients receiving TYSABRI
 Helpful Information for evaluation of new neurological symptoms in patients receiving TYSABRI This information is provided as an educational resource for healthcare providers and should be considered current
Helpful Information for evaluation of new neurological symptoms in patients receiving TYSABRI This information is provided as an educational resource for healthcare providers and should be considered current
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 3/12/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 11 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 3/12/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 11 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 15 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia)
 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 15 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A biopsy was performed on a 27-year-old man with no known travel history, presenting with a perianal ulcer. The specimen was preserved in formalin
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 15 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A biopsy was performed on a 27-year-old man with no known travel history, presenting with a perianal ulcer. The specimen was preserved in formalin
Innate Immunity. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Innate Immunity Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The vertebrate, including human, immune system is a complex multilayered system for defending against external and internal threats to the integrity of the body. The
Innate Immunity Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The vertebrate, including human, immune system is a complex multilayered system for defending against external and internal threats to the integrity of the body. The
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DISTINGUISHING MORPHOLOGIC LOOK-ALIKES
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DISTINGUISHING MORPHOLOGIC LOOK-ALIKES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DISTINGUISHING MORPHOLOGIC LOOK-ALIKES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
Free Living Ameba Case Report
 Revised 1/27/2012 Free Living Ameba Case Report CDC USE ONLY Date of Report: Demographics Patient s Last Name First M.I. Age Gender: Ethnicity: Hispanic n-hispanic Race: White Black Asian/Pacific Islander
Revised 1/27/2012 Free Living Ameba Case Report CDC USE ONLY Date of Report: Demographics Patient s Last Name First M.I. Age Gender: Ethnicity: Hispanic n-hispanic Race: White Black Asian/Pacific Islander
Unit VIII Problem 6 Pathology: Meningitis
 Unit VIII Problem 6 Pathology: Meningitis - Important terms: Meningitis: it is inflammation of meninges (coverings of the central nervous system) caused by infection. They are classified to: Pachymeningitis:
Unit VIII Problem 6 Pathology: Meningitis - Important terms: Meningitis: it is inflammation of meninges (coverings of the central nervous system) caused by infection. They are classified to: Pachymeningitis:
COPYRIGHT 2012 THE TRANSVERSE MYELITIS ASSOCIATION. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
 The Transverse Myelitis Association...advocating for those with acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, neuromyelitis optica, optic neuritis and transverse myelitis ACUTE DISSEMINATED ENCEPHALOMYELITIS (ADEM)
The Transverse Myelitis Association...advocating for those with acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, neuromyelitis optica, optic neuritis and transverse myelitis ACUTE DISSEMINATED ENCEPHALOMYELITIS (ADEM)
Neuropathology Inflammation, Infection, Demyelination in the CNS
 Neuropathology Inflammation, Infection, Demyelination in the CNS PathoBasic 2016-09-20 Jürgen Hench Inflammation in the CNS inflammation generally as a reaction against pathogen, substance, necrotic, or
Neuropathology Inflammation, Infection, Demyelination in the CNS PathoBasic 2016-09-20 Jürgen Hench Inflammation in the CNS inflammation generally as a reaction against pathogen, substance, necrotic, or
African Trypanosomes
 African Trypanosomes Giemsa-stained blood smear of African trypanosomes viewed under the 100X objective lens. The block arrows denote trypomastigote forms of the African trypanosomes found within the blood
African Trypanosomes Giemsa-stained blood smear of African trypanosomes viewed under the 100X objective lens. The block arrows denote trypomastigote forms of the African trypanosomes found within the blood
Free living amoebae and human disease
 Free living amoebae and human disease Evan Bursle Sullivan Nicolaides Pathology Whitmore Street Taringa, Qld 4068, Australia Email: evanbursle@gmail.com Jennifer Robson Sullivan Nicolaides Pathology Whitmore
Free living amoebae and human disease Evan Bursle Sullivan Nicolaides Pathology Whitmore Street Taringa, Qld 4068, Australia Email: evanbursle@gmail.com Jennifer Robson Sullivan Nicolaides Pathology Whitmore
Definitions. Canine Encephalitis. Neurodiagnostic Tools. Neurologic Examination. CSF Risks and Drawbacks. CSF Analysis
 Definitions Canine Encephalitis Christopher L. Mariani, DVM, PhD, DACVIM (Neurology) Assistant Professor College of Veterinary Medicine North Carolina State University Encephalitis: Inflammation of the
Definitions Canine Encephalitis Christopher L. Mariani, DVM, PhD, DACVIM (Neurology) Assistant Professor College of Veterinary Medicine North Carolina State University Encephalitis: Inflammation of the
MINI REVIEW PRIMARY MENINGOENCEPHALITIS CAUSED BY NAEGLERIA FOWLERI: A MINI REVIEW
 MINI REVIEW PRIMARY MENINGOENCEPHALITIS CAUSED BY NAEGLERIA FOWLERI: A MINI REVIEW Hassan Bin-Asif, Syed Abid Ali * H.E.J. Research Institute of Chemistry, International Centre for Chemical and Biological
MINI REVIEW PRIMARY MENINGOENCEPHALITIS CAUSED BY NAEGLERIA FOWLERI: A MINI REVIEW Hassan Bin-Asif, Syed Abid Ali * H.E.J. Research Institute of Chemistry, International Centre for Chemical and Biological
Viral Meningitis. 2. Use the information on the Possible Diseases sheet to complete the other four columns in the chart.
 Disease Detectives Part 1: What is wrong with Mike? Yesterday, Mike Wright developed a severe headache, a high fever, and a stiff neck. Then, he became nauseated and began vomiting. He just wanted medicine
Disease Detectives Part 1: What is wrong with Mike? Yesterday, Mike Wright developed a severe headache, a high fever, and a stiff neck. Then, he became nauseated and began vomiting. He just wanted medicine
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings of Eosinophilic Meningoencephalitis Caused by Angiostrongyliasis
 Chin J Radiol 2001; 26: 45-49 45 CASE REPORT Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings of Eosinophilic Meningoencephalitis Caused by Angiostrongyliasis TSYH-JYI HSIEH 1 GIN-CHUNG LIU 1 CHUAN-MIN YEN 2 YU-TING
Chin J Radiol 2001; 26: 45-49 45 CASE REPORT Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings of Eosinophilic Meningoencephalitis Caused by Angiostrongyliasis TSYH-JYI HSIEH 1 GIN-CHUNG LIU 1 CHUAN-MIN YEN 2 YU-TING
Case Report. Herpes simplex virus encephalitis presenting as frontal lobe hemorrhage
 1 Case Report Herpes simplex virus encephalitis presenting as frontal lobe hemorrhage Authors: Shila, MD, *Jessica Erfan, MPAS, PA-C, Ray Bogitch, MD, Jefferson T. Miley, MD Department of Neurology, Dell
1 Case Report Herpes simplex virus encephalitis presenting as frontal lobe hemorrhage Authors: Shila, MD, *Jessica Erfan, MPAS, PA-C, Ray Bogitch, MD, Jefferson T. Miley, MD Department of Neurology, Dell
Isolation and Genotyping of Acanthamoeba Strains from Corneal Scraps
 Isolation and Genotyping of Acanthamoeba Strains from Corneal Scraps MirMostafa Ghamilouie, MSc 1 Zarrintaj Valadkhani, PhD 1 Firoozeh Rahimi, MD 2 Fariba Khoshzaban, PhD 3 Zohreh Aghighi, MSc 1 Nayerreh
Isolation and Genotyping of Acanthamoeba Strains from Corneal Scraps MirMostafa Ghamilouie, MSc 1 Zarrintaj Valadkhani, PhD 1 Firoozeh Rahimi, MD 2 Fariba Khoshzaban, PhD 3 Zohreh Aghighi, MSc 1 Nayerreh
Pneumococcal Meningitis Meningitis is an inflammation of the lining around the brain and spinal cord. Most severe cases
 Pneumococcal Meningitis Meningitis is an inflammation of the lining around the brain and spinal cord. Most severe cases are caused by bacteria. Pneumococcal bacteria (Streptococcus pneumoniae) are the
Pneumococcal Meningitis Meningitis is an inflammation of the lining around the brain and spinal cord. Most severe cases are caused by bacteria. Pneumococcal bacteria (Streptococcus pneumoniae) are the
Protozoa: Introduction and classification Amoebae I. Pathogenic amoebae: Entamoeba histolytica, Naegleria fowleri, Acanthamoeba spp.
 Protozoa: Introduction and classification Amoebae I. Pathogenic amoebae: Entamoeba histolytica, Naegleria fowleri, Acanthamoeba spp. Nimit Morakote, Ph.D. 1 Protozoa-Simple classification Amoebapseudopodium(a)
Protozoa: Introduction and classification Amoebae I. Pathogenic amoebae: Entamoeba histolytica, Naegleria fowleri, Acanthamoeba spp. Nimit Morakote, Ph.D. 1 Protozoa-Simple classification Amoebapseudopodium(a)
Granulomatous amebic encephalitis in a child with acute. lymphoblastic leukemia successfully treated with
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 17 November 2010 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.01456-10 Copyright 2010, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 17 November 2010 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.01456-10 Copyright 2010, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All
BIOCYT. Revista BIOCYT es editada en la Facultad de Estudios Superiores Iztacala, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México
 BIOCYT www.iztacala.unam.mx/biocyt 7(25): 474-48, 204 ISSN 2007-2082 enero-marzo Revista BIOCYT es editada en la Facultad de Estudios Superiores Iztacala, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México PATHOGENIC
BIOCYT www.iztacala.unam.mx/biocyt 7(25): 474-48, 204 ISSN 2007-2082 enero-marzo Revista BIOCYT es editada en la Facultad de Estudios Superiores Iztacala, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México PATHOGENIC
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY #14 (BLOOD PARASITES) (Lynne S. Garcia)
 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY #14 (BLOOD PARASITES) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 37-year-old woman, who had traveled to New Guinea for several weeks, presented to the medical clinic with fever, chills, and rigors within
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY #14 (BLOOD PARASITES) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 37-year-old woman, who had traveled to New Guinea for several weeks, presented to the medical clinic with fever, chills, and rigors within
Role of MRI in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis
 Original Research Article Role of MRI in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis Shashvat Modiya 1*, Jayesh Shah 2, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 1 st year resident, 2 Associate Professor, 3 HOD and Professor Department
Original Research Article Role of MRI in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis Shashvat Modiya 1*, Jayesh Shah 2, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 1 st year resident, 2 Associate Professor, 3 HOD and Professor Department
Protozoa: Introduction and classification Amoebae I. Pathogenic amoebae: Entamoeba histolytica, Naegleria fowleri, Acanthamoeba spp.
 Protozoa: Introduction and classification Amoebae I. Pathogenic amoebae: Entamoeba histolytica, Naegleria fowleri, Acanthamoeba spp. Nimit Morakote, Ph.D. Protozoa-Simple classification Amoeba- pseudopodium(a)
Protozoa: Introduction and classification Amoebae I. Pathogenic amoebae: Entamoeba histolytica, Naegleria fowleri, Acanthamoeba spp. Nimit Morakote, Ph.D. Protozoa-Simple classification Amoeba- pseudopodium(a)
Cerebral Toxoplasmosis in HIV-Infected Patients. Ahmed Saad,MD,FACP
 Cerebral Toxoplasmosis in HIV-Infected Patients Ahmed Saad,MD,FACP Introduction Toxoplasmosis: Caused by the intracellular protozoan, Toxoplasma gondii. Immunocompetent persons with primary infection
Cerebral Toxoplasmosis in HIV-Infected Patients Ahmed Saad,MD,FACP Introduction Toxoplasmosis: Caused by the intracellular protozoan, Toxoplasma gondii. Immunocompetent persons with primary infection
Successful flow cytometric immunophenotyping of body fluid specimens
 Successful flow cytometric immunophenotyping of body fluid specimens Fiona E. Craig, MD Division of Hematopathology Mayo Clinic Arizona 2017 MFMER slide-1 Financial disclosure No conflicts 2017 MFMER slide-2
Successful flow cytometric immunophenotyping of body fluid specimens Fiona E. Craig, MD Division of Hematopathology Mayo Clinic Arizona 2017 MFMER slide-1 Financial disclosure No conflicts 2017 MFMER slide-2
Central nervous system
 Central nervous system By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 7 th Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Symptoms, signs & tests. Specific diseases. Review of structure
Central nervous system By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 7 th Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Symptoms, signs & tests. Specific diseases. Review of structure
CNS Infections in the Pediatric Age Group
 CNS Infections in the Pediatric Age Group Introduction CNS infections are frequently life-threatening In the Philippines, bacterial meningitis is one of the top leading causes of mortality in children
CNS Infections in the Pediatric Age Group Introduction CNS infections are frequently life-threatening In the Philippines, bacterial meningitis is one of the top leading causes of mortality in children
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY - CLUE CELL MORPHOLOGY: DIAGNOSTIC CONSIDERATIONS
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY - CLUE CELL MORPHOLOGY: DIAGNOSTIC CONSIDERATIONS Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY - CLUE CELL MORPHOLOGY: DIAGNOSTIC CONSIDERATIONS Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE
Nasreen A. Syed, MD F.C. Blodi Eye Pathology Laboratory University of Iowa
 Nasreen A. Syed, MD F.C. Blodi Eye Pathology Laboratory University of Iowa No financial interest in any of the material discussed in this presentation There will be discussion of off label use of medications,
Nasreen A. Syed, MD F.C. Blodi Eye Pathology Laboratory University of Iowa No financial interest in any of the material discussed in this presentation There will be discussion of off label use of medications,
ID Emergencies. BGSMC Internal Medicine Edwin Yu
 ID Emergencies BGSMC Internal Medicine Edwin Yu Learning Objectives Bacterial meningitis IDSA guidelines: Clin Infect Dis 2004; 39:1267-84 HSV encephalitis IDSA guidelines: Clin Infect Dis 2008; 47:303-27
ID Emergencies BGSMC Internal Medicine Edwin Yu Learning Objectives Bacterial meningitis IDSA guidelines: Clin Infect Dis 2004; 39:1267-84 HSV encephalitis IDSA guidelines: Clin Infect Dis 2008; 47:303-27
Literature List Body Fluids
 Literature List Body Fluids Customer Information March 2018 Date: March 2018 Subject: Literature List body fluids Issued by: Scientific Customer Services Number: 180312 Note: Whether references are given
Literature List Body Fluids Customer Information March 2018 Date: March 2018 Subject: Literature List body fluids Issued by: Scientific Customer Services Number: 180312 Note: Whether references are given
Dilemmas in the Management of Meningitis & Encephalitis HEADACHE AND FEVER. What is the best initial approach for fever, headache, meningisums?
 Dilemmas in the Management of Meningitis & Encephalitis Paul D. Holtom, MD Professor of Medicine and Orthopaedics USC Keck School of Medicine HEADACHE AND FEVER What is the best initial approach for fever,
Dilemmas in the Management of Meningitis & Encephalitis Paul D. Holtom, MD Professor of Medicine and Orthopaedics USC Keck School of Medicine HEADACHE AND FEVER What is the best initial approach for fever,
BODY FLUID ANALYSIS. Synovial Fluid. Synovial Fluid Classification. CLS 426 Urinalysis and Body Fluid Analysis Body Fluid Lecture Session 1
 BODY FLUID ANALYSIS Synovial Fluid Serous fluids the 3 P s Peritoneal Pleural Pericardial Cerebrospinal Fluid Karen Keller, MT(ASCP), SH Synovial Fluid Lubricant and sole nutrient source of joint. Normal
BODY FLUID ANALYSIS Synovial Fluid Serous fluids the 3 P s Peritoneal Pleural Pericardial Cerebrospinal Fluid Karen Keller, MT(ASCP), SH Synovial Fluid Lubricant and sole nutrient source of joint. Normal
OpenStax-CNX module: m Innate Immunity. OpenStax College. Abstract
 OpenStax-CNX module: m45542 1 Innate Immunity OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
OpenStax-CNX module: m45542 1 Innate Immunity OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
Syndromic Testing for Infectious Diseases
 Syndromic Testing for Infectious Diseases Part 3: Central Nervous System Infections HOT TOPIC / 2017 Presenter: Elitza S. Theel, Ph.D., D(ABMM) Director of Infectious Diseases Serology Department of Laboratory
Syndromic Testing for Infectious Diseases Part 3: Central Nervous System Infections HOT TOPIC / 2017 Presenter: Elitza S. Theel, Ph.D., D(ABMM) Director of Infectious Diseases Serology Department of Laboratory
Yersinia pestis. Yersinia and plague. Dr. Hala Al Daghistani
 Yersinia pestis Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Yersinia species Short, pleomorphic gram-negative rods that can exhibit bipolar staining. Catalase positive, and microaerophilic or facultatively anaerobic. Animals
Yersinia pestis Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Yersinia species Short, pleomorphic gram-negative rods that can exhibit bipolar staining. Catalase positive, and microaerophilic or facultatively anaerobic. Animals
DISORDERS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 DISORDERS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Bell Work What s your reaction time? Go to this website and check it out: https://www.justpark.com/creative/reaction-timetest/ Read the following brief article and summarize
DISORDERS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Bell Work What s your reaction time? Go to this website and check it out: https://www.justpark.com/creative/reaction-timetest/ Read the following brief article and summarize
Case 3: what grew? BA Gram stain morphology Mucoid colonies on BA
 Case 3: what grew? BA Gram stain morphology Mucoid colonies on BA 43 Case 3: probability split! Gram variable, grows on BA, MAC, barely on CHOC Oxidase positive Vitek: probability split, Acinetobacter
Case 3: what grew? BA Gram stain morphology Mucoid colonies on BA 43 Case 3: probability split! Gram variable, grows on BA, MAC, barely on CHOC Oxidase positive Vitek: probability split, Acinetobacter
Alberta Health Public Health Notifiable Disease Management Guidelines December Subacute Sclerosing Panencephalitis (SSPE)
 December 2015 Subacute Sclerosing Panencephalitis (SSPE) Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) Case Definition
December 2015 Subacute Sclerosing Panencephalitis (SSPE) Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) Case Definition
Emergency Neurological Life Support Meningitis and Encephalitis
 Emergency Neurological Life Support Meningitis and Encephalitis Version: 2.0 Last Updated: 19-Mar-2016 Checklist & Communication Meningitis and Encephalitis Table of Contents Emergency Neurological Life
Emergency Neurological Life Support Meningitis and Encephalitis Version: 2.0 Last Updated: 19-Mar-2016 Checklist & Communication Meningitis and Encephalitis Table of Contents Emergency Neurological Life
Risk for Transmission of Naegleria fowleri From Solid Organ Transplantation
 Risk for Transmission of Naegleria fowleri From Solid Organ Transplantation SL Roy, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention R Metzger, TransLife Organ Procurement Organization JG Chen, Arnold Palmer
Risk for Transmission of Naegleria fowleri From Solid Organ Transplantation SL Roy, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention R Metzger, TransLife Organ Procurement Organization JG Chen, Arnold Palmer
Lumbar puncture. Invasive procedure: diagnostic or therapeutic. The subarachnoid space 4-13 ys: ml Replenished: 4-6 h Routine LP (3-5 ml): <1h
 Lumbar puncture Lumbar puncture Invasive procedure: diagnostic or therapeutic. The subarachnoid space 4-13 ys: 65-150ml Replenished: 4-6 h Routine LP (3-5 ml):
Lumbar puncture Lumbar puncture Invasive procedure: diagnostic or therapeutic. The subarachnoid space 4-13 ys: 65-150ml Replenished: 4-6 h Routine LP (3-5 ml):
An Intriguing Case of Meningitis. Tiffany Mylius MLS (ASCP)
 An Intriguing Case of Meningitis { Tiffany Mylius MLS (ASCP) A 4yo male presents with 2wk history of URI symptoms. On the day of admission, the patient woke up with a HA in the morning, took a nap later
An Intriguing Case of Meningitis { Tiffany Mylius MLS (ASCP) A 4yo male presents with 2wk history of URI symptoms. On the day of admission, the patient woke up with a HA in the morning, took a nap later
Central Nervous System Infection
 Central Nervous System Infection Lingyun Shao Department of Infectious Diseases Huashan Hospital, Fudan University Definition Meningitis: an inflammation of the arachnoid membrane, the pia mater, and the
Central Nervous System Infection Lingyun Shao Department of Infectious Diseases Huashan Hospital, Fudan University Definition Meningitis: an inflammation of the arachnoid membrane, the pia mater, and the
Vasculitides in Surgical Neuropathology Practice
 Vasculitides in Surgical Neuropathology Practice USCAP requires that all faculty in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS
Vasculitides in Surgical Neuropathology Practice USCAP requires that all faculty in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS
CEREBROSPINAL FLUID [CSF]
![CEREBROSPINAL FLUID [CSF] CEREBROSPINAL FLUID [CSF]](/thumbs/89/100552494.jpg) CEREBROSPINAL FLUID [CSF] All question is compulsory Minimum passing mark is 15. 1. Full form of a) CSF = b) LDH = c) ADA = 2. If patient serum glucose level is 300 mg%,than expected csf glucose level
CEREBROSPINAL FLUID [CSF] All question is compulsory Minimum passing mark is 15. 1. Full form of a) CSF = b) LDH = c) ADA = 2. If patient serum glucose level is 300 mg%,than expected csf glucose level
Educational Introduction and Protocol for Molecular diagnosis of Acanthamoeba infection
 Educational Introduction and Protocol for Molecular diagnosis of Acanthamoeba infection Introduction: Acanthamoeba spp. are a family of free-living protozoans ubiquitously distributed in the environment,
Educational Introduction and Protocol for Molecular diagnosis of Acanthamoeba infection Introduction: Acanthamoeba spp. are a family of free-living protozoans ubiquitously distributed in the environment,
 Malaria parasites Malaria parasites are micro-organisms that belong to the genus Plasmodium. There are more than 100 species of Plasmodium, which can infect many animal species such as reptiles, birds,
Malaria parasites Malaria parasites are micro-organisms that belong to the genus Plasmodium. There are more than 100 species of Plasmodium, which can infect many animal species such as reptiles, birds,
Cerebrospinal fluid - role
 Cerebrospinal fluid Cerebrospinal fluid CSF is a mixture of fluid generated locally in the brain and filtered serum Total volume 150 ml (the fluid that fills the cerebral ventricles, subarachnoid space
Cerebrospinal fluid Cerebrospinal fluid CSF is a mixture of fluid generated locally in the brain and filtered serum Total volume 150 ml (the fluid that fills the cerebral ventricles, subarachnoid space
MLAB 1211 Body Fluids BF Differentials - pretest
 MLAB 1211 BF Differentials - pretest Instructor: Carolyn Ragland MLAB 1211 pre-test #2 Spring No Extra Materials Needed Name Date Instructions: Neatly write your answer in the space provided. Unless otherwise
MLAB 1211 BF Differentials - pretest Instructor: Carolyn Ragland MLAB 1211 pre-test #2 Spring No Extra Materials Needed Name Date Instructions: Neatly write your answer in the space provided. Unless otherwise
Fungal Meningitis. Stefan Zimmerli Institute for infectious diseases University of Bern Friedbühlstrasse Bern
 Fungal Meningitis Stefan Zimmerli Institute for infectious diseases University of Bern Friedbühlstrasse 51 3010 Bern Death due to infectious diseases in sub-saharan Africa Park BJ. Et al AIDS 2009;23:525
Fungal Meningitis Stefan Zimmerli Institute for infectious diseases University of Bern Friedbühlstrasse 51 3010 Bern Death due to infectious diseases in sub-saharan Africa Park BJ. Et al AIDS 2009;23:525
Disseminated Balamuthia mandrillaris infection. 1 Wake Forest University Health Sciences, 2 University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, 3
 JCM Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 1 July 2015 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.01549-15 Copyright 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 Disseminated Balamuthia mandrillaris
JCM Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 1 July 2015 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.01549-15 Copyright 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 Disseminated Balamuthia mandrillaris
The Diagnostic Accuracy of Kernig s Sign, Brudzinski s Sign, and Nuchal Rigidity in Adults with Suspected Meningitis
 MAJOR ARTICLE The Diagnostic Accuracy of Kernig s Sign, Brudzinski s Sign, and Nuchal Rigidity in Adults with Suspected Meningitis Karen E. Thomas, 1 Rodrigo Hasbun, 1 James Jekel, 2 and Vincent J. Quagliarello
MAJOR ARTICLE The Diagnostic Accuracy of Kernig s Sign, Brudzinski s Sign, and Nuchal Rigidity in Adults with Suspected Meningitis Karen E. Thomas, 1 Rodrigo Hasbun, 1 James Jekel, 2 and Vincent J. Quagliarello
Induced encystment improves resistance to preservation and storage of Acanthamoeba castellanii
 Induced encystment improves resistance to preservation and storage of Acanthamoeba castellanii 141 S. J. CAMPBELL 1,P.R.INGRAM 2, C. W. ROBERTS 2 and F. L. HENRIQUEZ 1 * 1 School of Engineering and Science,
Induced encystment improves resistance to preservation and storage of Acanthamoeba castellanii 141 S. J. CAMPBELL 1,P.R.INGRAM 2, C. W. ROBERTS 2 and F. L. HENRIQUEZ 1 * 1 School of Engineering and Science,
Dr Paul Holmes Guy s and St Thomas NHS Foundation Trust, London
 Dr Paul Holmes Guy s and St Thomas NHS Foundation Trust, London HIV and Lumbar punctures in 2018 Paul Holmes Consultant Neurologist Guy s and St Thomas Hospitals I have no competing interests Summary of
Dr Paul Holmes Guy s and St Thomas NHS Foundation Trust, London HIV and Lumbar punctures in 2018 Paul Holmes Consultant Neurologist Guy s and St Thomas Hospitals I have no competing interests Summary of
ANTIBIOTIC GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF COMMUNITY-ACQUIRED MENINGITIS AND ENCEPHALITIS IN ADULTS
 ANTIBIOTIC GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF COMMUNITY-ACQUIRED MENINGITIS AND ENCEPHALITIS IN ADULTS Version 4.0 Date ratified February 2009 Review date February 2011 Ratified by Authors Consultation Evidence
ANTIBIOTIC GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF COMMUNITY-ACQUIRED MENINGITIS AND ENCEPHALITIS IN ADULTS Version 4.0 Date ratified February 2009 Review date February 2011 Ratified by Authors Consultation Evidence
Synergistic Activity of Azithromycin and Amphotericin B against Naegleria fowleri In ACCEPTED. Shannon M. Soltow* and George M.
 AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on October 00 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:./aac.00-0 Copyright 00, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on October 00 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:./aac.00-0 Copyright 00, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
AMSER Case of the Month July 2018 Complicated Headache with Fever
 AMSER Case of the Month July 2018 Complicated Headache with Fever Benjamin Park, MS IV Dr. Karen Xie Department of Radiology University of Illinois College of Medicine at Chicago Patient Presentation CC:
AMSER Case of the Month July 2018 Complicated Headache with Fever Benjamin Park, MS IV Dr. Karen Xie Department of Radiology University of Illinois College of Medicine at Chicago Patient Presentation CC:
Vascular Disorders. Nervous System Disorders (Part B-1) Module 8 -Chapter 14. Cerebrovascular disease S/S 1/9/2013
 Nervous System Disorders (Part B-1) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview ACUTE NEUROLOGIC DISORDERS Vascular Disorders Infections/Inflammation/Toxins Metabolic, Endocrinologic, Nutritional, Toxic Neoplastic Traumatic
Nervous System Disorders (Part B-1) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview ACUTE NEUROLOGIC DISORDERS Vascular Disorders Infections/Inflammation/Toxins Metabolic, Endocrinologic, Nutritional, Toxic Neoplastic Traumatic
2008 CAP TODAY Q & A
 2008 CAP TODAY Q & A Q. How often should we document hematology competencies to ensure consistency of morphologic observations for manual differentials and fluids? Should we do this every six months or
2008 CAP TODAY Q & A Q. How often should we document hematology competencies to ensure consistency of morphologic observations for manual differentials and fluids? Should we do this every six months or
A cross sectional study of prevalance of tuberculous meningitis in Rohilkhand hospital in children
 Original article A cross sectional study of prevalance of tuberculous meningitis in Rohilkhand hospital in children Sumit Sachan, Ravi Singh Chauhan, Ajay Kumar Dept of Pediatrics, Rohilkhand Medical College
Original article A cross sectional study of prevalance of tuberculous meningitis in Rohilkhand hospital in children Sumit Sachan, Ravi Singh Chauhan, Ajay Kumar Dept of Pediatrics, Rohilkhand Medical College
Cryptococcal Meningitis
 Cryptococcal Meningitis Dr N Thumbiran Infectious Diseases Department UKZN Index patient 27 year old female Presented to King Edward Hospital on 17/07/2005 with: Severe headaches Vomiting Photophobia X
Cryptococcal Meningitis Dr N Thumbiran Infectious Diseases Department UKZN Index patient 27 year old female Presented to King Edward Hospital on 17/07/2005 with: Severe headaches Vomiting Photophobia X
ECMM Excellence Centers Quality Audit
 ECMM Excellence Centers Quality Audit Person in charge: Department: Head of Department: Laboratory is accredited according to ISO 15189 (Medical Laboratories Requirements for quality and competence) Inspected
ECMM Excellence Centers Quality Audit Person in charge: Department: Head of Department: Laboratory is accredited according to ISO 15189 (Medical Laboratories Requirements for quality and competence) Inspected
Streptococcus Pneumoniae
 Streptococcus Pneumoniae (Invasive Pneumococcal Disease) DISEASE REPORTABLE WITHIN 24 HOURS OF DIAGNOSIS Per N.J.A.C. 8:57, healthcare providers and administrators shall report by mail or by electronic
Streptococcus Pneumoniae (Invasive Pneumococcal Disease) DISEASE REPORTABLE WITHIN 24 HOURS OF DIAGNOSIS Per N.J.A.C. 8:57, healthcare providers and administrators shall report by mail or by electronic
Fungal Meningitis in an Immunocompetent Patient
 Clin Drug Investig (2013) 33 (Suppl 1):S47 S50 DOI 10.1007/s40261-012-0021-5 CASE REPORT Fungal Meningitis in an Immunocompetent Patient Ricardo Louro Rui Ferreira Catarina Pinheiro Helena Parada Domitília
Clin Drug Investig (2013) 33 (Suppl 1):S47 S50 DOI 10.1007/s40261-012-0021-5 CASE REPORT Fungal Meningitis in an Immunocompetent Patient Ricardo Louro Rui Ferreira Catarina Pinheiro Helena Parada Domitília
ID Emergencies. BUMC-P Internal Medicine Edwin Yu
 ID Emergencies BUMC-P Internal Medicine Edwin Yu Learning Objectives Bacterial meningitis IDSA guidelines: Clin Infect Dis 2004; 39:1267-84 HSV encephalitis IDSA guidelines: Clin Infect Dis 2008; 47:303-27
ID Emergencies BUMC-P Internal Medicine Edwin Yu Learning Objectives Bacterial meningitis IDSA guidelines: Clin Infect Dis 2004; 39:1267-84 HSV encephalitis IDSA guidelines: Clin Infect Dis 2008; 47:303-27
Full Blood Count analysis Is a 3 part-diff good enough? Dr Marion Münster, Sysmex South Africa
 Full Blood Count analysis Is a 3 part-diff good enough? Dr Marion Münster, Sysmex South Africa The Role of the FBC in clinical decision making History Examination Investigations Decision 70% FBC Laboratory
Full Blood Count analysis Is a 3 part-diff good enough? Dr Marion Münster, Sysmex South Africa The Role of the FBC in clinical decision making History Examination Investigations Decision 70% FBC Laboratory
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY BLOOD AND LYMPHATICS SYSTEM
 HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY BLOOD AND LYMPHATICS SYSTEM Login: http://histopath.westernu.edu Histology Atlas AND Virtual Histology links. I. HEMATOLOGY - PERIPHERAL BLOOD Purpose: To be able to identify
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY BLOOD AND LYMPHATICS SYSTEM Login: http://histopath.westernu.edu Histology Atlas AND Virtual Histology links. I. HEMATOLOGY - PERIPHERAL BLOOD Purpose: To be able to identify
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007
 Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA) Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA)
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA) Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA)
Lymphoma Tumor Board Quiz! Laboratory Hematology: Basic Cell Morphology
 Lymphoma Tumor Board Quiz! Laboratory Hematology: Basic Cell Morphology CABOT RINGS Cabot rings in a patient with hemolytic anemia. Cabot ring (red arrow) and Howell-Jolly body (blue arrow). Observed in
Lymphoma Tumor Board Quiz! Laboratory Hematology: Basic Cell Morphology CABOT RINGS Cabot rings in a patient with hemolytic anemia. Cabot ring (red arrow) and Howell-Jolly body (blue arrow). Observed in
Case Presentation. Intern Tutor VS 2007/01/26
 Case Presentation Intern 8931150 Tutor VS 2007/01/26 About The Patient 38 years old worker ID: M120794700 Admission date: 2006/12/28 C.C.: Fever with headache for 2 days Present Illness Smoker, alcoholism
Case Presentation Intern 8931150 Tutor VS 2007/01/26 About The Patient 38 years old worker ID: M120794700 Admission date: 2006/12/28 C.C.: Fever with headache for 2 days Present Illness Smoker, alcoholism
DENGUE WITH CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM INVOLVEMENT
 DENGUE WITH CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM INVOLVEMENT Usa Thisyakorn and Chule Thisyakorn Department of Pediatrics, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand Abstract. Dengue has spread
DENGUE WITH CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM INVOLVEMENT Usa Thisyakorn and Chule Thisyakorn Department of Pediatrics, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand Abstract. Dengue has spread
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING. James Chen (MS IV)
 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
Symptoms of a brain tumour in adults
 Symptoms of a brain tumour in adults A tumour is an abnormal growth caused by cells dividing in an uncontrolled manner. Approximately 9,300 people are diagnosed with a primary brain tumour each year. (Primary
Symptoms of a brain tumour in adults A tumour is an abnormal growth caused by cells dividing in an uncontrolled manner. Approximately 9,300 people are diagnosed with a primary brain tumour each year. (Primary
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY THROAT CULTURES LEARNING OUTCOMES. Upon completion of this exercise, the participant should be able to:
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY THROAT CULTURES LEARNING OUTCOMES Upon completion of this exercise, the participant should be able to: distinguish three types of hemolysis produced by bacterial colonies. discuss
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY THROAT CULTURES LEARNING OUTCOMES Upon completion of this exercise, the participant should be able to: distinguish three types of hemolysis produced by bacterial colonies. discuss
