Frontal Sinus Pneumatization Pattern With Age
|
|
|
- Cuthbert Marshall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
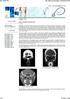
1 Journal of Experimental Research. March 2013, Vol. 1 No l editor-in-chief@ er-journal.com Received: Jan. 10, 2013 Accepted for publication: Mar. 15, 2013 Frontal Sinus Pneumatization Pattern With Age U.K. EZEMAGU, N. MGBOR, C.I.P. ANIBEZE, F.C. AKPUAKA Department of Anatomy, Enugu State University of Science and Technology, Enugu. 1 Department of Otorhinolaryngology, College Of Medicine, UNEC Enugu. 2 Department of Anatomy, Abia State University Uturu. 3 College of Health Sciences Anambra State University, Uli. * Author of Correspondence. 1 Abstract Understanding the mechanism of frontal sinus pneumatization depends on availability of accurate anatomical, physiological and pathological information in sufficient detail. It will also involve verification of certain prognostic factors, which may include simple anthropometric parameters. This study demonstrated the relationship between the variation in frontal sinus dimensions with age. In this study, lateral and anteroposterior radiographs of 74 males and 46 females between the ages of 9 and 75 years were measured. The three parameters of height, breath and length of the frontal sinus were taken from the radiographs. Data were analyzed using excel package of a tabletop computer, employing chi-square test 2 (x ) to determine the association between sinus dimensions and age. The results demonstrated a strong positive relationship between variation in sinus height and breadth (pneumatization in vertical portion of the frontal bone) with variation in age while variation in depth may not depend on age. Thus establishing the fact that some metric and morphologic characteristics of the frontal sinus vary with age. Therefore, it follows that advancement in age leads to increase in size of frontal sinus. Keywords. Age, frontal sinus, pneumatization, morphometries INTRODUCTION The paranasal sinuses are cavities in the bones of the face and the cranium that contain air which function in speech and also serve to lighten the skull(waugh and Grant,2005). The frontal sinus are between the outer and inner tables of the frontal bone, posterior to the superciliary arches and the root of the nose. The frontal sinus begins as an evagination of the anterior superior portion of the middle meatus known as the frontal recess. These bony air cells are produced in growth by the advancement of osteoclastic epithelial diverticulata; the resulting sinuses are found in the facial skeleton of both eutherian mammals and archosaurs (Rae et al; 2002). Extent of frontal sinuses varies among individuals and between the two sides. The pneumatization of the frontal sinus may extends in to the vertical part and the horizontal part of the frontal bone; extension into the roof of the orbit to the lesser wing of the sphenoid may also be present (Romanes, 1981). This results from an often irregular resorption of the diploe in the vertical portion of the frontal bone. Variation in frontal sinus may be attributable to both age and pathology. Variability due to the effect of age and pathology includes enlargement due to the thinning of frontal sinus walls which is in turn due to old age, post-menopausal symmetrical hyperostosis on the inner surface of the forehead causing reduction, chronic inflammatory conditions causing the thinning or thickening of the compact lamina and subsequent enlargement or reduction of the frontal sinus, injuries, tumors and obstruction of the front-nasal duct causing frontal sinus enlargement (Ezemagu et al;2005a). Trinkaus (1973) stated that the frontal sinus dimensions of Fontechevade 1 is an indicator of age. Showing that the inter-orbital breadth and frontal squamous thickness of Fontechevade 1, suggest juvenile status, while the size of the frontal sinus indicates a slightly older individual. In addition, variability due to sex and race are recognized (Stringer et a1; 1984) The dimensions of the frontal sinus are higher for males than females with mean length and width of frontal with previous sinus operation. sinuses as 35.36mm, 39
2 63.87mm for males and 28.70mm, 60.73mm for females respectively, in a population of South East Nigerians (Ezemagu et al; 2005a). European Neanderthal have a frontal sinus that extends laterally, not superiorly (Stringer et al;1984). Since sinusitis affects more than 31 million people in the US and is the most common health care complaint in the country (Shankar,1994), information on pneumatization pattern of this structure may be useful. Also, understanding the manner of growth direction and approximate extent at any particular age is of importance in carrying out the operation of sinus wash out on children, for allowance must be made for the probable position of the sinus at any particular stage in its development (Colman,1992). In quest for aggressive medical management with a low index of suspicion for development of complications requiring surgical intervention, any additional information on metric and morphologic characteristics of frontal sinus aid otorhinolaryngologist and neurosurgeons in evaluation of sinuses. Researchers in paleontology (Oyen et al; 1979) are concerned with the development of the supra orbital region. If it can be shown that supra orbital development involving frontal sinus is even partially correlated with certain sinus morphometries and that sinus pnuematization is correlated with age, it adds an additional factor to the puzzle of the meaning of supra orbital development. MATERIALS AND METHOD A total of 120 radiographs (74 males and 46 females) with age ranging from 9-75 years taken within 18'h August, 2003 and 12'h July, 2004 with lateral and Caldwell views were measured at Ebonyi State Teaching Hospital, Abakaliki, University of Nigeria Teaching Hospital Enugu and Hansa Clinic Enugu. Although the samples of radiographs used were collected from different places, the focus film distance used was the same (90cm as indicated from the centers where the samples were collected). Radiographs of sinus used include those reported normal by the radiologists and those not affected by any pathological conditions or The three parameters measured were height, breadth and depth of frontal sinuses. The height and depth of the frontal sinuses were taken from the lateral view radiographs. Frontal sinus mostly appears as J shadow with its apex superiorly and basel floor inferiorly shown. The height was measured in vertical plane from the apex to the base. The depth or anteroposterior dimension was taken as the longest line perpendicular to the height and touching the anterior and posterior tables of the frontal sinus at its floor using the protractor and metric rule, because of its irregularly shaped floor. The breadth of the frontal sinus was taken from the anteroposterior view radiographs. It appears as a crescent shaped shadow in this view separated in to two or three lobes by thin septa. Because of difficulty delimiting the inferior borders of the frontal sinus previous researchers have often drawn a base line tangential to the superior borders of the orbit (Francis et al; 1990, Ezemagu et al;2005a) The breadth was taken as the longest line parallel to the baseline touching the left and right lateral edges of the frontal sinus using the sets of squares and metric rule. In cases of smaller frontal sinuses, which may be partially or completely eliminated in these procedures, the parallel line was, taken midway between the baseline and the nasion (the midpoint of the nasofrontal suture). RESULT The relationships between age and height or breadth of frontal sinus as shown in Tables I and II showed that null hypothesis of no association should be rejected at a The degree of dependency showed that about 70% and 69% of the variation in height and breadth of the frontal sinus respectively was related to variation in age. The relationship between age and depth of the frontal sinus as shown in Table III, was indicative of the fact that the evidence to reject the null hypothesis of no association was lacked at a Also, the pattern of pneumatization shows that frontal sinus extend both superiorly and laterally but more laterally especially in females. 40
3 Table 1: Relationship of frontal sinus height and age Table II: Relationship of frontal sinus breadth and age 41
4 Regression Analysis The regression line for age and other variables with high value of correlation coefficient, using age as an independent variable shows that for age < 15 years: Male frontal sinus breadth 0.581age Male frontal sinus height age Female frontal sinus breadth age Female frontal sinus height age It also showed that for all ages in the sample that there is no regression line to explain the variation. DISCUSSION The study showed that the frontal sinus depth may not vary with age but the relationship between age and height or breadth of frontal sinus, which are in the vertical portion of the frontal bone showed that null hypothesis of no association, should be rejected. There is a high degree of dependency between variation in height or breadth (vertical portion of the sinus) and age. Therefore, it follows that advancement in age leads to increase in size of frontal sinus. The development of frontal sinus is the result of two simultaneous processes; the progressive advancement of the sinus mucosa and concomitant resorption of the overlying bone or an often-irregular resorption of the diploe in the vertical portion of the frontal bone (Ezemagu et al; 2005a). Rae et al (2002) staten that the development of frontal sinus is due to the advancement of osteoclastic epithelial diverticulata. The functions of paranasal sinuses which include lighten the skull, was supported by this finding since pneumatization will reduce the weight.of the skull bone. There is increasing pneumatization of maxillary sinus at the rate of 2mm and 3mm per year for eight years in the vertical and anteroposterior planes respectively (Ezemagu et al; 2005b). Also, the transverse limit of expansion is reached in ninth year, when the sinus penetrates the molars bone, thereafter progress is slow and ceases at 15years, except the inferior angle, which descends after eruption of the third molar. Shankar (1994) stated as follows; the frontal sinus undeveloped at birth appears in the second year as a result of the pneumatization of the anterior portion of the frontal recess or from an anterior ethmoid cell, frontal sinus usually reaches adult size by age 18, and may continue to grow slowly throughout adulthood, by the middle of third year, cupola of the sinus appears above the level of nasion, by eight years of age the superior border extends to the height of the supraorbital rim and by ten years of age, it may reach superiorly into the supercilliary region. From the regression 42
5 analysis of this work, it follows that pneumatization of male frontal sinus breadth reach the size of mm at age 9 and increase at the rate of O.581mm per year till age 15. Male frontal sinus reach the height of mm at age 9 and increase at the rate of per year till age 15. Female frontal sinus breadth reach the size of mm at age 9 and increase at the rate of 6.409mm per year till age 15. Also, female frontal sinus reach the height of 7.179mm at age 9 and increase at the rate of 2.977mm per year till age 15 This result therefore shows that frontal sinus extend both superiorly and laterally but more laterally especially in females. Also, it demonstrated a strong association between age and height or breadth of frontal sinus, though could not demonstrate a linear relationship for age above 15. Clearly, additional tests are necessary to explore the role played by genetic and epigenetic factors in the morphology of the paranasal sinuses. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT The authors thank P.J. Eze for advice and support, Hansa Clinic for access to the radiograph facilities and Felix Aguboshim for helping in the statistical analysis of this work. REFERENCES Colman B.H (1992) Disease of Nose, Throat, Ear, Head and th Neck. Hall and Colman's 14 Ed. Churchill Livingstone New York. Ezemagu U.K, Mgbor N, Anibeze Cf.P, Akpuaka F.C (2005a). Anthropometrical profiles of frontal sinus in population of southeast Nigerians. j.expt. & din Anat 4(1 ):42-46 Ezemagu U.K, Mgbor N, Anibeze ClP, Akpuaka F.C (2005b). Age and sex related variations in the maxillary sinuses of south East Nigerians.. j.expt. & clin Anat 4(1): Francis P, Raman, R, Korula, P. and Korah, I (1990). Pneumatization of-the paranasal simises (Maxillary and frontal) in cleft lip and palate. Arch otolaryngol Head and Neck Surg. 116: Oyen O et al Browridge structure and function in Extant primates and Neanderthals. American Journal of physical anthropology 51: Rae, T.E., Koppe, T., Spoor, F. Benefit et al Ancestral Loss of the maxillary sinuses in old world monkeys and independent Acquisition in Macaca, American Journal of Physical Anthropology 177: Romanes G.J.(1981). Cunningham's textbook of Anatomy. 12'" Ed.,Oxford University Press, New York, Shankar L (1994). An Atlas of imaging of the paranasal sinuses. J.B. Lippincott company, Philadelphia 8. Stringer CB, Hublin J and Vandcrrnecrsch (lq84) The origin of anatomically modern humans in Western Europe. In : The origin of modern humans. Ed Smith F.H and Spencer F. Alan R. Liss, New York Trinkaus E (1973). A reconsideration of the Fontcchcvade fossils. American journal of Physical Anthropology 39: Waugh A and Grant A (2005).Anatomy and Physiology in Health and Illness. Ross and Wilson 9th Ed. Churchill Livingstone, London,
Nasal region. cartilages: septal cartilage (l); lateral nasal cartilage (2); greater alar cartilages (2); lesser alar cartilages (?
 Nasal region skull bones: nasal and frontal processes of maxilla cartilages: septal cartilage (l); lateral nasal cartilage (2); greater alar cartilages (2); lesser alar cartilages (?) 1 Nasal cavity Roof
Nasal region skull bones: nasal and frontal processes of maxilla cartilages: septal cartilage (l); lateral nasal cartilage (2); greater alar cartilages (2); lesser alar cartilages (?) 1 Nasal cavity Roof
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Positioning for Exams of the Cranium, Sinuses, and Mandible. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 5 Positioning for Exams of the Cranium, Sinuses, and Mandible. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 5-1 through 5-9. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 5 Positioning for Exams of the Cranium, Sinuses, and Mandible. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 5-1 through 5-9. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able
Radiological anatomy of frontal sinus By drtbalu
 2009 Radiological anatomy of frontal sinus By drtbalu Anatomy of frontal sinus is highly variable. Precise understanding of these variables will help a surgeon to avoid unnecessary complications during
2009 Radiological anatomy of frontal sinus By drtbalu Anatomy of frontal sinus is highly variable. Precise understanding of these variables will help a surgeon to avoid unnecessary complications during
Anatomy and Physiology. Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Maxillary Sinus Measurements in Different Age Groups of Human Cadavers
 Tikrit Journal for Dental Sciences 1(2013)107-112 Maxillary Sinus Measurements in Different Age Groups of Human Cadavers Mohammad A. Abd-alla BDS, MSc., Ph.D. (1) Abdul-Jabbar J. Mahdi BDS, MSc., Ph.D.
Tikrit Journal for Dental Sciences 1(2013)107-112 Maxillary Sinus Measurements in Different Age Groups of Human Cadavers Mohammad A. Abd-alla BDS, MSc., Ph.D. (1) Abdul-Jabbar J. Mahdi BDS, MSc., Ph.D.
Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton
 Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton Why This Matters Understanding the anatomy of the skeleton enables you to anticipate problems such as pelvic dimensions that may affect labor and delivery The Skeleton The
Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton Why This Matters Understanding the anatomy of the skeleton enables you to anticipate problems such as pelvic dimensions that may affect labor and delivery The Skeleton The
Bones of the skull & face
 Bones of the skull & face Cranium= brain case or helmet Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The cranium is composed of eight bones : frontal Occipital
Bones of the skull & face Cranium= brain case or helmet Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The cranium is composed of eight bones : frontal Occipital
Cranium Facial bones. Sternum Rib
 Figure 7.1 The human skeleton. Skull Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) Cranium Facial bones Sternum Rib Bones of pectoral girdle Vertebral column Sacrum Vertebra Bones of pelvic girdle (a) Anterior view
Figure 7.1 The human skeleton. Skull Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) Cranium Facial bones Sternum Rib Bones of pectoral girdle Vertebral column Sacrum Vertebra Bones of pelvic girdle (a) Anterior view
SINUS ANATOMY AND FUNCTION
 EMBRYOLOGY AND DEVELOPMENT SINUS ANATOMY AND FUNCTION -4 th week gestation: -frontonasal process identified, arises over developing forebrain -ectodermal -contributes to nasal capsule -9 th and 10 th week
EMBRYOLOGY AND DEVELOPMENT SINUS ANATOMY AND FUNCTION -4 th week gestation: -frontonasal process identified, arises over developing forebrain -ectodermal -contributes to nasal capsule -9 th and 10 th week
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section. REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
Dr. Sami Zaqout, IUG Medical School
 The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
Chapter 7. Skeletal System
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
NEUROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM
 LECTURE 4 SKULL NEUROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM CRANIUM NEUROCRANIUM (protective case around brain) VISCEROCRANIUM (skeleton of face) NASOMAXILLARY COMPLEX MANDIBLE (DESMOCRANIUM)
LECTURE 4 SKULL NEUROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM CRANIUM NEUROCRANIUM (protective case around brain) VISCEROCRANIUM (skeleton of face) NASOMAXILLARY COMPLEX MANDIBLE (DESMOCRANIUM)
Skeletal System -Axial System. Chapter 7 Part A
 Skeletal System -Axial System Chapter 7 Part A Skeleton Learn: Names of the s. Identify specific landmarks that allow: Bones to fit into each other, Organs to fit into the cavities, Muscles to attach,
Skeletal System -Axial System Chapter 7 Part A Skeleton Learn: Names of the s. Identify specific landmarks that allow: Bones to fit into each other, Organs to fit into the cavities, Muscles to attach,
Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1996, v. 18 n. 12, p
 Title Radiological conference. Frontal sinus osteoma complicated by pneumocephalus Author(s) Fung, WT; Peh, WCG Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1996, v. 18 n. 12, p. 658-662 Issued Date 1996 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/44655
Title Radiological conference. Frontal sinus osteoma complicated by pneumocephalus Author(s) Fung, WT; Peh, WCG Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1996, v. 18 n. 12, p. 658-662 Issued Date 1996 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/44655
Jefferson Cephalometric Analysis--Face and Health Focused
 Jefferson Cephalometric Analysis--Face and Health Focused Google: Jefferson Ceph Analysis Video Instruction for video instruction. Note: video instruction teaches how to find Center O. Center O is now
Jefferson Cephalometric Analysis--Face and Health Focused Google: Jefferson Ceph Analysis Video Instruction for video instruction. Note: video instruction teaches how to find Center O. Center O is now
AXIAL SKELETON SKULL
 AXIAL SKELETON SKULL CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired) 1. Frontal forms forehead & upper portion of eyesocket (orbital) 2. Parietal paired bones; form superior & lateral walls of cranium 3.
AXIAL SKELETON SKULL CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired) 1. Frontal forms forehead & upper portion of eyesocket (orbital) 2. Parietal paired bones; form superior & lateral walls of cranium 3.
Bones Ethmoid bone Inferior nasal concha Lacrimal bone Maxilla Nasal bone Palatine bone Vomer Zygomatic bone Mandible
 splanchnocranium - Consists of part of skull that is derived from branchial arches - The facial bones are the bones of the anterior and lower human skull Bones Ethmoid bone Inferior nasal concha Lacrimal
splanchnocranium - Consists of part of skull that is derived from branchial arches - The facial bones are the bones of the anterior and lower human skull Bones Ethmoid bone Inferior nasal concha Lacrimal
FRONTAL SINUPLASTY P R E P A R E D A N D P R E S E N T E D B Y : D R. Y A H Y A F A G E E H R 4 16/ 12/ 2013
 FRONTAL SINUPLASTY P R E P A R E D A N D P R E S E N T E D B Y : D R. Y A H Y A F A G E E H R 4 16/ 12/ 2013 ANATOMY: FRONTAL SINUS Not present at birth Starts developing at 4 years Radiographically visualized
FRONTAL SINUPLASTY P R E P A R E D A N D P R E S E N T E D B Y : D R. Y A H Y A F A G E E H R 4 16/ 12/ 2013 ANATOMY: FRONTAL SINUS Not present at birth Starts developing at 4 years Radiographically visualized
Intranasal location of lacrimal sac in Thai cadavers
 Asian Biomedicine Vol. 4 No. 2 April 2010; 323-327 Clinical report Napas Tanamai a, Teeraporn Ratanaanekchai a, Sanguansak Thanaviratananich a, Kowit Chaisiwamongkol b, Thanarat Chantaumpalee b a Department
Asian Biomedicine Vol. 4 No. 2 April 2010; 323-327 Clinical report Napas Tanamai a, Teeraporn Ratanaanekchai a, Sanguansak Thanaviratananich a, Kowit Chaisiwamongkol b, Thanarat Chantaumpalee b a Department
Skeletal system. Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
 www.oralradiologists.com CONE BEAM CT REPORT CASE XXXX Patient information Patient Name: - Referring Doctor: - Patient DOB: - Scan Date: [Start date] Reason for Exam: Maxillary facial pain Doctor Notes:
www.oralradiologists.com CONE BEAM CT REPORT CASE XXXX Patient information Patient Name: - Referring Doctor: - Patient DOB: - Scan Date: [Start date] Reason for Exam: Maxillary facial pain Doctor Notes:
Human, Male, Single gunshot wound
 Human, Male, Single gunshot wound Product Number: Specimen Evaluated: Skeletal Inventory: BC-152 Bone Clones replica 1 intact cranium - left inferior nasal concha absent - middle nasal conchae absent 1
Human, Male, Single gunshot wound Product Number: Specimen Evaluated: Skeletal Inventory: BC-152 Bone Clones replica 1 intact cranium - left inferior nasal concha absent - middle nasal conchae absent 1
Anatomic Relations Summary. Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh
 Anatomic Relations Summary Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh Anatomic Relations Lecture 1 Part-1 - The medial wall of the nose is the septum. - The vestibule lies directly inside the nostrils (Nares). -
Anatomic Relations Summary Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh Anatomic Relations Lecture 1 Part-1 - The medial wall of the nose is the septum. - The vestibule lies directly inside the nostrils (Nares). -
The cribriform plate. ethmoid bone. Ethmoid bone consists from: 1) A horizontal cribriform plate. 2) A perpendicular plate. 3) Two lateral labyrinths.
 ethmoid bone Ethmoid bone consists from: 1) A horizontal cribriform plate. 2) A perpendicular plate. 3) Two lateral labyrinths. The cribriform plate 1) Connect the two labyrinths to the perpendicular plate.
ethmoid bone Ethmoid bone consists from: 1) A horizontal cribriform plate. 2) A perpendicular plate. 3) Two lateral labyrinths. The cribriform plate 1) Connect the two labyrinths to the perpendicular plate.
Skull-2. Norma Basalis Interna. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the skull is divided into
Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the skull is divided into
The orbit-1. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 The orbit-1 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Orbital plate of frontal bone Orbital plate of ethmoid bone Lesser wing of sphenoid Greater wing of sphenoid Lacrimal bone Orbital
The orbit-1 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Orbital plate of frontal bone Orbital plate of ethmoid bone Lesser wing of sphenoid Greater wing of sphenoid Lacrimal bone Orbital
SKULL AS A WHOLE + ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA
 SKULL AS A WHOLE + ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture, the student should be able to know: Parts of skeleton (axial and appendicular) Parts of skull Sutures of skull
SKULL AS A WHOLE + ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture, the student should be able to know: Parts of skeleton (axial and appendicular) Parts of skull Sutures of skull
Chapter 7: Head & Neck
 Chapter 7: Head & Neck Osteology I. Overview A. Skull The cranium is composed of irregularly shaped bones that are fused together at unique joints called sutures The skull provides durable protection from
Chapter 7: Head & Neck Osteology I. Overview A. Skull The cranium is composed of irregularly shaped bones that are fused together at unique joints called sutures The skull provides durable protection from
Assessment of the relative location of greater palatine foramen in adult Indian skulls: Consideration for maxillary nerve block
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Eur J Anat, 15 (3): 150-154 (2011) Assessment of the relative location of greater palatine foramen in adult Indian skulls: Consideration for maxillary nerve block Ajay Kumar, Anu Sharma,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Eur J Anat, 15 (3): 150-154 (2011) Assessment of the relative location of greater palatine foramen in adult Indian skulls: Consideration for maxillary nerve block Ajay Kumar, Anu Sharma,
o Diaphysis o Area where red marrow is found o Area where yellow marrow is found o Epiphyseal plate AXIAL SKELETON Skull
 64 Anatomy & Physiology Coloring Workbook 7. Figure 5-2A is a midlevel, cross-sectional view of the diaphysis of the femur. Label the membrane that lines the cavity and the membrane that covers the outside
64 Anatomy & Physiology Coloring Workbook 7. Figure 5-2A is a midlevel, cross-sectional view of the diaphysis of the femur. Label the membrane that lines the cavity and the membrane that covers the outside
Anatomy Made Easy MSS
 Anatomy Made Easy MSS part #1 هذا الملف يشمل تفريغ المحاضرة الثانية لعون بدءا من الصفحة 11 وحتى األخير Done By :MohamedA. Diabat Edited by Awn Academic team The Axial Skeleton The axial skeleton consist
Anatomy Made Easy MSS part #1 هذا الملف يشمل تفريغ المحاضرة الثانية لعون بدءا من الصفحة 11 وحتى األخير Done By :MohamedA. Diabat Edited by Awn Academic team The Axial Skeleton The axial skeleton consist
Imaging Orbit/Periorbital Injury
 Imaging Orbit/Periorbital Injury 9 th Nordic Trauma Radiology Course 2016 Stuart E. Mirvis, M.D., FACR Department of Radiology University of Maryland School of Medicine Fireworks Topics to Cover Struts
Imaging Orbit/Periorbital Injury 9 th Nordic Trauma Radiology Course 2016 Stuart E. Mirvis, M.D., FACR Department of Radiology University of Maryland School of Medicine Fireworks Topics to Cover Struts
Skull-2. Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the
Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the
Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki
 Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki MAXILLA Premaxillary/median palatal suture (radiolucent). Incisive fossa and foramen (radiolucent). Nasal passages (radiolucent). Nasal septum (radiopaque). Anterior nasal spine
Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki MAXILLA Premaxillary/median palatal suture (radiolucent). Incisive fossa and foramen (radiolucent). Nasal passages (radiolucent). Nasal septum (radiopaque). Anterior nasal spine
Core Curriculum Syllabus Emergencies in Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery FACIAL FRACTURES
 Core Curriculum Syllabus Emergencies in Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery A. General Considerations FACIAL FRACTURES Look for other fractures like skull and/or cervical spine fractures Test function
Core Curriculum Syllabus Emergencies in Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery A. General Considerations FACIAL FRACTURES Look for other fractures like skull and/or cervical spine fractures Test function
Bisection of Head & Nasal Cavity 頭部對切以及鼻腔. 解剖學科馮琮涵副教授 分機
 Bisection of Head & Nasal Cavity 頭部對切以及鼻腔 解剖學科馮琮涵副教授 分機 3250 E-mail: thfong@tmu.edu.tw Outline: The structure of nose The concha and meatus in nasal cavity The openings of paranasal sinuses Canals, foramens
Bisection of Head & Nasal Cavity 頭部對切以及鼻腔 解剖學科馮琮涵副教授 分機 3250 E-mail: thfong@tmu.edu.tw Outline: The structure of nose The concha and meatus in nasal cavity The openings of paranasal sinuses Canals, foramens
 www.oralradiologists.com CONE BEAM CT REPORT CASE ---- Case Information Referring Doctor: - Patient Name: - Scan Date: December 1, 2015 Patient DOB: - Reason for Exam: - Study Details: icat Flex, 160x160x112
www.oralradiologists.com CONE BEAM CT REPORT CASE ---- Case Information Referring Doctor: - Patient Name: - Scan Date: December 1, 2015 Patient DOB: - Reason for Exam: - Study Details: icat Flex, 160x160x112
Chapter Five. 1 of 8 11/3/2008 2:52 PM.
 1 of 8 11/3/2008 2:52 PM Email : myousefmian@hotmail.com Chapter Five FRONT COVER Introduction Acknowledgement CHAPTERS Chapter One Chapter Two Chapter Three Chapter Four Chapter Five Chapter Six Chapter
1 of 8 11/3/2008 2:52 PM Email : myousefmian@hotmail.com Chapter Five FRONT COVER Introduction Acknowledgement CHAPTERS Chapter One Chapter Two Chapter Three Chapter Four Chapter Five Chapter Six Chapter
Postnatal Growth. The study of growth in growing children is for two reasons : -For health and nutrition assessment
 Growth of The Soft Tissues Postnatal Growth Postnatal growth is defined as the first 20 years of growth after birth krogman 1972 The study of growth in growing children is for two reasons : -For health
Growth of The Soft Tissues Postnatal Growth Postnatal growth is defined as the first 20 years of growth after birth krogman 1972 The study of growth in growing children is for two reasons : -For health
Anatomy #1; Respiratory Nose and the Nasal Cavity December 1st, 2013
 Note #1: the doctor skipped some slides in the lecture. Those slides are not included in this sheet and so you will have to review the slides to study them. The reason they were not included is because
Note #1: the doctor skipped some slides in the lecture. Those slides are not included in this sheet and so you will have to review the slides to study them. The reason they were not included is because
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM. Focus on the Skull
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Focus on the Skull Review Anatomical Terms Anterior/Posterior Dorsal/Ventral Medial/Lateral Superior/Inferior Bone Markings - Review Projections for attachment of muscles, ligaments
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Focus on the Skull Review Anatomical Terms Anterior/Posterior Dorsal/Ventral Medial/Lateral Superior/Inferior Bone Markings - Review Projections for attachment of muscles, ligaments
Omran Saeed. Luma Taweel. Mohammad Almohtaseb. 1 P a g e
 2 Omran Saeed Luma Taweel Mohammad Almohtaseb 1 P a g e I didn t include all the photos in this sheet in order to keep it as small as possible so if you need more clarification please refer to slides In
2 Omran Saeed Luma Taweel Mohammad Almohtaseb 1 P a g e I didn t include all the photos in this sheet in order to keep it as small as possible so if you need more clarification please refer to slides In
Periodontal Disease. Radiology of Periodontal Disease. Periodontal Disease. The Role of Radiology in Assessment of Periodontal Disease
 Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
Biology 210 Chapter 8: Skeletal Tissues Supplement 1
 Biology 210 Chapter 8: Skeletal Tissues Supplement 1 By John McGill Material contributed by Beth Wyatt & Jack Bagwell DIVISIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM AXIAL SKELETON (80 BONES) Bones of the Head, Neck,
Biology 210 Chapter 8: Skeletal Tissues Supplement 1 By John McGill Material contributed by Beth Wyatt & Jack Bagwell DIVISIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM AXIAL SKELETON (80 BONES) Bones of the Head, Neck,
Infratemporal fossa: Tikrit University college of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck Anatomy 2 nd y.
 Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Exercise 10. The Axial Skeleton
 Exercise 10 The Axial Skeleton The Axial Skeleton Consists of the skeletal structures found along the midline of the body. Includes the skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, and sacrum. The cartilages
Exercise 10 The Axial Skeleton The Axial Skeleton Consists of the skeletal structures found along the midline of the body. Includes the skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, and sacrum. The cartilages
Structure Location Function
 Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
Extraoral radiography Introduction: Extraoral radiographs (outside the mouth) are taken when large areas of the skull or jaw must be examined or when
 Extraoral radiography Introduction: Extraoral radiographs (outside the mouth) are taken when large areas of the skull or jaw must be examined or when patients are unable to open their mouths for film placement.
Extraoral radiography Introduction: Extraoral radiographs (outside the mouth) are taken when large areas of the skull or jaw must be examined or when patients are unable to open their mouths for film placement.
Respiratory System. Ling Shucai
 Respiratory System Ling Shucai General Description Ⅰ. Constituents: Respiratory tract Lungs Pleura and plural cavity Ⅱ. Function: exchange O 2 and CO 2 mainly Mediastinum Respiratory tract Upper respiratory
Respiratory System Ling Shucai General Description Ⅰ. Constituents: Respiratory tract Lungs Pleura and plural cavity Ⅱ. Function: exchange O 2 and CO 2 mainly Mediastinum Respiratory tract Upper respiratory
APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 AXIAL SKELETON SKELETAL SYSTEM. Cranium. Skull. Face. Skull and associated bones. Auditory ossicles. Associated bones.
 SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 26 Skull Skull and associated s 29 Cranium Face Auditory ossicles 8 4 6 Associated s Hyoid Thoracic cage 25 Sternum Ribs 24 Vertebrae 24 column
SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 26 Skull Skull and associated s 29 Cranium Face Auditory ossicles 8 4 6 Associated s Hyoid Thoracic cage 25 Sternum Ribs 24 Vertebrae 24 column
Radiological Analysis of Sella Turcica
 Radiological Analysis of Sella Turcica S. R. Chavan 1, M. A. Kathole 1, A. S. Katti 2, N. G. Herekar 3 { 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Associate Professor, 3 Professor and Head}Dept. of Anatomy, Govt. Medical
Radiological Analysis of Sella Turcica S. R. Chavan 1, M. A. Kathole 1, A. S. Katti 2, N. G. Herekar 3 { 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Associate Professor, 3 Professor and Head}Dept. of Anatomy, Govt. Medical
Nose & Mouth OUTLINE. Nose. - Nasal Cavity & Its Walls. - Paranasal Sinuses. - Neurovascular Structures. Mouth. - Oral Cavity & Its Contents
 Dept. of Human Anatomy, Si Chuan University Zhou hongying eaglezhyxzy@163.com Nose & Mouth OUTLINE Nose - Nasal Cavity & Its Walls - Paranasal Sinuses - Neurovascular Structures Mouth - Oral Cavity & Its
Dept. of Human Anatomy, Si Chuan University Zhou hongying eaglezhyxzy@163.com Nose & Mouth OUTLINE Nose - Nasal Cavity & Its Walls - Paranasal Sinuses - Neurovascular Structures Mouth - Oral Cavity & Its
Head and Neck Examination
 Head and Neck Examination Statement of Goals Understand and perform an examination of the head and neck. Learning Objectives Head Ears Nose Sinus A. Describe the anatomy of the head, including regions
Head and Neck Examination Statement of Goals Understand and perform an examination of the head and neck. Learning Objectives Head Ears Nose Sinus A. Describe the anatomy of the head, including regions
YOU MUST BRING YOUR OWN GLOVES FOR THIS ACTIVITY.
 ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :
![Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :](/thumbs/88/115294566.jpg) Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
Dr. Sami Zaqout Faculty of Medicine IUG
 The Nose External Nose Nasal Cavity External Nose Blood and Nerve Supplies of the External Nose Blood Supply of the External Nose The skin of the external nose Branches of the ophthalmic and the maxillary
The Nose External Nose Nasal Cavity External Nose Blood and Nerve Supplies of the External Nose Blood Supply of the External Nose The skin of the external nose Branches of the ophthalmic and the maxillary
in compact bone, large vertical canals carrying blood vessels and nerves. in compact bone, large horizontal canals carrying blood vessels and nerves.
 Carl Christensen, PhD Skeletal System (Bones`) Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy 1. Identify a term for each of the following: shaft of a long bone ends of a long bone ossified remnant of the "growth plate" connective
Carl Christensen, PhD Skeletal System (Bones`) Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy 1. Identify a term for each of the following: shaft of a long bone ends of a long bone ossified remnant of the "growth plate" connective
Skull basic structures. Neurocranium
 Assoc. Prof. Květuše Lovásová, M.V.D., PhD. Skull basic structures Skull consists of two groups of bones: neurocranium (bones forming the brain box) splanchnocranium (bones forming the facial skeleton)
Assoc. Prof. Květuše Lovásová, M.V.D., PhD. Skull basic structures Skull consists of two groups of bones: neurocranium (bones forming the brain box) splanchnocranium (bones forming the facial skeleton)
MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS
 MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS Squamous cell carcinoma Osteogenic sarcoma Chondrosarcoma Fibrosarcoma Malignant lymphomas (incl. Burkitt s) Multiple myeloma Ameloblastoma Secondary
MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS Squamous cell carcinoma Osteogenic sarcoma Chondrosarcoma Fibrosarcoma Malignant lymphomas (incl. Burkitt s) Multiple myeloma Ameloblastoma Secondary
*in general the blood supply of the nose comes from branches of the internal and external carotid arteries.
 In the previous lecture we talked about the anatomy of the nasal cavity, today we will talk about its blood supply, venous drainage, innervations, and finally about the paranasal sinuses. When we describe
In the previous lecture we talked about the anatomy of the nasal cavity, today we will talk about its blood supply, venous drainage, innervations, and finally about the paranasal sinuses. When we describe
McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT-B and PHRN Optional Continuing Education 2019 #1 Facial Trauma
 McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT-B and PHRN Optional Continuing Education 2019 #1 Facial Trauma The face is vital to human appearance and function. Facial injuries can impair a patient
McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT-B and PHRN Optional Continuing Education 2019 #1 Facial Trauma The face is vital to human appearance and function. Facial injuries can impair a patient
Musculoskeletal System (Part A-1) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview. Functions
 Musculoskeletal System (Part A-1) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/8/13 Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations
Musculoskeletal System (Part A-1) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/8/13 Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations
Human, Female, Black, Shotgun wound
 Human, Female, Black, Shotgun wound Product Number: Specimen Evaluated: Skeletal Inventory: BC-196 Bone Clones replica 1 intact cranium 2 fragments of mandible: - portion of left body, ramus, coronoid
Human, Female, Black, Shotgun wound Product Number: Specimen Evaluated: Skeletal Inventory: BC-196 Bone Clones replica 1 intact cranium 2 fragments of mandible: - portion of left body, ramus, coronoid
Basic Anatomy and Physiology of the Lips and Oral Cavity. Dr. Faghih
 Basic Anatomy and Physiology of the Lips and Oral Cavity Dr. Faghih It is divided into seven specific subsites : 1. Lips 2. dentoalveolar ridges 3. oral tongue 4. retromolar trigone 5. floor of mouth 6.
Basic Anatomy and Physiology of the Lips and Oral Cavity Dr. Faghih It is divided into seven specific subsites : 1. Lips 2. dentoalveolar ridges 3. oral tongue 4. retromolar trigone 5. floor of mouth 6.
Boundaries Septum Turbinates & Meati Lamellae Drainage Pathways Variants
 The Fastest 20 Minutes in Michelle A. Michel, MD Professor of Radiology and Otolaryngology Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee Overview Nasal cavity Anterior skull base Ostiomeatal complex Frontal
The Fastest 20 Minutes in Michelle A. Michel, MD Professor of Radiology and Otolaryngology Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee Overview Nasal cavity Anterior skull base Ostiomeatal complex Frontal
Blair Radiology Exam Examination Packet
 Blair Radiology Exam Examination Packet This packet is made of up five sections: Examiner s Instructions, Applicant Requirements, Analysis Rubric, Overall Result and Comments and Exam Form. The Exam Form
Blair Radiology Exam Examination Packet This packet is made of up five sections: Examiner s Instructions, Applicant Requirements, Analysis Rubric, Overall Result and Comments and Exam Form. The Exam Form
Anatomy of. External NOSE. By Dr Farooq Aman Ullah Khan PMC
 Anatomy of External NOSE By Dr Farooq Aman Ullah Khan PMC 24 th Nov. 2017 The External Nose Descriptions of the nose always begin with that part of it which is covered by the skin, i.e., the EXPOSED PART
Anatomy of External NOSE By Dr Farooq Aman Ullah Khan PMC 24 th Nov. 2017 The External Nose Descriptions of the nose always begin with that part of it which is covered by the skin, i.e., the EXPOSED PART
Endoscopic Management Of A Giant Ethmoid Mucocele
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 6 Number 1 S Ceylan, F Bora Citation S Ceylan, F Bora.. The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology. 2006 Volume 6 Number 1. Abstract We present
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 6 Number 1 S Ceylan, F Bora Citation S Ceylan, F Bora.. The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology. 2006 Volume 6 Number 1. Abstract We present
Measurement of the Maxilla and Zygoma as an Aid in Installing Zygomatic Implants
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 59:1193-1198, 2001 Measurement of the Maxilla and Zygoma as an Aid in Installing Zygomatic Implants Yuki Uchida, DDS, PhD,* Masaaki Goto, DDS, PhD, Takeshi Katsuki DDS, PhD, and
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 59:1193-1198, 2001 Measurement of the Maxilla and Zygoma as an Aid in Installing Zygomatic Implants Yuki Uchida, DDS, PhD,* Masaaki Goto, DDS, PhD, Takeshi Katsuki DDS, PhD, and
Bony orbit Roof The orbital plate of the frontal bone Lateral wall: the zygomatic bone and the greater wing of the sphenoid
 Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
ISPUB.COM. Position Of The Ear In Relation To Facial Midline Landmarks In Nigerians. A Akinlolu, B Akinola, A Hussein INTRODUCTION
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Human Anatomy Volume 2 Number 1 Position Of The Ear In Relation To Facial Midline Landmarks In Nigerians. A Akinlolu, B Akinola, A Hussein Citation A Akinlolu, B Akinola,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Human Anatomy Volume 2 Number 1 Position Of The Ear In Relation To Facial Midline Landmarks In Nigerians. A Akinlolu, B Akinola, A Hussein Citation A Akinlolu, B Akinola,
Introduction to Local Anesthesia and Review of Anatomy
 5-Sep Introduction and Anatomy Review 12-Sep Neurophysiology and Pain 19-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 1 26-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 2 Introduction to Local Anesthesia and Review of
5-Sep Introduction and Anatomy Review 12-Sep Neurophysiology and Pain 19-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 1 26-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 2 Introduction to Local Anesthesia and Review of
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Respiration Includes Pulmonary ventilation Air moves in and out of lungs Continuous replacement of gases in alveoli (air sacs) External respiration Gas exchange between blood and
The Respiratory System Respiration Includes Pulmonary ventilation Air moves in and out of lungs Continuous replacement of gases in alveoli (air sacs) External respiration Gas exchange between blood and
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 09 Page September 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i9.52 Relationship of Agger Nasi Cell and Uncinate
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i9.52 Relationship of Agger Nasi Cell and Uncinate
Homo and Maccrca. A Comparative Study of Facial Growth in
 A Comparative Study of Facial Growth in Homo and Maccrca DONALD H. ENLOW Department of Anatomy and Center for Human Growth and Development, The University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan ABSTRACT Sections
A Comparative Study of Facial Growth in Homo and Maccrca DONALD H. ENLOW Department of Anatomy and Center for Human Growth and Development, The University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan ABSTRACT Sections
The characteristics of profile facial types and its relation with mandibular rotation in a sample of Iraqi adults with different skeletal relations
 The characteristics of profile facial types and its relation with mandibular rotation in a sample of Iraqi adults with different skeletal relations Sara M. Al-Mashhadany, B.D.S., M.Sc. (1) Nagham M.J.
The characteristics of profile facial types and its relation with mandibular rotation in a sample of Iraqi adults with different skeletal relations Sara M. Al-Mashhadany, B.D.S., M.Sc. (1) Nagham M.J.
04 Development of the Face and Neck. Development of the Face Development of the neck
 04 Development of the Face and Neck Development of the Face Development of the neck Development of the face Overview of facial development The fourth week ~ the twelfth week of prenatal development Between
04 Development of the Face and Neck Development of the Face Development of the neck Development of the face Overview of facial development The fourth week ~ the twelfth week of prenatal development Between
Upper Respiratory Tract
 Upper Respiratory Tract Lectures Objectives Describe the structure of nasal cavity including nasal septum. Describe the structure of lateral wall of nasal cavity including conchae and meatuses. Locate
Upper Respiratory Tract Lectures Objectives Describe the structure of nasal cavity including nasal septum. Describe the structure of lateral wall of nasal cavity including conchae and meatuses. Locate
Communication issue - What should the radiologist report before functional endoscopic sinus surgery
 Communication issue - What should the radiologist report before functional endoscopic sinus surgery Poster No.: C-0509 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. M. Dobra 1, C. A. Badiu 1,
Communication issue - What should the radiologist report before functional endoscopic sinus surgery Poster No.: C-0509 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. M. Dobra 1, C. A. Badiu 1,
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION COW BONE DISSECTION
 ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy
 Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
Reasons for Failure and Surgical Revisions. Stil Kountakis, MD, PhD Professor and Chief, Division of Rhinology
 Reasons for Failure and Surgical Revisions Stil Kountakis, MD, PhD Professor and Chief, Division of Rhinology Medical College of Georgia of Georgia Regents University Department of Otolaryngology / Head
Reasons for Failure and Surgical Revisions Stil Kountakis, MD, PhD Professor and Chief, Division of Rhinology Medical College of Georgia of Georgia Regents University Department of Otolaryngology / Head
An important indication for imaging the anterior skull base
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH D.C. Hughes M.J. Kaduthodil D.J.A. Connolly P.D. Griffiths Dimensions and Ossification of the Normal Anterior Cranial Fossa in Children BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Interpretation of CT of
ORIGINAL RESEARCH D.C. Hughes M.J. Kaduthodil D.J.A. Connolly P.D. Griffiths Dimensions and Ossification of the Normal Anterior Cranial Fossa in Children BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Interpretation of CT of
Classification of bones
 Classification of bones compact intramembranous axial histology development regional spongy Intra cartilaginous appendicular flat Irregular shape Sesamoid Long Short Wormian pneumatic Classification
Classification of bones compact intramembranous axial histology development regional spongy Intra cartilaginous appendicular flat Irregular shape Sesamoid Long Short Wormian pneumatic Classification
Human, Male, White, Calvarium cut
 Human, Male, White, Calvarium cut Product Number: Specimen Evaluated: Skeletal Inventory: BC-293 Bone Clones replica 1 intact cranium 1 intact mandible General observations: **NOTE The demographic features
Human, Male, White, Calvarium cut Product Number: Specimen Evaluated: Skeletal Inventory: BC-293 Bone Clones replica 1 intact cranium 1 intact mandible General observations: **NOTE The demographic features
The sebaceous glands (glands of Zeis) open directly into the eyelash follicles, ciliary glands (glands of Moll) are modified sweat glands that open
 The Orbital Region The orbits are a pair of bony cavities that contain the eyeballs; their associated muscles, nerves, vessels, and fat; and most of the lacrimal apparatus upper eyelid is larger and more
The Orbital Region The orbits are a pair of bony cavities that contain the eyeballs; their associated muscles, nerves, vessels, and fat; and most of the lacrimal apparatus upper eyelid is larger and more
The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR.
 The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR Made of A-AURICLE B-EXTERNAL AUDITORY MEATUS A-AURICLE It consists
The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR Made of A-AURICLE B-EXTERNAL AUDITORY MEATUS A-AURICLE It consists
CT of Maxillofacial Injuries
 CT of Maxillofacial Injuries Stuart E. Mirvis, M.D., FACR Department of Radiology University of Maryland School of Medicine Viking 1 1976 MGS 2001 Technology changes the diagnosis Technologic Evolution
CT of Maxillofacial Injuries Stuart E. Mirvis, M.D., FACR Department of Radiology University of Maryland School of Medicine Viking 1 1976 MGS 2001 Technology changes the diagnosis Technologic Evolution
TRAUMA TO THE FACE AND MOUTH
 Dr.Yahya A. Ali 3/10/2012 F.I.C.M.S TRAUMA TO THE FACE AND MOUTH Bailey & Love s 25 th edition Injuries to the orofacial region are common, but the majority are relatively minor in nature. A few are major
Dr.Yahya A. Ali 3/10/2012 F.I.C.M.S TRAUMA TO THE FACE AND MOUTH Bailey & Love s 25 th edition Injuries to the orofacial region are common, but the majority are relatively minor in nature. A few are major
Skull Base Danger Zones in FESS
 Skull Base Danger Zones in FESS Poster No.: C-2278 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Renza Lozada, R. Carreño Gonzalez, G. Quintana Sanchez, 1 2 1 1 1 2 R. E. Figueroa ; Malaga/ES,
Skull Base Danger Zones in FESS Poster No.: C-2278 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Renza Lozada, R. Carreño Gonzalez, G. Quintana Sanchez, 1 2 1 1 1 2 R. E. Figueroa ; Malaga/ES,
Assessment of the relationship between maxillary sinus floor and maxillary posterior teeth root apices using spiral CT scan
 Assessment of the relationship between maxillary sinus floor and maxillary posterior teeth root apices using spiral CT scan Zainab Abdulhasan Hussein, B.D.S. (1) (2) Lamia H. Al-Nakib, B.D.S., M.Sc. ABSTRACT
Assessment of the relationship between maxillary sinus floor and maxillary posterior teeth root apices using spiral CT scan Zainab Abdulhasan Hussein, B.D.S. (1) (2) Lamia H. Al-Nakib, B.D.S., M.Sc. ABSTRACT
 ISSN 1560-1587 81 7.18 11.51 9.21 72.84 4.94 22.22 4 Exploring the distance between upper central incisor edge and incisive papilla in Taiwanese population Sheau-Jiuan Huang 1, Tsau-Mau Chou 1, Huey-Er
ISSN 1560-1587 81 7.18 11.51 9.21 72.84 4.94 22.22 4 Exploring the distance between upper central incisor edge and incisive papilla in Taiwanese population Sheau-Jiuan Huang 1, Tsau-Mau Chou 1, Huey-Er
Normal Radiographic Anatomy Maxillary Central Area
 VARIA Normal Radiographic Anatomy Maxillary Central Area Carmen Elena Georgescu 1, Gabriela Tãnase 2, Augustin Mihai 3 Bucharest, Romania Summary The radiopgraphic recognition of disease requires knowledge
VARIA Normal Radiographic Anatomy Maxillary Central Area Carmen Elena Georgescu 1, Gabriela Tãnase 2, Augustin Mihai 3 Bucharest, Romania Summary The radiopgraphic recognition of disease requires knowledge
Human, Male, White, Healed hammer blows
 Human, Male, White, Healed hammer blows Product Number: Specimen Evaluated: Skeletal Inventory: BC-217 Bone Clones replica 1 intact cranium General observations: In general, the molding process has preserved
Human, Male, White, Healed hammer blows Product Number: Specimen Evaluated: Skeletal Inventory: BC-217 Bone Clones replica 1 intact cranium General observations: In general, the molding process has preserved
BONE CHALLENGE DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD
 BONE CHALLENGE DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD Bone Basic functions? A. support B. protection C. movement assistance in D. RBC formation-hemopoiesis E. mineral homeostasis +importance of calcium F. energy supply -yellow
BONE CHALLENGE DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD Bone Basic functions? A. support B. protection C. movement assistance in D. RBC formation-hemopoiesis E. mineral homeostasis +importance of calcium F. energy supply -yellow
Upper arch. 1Prosthodontics. Dr.Bassam Ali Al-Turaihi. Basic anatomy & & landmark of denture & mouth
 1Prosthodontics Lecture 2 Dr.Bassam Ali Al-Turaihi Basic anatomy & & landmark of denture & mouth Upper arch Palatine process of maxilla: it form the anterior three quarter of the hard palate. Horizontal
1Prosthodontics Lecture 2 Dr.Bassam Ali Al-Turaihi Basic anatomy & & landmark of denture & mouth Upper arch Palatine process of maxilla: it form the anterior three quarter of the hard palate. Horizontal
