LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS
|
|
|
- Kenneth Sullivan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. Human heart has (a) one auricle and one ventricle (b) two auricles and one ventricle (c) two auricles and two ventricles (d) one auricle and two ventricles 2. The blood cells which are carriers of oxygen are (a) RBCs (b) platelets (c) WBCs (d) all the above Ans. (a) 3. The blood cells which protect the body from infection are (a) RBCs (b) platelets (c) WBCs (d) all the above 4. The four blood groups in humans are (a) A, B, C and D (b) A, B, AB and C (c) A, B, AB and O (d) A, B, AB and OO 5. Movement of water in the plant body takes place through (a) xylem (b) vascular tissues (c) phloem (d) stomata Ans. (a) 6. Prepared food material is carried through (a) xylem (b) vascular tissues (c) phloem (d) stomata 7. Water from the soil enters the root xylem by the process of (a) diffusion (b) evaporation (c) osmosis (d) transpiration Ans. (d) 8. The heart beat is measured by an instrument called (a) thermometer (b) sphygmomanometer (c) stethoscope (d) none of the above Biology Class VIII 1 Question Bank
2 9. Nucleus is present in (a) RBCs (b) WBCs (c) blood platelets (d) all the above Ans. (b) 10. Arteries are the blood vessels that carry blood (a) away from the heart (b) to the heart (c) both (d) none of these Ans. (a) 11. Pulmonary vein carries (a) deoxygenated blood (b) oxygenated blood (c) lymph (d) none Ans. (b) 12. The blood group which is called universal recipient (a) A (b) AB (c) B (d) O Ans. (b) 13. Wall of arteries are (a) thin and muscular (b) thick and muscular (c) single cell thick (d) thin and valved Ans. (b) 14. Valves prevent blood from (a) entering the heart (b) leaving the heart (c) flowing backward in the heart (d) flowing forward in the heart 15. Blood cells responsible for clotting are (a) RBCs (b) WBCs (c) blood platelets (d) all of these 16. The finest blood vessels are (a) veins (b) arteries (c) aorta (d) capillaries Ans. (d) 17. Blood cells without nucleus are (a) RBCs (b) WBCs (c) blood platelets (d) all of these Ans. (a) Biology Class VIII 2 Question Bank 2
3 18. The only artery which carries deoxygenated blood is (a) aorta (b) pulmonary artery (c) superior vena cava (d) inferior vena cava Ans. (b) 19. The artery which supplies blood to all parts of the body is (a) pulmonary artery (b) superior vena cava (c) inferior vena cava (d) aorta Ans. (d) 20. Capillary is a/an (a) broad tube (b) artery with thick wall (c) vein with large lumen (d) narrow tube made up of endothelium only Ans. (d) II. Fill in the blanks. 1. Water passes into a root by the process called Osmosis occurs through a... membrane. 3. Movement of water occurs from a... solution into a... solution in osmosis. 4. Water is lost from the leaves by Upward movement of water takes place through In human body, heart is located on the... side of the chest cavity. 7. The blood vessels which carry blood from the heart to different parts of the body are called carry pure blood. 9. The red-coloured pigment present in RBCs is called The fluid part of blood is called Pus contains... and The largest artery in the body is the The two upper chambers of the heart are called The two lower chambers of the heart are called The clear, colourless, liquid part of the blood is called The pulmonary artery carries blood from the... to the.... Biology Class VIII 3 Question Bank
4 17. A person suffering from... has few... in his blood. 18. Red blood cells are formed in the are the blood vessels which carry blood towards the heart. 20. The stretching and relaxing of arteries with each heartbeat felt as throbbing is called Blood cells which fight against infection are Oxygenated blood is found on the... side of the heart tissue is involved in transportation of food in plants. 24. The blood loaded with the carbon dioxide from the body comes into the... of the heart. 25. The carbon dioxide loaded blood from the right ventricle is pumped into the lungs through... artery. Ans. 1. Osmosis 2. Partially permeable 3. Weaker, Stronger 4. Stomata 5. Xylem 6. Left 7. Arteries 8. Arteries 9. Haemoglobin 10. Plasma 11. Destroyed tissue cells, Erythrocytes 12. Aorta 13. Auricles 14. Ventricles 15. Plasma 16. Heart, Lungs 17. Infection, WBCs 18. Bone marrow 19. Veins 20. Pulse 21. White blood corpuscles 22. Left 23. Phloem 24. Right auricle 25. Pulmonary. III. Write true or false in front of the statements given below: 1. In Spirogyra, transport of materials take place through osmosis. 2. Xylem and phloem are vascular tissues. 3. Girdling experiment demonstrates food synthesis in plants. 4. Platelets help in clotting of blood. 5. The four blood groups in human beings are A, B, AB and AO. 6. People with blood group O are called universal recipients. 7. Blood group A has antigen A. 8. Impure blood is received by the right auricle. 9. The solid part of blood is called plasma. Biology Class VIII 4 Question Bank 4
5 10. Leucocytes are larger than erythrocytes and contain haemoglobin. 11. Haemoglobin combines with oxygen to form carboxyhaemoglobin. 12. Veins connect arteries with capillaries. 13. Heart is enclosed by a single membrane called pericardium. 14. Impure blood is received by the right auricle. 15. Walls of auricles are thinner than the walls of ventricles. Ans. 1. T 2. T 3. F 4. T 5. T 6. F 7. T 8. T 9. F 10. T 11. T 12. T 13. F 14. T 15. T IV. A. Match the statements in Column A with those in Column B. Column A Column B 1. Heart (a) Movement of materials 2. Food and oxygen (b) Pipes for transport in man 3. Carrier of oxygen (c) A living pump 4. Circulation (d) Materials needed by every living being 5. Arteries and veins (e) Red blood cells Ans. A. 1. c 2. d 3. e 4. a 5. b B. Match the column I with column II. Column I Column II 1. Universal Donor (a) Platelets 2. Blood Clotting (b) Heart 3. Rhessus factor (c) Veins 4. Vessel with valves (d) Rh factor 5. S-A node (e) O group Ans. B. 1. e 2. a 3. d 4. c 5. b V. Describe the function of the following: 1. Heart Ans. Heart acts as a pumping organ. It pumps blood to all the body organs. 2. Blood vessels Ans. Blood vessels carry blood from heart to different organs and also carry blood from different organs to heart. So they act as Biology Class VIII 5 Question Bank
6 channel between heart and different body organs. 3. Red blood cells Ans. Red blood cells have a red pigment called haemoglobin. Due to this pigment, RBCs act as a oxygen carrier from lungs to different body organs and also take in carbon dioxide from different body organs to lungs. 4. White blood cells Ans. These cells act as soldiers for body because they engulf viruses and bacteria in the body. 5. Platelets Ans. These blood cells help in blood clotting. VI. Answer the following Question. 1. Name the main parts of the circulatory system. Ans. Circulatory system is mainly composed of three parts (i) Heart (pumping system) (ii) Blood vessels (Arteries & Vains) (iii) Blood (blood cells & plasma) 2. Name the organ from which oxygenated blood goes into the heart. Ans. Lungs are the organs from which oxygenated blood goes into the heart with the help of haemoglobin. 3. Name the two aspects of transport in higher plants. Ans. In higher plants theee are some vascular tissues through which transportation of food and water occur. These vascular tissues consists of two tube-like structures called xylem and phloem. 4. How does transport of materials take place in unicellular plants? Ans. In unicellular plants like Chlamydomonas, transport of material takes place by a process called diffusion. It is a major method of transport in unicellular plants. 5. What are root hairs? Mention the function performed by root hairs. Ans. Root hairs are the microscopic, unicellular structures. These hairs develope from epidermis. Biology Class VIII 6 Question Bank 6
7 Root hairs greatly increase the surface area for the absorption of water and minerals. 6. How does movement and absorption of water take place through root? Ans. In plants, movement of water and minerals from roots to stems takes place through a conducting tissue called xylem. Water and minerals in roots are absorbed by root hairs from the soil. And in these root hairs water passes by a process called osmosis. Osmosis is the movement of water molecule from high concentration region to low concentration region through a partially permeable membrane. Osmosis in plant cells. In plants, water absorb through root hairs by the process of osmosis. Cell membrane of the plant cell is partially permeable membrane and the cell sap inside the cell is a strong solution. Due to this strong solution, water enters in the cell through partially permeable membrane by the process of osmosis. Now this cell sap is weaker than the second cell. Again osmosis takes place between these cells and this process is going on. 7. Name the process by which water loss takes place through leaves. Ans. Transpiration is the process by which loss of water takes place. 8. Mention the significance of transpiration. Ans. Transpiration is a necessary evil because there is loss of water in the form of water vapour. But it also has many significance which are as follows: (i) Transpiration stream. When water is lost through leaves in the form of water vapour than water is sucked up from the xylem vessels and xylem vessels from roots. So, there is a continuous flow of water from roots to leaves. This movement of water is called transpiration stream. (ii) Transport of salts. With the absorption of water some Biology Class VIII 7 Question Bank
8 mineral salts are also absorbed and carried from root to leaves. (iii) Cooling. Due to rapid transpiration of water from leaf surface and the consequent absorption of latent heat from the leaf tissue help in keeping the temperature low. 9. List important functions of the blood. Ans. Functions of blood. (i) The major function of blood is to carry oxygen with the help of haemoglobin from lung tissues to other tissues. (ii) It carries food and vitamins in dissolved form with the help of plasma. (iii) It carries nitrogenous waste products from tissues to excretory organs. (iv) It regulates the body temperature by distributing the heat equally. (v) It also protects body against bacterial infection by supplying leucocytes (WBCs) when needed. 10. How do the red blood corpuscles differ from other cells of the body? Ans. Red blood corpuscles (RBCs) are non-nucleated cells (unlike other cells). These cells are also have a oxygen-carrying pigment haemoglobin, which is red in colour. This pigment carries oxygen from lungs to other tissues. 11. How does blood clot? Name a disease in which the blood fails to clot. Ans. The production of a mass of semisolid material at the site of injury that prevents the further loss of blood is called blood clotting. At the site of wound, a network is formed of a substance called fibrin. Fibrin is formed from a substance called fibrinogen. Fibrinogen reacts with thrombin which is produced by platelets and form fibrin. Calcium is also an important factor which is required in blood clotting. Biology Class VIII 8 Question Bank 8
9 Haemophilia is a genetic disease in which blood clotting does not occur. It has been called the royal disease because it suddenly showed up as a genetic mutation in Queen Victoria of Britain. 12. Give the important differences between arteries and veins. Ans. Difference between arteries and veins. Arteries Veins (1) These are blood vessels that (1) These are the blood vessels carry blood from heart to that carry blood from different body organs. different organs of the body to heart. (2) Arteries carry oxygenated (2) Veins carry de-oxygenated blood except pulmonary blood except pulmonary artery. vein. (3) Arteries are made of thick (3) Veins are made of thin and and elastic wall. less elastic wall. (4) Arteries are deep in the (4) Veins are present towards body. the surface of the body. 13. What are the functions of heart? Ans. In mammals, heart is four-chembered and it acts as a pumping organ in the body. It receives deoxygenated blood from various organs of the body and pump oxygenated blood to various organs of the body. 14. What first aid you would give to a patient suffering from haemorrhage? Ans. Haemorrhage means excessive bleeding. In case of haemorrhage, we should tie a bandage over the bleeding part, towards the heat, so that bleeding can be minimised. In case of arms or legs, a ligature can be used. A rubber band or a handkirchief can be used as ligature. 15. What is the function of haemoglobin in the blood? Ans. Function of haemoglobin. Haemoglobin is a red pigment and Biology Class VIII 9 Question Bank
10 consists of protein and iron. It is an oxygen-carrying pigment and carry oxygen from lungs to different organs and it also carries carbon dioxide from different organs to lungs. 16. What is the composition of blood? Ans. Blood is composed of plasma and blood cells. (i) Red Blood Cells (RBCs) (ii) White Blood Cells (WBCs) (iii) Platelets 17. State where oxygen and carbon dioxide enter the blood stream and where they leave it. Ans. From lungs oxygen enters into the blood stream with the help of haemoglobin. Carbon dioxide released from different body organs enter into the blood stream and leave out with the help of lungs. 18. Name a vein which carries oxygenated blood and an artery which carries deoxygenated blood. Ans. All the arteries have oxygenated blood except pulmonary artery which has deoxygenated blood. All the veins have deoxygenated blood except pulmonary vein which has oxygenated blood. 19. What is the function of valve in the heart? Ans. The valve in the heart allows the blood to flow in one direction only that is, from the auricles into the ventricles, and not back from the ventricles. 20. Which blood cells can be called as the soldiers of the body? Ans. WBCs are called the soldiers of the body because they protect the body from infection by ingesting foreign bodies like bacteria and viruses. 21. What prevents the blood from going in the wrong direction in the heart? Ans. In heart, valves are present which allow the blood to flow only in one direction, not in wrong direction. Biology Class VIII 10 Question Bank 10
11 22. What are four blood groups? On what basis they are formed? Ans. There are four types of blood group: A, B, AB, and O Blood group are based on the basis of antigens. For example, Blood group A has antigen A Blood group B has antigen B Blood group AB has both antigen A & B Blood group O has neither antigen A nor B. 23. Why a person with blood group O is called a universal donor and a person with blood group AB called a universal recipient? Ans. A person with blood group O is called universal donor because RBCs of blood group O have no antigens. A person with blood group AB is called universal recipient because it has no antibodies. 24. What is the relationship between the rate of heart beat and pulse rate? Ans. Rate of pulse is directly proportional to rate of heart beat. The stretching and relaxing of the arteries with each heart beat is felt as a throbbing called pulse. 25. Why does rate of heart beat increase after running? Ans. After running, heart beat increases because during running we require more oxygen. To complete the demand of oxygen the heart has to pump more blood. Due to this reason, heart beat increases. 26. What is lymph? How is it different from blood? Ans. When blood reaches at the capillaries, some of the water and dissolved solutes are filtered out from blood plasma into tissue spaces and form tissue fluid. Some of the tissue fluid entre into lymph vessels which is called lymph. Lymph has all the elements of the blood except RBCs and blood platelets. Biology Class VIII 11 Question Bank
12 27. What is transpiration? Ans. Transpiration is the loss of water from leaves in the form of vapour into the atmosphere. It is a necessary evil. 28. What is translocation? Ans. Translocation is the movement of food molecules formed during photosynthesis throughout the plant through phloem. 29. Define wilting. Ans. During transpiration, when water is absorbed more quickly than their absorption rate then plant cell will lose water. In this condition, the leaves, the stem and the flowers will drop. This condition is called wilting. 30. What is active transportation of minerals? Ans. The movement of minerals through membranes in living cells, often against a concentration gradient is called active transportation of minerals. This process requires energy. Although, minerals are transported through xylem to all parts of the plants. **** Biology Class VIII 12 Question Bank 12
TRANSPORTATION IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS
 TRANSPORTATION IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS Circulatory system: organ system for the circulation of materials inside the body Materials transported in the body: Water, Oxygen, Carbon dioxide, Nutrients, Hormones
TRANSPORTATION IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS Circulatory system: organ system for the circulation of materials inside the body Materials transported in the body: Water, Oxygen, Carbon dioxide, Nutrients, Hormones
Life Processes. dronstudy.com
 Human Circulatory System Life Processes Circulatory system is responsible for transportation of various substances in human beings. It is composed of heart, arteries, veins and blood capillaries. Blood
Human Circulatory System Life Processes Circulatory system is responsible for transportation of various substances in human beings. It is composed of heart, arteries, veins and blood capillaries. Blood
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT
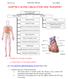 CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
perfect practice makes perfect
 CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT PLANTS Function of heart Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Wilting Transpiration: function
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT PLANTS Function of heart Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Wilting Transpiration: function
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Science Matters Chapter 8 Introduction Living things need a transport system to carry things around the body. In humans its called The Circulatory system. The parts of the system
The Circulatory System Science Matters Chapter 8 Introduction Living things need a transport system to carry things around the body. In humans its called The Circulatory system. The parts of the system
The Cardiovascular System home study course
 The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
Transportation and Excretion 7 th Biology
 Page1 Transportation and Excretion 7 th Biology William Harvey was an English physician was the first to give the details of blood circulation, the properties of blood and the pumping of blood by the heart.
Page1 Transportation and Excretion 7 th Biology William Harvey was an English physician was the first to give the details of blood circulation, the properties of blood and the pumping of blood by the heart.
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans
 Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
Organisation. AQA Biology topic 2
 Organisation AQA Biology topic 2 2.1 Principles of Organisation Cells, tissues, organs and systems Basically, all living things are made up of cells A group of CELLS makes up a TISSUE A group of TISSUES
Organisation AQA Biology topic 2 2.1 Principles of Organisation Cells, tissues, organs and systems Basically, all living things are made up of cells A group of CELLS makes up a TISSUE A group of TISSUES
Transport Systems in Plants and Animals
 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Bronze Level Mark Scheme Time
Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Bronze Level Mark Scheme Time
Lower Secondary Science Blood Circulatory System Notes / Advanced Notes
 Lower Secondary Science Blood Circulatory System Notes / Advanced Notes Double Circulation in Mammals In mammals, there is a double circulation (i.e. blood passes through the heart twice in one complete
Lower Secondary Science Blood Circulatory System Notes / Advanced Notes Double Circulation in Mammals In mammals, there is a double circulation (i.e. blood passes through the heart twice in one complete
The circulatory system
 The circulatory system Key words Vessels heart blood plasma platelets haemoglobin To engulf arteries capillaries veins venules lymphocytes Atrium / - a ventricle tricuspid bicuspid cardiac coronary Humans
The circulatory system Key words Vessels heart blood plasma platelets haemoglobin To engulf arteries capillaries veins venules lymphocytes Atrium / - a ventricle tricuspid bicuspid cardiac coronary Humans
Chapter 16: Circulation
 Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
Multicellular Organisms. Sub-Topic 2.6 Transport Systems in Animals
 Multicellular Organisms Sub-Topic 2.6 Transport Systems in Animals On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to state that: In mammals a transport system is required to deliver essential substances
Multicellular Organisms Sub-Topic 2.6 Transport Systems in Animals On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to state that: In mammals a transport system is required to deliver essential substances
It s Totally Tubular, Dude!
 It s Totally Tubular, Dude! Objective: To learn the structure and function of the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Bell Work: For the following, place the items in order from most simple to most complex:
It s Totally Tubular, Dude! Objective: To learn the structure and function of the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Bell Work: For the following, place the items in order from most simple to most complex:
The Circulatory System. The circulatory system includes the Heart, Blood Tissue and the Blood Vessels.
 The Circulatory System The circulatory system includes the Heart, Blood Tissue and the Blood Vessels. The Circulatory System-Transport The absorption and circulation of materials throughout an organism
The Circulatory System The circulatory system includes the Heart, Blood Tissue and the Blood Vessels. The Circulatory System-Transport The absorption and circulation of materials throughout an organism
Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93)
 Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
They need to transport all these to various parts of their body. Further, animal need to transport wastes to parts from where they can be removed.
 They need to transport all these to various parts of their body. Further, animal need to transport wastes to parts from where they can be removed. PLASMA Carry various substances. Blood is a liquid, which
They need to transport all these to various parts of their body. Further, animal need to transport wastes to parts from where they can be removed. PLASMA Carry various substances. Blood is a liquid, which
The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide.
 Section 1: The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What
Section 1: The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What
CIE Biology GCSE. 9: Transport in animals. Notes.
 CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
07 Human transport Biology Notes IGCSE Cambridge #69 Transport in humans - the circulatory system
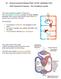 07 Human transport Biology Notes IGCSE Cambridge 2014 #69 Transport in humans - the circulatory system The main transport system of human is the circulatory system, a system of tubes (blood vessels) with
07 Human transport Biology Notes IGCSE Cambridge 2014 #69 Transport in humans - the circulatory system The main transport system of human is the circulatory system, a system of tubes (blood vessels) with
Blood flows away from the heart in arteries, to the capillaries and back to the heart in the veins
 Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Blood 10/22/2012
 Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
The Function. To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body.
 The Function To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body. What makes up the circulatory system? 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood vessels Blood travels from the heart to the body
The Function To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body. What makes up the circulatory system? 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood vessels Blood travels from the heart to the body
Monday 14 th May The Body Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 10 Cardio-Respiratory System
 Monday 14 th May 2018 The Body Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 10 Cardio-Respiratory System Homework 1. What is the function of the cardiovascular system? 2. List the main components of blood and describe
Monday 14 th May 2018 The Body Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 10 Cardio-Respiratory System Homework 1. What is the function of the cardiovascular system? 2. List the main components of blood and describe
Circulatory System. Circulatory System
 Circulatory System Transportation system of the body There are two types of circulatory systems: 1. Open Circulatory System pumps blood to open ended vessels into the body cavities containing organs, then
Circulatory System Transportation system of the body There are two types of circulatory systems: 1. Open Circulatory System pumps blood to open ended vessels into the body cavities containing organs, then
OB16 Demonstrate the effect of exercise and rest on pulse and breathing rate and appreciate that a balance of each promotes good health
 Biology: 6. The Circulation System Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier Syllabus OB13 Describe the function and composition of blood
Biology: 6. The Circulation System Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier Syllabus OB13 Describe the function and composition of blood
Circulatory System Objective sheet 3
 Circulatory System Objective sheet 3 10. Functions of blood 1) Transport oxygen and nutrients 2) Transport of carbon dioxide and waste 3) Protection against disease causing micro-organisms 4) Clotting
Circulatory System Objective sheet 3 10. Functions of blood 1) Transport oxygen and nutrients 2) Transport of carbon dioxide and waste 3) Protection against disease causing micro-organisms 4) Clotting
Cells & Systems The Circulatory System
 Cells & Systems The Circulatory System The Circulatory System What does it do? Your body s transportation network Transports Oxygen (O) Transports Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 ) Removes Waste products Delivers
Cells & Systems The Circulatory System The Circulatory System What does it do? Your body s transportation network Transports Oxygen (O) Transports Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 ) Removes Waste products Delivers
Life Functions Common to Living Things
 Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
learningobjectives At the end of the lesson, you should be able to: - Humans Explain the need for a transport system in multicellular
 transport in humans learningobjectives At the end of the lesson, you should be able to: - Humans Explain the need for a transport system in multicellular organisms Identify the parts of the human circulatory
transport in humans learningobjectives At the end of the lesson, you should be able to: - Humans Explain the need for a transport system in multicellular organisms Identify the parts of the human circulatory
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY
 TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
2. What makes up the most of your blood? least of your blood? 1. Look like red discs, have a pale center, no nucleus, similar in size
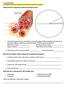 I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
Learning Objectives; 1. Identify the key features of the cardiovascular system. 2. Describe the function of the cardiovascular system.
 Learning Objectives; 1. Identify the key features of the cardiovascular system. 2. Describe the function of the cardiovascular system. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yaxna8lmoiy The Circulatory System
Learning Objectives; 1. Identify the key features of the cardiovascular system. 2. Describe the function of the cardiovascular system. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yaxna8lmoiy The Circulatory System
12.1 The Function of Circulation
 12.1 The Function of Circulation The Circulatory System Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) Heart pump beats 100 000 times a day Deliver oxygen and nutrients Function of Circulation Multicellular organisms
12.1 The Function of Circulation The Circulatory System Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) Heart pump beats 100 000 times a day Deliver oxygen and nutrients Function of Circulation Multicellular organisms
Class X Chapter 7 The Circulatory System Biology REVIEW QUESTIONS: A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE: (Select the most appropriate option in each case)
 REVIEW QUESTIONS: A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE: (Select the most appropriate option in each case) Question 1: Agranulocytes are: (a) lymphocytes and monocytes (b) lymphocytes and basophils (c) eosinophils and
REVIEW QUESTIONS: A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE: (Select the most appropriate option in each case) Question 1: Agranulocytes are: (a) lymphocytes and monocytes (b) lymphocytes and basophils (c) eosinophils and
1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary.
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems
 34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems section 1 Circulatory System Before You Read Press the tips of two fingers to the inside of your wrist, at a point just below your thumb. Can you feel
34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems section 1 Circulatory System Before You Read Press the tips of two fingers to the inside of your wrist, at a point just below your thumb. Can you feel
Equine biological systems
 Equine biological systems Pack 3 Circulation Pack Code: EBS3 This pack you will help you to: describe how blood circulates round the horse's body. www.lbcnc.org.uk About this pack Objectives When you have
Equine biological systems Pack 3 Circulation Pack Code: EBS3 This pack you will help you to: describe how blood circulates round the horse's body. www.lbcnc.org.uk About this pack Objectives When you have
2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system
 2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system Essential questions What are the structures of blood? What are the structures of the circulatory system? circulatory system 2 Structures of the circulatory
2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system Essential questions What are the structures of blood? What are the structures of the circulatory system? circulatory system 2 Structures of the circulatory
How does the Circulatory System maintain
 How does the Circulatory System maintain -It supplies cells throughout the body with oxygen and nutrients while also ridding them of wastes. Transports materials such as: (to cells) (to attack foreign
How does the Circulatory System maintain -It supplies cells throughout the body with oxygen and nutrients while also ridding them of wastes. Transports materials such as: (to cells) (to attack foreign
2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles:
 1. Label these diagrams of cells: 2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles: Organelle Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplast Mitochondria Vacuole 3. State 2 differences between
1. Label these diagrams of cells: 2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles: Organelle Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplast Mitochondria Vacuole 3. State 2 differences between
The Cardiovascular. Parts and Functions
 The Cardiovascular Parts and Functions Parts The cardiovascular system consists of 3 major parts that work together. 1- Heart 2- Lungs 3- Blood Vessels Blood Vessels There are blood vessels that carry
The Cardiovascular Parts and Functions Parts The cardiovascular system consists of 3 major parts that work together. 1- Heart 2- Lungs 3- Blood Vessels Blood Vessels There are blood vessels that carry
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 5090 BIOLOGY. 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 5090 BIOLOGY 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80 This mark scheme is published as
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 5090 BIOLOGY 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80 This mark scheme is published as
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System
 Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
DISCUSSION QUESTIONS: BLOOD AND TRANSPORT IN ANIMALS
 DISCUSSION QUESTIONS: BLOOD AND TRANSPORT IN ANIMALS 1. A person with blood group O is used to be a universal donor because 2. A person with blood group O is used to be a universal donor because 3. Which
DISCUSSION QUESTIONS: BLOOD AND TRANSPORT IN ANIMALS 1. A person with blood group O is used to be a universal donor because 2. A person with blood group O is used to be a universal donor because 3. Which
37 1 The Circulatory System
 H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation
 1 Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Section 9.1 Homeostasis: Life in the Balance Outcomes: I can explain homeostasis I can describe the importance of homeostasis to living things I can explain the
1 Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Section 9.1 Homeostasis: Life in the Balance Outcomes: I can explain homeostasis I can describe the importance of homeostasis to living things I can explain the
Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System
 Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System This color-enhanced image was made with an electron microscope, so the objects it depicts are extremely small. Do you know what they are? This incredible photo shows red
Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System This color-enhanced image was made with an electron microscope, so the objects it depicts are extremely small. Do you know what they are? This incredible photo shows red
Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels
 Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels Most animals have a closed blood system. The blood flows continuously in vessels back to the heart. In an open system the blood is pumped into open ended tubes and
Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels Most animals have a closed blood system. The blood flows continuously in vessels back to the heart. In an open system the blood is pumped into open ended tubes and
KS4 Physical Education
 KS4 Physical Education The Circulatory System These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities created
KS4 Physical Education The Circulatory System These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities created
Topic Page: Circulatory system
 Topic Page: Circulatory system Definition: circulatory system from Collins English Dictionary n 1 anatomy, zoology the system concerned with the transport of blood and lymph, consisting of the heart, blood
Topic Page: Circulatory system Definition: circulatory system from Collins English Dictionary n 1 anatomy, zoology the system concerned with the transport of blood and lymph, consisting of the heart, blood
Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for
 Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for hyperlipidemia! Agenda! - Review objectives for 6.2! - Video of circulatory
Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for hyperlipidemia! Agenda! - Review objectives for 6.2! - Video of circulatory
The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle.
 The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle. From this camber, it passes through the pulmonary semilunar valve
The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle. From this camber, it passes through the pulmonary semilunar valve
Angel International School - Manipay
 c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November 2016 Biology Duration: 3Hours Index No:- Choose the correct answer and underline it. (1) When a red stain is added to a culture
c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November 2016 Biology Duration: 3Hours Index No:- Choose the correct answer and underline it. (1) When a red stain is added to a culture
THE HEART. Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration
 THE HEART Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration The Circulatory System Also called the Cardiovascular System Circulates blood in the body Transports nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood
THE HEART Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration The Circulatory System Also called the Cardiovascular System Circulates blood in the body Transports nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood
CIE Biology A-level Topic 8: Transport in mammals
 CIE Biology A-level Topic 8: Transport in mammals Notes Circulatory systems can either be open, for instance in insects, or closed, like in fish and mammals where the blood is confined to blood vessels
CIE Biology A-level Topic 8: Transport in mammals Notes Circulatory systems can either be open, for instance in insects, or closed, like in fish and mammals where the blood is confined to blood vessels
Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Name Date Class Circulation 33 Chapter 19 Circulation Section 1 The
 Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Name Date Class Circulation 33 Chapter 19 Circulation Section 1 The Circulatory System A. Your system includes the blood, heart,
Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Name Date Class Circulation 33 Chapter 19 Circulation Section 1 The Circulatory System A. Your system includes the blood, heart,
Biology Unit 3 The Human Heart P
 Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
aliasyraf.wordpress.com
 aliasyraf.wordpress.com 1.1 Understanding the importance of having a transport system in some multicellular organisms 1.1 Understanding the importance of having a transport system in some multicellular
aliasyraf.wordpress.com 1.1 Understanding the importance of having a transport system in some multicellular organisms 1.1 Understanding the importance of having a transport system in some multicellular
Levels of Organization. Chapter 19 6/11/2012. Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body. 4 Primary Tissues
 Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process:
 Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: a. erythrocytes b. leukocytes c. melanocytes d. thrombocytes Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process: a. erythrocytes
Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: a. erythrocytes b. leukocytes c. melanocytes d. thrombocytes Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process: a. erythrocytes
Glossary: The Cardiovascular System
 This glossary includes terms that have been introduced in Lesson 14. Student Resource 14.14 Glossary: The Cardiovascular System Anatomy Terms aorta Large artery that transports blood from the left ventricle
This glossary includes terms that have been introduced in Lesson 14. Student Resource 14.14 Glossary: The Cardiovascular System Anatomy Terms aorta Large artery that transports blood from the left ventricle
The Human Body. Mrs. Green
 The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes. Circulation
 1 7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood Vessels Sect. 3: Blood and Lymph Sect. 4: Cardiovascular Health Sect. 1:
1 7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood Vessels Sect. 3: Blood and Lymph Sect. 4: Cardiovascular Health Sect. 1:
Contact us:
 Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels
 Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels 3.2 Learning Objectives 3.2.2 Organisational Complexity of the human 1. Describe the structures and organisation of tissues in the closed circulatory system. 2. Discuss
Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels 3.2 Learning Objectives 3.2.2 Organisational Complexity of the human 1. Describe the structures and organisation of tissues in the closed circulatory system. 2. Discuss
Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Blood o Red blood cells: heamoglobin and oxygen transport o White blood cells: phagocyte phagocytosis (engulf pathogen, vesicles fuse with vacuole,
Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Blood o Red blood cells: heamoglobin and oxygen transport o White blood cells: phagocyte phagocytosis (engulf pathogen, vesicles fuse with vacuole,
 CHAPTER 6 LIFE PROCESSES All living things perform certain life processes like growth, excretion, respiration, circulation etc. All the processes like respiration, digestion, which together keep the living
CHAPTER 6 LIFE PROCESSES All living things perform certain life processes like growth, excretion, respiration, circulation etc. All the processes like respiration, digestion, which together keep the living
1 Which substances are dissolved in human blood plasma? carbon dioxide, haemoglobin and glucose. carbon dioxide, oxygen and haemoglobin
 1 Which substances are dissolved in human blood plasma? carbon dioxide, haemoglobin and glucose carbon dioxide, oxygen and haemoglobin glucose, hormones and urea oxygen, urea and starch 2 Which chamber
1 Which substances are dissolved in human blood plasma? carbon dioxide, haemoglobin and glucose carbon dioxide, oxygen and haemoglobin glucose, hormones and urea oxygen, urea and starch 2 Which chamber
PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark)
 1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
2. What makes up the most of your blood? least of your blood? 1. Look like red discs, have a pale center, no nucleus, similar in size
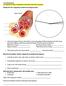 .I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
.I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like
 Page 95»Question» Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess complex body designs.
Page 95»Question» Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess complex body designs.
Bellwork Define: hemostasis anticoagulation hemophilia (Then write the underline portion of the two state standards in your notes).
 Bellwork Define: hemostasis anticoagulation hemophilia (Then write the underline portion of the two state standards in your notes). A&P Standards 31) Identify the liquid and cellular components of blood
Bellwork Define: hemostasis anticoagulation hemophilia (Then write the underline portion of the two state standards in your notes). A&P Standards 31) Identify the liquid and cellular components of blood
CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) CHAPTER-18 BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION
 CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) CHAPTER-18 BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION Body fluids are the medium of transport of nutrients, oxygen and other important substance in the body. Body Fluids Intracellular
CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) CHAPTER-18 BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION Body fluids are the medium of transport of nutrients, oxygen and other important substance in the body. Body Fluids Intracellular
Page 2. Q1.Substances can move into and out of cells. (a) (i) How does oxygen move into and out of cells? Draw a ring around one answer.
 Q1.Substances can move into and out of cells. (a) (i) How does oxygen move into and out of cells? Draw a ring around one answer. diffusion digestion photosynthesis (ii) Diagram 1 shows the percentage concentration
Q1.Substances can move into and out of cells. (a) (i) How does oxygen move into and out of cells? Draw a ring around one answer. diffusion digestion photosynthesis (ii) Diagram 1 shows the percentage concentration
 Caledonia Science the system that circulates blood and lymph through the body, consisting of the heart, blood vessels, The is the muscle that moves the blood throughout the highway system of vessles. The
Caledonia Science the system that circulates blood and lymph through the body, consisting of the heart, blood vessels, The is the muscle that moves the blood throughout the highway system of vessles. The
The Body s Transportation System (pages )
 The Body s Transportation System (pages 100-106) Use the diagram to answer the following questions. Name Date Class Circulatory Packet 1. Draw arrows on the diagram to show the path of the blood flow throughout
The Body s Transportation System (pages 100-106) Use the diagram to answer the following questions. Name Date Class Circulatory Packet 1. Draw arrows on the diagram to show the path of the blood flow throughout
Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The list gives some structures in the blood and circulatory system.
 Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The list gives some structures in the blood and circulatory system. heart artery red blood cell ventricle capillary plasma vein white blood cell platelets Which of
Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The list gives some structures in the blood and circulatory system. heart artery red blood cell ventricle capillary plasma vein white blood cell platelets Which of
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems. Chapter 37: Biology II
 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Chapter 37: Biology II The Circulatory System Larger organisms cannot rely on diffusion to move oxygen, nutrients and wastes through cells The Circulatory System Closed
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Chapter 37: Biology II The Circulatory System Larger organisms cannot rely on diffusion to move oxygen, nutrients and wastes through cells The Circulatory System Closed
Circulation and Respiration
 CHAPTER 20 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET Circulation and Respiration As you read Chapter 20, which begins on page 486 of your textbook, answer the following questions. This Really Happened... (p. 486) 1.
CHAPTER 20 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET Circulation and Respiration As you read Chapter 20, which begins on page 486 of your textbook, answer the following questions. This Really Happened... (p. 486) 1.
Main Menu. Circulatory System. click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 Circulatory System click here Main Menu http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/ap6/ap6entry.htm[3/20/18, 12:56:19 PM] Circulatory System The vascular or circulatory system controls the circulation
Circulatory System click here Main Menu http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/ap6/ap6entry.htm[3/20/18, 12:56:19 PM] Circulatory System The vascular or circulatory system controls the circulation
Revision Question Bank
 Revision Question Bank Life Processes 1. Name the passage in sequence through which urine passes from kidney to the outside in human. How is urine prevented from flowing back into the ureter? The passage
Revision Question Bank Life Processes 1. Name the passage in sequence through which urine passes from kidney to the outside in human. How is urine prevented from flowing back into the ureter? The passage
(a) (i) Describe how the structure of an artery is different from the structure of a vein.
 The circulatory system contains arteries and veins. (a) (i) Describe how the structure of an artery is different from the structure of a vein. (2) A comparison is made between blood taken from an artery
The circulatory system contains arteries and veins. (a) (i) Describe how the structure of an artery is different from the structure of a vein. (2) A comparison is made between blood taken from an artery
Lecture 8. Heart and Circulatory System. Lecture 8
 Lecture 8 Heart and Circulatory System Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Blood 3. Blood Vessels & Blood Pressure 4. The Heart 5. Cardiovascular (Circulatory) System 2 1 Circulatory System Function 1. Transport
Lecture 8 Heart and Circulatory System Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Blood 3. Blood Vessels & Blood Pressure 4. The Heart 5. Cardiovascular (Circulatory) System 2 1 Circulatory System Function 1. Transport
Cardiovascular System. Supplementary Information
 Cardiovascular System Supplementary Information THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM - 1 - THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM FUNCTION Transport system carrying nutrient, gases, hormones and waste products to and from the
Cardiovascular System Supplementary Information THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM - 1 - THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM FUNCTION Transport system carrying nutrient, gases, hormones and waste products to and from the
Chapter 12. Capillaries. Circulation. The circulatory system connects with all body tissues
 Chapter 12 Circulation The circulatory system connects with all body s In many animals, microscopic blood vessels called capillaries Form an intricate network among the Red blood cell song Figure 23.1A
Chapter 12 Circulation The circulatory system connects with all body s In many animals, microscopic blood vessels called capillaries Form an intricate network among the Red blood cell song Figure 23.1A
TRANSPORT SYSTEM IN LIVING SMPK PENABUR JAKARTA
 TRANSPORT SYSTEM IN LIVING ORGANISM SMPK PENABUR JAKARTA Part 1 PLANT TRANSPORTATION SYSTEM A. PLANT TRANSPORT SYSTEM Transport tissue? Where? A. 1. Water Transport Water liquid matter Affected by environment
TRANSPORT SYSTEM IN LIVING ORGANISM SMPK PENABUR JAKARTA Part 1 PLANT TRANSPORTATION SYSTEM A. PLANT TRANSPORT SYSTEM Transport tissue? Where? A. 1. Water Transport Water liquid matter Affected by environment
Bodies and Systems. What is your body made of?
 What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
Capillary Action and Blood Components. Biology 20 Unit D: Body Systems Circulation
 Capillary Action and Blood Components Biology 20 Unit D: Body Systems Circulation 1 Remember. Capillaries are so small that blood cells can only pass through single file Important because they are the
Capillary Action and Blood Components Biology 20 Unit D: Body Systems Circulation 1 Remember. Capillaries are so small that blood cells can only pass through single file Important because they are the
BLOOD RUNS THROUGH YOUR BODY
 BLOOD RUNS THROUGH YOUR BODY WORKSHEET A Your heart and blood vessels make up your blood system. At the centre of your blood system is your heart. Its job is to pump the blood around your body. The rest
BLOOD RUNS THROUGH YOUR BODY WORKSHEET A Your heart and blood vessels make up your blood system. At the centre of your blood system is your heart. Its job is to pump the blood around your body. The rest
Blood Vessels. veins. valve. to the heart. capillaries from the heart. arteries. Visual 25-1
 Blood Vessels veins valve to the heart capillaries from the heart arteries Visual 25-1 Human Heart pulmonary arteries superior vena cava aorta pulmonary veins semilunar valves right atrium pulmonary arteries
Blood Vessels veins valve to the heart capillaries from the heart arteries Visual 25-1 Human Heart pulmonary arteries superior vena cava aorta pulmonary veins semilunar valves right atrium pulmonary arteries
The circulatory system brings many different materials to all the cells of the body and picks up waste from the same cells.
 CIRCULATION AND IMMUNITY The Circulatory System The circulatory system, otherwise known as the cardiovascular system, consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. This important system is a large network
CIRCULATION AND IMMUNITY The Circulatory System The circulatory system, otherwise known as the cardiovascular system, consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. This important system is a large network
As a courtesy to your fellow classmates please refrain from talking, beating, or snoring. And Now Our Feature Presentation.
 As a courtesy to your fellow classmates please refrain from talking, beating, or snoring. And Now Our Feature Presentation. Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood
As a courtesy to your fellow classmates please refrain from talking, beating, or snoring. And Now Our Feature Presentation. Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood
Cardiovascular System. I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart
 Cardiovascular System I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart 1. : Pericardial Cavity serous fluid filled space between the heart and the pericardium B. Heart Wall 1.
Cardiovascular System I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart 1. : Pericardial Cavity serous fluid filled space between the heart and the pericardium B. Heart Wall 1.
DAY ONE BLOOD. What do you know about blood? What does it do? What is it made of? Where is it made?
 BLOOD AND THE HEART DAY ONE BLOOD What do you know about blood? What does it do? What is it made of? Where is it made? BLOOD Transports gases Brings in oxygen Removes carbon dioxide MAIN FUNCTIONS OF
BLOOD AND THE HEART DAY ONE BLOOD What do you know about blood? What does it do? What is it made of? Where is it made? BLOOD Transports gases Brings in oxygen Removes carbon dioxide MAIN FUNCTIONS OF
Book Second Term Test Model Answers. Page 84 to 87
 1. Write the scientific term: a. Red blood cells b. Aorta c. Ball bearings d. Air resistance e. silt soil f. sand soil 2. Write a brief account: Book Second Term Test Model Answers Page 84 to 87 a. friction:
1. Write the scientific term: a. Red blood cells b. Aorta c. Ball bearings d. Air resistance e. silt soil f. sand soil 2. Write a brief account: Book Second Term Test Model Answers Page 84 to 87 a. friction:
Circulation and Gas Exchange
 Circulation and Gas Exchange Sponges (porifera) Flat worms (platyhelminthes) Round worms (nematoda) Segmented worms (annelida) Stinging celled (cnidaria) Squishy (mollusca) Hard shelled (arthropods) Spiny
Circulation and Gas Exchange Sponges (porifera) Flat worms (platyhelminthes) Round worms (nematoda) Segmented worms (annelida) Stinging celled (cnidaria) Squishy (mollusca) Hard shelled (arthropods) Spiny
One system involved in exercising is the respiratory system. The respiratory system includes three main parts breathing, lungs and blood.
 By Andrea.K 2012 Grade 3 There are many different systems that help us exercise and the three main systems are the respiratory system which is about how we breathe, the circulatory system which is about
By Andrea.K 2012 Grade 3 There are many different systems that help us exercise and the three main systems are the respiratory system which is about how we breathe, the circulatory system which is about
