Study Title: Study of Hypertenol on the development of Hypertension in the SHR INTRODUCTION
|
|
|
- Elfrieda Newton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 P.O. No.: HYPERTENOL Pharmacodynamical Study (Efficacy Study) LIIDHATIRY IEPD,RT Test Facilitv: Institut de Cardiologie De Montreal, Canada Sponsor: Hamida Pharma, Inc, USA
2 PHARMACODYNAMICAL STUDY (EFFICACY STUDY) REPORT Study Title: Study of Hypertenol on the development of Hypertension in the SHR Test Article: Hypertenol Identification No.: ESHP-I 002 Test Facility: Physiological Dept. Institut de Cardiologie de Montreal, Canada Sponsor: Hamida Pharma, Inc. Study and Supervisory Personnel: Angelo Calderone, Ph.D. Amine Yacine, Ph.D. INTRODUCTION The spontaneous hypertensive rat (SHR) model has been extensively used to examine the underlying mechanisms implicated in the development of essential hypertension. During the early growth phase (0-30 days following birth) mean arterial pressure ( MAP) was equivalent to its control Wistar- Kyoto (WKY.) However, 40 days following birth, MAP was found to be higher in the SHR as compared to WKY, and continued to increase until it reached a plateau of mm Hg at 80 days of age (WKY= 125 mm Hg.) Although the SHR model represents a genetic model of hypertension, the genetic abnormalities contributing to the disease state remain undetermined. Nonetheless, Numerous studies have identified various abnormalities which are believed to contribute to the progression of hypertension. Circulating angitensin II levels were found significantly increased in the SHR model, and the vasoconstrictor response. Thirdly, left ventricular hypertrophy, and fibrosis represent prominent features in the SHR, and leads to cardiac contractile dysfunction, and subsequent heart failure. Lastly, increased oxidative stress has been documents in the SHR, and it is believed that the interest in free radicals binds to and inactive nitric oxide; an intrinsic cardiprotective mechanism. Based on this latter observation, the administration of anti-oxidants could potentially represent a
3 therapeutic approach to attenuate and/or abrogate established hypertension in the SHR model. The drug Hypertenol has been reported to possess anti-oxidant properties, and in this regard, the efficacy of this drug to alleviate the presence of established hypertension in the SHR model was investigated. METHODS Male SHR rats (Charles River) 9 weeks of age with an average MAP of 176 mm Hg were used in the present study. Hypertenol at a dose of either 20, 40, 100 mg/kg/day was added to the rat chow, changed every three days, and continued for a period of 5 weeks. Each group consisted of 5 rats. At 10, 11, 12, and 13 weeks of age, tail cuff blood pressure readings were made. At 14 weeks, the rats were anesthetized with a ketamine (50 mg/kg/xylazine (10mg/kg) mixtures A microtip pressure transducer (Millar 2F) was inserted into the right carotid artery to obtain mean arterial pressure. The transducer was subsequently advanced into the left ventricle to measure systolic, end- diastolic pressures, and the left ventricular rate of contraction (dp/dt). Lastly, the transducer was inserted into the right jugular vein, and advanced into the right ventricle to measure right ventricular contractile function. Following the assessment of contractile function, blood was withdrawn to measure plasma catecholamine levels, tissues were removed and immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen, and subsequently stored at -80 C. All tissue weight are in grams. RESULTS In the Hypertenol- Morphometric Measurements treated SHR, regardless the doe, an increase in body weight gain was observed during the 5 weeks treatment. Liver and kidney weight was unchanged in the Hypertenol- treated SHR, as compared to untreated SHR, regardless the dose. Interestingly, the lung weight/body weight ratio was decreased in the Hypertenol- treated SHR, regardless the dose, as compared to the untreated SHR ( Figure 1).
4 -.'he effe<.~t of Hyper-tel1ol on Lung '\Veight in the SHR nit o '" :c _= S H R a Figure 1 However, a statistical significance was observed only for the 20 and 100 mg dose regiment. Likewise, right ventricular weight/body weight ratio was decreased in the Hypertenol-treated SHR, regardless the dose, as compared to untreated SHR (Figure 2). However, statistical significance was observed only with the 40 and 100 mg dose of Hypertenol (figure 2). The effect of Ilypertcnul on Right Vl'ntTlcul:u' ''-'eight in the SH R njt I).6 * 1)~ IWt( S p<li.u5 ~'~'I'SIlSSUR: 11=5cnd1 ~rnup,:;,-;: - I) 7 o H S 1-1 R 2 0.-; Figure 2
5 91 5 D I, Tail Cuff Blood Pressure Measurements (Figure 3) Th~ ~rrcct of 1-I)'p. '-tl.. [l1i1on T.,if Cuff Blood Pressure in the SIIR n'l :7 0 (1.- SHR~20 SHR~40 ~//. I 9 0 l "" 1, es, 0e - H 1 k1 R0s ",. /"" ""A _._-" --2f Figure 3 1.A. 7 0 I I> 0 I- f- ','01 The average MAP of the SHR rats prior to Hypertenol treatment was 176 mm Hg. Following the first week of Hypertenol treatment, a marked reduction in tail cuff MAP was observed. In the 20 mg treated SHR, a reduction of 23 mm Hg was observed, whereas the 40 and 100 mg treated SHR, a reduction of 11 and 17 mm Hg was observed, respectively. Following the second to fourth week of treatment, MAP slowly returned to baseline levels observed prior to the administration of Hypertenol, regardless the dose. By contrast, in the untreated SHR, MAP remained unchanged, and markedly increased during the 13th week. In Vivo Hemodynamic Measurements & Plasma Catecholamine Levels Following 5 weeks of Hypertenol treatment, the rats were anesthetized cardiac contractile function were assessed. Hg, and Hypertenol treatment reduced MAP (Figure 4). and MAP, and In the untreated SHR rat, MAP was 165 mm The cfft'ct of Hypcrtcnol on j\. lcan A,'tcria! P"CSSlII'C in the SHR rat = ',\::Den"tl'" r.<n.ns versus SHR: n=::; 1 :I<.'h~rC1U(J E -E <r: I a.. 1 ~ S H R Figure 4
6 A significant reduction of35 and 47 mm Hg was observed in the 20 and 40 mg treated SHR (Figure 4), Likewise, the 100 mg dose of Hypertenol resulted in a 24 mm Hg reduction of MAP, but was not statistically significant, as compared to untreated SHR (Figure 4). Left ventricular systolic function was elevated in the untreated SHR, and a significant decrease was observed in the Hypertenol-treated (Figure 5). rat, regardless the dose Thl' effect of Hypcr"lennl 011 Ll'fI Vcntricular Syslolic PI'I~ssurl' in the SHR nil :r; E 'k DC'n"I ~ p<ii,u:- \'cn"~ SIIR: 11=::; :lch ~rol1l) CL (/) > -' S H R Figure 5 Consistent with theses data, the rate of left ventricular contraction (dp/dt) was increased in the SHR, and Hypertenol treatment markedly improved dp/dt (Figure 6). Thl' efft,cc of Hypcr'lennl on Left Vcntricul:lr Systolic I'r'csSlIl'l' ill the SHR nit :r; E E "" 2? 50 0 k nchu.c~ p<o..05 \-cr.'li~ SIIR: 11=:' c:ach }..:r"oup a > -' 1" 0 S H R 2 0 < Figure 6 A significant reduction of dp/dt was observed with 20 and 40 mg Hypertenol, whereas a non-significant decease was observed with 100 mg (Figure 6). Left ventricular relaxation, as measured by left ventricular end-diastolic pressure (LVEPD) was elevated in the SHR, and a reduction was observed following Hypertenol treatment (Figure7).
7 The effect o!" Hypcr'tcllol on Left Ventr'icu!:u' End-Diastolic Pn'ssurc in the SHR I'a' 0) I E E i 2 I 0 II ~t Dl'IIU[e~ p<ilu5 \erc~ljs SIIR; n=:- each gnlllp (L o 4 u.j > 2 SHR Figure 7 The 20 and 49 mg dose normalized LVEDP in the SHR, whereas the 100 mg nonsignificantly decreased LVEDP (Figure 7). Right ventricular systolic pressure was modestly increased in the SHR, and Hypertenol caused a non-significant reduction, regardless the dose. Lastly, plasma catecholamine levels were unchanged in the Hypertenol treated SHR, regardless he dose, as compared to untreated SHR (data not shown). DISCUSSION One week following Hypertenol treatment, a marked reduction of MAP via the tail cuff method was observed, regardless the dose. However, during the following three weeks of treatment with Hypertenol, MAP returned to baseline levels, prior to drug administration. These latter observations suggests that Hypertenol can indeed reduce MAP. Albeit, during the latter weeks, an increased stress level was observed in the rats, and this may have masked the beneficial effect of Hypertenol. Indeed, this latter conclusion is valid since in the anesthetized animal, MAP was markedly reduced in the Hypertenol treated SHR, regardless the dose. Secondly, left ventricular systolic pressure (LVSP), an index of contractility was elevated in the SHR, and Hypertenol treatment significantly improved LVSP, regardless the dose. Moreover, the rate of left ventricular contraction dp/dt was also improved with Hypertenol treatment, thereby supporting the premise that Hypertenol alleviation of MAP was associated with improved left ventricular function. Thirdly, left ventricular relaxation as assessed by left ventricular
8 end diastolic pressure (L VEDP) was significantly reduced by Hypertenol treatment. This latter therapeutic action of Hypertenol is important since an increase in LVEDP leads to impaired ventricular relaxation, resulting in ventricular dilation, and subsequent heart failure. Moreover, elevated LVEDP can result in pulmonary hypertension, and in the present study, Hypertenol reduction of LVEDP was associated with a decrease in lung weight/body weight ratio. Consistent with this latter result, right ventricular hypertrophy was also reduced wit Hypertenol therapy. Thus, Hypertenol may be beneficial in the treatment of pulmonary hypertension via its therapeutic action on LVEDP. In conclusion, the treatment of SHR with established essential hypertension with Hypertenol significantly improved MAP, and left ventricular contractile function. Based on the antioxidant property of Hypertenol, the reduction of free radicals in the SHR may result in a secondary increase in nitric oxide, thereby recruiting the intrinsic cardioprotective mechanism. Moreover, the growing evidence supporting a nefarious role of increased oxidative stress in other cardiovascular disease states warrants further investigation regarding the potential therapeutic effect of Hypertenol.
9 A pilot trial of oral administration of Hypertenol in the treatment of High blood pressure OBJECTIVE: To evaluate the efficacy of oral administration pressure. of Hypertenol in treatment of high blood METHODS: After initial screening, 29 patients with high blood pressure (Systolic> l30mmhg or Diastolic >85mmHg) were selected to join this pilot study. The patients were treated with Hypertenol by chewing 1-3 tablets each time, 1-2 time during 24 hours. The blood pressure was measured before taking Hypertenol and in some time after taking Hypertenol. Efficacy parameters including Systolic, Diastolic, Pulse, Pulse Press and Arterial Stiffness Index (ASI), were assessed by Cardiovision Machine. RESULTS: All 29 patients have completed the full course of therapy and observation and had reductions in Systolic after taking Hypertenol in at least 4 minutes. The Diastolic tends to normal range. Mean values for other efficacy parameters also showed improvement. There were no adverse events that were considered to be treatment related. (See enclosed Table and Figure) CONCLUSION: Oral administration of Hypertenol may be an effective therapy for hypertension.
10 Page Sex Patients 6. L'1SP 6.SP 45 9/23/ /15/ /15/ /17/ /17/ /18/ /15/ /24/00 3/17/ /13/00 7/15/ Age 3/25/00 6/15/00 3/16/00 7/16/ /2/00 7/14/ /1/ /4/00 M F Start First L'1Time Time K.AHN 32 D.GS1 75 Last T.NHN K.DS /16/00 7/15/ J.AHN L.DHN K.LS1 G.IS1 W.AS2 93 6/16/ /23/00 3/24/00 7/1100 7/15/ /17/ /13/00 L.LS1 M.CS1 R.GS2 8/2/ /4/ /25/00 6/15/00 7/15/ /18/00 7/14/ /15/ M.S1 RayS1 L'1DP G.RS2 K.M End P.CS1 S.BS1 C.LS2 E.BS2 H.BS2 7/16/ :06 0:12 2:47 0:11 0:09 0:05 0:08 0:27 0:07 2:19 0:15 5:40 0:25 0:04 S2/L Hypertenol After name Time Stage takingbefore Sex taking Diastolic Period (mmhg) Before Hypertenol taking Hypertenol Blood Pressure before/after taking Hypertenol Systolic (mmhg)
11 Page 22 Total 80 7/27/ /23/ /26/00 6/16/ /20/00 9/9/2000 9/9/00 7/15/ M7/8/00 F ± ± /10/ ± ± ± ± ± /23/ /16/ /20/00 7/27/00 5/29/00 7/8/00 9/9/ /15/ V.MS4 0:00 4:52 C.RS3 157± ±7.09 E.BS2 K.BS2 P.HS3 V.LS3 B.RS3 0:10 K.AS3 R.LL 0:54 136± :18 S.IL 0:14 0:06 148±6.26 0:12 1:12 0:34 144± ± ± ± ± :56 106± :58 S2
In the name of GOD. Animal models of cardiovascular diseases: myocardial infarction & hypertension
 In the name of GOD Animal models of cardiovascular diseases: myocardial infarction & hypertension 44 Presentation outline: Cardiovascular diseases Acute myocardial infarction Animal models for myocardial
In the name of GOD Animal models of cardiovascular diseases: myocardial infarction & hypertension 44 Presentation outline: Cardiovascular diseases Acute myocardial infarction Animal models for myocardial
2. Langendorff Heart
 2. Langendorff Heart 2.1. Principle Langendorff heart is one type of isolated perfused heart which is widely used for biochemical, physiological, morphological and pharmacological researches. It provides
2. Langendorff Heart 2.1. Principle Langendorff heart is one type of isolated perfused heart which is widely used for biochemical, physiological, morphological and pharmacological researches. It provides
Disclosures. Objectives 6/16/2016. A Look at the Other Side: Focus on the Right Ventricle and Pulmonary Hypertension
 A Look at the Other Side: Focus on the Right Ventricle and Pulmonary Hypertension Susan P. D Anna MSN, APN-BC, CHFN June 24, 2016 Disclosures Objectives Differentiate structure and function of RV and LV
A Look at the Other Side: Focus on the Right Ventricle and Pulmonary Hypertension Susan P. D Anna MSN, APN-BC, CHFN June 24, 2016 Disclosures Objectives Differentiate structure and function of RV and LV
Blood pressure. Formation of the blood pressure: Blood pressure. Formation of the blood pressure 5/1/12
 Blood pressure Blood pressure Dr Badri Paudel www.badripaudel.com Ø Blood pressure means the force exerted by the blood against the vessel wall Ø ( or the force exerted by the blood against any unit area
Blood pressure Blood pressure Dr Badri Paudel www.badripaudel.com Ø Blood pressure means the force exerted by the blood against the vessel wall Ø ( or the force exerted by the blood against any unit area
Fetal gene upregulation by 1-wk TAC is significantly increased in mice lacking RGS2.
 3562-RG-1 Supplementary Figure 1 Fetal gene upregulation by 1-wk is significantly increased in mice lacking RGS2. ANP(Nppa) /BNP(Nppb) A-type and B-type natriuretic peptide; β-mhc (Myh7) beta myosin heavy
3562-RG-1 Supplementary Figure 1 Fetal gene upregulation by 1-wk is significantly increased in mice lacking RGS2. ANP(Nppa) /BNP(Nppb) A-type and B-type natriuretic peptide; β-mhc (Myh7) beta myosin heavy
Special circulations, Coronary, Pulmonary. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD
 Special circulations, Coronary, Pulmonary Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Describe the control of blood flow to different circulations (Skeletal muscles, pulmonary and coronary) Point out special
Special circulations, Coronary, Pulmonary Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Describe the control of blood flow to different circulations (Skeletal muscles, pulmonary and coronary) Point out special
CARDIAC CYCLE CONTENTS. Divisions of cardiac cycle 11/13/13. Definition. Badri Paudel GMC
 CARDIAC CYCLE Badri Paudel GMC CONTENTS Ø DEFINATION Ø DIVISION OF CARDIAC CYCLE Ø SUB DIVISION AND DURATION OF CARDIAC CYCLE Ø SYSTOLE Ø DIASTOLE Ø DESCRIPTION OF EVENTS OF CARDIAC CYCLE Ø SUMMARY Ø ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY
CARDIAC CYCLE Badri Paudel GMC CONTENTS Ø DEFINATION Ø DIVISION OF CARDIAC CYCLE Ø SUB DIVISION AND DURATION OF CARDIAC CYCLE Ø SYSTOLE Ø DIASTOLE Ø DESCRIPTION OF EVENTS OF CARDIAC CYCLE Ø SUMMARY Ø ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY
Hemodynamic Monitoring
 Perform Procedure And Interpret Results Hemodynamic Monitoring Tracheal Tube Cuff Pressure Dean R. Hess PhD RRT FAARC Hemodynamic Monitoring Cardiac Rate and Rhythm Arterial Blood Pressure Central Venous
Perform Procedure And Interpret Results Hemodynamic Monitoring Tracheal Tube Cuff Pressure Dean R. Hess PhD RRT FAARC Hemodynamic Monitoring Cardiac Rate and Rhythm Arterial Blood Pressure Central Venous
Blood Pressure Regulation. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD
 Blood Pressure Regulation Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the short term and long term regulators of BP Know how baroreceptors and chemoreceptors work Know function of the atrial reflex.
Blood Pressure Regulation Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the short term and long term regulators of BP Know how baroreceptors and chemoreceptors work Know function of the atrial reflex.
Cardiac output and Venous Return. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD
 Cardiac output and Venous Return Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Objectives Define cardiac output and venous return Describe the methods of measurement of CO Outline the factors that regulate cardiac output
Cardiac output and Venous Return Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Objectives Define cardiac output and venous return Describe the methods of measurement of CO Outline the factors that regulate cardiac output
Cardiovascular Structure & Function
 Cardiovascular Structure & Function Cardiovascular system: The heart Arteries Veins Capillaries Lymphatic vessels Weighting of the heart ceremony: Ancient Egyptians William Harvey and Blood Flow April
Cardiovascular Structure & Function Cardiovascular system: The heart Arteries Veins Capillaries Lymphatic vessels Weighting of the heart ceremony: Ancient Egyptians William Harvey and Blood Flow April
Control of blood tissue blood flow. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD
 Control of blood tissue blood flow Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives List factors that affect tissue blood flow. Describe the vasodilator and oxygen demand theories. Point out the mechanisms of autoregulation.
Control of blood tissue blood flow Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives List factors that affect tissue blood flow. Describe the vasodilator and oxygen demand theories. Point out the mechanisms of autoregulation.
Therefore MAP=CO x TPR = HR x SV x TPR
 Regulation of MAP Flow = pressure gradient resistance CO = MAP TPR Therefore MAP=CO x TPR = HR x SV x TPR TPR is the total peripheral resistance: this is the combined resistance of all blood vessels (remember
Regulation of MAP Flow = pressure gradient resistance CO = MAP TPR Therefore MAP=CO x TPR = HR x SV x TPR TPR is the total peripheral resistance: this is the combined resistance of all blood vessels (remember
Anaesthesia for non-cardiac surgery in patients left ventricular outflow tract obstruction (LVOTO)
 Anaesthesia for non-cardiac surgery in patients left ventricular outflow tract obstruction (LVOTO) Dr. Siân Jaggar Consultant Anaesthetist Royal Brompton Hospital London UK Congenital Cardiac Services
Anaesthesia for non-cardiac surgery in patients left ventricular outflow tract obstruction (LVOTO) Dr. Siân Jaggar Consultant Anaesthetist Royal Brompton Hospital London UK Congenital Cardiac Services
Cardiovascular system
 Cardiovascular system L-4 Blood pressure & special circulation Dr Than Kyaw 27 February 2012 Blood Pressure (BP) Pressure generation and flow Blood is under pressure within its closed system. Pressure
Cardiovascular system L-4 Blood pressure & special circulation Dr Than Kyaw 27 February 2012 Blood Pressure (BP) Pressure generation and flow Blood is under pressure within its closed system. Pressure
Topics to be Covered. Cardiac Measurements. Distribution of Blood Volume. Distribution of Pulmonary Ventilation & Blood Flow
 Topics to be Covered MODULE F HEMODYNAMIC MONITORING Cardiac Output Determinants of Stroke Volume Hemodynamic Measurements Pulmonary Artery Catheterization Control of Blood Pressure Heart Failure Cardiac
Topics to be Covered MODULE F HEMODYNAMIC MONITORING Cardiac Output Determinants of Stroke Volume Hemodynamic Measurements Pulmonary Artery Catheterization Control of Blood Pressure Heart Failure Cardiac
Cardiovascular Responses to Exercise
 CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY 69 Case 13 Cardiovascular Responses to Exercise Cassandra Farias is a 34-year-old dietician at an academic medical center. She believes in the importance of a healthy lifestyle
CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY 69 Case 13 Cardiovascular Responses to Exercise Cassandra Farias is a 34-year-old dietician at an academic medical center. She believes in the importance of a healthy lifestyle
PART I: HEART ANATOMY
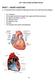 Lab 7: Heart Sounds and Blood Pressure PART I: HEART ANATOMY a) You should be able to identify the following structures on an adult human heart diagram. the 4 chambers the bicuspid (mitral) and tricuspid
Lab 7: Heart Sounds and Blood Pressure PART I: HEART ANATOMY a) You should be able to identify the following structures on an adult human heart diagram. the 4 chambers the bicuspid (mitral) and tricuspid
Heart Pump and Cardiac Cycle. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD
 Heart Pump and Cardiac Cycle Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Objectives To understand the volume, mechanical, pressure and electrical changes during the cardiac cycle To understand the inter-relationship
Heart Pump and Cardiac Cycle Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Objectives To understand the volume, mechanical, pressure and electrical changes during the cardiac cycle To understand the inter-relationship
End of chapter exercises
 End of chapter exercises Problem 1: The following diagrams show the heart during the cardiac cycle. The arrows represent the flow of blood. Study the diagrams and answer the questions that follow: Figure
End of chapter exercises Problem 1: The following diagrams show the heart during the cardiac cycle. The arrows represent the flow of blood. Study the diagrams and answer the questions that follow: Figure
Blood Pressure. a change in any of these could cause a corresponding change in blood pressure
 Blood Pressure measured as mmhg Main factors affecting blood pressure: 1. cardiac output 2. peripheral resistance 3. blood volume a change in any of these could cause a corresponding change in blood pressure
Blood Pressure measured as mmhg Main factors affecting blood pressure: 1. cardiac output 2. peripheral resistance 3. blood volume a change in any of these could cause a corresponding change in blood pressure
AGENDA for 04/04/14 AGENDA: HOMEWORK: Due Tues, Online Quiz: OBJECTIVES:
 AGENDA for 04/04/14 AGENDA: 1. Pump Your Blood Performances 2. 4.2.2: Blood Pressure Experimental Design and Writing a Formal Lab Report OBJECTIVES: 1. Measure blood pressure and use the reading to indicate
AGENDA for 04/04/14 AGENDA: 1. Pump Your Blood Performances 2. 4.2.2: Blood Pressure Experimental Design and Writing a Formal Lab Report OBJECTIVES: 1. Measure blood pressure and use the reading to indicate
McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT-B and PHRN Optional Continuing Education 2018 #12 Understanding Preload and Afterload
 McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT-B and PHRN Optional Continuing Education 2018 #12 Understanding Preload and Afterload Cardiac output (CO) represents the volume of blood that is delivered
McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT-B and PHRN Optional Continuing Education 2018 #12 Understanding Preload and Afterload Cardiac output (CO) represents the volume of blood that is delivered
What is the mechanism of the audible carotid bruit? How does one calculate the velocity of blood flow?
 CASE 8 A 65-year-old man with a history of hypertension and coronary artery disease presents to the emergency center with complaints of left-sided facial numbness and weakness. His blood pressure is normal,
CASE 8 A 65-year-old man with a history of hypertension and coronary artery disease presents to the emergency center with complaints of left-sided facial numbness and weakness. His blood pressure is normal,
Selected age-associated changes in the cardiovascular system
 Selected age-associated changes in the cardiovascular system Tamara Harris, M.D., M.S. Chief, Interdisciplinary Studies of Aging Acting Co-Chief, Laboratory of Epidemiology and Population Sciences Intramural
Selected age-associated changes in the cardiovascular system Tamara Harris, M.D., M.S. Chief, Interdisciplinary Studies of Aging Acting Co-Chief, Laboratory of Epidemiology and Population Sciences Intramural
Technique. Technique. Technique. Monitoring 1. Local anesthetic? Aseptic technique Hyper-extend (if radial)
 Critical Care Monitoring Hemodynamic Monitoring Arterial Blood Pressure Cannulate artery Uses 2 Technique Sites Locate artery, prep 3 1 Technique Local anesthetic? Aseptic technique Hyper-extend (if radial)
Critical Care Monitoring Hemodynamic Monitoring Arterial Blood Pressure Cannulate artery Uses 2 Technique Sites Locate artery, prep 3 1 Technique Local anesthetic? Aseptic technique Hyper-extend (if radial)
Copyright 2011, 2007 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Normal Cardiac Anatomy
 Mosby,, an affiliate of Elsevier Normal Cardiac Anatomy Impaired cardiac pumping Results in vasoconstriction & fluid retention Characterized by ventricular dysfunction, reduced exercise tolerance, diminished
Mosby,, an affiliate of Elsevier Normal Cardiac Anatomy Impaired cardiac pumping Results in vasoconstriction & fluid retention Characterized by ventricular dysfunction, reduced exercise tolerance, diminished
Blood Pressure Laboratory
 Introduction The blood that circulates throughout the body maintains a flow and pressure. The nervous system can change the flow and pressure based on the particular needs at a given time. For example,
Introduction The blood that circulates throughout the body maintains a flow and pressure. The nervous system can change the flow and pressure based on the particular needs at a given time. For example,
Cardiac Cycle MCQ. Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology. Cairo University 2007
 Cardiac Cycle MCQ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim Ahmed, MD Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology Cairo University 2007 1- Regarding the length of systole and diastole: a- At heart rate 75 b/min, the duration of
Cardiac Cycle MCQ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim Ahmed, MD Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology Cairo University 2007 1- Regarding the length of systole and diastole: a- At heart rate 75 b/min, the duration of
Biology 236 Spring 2002 Campos/Wurdak/Fahey Laboratory 4. Cardiovascular and Respiratory Adjustments to Stationary Bicycle Exercise.
 BACKGROUND: Cardiovascular and Respiratory Adjustments to Stationary Bicycle Exercise. The integration of cardiovascular and respiratory adjustments occurring in response to varying levels of metabolic
BACKGROUND: Cardiovascular and Respiratory Adjustments to Stationary Bicycle Exercise. The integration of cardiovascular and respiratory adjustments occurring in response to varying levels of metabolic
-12. -Ensherah Mokheemer - ABDULLAH ZREQAT. -Faisal Mohammad. 1 P a g e
 -12 -Ensherah Mokheemer - ABDULLAH ZREQAT -Faisal Mohammad 1 P a g e In the previous lecture we talked about: - cardiac index: we use the cardiac index to compare the cardiac output between different individuals,
-12 -Ensherah Mokheemer - ABDULLAH ZREQAT -Faisal Mohammad 1 P a g e In the previous lecture we talked about: - cardiac index: we use the cardiac index to compare the cardiac output between different individuals,
3/10/2009 VESSELS PHYSIOLOGY D.HAMMOUDI.MD. Palpated Pulse. Figure 19.11
 VESSELS PHYSIOLOGY D.HAMMOUDI.MD Palpated Pulse Figure 19.11 1 shows the common sites where the pulse is felt. 1. Temporal artery at the temple above and to the outer side of the eye 2. External maxillary
VESSELS PHYSIOLOGY D.HAMMOUDI.MD Palpated Pulse Figure 19.11 1 shows the common sites where the pulse is felt. 1. Temporal artery at the temple above and to the outer side of the eye 2. External maxillary
Age-related changes in cardiovascular system. Dr. Rehab Gwada
 Age-related changes in cardiovascular system Dr. Rehab Gwada Objectives explain the main structural and functional changes in cardiovascular system associated with normal aging Introduction aging results
Age-related changes in cardiovascular system Dr. Rehab Gwada Objectives explain the main structural and functional changes in cardiovascular system associated with normal aging Introduction aging results
Physiologic Based Management of Circulatory Shock Kuwait 2018
 Physiologic Based Management of Circulatory Shock Kuwait 2018 Dr. Yasser Elsayed, MD, PhD Director of the Targeted Neonatal Echocardiography, Point of Care and Hemodynamics Program Staff Neonatologist
Physiologic Based Management of Circulatory Shock Kuwait 2018 Dr. Yasser Elsayed, MD, PhD Director of the Targeted Neonatal Echocardiography, Point of Care and Hemodynamics Program Staff Neonatologist
The effect of sildenafil on electrostimulation-induced erection in the rat model
 (2002) 14, 251 255 ß 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0955-9930/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/ijir The effect of sildenafil on electrostimulation-induced erection in the rat model N Ueno 1,
(2002) 14, 251 255 ß 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0955-9930/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/ijir The effect of sildenafil on electrostimulation-induced erection in the rat model N Ueno 1,
CATCH A WAVE.. INTRODUCTION NONINVASIVE HEMODYNAMIC MONITORING 4/12/2018
 WAVES CATCH A WAVE.. W I S C O N S I N P A R A M E D I C S E M I N A R A P R I L 2 0 1 8 K E R I W Y D N E R K R A U S E R N, C C R N, E M T - P Have you considered that if you don't make waves, nobody
WAVES CATCH A WAVE.. W I S C O N S I N P A R A M E D I C S E M I N A R A P R I L 2 0 1 8 K E R I W Y D N E R K R A U S E R N, C C R N, E M T - P Have you considered that if you don't make waves, nobody
HOW LOW CAN YOU GO? HYPOTENSION AND THE ANESTHETIZED PATIENT.
 HOW LOW CAN YOU GO? HYPOTENSION AND THE ANESTHETIZED PATIENT. Donna M. Sisak, CVT, LVT, VTS (Anesthesia/Analgesia) Seattle Veterinary Specialists Kirkland, WA dsisak@svsvet.com THE ANESTHETIZED PATIENT
HOW LOW CAN YOU GO? HYPOTENSION AND THE ANESTHETIZED PATIENT. Donna M. Sisak, CVT, LVT, VTS (Anesthesia/Analgesia) Seattle Veterinary Specialists Kirkland, WA dsisak@svsvet.com THE ANESTHETIZED PATIENT
The Arterial and Venous Systems Roland Pittman, Ph.D.
 The Arterial and Venous Systems Roland Pittman, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. State the primary characteristics of the arterial and venous systems. 2. Describe the elastic properties of arteries in terms of pressure,
The Arterial and Venous Systems Roland Pittman, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. State the primary characteristics of the arterial and venous systems. 2. Describe the elastic properties of arteries in terms of pressure,
HISTORY. Question: What category of heart disease is suggested by the fact that a murmur was heard at birth?
 HISTORY 23-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance of several years duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: The patient is the product of an uncomplicated term pregnancy. A heart murmur was discovered
HISTORY 23-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance of several years duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: The patient is the product of an uncomplicated term pregnancy. A heart murmur was discovered
Evalua&on)of)Le-)Ventricular)Diastolic) Dysfunc&on)by)Echocardiography:) Role)of)Ejec&on)Frac&on)
 Evalua&on)of)Le-)Ventricular)Diastolic) Dysfunc&on)by)Echocardiography:) Role)of)Ejec&on)Frac&on) N.Koutsogiannis) Department)of)Cardiology) University)Hospital)of)Patras)! I have no conflicts of interest
Evalua&on)of)Le-)Ventricular)Diastolic) Dysfunc&on)by)Echocardiography:) Role)of)Ejec&on)Frac&on) N.Koutsogiannis) Department)of)Cardiology) University)Hospital)of)Patras)! I have no conflicts of interest
Blood Flow, Blood Pressure, Cardiac Output. Blood Vessels
 Blood Flow, Blood Pressure, Cardiac Output Blood Vessels Blood Vessels Made of smooth muscle, elastic and fibrous connective tissue Cells are not electrically coupled Blood Vessels Arteries arterioles
Blood Flow, Blood Pressure, Cardiac Output Blood Vessels Blood Vessels Made of smooth muscle, elastic and fibrous connective tissue Cells are not electrically coupled Blood Vessels Arteries arterioles
The Mammalian Circulatory System
 The Mammalian Heart The Mammalian Circulatory System Recall: What are the 3 cycles of the mammalian circulatory system? What are their functions? What are the three main vessel types in the mammalian circulatory
The Mammalian Heart The Mammalian Circulatory System Recall: What are the 3 cycles of the mammalian circulatory system? What are their functions? What are the three main vessel types in the mammalian circulatory
Cardiac Output (C.O.) Regulation of Cardiac Output
 Cardiac Output (C.O.) Is the volume of the blood pumped by each ventricle per minute (5 Litre) Stroke volume: Is the volume of the blood pumped by each ventricle per beat. Stroke volume = End diastolic
Cardiac Output (C.O.) Is the volume of the blood pumped by each ventricle per minute (5 Litre) Stroke volume: Is the volume of the blood pumped by each ventricle per beat. Stroke volume = End diastolic
Left ventricular hypertrophy: why does it happen?
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2003) 18 [Suppl 8]: viii2 viii6 DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfg1083 Left ventricular hypertrophy: why does it happen? Gerard M. London Department of Nephrology and Dialysis, Manhes Hospital,
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2003) 18 [Suppl 8]: viii2 viii6 DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfg1083 Left ventricular hypertrophy: why does it happen? Gerard M. London Department of Nephrology and Dialysis, Manhes Hospital,
Physiology lecture 15 Hemodynamic
 Physiology lecture 15 Hemodynamic Dispensability (D) : proportional change in volume per unit change in pressure D = V/ P*V It is proportional (divided by the original volume). Compliance (C) : total change
Physiology lecture 15 Hemodynamic Dispensability (D) : proportional change in volume per unit change in pressure D = V/ P*V It is proportional (divided by the original volume). Compliance (C) : total change
HISTORY. Question: How do you interpret the patient s history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: 45-year-old man.
 HISTORY 45-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: His dyspnea began suddenly and has been associated with orthopnea, but no chest pain. For two months he has felt
HISTORY 45-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: His dyspnea began suddenly and has been associated with orthopnea, but no chest pain. For two months he has felt
1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary.
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1. Resting membrane potential of the ventricular myocardium is: A. -55 to-65mv B. --65 to-75mv C. -75 to-85mv D. -85 to-95 mv E. -95 to-105mv 2. Regarding myocardial contraction:
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1. Resting membrane potential of the ventricular myocardium is: A. -55 to-65mv B. --65 to-75mv C. -75 to-85mv D. -85 to-95 mv E. -95 to-105mv 2. Regarding myocardial contraction:
Comparative Biosciences Model of Monocrotaline-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension in Rats
 Comparative Biosciences Model of Monocrotaline-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension in Rats Comparative Biosciences, Inc. 786 Lucerne Drive Sunnyvale, CA 94085 Telephone: 408.738.9260 www.compbio.com Comparative
Comparative Biosciences Model of Monocrotaline-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension in Rats Comparative Biosciences, Inc. 786 Lucerne Drive Sunnyvale, CA 94085 Telephone: 408.738.9260 www.compbio.com Comparative
Activity Vital Signs: Heart Rate and Blood Pressure
 Activity 8.1.2 Vital Signs: Heart Rate and Blood Pressure Introduction The human body is an amazing machine that automatically monitors and adjusts itself in order to maintain equilibrium or homeostasis.
Activity 8.1.2 Vital Signs: Heart Rate and Blood Pressure Introduction The human body is an amazing machine that automatically monitors and adjusts itself in order to maintain equilibrium or homeostasis.
RAPID COMMUNICATION. Vascular Reactivity in Isolated Lungs of Rats with Spontaneous Systemic Hypertension
 Physiol. Res. 40:367-371,1991 RAPID COMMUNICATION Vascular Reactivity in Isolated Lungs of Rats with Spontaneous Systemic Hypertension V. HAMPL, J. HERGET Department of Physiology, 2nd Medical School,
Physiol. Res. 40:367-371,1991 RAPID COMMUNICATION Vascular Reactivity in Isolated Lungs of Rats with Spontaneous Systemic Hypertension V. HAMPL, J. HERGET Department of Physiology, 2nd Medical School,
Control of blood tissue blood flow. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD
 Control of blood tissue blood flow Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives List factors that affect tissue blood flow. Describe the vasodilator and oxygen demand theories. Point out the mechanisms of autoregulation.
Control of blood tissue blood flow Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives List factors that affect tissue blood flow. Describe the vasodilator and oxygen demand theories. Point out the mechanisms of autoregulation.
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiol I (Kristan) Lecture 14 Cardiovascular control mechanisms p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiol I (Kristan) Lecture 14 Cardiovascular control mechanisms p. 1 Terms you should understand: hemorrhage, intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms, anoxia, myocardial contractility, residual
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiol I (Kristan) Lecture 14 Cardiovascular control mechanisms p. 1 Terms you should understand: hemorrhage, intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms, anoxia, myocardial contractility, residual
Physiology Unit 3 CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY: THE VASCULAR SYSTEM
 Physiology Unit 3 CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY: THE VASCULAR SYSTEM In Physiology Today Hemodynamics F = ΔP/R Blood flow (F) High to low pressure Rate = L/min Pressure (P) Hydrostatic pressure Pressure exerted
Physiology Unit 3 CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY: THE VASCULAR SYSTEM In Physiology Today Hemodynamics F = ΔP/R Blood flow (F) High to low pressure Rate = L/min Pressure (P) Hydrostatic pressure Pressure exerted
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD)
 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
Brief View of Calculation and Measurement of Cardiac Hemodynamics
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC CARDIOLOGY Review Article Brief View of Calculation and Measurement of Cardiac Hemodynamics Samah Alasrawi* Pediatric Cardiologist, Al Jalila Children Heart Center, Dubai, UAE *
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC CARDIOLOGY Review Article Brief View of Calculation and Measurement of Cardiac Hemodynamics Samah Alasrawi* Pediatric Cardiologist, Al Jalila Children Heart Center, Dubai, UAE *
Introduction. Invasive Hemodynamic Monitoring. Determinants of Cardiovascular Function. Cardiovascular System. Hemodynamic Monitoring
 Introduction Invasive Hemodynamic Monitoring Audis Bethea, Pharm.D. Assistant Professor Therapeutics IV January 21, 2004 Hemodynamic monitoring is necessary to assess and manage shock Information obtained
Introduction Invasive Hemodynamic Monitoring Audis Bethea, Pharm.D. Assistant Professor Therapeutics IV January 21, 2004 Hemodynamic monitoring is necessary to assess and manage shock Information obtained
Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1984, 29
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Efficacy of Coenzyme Q10 Administra Aortic Stenosis and Pacemaker Induc Igarashi, Katsuro Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1984, 29 Issue Date 1984-10-25
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Efficacy of Coenzyme Q10 Administra Aortic Stenosis and Pacemaker Induc Igarashi, Katsuro Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1984, 29 Issue Date 1984-10-25
IABP Timing & Fidelity. Pocket Reference Guide
 IABP Timing & Fidelity Pocket Reference Guide Correct IABP Timing A = One complete cardiac cycle R B = Unassisted aortic end diastolic pressure P T C = Unassisted systolic pressure D = Diastolic augmentation
IABP Timing & Fidelity Pocket Reference Guide Correct IABP Timing A = One complete cardiac cycle R B = Unassisted aortic end diastolic pressure P T C = Unassisted systolic pressure D = Diastolic augmentation
Lab 16. The Cardiovascular System Heart and Blood Vessels. Laboratory Objectives
 Lab 16 The Cardiovascular System Heart and Blood Vessels Laboratory Objectives Describe the anatomical structures of the heart to include the pericardium, chambers, valves, and major vessels. Describe
Lab 16 The Cardiovascular System Heart and Blood Vessels Laboratory Objectives Describe the anatomical structures of the heart to include the pericardium, chambers, valves, and major vessels. Describe
Blood Pressure Regulation 2. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD
 Blood Pressure Regulation 2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the intermediate term and long term regulators of ABP. Describe the role of Epinephrine, Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone
Blood Pressure Regulation 2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the intermediate term and long term regulators of ABP. Describe the role of Epinephrine, Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone
Exam KEY. NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 Exam # 2 October 23, 2015 Total POINTS: % of grade in class
 NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 Exam # 2 October 23, 2015 Total POINTS: 100 20% of grade in class 1) Arterial and venous blood samples are taken, and other physiological measures are obtained, from a
NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 Exam # 2 October 23, 2015 Total POINTS: 100 20% of grade in class 1) Arterial and venous blood samples are taken, and other physiological measures are obtained, from a
Disclosures. Objectives. RV vs LV. Structure and Function 9/25/2016. A Look at the Other Side: Focus on the Right Ventricle and Pulmonary Hypertension
 Disclosures A Look at the Other Side: Focus on the Right Ventricle and Pulmonary Hypertension No financial relationships Susan P. D Anna MSN, APN BC, CHFN September 29, 2016 Objectives RV vs LV Differentiate
Disclosures A Look at the Other Side: Focus on the Right Ventricle and Pulmonary Hypertension No financial relationships Susan P. D Anna MSN, APN BC, CHFN September 29, 2016 Objectives RV vs LV Differentiate
Hemodynamics of Exercise
 Hemodynamics of Exercise Joe M. Moody, Jr, MD UTHSCSA and ALMMVAH, STVAHCS Exercise Physiology - Acute Effects Cardiac Output (Stroke volume, Heart Rate ) Oxygen Extraction (Arteriovenous O 2 difference,
Hemodynamics of Exercise Joe M. Moody, Jr, MD UTHSCSA and ALMMVAH, STVAHCS Exercise Physiology - Acute Effects Cardiac Output (Stroke volume, Heart Rate ) Oxygen Extraction (Arteriovenous O 2 difference,
Clinical Study Synopsis
 Clinical Study Synopsis This document is not intended to replace the advice of a healthcare professional and should not be considered as a recommendation. Patients should always seek medical advice before
Clinical Study Synopsis This document is not intended to replace the advice of a healthcare professional and should not be considered as a recommendation. Patients should always seek medical advice before
HEART FAILURE PHARMACOLOGY. University of Hawai i Hilo Pre- Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita Narciso Pharm D
 HEART FAILURE PHARMACOLOGY University of Hawai i Hilo Pre- Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita Narciso Pharm D 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand the effects of heart failure in the body
HEART FAILURE PHARMACOLOGY University of Hawai i Hilo Pre- Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita Narciso Pharm D 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand the effects of heart failure in the body
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM
 IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein THE BLOOD SYSTEM 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein THE BLOOD SYSTEM 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
Major Function of the Cardiovascular System. Transportation. Structures of the Cardiovascular System. Heart - muscular pump
 Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Ventricular-Pulmonary Vascular Coupling after the Total Cavopulmonary Anastomosis (Fontan)
 Ventricular-Pulmonary Vascular Coupling after the Total Cavopulmonary Anastomosis (Fontan) 6th International Neonatal & Childhood Pulmonary Vascular Disease Conference Fontan Physiology Single ventricular
Ventricular-Pulmonary Vascular Coupling after the Total Cavopulmonary Anastomosis (Fontan) 6th International Neonatal & Childhood Pulmonary Vascular Disease Conference Fontan Physiology Single ventricular
RV dysfunction and failure PATHOPHYSIOLOGY. Adam Torbicki MD, Dept Chest Medicine Institute of Tuberculosis and Lung Diseases Warszawa, Poland
 RV dysfunction and failure PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Adam Torbicki MD, Dept Chest Medicine Institute of Tuberculosis and Lung Diseases Warszawa, Poland Normal Right Ventricle (RV) Thinner wall Weaker myocytes Differences
RV dysfunction and failure PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Adam Torbicki MD, Dept Chest Medicine Institute of Tuberculosis and Lung Diseases Warszawa, Poland Normal Right Ventricle (RV) Thinner wall Weaker myocytes Differences
Circulation. Blood Pressure and Antihypertensive Medications. Venous Return. Arterial flow. Regulation of Cardiac Output.
 Circulation Blood Pressure and Antihypertensive Medications Two systems Pulmonary (low pressure) Systemic (high pressure) Aorta 120 mmhg Large arteries 110 mmhg Arterioles 40 mmhg Arteriolar capillaries
Circulation Blood Pressure and Antihypertensive Medications Two systems Pulmonary (low pressure) Systemic (high pressure) Aorta 120 mmhg Large arteries 110 mmhg Arterioles 40 mmhg Arteriolar capillaries
Nothing to Disclose. Severe Pulmonary Hypertension
 Severe Ronald Pearl, MD, PhD Professor and Chair Department of Anesthesiology Stanford University Rpearl@stanford.edu Nothing to Disclose 65 year old female Elective knee surgery NYHA Class 3 Aortic stenosis
Severe Ronald Pearl, MD, PhD Professor and Chair Department of Anesthesiology Stanford University Rpearl@stanford.edu Nothing to Disclose 65 year old female Elective knee surgery NYHA Class 3 Aortic stenosis
Properties of Pressure
 OBJECTIVES Overview Relationship between pressure and flow Understand the differences between series and parallel circuits Cardiac output and its distribution Cardiac function Control of blood pressure
OBJECTIVES Overview Relationship between pressure and flow Understand the differences between series and parallel circuits Cardiac output and its distribution Cardiac function Control of blood pressure
Circulatory System Review
 Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
Chapter 9. Body Fluid Compartments. Body Fluid Compartments. Blood Volume. Blood Volume. Viscosity. Circulatory Adaptations to Exercise Part 4
 Body Fluid Compartments Chapter 9 Circulatory Adaptations to Exercise Part 4 Total body fluids (40 L) Intracellular fluid (ICF) 25 L Fluid of each cell (75 trillion) Constituents inside cell vary Extracellular
Body Fluid Compartments Chapter 9 Circulatory Adaptations to Exercise Part 4 Total body fluids (40 L) Intracellular fluid (ICF) 25 L Fluid of each cell (75 trillion) Constituents inside cell vary Extracellular
OHTAC Recommendation: Twenty-Four-Hour Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring in Hypertension. Ontario Health Technology Advisory Committee
 OHTAC Recommendation: Twenty-Four-Hour Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring in Hypertension Ontario Health Technology Advisory Committee May 2012 Background Hypertension in Canada Hypertension occurs when
OHTAC Recommendation: Twenty-Four-Hour Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring in Hypertension Ontario Health Technology Advisory Committee May 2012 Background Hypertension in Canada Hypertension occurs when
Exercise in Adverse Cardiac Remodeling: of Mice and Men
 Exercise in Adverse Cardiac Remodeling: of Mice and Men 17-01-2013 Dirk J Duncker Experimental Cardiology, Cardiology, Thoraxcenter Cardiovascular Research Institute COEUR Erasmus MC, University Medical
Exercise in Adverse Cardiac Remodeling: of Mice and Men 17-01-2013 Dirk J Duncker Experimental Cardiology, Cardiology, Thoraxcenter Cardiovascular Research Institute COEUR Erasmus MC, University Medical
THE DIASTOLIC STRESS TEST: A NEW CLINICAL TOOL? THE CONCEPT OF DIASTOLIC RESERVE
 Thierry C. Gillebert University of Ghent ESC Education Committee THE DIASTOLIC STRESS TEST: A NEW CLINICAL TOOL? THE CONCEPT OF DIASTOLIC RESERVE 1 Case: Ann, 63 years Suffered from metabolic syndrome
Thierry C. Gillebert University of Ghent ESC Education Committee THE DIASTOLIC STRESS TEST: A NEW CLINICAL TOOL? THE CONCEPT OF DIASTOLIC RESERVE 1 Case: Ann, 63 years Suffered from metabolic syndrome
Chapter 9, Part 2. Cardiocirculatory Adjustments to Exercise
 Chapter 9, Part 2 Cardiocirculatory Adjustments to Exercise Electrical Activity of the Heart Contraction of the heart depends on electrical stimulation of the myocardium Impulse is initiated in the right
Chapter 9, Part 2 Cardiocirculatory Adjustments to Exercise Electrical Activity of the Heart Contraction of the heart depends on electrical stimulation of the myocardium Impulse is initiated in the right
Journal of Anesthesia & Clinical
 Journal of Anesthesia & Clinical Research ISSN: 2155-6148 Journal of Anesthesia & Clinical Research Balasubramanian and Menaha, J Anesth Clin Res 2017, 8:12 DOI: 10.4172/2155-6148.1000791 Research Article
Journal of Anesthesia & Clinical Research ISSN: 2155-6148 Journal of Anesthesia & Clinical Research Balasubramanian and Menaha, J Anesth Clin Res 2017, 8:12 DOI: 10.4172/2155-6148.1000791 Research Article
Weeks 1-3:Cardiovascular
 Weeks 1-3:Cardiovascular Cardiac Output The total volume of blood ejected from the ventricles in one minute is known as the cardiac output. Heart Rate (HR) X Stroke Volume (SV) = Cardiac Output Normal
Weeks 1-3:Cardiovascular Cardiac Output The total volume of blood ejected from the ventricles in one minute is known as the cardiac output. Heart Rate (HR) X Stroke Volume (SV) = Cardiac Output Normal
The circulatory system
 Introduction to Physiology (Course # 72336) 1 הלב עקרונות בסיסיים (הכנה למעבדת לב) Adi Mizrahi mizrahia@cc.huji.ac.il Textbook Chapter 12 2 The circulatory system To the heart Away from the heart 3 L 2.5
Introduction to Physiology (Course # 72336) 1 הלב עקרונות בסיסיים (הכנה למעבדת לב) Adi Mizrahi mizrahia@cc.huji.ac.il Textbook Chapter 12 2 The circulatory system To the heart Away from the heart 3 L 2.5
HYPERTENSION: Sustained elevation of arterial blood pressure above normal o Systolic 140 mm Hg and/or o Diastolic 90 mm Hg
 Lecture 39 Anti-Hypertensives B-Rod BLOOD PRESSURE: Systolic / Diastolic NORMAL: 120/80 Systolic = measure of pressure as heart is beating Diastolic = measure of pressure while heart is at rest between
Lecture 39 Anti-Hypertensives B-Rod BLOOD PRESSURE: Systolic / Diastolic NORMAL: 120/80 Systolic = measure of pressure as heart is beating Diastolic = measure of pressure while heart is at rest between
Ventriculo-arterial coupling and diastolic elastance. MasterclassIC Schiermonnikoog 2015
 Ventriculo-arterial coupling and diastolic elastance MasterclassIC Schiermonnikoog 2015 Ventriculo-arterial coupling Dynamic interaction between heart and systemic circulation (modulation of compliance
Ventriculo-arterial coupling and diastolic elastance MasterclassIC Schiermonnikoog 2015 Ventriculo-arterial coupling Dynamic interaction between heart and systemic circulation (modulation of compliance
Physiology of the heart I.
 Physiology of the heart I. Features of the cardiac muscle The cardiac cycle Theheart as a pump Cardiac sounds (Learning objectives 35-36) prof. Gyula Sáry Cardiovascular physiology Cardiac function, pumping
Physiology of the heart I. Features of the cardiac muscle The cardiac cycle Theheart as a pump Cardiac sounds (Learning objectives 35-36) prof. Gyula Sáry Cardiovascular physiology Cardiac function, pumping
AT1 RECEPTOR BLOCKADE ATTENUATES INSULIN RESISTANCE AND MYOCARDIAL REMODELING IN RATS WITH DIET-INDUCED OBESITY
 AT1 RECEPTOR BLOCKADE ATTENUATES INSULIN RESISTANCE AND MYOCARDIAL REMODELING IN RATS WITH DIET-INDUCED OBESITY SA Oliveira Jr, MP Okoshi, PF Martinez, DM Guizoni, BP Torres, M Dal Pai-Silva, K Okoshi,
AT1 RECEPTOR BLOCKADE ATTENUATES INSULIN RESISTANCE AND MYOCARDIAL REMODELING IN RATS WITH DIET-INDUCED OBESITY SA Oliveira Jr, MP Okoshi, PF Martinez, DM Guizoni, BP Torres, M Dal Pai-Silva, K Okoshi,
REGULATION OF CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 REGULATION OF CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Jonas Addae Medical Sciences, UWI REGULATION OF CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Intrinsic Coupling of cardiac and vascular functions - Autoregulation of vessel diameter Extrinsic
REGULATION OF CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Jonas Addae Medical Sciences, UWI REGULATION OF CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Intrinsic Coupling of cardiac and vascular functions - Autoregulation of vessel diameter Extrinsic
Introduction to Physiology (Course # 72336) 1. Adi Mizrahi Textbook Chapter 12
 Introduction to Physiology (Course # 72336) 1 עקרונות בסיסיים (הכנה למעבדת לב) הלב Adi Mizrahi mizrahia@cc.huji.ac.il Textbook Chapter 12 2 The circulatory system To the heart Away from the heart 3 L 2.5
Introduction to Physiology (Course # 72336) 1 עקרונות בסיסיים (הכנה למעבדת לב) הלב Adi Mizrahi mizrahia@cc.huji.ac.il Textbook Chapter 12 2 The circulatory system To the heart Away from the heart 3 L 2.5
Large Arteries of Heart
 Cardiovascular System (Part A-2) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Arteries Capillaries Veins Heart Anatomy Conduction System Blood pressure Fetal circulation Susie Turner, M.D. 1/5/13 Large Arteries of Heart
Cardiovascular System (Part A-2) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Arteries Capillaries Veins Heart Anatomy Conduction System Blood pressure Fetal circulation Susie Turner, M.D. 1/5/13 Large Arteries of Heart
The Causes of Heart Failure
 The Causes of Heart Failure Andy Birchall HFSN Right heart failure LVSD - HFREF Valve regurgitation or stenosis Dropsy CCF congestive cardiac failure Cor pulmonale Pulmonary hypertension HFPEF LVF Definitions
The Causes of Heart Failure Andy Birchall HFSN Right heart failure LVSD - HFREF Valve regurgitation or stenosis Dropsy CCF congestive cardiac failure Cor pulmonale Pulmonary hypertension HFPEF LVF Definitions
Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93)
 Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
SCVMC RESPIRATORY CARE PROCEDURE
 Page 1 of 7 New: 12/08 R: 4/11 R NC: 7/11, 7/12 B7180-63 Definitions: Inhaled nitric oxide (i) is a medical gas with selective pulmonary vasodilator properties. Vaso-reactivity is the evidence of acute
Page 1 of 7 New: 12/08 R: 4/11 R NC: 7/11, 7/12 B7180-63 Definitions: Inhaled nitric oxide (i) is a medical gas with selective pulmonary vasodilator properties. Vaso-reactivity is the evidence of acute
Closing ASDs with pulmonary hypertension. Shakeel A Qureshi Evelina Children s Hospital London
 Closing ASDs with pulmonary hypertension Shakeel A Qureshi Evelina Children s Hospital London Ho Chi Minh, Vietnam, January 2012 ACC/AHA 2008 Guidelines ASD closure Closure is indicated for right atrial
Closing ASDs with pulmonary hypertension Shakeel A Qureshi Evelina Children s Hospital London Ho Chi Minh, Vietnam, January 2012 ACC/AHA 2008 Guidelines ASD closure Closure is indicated for right atrial
TITLE: Epicatechin as a therapeutic strategy to mitigate the development of cardiac remodeling and fibrosis
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-16-1-0244 TITLE: Epicatechin as a therapeutic strategy to mitigate the development of cardiac remodeling and fibrosis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Francisco Villarreal CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-16-1-0244 TITLE: Epicatechin as a therapeutic strategy to mitigate the development of cardiac remodeling and fibrosis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Francisco Villarreal CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
Transportation and Excretion 7 th Biology
 Page1 Transportation and Excretion 7 th Biology William Harvey was an English physician was the first to give the details of blood circulation, the properties of blood and the pumping of blood by the heart.
Page1 Transportation and Excretion 7 th Biology William Harvey was an English physician was the first to give the details of blood circulation, the properties of blood and the pumping of blood by the heart.
Pregnancy and Heart Disease Sharon L. Roble, MD Echo Hawaii 2016
 1 Pregnancy and Heart Disease Sharon L. Roble, MD Echo Hawaii 2016 DISCLOSURES I have no disclosures relevant to today s talk 2 Cardiovascular Effects of Pregnancy Anatomic Ventricular muscle mass increases
1 Pregnancy and Heart Disease Sharon L. Roble, MD Echo Hawaii 2016 DISCLOSURES I have no disclosures relevant to today s talk 2 Cardiovascular Effects of Pregnancy Anatomic Ventricular muscle mass increases
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 20 The Cardiovascular System: The Heart Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Learn about the components of the cardiovascular system
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 20 The Cardiovascular System: The Heart Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Learn about the components of the cardiovascular system
