Evaluation of Related Factors and the Outcome in Cardiac Arrest Resuscitation at Thammasat Emergency Department
|
|
|
- Gervase Pope
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Evaluation of Related Factors and the Outcome in Cardiac Arrest Resuscitation at Thammasat Emergency Department Kumpol Amnuaypattanapon MD* Umaporn Udomsubpayakul MSc** * Department of Emergency Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Thammasat University, Pathumthani, Thailand ** Section for Clinical Epidemiology and Biostatistics of Research Center, Faculty of Medicine, Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand Objective: In the present study, we aimed to define the factors contributing to patient survival after treatment by cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) following cardiac arrest. Material and Method: Retrospective analysis was performed on cardiac arrest patients (n = 138) who had CPR in the emergency department (ED) at Thammasat University hospital from Logistic regression was used to analyze factors that related to the sustained return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) for 20 minutes, survival until discharge, and survival up to 1 month post discharge. Results: The sustained ROSC was 22.5%, survival to discharge 5.6%, and survival from discharge to 1 month 3.6%. Significant factors related to sustained ROSC was the location of cardiac arrest, the cause of arrest, shockable rhythm with defibrillation, the time until chest compression, and CPR duration. The factor influencing survival to discharge was chest compression performed within 15 minutes after cardiac arrest (p = 0.048). No factor however could be attributed to survivability up to 1 month following discharge. Conclusion: Our findings attribute six factors associated to ROSC including the location of arrest, the cause of cardiac arrest, initial cardiac rhythm, shockable rhythm with defibrillation, the time until chest compression and CPR duration. Statistically, resuscitation performed within 15 minutes of cardiac arrest increases the survivability of patients until discharge. However, no factors could be related to the percentage of patients surviving up to 1 month post discharge. Keywords: Cardiopulmonary resuscitation, Outcomes, Factors J Med Assoc Thai 2010; 93 (Suppl. 7) : S26-S34 Full text. e-journal: In Thailand, investigations on patient survival following cardiac arrest and ED resuscitation are limited. In 2006, the National Registry of CPR reported patients who were resuscitated after cardiac arrest have higher rates of death up to 55-67%. This is comparable to research findings conducted in the United Kingdom in 2007, which reported that 71% of resuscitated cardiac arrest patients died soon after CPR (1). At present, there is a plethora of literature documenting factors contributing to sustained ROSC, and can be divided into 2 groups including factors outside the hospital and factors within the hospital. Factors outside the hospital include patients condition, Correspondence to: Amnuaypattanapon K, Department of Emergency Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Thammasat University, Pathumthani 12120, Thailand. Phone: , Fax: kumpona@hotmail.com witness of arrest and pre-hospital resuscitation (1-5). Factors within the hospital are monitoring of initial cardiac rhythm, procedures applied during resuscitation, resuscitation team and team commander (6-20). However, all of these studies do show variance. This is most likely due to each hospital differing in administration, the handling of patients during resuscitation and the roles of a resuscitation team. It has been shown that death rates of resuscitated patients in ED can be key indicators of the quality and efficiency of a hospital. For example if successful resuscitation is performed promptly after the onset of cardiac arrest, not only does a patient s chance of survivability increase, but also the chance to reduce detrimental side effects (1-5). Therefore studies of factors influencing survival of resuscitated patients are necessary as they can help in the improvement and development of resuscitation team and the organization. S26 J Med Assoc Thai Vol. 93 Suppl
2 In this study, we aim to observe the general characteristics, outcomes and factors that influence the survivability of cardiac arrest patients after resuscitation. Material and Method Patient population This retrospective analysis was conducted on cardiac arrest patients (n = 138) who had CPR in the emergency department (ED) at Thammasat University hospital from October 2007 to March The exclusion criteria was based on physician order DNAR do not attempt resuscitation and patients with incomplete medical records. The patients meeting inclusion criteria were divided into 2 groups: group 1 the patients with ROSC > 20 minutes. Group 2 the patients deceased during resuscitation or with ROSC of < 20 minutes. The two groups were studied and compared for their distinctive characteristics. A followup on group 1 patients was performed to see how they were since the administration to the day of discharge. After discharge a telephone follow-up was initiated with the patients themselves or the relatives to assess patient survivability up to 1 month post discharge. Statistical analysis Demographic data was shown as numbers of patients (n), percentage of survivability (%), mean + SD and median. The data was analyzed by comparison of continuous variables using unpaired t-test. A stepwise logistic regression analysis was used to select independent predictors to dichotomous dependent variables between sustained ROSC and non-sustained ROSC patients. Significance was accepted at p < Results Of the admitted patients, 138 patients met the criteria for the case study. Thirty-one patients had sustained ROSC of more than 20 minutes and of these, 30 patients (22.5%) were admitted, 1 transferred to another hospital, with 8 surviving to discharge (5.6%), and 5 survived up to 1 month post discharge (3.6%). This is shown in Fig. 1 and demographic data of the subjects in Table 1. The related factors associated with resuscitation of cardiac arrest patient with sustained ROSC are shown in Table 2. A result of this present study in relation to the factors and its impact with sustained ROSC using the univariate analysis, revealed that they were statistically significant (p < 0.05) to many key factors, such as in-hospital cardiac arrest with an odd ratio of 3.57 (95%, CI, ), known causes 6.57 (95% CI, ), shockable rhythm 3.25 (95% CI, ) and defibrillation 4.46 (95% CI, ). The time to the first chest compression was performed Fig. 1 Flow of the study J Med Assoc Thai Vol. 93 Suppl S27
3 Table 1. Characteristics of the cardiac arrest patients Cardiac arrest patients (n = 138) Characteristics No. (%) Characteristics No. (%) Gender Male 93 (67.4) Lethal arrhythmia 26 (18.8) Female 45 (32.6) Non arrhythmia Age(y/o), mean + 2SD Hypotension 6 (4.3) Location of arrest Respiratory depression 17 (12.3) Out-of hospital Metabolic 4 (2.9) Home 85 (61.5) AMI 7 (5.1) Transport 11 (8.0) Unknown 78 (56.6) Office 8 (5.8) Initial rhythm Road 3 (2.2) Shockable Hospital VF 15 (10.9) ER 31 (22.5) Pulseless VT 7 (5.1) Witness arrest Nonshockable Yes 72 (52.2) Asystole 97 (70.3) No 66 (47.8) PEA 17 (12.3) Prehospital CPR n/a 2 (1.4) No 132 (95.6) Shift Yes Day 54 (39.1) LR 5 (3.6) Afternoon 52 (37.7) HCP 1 (0.7) Night 32 (23.2) Mode of transport Time to 1 st chest compression (min),median Family 126 (91.3) (Min-Max) 20 (0-120) EMS 12 (8.7) Total CPR times(min), median Underlying disease (Min-Max) 30 (2-180) None 38 (27.5) Stop CPR why? Unknown 39 (28.2) ROSC 30 (21.7) CVS 34 (24.6) Death 108 (78.3) CNS 15 (10.9) ROSC Metabolic/endocrine 26 (18.8) >20 min 31 (22.5) ESRD 8 (5.8) < 20 min 107 (77.5) Respiratory 11 (8.0) ED disposition Terminal case Death 107 (77.6) Yes 21 (15.2) Refer 1 (0.7) No 105 (76.1) Admit with ROSC Unknown 12 (8.7) 20 min<rosc<24 h 8 (5.8) ACLS intervention 24< ROSC<72 h 1 (0.7) Complete 138 (100) >72h 21 (15.2) Incomplete 0 Hospital course Type of arrest Death 22 (15.9) Trauma 27 (19.6) Discharge 8 (5.6) Non-trauma 111(80.4) LOH(day), median(min-max) 4.5 (1-29) Type of trauma Time to death (day), median(min-max) 4.0 (1-21) Blunt 27 (19.6) 1 mo survival 5 (3.6) Penetrating 0 *ER; emergency room, LR; lay rescuer, HCP; health care provider, EMS; emergency medical service,cvs; cardio vascular disease, CNS; central nervous system, ESRD; end stage renal disease, AMI; acute myocardial infraction, VF; ventricular fibrillation, VT; ventricular tachycardia, PEA; pulseless electrical activity, n/a; non access, ROSC; reverse of spontaneous circulation, LOH; length of hospital stay. S28 J Med Assoc Thai Vol. 93 Suppl
4 Table 2. Related factors associated with sustained ROSC in cardiac arrest patients (n = 138) Characteristics Sustained ROSC > 20 min p-value 31 Success; 107 Failure; n (%) n (%) Gender Male 21 (67.7) 72 (67.3) Female 10 (32.3) 35 (32.7) Age(y/o), mean + 2SD Location of arrest Out-of hospital Home 14 (45.2) 71 (66.4) Transport 3 (9.7) 8 (7.5) Office 1 (3.2) 7 (6.5) Road 0 3 (2.8) Hospital ER 13 (41.9) 18 (16.8) Witness arrest Yes 21 (67.7) 51 (47.7) No 10 (32.3) 56 (52.3) Mode of transport Family 29 (93.5) 97 (90.7) EMS 2 (6.5) 10 (9.3) Underlying disease None 8 (25.8) 30 (28.0) Unknown 8 (25.8) 31 (29.0) CVS 9 (29.0) 25 (23.4) CNS 3 (9.7) 12 (11.2) Metabolic/endocrine 7 (22.6) 15 (14.0) ESRD 2 (6.5) 6 (5.6) Respiratory 5 (16.1) 6 (5.6) Terminal case Yes 2 (6.5) 19 (18.7) No 25 (80.6) 80 (74.8) Unknown 4 (12.9) 8 (7.5) Type of arrest Trauma 3 (9.7) 24 (22.4) Non-trauma 28 (90.3) 83 (77.6) Lethal arrhythmia 12 (38.7) 14 (13.0) Non arrhythmia Hypotension 1 (3.2) 5 (4.7) Respiratory 6 (19.4) 11 (10.3) Metabolic 1 (3.2) 3 (2.8) AMI 2 (6.5) 5 (4.7) Unknown 9 (29.0) 69 (64.5) Initial rhythm Shockable VF 8 (25.8) 7 (6.5) Pulseless VT 1 (3.2) 6 (5.6) Nonshockable Asystole 16 (51.6) 81 (75.7) PEA 4 (12.9) 13 (12.2) n/a 2 (6.5) 0 Defibrillation yes 9 (29.0) 9 (8.4) No 22 (71.0) 98 (91.6) J Med Assoc Thai Vol. 93 Suppl S29
5 Table 2. (Cont.) Characteristics Sustained ROSC >20 min p-value 31 Success; 107 Failure; n (%) n (%) Shift Day 15 (83.4) 39 (36.4) Afternoon 11 (35.5) 41 (38.3) Night 5 (16.1) 27 (25.3) Time to 1 st chest compression (min), (0-30) (0-120) median(min-max) Time to 1 st chest compression (min) < 15 min 15 (55.6) 25 (27.5) > 15 min 12 (44.4) 66 (72.5) Total CPR times (min), median (Min-Max) (2-60) (10-180) < Total CPR times (min) < 15 min 13 (41.9) 5 (4.7) < > 15 min 18 (58.1) 102 (95.3) within the first 15 minutes 3.30 (95% CI, ) and CPR duration less than 15 minutes (95% CI, ) are shown in Table 3. Using multivariate analysis with backward logistic regression revealed that the impact of six factors related to resuscitation of cardiac arrest patients with sustained ROSC more than or equal to 20 minutes. The impact of 2 factors is shown in Table 4, being causes of cardiac arrest. These are classified as lethal arrhythmia factor 9.17 ( ) and total CPR time less than 15 minutes ( ). Only one factor influenced survival to discharge, which was the time to the 1 st chest compression, being less than 15 minutes (Table 5). No statistically significant factor influencing survival to 1 month was found in this study. Discussion The outcome of CPR in this study is much lower when compared to statistic figures of overseas researches. The main cause being that, in developed countries a pre-hospital care system was set in place for the emergency teams. From the many researches studied, it was clear that cardiac arrest patients have a higher chance of survival if chest compression was performed as soon as possible. However, from this study 77.5% of the patients had cardiac arrest outside the hospital and of this 95.6% did not receive prehospital basic life support. In countries with successful resuscitation of cardiac arrest patients, it was clear that there is an effective system in place to assist and transport patients, effective hotline center, well equipped ambulance, and a highly skilled and experienced pre-hospital care team. With this system, in some countries advance resuscitation is performed at the location of the arrest (2,16,18,20-22). In Thailand, however a system for Emergency Medical Service is in a developing stage as there has recently been an Emergency Medical Institution of Thailand established in 2008 with a hotline number Inside information (as of 30 September 2009) from the institution s report in regards to the call through 1669 only 52.61% if the population uses this number and in Pathumthani-where Thammasat University hospital is located the use of this number is only 32%. This supports the research finding that 91.3% of the patients were transported to the hospital by members of the family. In order for the patients to receive assistance as soon as possible it is very important to promote the use of the hotline number 1669, as well as to expand the zone of this service. However, it is vital that relatives and the general public be educated on first aid and basic resuscitation so necessary assistance can be provided to the patients prior to the medical team arrival. In this aspect, hospital or concerned organization should implement and continue training these people. The sustained ROSC > 20 minutes is a patient survival success indicator because by this time all of the organs can be recovered to full functionality (1), and was employed in the present study. These groups of patients rate of survival to discharge are higher than S30 J Med Assoc Thai Vol. 93 Suppl
6 Table 3. Univariate logistic regression analysis of related factors for sustained ROSC in cardiac arrest patients. Factors Coefficient Standard error OR (95% CI) p-value Location of arrest Hospital ( ) Out-of-hospital 1 Lethal arrhythmia (VF, pulseless VT) ( ) <0.001 Non arrhythmia ( ) Unknown 1 Shockable rhythm Yes ( ) No 1 Defibrillation Yes ( ) No 1 Time to 1 st chest compression < 15 min ( ) > 15 min 1 Total CPR time < 15 min ( ) <0.001 > 15 min 1 OR, Odds ratio; CI, Confidence interval Table 4. Multivariate logistic regression analysis of related factors for sustained ROSC in cardiac arrest patients Factors Coefficient Standard error OR (95% CI) p-value Lethal arrhythmia (VF, pulseless VT) ( ) < Non arrhythmia ( ) Unknown 1 Total CPR time <15 min ( ) < > 15 min 1 that of resuscitated patients with ROSC less than 20 minutes, which normally die soon after. The percentage of surviving patients also occurred in higher frequency in cases where there was in-hospital cardiac arrest. Patients attended by medical staff are instant unlike that of out of hospital cardiac arrest having to be transported for help. Patients with cardiac arrest, especially in shockable cardiac rhythm such as: pulseless VT and VF, have a high chance of survival if help was given instantly. The results are similar to the overseas studies that if resuscitation is performed within 10 minutes (2,9,10,16,23). Therefore in crowded locations like department stores and airports an Automatic External Defibrillator (AED) should be a vailable and accessible so that if necessary, can be used on patients if required, prior to the arrival of the medical team. From this research study, no relevant statistic factors were found on factors influencing survival to one month. This may be due to the minimal number of patients fitting the criteria, as well as incomplete information recorded by the registry staff. If provided, more time to gather more samples and with a better recording system, the related factors could be found and may enhance in a greater survival number. Conclusion From 138 cardiac arrest patients resuscitated in the ED, 22.5% regained sustained ROSC, 5.6% J Med Assoc Thai Vol. 93 Suppl S31
7 Table 5. Related factors associated with survival to discharge Factors Hospital course p-value 22 hospital 8 Survival to death; n (%) discharge; n (%) Location of cardiac arrest Hospital 8 (36.4) 5 (62.5) Out-of-hospital 14 (63.6) 3 (37.5) Witness Yes 15 (68.2) 6 (75.0) No 7 (31.8) 2 (25.0) Lethal arrhythmia 8 (36.4) 3 (37.5) Non arrhythmia 7 (31.8) 3 (37.5) Unknown 7 (31.8) 2 (25.0) Initial rhythm Shockable 4 (18.2) 3 (37.5) Nonshockable 18 (81.8) 5 (62.5) Time to 1 st chest compression < 15 min 8 (36.4) 7 (87.5) > 15 min 14 (63.6) 1 (12.5) survived to discharge and 3.6% survived up to one month after discharge. Statistically factors influencing sustained ROSC are: the location of arrest, the cause of cardiac arrest, initial cardiac rhythm, shockable rhythm with defibrillation, the time until chest compression and CPR duration. Factors influencing survival to discharge are resuscitation performed within 15 minutes (p = 0.048). There was no relevant factor found in regards to one month survival after discharge, however. Study limitations From the statistic record of resuscitated patients in the ED of Thammasat University hospital from year 2007 to 2009, there were 353 patients, but only 138 met the criteria for this study. Part of the reason for the small number of patients meeting the criteria is because of an incomplete CPR record form. The form in use today is non-practical as it is not user friendly and is time consumable. Another reason is the misplacing of patient records. If a record is lost, it means a loss of an example. In the future the Utstein template should be applied and circulated for use (24). Acknowledgements We would like to thank Dr. Michael Stewart, Faculty of Heath and Behavioral Science, School of Medicine, Deakin University, Australia for editing manuscript. References 1. Nolan JP, Neumar RW, Adrie C, Aibiki M, Berg RA, Bottiger BW, et al. Post-cardiac arrest syndrome: epidemiology, pathophysiology, treatment, and prognostication. A Scientific Statement from the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation; the American Heart Association Emergency Cardiovascular Care Committee; the Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia; the Council on Cardiopulmonary, Perioperative, and Critical Care; the Council on Clinical Cardiology; the Council on Stroke. Resuscitation 2008; 79: Eckstein M, Stratton SJ, Chan LS. Cardiac arrest resuscitation evaluation in Los Angeles: CARE- LA. Ann Emerg Med 2005; 45: Eisenberg MS. Improving survival from out-ofhospital cardiac arrest: back to the basics. Ann Emerg Med 2007; 49: Herlitz J, Svensson L, Engdahl J, Gelberg J, Silfverstolpe J, Wisten A, et al. Characteristics of cardiac arrest and resuscitation by age group: an analysis from the Swedish Cardiac Arrest Registry. Am J Emerg Med 2007; 25: Herlitz J, Svensson L, Engdahl J, Silfverstolpe J. Characteristics and outcome in out-of-hospital S32 J Med Assoc Thai Vol. 93 Suppl
8 cardiac arrest when patients are found in a nonshockable rhythm. Resuscitation 2008; 76: Abe T, Tokuda Y, Ishimatsu S. Predictors for good cerebral performance among adult survivors of outof-hospital cardiac arrest. Resuscitation 2009; 80: Adams BD, Zeiler K, Jackson WO, Hughes B. Emergency medicine residents effectively direct inhospital cardiac arrest teams. Am J Emerg Med 2005; 23: Arrich J, Zeiner A, Sterz F, Janata A, Uray T, Richling N, et al. Factors associated with a change in functional outcome between one month and six months after cardiac arrest: a retrospective cohort study. Resuscitation 2009; 80: Cooper S, Janghorbani M, Cooper G. A decade of in-hospital resuscitation: outcomes and prediction of survival? Resuscitation 2006; 68: Hajbaghery MA, Mousavi G, Akbari H. Factors influencing survival after in-hospital cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Resuscitation 2005; 66: Kayser RG, Ornato JP, Peberdy MA. Cardiac arrest in the Emergency Department: a report from the National Registry of Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation. Resuscitation 2008; 78: Kellum MJ, Kennedy KW, Barney R, Keilhauer FA, Bellino M, Zuercher M, et al. Cardiocerebral resuscitation improves neurologically intact survival of patients with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Ann Emerg Med 2008; 52: Kramer-Johansen J, Edelson DP, Losert H, Kohler K, Abella BS. Uniform reporting of measured quality of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). Resuscitation 2007; 74: Lin YR, Wu HP, Huang CY, Chang YJ, Lin CY, Chou CC. Significant factors in predicting sustained ROSC in paediatric patients with traumatic out-ofhospital cardiac arrest admitted to the emergency department. Resuscitation 2007; 74: Matot I, Shleifer A, Hersch M, Lotan C, Weiniger CF, Dror Y, et al. In-hospital cardiac arrest: is outcome related to the time of arrest? Resuscitation 2006; 71: Nishiuchi T, Hayashino Y, Fukuhara S, Iwami T, Hayashi Y, Hiraide A, et al. Survival rate and factors associated with 1-month survival of witnessed out-of-hospital cardiac arrest of cardiac origin with ventricular fibrillation and pulseless ventricular tachycardia: the Utstein Osaka project. Resuscitation 2008; 78: Perkins GD, Boyle W, Bridgestock H, Davies S, Oliver Z, Bradburn S, et al. Quality of CPR during advanced resuscitation training. Resuscitation 2008; 77: Spaite DW, Bobrow BJ, Vadeboncoeur TF, Chikani V, Clark L, Mullins T, et al. The impact of prehospital transport interval on survival in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: implications for regionalization of post-resuscitation care. Resuscitation 2008; 79: Suraseranivongse S, Chawaruechai T, Saengsung P, Komoltri C. Outcome of cardiopulmonary resuscitation in a 2300-bed hospital in a developing country. Resuscitation 2006; 71: Vukmir RB. Survival from prehospital cardiac arrest is critically dependent upon response time. Resuscitation 2006; 69: Yanagawa Y, Sakamoto T. Analysis of prehospital care for cardiac arrest in an urban setting in Japan. J Emerg Med 2010; 38: Odegaard S, Olasveengen T, Steen PA, Kramer- Johansen J. The effect of transport on quality of cardiopulmonary resuscitation in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Resuscitation 2009; 80: Jacobs I, Nadkarni V, Bahr J, Berg RA, Billi JE, Bossaert L, et al. Cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation outcome reports: update and simplification of the Utstein templates for resuscitation registries. A statement for healthcare professionals from a task force of the international liaison committee on resuscitation (American Heart Association, European Resuscitation Council, Australian Resuscitation Council, New Zealand Resuscitation Council, Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada, InterAmerican Heart Foundation, Resuscitation Council of Southern Africa). Resuscitation 2004; 63: J Med Assoc Thai Vol. 93 Suppl S33
9 ศ กษาป จจ ย และผลของการก ช พต อการรอดช ว ตของผ ป วยภาวะห วใจหย ดเต นเฉ ยบพล น ในห อง ฉ กเฉ นโรงพยาบาลธรรมศาสตร เฉล มพระเก ยรต ก มพล อำนวยพ ฒนพล, อ มาพร อ ดมทร พยาก ล ว ตถ ประสงค : เพ อศ กษาผลของการก ช พและป จจ ยท ม ผลต อการรอดช ว ตหล งการก ช พ ว สด และว ธ การ: ศ กษาผลของการก ช พและใช สถ ต ช วยหาป จจ ยท ม ผลต อการรอดช ว ตของผ ป วยภาวะห วใจ หย ดเต นเฉ ยบพล น หล งการก ช พ ระหว าง ต ลาคม พ.ศ ถ ง ม นาคม พ.ศ โดยว ดความสำเร จของการก ช พ จากการ ม ช พจร และการไหลเว ยนกล บค นมานานกว าหร อเท าก บ 20 นาท การม ช ว ตรอดจนสามารถจำหน ายออกจาก โรงพยาบาล และม ช ว ตรอดจนถ งหน งเด อน ผลการศ กษา: ม ผ ป วยท ตรงเกณฑ จำนวน 138 ราย ในจำนวนน ม ช พจรและการไหลเว ยนกล บค นมานานมากกว าหร อ เท าก บ 20 นาท ร อยละ 22.5 สามารถจำหน ายออกจากโรงพยาบาลได ร อยละ 5.6 และม ช ว ตรอดจนถ งหน งเด อน ร อยละ 3.6 ป จจ ยท ทำให ผ ป วยม ช พจร และการไหลเว ยนกล บค นมานานมากกว าหร อเท าก บ 20 นาท (p < 0.05) ได แก สถานท เก ดเหต ทราบสาเหต ล กษณะคล นห วใจท สามารถใช เคร องช อกไฟฟ าห วใจ การทำการช อกห วใจ ด วยไฟฟ า ระยะเวลาท เร มม การกดหน าอก ระยะเวลาท ใช ก ช พ ป จจ ยท ม ผลต อการรอดช ว ตจนสามารถจำหน ายออก จากโรงพยาบาลค อการท ผ ป วยได ร บการกดหน าอกภายใน 15 นาท และไม พบป จจ ยท ม ผลก บการรอดช ว ต จนถ ง หน งเด อน สร ป: ผลของการก ช พ และป จจ ยต างๆ ท ม ผลต อการรอดช ว ตของผ ป วย หล งการก ช พเป นข อม ลท ม ประโยชน ต อท มก ช พ ในด านการด แลร กษา และพ ฒนามาตรฐานของการก ช พต อไป S34 J Med Assoc Thai Vol. 93 Suppl
WORKSHEET for Evidence-Based Review of Science for Veterinary CPCR
 RECOVER 2011 1 of 7 WORKSHEET for Evidence-Based Review of Science for Veterinary CPCR 1. Basic Demographics Worksheet author(s) Kate Hopper Mailing address: Dept Vet Surgical & Radiological Sciences Room
RECOVER 2011 1 of 7 WORKSHEET for Evidence-Based Review of Science for Veterinary CPCR 1. Basic Demographics Worksheet author(s) Kate Hopper Mailing address: Dept Vet Surgical & Radiological Sciences Room
Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: incidence, process of care, and outcomes in an urban city, Korea
 Clin Exp Emerg Med 2014;1(2):94-100 http://dx.doi.org/10.15441/ceem.14.021 Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: incidence, process of care, and outcomes in an urban city, Korea Hanjin Cho 1, Sungwoo Moon 1,
Clin Exp Emerg Med 2014;1(2):94-100 http://dx.doi.org/10.15441/ceem.14.021 Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: incidence, process of care, and outcomes in an urban city, Korea Hanjin Cho 1, Sungwoo Moon 1,
Protocol. This trial protocol has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work.
 Protocol This trial protocol has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Protocol for: Hasselqvist-Ax I, Riva G, Herlitz J, et al. Early cardiopulmonary resuscitation
Protocol This trial protocol has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Protocol for: Hasselqvist-Ax I, Riva G, Herlitz J, et al. Early cardiopulmonary resuscitation
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Hasegawa K, Hiraide A, Chang Y, Brown DFM. Association of prehospital advancied airway management with neurologic outcome and survival in patients with out-of-hospital cardiac
Supplementary Online Content Hasegawa K, Hiraide A, Chang Y, Brown DFM. Association of prehospital advancied airway management with neurologic outcome and survival in patients with out-of-hospital cardiac
Are There Major & Minor Changes In the Guideline 2008?
 How to Update CPR? Are There Major & Minor Changes In the Guideline 2008? Are There Major & Minor Changes In the Guideline 2008? Are Nurse anesthetists important for CPR? Sudta Parakkamodom,RN,CRNA,Sc.M
How to Update CPR? Are There Major & Minor Changes In the Guideline 2008? Are There Major & Minor Changes In the Guideline 2008? Are Nurse anesthetists important for CPR? Sudta Parakkamodom,RN,CRNA,Sc.M
In the past decade, two large randomized
 Mild therapeutic hypothermia improves outcomes compared with normothermia in cardiac-arrest patients a retrospective chart review* David Hörburger, MD; Christoph Testori, MD; Fritz Sterz, MD; Harald Herkner,
Mild therapeutic hypothermia improves outcomes compared with normothermia in cardiac-arrest patients a retrospective chart review* David Hörburger, MD; Christoph Testori, MD; Fritz Sterz, MD; Harald Herkner,
CLINICAL RESEARCH STUDY
 CLINICAL RESEARCH STUDY The Effects of Sex on Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Outcomes Manabu Akahane, MD, PhD, a Toshio Ogawa, MSc, a Soichi Koike, MD, PhD, b Seizan Tanabe, MD, c Hiromasa Horiguchi, PhD,
CLINICAL RESEARCH STUDY The Effects of Sex on Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Outcomes Manabu Akahane, MD, PhD, a Toshio Ogawa, MSc, a Soichi Koike, MD, PhD, b Seizan Tanabe, MD, c Hiromasa Horiguchi, PhD,
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Chan PS, Nallamothu BK, Krumholz HM, et al. Long-term outcomes
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Chan PS, Nallamothu BK, Krumholz HM, et al. Long-term outcomes
But unfortunately, the first sign of cardiovascular disease is often the last. Chest-Compression-Only Resuscitation Gordon A.
 THE UNIVERSITY OF ARIZONA Sarver Heart Center 1 THE UNIVERSITY OF ARIZONA Sarver Heart Center 2 But unfortunately, the first sign of cardiovascular disease is often the last 3 4 1 5 6 7 8 2 Risk of Cardiac
THE UNIVERSITY OF ARIZONA Sarver Heart Center 1 THE UNIVERSITY OF ARIZONA Sarver Heart Center 2 But unfortunately, the first sign of cardiovascular disease is often the last 3 4 1 5 6 7 8 2 Risk of Cardiac
JUST SAY NO? THE LATEST LOOK AT ACLS MEDICATIONS BRIDGETTE SVANCAREK, MD
 JUST SAY NO? THE LATEST LOOK AT ACLS MEDICATIONS BRIDGETTE SVANCAREK, MD OBJECTIVES Review the progression of the American Heart Association s ACLS cardiac arrest medication guidelines Identify the latest
JUST SAY NO? THE LATEST LOOK AT ACLS MEDICATIONS BRIDGETTE SVANCAREK, MD OBJECTIVES Review the progression of the American Heart Association s ACLS cardiac arrest medication guidelines Identify the latest
Medical Referral of Patients with Acute Respiratory Failure: Lessons learned from a Large Outbreak of Botulism in Northern Thailand
 Medical Referral of Patients with Acute Respiratory Failure: Lessons learned from a Large Outbreak of Botulism in Northern Thailand Sompop Pantukosit MD, FICS* * Department of Medical Services, Ministry
Medical Referral of Patients with Acute Respiratory Failure: Lessons learned from a Large Outbreak of Botulism in Northern Thailand Sompop Pantukosit MD, FICS* * Department of Medical Services, Ministry
Incisional Surgical Site Infection in Colorectal Surgery Patients
 Incisional Surgical Site Infection in Colorectal Surgery Patients Sahaphol Anannamcharoen MD*, Sitthichai Vachirasrisirikul MD*, Chinakrit Boonya-assadorn MD* * Department of Surgery, Phramongkutklao Hospital,
Incisional Surgical Site Infection in Colorectal Surgery Patients Sahaphol Anannamcharoen MD*, Sitthichai Vachirasrisirikul MD*, Chinakrit Boonya-assadorn MD* * Department of Surgery, Phramongkutklao Hospital,
Outcomes of Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Performed in Emergency Department, Hospital Universiti Sains Malaysia
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Outcomes of Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Performed in Emergency Department, Hospital Universiti Sains Malaysia K S Chew*, Z M Idzwan*, N A R Hisamuddin*, J Kamaruddin**, W A Wan Aasim**
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Outcomes of Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Performed in Emergency Department, Hospital Universiti Sains Malaysia K S Chew*, Z M Idzwan*, N A R Hisamuddin*, J Kamaruddin**, W A Wan Aasim**
Key statistics from the National Cardiac Arrest Audit: Paediatric arrests April 2012 to March 2017
 Key statistics from the National Cardiac Arrest Audit: Paediatric arrests April 12 to March 17 Supported by Resuscitation Council (UK) and Intensive Care National Audit & Research Centre (ICNARC) Data
Key statistics from the National Cardiac Arrest Audit: Paediatric arrests April 12 to March 17 Supported by Resuscitation Council (UK) and Intensive Care National Audit & Research Centre (ICNARC) Data
Factors Related to Mortality after Osteoporotic Hip Fracture Treatment at Chiang Mai University Hospital, Thailand, during 2006 and 2007
 Factors Related to Mortality after Osteoporotic Hip Fracture Treatment at Chiang Mai University Hospital, Thailand, during 2006 and 2007 Rathasart Chaysri MD*, Taninnit Leerapun MD*, Kasisin Klunklin MD*,
Factors Related to Mortality after Osteoporotic Hip Fracture Treatment at Chiang Mai University Hospital, Thailand, during 2006 and 2007 Rathasart Chaysri MD*, Taninnit Leerapun MD*, Kasisin Klunklin MD*,
Outcomes of Therapeutic Hypothermia in Cardiac Arrest. Saad Mohammed Shariff, MBBS Aravind Herle, MD, FACC
 Outcomes of Therapeutic Hypothermia in Cardiac Arrest Saad Mohammed Shariff, MBBS Aravind Herle, MD, FACC https://my.americanheart.org/idc/groups/ahamah-public/@wcm/@sop/@scon/documents/downloadable/ucm_427331.pdf
Outcomes of Therapeutic Hypothermia in Cardiac Arrest Saad Mohammed Shariff, MBBS Aravind Herle, MD, FACC https://my.americanheart.org/idc/groups/ahamah-public/@wcm/@sop/@scon/documents/downloadable/ucm_427331.pdf
Compression-Only CPR or Standard CPR in Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest
 The new england journal of medicine original article Compression-Only or Standard in Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Leif Svensson, M.D., Ph.D., Katarina Bohm, R.N., Ph.D., Maaret Castrèn, M.D., Ph.D.,
The new england journal of medicine original article Compression-Only or Standard in Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Leif Svensson, M.D., Ph.D., Katarina Bohm, R.N., Ph.D., Maaret Castrèn, M.D., Ph.D.,
Reliability and Validity of Long Case and Short Case in Internal Medicine Board Certification Examination
 Reliability and Validity of Long Case and Short Case in Internal Medicine Board Certification Examination Nitipatana Chierakul MD*, **, Somwang Danchaivijitr MD*, **, Paka Kontee BBA*, Chana Naruman MSc**
Reliability and Validity of Long Case and Short Case in Internal Medicine Board Certification Examination Nitipatana Chierakul MD*, **, Somwang Danchaivijitr MD*, **, Paka Kontee BBA*, Chana Naruman MSc**
Early Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation in Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest
 Original Article Early Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation in Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Ingela Hasselqvist Ax, R.N., Gabriel Riva, M.D., Johan Herlitz, M.D., Ph.D., Mårten Rosenqvist, M.D., Ph.D., Jacob
Original Article Early Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation in Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Ingela Hasselqvist Ax, R.N., Gabriel Riva, M.D., Johan Herlitz, M.D., Ph.D., Mårten Rosenqvist, M.D., Ph.D., Jacob
Update on Sudden Cardiac Death and Resuscitation
 Update on Sudden Cardiac Death and Resuscitation Ashish R. Panchal, MD, PhD Medical Director Center for Emergency Medical Services Assistant Professor Clinical Department of Emergency Medicine The Ohio
Update on Sudden Cardiac Death and Resuscitation Ashish R. Panchal, MD, PhD Medical Director Center for Emergency Medical Services Assistant Professor Clinical Department of Emergency Medicine The Ohio
WORKSHEET for Evidence-Based Review of Science for Veterinary CPCR
 RECOVER 2011 1 of 6 WORKSHEET for Evidence-Based Review of Science for Veterinary CPCR 1. Basic Demographics Worksheet author(s) James Barr Mailing address: 4474 TAMU Texas A&M University College Station,
RECOVER 2011 1 of 6 WORKSHEET for Evidence-Based Review of Science for Veterinary CPCR 1. Basic Demographics Worksheet author(s) James Barr Mailing address: 4474 TAMU Texas A&M University College Station,
Influence of Heart Rate on Image Quality to Identify the Best Cardiac Phase in 16-Slice Coronary CT Angiography
 Influence of Heart Rate on Image Quality to Identify the Best Cardiac Phase in 16-Slice Coronary CT Angiography Sureeporn Mayurasakorn MD*, Thanongchai Siriapisith MD*, Jitladda Wasinrat MD* * Department
Influence of Heart Rate on Image Quality to Identify the Best Cardiac Phase in 16-Slice Coronary CT Angiography Sureeporn Mayurasakorn MD*, Thanongchai Siriapisith MD*, Jitladda Wasinrat MD* * Department
Alvarado Score for the Acute Appendicitis in a Provincial Hospital
 Alvarado Score for the Acute Appendicitis in a Provincial Hospital Chairoek Limpawattanasiri MD* * Chachoengsao Hospital, Chachoengsao, Thailand Objective: To assess the accuracy of Alvarado Score in predicting
Alvarado Score for the Acute Appendicitis in a Provincial Hospital Chairoek Limpawattanasiri MD* * Chachoengsao Hospital, Chachoengsao, Thailand Objective: To assess the accuracy of Alvarado Score in predicting
Developments in Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Guidelines
 Developments in Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Guidelines Bernd W. Böttiger Seite 1 To preserve human life by making high quality resuscitation available to all Outcome after CPR in Germany ROSC ( Return
Developments in Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Guidelines Bernd W. Böttiger Seite 1 To preserve human life by making high quality resuscitation available to all Outcome after CPR in Germany ROSC ( Return
Netherlands Heart Journal High survival rate of 43% in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest patients in an optimized chain of survival.
 Netherlands Heart Journal High survival rate of 43% in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest patients in an optimized chain of survival. --Manuscript Draft-- Manuscript Number: Full Title: Article Type: Keywords:
Netherlands Heart Journal High survival rate of 43% in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest patients in an optimized chain of survival. --Manuscript Draft-- Manuscript Number: Full Title: Article Type: Keywords:
Free Survival Time of Recurrence and Malignant Transformation and Associated Factors in Patients with Supratentorial Low-Grade Gliomas
 Free Survival Time of Recurrence and Malignant Transformation and Associated Factors in Patients with Supratentorial Low-Grade Gliomas Ittichai Sakarunchai MD*, Rassamee Sangthong MD, PhD**, Nakornchai
Free Survival Time of Recurrence and Malignant Transformation and Associated Factors in Patients with Supratentorial Low-Grade Gliomas Ittichai Sakarunchai MD*, Rassamee Sangthong MD, PhD**, Nakornchai
The ARREST Trial: Amiodarone for Resuscitation After Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Due to Ventricular Fibrillation
 The ARREST Trial: Amiodarone for Resuscitation After Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Due to Ventricular Fibrillation Introduction The ARREST (Amiodarone in out-of-hospital Resuscitation of REfractory Sustained
The ARREST Trial: Amiodarone for Resuscitation After Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Due to Ventricular Fibrillation Introduction The ARREST (Amiodarone in out-of-hospital Resuscitation of REfractory Sustained
ANZCOR Guideline 11.1 Introduction to Advanced Life Support
 ANZCOR Guideline 11.1 Introduction to Advanced Life Support Who does this guideline apply to? Summary This guideline applies to adults who require advanced life support. Who is the audience for this guideline?
ANZCOR Guideline 11.1 Introduction to Advanced Life Support Who does this guideline apply to? Summary This guideline applies to adults who require advanced life support. Who is the audience for this guideline?
Consensus Paper on Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest in England
 Consensus Paper on Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest in England Date: 16 th October 2014 Revision Date: 16 th October 2015 Introduction The purpose of this paper is to bring some clarity to the analysis of
Consensus Paper on Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest in England Date: 16 th October 2014 Revision Date: 16 th October 2015 Introduction The purpose of this paper is to bring some clarity to the analysis of
Accuracy of Amsler Grid in Screening for Chloroquine Retinopathy
 Accuracy of Amsler Grid in Screening for Chloroquine Retinopathy Apichat Suansilpong MD*, Somchai Uaratanawong MD** * Department of Ophthalmology, BMA Medical College and Vajira Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand
Accuracy of Amsler Grid in Screening for Chloroquine Retinopathy Apichat Suansilpong MD*, Somchai Uaratanawong MD** * Department of Ophthalmology, BMA Medical College and Vajira Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand
Krittin Silanun MD, MSc*, Naesinee Chaiear MD, MMedSc, Ph D*, Wipa Rechaipichitkul MD**
 Prevalence of Silicosis in Stone Carving Workers Being Exposed to Inorganic Dust at Sikhiu District Nakhonratchasima Province, Thailand; Preliminary Results Krittin Silanun MD, MSc*, Naesinee Chaiear MD,
Prevalence of Silicosis in Stone Carving Workers Being Exposed to Inorganic Dust at Sikhiu District Nakhonratchasima Province, Thailand; Preliminary Results Krittin Silanun MD, MSc*, Naesinee Chaiear MD,
Is Radical Prostatectomy in Thai Men a High Morbidity Surgery for Localized or Locally Advanced Prostate Cancer?
 Is Radical Prostatectomy in Thai Men a High Morbidity Surgery for Localized or Locally Advanced Prostate Cancer? Sunai Leewansangtong MD*, Suchai Soontrapa MD*, Chaiyong Nualyong MD*, Sittiporn Srinualnad
Is Radical Prostatectomy in Thai Men a High Morbidity Surgery for Localized or Locally Advanced Prostate Cancer? Sunai Leewansangtong MD*, Suchai Soontrapa MD*, Chaiyong Nualyong MD*, Sittiporn Srinualnad
Update on Sudden Cardiac Death and Resuscitation
 Update on Sudden Cardiac Death and Resuscitation Ashish R. Panchal, MD, PhD Medical Director Center for Emergency Medical Services Assistant Professor Clinical Department of Emergency Medicine The Ohio
Update on Sudden Cardiac Death and Resuscitation Ashish R. Panchal, MD, PhD Medical Director Center for Emergency Medical Services Assistant Professor Clinical Department of Emergency Medicine The Ohio
A mong patients who have an out-of-hospital cardiac
 1114 CARDIOVASCULAR MEDICINE Can we define patients with no chance of survival after outof-hospital cardiac arrest? J Herlitz, J Engdahl, L Svensson, M Young, K-A Ängquist, S Holmberg... See end of article
1114 CARDIOVASCULAR MEDICINE Can we define patients with no chance of survival after outof-hospital cardiac arrest? J Herlitz, J Engdahl, L Svensson, M Young, K-A Ängquist, S Holmberg... See end of article
Predicting Factors for Risk of Depression in Adolescents with Learning Disorders
 Predicting Factors for Risk of Depression in Adolescents with Learning Disorders Manika Phetcharat RN, MNS (Mental Health and Psychiatric Nursing)*, Wimolnun Putdivarnichapong RN, DNS**, Yajai Sitthimongkol
Predicting Factors for Risk of Depression in Adolescents with Learning Disorders Manika Phetcharat RN, MNS (Mental Health and Psychiatric Nursing)*, Wimolnun Putdivarnichapong RN, DNS**, Yajai Sitthimongkol
Advanced Resuscitation - Adolescent
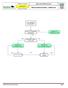 C02B Resuscitation 2017-03-23 10 up to 17 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adolescent Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia
C02B Resuscitation 2017-03-23 10 up to 17 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adolescent Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia
Coronary Artery Disease in the Thai Population: Data from Health Situation Analysis 2010
 Coronary Artery Disease in the Thai Population: Data from Health Situation Analysis 2010 J Med Assoc Thai 2012; 95 (Suppl. 7): S149-S155 Full text. e-journal: http://jmat.mat.or.th Songsak Kiatchoosakun
Coronary Artery Disease in the Thai Population: Data from Health Situation Analysis 2010 J Med Assoc Thai 2012; 95 (Suppl. 7): S149-S155 Full text. e-journal: http://jmat.mat.or.th Songsak Kiatchoosakun
Department of Surgery, Division of Cardiothoracic Surgery
 Review of In-Hospital and Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrests at a Tertiary Community Hospital for Potential ECPR Rescue Amanda Broderick 1, Jordan Williams 1, Alexandra Maryashina 1, & James Wu, MD 1 1 Department
Review of In-Hospital and Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrests at a Tertiary Community Hospital for Potential ECPR Rescue Amanda Broderick 1, Jordan Williams 1, Alexandra Maryashina 1, & James Wu, MD 1 1 Department
Advanced Resuscitation - Child
 C02C Resuscitation 2017-03-23 1 up to 10 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Child Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
C02C Resuscitation 2017-03-23 1 up to 10 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Child Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
Efficacy and Safety of Enoxaparin during Hemodialysis: Results from the HENOX Study
 Efficacy and Safety of Enoxaparin during Hemodialysis: Results from the HENOX Study Kriengsak Vareesangthip MD, PhD*, Supachai Thitiarchakul MD**, Inseey Kanjanakul MD***, Vasant Sumethkul MD****, Udom
Efficacy and Safety of Enoxaparin during Hemodialysis: Results from the HENOX Study Kriengsak Vareesangthip MD, PhD*, Supachai Thitiarchakul MD**, Inseey Kanjanakul MD***, Vasant Sumethkul MD****, Udom
Clinical Presentations of Bipolar Disorder in Children and Adolescents
 Clinical Presentations of Bipolar Disorder in Children and Adolescents J Med Assoc Thai 2014; 97 (2): 179-83 Full text. e-journal: http://www.jmatonline.com Nida Limsuwan MD* * Department of Psychiatry,
Clinical Presentations of Bipolar Disorder in Children and Adolescents J Med Assoc Thai 2014; 97 (2): 179-83 Full text. e-journal: http://www.jmatonline.com Nida Limsuwan MD* * Department of Psychiatry,
Clinical Manifestation, Diagnosis, Management, and Treatment Outcome of Pericarditis in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
 Clinical Manifestation, Diagnosis, Management, and Treatment Outcome of Pericarditis in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Tanas Buppajarntham MD*, Nattawan Palavutitotai MD*, Wanruchada Katchamart
Clinical Manifestation, Diagnosis, Management, and Treatment Outcome of Pericarditis in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Tanas Buppajarntham MD*, Nattawan Palavutitotai MD*, Wanruchada Katchamart
Automated external defibrillators and survival after in-hospital cardiac arrest: early experience at an Australian teaching hospital
 Automated external defibrillators and survival after in-hospital cardiac arrest: early experience at an Australian teaching hospital Roger J Smith, Bernadette B Hickey and John D Santamaria Early defibrillation
Automated external defibrillators and survival after in-hospital cardiac arrest: early experience at an Australian teaching hospital Roger J Smith, Bernadette B Hickey and John D Santamaria Early defibrillation
Management of Patients with Severe Hypertension in Emergency Department, Maharaj Nakorn Chiang Mai Hospital
 Management of Patients with Severe Hypertension in Emergency Department, Maharaj Nakorn Chiang Mai Hospital Kamphee Sruamsiri MD*, Boriboon Chenthanakij MD*, Borwon Wittayachamnankul MD* * Department of
Management of Patients with Severe Hypertension in Emergency Department, Maharaj Nakorn Chiang Mai Hospital Kamphee Sruamsiri MD*, Boriboon Chenthanakij MD*, Borwon Wittayachamnankul MD* * Department of
Spontaneous Breathing Trial with Low Pressure Support Protocol for Weaning Respirator in Surgical ICU
 Spontaneous Breathing Trial with Low Pressure Support Protocol for Weaning Respirator in Surgical ICU Kaweesak Chittawatanarat MD, FRCST, Thai Board of Critical Care Medicine*, Chaweewan Thongchai RN,
Spontaneous Breathing Trial with Low Pressure Support Protocol for Weaning Respirator in Surgical ICU Kaweesak Chittawatanarat MD, FRCST, Thai Board of Critical Care Medicine*, Chaweewan Thongchai RN,
Management of Cardiac Arrest Based on : 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines
 Management of Cardiac Arrest Based on : 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines www.circ.ahajournals.org Elham Pishbin. M.D Assistant Professor of Emergency Medicine MUMS C H E S Advanced Life Support
Management of Cardiac Arrest Based on : 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines www.circ.ahajournals.org Elham Pishbin. M.D Assistant Professor of Emergency Medicine MUMS C H E S Advanced Life Support
Out-Of-Hospital Management and Outcomes of Sudden Cardiac Death Abdelouahab BELLOU, MD, PhD
 Out-Of-Hospital Management and Outcomes of Sudden Cardiac Death Abdelouahab BELLOU, MD, PhD Professor of Internal Medicine, Emergency Medicine, Therapeutics. Past President of the European Society for
Out-Of-Hospital Management and Outcomes of Sudden Cardiac Death Abdelouahab BELLOU, MD, PhD Professor of Internal Medicine, Emergency Medicine, Therapeutics. Past President of the European Society for
Abstract. Introduction. Kitigon Vichairuangthum, MD 1, Anawat Sermsawan, MD 1, and Mala Treewatchareekorn, MSc 2
 Troponin I Assessment Provides Incremental Prognostic Information in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndromes and Borderline Troponin T Values upon Admission Kitigon Vichairuangthum, MD 1, Anawat Sermsawan,
Troponin I Assessment Provides Incremental Prognostic Information in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndromes and Borderline Troponin T Values upon Admission Kitigon Vichairuangthum, MD 1, Anawat Sermsawan,
Factors modifying the effect of bystander cardiopulmonary resuscitation on survival in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest patients in Sweden
 European Heart Journal (2001) 22, 511 519 doi:10.1053/euhj.2000.2421, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Factors modifying the effect of bystander cardiopulmonary resuscitation on survival
European Heart Journal (2001) 22, 511 519 doi:10.1053/euhj.2000.2421, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Factors modifying the effect of bystander cardiopulmonary resuscitation on survival
Passive Oxygen Insufflation Is Superior to Bag-Valve-Mask Ventilation for Witnessed Ventricular Fibrillation Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest
 EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES/ORIGINAL RESEARCH Passive Oxygen Insufflation Is Superior to Bag-Valve-Mask Ventilation for Witnessed Ventricular Fibrillation Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Bentley J. Bobrow,
EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES/ORIGINAL RESEARCH Passive Oxygen Insufflation Is Superior to Bag-Valve-Mask Ventilation for Witnessed Ventricular Fibrillation Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Bentley J. Bobrow,
Pulseless electrical activity and successful out-of-hospital resuscitation long-term survival and quality of life: an observational cohort study
 Saarinen et al. Scandinavian Journal of Trauma, Resuscitation and Emergency Medicine 2012, 20:74 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Open Access Pulseless electrical activity and successful out-of-hospital resuscitation
Saarinen et al. Scandinavian Journal of Trauma, Resuscitation and Emergency Medicine 2012, 20:74 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Open Access Pulseless electrical activity and successful out-of-hospital resuscitation
Tomohide Komatsu, Kosaku Kinoshita, Atsushi Sakurai, Takashi Moriya, Junko Yamaguchi, Atsunori Sugita, Rikimaru Kogawa, Katsuhisa Tanjoh
 Division of Emergency and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Acute Medicine, Nihon University School of Medicine, Itabashi-ku, Tokyo, Japan Correspondence to Dr Atsushi Sakurai, Division of Emergency
Division of Emergency and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Acute Medicine, Nihon University School of Medicine, Itabashi-ku, Tokyo, Japan Correspondence to Dr Atsushi Sakurai, Division of Emergency
Chaiyut Thanapaisal MD*, Puthipong Saksaen MD**
 A Comparison of the Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHE) II Score and The Trauma-Injury Severity Score (TRISS) for Outcome Assessment in Srinagarind Intensive Care Unit Trauma Patients
A Comparison of the Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHE) II Score and The Trauma-Injury Severity Score (TRISS) for Outcome Assessment in Srinagarind Intensive Care Unit Trauma Patients
Initial Rhythms and Outcomes for In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest in Kenya
 Initial Rhythms and Outcomes for In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest in Kenya Presented By Dr. Mohamed Hasham Varwani 1 On behalf of the authors: Dr Mzee Ngunga 1, Prof Gerald Yonga 1, Dr Benjamin Wachira 1, Dr
Initial Rhythms and Outcomes for In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest in Kenya Presented By Dr. Mohamed Hasham Varwani 1 On behalf of the authors: Dr Mzee Ngunga 1, Prof Gerald Yonga 1, Dr Benjamin Wachira 1, Dr
2015 AHA Guidelines: Pediatric Updates
 2015 AHA Guidelines: Pediatric Updates Advances in Pediatric Emergency Medicine December 9, 2016 Karen O Connell, MD, MEd Associate Professor of Pediatrics and Emergency Medicine Emergency Medicine and
2015 AHA Guidelines: Pediatric Updates Advances in Pediatric Emergency Medicine December 9, 2016 Karen O Connell, MD, MEd Associate Professor of Pediatrics and Emergency Medicine Emergency Medicine and
An Analysis of Continuous Chest Compression CPR for EMS Providers During Out of Hospital Cardiac Arrest
 Illinois Wesleyan University Digital Commons @ IWU Honors Projects Psychology 2010 An Analysis of Continuous Chest Compression CPR for EMS Providers During Out of Hospital Cardiac Arrest Megan L. Gleason
Illinois Wesleyan University Digital Commons @ IWU Honors Projects Psychology 2010 An Analysis of Continuous Chest Compression CPR for EMS Providers During Out of Hospital Cardiac Arrest Megan L. Gleason
RESEARCH ABSTRACT. those with arrests of non-cardiac origin and younger people, and people in whom there was delay in the start of CPR.
 Outcomes of chest compression only CPR versus conventional CPR conducted by lay people in patients with out of hospital cardiopulmonary arrest witnessed by bystanders: nationwide population based observational
Outcomes of chest compression only CPR versus conventional CPR conducted by lay people in patients with out of hospital cardiopulmonary arrest witnessed by bystanders: nationwide population based observational
Advanced Resuscitation - Adult
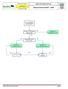 C02A Resuscitation 2017-03-23 17 years & older Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adult Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
C02A Resuscitation 2017-03-23 17 years & older Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adult Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
Reagent Strip Testing for Antenatal Screening and First Meaningful of Asymptomatic Bacteriuria in Pregnant Women
 Reagent Strip Testing for Antenatal Screening and First Meaningful of Asymptomatic Bacteriuria in Pregnant Women Ekachai Kovavisarach MD*, Maytina Vichaipruck MD*, Suwattana Kanjanahareutai MSc** * Department
Reagent Strip Testing for Antenatal Screening and First Meaningful of Asymptomatic Bacteriuria in Pregnant Women Ekachai Kovavisarach MD*, Maytina Vichaipruck MD*, Suwattana Kanjanahareutai MSc** * Department
Result of Ambulatory Diet Therapy in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
 Result of Ambulatory Diet Therapy in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Prasert Sunsaneevithayakul MD*, Sujin Kanokpongsakdi MD*, Anuwat Sutanthavibul MD*, Pornpimol Ruangvutilert MD, PhD*, Dittakarn Boriboohirunsarn
Result of Ambulatory Diet Therapy in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Prasert Sunsaneevithayakul MD*, Sujin Kanokpongsakdi MD*, Anuwat Sutanthavibul MD*, Pornpimol Ruangvutilert MD, PhD*, Dittakarn Boriboohirunsarn
Prof Gavin Perkins Co-Chair ILCOR
 Epidemiology of out of hospital cardiac arrest how to improve survival Prof Gavin Perkins Co-Chair ILCOR Chair, Community Resuscitation Committee, Resuscitation Council (UK) Conflict of interest Commercial
Epidemiology of out of hospital cardiac arrest how to improve survival Prof Gavin Perkins Co-Chair ILCOR Chair, Community Resuscitation Committee, Resuscitation Council (UK) Conflict of interest Commercial
Resuscitation Science. Bystander-Initiated Rescue Breathing for Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrests of Noncardiac Origin
 Resuscitation Science Bystander-Initiated Rescue Breathing for Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrests of Noncardiac Origin Tetsuhisa Kitamura, MD, MS; Taku Iwami, MD, PhD; Takashi Kawamura, MD, PhD; Ken Nagao,
Resuscitation Science Bystander-Initiated Rescue Breathing for Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrests of Noncardiac Origin Tetsuhisa Kitamura, MD, MS; Taku Iwami, MD, PhD; Takashi Kawamura, MD, PhD; Ken Nagao,
Out-of-hospital Cardiac Arrest. Franz R. Eberli MD, FESC, FAHA Cardiology Triemli Hospital Zurich, Switzerland
 Out-of-hospital Cardiac Arrest Franz R. Eberli MD, FESC, FAHA Cardiology Triemli Hospital Zurich, Switzerland Conflict of Interest I have no conflict of interest to disclose regarding this presentation.
Out-of-hospital Cardiac Arrest Franz R. Eberli MD, FESC, FAHA Cardiology Triemli Hospital Zurich, Switzerland Conflict of Interest I have no conflict of interest to disclose regarding this presentation.
Incidence and Risk Factors of Hypotension During Spinal Anesthesia for Cesarean Section at Siriraj Hospital
 Incidence and Risk Factors of Hypotension During Spinal Anesthesia for Cesarean Section at Siriraj Hospital Saowapark Chumpathong MD*, Thitima Chinachoti MD*, Shusee Visalyaputra MD*, Thongporn Himmunngan
Incidence and Risk Factors of Hypotension During Spinal Anesthesia for Cesarean Section at Siriraj Hospital Saowapark Chumpathong MD*, Thitima Chinachoti MD*, Shusee Visalyaputra MD*, Thongporn Himmunngan
Potential Effectiveness of Health Warning Labels among Employees in Thailand
 Potential Effectiveness of Health Warning Labels among Employees in Thailand Pimpan Silpasuwan EdD*, Yaowaluk Ngoenwiwatkul DrPH**, Chukiat Viwatwongkasem PhD***, Pratana Satitvipawee MPH***, Nithat Sirichotiratana
Potential Effectiveness of Health Warning Labels among Employees in Thailand Pimpan Silpasuwan EdD*, Yaowaluk Ngoenwiwatkul DrPH**, Chukiat Viwatwongkasem PhD***, Pratana Satitvipawee MPH***, Nithat Sirichotiratana
EPIDEMIOLOGY AND TREATMENT OF CARDIOVASCULAR EMERGENCIES IN URBAN VS. REMOTE AREAS
 EPIDEMIOLOGY AND TREATMENT OF CARDIOVASCULAR EMERGENCIES IN URBAN VS. REMOTE AREAS Andrea Semplicini Medicina Interna 1 Ospedale SS. Giovanni e Paolo - Venezia Azienda ULSS 12 Veneziana Dipartimento Medicina
EPIDEMIOLOGY AND TREATMENT OF CARDIOVASCULAR EMERGENCIES IN URBAN VS. REMOTE AREAS Andrea Semplicini Medicina Interna 1 Ospedale SS. Giovanni e Paolo - Venezia Azienda ULSS 12 Veneziana Dipartimento Medicina
First Documented Rhythm and Clinical Outcome From In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Among Children and Adults
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION First Documented Rhythm and Clinical Outcome From In-Hospital Among Children and s Vinay M. Nadkarni, MD Gregory Luke Larkin, MD Mary Ann Peberdy, MD Scott M. Carey William Kaye,
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION First Documented Rhythm and Clinical Outcome From In-Hospital Among Children and s Vinay M. Nadkarni, MD Gregory Luke Larkin, MD Mary Ann Peberdy, MD Scott M. Carey William Kaye,
2015 Interim Training Materials
 2015 Interim Training Materials ACLS Manual and ACLS EP Manual Comparison Chart Assessment sequence Manual, Part 2: The Systematic Approach, and Part BLS Changes The HCP should check for response while
2015 Interim Training Materials ACLS Manual and ACLS EP Manual Comparison Chart Assessment sequence Manual, Part 2: The Systematic Approach, and Part BLS Changes The HCP should check for response while
Thanainit Chotanaphuti MD*, Pipat Ongnamthip MD*, Krit Karnchanalerk MD*, Phichai Udombuathong MD*
 Comparative Study between 2 cm Limited Quadriceps Exposure Minimal Invasive Surgery and Conventional Total Knee Arthroplasty in Quadriceps Function: Prospective Randomized Controlled Trial Thanainit Chotanaphuti
Comparative Study between 2 cm Limited Quadriceps Exposure Minimal Invasive Surgery and Conventional Total Knee Arthroplasty in Quadriceps Function: Prospective Randomized Controlled Trial Thanainit Chotanaphuti
ACP Recertification Pre-Course: Pediatric Manual Defibrillation
 2010-2011 ACP Recertification Pre-Course: Pediatric Manual Defibrillation Pediatric Defibrillation - Overview Objectives Overview of Pediatric Defibrillation Etiology and Pathophysiology of Pediatric Defibrillation
2010-2011 ACP Recertification Pre-Course: Pediatric Manual Defibrillation Pediatric Defibrillation - Overview Objectives Overview of Pediatric Defibrillation Etiology and Pathophysiology of Pediatric Defibrillation
Australian Resuscitation Outcomes Consortium (Aus-ROC)
 Australian Resuscitation Outcomes Consortium (Aus-ROC) A NHMRC Centre of Research Excellence (CRE) in Clinical Research, #1029983 Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest registry ( Epistry ) Presented by Prof Judith
Australian Resuscitation Outcomes Consortium (Aus-ROC) A NHMRC Centre of Research Excellence (CRE) in Clinical Research, #1029983 Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest registry ( Epistry ) Presented by Prof Judith
Disclosures. Overview. Cardiopulmonary Arrest: Quality Measures 5/29/2014. In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest: Measuring Effectiveness and Improving Outcomes
 Disclosures In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest: Measuring Effectiveness and Improving Outcomes Research support from UCOP CHQI award J. Matthew Aldrich, MD Anesthesia & Critical Care UCSF Overview Epidemiology
Disclosures In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest: Measuring Effectiveness and Improving Outcomes Research support from UCOP CHQI award J. Matthew Aldrich, MD Anesthesia & Critical Care UCSF Overview Epidemiology
Wariya Sukhupragarn MD*, Prangmalee Leurcharusmee MD*, Thitipan Sotthisopha MD*
 Cardiovascular Effects of Volatile Induction and Maintenance of Anesthesia (VIMA) and Total Intravenous Anesthesia (TIVA) for Laryngeal Mask Airway (LMA) Anesthesia: A Comparison Study Wariya Sukhupragarn
Cardiovascular Effects of Volatile Induction and Maintenance of Anesthesia (VIMA) and Total Intravenous Anesthesia (TIVA) for Laryngeal Mask Airway (LMA) Anesthesia: A Comparison Study Wariya Sukhupragarn
* Division of Colorectal Surgery, Department of Surgery, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand
 A Comparison of Early Postoperative Results between Urgent Closed Hemorrhoidectomy for Prolapsed Thrombosed Hemorrhoids and Elective Closed Hemorrhoidectomy Jirawat Pattana-arun MD*, Warin Wesarachawit
A Comparison of Early Postoperative Results between Urgent Closed Hemorrhoidectomy for Prolapsed Thrombosed Hemorrhoids and Elective Closed Hemorrhoidectomy Jirawat Pattana-arun MD*, Warin Wesarachawit
Growth Rate of Aortic Diameter in Post Treatment of Aortic Dissection
 Growth Rate of Aortic Diameter in Post Treatment of Aortic Dissection Jitladda Wasinrat MD*, Methininat Lertkowit MD*, Thanongchai Siriapisith MD* * Division of Diagnostic Radiology, Department of Radiology,
Growth Rate of Aortic Diameter in Post Treatment of Aortic Dissection Jitladda Wasinrat MD*, Methininat Lertkowit MD*, Thanongchai Siriapisith MD* * Division of Diagnostic Radiology, Department of Radiology,
Comparison of Aortic Diameter in Normal Subjects and Patients with Systemic Hypertension
 Comparison of Aortic Diameter in Normal Subjects and Patients with Systemic Hypertension Decho Jakrapanichakul MD*, Srisakul Chirakarnjanakorn MD* * Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine, Siriraj
Comparison of Aortic Diameter in Normal Subjects and Patients with Systemic Hypertension Decho Jakrapanichakul MD*, Srisakul Chirakarnjanakorn MD* * Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine, Siriraj
Observational study II
 Observational study II (QUANTITATIVE METHOD IV) หล กส ตรเวชศาสตร ช มชน RACM 302 1 AIMS Observational study and analytic study designs : Case-control study Cross-sectional study Ecological study Calculate
Observational study II (QUANTITATIVE METHOD IV) หล กส ตรเวชศาสตร ช มชน RACM 302 1 AIMS Observational study and analytic study designs : Case-control study Cross-sectional study Ecological study Calculate
Extracardiac Conduit versus Lateral Tunnel for Total Cavopulmonary Connections
 Cases Report Extracardiac Conduit versus Lateral Tunnel for Total Cavopulmonary Connections Sukasom Attanavanich MD*, Panuwat Lertsithichai MD* * Cardiovascular Thoracic Unit, Division of Surgery, Faculty
Cases Report Extracardiac Conduit versus Lateral Tunnel for Total Cavopulmonary Connections Sukasom Attanavanich MD*, Panuwat Lertsithichai MD* * Cardiovascular Thoracic Unit, Division of Surgery, Faculty
Therapeutic Hypothermia After Resuscitation From a Non-Shockable Rhythm Improves Outcomes in a Regionalized System of Cardiac Arrest Care
 DOI 10.1007/s12028-015-0184-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE Therapeutic Hypothermia After Resuscitation From a Non-Shockable Rhythm Improves Outcomes in a Regionalized System of Cardiac Arrest Care Gene Sung 1 Nichole
DOI 10.1007/s12028-015-0184-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE Therapeutic Hypothermia After Resuscitation From a Non-Shockable Rhythm Improves Outcomes in a Regionalized System of Cardiac Arrest Care Gene Sung 1 Nichole
Effect of Oral Contraceptives on Risk of Cervical Cancer
 Effect of Oral Contraceptives on Risk of Cervical Cancer Natthakan Vanakankovit MD*, Surasak Taneepanichskul MD* * Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Faculty of Medicine, King Chulalongkorn Memorial
Effect of Oral Contraceptives on Risk of Cervical Cancer Natthakan Vanakankovit MD*, Surasak Taneepanichskul MD* * Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Faculty of Medicine, King Chulalongkorn Memorial
Manual Defibrillation. CPR AGE: 18 years LOA: Altered HR: N/A RR: N/A SBP: N/A Other: N/A
 ROC AMIODARONE, LIDOCAINE OR PLACEBO FOR OUT OF HOSPITAL CARDIAC ARREST DUE TO VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION OR TACHYCARDIA (ALPS) STUDY: MEDICAL CARDIAC ARREST MEDICAL DIRECTIVE An Advanced Care Paramedic
ROC AMIODARONE, LIDOCAINE OR PLACEBO FOR OUT OF HOSPITAL CARDIAC ARREST DUE TO VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION OR TACHYCARDIA (ALPS) STUDY: MEDICAL CARDIAC ARREST MEDICAL DIRECTIVE An Advanced Care Paramedic
Nawanant Piyavhatkul MD*, Thawatchai Krisanaprakornkit MD*, Suchat Paholpak MD*
 Stress and Adjustment Disorder Section of WHO Schedules for Clinical Assessment in Neuropsychiatry (SCAN) - Thai Version: Validity and Reliability Study Nawanant Piyavhatkul MD*, Thawatchai Krisanaprakornkit
Stress and Adjustment Disorder Section of WHO Schedules for Clinical Assessment in Neuropsychiatry (SCAN) - Thai Version: Validity and Reliability Study Nawanant Piyavhatkul MD*, Thawatchai Krisanaprakornkit
Value and Validation of RCOST and TOPF Clinical Practice Guideline for Osteoporosis Treatment
 Value and Validation of RCOST and TOPF Clinical Practice Guideline for Osteoporosis Treatment Chatlert Pongchaiyakul MD*, Taninnit Leerapun MD**, Sunton Wongsiri MD***, Thawee Songpattanasilp MD, PhD****,
Value and Validation of RCOST and TOPF Clinical Practice Guideline for Osteoporosis Treatment Chatlert Pongchaiyakul MD*, Taninnit Leerapun MD**, Sunton Wongsiri MD***, Thawee Songpattanasilp MD, PhD****,
Outcome and prognostic factors of patients in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests presenting with non-shockable rhythm in Hong Kong
 Hong Kong Journal of Emergency Medicine Outcome and prognostic factors of patients in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests presenting with non-shockable rhythm in Hong Kong KL Leung, CT Lui, KH Cheung, KL Tsui,
Hong Kong Journal of Emergency Medicine Outcome and prognostic factors of patients in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests presenting with non-shockable rhythm in Hong Kong KL Leung, CT Lui, KH Cheung, KL Tsui,
Outcome of Recombinant Tissue Plasminogen Activator in ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction in Buriram Hospital
 Outcome of Recombinant Tissue Plasminogen Activator in ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction in Buriram Hospital Phattaraphong Pheerawong MD*, Bulan Plienthaisong RN* * Department of Medicine, Buriram
Outcome of Recombinant Tissue Plasminogen Activator in ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction in Buriram Hospital Phattaraphong Pheerawong MD*, Bulan Plienthaisong RN* * Department of Medicine, Buriram
Traumatic cardiac arrest in Sweden a population-based national cohort study
 Djarv et al. Scandinavian Journal of Trauma, Resuscitation and Emergency Medicine (2018) 26:30 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13049-018-0500-7 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Traumatic cardiac arrest in Sweden 1990-2016 -
Djarv et al. Scandinavian Journal of Trauma, Resuscitation and Emergency Medicine (2018) 26:30 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13049-018-0500-7 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Traumatic cardiac arrest in Sweden 1990-2016 -
Prospective Study of Hypotension and Bradycardia during Spinal Anesthesia with Bupivacaine: Incidence and Risk Factors, Part Two
 Prospective Study of Hypotension and Bradycardia during Spinal Anesthesia with Bupivacaine: Incidence and Risk Factors, Part Two Thitima Chinachoti MD*, Thara Tritrakarn MD* * Department of Anesthesiology,
Prospective Study of Hypotension and Bradycardia during Spinal Anesthesia with Bupivacaine: Incidence and Risk Factors, Part Two Thitima Chinachoti MD*, Thara Tritrakarn MD* * Department of Anesthesiology,
Epinephrine Cardiovascular Emergencies Symposium 2018
 Epinephrine Cardiovascular Emergencies Symposium 218 Corey M. Slovis, M.D. Vanderbilt University Medical Center Metro Nashville Fire Department Nashville International Airport Nashville, TN High Quality
Epinephrine Cardiovascular Emergencies Symposium 218 Corey M. Slovis, M.D. Vanderbilt University Medical Center Metro Nashville Fire Department Nashville International Airport Nashville, TN High Quality
People Living with HIV/AIDS in the City of Bangkok: Quality of Life and Related Factors
 People Living with HIV/AIDS in the City of Bangkok: Quality of Life and Related Factors Chokchai Munsawaengsub MD*, Basamat Berair Ebella Mohammed Khair MPH**, Sutham Nanthamongkolchai PhD* * Department
People Living with HIV/AIDS in the City of Bangkok: Quality of Life and Related Factors Chokchai Munsawaengsub MD*, Basamat Berair Ebella Mohammed Khair MPH**, Sutham Nanthamongkolchai PhD* * Department
Benefit of Electrocardiography during Front-Line Combination Paclitaxel and Carboplatin Chemotherapy for Epithelial Ovarian Cancer
 Benefit of Electrocardiography during Front-Line Combination Paclitaxel and Carboplatin Chemotherapy for Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Chumnan Kietpeerakool MD*, Jitima Tiyayon MD*, Prapaporn Suprasert MD*,
Benefit of Electrocardiography during Front-Line Combination Paclitaxel and Carboplatin Chemotherapy for Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Chumnan Kietpeerakool MD*, Jitima Tiyayon MD*, Prapaporn Suprasert MD*,
PERIOPERATIVE cardiopulmonary arrests are
 Predictors of Survival from Perioperative Cardiopulmonary Arrests A Retrospective Analysis of 2,524 Events from the Get With The Guidelines-Resuscitation Registry Satya Krishna Ramachandran, M.D., F.R.C.A.,*
Predictors of Survival from Perioperative Cardiopulmonary Arrests A Retrospective Analysis of 2,524 Events from the Get With The Guidelines-Resuscitation Registry Satya Krishna Ramachandran, M.D., F.R.C.A.,*
Breast Pain and Service Satisfaction during Digital Mammography
 Breast Pain and Service Satisfaction during Digital Mammography Cholatip Wiratkapun MD*, Panuwat Lertsithichai MD, MSc**, Bussanee Wibulpolprasert MD*, Montira Leelaswattanakul BSc*, Jantarika Detakarat
Breast Pain and Service Satisfaction during Digital Mammography Cholatip Wiratkapun MD*, Panuwat Lertsithichai MD, MSc**, Bussanee Wibulpolprasert MD*, Montira Leelaswattanakul BSc*, Jantarika Detakarat
Validation Study of the Thai ID Pain Scale
 Validation Study of the Thai ID Pain Scale Wasuwat Kitisomprayoonkul MD* * Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok,
Validation Study of the Thai ID Pain Scale Wasuwat Kitisomprayoonkul MD* * Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok,
Continuation of cardiopulmonary resuscitation in a Chinese hospital after unsuccessful EMS resuscitation
 142 Journal of Geriatric Cardiology September 2009 Vol 6 No 3 Clinical Research Continuation of cardiopulmonary resuscitation in a Chinese hospital after unsuccessful EMS resuscitation Xiao-Bo Yang 1,
142 Journal of Geriatric Cardiology September 2009 Vol 6 No 3 Clinical Research Continuation of cardiopulmonary resuscitation in a Chinese hospital after unsuccessful EMS resuscitation Xiao-Bo Yang 1,
Comparative Study between Preoperative and Postoperative Histologic Grading in Adenocarcinoma of the Colon and Rectum
 Comparative Study between Preoperative and Postoperative Histologic Grading in Adenocarcinoma of the Colon and Rectum Bunlue Chaleoykitti MD* * Division of Colorectal Surgery, Department of Surgery, Phramongkutklao
Comparative Study between Preoperative and Postoperative Histologic Grading in Adenocarcinoma of the Colon and Rectum Bunlue Chaleoykitti MD* * Division of Colorectal Surgery, Department of Surgery, Phramongkutklao
Refractive Outcomes of Femtosecond LASIK for Myopic Correction at Siriraj Hospital, Thailand
 Refractive Outcomes of Femtosecond LASIK for Myopic Correction at Siriraj Hospital, Thailand Sabong Srivannaboon MD*, **, Pornlada Sunlakaviset MD*, Panida Kosrirukvongs MD*, **, Pinnita Prabhasawat, MD*,
Refractive Outcomes of Femtosecond LASIK for Myopic Correction at Siriraj Hospital, Thailand Sabong Srivannaboon MD*, **, Pornlada Sunlakaviset MD*, Panida Kosrirukvongs MD*, **, Pinnita Prabhasawat, MD*,
Disposable Laryngeal Mask Airway (Soft Seal ) for Endotracheal Intubation: FOB Guidance Technique and Blind Technique
 Disposable Laryngeal Mask Airway (Soft Seal ) for Endotracheal Intubation: FOB Guidance Technique and Blind Technique Suhattaya Boonmak MD*, Polpun Boonmak MD*, Piyaporn Bunsaengjaroen MD*, Somyong Srichaipanha
Disposable Laryngeal Mask Airway (Soft Seal ) for Endotracheal Intubation: FOB Guidance Technique and Blind Technique Suhattaya Boonmak MD*, Polpun Boonmak MD*, Piyaporn Bunsaengjaroen MD*, Somyong Srichaipanha
A bs tr ac t. Conclusions Delayed defibrillation is common and is associated with lower rates of survival after in-hospital cardiac arrest.
 The new england journal of medicine established in 1812 january 3, 2008 vol. 358 no. 1 Delayed Time after In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Paul S. Chan, M.D., Harlan M. Krumholz, M.D., Graham Nichol, M.D., M.P.H.,
The new england journal of medicine established in 1812 january 3, 2008 vol. 358 no. 1 Delayed Time after In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Paul S. Chan, M.D., Harlan M. Krumholz, M.D., Graham Nichol, M.D., M.P.H.,
The Effects of Systematic Management on Maternal and Neonatal Complications in Gestational Diabetes Subjects
 The Effects of Systematic Management on Maternal and Neonatal Complications in Gestational Diabetes Subjects Pitvara Panpitpat MNS*, Thipaporn Tharavanij MD, MSc**, Charintip Somprasit MD***, Chamnan Tanprasertkul
The Effects of Systematic Management on Maternal and Neonatal Complications in Gestational Diabetes Subjects Pitvara Panpitpat MNS*, Thipaporn Tharavanij MD, MSc**, Charintip Somprasit MD***, Chamnan Tanprasertkul
Sudden Cardiac Arrest
 Sudden Cardiac Arrest Amit Sharma, MD, FACP, FACC Interventional Cardiologist Rockledge Regional Medical Center Assistant Professor of Medicine University of Central Florida Disclosures No relevant financial
Sudden Cardiac Arrest Amit Sharma, MD, FACP, FACC Interventional Cardiologist Rockledge Regional Medical Center Assistant Professor of Medicine University of Central Florida Disclosures No relevant financial
