Warfarin. Living. with. Further information
|
|
|
- Bruno Flynn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Further information Anticoagulation UK is committed to the prevention of thrombosis and to providing information and support to help people maintain their quality of life whilst on anticoagulant or antiplatelet therapy. For more information please contact us, see below for details. Anticoagulation UK Ace house, 2 Appledore close, bromley, br2 9bZ telephone: info@anticoagulationuk.org Web: Follow us on ACUK is a registered charity and relies on membership donations and sponsorship to continue its work. To make a donation please send a cheque or postal order to the address above, or you can donate online at our website. Living with Warfarin Registered charity number: January 2019
2 Warfarin Tablets Warfarin tablets in the UK are colour coded to help you take the correct dose. PINK 5mg BLUE 3mg They are available in 5mg (pink), 3mg (blue), 1mg (light brown) and 0.5mg (white). You should remember what dose you are taking and not just the colour. LIGHT BROWN 1mg WHITE 0.5mg Keep your warfarin tablets in a safe dry place out of reach of children. It is not advisable to store them in a bathroom cabinet or near the kettle in the kitchen because steam and damp will make them deteriorate. Always take your warfarin tablets at the same time each day. Swallow your tablets whole, do not crush or chew them. Tell your doctor or nurse if you have diffi culty in swallowing your tablets. If you miss a dose try to take your tablets shortly afterwards. Never take a double dose. Phone your clinic or GP for advice if you know you have completely missed a dose or if you have taken too many tablets.
3 How does warfarin work? Warfarin stops your blood from clotting inside your blood vessels. It is also used to stop existing clots getting bigger as in deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and to stop parts of a clot breaking off and travelling to the lungs, as in pulmonary embolism (PE). You may hear warfarin referred to as a blood thinner, although that is not what it does. The blood is not actually made any thinner, it just takes longer to clot whilst you are taking anticoagulants because warfarin is a vitamin K antagonist. This means it slows down the production of vitamin K (which helps your blood to clot) in your liver thus making your blood take longer to clot. How will my treatment be monitored? Treatment with warfarin is safe as long as you follow the advice of your anticoagulant clinic or GP. You will need to have your blood tested at regular intervals. This may be at an anticoagulant clinic at the hospital, at your doctors surgery, at your local pharmacy or at home by self-monitoring. If you want to self-monitor you should discuss this with your current provider of your anticoagulant service. ACE supports this concept and can provide advice and put you in touch with someone who has experience of self-monitoring. The national Institute for Health and Care Excellence has recommended self-monitoring for people with replacement valves and for those with atrial fibrillation. The reading obtained by testing the blood is called your INR (International Normalised Ratio). Your INR reading may vary but it will need to be kept within a certain range depending on the reason why you are taking warfarin. This is called your therapeutic range and will be decided by your GP or consultant. Conditions for which warfarin is prescribed 1. Atrial Fibrillation (AF) This is a condition in which the collecting chambers of the heart (the atria) fail to beat normally. Instead they fibrillate, making repetitive fine twitching movements that do not propel the blood forwards into the pumping chambers (the ventricles). 2.8 As a result, the normal co-ordination of the heart beat (with the atria contracting first and then the ventricles) is lost. The ventricles beat irregularly, making your pulse feel irregular.
4 People often describe this as feeling like their heart is beating faster than normal and at irregular intervals. The lack of normal contraction in the atria means that there is a degree of blood stagnation (pooling at the bottom of the chamber). This increases the risk of blood clots forming in the atria. Such blood clots are usually firmly attached to the wall of the atrium, but there is always a risk that they may break off, travel to another part of the body (embolism) and cause severe damage (e.g. a stroke if the clot travels to the brain). Warfarin is needed for as long as the atrial fibrillation persists, which may be for life. Sometimes the atrial fibrillation can be converted back to a normal rhythm with drugs, cardioversion (electrical therapy), catheter treatment or surgery. You should discuss this with your doctor. Warfarin does not cure your atrial fibrillation but will help reduce the risk of a stroke. 2. ArtiFiciAl heart valve (Avr or Mvr) If you have had one or more of your heartvalves replaced with a mechanical valve (prosthetic), you will need warfarin for life to prevent clots forming on or near the valve. Such blood clots can interfere with the function of the valve or break off and travel to the brain, causing a stroke. It is therefore very important to take your warfarin every day as prescribed. If another doctor suggests that you stop taking warfarin for any reason (e.g. if you need a non-cardiac operation), it is important to check with your cardiac consultant first. For minor operations (including dental extractions) and for some operations, it may not be necessary to stop warfarin. Sometimes you may be asked to reduce your INR level. Always check first before allowing anyone to stop your warfarin. Remember, it is your valve and your life that may be at risk. You may have been given a tissue valve also known as a bioprosthesis. If the rhythm of your heart valve is normal, you will probably only need to take warfarin for the first three months after your operation, until the sewing ring of the valve has healed and become largely covered with the body s own tissue. You should be told how long you will need to take warfarin. If not, do not hesitate to ask when you can safely stop taking warfarin.
5 3. DeeP vein thrombosis (Dvt) This is where a clot lodges in one of the larger veins of a leg or arm. The presence of a clot may produce pain and swelling of the affected area, however some people may have no recognisable symptoms. The clot may take some time to disperse, so warfarin is given to stop the clot getting bigger. Warfarin is also used to prevent small clots breaking off, travelling in the circulation, and lodging in places such as the lungs. Treatment is usually given for between three and six months. If you have more than one DVT, or have other risk factors, you may need to take warfarin for life. 4. PUlMonArY embolism (Pe) This is where a clot obstructs the blood supply to the lungs. Its presence may cause chest pain or breathlessness. Most of these clots form in the legs or pelvis and then break off and travel in the circulation until they lodge in the lungs. 5. heart AttAcK (MYocArDiAl infarction) or ischaemic heart DiSeASe Any narrowing or blockage of the vessels that supply the heart may cause irreversible damage to the heart muscle. Warfarin may be given to prevent a blood clot forming within the heart and to allow better blood flow through the arteries that supply the heart. The treatment may be for a short-term or for life. This depends on your condition and will be decided by your clinician. 6. Prevention of blood clots Certain groups of people have a particular tendency to form clots. This can be inherited, or be a result of some other condition. In these circumstances, warfarin is given to prevent the formation of clots. The consultant, haematologist or GP who started your treatment will tell you how long you will need to keep taking warfarin. This condition is a complication of a deep vein thrombosis. Treatment is normally for six months, but as with a DVT it may be for life. A pulmonary embolism is a serious condition and can be life threatening. If you think you may have a PE urgent medical treatment is required.
6 Side Effects The most common warfarin side effects are bleeding and bruising. These side effects can take the form of prolonged bleeding from cuts; bleeding that does not stop by itself; nose bleeds; small or large bruises under the skin; bleeding gums when brushing the teeth; red or dark brown urine; red or black stools; or coughing or vomiting blood stained fluid. All of these side effects should be reported to your clinic or GP. If your next appointment is not for some time please phone them. If you experience other side effects tell your clinic or GP. Do not stop taking warfarin without advice from your clinician. In the event of prolonged bleeding, inform your GP or go to the nearest casualty department for urgent treatment. What else should I know? If you are ill and are unable to eat properly or if you suffer from a period of diarrhoea and sickness this may affect the way your body absorbs the warfarin. This may mean that your INR level will alter and you may go out of your therapeutic range. Contact your clinic or GP if symptoms persist beyond two or three days as they may need to test your INR. Even if you are able to resume normal eating habits after a couple of days do not forget to tell your clinic next time you go. Other Medications It is important to continue taking all medications that have been prescribed for you by your consultant or GP. Some drugs affect how warfarin works. If your doctor prescribes any new medication, please ask them whether it may interfere with warfarin. If it does, then contact your anticoagulant clinic and tell them about your new medicine. Antibiotics in particular often cause problems with INR readings. If you are prescribed antibiotics, you should inform your clinic as soon as possible - they may want you to attend earlier than usual for a blood test. Also contact them if you are stopping a drug that is known to affect warfarin.
7 A list of some of the food and drugs that may affect your warfarin therapy can be found on our website under publications or send a large envelope with two first class stamps to AntiCoagulation Europe at the address on the back page of this leaflet. No list can be comprehensive, so contact your INR clinic if there is any possibility that a change in medication may alter your INR. Avoid all aspirin-based drugs, including non-steroidal anti-inflammatory preparations such as ibuprofen unless prescribed by your doctor. These may be referred to as NSAIDS. Paracetamol can be taken safely with warfarin for pain, although they can affect INR control if taken for prolonged periods. Aspirin can only be taken if your doctor has advised you to take it. Vitamins and Herbal Supplements Most vitamins and supplements have the potential to interact with warfarin. This does not necessarily mean that you cannot take them. Always seek advice from a pharmacist about possible interactions before purchasing any over the counter medicines, food or health supplements (this includes creams and ointments). Remember that even common over the counter medicines such as cold remedies and cough medicine may interact with warfarin. Some may contain aspirin. Always tell your pharmacist that you are taking warfarin and check anything that you intend to buy with them. If you wish to take vitamins or supplements tell your clinic when you are going to start taking them as they may want to monitor your INR levels more frequently for a while. Also tell them if you stop taking them. How warfarin will affect your lifestyle? Diet There are virtually no dietary restrictions while you are on warfarin, as long as you eat a healthy well balanced diet and avoid strict diets or crash dieting. Also avoid dramatic changes in the amount and type of food you eat, particularly green vegetables and liver products. You should not drink cranberry juice as this has been shown to reduce INR levels in some people and increase INR levels for others. It is also advisable not to drink grapefruit juice as this may affect absorption of some drugs.
8 Alcohol Alcohol may affect your INR reading. But drinking in moderation may do you some good. Moderation is normally defined as up to two units a day. Half a pint of beer or a small glass of wine or one measure of spirit is one unit. Binge drinking or a sudden increase or decrease in the amount of alcohol you drink may alter your INR levels. Remember it may be a combination of eating and drinking that will affect you. Travel It is advisable to have your INR checked before any overseas travel, so you can be sure of the correct dose whilst away from home. You may also need to have your INR checked while you are abroad, depending on the length of time you intend to be away. Please ensure that you have valid medical insurance for your trip. You must tell your insurance company about the conditions you suffer from and also that you are taking warfarin (receiving anticoagulant therapy). Adequate travel insurance when you have a medical condition, and are on warfarin is, almost always, going to cost more than normal. But it may literally save your life if you need emergency treatment abroad. It is always advisable to get two or three quotes and always read the small print. Make sure you have any Government health cards, such as the European Health Insurance Card. Remember to pack sufficient quantities of your tablets for the length of your stay. It is advisable to take two packs, one in your main luggage and one in your hand luggage. Don t forget that temperatures may be different when you travel abroad so always look at the patient information leaflet of your medication for storage instructions. Remember to take your yellow book or other information card. If you have a smart phone you may want to consider using an App that lets you record your INR, set daily dosage reminders and keep your clinic appointment dates. Visit Travel insurance When you take out travel insurance you must check that it will cover your specific condition. Declare all your past and present health conditions. Making a mistake or omission could result in a claim being refused. For travel in Europe, make sure you have a European Health Insurance Card (EHIC). This entitles you to reduced-cost and sometimes free medical treatment. Take out travel insurance as well because an EHIC may not cover all the costs of your treatment. An EHIC will not cover the cost of being flown back to the UK.
9 DentAl SUrGerY You should tell your dentist that you are taking warfarin and also any other medication, including ones that you have bought yourself over the counter, so that it can be added to your dental records. If you require a dental check up or small filling, then you may need to take no action with regard to your warfarin. If you require a tooth extraction, then please contact your clinic for advice as you may need a warfarin test before your appointment. If possible get in touch with the clinic at least a week in advance of the extraction, telling them the date of the treatment, so that if it is necessary they can adjust your warfarin level. Do not let a dentist remove your tooth without knowing your INR level. Your dentist may give instructions themselves or may contact your clinic directly. It is not usually necessary to stop taking warfarin for a dental extraction. It is important that you have good dental hygiene so make sure that you have regular check ups with your dentist and the dental hygienist. remember: If you are given a yellow book, or other information pack, try to carry it with you at all times. If you fi nd this is inconvenient, or you forget it, you may want to have some other means of identifying to others that you are on warfarin. In an emergency it can be vital that a doctor or paramedic knows you are on warfarin, and remember you may not always be conscious or able to tell them. Always tell the pharmacist (chemist) that you are taking warfarin when buying any over the counter preparation, even something that you think may be harmless, such as cough medicine. Always tell the dentist that you are taking warfarin. Never stop taking warfarin unless you have consulted your clinic, consultant or GP. If you have prolonged or serious bleeding and cannot contact your clinic or GP go to the accident and emergency department at your nearest hospital. If you are in doubt about anything do not be afraid to ask questions.
10 Notes Anticoagulation UK... Publishes regular newsletters, with up to date information, helpful articles and advice, patient stories, the latest clinical evidence and much more. Anticoagulation UK 2018 ISSUE 59 The Ne WSLe TTe R for peopl e TAKi Ng ANTicoA g ULANT T herapy LumiraDx Care SolutionS LumiraDx Care Solutions has won the Best Digital Innovation in Healthcare category at the 2018 Cornwall Live EDGE Page 2 What is it Like to be a Patient representative for acuk? In June and September this year, Anticoagulation UK was asked to provide a patient representative to be involved in the review committees has a comprehensive website Provides information booklets For a full list please write or to the address on the back page of this booklet. Leaflets can also be read or downloaded on line. ImPlemenTATIOn OF A STAndARdISed AnTICOAgUlATIOn RevIew In PRImARy CARe Membership is per year, you can join or renew on line or by sending a cheque made payable to Anticoagulation UK to the address on the back page. AcUK is a registered charity ( ) and relies on membership, sponsorship and donations to continue our work. You can donate on line or by sending a cheque or postal order made payable to Anticoagulation UK. You can also donate from your mobile phone. Text ACED44 3 to Shop on line and raise funds at no cost to you by going to and then follow instructions. You may need to type Anticoagulation UK as your charity to support. for a grants process led by a large pharmaceutical firm. These grants were for Improving Patient Care in Anticoagulation and Improving Care of Patients with Atrial Fibrillation in Order to Reduce Stroke Risk. Page 3 Direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) are now recommended by NICE as alternatives to warfarin for stroke prevention in non-valvular atrial fibrillation (NVAF) and for the treatment/prevention of venous thromboembolism (VTE) (NICE CG180 and QS29). The DOACs, compared to warfarin, have a number of advantages such as, a lower risk of life-threatening bleeding, less interactions with food/medication and a lack of INR monitoring (Hicks et al. 2016). As a result, the DOACs are now often used over warfarin as first line treatment. In addition, a significant number of patients are being switched from warfarin to DOACs. Patients with a time in therapeutic range (TTR) of <50% are at high risk of harm by taking warfarin (Abdou, J. K et al. 2015). NICE suggests that patients taking warfarin should aim to have a TTR of >65% to be getting to the optimum use from the warfarin therapy (NICE CG180). Other studies have suggested higher TTR targets (Kılıç et al. 2017). For many patients this is hard to achieve and treatment with a DOAC may be more appropriate. Anticoagulation UK 2018 ISSUE 59 The Ne WSLe TTe R for peopl e TAKi Ng ANTicoA g ULANT T herapy LumiraDx Care SolutionS LumiraDx Care Solutions has won the Best Digital Innovation in Healthcare category at the 2018 Cornwall Live EDGE Page 2 ImPlemenTATIOn OF A STAndARdISed AnTICOAgUlATIOn RevIew In PRImARy CARe What is it Like to be a Patient representative for acuk? In June and September this year, Anticoagulation UK was asked to provide a patient representative to be involved in the review committees for a grants process led by a large pharmaceutical firm. These grants were for Improving Patient Care in Anticoagulation and Improving Care of Patients with Atrial Fibrillation in Order to Reduce Stroke Risk. Page 3 Page 4 Direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) are now recommended by NICE as alternatives to warfarin for stroke prevention in non-valvular atrial fibrillation (NVAF) and for the treatment/prevention of venous thromboembolism (VTE) (NICE CG180 and QS29). The DOACs, compared to warfarin, have a number of advantages such as, a lower risk of life-threatening bleeding, less interactions with food/medication and a lack of INR monitoring (Hicks et al. 2016). As a result, the DOACs are now often used over warfarin as first line treatment. In addition, a significant number of patients are being switched from warfarin to DOACs. Patients with a time in therapeutic range (TTR) of <50% are at high risk of harm by taking warfarin (Abdou, J. K et al. 2015). NICE suggests that patients taking warfarin should aim to have a TTR of >65% to be getting to the optimum use from the warfarin therapy (NICE CG180). Other studies have suggested higher TTR targets (Kılıç et al. 2017). For many patients this is hard to achieve and treatment with a DOAC may be more appropriate. Page 4
WARFARIN ANTICOAGULANT RECORD
 WARFARIN ANTICOAGULANT RECORD Provided as a service to medicine by Concordia International Rx UK Ltd HOSPITAL/GP PRACTICE:... Telephone:... ANTICOAGULANT CLINIC Telephone:... Name:... Address:...... Telephone:...
WARFARIN ANTICOAGULANT RECORD Provided as a service to medicine by Concordia International Rx UK Ltd HOSPITAL/GP PRACTICE:... Telephone:... ANTICOAGULANT CLINIC Telephone:... Name:... Address:...... Telephone:...
 Appendix 8 Patient Information Leaflet A. NPSA Web Link www.npsa.nhs.uk/easysiteweb/gatewaylink.aspx?alid=19112 B. Supplementary NT 1. WHY AM I ON WARFARIN? Your doctors have told you that you have a condition
Appendix 8 Patient Information Leaflet A. NPSA Web Link www.npsa.nhs.uk/easysiteweb/gatewaylink.aspx?alid=19112 B. Supplementary NT 1. WHY AM I ON WARFARIN? Your doctors have told you that you have a condition
Direct Oral Anticoagulant (DOAC)Therapy. Important information for patients prescribed: Apixaban, Dabigatran, Edoxaban or Rivaroxaban
 Direct Oral Anticoagulant (DOAC)Therapy Important information for patients prescribed: Apixaban, Dabigatran, Edoxaban or Rivaroxaban Patient Name: Address: Postcode: CHI Number: Condition requiring treatment:
Direct Oral Anticoagulant (DOAC)Therapy Important information for patients prescribed: Apixaban, Dabigatran, Edoxaban or Rivaroxaban Patient Name: Address: Postcode: CHI Number: Condition requiring treatment:
Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
 Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Normally blood moves freely throughout the body without any problems. However, if a blood clot forms in a vein it can block the vein and stop the blood from flowing properly. Sometimes
Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Normally blood moves freely throughout the body without any problems. However, if a blood clot forms in a vein it can block the vein and stop the blood from flowing properly. Sometimes
Fibrillation. Living. withatrial. Further information
 Further information Anticoagulation UK is committed to the prevention of thrombosis and to providing information and support to help people maintain their quality of life whilst on anticoagulant or antiplatelet
Further information Anticoagulation UK is committed to the prevention of thrombosis and to providing information and support to help people maintain their quality of life whilst on anticoagulant or antiplatelet
Warfarin. Information for patients taking warfarin
 Warfarin Information for patients taking warfarin Read this booklet to learn: what warfarin is and why you are taking it what blood tests you need to use warfarin safely how other medicines and diet can
Warfarin Information for patients taking warfarin Read this booklet to learn: what warfarin is and why you are taking it what blood tests you need to use warfarin safely how other medicines and diet can
Banner Health Center
 Banner Health Center Coumadin Education Class Anticoagulation Clinic Please turn cell phones off. Thank you! The History of Coumadin 1920s: cattle deaths due to anti-clotting agent found in clover Mid-1940s:
Banner Health Center Coumadin Education Class Anticoagulation Clinic Please turn cell phones off. Thank you! The History of Coumadin 1920s: cattle deaths due to anti-clotting agent found in clover Mid-1940s:
Thrombosis and Anticoagulation Team. Warfarin. Information for patients, relatives and carers
 Thrombosis and Anticoagulation Team Warfarin Information for patients, relatives and carers What is warfarin? Warfarin is an anticoagulant. Anticoagulants are drugs which prevent harmful blood clots forming
Thrombosis and Anticoagulation Team Warfarin Information for patients, relatives and carers What is warfarin? Warfarin is an anticoagulant. Anticoagulants are drugs which prevent harmful blood clots forming
Things to Know When Taking Warfarin (Coumadin ) Anticoagulation Therapy
 Things to Know When Taking Warfarin (Coumadin ) Anticoagulation Therapy Table of Contents Highlights... 1 Why Do I Need Warfarin (Coumadin )?... 1 Who is Going to be Taking Care of My Warfarin?... 1 What
Things to Know When Taking Warfarin (Coumadin ) Anticoagulation Therapy Table of Contents Highlights... 1 Why Do I Need Warfarin (Coumadin )?... 1 Who is Going to be Taking Care of My Warfarin?... 1 What
Atrial Fibrillation and Anticoagulants
 Atrial Fibrillation and Anticoagulants A guide to your diagnosis and treatment Information for patients, relatives and carers For more information, please contact: York Anticoagulant Clinic Tel: 01904
Atrial Fibrillation and Anticoagulants A guide to your diagnosis and treatment Information for patients, relatives and carers For more information, please contact: York Anticoagulant Clinic Tel: 01904
Helping to prevent stroke caused by non-valvular atrial fibrillation Information booklet
 Helping to prevent stroke caused by non-valvular atrial fibrillation Information booklet IF FOUND, PLEASE RETURN TO: Name Address Phone number Contents ALERT CARD...2 BOOKLET INFORMATION...3 What is atrial
Helping to prevent stroke caused by non-valvular atrial fibrillation Information booklet IF FOUND, PLEASE RETURN TO: Name Address Phone number Contents ALERT CARD...2 BOOKLET INFORMATION...3 What is atrial
Warfarin PATIENT EDUCATION
 Warfarin PATIENT EDUCATION Information for patients taking warfarin Read this booklet to learn: What warfarin is and why you are taking it What blood tests you need to use warfarin safely How other medicines
Warfarin PATIENT EDUCATION Information for patients taking warfarin Read this booklet to learn: What warfarin is and why you are taking it What blood tests you need to use warfarin safely How other medicines
What is Warfarin? 1 Light Brown 3 Light Blue 5 Pink
 Pharmacy Warfarin What is Warfarin? Warfarin is an anticoagulant, sometimes called a blood thinner. It prevents blood clots from forming and also prevents existing clots in the blood vessels from getting
Pharmacy Warfarin What is Warfarin? Warfarin is an anticoagulant, sometimes called a blood thinner. It prevents blood clots from forming and also prevents existing clots in the blood vessels from getting
Understanding your risk of blood clots from hospital to home and how Bevyxxa may help
 Understanding your risk of blood clots from hospital to home and how Bevyxxa may help People who take Bevyxxa and have medicine injected into their spinal and epidural area, or have a spinal puncture,
Understanding your risk of blood clots from hospital to home and how Bevyxxa may help People who take Bevyxxa and have medicine injected into their spinal and epidural area, or have a spinal puncture,
Date of preparation: September 2014 L.GB d
 Date of preparation: September 2014 L.GB.12.2013.4666d This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. If you get any side effects, talk
Date of preparation: September 2014 L.GB.12.2013.4666d This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. If you get any side effects, talk
Clinical Guide - Patient Information (January 2007)
 Clinical Guide - Patient Information (January 2007) Principal Developer: B. Bartle Secondary Developers: J. Johnson, M-F. Scully, L. Vickars Information For Patients Taking Oral Anticoagulants You are
Clinical Guide - Patient Information (January 2007) Principal Developer: B. Bartle Secondary Developers: J. Johnson, M-F. Scully, L. Vickars Information For Patients Taking Oral Anticoagulants You are
Rivaroxaban. medication do? Xarelto. is a blood. Medication. Emboli (PE).
 Medication Information (Ri va rox xa - ban) Other names for this medication: Xarelto What does this medication do? This medication is a blood thinner, also called an anticoagulant. It prevents a blood
Medication Information (Ri va rox xa - ban) Other names for this medication: Xarelto What does this medication do? This medication is a blood thinner, also called an anticoagulant. It prevents a blood
To prevent blood clots after hip or knee replacement surgery This booklet contains information for those who have been prescribed ELIQUIS (apixaban)
 To prevent blood clots after hip or knee replacement surgery This booklet contains information for those who have been prescribed ELIQUIS (apixaban) after hip or knee replacement surgery Always read the
To prevent blood clots after hip or knee replacement surgery This booklet contains information for those who have been prescribed ELIQUIS (apixaban) after hip or knee replacement surgery Always read the
Preventing Blood Clots in Adult Patients
 Manchester Royal Eye Hospital Surgical Services Information for Patients Preventing Blood Clots in Adult Patients This leaflet will give you information on how to reduce the risk of developing blood clots
Manchester Royal Eye Hospital Surgical Services Information for Patients Preventing Blood Clots in Adult Patients This leaflet will give you information on how to reduce the risk of developing blood clots
DO YOU HAVE AFIB OR DVT/PE BLOOD CLOTS?
 To significantly reduce stroke risk from AFib and to treat and help prevent DVT and PE blood clots DO YOU HAVE AFIB OR DVT/PE BLOOD CLOTS? GET TO KNOW HOW THIS LATEST-GENERATION BLOOD THINNER HELPS PROTECT
To significantly reduce stroke risk from AFib and to treat and help prevent DVT and PE blood clots DO YOU HAVE AFIB OR DVT/PE BLOOD CLOTS? GET TO KNOW HOW THIS LATEST-GENERATION BLOOD THINNER HELPS PROTECT
Treatment with Rivaroxaban Xarelto
 Treatment with Rivaroxaban Xarelto Anticoagulation Clinic This handout explains the medicine rivaroxaban, a drug that helps prevent blood clots. What is rivaroxaban? Rivaroxaban (brand name Xarelto) is
Treatment with Rivaroxaban Xarelto Anticoagulation Clinic This handout explains the medicine rivaroxaban, a drug that helps prevent blood clots. What is rivaroxaban? Rivaroxaban (brand name Xarelto) is
Dabigatran. (Da. medication do? What does this. Medication. very fast.
 Medication Information (Da big a tran) Other names for this medication are: Pradaxa What does this medication do? This medication is a blood thinner, also called an anticoagulant. It prevents a blood clot
Medication Information (Da big a tran) Other names for this medication are: Pradaxa What does this medication do? This medication is a blood thinner, also called an anticoagulant. It prevents a blood clot
Treatment with Apixaban Eliquis
 Treatment with Apixaban Eliquis Anticoagulation Clinic 416-530-6000 ext 3477 This handout explains the medicine rivaroxaban, a drug that helps prevent blood clots. What is apixaban? Apixaban (brand name
Treatment with Apixaban Eliquis Anticoagulation Clinic 416-530-6000 ext 3477 This handout explains the medicine rivaroxaban, a drug that helps prevent blood clots. What is apixaban? Apixaban (brand name
Diagnosed with AFib? Your journey with XARELTO starts here.
 THERE S MORE TO KNOW Diagnosed with AFib? Your journey with XARELTO starts here. Do not stop taking XARELTO without talking to your doctor. Stopping XARELTO increases your risk of having a stroke. 2 Welcome
THERE S MORE TO KNOW Diagnosed with AFib? Your journey with XARELTO starts here. Do not stop taking XARELTO without talking to your doctor. Stopping XARELTO increases your risk of having a stroke. 2 Welcome
Diagnosed with DVT/PE blood clots? Your journey with XARELTO starts here.
 THERE S MORE TO KNOW Diagnosed with DVT/PE blood clots? Your journey with XARELTO starts here. Do not stop taking XARELTO without talking to your doctor. Stopping XARELTO increases your risk of having
THERE S MORE TO KNOW Diagnosed with DVT/PE blood clots? Your journey with XARELTO starts here. Do not stop taking XARELTO without talking to your doctor. Stopping XARELTO increases your risk of having
Blood Thinning in Atrial Fibrillation (AF)
 AF A Blood Thinning in Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary Antiarrhythmic
AF A Blood Thinning in Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary Antiarrhythmic
Novel oral anticoagulant therapy (NOAC)
 Haematology Department Novel oral anticoagulant therapy (NOAC) Information for patients, relatives and carers What is novel oral anticoagulant therapy? Novel oral anticoagulants, or NOACs, are drugs which
Haematology Department Novel oral anticoagulant therapy (NOAC) Information for patients, relatives and carers What is novel oral anticoagulant therapy? Novel oral anticoagulants, or NOACs, are drugs which
Pradaxa. [dabigatran etexilate] patient support booklet
![Pradaxa. [dabigatran etexilate] patient support booklet Pradaxa. [dabigatran etexilate] patient support booklet](/thumbs/78/77038668.jpg) Pradaxa [dabigatran etexilate] patient support booklet Important information about your medication and how to take it to help you reduce your risk of stroke associated with atrial fibrillation You have
Pradaxa [dabigatran etexilate] patient support booklet Important information about your medication and how to take it to help you reduce your risk of stroke associated with atrial fibrillation You have
Understand. your risk of. blood clot
 Going into hospital? Understand how to reduce your risk of developing a blood clot Printing of this leaflet has been supported by a donation from Bayer HealthCare. Bayer HealthCare has had no editorial
Going into hospital? Understand how to reduce your risk of developing a blood clot Printing of this leaflet has been supported by a donation from Bayer HealthCare. Bayer HealthCare has had no editorial
Venous Thrombo-Embolism (VTE)
 Venous Thrombo-Embolism (VTE) Information for service users and carers RDaSH leading the way with care Older People s Mental Health Services Reducing risk of unwanted blood clots whilst in hospital About
Venous Thrombo-Embolism (VTE) Information for service users and carers RDaSH leading the way with care Older People s Mental Health Services Reducing risk of unwanted blood clots whilst in hospital About
Rivaroxaban to prevent blood clots for patients who have a lower limb plaster cast. Information for patients Pharmacy
 Rivaroxaban to prevent blood clots for patients who have a lower limb plaster cast Information for patients Pharmacy Your doctor has prescribed a tablet called rivaroxaban. This leaflet tells you about
Rivaroxaban to prevent blood clots for patients who have a lower limb plaster cast Information for patients Pharmacy Your doctor has prescribed a tablet called rivaroxaban. This leaflet tells you about
HELPING TO TREAT DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS AND PULMONARY EMBOLISM
 HELPING TO TREAT DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS AND PULMONARY EMBOLISM AND PREVENT THEIR RECURRENCE PATIENT INFORMATION BOOKLET IF FOUND, PLEASE RETURN TO: If found, please return to: Name Address Phone number It
HELPING TO TREAT DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS AND PULMONARY EMBOLISM AND PREVENT THEIR RECURRENCE PATIENT INFORMATION BOOKLET IF FOUND, PLEASE RETURN TO: If found, please return to: Name Address Phone number It
SAMPLE ONLY. Your Child s Health. A Pediatric Patient s Guide to Using Warfarin. Please order from Documents, Media and Mail: 415/
 Physician Referral Service: 888/689-UCSF Your Child s Health A Pediatric Patient s Guide to Using Warfarin Warfarin (WAR-far-in) Brand Name: Coumadin The purpose of this brochure is to inform you about
Physician Referral Service: 888/689-UCSF Your Child s Health A Pediatric Patient s Guide to Using Warfarin Warfarin (WAR-far-in) Brand Name: Coumadin The purpose of this brochure is to inform you about
pat hways Key therapeutic topic Published: 26 February 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ktt16
 pat hways Anticoagulants, including non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants (NOACs) Key therapeutic topic Published: 26 February 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ktt16 Options for local implementation NICE
pat hways Anticoagulants, including non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants (NOACs) Key therapeutic topic Published: 26 February 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ktt16 Options for local implementation NICE
Medicines and You: A Guide for Older Adults
 Medicines and You: A Guide for Older Adults Council on Family Health Provided in cooperation with U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration and the Administration on Aging
Medicines and You: A Guide for Older Adults Council on Family Health Provided in cooperation with U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration and the Administration on Aging
Venous Thromboembolic Events (VTEs)
 Venous Thromboembolic Events (VTEs) This Infosheet explains what a VTE is, what the causes and risk factors for VTEs are, the symptoms of a VTE, how they can be treated and some tips for self-management.
Venous Thromboembolic Events (VTEs) This Infosheet explains what a VTE is, what the causes and risk factors for VTEs are, the symptoms of a VTE, how they can be treated and some tips for self-management.
About Blood Clots and How to Treat Them
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION About Blood Clots and How to Treat Them This information describes what a blood clot is and how it is treated. About Blood Clots When you have a cut or an injury, your blood
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION About Blood Clots and How to Treat Them This information describes what a blood clot is and how it is treated. About Blood Clots When you have a cut or an injury, your blood
MEDICATION GUIDE ELIQUIS (ELL eh kwiss) (apixaban) tablets
 MEDICATION GUIDE ELIQUIS (ELL eh kwiss) (apixaban) tablets What is the most important information I should know about ELIQUIS? For people taking ELIQUIS for atrial fibrillation: People with atrial fibrillation
MEDICATION GUIDE ELIQUIS (ELL eh kwiss) (apixaban) tablets What is the most important information I should know about ELIQUIS? For people taking ELIQUIS for atrial fibrillation: People with atrial fibrillation
Warfarin - Introduction for New Users
 Warfarin - Introduction for New Users Introduction Blood clots are frequent in patients who have diseases of the blood vessels or heart. Blood clots may pose a dangerous threat to some people, as they
Warfarin - Introduction for New Users Introduction Blood clots are frequent in patients who have diseases of the blood vessels or heart. Blood clots may pose a dangerous threat to some people, as they
Oral anti-cancer treatment
 Oral anti-cancer treatment Information for patients Chemotherapy Name Hospital No Your consultant is Anti-cancer treatment is the term used to describe medicines used to treat cancer, including chemotherapy.
Oral anti-cancer treatment Information for patients Chemotherapy Name Hospital No Your consultant is Anti-cancer treatment is the term used to describe medicines used to treat cancer, including chemotherapy.
Monitoring my anticoagulation treatment
 Information for patients My pharmacist and me Monitoring my anticoagulation treatment With your pharmacist s help, your treatment is easier than ever L Association québécoise des pharmaciens propriétaires
Information for patients My pharmacist and me Monitoring my anticoagulation treatment With your pharmacist s help, your treatment is easier than ever L Association québécoise des pharmaciens propriétaires
I know my value. Be an active part of your anticoagulation therapy with INR self-monitoring
 I know my value Be an active part of your anticoagulation therapy with INR self-monitoring INR* self-monitoring needs only a drop of blood, is easy, fast and decreases the possibility Be involved in your
I know my value Be an active part of your anticoagulation therapy with INR self-monitoring INR* self-monitoring needs only a drop of blood, is easy, fast and decreases the possibility Be involved in your
How Entecavir GH Works
 entecavir monohydrate tablets ENTECAVIR GH Tablets Consumer Medicine Information What is in this leaflet Read this leaflet carefully before taking. This leaflet answers some common questions about. It
entecavir monohydrate tablets ENTECAVIR GH Tablets Consumer Medicine Information What is in this leaflet Read this leaflet carefully before taking. This leaflet answers some common questions about. It
Hospital No. Weston Park Hospital contact number
 Pemetrexed Information for patients Chemotherapy Name Hospital No Your consultant is Important Advice Always carry your chemotherapy alert card. It is important that you know what to do if you feel ill
Pemetrexed Information for patients Chemotherapy Name Hospital No Your consultant is Important Advice Always carry your chemotherapy alert card. It is important that you know what to do if you feel ill
For the Patient: UMYLDREL
 For the Patient: UMYLDREL Other Names: Treatment of Multiple Myeloma Using Lenalidomide (REVLIMID ) and Dexamethasone MY = MYeloma (tumour group) L = Lenalidomide D = Dexamethasone REL = RELapse Uses:
For the Patient: UMYLDREL Other Names: Treatment of Multiple Myeloma Using Lenalidomide (REVLIMID ) and Dexamethasone MY = MYeloma (tumour group) L = Lenalidomide D = Dexamethasone REL = RELapse Uses:
ARE YOU HAVING HIP OR KNEE REPLACEMENT SURGERY?
 ARE YOU HAVING HIP OR KNEE REPLACEMENT SURGERY? GET TO KNOW HOW THIS LATEST-GENERATION BLOOD THINNER HELPS PROTECT YOU FROM BLOOD CLOTS. Once I got the facts, my doctor and I chose XARELTO Do not stop
ARE YOU HAVING HIP OR KNEE REPLACEMENT SURGERY? GET TO KNOW HOW THIS LATEST-GENERATION BLOOD THINNER HELPS PROTECT YOU FROM BLOOD CLOTS. Once I got the facts, my doctor and I chose XARELTO Do not stop
Information about TIA
 Information about TIA Transient Ischemic Attack (mini-stroke) Did I have a TIA? Did you have stroke-like symptoms such as slurred speech or weakness in one arm that seemed to go away after a few minutes
Information about TIA Transient Ischemic Attack (mini-stroke) Did I have a TIA? Did you have stroke-like symptoms such as slurred speech or weakness in one arm that seemed to go away after a few minutes
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO THE LEFT ATRIAL APPENDAGE CLOSURE. Reducing the risk of stroke in atrial fibrillation
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO THE LEFT ATRIAL APPENDAGE CLOSURE Reducing the risk of stroke in atrial fibrillation TABLE OF CONTENTS IMPORTANT Please Note: Information provided by Boston Scientific Corporation
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO THE LEFT ATRIAL APPENDAGE CLOSURE Reducing the risk of stroke in atrial fibrillation TABLE OF CONTENTS IMPORTANT Please Note: Information provided by Boston Scientific Corporation
Mitral valve surgery. Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England.
 Mitral valve surgery Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained the information
Mitral valve surgery Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained the information
Drug information. Baricitinib BARICITINIB. is used to treat rheumatoid arthritis. Helpline
 Drug information Baricitinib BARICITINIB is used to treat rheumatoid arthritis Helpline 0800 5200 520 1 Introduction Baricitinib is a drug that can help prevent your condition causing damage to your body.
Drug information Baricitinib BARICITINIB is used to treat rheumatoid arthritis Helpline 0800 5200 520 1 Introduction Baricitinib is a drug that can help prevent your condition causing damage to your body.
Anticoagulation in Atrial Fibrillation Patient information
 Anticoagulation in Atrial Fibrillation Patient information Introduction This leaflet will help you understand your new medicine. Your new medicine is commonly known as a blood thinner because that is what
Anticoagulation in Atrial Fibrillation Patient information Introduction This leaflet will help you understand your new medicine. Your new medicine is commonly known as a blood thinner because that is what
Patient Information. Preventing and treating blood clots
 Patient Information Preventing and treating blood clots 1_Clexane_Patient_Booklet_AW05.indd 1 8/04/2016 11:26 a The information provided in this document is for patients prescribed CLEXANE, and should
Patient Information Preventing and treating blood clots 1_Clexane_Patient_Booklet_AW05.indd 1 8/04/2016 11:26 a The information provided in this document is for patients prescribed CLEXANE, and should
Atrial fibrillation. Understanding NICE guidance
 Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services Atrial fibrillation NICE clinical guidelines advise the NHS on caring for people with specific conditions or diseases and the treatments
Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services Atrial fibrillation NICE clinical guidelines advise the NHS on caring for people with specific conditions or diseases and the treatments
Drug information. Tofacitinib TOFACITINIB. is used to treat rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis. Helpline
 Drug information Tofacitinib TOFACITINIB is used to treat rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis Helpline 0800 5200 520 1 Introduction Tofacitinib is a drug that can help prevent your condition causing
Drug information Tofacitinib TOFACITINIB is used to treat rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis Helpline 0800 5200 520 1 Introduction Tofacitinib is a drug that can help prevent your condition causing
Deep Vein Thrombosis or Pulmonary Embolism
 What You Need to Know After Deep Vein Thrombosis or Pulmonary Embolism The content provided here is for informational purposes only. It is not intended to diagnose or treat a health problem or disease,
What You Need to Know After Deep Vein Thrombosis or Pulmonary Embolism The content provided here is for informational purposes only. It is not intended to diagnose or treat a health problem or disease,
Living with a New Oral Anticoagulant (NOAC)
 Living with a New Oral Anticoagulant (NOAC) dabigatran (Pradaxa ) rivaroxaban (Xarelto ) apixaban (Eliquis ) Information for patients Produced and made available by the Western Australian Medication Safety
Living with a New Oral Anticoagulant (NOAC) dabigatran (Pradaxa ) rivaroxaban (Xarelto ) apixaban (Eliquis ) Information for patients Produced and made available by the Western Australian Medication Safety
References: Murtagh J. Murtagh s General Practice. 5 th edn. Sydney: McGraw Hill; 2010.
 This presentation is designed to be delivered to people who work in a health care setting; such as nurses, carers and other nursing home staff. If you are an accredited pharmacist, you can use this presentation
This presentation is designed to be delivered to people who work in a health care setting; such as nurses, carers and other nursing home staff. If you are an accredited pharmacist, you can use this presentation
Atrial fibrillation and anticoagulation therapy
 Atrial fibrillation and anticoagulation therapy This leaflet offers more information about atrial fibrillation for patients who have been advised that they need anticoagulation therapy. If you have any
Atrial fibrillation and anticoagulation therapy This leaflet offers more information about atrial fibrillation for patients who have been advised that they need anticoagulation therapy. If you have any
Aortic valve replacement. Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England.
 Aortic replacement Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained the information in
Aortic replacement Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained the information in
Anticoagulants and Antiplatelet. Therapy
 Anticoagulants and Antiplatelet Therapy Your Heart and Blood Clots You ve been told by your healthcare provider that you have a condition that can cause blood clots. This may be due to several factors,
Anticoagulants and Antiplatelet Therapy Your Heart and Blood Clots You ve been told by your healthcare provider that you have a condition that can cause blood clots. This may be due to several factors,
Reducing the Risk of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) whilst in hospital and following your discharge home
 Reducing the Risk of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) whilst in hospital and following your discharge home 1 Part of: South Tyneside and Sunderland Healthcare Group Introduction This leaflet explains what Deep
Reducing the Risk of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) whilst in hospital and following your discharge home 1 Part of: South Tyneside and Sunderland Healthcare Group Introduction This leaflet explains what Deep
Intravenous anti-cancer treatment
 Intravenous anti-cancer treatment Information for patients Chemotherapy Name Hospital No Your consultant is Anti-cancer treatment is the term used to describe medicines used to treat cancer including chemotherapy.
Intravenous anti-cancer treatment Information for patients Chemotherapy Name Hospital No Your consultant is Anti-cancer treatment is the term used to describe medicines used to treat cancer including chemotherapy.
Information for patients, parents and guardians. Your child s doctor has recommended that your child has a procedure called an ablation.
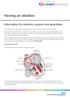 Having an ablation Information for patients, parents and guardians Your child s doctor has recommended that your child has a procedure called an ablation. An ablation is a treatment for an abnormal heartbeat.
Having an ablation Information for patients, parents and guardians Your child s doctor has recommended that your child has a procedure called an ablation. An ablation is a treatment for an abnormal heartbeat.
Dabigatran (Pradaxa )
 What is dabigatran (Pradaxa )? Dabigatran is also called Pradaxa Dabigatran (Pradaxa ) is used to reduce the risk of blood clots and stroke in people with an abnormal heart rhythm known as atrial fibrillation,
What is dabigatran (Pradaxa )? Dabigatran is also called Pradaxa Dabigatran (Pradaxa ) is used to reduce the risk of blood clots and stroke in people with an abnormal heart rhythm known as atrial fibrillation,
Blood-thinning medication after stroke
 Call the Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 or email: info@stroke.org.uk Blood-thinning medication after stroke Blood-thinning medicines are drugs that help to prevent clots forming in your blood. They are
Call the Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 or email: info@stroke.org.uk Blood-thinning medication after stroke Blood-thinning medicines are drugs that help to prevent clots forming in your blood. They are
Methotrexate for inflammatory bowel disease: what you need to know
 Methotrexate for inflammatory bowel disease: what you need to know This leaflet aims to answer your questions about taking methotrexate for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). If you have any questions or
Methotrexate for inflammatory bowel disease: what you need to know This leaflet aims to answer your questions about taking methotrexate for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). If you have any questions or
Pathology Service User Guide Haematology
 Pathology Service User Guide Haematology St Richard s This section of the Pathology Service User Guide includes: Anticoagulant Therapy Information about the Anticoagulant Clinic Low Molecular Weight Heparin
Pathology Service User Guide Haematology St Richard s This section of the Pathology Service User Guide includes: Anticoagulant Therapy Information about the Anticoagulant Clinic Low Molecular Weight Heparin
Blood Thinners. Staying Safe and Healthy While Using Warfarin PATIENT SAFETY ISSUE
 PATIENT SAFETY ISSUE Blood Thinners Staying Safe and Healthy While Using Warfarin Q: What are blood thinners? A: Some prescription medications are commonly called blood thinners. They may also be called
PATIENT SAFETY ISSUE Blood Thinners Staying Safe and Healthy While Using Warfarin Q: What are blood thinners? A: Some prescription medications are commonly called blood thinners. They may also be called
Reducing the risk of venous thrombo-embolism (VTE) in hospital and after discharge
 Reducing the risk of venous thrombo-embolism (VTE) in hospital and after discharge What is a venous thromboembolism (VTE)? This is a medical term that describes a blood clot that develops in a deep vein
Reducing the risk of venous thrombo-embolism (VTE) in hospital and after discharge What is a venous thromboembolism (VTE)? This is a medical term that describes a blood clot that develops in a deep vein
Atrial Fibrillation Your quick guide
 Atrial Fibrillation Your quick guide Coronary heart disease is the UK s single biggest killer. For over 50 years we ve pioneered research that s transformed the lives of people living with heart and circulatory
Atrial Fibrillation Your quick guide Coronary heart disease is the UK s single biggest killer. For over 50 years we ve pioneered research that s transformed the lives of people living with heart and circulatory
A Guide for Patients Prescribed Oral Anticoagulant Therapy
 A Guide for Patients Prescribed Oral Anticoagulant Therapy www.heartrhythmalliance.org Contents Glossary Introduction 3 5 Why have I been prescribed an anticoagulant? 6 What are the available anticoagulant
A Guide for Patients Prescribed Oral Anticoagulant Therapy www.heartrhythmalliance.org Contents Glossary Introduction 3 5 Why have I been prescribed an anticoagulant? 6 What are the available anticoagulant
Abdominal surgery for Crohn's disease. Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England.
 Abdominal surgery for Crohn's disease Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained
Abdominal surgery for Crohn's disease Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained
Pulmonary embolism. Information for patients Specialised Medicine
 Pulmonary embolism Information for patients Specialised Medicine page 2 of 8 What is a pulmonary embolism? A blood clot that has formed inside one of your veins, usually in your leg, is called a deep vein
Pulmonary embolism Information for patients Specialised Medicine page 2 of 8 What is a pulmonary embolism? A blood clot that has formed inside one of your veins, usually in your leg, is called a deep vein
Blood-thinning medication after stroke
 Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Blood-thinning medication after stroke Blood-thinning medicines are drugs that help to prevent clots forming in your blood. They are often prescribed
Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Blood-thinning medication after stroke Blood-thinning medicines are drugs that help to prevent clots forming in your blood. They are often prescribed
Mohs surgery. Information for patients Dermatology
 Mohs surgery Information for patients Dermatology Why have I been given this leaflet? You have been given this leaflet because you are going to have a procedure known as Mohs surgery. This leaflet explains
Mohs surgery Information for patients Dermatology Why have I been given this leaflet? You have been given this leaflet because you are going to have a procedure known as Mohs surgery. This leaflet explains
Pazopanib (Votrient ) oral for renal tumours
 Pazopanib (Votrient )oral for renal tumours Pazopanib (Votrient ) oral for renal tumours This leaflet is offered as a guide to you and your family. Pazopanib (Votrient ) is a type of medicine called a
Pazopanib (Votrient )oral for renal tumours Pazopanib (Votrient ) oral for renal tumours This leaflet is offered as a guide to you and your family. Pazopanib (Votrient ) is a type of medicine called a
Bevacizumab (Avastin ) treatment for Neurofibromatosis Type 2 (NF2) Information for patients
 Bevacizumab (Avastin ) treatment for Neurofibromatosis Type 2 (NF2) Information for patients This booklet has been written to give you more information about bevacizumab (commonly known as Avastin). This
Bevacizumab (Avastin ) treatment for Neurofibromatosis Type 2 (NF2) Information for patients This booklet has been written to give you more information about bevacizumab (commonly known as Avastin). This
Traztuzumab (Herceptin)
 Traztuzumab (Herceptin) Information for patients Chemotherapy Name Hospital No Your consultant is Important Advice Always carry your chemotherapy alert card. It is important that you know what to do if
Traztuzumab (Herceptin) Information for patients Chemotherapy Name Hospital No Your consultant is Important Advice Always carry your chemotherapy alert card. It is important that you know what to do if
Treating your abdominal aortic aneurysm by open repair (surgery)
 Patient information Abdominal aortic aneurysm open surgery Treating your abdominal aortic aneurysm by open repair (surgery) Introduction This leaflet tells you about open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm,
Patient information Abdominal aortic aneurysm open surgery Treating your abdominal aortic aneurysm by open repair (surgery) Introduction This leaflet tells you about open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm,
Capecitabine (Xeloda) tablets
 Capecitabine (Xeloda) tablets This is used with radiotherapy to treat colorectal cancer Information for patients Chemotherapy Name Hospital No Your consultant is Important Advice Always carry your chemotherapy
Capecitabine (Xeloda) tablets This is used with radiotherapy to treat colorectal cancer Information for patients Chemotherapy Name Hospital No Your consultant is Important Advice Always carry your chemotherapy
A Guide for Patients Prescribed Oral Anticoagulant Therapy
 A Guide for Patients Prescribed Oral Anticoagulant Therapy Contents Glossary 3 Introduction 4 Why have I been prescribed an anticoagulant? 4 What are the available anticoagulant options? 8 How do anticoagulant
A Guide for Patients Prescribed Oral Anticoagulant Therapy Contents Glossary 3 Introduction 4 Why have I been prescribed an anticoagulant? 4 What are the available anticoagulant options? 8 How do anticoagulant
Direct Current (DC) Cardioversion
 Page 1 of 10 Direct Current (DC) Cardioversion Introduction This leaflet is to inform you about your planned Direct Current (DC) electrical cardioversion. A cardioversion is an electrical treatment which
Page 1 of 10 Direct Current (DC) Cardioversion Introduction This leaflet is to inform you about your planned Direct Current (DC) electrical cardioversion. A cardioversion is an electrical treatment which
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Treating Blood Clots. What is a blood clot? DRAFT
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Treating Blood Clots About deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) and how they are treated This handout explains blood clots, their symptoms, and how they
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Treating Blood Clots About deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) and how they are treated This handout explains blood clots, their symptoms, and how they
A Guide for Patients Prescribed Oral Anticoagulant Therapy
 A Guide for Patients Prescribed Oral Anticoagulant Therapy Contents Glossary Introduction Why have I been prescribed an anticoagulant? What are the available anticoagulant options? How do anticoagulant
A Guide for Patients Prescribed Oral Anticoagulant Therapy Contents Glossary Introduction Why have I been prescribed an anticoagulant? What are the available anticoagulant options? How do anticoagulant
Abemaciclib (Verzenios ) Abemaciclib (Verzenios )
 Abemaciclib (Verzenios ) Abemaciclib (Verzenios ) Abemaciclib is a targeted (biological) therapy. This group of drugs block the growth and spread of cancer. They target and interfere with processes in
Abemaciclib (Verzenios ) Abemaciclib (Verzenios ) Abemaciclib is a targeted (biological) therapy. This group of drugs block the growth and spread of cancer. They target and interfere with processes in
Heart Valve Replacement
 Heart Valve Replacement Introduction Sometimes people have serious problems with the valves in their hearts. A heart valve repair or replacement surgery restores or replaces a defective heart valve. If
Heart Valve Replacement Introduction Sometimes people have serious problems with the valves in their hearts. A heart valve repair or replacement surgery restores or replaces a defective heart valve. If
Listen to Your Heart. What Everyone Needs To Know About Atrial Fibrillation & Stroke. The S-ICD System. The protection you need
 Listen to Your Heart The S-ICD System What Everyone Needs To Know About Atrial Fibrillation & Stroke The protection you need without Stroke. touching Are you your at heart risk? Increase your knowledge.
Listen to Your Heart The S-ICD System What Everyone Needs To Know About Atrial Fibrillation & Stroke The protection you need without Stroke. touching Are you your at heart risk? Increase your knowledge.
HIGHLANDS SURGERY NEWSLETTER
 HIGHLANDS SURGERY NEWSLETTER Spring 2017 Inside This Issue 1 Virtual GP service (babylon) 2 Website Did Not Attend 3 Who to contact when you are not feeling well 4 Who to contact when you are not feeling
HIGHLANDS SURGERY NEWSLETTER Spring 2017 Inside This Issue 1 Virtual GP service (babylon) 2 Website Did Not Attend 3 Who to contact when you are not feeling well 4 Who to contact when you are not feeling
bpac better e m dicine
 INR Testing Quiz Feedback bpac nz better medicin e Contents INR Testing Quiz 2 Quiz Feedback: Responses from Colleagues, and Expert Review 4 bpac nz Review : Dr Janine Bailey, Motueka Dr Stephen Kuzmich,
INR Testing Quiz Feedback bpac nz better medicin e Contents INR Testing Quiz 2 Quiz Feedback: Responses from Colleagues, and Expert Review 4 bpac nz Review : Dr Janine Bailey, Motueka Dr Stephen Kuzmich,
1. Wounds may be left exposed with some ointment applied to the stitch line:
 GENERAL AFTERCARE AT HOME Elevation If you have had surgery to your face or the chest area it is important that you try to elevate this area in the first couple of days as there is the tendency to swelling.
GENERAL AFTERCARE AT HOME Elevation If you have had surgery to your face or the chest area it is important that you try to elevate this area in the first couple of days as there is the tendency to swelling.
Pemetrexed APOTEX Powder for Injection Contains the active ingredient pemetrexed (as disodium)
 Pemetrexed APOTEX Powder for Injection Contains the active ingredient pemetrexed (as disodium) Consumer Medicine Information For a copy of a large print leaflet, Ph: 1800 195 055 What is in this leaflet
Pemetrexed APOTEX Powder for Injection Contains the active ingredient pemetrexed (as disodium) Consumer Medicine Information For a copy of a large print leaflet, Ph: 1800 195 055 What is in this leaflet
Oral Systemic Therapy
 Patient & Family Guide 2018 Oral Systemic Therapy www.nscancercare.ca Patient s Name: Type of Treatment: Cancer Doctor: Cancer Clinic: Phone Number: Emergency Department Phone Number: Who do I call if
Patient & Family Guide 2018 Oral Systemic Therapy www.nscancercare.ca Patient s Name: Type of Treatment: Cancer Doctor: Cancer Clinic: Phone Number: Emergency Department Phone Number: Who do I call if
Medicines in Scotland: What s the right treatment for me? Information for patients and the public
 Medicines in Scotland: What s the right treatment for me? Information for patients and the public You can read and download this document from our website. We are happy to consider requests for other languages
Medicines in Scotland: What s the right treatment for me? Information for patients and the public You can read and download this document from our website. We are happy to consider requests for other languages
APO-Ondansetron Contains the active ingredient, ondansetron (as hydrochloride dihydrate)
 APO-Ondansetron Contains the active ingredient, ondansetron (as hydrochloride dihydrate) Consumer Medicine Information For a copy of a large print leaflet, Ph: 1800 195 055 What is in this leaflet Read
APO-Ondansetron Contains the active ingredient, ondansetron (as hydrochloride dihydrate) Consumer Medicine Information For a copy of a large print leaflet, Ph: 1800 195 055 What is in this leaflet Read
Rheumatology Department Patient Information Leaflet
 Methotrexate Rheumatology Department Patient Information Leaflet Please keep this information in a safe place Introduction This leaflet provides information about methotrexate which will be discussed with
Methotrexate Rheumatology Department Patient Information Leaflet Please keep this information in a safe place Introduction This leaflet provides information about methotrexate which will be discussed with
MEDICATION GUIDE JANTOVEN (JAN-to-ven) Tablets (Warfarin Sodium Tablets, USP)
 MEDICATION GUIDE JANTOVEN (JAN-to-ven) Tablets (Warfarin Sodium Tablets, USP) Read this Medication Guide before you start taking JANTOVEN (Warfarin Sodium Tablets, USP) and each time you get a refill.
MEDICATION GUIDE JANTOVEN (JAN-to-ven) Tablets (Warfarin Sodium Tablets, USP) Read this Medication Guide before you start taking JANTOVEN (Warfarin Sodium Tablets, USP) and each time you get a refill.
MEDICATION GUIDE PRADAXA (pra dax a) (dabigatran etexilate mesylate) capsules
 MEDICATION GUIDE PRADAXA (pra dax a) (dabigatran etexilate mesylate) capsules Read this Medication Guide before you start taking PRADAXA and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This
MEDICATION GUIDE PRADAXA (pra dax a) (dabigatran etexilate mesylate) capsules Read this Medication Guide before you start taking PRADAXA and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This
Methotrexate. Information for patients. Paediatric Rheumatology. Feedback
 Feedback We appreciate and encourage feedback. If you need advice or are concerned about any aspect of care or treatment please speak to a member of staff or contact the Patient Advice and Liaison Service
Feedback We appreciate and encourage feedback. If you need advice or are concerned about any aspect of care or treatment please speak to a member of staff or contact the Patient Advice and Liaison Service
SAFE study A-fib ED Anticoagulation Package
 SAFE study A-fib ED Anticoagulation Package In this package you will find documents to help you make decision making easy for the Anticoagulation of New AFib patients being discharged from the ED: 1. Anticoagulation
SAFE study A-fib ED Anticoagulation Package In this package you will find documents to help you make decision making easy for the Anticoagulation of New AFib patients being discharged from the ED: 1. Anticoagulation
