Appendix 3. Comparison of plasma neurohormones in congestive heart failure patients with atrial fibrillation versus patients with sinus rhythm
|
|
|
- Adele Bates
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Appendix 3 Comparison of plasma neurohormones in congestive heart failure patients with atrial fibrillation versus patients with sinus rhythm Anton E. Tuinenburg, Dirk J. Van Veldhuisen, Frans Boomsma*, Maarten P. Van Den Berg, Pieter J. De Kam, Harry J.G.M. Crijns From the Department of Cardiology, Thoraxcenter, University Hospital Groningen, Groningen; and the Department of Internal Medicine I/ COEUR*, University Hospital Dijkzigt, Rotterdam, The Netherlands Am J Cardiol 1998;81:
2
3 Appendix 3 MINI-ABSTRACT Plasma atrial natriuretic peptide and endothelin are further elevated in patients with congestive heart failure and atrial fibrillation, compared to those with sinus rhythm. The higher plasma endothelin suggests that vasoconstriction is an important mechanism for hemodynamic compensation in these patients. INTRODUCTION A large number of studies have shown that neurohumoral activation plays an important role in the pathophysiology of congestive heart failure (CHF). However, these studies have mainly focused on patients with sinus rhythm (SR) and not on patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) since patients with AF were either excluded from these studies or not separately analyzed. Yet, AF is very common in CHF patients (up to 40%), and there is reason to presume that AF has an additional effect on neurohumoral activation because AF as such has potentially important hemodynamic consequences in the setting of CHF. 1 The present study investigates neurohumoral activation in a large group of patients with advanced CHF, comparing patients with AF and SR. METHODS AND RESULTS We studied 269 patients who participated in a neurohumoral substudy of the PRIME II study, a survival study with ibopamine in moderate to severe CHF. 2 Baseline data of the PRIME II study were used in this neurohumoral substudy, i.e., before any study medication was given. To eliminate effects on neurohormone values by differences in etiology of CHF, only patients with ischemic heart disease underlying CHF were included. CHF had to be characterized by symptoms at rest or a recent hospital admission for CHF, equivalent to functional class III-IV according to the New York Heart Association. Left ventricular dysfunction had to be proven by one of the following: A) left ventricular ejection fraction < 0.35, B) left ventricular internal end-diastolic diameter > 60 mm, C) left ventricular fractional shortening < 20% or D) cardiothoracic ratio on standard chest X-ray > Patients were on optimal medical treatment 95
4 Table I. Clinical characteristics comparing patients with sinus rhythm and atrial fibrillation Characteristic SR patients AF patients p-value (n=225) (n=44) Age (years) 67±8 71± Male 179 (80%) 39 (89%) NS NYHA Functional Class NS III 157 (70%) 28 (64%) III/IV 63 (28%) 14 (32%) IV 5 (2%) 2 (4%) Duration of CHF (months) 35±35 43±43 NS Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction 0.23± ±0.07 NS Heart Rate (beats min -1 ) 80±14 78±11 NS Systolic Blood Pressure (mm Hg) 126±18 121±19 NS Diastolic Blood Pressure (mm Hg) 76±9 74±10 NS Creatinine (µmol/l) 120±42 122±29 NS Medication ACE Inhibitor 216 (96%) 42 (95%) NS Anti-Arrhythmic Drug 35 (16%) 9 (20%) NS Anti-Platelet Drug 44 (20%) 7 (16%) NS Beta-Blocker 25 (11%) 5 (11%) NS Calcium Entry Blocker 14 (6%) 3 (7%) NS Digoxin 116 (52%) 38 (86%) < Diuretic 224 (100%) 44 (100%) NS Long Acting Nitrate 122 (54%) 26 (59%) NS Warfarin 154 (68%) 34 (77%) NS ACE= Angiotensin Converting Enzyme, AF= Atrial Fibrillation, CHF= Congestive Heart Failure, NS= Not Significant, NYHA= New York Heart Association, SR= Sinus Rhythm. for CHF, including angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and diuretics. The diuretic dose was either = 40 mg furosemide or = 80 mg furosemide (or equivalent) if angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors were not prescribed. Use of digoxin or a vasodilator was allowed. The exclusion criteria included obstructive valve disease, obstructive or restrictive cardiomyopathy, transient heart failure (e.g. acute myocarditis), myocardial infarction or cardiac surgery within the preceding 3 months, uncontrolled arrhythmias and need for intravenous inotropic support. To be designated as AF patient, AF had to be chronic and electrocardiographically documented on two separate occasions at least 96
5 Appendix 3 24 hours apart. Patients with ventricular pacemakers were excluded from the study. Blood sampling for plasma neurohormone determination was done from an intravenous canula after resting for at least 30 minutes in the supine position. Samples for measurement of norepinephrine, epinephrine, dopamine, renin and aldosterone were poured into chilled heparinized tubes containing glutathione; for measurement of atrial natriuretic peptide, N-terminal atrial natriuretic peptide, and endothelin, chilled tubes containing EDTA and aprotonin were used. After centrifugation the plasma samples were deep frozen at -70 C and sent to the core laboratory at the University Hospital Dijkzigt, Rotterdam, The Netherlands. Norepinephrine, epinephrine and dopamine were analyzed using high-performance liquid chromatography with fluormetric detection. Renin was determined according to a method previously described. 3 Atrial natriuretic peptide and endothelin were determined with commercially available radioimmunoassay kits from the Nichols Institute, Wijchen, The Netherlands, as previously described. 4,5 Commercially available radioimmunoassay kits were also used for determination of N-terminal atrial natriuretic peptide (Biotop, Oulo, Finland) and aldosterone (Coat-a-Count, Diagnostic Products Corporation, Los Angeles, CA). Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation; median values with ranges are used in case of a non-parametric distribution. Table II. Neurohormone plasma concentrations in patients with sinus rhythm versus atrial fibrillation Neurohormone * Normal SR patients AF patients Uni Multi range variate variate (n=225) (n=44) p-value p-value Norepinephrine (pg/ml) ( ) 519 ( ) 506 ( ) NS NS Epinephrine (pg/ml) (10-70) 36 (5-271) 47 (9-163) NS NS Dopamine (pg/ml) (5-50) 20 (1-172) 17 (1-133) NS NS Renin (µu/ml) (5-50) 74 (3-2516) 100 (6-3598) NS NS Aldosterone (pg/ml) (50-250) 100 (8-933) 116 (1-715) NS NS ANP (pmol/l) (15-35) 285 ( ) 380 ( ) < N-ANP (nmol/l) ( ) 1.00 ( ) 1.46 ( ) <0.001 NS Endothelin (pg/ml) (1-5) 4.9 (0-35.0) 7.0 (0-30.7) * = Values are expressed as median with range. AF= Atrial Fibrillation, ANP= Atrial Natriuretic Peptide, N-ANP= N-terminal Atrial Natriuretic Peptide, SR= Sinus Rhythm. 97
6 Data were analyzed using univariate and multiple regression analysis. To realize a constant variance in these analyses, the neurohormone values were logarithmically transformed. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Clinical characteristics are given in Table I, comparing AF patients with SR patients. The AF and SR groups were comparable for general characteristics of CHF (New York Heart Association class for exercise tolerance, left ventricular ejection fraction, and blood pressure). Ventricular rate was controlled in AF patients and their heart rate was comparable with heart rate in SR patients. Medication use was equally distributed between the two groups, with the exception of digoxin. Not surprisingly, digoxin was used more frequently in the AF group. Also, AF patients were slightly older, but renal function, as assessed by serum creatinine level, was comparable with SR patients. Neurohumoral data are presented in Table II. In the univariate analysis, atrial natriuretic peptide, N-terminal atrial natriuretic peptide and endothelin were significantly higher in AF patients. In the multiple regression analysis, only the levels of atrial natriuretic peptide and endothelin remained significantly higher in AF patients. DISCUSSION Our main finding is that AF in patients with advanced CHF is associated with an additional increase in plasma endothelin. Three isoforms endothelin have been identified (endothelin-1, endothelin-2 and endothelin-3), from which endothelin-1 exercises the most important effects. This 21-amino acid peptide is predominantly produced in the endothelium, and causes potent vasoconstriction, myocyte cell growth and positive inotropy. Different cardiovascular conditions are associated with an increase in endothelin, including CHF. 6,7 In addition to the endothelium, the myocardium itself appears to be an important site of production in CHF. 8 Since vasoconstriction is one of the compensatory mechanisms in CHF, it is conceivable why CHF leads to higher endothelin concentrations. The question remains why AF is associated with an additional increase in endothelin in patients with CHF. The design of our study did not allow investigation of the underlying mechanism, but it seems reasonable to presume that the hemodynamic effects of AF play a crucial role in this connection. 98
7 Appendix 3 AF per se, i.e. irrespective of CHF, may cause hemodynamic deterioration due to loss of atrial contractile function, irregularity of ventricular rhythm and an altered chronotropic response. Importantly, however, further worsening of hemodynamic function has been observed in patients with CHF who develop AF. 1 It is thus conceivable that the already elevated endothelin production increases even more in case of concomitant AF. This explanation is supported by our previous work which showed altered peripheral flow after electrical cardioversion of AF. 9 A reduced calf blood flow was found in patients with AF (functional class I-II according to the New York Heart Association), but this normalized after restoration of SR, suggesting that vasoconstriction plays an important role as a compensatory mechanism in AF patients. Atrial natriuretic peptide and N-terminal atrial natriuretic peptide were significantly elevated in the univariate analysis, and to the same extent as endothelin (factor ± 1.4). In the multivariate analysis, atrial natriuretic peptide remained significantly higher in AF patients. Previous data showed that AF is associated with an increase in atrial natriuretic peptide, 10 but this observation pertained to acute AF without concomitant CHF. We have shown recently that atrial natriuretic peptide levels in patients with AF and CHF are a function of time, longer duration of AF being associated with lower atrial natriuretic peptide levels. 11 During the course of AF, atrial atrophy and fibrosis develop, which may cause this decline in atrial natriuretic peptide production. In fact, during atrial standstill, after long standing AF, atrial natriuretic peptide falls to even undetectably low levels ( endocrinologic silence ). 12 The duration of AF is unknown in our patients, so a relation between atrial natriuretic peptide level and the duration of AF could not be made. It is shown though that atrial natriuretic peptide levels are higher in AF patients with a duration of CHF comparable with SR patients. The clinical relevance of our findings is that, in addition to well known other considerations, attempts should be undertaken to restore and maintain SR, as neurohormone levels (endothelin in particular) are lower during SR. The results from the univariate analysis might be attributed to differences in clinical characteristics. However, the multivariate analysis points out that these differences in clinical characteristics do not explain the higher endothelin and atrial natriuretic peptide levels in the AF group. Furthermore, the study is observational in design, and therefore has its limitations; 99
8 pathophysiological mechanisms and hemodynamics were not analyzed. Finally, the results are only applicable to patients with ischemic heart disease. References 1. Cioffi G, Pozzoli M, Traversi E, Forni G, Gola A, Franchini M, Tavazzi L: Predictors and consequences of the development of atrial fibrillation in patients with chronic heart failure. A prospective study in 344 patients with baseline sinus rhythm (abstr). Circulation 1996;94:I Hampton JR, Van Veldhuisen DJ, Kleber FX, Cowley AJ, Ardia A, Block P, Cortina A, Cserhalmi L, Follath F, Jensen G, Kayanakis J, Lie KI, Mancia G, Skene AM: Randomised study of effect of ibopamine on survival in patients with advanced severe heart failure. Lancet 1997;349: Derkx FHM, Tan Tjiong L, Wenting GJ, Boomsma F, Man in t Veld AJ, Schalekamp MA: Asynchronous changes in prorenin and renin secretion after captopril in patients with renal artery stenosis. Hypertension 1983;5: Boomsma F, Bhaggoe UM, Man in t Veld AJ, Schalekamp MA: Comparison of N-terminal pro-atrial natriuretic peptide and atrial natriuretic peptide in human plasma as measured with commercially available radioimmunoassay kits. Clin Chim Acta 1996;252: Florijn KW, Derkx FHM, Visser W, Hofman JA, Rosmalen FM, Wallenburg HC, Schalekamp MA: Plasma immunoreactive endothelin-1 in pregnant women with and without pre-eclampsia. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1991;17 (suppl 7):S446-S McMurray JJ, Ray SG, Abdullah I, Dargie HJ, Morton JJ: Plasma endothelin in chronic heart failure. Circulation 1992;85: Cody RJ, Haas GJ, Binkley PF, Capers Q, Kelley R: Plasma endothelin correlates with the extent of pulmonary hypertension in patients with chronic congestive heart failure. Circulation 1992;85: Sakai S, Miyauchi T, Sakurai T, Kasuya Y, Ihara M, Yamaguchi I, Goto K, Sugishita Y: Endogenous endothelin-1 participates in the maintenance of cardiac function in rats with congestive heart failure. Marked increase in endothelin-1 production in the failing heart. Circulation 1996;93: Gosselink ATM, Smit AJ, Crijns HJGM, Hillege HL, Landsman ML, Lie KI: Alteration of peripheral vasodilatory reserve capacity after cardioversion of atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J 1996;17: Roy D, Paillard F, Cassidy D, Bourassa MG, Gutkowska J, Genest J, Cantin M: Atrial natriuretic factor during atrial fibrillation and supraventricular tachycardia. J Am Coll Cardiol 1987;9: Van den Berg MP, Crijns HJGM, Van Veldhuisen DJ, Van Gelder IC, De Kam PJ, Lie KI: Atrial natriuretic peptide in patients with heart failure and chronic atrial fibrillation: role of duration of atrial fibrillation. Am Heart J 1998;135: Seino Y, Shimai S, Ibuki C, Itoh K, Takano T, Hayakawa H: Disturbed secretion of atrial natriuretic peptide in patients with persistent atrial standstill: endocrinologic silence. J Am Coll Cardiol 1991;18:
Concomitant Recovery of Atrial Mechanical and Endocrine Function After Cardioversion in Patients With Persistent Atrial Fibrillation
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 41, No. 10, 2003 2003 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/03/$30.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/s0735-1097(03)00306-1
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 41, No. 10, 2003 2003 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/03/$30.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/s0735-1097(03)00306-1
Chronic heart failure (CHF) is caused by a loss of
 Renal Function, Neurohormonal Activation, and Survival in Patients With Chronic Heart Failure Hans L. Hillege, MD; Armand R.J. Girbes, MD; Pieter J. de Kam, MSc; Frans Boomsma, PhD; Dick de Zeeuw, MD;
Renal Function, Neurohormonal Activation, and Survival in Patients With Chronic Heart Failure Hans L. Hillege, MD; Armand R.J. Girbes, MD; Pieter J. de Kam, MSc; Frans Boomsma, PhD; Dick de Zeeuw, MD;
University of Groningen. BNP and NT-proBNP in heart failure Hogenhuis, Jochem
 University of Groningen BNP and NT-proBNP in heart failure Hogenhuis, Jochem IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
University of Groningen BNP and NT-proBNP in heart failure Hogenhuis, Jochem IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
Depletion of atrial natriuretic peptide during longstanding atrial fibrillation
 Europace (2004) 6, 433e437 REVIEW ARTICLE Depletion of atrial natriuretic peptide during longstanding atrial fibrillation Maarten P. van den Berg ), Isabelle C. van Gelder, Dirk J. van Veldhuisen Department
Europace (2004) 6, 433e437 REVIEW ARTICLE Depletion of atrial natriuretic peptide during longstanding atrial fibrillation Maarten P. van den Berg ), Isabelle C. van Gelder, Dirk J. van Veldhuisen Department
Low pulse pressure is independently related to elevated natriuretic peptides and increased mortality in advanced chronic heart failure
 European Heart Journal (2005) 26, 1759 1764 doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehi270 Clinical research Low pulse pressure is independently related to elevated natriuretic peptides and increased mortality in advanced
European Heart Journal (2005) 26, 1759 1764 doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehi270 Clinical research Low pulse pressure is independently related to elevated natriuretic peptides and increased mortality in advanced
Definition of Congestive Heart Failure
 Heart Failure Definition of Congestive Heart Failure A clinical syndrome of signs & symptoms resulting from the heart s inability to supply adequate tissue perfusion. CHF Epidemiology Affects 4.7 million
Heart Failure Definition of Congestive Heart Failure A clinical syndrome of signs & symptoms resulting from the heart s inability to supply adequate tissue perfusion. CHF Epidemiology Affects 4.7 million
ATRIAL fibrillation is one of the most common cardiac arrhythmias and has
 Distinct Increase in Hematocrit Associated with Paroxysm of Atrial Fibrillation Shigeru OKUNO, MD*, Terunao ASHIDA, MD, Aya EBIHARA, MD, Takao SUGIYAMA, MD, and Jun FUJII, MD SUMMARY In a previous study
Distinct Increase in Hematocrit Associated with Paroxysm of Atrial Fibrillation Shigeru OKUNO, MD*, Terunao ASHIDA, MD, Aya EBIHARA, MD, Takao SUGIYAMA, MD, and Jun FUJII, MD SUMMARY In a previous study
Online Appendix (JACC )
 Beta blockers in Heart Failure Collaborative Group Online Appendix (JACC013117-0413) Heart rate, heart rhythm and prognostic effect of beta-blockers in heart failure: individual-patient data meta-analysis
Beta blockers in Heart Failure Collaborative Group Online Appendix (JACC013117-0413) Heart rate, heart rhythm and prognostic effect of beta-blockers in heart failure: individual-patient data meta-analysis
Influence of Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation Attack on Brain Natriuretic Peptide Secretion
 Influence of Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation Attack on Brain Natriuretic Peptide Secretion Keizo Kazuhiko TSUCHIDA,MD TANABE, MD Abstract Objectives. Plasma brain natriuretic peptide BNP concentration is
Influence of Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation Attack on Brain Natriuretic Peptide Secretion Keizo Kazuhiko TSUCHIDA,MD TANABE, MD Abstract Objectives. Plasma brain natriuretic peptide BNP concentration is
Cardiac Drugs: Chapter 9 Worksheet Cardiac Agents. 1. drugs affect the rate of the heart and can either increase its rate or decrease its rate.
 Complete the following. 1. drugs affect the rate of the heart and can either increase its rate or decrease its rate. 2. drugs affect the force of contraction and can be either positive or negative. 3.
Complete the following. 1. drugs affect the rate of the heart and can either increase its rate or decrease its rate. 2. drugs affect the force of contraction and can be either positive or negative. 3.
Topic Page: congestive heart failure
 Topic Page: congestive heart failure Definition: congestive heart f ailure from Merriam-Webster's Collegiate(R) Dictionary (1930) : heart failure in which the heart is unable to maintain an adequate circulation
Topic Page: congestive heart failure Definition: congestive heart f ailure from Merriam-Webster's Collegiate(R) Dictionary (1930) : heart failure in which the heart is unable to maintain an adequate circulation
Heart Failure Clinician Guide JANUARY 2016
 Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Heart Failure Clinician Guide JANUARY 2016 Introduction This evidence-based guideline summary is based on the 2016 National Heart Failure Guideline.
Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Heart Failure Clinician Guide JANUARY 2016 Introduction This evidence-based guideline summary is based on the 2016 National Heart Failure Guideline.
Pathophysiology: Heart Failure
 Pathophysiology: Heart Failure Mat Maurer, MD Irving Assistant Professor of Medicine Outline Definitions and Classifications Epidemiology Muscle and Chamber Function Pathophysiology Heart Failure: Definitions
Pathophysiology: Heart Failure Mat Maurer, MD Irving Assistant Professor of Medicine Outline Definitions and Classifications Epidemiology Muscle and Chamber Function Pathophysiology Heart Failure: Definitions
Heart Failure Update John Coyle, M.D.
 Heart Failure Update 2011 John Coyle, M.D. Causes of Heart Failure Anderson,B.Am Heart J 1993;126:632-40 It It is now well-established that at least one-half of the patients presenting with symptoms and
Heart Failure Update 2011 John Coyle, M.D. Causes of Heart Failure Anderson,B.Am Heart J 1993;126:632-40 It It is now well-established that at least one-half of the patients presenting with symptoms and
Influence of age on neurohormonal activation and prognosis in patients with chronic heart failure
 European Heart Journal (1998) 19, 753 76 Influence of age on neurohormonal activation and prognosis in patients with chronic heart failure D. J. van Veldhuisen*, F. Boomsma, P. J. de Kam*, A. J. Man in
European Heart Journal (1998) 19, 753 76 Influence of age on neurohormonal activation and prognosis in patients with chronic heart failure D. J. van Veldhuisen*, F. Boomsma, P. J. de Kam*, A. J. Man in
Chapter 10. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives 9/11/2012. Congestive Heart Failure
 Chapter 10 Congestive Heart Failure Learning Objectives Explain concept of polypharmacy in treatment of congestive heart failure Explain function of diuretics Learning Objectives Discuss drugs used for
Chapter 10 Congestive Heart Failure Learning Objectives Explain concept of polypharmacy in treatment of congestive heart failure Explain function of diuretics Learning Objectives Discuss drugs used for
Diagnosis & Management of Heart Failure. Abena A. Osei-Wusu, M.D. Medical Fiesta
 Diagnosis & Management of Heart Failure Abena A. Osei-Wusu, M.D. Medical Fiesta Learning Objectives: 1) Become familiar with pathogenesis of congestive heart failure. 2) Discuss clinical manifestations
Diagnosis & Management of Heart Failure Abena A. Osei-Wusu, M.D. Medical Fiesta Learning Objectives: 1) Become familiar with pathogenesis of congestive heart failure. 2) Discuss clinical manifestations
The benefit of treatment with -blockers in heart failure is
 Heart Rate and Cardiac Rhythm Relationships With Bisoprolol Benefit in Chronic Heart Failure in CIBIS II Trial Philippe Lechat, MD, PhD; Jean-Sébastien Hulot, MD; Sylvie Escolano, MD, PhD; Alain Mallet,
Heart Rate and Cardiac Rhythm Relationships With Bisoprolol Benefit in Chronic Heart Failure in CIBIS II Trial Philippe Lechat, MD, PhD; Jean-Sébastien Hulot, MD; Sylvie Escolano, MD, PhD; Alain Mallet,
Outline. Pathophysiology: Heart Failure. Heart Failure. Heart Failure: Definitions. Etiologies. Etiologies
 Outline Pathophysiology: Mat Maurer, MD Irving Assistant Professor of Medicine Definitions and Classifications Epidemiology Muscle and Chamber Function Pathophysiology : Definitions An inability of the
Outline Pathophysiology: Mat Maurer, MD Irving Assistant Professor of Medicine Definitions and Classifications Epidemiology Muscle and Chamber Function Pathophysiology : Definitions An inability of the
Akash Ghai MD, FACC February 27, No Disclosures
 Akash Ghai MD, FACC February 27, 2015 No Disclosures Epidemiology Lifetime risk is > 20% for American s older than 40 years old. > 650,000 new cases diagnosed each year. Incidence increases with age: 2%
Akash Ghai MD, FACC February 27, 2015 No Disclosures Epidemiology Lifetime risk is > 20% for American s older than 40 years old. > 650,000 new cases diagnosed each year. Incidence increases with age: 2%
Therapeutic Targets and Interventions
 Therapeutic Targets and Interventions Ali Valika, MD, FACC Advanced Heart Failure and Pulmonary Hypertension Advocate Medical Group Midwest Heart Foundation Disclosures: 1. Novartis: Speaker Honorarium
Therapeutic Targets and Interventions Ali Valika, MD, FACC Advanced Heart Failure and Pulmonary Hypertension Advocate Medical Group Midwest Heart Foundation Disclosures: 1. Novartis: Speaker Honorarium
Comparison with plasma angiotensin II and endothelin-1
 European Heart Journal (1999) 2, 1799 187 Article No. euhj.1999.1746, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Plasma brain natriuretic peptide level as a biochemical marker of morbidity and mortality
European Heart Journal (1999) 2, 1799 187 Article No. euhj.1999.1746, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Plasma brain natriuretic peptide level as a biochemical marker of morbidity and mortality
Heart Failure. Subjective SOB (shortness of breath) Peripheral edema. Orthopnea (2-3 pillows) PND (paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea)
 Pharmacology I. Definitions A. Heart Failure (HF) Heart Failure Ezra Levy, Pharm.D. HF Results when one or both ventricles are unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the body s needs There are 2 types
Pharmacology I. Definitions A. Heart Failure (HF) Heart Failure Ezra Levy, Pharm.D. HF Results when one or both ventricles are unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the body s needs There are 2 types
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment
 Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a disorder seen
 This Just In... An Update on Arrhythmia What do recent studies reveal about arrhythmia? In this article, the authors provide an update on atrial fibrillation and ventricular arrhythmia. Beth L. Abramson,
This Just In... An Update on Arrhythmia What do recent studies reveal about arrhythmia? In this article, the authors provide an update on atrial fibrillation and ventricular arrhythmia. Beth L. Abramson,
University of Groningen. Atrial remodeling due to atrial tachycardia and heart failure Schoonderwoerd, Bas Arjan
 University of Groningen Atrial remodeling due to atrial tachycardia and heart failure Schoonderwoerd, Bas Arjan IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you
University of Groningen Atrial remodeling due to atrial tachycardia and heart failure Schoonderwoerd, Bas Arjan IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you
Intravenous Inotropic Support an Overview
 Intravenous Inotropic Support an Overview Shaul Atar, MD Western Galilee Medical Center, Nahariya Affiliated with the Faculty of Medicine of the Galilee, Safed, Israel INOTROPES in Acute HF (not vasopressors)
Intravenous Inotropic Support an Overview Shaul Atar, MD Western Galilee Medical Center, Nahariya Affiliated with the Faculty of Medicine of the Galilee, Safed, Israel INOTROPES in Acute HF (not vasopressors)
Diastolic Heart Failure. Edwin Tulloch-Reid MBBS FACC Consultant Cardiologist Heart Institute of the Caribbean December 2012
 Diastolic Heart Failure Edwin Tulloch-Reid MBBS FACC Consultant Cardiologist Heart Institute of the Caribbean December 2012 Disclosures Have spoken for Merck, Sharpe and Dohme Sat on a physician advisory
Diastolic Heart Failure Edwin Tulloch-Reid MBBS FACC Consultant Cardiologist Heart Institute of the Caribbean December 2012 Disclosures Have spoken for Merck, Sharpe and Dohme Sat on a physician advisory
ESC Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure
 Patients t with acute heart failure frequently develop chronic heart failure Patients with chronic heart failure frequently decompensate acutely ESC Guidelines for the Diagnosis and A clinical response
Patients t with acute heart failure frequently develop chronic heart failure Patients with chronic heart failure frequently decompensate acutely ESC Guidelines for the Diagnosis and A clinical response
NCAP NATIONAL CARDIAC AUDIT PROGR AMME NATIONAL HEART FAILURE AUDIT 2016/17 SUMMARY REPORT
 NCAP NATIONAL CARDIAC AUDIT PROGR AMME NATIONAL HEART FAILURE AUDIT 2016/17 SUMMARY REPORT CONTENTS PATIENTS ADMITTED WITH HEART FAILURE...4 Demographics... 4 Trends in Symptoms... 4 Causes and Comorbidities
NCAP NATIONAL CARDIAC AUDIT PROGR AMME NATIONAL HEART FAILURE AUDIT 2016/17 SUMMARY REPORT CONTENTS PATIENTS ADMITTED WITH HEART FAILURE...4 Demographics... 4 Trends in Symptoms... 4 Causes and Comorbidities
Effects of Cilostazol in Patients With Bradycardiac Atrial Fibrillation
 J Cardiol 2001 ; 37: 27 33 Effects of Cilostazol in Patients With Bradycardiac Atrial Fibrillation 1 2 1 Masato Kouki KISHIDA, MD WATANABE, MD Abstract Objectives. Cilostazol, an antithrombotic agent,
J Cardiol 2001 ; 37: 27 33 Effects of Cilostazol in Patients With Bradycardiac Atrial Fibrillation 1 2 1 Masato Kouki KISHIDA, MD WATANABE, MD Abstract Objectives. Cilostazol, an antithrombotic agent,
Χριστίνα Χρυσοχόου Καρδιολόγος Επι,Α Καρδιολογική Κλινική Πανεπιστηίου Αθηνών, ΙΓΝΑ
 Χριστίνα Χρυσοχόου Καρδιολόγος Επι,Α Καρδιολογική Κλινική Πανεπιστηίου Αθηνών, ΙΓΝΑ Digitalisis a genus of about 20 species of herbaceousperennials, shrubs, and biennialsthat are commonly called foxgloves.
Χριστίνα Χρυσοχόου Καρδιολόγος Επι,Α Καρδιολογική Κλινική Πανεπιστηίου Αθηνών, ΙΓΝΑ Digitalisis a genus of about 20 species of herbaceousperennials, shrubs, and biennialsthat are commonly called foxgloves.
Heart Failure Clinician Guide JANUARY 2018
 Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Heart Failure Clinician Guide JANUARY 2018 Introduction This evidence-based guideline summary is based on the 2018 National Heart Failure Guideline.
Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Heart Failure Clinician Guide JANUARY 2018 Introduction This evidence-based guideline summary is based on the 2018 National Heart Failure Guideline.
Treatment of Heart Failure: Current Recommendation Waiz A
 Treatment of Heart Failure: Current Recommendation Waiz A The impaired left ventricular emptying that characterizes heart failure may result from a variety of cardiac diseases, including myocardial ischaemia
Treatment of Heart Failure: Current Recommendation Waiz A The impaired left ventricular emptying that characterizes heart failure may result from a variety of cardiac diseases, including myocardial ischaemia
HEART FAILURE PHARMACOLOGY. University of Hawai i Hilo Pre- Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita Narciso Pharm D
 HEART FAILURE PHARMACOLOGY University of Hawai i Hilo Pre- Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita Narciso Pharm D 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand the effects of heart failure in the body
HEART FAILURE PHARMACOLOGY University of Hawai i Hilo Pre- Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita Narciso Pharm D 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand the effects of heart failure in the body
Heart Failure. Dr. William Vosik. January, 2012
 Heart Failure Dr. William Vosik January, 2012 Questions for clinicians to ask Is this heart failure? What is the underlying cause? What are the associated disease processes? Which evidence-based treatment
Heart Failure Dr. William Vosik January, 2012 Questions for clinicians to ask Is this heart failure? What is the underlying cause? What are the associated disease processes? Which evidence-based treatment
Dysrhythmias. Dysrythmias & Anti-Dysrhythmics. EKG Parameters. Dysrhythmias. Components of an ECG Wave. Dysrhythmias
 Dysrhythmias Dysrythmias & Anti-Dysrhythmics Rhythm bad in the heart: Whitewater rafting Electrical impulses coordinate heart Reduction in Cardiac Output PEA Asystole Components of an ECG Wave EKG Parameters
Dysrhythmias Dysrythmias & Anti-Dysrhythmics Rhythm bad in the heart: Whitewater rafting Electrical impulses coordinate heart Reduction in Cardiac Output PEA Asystole Components of an ECG Wave EKG Parameters
Innovation therapy in Heart Failure
 Innovation therapy in Heart Failure P. Laothavorn September 2015 Topics of discussion Basic Knowledge about heart failure Standard therapy New emerging therapy References: standard Therapy in Heart Failure
Innovation therapy in Heart Failure P. Laothavorn September 2015 Topics of discussion Basic Knowledge about heart failure Standard therapy New emerging therapy References: standard Therapy in Heart Failure
Antihypertensive Agents Part-2. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Antihypertensive Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Agents that block production or action of angiotensin Angiotensin-converting
Antihypertensive Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Agents that block production or action of angiotensin Angiotensin-converting
Heart Failure: Combination Treatment Strategies
 Heart Failure: Combination Treatment Strategies M. McDonald MD, FRCP State of the Heart Symposium May 28, 2011 None Disclosures Case 69 F, prior MIs (LV ejection fraction 25%), HTN No demonstrable ischemia
Heart Failure: Combination Treatment Strategies M. McDonald MD, FRCP State of the Heart Symposium May 28, 2011 None Disclosures Case 69 F, prior MIs (LV ejection fraction 25%), HTN No demonstrable ischemia
Appendix 7. Cardioversion of atrial fibrillation in the setting of mild to moderate heart failure
 Appendix 7 Cardioversion of atrial fibrillation in the setting of mild to moderate heart failure Maarten P. van den Berg, Anton E. Tuinenburg, Dirk J. van Veldhuisen, Pieter J. de Kam, Harry J.G.M. Crijns
Appendix 7 Cardioversion of atrial fibrillation in the setting of mild to moderate heart failure Maarten P. van den Berg, Anton E. Tuinenburg, Dirk J. van Veldhuisen, Pieter J. de Kam, Harry J.G.M. Crijns
Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition
 Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition Table of Contents Volume 1 Chapter 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology Basic Cardiac
Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition Table of Contents Volume 1 Chapter 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology Basic Cardiac
Δακτυλίτιδα και Ινότροπα Φάρμακα στην Καρδιακή Ανεπάρκεια. Ι.Κανονίδης
 Δακτυλίτιδα και Ινότροπα Φάρμακα στην Καρδιακή Ανεπάρκεια Ι.Κανονίδης Cardiac Glycosides Chronic Congestive Heart Failure DIGOXIN Na-K ATPase Na + K + Na-Ca Exchange Na + Ca ++ Ca ++ K + Na + Myofilaments
Δακτυλίτιδα και Ινότροπα Φάρμακα στην Καρδιακή Ανεπάρκεια Ι.Κανονίδης Cardiac Glycosides Chronic Congestive Heart Failure DIGOXIN Na-K ATPase Na + K + Na-Ca Exchange Na + Ca ++ Ca ++ K + Na + Myofilaments
Images have been removed from the PowerPoint slides in this handout due to copyright restrictions.
 Heart Failure Heart Failure Introduction and History AHA 2015 Statistics About 6 million Americans 870,000 new cases each year 1 in 9 deaths related to HF Almost 1 million hospitalizations each year (cost
Heart Failure Heart Failure Introduction and History AHA 2015 Statistics About 6 million Americans 870,000 new cases each year 1 in 9 deaths related to HF Almost 1 million hospitalizations each year (cost
CKD Satellite Symposium
 CKD Satellite Symposium Recommended Therapy by Heart Failure Stage AHA/ACC Task Force on Practice Guideline 2001 Natural History of Heart Failure Patients surviving % Mechanism of death Sudden death 40%
CKD Satellite Symposium Recommended Therapy by Heart Failure Stage AHA/ACC Task Force on Practice Guideline 2001 Natural History of Heart Failure Patients surviving % Mechanism of death Sudden death 40%
Heart Failure. Dr. Alia Shatanawi
 Heart Failure Dr. Alia Shatanawi Left systolic dysfunction secondary to coronary artery disease is the most common cause, account to 70% of all cases. Heart Failure Heart is unable to pump sufficient blood
Heart Failure Dr. Alia Shatanawi Left systolic dysfunction secondary to coronary artery disease is the most common cause, account to 70% of all cases. Heart Failure Heart is unable to pump sufficient blood
Atrial Fibrillation Ablation in Patients with Heart Failure
 Atrial Fibrillation Ablation in Patients with Heart Failure Eleftherios M. Kallergis, MD, PhD, FESC Cardiology Department, Heraklion University Hospital Since auricular fibrillation so often complicates
Atrial Fibrillation Ablation in Patients with Heart Failure Eleftherios M. Kallergis, MD, PhD, FESC Cardiology Department, Heraklion University Hospital Since auricular fibrillation so often complicates
Heart Failure Treatments
 Heart Failure Treatments Past & Present www.philippelefevre.com Background Background Chronic heart failure Drugs Mechanical Electrical Background Chronic heart failure Drugs Mechanical Electrical Sudden
Heart Failure Treatments Past & Present www.philippelefevre.com Background Background Chronic heart failure Drugs Mechanical Electrical Background Chronic heart failure Drugs Mechanical Electrical Sudden
Dobutamine-induced increase in heart rate is blunted by ivabradine treatment in patients with acutely decompensated heart failure
 Dobutamine-induced increase in heart rate is blunted by ivabradine treatment in patients with acutely decompensated heart failure Yuksel Cavusoglu, KU Mert, A Nadir, F Mutlu, E Gencer, T Ulus, A Birdane
Dobutamine-induced increase in heart rate is blunted by ivabradine treatment in patients with acutely decompensated heart failure Yuksel Cavusoglu, KU Mert, A Nadir, F Mutlu, E Gencer, T Ulus, A Birdane
AF in the ER: Common Scenarios CASE 1. Fast facts. Diagnosis. Management
 AF in the ER: Common Scenarios Atrial fibrillation is a common problem with a wide spectrum of presentations. Below are five common emergency room scenarios and the management strategies for each. Evan
AF in the ER: Common Scenarios Atrial fibrillation is a common problem with a wide spectrum of presentations. Below are five common emergency room scenarios and the management strategies for each. Evan
Heart Failure. Acute. Plasma [NE] (pg/ml) 24 Hours. Chronic
![Heart Failure. Acute. Plasma [NE] (pg/ml) 24 Hours. Chronic Heart Failure. Acute. Plasma [NE] (pg/ml) 24 Hours. Chronic](/thumbs/90/103241154.jpg) Heart Failure Heart failure is the inability of the heart to deliver sufficient blood to the tissues to ensure adequate oxygen supply. Clinically it is characterized by signs of volume overload or symptoms
Heart Failure Heart failure is the inability of the heart to deliver sufficient blood to the tissues to ensure adequate oxygen supply. Clinically it is characterized by signs of volume overload or symptoms
The ACC Heart Failure Guidelines
 The ACC Heart Failure Guidelines Fakhr Alayoubi, Msc,R Ph President of SCCP Cardiology Clinical Pharmacist Assistant Professor At King Saud University King Khalid University Hospital Riyadh-KSA 2017 ACC/AHA/HFSA
The ACC Heart Failure Guidelines Fakhr Alayoubi, Msc,R Ph President of SCCP Cardiology Clinical Pharmacist Assistant Professor At King Saud University King Khalid University Hospital Riyadh-KSA 2017 ACC/AHA/HFSA
Polypharmacy - arrhythmic risks in patients with heart failure
 Influencing sudden cardiac death by pharmacotherapy Polypharmacy - arrhythmic risks in patients with heart failure Professor Dan Atar Head, Dept. of Cardiology Oslo University Hospital Ullevål Norway 27.8.2012
Influencing sudden cardiac death by pharmacotherapy Polypharmacy - arrhythmic risks in patients with heart failure Professor Dan Atar Head, Dept. of Cardiology Oslo University Hospital Ullevål Norway 27.8.2012
Interventional solutions for atrial fibrillation in patients with heart failure
 Interventional solutions for atrial fibrillation in patients with heart failure Advances in Cardiovascular Arrhythmias Great Innovations in Cardiology Matteo Anselmino, MD PhD Division of Cardiology Department
Interventional solutions for atrial fibrillation in patients with heart failure Advances in Cardiovascular Arrhythmias Great Innovations in Cardiology Matteo Anselmino, MD PhD Division of Cardiology Department
DOWNLOAD PDF ABC OF HEART FAILURE
 Chapter 1 : The ABCs of managing systolic heart failure: Past, present, and future Heart failure is a multisystem disorder which is characterised by abnormalities of cardiac, skeletal muscle, and renal
Chapter 1 : The ABCs of managing systolic heart failure: Past, present, and future Heart failure is a multisystem disorder which is characterised by abnormalities of cardiac, skeletal muscle, and renal
Atrial Fibrillation Ablation in Patients with Heart Failure
 Atrial Fibrillation Ablation in Patients with Heart Failure Eleftherios M. Kallergis, MD, PhD, FESC Cardiology Department, Heraklion University Hospital Since auricular fibrillation so often complicates
Atrial Fibrillation Ablation in Patients with Heart Failure Eleftherios M. Kallergis, MD, PhD, FESC Cardiology Department, Heraklion University Hospital Since auricular fibrillation so often complicates
Relationship between cardiac dysfunction, HF and HF rendered asymptomatic
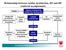 Relationship between cardiac dysfunction, HF and HF rendered asymptomatic NORMAL CARDIAC DYSFUNCTION CORRECTED OR RESOLVED Therapy CAN be withdrawn without recurrence of symptoms Transient Heart Failure
Relationship between cardiac dysfunction, HF and HF rendered asymptomatic NORMAL CARDIAC DYSFUNCTION CORRECTED OR RESOLVED Therapy CAN be withdrawn without recurrence of symptoms Transient Heart Failure
LCZ696 A First-in-Class Angiotensin Receptor Neprilysin Inhibitor
 The Angiotensin Receptor Neprilysin Inhibitor LCZ696 in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction The Prospective comparison of ARNI with ARB on Management Of heart failure with preserved ejection
The Angiotensin Receptor Neprilysin Inhibitor LCZ696 in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction The Prospective comparison of ARNI with ARB on Management Of heart failure with preserved ejection
Atrial fibrillation in the ICU
 Atrial fibrillation in the ICU Atrial fibrillation Preexisting or incident (new onset) among nearly one in three critically ill patients Formation of arrhythogenic substrate usually fibrosis (CHF, hypertension,
Atrial fibrillation in the ICU Atrial fibrillation Preexisting or incident (new onset) among nearly one in three critically ill patients Formation of arrhythogenic substrate usually fibrosis (CHF, hypertension,
A Guide to the Etiology, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Heart Failure. Part I: Etiology and Pathophysiology of Heart Failure
 A Guide to the Etiology, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Heart Failure Dr Badri Paudel GMC Part I: Etiology and Pathophysiology of Heart Failure Heart Failure (HF) Definition A complex clinical
A Guide to the Etiology, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Heart Failure Dr Badri Paudel GMC Part I: Etiology and Pathophysiology of Heart Failure Heart Failure (HF) Definition A complex clinical
Cardiovascular Disorders. Heart Disorders. Diagnostic Tests for CV Function. Bio 375. Pathophysiology
 Cardiovascular Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology Heart Disorders Heart disease is ranked as a major cause of death in the U.S. Common heart diseases include: Congenital heart defects Hypertensive heart
Cardiovascular Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology Heart Disorders Heart disease is ranked as a major cause of death in the U.S. Common heart diseases include: Congenital heart defects Hypertensive heart
Protocol Identifier Subject Identifier Visit Description. [Y] Yes [N] No. [Y] Yes [N] N. If Yes, admission date and time: Day Month Year
![Protocol Identifier Subject Identifier Visit Description. [Y] Yes [N] No. [Y] Yes [N] N. If Yes, admission date and time: Day Month Year Protocol Identifier Subject Identifier Visit Description. [Y] Yes [N] No. [Y] Yes [N] N. If Yes, admission date and time: Day Month Year](/thumbs/76/74263761.jpg) PAST MEDICAL HISTORY Has the subject had a prior episode of heart failure? o Does the subject have a prior history of exposure to cardiotoxins, such as anthracyclines? URGENT HEART FAILURE VISIT Did heart
PAST MEDICAL HISTORY Has the subject had a prior episode of heart failure? o Does the subject have a prior history of exposure to cardiotoxins, such as anthracyclines? URGENT HEART FAILURE VISIT Did heart
Arrhythmias and Heart Failure Dr Chris Lang Consultant Cardiologist and Electrophysiologist Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh
 Arrhythmias and Heart Failure Dr Chris Lang Consultant Cardiologist and Electrophysiologist Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh Arrhythmias and Heart Failure Ventricular Supraventricular VT/VF Primary prevention
Arrhythmias and Heart Failure Dr Chris Lang Consultant Cardiologist and Electrophysiologist Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh Arrhythmias and Heart Failure Ventricular Supraventricular VT/VF Primary prevention
AF Today: W. For the majority of patients with atrial. are the Options? Chris Case
 AF Today: W hat are the Options? Management strategies for patients with atrial fibrillation should depend on the individual patient. Treatment with medications seems adequate for most patients with atrial
AF Today: W hat are the Options? Management strategies for patients with atrial fibrillation should depend on the individual patient. Treatment with medications seems adequate for most patients with atrial
Diagnosis is it really Heart Failure?
 ESC Congress Munich - 25-29 August 2012 Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction From Bench to Bedside Diagnosis is it really Heart Failure? Prof. Burkert Pieske Department of Cardiology Med.University
ESC Congress Munich - 25-29 August 2012 Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction From Bench to Bedside Diagnosis is it really Heart Failure? Prof. Burkert Pieske Department of Cardiology Med.University
Treating HF Patients with ARNI s Why, When and How?
 Treating HF Patients with ARNI s Why, When and How? 19 th Annual San Diego Heart Failure Symposium for Primary Care Physicians January 11-12, 2019 La Jolla, CA Barry Greenberg M.D. Distinguished Professor
Treating HF Patients with ARNI s Why, When and How? 19 th Annual San Diego Heart Failure Symposium for Primary Care Physicians January 11-12, 2019 La Jolla, CA Barry Greenberg M.D. Distinguished Professor
Mission Statement for our Arrhythmia Care
 Mission Statement for our Arrhythmia Care We are dedicated to provide a compassionate and an outstanding care for patients with cardiac arrhythmias. We will be utilizing the cutting edge and the most advanced
Mission Statement for our Arrhythmia Care We are dedicated to provide a compassionate and an outstanding care for patients with cardiac arrhythmias. We will be utilizing the cutting edge and the most advanced
Copyright 2011, 2007 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Normal Cardiac Anatomy
 Mosby,, an affiliate of Elsevier Normal Cardiac Anatomy Impaired cardiac pumping Results in vasoconstriction & fluid retention Characterized by ventricular dysfunction, reduced exercise tolerance, diminished
Mosby,, an affiliate of Elsevier Normal Cardiac Anatomy Impaired cardiac pumping Results in vasoconstriction & fluid retention Characterized by ventricular dysfunction, reduced exercise tolerance, diminished
Satish K Surabhi, MD.FACC,FSCAI,RPVI Medical Director, Cardiac Cath Labs AnMed Health Heart & Vascular Care
 Satish K Surabhi, MD.FACC,FSCAI,RPVI Medical Director, Cardiac Cath Labs AnMed Health Heart & Vascular Care None Fig. 1. Progression of Heart Failure.With each hospitalization for acute heart failure,
Satish K Surabhi, MD.FACC,FSCAI,RPVI Medical Director, Cardiac Cath Labs AnMed Health Heart & Vascular Care None Fig. 1. Progression of Heart Failure.With each hospitalization for acute heart failure,
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 43, No. 2, by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN /04/$30.
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 43, No. 2, 2004 2004 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/04/$30.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2003.08.037
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 43, No. 2, 2004 2004 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/04/$30.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2003.08.037
Intermittent low dose digoxin may be effective and safe in patients with chronic heart failure undergoing maintenance hemodialysis
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 8: 1689-1694, 2014 Intermittent low dose digoxin may be effective and safe in patients with chronic heart failure undergoing maintenance hemodialysis XIAOZHAO LI 1,
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 8: 1689-1694, 2014 Intermittent low dose digoxin may be effective and safe in patients with chronic heart failure undergoing maintenance hemodialysis XIAOZHAO LI 1,
Trials Enrolled subjects Findings Fox et al. 2014, SIGNIFY 1
 Appendix 5 (as supplied by the authors): Published trials on the effect of ivabradine on outcomes including mortality in patients with different cardiovascular diseases Trials Enrolled subjects Findings
Appendix 5 (as supplied by the authors): Published trials on the effect of ivabradine on outcomes including mortality in patients with different cardiovascular diseases Trials Enrolled subjects Findings
Lack of prevention of heart failure by serial electrical cardioversion in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation
 48 Department of Cardiology, Thoraxcenter, University Hospital Groningen, 97 RB Groningen, Netherlands A E Tuinenburg I C Van Gelder M P Van Den Berg J Brügemann PJDeKam HJGMCrijns Correspondence to: Dr
48 Department of Cardiology, Thoraxcenter, University Hospital Groningen, 97 RB Groningen, Netherlands A E Tuinenburg I C Van Gelder M P Van Den Berg J Brügemann PJDeKam HJGMCrijns Correspondence to: Dr
Dos and Don t in Cardiac Arrhythmia. Case 1 -ECG. Case 1. Management. Emergency Admissions. Reduction of TE risk -CHADS 2 score. Hospital Admissions
 Emergency Admissions Dos and Don t in Cardiac Arrhythmia Tom Wong, MD, FESC Consultant Cardiologist, Honorary Senior Lecturer Royal Brompton & Harefield Hospitals National Heart and Lung Institute, Imperial
Emergency Admissions Dos and Don t in Cardiac Arrhythmia Tom Wong, MD, FESC Consultant Cardiologist, Honorary Senior Lecturer Royal Brompton & Harefield Hospitals National Heart and Lung Institute, Imperial
Index of subjects. effect on ventricular tachycardia 30 treatment with 101, 116 boosterpump 80 Brockenbrough phenomenon 55, 125
 145 Index of subjects A accessory pathways 3 amiodarone 4, 5, 6, 23, 30, 97, 102 angina pectoris 4, 24, 1l0, 137, 139, 140 angulation, of cavity 73, 74 aorta aortic flow velocity 2 aortic insufficiency
145 Index of subjects A accessory pathways 3 amiodarone 4, 5, 6, 23, 30, 97, 102 angina pectoris 4, 24, 1l0, 137, 139, 140 angulation, of cavity 73, 74 aorta aortic flow velocity 2 aortic insufficiency
Medical Management of Acute Heart Failure
 Critical Care Medicine and Trauma Medical Management of Acute Heart Failure Mary O. Gray, MD, FAHA Associate Professor of Medicine University of California, San Francisco Staff Cardiologist and Training
Critical Care Medicine and Trauma Medical Management of Acute Heart Failure Mary O. Gray, MD, FAHA Associate Professor of Medicine University of California, San Francisco Staff Cardiologist and Training
DISCLAIMER: ECHO Nevada emphasizes patient privacy and asks participants to not share ANY Protected Health Information during ECHO clinics.
 DISCLAIMER: Video will be taken at this clinic and potentially used in Project ECHO promotional materials. By attending this clinic, you consent to have your photo taken and allow Project ECHO to use this
DISCLAIMER: Video will be taken at this clinic and potentially used in Project ECHO promotional materials. By attending this clinic, you consent to have your photo taken and allow Project ECHO to use this
Disclosure of Relationships
 Disclosure of Relationships Over the past 12 months Dr Ruilope has served as Consultant and Speakers Bureau member of Astra-Zeneca, Bayer, Daiichi-Sankyo, Menarini, Novartis, Otsuka, Pfizer, Relypsa, Servier
Disclosure of Relationships Over the past 12 months Dr Ruilope has served as Consultant and Speakers Bureau member of Astra-Zeneca, Bayer, Daiichi-Sankyo, Menarini, Novartis, Otsuka, Pfizer, Relypsa, Servier
Evaluation of a diagnostic pathway in heart failure in primary care, using electrocardiography and brain natriuretic peptide guided echocardiography
 Evaluation of a diagnostic pathway in heart failure in primary care, using electrocardiography and brain natriuretic peptide guided echocardiography Rebecka Karlsson Pardeep Jhund 1 Material and methods
Evaluation of a diagnostic pathway in heart failure in primary care, using electrocardiography and brain natriuretic peptide guided echocardiography Rebecka Karlsson Pardeep Jhund 1 Material and methods
(D) (E) (F) 6. The extrasystolic beat would produce (A) increased pulse pressure because contractility. is increased. increased
 Review Test 1. A 53-year-old woman is found, by arteriography, to have 5% narrowing of her left renal artery. What is the expected change in blood flow through the stenotic artery? Decrease to 1 2 Decrease
Review Test 1. A 53-year-old woman is found, by arteriography, to have 5% narrowing of her left renal artery. What is the expected change in blood flow through the stenotic artery? Decrease to 1 2 Decrease
Disclosures for Presenter
 A Comparison of Angiotensin Receptor- Neprilysin Inhibition (ARNI) With ACE Inhibition in the Long-Term Treatment of Chronic Heart Failure With a Reduced Ejection Fraction Milton Packer, John J.V. McMurray,
A Comparison of Angiotensin Receptor- Neprilysin Inhibition (ARNI) With ACE Inhibition in the Long-Term Treatment of Chronic Heart Failure With a Reduced Ejection Fraction Milton Packer, John J.V. McMurray,
BUSINESS. Articles? Grades Midterm Review session
 BUSINESS Articles? Grades Midterm Review session REVIEW Cardiac cells Myogenic cells Properties of contractile cells CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART Conduction pathway SA node (pacemaker) atrial depolarization
BUSINESS Articles? Grades Midterm Review session REVIEW Cardiac cells Myogenic cells Properties of contractile cells CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART Conduction pathway SA node (pacemaker) atrial depolarization
Advances in the Monitoring & Treatment of Heart Failure
 Advances in the Monitoring & Treatment of Heart Failure Darrell J. Solet, MD - Cardiologist & Medical Director - Cardiovascular Institute of the South of Morgan City, Louisiana - Clinical Assistant Professor
Advances in the Monitoring & Treatment of Heart Failure Darrell J. Solet, MD - Cardiologist & Medical Director - Cardiovascular Institute of the South of Morgan City, Louisiana - Clinical Assistant Professor
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acute coronary syndrome(s), anticoagulant therapy in, 706, 707 antiplatelet therapy in, 702 ß-blockers in, 703 cardiac biomarkers in,
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acute coronary syndrome(s), anticoagulant therapy in, 706, 707 antiplatelet therapy in, 702 ß-blockers in, 703 cardiac biomarkers in,
Crisis Management During Liver Transplant Surgery Liver and Intensive Care Group of Europe Newcastle upon Tyne 2005
 Crisis Management During Liver Transplant Surgery Liver and Intensive Care Group of Europe Newcastle upon Tyne 2005 M. Susan Mandell M.D. Ph. D. Department of Anesthesiology University of Colorado Health
Crisis Management During Liver Transplant Surgery Liver and Intensive Care Group of Europe Newcastle upon Tyne 2005 M. Susan Mandell M.D. Ph. D. Department of Anesthesiology University of Colorado Health
Report on the Expert Group Meeting of Paediatric Heart Failure, London 29 November 2010
 Report on the Expert Group Meeting of Paediatric Heart Failure, London 29 November Clinical trials in Paediatric Heart Failure List of participants: Michael Burch, Hugo Devlieger, Angeles Garcia, Daphne
Report on the Expert Group Meeting of Paediatric Heart Failure, London 29 November Clinical trials in Paediatric Heart Failure List of participants: Michael Burch, Hugo Devlieger, Angeles Garcia, Daphne
Performance and Quality Measures 1. NQF Measure Number. Coronary Artery Disease Measure Set
 Unless indicated, the PINNACLE Registry measures are endorsed by the American College of Cardiology Foundation and the American Heart Association and may be used for purposes of health care insurance payer
Unless indicated, the PINNACLE Registry measures are endorsed by the American College of Cardiology Foundation and the American Heart Association and may be used for purposes of health care insurance payer
Peripartum Cardiomyopathy. Lavanya Rai Manipal
 Peripartum Cardiomyopathy Lavanya Rai Manipal Definition - PPCM - Dilated cardiomyopathy of unknown cause resulting in cardiac failure that occurs in the peripartum period in women without any preexisting
Peripartum Cardiomyopathy Lavanya Rai Manipal Definition - PPCM - Dilated cardiomyopathy of unknown cause resulting in cardiac failure that occurs in the peripartum period in women without any preexisting
DR ALEXIA STAVRATI CARDIOLOGIST, DIRECTOR OF CARDIOLOGY DEPT, "G. PAPANIKOLAOU" GH, THESSALONIKI
 The Impact of AF on Natural History of CAD DR ALEXIA STAVRATI CARDIOLOGIST, DIRECTOR OF CARDIOLOGY DEPT, "G. PAPANIKOLAOU" GH, THESSALONIKI CAD MOST COMMON CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE MOST COMMON CAUSE OF DEATH
The Impact of AF on Natural History of CAD DR ALEXIA STAVRATI CARDIOLOGIST, DIRECTOR OF CARDIOLOGY DEPT, "G. PAPANIKOLAOU" GH, THESSALONIKI CAD MOST COMMON CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE MOST COMMON CAUSE OF DEATH
The Who, How and When of Advanced Heart Failure Therapies. Disclosures. What is Advanced Heart Failure?
 The Who, How and When of Advanced Heart Failure Therapies 9 th Annual Dartmouth Conference on Advances in Heart Failure Therapies Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center Lebanon, NH May 20, 2013 Joseph G. Rogers,
The Who, How and When of Advanced Heart Failure Therapies 9 th Annual Dartmouth Conference on Advances in Heart Failure Therapies Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center Lebanon, NH May 20, 2013 Joseph G. Rogers,
Heart Failure Medical and Surgical Treatment
 Heart Failure Medical and Surgical Treatment Daniel S. Yip, M.D. Medical Director, Heart Failure and Transplantation Mayo Clinic Second Annual Lakeland Regional Health Cardiovascular Symposium February
Heart Failure Medical and Surgical Treatment Daniel S. Yip, M.D. Medical Director, Heart Failure and Transplantation Mayo Clinic Second Annual Lakeland Regional Health Cardiovascular Symposium February
Evidence Supporting Post-MI Use of
 Addressing the Gap in the Management of Patients After Acute Myocardial Infarction: How Good Is the Evidence Supporting Current Treatment Guidelines? Michael B. Fowler, MB, FRCP Beta-adrenergic blocking
Addressing the Gap in the Management of Patients After Acute Myocardial Infarction: How Good Is the Evidence Supporting Current Treatment Guidelines? Michael B. Fowler, MB, FRCP Beta-adrenergic blocking
Rehospitalization Prognostic Factors in Patients with Heart Failure: a Prospective Follow-up Study
 ARC Journal of Cardiology Volume2, Issue 2, 2016, PP 13-18 ISSN No. (Online) 2455-5991 http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2455-5991.0202002 www.arcjournals.org Rehospitalization Prognostic Factors in Patients
ARC Journal of Cardiology Volume2, Issue 2, 2016, PP 13-18 ISSN No. (Online) 2455-5991 http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2455-5991.0202002 www.arcjournals.org Rehospitalization Prognostic Factors in Patients
AF#in#pa(ents#with#CAD# Is#dronedarone#a#good#choice?!
 AF#in#pa(ents#with#CAD# Is#dronedarone#a#good#choice?! DRUG#PROPHYLAXIS#OF#AF:# FOCUS#ON#DRONEDARONE# Friday#16C10C2015# Harry%JGM%Crijns% Maastricht,%The%Netherlands% Disclosures Harry Crijns - research
AF#in#pa(ents#with#CAD# Is#dronedarone#a#good#choice?! DRUG#PROPHYLAXIS#OF#AF:# FOCUS#ON#DRONEDARONE# Friday#16C10C2015# Harry%JGM%Crijns% Maastricht,%The%Netherlands% Disclosures Harry Crijns - research
Management of atrial fibrillation in heart failure
 Nationale hartfalendag 2017 Zeist Management of atrial fibrillation in heart failure Isabelle C Van Gelder University of Groningen University Medical Center Groningen The Netherlands Disclosures Grant
Nationale hartfalendag 2017 Zeist Management of atrial fibrillation in heart failure Isabelle C Van Gelder University of Groningen University Medical Center Groningen The Netherlands Disclosures Grant
Disclosure Information : No conflict of interest
 Intravenous nicorandil improves symptoms and left ventricular diastolic function immediately in patients with acute heart failure : a randomized, controlled trial M. Shigekiyo, K. Harada, A. Okada, N.
Intravenous nicorandil improves symptoms and left ventricular diastolic function immediately in patients with acute heart failure : a randomized, controlled trial M. Shigekiyo, K. Harada, A. Okada, N.
How much atrial fibrillation causes symptoms of heart failure?
 ORIGINAL PAPER How much atrial fibrillation causes symptoms of heart failure? M. Guglin, R. Chen Linked Comment: Lip. Int J Clin Pract 2014; 68: 408 9. SUMMARY Introduction: Patients with atrial fibrillation
ORIGINAL PAPER How much atrial fibrillation causes symptoms of heart failure? M. Guglin, R. Chen Linked Comment: Lip. Int J Clin Pract 2014; 68: 408 9. SUMMARY Introduction: Patients with atrial fibrillation
Heart Failure and Atrial Fibrillation
 Heart Failure and Atrial Fibrillation 신미승 가천의대심장내과 Prevalence of AF & CHF AF : the most common cardiac arrhythmia more than 2.2 million Americans -- 2007 ACC CHF : more than 5 million Americans The prevalence
Heart Failure and Atrial Fibrillation 신미승 가천의대심장내과 Prevalence of AF & CHF AF : the most common cardiac arrhythmia more than 2.2 million Americans -- 2007 ACC CHF : more than 5 million Americans The prevalence
Disclosure Statement. Heart Failure: Refreshers and Updates. Objectives. CHF: Chronic Heart Failure. Definitions. Definitions 2/19/2018
 Disclosure Statement Heart Failure: Refreshers and Updates Tracy K. Pettinger, PharmD Clinical Associate Professor College of Pharmacy The planners and presenter of this presentation have disclosed no
Disclosure Statement Heart Failure: Refreshers and Updates Tracy K. Pettinger, PharmD Clinical Associate Professor College of Pharmacy The planners and presenter of this presentation have disclosed no
Our Readers Have An Attitude Toward Living
 February 2007 America s Wellness Guide Number 43 FREE at Doctor s Offices, Hospitals, Clinics and Kroger Pharmacies in the Midsouth COVER Standard of Care for Heart Failure Management By Arie Szatkowski,
February 2007 America s Wellness Guide Number 43 FREE at Doctor s Offices, Hospitals, Clinics and Kroger Pharmacies in the Midsouth COVER Standard of Care for Heart Failure Management By Arie Szatkowski,
