Oncologic Emergencies
|
|
|
- Ezra Lindsey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Oncologic Emergencies Luca Delatore, MD James Emergency Department Medical Director Associate Professor Clinical Department of Emergency Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Prevalence of cancer: American Cancer Society 13.7 million Americans are living with cancer or history of the disease American Cancer Society projects 1.6 million new diagnoses this year Cancer is the 2 nd leading cause of death in the US (Heart disease #1) Cancer accounts for more than 500,000 deaths per year Prevalence of cancer New therapies have led to longer survival New drugs Radiation Bone marrow transplants Immunotherapy-most recent and area of growth at OSU Cancer-related ED visits Patients with high acuity Admission rate of 60-70% Often (~5%) a new diagnosis made in the ED Frequently the more acute patients with lower survival rates present to the ED Also older patients and those with limited healthcare access present to the ED 1
2 Cancer-related ED visits Resisting labels is critical for appropriate treatment Cancer does not mean terminal Cancer does not assume DNR Treatment is indicated Pain Dehydration Vomiting Infection Palliative Why a specific Emergency Department? Provide specialized care in the emergency setting for cancer patients Improve access to unique treatment and research opportunities for patients with cancer Establish hospital based guidelines for emergency department care Evaluation of patient outcome Admissions Inpatient length of stay Infection rates Patient Satisfaction Classification of Oncologic Emergencies Can be broken down into 3 main areas Structural Metabolic/endocrine Hematologic Structural Oncologic Emergencies Spinal Cord Compression Malignant pericardial effusion Brain metastases Superior Vena Cava Syndrome 2
3 Spinal Cord Compression Major emergency requiring radiation treatment Most are due to metastatic lesions Most common in the thoracic spine (70%) and lumbrosacral (20%) Most common early symptom is pain (95%) Pain is positional and usually worse when supine Occurs in approximately 5% of all cancer patients Most common in breast, lung and prostate cancer, renal, lymphoma Life threatening if above C3 Spinal Cord Compression- Exam findings Tenderness to palpation Weakness Spasticity Abnormal reflexes Sensory deficits Good indicator of location of lesion Palpable bladder Decreased rectal tone Spinal Cord Compression Early recognition is key. Early MRI imaging Prognosis is closely related to pretreatment level of function Late Signs Autonomic dysfunction Urinary retention Constipation Transport for rapid evaluation of emergent radiation therapy and steroids Surgery for tissue diagnosis and stabilization Treatment delays may result in loss of bowel or bladder function Malignant pericardial effusion Due to neoplastic infiltration or radiation treatment Can lead to cardiac tamponade Difficult diagnosis to make and often misdiagnosed as CHF, PE or anxiety Beat to beat alteration of the QRS Symptoms Dyspnea Orthopnea Cough Chest pain Weakness 3
4 Malignant pericardial effusion Physical exam findings: muffled heart sounds Increased JVP Decreased systolic blood pressure Echocardiogram (Most Helpful Tool) Diastolic collapse of RA and RV Dilated IVC Malignant pericardial effusion Cardiac tamponade Initial treatment is temporizing Oxygen, IVF, vasopressors May require pericardiocentesis, pericardial window 60% of malignant effusions reaccummulate Treat underlying malignancy Brain Metastases Most common form of malignant CNS involvement Common associated cancers: Lung (most common) Breast Melanoma Leukemia/lymphoma Causes symptoms via compression and edema Headache Seizures Focal weakness Exam may be normal Brain Metastases Diagnosis: Find the primary tumor CT scan of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis If negative, then consider mammogram or other imaging study In 30% of patients no primary tumor is identified 4
5 Brain Metastases Alleviate Symptoms ie palliation Radiation is the primary treatment for brain metastases If single brain lesion, then surgery may be reasonable with or without radiation Corticosteroids Especially if signs of edema Chemotherapy Anti-seizure medications tend to improve quality of life Superior Vena Cava Syndrome Obstruction of the SVC which carries blood back into the heart Approximately 90% caused by cancer Lung cancer is the most common (65%) Clinical features: Edema of the face and arms Swollen collateral veins on the chest Shortness of breath Coughing Difficulty swallowing Headache Superior Vena Cava Syndrome Lung cancer patients account for 65% of all SVCS cases 3 15% of patients with Lung CA Four times more likely in right vs left sided tumors Lymphoma - 8% Usually in the anterior mediastinum Breast and other mediastinal tumors 10% Non-malignant conditions account for remainder Superior Vena Cava Syndrome Supportive care and transport Elevate the head of the bed and provide oxygen if hypoxic Immediate radiation therapy consultation Consider anticoagulation (50% will have clot present) Radiation is the definitive treatment Surgery and chemotherapy in selected cases Intravenous stents, balloon angioplasty and surgical bypass are becoming more common 5
6 Oncologic Emergencies Joseph Flynn, DO, MPH, FACP Associate Professor Clinical Division of Hematology & Oncology The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Overview General Considerations Hypercalcemia of malignancy Tumor Lysis Syndrome Septic Shock General Considerations Oncologic Emergencies Have Increased Rapid Recognition Required Aggressive Treatment is Indicated If due to underlying cancer, then treat the cancer Palliation in Advanced Malignancies Must Consider Doing Nothing Case # 1 A 60 y/o white female is brought to the ER by her family for new onset worsening confusion The patient notes only vague abdominal pain and constipation PE: HR 115, BP 88/40, RR 10, T Elderly appearing female Dry mucous membranes Tachycardia, no murmurs Lungs are clear Abdomen w/ decreased bowel sounds 6
7 Laboratory Hypercalcemia of Malignancy Most Common Metabolic Emergency in Cancer Occurs in about 10%-20% of Cancer Patients Most Often Seen with Lung, Breast Hematologic Malignancies BLT with a Kosher Pickle and Mayonaisse Cancers that go to bone Breast Lung / Lymphoma Thyroid Kidney Prostate Myeloma Hypercalcemia Etiology Syndrome Mediated by Production of PTHrP Parathyroid hormone-related peptide which binds to parathyroid hormone receptors, mobilizing calcium from bones, and increasing renal reabsorption of calcium. This Activates Osteoclast Activity Level of Boney Metastasis Does Not Necessarily Correlate with Level of Calcium Direct Tumor Invasion into Bony Structures Individual tumor cells secrete a variety of mediators that upregulate local osteoclastic activity, causing calcium to be released into the serum. * Immobility May Contribute to Hypercalcemia 7
8 Hypercalcemia Acute Symptoms Early Nausea Vomiting Constipation Muscle Weakness Mental Status Changes Acute Renal Insufficiency Late Oliguria Renal failure Stupor, coma Ileus Heart block Hypercalcemia Acute Symptoms Early Nausea Vomiting Constipation Muscle Weakness Mental Status Changes Acute Renal Insufficiency Late Oliguria Renal failure Stupor, coma Ileus Heart block Hypercalcemia Symptoms CNS Cardia GI Renal Weakness Bradycardia Nausea / Vomiting Polyuria Hypotonia Decreased QT Constipation Calcinosis Proximal Myopathy Prolonged PR Interval Ileus Hypercalcemia Diagnosis History and Physical Serum calcium (>11 mg/dl) Phosphorus is low or normal Mental Status Changes Widened T wave Pancreatitis Seizure /Coma Arrhythmias Dyspepsia Adapted from Escalante et al, Cancer Management, May
9 Treatment General Approach If Ca++ < 12 and Asymptomatic can be Treated as Outpatient Reduce or Eliminate Causative Malignancy Hydration with IVF ( ml/Hr based on UOP) Usually Doesn t Normalize Calcium Alone Diuresis With Loop Diuretic after Hydration Biphosphonates inhibit osteoclastic activity and calcium resorption from bone Denosumab HypercalcemiaTreatment Bisphosphonates Bind to hydroxyapatite crystals Onset around 48 hours Duration 2-4 weeks Pamidronate 60 90mg IV Zoledronic Acide 4 8 mg Corticosteroids Limited Value Outside Hematological Malignancies Onset 1 to 5 days Duration 2-4 weeks Dose: Varied Calcitonin Binds directly to osteoclasts Onset: 2 6 hours Duration: 6-12 hours Dose: 4 IU/Kg SQ q12hr Gallium Onset: hours Duration: 2 3 weeks Dose: 200mg/m2 CIV for 5 days Consider Corticosteroids Volume Expansion Loop Diuretic Maintain Urine output ~ 200ml per hour Bisphosphonate Denosumab Hypercalcemia Treatment Chronic / Prevention Supportive Measures / Bisphosphonate Dialysis Cancer Directed Therapy Denosumab Potent inhibitor of osteoclast-mediated bone resorption Fully humanized monoclonal antibody Binds RANKL (receptor activator of nuclear factor kb ligand) to inhibit the formation, function, and survival of osteoclasts Reduces serum calcium in patients with bisphosphonate-refractory hypercalcemia of malignancy 9
10 Case #2 59-year-old woman who was diagnosed with non-hodgkins Lymphoma Presented to Hematology 1 day post treatment and was found to have worsening urinary output. Physical examination notable for diffuse lymphadenopathy Otherwise Normal Tumor Lysis Syndrome (TLS) Result of a high rate of cell turnover. Results in the release of intracellular products into the circulation. Overwhelms normal homeostatic mechanisms that control potassium, calcium, phosphorus and uric acid. Hyperkalemia, Hypocalcemia, Hyperphosphatemia and Hyperuricemia may occur alone or in combination with one another. Tumor Lysis Syndrome (con t) Can occur with a variety of tumors Most commonly with hematological malignancies Poorly differentiated lymphomas Post Treatment Myeloproliferative disorders Leukemias Acute myelogenous & acute lymphocytic Leukemia Chronic myelogenous leukemia Chronic Lymphocytic leukemia 10
11 Tumor Lysis Syndrome Features of TLS Hyperkalemia Most Life-threatening Component of TLS Sudden Increase Can Cause Cardiac Arrhythmias and Death Must Rule Out Other Causes Treatment is Based on the Underlying Cause Tumor Lysis Syndrome Additional symptoms Paresthesias Altered level of consciousness Seizure Nausea/vomiting Anorexia Flank pain Oliguria, hematuria edema Tumor Lysis Syndrome Diagnosis Labs: Serum potassium Calcium Phosphorus Uric acid Creatinine Cairo-Bishop Classification of TLS Uric Acid > 8 mg/dl (> 476 umol/l) or 25% increase from baseline Potassium > 6 meq/l (>6 mmol/l) or 25% increase from baseline Phosphorus > 6.5 mg/dl (>2.1 mmol/l) or 25% increase from baseline Calcium < 7 mg/dl (< 1.75 mmol/l) or 25% decrease from baseline Creatinine > 1.5 times the ULN Cardiac Arrhythmia or Sudden Death Seizure Two or More Laboratory Changes Must be Observed within 3 Days Before or 7 Days After Cytotoxic Therapy The same criteria do not apply to spontaneous TLS Lewis et al CA CANCER J CLIN 2011;61:
12 Tumor Lysis Syndrome Hyperuricemia Prophylactic Measures Prior to the Initiation of Chemotherapy. Avoid Drugs That Increase Serum Urate or Produce Acidic Urine Thiazides Diuretics and Salicylates Alkalinization of the Urine Should be Initiated to Maintain a Urine ph > 7.0. Sodium Bicarbonate Solution ( mmol/l) Adjusted so that an Alkaline Urinary ph is Maintained. Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitor, Acetazolamide May be Used to Increase the Effects of Alkalinization. Tumor Lysis Syndrome Hyperuricemia Prior to Era of Allopurinol Use Acute uric acid nephropathy developed in as many as 10 percent of patients treated with acute lymphoblastic leukemias Gouty Arthritis May Be Seen Biggest Risk ARF Treat with Allopurinol Start 1 2 days Prior to Chemotherapy 10mg/kg/d q 8 hrs Careful in Renal Disease Rasburicase: mg/kg Dialysis May Be Required Tumor Lysis Syndrome Hyperphosphatemia and hypocalcemia Phosphate Levels May Reach Four Times Normal As Concentration of Phosphate Increases, it Combines with Calcium and Precipitates in the Renal Tubule and in Soft Tissues : Malignant Calcemia Result is Renal Failure Symptoms Include Agitation, Tetany and Bone Pain Aluminum Hydroxide: mg/kg/d divided q 4 6 hours Dialysis Hypocalcemia: Treat with Calcium Gluconate if Symptomatic Tumor Lysis Syndrome Treatment of Hyperkalemia Sodium Polystyrene gm Normal Saline Regular Insulin: 10 U IV Follow BG Dextrose 50% with Insulin Sodium Bicarbonate: 50 meq IV Calcium Chloride mg IV Albuterol nebulized Dialysis 12
13 Case # 3 Patient is a 85 year old white female who resides in an ECF who experienced worsening abominal pain over days was transferred to your facility with dizziness and fevers to 102.5F BP 78/38, pulse 133, pulse ox 92% RA Pulmonary: crackles bilateral bases Abdomen: soft, tender to palpation in the hypogastrum Patient minimally responsive Start Dopamine to 10mcg / hr Blood pressure 100/50, pulse 120 Septic Shock A response to overwhelming infection Marked by: Hemodynamic instabillity Altered metabolism Abnormal coagulation 75% of cancer patients who get septic shock die if not treated immediately. Most common cause - gram-negative bacteria. Septic Shock (con t) Early Warm, flushed, skin May be febrile/have chills Tachypnea Anxiety Altered mental status Progressive hypotension Decreased urine output Late Cold, clammy skin Temperature probably sub-normal Vasoconstriction Systemic vascular resistance Decreased cardiac output Rapid, thready pulse Low/unobtainable B/P Lips/nailbeds cyanotic Decreased urine output Altered level of consciousness Septic Shock Diagnosis Laboratory findings Blood Cultures Positive WBC Increased or Decreased, with left shift (increased segs and bands) Increased PT/PTT Decreased Platelets/Fibrinogen levels Increased BUN/creatinine ABGs Reveal Respiratory Alkalosis Progresses to Metabolic Acidosis 13
14 Septic Shock Treatment Fluid resuscitation Raise B/P, Improve Perfusion Dopamine Improve Renal Perfusion Increase Peripheral Vascular Resistance Broad Spectrum Antibiotics Immediately After Cultures Supportive Electrolyte Replacement 14
Oncologic Emergencies
 Oncologic Emergencies Luca Delatore, MD James Emergency Department Medical Director Associate Professor Clinical Department of Emergency Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Prevalence
Oncologic Emergencies Luca Delatore, MD James Emergency Department Medical Director Associate Professor Clinical Department of Emergency Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Prevalence
Professor Dr. Saiyeedur Rahman Professor and Head Department of Medicine SBMCH, Barisal
 Professor Dr. Saiyeedur Rahman Professor and Head Department of Medicine SBMCH, Barisal What is Oncologic Emergency? An oncologic emergency is an acute, potentially life-threatening event resulting from
Professor Dr. Saiyeedur Rahman Professor and Head Department of Medicine SBMCH, Barisal What is Oncologic Emergency? An oncologic emergency is an acute, potentially life-threatening event resulting from
It s Not A Tumor! Oncologic Emergencies
 It s Not A Tumor! Diane M. Birnbaumer, M.D., FACEP Professor of Medicine University of California, Los Angeles Senior Clinical Educator Department of Emergency Medicine Harbor-UCLA Medical Center Increasing
It s Not A Tumor! Diane M. Birnbaumer, M.D., FACEP Professor of Medicine University of California, Los Angeles Senior Clinical Educator Department of Emergency Medicine Harbor-UCLA Medical Center Increasing
Oncologic Emergencies
 Oncologic Emergencies Objectives Identify the major oncologic emergencies Describe the assessment for each emergency Outline the standard of care of patients experiencing oncologic emergencies Structural
Oncologic Emergencies Objectives Identify the major oncologic emergencies Describe the assessment for each emergency Outline the standard of care of patients experiencing oncologic emergencies Structural
Managing patients with bulky cancers
 SIOP PODC Supportive Care Education (ICON 2016) Presentation Date: 23 rd January 2016 Recording Link at www.cure4kids.org: https://www.cure4kids.org/ums/home/conference_rooms/enter.php?room=p2pjfjp8nha
SIOP PODC Supportive Care Education (ICON 2016) Presentation Date: 23 rd January 2016 Recording Link at www.cure4kids.org: https://www.cure4kids.org/ums/home/conference_rooms/enter.php?room=p2pjfjp8nha
GUIDELINE FOR THE MANAGEMENT AND PREVENTION OF ACUTE TUMOUR LYSIS SYNDROME IN HAEMATOLOGICAL MALIGNANCIES
 GUIDELINE FOR THE MANAGEMENT AND PREVENTION OF ACUTE TUMOUR LYSIS SYNDROME IN HAEMATOLOGICAL MALIGNANCIES Full Title of Guideline: Author (include email and role): Division & Speciality: Scope (Target
GUIDELINE FOR THE MANAGEMENT AND PREVENTION OF ACUTE TUMOUR LYSIS SYNDROME IN HAEMATOLOGICAL MALIGNANCIES Full Title of Guideline: Author (include email and role): Division & Speciality: Scope (Target
Outcome of Tumor Lysis Syndrome with Hydration and Alkalinization in Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
 Bangladesh Journal of Medical Science Vol. 11 No. 04 Oct 12 Original article Outcome of Tumor Lysis Syndrome with Hydration and Alkalinization in Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Sultana A 1,
Bangladesh Journal of Medical Science Vol. 11 No. 04 Oct 12 Original article Outcome of Tumor Lysis Syndrome with Hydration and Alkalinization in Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Sultana A 1,
Hematologic Emergencies. Udomsak Bunworasate Chulalongkorn University
 Hematologic Emergencies Udomsak Bunworasate Chulalongkorn University Hematologic Emergencies Hyperleukocytosis Tumor lysis syndrome SVC syndrome Spinal cord compression Hypercalcemia 1. Hyperleukocytosis
Hematologic Emergencies Udomsak Bunworasate Chulalongkorn University Hematologic Emergencies Hyperleukocytosis Tumor lysis syndrome SVC syndrome Spinal cord compression Hypercalcemia 1. Hyperleukocytosis
Educational Session: Oncology Emergencies
 Educational Session: Oncology Emergencies Diane M. Birnbaumer, MD, FACEP 3/24/2010 10:00 AM - 11:00 AM Oncologic Emergencies Diane M. Birnbaumer, M.D., FACEP Professor of Medicine University of California,
Educational Session: Oncology Emergencies Diane M. Birnbaumer, MD, FACEP 3/24/2010 10:00 AM - 11:00 AM Oncologic Emergencies Diane M. Birnbaumer, M.D., FACEP Professor of Medicine University of California,
HYPERCALCEMIA. Babak Tamizi Far MD. Assistant professor of internal medicine Al-zahra hospital, Isfahan university of medical sciences
 HYPERCALCEMIA Babak Tamizi Far MD. Assistant professor of internal medicine Al-zahra hospital, Isfahan university of medical sciences ESSENTIALS OF DIAGNOSIS Serum calcium level > 10.5 mg/dl Serum ionized
HYPERCALCEMIA Babak Tamizi Far MD. Assistant professor of internal medicine Al-zahra hospital, Isfahan university of medical sciences ESSENTIALS OF DIAGNOSIS Serum calcium level > 10.5 mg/dl Serum ionized
Oncologic Emergencies
 Oncologic Emergencies Peter Bjerkerot RN, OCN 1339 Normandy Drive Atlanta, GA 30306-2574 404.754.5952 WebPage http://boyrn.com peter.bjerkerot@mindspring.com Full Disclosure Statement Celgene Nurse Advisory
Oncologic Emergencies Peter Bjerkerot RN, OCN 1339 Normandy Drive Atlanta, GA 30306-2574 404.754.5952 WebPage http://boyrn.com peter.bjerkerot@mindspring.com Full Disclosure Statement Celgene Nurse Advisory
Palliative Care Emergencies
 Palliative Care Emergencies LAURA BARNFIELD What might constitute an emergency in Palliative Care? 1 Palliative Care Emergencies Major haemorrhage Metastatic Spinal Cord Compression (MSCC) Superior Vena
Palliative Care Emergencies LAURA BARNFIELD What might constitute an emergency in Palliative Care? 1 Palliative Care Emergencies Major haemorrhage Metastatic Spinal Cord Compression (MSCC) Superior Vena
Current Management of Metastatic Bone Disease
 Current Management of Metastatic Bone Disease Evaluation and Medical Management Dr. Sara Rask Head, Medical Oncology Simcoe Muskoka Regional Cancer Centre www.rvh.on.ca Objectives 1. Outline an initial
Current Management of Metastatic Bone Disease Evaluation and Medical Management Dr. Sara Rask Head, Medical Oncology Simcoe Muskoka Regional Cancer Centre www.rvh.on.ca Objectives 1. Outline an initial
Oncologic Emergencies
 Oncologic Emergencies Francis L. Counselman, M.D., CPE, FACEP Department of Emergency Medicine Eastern Virginia Medical School Norfolk, Virginia Superior Vena Cava Syndrome Compression of SVC by mediastinal
Oncologic Emergencies Francis L. Counselman, M.D., CPE, FACEP Department of Emergency Medicine Eastern Virginia Medical School Norfolk, Virginia Superior Vena Cava Syndrome Compression of SVC by mediastinal
Oncological emergencies. Harmesh Naik, MD. Medical Oncology Hope Cancer Clinic
 Oncological emergencies Harmesh Naik, MD. Medical Oncology Hope Cancer Clinic Presentation to Internal Medicine GME resident physicians: October 24, 2013 Presentation goals Briefly review clinical presentation,
Oncological emergencies Harmesh Naik, MD. Medical Oncology Hope Cancer Clinic Presentation to Internal Medicine GME resident physicians: October 24, 2013 Presentation goals Briefly review clinical presentation,
CCRN Review - Renal. CCRN Review - Renal 10/16/2014. CCRN Review Renal. Sodium Critical Value < 120 meq/l > 160 meq/l
 CCRN Review Renal Leanna R. Miller, RN, MN, CCRN-CMC, PCCN-CSC, CEN, CNRN, CMSRN, NP Education Specialist LRM Consulting Nashville, TN Sodium 136-145 Critical Value < 120 meq/l > 160 meq/l Sodium Etiology
CCRN Review Renal Leanna R. Miller, RN, MN, CCRN-CMC, PCCN-CSC, CEN, CNRN, CMSRN, NP Education Specialist LRM Consulting Nashville, TN Sodium 136-145 Critical Value < 120 meq/l > 160 meq/l Sodium Etiology
Bone Metastases. Sukanda Denjanta, M.Sc., BCOP Pharmacy Department, Chiangrai Prachanukroh Hospital
 Bone Metastases Sukanda Denjanta, M.Sc., BCOP Pharmacy Department, Chiangrai Prachanukroh Hospital 1 Outline Pathophysiology Signs & Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Spinal Cord Compression 2 General Information
Bone Metastases Sukanda Denjanta, M.Sc., BCOP Pharmacy Department, Chiangrai Prachanukroh Hospital 1 Outline Pathophysiology Signs & Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Spinal Cord Compression 2 General Information
5/18/2017. Specific Electrolytes. Sodium. Sodium. Sodium. Sodium. Sodium
 Specific Electrolytes Hyponatremia Hypervolemic Replacing water (not electrolytes) after perspiration Freshwater near-drowning Syndrome of Inappropriate ADH Secretion (SIADH) Hypovolemic GI disease (decreased
Specific Electrolytes Hyponatremia Hypervolemic Replacing water (not electrolytes) after perspiration Freshwater near-drowning Syndrome of Inappropriate ADH Secretion (SIADH) Hypovolemic GI disease (decreased
Spontaneous Tumor Lysis Syndrome in Small Cell Lung Cancer
 Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.1017 Spontaneous Tumor Lysis Syndrome in Small Cell Lung Cancer Venkatkiran Kanchustambham 1, Swetha Saladi 2, Setu Patolia 2, David Stoeckel 2 1. Pulmonary
Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.1017 Spontaneous Tumor Lysis Syndrome in Small Cell Lung Cancer Venkatkiran Kanchustambham 1, Swetha Saladi 2, Setu Patolia 2, David Stoeckel 2 1. Pulmonary
2.1 mmol/l or 25% increase from baseline mmol/l or 25% decrease from baseline
 22.1 Hyperleukocytosis and tumour lysis syndrome The guideline is addressed for ALL patients with hyperleukocytosis (WBC 100 x109/l) only and should not be used without modifications in case of other diseases
22.1 Hyperleukocytosis and tumour lysis syndrome The guideline is addressed for ALL patients with hyperleukocytosis (WBC 100 x109/l) only and should not be used without modifications in case of other diseases
Electrolyte Imbalance and Resuscitation. Dr. Mehmet Okumuş Sütçü Imam University Faculty of Medicine Department of Emergency Medicine
 Electrolyte Imbalance and Resuscitation Dr. Mehmet Okumuş Sütçü Imam University Faculty of Medicine Department of Emergency Medicine Presentation plan Definition of the electrolyte disturbances Conditions
Electrolyte Imbalance and Resuscitation Dr. Mehmet Okumuş Sütçü Imam University Faculty of Medicine Department of Emergency Medicine Presentation plan Definition of the electrolyte disturbances Conditions
Nursing Process Focus: Patients Receiving Dextran 40 (Gentran 40)
 Assess for presence/history of hypovolemia, shock, venous thrombosis. Assess vital signs: Hypovolemic shock secondary to surgery, burns, hemorrhage, other serious condition PT and PTT abnormalities Venous
Assess for presence/history of hypovolemia, shock, venous thrombosis. Assess vital signs: Hypovolemic shock secondary to surgery, burns, hemorrhage, other serious condition PT and PTT abnormalities Venous
WATER, SODIUM AND POTASSIUM
 WATER, SODIUM AND POTASSIUM Attila Miseta Tamás Kőszegi Department of Laboratory Medicine, 2016 1 Average daily water intake and output of a normal adult 2 Approximate contributions to plasma osmolality
WATER, SODIUM AND POTASSIUM Attila Miseta Tamás Kőszegi Department of Laboratory Medicine, 2016 1 Average daily water intake and output of a normal adult 2 Approximate contributions to plasma osmolality
-Cardiogenic: shock state resulting from impairment or failure of myocardium
 Shock chapter Shock -Condition in which tissue perfusion is inadequate to deliver oxygen, nutrients to support vital organs, cellular function -Affects all body systems -Classic signs of early shock: Tachycardia,tachypnea,restlessness,anxiety,
Shock chapter Shock -Condition in which tissue perfusion is inadequate to deliver oxygen, nutrients to support vital organs, cellular function -Affects all body systems -Classic signs of early shock: Tachycardia,tachypnea,restlessness,anxiety,
Acute tumor lysis syndrome (ATLS), although
 ACUTE TUMOR LYSIS SYNDROME Michele Cohen, DVM, DACVIM (Oncology) College of Veterinary Medicine Auburn University Auburn, Alabama Acute tumor lysis syndrome (ATLS), although uncommon, can be a serious
ACUTE TUMOR LYSIS SYNDROME Michele Cohen, DVM, DACVIM (Oncology) College of Veterinary Medicine Auburn University Auburn, Alabama Acute tumor lysis syndrome (ATLS), although uncommon, can be a serious
Saint-Antoine Hospital, Paris. Medical Intensive Unit Care. Hafid Ait-Oufella, MD.PhD. Dyscalcemia. Dyskalemia
 Dyskalemia Dyscalcemia Hafid Ait-Oufella, MD.PhD. Medical Intensive Unit Care Saint-Antoine Hospital, Paris Potassium K + Molecular weight: 39 1gr K + =2.5mmol Potassium disorders in ICU : Our experience
Dyskalemia Dyscalcemia Hafid Ait-Oufella, MD.PhD. Medical Intensive Unit Care Saint-Antoine Hospital, Paris Potassium K + Molecular weight: 39 1gr K + =2.5mmol Potassium disorders in ICU : Our experience
Nephrology / Urology. Hyperkalemia Causes and Definition Lecturio Online Medical Library. Definition. Epidemiology of Hyperkalemia.
 Nephrology / Urology Hyperkalemia Causes and Definition Lecturio Online Medical Library See online here Hyperkalemia is defined by the serum potassium level when it is higher than 5.5mEq/L. It is usually
Nephrology / Urology Hyperkalemia Causes and Definition Lecturio Online Medical Library See online here Hyperkalemia is defined by the serum potassium level when it is higher than 5.5mEq/L. It is usually
RENAL FAILURE IN CHILDREN Dr. Mai Mohamed Elhassan Assistant Professor Jazan University
 RENAL FAILURE IN CHILDREN Dr. Mai Mohamed Elhassan Assistant Professor Jazan University OBJECTIVES By the end of this lecture each student should be able to: Define acute & chronic kidney disease(ckd)
RENAL FAILURE IN CHILDREN Dr. Mai Mohamed Elhassan Assistant Professor Jazan University OBJECTIVES By the end of this lecture each student should be able to: Define acute & chronic kidney disease(ckd)
IV Fluids. I.V. Fluid Osmolarity Composition 0.9% NaCL (Normal Saline Solution, NSS) Uses/Clinical Considerations
 IV Fluids When administering IV fluids, the type and amount of fluid may influence patient outcomes. Make sure to understand the differences between fluid products and their effects. Crystalloids Crystalloid
IV Fluids When administering IV fluids, the type and amount of fluid may influence patient outcomes. Make sure to understand the differences between fluid products and their effects. Crystalloids Crystalloid
BCCA Protocol Summary Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Malignancy Related Hypercalcemia
 BCCA Protocol Summary Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Malignancy Related Hypercalcemia Protocol Code Tumour Group Supportive Care Group Contacts SCHYPCAL Supportive Care Lisa Wanbon (VIC)
BCCA Protocol Summary Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Malignancy Related Hypercalcemia Protocol Code Tumour Group Supportive Care Group Contacts SCHYPCAL Supportive Care Lisa Wanbon (VIC)
SHOCK Susanna Hilda Hutajulu, MD, PhD
 SHOCK Susanna Hilda Hutajulu, MD, PhD Div Hematology and Medical Oncology Department of Internal Medicine Universitas Gadjah Mada Yogyakarta Outline Definition Epidemiology Physiology Classes of Shock
SHOCK Susanna Hilda Hutajulu, MD, PhD Div Hematology and Medical Oncology Department of Internal Medicine Universitas Gadjah Mada Yogyakarta Outline Definition Epidemiology Physiology Classes of Shock
Cardiorenal and Renocardiac Syndrome
 And Renocardiac Syndrome A Vicious Cycle Cardiorenal and Renocardiac Syndrome Type 1 (acute) Acute HF results in acute kidney injury Type 2 Chronic cardiac dysfunction (eg, chronic HF) causes progressive
And Renocardiac Syndrome A Vicious Cycle Cardiorenal and Renocardiac Syndrome Type 1 (acute) Acute HF results in acute kidney injury Type 2 Chronic cardiac dysfunction (eg, chronic HF) causes progressive
Contents. Contributors. Reviewers. Acknowledgements I CARDIOVASCULAR COMPLICATIONS
 Contributors Reviewers Acknowledgements Preface xii xvi xvii xviii I CARDIOVASCULAR COMPLICATIONS 1 Cardiac Complications of Cancer and Anticancer Treatment 3 Introduction 3 Malignant Pericardial Effusion
Contributors Reviewers Acknowledgements Preface xii xvi xvii xviii I CARDIOVASCULAR COMPLICATIONS 1 Cardiac Complications of Cancer and Anticancer Treatment 3 Introduction 3 Malignant Pericardial Effusion
It s Not A Tumor! Oncologic Emergencies
 It s Not A Tumor! Diane M. Birnbaumer, M.D., FACEP Professor of Medicine University of California, Los Angeles Senior Clinical Educator Department of Emergency Medicine Harbor-UCLA Medical Center Increasing
It s Not A Tumor! Diane M. Birnbaumer, M.D., FACEP Professor of Medicine University of California, Los Angeles Senior Clinical Educator Department of Emergency Medicine Harbor-UCLA Medical Center Increasing
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominal tumors, in children, 530 531 Alkalinization, in tumor lysis syndrome, 516 Allopurinol, in tumor lysis syndrome, 515 Anaphylaxis, drug
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominal tumors, in children, 530 531 Alkalinization, in tumor lysis syndrome, 516 Allopurinol, in tumor lysis syndrome, 515 Anaphylaxis, drug
Case Scenario 3: Shock and Sepsis
 Name: Molly Boyle 1. Define the term shock (Lewis textbook): Shock is a syndrome characterized by decreased perfusion and impaired metabolism. Shock can have a number of causes that result in damage to
Name: Molly Boyle 1. Define the term shock (Lewis textbook): Shock is a syndrome characterized by decreased perfusion and impaired metabolism. Shock can have a number of causes that result in damage to
Electrolyte Emergencies
 Electrolyte Emergencies Hyponatremia/hypernatremia Hypokalemia/hyperkalemia Hypocalcemia/hypercalcemia Hypomagnesemia/hypermagnesemia Hypophosphatemia/hyperphosphatemia Hyponatremia Symptomatic: headaches,
Electrolyte Emergencies Hyponatremia/hypernatremia Hypokalemia/hyperkalemia Hypocalcemia/hypercalcemia Hypomagnesemia/hypermagnesemia Hypophosphatemia/hyperphosphatemia Hyponatremia Symptomatic: headaches,
3/9/2017. Chapter 56. Care of the Patient with Cancer. Cancer Rates in the US. Carcinogenesis
 Chapter 56 Care of the Patient with Cancer All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Cancer Rates in the US 1 in 2 men and 1 in 3 women
Chapter 56 Care of the Patient with Cancer All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Cancer Rates in the US 1 in 2 men and 1 in 3 women
UNIT VI: ACID BASE IMBALANCE
 UNIT VI: ACID BASE IMBALANCE 1 Objectives: Review the physiological mechanism responsible to regulate acid base balance in the body i.e.: Buffers (phosphate, hemoglobin, carbonate) Renal mechanism Respiratory
UNIT VI: ACID BASE IMBALANCE 1 Objectives: Review the physiological mechanism responsible to regulate acid base balance in the body i.e.: Buffers (phosphate, hemoglobin, carbonate) Renal mechanism Respiratory
W. Heath Giles, M.D. University of Tennessee College of Medicine Chattanooga Assistant Professor of Surgery Associate Residency Program Director
 W. Heath Giles, M.D. University of Tennessee College of Medicine Chattanooga Assistant Professor of Surgery Associate Residency Program Director It is our duty to each learner to honor your right to expect
W. Heath Giles, M.D. University of Tennessee College of Medicine Chattanooga Assistant Professor of Surgery Associate Residency Program Director It is our duty to each learner to honor your right to expect
Approach to a patient with hypercalcemia
 Approach to a patient with hypercalcemia Ana-Maria Chindris, MD Division of Endocrinology Mayo Clinic Florida 2013 MFMER slide-1 Background Hypercalcemia is a problem frequently encountered in clinical
Approach to a patient with hypercalcemia Ana-Maria Chindris, MD Division of Endocrinology Mayo Clinic Florida 2013 MFMER slide-1 Background Hypercalcemia is a problem frequently encountered in clinical
Tumor Lysis Syndrome Nephrology Grand Rounds Tuesday, July 27 th, 2010 Aditya Mattoo
 Tumor Lysis Syndrome Nephrology Grand Rounds Tuesday, July 27 th, 2010 Aditya Mattoo Outline Background/Definition Epidemiology/Risk Stratification Pathophysiology Treatment Renal Replacement Therapy Background/Definition
Tumor Lysis Syndrome Nephrology Grand Rounds Tuesday, July 27 th, 2010 Aditya Mattoo Outline Background/Definition Epidemiology/Risk Stratification Pathophysiology Treatment Renal Replacement Therapy Background/Definition
Easy Trick to Spot Leukemia for Pediatricians
 Easy Trick to Spot Leukemia for Pediatricians Piya Rujkijyanont, MD Division of Hematology-Oncology Department of Pediatrics Phramongkutklao Hospital Most Common Pediatric Cancers Age 0-14 Leukemia 32%
Easy Trick to Spot Leukemia for Pediatricians Piya Rujkijyanont, MD Division of Hematology-Oncology Department of Pediatrics Phramongkutklao Hospital Most Common Pediatric Cancers Age 0-14 Leukemia 32%
Normal range of serum potassium is meq/l true hyperkalemia manifests clinically as : Clinical presentation : muscle and cardiac dysfunction
 Potassium Disorders hyperkalemia Potassium is mainly an cation? What is the major physiological role of potassium in the body? What is the major regulatory system of serum potassium level? Which part of
Potassium Disorders hyperkalemia Potassium is mainly an cation? What is the major physiological role of potassium in the body? What is the major regulatory system of serum potassium level? Which part of
Calcium (Ca 2+ ) mg/dl
 Quick Guide to Laboratory Values Use this handy cheat-sheet to help you monitor laboratory values related to fluid and electrolyte status. Remember, normal values may vary according to techniques used
Quick Guide to Laboratory Values Use this handy cheat-sheet to help you monitor laboratory values related to fluid and electrolyte status. Remember, normal values may vary according to techniques used
Major intra and extracellular ions Lec: 1
 Major intra and extracellular ions Lec: 1 The body fluids are solutions of inorganic and organic solutes. The concentration balance of the various components is maintained in order for the cell and tissue
Major intra and extracellular ions Lec: 1 The body fluids are solutions of inorganic and organic solutes. The concentration balance of the various components is maintained in order for the cell and tissue
Oncologic Emergencies. Melissa Davis, MSN, APRN, AOCNP
 Oncologic Emergencies Melissa Davis, MSN, APRN, AOCNP Objectives For each oncologic emergency, review: Definition Signs and symptoms Risk factors Diagnostics Management Metabolic Emergencies: Disseminated
Oncologic Emergencies Melissa Davis, MSN, APRN, AOCNP Objectives For each oncologic emergency, review: Definition Signs and symptoms Risk factors Diagnostics Management Metabolic Emergencies: Disseminated
Oncology Emergency Essentials: Addressing Tumor Lysis Syndrome in Your Practice
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of a continuing medical education (CME) activity accessible on the ReachMD network. Additional media formats for the activity and full activity details (including
Transcript Details This is a transcript of a continuing medical education (CME) activity accessible on the ReachMD network. Additional media formats for the activity and full activity details (including
Emergencies in Palliative Medicine
 Emergencies in Palliative Medicine Objectives Recognise palliative care emergencies Be aware of their existence Recognise signs and symptoms of common emergencies Anticipate occurrence of emergencies Manage
Emergencies in Palliative Medicine Objectives Recognise palliative care emergencies Be aware of their existence Recognise signs and symptoms of common emergencies Anticipate occurrence of emergencies Manage
What is sepsis? RECOGNITION. Sepsis I Know It When I See It 9/21/2017
 Sepsis I Know It When I See It September 15, 2017 Matthew Exline, MD MPH Medical Director, Medical ICU What is sepsis? I shall not today attempt further to define the kinds of material [b]ut I know it
Sepsis I Know It When I See It September 15, 2017 Matthew Exline, MD MPH Medical Director, Medical ICU What is sepsis? I shall not today attempt further to define the kinds of material [b]ut I know it
9/3/2014. Conflict of Interest Disclosures. Learning Objectives. Definitions of Nausea/Vomiting. Definitions of Nausea/Vomiting
 Conflict of Interest Disclosures LeAnn B. Norris Teva Pharmaceuticals Last Chance Webinar 2014 Oncology Supportive Care LeAnn B. Norris, PharmD, BCPS, BCOP Assistant Professor South Carolina College of
Conflict of Interest Disclosures LeAnn B. Norris Teva Pharmaceuticals Last Chance Webinar 2014 Oncology Supportive Care LeAnn B. Norris, PharmD, BCPS, BCOP Assistant Professor South Carolina College of
1/3/2008. Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown. Medical-Surgical Nursing Care, 2e Karen Burke, Priscilla LeMone, and Elaine Mohn-Brown
 Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 7 Caring for Clients with Altered Fluid, Electrolyte, or Acid-Base Balance Water Primary component of
Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 7 Caring for Clients with Altered Fluid, Electrolyte, or Acid-Base Balance Water Primary component of
Basic Fluid and Electrolytes
 Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Chapter 22 Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Introduction Infants and young children have a greater need for water and are more vulnerable to alterations in fluid and electrolyte
Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Chapter 22 Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Introduction Infants and young children have a greater need for water and are more vulnerable to alterations in fluid and electrolyte
Sepsis Awareness and Education
 Sepsis Awareness and Education Meets the updated New York State Department of Health (NYSDOH) requirements for Infection Control and Barrier Precautions coursework Element VII: Sepsis Awareness and Education
Sepsis Awareness and Education Meets the updated New York State Department of Health (NYSDOH) requirements for Infection Control and Barrier Precautions coursework Element VII: Sepsis Awareness and Education
Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
 Early Treatment is the Key Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Stage Description GFR (ml/min/1.73 m 2 ) >90 1 Kidney damage with normal or GFR 2 Mild decrease in GFR 60-89 3 Moderate decrease in GFR
Early Treatment is the Key Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Stage Description GFR (ml/min/1.73 m 2 ) >90 1 Kidney damage with normal or GFR 2 Mild decrease in GFR 60-89 3 Moderate decrease in GFR
Suspecting Tumors, or Could it be cancer?
 Suspecting Tumors, or Could it be cancer? Donna E. Reece, M.D. Princess Margaret Cancer Centre University Health Network Toronto, ON CANADA 07 February 2018 Background Low back pain is common However,
Suspecting Tumors, or Could it be cancer? Donna E. Reece, M.D. Princess Margaret Cancer Centre University Health Network Toronto, ON CANADA 07 February 2018 Background Low back pain is common However,
hypercalcemia of malignancy hyperparathyroidism PHPT the most common cause of hypercalcemia in the outpatient setting the second most common cause
 hyperparathyroidism A 68-year-old woman with documented osteoporosis has blood tests showing elevated serum calcium and parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels: 11.2 mg/dl (8.8 10.1 mg/dl) and 88 pg/ml (10-60),
hyperparathyroidism A 68-year-old woman with documented osteoporosis has blood tests showing elevated serum calcium and parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels: 11.2 mg/dl (8.8 10.1 mg/dl) and 88 pg/ml (10-60),
Hemodynamic Changes in Obstetric Anesthesia. Sonia Vaida PANA, Hershey, April 2009
 Hemodynamic Changes in Obstetric Anesthesia Sonia Vaida PANA, Hershey, April 2009 Pregnancy is a normal healthy condition and is simultaneously the most common altered physiologic state to which human
Hemodynamic Changes in Obstetric Anesthesia Sonia Vaida PANA, Hershey, April 2009 Pregnancy is a normal healthy condition and is simultaneously the most common altered physiologic state to which human
Fluid and Electrolytes P A R T 4
 Fluid and Electrolytes P A R T 4 Mechanisms that control acid-base homeostasis Acids and bases continually enter and leave body Hydrogen ions also result from metabolic activity Acids Hydrogen ion donors
Fluid and Electrolytes P A R T 4 Mechanisms that control acid-base homeostasis Acids and bases continually enter and leave body Hydrogen ions also result from metabolic activity Acids Hydrogen ion donors
Oncologic Emergencies: When to call the Radiation Oncologist
 Oncologic Emergencies: When to call the Radiation Oncologist Dr. Shrinivas Rathod Radiation Oncologist Radiation Oncology Program CancerCare Manitoba and University of Manitoba Disclosures Speaker s name:
Oncologic Emergencies: When to call the Radiation Oncologist Dr. Shrinivas Rathod Radiation Oncologist Radiation Oncology Program CancerCare Manitoba and University of Manitoba Disclosures Speaker s name:
Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS): Cytokine release syndrome and neurological toxicities
 Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS): Cytokine release syndrome and neurological toxicities A REMS is a program required by the FDA to manage known or potential serious risks associated with
Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS): Cytokine release syndrome and neurological toxicities A REMS is a program required by the FDA to manage known or potential serious risks associated with
Patient Information VERSACLOZ (VER sa kloz) (clozapine) Oral Suspension
 Patient Information VERSACLOZ (VER sa kloz) (clozapine) Oral Suspension Read this Patient Information before you start taking VERSACLOZ and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This
Patient Information VERSACLOZ (VER sa kloz) (clozapine) Oral Suspension Read this Patient Information before you start taking VERSACLOZ and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Undergraduate nurse education
 Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Undergraduate nurse education Year One Developed Summer 2017 Overview Basic A & P of: Urinary system Kidneys Followed by: Introduction to Acute Kidney Injury Urinary System The
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Undergraduate nurse education Year One Developed Summer 2017 Overview Basic A & P of: Urinary system Kidneys Followed by: Introduction to Acute Kidney Injury Urinary System The
2018 OCN Keywords January 22, 2018 Subject Area Weight Keywords
 Subject Area Weight Keywords Care Continuum 19% Care Continuum Coordination of Care Navigation Psychosocial Symptom Management Health Promotion/Screening and Early Detection Disease Prevention High-Risk
Subject Area Weight Keywords Care Continuum 19% Care Continuum Coordination of Care Navigation Psychosocial Symptom Management Health Promotion/Screening and Early Detection Disease Prevention High-Risk
John Park, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine
 John Park, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Faculty photo will be placed here park.john@mayo.edu 2015 MFMER 3543652-1 Sepsis Out with the Old, In with the New Mayo School of Continuous Professional Development
John Park, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Faculty photo will be placed here park.john@mayo.edu 2015 MFMER 3543652-1 Sepsis Out with the Old, In with the New Mayo School of Continuous Professional Development
Electrolytes and other equally exciting topics
 Electrolytes and other equally exciting topics Rebecca A. Snyder Summer School 2010 Why do we care? Why do we care? Why do we care? Torsades is bad. Because medical records cares even more. Because apparently
Electrolytes and other equally exciting topics Rebecca A. Snyder Summer School 2010 Why do we care? Why do we care? Why do we care? Torsades is bad. Because medical records cares even more. Because apparently
Transfusion Reactions
 Transfusion Reactions From A to T Provincial Blood Coordinating Program Daphne Osborne MN PANC (C) RN We want you to know Definition Appropriate actions Classification Complete case studies Transfusion
Transfusion Reactions From A to T Provincial Blood Coordinating Program Daphne Osborne MN PANC (C) RN We want you to know Definition Appropriate actions Classification Complete case studies Transfusion
Chapter 26 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid- Base Balance
 Chapter 26 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid- Base Balance 1 Body Water Content Infants: 73% or more water (low body fat, low bone mass) Adult males: ~60% water Adult females: ~50% water (higher fat content,
Chapter 26 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid- Base Balance 1 Body Water Content Infants: 73% or more water (low body fat, low bone mass) Adult males: ~60% water Adult females: ~50% water (higher fat content,
Hypocalcemia 6/8/12. Normal value. Physiologic functions. Nephron a functional unit of kidney. Influencing factors in Calcium and Phosphate Balance
 Normal value Hypocalcemia Serum calcium Total mg/dl Ionized mg/dl Cord blood 9.0 ~ 11.5 5.0 ~ 6.o New born (1 st 24 hrs) 9.0 ~ 10.6 4.3 ~ 5.1 24~ 48 hrs 7.0 ~12.0 4.0 ~4.7 Child 8.8 ~10.8 4.8 ~4.92 There
Normal value Hypocalcemia Serum calcium Total mg/dl Ionized mg/dl Cord blood 9.0 ~ 11.5 5.0 ~ 6.o New born (1 st 24 hrs) 9.0 ~ 10.6 4.3 ~ 5.1 24~ 48 hrs 7.0 ~12.0 4.0 ~4.7 Child 8.8 ~10.8 4.8 ~4.92 There
Prehospital Resuscitation for the 21 st Century Simulation Case. VF/Asystole
 Prehospital Resuscitation for the 21 st Century Simulation Case VF/Asystole Case History 1 (hypovolemic cardiac arrest secondary to massive upper GI bleed) 56 year-old male patient who fainted in the presence
Prehospital Resuscitation for the 21 st Century Simulation Case VF/Asystole Case History 1 (hypovolemic cardiac arrest secondary to massive upper GI bleed) 56 year-old male patient who fainted in the presence
RENAL & HEMATOLOGY EMERGENCIES JEFF SIMONS B.S. F-PC
 RENAL & HEMATOLOGY EMERGENCIES JEFF SIMONS B.S. F-PC GOALS Overview of renal system anatomy / physiology Discuss common medical / trauma renal issues Identify associated assessment keys GOALS Introduction
RENAL & HEMATOLOGY EMERGENCIES JEFF SIMONS B.S. F-PC GOALS Overview of renal system anatomy / physiology Discuss common medical / trauma renal issues Identify associated assessment keys GOALS Introduction
1/3/2008. Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown. Medical-Surgical Nursing Care, 2e Karen Burke, Priscilla LeMone, and Elaine Mohn-Brown
 Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 12 Caring for Clients with Cancer Cancer Disease that results when normal cells mutate into abnormal,
Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 12 Caring for Clients with Cancer Cancer Disease that results when normal cells mutate into abnormal,
What Lung Cancer Patients Need to Know About Bone Health. A Publication of The Bone and Cancer Foundation
 What Lung Cancer Patients Need to Know About Bone Health A Publication of The Bone and Cancer Foundation Contents THIS PUBLICATION PROVIDES IMPORTANT INFORMATION ABOUT THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN LUNG CANCER
What Lung Cancer Patients Need to Know About Bone Health A Publication of The Bone and Cancer Foundation Contents THIS PUBLICATION PROVIDES IMPORTANT INFORMATION ABOUT THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN LUNG CANCER
Acid-Base Balance 11/18/2011. Regulation of Potassium Balance. Regulation of Potassium Balance. Regulatory Site: Cortical Collecting Ducts.
 Influence of Other Hormones on Sodium Balance Acid-Base Balance Estrogens: Enhance NaCl reabsorption by renal tubules May cause water retention during menstrual cycles Are responsible for edema during
Influence of Other Hormones on Sodium Balance Acid-Base Balance Estrogens: Enhance NaCl reabsorption by renal tubules May cause water retention during menstrual cycles Are responsible for edema during
Announcements. Learning Objectives. Introduction. Prevention and Treatment of an Oncologic Emergency: Focus on Tumor Lysis Syndrome
 Prevention and Treatment of an Oncologic Emergency: Focus on Tumor Lysis Syndrome Kamakshi V. Rao, Pharm.D., BCOP Oncology Clinical Pharmacy Specialist University of North Carolina Hospitals and Clinics
Prevention and Treatment of an Oncologic Emergency: Focus on Tumor Lysis Syndrome Kamakshi V. Rao, Pharm.D., BCOP Oncology Clinical Pharmacy Specialist University of North Carolina Hospitals and Clinics
Example Clinician Educational Material for Providers of Immune Effector Cellular Therapy
 Example Clinician Educational Material for Providers of Immune Effector Cellular Therapy Disclaimer: This example is just one of many potential examples of clinician education material that can be provided
Example Clinician Educational Material for Providers of Immune Effector Cellular Therapy Disclaimer: This example is just one of many potential examples of clinician education material that can be provided
Staging Sepsis for the Emergency Department: Physician
 Staging Sepsis for the Emergency Department: Physician Sepsis Continuum 1 Sepsis Continuum SIRS = 2 or more clinical criteria, resulting in Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome Sepsis = SIRS + proven/suspected
Staging Sepsis for the Emergency Department: Physician Sepsis Continuum 1 Sepsis Continuum SIRS = 2 or more clinical criteria, resulting in Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome Sepsis = SIRS + proven/suspected
Supplement Table 1. Definitions for Causes of Death
 Supplement Table 1. Definitions for Causes of Death 3. Cause of Death: To record the primary cause of death. Record only one answer. Classify cause of death as one of the following: 3.1 Cardiac: Death
Supplement Table 1. Definitions for Causes of Death 3. Cause of Death: To record the primary cause of death. Record only one answer. Classify cause of death as one of the following: 3.1 Cardiac: Death
SHOCK AETIOLOGY OF SHOCK (1) Inadequate circulating blood volume ) Loss of Autonomic control of the vasculature (3) Impaired cardiac function
 SHOCK Shock is a condition in which the metabolic needs of the body are not met because of an inadequate cardiac output. If tissue perfusion can be restored in an expeditious fashion, cellular injury may
SHOCK Shock is a condition in which the metabolic needs of the body are not met because of an inadequate cardiac output. If tissue perfusion can be restored in an expeditious fashion, cellular injury may
Instruct patient and caregivers: Need for constant monitoring Potential complications of drug therapy
 Assessment Prior to administration: Assess patient for chest pain, dysrhythmias, and vital signs (initially and throughout therapy) Obtain complete medical history, including allergies, especially heart
Assessment Prior to administration: Assess patient for chest pain, dysrhythmias, and vital signs (initially and throughout therapy) Obtain complete medical history, including allergies, especially heart
Acute Kidney Injury in the ED
 + Acute Kidney Injury in the ED + Dr Eric Clark, MD FRCPC University of Ottawa Canada Canadian Association of Emergency Physicians + Outline 1. Diagnostic challenges 2. ED treatment 3. Contrast induced
+ Acute Kidney Injury in the ED + Dr Eric Clark, MD FRCPC University of Ottawa Canada Canadian Association of Emergency Physicians + Outline 1. Diagnostic challenges 2. ED treatment 3. Contrast induced
Shock is defined as a state of cellular and tissue hypoxia due to : reduced oxygen delivery and/or increased oxygen consumption or inadequate oxygen
 Shock is defined as a state of cellular and tissue hypoxia due to : reduced oxygen delivery and/or increased oxygen consumption or inadequate oxygen utilization The effects of shock are initially reversible
Shock is defined as a state of cellular and tissue hypoxia due to : reduced oxygen delivery and/or increased oxygen consumption or inadequate oxygen utilization The effects of shock are initially reversible
Care for patients with Neurological disorders
 King Saud University College of Nursing Medical Surgical Department Application of Adult Health Nursing Skills ( NUR 317 ) Care for patients with Neurological disorders Outline; EEG Overview. Nursing Interventions;
King Saud University College of Nursing Medical Surgical Department Application of Adult Health Nursing Skills ( NUR 317 ) Care for patients with Neurological disorders Outline; EEG Overview. Nursing Interventions;
Medical PANRE. Physician Assistant National Recertifying Exam.
 Medical PANRE Physician Assistant National Recertifying Exam https://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/panre Question: 60 A patient comes to the office presenting with paroxysmal or sustained hypertension,
Medical PANRE Physician Assistant National Recertifying Exam https://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/panre Question: 60 A patient comes to the office presenting with paroxysmal or sustained hypertension,
SHOCK. Emergency pediatric PICU division Pediatric Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara H. Adam Malik Hospital
 SHOCK Emergency pediatric PICU division Pediatric Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara H. Adam Malik Hospital 1 Definition Shock is an acute, complex state of circulatory dysfunction
SHOCK Emergency pediatric PICU division Pediatric Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara H. Adam Malik Hospital 1 Definition Shock is an acute, complex state of circulatory dysfunction
Case 4 Generalised bone pain
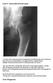 Case 4 Generalised bone pain C A 34- year- old woman presented complaining of multifocal pain in her chest and legs. The pain was intermittent, was aggravated by weight bearing. Initially was alleviated
Case 4 Generalised bone pain C A 34- year- old woman presented complaining of multifocal pain in her chest and legs. The pain was intermittent, was aggravated by weight bearing. Initially was alleviated
Tarek ElBaz, MD. Prof. Internal Medicine Chief, Division of Renal Medicine Al Azhar University President, ESNT
 The Kidney in Multiple Myeloma Tarek ElBaz, MD. Prof. Internal Medicine Chief, Division of Renal Medicine Al Azhar University President, ESNT Normal Cell Plasma cells produce antibodies that bind to antigens,
The Kidney in Multiple Myeloma Tarek ElBaz, MD. Prof. Internal Medicine Chief, Division of Renal Medicine Al Azhar University President, ESNT Normal Cell Plasma cells produce antibodies that bind to antigens,
Salicylate (Aspirin) Ingestion California Poison Control Background 1. The prevalence of aspirin-containing analgesic products makes
 Salicylate (Aspirin) Ingestion California Poison Control 1-800-876-4766 Background 1. The prevalence of aspirin-containing analgesic products makes these agents, found in virtually every household, common
Salicylate (Aspirin) Ingestion California Poison Control 1-800-876-4766 Background 1. The prevalence of aspirin-containing analgesic products makes these agents, found in virtually every household, common
Pediatric GU Dysfunction
 Pediatric GU Dysfunction Assessment of pediatric renal function Signs and symptoms Laboratory tests Radiological tests Nursing considerations Psychosocial and developmental considerations GU Disorders
Pediatric GU Dysfunction Assessment of pediatric renal function Signs and symptoms Laboratory tests Radiological tests Nursing considerations Psychosocial and developmental considerations GU Disorders
Zerlinda (MRP DK/H/2265/001)
 Zerlinda (MRP DK/H/2265/001) VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Prevention of bone complications, e.g. fractures, in adult patients with bone metastases (spread
Zerlinda (MRP DK/H/2265/001) VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Prevention of bone complications, e.g. fractures, in adult patients with bone metastases (spread
Acid/Base Disorders 2015
 Objectives - 2 1. Identify acid/base disorders 2. Discuss etiologies for 1 0 acid/base disorders (will not include mixed disorders) 3. Interpret acid/base disorders by interpreting arterial blood gas &
Objectives - 2 1. Identify acid/base disorders 2. Discuss etiologies for 1 0 acid/base disorders (will not include mixed disorders) 3. Interpret acid/base disorders by interpreting arterial blood gas &
Amjad Bani Hani Ass.Prof. of Cardiac Surgery & Intensive Care FLUIDS AND ELECTROLYTES
 Amjad Bani Hani Ass.Prof. of Cardiac Surgery & Intensive Care FLUIDS AND ELECTROLYTES Body Water Content Water Balance: Normal 2500 2000 1500 1000 500 Metab Food Fluids Stool Breath Sweat Urine
Amjad Bani Hani Ass.Prof. of Cardiac Surgery & Intensive Care FLUIDS AND ELECTROLYTES Body Water Content Water Balance: Normal 2500 2000 1500 1000 500 Metab Food Fluids Stool Breath Sweat Urine
Shock Management. Seyed Tayeb Moradian MSc, Critical Care Nursing Ph.D Candidate. PDF created with pdffactory Pro trial version
 Shock Management Seyed Tayeb Moradian MSc, Critical Care Nursing Ph.D Candidate Definition of Shock The definition of shock does not involve low blood pressure, rapid pulse or cool clammy skin - these
Shock Management Seyed Tayeb Moradian MSc, Critical Care Nursing Ph.D Candidate Definition of Shock The definition of shock does not involve low blood pressure, rapid pulse or cool clammy skin - these
2 Diagnosis and Staging of Cancer 2.1 Pathophysiology of cancer 2.2 Classification and staging 2.3 Diagnostic measures for specific cancer types
 Oncology Nursing Sub-Specialty Module Reference: Gobel B. M., Triest-Robertson S. & Vogel W.H. (Eds). (205). Advanced Oncology Nursing Certificate Review and Resources Manual. Pittsburgh: Oncology Nursing
Oncology Nursing Sub-Specialty Module Reference: Gobel B. M., Triest-Robertson S. & Vogel W.H. (Eds). (205). Advanced Oncology Nursing Certificate Review and Resources Manual. Pittsburgh: Oncology Nursing
FLUIDS AND ELECTROLYTES
 FLUIDS AND ELECTROLYTES J a s leen G r ewal, M D J u ly 2 017 A d a p te d f ro m B indu S waro o p, M D W illiam G r a h a m, M D S a m Lai, M D FLUIDS & ELECTROLY TES: OBJECTIVES Understand replacement
FLUIDS AND ELECTROLYTES J a s leen G r ewal, M D J u ly 2 017 A d a p te d f ro m B indu S waro o p, M D W illiam G r a h a m, M D S a m Lai, M D FLUIDS & ELECTROLY TES: OBJECTIVES Understand replacement
Malignant related superior vena cava (SVC) syndrome
 Malignant related superior vena cava (SVC) syndrome Manit Sae-teaw B.Pharm, BCP, BCOP Grad dip in Pharmacotherapy Faculty of pharmaceutical sciences Ubon Ratchathani University 1 Outline Introduction Etiology
Malignant related superior vena cava (SVC) syndrome Manit Sae-teaw B.Pharm, BCP, BCOP Grad dip in Pharmacotherapy Faculty of pharmaceutical sciences Ubon Ratchathani University 1 Outline Introduction Etiology
Volume and Electrolytes. Fluid and Electrolyte Management. Why 125ml? Question. Normal fluid requirement. Normal losses
 Volume and Electrolytes Fluid and Electrolyte Management Pre-existing deficits of excesses Ongoing losses or gains Ajai K. Malhotra, MD VCU School of Medicine 1 2 Question Why 125ml? Intern said so Chief
Volume and Electrolytes Fluid and Electrolyte Management Pre-existing deficits of excesses Ongoing losses or gains Ajai K. Malhotra, MD VCU School of Medicine 1 2 Question Why 125ml? Intern said so Chief
The management and treatment options for secondary bone disease. Dr Jason Lester Clinical Oncologist Velindre Cancer Centre
 The management and treatment options for secondary bone disease Dr Jason Lester Clinical Oncologist Velindre Cancer Centre Aims Overview of bone metastases management in castrate-refractory prostate cancer
The management and treatment options for secondary bone disease Dr Jason Lester Clinical Oncologist Velindre Cancer Centre Aims Overview of bone metastases management in castrate-refractory prostate cancer
Instrumental determination of electrolytes in urine. Amal Alamri
 Instrumental determination of electrolytes in urine Amal Alamri What is the Electrolytes? Electrolytes are positively and negatively chargedions, Found in Within body's cells extracellular fluids, including
Instrumental determination of electrolytes in urine Amal Alamri What is the Electrolytes? Electrolytes are positively and negatively chargedions, Found in Within body's cells extracellular fluids, including
Acid Base Balance. Chapter 26 Balance. ph Imbalances. Acid Base Balance. CO 2 and ph. Carbonic Acid. Part 2. Acid/Base Balance
 Acid Base Balance Chapter 26 Balance Part 2. Acid/Base Balance Precisely balances production and loss of hydrogen ions (ph) The body generates acids during normal metabolism, tends to reduce ph Kidneys:
Acid Base Balance Chapter 26 Balance Part 2. Acid/Base Balance Precisely balances production and loss of hydrogen ions (ph) The body generates acids during normal metabolism, tends to reduce ph Kidneys:
