In the US: More than 1000 cases of HF exposure are reported annually. Actual incidence rate is unknown.
|
|
|
- Erick Chambers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Hydrofluoric Acid Burns Last Updated: May 7, 2001 Synonyms and related keywords: HF acid Author: Garry Wilkes, MD, Director of Emergency Medicine, Clinical Senior Lecturer, University of Queensland, Department of Emergency Medicine, Bunbury Regional Hospital Editor(s): Edward A Michelson, MD, Program Director, Associate Professor, Department of Emergency Medicine, Northwestern University Medical Center; John T VanDeVoort, PharmD, DABAT, Manager, Clinical Assistant Professor, Pharmacy Department, Regions Hospital; Richard Sinert, DO, Associate Professor of Emergency Medicine, Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine, State University of New York College of Medicine; Consulting Staff, Department of Emergency Medicine, Kings County Hospital Center; John Halamka, MD, Chief Information Officer, CareGroup Healthcare System, Assistant Professor of Medicine, Department of Emergency Medicine, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center; Assistant Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School; and Raymond J Roberge, MD, MPH, FAAEM, FACMT, Research Director, Department of Emergency Medicine, Ohio Valley Medical Center; Clinical Associate Professor, Department of Emergency Medicine, University of Pittsburgh Introduction Background: Hydrofluoric (HF) acid, one of the strongest inorganic acids, is used mainly for industrial purposes (eg, glass etching, metal cleaning, electronics manufacturing). HF acid also may be found in home rust removers. Exposure usually is accidental and often is due to inadequate use of protective measures. HF acid burns are a unique clinical entity. Dilute solutions deeply penetrate before dissociating, thus causing delayed injury and symptoms. Burns to the fingers and nail beds may leave the overlying nails intact. Severe burns occur after exposure of concentrated (ie, 50% or stronger solution) HF acid to 1% or more body surface area (BSA), exposure to HF acid of any concentration to 5% or more BSA, or inhalation of HF acid fumes from a 60% or stronger solution. The vast majority of cases involve only small areas of exposure, usually on the digits. Pathophysiology: The 2 mechanisms that cause tissue damage are corrosive burn from the free hydrogen ions and chemical burn from tissue penetration of the fluoride ions. Fluoride ions penetrate and form insoluble salts with calcium and magnesium. Soluble salts also are formed with other cations but dissociate rapidly. Consequently, fluoride ions release, and further tissue destruction occurs. Frequency: In the US: More than 1000 cases of HF exposure are reported annually. Actual incidence rate is unknown. Mortality/Morbidity: Local effects include tissue destruction and necrosis. Burns may involve underlying bone. Systemic fluoride ion poisoning from severe burns is associated with hypocalcemia, hyperkalemia, hypomagnesemia, and sudden death. Deaths have been reported from concentrated acid burns to as little as 2.5% BSA. Sex: Males are affected more commonly, which reflects occupational patterns. Age: The majority of exposures occur in adults. From: [5/10/ :53:27 AM] Page 1 of 9
2 Clinical History: Time of exposure to onset of symptoms is related to the concentration of the HF acid. - Solutions of 14.5% immediately produce symptoms. - Solutions of 12% may take up to an hour to produce symptoms. - Solutions of less than 7% may take several hours before onset of symptoms, resulting in delayed presentation, deeper penetration of the undissociated HF acid, and a more severe burn. - Concentrated solutions cause immediate pain and produce surface burns similar to those produced by other common acids (eg, erythema, blistering, necrosis). - Pain typically is described as deep, burning, or throbbing. - Pain often is disproportionate to apparent skin involvement. Obtain history of potential exposure to cleaning solutions within the last 24 hours, to include the following: - Duration of exposure - Concentration of acid - Use of protective measures - Other agents in the solution - Symptoms of hypocalcemia - Tetany - Chvostek sign - Trousseau sign - Cardiac arrhythmias Additionally, obtain history of medications and intercurrent illness that predispose patient to hypocalcemia or hypomagnesemia. Physical: Weaker solutions penetrate before dissociating. Surface involvement in these cases is minimal and may be absent. Three categories of appearance include the following: - A white burn mark and/or erythema and pain - A white burn mark and/or erythema and pain, plus edema and blistering - Ocular burns, which present with severe pain Patients with inhalation burns may develop acute pulmonary edema. From: [5/10/ :53:27 AM] Page 2 of 9
3 Differentials See: Burns, Chemical See: Burns, Ocular Workup Lab Studies: Electrolytes - Severe disturbances can occur, especially the following: - Hypocalcemia - Hypomagnesemia - Hyperkalemia Imaging Studies: Radiographs - Obtain chest x-ray (CXR) if pulmonary edema is suspected. - If burns to the fingers exist, perform digital x-rays to evaluate bone integrity. Other Tests: Electrocardiogram - Cardiac monitoring is necessary if burn is significant. - Arrhythmias are a primary cause of death. - Monitor for QT prolongation from hypocalcemia or signs of hyperkalemia. From: [5/10/ :53:27 AM] Page 3 of 9
4 Treatment Prehospital Care: Treatment for HF acid burns includes basic life support and appropriate decontamination, followed by neutralization of the acid by use of calcium gluconate. If exposure occurs at an industrial site, obtain and transport any available treatment literature. Assess and manage acute life threatening conditions in the usual manner. Emergency Medical Services (EMS) personnel should use gloves, masks, and gowns, if necessary. Remove soiled clothing. Initially decontaminate by irrigation with copious amounts of water. Ice packs on the affected area may alleviate symptoms by retarding diffusion of the ion. If calcium gluconate gel is available, apply liberally to the affected area. For digital burns, if calcium gluconate gel is not available, the fingers may be soaked in magnesium hydroxide containing antacid preparations (eg, Mylanta) en route to a medical facility. Treat inhalation injuries with oxygen and 2.5% calcium gluconate nebulizer. Transport the patient to the nearest appropriate medical facility. Emergency Department Care: Remove soiled clothing. Decontaminate by irrigation with copious amounts of water. Assess and manage life-threatening conditions as with any other cause. Commence comprehensive monitoring for significant exposures. With any evidence of hypocalcemia, immediately administer 10% calcium gluconate IV. Apply 2.5% calcium gluconate gel to the affected area. If the proprietary gel is not available, constitute by dissolving 10% calcium gluconate solution in 3 times the volume of a water-soluble lubricant (eg, KY gel). For burns to the fingers, retain gel in a latex glove. If pain persists for more than 30 minutes after application of calcium gluconate gel, further treatment is required. Subcutaneous infiltration of calcium gluconate is recommended at a dose of 0.5 ml of a 10% solution per square centimeter of surface burn extending 0.5 cm beyond the margin of involved tissue. Do not use the chloride salt because it is an irritant and may cause tissue damage. Burns to the digits: Local infiltration of digits is not recommended because of pain, disfigurement, and potential complications. Alternative treatment methods follow. - IV regional calcium gluconate: ml of 10% calcium gluconate plus 5000 units of heparin diluted up to 40 ml in 5% dextrose. Use a Bier ischemic arm block technique to infuse the solution intravenously. Release the cuff when any of the following conditions first occur: (1) pain from the digits resolves, (2) the cuff becomes more painful than the burn, or (3) 20 minutes of ischemic time elapses. Treatment can be repeated after 4 hours if needed. Continuous ECG and clinical monitoring are essential during this procedure. - Intra-arterial calcium gluconate: Place an arterial catheter in the radial or brachial artery to perfuse the affected digits. Infuse a solution of 10 ml of 10% calcium gluconate in 40 ml of 5% dextrose over a 4-hour period. Follow with further infusions repeated after 4-8 hours, if necessary. Several treatments may be needed. Exercise great care to ensure that the catheter is appropriately placed intravascularly (ie, by continuous waveform analysis), as tissue necrosis and digit loss have occurred following extravasation of From: [5/10/ :53:27 AM] Page 4 of 9
5 calcium salts. Continuous ECG and clinical monitoring are essential during this procedure. Ocular burns: Generously irrigate with sterile water or saline for at least 5 minutes. Local anesthetic may be required. If pain persists, irrigate with a 1% solution of calcium gluconate, which is made by diluting the 10% solution in 10 times the volume of normal saline. Do not use undiluted 10% calcium gluconate. Inhalation burns: Exposures to the head and neck should arouse suspicion of pulmonary involvement. If any doubt is present, admission for observation is advised. Specific treatment - Provide 100% oxygen by mask, 2.5% calcium gluconate by nebulizer with 100% oxygen, continuous pulse oximetry, ECG, and clinical monitoring. - Pulmonary edema is treated along conventional lines, as needed. - Despite concerns of perforation, consider gastric lavage with calcium chloride (ie, 20 mmol calcium in 1000 cc normal saline solution) early in overdose. One series of autopsies performed on decedents who had received calcium chloride lavage after HF acid ingestion demonstrated hemorrhagic gastritis; however, no evidence of perforation was revealed. Secure the airway prior to gastric lavage. Consultations: Consultation with specialty units may be required depending on individual circumstances. Toxicology service Burn surgery Intensive care Ophthalmology Hand surgery Gastroenterologist (following ingestions) From: [5/10/ :53:27 AM] Page 5 of 9
6 Medication The goal of pharmacotherapy is to reduce morbidity and prevent complications. Drug Category: Pharmacologic antidote The major pharmacologic intervention is with calcium gluconate. Depending on the clinical situation, it may be used in a gel, intravenously, or intra-arterially. May also be used to irrigate ocular burns. Drug Name Adult Dose Pediatric Dose Contraindications Interactions Pregnancy Precautions Calcium gluconate (Kalcinate) -- Moderates nerve and muscle performance and facilitates normal cardiac function. For systemic hypocalcemia, can be given IV initially, and calcium levels maintained with high calcium diet. Some patients will require oral calcium supplementation. For topical pain, can be applied as a water-soluble gel mixture. For IV, intra-arterial, or ocular administration, please refer to discussion in Treatment. May apply 2.5-5% calcium gluconate to affected area; repeat prn pain; if not available commercially, can be prepared by simple 3:1 (for 2.5%) or 1:1 (for 5%) dilution of a 10% IV solution in a water-soluble surgical gel or similar sterile base Apply as in adults Renal calculi; hypercalcemia; hypophosphatemia; renal or cardiac disease; digitalis toxicity May decrease effects of tetracyclines, atenolol, salicylates, iron salts, and fluoroquinolones; antagonizes effects of verapamil; large intakes of dietary fiber may decrease calcium absorption and levels B - Usually safe but benefits must outweigh the risks. Caution in digitalized patients, respiratory failure, acidosis, or severe hyperphosphatemia Serum calcium should be monitored when calcium gluconate is given parenterally Drug Name Adult Dose Pediatric Dose Contraindications Interactions Pregnancy Precautions Calcium chloride -- Manages underlying hypocalcemic effects. Initial dose: 1-2 g (1-2 ampules) IV slow push of 10% calcium chloride solution (10 ml each); repeat doses to obtain desired serum calcium level; for severe poisoning, may need to give multiple grams for the first several h mg/kg IV push of calcium chloride; repeat prn; may need massive doses with severe poisoning Ventricular fibrillation not associated with hyperkalemia; digitalis toxicity; hypercalcemia; renal insufficiency; cardiac disease Coadministration with digoxin may cause arrhythmias; with thiazides, may induce hypercalcemia; may antagonize effects of calcium channel blockers, atenolol, and sodium polystyrene sulfonate B - Usually safe but benefits must outweigh the risks. Administer slowly (not to exceed ml/min) to avoid extravasation; hypercalcemia may occur in renal failure From: [5/10/ :53:27 AM] Page 6 of 9
7 Follow-Up Further Inpatient Care: Admission to a burn service or ICU may be required if burns are extensive or if any clinical, laboratory, or electrocardiographic evidence of complications is present. Further Outpatient Care: Patients are suitable for discharge only when pain has been controlled adequately. Patients with serious exposures can be discharged once electrolytes return to normal, arrhythmias are absent, and ECG is normal, provided other complications are managed adequately. Patients with finger burns can be discharged with calcium gluconate gel on the affected digits. Instruct patients to keep affected digits in a latex glove for 24 hours. Prudence requires physicians to provide follow-up care with all patients after 24 hours, at least by telephone. Deterrence/Prevention: Most burns are a result of inadequate use of safety devices. Patient education is important to prevent recurrences. Complications: Airway compromise Systemic fluorosis Pulmonary edema Electrolyte abnormalities Arrhythmias Scarring Loss of digits Corneal perforation Blindness Prognosis: Prognosis varies depending on burn severity and site. Poor prognosis follows fluoride inhalation. From: [5/10/ :53:27 AM] Page 7 of 9
8 Miscellaneous Medical/Legal Pitfalls: Several features of HF acid burns may lead to delayed or missed diagnosis. - Significant delays may occur between exposure and onset of symptoms. - Marked pain in the absence of significant surface dermal injury should raise suspicion of HF acid burns. - HF acid penetrates fingernails and burns the pulp beneath without destroying the nails. Adequate treatment of these cases requires removal of the nails and/or IV and/or intraarterial infusion of calcium gluconate. - Severe burns may produce severe electrolyte disturbances and arrhythmias. These must be monitored expediently and corrected. - All exposures to the head and neck may be associated with respiratory burns. Keep patients for observation with that possibility in mind. - Although 10% calcium gluconate is the agent of choice for counteracting most sites of exposure, irrigate burns to the eye with 1-2% dilute solution. Dislodgement of intra-arterial catheter may result in extravasation of calcium salts and subsequent tissue necrosis and/or digit loss. Pictures Caption: Picture 1. Grade 1 hydrofluoric (HF) acid burns of the fingertips. The patient has severe pain (maximum middle digit) with only minimal redness of the nail beds. Caption: Picture 2. Grade 3 hydrofluoric (HF) acid burns of the fingertips. Note how the nailbed and tip of the fingers have severely been injured, but the nails show no damage. From: [5/10/ :53:27 AM] Page 8 of 9
9 Bilbiography Bertolini JC: Hydrofluoric acid: a review of toxicity. J Emerg Med 1992 Mar-Apr; 10(2): 163-8[Medline]. Chan BS, Duggin GG: Survival after a massive hydrofluoric acid ingestion. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol 1997; 35(3): 307-9[Medline]. Dunn BJ, MacKinnon MA, Knowlden NF, et al: Topical treatments for hydrofluoric acid dermal burns. Further assessment of efficacy using an experimental piq model. J Occup Environ Med 1996 May; 38(5): [Medline]. Graudins A, Burns MJ, Aaron CK: Regional intravenous infusion of calcium gluconate for hydrofluoric acid burns of the upper extremity. Ann Emerg Med 1997 Nov; 30(5): 604-7[Medline]. Greco RJ, Hartford CE, Haith LR Jr, et al: Hydrofluoric acid-induced hypocalcemia. J Trauma 1988 Nov; 28(11): [Medline]. Henry JA, Hla KK: Intravenous regional calcium gluconate perfusion for hydrofluoric acid burns. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol 1992; 30(2): 203-7[Medline]. Koehnlein HE, Seitz HD, Achinger R: Abstracts of 5th International Congress on Burn Injuries. Stockholm, Sweden; Mayer TG, Gross PL: Fatal systemic fluorosis due to hydrofluoric acid burns. Ann Emerg Med 1985 Feb; 14(2): [Medline]. McIvor ME, Cummings CE, Mower MM, et al: Sudden cardiac death from acute fluoride intoxication: the role of potassium. Ann Emerg Med 1987 Jul; 16(7): [Medline]. Ryan JM, McCarthy GM, Plunkett PK: Regional intravenous calcium--an effective method of treating hydrofluoric acid burns to limb peripheries. J Accid Emerg Med 1997 Nov; 14(6): 401-4[Medline]. Shewmake SW, Anderson BG: Hydrofluoric acid burns. A report of a case and review of the literature. Arch Dermatol 1979 May; 115(5): 593-6[Medline]. Vance MV, Curry SC, Kunkel DB, et al: Digital hydrofluoric acid burns: treatment with intraarterial calcium infusion. Ann Emerg Med 1986 Aug; 15(8): 890-6[Medline]. Velvart J: Arterial perfusion for hydrofluoric acid burns. Hum Toxicol 1983 Apr; 2(2): 233-8[Medline]. Wilkes GJ: Intravenous regional calcium gluconate for hydrofluoric acid burns of the digits. Emerg Med (Aust) 1993; 5: Wilkes GJ, Morel DG: Hydrofluoric acid burns of the hands. In: Abstracts of the 6th International Conference on Emergency Medicine Sydney; Note: Medicine is a constantly changing science and not all therapies are clearly established. New research changes drug and treatment therapies daily. The authors, editors, and publisher of this journal have used their best efforts to provide information that is up-to-date and accurate and is generally accepted within medical standards at the time of publication. However, as medical science is constantly changing and human error is always possible, the authors, editors, and publisher or any other party involved with the publication of this article do not warrant the information in this article is accurate or complete, nor are they responsible for omissions or errors in the article or for the results of using this information. The reader should confirm the information in this article from other sources prior to use. In particular, all drug doses, indications, and contraindications should be confirmed in the package insert. FULL DISCLAIMER Hydrofluoric Acid Burns excerpt Copyright 2002, emedicine.com, Inc. From: [5/10/ :53:27 AM] Page 9 of 9
INTRODUCTION. Objectives. When the student has finished this module, he/she will be able to:
 Hydrofluoric Acid Burns WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed September 2017, Expires September 2019 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2017 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG,
Hydrofluoric Acid Burns WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed September 2017, Expires September 2019 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2017 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG,
Hydrofluoric acid (HF) C 1
 BASF Chemical Emergency Medical Guidelines Hydrofluoric acid (HF) C 1 Information and recommendations for doctors at hospitals/emergency departments Patients whose clothing or skin is contaminated with
BASF Chemical Emergency Medical Guidelines Hydrofluoric acid (HF) C 1 Information and recommendations for doctors at hospitals/emergency departments Patients whose clothing or skin is contaminated with
PRODUCT INFORMATION RESONIUM A. Na m
 PRODUCT INFORMATION RESONIUM A NAME OF THE MEDICINE Non-proprietary Name Sodium polystyrene sulfonate Chemical Structure CH - 2 CH SO 3 Na + n CAS Number 28210-41-5 [9003-59-2] CH 2 CH SO - 3 m DESCRIPTION
PRODUCT INFORMATION RESONIUM A NAME OF THE MEDICINE Non-proprietary Name Sodium polystyrene sulfonate Chemical Structure CH - 2 CH SO 3 Na + n CAS Number 28210-41-5 [9003-59-2] CH 2 CH SO - 3 m DESCRIPTION
Standard Operating Procedure (SOP)
 INTRODUCTION This SOP applies to HYDROFLUORIC ACID (HF). HYDROFLUORIC ACID is one of the strongest acids. It is extremely destructive to tissue and potentially fatal. HF causes such severe burns because
INTRODUCTION This SOP applies to HYDROFLUORIC ACID (HF). HYDROFLUORIC ACID is one of the strongest acids. It is extremely destructive to tissue and potentially fatal. HF causes such severe burns because
Hydrofluoric Acid Toxicity Author: Z. Kazzi / E. A. Numur / S. Kini. Target Audience: Emergency Medicine Residents
 Hydrofluoric Acid Toxicity Author: Z. Kazzi / E. A. Numur / S. Kini Reviewer: S. M. Varney Target Audience: Emergency Medicine Residents Primary Learning Objectives: 1. Demonstrate a general approach to
Hydrofluoric Acid Toxicity Author: Z. Kazzi / E. A. Numur / S. Kini Reviewer: S. M. Varney Target Audience: Emergency Medicine Residents Primary Learning Objectives: 1. Demonstrate a general approach to
Hypoparathyroidism By John Halpern, DO, FACEP Coauthored by N. Ewen Wang, MD
 Hypoparathyroidism By John Halpern, DO, FACEP Coauthored by N. Ewen Wang, MD Reprinted with permission from: E-Medicine: Instant Access to the Minds of Medicine http://www.emedicine.com/emerg/topic276.htm
Hypoparathyroidism By John Halpern, DO, FACEP Coauthored by N. Ewen Wang, MD Reprinted with permission from: E-Medicine: Instant Access to the Minds of Medicine http://www.emedicine.com/emerg/topic276.htm
SODIUM POLYSTYRENE SULFONATE Suspension, USP
 SODIUM POLYSTYRENE SULFONATE Suspension, USP DESCRIPTION Sodium Polystyrene Sulfonate Suspension, USP can be administered orally or in an enema. It is a cherryflavored suspension containing 15 grams of
SODIUM POLYSTYRENE SULFONATE Suspension, USP DESCRIPTION Sodium Polystyrene Sulfonate Suspension, USP can be administered orally or in an enema. It is a cherryflavored suspension containing 15 grams of
Limited Efficacy of Calcium and Magnesium in a Porcine Model of Hydrofluoric Acid Ingestion
 Toxicology Investigations Limited Efficacy of Calcium and Magnesium in a Porcine Model of Hydrofluoric Acid Ingestion Jason A. Coffey, MD a, Kori L. Brewer, PhD a, Robert Carroll, PhD b, John Bradfield,
Toxicology Investigations Limited Efficacy of Calcium and Magnesium in a Porcine Model of Hydrofluoric Acid Ingestion Jason A. Coffey, MD a, Kori L. Brewer, PhD a, Robert Carroll, PhD b, John Bradfield,
Magnesium Sulphate - Management of Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy
 1. Purpose Magnesium sulphate is the anticonvulsant of choice for pre-eclampsia prophylaxis and treatment. This clinical guideline outlines the indications, contraindications, administration and monitoring
1. Purpose Magnesium sulphate is the anticonvulsant of choice for pre-eclampsia prophylaxis and treatment. This clinical guideline outlines the indications, contraindications, administration and monitoring
Clinical Pathway: Management Of The Life-Threatening Overdose
 Clinical Pathway: Management Of The Life-Threatening Overdose Intravenous access Oxygen Pulse oximetry n-invasive blood pressure monitoring Accu-Check ECG monitoring and ECG Chest x-ray Respiratory depression?
Clinical Pathway: Management Of The Life-Threatening Overdose Intravenous access Oxygen Pulse oximetry n-invasive blood pressure monitoring Accu-Check ECG monitoring and ECG Chest x-ray Respiratory depression?
ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments
 ADENOSINE Paroxysmal SVT 1 st Dose 6 mg rapid IV 2 nd & 3 rd Doses 12 mg rapid IV push Follow each dose with rapid bolus of 20 ml NS May cause transient heart block or asystole. Side effects include chest
ADENOSINE Paroxysmal SVT 1 st Dose 6 mg rapid IV 2 nd & 3 rd Doses 12 mg rapid IV push Follow each dose with rapid bolus of 20 ml NS May cause transient heart block or asystole. Side effects include chest
POISON ANTIDOTE DOSE* COMMENTS
 Antidotes Acetaminophen N-acetylcysteine 140 mg/kg initial oral dose, followed Most effective within 16 24 hr; may by 70 mg/kg every 4 hr 17 doses be useful after chronic intoxication or intravenously
Antidotes Acetaminophen N-acetylcysteine 140 mg/kg initial oral dose, followed Most effective within 16 24 hr; may by 70 mg/kg every 4 hr 17 doses be useful after chronic intoxication or intravenously
Basic Fluid and Electrolytes
 Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Chapter 22 Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Introduction Infants and young children have a greater need for water and are more vulnerable to alterations in fluid and electrolyte
Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Chapter 22 Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Introduction Infants and young children have a greater need for water and are more vulnerable to alterations in fluid and electrolyte
Comparative Efficacy of Injectable Calcium and Magnesium Salts in the Therapy of Hydrofluoric Acid Burns
 CLINICAL TOXICOLOGY, 18(9), pp. 1027-1032 (1981) Comparative Efficacy of Injectable Calcium and Magnesium Salts in the Therapy of Hydrofluoric Acid Burns JOHN C. HARRIS, MD, and BARRY H. RUMACK,* MD University
CLINICAL TOXICOLOGY, 18(9), pp. 1027-1032 (1981) Comparative Efficacy of Injectable Calcium and Magnesium Salts in the Therapy of Hydrofluoric Acid Burns JOHN C. HARRIS, MD, and BARRY H. RUMACK,* MD University
PACKAGE INSERT CALCIUM GLUCONATE INJECTION, USP 10% Electrolyte Replenisher mosmol/ml 680 mosmol/l Ca meq/ml ph
 CALCIUM GLUCONATE INJECTION, USP 10% Electrolyte Replenisher 0.68 mosmol/ml 680 mosmol/l Ca ++ 0.465 meq/ml ph 6.0 8.2 DESCRIPTION Calcium Gluconate Injection, USP is a sterile, nonpyrogenic supersaturated
CALCIUM GLUCONATE INJECTION, USP 10% Electrolyte Replenisher 0.68 mosmol/ml 680 mosmol/l Ca ++ 0.465 meq/ml ph 6.0 8.2 DESCRIPTION Calcium Gluconate Injection, USP is a sterile, nonpyrogenic supersaturated
CRACKCast Episode Hydrocarbons (Ch th )
 CRACKCast Episode Hydrocarbons (Ch. 152 9 th ) Episode Overview Key Concepts: Aspiration is the major toxic risk of hydrocarbon poisoning. Hydrocarbons may cause systemic toxicity, burns, seizures, cardiac
CRACKCast Episode Hydrocarbons (Ch. 152 9 th ) Episode Overview Key Concepts: Aspiration is the major toxic risk of hydrocarbon poisoning. Hydrocarbons may cause systemic toxicity, burns, seizures, cardiac
Drug Max dose approved for IVP Dilution Rate Monitoring Parameters. Dilution not necessary (Available in prefilled syringe)
 Drug Max dose approved for IVP Dilution Rate Monitoring Parameters Acetazolamide 500 mg Reconstitute with at least 5ml sterile water (max concentration should not exceed 100mg/ml) 100-500 mg/min Hypotension
Drug Max dose approved for IVP Dilution Rate Monitoring Parameters Acetazolamide 500 mg Reconstitute with at least 5ml sterile water (max concentration should not exceed 100mg/ml) 100-500 mg/min Hypotension
Honeywell Hydrofluoric Acid. Recommended Medical Treatment for Hydrofluoric Acid Exposure
 Honeywell Hydrofluoric Acid Recommended Medical Treatment for Hydrofluoric Acid Exposure Hydrofluoric Acid Treatment Quick Reference Chart FOLD OUT HERE This booklet describes the special First Aid and
Honeywell Hydrofluoric Acid Recommended Medical Treatment for Hydrofluoric Acid Exposure Hydrofluoric Acid Treatment Quick Reference Chart FOLD OUT HERE This booklet describes the special First Aid and
Document 3 Summary of Data and Guidance for Medical Professionals
 Document 3 Summary of Data and Guidance for Medical Professionals Anvirzel Anvirzel is a novel antitumor compound extracted from the plant Nerium oleander, which belongs to the family Apocynaceae. Anvirzel
Document 3 Summary of Data and Guidance for Medical Professionals Anvirzel Anvirzel is a novel antitumor compound extracted from the plant Nerium oleander, which belongs to the family Apocynaceae. Anvirzel
Hydrofluoric Acid Exposure A Double Whammy That s Not Just Skin Deep
 he following report was submitted to PA-PSRS. T A patient came to the Emergency Department complaining of chest pains. He also stated he received an acid burn of the hand prior to his arrival. The ED physician
he following report was submitted to PA-PSRS. T A patient came to the Emergency Department complaining of chest pains. He also stated he received an acid burn of the hand prior to his arrival. The ED physician
Approved By: Airway and Breathing A. Initially give humidified high flow oxygen at 15 L (100%) using a nonrebreather
 Subject: BURN CARE CLINICAL GUIDELINE Originator: Approval Date: 2015 Approved By: Policy: All burn patients presenting to XXXXXX Hospital will have appropriate assessment, stabilization and evaluation
Subject: BURN CARE CLINICAL GUIDELINE Originator: Approval Date: 2015 Approved By: Policy: All burn patients presenting to XXXXXX Hospital will have appropriate assessment, stabilization and evaluation
Industrial Fluorines. Recommended Medical Treatment for Hydrofluoric Acid Exposure
 Industrial Fluorines Recommended Medical Treatment for Hydrofluoric Acid Exposure This booklet describes the special First Aid and Medical Treatment measures necessary following exposure to or injury from
Industrial Fluorines Recommended Medical Treatment for Hydrofluoric Acid Exposure This booklet describes the special First Aid and Medical Treatment measures necessary following exposure to or injury from
DRUGS FOR VIVA. IAP UG Teaching slides
 DRUGS FOR VIVA 1 Q:1 INJ SODIUM BICARBONATE 1. What all strengths are available? 2. What are the clinical indications for IV sodium bicarbonate? 3. How do you administer this drug? 2 ANS: 1. Available
DRUGS FOR VIVA 1 Q:1 INJ SODIUM BICARBONATE 1. What all strengths are available? 2. What are the clinical indications for IV sodium bicarbonate? 3. How do you administer this drug? 2 ANS: 1. Available
Calcium (Ca 2+ ) mg/dl
 Quick Guide to Laboratory Values Use this handy cheat-sheet to help you monitor laboratory values related to fluid and electrolyte status. Remember, normal values may vary according to techniques used
Quick Guide to Laboratory Values Use this handy cheat-sheet to help you monitor laboratory values related to fluid and electrolyte status. Remember, normal values may vary according to techniques used
DBL MAGNESIUM SULFATE CONCENTRATED INJECTION
 DBL MAGNESIUM SULFATE CONCENTRATED INJECTION NAME OF MEDICINE Magnesium Sulfate BP DESCRIPTION DBL Magnesium Sulfate Concentrated Injection is a clear, colourless, sterile solution. Each ampoule contains
DBL MAGNESIUM SULFATE CONCENTRATED INJECTION NAME OF MEDICINE Magnesium Sulfate BP DESCRIPTION DBL Magnesium Sulfate Concentrated Injection is a clear, colourless, sterile solution. Each ampoule contains
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS PRODUCT SUMMARY 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Sterile Potassium Chloride Concentrate 15%. 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 15% of Potassium Chloride in
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS PRODUCT SUMMARY 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Sterile Potassium Chloride Concentrate 15%. 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 15% of Potassium Chloride in
NORMOSOL -R MULTIPLE ELECTROLYTES INJECTION TYPE 1, USP For Replacing Acute Losses of Extracellular Fluid Flexible Plastic Container
 NORMOSOL -R MULTIPLE ELECTROLYTES INJECTION TYPE 1, USP For Replacing Acute Losses of Extracellular Fluid Flexible Plastic Container R x only DESCRIPTION Normosol-R is a sterile, nonpyrogenic isotonic
NORMOSOL -R MULTIPLE ELECTROLYTES INJECTION TYPE 1, USP For Replacing Acute Losses of Extracellular Fluid Flexible Plastic Container R x only DESCRIPTION Normosol-R is a sterile, nonpyrogenic isotonic
Major intra and extracellular ions Lec: 1
 Major intra and extracellular ions Lec: 1 The body fluids are solutions of inorganic and organic solutes. The concentration balance of the various components is maintained in order for the cell and tissue
Major intra and extracellular ions Lec: 1 The body fluids are solutions of inorganic and organic solutes. The concentration balance of the various components is maintained in order for the cell and tissue
I write in response to your request for information in relation to pharmacy drug guidelines within NHS Lothian.
 Lothian NHS Board = Waverley Gate 2-4 Waterloo Place Edinburgh EH1 3EG = Telephone: 0131 536 9000 www.nhslothian.scot.nhs.uk www.nhslothian.scot.nhs.uk Dear FREEDOM OF INFORMATION IV POLICIES Date: 03/10/2016
Lothian NHS Board = Waverley Gate 2-4 Waterloo Place Edinburgh EH1 3EG = Telephone: 0131 536 9000 www.nhslothian.scot.nhs.uk www.nhslothian.scot.nhs.uk Dear FREEDOM OF INFORMATION IV POLICIES Date: 03/10/2016
DATA SHEET. Product Summary. 1. Trade Name of Medicinal Product. Protamine Sulphate Injection BP. 2. Qualitative and Quantitative Composition
 DATA SHEET Product Summary 1. Trade Name of Medicinal Product Protamine Sulphate Injection BP 2. Qualitative and Quantitative Composition Protamine Sulphate 10mg/ml 3. Pharmaceutical Form Solution for
DATA SHEET Product Summary 1. Trade Name of Medicinal Product Protamine Sulphate Injection BP 2. Qualitative and Quantitative Composition Protamine Sulphate 10mg/ml 3. Pharmaceutical Form Solution for
Clinical Toxicology Toxicity of Digitalis Glycosides 5 th Year (Lab 3)
 Clinical Toxicology Toxicity of Digitalis Glycosides 5 th Year (Lab 3) Lecturer: Rua Abbas Al-Hamdy Department of Pharmacology & Toxicology University of Al-Mustansiriyah 2017-2018 Introduction: Digitalis
Clinical Toxicology Toxicity of Digitalis Glycosides 5 th Year (Lab 3) Lecturer: Rua Abbas Al-Hamdy Department of Pharmacology & Toxicology University of Al-Mustansiriyah 2017-2018 Introduction: Digitalis
1/3/2008. Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown. Medical-Surgical Nursing Care, 2e Karen Burke, Priscilla LeMone, and Elaine Mohn-Brown
 Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 7 Caring for Clients with Altered Fluid, Electrolyte, or Acid-Base Balance Water Primary component of
Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 7 Caring for Clients with Altered Fluid, Electrolyte, or Acid-Base Balance Water Primary component of
Chapter 20 8/23/2016. Fluids and Electrolytes. Fluid (Water) Fluid (Water) (Cont.) Functions
 Chapter 20 Fluids and Electrolytes All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Fluid (Water) Functions Provides an extracellular transportation
Chapter 20 Fluids and Electrolytes All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Fluid (Water) Functions Provides an extracellular transportation
EmergencyKT: Management of Thermal Injury in Adult Patients
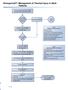 EmergencyKT: Management of Thermal Injury in Adult Patients Remove patient from source of injury, including burned clothing and jewelry Does patient appear to have minor burns? (See Box A) No Notify Burn
EmergencyKT: Management of Thermal Injury in Adult Patients Remove patient from source of injury, including burned clothing and jewelry Does patient appear to have minor burns? (See Box A) No Notify Burn
SAFETY DATA SHEET. Oxycodone Hydrochloride (CII) Capsule, 5mg, 100 count bottle NDC
 SAFETY DATA SHEET SECTION 1 - IDENTIFICATION Product Identification: Oxycodone Hydrochloride (CII) Capsule, 5mg, 100 count bottle NDC 64950-901-10 Recommended use and restrictions: Oxycodone Hydrochloride
SAFETY DATA SHEET SECTION 1 - IDENTIFICATION Product Identification: Oxycodone Hydrochloride (CII) Capsule, 5mg, 100 count bottle NDC 64950-901-10 Recommended use and restrictions: Oxycodone Hydrochloride
Used for removing granulation tissue, warts (including verrucas), for cautery and as a caustic
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Avoca Caustic Pencil 95% w/w Cutaneous Stick Avoca Caustic Applicator 95% w/w Cutaneous Stick Avoca Wart & Verruca Treatment 95% w/w
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Avoca Caustic Pencil 95% w/w Cutaneous Stick Avoca Caustic Applicator 95% w/w Cutaneous Stick Avoca Wart & Verruca Treatment 95% w/w
Electrolyte Imbalance and Resuscitation. Dr. Mehmet Okumuş Sütçü Imam University Faculty of Medicine Department of Emergency Medicine
 Electrolyte Imbalance and Resuscitation Dr. Mehmet Okumuş Sütçü Imam University Faculty of Medicine Department of Emergency Medicine Presentation plan Definition of the electrolyte disturbances Conditions
Electrolyte Imbalance and Resuscitation Dr. Mehmet Okumuş Sütçü Imam University Faculty of Medicine Department of Emergency Medicine Presentation plan Definition of the electrolyte disturbances Conditions
50% Concentrated Injection
 NAME OF THE MEDICINE. The molecular weight of the compound is 246.5 and the CAS registry number is 10034-99-8. The molecular formula is MgSO4, 7H2O. DESCRIPTION MAGNESIUM SULFATE HEPTAHYDRATE 50% CONCENTRATED
NAME OF THE MEDICINE. The molecular weight of the compound is 246.5 and the CAS registry number is 10034-99-8. The molecular formula is MgSO4, 7H2O. DESCRIPTION MAGNESIUM SULFATE HEPTAHYDRATE 50% CONCENTRATED
Nephrology / Urology. Hyperkalemia Causes and Definition Lecturio Online Medical Library. Definition. Epidemiology of Hyperkalemia.
 Nephrology / Urology Hyperkalemia Causes and Definition Lecturio Online Medical Library See online here Hyperkalemia is defined by the serum potassium level when it is higher than 5.5mEq/L. It is usually
Nephrology / Urology Hyperkalemia Causes and Definition Lecturio Online Medical Library See online here Hyperkalemia is defined by the serum potassium level when it is higher than 5.5mEq/L. It is usually
GPS* Safety Summary for Sodium Hydroxide
 GPS* Safety Summary for Sodium Hydroxide Select a Topic: Names Product Overview Manufacture of Product Product Description Product Uses Exposure Potential Health Information Environmental Information Physical
GPS* Safety Summary for Sodium Hydroxide Select a Topic: Names Product Overview Manufacture of Product Product Description Product Uses Exposure Potential Health Information Environmental Information Physical
Cyanide Poisoning. Daniel Shodell MD, MPH. Anne Arundel County DOH,
 Cyanide Poisoning Daniel Shodell MD, MPH Anne Arundel County DOH, 2004 1 Learning objectives Describe the clinical syndrome, treatment, and epidemiology of cyanide Identify the key public health agency
Cyanide Poisoning Daniel Shodell MD, MPH Anne Arundel County DOH, 2004 1 Learning objectives Describe the clinical syndrome, treatment, and epidemiology of cyanide Identify the key public health agency
Ammonia (NH 3 ) B 1. Information and recommendations for paramedics and doctors at the site. BASF Chemical Emergency Medical Guidelines
 BASF Chemical Emergency Medical Guidelines Ammonia (NH 3 ) B 1 Information and recommendations for paramedics and doctors at the site Before approaching the patient the paramedics and doctors at the site
BASF Chemical Emergency Medical Guidelines Ammonia (NH 3 ) B 1 Information and recommendations for paramedics and doctors at the site Before approaching the patient the paramedics and doctors at the site
NHS Grampian Staff Guideline for the Management of Acute Hypokalaemia in Adults
 NHS Grampian Staff Guideline for the Management of Acute Hypokalaemia in Adults Co-ordinators: Medicines Information Pharmacist Consultation Group: See relevant page in guidance Approver: Medicine Guidelines
NHS Grampian Staff Guideline for the Management of Acute Hypokalaemia in Adults Co-ordinators: Medicines Information Pharmacist Consultation Group: See relevant page in guidance Approver: Medicine Guidelines
Advanced Resuscitation - Child
 C02C Resuscitation 2017-03-23 1 up to 10 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Child Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
C02C Resuscitation 2017-03-23 1 up to 10 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Child Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
PHENTOLAMINE MESYLATE INJECTION SANDOZ STANDARD 5 mg/ ml THERAPEUTIC CLASSIFICATION Alpha-adrenoreceptor Blocker
 PACKAGE INSERT Pr PHENTOLAMINE MESYLATE INJECTION SANDOZ STANDARD 5 mg/ ml THERAPEUTIC CLASSIFICATION Alpha-adrenoreceptor Blocker ACTIONS AND CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY Phentolamine produces an alpha-adrenergic
PACKAGE INSERT Pr PHENTOLAMINE MESYLATE INJECTION SANDOZ STANDARD 5 mg/ ml THERAPEUTIC CLASSIFICATION Alpha-adrenoreceptor Blocker ACTIONS AND CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY Phentolamine produces an alpha-adrenergic
February 12, Re: 10% Calcium Chloride Injection, USP. Dear Healthcare Professional,
 Re: 10% Calcium Chloride Injection, USP Dear Healthcare Professional, In an effort to reduce medication errors and ensure patient safety, American Regent, Inc. is informing you of recent changes to the
Re: 10% Calcium Chloride Injection, USP Dear Healthcare Professional, In an effort to reduce medication errors and ensure patient safety, American Regent, Inc. is informing you of recent changes to the
A case of nonfatal non-collapsed patient with extreme hyperkalaemia
 Hong Kong Journal of Emergency Medicine A case of nonfatal non-collapsed patient with extreme hyperkalaemia YH Lim and J Hendricks This is a report of a non-collapsed patient with nonfatal, extreme hyperkalaemia
Hong Kong Journal of Emergency Medicine A case of nonfatal non-collapsed patient with extreme hyperkalaemia YH Lim and J Hendricks This is a report of a non-collapsed patient with nonfatal, extreme hyperkalaemia
ALS MODULE 7 Pharmacology
 ALS MODULE 7 Pharmacology Relates to HLT404C Apply Advanced Resuscitation Techniques Introduction There are no studies that addressed the order of drug administration. There is inadequate evidence to define
ALS MODULE 7 Pharmacology Relates to HLT404C Apply Advanced Resuscitation Techniques Introduction There are no studies that addressed the order of drug administration. There is inadequate evidence to define
Instruct patient and caregivers: Need for constant monitoring Potential complications of drug therapy
 Assessment Prior to administration: Assess patient for chest pain, dysrhythmias, and vital signs (initially and throughout therapy) Obtain complete medical history, including allergies, especially heart
Assessment Prior to administration: Assess patient for chest pain, dysrhythmias, and vital signs (initially and throughout therapy) Obtain complete medical history, including allergies, especially heart
DBL CALCIUM GLUCONATE INJECTION BP
 Description DBL CALCIUM GLUCONATE INJECTION BP DBL Calcium Gluconate Injection BP is a clear, colourless solution containing in each 10 ml, Calcium Gluconate BP 953 mg and Calcium Saccharate U.S.P. 30
Description DBL CALCIUM GLUCONATE INJECTION BP DBL Calcium Gluconate Injection BP is a clear, colourless solution containing in each 10 ml, Calcium Gluconate BP 953 mg and Calcium Saccharate U.S.P. 30
Adult Drug Reference. Dopamine Drip Chart. Pediatric Drug Reference. Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES
 Adult Drug Reference Dopamine Drip Chart Pediatric Drug Reference Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments ADENOSINE Paroxysmal
Adult Drug Reference Dopamine Drip Chart Pediatric Drug Reference Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments ADENOSINE Paroxysmal
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER. CALCICLO STEROP 11 meq 10 ml Solution for injection. Dihydrated Calcium Chloride
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER CALCICLO STEROP 11 meq 10 ml Solution for injection Dihydrated Calcium Chloride Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER CALCICLO STEROP 11 meq 10 ml Solution for injection Dihydrated Calcium Chloride Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because
Unit 11. Objectives. Indications for IV Therapy. Intravenous Access Devices & Common IV Fluids. 3 categories. Maintenance Replacement Restoration
 Unit 11 Fluids, Electrolytes and Acid Base Imbalances Intravenous Access Devices & Common IV Fluids Objectives Review the purpose and types of intravenous (IV) therapy. Recall the nursing care related
Unit 11 Fluids, Electrolytes and Acid Base Imbalances Intravenous Access Devices & Common IV Fluids Objectives Review the purpose and types of intravenous (IV) therapy. Recall the nursing care related
Calcium Chloride 10% Injection 1g in 10 ml (as calcium chloride dihydrate containing 6.8 mmol calcium ions in 10 ml)
 10% Injection 1g in 10 ml (as calcium chloride dihydrate containing 6.8 mmol calcium ions in 10 ml) NAME OF THE MEDICINE Name: Calcium chloride dihydrate Molecular formula: CaCl2.2H20 Molecular weight:
10% Injection 1g in 10 ml (as calcium chloride dihydrate containing 6.8 mmol calcium ions in 10 ml) NAME OF THE MEDICINE Name: Calcium chloride dihydrate Molecular formula: CaCl2.2H20 Molecular weight:
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION. Sodium Bicarbonate Injection USP 42mg/ml (4.2%), 75mg/ml (7.5%), 84mg/ml (8.4%) Sterile solution ALKALIZER
 PRESCRIBING INFORMATION Sodium Bicarbonate Injection USP 42mg/ml (4.2%), 75mg/ml (7.5%), 84mg/ml (8.4%) Sterile solution Lifeshield ABBOJECT Single-dose Syringes and Flipp Vial ALKALIZER FOR CORRECTION
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION Sodium Bicarbonate Injection USP 42mg/ml (4.2%), 75mg/ml (7.5%), 84mg/ml (8.4%) Sterile solution Lifeshield ABBOJECT Single-dose Syringes and Flipp Vial ALKALIZER FOR CORRECTION
Cardiac Pathophysiology
 Cardiac Pathophysiology Evaluation Components Medical history Physical examination Routine laboratory tests Optional tests Medical History Duration and classification of hypertension. Patient history of
Cardiac Pathophysiology Evaluation Components Medical history Physical examination Routine laboratory tests Optional tests Medical History Duration and classification of hypertension. Patient history of
2
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Please check regional policy on Tetracaine and Morgan Lens this may be optional in your region. *Ketamine and Fentanyl must be added to your controlled substance license if required by
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Please check regional policy on Tetracaine and Morgan Lens this may be optional in your region. *Ketamine and Fentanyl must be added to your controlled substance license if required by
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT "Carbellon" Tablets. 2. Qualitative and Quantitative Composition Active Constituents: Activated Charcoal Ph.Eur. Magnesium Hydroxide Ph.Eur.
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT "Carbellon" Tablets. 2. Qualitative and Quantitative Composition Active Constituents: Activated Charcoal Ph.Eur. Magnesium Hydroxide Ph.Eur.
Chemical Safety for SRF Work Introduction
 Chemical Safety for SRF Work Introduction John Mammosser (ORNL/SNS) USPAS Course: SRF Technology: Practices and Hands-On Measurements January 2015 J. Mammosser HF Safety Non-HF Acid Exposures Treated with
Chemical Safety for SRF Work Introduction John Mammosser (ORNL/SNS) USPAS Course: SRF Technology: Practices and Hands-On Measurements January 2015 J. Mammosser HF Safety Non-HF Acid Exposures Treated with
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS. Potassium Chloride 0.15% w/v & Sodium Chloride 0.9% w/v Solution for Infusion
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Potassium Chloride 0.15% w/v & Sodium Chloride 0.9% w/v Solution for Infusion 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Potassium Chloride
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Potassium Chloride 0.15% w/v & Sodium Chloride 0.9% w/v Solution for Infusion 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Potassium Chloride
Chapter 13. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives 9/11/2012. Poisonings, Overdoses, and Intoxications
 Chapter 13 Poisonings, Overdoses, and Intoxications Learning Objectives Discuss use of activated charcoal in treatment of poisonings List treatment options for acetaminophen overdose List clinical manifestations
Chapter 13 Poisonings, Overdoses, and Intoxications Learning Objectives Discuss use of activated charcoal in treatment of poisonings List treatment options for acetaminophen overdose List clinical manifestations
Acid-Base Balance 11/18/2011. Regulation of Potassium Balance. Regulation of Potassium Balance. Regulatory Site: Cortical Collecting Ducts.
 Influence of Other Hormones on Sodium Balance Acid-Base Balance Estrogens: Enhance NaCl reabsorption by renal tubules May cause water retention during menstrual cycles Are responsible for edema during
Influence of Other Hormones on Sodium Balance Acid-Base Balance Estrogens: Enhance NaCl reabsorption by renal tubules May cause water retention during menstrual cycles Are responsible for edema during
Sodium Bicarbonate Injection, USP
 Sodium Bicarbonate Injection, USP FOR THE CORRECTION OF METABOLIC ACIDOSIS AND OTHER CONDITIONS REQUIRING SYSTEMIC ALKALINIZATION. Plastic Ansyr II Syringe R x only DESCRIPTION Sodium Bicarbonate Injection,
Sodium Bicarbonate Injection, USP FOR THE CORRECTION OF METABOLIC ACIDOSIS AND OTHER CONDITIONS REQUIRING SYSTEMIC ALKALINIZATION. Plastic Ansyr II Syringe R x only DESCRIPTION Sodium Bicarbonate Injection,
Fluid and Electrolytes P A R T 4
 Fluid and Electrolytes P A R T 4 Mechanisms that control acid-base homeostasis Acids and bases continually enter and leave body Hydrogen ions also result from metabolic activity Acids Hydrogen ion donors
Fluid and Electrolytes P A R T 4 Mechanisms that control acid-base homeostasis Acids and bases continually enter and leave body Hydrogen ions also result from metabolic activity Acids Hydrogen ion donors
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment
 Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
Trichuris Trichiura. AUTHOR INFORMATION Section 1 of 9
 Febr (advertisement) Home Specialties CME PDA Contributor Recruitment Patient Education Articles Images CME Patient Education Advanced Search Li Back to: emedicine Specialties > Emergency Medicine > Infectious
Febr (advertisement) Home Specialties CME PDA Contributor Recruitment Patient Education Articles Images CME Patient Education Advanced Search Li Back to: emedicine Specialties > Emergency Medicine > Infectious
Formaldehyde (HCHO) C 1
 BASF Chemical Emergency Medical Guidelines Formaldehyde (HCHO) C 1 Information and recommendations for doctors at hospitals/emergency departments Patients exposed only to formaldehyde gas or vapor do not
BASF Chemical Emergency Medical Guidelines Formaldehyde (HCHO) C 1 Information and recommendations for doctors at hospitals/emergency departments Patients exposed only to formaldehyde gas or vapor do not
GUIDELINE FOR THE MANAGEMENT AND PREVENTION OF ACUTE TUMOUR LYSIS SYNDROME IN HAEMATOLOGICAL MALIGNANCIES
 GUIDELINE FOR THE MANAGEMENT AND PREVENTION OF ACUTE TUMOUR LYSIS SYNDROME IN HAEMATOLOGICAL MALIGNANCIES Full Title of Guideline: Author (include email and role): Division & Speciality: Scope (Target
GUIDELINE FOR THE MANAGEMENT AND PREVENTION OF ACUTE TUMOUR LYSIS SYNDROME IN HAEMATOLOGICAL MALIGNANCIES Full Title of Guideline: Author (include email and role): Division & Speciality: Scope (Target
Organ Donor Management Recommended Guidelines ADULT CARDIAC DEATH (DCD)
 Date: Time: = Always applicable = Check if applicable ADMISSION INSTRUCTIONS Move to Comfort Care Note in chart. Contact initiated with BC Transplant Consent for Organ Donation obtained Code Status: Full
Date: Time: = Always applicable = Check if applicable ADMISSION INSTRUCTIONS Move to Comfort Care Note in chart. Contact initiated with BC Transplant Consent for Organ Donation obtained Code Status: Full
Instrumental determination of electrolytes in urine. Amal Alamri
 Instrumental determination of electrolytes in urine Amal Alamri What is the Electrolytes? Electrolytes are positively and negatively chargedions, Found in Within body's cells extracellular fluids, including
Instrumental determination of electrolytes in urine Amal Alamri What is the Electrolytes? Electrolytes are positively and negatively chargedions, Found in Within body's cells extracellular fluids, including
For more information about Thomson Reuters Micromedex, visit Information valid as of March 17, 2011.
 pentetate calcium trisodium Micromedex drugpoints Summary DrugPoints Summaries provide information on dosage, pharmacokinetics, cautions, interactions, clinical applications, adverse effects, comparative
pentetate calcium trisodium Micromedex drugpoints Summary DrugPoints Summaries provide information on dosage, pharmacokinetics, cautions, interactions, clinical applications, adverse effects, comparative
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION. Dextrose Injection USP. (Concentrated Dextrose for Intravenous Administration) 50% (500 mg/ml) Fluid and Nutrient Replenisher
 PRESCRIBING INFORMATION Dextrose Injection USP (Concentrated Dextrose for Intravenous Administration) 50% (500 mg/ml) Fluid and Nutrient Replenisher Pfizer Canada Inc. 17300 Trans-Canada Highway Kirkland,
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION Dextrose Injection USP (Concentrated Dextrose for Intravenous Administration) 50% (500 mg/ml) Fluid and Nutrient Replenisher Pfizer Canada Inc. 17300 Trans-Canada Highway Kirkland,
Children's National Medical Center The Division of Trauma and Burn Burn Education Module Post-test
 Children's National Medical Center The Division of Trauma and Burn Burn Education Module Post-test Purpose: To provide nurses with on overview of burn injuries in pediatric patients. Learning Objectives:
Children's National Medical Center The Division of Trauma and Burn Burn Education Module Post-test Purpose: To provide nurses with on overview of burn injuries in pediatric patients. Learning Objectives:
2. What you need to know before you use Compound Sodium Lactate
 Package leaflet: Information for the user Compound Sodium Lactate Intravenous Infusion BP, Ecobag (Hartmann s Solution) Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it
Package leaflet: Information for the user Compound Sodium Lactate Intravenous Infusion BP, Ecobag (Hartmann s Solution) Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it
Composition Each ml of Ventol solution for inhalation contains 5 mg Salbutamol (as sulphate).
 VENTOL Composition Each ml of Ventol solution for inhalation contains 5 mg Salbutamol (as sulphate). Respiratory Solution Action Salbutamol is a short-acting, relatively selective beta2-adrenoceptor agonist.
VENTOL Composition Each ml of Ventol solution for inhalation contains 5 mg Salbutamol (as sulphate). Respiratory Solution Action Salbutamol is a short-acting, relatively selective beta2-adrenoceptor agonist.
ISPUB.COM. Electrolyte Replacement: A Review. B Phillips INTRODUCTION ELECTROLYTES I. CALCIUM
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Internal Medicine Volume 5 Number 1 Electrolyte Replacement: A Review B Phillips Citation B Phillips. Electrolyte Replacement: A Review. The Internet Journal of Internal
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Internal Medicine Volume 5 Number 1 Electrolyte Replacement: A Review B Phillips Citation B Phillips. Electrolyte Replacement: A Review. The Internet Journal of Internal
Pediatrics. Arrhythmias in Children: Bradycardia and Tachycardia Diagnosis and Treatment. Overview
 Pediatrics Arrhythmias in Children: Bradycardia and Tachycardia Diagnosis and Treatment See online here The most common form of cardiac arrhythmia in children is sinus tachycardia which can be caused by
Pediatrics Arrhythmias in Children: Bradycardia and Tachycardia Diagnosis and Treatment See online here The most common form of cardiac arrhythmia in children is sinus tachycardia which can be caused by
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS Page 1 of 9 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Magnesium sulfate-kalceks 500 mg/ml solution for injection, BP * 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1 ml of solution
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS Page 1 of 9 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Magnesium sulfate-kalceks 500 mg/ml solution for injection, BP * 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1 ml of solution
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER. SODIPHOS 22mEq / 10ml Concentrate for solution for infusion. Disodium phosphate dihydrate
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER SODIPHOS 22mEq / 10ml Concentrate for solution for infusion Disodium phosphate dihydrate Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine.
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER SODIPHOS 22mEq / 10ml Concentrate for solution for infusion Disodium phosphate dihydrate Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine.
EL DORADO COUNTY EMS AGENCY FIELD PROCEDURES
 EL DORADO COUNTY EMS AGENCY FIELD PROCEDURES Effective: July 1, 2017 Reviewed: November 9, 2016 Revised: November 9, 2016 EMS Agency Medical Director INTRAOSSEOUS INFUSION PURPOSE: To establish immediate
EL DORADO COUNTY EMS AGENCY FIELD PROCEDURES Effective: July 1, 2017 Reviewed: November 9, 2016 Revised: November 9, 2016 EMS Agency Medical Director INTRAOSSEOUS INFUSION PURPOSE: To establish immediate
Draft Labeling Package Insert Not Actual Size. BRAINTREE LABORATORIES, INC. PhosLo Capsules (Calcium Acetate)
 Draft Labeling Package Insert Not Actual Size BRAINTREE LABORATORIES, INC. PhosLo Capsules (Calcium Acetate) DESCRIPTION: Full Size: Each opaque capsule with a white cap and white body is spin printed
Draft Labeling Package Insert Not Actual Size BRAINTREE LABORATORIES, INC. PhosLo Capsules (Calcium Acetate) DESCRIPTION: Full Size: Each opaque capsule with a white cap and white body is spin printed
Diabetic Ketoacidosis: When Sugar Isn t Sweet!!!
 Diabetic Ketoacidosis: When Sugar Isn t Sweet!!! W Ricks Hanna Jr MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics University of Tennessee Health Science Center LeBonheur Children s Hospital Introduction Diabetes
Diabetic Ketoacidosis: When Sugar Isn t Sweet!!! W Ricks Hanna Jr MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics University of Tennessee Health Science Center LeBonheur Children s Hospital Introduction Diabetes
3M Tegaderm CHG Chlorhexidine Gluconate I.V. Securement Dressing Description 3M Tegaderm CHG Chlorhexidine Gluconate I.V. Securement Dressing is used
 3M Tegaderm CHG Chlorhexidine Gluconate I.V. Securement Dressing Description 3M Tegaderm CHG Chlorhexidine Gluconate I.V. Securement Dressing is used to cover and protect catheter sites and to secure devices
3M Tegaderm CHG Chlorhexidine Gluconate I.V. Securement Dressing Description 3M Tegaderm CHG Chlorhexidine Gluconate I.V. Securement Dressing is used to cover and protect catheter sites and to secure devices
Material Safety Data Sheet CISPLATIN INJECTION SECTION 2 COMPOSITION, INFORMATION ON INGREDIENTS
 Material Safety Data Sheet CISPLATIN INJECTION SECTION 1 - PRODUCT MSDS NAME: Cisplatin Injection, BP SYNONYMS: Cis-Diamminedi-chloroplatinum (II) SECTION 2 COMPOSITION, INFORMATION ON INGREDIENTS Active:
Material Safety Data Sheet CISPLATIN INJECTION SECTION 1 - PRODUCT MSDS NAME: Cisplatin Injection, BP SYNONYMS: Cis-Diamminedi-chloroplatinum (II) SECTION 2 COMPOSITION, INFORMATION ON INGREDIENTS Active:
Important Prescribing Information
 Important Prescribing Information Subject: Temporary importation of Potassium Chloride (KCl) Injection, Concentrate, 2 meq/ml to address drug shortage issues July 11, 2018 Dear Healthcare Professional,
Important Prescribing Information Subject: Temporary importation of Potassium Chloride (KCl) Injection, Concentrate, 2 meq/ml to address drug shortage issues July 11, 2018 Dear Healthcare Professional,
PDP 406 CLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
 PDP 406 CLINICAL TOXICOLOGY Pharm.D Fourth Year Mr.D.Raju.M.Pharm., Lecturer INTRODUCTION It is the process of freeing of a person or object of some contaminating substance from intestine which further
PDP 406 CLINICAL TOXICOLOGY Pharm.D Fourth Year Mr.D.Raju.M.Pharm., Lecturer INTRODUCTION It is the process of freeing of a person or object of some contaminating substance from intestine which further
Waitin In The Wings. Esophageal/Tracheal Double Lumen Airway (Combitube ) Indications and Use for the Pre-Hospital Provider
 Waitin In The Wings Esophageal/Tracheal Double Lumen Airway (Combitube ) Indications and Use for the Pre-Hospital Provider 1 CombiTube Kit General Description The CombiTube is A double-lumen tube with
Waitin In The Wings Esophageal/Tracheal Double Lumen Airway (Combitube ) Indications and Use for the Pre-Hospital Provider 1 CombiTube Kit General Description The CombiTube is A double-lumen tube with
Amjad Bani Hani Ass.Prof. of Cardiac Surgery & Intensive Care FLUIDS AND ELECTROLYTES
 Amjad Bani Hani Ass.Prof. of Cardiac Surgery & Intensive Care FLUIDS AND ELECTROLYTES Body Water Content Water Balance: Normal 2500 2000 1500 1000 500 Metab Food Fluids Stool Breath Sweat Urine
Amjad Bani Hani Ass.Prof. of Cardiac Surgery & Intensive Care FLUIDS AND ELECTROLYTES Body Water Content Water Balance: Normal 2500 2000 1500 1000 500 Metab Food Fluids Stool Breath Sweat Urine
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Magnesium Trisilicate Mixture B.P. 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Magnesium Trisilicate B.P. 250 mg/5 ml Light Magnesium
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Magnesium Trisilicate Mixture B.P. 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Magnesium Trisilicate B.P. 250 mg/5 ml Light Magnesium
Normosol -R and 5% Dextrose Injection MULTIPLE ELECTROLYTES AND 5% DEXTROSE INJECTION TYPE 1, USP For Replacing Acute Losses of Extracellular Fluid
 Normosol -R and 5% Dextrose Injection MULTIPLE ELECTROLYTES AND 5% DEXTROSE INJECTION TYPE 1, USP For Replacing Acute Losses of Extracellular Fluid R x only Flexible Plastic Container DESCRIPTION Normosol-R
Normosol -R and 5% Dextrose Injection MULTIPLE ELECTROLYTES AND 5% DEXTROSE INJECTION TYPE 1, USP For Replacing Acute Losses of Extracellular Fluid R x only Flexible Plastic Container DESCRIPTION Normosol-R
Yolo County Health & Human Services Agency
 Yolo County Health & Human Services Agency Kristin Weivoda EMS Administrator John S. Rose, MD, FACEP Medical Director DATE: December 28, 2017 TO: Yolo County Providers and Agencies FROM: Yolo County EMS
Yolo County Health & Human Services Agency Kristin Weivoda EMS Administrator John S. Rose, MD, FACEP Medical Director DATE: December 28, 2017 TO: Yolo County Providers and Agencies FROM: Yolo County EMS
Westco Chemicals, Inc Saticoy Street South - North Hollywood, CA TEL: FAX:
 Westco Chemicals, Inc. 12551-61 Saticoy Street South - North Hollywood, CA 91605 TEL:323-877-0077 818-255-3655 FAX: 818-255-3650 Data Sheet MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET SECTION 1: CHEMICAL PRODUCTS & COMPANY
Westco Chemicals, Inc. 12551-61 Saticoy Street South - North Hollywood, CA 91605 TEL:323-877-0077 818-255-3655 FAX: 818-255-3650 Data Sheet MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET SECTION 1: CHEMICAL PRODUCTS & COMPANY
Electrolytes and other equally exciting topics
 Electrolytes and other equally exciting topics Rebecca A. Snyder Summer School 2010 Why do we care? Why do we care? Why do we care? Torsades is bad. Because medical records cares even more. Because apparently
Electrolytes and other equally exciting topics Rebecca A. Snyder Summer School 2010 Why do we care? Why do we care? Why do we care? Torsades is bad. Because medical records cares even more. Because apparently
Poison (Toxicant): any substance or agent capable of producing a deleterious response in a biological system or living organism.
 Poison (Toxicant): any substance or agent capable of producing a deleterious response in a biological system or living organism. Poisoning= overdose toxicity intoxication= toxicity due to foreign substance
Poison (Toxicant): any substance or agent capable of producing a deleterious response in a biological system or living organism. Poisoning= overdose toxicity intoxication= toxicity due to foreign substance
Sodium Reference Electrode Filling Solution 2M NH 4 Cl Material Safety Data Sheet
 900010 Sodium Reference Electrode Filling Solution 2M NH 4 Cl I. PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION: Sodium Reference Electrode Filling Solution 2M NH 4 Cl 900010 NFPA RATINGS: HEALTH: 1 FLAMMABILITY: 0 REACTIVITY:
900010 Sodium Reference Electrode Filling Solution 2M NH 4 Cl I. PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION: Sodium Reference Electrode Filling Solution 2M NH 4 Cl 900010 NFPA RATINGS: HEALTH: 1 FLAMMABILITY: 0 REACTIVITY:
Clodronate BE/H/PSUR/001/001 October 2011 Agreed CSP
 Clodronate BE/H/PSUR/001/001 October 2011 Agreed CSP 4. CLINICAL PARTICULARS 4.1 Therapeutic indications Intravenous use Treatment of hypercalcemia due to malignancy. Oral use Treatment of hypercalcemia
Clodronate BE/H/PSUR/001/001 October 2011 Agreed CSP 4. CLINICAL PARTICULARS 4.1 Therapeutic indications Intravenous use Treatment of hypercalcemia due to malignancy. Oral use Treatment of hypercalcemia
Case Files of the Toxikon Consortium in Chicago: Survival after Intentional Ingestion of Hydrofluoric Acid
 J. Med. Toxicol. (2010) 6:349 354 DOI 10.1007/s13181-010-0088-4 TOXICOLOGY CASE FILES Case Files of the Toxikon Consortium in Chicago: Survival after Intentional Ingestion of Hydrofluoric Acid Patrick
J. Med. Toxicol. (2010) 6:349 354 DOI 10.1007/s13181-010-0088-4 TOXICOLOGY CASE FILES Case Files of the Toxikon Consortium in Chicago: Survival after Intentional Ingestion of Hydrofluoric Acid Patrick
Ventricular Tachycardia in Structurally Normal Hearts (Idiopathic VT) Patient Information
 Melbourne Heart Rhythm Ventricular Tachycardia in Structurally Normal Hearts (Idiopathic VT) Patient Information What is Ventricular Tachycardia? Ventricular tachycardia (VT) is an abnormal rapid heart
Melbourne Heart Rhythm Ventricular Tachycardia in Structurally Normal Hearts (Idiopathic VT) Patient Information What is Ventricular Tachycardia? Ventricular tachycardia (VT) is an abnormal rapid heart
RNZ INTERNATIONAL FZE MSDS. SECTION 1. Product And Company Identification. Company Name: RNZ INTERNATIONAL FZE
 MSDS Material Safety Data Sheet POTASSIUM SULPHATE SECTION 1. Product And Company Identification Chemical Product Product Name: POTASSIUM SULPHATE Company Name: RNZ INTERNATIONAL FZE Company Address: PO
MSDS Material Safety Data Sheet POTASSIUM SULPHATE SECTION 1. Product And Company Identification Chemical Product Product Name: POTASSIUM SULPHATE Company Name: RNZ INTERNATIONAL FZE Company Address: PO
Advanced Resuscitation - Adult
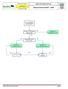 C02A Resuscitation 2017-03-23 17 years & older Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adult Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
C02A Resuscitation 2017-03-23 17 years & older Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adult Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
