Utility of Exercise-Induced Zero TBI Sign in Patients on Maintenance Hemodialysis
|
|
|
- Eric Fitzgerald
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2016 Annals of Vascular Diseases doi: /avd.oa Original Article Utility of Exercise-Induced Zero TBI Sign in Patients on Maintenance Hemodialysis Kazuo Tsuyuki, CVT, PhD, 1 Kenji Kohno, PhD, 1 Kunio Ebine, MD, PhD, 2 Susumu Tamura, MD, PhD, 2 Yasuhiro Ohzeki, MD, PhD, 2 Toshifumi Murase, MD, 2 Takehiro Ohara, MD, PhD, 3 Yujin Kunugi, MD, 3 Fumihiko Iida, MT, 4 Yoshie Mochizuki, MT, 4 Mutsumi Sorimachi, CE, BS, 1,5 and Shinichi Watanabe, PhD 5 It is uncertain whether exercise-induced zero toe brachial index sign (e-zets) is beneficial to prevent advanced perfusion disturbance in maintenance hemodialysis (HD) patients. In HD patients, we compared the clinical findings and prognoses among 22 toes in a resting zero toe brachial index sign (r-zets) group, 22 toes in an e-zets group, and 63 toes in a non-e-zets group. The hemodynamics of the lower extremities in the e-zets group is intermediate between the r-zets and non-e-zets groups. As the result of a 36-month followup observation, the r-zets avoidance rate was significantly lower in the e-zets group (63.6%; P <0.001) than the none-zets group (98.4%), showing that it was difficult to avoid advanced perfusion disturbance. The e-zets in HD patients may appear before r-zets, being beneficial as a predictor for advanced perfusion disturbance. (This is a translation of J Jpn Coll Angiol 2015; 55: ) Keyword: peripheral arterial disease, critical limb ischemia, hemodialysis, toe brachial pressure index, exercise Introduction The great toe in humans is particularly important in daily life, playing a central role in maintaining the standing 1 Laboratory of Physiology, Odawara Cardiovascular Hospital, Odawara, Kanagawa, Japan 2 Division of Cardiovascular Surgery, Odawara Cardiovascular Hospital, Odawara, Kanagawa, Japan 3 Division of Nephrology, Odawara Cardiovascular Hospital, Odawara, Kanagawa, Japan 4 Division of Medical Technology, Odawara Cardiovascular Hospital, Odawara, Kanagawa, Japan 5 Department of Clinical Engineering, Kanagawa Institute of Technology, Atsugi, Kanagawa, Japan Received: July 19, 2016; Accepted: July 23, 2016 Corresponding author: Kazuo Tsuyuki, CVT, PhD. Laboratory of Physiology, Odawara Cardiovascular Hospital, Yahagi, Odawara, Kanagawa , Japan Tel: , Fax: tsuyuki47msd@yahoo.co.jp This is a translation of J Jpn Coll Angiol 2015; 55: posture and producing a driving force in walking. However, patients on maintenance hemodialysis (HD patients) sometimes undergo great toe amputation due to critical limb ischemia (CLI), resulting in a marked decrease in the activity of daily life. 1) CLI is often treated by revascularization, when revascularization is not indicated, perfusion disorders should be diagnosed as early as possible, and efforts should be made to prevent CLI. Since CLI is closely associated with a poor prognosis, even earlier diagnosis is required. As a diagnostic method for perfusion disorders at the toe level, the ratio of the toe to brachial blood pressure (toe brachial pressure index: TBI) is widely used. Matsui et al. 2) called the state not allowing TBI measurement the zero TBI sign, and reported that this sign is a good parameter indicating severe perfusion disorders of the toe. This zero TBI sign (resting zero TBI sign: r-zets) represents a state in which the toe pressure is below 40 mmhg as the measurement threshold of automatic devices for blood pressure measurement. Findings such as ischemic resting pain, ulceration, or gangrene in addition to such a hemodynamic state lead to CLI. Therefore, r-zets is an important factor for the diagnosis of CLI, and measurement for its detection is indispensable. However, in terms of early diagnosis and treatment, measurement for r-zets detection is not performed at an appropriate timing. In daily clinical practice, regular TBI measurements are important for the early diagnosis of the condition as the gateway to severe perfusion disorders including CLI. However, there is no clear TBI cut-off value indicating this condition. In HD patients, the complication rate of severe perfusion disorders is high, and CLI sometimes suddenly develops in the absence of intermittent claudication. Therefore, it is necessary to detect objective signs indicating the gateway to severe perfusion disorders including CLI and take active preventive measures. We speculated that the exercise-induced zero TBI sign (e-zets) can 1
2 Tsuyuki K, et al. Table 1 Clinical characteristics of patients All patients Patients who underwent Ex-TBI test Number of limbs Number of patients Gender (men/women) 102/54 30/15 Age (years) 66.3 ± ± 11.2 Dialysis duration (years) 6.6 ± ± 7.0 CTR (%) 48.9 ± ± 4.3 Hemoglobin (mg/dl) 10.9 ± ± 1.0 ABI 1.12 ± ± 0.22 TBI 0.64 ± ± 0.30 Intermittent claudication (limbs) 44 (14.1) 20 (23.5) Coldness (limbs) 109 (34.9) 26 (30.6) Numbness (limbs) 61 (19.6) 18 (21.2) Cyanosis (limbs) 10 (3.2) 2 (2.4) Resting pain (limbs) 2 (0.6) 0 Ulcer (limbs) 3 (1.0) 2 (2.4) Gangrene (limbs) 0 0 Diabetes mellitus 62 (39.7) 20 (44.4) Hypertension 108 (69.2) 33 (73.3) Coronary artery disease 36 (23.1) 10 (22.2) Cerebrovascular disease 10 (6.4) 3 (6.7) CTR: cardiothoracic ratio; Ex: exercise; ABI: ankle-brachial pressure index; TBI: toe brachial pressure index; ( ): % indicate severe perfusion disorders including CLI. In this study, the usefulness of the e-zets was clarified. Subjects and Methods Subjects The subjects consisted of 156 HD outpatients (312 toes) in whom the ankle-brachial pressure index (ABI) and toe-brachial pressure index (TBI) were measured, and the lower limbs were observed at the time of foot care between May 2009 and June 2014 (Table 1). Of the 156 patients, 45 (90 toes) gave consent to participate in this study, and underwent TBI measurement after walking. After excluding 5 toes already showing r-zets, the other 85 toes were included in the evaluation of toe blood flow during exercise (Table 1). This study was performed with the approval of the ethical committee of our hospital (approval No ). ABI and TBI After 15 minutes of rest in the supine position, the ABI and TBI were measured with an automatic device for blood pressure and pulse volume recording (PVR) (Form PWV/ ABI First, Omron Colin) and using the oscillometric method. 3) The ABI and TBI were obtained by dividing the arterial pressures of the ankle and the great toe, respectively, by the systolic brachial artery pressure on the arm without an arteriovenous fistula. According to the Guidelines of the TASC II 4) and the Japanese Society of Dialysis Therapy, 5) an ABI <0.9 and TBI <0.6 were used as the positive criteria. Exercise TBI measurement On a non-hd day, immediately after 1-minute walking using a treadmill (Series, 2000, Marquette Electronics) at a speed of 2.4 km/h with a slope of 12%, the TBI was measured using a manual mode in the supine position. For this measurement, pressure was applied to the cuff around the toe within 15 seconds after the walking, and measurement was performed at 2-minute intervals for 10 minutes. However, in terms of safety, the walking speed was reduced to 2.0 km/h in patients aged 70 years or showing decreased left ventricular function or decreased walking ability. 3) During the exercise TBI measurement, 12-lead ECG records were monitored using a cardiac assessment system for exercise testing (CASE 8000, Marquette Electronics). Walking was discontinued when one of the following symptoms appeared: 1) horizontal or downsloping ST depression of 0.1 mv compared with the resting ST at 80 m/sec after the J point; 2) abnormal blood pressure responses (systolic pressure 250 mmhg, diastolic pressure 120 mmhg); 3) dangerous or potentially dangerous arrhythmias; 4) the maximum heart rate obtained using the equation 220 age ; 5) difficulty in walking due to lower limb pain, and 6) symptoms of the cardiopulmonary or neurological system. 3) Definition of e-zets When all the following criteria were fulfilled, the e-zets was considered to be present: 1) Measurement was performed with an automatic device for blood pressure and 2
3 Exercise-Induced Zero TBI Sign Pre walk Post walk Recovery 3 min Recovery 5 min Brachial Right toe Left toe Fig. 1 Exercise-induced zero TBI sign (e-zets). Toe pressure disappeared after walking; and reappeared sometime after walking. TBI: toe brachial pressure index Table 2 Four kinds of measurements for PAD in HD patients Measurements Number of patients Number of positive tests Incidence (%) ABI below TBI below r-zets e-zets ABI: ankle-brachial pressure index; TBI: toe brachial pressure index; r-zets: resting zero TBI sign; e-zets: exercise-induced zero TBI sign; HD: hemodialysis; PAD: peripheral arterial disease PVR using the oscillometric method; 2) The resting TBI could be measured; 3) The PVR of the toe became flat immediately after walking; 4) The PVR of the toe that once became flat after walking gradually reappeared with the time course (Fig. 1). Outcome survey The 85 toes examined by exercise TBI measurement were classified into 22 with and 63 without e-zets, and outcomes were prospectively observed. The observation period was 36 months, and the endpoint was the appearance of r-zets. Statistical analysis Each factor was expressed as the mean value ± SD. Between two independent groups, differences in the mean values were analyzed using the unpaired t-test, and the ratio was analyzed using the c 2 test. Among multiple groups, differences in the mean value were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance, and the ratio was analyzed using the c 2 test and r k contingency table (Pearson type), but when 0 is included in N (sample number), the G test (likelihood ratio test) was used. Outcomes were analyzed using the Kaplan-Meier method and the Logrank test (Stat Mate IV). P <0.05 was regarded as significant. Results Incidence of r-zets Of the 156 patients, 15 (9.6%) showed r-zets (Table 2), consisting of 8 (5.1%) with this sign in the single foot and 7 (4.5%) with this sign in the both feet. Incidence of e-zets Of the 45 patients who underwent exercise TBI measurement, 14 (31.1%) showed e-zets (Table 2), consisting of 3
4 Tsuyuki K, et al. Table 3 Comparison of clinical findings among the three stages of zero TBI sign in HD patients r-zets group e-zets group Non-e-ZETS group χ 2 or G test Number of limbs ABI 0.99 ± 0.31 ** 1.0 ± 0.27 ** 1.20 ± 0.15 TBI Zero sign ** 0.58 ± 0.20 * 0.79 ± 0.17 Toe pressure Zero sign ** 75.5 ± 27.4 * ± 27.1 Intermittent claudication (limbs) 13 (59.1) 12 (54.5) 8 (12.7) p <0.001 Coldness (limbs) 16 (72.7) 14 (63.6) 12 (19.0) p <0.001 Numbness (limbs) 11 (50.0) 7 (31.8) 12 (19.0) p <0.05 Cyanosis (limbs) 6 (27.3) 0 2 (3.2) p <0.01 Resting pain (limbs) 2 (9.1) 0 0 NS Ulcer (limbs) 1 (4.5) 0 2 (3.2) NS Gangrene (limbs) NS ABI: ankle-brachial pressure index; TBI: toe brachial pressure index; r-zets: resting zero TBI sign; e-zets: exercise-induced zero TBI sign; ( ): %; ** : p <0.001; * : p <0.01 (comparison with Non-e-ZETS group); : p <0.001 (comparison with r-zets group); HD: hemodialysis 6 (13.3%) with this sign in the single foot and 8 (17.8%) with this sign in the both feet. Clinical findings Hemodynamics in the lower limbs, symptoms, and skin lesions were compared among the 22 toes showing r-zets (r-zets group), 22 showing e-zets (e-zets group), and 63 without e-zets (non-e-zets group) (Table 3). The ABI was significantly lower in the r-zets and e-zets groups than in the non-e-zets group, but did not differ between the former two groups. The TBI and toe systolic pressure significantly differed among the three groups (p <0.001 or p <0.01). The resting TBI in the e-zets group was 0.6 in 9 toes and <0.6 in the other 13 toes. The incidences of intermittent claudication, coldness, and numbness were highest in the r-zets group, followed in order by the e-zets group and non-e-zets group (p <0.001). The incidence of cyanosis was high in the r-zet group (p <0.01), but the incidence of ischemic resting pain, ulceration, or gangrene did not significantly differ among the groups. Outcomes in toes showing e-zets As a result of a 36-month follow-up survey, progression to the r-zets was observed in 8 (36.4%) of the 22 toes in the e-zets group, including 3 (13.6%) with CLI. In the non-e-zets group, 1 (1.6%) of the 63 toes showed progression to the r-zets. The r-zets avoidance rate significantly differed (p <0.001) between the e-zets and non-e-zets groups (Fig. 2). Discussion r-zets in HD patients Okamoto et al. 6) reported peripheral arterial disease (PAD) showing an ABI <0.9 in 20.0% of HD patients. In our study, the ABI was <0.9 in 20.5% of the HD Zero TBI sign free survival (%) Non-e-ZETS e-zets Logrank test: p< Duration of follow-up (month) Fig. 2 Comparison of resting zero TBI sign (r-zets) free survival between the e-zets and non-e-zets groups in HD patients. While 1.6% of patients developed r-zets for 36 months in the non-e-zets group, 36.4% of cases progressed to r-zets for 36 months in the e-zets group. TBI: toe-brachial pressure index; r-zets: resting zero TBI sign; e-zets: exercise-induced zero TBI sign; HD: hemodialysis patients, which was similar to the percentage reported by Okamoto et al. In our study, the r-zets as another parameter for the detection of PAD was observed in 9.6%. These results suggest the presence of severe perfusion disorder (toe pressure <40 mmhg) in about 50% of patients with PAD as a complication of HD. In the r-zets group, cyanosis was present in 27.3% while the incidences of ischemic resting pain and ulceration were low, and gangrene was not observed. Thus, although HD outpatients with the r-zets may partly include those with CLI, most of them may have severe perfusion disorder in the pre-cli stage without lower limb symptoms and tissue defects. Clinical importance of the e-zets This study confirmed the phenomenon of the appearance of the r-zets after 1-minute walking in HD patients, i.e., 4
5 Exercise-Induced Zero TBI Sign the existence of the e-zets, and also was the first to clarify that its incidence was 31.1%. These results suggest that the r-zets as severe perfusion disorder is present in about 10% of HD patients, and toe perfusion disorder that is not manifested by routine TBI measurement is present in about three times as high as this percentage. The TBI in the non-e-zets group was in the normal range, but that in the e-zets group (0.58) was slightly lower than the normal range. Ohtake et al. 7) described that the desirable cut-off value for diagnosing PAD using the TBI in HD patients is 0.6, and recommended a cut-off value of 0.25 for detecting CLI. Their study suggests that the e-zets is mild perfusion disorder and a hemodynamic state far from CLI. This is supported by the absence of cyanosis, ischemic resting pain, ulceration, or gangrene in the e-zets group. However, progression to the r-zets during a 36-month follow-up period was observed only in 1.6% in the non-e-zets group but in 36.4% in the e-zets group, and the latter included toes showing CLI. Based on these results, the e-zets observed in HD patients may be an adequate marker showing that perfusion disorders is mild at present but can progress to severe perfusion disorders in the near future. In daily clinical practice, the prediction of severe perfusion disorders in the future by regular TBI measurements is required, but there is no definite TBI cut-off value as its gateway. In terms of this, the e-zets may be the gateway to severe perfusion disorders including CLI because of the high incidence of progression to the r-zets within 36 months after the e-zets. Therefore, the evaluation of the e-zets can be the evaluation of latent perfusion disorders of the toe, and is useful for predicting the development of the r-zets and CLI. Limitations and problems of this study The number of patients in whom outcomes were evaluated was small in this study. In the future, evaluation in additional cases is necessary. Conclusion The e-zets is useful for predicting severe perfusion disorders of the toe. Disclosure Statement The first author and co-authors have no conflicts of interest. References 1) Takagi T, Morishita T, Teramoto H, et al. Lower extremity amputations in gangrene patients. Jpn J Clin Dial 2010; 26: (in Japanese) 2) Matsui K, Murakami Y, Shimada K, et al. Non-invasive Evaluation for Therapeutic Angiogenesis. J Jpn Coll Angio 2005; 45: (in Japanese) 3) Tsuyuki K, Kohno K, Ebine K, et al. Exercise-ankle brachial pressure index with one-minute treadmill walking in patients on maintenance hemodialysis. Ann Vasc Dis 2013; 6: ) Norgren L, Hiatt WR, Dormandy JA, et al. Inter-Society Consensus for the management of PAD. C intermittent claudication. Tokyo: Medical Tribune, 2009: (in Japanese) 5) Working group for Clinical Guidelines for the Evaluation and the Treatment of Cardiovascular Complications in Hemodialysis Patients. Clinical Guidelines for the Evaluation and the Treatment of Cardiovascular Complications in Hemodialysis Patients: Chapter 8, peripheral artery disease. J Jpn Soc Dial Ther 2011; 44: (in Japanese) 6) Okamoto K, Oka M, Maesato K, et al. Peripheral arterial occlusive disease is more prevalent in patients with hemodialysis: comparison with the findings of multidetector-row computed tomography. Am J Kidney Dis 2006; 48: ) Ohtake T, Oka M, Ikee R, et al. Impact of lower limbs arterial calcification on the prevalence and severity of PAD in patients on hemodialysis. J Vasc Surg 2011; 53:
Vascular screening in diabetic patients: how aggressive should we be and when to intervene?
 Vascular screening in diabetic patients: how aggressive should we be and when to intervene? Roberto Ferraresi Peripheral Interventional Unit Bergamo Italy Disclosure Speaker name: ROBERTO FERRARESI X X
Vascular screening in diabetic patients: how aggressive should we be and when to intervene? Roberto Ferraresi Peripheral Interventional Unit Bergamo Italy Disclosure Speaker name: ROBERTO FERRARESI X X
Due to Perimed s commitment to continuous improvement of our products, all specifications are subject to change without notice.
 A summary Disclaimer The information contained in this document is intended to provide general information only. It is not intended to be, nor does it constitute, medical advice. Under no circumstances
A summary Disclaimer The information contained in this document is intended to provide general information only. It is not intended to be, nor does it constitute, medical advice. Under no circumstances
Objective assessment of CLI patients Hemodynamic parameters
 Objective assessment of CLI patients Hemodynamic parameters Worth anything in end stage patients? Marianne Brodmann Angiology, Medical University Graz, Austria Disclosure Speaker name: Marianne Brodmann
Objective assessment of CLI patients Hemodynamic parameters Worth anything in end stage patients? Marianne Brodmann Angiology, Medical University Graz, Austria Disclosure Speaker name: Marianne Brodmann
National Clinical Conference 2018 Baltimore, MD
 National Clinical Conference 2018 Baltimore, MD No relevant financial relationships to disclose Wound Care Referral The patient has been maximized from a vascular standpoint. She has no other options.
National Clinical Conference 2018 Baltimore, MD No relevant financial relationships to disclose Wound Care Referral The patient has been maximized from a vascular standpoint. She has no other options.
Disclosures. Critical Limb Ischemia. Vascular Testing in the CLI Patient. Vascular Testing in Critical Limb Ischemia UCSF Vascular Symposium
 Disclosures Vascular Testing in the CLI Patient None 2015 UCSF Vascular Symposium Warren Gasper, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery UCSF Division of Vascular Surgery Critical Limb Ischemia Chronic Limb
Disclosures Vascular Testing in the CLI Patient None 2015 UCSF Vascular Symposium Warren Gasper, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery UCSF Division of Vascular Surgery Critical Limb Ischemia Chronic Limb
Perfusion Assessment in Chronic Wounds
 Perfusion Assessment in Chronic Wounds American Society of Podiatric Surgeons Surgical Conference September 22, 2018 Michael Maier, DPM, FACCWS Cardiovascular Medicine Cleveland Clinic Disclosures Speaker,
Perfusion Assessment in Chronic Wounds American Society of Podiatric Surgeons Surgical Conference September 22, 2018 Michael Maier, DPM, FACCWS Cardiovascular Medicine Cleveland Clinic Disclosures Speaker,
Current Vascular and Endovascular Management in Diabetic Vasculopathy
 Current Vascular and Endovascular Management in Diabetic Vasculopathy Yang-Jin Park Associate professor Vascular Surgery, Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Peripheral artery
Current Vascular and Endovascular Management in Diabetic Vasculopathy Yang-Jin Park Associate professor Vascular Surgery, Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Peripheral artery
3-year results of the OLIVE registry:
 3-year results of the OLIVE registry: A prospective multicenter study in patients with critical limb ischemia Osamu Iida, MD Kansai Rosai Hospital Cardiovascular Center Amagasaki, Hyogo, Japan Disclosure
3-year results of the OLIVE registry: A prospective multicenter study in patients with critical limb ischemia Osamu Iida, MD Kansai Rosai Hospital Cardiovascular Center Amagasaki, Hyogo, Japan Disclosure
Practical Point in Holistic Diabetic Foot Care 3 March 2016
 Diabetic Foot Ulcer : Vascular Management Practical Point in Holistic Diabetic Foot Care 3 March 2016 Supapong Arworn, MD Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Department of Surgery, Chiang Mai
Diabetic Foot Ulcer : Vascular Management Practical Point in Holistic Diabetic Foot Care 3 March 2016 Supapong Arworn, MD Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Department of Surgery, Chiang Mai
Practical Point in Diabetic Foot Care 3-4 July 2017
 Diabetic Foot Ulcer : Role of Vascular Surgeon Practical Point in Diabetic Foot Care 3-4 July 2017 Supapong Arworn, MD Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Department of Surgery, Chiang Mai University
Diabetic Foot Ulcer : Role of Vascular Surgeon Practical Point in Diabetic Foot Care 3-4 July 2017 Supapong Arworn, MD Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Department of Surgery, Chiang Mai University
World s Fastest Ankle-Brachial Index Screening Device
 World s Fastest Ankle-Brachial Index Screening Device Accurate and objective Peripheral Arterial Disease diagnosis E S S E N T I A L T O H E A LT H NOTE: Brošura - A4 format na poli A3 What is Peripheral
World s Fastest Ankle-Brachial Index Screening Device Accurate and objective Peripheral Arterial Disease diagnosis E S S E N T I A L T O H E A LT H NOTE: Brošura - A4 format na poli A3 What is Peripheral
UC SF. Disclosures. Vascular Assessment of the Diabetic Foot. What are the best predictors of wound healing? None. Non-Invasive Vascular Studies
 Disclosures Vascular Assessment of the Diabetic Foot What are the best predictors of wound healing? None Shant Vartanian MD Assistant Professor of Vascular Surgery UCSF Vascular Symposium April 20, 2013
Disclosures Vascular Assessment of the Diabetic Foot What are the best predictors of wound healing? None Shant Vartanian MD Assistant Professor of Vascular Surgery UCSF Vascular Symposium April 20, 2013
Peripheral Arterial Disease Management A Practical Guide for Internists. EFIM Vascular Working Group
 2 Peripheral Arterial Disease Management A Practical Guide for Internists EFIM Vascular Working Group 1 Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) is a growing concern among our aging population. More than 27 million
2 Peripheral Arterial Disease Management A Practical Guide for Internists EFIM Vascular Working Group 1 Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) is a growing concern among our aging population. More than 27 million
Usefulness of the transfer function index for diagnosing peripheral arterial disease in patients with arterial calcification
 29 2016; 63: 29-35 A. Zainuer et al. Original Article Usefulness of the transfer function index for diagnosing peripheral arterial disease in patients with arterial calcification Abulimiti Zainuer 1),
29 2016; 63: 29-35 A. Zainuer et al. Original Article Usefulness of the transfer function index for diagnosing peripheral arterial disease in patients with arterial calcification Abulimiti Zainuer 1),
STPH Clinic for Wound Care and Hyperbaric Medicine
 STPH Clinic for Wound Care and Hyperbaric Medicine Ochsner/St. Tammany Partnership John Kessels, MD Medical Director St. Tammany Wound Center Chantal Lorio, DPM Associate Medical Director Ochsner Wound
STPH Clinic for Wound Care and Hyperbaric Medicine Ochsner/St. Tammany Partnership John Kessels, MD Medical Director St. Tammany Wound Center Chantal Lorio, DPM Associate Medical Director Ochsner Wound
PERIPHERAL ARTERIAL occlusive disease
 Dialysis Therapies Peripheral Arterial Occlusive Disease Is More Prevalent in Patients With Hemodialysis: Comparison With the Findings of Multidetector-Row Computed Tomography Koji Okamoto, MD, Machiko
Dialysis Therapies Peripheral Arterial Occlusive Disease Is More Prevalent in Patients With Hemodialysis: Comparison With the Findings of Multidetector-Row Computed Tomography Koji Okamoto, MD, Machiko
Larry Diaz, MD, FSCAI Mehdi H. Shishehbor, DO, FSCAI
 PAD Diagnosis Larry Diaz, MD, FSCAI Metro Health / University of Michigan Health, Wyoming, MI Mehdi H. Shishehbor, DO, FSCAI University Hospitals Harrington Heart & Vascular Institute, Cleveland, OH PAD:
PAD Diagnosis Larry Diaz, MD, FSCAI Metro Health / University of Michigan Health, Wyoming, MI Mehdi H. Shishehbor, DO, FSCAI University Hospitals Harrington Heart & Vascular Institute, Cleveland, OH PAD:
Maximally Invasive Vascular Surgery for the Treatment of Critical Limb Ischemia
 Maximally Invasive Vascular Surgery for the Treatment of Critical Limb Ischemia Traci A. Kimball, MD Department of Surgery Grand Rounds Septemember 13, 2010 Overview Defining Critical Limb Ischemia Epidemiology
Maximally Invasive Vascular Surgery for the Treatment of Critical Limb Ischemia Traci A. Kimball, MD Department of Surgery Grand Rounds Septemember 13, 2010 Overview Defining Critical Limb Ischemia Epidemiology
Measurement of Skin Perfusion Pressure in Hemodialyzed Patients: Association with Toe/Brachial Index
 Measurement of Skin Perfusion Pressure in Hemodialyzed Patients: Association with Toe/Brachial Index Masaru Shimazaki, MD; Takayuki Matsuki, MD; Kazuaki Yamauchi, MD; Michihiro Iwata, MD; Hiroshi Takahashi,
Measurement of Skin Perfusion Pressure in Hemodialyzed Patients: Association with Toe/Brachial Index Masaru Shimazaki, MD; Takayuki Matsuki, MD; Kazuaki Yamauchi, MD; Michihiro Iwata, MD; Hiroshi Takahashi,
World s Fastest Ankle-Brachial Index Screening Device
 World s Fastest Ankle-Brachial Index Screening Device Accurate and objective Peripheral Arterial Disease diagnosis From secondary to primary healthcare with the help of technology. MESI founders identified
World s Fastest Ankle-Brachial Index Screening Device Accurate and objective Peripheral Arterial Disease diagnosis From secondary to primary healthcare with the help of technology. MESI founders identified
Clinical Approach to CLI and Related Diagnostics: What You Need to Know
 Clinical Approach to CLI and Related Diagnostics: What You Need to Know Ido Weinberg, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Massachusetts General Hospital None Disclosures Critical
Clinical Approach to CLI and Related Diagnostics: What You Need to Know Ido Weinberg, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Massachusetts General Hospital None Disclosures Critical
Lower Extremity Arterial Disease
 Lower Extremity Arterial Disease Circulating the Facts About Peripheral Disease Brought to you by the Education Committee of the Society for 1 www.svnnet.org Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) Many people
Lower Extremity Arterial Disease Circulating the Facts About Peripheral Disease Brought to you by the Education Committee of the Society for 1 www.svnnet.org Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) Many people
Peripheral Arterial Disease: Objectives. Disclosure. Definition: Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD)
 Geriatric Grand Rounds Tuesday, April 21, 2009 12:00 noon Dr. Bill Black Auditorium Glenrose Rehabilitation Hospital In keeping with Glenrose Rehabilitation Hospital policy, speakers participating in this
Geriatric Grand Rounds Tuesday, April 21, 2009 12:00 noon Dr. Bill Black Auditorium Glenrose Rehabilitation Hospital In keeping with Glenrose Rehabilitation Hospital policy, speakers participating in this
Berman distal revascularization-interval
 13 487 491 2004 distal revascularization-interval ligation DRIL 75 2003 11 10 20 0 mmhg 35 distal revascularization-interval ligation DRIL 90mmHg 0.56 DRIL 13 487 491 2004 70 1 dialysis access-associated
13 487 491 2004 distal revascularization-interval ligation DRIL 75 2003 11 10 20 0 mmhg 35 distal revascularization-interval ligation DRIL 90mmHg 0.56 DRIL 13 487 491 2004 70 1 dialysis access-associated
Role of ABI in Detecting and Quantifying Peripheral Arterial Disease
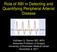 Role of ABI in Detecting and Quantifying Peripheral Arterial Disease Difference in AAA size between US and Surgeon 2 1 0-1 -2-3 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Mean AAA size between US and Surgeon Kathleen G. Raman MD,
Role of ABI in Detecting and Quantifying Peripheral Arterial Disease Difference in AAA size between US and Surgeon 2 1 0-1 -2-3 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Mean AAA size between US and Surgeon Kathleen G. Raman MD,
Peripheral Arterial Disease Extremity
 Peripheral Arterial Disease Lower Extremity 05 Contributor Dr Steven Chong Advisors Dr Ashish Anil Dr Tay Jam Chin Introduction Risk Factors Clinical Presentation Classification History PHYSICAL examination
Peripheral Arterial Disease Lower Extremity 05 Contributor Dr Steven Chong Advisors Dr Ashish Anil Dr Tay Jam Chin Introduction Risk Factors Clinical Presentation Classification History PHYSICAL examination
Peripheral Arterial Disease: the growing role of endovascular management
 Peripheral Arterial Disease: the growing role of endovascular management Poster No.: C-1931 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. M. C. Guedes Pinto, E. Rosado, D. Penha, P. Cabral,
Peripheral Arterial Disease: the growing role of endovascular management Poster No.: C-1931 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. M. C. Guedes Pinto, E. Rosado, D. Penha, P. Cabral,
Case Study: Chris Arden. Peripheral Arterial Disease
 Case Study: Chris Arden Peripheral Arterial Disease Patient Presentation Diane is a 65-year-old retired school teacher She complains of left calf pain when walking 50 metres; the pain goes away after she
Case Study: Chris Arden Peripheral Arterial Disease Patient Presentation Diane is a 65-year-old retired school teacher She complains of left calf pain when walking 50 metres; the pain goes away after she
DON T LET LEG PAIN BECOME A REAL THREAT.
 DON T LET LEG PAIN BECOME A REAL THREAT. These three words have the power to change lives. Between 8 to 10 million Americans are estimated to suffer from poor blood flow to the legs and feet potentially
DON T LET LEG PAIN BECOME A REAL THREAT. These three words have the power to change lives. Between 8 to 10 million Americans are estimated to suffer from poor blood flow to the legs and feet potentially
I have no financial disclosures
 Manpreet Singh MD I have no financial disclosures Exercise Treadmill Bicycle Functional capacity assessment Well validated prognostic value Ischemic assessment ECG changes ST segments Arrhythmias Hemodynamic
Manpreet Singh MD I have no financial disclosures Exercise Treadmill Bicycle Functional capacity assessment Well validated prognostic value Ischemic assessment ECG changes ST segments Arrhythmias Hemodynamic
LIBERTY 360 Study. 15-Jun-2018 Data 1. Olinic Dm, et al. Int Angiol. 2018;37:
 LIBERTY 360 Study LIBERTY is a prospective, observational, multi-center study to evaluate procedural and long-term clinical and economic outcomes of endovascular device interventions in patients with symptomatic
LIBERTY 360 Study LIBERTY is a prospective, observational, multi-center study to evaluate procedural and long-term clinical and economic outcomes of endovascular device interventions in patients with symptomatic
Imaging for Peripheral Vascular Disease
 Imaging for Peripheral Vascular Disease James G. Jollis, MD Director, Rex Hospital Cardiovascular Imaging Imaging for Peripheral Vascular Disease 54 year old male with exertional calf pain in his right
Imaging for Peripheral Vascular Disease James G. Jollis, MD Director, Rex Hospital Cardiovascular Imaging Imaging for Peripheral Vascular Disease 54 year old male with exertional calf pain in his right
USWR 23: Outcome Measure: Non Invasive Arterial Assessment of patients with lower extremity wounds or ulcers for determination of healing potential
 USWR 23: Outcome Measure: Non Invasive Arterial Assessment of patients with lower extremity wounds or ulcers for determination of healing potential MEASURE STEWARD: The US Wound Registry [Note: This measure
USWR 23: Outcome Measure: Non Invasive Arterial Assessment of patients with lower extremity wounds or ulcers for determination of healing potential MEASURE STEWARD: The US Wound Registry [Note: This measure
Novel distal popliteal artery puncture technique in supine position for chronic femoropopliteal arterial occlusion; frontal popliteal puncture
 Novel distal popliteal artery puncture technique in supine position for chronic femoropopliteal arterial occlusion; frontal popliteal puncture Miyazaki Medical Association Hospital Cardiovascular Center
Novel distal popliteal artery puncture technique in supine position for chronic femoropopliteal arterial occlusion; frontal popliteal puncture Miyazaki Medical Association Hospital Cardiovascular Center
Hypothesis: When compared to conventional balloon angioplasty, cryoplasty post-dilation decreases the risk of SFA nses in-stent restenosis
 Cryoplasty or Conventional Balloon Post-dilation of Nitinol Stents For Revascularization of Peripheral Arterial Segments Background: Diabetes mellitus is associated with increased risk of in-stent restenosis
Cryoplasty or Conventional Balloon Post-dilation of Nitinol Stents For Revascularization of Peripheral Arterial Segments Background: Diabetes mellitus is associated with increased risk of in-stent restenosis
Disclosure. Speaker name: Prof. Hesham Aly Sharaf El-Din. I do not have any potential conflict of interest
 Disclosure Speaker name: Prof. Hesham Aly Sharaf El-Din I do not have any potential conflict of interest Introduction 5% of patients with upper limb AVF develop ipsilateral hand ischemia, recently termed
Disclosure Speaker name: Prof. Hesham Aly Sharaf El-Din I do not have any potential conflict of interest Introduction 5% of patients with upper limb AVF develop ipsilateral hand ischemia, recently termed
The relation of 2D perfusion angiography after BTK intervention and wound healing in patient with CLI - Single center prospective study -
 The relation of 2D perfusion angiography after BTK intervention and wound healing in patient with CLI - Single center prospective study - Shinya Sasaki, MD. Saka General Hospital Miyagi, JAPAN Disclosure
The relation of 2D perfusion angiography after BTK intervention and wound healing in patient with CLI - Single center prospective study - Shinya Sasaki, MD. Saka General Hospital Miyagi, JAPAN Disclosure
John E. Campbell, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery and Medicine Department of Vascular Surgery West Virginia University, Charleston Division
 John E. Campbell, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery and Medicine Department of Vascular Surgery West Virginia University, Charleston Division John Campbell, MD For the 12 months preceding this CME activity,
John E. Campbell, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery and Medicine Department of Vascular Surgery West Virginia University, Charleston Division John Campbell, MD For the 12 months preceding this CME activity,
GLOBAL VASCULAR GUIDELINES: A NEW PATHWAY FOR LIMB SALVAGE
 GLOBAL VASCULAR GUIDELINES: A NEW PATHWAY FOR LIMB SALVAGE Michael S. Conte MD Professor and Chief, Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Co-Director, Center for Limb Preservation Co-Director, Heart and Vascular
GLOBAL VASCULAR GUIDELINES: A NEW PATHWAY FOR LIMB SALVAGE Michael S. Conte MD Professor and Chief, Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Co-Director, Center for Limb Preservation Co-Director, Heart and Vascular
Arterial Studies And The Diabetic Foot Patient
 Arterial Studies And The Patient George L. Berdejo, BA, RVT, FSVU gberdejo@wphospital.org Disclosures I have nothing to disclose! Diabetes mellitus continues to grow in global prevalence and to consume
Arterial Studies And The Patient George L. Berdejo, BA, RVT, FSVU gberdejo@wphospital.org Disclosures I have nothing to disclose! Diabetes mellitus continues to grow in global prevalence and to consume
When to screen for PAD? Prof. Dr.Tine De Backer Prof. Dr. Jean-Claude Wautrecht
 When to screen for PAD? Prof. Dr.Tine De Backer Prof. Dr. Jean-Claude Wautrecht How do we define asymptomatic PAD? A. ABI < 1 B. ABI < 0.9 C. ABI < 0.8 D. ABI > 1 How do we define asymptomatic PAD? A.
When to screen for PAD? Prof. Dr.Tine De Backer Prof. Dr. Jean-Claude Wautrecht How do we define asymptomatic PAD? A. ABI < 1 B. ABI < 0.9 C. ABI < 0.8 D. ABI > 1 How do we define asymptomatic PAD? A.
Wifi classification does not predict limb amputation risk in dialysis patients following critical limb ischemia revascularization
 Wifi classification does not predict limb amputation risk in dialysis patients following critical limb ischemia revascularization A Sonetto, M Abualhin, M Gargiulo, GL Faggioli, A Stella Disclosure Speaker
Wifi classification does not predict limb amputation risk in dialysis patients following critical limb ischemia revascularization A Sonetto, M Abualhin, M Gargiulo, GL Faggioli, A Stella Disclosure Speaker
Skin Perfusion Pressure (SPP) Assessments with the moorvms-vasc Application note #105
 innovation in microvascular assessment Skin Perfusion Pressure (SPP) Assessments with the moorvms-vasc Application note #105 Application Skin Perfusion Pressure (SPP) is the pressure required for restoring
innovation in microvascular assessment Skin Perfusion Pressure (SPP) Assessments with the moorvms-vasc Application note #105 Application Skin Perfusion Pressure (SPP) is the pressure required for restoring
CRITICAL LIMB ISCHEMIA UNITED STATES EPIDEMIOLOGY TABLE OF CONTENTS
 CRITICAL LIMB ISCHEMIA UNITED STATES EPIDEMIOLOGY TABLE OF CONTENTS CRITICAL LIMB ISCHEMIA... 1 CONCLUSION... 9 U.S. CRITICAL LIMB ISCHEMIA PREVALENCE... 9 MARKET OPPORTUNITY ENDOVASCULAR... 9 MARKET OPPORTUNITY
CRITICAL LIMB ISCHEMIA UNITED STATES EPIDEMIOLOGY TABLE OF CONTENTS CRITICAL LIMB ISCHEMIA... 1 CONCLUSION... 9 U.S. CRITICAL LIMB ISCHEMIA PREVALENCE... 9 MARKET OPPORTUNITY ENDOVASCULAR... 9 MARKET OPPORTUNITY
Making the difference with Live Image Guidance
 Live Image Guidance 2D Perfusion Making the difference with Live Image Guidance In Peripheral Arterial Disease Real-time results, instant assessment Severe foot complications the result of hampered blood
Live Image Guidance 2D Perfusion Making the difference with Live Image Guidance In Peripheral Arterial Disease Real-time results, instant assessment Severe foot complications the result of hampered blood
A study on diabetic foot and its association with peripheral artery disease
 International Surgery Journal Muthiah A et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Apr;4(4):1217-1221 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20170937
International Surgery Journal Muthiah A et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Apr;4(4):1217-1221 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20170937
Dapagliflozin and Outcomes in Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease: Insights from DECLARE-TIMI 58
 Dapagliflozin and Outcomes in Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease: Insights from DECLARE-TIMI 58 Marc P. Bonaca MD MPH for the DECLARE TIMI 58 Investigators American College of Cardiology March 2019
Dapagliflozin and Outcomes in Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease: Insights from DECLARE-TIMI 58 Marc P. Bonaca MD MPH for the DECLARE TIMI 58 Investigators American College of Cardiology March 2019
ANTIHYPERTENSIVE DRUG THERAPY IN CONSIDERATION OF CIRCADIAN BLOOD PRESSURE VARIATION*
 Progress in Clinical Medicine 1 ANTIHYPERTENSIVE DRUG THERAPY IN CONSIDERATION OF CIRCADIAN BLOOD PRESSURE VARIATION* Keishi ABE** Asian Med. J. 44(2): 83 90, 2001 Abstract: J-MUBA was a large-scale clinical
Progress in Clinical Medicine 1 ANTIHYPERTENSIVE DRUG THERAPY IN CONSIDERATION OF CIRCADIAN BLOOD PRESSURE VARIATION* Keishi ABE** Asian Med. J. 44(2): 83 90, 2001 Abstract: J-MUBA was a large-scale clinical
Is estimation of laser Doppler skin perfusion pressure appropriate during hemodialysis enforcement?
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Cardiovascular Research Volume 6 Number 2 Is estimation of laser Doppler skin perfusion pressure appropriate during hemodialysis enforcement? M Shimazaki Citation M Shimazaki.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Cardiovascular Research Volume 6 Number 2 Is estimation of laser Doppler skin perfusion pressure appropriate during hemodialysis enforcement? M Shimazaki Citation M Shimazaki.
PATIENT SPECIFIC STRATEGIES IN CRITICAL LIMB ISCHEMIA. Dr. Manar Trab Consultant Vascular Surgeon European Vascular Clinic DMCC Dubai, UAE
 PATIENT SPECIFIC STRATEGIES IN CRITICAL LIMB ISCHEMIA Dr. Manar Trab Consultant Vascular Surgeon European Vascular Clinic DMCC Dubai, UAE Disclosure Speaker name: DR. Manar Trab I have the following potential
PATIENT SPECIFIC STRATEGIES IN CRITICAL LIMB ISCHEMIA Dr. Manar Trab Consultant Vascular Surgeon European Vascular Clinic DMCC Dubai, UAE Disclosure Speaker name: DR. Manar Trab I have the following potential
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article A Study to Assess the Effectiveness of Buerger Allen Exercise on Foot Perfusion among Patients
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article A Study to Assess the Effectiveness of Buerger Allen Exercise on Foot Perfusion among Patients
Is there an association between atherosclerosis and chronic venous disease?
 Is there an association between atherosclerosis and chronic venous disease? Karel Roztocil, IKEM, Praha Hungarian Society of Angiology and Vascular Surgery Congress, Szombathely 2017 Disclosure Nothing
Is there an association between atherosclerosis and chronic venous disease? Karel Roztocil, IKEM, Praha Hungarian Society of Angiology and Vascular Surgery Congress, Szombathely 2017 Disclosure Nothing
Limb Salvage in Diabetic Ischemic Foot. Kritaya Kritayakirana, MD, FACS Assistant Professor Chulalongkorn University April 30, 2017
 Limb Salvage in Diabetic Ischemic Foot Kritaya Kritayakirana, MD, FACS Assistant Professor Chulalongkorn University April 30, 2017 Case Male 67 years old Underlying DM, HTN, TVD Present with gangrene
Limb Salvage in Diabetic Ischemic Foot Kritaya Kritayakirana, MD, FACS Assistant Professor Chulalongkorn University April 30, 2017 Case Male 67 years old Underlying DM, HTN, TVD Present with gangrene
Detection of peripheral vascular disease in patients with type-2 DM using Ankle Brachial Index (ABI)
 Original article: Detection of peripheral vascular disease in patients with type-2 DM using Ankle Brachial Index (ABI) 1DR Anu N Gaikwad, 2 Dr Vikrant V Rasal, 3 Dr S A Kanitkar, 4 Dr Meenakshi Kalyan
Original article: Detection of peripheral vascular disease in patients with type-2 DM using Ankle Brachial Index (ABI) 1DR Anu N Gaikwad, 2 Dr Vikrant V Rasal, 3 Dr S A Kanitkar, 4 Dr Meenakshi Kalyan
The clinical trial information provided in this public disclosure synopsis is supplied for informational purposes only.
 The clinical trial information provided in this public disclosure synopsis is supplied for informational purposes only. Please note that the results reported in any single trial may not reflect the overall
The clinical trial information provided in this public disclosure synopsis is supplied for informational purposes only. Please note that the results reported in any single trial may not reflect the overall
Listing Form: Heart or Cardiovascular Impairments. Medical Provider:
 Listing Form: Heart or Cardiovascular Impairments Medical Provider: Printed Name Signature Patient Name: Patient DOB: Patient SS#: Date: Dear Provider: Please indicate whether your patient s condition
Listing Form: Heart or Cardiovascular Impairments Medical Provider: Printed Name Signature Patient Name: Patient DOB: Patient SS#: Date: Dear Provider: Please indicate whether your patient s condition
The results of EVT for Chronic Aortic Occlusion - a multicenter retrospective study - Taku Kato, MD Rakuwakai Otowa Hospital, Kyoto, Japan
 The results of EVT for Chronic Aortic Occlusion - a multicenter retrospective study - Taku Kato, MD Rakuwakai Otowa Hospital, Kyoto, Japan COI disclosure Disclosure Speaker name: Taku Kato... I have the
The results of EVT for Chronic Aortic Occlusion - a multicenter retrospective study - Taku Kato, MD Rakuwakai Otowa Hospital, Kyoto, Japan COI disclosure Disclosure Speaker name: Taku Kato... I have the
Index. cardiology.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ABI. See Ankle-brachial index (ABI). Afterload, deconstructing of, in ventricular vascular interaction in heart failure, 449 Air plethysmography
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ABI. See Ankle-brachial index (ABI). Afterload, deconstructing of, in ventricular vascular interaction in heart failure, 449 Air plethysmography
Global Vascular Guideline on the Management of Chronic Limb Threatening Ischemia -a new foundation for evidence-based care
 Global Vascular Guideline on the Management of Chronic Limb Threatening Ischemia -a new foundation for evidence-based care Michael S. Conte MD Professor and Chief, Division of Vascular and Endovascular
Global Vascular Guideline on the Management of Chronic Limb Threatening Ischemia -a new foundation for evidence-based care Michael S. Conte MD Professor and Chief, Division of Vascular and Endovascular
Nephrology Unit- CHU Liège- Ulg- Belgium
 Are the complications of arteriovenous fistulas associated with an abnormal Ankle-Brachial Index in Hemodialysis? A 4y study P. Xhignesse, A. Saint-Remy, B. Dubois, JC. Philips, JM. Krzesinski Nephrology
Are the complications of arteriovenous fistulas associated with an abnormal Ankle-Brachial Index in Hemodialysis? A 4y study P. Xhignesse, A. Saint-Remy, B. Dubois, JC. Philips, JM. Krzesinski Nephrology
Introduction. Risk factors of PVD 5/8/2017
 PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND CLINICAL FEATURES OF PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASE Dr. Muhamad Zabidi Ahmad Radiologist and Section Chief, Radiology, Oncology and Nuclear Medicine Section, Advanced Medical and Dental
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND CLINICAL FEATURES OF PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASE Dr. Muhamad Zabidi Ahmad Radiologist and Section Chief, Radiology, Oncology and Nuclear Medicine Section, Advanced Medical and Dental
Long-Term Results of Treatment for Critical Limb Ischemia
 2015 Annals of Vascular Diseases doi:10.3400/avd.oa.15-00074 Original Article Long-Term Results of Treatment for Critical Limb Ischemia Takuya Miyahara, MD, PhD, 1 Masamitsu Suhara, MD, 1 Yoko Nemoto,
2015 Annals of Vascular Diseases doi:10.3400/avd.oa.15-00074 Original Article Long-Term Results of Treatment for Critical Limb Ischemia Takuya Miyahara, MD, PhD, 1 Masamitsu Suhara, MD, 1 Yoko Nemoto,
LD TECHNOLOGY PRODUCT CATALOG
 LD TECHNOLOGY M A K I N G A D I F F E R E N C E EARLY DETECTION OF DIABETES COMPLICATIONS AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM AND ARTERY ASSESSEMENT BLOOD PRESSURE AND ARTERIAL STIFFNESS ANALYSIS Monitoring and Treatment
LD TECHNOLOGY M A K I N G A D I F F E R E N C E EARLY DETECTION OF DIABETES COMPLICATIONS AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM AND ARTERY ASSESSEMENT BLOOD PRESSURE AND ARTERIAL STIFFNESS ANALYSIS Monitoring and Treatment
DETECT-PAD Computerized and patient specific model to determine pressure gradients in borderline iliac artery stenosis with MRA/ CTA
 DETECT-PAD Computerized and patient specific model to determine pressure gradients in borderline iliac artery stenosis with MRA/ CTA Jean-Paul P.M. de Vries Head Department of Surgery University Medical
DETECT-PAD Computerized and patient specific model to determine pressure gradients in borderline iliac artery stenosis with MRA/ CTA Jean-Paul P.M. de Vries Head Department of Surgery University Medical
ESM 1. Survey questionnaire sent to French GPs. Correct answers are in bold. Part 2: Clinical cases: (Good answer are in bold) Clinical Case 1:
 ESM 1. Survey questionnaire sent to French GPs. Correct answers are in bold. Part 2: Clinical cases: (Good answer are in bold) Clinical Case 1: to your office at 2 pm for a feeling of weakness and numbness
ESM 1. Survey questionnaire sent to French GPs. Correct answers are in bold. Part 2: Clinical cases: (Good answer are in bold) Clinical Case 1: to your office at 2 pm for a feeling of weakness and numbness
V.A. is a 62-year-old male who presents in referral
 , LLC an HMP Communications Holdings Company Clinical Case Update Latest Trends in Critical Limb Ischemia Imaging Amit Srivastava, MD, FACC, FABVM Interventional Cardiologist Bay Area Heart Center St.
, LLC an HMP Communications Holdings Company Clinical Case Update Latest Trends in Critical Limb Ischemia Imaging Amit Srivastava, MD, FACC, FABVM Interventional Cardiologist Bay Area Heart Center St.
The distinguishing traits of CLI: what makes it so different? Roberto Ferraresi Cardiovascular CathLab
 The distinguishing traits of CLI: what makes it so different? Roberto Ferraresi Cardiovascular CathLab Potential conflicts of interest Roberto Ferraresi, MD I have the following potential conflicts of
The distinguishing traits of CLI: what makes it so different? Roberto Ferraresi Cardiovascular CathLab Potential conflicts of interest Roberto Ferraresi, MD I have the following potential conflicts of
What s New in the Management of Peripheral Arterial Disease
 What s New in the Management of Peripheral Arterial Disease Sibu P. Saha, MD, MBA Professor of Surgery Chairman, Directors Council Gill Heart Institute University of Kentucky Lexington, KY Disclosure My
What s New in the Management of Peripheral Arterial Disease Sibu P. Saha, MD, MBA Professor of Surgery Chairman, Directors Council Gill Heart Institute University of Kentucky Lexington, KY Disclosure My
SAVE LIMBS SAVE LIVES!
 SAVE LIMBS SAVE LIVES! PAD Awareness: The Key to Limb Preservation By Frank J Tursi, D.P.M., F.A.C.F.A.S. Epidemiology Over 12 million people are afflicted with PAD 11 Million of these-dm 4 Million DFU
SAVE LIMBS SAVE LIVES! PAD Awareness: The Key to Limb Preservation By Frank J Tursi, D.P.M., F.A.C.F.A.S. Epidemiology Over 12 million people are afflicted with PAD 11 Million of these-dm 4 Million DFU
Peripheral Arterial Occlusive Disease- The Challenge in patients with diabetes
 Peripheral Arterial Occlusive Disease- The Challenge in patients with diabetes Ashok Handa Reader in Surgery and Consultant Surgeon Nuffield Department of Surgery University of Oxford Introduction Vascular
Peripheral Arterial Occlusive Disease- The Challenge in patients with diabetes Ashok Handa Reader in Surgery and Consultant Surgeon Nuffield Department of Surgery University of Oxford Introduction Vascular
Improved Assessment of Aortic Calcification in Japanese Patients Undergoing Maintenance Hemodialysis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Improved Assessment of Aortic Calcification in Japanese Patients Undergoing Maintenance Hemodialysis Masaki Ohya 1, Haruhisa Otani 2,KeigoKimura 3, Yasushi Saika 4, Ryoichi Fujii 4, Susumu
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Improved Assessment of Aortic Calcification in Japanese Patients Undergoing Maintenance Hemodialysis Masaki Ohya 1, Haruhisa Otani 2,KeigoKimura 3, Yasushi Saika 4, Ryoichi Fujii 4, Susumu
Introduction to Peripheral Arterial Disease. Stacey Clegg, MD Interventional Cardiology August
 Introduction to Peripheral Arterial Disease Stacey Clegg, MD Interventional Cardiology August 20 2014 Outline (and for the ABIM board exam * ** ***) Prevalence* Definitions Lower Extremity: Aorta*** Claudication***
Introduction to Peripheral Arterial Disease Stacey Clegg, MD Interventional Cardiology August 20 2014 Outline (and for the ABIM board exam * ** ***) Prevalence* Definitions Lower Extremity: Aorta*** Claudication***
Synchronous TBI and ABI measurement Scheme for Diabetes Patients Synchronous Sphygmomanometer of Four Limbs
 Synchronous Sphygmomanometer of Four Limbs Sung-Tsun Shih 1, Kuan-Yu Chang 2 Department of Electronic Engineering, Cheng Shiu University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan. 2 Mackay Memorial Hospital Taitung Branch, Taitung,
Synchronous Sphygmomanometer of Four Limbs Sung-Tsun Shih 1, Kuan-Yu Chang 2 Department of Electronic Engineering, Cheng Shiu University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan. 2 Mackay Memorial Hospital Taitung Branch, Taitung,
John E. Campbell, MD. Assistant Professor of Surgery and Medicine Department of Vascular Surgery West Virginia University, Charleston Division
 John E. Campbell, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery and Medicine Department of Vascular Surgery West Virginia University, Charleston Division John Campbell, MD For the 12 months preceding this CME activity,
John E. Campbell, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery and Medicine Department of Vascular Surgery West Virginia University, Charleston Division John Campbell, MD For the 12 months preceding this CME activity,
Olive registry: 3-years outcome of BTK intervention in Japan. Osamu Iida, MD Kansai Rosai Hospital Amagasaki, Hyogo, Japan
 Olive registry: 3-years outcome of BTK intervention in Japan Osamu Iida, MD Kansai Rosai Hospital Amagasaki, Hyogo, Japan What is the optimal treatment for the patient with critical limb ischemia (CLI)?
Olive registry: 3-years outcome of BTK intervention in Japan Osamu Iida, MD Kansai Rosai Hospital Amagasaki, Hyogo, Japan What is the optimal treatment for the patient with critical limb ischemia (CLI)?
Will it heal? How to assess the probability of wound healing
 Will it heal? How to assess the probability of wound healing Richard F. Neville, M.D. Professor of Surgery Chief, Division of Vascular Surgery George Washington University Limb center case 69 yr old male
Will it heal? How to assess the probability of wound healing Richard F. Neville, M.D. Professor of Surgery Chief, Division of Vascular Surgery George Washington University Limb center case 69 yr old male
Relationship between Arterial Stiffness and the Risk of Coronary Artery Disease in Subjects with and without Metabolic Syndrome
 243 Original Article Hypertens Res Vol.30 (2007) No.3 p.243-247 Relationship between Arterial Stiffness and the Risk of Coronary Artery Disease in Subjects with and without Metabolic Syndrome Yutaka KOJI
243 Original Article Hypertens Res Vol.30 (2007) No.3 p.243-247 Relationship between Arterial Stiffness and the Risk of Coronary Artery Disease in Subjects with and without Metabolic Syndrome Yutaka KOJI
Clinical Features and Subtypes of Ischemic Stroke Associated with Peripheral Arterial Disease
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC NEUROLOGY Research Article Clinical Features and Subtypes of Ischemic Stroke Associated with Peripheral Arterial Disease Jin Ok Kim, Hyung-IL Kim, Jae Guk Kim, Hanna Choi, Sung-Yeon
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC NEUROLOGY Research Article Clinical Features and Subtypes of Ischemic Stroke Associated with Peripheral Arterial Disease Jin Ok Kim, Hyung-IL Kim, Jae Guk Kim, Hanna Choi, Sung-Yeon
My Diabetic Patient Has No Pulses; What Should I Do?
 Emily Malgor, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery University of Oklahoma, Oklahoma City My Diabetic Patient Has No Pulses; What Should I Do? There are no disclosures. Background Diabetes affects 387 million
Emily Malgor, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery University of Oklahoma, Oklahoma City My Diabetic Patient Has No Pulses; What Should I Do? There are no disclosures. Background Diabetes affects 387 million
Garland Green, MD Interventional Cardiologist. Impact of PAD: Prevalence, Risk Factors, Testing, and Medical Management
 Garland Green, MD Interventional Cardiologist Impact of PAD: Prevalence, Risk Factors, Testing, and Medical Management Peripheral Arterial Disease Affects over 8 million Americans Affects 12% of the general
Garland Green, MD Interventional Cardiologist Impact of PAD: Prevalence, Risk Factors, Testing, and Medical Management Peripheral Arterial Disease Affects over 8 million Americans Affects 12% of the general
LD TECHNOLOGY PRODUCT CATALOG
 LD TECHNOLOGY M A K I N G A D I F F E R E N C E EARLY DETECTION OF DIABETES COMPLICATIONS AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM AND VASCULAR FUNCTION ASSESSMENTS BLOOD PRESSURE AND ARTERIAL STIFFNESS ANALYSIS Monitoring
LD TECHNOLOGY M A K I N G A D I F F E R E N C E EARLY DETECTION OF DIABETES COMPLICATIONS AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM AND VASCULAR FUNCTION ASSESSMENTS BLOOD PRESSURE AND ARTERIAL STIFFNESS ANALYSIS Monitoring
Experiment HC-1: Blood Pressure, Peripheral Circulation, and Body Position
 Experiment HC-1: Blood Pressure, Peripheral Circulation, and Body Position Exercise 1: Blood Pressures from the Left Arm Aim: To determine the systolic and diastolic blood pressures in a reclining subject,
Experiment HC-1: Blood Pressure, Peripheral Circulation, and Body Position Exercise 1: Blood Pressures from the Left Arm Aim: To determine the systolic and diastolic blood pressures in a reclining subject,
Cardiovascular Diseases in CKD
 1 Cardiovascular Diseases in CKD Hung-Chun Chen, MD, PhD. Kaohsiung Medical University Taiwan Society of Nephrology 1 2 High Prevalence of CVD in CKD & ESRD Foley RN et al, AJKD 1998; 32(suppl 3):S112-9
1 Cardiovascular Diseases in CKD Hung-Chun Chen, MD, PhD. Kaohsiung Medical University Taiwan Society of Nephrology 1 2 High Prevalence of CVD in CKD & ESRD Foley RN et al, AJKD 1998; 32(suppl 3):S112-9
Endovascular treatment (EVT) has markedly advanced,
 Ann Vasc Dis Vol. 6, No. 3; 2013; pp 573 577 Online August 12, 2013 2013 Annals of Vascular Diseases doi:10.3400/avd.oa.13-00055 Original Article A Review of Surgically Treated Patients with Obstruction
Ann Vasc Dis Vol. 6, No. 3; 2013; pp 573 577 Online August 12, 2013 2013 Annals of Vascular Diseases doi:10.3400/avd.oa.13-00055 Original Article A Review of Surgically Treated Patients with Obstruction
Does Patient-Prosthesis Mismatch Affect Long-term Results after Mitral Valve Replacement?
 Original Article Does Patient-Prosthesis Mismatch Affect Long-term Results after Mitral Valve Replacement? Hiroaki Sakamoto, MD, PhD, and Yasunori Watanabe, MD, PhD Background: Recently, some articles
Original Article Does Patient-Prosthesis Mismatch Affect Long-term Results after Mitral Valve Replacement? Hiroaki Sakamoto, MD, PhD, and Yasunori Watanabe, MD, PhD Background: Recently, some articles
ASSESSING THE VASCULAR STATUS OF THE FEET FOR PATIENTS WITH DIABETES
 ASSESSING THE VASCULAR STATUS OF THE FEET FOR PATIENTS WITH DIABETES Caroline McIntosh is Senior Lecturer in Podiatry, University of Huddersfield, Yorkshire A reduced blood supply to the lower limb, due
ASSESSING THE VASCULAR STATUS OF THE FEET FOR PATIENTS WITH DIABETES Caroline McIntosh is Senior Lecturer in Podiatry, University of Huddersfield, Yorkshire A reduced blood supply to the lower limb, due
Nomogram of the Relation of Brachial-Ankle Pulse Wave Velocity with Blood Pressure
 801 Original Article Nomogram of the Relation of Brachial-Ankle Pulse Wave Velocity with Blood Pressure Akira YAMASHINA, Hirofumi TOMIYAMA, Tomio ARAI, Yutaka KOJI, Minoru YAMBE, Hiroaki MOTOBE, Zydem
801 Original Article Nomogram of the Relation of Brachial-Ankle Pulse Wave Velocity with Blood Pressure Akira YAMASHINA, Hirofumi TOMIYAMA, Tomio ARAI, Yutaka KOJI, Minoru YAMBE, Hiroaki MOTOBE, Zydem
Angiosome concept myth or truth? Does it make a real difference in real world cases?
 Angiosome concept myth or truth? Does it make a real difference in real world cases? Osamu Iida, MD, FACC Kansai Rosai Hospital Amagasaki, Hyogo, Japan Disclosure Speaker name:... I have the following
Angiosome concept myth or truth? Does it make a real difference in real world cases? Osamu Iida, MD, FACC Kansai Rosai Hospital Amagasaki, Hyogo, Japan Disclosure Speaker name:... I have the following
ARTERIAL STIFFNESS ASSESSMENT COMMENTS:
 ARTERIAL STIFFNESS ASSESSMENT 10% Low small artery stiffness risk. However, we detect mild vasoconstriction in small artery. No large arterial stiffness has been detected. High Blood Pressure & Arterial
ARTERIAL STIFFNESS ASSESSMENT 10% Low small artery stiffness risk. However, we detect mild vasoconstriction in small artery. No large arterial stiffness has been detected. High Blood Pressure & Arterial
Lower Extremity Peripheral Arterial Disease: Less is Sometimes More. Spence M Taylor, M.D.
 Lower Extremity Peripheral Arterial Disease: Less is Sometimes More Spence M Taylor, M.D. President, Greenville Health System Clinical University Senior Associate Dean for Academic Affairs and Diversity
Lower Extremity Peripheral Arterial Disease: Less is Sometimes More Spence M Taylor, M.D. President, Greenville Health System Clinical University Senior Associate Dean for Academic Affairs and Diversity
Clinical and morphological features of patients who underwent endovascular interventions for lower extremity arterial occlusive diseases
 Original paper Clinical and morphological features of patients who underwent endovascular interventions for lower extremity arterial occlusive diseases Sakir Arslan, Isa Oner Yuksel, Erkan Koklu, Goksel
Original paper Clinical and morphological features of patients who underwent endovascular interventions for lower extremity arterial occlusive diseases Sakir Arslan, Isa Oner Yuksel, Erkan Koklu, Goksel
2.0 Synopsis. ABT-358/Paricalcitol M Clinical Study Report R&D/09/1255. (For National Authority Use Only) to Part of Dossier: Volume:
 2.0 Synopsis Title of Study: Late Phase II Study of Paricalcitol Injection Dose-response study of paricalcitol injection in chronic kidney disease subjects receiving hemodialysis with secondary hyperparathyroidism
2.0 Synopsis Title of Study: Late Phase II Study of Paricalcitol Injection Dose-response study of paricalcitol injection in chronic kidney disease subjects receiving hemodialysis with secondary hyperparathyroidism
Abstract. Key words: peripheral artery disease, lower limb, endovascular therapy, Iran
 The evaluation of the success rate, complications and midterm follow up results of patients with peripheral arterial disease of lower limb treated using endovascular therapy: A single center study Mohammad
The evaluation of the success rate, complications and midterm follow up results of patients with peripheral arterial disease of lower limb treated using endovascular therapy: A single center study Mohammad
A Comparative Study of Health Checkup Results between Early and Late Elderly
 Original Article A Comparative Study of Health Checkup Results between Early and Late Elderly Keito Torikai, MD, PhD 1), Nobuyoshi Narita, MD, PhD 1), Takahide Matsuda, MD, PhD 1), Yuko Tohyo, MD, PhD
Original Article A Comparative Study of Health Checkup Results between Early and Late Elderly Keito Torikai, MD, PhD 1), Nobuyoshi Narita, MD, PhD 1), Takahide Matsuda, MD, PhD 1), Yuko Tohyo, MD, PhD
iworx Sample Lab Experiment HC-5: Body Position, Exercise, and Cardiac Output
 Experiment HC-5: Body Position, Exercise, and Cardiac Output Exercise 1: Cardiac Output While Reclining Aim: To determine the cardiac output of a subject through the measurement of blood pressures and
Experiment HC-5: Body Position, Exercise, and Cardiac Output Exercise 1: Cardiac Output While Reclining Aim: To determine the cardiac output of a subject through the measurement of blood pressures and
Diagnosis and Endovascular Treatment of Critical Limb Ischemia: What You Need to Know S. Jay Mathews, MD, MS, FACC
 Diagnosis and Endovascular Treatment of Critical Limb Ischemia: What You Need to Know S. Jay Mathews, MD, MS, FACC Interventional Cardiologist/Endovascular Specialist Bradenton Cardiology Center Bradenton,
Diagnosis and Endovascular Treatment of Critical Limb Ischemia: What You Need to Know S. Jay Mathews, MD, MS, FACC Interventional Cardiologist/Endovascular Specialist Bradenton Cardiology Center Bradenton,
Nurse and Technician Forum Part II Critical Limb Ischemia: Optimal care, an interdisciplinary challenge
 L E I P Z I G I N T E R V E N T I O N A L C O U R S E 2017 Nurse and Technician Forum Part II Critical Limb Ischemia: Optimal care, an interdisciplinary challenge Markus Haumer Landesklinikum Baden-Mödling
L E I P Z I G I N T E R V E N T I O N A L C O U R S E 2017 Nurse and Technician Forum Part II Critical Limb Ischemia: Optimal care, an interdisciplinary challenge Markus Haumer Landesklinikum Baden-Mödling
Endovascular Should Be Considered First Line Therapy
 Revascularization of Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia Endovascular Should Be Considered First Line Therapy Michael Conte David Dawson David L. Dawson, MD Revised Presentation Title A Selective Approach
Revascularization of Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia Endovascular Should Be Considered First Line Therapy Michael Conte David Dawson David L. Dawson, MD Revised Presentation Title A Selective Approach
The incidence of peripheral artery disease (PAD)
 Pharmacologic Options for Treating Restenosis The role of cilostazol in the treatment of patients with infrainguinal lesions. By Osamu Iida, MD, and Yoshimitsu Soga, MD The incidence of peripheral artery
Pharmacologic Options for Treating Restenosis The role of cilostazol in the treatment of patients with infrainguinal lesions. By Osamu Iida, MD, and Yoshimitsu Soga, MD The incidence of peripheral artery
Pedal Bypass With Deep Venous Arterialization:
 Pedal Bypass With Deep Venous Arterialization: Long Term Result For Critical Limb Ischemia With Unreconstructable Distal Arteries Pramook Mutirangura Professor of Vascular Surgery Faculty of Medicine Siriraj
Pedal Bypass With Deep Venous Arterialization: Long Term Result For Critical Limb Ischemia With Unreconstructable Distal Arteries Pramook Mutirangura Professor of Vascular Surgery Faculty of Medicine Siriraj
