Accelerated Atherosclerosis in Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases Prof. Andrea Doria
|
|
|
- Barrie Howard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Accelerated Atherosclerosis Andrea Doria Division of Rheumatology University of Padova 1 Endothelial Dysfunction Fatty-Streak Formation Endothelial Leukocyte Endothelial Leukocyte permeability migration adhesion adhesion Formation of an advanced lesion Smooth Adherence Adherence muscle Foam cell T-cell and and entry of migration formation activation aggregation leukocytes of platelets Unstable fibrous plaques Macrophage Formation of Fibrous cap accumulation necrotic core formation Russel Ross N Engl J Med 1999;34: Plaque rupture Thinning of fibrous cap Hemorrhage from plaque microvessels 2 Pathogenetic Steps in Atherosclerosis Monocyte Vessel lumen LDL Adhesion molecules MCP-1 P-D LDL Endothelium Cytokines oxidate LDL Growth factors Cell proliferation Macrophage Breakdown of fibrous cup Intima Ross R. N Engl J Med 1999;34: Foam cell MMP Matrix degradation 3 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 1
2 Triggers and Common Pathway in Atherosclerosis Infections CV risk factors Chronic inflammatory diseases Innate/adaptive immunity Endothelial dysfunction Atherosclerosis/inflammat ion Vessel lumen Endothelium Intima 4 Key Features of Innate and Adaptive Immunity in Atherogenesis Innate Immunity Rapid immune response to pathogen Antigen recognition driven by pattern recognition receptors which bind to highly conserved structures expressed by pathogens Effectors Phagocytes Pattern recognition receptors Pentraxines (CRP, PTX3) Complement Cytokine (TNFα, IL-1, IL-6) Chemokines (MCP-1) Inflammation Atherosclerosis Adaptive Immunity Require three to five days to mature Antigen recognition driven by T and B cell receptors; Very specific antigen recognition Effectors T and B cell T and B cell receptors Cytotoxic T cell Antibodies Cytokine (TNFα, IL-2, INFγ) Chemokines 5 Chronic Inflammatory Diseases CV Risk Factors Infectious Agents Innate immunity 6 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 2
3 Immunocytochemistry for CRP Distribution Within the Atherosclerotic Plaque m apl 7 Odds Ratios for Coronary Heart Disease Among 2459 Patients with Coronary Heart Disease and 3969 Controls Danesh, J. et al., N Engl J Med 24;35: Unstable Carotid Plaque (CARS) Macrophages Lymphocytes Pauletto P, Circulation 2; 12(7): The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 3
4 An Unusual Subset of T-Cells, CD4+CD28 null, Is Clonally Expanded in the Peripheral Blood and Infiltrates Coronary Plaques in UA CD4+ CD28 null T cells (%) CD4 + CD28 n u ll T cells expansion in UA 4 35 P < Stable Angina Unstable Angina Liuzzo G, Circulation 1999; 1: Infiltration of selected CD4 + CD28 n u ll T cells clones into the unstable plaque L = Left anterior descending coronary artery R = Right coronary artery, culprit lesion Liuzzo G, Circulation 2; 11: CD4+CD28 null Lymphocytes Undergo clonal proliferation Form long-lived clonal population Produce IFN-γ high levels (Liuzzo G, Circulation 1999; 1: ) Coexpress the CD57 NK cell marker Have cytolytic activity (Nakajima T, Circulation 22; 15: 57-5; Nakajima T, Circ Res 23; 93: ; Nakajima T, Circulation 22; 15: 57-5) Are autoreactive Enhanced number with increasing age in the blood of healthy subjects (Warrington KJ Blood 23;11:3543-9) 11 Frequency of CD4+CD28 - T Cells in 87 RA and 3 Control Subjects Gerli R, et al., Circulation 24,19: The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 4
5 Common Carotid IMT in RA Patients Subdivided According to the Presence or Absence of CD4+CD28- Cell Expansion Common carotid IMT (mm) Controls Gerli R, et al., Circulation 24,19: * * All RA CD4+CD28+ CD4+CD28-13 Atherosclerosis and Autoimmunity Anti-oxLDL Anti-β2GPI Anti-HSP6/65 Anti-ECA Anti-HDL Anti-APO A-1 Anti-LPL Doria A, Sherer Y, Meroni PL, Shoenfeld Y. Rheum Dis Clin N Am 25; 31: Oxidized LDL and other lipoproteins can be actively taken up by scavenger receptor mediated endocytosis, transforming macrophages into the so called foam cells Some anti-oxldl can enhance oxldl uptake by macrophages through the involvement of the Fcγ receptors rather than via the usually employed scavenger receptor favouring foam cell formation and macrophage activation oxldl Anti-oxLDL 15 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 5
6 Anti-oxLDL and Atherosclerosis Raised levels in some conditions linked to coronary artery disease in humans Lehtimaki T, et al., Arterioscl. Thromb. Vasc. Biol 19, 23-7, 1999 Maggi E, et al., Arterioscler Thromb 14, , 1994 Saloen J.T., et al., Lancet 339, 883-7, 1992 Meraviglia MV et al., Stroke 22, 33: George J, et al., Immunol Lett 1999;68:263-6 Immunization with oxldl of animals results in suppression rather than aggravation of early atherogenesis Palinski W. et al., Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92, , 1995 George J, et al., Atherosclerosis 138, , 1998 Ameli S, et al., Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 16, 174-9, 1996 Anti-oxLDL mabs inhibit uptake of oxldl by macrophages Show PX, et al., Atherosclerosis, Thrombosis & Vascular Biology 21, 1: 333-9, Anti-oxLDL and Atherosclerosis Protective Pathogenetic Help to clear the high levels of oxldl Aid the uptake of oxldl by macrophages turning them into foam cells within the atherosclerotic plaques IgM anti-oxldl IgG anti-oxldl 17 Antiphospholipid Antibodies Generally they are directed to phospholipids binding proteins (β 2 glycoprotein I, prothrombin, etc.) Detected by different tests as: Lupus anticoagulant, Anticardiolipin antibodies Anti β2gpi Anti prothrombin Anti ethanolamine Anti annexin Anti phospholipids Major cause of thromboembolic disorder in patients with autoimmune diseases and otherwise healthy subjects (antiphospholipid syndrome) 18 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 6
7 The Primary Structure of Human β2gpi and Location of Attachment Sites for Oligosaccharide Chains Characters of amino acid residues Positively charged Negatively charged Polar(-NH2) Polar(-OH,-SH) Hydrophobic glycine 19 2 β2gpi Adhered on Endothelial Cells Is a Target for Anti-Phospholipid Antibodies β 2GPI adhesion to endothelium in vivo (McIntyre 1993, La Rosa 1994) β2gpi β 2GPI binding to endothelial monolayers in vitro (Del Papa 1995, 1997, 1998) β 2GPI binds endothelium through the PL-binding site located at the fifth domain and through annexin II (Del Papa 1998; Keying 2) Endothelium ++ + β2gpi 21 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 7
8 - -- Accelerated Atherosclerosis Two Step Complex Formation Between OxLDL and β2gpi apob1 Free β 2GPI Intermediate complexes Stable complexes oxldl ph7.4 oxldl ph7.4 oxldl ph7.4 + Mg 2+ +heparin Matsuura E, et al., Lupus 25; 14: ph1 + Mg 2+ +heparin Electrostatic and dissociable complexes, formed with β 2GP ligands (ω -carboxyl), such as oxlig-1 and oxlig-2 (Schiff base etc.) Stable complexes (i.e., Schiff base adducts), formed with ω -aldehydes 22 Serum OxLDL/β2GPI Complexes May Be a Marker of Vascular Inflammation Disease Inflammation Oxidative Stress Lipid Modification Antibody Clinical manifestation SLE APS Chronic Autoimmune Vasculitis ++++ OxLDL/β2GPI IgG/IgM Premature Atherosclerosis + CVD SSc? +++ OxLDL/β2GPI IgG/IgM CVD Atherosclerosis DM-2 Infectious Endocarditis Chronic Hyperglycemia Blood Infection (Sepsis) OxLDL/β2GPI OxLDL/β2GPI IgM -- Premature Atherosclerosis + CVD No Atherosclerosis Healthy Matsuura E, et al., Lupus 25; 14: Age-related + risk Factors 23 The Role of β2gpi in Atherogenesis β 2GPI oxldl Anti-β 2GPI Da Koike T, The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 8
9 Immunolocalization of β 2 GPI (Apolipoprotein H) in Human Atherosclerotic Plaques: Potential Implications for Lesion Progression George et al., Circulation 9 9 :2227, 1999 A and B rabbit anti-β 2GPI antibody C, normal rabbit IgG D, hematoxylin- eosin E, anti-cd4 F, anti-cd8 25 Immunization with Human β2 Glycoprotein I In LDL-receptor-d eficient mice or Apo-E knock-out mice immunization with β 2GPI enhances atherosclerotic lesions which contain abundant CD4+ cells George J et al., Circulation 1998; Afek A et al., Pathobiology 1999 T cell depletion impairs reproduction of the experimental model!! The transfer of lymphocytes from mice immunized with β 2GPI to mice of similar genetic background increases atherosclerotic lesions compared to those occurring in animals tranferred with lymphocytes from control mice 26 Antiphospholipid Antibodies in Patients with Clinical and Subclinical Atherosclerosis The presence of antiphospholipid antibodies was found to be a risk factor for various manifestations of coronary artery disease such as angina, myocardial infarction or cardiac death, as well as being associated with subclinical atherosclerosis Vaarala O et al., Circulation 1995, 91:23; Sherer Y, Cardiology 21, 95: 2 Sherer Y et al., Am J Cardiology 2, 86: Vaarala O et al., Thromb Haemost 1996, 75:456 Shoenfeld Y, et al., Ann.Med. 2, 1:37-4 Glueck et al., Am J Cardiol :149; Nityanand S et al., J Intern Med 1995, 238:437 It has also been shown that patients with primary antiphospholipid syndrome have a high prevalence of increased carotid intima-media thickness or plaque Ames PRJ, et al., Lupus 22; 11: G. Medina, et al., Ann Rheum Dis 23;62:67-61 PG Vlachoyiannopoulos et al., Rheumatol23;42: The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 9
10 Reduction of Atherosclerosis in Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Deficient Mice by Passive Administration of Antiphospholipid Antibody In contrast to earlier studies of apl which were specific for oxidized forms of LDL, FB1 cross-reacted with both native LDL and oxldl In vivo, passive administration of FB1 significantly reduced plaque formation in atherosclerosis-prone LDLR(-/-) mice These results indicate that some apl may play a protective role in atherogenesis Nicolo D, et al., Arthritis Rheum 23; 48: Human HSP6 Intracellular chaperone protein Expressed on the surface of stressed cells Human HSPs are expressed on endothelial cells in response to stressors like hypertension, smoking, lipoproteins, etc. HSPs offer a target for autoimmunity under such circumstances HSP6 shows high inter-species homology 29 Anti-Heat Shock Protein (HSP) 6/65 Antibodies Patients with high levels of anti-hsp65 were found to be at increased risk of subsequent cardiovascular events and cardiovascular mortality SoRell R. Circulation 16: , 22 Xu Q, et al., Circulation 1: 1169, 1999 Subjects with sonographic evidence of carotid atherosclerotic lesions had significantly elevated levels of anti-hsp65 compared with controls Xu Q, et al., Lancet 341: 255, 1993 Immunization of animals with mycobacterial or recombinant antigen causes atherosclerotic lesions (rabbits, C57BL/6 mice fed with high cholesterol diet, or LDL receptor deficient mice) George J, et al., Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 19:55-51,1999 Xu Q, et al., Arterioscl Thromb 12: 789, 1999 Afek A, et al., J Autoimmun 14: 115, 2 3 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 1
11 Enhanced Atherosclerosis and Associated Factors in ARD Disease Evidence for enhanced ATS Factors involved in enhanced ATS RA SLE APS SSc Prevalence of CAD, increased extent of subclinical ATS Prevalence of CAD, increased extent of subclinical ATS Prevalence thrombosis, increased extent of subclinical ATS, apls are prevalent in patients with macrovascular disease, apls predict future CVD in the general population Prevalence of macrovascular disease, few studies on ATS Prevalence of classic risk factors for ATS, drugs used for treatment Prevalence of classic risk factors for ATS, corticosteroid therapy, long disease duration Animals models support a proatherogenic role of apl Oxidative stress, antiendothelial cell antibodies PSV SS Increased extent of subclinical ATS in WG; Not studied in other diseases Not studied Shoenfeld Y, Gerli R, Doria A, et al., Circulation 25; 112: Enhanced inflammation and excessive vascular remodelling Unknown 31 Marson P. et al., Reumatismo 24; 56: The Prevalence of Coronary Artery Disease Is Higher in RA Patients than in General Population RA patients have a 2-3 fold increase in rates of MI compared to the general population Solomon DHM, et al., Circulation 23;17: Del Rincon ID, et al., Arthritis Rheum 21; 44: They are more likely to experience silent ischaemia and sudden cardiac death Maradit-Kremers H, et al. Arthritis Rheum 25; 52: The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 11
12 Prevalence of Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) in Three Cohort of SLE Patients and in Women of Framingham Offspring Study Baltimore (1992) Toronto (1995) Pittsburgh (1997) Framingham Offspring Study Patients, N Prevalence of CAD 8,3% 1% 6,7% 1,6% Baltimore: Petri M, et al., Am J Med 1992; 93: Toronto: Abu-Shakra M, et al., J Rheumatol 1995; 22: Pittsburgh: Manzi S, et al., Am J Epidemiol 1997; 145: Incidence Rates of MI per 1 Person-Years in 498 Women with SLE, University of Pittsburgh, and 2,28 women, Framingham Offspring Heart Study, Age (years) Rate SLE 95% CI Rate Framingham 95% CI Rate ratio 95% CI Manzi S, et al., Am J Epidemiol 1997; 145: Risk Factors for Atherosclerosis in SLE The evaluation of risk factors for clinical atherosclerosis is difficult in SLE because of the low number of observed cardiovascular events due to the low prevalence of the disease The study of subclinical atherosclerosis has the advantage of providing a higher number of lesions leading to a more suitable evaluation of risk factors 36 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 12
13 Non-Invasive Techniques for the Detection of Subclinical Atherosclerosis Brachial flow mediated vasodilatation (BFMV) Pulse-Wave Velocity (PWV) Carotid Color Doppler Ultrasonography (US) Electron Beam Computed Tomography (CT) Scintigraphy (Thallium-21) Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) Thallium-21 Dual Isotope Myocardial Perfusion Imaging (DIMPI) 37 Duplex Ultrasonography Intima-media thickness (IMT) of common carotid artery 38 Evidence of Increased IMT in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Wallberg S, et al., J Rheumatol 21;28: Kumeda Y, et al., Arthritis Rheum 22;46: Park Y-B, et al., Arthritis Rheum 22;46: Alkaabi JK, et al., Rheumatology 23;42:292-7 Del Rincon, et al., Arthritis Rheum 23;48: Gonzales C, et al., Medicine 23;82:47-13 Nagata M, et al., Arthritis Rheum 23;48: The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 13
14 Traditional risk factors Age Sedentary life style Diabetes Dyslipidaemia Smoking Hypertension R.F. Drugs CysA Steroids HC MTX CIC Proinflammatory cytokines Cellular dysfunction Acute-phase Adhesion reactants molecules Chronic Inflammation Homocysteine Prothrombotic state Similarities between Atherosclerosis RA C-reactive protein Adhesion molecules Neoangiogenesis (UA) Macrophage activation TNF-α Metallopr. Expression IL-6 Mast cell activation B-cell activation Autoantibodies (oxldl, HS) Rheumatoid factor T-cell activation sil-2 receptor CD3+ DR+ CD4+ CD28- CD4+ IFN-γ Th1/Th2 balance or (UA) (UA) (UA) (UA) (UA) Th1 or 41 Th1 Patients n. Mean age (years) Female % White% Previous CVD % Plaque definition Plaque % Mean IMT (mm) Risk factor evaluation Carotid Ultrasound Studies in SLE Manzi et al. (1999) mm IMT (mean±sd) >5% than surrounding area Roman 4 MJ, et 65al. N Eng 38 J Med 23; 37349: ±.14.66±.15.6±.14 Cross sectional 1, 4 1, 2 1, 8, 6, 4, 2 Svenungsson et al. (21) SLE cases ±.16.67± Not reported SLE IMT>1 patients mm Cross sectional SLE controls p<.1 26 Roman et al. (23) 197 ~5 12 >5% than IMT>1.3 Healthy surrounding subjects mm area.61±.16 Cross sectional Shoenfeld Y, Gerli R, Doria A, et al. Circulation 25; 112: Doria et al. (23) ±.15 Prospective Selzer et al. (24) >5% than surrounding area 32.71±.1 Cross sectional 42 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 14
15 Traditional and Other Metabolic Risk Factors for ATS Age Sex Hypercholesterolaemia Hypertension Obesity in SLE Diabetes Sedentary life style Cigarette smoking Family history for CVD Hypertryglyceridaemia Mean number of CV risk factors per person Premature menopause Hyperhomocysteinaemia in SLE Insulin SLE patients resistance >>> General population Petri M, et al., Medicine (Baltimore) 1992; 71: ; Bruce IN, et al., Arthritis Rheum 23; 48: ; EL-Magadmi M, et al., J Rheumatol 23; 48: Cardiovascular Risk in Lupus SLE Overall Risk of CHD General population Low Traditional risk factors High Wajed et al., Rheumatol 24; 43: 7 44 Novel Risk Factors for Atherosclerosis Markers of inflammation Acute-phase proteins CRP Serum amyloid A Adhesion molecules ICAM-1 P selectin E selectin Cytokines IL-6 TNFα Immunological factors Adaptive immunity Anti-β 2GPI Anti-oxLDL Anti-HSP-65 Innate immunity Toll-like receptor (TLRs) TLR4 Scavenger receptors (SR) SR-A CD36 Lipoproteins and modified lipids Lipoprotein (a) Oxidized LDL Small, dense, LDL Abnormal coagulation factors Fibrinogen PAI-1 Homocysteine 45 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 15
16 CRP and Subclinical Atherosclerosis in SLE CRP was associated with plaques at univariate, but not at multivariate analysis Selzer F, et al., Arthritis Rheum 24; 5: CRP was not associated with plaques Roman MJ, et al., N Eng J Med 23; 349: Cross-Sectional Studies on the Relationship Between Autoantibodies and Atherosclerosis (ATS) in SLE Patients Zampieri S, Doria A, et al., Ann N Y Acad Sci 25; 151: Subclinical Atherosclerosis in SLE: Study Design Traditional risk factors Treatment during follow-up Carotid ultrasound examination 78 SLE pts T 5 year follow-up T1 SLE clinical and laboratory features SLE disease activity (ECLAM) SLE damage index (SLICC DI) Novel predictors: CRP, anti-oxldl, anti-β 2GPI, and anti-hsp65 Doria A, et al., Ann Rheum Dis 23; 62: The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 16
17 U/ml6 Correlation Between M-IMT and IgG Anti-oxLDL Levels IgG anti-oxldl levels at T r=.344, p=.2,,1,2 M-IMT Doria A, et al., Ann Rheum Dis 23; 62: ,3 mm 49 Conclusions The IgG role anti-oxldl of anti-β2gpi, may anti-hsp65 play a role and CRP seems in to the be masked accelerated by some atherosclerotic disease-related process features observed particularly in SLE prednisone patients cumulative dosage and renal involvement SLE-Related Risk Factors for Atherosclerosis SLE phenotype SLE activity Severe/mild SLE Glomerulonephritis Arthritis apl syndrome Other manifestations Doria A, et al., Ann Rheum Dis 23; 62: Disease duration Treatment Corticosteroids Immunosuppressants Others 5 Questions Which Should Be Addressed: 1) Who are at highest risk for accelerated atherosclerosis? Severe or mild SLE patients? Patients with renal involvement or those with skin or joint manifestations? 2) Are corticosteroids pro or anti-atherosclerotic? 51 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 17
18 Correlates of Accelerated Atherosclerosis in SLE Roman MJ, et al., N Eng J Med 23; : st Multivariate analysis Traditional risk factors Age Menopausal status Systolic BP Total cholesterol LDL cholesterol 2nd Multivariate analysis SLE related features Age at diagnosis Longer SLE duration SLICC damage index Pulmonary hypertension Anti-RNP Anti-Sm 5-yr daily dose of PDN Cyclophosphamide use Hydroxychloroquine use Significant in univariate and multivariate analyses 52 Severe or Mild SLE Patients: Who Are at Highest Risk for Accelerated Atherosclerosis? In Roman s study, patients with less severe disease were older than those with more severe disease The higher prevalence of plaque in the former group of patients could not be related to milder disease, but to age itself, a factor not considered by the authors in the multiple regression analysis for disease-related factors Doria A, et al., N Eng J Med 24; 35: Risk Factors for Carotid Plaques in SLE Doria A et al., Ann Rheum Dis 23; 6 2 : Multivariate analysis Traditional risk factors Age Hypertension Hypercholesterolemia SLE related features Renal involv. at T ECLAM >2 at T PDN 4 gr Azathioprine Significant in univariate and multivariate analyses 54 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 18
19 78 SLE Patients Traditional risk factors Lipoprotein subclasses SLE variables Novel risk factors 1 8 % Groups: A B C <18 g g >38 g Prednisone cumulative intake Doria A et al., Arthritis Rheum 24; 5: S191-S Mean (±SD) Prednisone (PRD) Cumulative Dosage in Patients with and Without Carotid Plaque Patients with plaque Patients without plaque * Adjusted for traditional risk factors including BP and lipoprotein subclasses Doria A et al., Arthritis Rheum 24; 5: S191-S Mean (±SD) Prednisone (PRD) Cumulative Dosage in Patients with and Without Carotid Plaque grams of PRD ±5.2 p=n.s. 29.3±2. Patients with plaque Patients without plaque PRD adjusted* * Adjusted for traditional risk factors and renal involvement Doria A et al., Arthritis Rheum 24; 5: S191-S The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 19
20 The Bimodal Mortality Pattern of SLE Urowitz MB, et al., Am J Med 1976; 6 : % Active SLE CHD Early mortality Late mortality Years After Diagnosis 58 Long-Term Prognosis in SLE Doria A, et al., Am J Med 26; : 7-6 % Years After Diagnosis Urowitz et al., Am J Med 1976 Doria et al., Am J Med Long-Term Prognosis in SLE Doria A, et al., Am J Med 26; : Mild disease 72 % 6 Severe disease Years After Diagnosis 6 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 2
21 Maximum effort should be made: To adequately treat severe lupus manifestations, particularly glomerulonephritis, using the lowest possible dosage of corticosteroids associated with corticosteroid sparing therapy To manage modifiable traditional risk factors for ATS, first of all hypertension and hypercholesterolemia, as quickly as possible Take Home Message To consider the use in these patients of low-dose aspirin, hydroxychloroquine, and ACE inhibitors 61 Triggers and Common Pathway in Atherosclerosis Infections CV risk factors Chronic inflammatory diseases Innate/adaptive immunity Endothelial dysfunction Vessel Lumen Endothelium Atherosclerosis/inflammat ion 62 Intima The Role of the Endothelium in the Maintenance of Vascular Homoeostasis Vasodilation Anti-inflammatory Anti-thrombotic Anti-coagulant Pro-fibrinolytic Vasoconstriction Pro-inflammatory Pro-thrombotic Pro-coagulant Anti-fibrinolytic Endothelium Vessel Lumen Intima 63 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 21
22 Assessment of Endothelial Function Circulating markers of vascular wall inflammation Endothelial vasomotor testing (endothelial stress test) Intra-arterial infusion of specific endotheliumdependent vasodilators (coronary microcirculation, brachial or femoral circulation) Ultrasound measurement of brachial artery reactivity to shear stress (upper arm occlusion) Lerman, A. et al., Circulation 25;111: Ultrasound Assessment of Endothelial- Dependent Flow-Mediated Vasodilation of Brachial Artery 65 Evidence of Endothelial Dysfunction as Predictor of CV Events Lerman, A. et al., Circulation 25;111: The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 22
23 Endothelial-Dependent FMV of Brachial Artery in Patients with ARD Endothelial dysfunction was reported in patients with: Rheumatoid arthritis Bergholm R et al., Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 22;22: Hurlimann D et al., Circulation 22;16: Van Doornum S et al., Arthritis Rheum 23;48:72-8 Systemic lupus erythematosus Lima et al., J Rheumatol 22; 29: 292 El-Magadmi et al., Circulation 24; 11: 399 Johnson SR et al., Lupus 24; 13:59-3 Primary antiphospholipid antibody syndrome Mercanoglu F, et al., Int J Clin Pract 24; 58: 13-7 Sjıgren syndrome Pirildar T, et al., Rheumatol Int 25; 25:536-9 Primary systemic vasculitis Booth AD, et al., Circulation 24; 19: ; Ozdemir R, et al., Am J Cardiol 24; 94: ; Raza K, et al., Circulation 2; 12: 147-2; Filer AD, et al., Ann Rheum Dis 23; 62: Why Patients with Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases Have a Diffuse Endothelial Dysfunction? 68 Vascular Endothelium at the Site of the Primary Inflammatory Response and at Distant Sites Local inflammation Distant effects Leucocyte recruitment Systemic TNF-α Systemic TNF-α /CRP etc. Endothelial dysfunction Stromal/endothelial interactions Buckley, C. D. et al., Rheumatology 25 44: The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 23
24 Acknowledgments Anna Ghirardello Luca Iaccarino Sandra Zampieri Silvia Arienti Maria Elisa Rampudda Nicola Bassi Yheuda Shoenfeld Paolo Pauletto Pier Luigi Meroni Roberto Gerli Angela Tincani 7 71 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 24
CIC Edizioni Internazionali. Cardio-metabolic comorbidities in rheumatoid arthritis and SLE. Review. 120 Clinical Dermatology 2013; 1 (2):
 Review Cardio-metabolic comorbidities in rheumatoid arthritis and SLE Andrea Doria Division of Rheumatology University of Padua, Italy Address for correspondence: Division of Rheumatology University of
Review Cardio-metabolic comorbidities in rheumatoid arthritis and SLE Andrea Doria Division of Rheumatology University of Padua, Italy Address for correspondence: Division of Rheumatology University of
THE CARDIOVASCULAR INFLAMMATORY CONTINUUM DR AB MAHARAJ
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR INFLAMMATORY CONTINUUM DR AB MAHARAJ Disclosures: On National Advisory Boards of: (1) Pfizer Pharmaceuticals (2) MSD (3) Roche Pharmaceuticals (4) Abbott International: AfME Rheumatology
THE CARDIOVASCULAR INFLAMMATORY CONTINUUM DR AB MAHARAJ Disclosures: On National Advisory Boards of: (1) Pfizer Pharmaceuticals (2) MSD (3) Roche Pharmaceuticals (4) Abbott International: AfME Rheumatology
Lupus as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease
 Lupus as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease SØREN JACOBSEN Department Rheumatology, Rigshospitalet Søren Jacobsen Main sponsors: Gigtforeningen Novo Nordisk Fonden Rigshospitalet Disclaimer: Novo
Lupus as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease SØREN JACOBSEN Department Rheumatology, Rigshospitalet Søren Jacobsen Main sponsors: Gigtforeningen Novo Nordisk Fonden Rigshospitalet Disclaimer: Novo
Not only...but also : factors that contribute to accelerated atherosclerosis and premature coronary heart disease in systemic lupus erythematosus
 Rheumatology 2005;44:1492 1502 Advance Access publication 18 October 2005 Review doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kei142 Michael Mason Prize Essay Not only...but also : factors that contribute to accelerated atherosclerosis
Rheumatology 2005;44:1492 1502 Advance Access publication 18 October 2005 Review doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kei142 Michael Mason Prize Essay Not only...but also : factors that contribute to accelerated atherosclerosis
Dyslipidemia Endothelial dysfunction Free radicals Immunologic
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS Hossein Mehrani Professor of Clinical Biochemistry Definition Atherosclerosis: Is a chronic inflammatory process characterized by plaque formation within the vessel wall of arteries and
ATHEROSCLEROSIS Hossein Mehrani Professor of Clinical Biochemistry Definition Atherosclerosis: Is a chronic inflammatory process characterized by plaque formation within the vessel wall of arteries and
PATIENTS AND METHODS:
 BACKGROUND: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic systemic inflammatory disease characterized by erosive synovitis that involves peripheral joints and implicates an important influence in the quality
BACKGROUND: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic systemic inflammatory disease characterized by erosive synovitis that involves peripheral joints and implicates an important influence in the quality
The 10 th International & 15 th National Congress on Quality Improvement in Clinical Laboratories
 The 10 th International & 15 th National Congress on Quality Improvement in Clinical Laboratories Cardiac biomarkers in atherosclerosis Najma Asadi MD-APCP Ross and Colleagues in 1973: Response to Injury
The 10 th International & 15 th National Congress on Quality Improvement in Clinical Laboratories Cardiac biomarkers in atherosclerosis Najma Asadi MD-APCP Ross and Colleagues in 1973: Response to Injury
Vascular disease. Structural evaluation of vascular disease. Goo-Yeong Cho, MD, PhD Seoul National University Bundang Hospital
 Vascular disease. Structural evaluation of vascular disease Goo-Yeong Cho, MD, PhD Seoul National University Bundang Hospital resistance vessels : arteries
Vascular disease. Structural evaluation of vascular disease Goo-Yeong Cho, MD, PhD Seoul National University Bundang Hospital resistance vessels : arteries
Pathophysiology of Lipid Disorders
 Pathophysiology of Lipid Disorders Henry Ginsberg, M.D. Division of Preventive Medicine and Nutrition CHD in the United States CHD is the single largest killer of men and women 12 million have history
Pathophysiology of Lipid Disorders Henry Ginsberg, M.D. Division of Preventive Medicine and Nutrition CHD in the United States CHD is the single largest killer of men and women 12 million have history
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis
 Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease
 Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth J. Kligerman, MD Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth Kligerman, MD Assistant Professor Medical Director of MRI University of Maryland Department of Radiology
Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth J. Kligerman, MD Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth Kligerman, MD Assistant Professor Medical Director of MRI University of Maryland Department of Radiology
ROLE OF INFLAMMATION IN HYPERTENSION. Dr Barasa FA Physician Cardiologist Eldoret
 ROLE OF INFLAMMATION IN HYPERTENSION Dr Barasa FA Physician Cardiologist Eldoret Outline Inflammation in CVDs the evidence Basic Science in Cardiovascular inflammation: The Main players Inflammation as
ROLE OF INFLAMMATION IN HYPERTENSION Dr Barasa FA Physician Cardiologist Eldoret Outline Inflammation in CVDs the evidence Basic Science in Cardiovascular inflammation: The Main players Inflammation as
Lupus and the heart. Lupus Foundation of America
 Lupus and the heart Lupus Foundation of America Teleconference FEB 2015 Premature Atherosclerotic ti Cardiovascular Disease in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Joan M. Von Feldt, MD, MSEd Professor of Medicine
Lupus and the heart Lupus Foundation of America Teleconference FEB 2015 Premature Atherosclerotic ti Cardiovascular Disease in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Joan M. Von Feldt, MD, MSEd Professor of Medicine
Cho et al., 2009 Journal of Cardiology (2009), 54:
 Endothelial Dysfunction, Increased Carotid Artery Intima-media Thickness and Pulse Wave Velocity, and Increased Level of Inflammatory Markers are Associated with Variant Angina Cho et al., 2009 Journal
Endothelial Dysfunction, Increased Carotid Artery Intima-media Thickness and Pulse Wave Velocity, and Increased Level of Inflammatory Markers are Associated with Variant Angina Cho et al., 2009 Journal
Role of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the development of atherosclerosis Jan Borén MD, PhD
 Role of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the development of atherosclerosis Jan Borén MD, PhD Our laboratory focuses on the role of apolipoprotein (apo) B- containing lipoproteins in normal
Role of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the development of atherosclerosis Jan Borén MD, PhD Our laboratory focuses on the role of apolipoprotein (apo) B- containing lipoproteins in normal
Inflammation and and Heart Heart Disease in Women Inflammation and Heart Disease
 Inflammation and Heart Disease in Women Inflammation and Heart Disease What is the link between een inflammation and atherosclerotic disease? What is the role of biomarkers in predicting cardiovascular
Inflammation and Heart Disease in Women Inflammation and Heart Disease What is the link between een inflammation and atherosclerotic disease? What is the role of biomarkers in predicting cardiovascular
Part 1 Risk Factors and Atherosclerosis. LO1. Define the Different Forms of CVD
 Week 3: Cardiovascular Disease Learning Outcomes: 1. Define the difference forms of CVD 2. Describe the various risk factors of CVD 3. Describe atherosclerosis and its stages 4. Describe the role of oxidation,
Week 3: Cardiovascular Disease Learning Outcomes: 1. Define the difference forms of CVD 2. Describe the various risk factors of CVD 3. Describe atherosclerosis and its stages 4. Describe the role of oxidation,
Classification of Endothelial Dysfunction. Stefano Taddei Department of Internal Medicine University of Pisa, Italy
 Classification of Endothelial Dysfunction Stefano Taddei Department of Internal Medicine University of Pisa, Italy Pathogenesis of atherosclerosis from endothelial dysfunction to clinical disease endothelial
Classification of Endothelial Dysfunction Stefano Taddei Department of Internal Medicine University of Pisa, Italy Pathogenesis of atherosclerosis from endothelial dysfunction to clinical disease endothelial
 Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Apolipoprotein
Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Apolipoprotein
Tracking a Killer Molecule
 Tracking a Killer Molecule Mercodia Oxidized LDL ELISA www.mercodia.com Mercodia Oxidized LDL ELISA products Product Catalog No Kit size Oxidized LDL ELISA 10-1143-01 96 wells Oxidized LDL competitive
Tracking a Killer Molecule Mercodia Oxidized LDL ELISA www.mercodia.com Mercodia Oxidized LDL ELISA products Product Catalog No Kit size Oxidized LDL ELISA 10-1143-01 96 wells Oxidized LDL competitive
Complications of Diabetes mellitus. Dr Bill Young 16 March 2015
 Complications of Diabetes mellitus Dr Bill Young 16 March 2015 Complications of diabetes Multi-organ involvement 2 The extent of diabetes complications At diagnosis as many as 50% of patients may have
Complications of Diabetes mellitus Dr Bill Young 16 March 2015 Complications of diabetes Multi-organ involvement 2 The extent of diabetes complications At diagnosis as many as 50% of patients may have
Low-density lipoprotein as the key factor in atherogenesis too high, too long, or both
 Low-density lipoprotein as the key factor in atherogenesis too high, too long, or both Lluís Masana Vascular Medicine and Metabolism Unit. Sant Joan University Hospital. IISPV. CIBERDEM Rovira i Virgili
Low-density lipoprotein as the key factor in atherogenesis too high, too long, or both Lluís Masana Vascular Medicine and Metabolism Unit. Sant Joan University Hospital. IISPV. CIBERDEM Rovira i Virgili
Atherosclerosis is a multifactorial process that commences
 Contemporary Reviews in Cardiovascular Medicine Accelerated Atherosclerosis in Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases Yehuda Shoenfeld, MD, FRCP (Hon); Roberto Gerli, MD; Andrea Doria, MD; Eiji Matsuura, PhD; Marco
Contemporary Reviews in Cardiovascular Medicine Accelerated Atherosclerosis in Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases Yehuda Shoenfeld, MD, FRCP (Hon); Roberto Gerli, MD; Andrea Doria, MD; Eiji Matsuura, PhD; Marco
The Study of Endothelial Function in CKD and ESRD
 The Study of Endothelial Function in CKD and ESRD Endothelial Diversity in the Human Body Aird WC. Circ Res 2007 Endothelial Diversity in the Human Body The endothelium should be viewed for what it is:
The Study of Endothelial Function in CKD and ESRD Endothelial Diversity in the Human Body Aird WC. Circ Res 2007 Endothelial Diversity in the Human Body The endothelium should be viewed for what it is:
Key words: antiphospholipid syndrome, trombosis, pathogenesis
 26. XI,. 4/2011,.,..,..,., -..,,. 2GPI. -,.,,., -,, -, -,,,,, IL-1, IL-2, IL-6, IL-8, IL-12, IL-10, TNF, INF-. :,, N. Stoilov, R. Rashkov and R. Stoilov. ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID SYNDROME HISTORICAL DATA, ETI-
26. XI,. 4/2011,.,..,..,., -..,,. 2GPI. -,.,,., -,, -, -,,,,, IL-1, IL-2, IL-6, IL-8, IL-12, IL-10, TNF, INF-. :,, N. Stoilov, R. Rashkov and R. Stoilov. ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID SYNDROME HISTORICAL DATA, ETI-
Dyslipidaemia. Is there any new information? Dr. A.R.M. Saifuddin Ekram
 Dyslipidaemia Is there any new information? Dr. A.R.M. Saifuddin Ekram PhD,FACP,FCPS(Medicine) Professor(c.c.) & Head Department of Medicine Rajshahi Medical College Rajshahi-6000 New features of ATP III
Dyslipidaemia Is there any new information? Dr. A.R.M. Saifuddin Ekram PhD,FACP,FCPS(Medicine) Professor(c.c.) & Head Department of Medicine Rajshahi Medical College Rajshahi-6000 New features of ATP III
IS PRE-CLINICAL AUTOIMMUNITY BENIGN?
 IS PRE-CLINICAL AUTOIMMUNITY BENIGN? Darcy S. Majka MD, MS Disclosures I have no significant financial or other relationship with the manufacturers of any product or services. Dr. Teodorescu (coauthor)
IS PRE-CLINICAL AUTOIMMUNITY BENIGN? Darcy S. Majka MD, MS Disclosures I have no significant financial or other relationship with the manufacturers of any product or services. Dr. Teodorescu (coauthor)
Which CVS risk reduction strategy fits better to carotid US findings?
 Which CVS risk reduction strategy fits better to carotid US findings? Dougalis A, Soulaidopoulos S, Cholongitas E, Chalevas P, Vettas Ch, Doumtsis P, Vaitsi K, Diavasti M, Mandala E, Garyfallos A 4th Department
Which CVS risk reduction strategy fits better to carotid US findings? Dougalis A, Soulaidopoulos S, Cholongitas E, Chalevas P, Vettas Ch, Doumtsis P, Vaitsi K, Diavasti M, Mandala E, Garyfallos A 4th Department
Association between arterial stiffness and cardiovascular risk factors in a pediatric population
 + Association between arterial stiffness and cardiovascular risk factors in a pediatric population Maria Perticone Department of Experimental and Clinical Medicine University Magna Graecia of Catanzaro
+ Association between arterial stiffness and cardiovascular risk factors in a pediatric population Maria Perticone Department of Experimental and Clinical Medicine University Magna Graecia of Catanzaro
LIPOPROTEIN-ASSOCIATED PHOSPHOLIPASE A 2 : EFFECTS OF LOW DENSITY LIPOPROTEIN APHERESIS
 LIPOPROTEIN-ASSOCIATED PHOSPHOLIPASE A 2 : EFFECTS OF LOW DENSITY LIPOPROTEIN APHERESIS Patrick M. Moriarty, M.D., FACP, Director, Atherosclerosis and LDL-Apheresis Center, University of Kansas Medical
LIPOPROTEIN-ASSOCIATED PHOSPHOLIPASE A 2 : EFFECTS OF LOW DENSITY LIPOPROTEIN APHERESIS Patrick M. Moriarty, M.D., FACP, Director, Atherosclerosis and LDL-Apheresis Center, University of Kansas Medical
Title for Paragraph Format Slide
 Title for Paragraph Format Slide Presentation Title: Month Date, Year Atherosclerosis A Spectrum of Disease: February 12, 2015 Richard Cameron Padgett, MD Executive Medical Director, OHVI Pt RB Age 38
Title for Paragraph Format Slide Presentation Title: Month Date, Year Atherosclerosis A Spectrum of Disease: February 12, 2015 Richard Cameron Padgett, MD Executive Medical Director, OHVI Pt RB Age 38
The New Gold Standard for Lipoprotein Analysis. Advanced Testing for Cardiovascular Risk
 The New Gold Standard for Lipoprotein Analysis Advanced Testing for Cardiovascular Risk Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing The Lipid Panel Total Cholesterol = VLDL + LDL + HDL Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing
The New Gold Standard for Lipoprotein Analysis Advanced Testing for Cardiovascular Risk Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing The Lipid Panel Total Cholesterol = VLDL + LDL + HDL Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing
Basic Mechanisms of Atherosclerosis and Plaque Rupture: Clinical Implications
 12 th Annual Cardiovascular Disease Prevention Symposium February 8, 2013 KEYNOTE ADDRESS Basic Mechanisms of Atherosclerosis and Plaque Rupture: Clinical Implications Ira Tabas, M.D., Ph.D. Richard J.
12 th Annual Cardiovascular Disease Prevention Symposium February 8, 2013 KEYNOTE ADDRESS Basic Mechanisms of Atherosclerosis and Plaque Rupture: Clinical Implications Ira Tabas, M.D., Ph.D. Richard J.
10/17/16. Assessing cardiovascular risk through use of inflammation testing
 Assessing cardiovascular risk through use of inflammation testing Anthony L. Lyssy, DO Medical Director and Managing Partner Diamond Physicians Dallas, TX Response to Injury Hypothesis Injury Response
Assessing cardiovascular risk through use of inflammation testing Anthony L. Lyssy, DO Medical Director and Managing Partner Diamond Physicians Dallas, TX Response to Injury Hypothesis Injury Response
Thrombophilia. Dr. A Sarrafnejad PhD Dep. Immunology School of public health TUMS
 Autoimmune Thrombophilia Dr. A Sarrafnejad PhD Dep. Immunology School of public health TUMS Saraf@sina.tums.ac.ir Acquired Thrombophilia HIT PNH Cyckle cell Anemia Myeloproliferative lf Diseases Thrombocytosis
Autoimmune Thrombophilia Dr. A Sarrafnejad PhD Dep. Immunology School of public health TUMS Saraf@sina.tums.ac.ir Acquired Thrombophilia HIT PNH Cyckle cell Anemia Myeloproliferative lf Diseases Thrombocytosis
1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones?
 1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones? 3How are dietary lipids transported? 4How lipids synthesized in the liver are transported? 5 Lipoprotien
1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones? 3How are dietary lipids transported? 4How lipids synthesized in the liver are transported? 5 Lipoprotien
Demir Baykal,MD,FACC,FASE Diplomat ABCL,SCCT Gwinnett Consultants in Cardiology Medical Software,LLC
 Demir Baykal,MD,FACC,FASE Diplomat ABCL,SCCT Gwinnett Consultants in Cardiology Medical Software,LLC 1950-1979 1980-1992 Gabriel, S. et al., Arthritis Rheum 1999;42:46-50. 1. Pericarditis 2. Myocarditis
Demir Baykal,MD,FACC,FASE Diplomat ABCL,SCCT Gwinnett Consultants in Cardiology Medical Software,LLC 1950-1979 1980-1992 Gabriel, S. et al., Arthritis Rheum 1999;42:46-50. 1. Pericarditis 2. Myocarditis
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. An Independent Risk Factor for Endothelial Dysfunction in Women
 Systemic Lupus Erythematosus An Independent Risk Factor for Endothelial Dysfunction in Women Masoud El-Magadmi, MB; Helena Bodill, MSc; Yasmeen Ahmad, MB, MRCP; Paul N. Durrington, MD, F Med Sci; Michael
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus An Independent Risk Factor for Endothelial Dysfunction in Women Masoud El-Magadmi, MB; Helena Bodill, MSc; Yasmeen Ahmad, MB, MRCP; Paul N. Durrington, MD, F Med Sci; Michael
Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice
 Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice Atherosclerosis, 2007 Chiba T, Shinozaki S, Nakazawa T, et al. Present by Sudaporn Pummoung Apolipoprotein E (apoe( apoe)
Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice Atherosclerosis, 2007 Chiba T, Shinozaki S, Nakazawa T, et al. Present by Sudaporn Pummoung Apolipoprotein E (apoe( apoe)
Hans Strijdom SA Heart Meeting November 2017
 Hans Strijdom SA Heart Meeting November 2017 HIV-infection and ART, but not high sensitivity CRP, are associated with markers of vascular function: Results from the Western Cape cohort of the EndoAfrica
Hans Strijdom SA Heart Meeting November 2017 HIV-infection and ART, but not high sensitivity CRP, are associated with markers of vascular function: Results from the Western Cape cohort of the EndoAfrica
Intima-Media Thickness
 European Society of Cardiology Stockholm, 30th August 2010 Intima-Media Thickness Integration of arterial assessment into clinical practice Prof Arno Schmidt-Trucksäss, MD Institute of Exercise and Health
European Society of Cardiology Stockholm, 30th August 2010 Intima-Media Thickness Integration of arterial assessment into clinical practice Prof Arno Schmidt-Trucksäss, MD Institute of Exercise and Health
Plasma lipoproteins & atherosclerosis by. Prof.Dr. Maha M. Sallam
 Biochemistry Department Plasma lipoproteins & atherosclerosis by Prof.Dr. Maha M. Sallam 1 1. Recognize structures,types and role of lipoproteins in blood (Chylomicrons, VLDL, LDL and HDL). 2. Explain
Biochemistry Department Plasma lipoproteins & atherosclerosis by Prof.Dr. Maha M. Sallam 1 1. Recognize structures,types and role of lipoproteins in blood (Chylomicrons, VLDL, LDL and HDL). 2. Explain
Mandana Nikpour 1,2, Murray B Urowitz 1*, Dominique Ibanez 1, Paula J Harvey 3 and Dafna D Gladman 1. Abstract
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Importance of cumulative exposure to elevated cholesterol and blood pressure in development of atherosclerotic coronary artery disease in systemic lupus erythematosus: a prospective
RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Importance of cumulative exposure to elevated cholesterol and blood pressure in development of atherosclerotic coronary artery disease in systemic lupus erythematosus: a prospective
Identifying and Quantifying Dynamic Risk Factors for Coronary Artery Disease in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
 Identifying and Quantifying Dynamic Risk Factors for Coronary Artery Disease in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus by Mandana Nikpour A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of
Identifying and Quantifying Dynamic Risk Factors for Coronary Artery Disease in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus by Mandana Nikpour A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of
Lipid/Lipoprotein Structure and Metabolism (Overview)
 Lipid/Lipoprotein Structure and Metabolism (Overview) Philip Barter President, International Atherosclerosis Society Centre for Vascular Research University of New South Wales Sydney, Australia Disclosures
Lipid/Lipoprotein Structure and Metabolism (Overview) Philip Barter President, International Atherosclerosis Society Centre for Vascular Research University of New South Wales Sydney, Australia Disclosures
Subclinical atherosclerosis in CVD: Risk stratification & management Raul Santos, MD
 Subclinical atherosclerosis in CVD: Risk stratification & management Raul Santos, MD Sao Paulo Medical School Sao Paolo, Brazil Subclinical atherosclerosis in CVD risk: Stratification & management Prof.
Subclinical atherosclerosis in CVD: Risk stratification & management Raul Santos, MD Sao Paulo Medical School Sao Paolo, Brazil Subclinical atherosclerosis in CVD risk: Stratification & management Prof.
Diabetes and Occult Coronary Artery Disease
 Diabetes and Occult Coronary Artery Disease Mun K. Hong, MD, FACC, FSCAI Director, Cardiac Catheterization Laboratory & Interventional Cardiology St. Luke s-roosevelt Hospital Center New York, New York
Diabetes and Occult Coronary Artery Disease Mun K. Hong, MD, FACC, FSCAI Director, Cardiac Catheterization Laboratory & Interventional Cardiology St. Luke s-roosevelt Hospital Center New York, New York
Invited Review. Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases
 Histol Histopathol (2000) 15: 557-571 Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Invited Review Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular
Histol Histopathol (2000) 15: 557-571 Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Invited Review Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular
Review of guidelines for management of dyslipidemia in diabetic patients
 2012 international Conference on Diabetes and metabolism (ICDM) Review of guidelines for management of dyslipidemia in diabetic patients Nan Hee Kim, MD, PhD Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University
2012 international Conference on Diabetes and metabolism (ICDM) Review of guidelines for management of dyslipidemia in diabetic patients Nan Hee Kim, MD, PhD Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University
Omics and coronary atherosclerosis
 Omics and coronary atherosclerosis Dr.ssa Rosalinda Madonna Centro Scienze dell Invecchiamento e Medicina Traslazionale CESI-Met Università G. d Annunzio Chieti Geographic Distribution of Relative Mortality
Omics and coronary atherosclerosis Dr.ssa Rosalinda Madonna Centro Scienze dell Invecchiamento e Medicina Traslazionale CESI-Met Università G. d Annunzio Chieti Geographic Distribution of Relative Mortality
Adipose Tissue as an Endocrine Organ. Abdel Moniem Ibrahim, MD Professor of Physiology Cairo University
 Adipose Tissue as an Endocrine Organ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim, MD Professor of Physiology Cairo University Functions of Adipose Tissue Adipose tissue expresses and secretes a variety of bioactive peptides,
Adipose Tissue as an Endocrine Organ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim, MD Professor of Physiology Cairo University Functions of Adipose Tissue Adipose tissue expresses and secretes a variety of bioactive peptides,
A Study of Atherosclerosis in Systemic Vasculitis
 Original Article A Study of Atherosclerosis in Systemic Vasculitis Silas Supragya Nelson, Sonjjay Pande, Avadhesh Pratap Singh Kushwah 3 Assistant Professor in the Department of Medicine, NSCB Medical
Original Article A Study of Atherosclerosis in Systemic Vasculitis Silas Supragya Nelson, Sonjjay Pande, Avadhesh Pratap Singh Kushwah 3 Assistant Professor in the Department of Medicine, NSCB Medical
Ischemic Heart and Cerebrovascular Disease. Harold E. Lebovitz, MD, FACE Kathmandu November 2010
 Ischemic Heart and Cerebrovascular Disease Harold E. Lebovitz, MD, FACE Kathmandu November 2010 Relationships Between Diabetes and Ischemic Heart Disease Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in Different Categories
Ischemic Heart and Cerebrovascular Disease Harold E. Lebovitz, MD, FACE Kathmandu November 2010 Relationships Between Diabetes and Ischemic Heart Disease Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in Different Categories
Subclinical inflammation and peripheral artery disease. Luigi M Biasucci, M.D. Institute of Cardiology Catholic University Rome, ITALY
 Subclinical inflammation and peripheral artery disease Luigi M Biasucci, M.D. Institute of Cardiology Catholic University Rome, ITALY ESC Congress 2010 Conflict of interest Research grants:sanofi-aventis,
Subclinical inflammation and peripheral artery disease Luigi M Biasucci, M.D. Institute of Cardiology Catholic University Rome, ITALY ESC Congress 2010 Conflict of interest Research grants:sanofi-aventis,
Novel Markers of Arterial Dysfunction
 혈관연구회창립심포지움, 3 월 3 일, 2005 Novel Markers of Arterial Dysfunction Kwang Kon Koh, MD, FACC, FAHA Cardiology Gachon Medical School Incheon, Korea Atherosclerosis: A progressive process PHASE I: Initiation
혈관연구회창립심포지움, 3 월 3 일, 2005 Novel Markers of Arterial Dysfunction Kwang Kon Koh, MD, FACC, FAHA Cardiology Gachon Medical School Incheon, Korea Atherosclerosis: A progressive process PHASE I: Initiation
Cardiovascular Complications of Diabetes
 VBWG Cardiovascular Complications of Diabetes Nicola Abate, M.D., F.N.L.A. Professor and Chief Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism The University of Texas Medical Branch Galveston, Texas Coronary
VBWG Cardiovascular Complications of Diabetes Nicola Abate, M.D., F.N.L.A. Professor and Chief Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism The University of Texas Medical Branch Galveston, Texas Coronary
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF ACUTE CORONARY SYNDROMES
 PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF ACUTE CORONARY SYNDROMES Brian R. Holroyd, MD, FACEP, FRCPC Professor and Director, Division of Emergency Medicine, Faculty of Medicine and Dentistry, University of Alberta, Edmonton,
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF ACUTE CORONARY SYNDROMES Brian R. Holroyd, MD, FACEP, FRCPC Professor and Director, Division of Emergency Medicine, Faculty of Medicine and Dentistry, University of Alberta, Edmonton,
1. Which one of the following patients does not need to be screened for hyperlipidemia:
 Questions: 1. Which one of the following patients does not need to be screened for hyperlipidemia: a) Diabetes mellitus b) Hypertension c) Family history of premature coronary disease (first degree relatives:
Questions: 1. Which one of the following patients does not need to be screened for hyperlipidemia: a) Diabetes mellitus b) Hypertension c) Family history of premature coronary disease (first degree relatives:
Demir Baykal,MD,FACC,FASE Diplomat ABCL,SCCT Gwinnett Consultants in Cardiology Medical Software,LLC
 Demir Baykal,MD,FACC,FASE Diplomat ABCL,SCCT Gwinnett Consultants in Cardiology Medical Software,LLC 1950-1979 1980-1992 Gabriel, S. et al., Arthritis Rheum 1999;42:46-50. 1 1. Pericarditis 2. Myocarditis
Demir Baykal,MD,FACC,FASE Diplomat ABCL,SCCT Gwinnett Consultants in Cardiology Medical Software,LLC 1950-1979 1980-1992 Gabriel, S. et al., Arthritis Rheum 1999;42:46-50. 1 1. Pericarditis 2. Myocarditis
C-reactive protein: a marker or a player?
 C-reactive protein: a marker or a player? Thomas Nyström, Thomas Nyström To cite this version: Thomas Nyström, Thomas Nyström. C-reactive protein: a marker or a player?. Clinical Science, Portland Press,
C-reactive protein: a marker or a player? Thomas Nyström, Thomas Nyström To cite this version: Thomas Nyström, Thomas Nyström. C-reactive protein: a marker or a player?. Clinical Science, Portland Press,
KEY COMPONENTS. Metabolic Risk Cardiovascular Risk Vascular Inflammation Markers
 CardioMetabolic Risk Poor blood sugar regulation and unhealthy triglyceride and lipoprotein levels often present long before the diagnosis of type 2 Diabetes. SpectraCell s CardioMetabolic and Pre-Diabetes
CardioMetabolic Risk Poor blood sugar regulation and unhealthy triglyceride and lipoprotein levels often present long before the diagnosis of type 2 Diabetes. SpectraCell s CardioMetabolic and Pre-Diabetes
Quinn Capers, IV, MD
 Heart Attacks Mended Hearts Presentation, January, 2017 Quinn Capers, IV, MD Associate Professor of Medicine (Cardiovascular Medicine) Director, Transradial Coronary Interventions Division of Cardiovascular
Heart Attacks Mended Hearts Presentation, January, 2017 Quinn Capers, IV, MD Associate Professor of Medicine (Cardiovascular Medicine) Director, Transradial Coronary Interventions Division of Cardiovascular
 Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Apolipoprotein B (APOB or ApoB) are the primary apolipoproteins of chylomicrons and low-density lipoproteins (LDL - known commonly by the misnomer "bad cholesterol"
Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Apolipoprotein B (APOB or ApoB) are the primary apolipoproteins of chylomicrons and low-density lipoproteins (LDL - known commonly by the misnomer "bad cholesterol"
Annals of RSCB Vol. XVI, Issue 1
 THE STUDY OF PROTHROBOTIC STATE IN PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES Oana Bădulescu 1, Codruţa Bădescu 2, Manuela Ciocoiu 1, Magda Bădescu 1 1 DEPARTMENT OF PATHOPHYSIOLOGY;
THE STUDY OF PROTHROBOTIC STATE IN PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES Oana Bădulescu 1, Codruţa Bădescu 2, Manuela Ciocoiu 1, Magda Bădescu 1 1 DEPARTMENT OF PATHOPHYSIOLOGY;
Assessment for Early Cardiovascular Risk in Pediatric Rheumatic Disease
 Assessment for Early Cardiovascular Risk in Pediatric Rheumatic Disease by Pascal Norman Tyrrell A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy Institute
Assessment for Early Cardiovascular Risk in Pediatric Rheumatic Disease by Pascal Norman Tyrrell A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy Institute
ATHEROSCLEROSIS زيد ثامر جابر. Zaid. Th. Jaber
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS زيد ثامر جابر Zaid. Th. Jaber Objectives 1- Review the normal histological features of blood vessels walls. 2-define the atherosclerosis. 3- display the risk factors of atherosclerosis.
ATHEROSCLEROSIS زيد ثامر جابر Zaid. Th. Jaber Objectives 1- Review the normal histological features of blood vessels walls. 2-define the atherosclerosis. 3- display the risk factors of atherosclerosis.
CLINICAL OUTCOME Vs SURROGATE MARKER
 CLINICAL OUTCOME Vs SURROGATE MARKER Statin Real Experience Dr. Mostafa Sherif Senior Medical Manager Pfizer Egypt & Sudan Objective Difference between Clinical outcome and surrogate marker Proper Clinical
CLINICAL OUTCOME Vs SURROGATE MARKER Statin Real Experience Dr. Mostafa Sherif Senior Medical Manager Pfizer Egypt & Sudan Objective Difference between Clinical outcome and surrogate marker Proper Clinical
Coronary Artery Calcification
 Coronary Artery Calcification Julianna M. Czum, MD OBJECTIVES CORONARY ARTERY CALCIFICATION Julianna M. Czum, MD Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center 1. To review the clinical significance of coronary heart
Coronary Artery Calcification Julianna M. Czum, MD OBJECTIVES CORONARY ARTERY CALCIFICATION Julianna M. Czum, MD Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center 1. To review the clinical significance of coronary heart
INFLAMMATION & REPAIR
 INFLAMMATION & REPAIR Lecture 7 Chemical Mediators of Inflammation Winter 2013 Chelsea Martin Special thanks to Drs. Hanna and Forzan Course Outline i. Inflammation: Introduction and generalities (lecture
INFLAMMATION & REPAIR Lecture 7 Chemical Mediators of Inflammation Winter 2013 Chelsea Martin Special thanks to Drs. Hanna and Forzan Course Outline i. Inflammation: Introduction and generalities (lecture
USING NON -TRADITIONAL RISK MARKERS IN ASSESSING CV RISK
 USING NON -TRADITIONAL RISK MARKERS IN ASSESSING CV RISK JAMES M FALKO MD PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF COLORADO Adapted from: Rader D. N Engl J Med. 2000 hs-crp (mg/l) 6 5 4 3 2 1 *p
USING NON -TRADITIONAL RISK MARKERS IN ASSESSING CV RISK JAMES M FALKO MD PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF COLORADO Adapted from: Rader D. N Engl J Med. 2000 hs-crp (mg/l) 6 5 4 3 2 1 *p
Diabetes and the Heart
 Diabetes and the Heart Association of Specialty Professors April 4, 2013 Jorge Plutzky, MD Co-Director, Preventive Cardiology Director, The Lipid Clinic Cardiovascular Division Brigham and Women s Hospital
Diabetes and the Heart Association of Specialty Professors April 4, 2013 Jorge Plutzky, MD Co-Director, Preventive Cardiology Director, The Lipid Clinic Cardiovascular Division Brigham and Women s Hospital
ΛΟΙΜΩΞΗ HIV. Ιγνάτιος Οικονομίδης,MD,FESC Β Πανεπιστημιακή Καρδιολογική
 ΛΟΙΜΩΞΗ HIV Ιγνάτιος Οικονομίδης,MD,FESC Β Πανεπιστημιακή Καρδιολογική Κλινική, Νοσοκομείο «Αττικόν» Infection Acute Myocardial Infarction p er 100,000 HIV/AIDS discharg es 800 700 600 500 400 300 200
ΛΟΙΜΩΞΗ HIV Ιγνάτιος Οικονομίδης,MD,FESC Β Πανεπιστημιακή Καρδιολογική Κλινική, Νοσοκομείο «Αττικόν» Infection Acute Myocardial Infarction p er 100,000 HIV/AIDS discharg es 800 700 600 500 400 300 200
Immune response to infection
 Immune response to infection Dr. Sandra Nitsche (Sandra.Nitsche@rub.de ) 20.06.2018 1 Course of acute infection Typical acute infection that is cleared by an adaptive immune reaction 1. invasion of pathogen
Immune response to infection Dr. Sandra Nitsche (Sandra.Nitsche@rub.de ) 20.06.2018 1 Course of acute infection Typical acute infection that is cleared by an adaptive immune reaction 1. invasion of pathogen
VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM AND CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE: IS THERE A LINK?
 VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM AND CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE: IS THERE A LINK? Ayman El-Menyar (1), MD, Hassan Al-Thani (2),MD (1)Clinical Research Consultant, (2) Head of Vascular Surgery, Hamad General Hospital
VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM AND CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE: IS THERE A LINK? Ayman El-Menyar (1), MD, Hassan Al-Thani (2),MD (1)Clinical Research Consultant, (2) Head of Vascular Surgery, Hamad General Hospital
Inflammation: Novel Target for Cardiovascular Risk Reduction
 Inflammation: Novel Target for Cardiovascular Risk Reduction Andrew Zalewski, M.D. Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia GlaxoSmithKline, Philadelphia Why inflammation? Population-based studies: low
Inflammation: Novel Target for Cardiovascular Risk Reduction Andrew Zalewski, M.D. Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia GlaxoSmithKline, Philadelphia Why inflammation? Population-based studies: low
Cardiovascular Disorders Lecture 3 Coronar Artery Diseases
 Cardiovascular Disorders Lecture 3 Coronar Artery Diseases By Prof. El Sayed Abdel Fattah Eid Lecturer of Internal Medicine Delta University Coronary Heart Diseases It is the leading cause of death in
Cardiovascular Disorders Lecture 3 Coronar Artery Diseases By Prof. El Sayed Abdel Fattah Eid Lecturer of Internal Medicine Delta University Coronary Heart Diseases It is the leading cause of death in
Berries and Cardiovascular Health
 Berries and Cardiovascular Health Britt Burton-Freeman, PhD Institute for Food Safety and Health Illinois Institute of Technology bburton@iit.edu Berry Health Benefits Symposium Westlake Village CA, 2011
Berries and Cardiovascular Health Britt Burton-Freeman, PhD Institute for Food Safety and Health Illinois Institute of Technology bburton@iit.edu Berry Health Benefits Symposium Westlake Village CA, 2011
All biomarkers at higher level in HIV group
 Supplemental Table S1: Summary of studies assessing mainly inflammatory biomarkers and their association with mortality and clinical endpoints in HIV infection First author, year, country Biomarkers measured
Supplemental Table S1: Summary of studies assessing mainly inflammatory biomarkers and their association with mortality and clinical endpoints in HIV infection First author, year, country Biomarkers measured
Rheumatoid Arthritis: An update for non rheumatologists
 Rheumatoid Arthritis: An update for non rheumatologists Dimitrios Pappas, M.D., M.P.H. Assistant Professor of Medicine Columbia University, College of Physicians & Surgeons Director of Rheumatology Athens
Rheumatoid Arthritis: An update for non rheumatologists Dimitrios Pappas, M.D., M.P.H. Assistant Professor of Medicine Columbia University, College of Physicians & Surgeons Director of Rheumatology Athens
Lipoprotein Particle Profile
 Lipoprotein Particle Profile 50% of people at risk for HEART DISEASE are not identified by routine testing. Why is LPP Testing The Most Comprehensive Risk Assessment? u Provides much more accurate cardiovascular
Lipoprotein Particle Profile 50% of people at risk for HEART DISEASE are not identified by routine testing. Why is LPP Testing The Most Comprehensive Risk Assessment? u Provides much more accurate cardiovascular
Term-End Examination December, 2009 MCC-006 : CARDIOVASCULAR EPIDEMIOLOGY
 MCC-006 POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN CLINICAL CARDIOLOGY (PGDCC) 00269 Term-End Examination December, 2009 MCC-006 : CARDIOVASCULAR EPIDEMIOLOGY Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 60 Note : There will be multiple
MCC-006 POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN CLINICAL CARDIOLOGY (PGDCC) 00269 Term-End Examination December, 2009 MCC-006 : CARDIOVASCULAR EPIDEMIOLOGY Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 60 Note : There will be multiple
Causes of death in Diabetes
 Rates of CV events in Diabetes patients Respiratory4.2 Cancer 7.6 Diabetes 1.3 CV disease 17.3 Causes of death in Diabetes 250 200 150 100 50 0 per 10,000 person-years 97 151 243 Framingham 5 X increase
Rates of CV events in Diabetes patients Respiratory4.2 Cancer 7.6 Diabetes 1.3 CV disease 17.3 Causes of death in Diabetes 250 200 150 100 50 0 per 10,000 person-years 97 151 243 Framingham 5 X increase
 Five chapters 1. What is CVD prevention 2. Why is CVD prevention needed 3. Who needs CVD prevention 4. How is CVD prevention applied 5. Where should CVD prevention be offered Shorter, more adapted to clinical
Five chapters 1. What is CVD prevention 2. Why is CVD prevention needed 3. Who needs CVD prevention 4. How is CVD prevention applied 5. Where should CVD prevention be offered Shorter, more adapted to clinical
Supplemental Figures and Legends
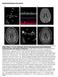 Supplemental Figures and Legends Online Figure 1. 18 year old female with SLE and acute homonymous hemianopsia, confusional state, and cognitive dysfunction. A. This TEE four chamber view demonstrates
Supplemental Figures and Legends Online Figure 1. 18 year old female with SLE and acute homonymous hemianopsia, confusional state, and cognitive dysfunction. A. This TEE four chamber view demonstrates
University of Pretoria
 University of Pretoria Serodiagnostic Procedures Performed in the Department of Immunology Dr Pieter WA Meyer 1.Autoimmune Diseases Automated Anti-nuclear antibodies Anti-gliadin/ tissue transglutaminase
University of Pretoria Serodiagnostic Procedures Performed in the Department of Immunology Dr Pieter WA Meyer 1.Autoimmune Diseases Automated Anti-nuclear antibodies Anti-gliadin/ tissue transglutaminase
Autoimmune Diseases. Betsy Kirchner CNP The Cleveland Clinic
 Autoimmune Diseases Betsy Kirchner CNP The Cleveland Clinic Disclosures (financial) No relevant disclosures Learning Objectives Explain the pathophysiology of autoimmune disease Discuss safe administration
Autoimmune Diseases Betsy Kirchner CNP The Cleveland Clinic Disclosures (financial) No relevant disclosures Learning Objectives Explain the pathophysiology of autoimmune disease Discuss safe administration
Pathogenesis of atherosclerosis in rheumatoid arthritis
 Pathogenesis of atherosclerosis in rheumatoid arthritis JR Pambudi 1, H Isbagio 1 1 Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, University of Indonesia School of Medicine/ Cipto Mangunkusumo
Pathogenesis of atherosclerosis in rheumatoid arthritis JR Pambudi 1, H Isbagio 1 1 Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, University of Indonesia School of Medicine/ Cipto Mangunkusumo
Who Cares About the Past?
 Risk Factors, the New Calcium Score, Rheology and Atherosclerosis Progression Arthur Agatston 2/21/15 The Vulnerable Plaque vs. Plaque Burden CT Angiogram Is There a Role for Coronary Artery Calcium Scoring
Risk Factors, the New Calcium Score, Rheology and Atherosclerosis Progression Arthur Agatston 2/21/15 The Vulnerable Plaque vs. Plaque Burden CT Angiogram Is There a Role for Coronary Artery Calcium Scoring
STABILITY Stabilization of Atherosclerotic plaque By Initiation of darapladib TherapY. Harvey D White on behalf of The STABILITY Investigators
 STABILITY Stabilization of Atherosclerotic plaque By Initiation of darapladib TherapY Harvey D White on behalf of The STABILITY Investigators Lipoprotein- associated Phospholipase A 2 (Lp-PLA 2 ) activity:
STABILITY Stabilization of Atherosclerotic plaque By Initiation of darapladib TherapY Harvey D White on behalf of The STABILITY Investigators Lipoprotein- associated Phospholipase A 2 (Lp-PLA 2 ) activity:
CRP and fibrinogen imply clinical outcome of patients with type-2 diabetes. and coronary artery disease
 CRP and fibrinogen imply clinical outcome of patients with type-2 diabetes and coronary artery disease Marijan Bosevski 1, *, Golubinka Bosevska 1, Lily Stojanovska 2, Vasso Apostolopoulos 2, * 1 University
CRP and fibrinogen imply clinical outcome of patients with type-2 diabetes and coronary artery disease Marijan Bosevski 1, *, Golubinka Bosevska 1, Lily Stojanovska 2, Vasso Apostolopoulos 2, * 1 University
The aorta is an integral part of the cardiovascular system and should not be considered as just a conduit for blood supply from the heart to the
 The aorta is an integral part of the cardiovascular system and should not be considered as just a conduit for blood supply from the heart to the limbs and major organs. A range of important pathologies
The aorta is an integral part of the cardiovascular system and should not be considered as just a conduit for blood supply from the heart to the limbs and major organs. A range of important pathologies
Acute coronary syndrome. Dr LM Murray Chemical Pathology Block SA
 Acute coronary syndrome Dr LM Murray Chemical Pathology Block SA13-2014 Acute myocardial infarction (MI) MI is still the leading cause of death in many countries It is characterized by severe chest pain,
Acute coronary syndrome Dr LM Murray Chemical Pathology Block SA13-2014 Acute myocardial infarction (MI) MI is still the leading cause of death in many countries It is characterized by severe chest pain,
The presenter does not have any potential conflicts of interest to disclose
 Carotid intima-media thickness as a predictor of multi territory atherosclerotic occlusive disease in patients with symptomatic subclavian artery obstruction Leszek Wrotniak 1, Anna Kabłak Ziembicka 1,
Carotid intima-media thickness as a predictor of multi territory atherosclerotic occlusive disease in patients with symptomatic subclavian artery obstruction Leszek Wrotniak 1, Anna Kabłak Ziembicka 1,
Accelerated atherosclerosis in patients with chronic inflammatory rheumatologic conditions
 Review International Journal of Clinical Rheumatology ith ns Accelerated atherosclerosis in patients with chronic inflammatory rheumatologic conditions Atherosclerosis is a complex inflammatory disease
Review International Journal of Clinical Rheumatology ith ns Accelerated atherosclerosis in patients with chronic inflammatory rheumatologic conditions Atherosclerosis is a complex inflammatory disease
Role of imaging in risk assessment models: the example of CIMT
 Role of imaging in risk assessment models: the example of CIMT Diederick E. Grobbee, MD, PhD, FESC Professor of Clinical Epidemiology Julius Center for Health Sciences and Primary Care, University Medical
Role of imaging in risk assessment models: the example of CIMT Diederick E. Grobbee, MD, PhD, FESC Professor of Clinical Epidemiology Julius Center for Health Sciences and Primary Care, University Medical
The inhibition of CETP: From simply raising HDL-c to promoting cholesterol efflux and lowering of atherogenic lipoproteins Prof Dr J Wouter Jukema
 The inhibition of CETP: From simply raising HDL-c to promoting cholesterol efflux and lowering of atherogenic lipoproteins Prof Dr J Wouter Jukema Dept Cardiology, Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden,
The inhibition of CETP: From simply raising HDL-c to promoting cholesterol efflux and lowering of atherogenic lipoproteins Prof Dr J Wouter Jukema Dept Cardiology, Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden,
Health and Disease of the Cardiovascular system
 1 Health and Disease of the Cardiovascular system DR CHRIS MOORE Instructions 2 USE THE ARROWS TO NAVIGATE, OR TAP OUTLINE AT THE TOP TO BRING DOWN A SLIDE MENU Click these where you see them to zoom or
1 Health and Disease of the Cardiovascular system DR CHRIS MOORE Instructions 2 USE THE ARROWS TO NAVIGATE, OR TAP OUTLINE AT THE TOP TO BRING DOWN A SLIDE MENU Click these where you see them to zoom or
Introduction to Immunopathology
 MICR2209 Introduction to Immunopathology Dr Allison Imrie 1 Allergy and Hypersensitivity Adaptive immune responses can sometimes be elicited by antigens not associated with infectious agents, and this
MICR2209 Introduction to Immunopathology Dr Allison Imrie 1 Allergy and Hypersensitivity Adaptive immune responses can sometimes be elicited by antigens not associated with infectious agents, and this
METABOLISM of ADIPOSE TISSUE
 METABOLISM of ADIPOSE TISSUE 2. LF UK Prof. Rudolf Poledne, PhD. TYPES OF ADIPOSE TISSUE brown adipose tissue subcutaneous adipose tissue visceral adipose tissue ADIPOSE TISSUE FUNCTIONS: thermal isolation
METABOLISM of ADIPOSE TISSUE 2. LF UK Prof. Rudolf Poledne, PhD. TYPES OF ADIPOSE TISSUE brown adipose tissue subcutaneous adipose tissue visceral adipose tissue ADIPOSE TISSUE FUNCTIONS: thermal isolation
JUPITER NEJM Poll. Panel Discussion: Literature that Should Have an Impact on our Practice: The JUPITER Study
 Panel Discussion: Literature that Should Have an Impact on our Practice: The Study Kaiser COAST 11 th Annual Conference Maui, August 2009 Robert Blumberg, MD, FACC Ralph Brindis, MD, MPH, FACC Primary
Panel Discussion: Literature that Should Have an Impact on our Practice: The Study Kaiser COAST 11 th Annual Conference Maui, August 2009 Robert Blumberg, MD, FACC Ralph Brindis, MD, MPH, FACC Primary
