Collateral ventilation, the ability of gas to move from one part of the lung to
|
|
|
- Lester Melton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Prolongation of patency of airway bypass stents with use of drug-eluting stents Cliff K. Choong, FRACS, a Loc Phan, BSC, b Patrick Massetti, BSC, b Fabio J. Haddad, MD, a Carlo Martinez, MD, a Edmund Roschak, BSC, b and Joel D. Cooper, MD a Drs Choong and Cooper From the Division of Cardiothoracic Surgery, Department of Surgery, Washington University School of Medicine, Barnes- Jewish Hospital, St Louis, Mo, a and Broncus Technologies Inc, b Mountain View, Calif. Supported in part by NIH grant RO1 HL , the Jacqueline Mariitz Lung Center at Barnes-Jewish Hospital, St Louis, Mo, and Broncus Technologies Inc, Mountain View, Calif. J.D.C. acts as a consultant for Broncus Technologies. Read at the Eighty-fifth Annual Meeting of The American Association for Thoracic Surgery, San Francisco, Calif, April 10-13, Received for publication April 11, 2005; revisions received July 7, 2005; accepted for publication July 11, Address for reprints: Joel D. Cooper, MD, Division of Cardiothoracic Surgery, Washington University School of Medicine, One Barnes-Jewish Hospital Plaza, 3108 Queeny Tower, St Louis, MO ( cooperjd@msnotes.wustl.edu). J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2006;131: /$32.00 Copyright 2006 by The American Association for Thoracic Surgery doi: /j.jtcvs Objective: Airway bypass by transbronchial fenestration has been shown to improve forced expiratory volume and flow in explanted emphysematous human lungs. We previously demonstrated the feasibility and safety of airway bypass stent placement in a canine model, but we found that most stents occluded within 1 week. The aim of this study was to evaluate the influence of controlled-release paclitaxel-eluting stents on prolongation of patency. Methods: With the subject dogs under general anesthesia, suitable segmental and subsegmental bronchial wall sites were selected by direct visualization with a flexible bronchoscope. A Doppler probe was used to detect and avoid sites with adjacent blood vessels. Transbronchial passages were formed with a 25-gauge transbronchial needle-tipped catheter and dilated with a 2.5-mm balloon integrated into the needle catheter. A specifically designed expandable stainless steel stent (3 mm long 3 mm wide) embedded in a sleeve of silicone rubber was placed within the passage and expanded until secured about the bronchial wall. Fifty control stents (no paclitaxel impregnation) and 107 paclitaxel-eluting stents were placed in 25 dogs. Animals underwent bronchoscopy at intervals to assess stent patency. Results: Eight instances of minor and brief bleeding occurred during stent placement; all resolved without incident. There were no pneumothoraces or deaths associated with stent placement. No delayed complications occurred. No identifiable paclitaxel-related toxicity was observed. At 1, 4, 8, and 12 weeks, the patency rates were 10%, 0%, 0%, and 0% for control stents and 100%, 96%, 76%, and 65% for paclitaxel stents. Conclusion: In an animal model, the use of specifically designed paclitaxel-eluting airway bypass stents was both feasible and safe. These stents resulted in a significant prolongation of patency. Collateral ventilation, the ability of gas to move from one part of the lung to another through nonanatomic pathways, was first observed by Van Allen and colleagues 1 in The importance of collateral ventilation is minimal in normal lungs, because the resistance to air flow is higher in collateral channels than in the airway. 2 However, the resistance of air flow in collateral channels is low in patients with emphysema relative to that in normal lungs. 2,3 In emphysematous lungs, collateral ventilation provides important channels for gas distribution and may be therapeutically useful. 4 We have previously demonstrated that creation of direct passages between emphysematous pulmonary parenchyma and bronchial airways (airway bypass) in excised emphysematous human lungs can improve expiratory flow and volume, which is otherwise limited by the collapse of the small, peripheral airways during expiration. 5 Our ex vivo study of 12 emphysematous human lungs demonstrated that creation of three passages improved mean forced expiratory volume in 1 second from 245 ml to 447 ml. The addition of two more passages further improved mean forced expiratory volume in 1 second to 666 ml. 60 The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery January 2006
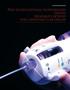
2 General Thoracic Surgery TABLE 1. Summary of stent patency Control stents (%) Paclitaxel-eluting stents (%) Week No. % No. % 1 5/50 10% 107/ % 2 2/50 4% 106/107 99% 4 0/50 0% 103/107 96% 6 85/107 79% 8 81/107 76% 10 79/107 74% 12 69/107 65% 14 23/35* 65% 16 23/35* 65% 18 23/35* 65% *After the 12th week of follow-up, 16 dogs were killed and the remaining 9 dogs were followed up until the 18th week, per the study protocol. Figure 1. Equipment used in procedure for airway bypass stent placement Equipment from top to bottom: 4.9-mm flexible bronchoscope, Doppler probe, 25-gauge retractable needle-tipped catheter integrated with 2.5-mm balloon, stent mounted on delivery device, expanded 3 3-mm stent from side and front views, expanded balloon of stent delivery device. We subsequently demonstrated that airway bypass passages can be safely created in patients with emphysema. 6 In a separate animal study, we showed that it was feasible and safe to place airway bypass stents in vivo. 7 Most of the stents, however, became occluded within 1 week after placement, and this would pose a major problem for potential clinical application. 7 The topical application of mitomycin, an anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic agent, has been reported to be useful in the treatment of airway stenosis. 8,9 We evaluated the influence of weekly topical mitomycin on airway bypass stent patency and found it to prolong stent patency. 7 The duration of stent patency was associated with the number of weekly topical mitomycin applications. However, it is not practical to subject patients to weekly bronchoscopic topical application of mitomycin to prolong stent patency. The aim of this study was therefore to evaluate the influence of controlled-release paclitaxel-eluting stents on prolongation of airway bypass stent patency. Materials and Methods Specially bred research mongrel dogs were used for the experiment. The weights of the dogs were between 20 and 25 kg. The airway bypass procedure was performed with the animals under general anesthesia, and each dog was mechanically ventilated via a single-lumen endotracheal tube. The equipment used is shown in Figure 1. A standard 4.9-mm external diameter flexible fiberoptic bronchoscope with a 2-mm working channel (BF-P160; Olympus America Inc, Melville, NY) was used to visualize the airway and to select appropriate target sites at the segmental or subsegmental bronchial level. A Doppler catheter (Broncus Technologies Inc, Mountain View, Calif) inserted through the bronchoscope channel was used to scan the target site and its adjacent area to detect and to avoid peribronchial vessels before transbronchial fenestration. Once an appropriate site had been identified, the Doppler probe was exchanged for a 25-gauge transbronchial retractable needletipped catheter with a 2.5-mm balloon integrated into the catheter. Transbronchial passages were formed with the 25-gauge transbronchial needle and dilated with the integrated 2.5-mm balloon. The needle-balloon catheter was withdrawn, and a balloon-expandable stent was passed through the bronchoscope channel and visually positioned in the newly created passage. The paclitaxeleluting stent used is made of stainless steel (3 mm long 3 mm wide) embedded within silicone rubber impregnated with paclitaxel (Exhale Stent; Broncus Technologies). This stent expands out on either end from its midportion (3 mm wide) to a 5.5-mm flange that helps to secure the stent (Figure 1). Fifty control stents (no paclitaxel impregnation) and 107 paclitaxel-eluting stents were placed in 25 dogs. Each paclitaxel-eluting airway bypass stent contains approximately 400 g paclitaxel. Most of the released drug is delivered within the first 90 days. Animals underwent bronchoscopy at intervals to assess stent patency. The stent was considered to be occluded if there was tissue ingrowth that completely filled the inside channel of the stent for at least half its length. The general health status of the dogs was assessed by daily clinical examination and weekly complete blood count, urea, and electrolyte laboratory blood tests. Weekly follow-up was performed to a maximum of 18 weeks. The study had animal studies ethics committee approval. All animals received humane care in compliance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals ( html). The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery Volume 131, Number 1 61
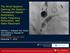
3 Figure 2. Kaplan-Meier freedom from stent closure. Results Eight episodes of minor and brief bleeding occurred during transbronchial passage formation. These were treated with dilute topical epinephrine solution and resolved without incident. There were no pneumothoraces or deaths associated with stent placement. No delayed hemorrhages or pneumothoraces occurred. The animals remained clinically well through out the study period, and there were no abnormal laboratory blood test results. Ninety percent of the control stents were found to be occluded at the first week of bronchoscopic follow-up, and the rest were occluded by the fourth week of follow-up (Table 1). In contrast, paclitaxeleluting stents had a significant prolongation of stent patency (Table 1, Figure 2). The median duration of stent patency in the paclitaxel group was greater than 18 weeks, because approximately two thirds of the paclitaxel-eluting stents were still patent at the 18-week conclusion of bronchoscopic follow-up. Examples of patent and occluded stents, as visualized with bronchoscopy, are shown in Figure 3. Discussion Emphysema is anatomically defined as irreversible increase in the size of the air spaces distal to the terminal bronchioles, resulting from the destructive activity of neutrophil and macrophage elastase. 10 It is associated with a loss of lung elastic recoil and progressive dynamic hyperinflation of the lungs. These changes result in enlargement of the thorax, flattening of the diaphragm, increased work of breathing, increased dyspnea, and reduced exercise tolerance. 11 The progressive loss of elastic recoil traps the patient in a state of hyperinflation in which forced expiratory effort cannot reduce the residual volume, because the force exerted to empty the lungs collapses the small airways and obstructs the outflow of gas. Progressive hyperinflation of the lungs and hyperextension of the chest wall also diminish inspiratory capacity. To maintain adequate minute ventilation, the respiratory rate must increase, resulting in an increase in the work of breathing and in dyspnea. 12 Surgical options in the treatment of emphysema include lung transplantation and lung volume reduction surgery. Both treatment modalities have specific indications, and their use is limited to selected patients. Our group embarked on an experimental study of airway bypass with the goal of developing a palliative treatment for patients with homogeneous severe emphysema who are not candidates for either lung transplantation or lung volume reduction surgery. We previously found that the creation of extra-anatomic bronchopulmonary passages in ex vivo emphysematous lungs resulted in the improvement of forced expiratory flow and Figure 3. Examples of patent and occluded stents visualized on bronchoscopy. a, Stent at time of placement. b, Occluded control stent at 1 week of follow-up. c, Patent paclitaxel-eluting stent at 3 weeks of follow-up. d, Patent paclitaxel-eluting stent at 13 weeks of follow-up. 62 The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery January 2006
4 General Thoracic Surgery volume. 5 The transbronchial passages created took advantage of the extensive collateral ventilation present in emphysematous lungs to allow additional removal of trapped gas and further reduction of residual volume not obtainable through the airways. The airway bypass stent was developed as a noncollapsing structure that would prevent the collapse and closure of these transbronchial passages. We initially used a radiofrequency probe to create the transbronchial passages, but we subsequently altered the technique to use a 22-gauge needle to create the transbronchial track and a 2.5-mm dilating balloon to expand the puncture site. 7 We now use an integrated needle-balloon device, as described in this article. This combined device has resulted in a significant ease, simplicity, and time saving in the formation of the transbronchial passages. Paclitaxel has been successfully applied to the prevention of coronary artery restenosis and works by inhibiting mitosis and prevention of neointimal proliferation while allowing healing and endothelialization. 13,14 In the prevention of coronary artery in-stent stenosis, paclitaxel is considered to be best delivered locally on a drug-eluting stent to achieve therapeutic concentrations without the risk of systemic toxicity. On the basis of these findings, we chose to assess the potential effect of paclitaxel-eluting stents on airway bypass stent patency. Our results suggest that paclitaxel was effective in maintaining airway bypass stent patency. The potential clinical application of an effective drug-eluting airway bypass stent is that it would obviate the need for patients to undergo regular bronchoscopic topical application of medications to maintain airway bypass stent patency. 7 Paclitaxel-eluting coronary stents have been found to be safe and without significant adverse effects, with the local delivery minimizing the risks of systemic toxicity. Paclitaxel is widely used as an effective anticancer chemotherapeutic agent, for which purpose it has been administered systemically at dosages in the range of 135 to 300 mg/m2 with satisfactory patient tolerance In comparison, the dose used in a paclitaxel-eluting coronary stent and also in the airway bypass stent (400 g in each stent) in this study is a small fraction of the systemic dose delivered for chemotherapy. In our study there were no local or systemic adverse effects seen as a result of the paclitaxel. All the animals remained clinically well throughout the study. Results of the weekly laboratory blood tests were also normal during the study period. Systemic absorption of paclitaxel and monitoring of the serum level are, however, important issues and as such require further future evaluation beyond the scope of this study. In summary, it was feasible and safe to perform airway bypass stent placement in vivo. In our canine model, most control stents became occluded within 1 week. Placement of paclitaxel-eluting airway bypass stents, however, resulted in a prolonged duration of stent patency. We thank Patricia Toeniskoetter, Naomi Still, and Katheryn Cook for their technical assistance in the project. References 1. Van Allen CM, Lindskog GE, Richter HT. Gaseous interchange between adjacent lung lobules. Yale J Biol Med. 1930;2: Hogg JC, Macklem PT, Thurlbeck WM. The resistance of collateral channels in excised human lungs. J Clin Invest. 1969;48: Terry PB, Traystman RJ, Newball HH, Batra G, Menkes HA. Collateral ventilation in man. N Engl J Med. 1978;298: Macklem PT. Collateral ventilation. N Engl J Med. 1978;298: Lausberg HF, Chino K, Patterson GA, Meyers BF, Toeniskoetter PD, Cooper JD. Bronchial fenestration improves expiratory flow in emphysematous human lungs. Ann Thorac Surg. 2003;75: Rendina EA, De Giacomo T, Venuta F, Coloni GF, Meyers BF, Patterson GA, et al. Feasibility and safety of the airway bypass procedure for patients with emphysema. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2003;152: Choong CK, Haddad FJ, Gee EY, Cooper JD. Feasibility and safety of airway bypass stent placement and influence of topical mitomycin C on stent patency. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2005;129: Erard AC, Monnier P, Spiloupoulos A, Nicod L. Mitomycin C for control of recurrent bronchial stenosis. Chest. 2001;120: Correa AJ, Reinisch L, Sanders DL, Huang S, Deriso W, Duncavage JA, et al. Inhibition of subglottic stenosis with mitomycin C in the canine model. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1999;108: The definition of emphysema. Report of a National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Division of Lung Disease Workshop. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985;132: Rochester D, Braun N, Arora N. Respiratory muscle strength in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979;119: Sharp JT, Danon J, Druz WS, Goldberg NB, Fishman H, Machnach W. Respiratory muscle function in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: its relationship to disability and to respiratory therapy. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1974;110: Schiff PB, Horwitz SB. Taxol stabilizes microtubules in mouse fibroblast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980;77: Kolodgie FD, John M, Khurana C, Farb A, Wilson PS, Acampado E, et al. Sustained reduction of in-stent neointimal growth with the use of a novel systemic nanoparticle paclitaxel. Circulation. 2002;106: Blagosklonny MV, Fojo T. Molecular effects of paclitaxel: myths and reality: a critical review. Int J Cancer. 1999;83: Bristol-Meyers Squibb Company. Semi-synthetic TAXOL (paclitaxel) injection. Full prescribing information. Available from: URL: Accessed April 11, Discussion Dr Steven J. Mentzer (Boston, Mass). We now have three major approaches to the endobronchial treatment of emphysema. The first is the bronchial valve, essentially a 1-way valve designed to induce distal atelectasis. The second is the instillation of bioactive agents to induce distal atelectasis and scarring. These two approaches are designed to reduce lung volumes. The third approach, presented here, is conceptually different. It relies on collateral ventilation to bypass obstructed airways and improve expiratory flow. A central question regarding this third approach to endobronchial treatment of emphysema is collateral ventilation in human beings. It s interesting, Dr Choong, that you chose the dog model. In pigs, as you may know, there is little if any collateral ventilation. The lobules in a pig lung prevent collateral ventilation. In dogs, there are essentially no fibrous septa, and the lung is basically unlobulated. In human beings, the situation is somewhere in The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery Volume 131, Number 1 63
5 between. Could you comment on how dependent your results are on the dog model? Dr. Choong. The purpose of this study was to assess the patency of paclitaxel-eluting airway bypass stents in a dog model. As previously mentioned, the dogs used in the study were normal dogs with normal lungs. We have previously provided the definition of an occluded stent as one with tissue ingrowth occupying half or more of the stent channel. The patency of the stents was therefore assessed in accordance with that definition. The purpose of this study was not to assess the effects of airway bypass stents on collateral ventilation. These normal dogs had normal lungs and therefore did not have significant collateral ventilation. Collateral ventilation is present in human beings and is especially significant in patients with emphysematous lungs. We believe that the airway bypass stents would take advantage of that situation and improve expiratory flow and volume in patients with emphysema. We have done experimental studies with explanted emphysematous human lungs obtained from lung transplant recipients during lung transplantations, with patient and ethics committee approval, and these studies demonstrated that airway bypass stents do take advantage of the significant collateral ventilation that is present in emphysematous lungs, leading to improvement in expiratory flow and volume and reduction in hyperinflation. Preliminary clinical studies in human patients have also confirmed these results. Dr Mentzer. However, one would imagine that if you have collateral ventilation, the chance of having continuous ventilation and a patent stent would improve. Conversely, if you have distal atelectasis, the amount of ventilation distal to the stent would be diminished. A related point regards the time constant of the stents. If the amount of time that it takes for air flow to go across the stent is relatively large relative to the ventilatory cycle, then the contribution of those stents to overall ventilatory function would be small. Clearly, the time constant is dependent on stent patency. As these stents start to occlude, you would expect the time constant to go up and the relative benefit of the stent to go down. Dr Choong. Exactly. I think one of the critical issues for this to be successful is to ensure that the stents stay patent. Dr Mentzer. It seems logical that if the stents are truly decompressing distal emphysematous lung, you might affect distal hyperinflation. For example, dynamic hyperinflation might be less and air flow improved with these additional air passages. Do you have any evidence, in animals or in human beings, that dynamic hyperinflation is in fact improved with stent therapy? Dr Choong. We are currently conducting experimental studies specifically looking at this area, together with Drs Peter Macklem, John Pierce, and Jim Hogg. In our studies, the airway bypass stents resulted in improvement in the physiologic and mechanical properties of explanted emphysematous human lungs. Preliminary clinical studies in human patients have confirmed these results. Dr Mentzer. Mechanical ventilation improved, but did you get improvement in blood gases? It seems plausible that you could simply be improving ventilation to dead space; that is, you may be increasing the overall air flow, but perhaps only by increasing your dead space ventilation. Dr Choong. In terms of looking at the blood gas values, we have not done this in the experimental or clinical studies that we re conducting. In our experimental and clinical studies, however, the airway bypass stents did result in a decrease in the trapped gas and the residual volumes of emphysematous lungs. Dr Joseph B. Shrager (Philadelphia, Pa). This was a nice presentation of obviously exciting work. I m particularly excited to see the picture you presented from the human lung, which is the first one I ve seen where you can actually visualize the lung parenchyma directly through the hole; on the other hand, in the pictures that you showed in the animals, at least the ones you presented here today, it s not entirely clear to me that you can tell objectively whether the stent is open. Is it a plus/minus obvious event whether the thing is open? Dr Choong. Yes. The picture I showed of the airway bypass stent that was placed in a patient with severe emphysema shows clearly the appearance of a patent stent and the markedly destroyed emphysematous lung seen through the stent channel. Dr Shrager. Isn t there a degree of subjective interpretation as to whether a stent has remained open? If it is a little bit subjective, is there something else you can do to make sure they are in fact open? Are there any adjunctive things that you are doing bronchoscopically to tell whether they are really open? Dr Choong. In the animal studies that we conducted, we used normal research mongrel dogs with normal lung tissues. They did not have emphysematous lungs. Therefore, in the pictures I have shown, you re looking at solid lung parenchyma at the other end of the stent channel. The way we define stent occlusion is that half or more of the stent channel is occupied by tissue. You are right that in emphysematous human lungs there is a definite, clear view of the destroyed lung tissue; unfortunately, we do not have this situation in the normal research mongrel dogs with normal lungs. Dr Shrager. So you are not really sure whether there is air flowing back and forth through these stents that you re calling open? Dr Choong. There is most likely no air flow in these normal lungs, but the purpose of this study was to look at the patency according to the definition previously described. We have, however, used the paclitaxel-eluting airway bypass stents in human clinical studies, and we have found encouraging results with these stents being patent and looking that way during follow-up. Dr Shrager. For how long do they elute paclitaxel? Dr Choong. Most of the elution occurs though a 3-month period. 64 The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery January 2006
Bronchial Fenestration Improves Expiratory Flow in Emphysematous Human Lungs
 Bronchial Fenestration Improves Expiratory Flow in Emphysematous Human Lungs Henning F. Lausberg, MD, Kimiaki Chino, MD, G. Alexander Patterson, MD, Bryan F. Meyers, MD, Patricia D. Toeniskoetter, MD,
Bronchial Fenestration Improves Expiratory Flow in Emphysematous Human Lungs Henning F. Lausberg, MD, Kimiaki Chino, MD, G. Alexander Patterson, MD, Bryan F. Meyers, MD, Patricia D. Toeniskoetter, MD,
Clinical application of airway bypass with paclitaxel-eluting stents: Early results
 Evolving Technology Clinical application of airway bypass with paclitaxel-eluting stents: Early results Paulo F. G. Cardoso, MD, PhD, a Gregory I. Snell, MD, MBBS, FRACP, b Peter Hopkins, MD, c Gerhard
Evolving Technology Clinical application of airway bypass with paclitaxel-eluting stents: Early results Paulo F. G. Cardoso, MD, PhD, a Gregory I. Snell, MD, MBBS, FRACP, b Peter Hopkins, MD, c Gerhard
Emphysema. Endoscopic lung volume reduction. PhD. Chief, department of chest diseases and thoracic oncology. JM VERGNON M.D, PhD.
 Emphysema Endoscopic lung volume reduction JM VERGNON M.D, PhD. PhD. Chief, department of chest diseases and thoracic oncology Genève 2010 INSERM IFR 143 Physiological concepts EMPHYSEMA Slide of Ch H
Emphysema Endoscopic lung volume reduction JM VERGNON M.D, PhD. PhD. Chief, department of chest diseases and thoracic oncology Genève 2010 INSERM IFR 143 Physiological concepts EMPHYSEMA Slide of Ch H
Introduction to Interventional Pulmonology
 Introduction to Interventional Pulmonology Alexander Chen, M.D. Director, Interventional Pulmonology Assistant Professor of Medicine and Surgery Divisions of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine and Cardiothoracic
Introduction to Interventional Pulmonology Alexander Chen, M.D. Director, Interventional Pulmonology Assistant Professor of Medicine and Surgery Divisions of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine and Cardiothoracic
Endobronchial valve insertion to reduce lung volume in emphysema
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Endobronchial valve insertion to reduce lung volume in emphysema Emphysema is a chronic lung disease that
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Endobronchial valve insertion to reduce lung volume in emphysema Emphysema is a chronic lung disease that
Methodological Aspects of Bronchoscopic Lung Volume Reduction with a Proprietary System
 Technical Review Respiration 2003;70:658 664 DOI: 10.1159/000075217 Received: November 12, 2002 Accepted after revision: July 4, 2003 Methodological Aspects of Bronchoscopic Lung Volume Reduction with
Technical Review Respiration 2003;70:658 664 DOI: 10.1159/000075217 Received: November 12, 2002 Accepted after revision: July 4, 2003 Methodological Aspects of Bronchoscopic Lung Volume Reduction with
Jay B. Brodsky, M.D. Professor Department of Anesthesia tel: (650) Stanford University School of Medicine fax: (650)
 Jay B. Brodsky, M.D. Professor Department of Anesthesia tel: (650) 725-5869 Stanford University School of Medicine fax: (650) 725-8544 Stanford, CA, 94305, USA e-mail: jbrodsky@stanford.edu RELIABLE SEPARATION
Jay B. Brodsky, M.D. Professor Department of Anesthesia tel: (650) 725-5869 Stanford University School of Medicine fax: (650) 725-8544 Stanford, CA, 94305, USA e-mail: jbrodsky@stanford.edu RELIABLE SEPARATION
Interventional procedures guidance Published: 20 December 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg600
 Endobronchial valve insertion to reduce lung volume in emphysema Interventional procedures guidance Published: 20 December 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg600 Your responsibility This guidance represents
Endobronchial valve insertion to reduce lung volume in emphysema Interventional procedures guidance Published: 20 December 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg600 Your responsibility This guidance represents
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide
 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide NOTE: A very useful Study Guide! This Pre-lab guide takes you through the important concepts that where discussed in the lab videos. There will be some conceptual questions
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide NOTE: A very useful Study Guide! This Pre-lab guide takes you through the important concepts that where discussed in the lab videos. There will be some conceptual questions
Therapeutic Bronchoscopy Etiology - Benign Stenosis Post - intubation Trauma Post - operative Inflammatory Idiopathic
 Endobronchial Palliation of Airway Disease Douglas E. Wood, MD Professor and Chief Division of Cardiothoracic Surgery Vice-Chair, Department of Surgery Endowed Chair in Lung Cancer Research University
Endobronchial Palliation of Airway Disease Douglas E. Wood, MD Professor and Chief Division of Cardiothoracic Surgery Vice-Chair, Department of Surgery Endowed Chair in Lung Cancer Research University
Стенты «Ella-cs» Уважаемые коллеги! Высылаем очередной выпуск «Issue of ELLA Abstracts»
 Уважаемые коллеги! Высылаем очередной выпуск «Issue of ELLA Abstracts» A. Esophageal Stenting and related topics 1 AMJG 2009; 104:1329 1330 Letters to Editor Early Tracheal Stenosis Post Esophageal Stent
Уважаемые коллеги! Высылаем очередной выпуск «Issue of ELLA Abstracts» A. Esophageal Stenting and related topics 1 AMJG 2009; 104:1329 1330 Letters to Editor Early Tracheal Stenosis Post Esophageal Stent
SPIRATION. VALVE SYSTEM For the Treatment of Emphysema or Air Leaks.
 SPIRATION VALVE SYSTEM For the Treatment of Emphysema or Air Leaks. 0000 ENGINEERED FOR AIRWAY MANAGEMENT Inspired by aerodynamics, the Spiration Valve redirects air away from diseased or damaged lung
SPIRATION VALVE SYSTEM For the Treatment of Emphysema or Air Leaks. 0000 ENGINEERED FOR AIRWAY MANAGEMENT Inspired by aerodynamics, the Spiration Valve redirects air away from diseased or damaged lung
Surgery has been proven to be beneficial for selected patients
 Thoracoscopic Lung Volume Reduction Surgery Robert J. McKenna, Jr, MD Surgery has been proven to be beneficial for selected patients with severe emphysema. Compared with medical management, lung volume
Thoracoscopic Lung Volume Reduction Surgery Robert J. McKenna, Jr, MD Surgery has been proven to be beneficial for selected patients with severe emphysema. Compared with medical management, lung volume
Interventional Pulmonology
 Interventional Pulmonology The Division of Thoracic Surgery Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery New York Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical College p: 212-746-6275 f: 212-746-8223 https://weillcornell.org/eshostak
Interventional Pulmonology The Division of Thoracic Surgery Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery New York Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical College p: 212-746-6275 f: 212-746-8223 https://weillcornell.org/eshostak
Bronchoscopic procedures for emphysema treatment
 European Journal of Cardio-thoracic Surgery 29 (2006) 281 287 Review Bronchoscopic procedures for emphysema treatment Federico Venuta *, Erino A. Rendina, Tiziano De Giacomo, Marco Anile, Daniele Diso,
European Journal of Cardio-thoracic Surgery 29 (2006) 281 287 Review Bronchoscopic procedures for emphysema treatment Federico Venuta *, Erino A. Rendina, Tiziano De Giacomo, Marco Anile, Daniele Diso,
EMPHYSEMA THERAPY. Information brochure for valve therapy in the treatment of emphysema.
 EMPHYSEMA THERAPY Information brochure for valve therapy in the treatment of emphysema. PATIENTS WITH EMPHYSEMA With every breath, lungs deliver oxygen to the rest of the body to perform essential life
EMPHYSEMA THERAPY Information brochure for valve therapy in the treatment of emphysema. PATIENTS WITH EMPHYSEMA With every breath, lungs deliver oxygen to the rest of the body to perform essential life
The Influence of Altered Pulmonarv
 The Influence of Altered Pulmonarv J Mechanics on the Adequacy of Controlled Ventilation Peter Hutchin, M.D., and Richard M. Peters, M.D. W ' hereas during spontaneous respiration the individual determines
The Influence of Altered Pulmonarv J Mechanics on the Adequacy of Controlled Ventilation Peter Hutchin, M.D., and Richard M. Peters, M.D. W ' hereas during spontaneous respiration the individual determines
H yperinflation and gas trapping are devastating consequences
 623 EMPHYSEMA Transpleural ventilation of explanted human lungs Cliff K Choong, Peter T Macklem, John A Pierce, Stephen S Lefrak, Jason C Woods, Mark S Conradi, Dimitry A Yablonskiy, James C Hogg, Kimiaki
623 EMPHYSEMA Transpleural ventilation of explanted human lungs Cliff K Choong, Peter T Macklem, John A Pierce, Stephen S Lefrak, Jason C Woods, Mark S Conradi, Dimitry A Yablonskiy, James C Hogg, Kimiaki
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lung volume reduction for severe emphysema: do we need a scalpel or a scope?
 Eur Respir Rev 2010; 19: 117, 242 247 DOI: 1183/09059180005810 CopyrightßERS 2010 REVIEW: ENDOSCOPY Lung volume reduction for severe emphysema: do we need a scalpel or a scope? D. Van Raemdonck* and V.
Eur Respir Rev 2010; 19: 117, 242 247 DOI: 1183/09059180005810 CopyrightßERS 2010 REVIEW: ENDOSCOPY Lung volume reduction for severe emphysema: do we need a scalpel or a scope? D. Van Raemdonck* and V.
Lung Cancer Resection
 Lung Cancer Resection Introduction The occurrence of lung cancer has increased dramatically over the last 50 years. Your health care provider may have recommended an operation to remove your lung cancer.
Lung Cancer Resection Introduction The occurrence of lung cancer has increased dramatically over the last 50 years. Your health care provider may have recommended an operation to remove your lung cancer.
Nonsurgical Management of Postoperative Pulmonary Vein Stenosis
 Nonsurgical Management of Postoperative Pulmonary Vein Stenosis 부산의대소아청소년과학교실부산대학교어린이병원심장센터 이형두 Postop pulmonary vein stenosis TAPVR or PAPVR repair Primary pulmonary vein stenosis Lung transplantation
Nonsurgical Management of Postoperative Pulmonary Vein Stenosis 부산의대소아청소년과학교실부산대학교어린이병원심장센터 이형두 Postop pulmonary vein stenosis TAPVR or PAPVR repair Primary pulmonary vein stenosis Lung transplantation
How does COPD really work?
 How does COPD really work? by Alex Goodell View online Where does COPD fit in the mix of respiratory diseases? I ve made a map of the major pathologies outlined in Robbins and First Aid (obviously these
How does COPD really work? by Alex Goodell View online Where does COPD fit in the mix of respiratory diseases? I ve made a map of the major pathologies outlined in Robbins and First Aid (obviously these
Thoracoscopy for Lung Cancer
 Thoracoscopy for Lung Cancer Introduction The occurrence of lung cancer has increased dramatically over the last 50 years. Your doctor may have recommended an operation to remove your lung cancer. The
Thoracoscopy for Lung Cancer Introduction The occurrence of lung cancer has increased dramatically over the last 50 years. Your doctor may have recommended an operation to remove your lung cancer. The
Reducing lung volume in emphysema Surgical Aspects
 Reducing lung volume in emphysema Surgical Aspects Simon Jordan Consultant Thoracic Surgeon Royal Brompton Hospital Thirteenth Cambridge Chest Meeting April 2015 Surgical aspects of LVR Why we should NOT
Reducing lung volume in emphysema Surgical Aspects Simon Jordan Consultant Thoracic Surgeon Royal Brompton Hospital Thirteenth Cambridge Chest Meeting April 2015 Surgical aspects of LVR Why we should NOT
Capnography (ILS/ALS)
 Capnography (ILS/ALS) Clinical Indications: 1. Capnography shall be used as soon as possible in conjunction with any airway management adjunct, including endotracheal, Blind Insertion Airway Devices (BIAD)
Capnography (ILS/ALS) Clinical Indications: 1. Capnography shall be used as soon as possible in conjunction with any airway management adjunct, including endotracheal, Blind Insertion Airway Devices (BIAD)
Endoscopy. Pulmonary Endoscopy
 Pulmonary 1 Direct visualization of TB tree Developed in 1890 s to remove foreign bodies - rigid metal tube Advances added light system, Sx Flexible fiberoptic scopes introduced in early 1960 s 2 Used
Pulmonary 1 Direct visualization of TB tree Developed in 1890 s to remove foreign bodies - rigid metal tube Advances added light system, Sx Flexible fiberoptic scopes introduced in early 1960 s 2 Used
TRACHEOSTOMY. Tracheostomy means creation an artificial opening in the trachea with tracheostomy tube insertion
 TRACHEOSTOMY Definition Tracheostomy means creation an artificial opening in the trachea with tracheostomy tube insertion Indications for tracheostomy 1-upper airway obstruction with stridor, air hunger,
TRACHEOSTOMY Definition Tracheostomy means creation an artificial opening in the trachea with tracheostomy tube insertion Indications for tracheostomy 1-upper airway obstruction with stridor, air hunger,
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
An Image Repository for Chest CT
 An Image Repository for Chest CT Francesco Frajoli for the Chest CT in Antibody Deficiency Group An Image Repository for Chest CT he Chest CT in Antibody Deficiency Group is an international and interdisciplinary
An Image Repository for Chest CT Francesco Frajoli for the Chest CT in Antibody Deficiency Group An Image Repository for Chest CT he Chest CT in Antibody Deficiency Group is an international and interdisciplinary
Prospective, randomized controlled study of paclitaxel-coated versus plain balloon angioplasty for the treatment of failing dialysis access
 Prospective, randomized controlled study of paclitaxel-coated versus plain balloon angioplasty for the treatment of failing dialysis access Disclosure Speaker name:... I have the following potential conflicts
Prospective, randomized controlled study of paclitaxel-coated versus plain balloon angioplasty for the treatment of failing dialysis access Disclosure Speaker name:... I have the following potential conflicts
Emphysema is a debilitating lung disease with a significant
 Bronchoscopic Lung-Volume Reduction With One-Way Valves in Patients With Heterogenous Emphysema Federico Venuta, MD, Tiziano de Giacomo, MD, Erino A. Rendina, MD, Anna Maria Ciccone, MD, Daniele Diso,
Bronchoscopic Lung-Volume Reduction With One-Way Valves in Patients With Heterogenous Emphysema Federico Venuta, MD, Tiziano de Giacomo, MD, Erino A. Rendina, MD, Anna Maria Ciccone, MD, Daniele Diso,
Regardless of whether you are a vascular surgeon,
 C A S E R E P O R T The Versatility of the GORE VIABAHN Endoprosthesis Several case reports highlighting its unique design and why it is a valuable tool for the interventionist. BY PETER WAYNE, MD Regardless
C A S E R E P O R T The Versatility of the GORE VIABAHN Endoprosthesis Several case reports highlighting its unique design and why it is a valuable tool for the interventionist. BY PETER WAYNE, MD Regardless
Keywords: bronchoscopy; emphysema; lung volume reduction
 Endoscopic Lung Volume Reduction An American Perspective Hans J. Lee 1 *, Samira Shojaee 2 *, and Daniel H. Sterman 3 1 Interventional Pulmonology, Pulmonary Disease, and Critical Care Medicine, The Johns
Endoscopic Lung Volume Reduction An American Perspective Hans J. Lee 1 *, Samira Shojaee 2 *, and Daniel H. Sterman 3 1 Interventional Pulmonology, Pulmonary Disease, and Critical Care Medicine, The Johns
VIRTUS: Trial Design and Primary Endpoint Results
 VIRTUS: Trial Design and Primary Endpoint Results Mahmood K. Razavi, MD St. Joseph Cardiac and Vascular Center Orange, CA, USA IMPORTANT INFORMATION: These materials are intended to describe common clinical
VIRTUS: Trial Design and Primary Endpoint Results Mahmood K. Razavi, MD St. Joseph Cardiac and Vascular Center Orange, CA, USA IMPORTANT INFORMATION: These materials are intended to describe common clinical
Review Article Bronchoscopic Lung Volume Reduction
 Pulmonary Medicine Volume 2011, Article ID 610802, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2011/610802 Review Article Bronchoscopic Lung Volume Reduction Armin Ernst 1 and Devanand Anantham 2 1 Pulmonary, Critical Care and
Pulmonary Medicine Volume 2011, Article ID 610802, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2011/610802 Review Article Bronchoscopic Lung Volume Reduction Armin Ernst 1 and Devanand Anantham 2 1 Pulmonary, Critical Care and
IN ARTERIOVENOUS FISTULA FAILURE
 DRUG ELUTING BALLOON ANGIOPLASTY IN ARTERIOVENOUS FISTULA FAILURE Nicola Troisi, MD GUIDELINES GUIDELINES VAS 2007 GUIDELINES VAS 2007 GUIDELINES VAS 2007 GUIDELINES VAS 2007 2007!!!!!!!!!! GUIDELINES
DRUG ELUTING BALLOON ANGIOPLASTY IN ARTERIOVENOUS FISTULA FAILURE Nicola Troisi, MD GUIDELINES GUIDELINES VAS 2007 GUIDELINES VAS 2007 GUIDELINES VAS 2007 GUIDELINES VAS 2007 2007!!!!!!!!!! GUIDELINES
October Paediatric Respiratory Workbook APCP RESPIRATORY COMMITTEE
 October 2017 Paediatric Respiratory Workbook APCP RESPIRATORY COMMITTEE This workbook is designed to introduce to you the difference between paediatric and adult anatomy and physiology. It will also give
October 2017 Paediatric Respiratory Workbook APCP RESPIRATORY COMMITTEE This workbook is designed to introduce to you the difference between paediatric and adult anatomy and physiology. It will also give
LVRS and Endobronchial Therapy for Emphysema: Is it Still Viable?
 LVRS and Endobronchial Therapy for Emphysema: Is it Still Viable? Malcolm M. DeCamp, MD Fowler McCormick Professor of Surgery Feinberg School of Medicine Chief, Division of Thoracic Surgery Disclosures
LVRS and Endobronchial Therapy for Emphysema: Is it Still Viable? Malcolm M. DeCamp, MD Fowler McCormick Professor of Surgery Feinberg School of Medicine Chief, Division of Thoracic Surgery Disclosures
Paramedic Rounds. Pre-Hospital Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP)
 Paramedic Rounds Pre-Hospital Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Morgan Hillier MD Class of 2011 Dr. Mike Peddle Assistant Medical Director SWORBHP Objectives Outline evidence for pre-hospital
Paramedic Rounds Pre-Hospital Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Morgan Hillier MD Class of 2011 Dr. Mike Peddle Assistant Medical Director SWORBHP Objectives Outline evidence for pre-hospital
DISEASES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 2018 DR HEYAM AWAD LECTURE 2: ATELECTASIS AND EMPHYSEMA
 DISEASES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 2018 DR HEYAM AWAD LECTURE 2: ATELECTASIS AND EMPHYSEMA INTRODUCTION In this lecture we will discuss atelectasis which is a complication of several medical and surgical
DISEASES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 2018 DR HEYAM AWAD LECTURE 2: ATELECTASIS AND EMPHYSEMA INTRODUCTION In this lecture we will discuss atelectasis which is a complication of several medical and surgical
DUMON-NOVATECH Y-STENTS: A FOUR-YEAR EXPERIENCE WITH 50 TRACHEOBRONCHIAL TUMORS INVOLVING THE CARINA
 Solunum 3, Özel Sayı 2: 260-264, 2001 DUMON-NOVATECH Y-STENTS: A FOUR-YEAR EXPERIENCE WITH 50 TRACHEOBRONCHIAL TUMORS INVOLVING THE CARINA Jean F DUMON* M C DUMON* SUMMARY This article reports a 4-year
Solunum 3, Özel Sayı 2: 260-264, 2001 DUMON-NOVATECH Y-STENTS: A FOUR-YEAR EXPERIENCE WITH 50 TRACHEOBRONCHIAL TUMORS INVOLVING THE CARINA Jean F DUMON* M C DUMON* SUMMARY This article reports a 4-year
Pulmonary. Pulmonary Endoscopy. Alair Bronchial Thermoplasty System. Transbronchial Aspiration Needles. Cytology Brushes.
 Pulmonary Endoscopy Alair Bronchial Thermoplasty System Alair Bronchial Thermoplasty System... 79 Airway Stents Dynamic (Y) Stent... 79 Polyflex Self-Expanding Silicone Airway Stent... 82 Ultraflex Partially
Pulmonary Endoscopy Alair Bronchial Thermoplasty System Alair Bronchial Thermoplasty System... 79 Airway Stents Dynamic (Y) Stent... 79 Polyflex Self-Expanding Silicone Airway Stent... 82 Ultraflex Partially
Pulmonary circulation. Lung Blood supply : lungs have a unique blood supply system :
 Dr. Ali Naji Pulmonary circulation Lung Blood supply : lungs have a unique blood supply system : 1. Pulmonary circulation 2. Bronchial circulation 1- Pulmonary circulation : receives the whole cardiac
Dr. Ali Naji Pulmonary circulation Lung Blood supply : lungs have a unique blood supply system : 1. Pulmonary circulation 2. Bronchial circulation 1- Pulmonary circulation : receives the whole cardiac
Respiratory System Mechanics
 M56_MARI0000_00_SE_EX07.qxd 8/22/11 3:02 PM Page 389 7 E X E R C I S E Respiratory System Mechanics Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Demonstrate the mechanics of the lungs during respiration if a bell jar
M56_MARI0000_00_SE_EX07.qxd 8/22/11 3:02 PM Page 389 7 E X E R C I S E Respiratory System Mechanics Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Demonstrate the mechanics of the lungs during respiration if a bell jar
Airway Remodeling: Preliminary Experience with Bio-Absorbable Airway Stents in Adults Jaus MO, Gonfiotti A, Barale D, Macchiarini P
 Airway Remodeling: Preliminary Experience with Bio-Absorbable Airway Stents in Adults Jaus MO, Gonfiotti A, Barale D, Macchiarini P University Hospital Careggi Florence, Italy Disclosure Statement THE
Airway Remodeling: Preliminary Experience with Bio-Absorbable Airway Stents in Adults Jaus MO, Gonfiotti A, Barale D, Macchiarini P University Hospital Careggi Florence, Italy Disclosure Statement THE
4/24/2017. Tracheal Stenosis. Tracheal Stenosis. Tracheal Stenosis. Tracheal Stenosis. Tracheal Stenosis Endoscopic & Surgical Management
 Endoscopic & Surgical Management Pressure ulceration Healing: granulation cicatrization contraction Ann Surg 1969;169:334-348 Gary Schwartz, MD Department of Thoracic Surgery and Lung Transplantation Baylor
Endoscopic & Surgical Management Pressure ulceration Healing: granulation cicatrization contraction Ann Surg 1969;169:334-348 Gary Schwartz, MD Department of Thoracic Surgery and Lung Transplantation Baylor
Disclosures. Learning Objectives. Coeditor/author. Associate Science Editor, American Heart Association
 Tracheotomy Challenges for airway specialists Elizabeth H. Sinz, MD Professor of Anesthesiology & Neurosurgery Associate Dean for Clinical Simulation Disclosures Coeditor/author Associate Science Editor,
Tracheotomy Challenges for airway specialists Elizabeth H. Sinz, MD Professor of Anesthesiology & Neurosurgery Associate Dean for Clinical Simulation Disclosures Coeditor/author Associate Science Editor,
Rigid Bronchoscopic Intervention in Patients with Respiratory Failure Caused by Malignant Central Airway Obstruction
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Rigid Bronchoscopic Intervention in Patients with Respiratory Failure Caused by Malignant Central Airway Obstruction Kyeongman Jeon, MD, Hojoong Kim, MD, Chang-Min Yu, MD, Won-Jung Koh,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Rigid Bronchoscopic Intervention in Patients with Respiratory Failure Caused by Malignant Central Airway Obstruction Kyeongman Jeon, MD, Hojoong Kim, MD, Chang-Min Yu, MD, Won-Jung Koh,
PCI in Patients with Transplant Coronary Artery Disease. Michael S. Lee, MD, FACC, FSCAI Assistant Professor UCLA School of Medicine
 PCI in Patients with Transplant Coronary Artery Disease Michael S. Lee, MD, FACC, FSCAI Assistant Professor UCLA School of Medicine Faculty Disclosure Honararia for Boston Scientific, BMS, Daiichi Sankyo,
PCI in Patients with Transplant Coronary Artery Disease Michael S. Lee, MD, FACC, FSCAI Assistant Professor UCLA School of Medicine Faculty Disclosure Honararia for Boston Scientific, BMS, Daiichi Sankyo,
MODERATOR Felix Rapaport, other members of this
 The First Lung Transplant in Man (1963) and the First Heart Transplant in Man (1964) J.D. Hardy MODERATOR Felix Rapaport, other members of this distinguished panel, and members of the audience, I will
The First Lung Transplant in Man (1963) and the First Heart Transplant in Man (1964) J.D. Hardy MODERATOR Felix Rapaport, other members of this distinguished panel, and members of the audience, I will
ANGIOPLASTY AND STENTING
 ANGIOPLASTY AND STENTING What is angioplasty and stenting? During an angioplasty, your vascular surgeon inflates a small balloon inside a narrowed blood vessel. This balloon helps to widen your blood vessel
ANGIOPLASTY AND STENTING What is angioplasty and stenting? During an angioplasty, your vascular surgeon inflates a small balloon inside a narrowed blood vessel. This balloon helps to widen your blood vessel
squamous-cell carcinoma1
 Thorax (1975), 30, 152. Local ablative procedures designed to destroy squamous-cell carcinoma1 J. M. LEE, FREDERICK P. STITIK, DARRYL CARTER, and R. ROBINSON BAKER Departments of Surgery, Pathology, and
Thorax (1975), 30, 152. Local ablative procedures designed to destroy squamous-cell carcinoma1 J. M. LEE, FREDERICK P. STITIK, DARRYL CARTER, and R. ROBINSON BAKER Departments of Surgery, Pathology, and
INDEPENDENT LUNG VENTILATION
 INDEPENDENT LUNG VENTILATION Giuseppe A. Marraro, MD Director Anaesthesia and Intensive Care Department Paediatric Intensive Care Unit Fatebenefratelli and Ophthalmiatric Hospital Milan, Italy gmarraro@picu.it
INDEPENDENT LUNG VENTILATION Giuseppe A. Marraro, MD Director Anaesthesia and Intensive Care Department Paediatric Intensive Care Unit Fatebenefratelli and Ophthalmiatric Hospital Milan, Italy gmarraro@picu.it
1. When a patient fails to ventilate or oxygenate adequately, the problem is caused by pathophysiological factors such as hyperventilation.
 Chapter 1: Principles of Mechanical Ventilation TRUE/FALSE 1. When a patient fails to ventilate or oxygenate adequately, the problem is caused by pathophysiological factors such as hyperventilation. F
Chapter 1: Principles of Mechanical Ventilation TRUE/FALSE 1. When a patient fails to ventilate or oxygenate adequately, the problem is caused by pathophysiological factors such as hyperventilation. F
Lessons & Perspectives: What is the role of Cryoplasty in SFA Intervention?
 Lessons & Perspectives: What is the role of Cryoplasty in SFA Intervention? Michael Wholey, MD, MBA San Antonio, TX USA 19/06/2009 at 09:35 during 4mn as a Speaker Session: Improving Femoral Artery Recanalization
Lessons & Perspectives: What is the role of Cryoplasty in SFA Intervention? Michael Wholey, MD, MBA San Antonio, TX USA 19/06/2009 at 09:35 during 4mn as a Speaker Session: Improving Femoral Artery Recanalization
Respiratory Physiology In-Lab Guide
 Respiratory Physiology In-Lab Guide Read Me Study Guide Check Your Knowledge, before the Practical: 1. Understand the relationship between volume and pressure. Understand the three respiratory pressures
Respiratory Physiology In-Lab Guide Read Me Study Guide Check Your Knowledge, before the Practical: 1. Understand the relationship between volume and pressure. Understand the three respiratory pressures
Bi-Level Therapy: Boosting Comfort & Compliance in Apnea Patients
 Bi-Level Therapy: Boosting Comfort & Compliance in Apnea Patients Objectives Describe nocturnal ventilation characteristics that may indicate underlying conditions and benefits of bilevel therapy for specific
Bi-Level Therapy: Boosting Comfort & Compliance in Apnea Patients Objectives Describe nocturnal ventilation characteristics that may indicate underlying conditions and benefits of bilevel therapy for specific
Bronchial valve treatment for pulmonary air leak after anatomic lung resection for cancer.
 ERJ Express. Published on November 14, 2013 as doi: 10.1183/09031936.00117613 Bronchial valve treatment for air leak. Bronchial valve treatment for pulmonary air leak after anatomic lung resection for
ERJ Express. Published on November 14, 2013 as doi: 10.1183/09031936.00117613 Bronchial valve treatment for air leak. Bronchial valve treatment for pulmonary air leak after anatomic lung resection for
Acute dissections of the descending thoracic aorta (Debakey
 Endovascular Treatment of Acute Descending Thoracic Aortic Dissections Nimesh D. Desai, MD, PhD, and Joseph E. Bavaria, MD Acute dissections of the descending thoracic aorta (Debakey type III or Stanford
Endovascular Treatment of Acute Descending Thoracic Aortic Dissections Nimesh D. Desai, MD, PhD, and Joseph E. Bavaria, MD Acute dissections of the descending thoracic aorta (Debakey type III or Stanford
Pathology of Cardiovascular Interventions. Body and Disease 2011
 Pathology of Cardiovascular Interventions Body and Disease 2011 Coronary Artery Atherosclerosis Intervention Goals: Acute Coronary Syndromes: Treat plaque rupture and thrombosis Significant Disease: Prevent
Pathology of Cardiovascular Interventions Body and Disease 2011 Coronary Artery Atherosclerosis Intervention Goals: Acute Coronary Syndromes: Treat plaque rupture and thrombosis Significant Disease: Prevent
Novatech Products for Interventional Pulmonology
 Novatech Products for Novatech and Boston Medical Products Bringing you the finest products for Novatech is a manufacturer of top-quality medical products used successfully worldwide in the growing specialty
Novatech Products for Novatech and Boston Medical Products Bringing you the finest products for Novatech is a manufacturer of top-quality medical products used successfully worldwide in the growing specialty
POSITION DESCRIPTION / PERFORMANCE EVALUATION
 POSITION DESCRIPTION / PERFORMANCE EVALUATION Job Title: Cardiopulmonary Services Manager Prepared by: Date: Supervised by: Cardiopulmonary Services Medical Director, CEO Approved by: Date: Job Summary:
POSITION DESCRIPTION / PERFORMANCE EVALUATION Job Title: Cardiopulmonary Services Manager Prepared by: Date: Supervised by: Cardiopulmonary Services Medical Director, CEO Approved by: Date: Job Summary:
EMS System for Metropolitan Oklahoma City and Tulsa 2017 Medical Control Board Treatment Protocols
 S O EMT EMT-INTERMEDIATE 85 ADVANCED EMT PARAMEDIC 3H WAVEFORM CAPNOGRAPHY ADULT & PEDIATRIC Indications: 1. Medical General Assessment/General Supportive Care. 2. Trauma General Assessment/Trauma & Hypovolemic
S O EMT EMT-INTERMEDIATE 85 ADVANCED EMT PARAMEDIC 3H WAVEFORM CAPNOGRAPHY ADULT & PEDIATRIC Indications: 1. Medical General Assessment/General Supportive Care. 2. Trauma General Assessment/Trauma & Hypovolemic
Respiratory Physiology
 Respiratory Physiology Dr. Aida Korish Associate Prof. Physiology KSU The main goal of respiration is to 1-Provide oxygen to tissues 2- Remove CO2 from the body. Respiratory system consists of: Passages
Respiratory Physiology Dr. Aida Korish Associate Prof. Physiology KSU The main goal of respiration is to 1-Provide oxygen to tissues 2- Remove CO2 from the body. Respiratory system consists of: Passages
Incomplete fissures are associated with increased alveolar ventilation via spiracles in severe emphysema
 Interactive CardioVascular and Thoracic Surgery 25 (2017) 851 855 doi:10.1093/icvts/ivx220 Advance Access publication 6 July 2017 THORACIC Cite this article as: Khauli S, Abston E, Sajjad H, Bolukbas S,
Interactive CardioVascular and Thoracic Surgery 25 (2017) 851 855 doi:10.1093/icvts/ivx220 Advance Access publication 6 July 2017 THORACIC Cite this article as: Khauli S, Abston E, Sajjad H, Bolukbas S,
Does the Presence of Preoperative Mild or Moderate Coronary Artery Disease Affect the Outcomes of Lung Transplantation?
 Does the Presence of Preoperative Mild or Moderate Coronary Artery Disease Affect the Outcomes of Lung Transplantation? Cliff K. Choong, FRACS, Bryan F. Meyers, MD, Tracey J. Guthrie, BSN, Elbert P. Trulock,
Does the Presence of Preoperative Mild or Moderate Coronary Artery Disease Affect the Outcomes of Lung Transplantation? Cliff K. Choong, FRACS, Bryan F. Meyers, MD, Tracey J. Guthrie, BSN, Elbert P. Trulock,
Endovascular Repair of Aortic Arch/Thoracic Aneurysms: Bolton RelayBranch Device
 Endovascular Repair of Aortic Arch/Thoracic Aneurysms: Bolton RelayBranch Device Luis A. Sanchez MD Gregorio A. Sicard Distinguished Professor of Surgery & Radiology Chief, Section of Vascular Surgery
Endovascular Repair of Aortic Arch/Thoracic Aneurysms: Bolton RelayBranch Device Luis A. Sanchez MD Gregorio A. Sicard Distinguished Professor of Surgery & Radiology Chief, Section of Vascular Surgery
Successful Endobronchial stenting for bronchial compression from a massive thoracic aortic aneurysm
 Successful Endobronchial stenting for bronchial compression from a massive thoracic aortic aneurysm Authors: David Comer (1), Amit Bedi (2), Peter Kennedy (2), Kieran McManus (2), and Werner McIlwaine
Successful Endobronchial stenting for bronchial compression from a massive thoracic aortic aneurysm Authors: David Comer (1), Amit Bedi (2), Peter Kennedy (2), Kieran McManus (2), and Werner McIlwaine
Branch Pulmonary Artery Stenosis Long-term Outcomes of Endovascular Stenting
 Branch Pulmonary Artery Stenosis Long-term Outcomes of Endovascular Stenting Lee Benson MD Professor Pediatrics (Cardiology) Director, Cardiac Diagnostic & Interventional Unit The Hospital for Sick Children
Branch Pulmonary Artery Stenosis Long-term Outcomes of Endovascular Stenting Lee Benson MD Professor Pediatrics (Cardiology) Director, Cardiac Diagnostic & Interventional Unit The Hospital for Sick Children
NEW INTERVENTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES
 by Lawrence M Prescott, PhD NEW INTERVENTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES EXPAND TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE Novel interventional techniques are proving to be of particular value in the treatment of
by Lawrence M Prescott, PhD NEW INTERVENTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES EXPAND TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE Novel interventional techniques are proving to be of particular value in the treatment of
Advanced Bronchoscopy
 Advanced Bronchoscopy Radial Jaw 4 Pulmonary Forceps Ultraflex Tracheobronchial Stent System CRE Pulmonary Balloon Alair Bronchial Thermoplasty Catheter CRE Pulmonary Balloon Radial Jaw 4 Pulmonary Forceps
Advanced Bronchoscopy Radial Jaw 4 Pulmonary Forceps Ultraflex Tracheobronchial Stent System CRE Pulmonary Balloon Alair Bronchial Thermoplasty Catheter CRE Pulmonary Balloon Radial Jaw 4 Pulmonary Forceps
Lung Isolation: Clinical Challenges and Strategies for Success
 Lung Isolation: Clinical Challenges and Strategies for Success 2017 Dr. Alan Jay Schwartz: Hello. This is Alan Jay Schwartz, Editor-in-Chief of the American Society of Anesthesiologists 2017 Refresher
Lung Isolation: Clinical Challenges and Strategies for Success 2017 Dr. Alan Jay Schwartz: Hello. This is Alan Jay Schwartz, Editor-in-Chief of the American Society of Anesthesiologists 2017 Refresher
WHAT IS. Helping your patients understand their type of PH. Educational program by. Material endorsed by
 Educational program by Material endorsed by WHAT IS CTEPH Helping your patients understand their type of PH Provided by Bayer to help education of the PH community What is ph? B lood travels from your
Educational program by Material endorsed by WHAT IS CTEPH Helping your patients understand their type of PH Provided by Bayer to help education of the PH community What is ph? B lood travels from your
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation Procedure (TAVI)
 Page 1 of 5 Procedure (TAVI) Introduction Aortic stenosis (AS) is a common heart valve problem associated with heart failure and death. Surgical valve repair or replacement is recommended if AS patients
Page 1 of 5 Procedure (TAVI) Introduction Aortic stenosis (AS) is a common heart valve problem associated with heart failure and death. Surgical valve repair or replacement is recommended if AS patients
Tracheal Stenosis Following Cuffed Tube Tracheostomy
 Tracheal Stenosis Following Cuffed Tube Tracheostomy Anatomical Variation and Selected Treatment Armand A. Lefemine, M.D., Kenneth MacDonnell, M.D., and Hyung S. Moon, M.D. ABSTRACT Tracheal stenosis resulting
Tracheal Stenosis Following Cuffed Tube Tracheostomy Anatomical Variation and Selected Treatment Armand A. Lefemine, M.D., Kenneth MacDonnell, M.D., and Hyung S. Moon, M.D. ABSTRACT Tracheal stenosis resulting
LUNG VOLUME REDUCTION SURGERY IN PATIENTS WITH COPD
 LUNG VOLUME REDUCTION SURGERY IN PATIENTS WITH COPD Walter WEDER, Ilhan INCI, Michaela TUTIC Division of Thoracic Surgery University Hospital, Zurich, Switzerland e-mail: walter.weder@usz.ch INTRODUCTION
LUNG VOLUME REDUCTION SURGERY IN PATIENTS WITH COPD Walter WEDER, Ilhan INCI, Michaela TUTIC Division of Thoracic Surgery University Hospital, Zurich, Switzerland e-mail: walter.weder@usz.ch INTRODUCTION
Bronchoscopes: Occurrence and Management
 ORIGIAL ARTICLES Res tk iratory Acidosis wi the Small Ston-Hopkins Bronchoscopes: Occurrence and Management Kang H. Rah, M.D., Arnold M. Salzberg, M.D., C. Paul Boyan, M.D., and Lazar J. Greenfield, M.D.
ORIGIAL ARTICLES Res tk iratory Acidosis wi the Small Ston-Hopkins Bronchoscopes: Occurrence and Management Kang H. Rah, M.D., Arnold M. Salzberg, M.D., C. Paul Boyan, M.D., and Lazar J. Greenfield, M.D.
A New Treatment Paradigm Outside-In
 A New Treatment Paradigm Outside-In 2 2013 Mercator MedSystems OneMedForum Jan 8, 2013 Outside-In Response: Signal Amplification Signal convection Signal amplification Modified from Michel 2007, ATVB 3
A New Treatment Paradigm Outside-In 2 2013 Mercator MedSystems OneMedForum Jan 8, 2013 Outside-In Response: Signal Amplification Signal convection Signal amplification Modified from Michel 2007, ATVB 3
Interventional Treatment for Complete Occlusion of Arteriovenous Shunt: Our Experience in 39 cases
 Chin J Radiol 2003; 28: 137-142 137 Interventional Treatment for Complete Occlusion of Arteriovenous Shunt: Our Experience in 39 cases SHE-MENG CHENG SUK-PING NG FEI-SHIH YANG SHIN-LIN SHIH Department
Chin J Radiol 2003; 28: 137-142 137 Interventional Treatment for Complete Occlusion of Arteriovenous Shunt: Our Experience in 39 cases SHE-MENG CHENG SUK-PING NG FEI-SHIH YANG SHIN-LIN SHIH Department
FOREIGN BODY ASPIRATION in children. Dr. Xayyavong Bouathongthip, M.D Emergency department, children s hospital
 FOREIGN BODY ASPIRATION in children Dr. Xayyavong Bouathongthip, M.D Emergency department, children s hospital How common is choking? About 3,000 people die/year from choking Figure remained unchanged
FOREIGN BODY ASPIRATION in children Dr. Xayyavong Bouathongthip, M.D Emergency department, children s hospital How common is choking? About 3,000 people die/year from choking Figure remained unchanged
Combine the best of both worlds
 S c i e n c e B a s e d E v o l u t i o n s l e a d t o R e v o l u t i o n a r y S o l u t i o n s PIONEER CoCr STENT ON DEB Combine the best of both worlds A next step in cardiovascular treatment should
S c i e n c e B a s e d E v o l u t i o n s l e a d t o R e v o l u t i o n a r y S o l u t i o n s PIONEER CoCr STENT ON DEB Combine the best of both worlds A next step in cardiovascular treatment should
A Place For Airway Clearance Therapy In Today s Healthcare Environment
 A Place For Airway Clearance Therapy In Today s Healthcare Environment Michigan Society for Respiratory Care 2015 Fall Conference K. James Ehlen, MD October 6, 2015 Objectives Describe patients who will
A Place For Airway Clearance Therapy In Today s Healthcare Environment Michigan Society for Respiratory Care 2015 Fall Conference K. James Ehlen, MD October 6, 2015 Objectives Describe patients who will
Journal of the COPD Foundation. Journal Club - Endobronchial Valve Bronchoscopic Lung Volume Reduction Ron Balkissoon, MD, MSc, DIH, FRCPC 1
 118 Journal Club: Endobronchial Valve Lung Volume Reduction Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal of the COPD Foundation Journal Club Journal Club - Endobronchial Valve Bronchoscopic Lung Volume
118 Journal Club: Endobronchial Valve Lung Volume Reduction Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal of the COPD Foundation Journal Club Journal Club - Endobronchial Valve Bronchoscopic Lung Volume
Saphenous Vein Autograft Replacement
 Saphenous Vein Autograft Replacement of Severe Segmental Coronary Artery Occlusion Operative Technique Rene G. Favaloro, M.D. D irect operation on the coronary artery has been performed in 180 patients
Saphenous Vein Autograft Replacement of Severe Segmental Coronary Artery Occlusion Operative Technique Rene G. Favaloro, M.D. D irect operation on the coronary artery has been performed in 180 patients
Airway Foreign Body in Children
 Joseph E. Dohar, M.D., M.S. Dr. Dohar Financial Disclosures Alcon consultant Incusmed consultant Otonomy consultant OrbiMed consultant Learning Objectives Identify clinical situations that may require
Joseph E. Dohar, M.D., M.S. Dr. Dohar Financial Disclosures Alcon consultant Incusmed consultant Otonomy consultant OrbiMed consultant Learning Objectives Identify clinical situations that may require
Surgical indications: Non-malignant pulmonary diseases. Punnarerk Thongcharoen
 Surgical indications: Non-malignant pulmonary diseases Punnarerk Thongcharoen Non-malignant Malignant as a pathological term: Cancer Non-malignant = not cancer Malignant as an adjective: Disposed to cause
Surgical indications: Non-malignant pulmonary diseases Punnarerk Thongcharoen Non-malignant Malignant as a pathological term: Cancer Non-malignant = not cancer Malignant as an adjective: Disposed to cause
Correspondence should be addressed to Haris Kalatoudis;
 Hindawi Case Reports in Critical Care Volume 2017, Article ID 3092457, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3092457 Case Report Bronchopleural Fistula Resolution with Endobronchial Valve Placement and
Hindawi Case Reports in Critical Care Volume 2017, Article ID 3092457, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3092457 Case Report Bronchopleural Fistula Resolution with Endobronchial Valve Placement and
Solving the Dilemma of Ostial Stenting: A Case Series Illustrating the Flash Ostial System
 Volume 1, Issue 1 Case Report Solving the Dilemma of Ostial Stenting: A Case Series Illustrating the Flash Ostial System Robert F. Riley * and Bill Lombardi University of Washington Medical Center, Division
Volume 1, Issue 1 Case Report Solving the Dilemma of Ostial Stenting: A Case Series Illustrating the Flash Ostial System Robert F. Riley * and Bill Lombardi University of Washington Medical Center, Division
Ventilatory Mechanics in Patients with Cardio-Pulmonary Diseases. Part III. On Pulmonary Fibrosis
 Ventilatory Mechanics in Patients with Cardio-Pulmonary Diseases Part III. On Pulmonary Fibrosis Kazuaki SERA, M.D. Pulmonary function studies have been undertaken on the pulmonary fibrosis as diagnosed
Ventilatory Mechanics in Patients with Cardio-Pulmonary Diseases Part III. On Pulmonary Fibrosis Kazuaki SERA, M.D. Pulmonary function studies have been undertaken on the pulmonary fibrosis as diagnosed
The Atrial Septum: Opening the Septum Transseptal Needle Perforation, Radio Frequency Perforation, and Stent Placement
 The Atrial Septum: Opening the Septum Transseptal Needle Perforation, Radio Frequency Perforation, and Stent Placement Matthew J. Gillespie MD, FSCAI The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia SCAI Fellows
The Atrial Septum: Opening the Septum Transseptal Needle Perforation, Radio Frequency Perforation, and Stent Placement Matthew J. Gillespie MD, FSCAI The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia SCAI Fellows
The Respiratory System. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
Department of Thoracic Medicine, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Lin-Kuo Branch, Chang Gung Medical Foundation; Abstract
 DOI 10.6314/JIMT.2017.28(4).07 2017 28 243-251 Impacts of Airway Self-expandable Metallic Stent on Ventilator Weaning and Survival of Mechanically Ventilated Patients with Esophageal Cancer and Cental
DOI 10.6314/JIMT.2017.28(4).07 2017 28 243-251 Impacts of Airway Self-expandable Metallic Stent on Ventilator Weaning and Survival of Mechanically Ventilated Patients with Esophageal Cancer and Cental
Double Y-stenting for tracheobronchial stenosis
 ERJ Express. Published on April 10, 2012 as doi: 10.1183/09031936.00015012 Double Y-stenting for tracheobronchial stenosis M. Oki and H. Saka AFFILIATIONS Dept of Respiratory Medicine, Nagoya Medical Center,
ERJ Express. Published on April 10, 2012 as doi: 10.1183/09031936.00015012 Double Y-stenting for tracheobronchial stenosis M. Oki and H. Saka AFFILIATIONS Dept of Respiratory Medicine, Nagoya Medical Center,
Examining the Biodegradable Stent
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/heart-matters/examining-the-biodegradable-stent/3983/
Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/heart-matters/examining-the-biodegradable-stent/3983/
CASE REPORTS. Idiopathic Unilateral Hyperlucent Lung
 CASE REPORTS Idiopathic Unilateral Hyperlucent Lung The Swyer-James Syndrome J. Judson McNamara, M.D., Harold C. Urschel, M.D., J. H. Arndt, M.D., Herman Ulevitch, M.D., and W. B. Kingsley, M.D. I diopathic
CASE REPORTS Idiopathic Unilateral Hyperlucent Lung The Swyer-James Syndrome J. Judson McNamara, M.D., Harold C. Urschel, M.D., J. H. Arndt, M.D., Herman Ulevitch, M.D., and W. B. Kingsley, M.D. I diopathic
Chapter 8. Other Important Tests and Procedures. Mosby items and derived items 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 8 Other Important Tests and Procedures 1 Introduction Additional important diagnostic studies include: Sputum examination Skin tests Endoscopic examination Lung biopsy Thoracentesis Hematology,
Chapter 8 Other Important Tests and Procedures 1 Introduction Additional important diagnostic studies include: Sputum examination Skin tests Endoscopic examination Lung biopsy Thoracentesis Hematology,
PHARMACOLOGICAL TREATMENT OF ARTERIAL RESTENOSIS
 PHARMACOLOGICAL TREATMENT OF ARTERIAL RESTENOSIS PACLITAXEL VS RAPAMYCIN Paclitaxel essentially freezes the microtubules that are in place during cell division. The cells cannot complete cell division
PHARMACOLOGICAL TREATMENT OF ARTERIAL RESTENOSIS PACLITAXEL VS RAPAMYCIN Paclitaxel essentially freezes the microtubules that are in place during cell division. The cells cannot complete cell division
Respiratory Pathophysiology Cases Linda Costanzo Ph.D.
 Respiratory Pathophysiology Cases Linda Costanzo Ph.D. I. Case of Pulmonary Fibrosis Susan was diagnosed 3 years ago with diffuse interstitial pulmonary fibrosis. She tries to continue normal activities,
Respiratory Pathophysiology Cases Linda Costanzo Ph.D. I. Case of Pulmonary Fibrosis Susan was diagnosed 3 years ago with diffuse interstitial pulmonary fibrosis. She tries to continue normal activities,
Airways Disease MDT - 6th May 2014
 Airways Disease MDT - 6th May 2014 The inaugural AD-MDT was held on 6/5/14. The AIM of the meeting is to develop the skills and knowledge to be able to run an AD-MDT - the time frame from the start to
Airways Disease MDT - 6th May 2014 The inaugural AD-MDT was held on 6/5/14. The AIM of the meeting is to develop the skills and knowledge to be able to run an AD-MDT - the time frame from the start to
