SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Classical presentation of a newborn infant with renal vein thrombosis
|
|
|
- Camilla Patrick
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Classical presentation of a newborn infant with renal vein thrombosis December 2017
2 Wendelspiess M, Schifferli A, Rudin C, Kaempfen S, Department of Neonatology (WM, KS), Department of Pediatric Nephrology (RC), Department of Oncology / Hematology (SA), University of Basel Children s Hospital (UKBB), Basel, Switzerland Title figure: Blood clot (source: Swiss Society of Neonatology, Thomas M Berger, Webmaster
3 3 Thrombosis in neonates is a rare event, but associated with significant morbidity and even mortality. Renal vein thrombosis (RVT) accounts for approximately 10 % of venous thromboses in neonates. Compared to other regions of thrombosis, RVT is less often asso ciated with central venous catheters (1). Various pathomechanisms, which may lead to a RVT, reduce blood flow to the kidneys or provoke hyperos molarity, hypercoagulability or increased blood viscosity (2, 3). Fetal/neonatal as well as maternal risk factors are summarized in Fig. 1. RVT can also occur as an extension of inferior vena cava thrombosis. INTRODUCTION Two thirds of neonatal RVTs are diagnosed during the first three days of life. RVTs are associated with male sex and preterm birth. Clinical presentation includes macrohematuria, thrombocytopenia and a palpable abdominal mass in approximately half of the cases (4, 5).
4 4 CASE REPORT This male infant was born to a 33-year-old G2/P2 at 38 0/7 weeks of gestation after an uncomplicated pregnancy. The mother developed fever during labor and received amoxicillin clavulanate prior to delivery for suspected chorioamnionitis. The infant was delivered by secondary Caesarean section and adapted well with Apgar scores of 8, 9 and 10 at 1, 5 and 10 minutes, respectively. Arterial and venous umbilical cord ph values were 7.28 and 7.42, respectively. Birth weight was 3160 g (P50), length 49 cm (P50) and head circumference 33 cm (P30). At 34 hours of age, the infant developed macrohematuria. Apart from a palpable mass in the right flank, physical examination was normal. On admission to the NICU, vital signs including blood pressure (80/40 (56) mmhg) were normal. Laboratory investigations showed thrombocytopenia (61 G/l) and renal failure (serum creatinine 124 µmol/l with a maternal serum creatinine prior to delivery of 49 µmol/l). Hemoglobin concentration was 135 g/l, and clotting studies (INR, aptt, fibrinogen) were within the normal range. Markers of inflammation were not elevated. Urine analysis confirmed macrohematuria, and the urine output was normal (3.1 ml/kg/hour). An abdominal ultrasound examination showed an enlarged right kidney with abolished corticomedullary differentiation and echogenic streaks in the lower pole, compatible with partial renal venous thrombosis (Fig. 2, 3). Apart from a persistent foramen ovale, echocardiography was normal.
5 5 Fetal/neonatal risk factors Catheters CHD RDS Sepsis Dehydration Birth asphyxia Polycythemia Inherited thrombophilia Prematurity T H R O M B O S I S Maternal risk factors Infertility Oligohydramnion Thrombotic states Chorioamnionitis Preeclampsia Diabetes mellitus Antiphospholipid syndrome In utero twin death Fig. 1 Risk factors for neonatal thrombosis (CHD: congenital heart disease; RDS: respiratory distress syndrome) (17).
6 6 Fig. 2 Renal ultrasound examination on DOL 2: enlarged right kidney (5.35 cm, normal range cm).
7 7 Fig. 3 Renal ultrasound examination on DOL 3: right kidney with echogenic streaks and abolished corticomedullary differentiation.
8 8 On follow-up ultrasound examination a few hours later there was extension of the thrombus into the inferior vena cava (IVC) over a length of 2 cm and partial thrombosis of the left renal vein (Fig. 4). After interdisciplinary discussions, anticoagulation with unfractionated heparin (UFH) was started with a heparin bolus, followed by a continuous infusion. Anti coagulation was adjusted using the protocol published by Michelson et al. (6) (Table), aiming at an appt of 60 to 85 seconds. Loading dose: 75 units/kg i.v. over 10 minutes Initial maintenance dose: 28 units/kg/hour for infants < 1 year Adjust infusion rate to maintain aptt between seconds or anti-xa between IU/ml aptt (seconds) Bolus (units/kg) Hold (minutes) Infusion rate change Repeat aptt < % 4 hours % 4 hours no change next day % 4 hours % 4 hours > % 4 hours Protocol for systemic unfractionated heparin (UFH) administration and dose adjustments for pediatric patients (6).
9 9 Repeated cranial ultrasound examinations (including one obtained prior to starting anticoagulation) showed no signs of intracerebral hemorrhage. After initiation of heparin treatment, no further extension of the thrombosis was documented. Serum creatinine concentrations decreased to 79 µmol/l within 96 hours. Macrohematuria disappeared after one week of life. Blood pressure remained normal. After eight days of intravenous UFH, anticoagulation was changed to enoxaparin, a low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH), administered subcutaneously via an Insuflon catheter. On day 13, improved blood flow in the IVC could be demonstrated on ultrasound. The infant was discharged home on day of life 14. At one month of age, the thrombi in the IVC and the left kidney had completely resolved, and only discreet signs of the thrombosis in the lower pole of the right kidney were still detectable. Renal function had normalized (serum creatinine of 33 µmol/l). Treatment with subcutaneous LMWH was continued for a total of 3 months. Most recently, one year after discharge, renal function, blood pressure, and renal ultrasound examinations have been normal. Family history was positive for sickle cell anemia in two paternal uncles and for pulmonary embolism in a grandmother at the age of 60 years. The patient s parents already had one healthy child. Investigations
10 10 Fig. 4 Abdominal ultrasound examination on DOL 3: absent flow in the inferior vena cava.
11 11 for hereditary thrombophilias were negative. Sickle cell trait was excluded by hemoglobin electrophoresis at the age of six months. The etiology of RVT remained unexplained in our patient. Chorionamnionitis was the only maternal risk factor (Fig. 1), however, the baby had no signs of a neonatal infection.
12 12 DISCUSSION This case report describes an infant with the so-called classical clinical presentation of RVT (macrohematuria, palpable renal mass, and thrombocytopenia). However, the full triad has been reported to be only present in 13 % of RVT cases (7). If RVT is suspected, the diagnosis must be confirmed by imaging. In neonates, the initial method of choice is Doppler ultrasonography (8). In addition, laboratory markers such as full blood count and renal function tests should be analyzed. Coagulation tests, including activated partial thromboplastin time (aptt), fibrinogen and INR, are crucial to exclude an acute hemostatic problem such as DIC and to acquire base-line values before starting treatment. If bilateral RVT is diagnosed, renal function tests, electrolytes and diuresis must be monitored because of the risk of acute renal failure. In unilateral disease, creatinine and urea concentrations usually remain normal. Arterial hypertension can develop after RVT and blood pressure must therefore be monitored regularly. The role of anticoagulation in RVT is controversially discussed in the literature. Strategies regarding initiation of treatment, route of application, choice of anticoagulants and treatment duration differ widely due to a lack of randomized controlled trials (9, 10).
13 13 In cases of isolated unilateral RVT, supportive care with close monitoring is suggested since no benefit has been demonstrated while bleeding complications can occur. In contrast, for patients with unilateral RVT and extension into the IVC, anticoagulation for six weeks to three months should be considered. If both kidneys are affected with renal impairment, either thrombolytic treatment with systemic tissue plasminogen activator (tpa) followed by anticoagulation or anticoagulation only for six weeks to three months is generally recommended. Suggested strategies include treatment either with LMWH alone or to start with UFH followed by LMWH. We chose to start with UFH because of its rapid onset of action, its short half life and its reversibility by protamine sulfate should side effects (bleeding, heparin induced thrombocytopenia) occur. Disadvantages of anticoagulation with UFH include the need for intravenous administration, frequent blood tests and dose adjustments. Once adequate anticoagulation has been established and the patient is stable, treatment can be changed to subcutaneous LMWH. Major bleeding episodes in children receiving UFH treatment have been described in 1.5 % to 24 % of patients (11). Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia by UFH is relatively rare, occurring in less than 2.5 % of pediatric patients (12).
14 14 Therapeutic dosing of LMWH is based on anti-fxa levels. The suggested dose for subcutaneously administered enoxaparin in infants < 2 months of age is 1.5 mg/kg 12 hourly. Anti-FXa levels 4 6 hours after subcutaneous injection should be between U/ ml. Enoxaparin is easy to administer, even in an outpatient setting (12). Although adverse events are considered to be rare, several major complications including major bleeding episodes, hematoma formation at the administration site, gastrointestinal bleeding, and intracranial hemorrhage have been described with an overall incidence of approximately 5 % (13 14). Inherited prothrombotic conditions like protein C or S deficiency, antithrombin deficiency, factor V Leiden, and mutation of prothrombin 20210A are more common in newborns with RVT as compared to the general population and should be tested in patients with an unclear origin of RVT. Babies born to mothers with antiphospholipid syndrome or lupus should be screened for lupus anticoagulant. Survival rates of infants with RVT are excellent. However, long-term sequelae, including irreversible renal damage (71%) and arterial hypertension (19 %) can occur (4). Therefore, nephrology follow-up is required. Importantly, there is a 6.8 % risk for a second episode of venous thrombosis during puberty.
15 15 RVT should be suspected in newborns with hematuria, palpable abdominal mass and/or thrombocyto penia, especially if neonatal or maternal risk factors for hemostasis imbalance are present. The aim of heparin treatment is to prevent life-threatening events, thrombus extension, and long-term complications. However, there is limited evidence to guide decision-making and anticoagulation significantly increases the risk of bleeding. CONCLUSION
16 16 REFERENCES 1. Schmidt B, Andrew M. Neonatal thrombosis: report of a prospective Canadian and international registry. Pediatrics 1995;96: (Abstract) 2. Marks SD, Massicotte MP, Steele BT, et al. Neonatal renal venous thrombosis: clinical outcomes and prevalence of prothrombotic disorders. J Pediatr 2005;146: (Abstract) 3. Kosh A, Kuwertz-Bröking E, Heller C, Kumik K, Schobess R, Nowak-Göttl U. Renal venous thrombosis in neonates: prothrombotic risk factors and long-term follow-up. Blood 2004;104: (Abstract) 4. Lau KK, Stoffman JM, Williams S, et al. for the Canadian Pediatric Thrombosis Network. Neonatal renal vein thrombosis: review of the English-language literature between 1992 and Pediatrics 2007;120:e1278-e1284 (Abstract) 5. Bidadi B, Nageswara A, Kaur D, Kahn S, Rodrriguez V. Neonatal renal vein thrombosis: role of anticoagulation and thrombolysis an institutional review. Pediatr Hematol Oncol 2016;33:59 66 (Abstract) 6. Michelson AD, Bovill E, Andrew M. Antithrombotic therapy in children. Chest 1995;108:506S-522S (no abstract available) 7. Zigman A, Yazbeck S, Emil S, Nguyen L. Renal vein thrombosis: a 10-year review. J Pediatr Surg 2000;35: (Abstract) 8. Roy M, Turner-Gomes S, Gill G, Way C, Mernagh J, Schmidt B. Accuracy of Doppler echocardiography for the diagnosis of thrombosis associated with umbilical venous catheters. J Pediatr 2002;140: (Abstract)
17 9. Williams MD, Chalmers EA, Gibson BE, Haemostasis and Thrombosis Task Force, British Committee for Standards in Haematology. The investigation and management of neonatal haemostasis and thrombosis. Br J Haematol 2002;119: (Abstract) 10. Monagle P, Chalmers E, Chan A, deverber G, et al. Antithrombotic therapy in neonates and children. American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition) 2008;133:887S-968S (Abstract) 11. Kuhle S, Eulmesekian P, Kavanagh B, Massicotte P, Vegh P, Mitchell LG. A clinically significant incidence of bleeding in critically ill children receiving therapeutic doses of unfractionated heparin: a prospective cohort study. Hematologica 2007;92: (Abstract) 12. Schmugge M, Risch L, Huber AR, Benn A, Fischer JE. Heparininduced thrombocytopenia-associated thrombosis in pediatric intensive care patients. Pediatrics 2002;109:E10 (Abstract) 13. Malowany JI, Monagle P, Knoppert DC, et al. Enoxaparin for neonatal thrombosis: a call for a higher dose for neonates. Thromb Res 2008;122: (Abstract) 14. Romantsik O, Bruschettini M, Zappettini S, Ramenghi LA, Calevo MG. Heparin for the treatment of thrombosis in neonates. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2016;CD (Abstract)
18 concept & design by mesch.ch SUPPORTED BY CONTACT Swiss Society of Neonatology
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Neonatal cerebral infarction
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Neonatal cerebral infarction May 2002 2 Mann C, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit, Landeskrankenhaus und Akademisches Lehrkrankenhaus Feldkirch, Austria Swiss Society
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Neonatal cerebral infarction May 2002 2 Mann C, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit, Landeskrankenhaus und Akademisches Lehrkrankenhaus Feldkirch, Austria Swiss Society
VTE in Children: Practical Issues
 VTE in Children: Practical Issues Wasil Jastaniah MBBS,FAAP,FRCPC Consultant Pediatric Hem/Onc/BMT May 2012 Top 10 Reasons Why Pediatric VTE is Different 1. Social, ethical, and legal implications. 2.
VTE in Children: Practical Issues Wasil Jastaniah MBBS,FAAP,FRCPC Consultant Pediatric Hem/Onc/BMT May 2012 Top 10 Reasons Why Pediatric VTE is Different 1. Social, ethical, and legal implications. 2.
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Local fibrinolysis with r-tpa in a newborn with brachial artery thrombosis
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Local fibrinolysis with r-tpa in a newborn with brachial artery thrombosis January 2001 2 Dyroff C, Berger TM, Treumann T, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (DC, BTM),
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Local fibrinolysis with r-tpa in a newborn with brachial artery thrombosis January 2001 2 Dyroff C, Berger TM, Treumann T, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (DC, BTM),
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Spontaneous intestinal perforation or necrotizing enterocolitis?
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Spontaneous intestinal perforation or necrotizing enterocolitis? June 2004 2 Stocker M, Berger TM, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit, Children s Hospital of Lucerne,
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Spontaneous intestinal perforation or necrotizing enterocolitis? June 2004 2 Stocker M, Berger TM, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit, Children s Hospital of Lucerne,
Mabel Labrada, MD Miami VA Medical Center
 Mabel Labrada, MD Miami VA Medical Center *1-Treatment for acute DVT with underlying malignancy is for 3 months. *2-Treatment of provoked acute proximal DVT can be stopped after 3months of treatment and
Mabel Labrada, MD Miami VA Medical Center *1-Treatment for acute DVT with underlying malignancy is for 3 months. *2-Treatment of provoked acute proximal DVT can be stopped after 3months of treatment and
Anticoagulant Therapy in Neonates By Nancy Burke RNC-NIC, MSN, ARNP
 Anticoagulant Therapy in Neonates By Nancy Burke RNC-NIC, MSN, ARNP 1 Objectives: Upon completion, the participant will be able to: Name at least 3 things have been identified as risk factors for developing
Anticoagulant Therapy in Neonates By Nancy Burke RNC-NIC, MSN, ARNP 1 Objectives: Upon completion, the participant will be able to: Name at least 3 things have been identified as risk factors for developing
DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT): TREATMENT
 DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT): TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide an evidence-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis (DVT). BACKGROUND: An estimated 45,000 patients in Canada
DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT): TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide an evidence-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis (DVT). BACKGROUND: An estimated 45,000 patients in Canada
Neonatal thrombosis. E A Chalmers
 J Clin Pathol 2000;53:419 423 419 Neonatal thrombosis Department of Haematology, Royal Hospital for Sick Children, Yorkhill, Glasgow G3 8SJ, UK E A Chalmers Correspondence to: Dr Chalmers e-mail: lizchalmers@btinternet.com
J Clin Pathol 2000;53:419 423 419 Neonatal thrombosis Department of Haematology, Royal Hospital for Sick Children, Yorkhill, Glasgow G3 8SJ, UK E A Chalmers Correspondence to: Dr Chalmers e-mail: lizchalmers@btinternet.com
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Severe apnea and bradycardia in a term infant
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Severe apnea and bradycardia in a term infant October 2014 2 Walker JH, Arlettaz Mieth R, Däster C, Division of Neonatology, University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland Swiss Society
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Severe apnea and bradycardia in a term infant October 2014 2 Walker JH, Arlettaz Mieth R, Däster C, Division of Neonatology, University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland Swiss Society
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Fatal pulmonary embolism in a premature neonate after twin-twin transfusion syndrome
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Fatal pulmonary embolism in a premature neonate after twin-twin transfusion syndrome February 2010 2 Schlapbach LJ, Riedel T, Genitsch V, Nelle M, McDougall FJ, Department
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Fatal pulmonary embolism in a premature neonate after twin-twin transfusion syndrome February 2010 2 Schlapbach LJ, Riedel T, Genitsch V, Nelle M, McDougall FJ, Department
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Neonatal sinovenous thrombosis
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Neonatal sinovenous thrombosis August 2006 2 Hauri-Hohl A, Zeilinger G, Pasquier S, Children s Hospital of Aarau, Switzerland Swiss Society of Neonatology, Thomas M Berger,
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Neonatal sinovenous thrombosis August 2006 2 Hauri-Hohl A, Zeilinger G, Pasquier S, Children s Hospital of Aarau, Switzerland Swiss Society of Neonatology, Thomas M Berger,
Risk factors for DVT. Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism. Anticoagulation (cont d) Diagnosis 1/5/2018. Ahmed Mahmoud, MD
 Risk factors for DVT Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism Ahmed Mahmoud, MD Surgery ; post op especially for long cases, pelvic operations (THR), Trauma ; long bone fractures, pelvic fractures (posterior
Risk factors for DVT Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism Ahmed Mahmoud, MD Surgery ; post op especially for long cases, pelvic operations (THR), Trauma ; long bone fractures, pelvic fractures (posterior
Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism. Ahmed Mahmoud, MD
 Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism Ahmed Mahmoud, MD Risk factors for DVT Surgery ; post op especially for long cases, pelvic operations (THR), Trauma ; long bone fractures, pelvic fractures (posterior
Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism Ahmed Mahmoud, MD Risk factors for DVT Surgery ; post op especially for long cases, pelvic operations (THR), Trauma ; long bone fractures, pelvic fractures (posterior
Venous thrombosis is common and often occurs spontaneously, but it also frequently accompanies medical and surgical conditions, both in the community
 Venous Thrombosis Venous Thrombosis It occurs mainly in the deep veins of the leg (deep vein thrombosis, DVT), from which parts of the clot frequently embolize to the lungs (pulmonary embolism, PE). Fewer
Venous Thrombosis Venous Thrombosis It occurs mainly in the deep veins of the leg (deep vein thrombosis, DVT), from which parts of the clot frequently embolize to the lungs (pulmonary embolism, PE). Fewer
Treatment of Pediatric Venous Thromboembolism
 Treatment of Pediatric Venous Thromboembolism An Educational Slide Set American Society of Hematology 2018 Guidelines for Management of Venous Thromboembolism Slide set authors: Eric Tseng MD, MScCH, University
Treatment of Pediatric Venous Thromboembolism An Educational Slide Set American Society of Hematology 2018 Guidelines for Management of Venous Thromboembolism Slide set authors: Eric Tseng MD, MScCH, University
Draft Agreed by Cardiovascular Working Party 28 September Adoption by CHMP for release for consultation 12 October 2017
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 12 October 2017 EMA/230866/2017 Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) Concept paper on the need for a paediatric addendum of the guideline on clinical investigation
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 12 October 2017 EMA/230866/2017 Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) Concept paper on the need for a paediatric addendum of the guideline on clinical investigation
PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE): DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT
 PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE): DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide a diagnostic algorithm and treatment options for patients with acute pulmonary embolism (PE). BACKGROUND: Venous thromboembolism (VTE)
PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE): DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide a diagnostic algorithm and treatment options for patients with acute pulmonary embolism (PE). BACKGROUND: Venous thromboembolism (VTE)
Approach to Thrombosis
 Approach to Thrombosis Theera Ruchutrakool, M.D. Division of Hematology Department of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Faculty of Medicine Mahidol University Approach to Thrombosis Thrombosis: thrombus formation
Approach to Thrombosis Theera Ruchutrakool, M.D. Division of Hematology Department of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Faculty of Medicine Mahidol University Approach to Thrombosis Thrombosis: thrombus formation
The evaluation and management of postnatal thromboses
 STATE-OF-THE-ART The evaluation and management of postnatal thromboses (2009) 29, 467 478 r 2009 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved. 0743-8346/09 $32 www.nature.com/jp Division of Neonatology,
STATE-OF-THE-ART The evaluation and management of postnatal thromboses (2009) 29, 467 478 r 2009 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved. 0743-8346/09 $32 www.nature.com/jp Division of Neonatology,
Thromboembolic Disease and Antithrombotic Therapy in Newborns
 Thromboembolic Disease and Antithrombotic Therapy in Newborns Maureen E. Andrew,* Paul Monagle, Gabrielle deveber, and Anthony K.C. Chan This update uses an evidence based approach to analyze and present
Thromboembolic Disease and Antithrombotic Therapy in Newborns Maureen E. Andrew,* Paul Monagle, Gabrielle deveber, and Anthony K.C. Chan This update uses an evidence based approach to analyze and present
Guidelines for Anticoagulation in Paediatric Cardiac Patients
 Leeds Children s Hospital Guidelines for Anticoagulation in Paediatric Cardiac Patients SURGICAL PATIENTS Preoperative Management Blalock-Taussig (BT) Shunt / Fontan circulation / Sano Shunt and Severe
Leeds Children s Hospital Guidelines for Anticoagulation in Paediatric Cardiac Patients SURGICAL PATIENTS Preoperative Management Blalock-Taussig (BT) Shunt / Fontan circulation / Sano Shunt and Severe
BLOOD RESEARCH. Venous thromboembolism in pediatric patients: a single institution experience in Korea
 BLOOD RESEARCH VOLUME 5 ㆍ NUMBER September 6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Venous thromboembolism in pediatric patients: a single institution experience in Korea Hyoung Soo Choi, Chang Won Choi, Heon Min Kim, Hye Won
BLOOD RESEARCH VOLUME 5 ㆍ NUMBER September 6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Venous thromboembolism in pediatric patients: a single institution experience in Korea Hyoung Soo Choi, Chang Won Choi, Heon Min Kim, Hye Won
10/24/2013. Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia (HIT) Anticoagulation Management in ECMO Therapy:
 Anticoagulation Management in ECMO Therapy: Heparin-Induced (HIT) Michael H. Creer, MD Professor of Pathology Director, Clinical Laboratories, Medical Co- Director, Hematopathology and Chief, Division
Anticoagulation Management in ECMO Therapy: Heparin-Induced (HIT) Michael H. Creer, MD Professor of Pathology Director, Clinical Laboratories, Medical Co- Director, Hematopathology and Chief, Division
THROMBOPHILIA TESTING: PROS AND CONS SHANNON CARPENTER, MD MS CHILDREN S MERCY HOSPITAL KANSAS CITY, MO
 THROMBOPHILIA TESTING: PROS AND CONS SHANNON CARPENTER, MD MS CHILDREN S MERCY HOSPITAL KANSAS CITY, MO DISCLAIMER I m a pediatrician I will be discussing this issue primarily from a pediatric perspective
THROMBOPHILIA TESTING: PROS AND CONS SHANNON CARPENTER, MD MS CHILDREN S MERCY HOSPITAL KANSAS CITY, MO DISCLAIMER I m a pediatrician I will be discussing this issue primarily from a pediatric perspective
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Vein of Galen aneurysm: Aneurysmal characteristics and clinical features as predictive factors
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Vein of Galen aneurysm: Aneurysmal characteristics and clinical features as predictive factors April 2010 2 Pronzini F, Fontijn J, Fauchère JC, Bucher HU, Clinic of Neonatology,
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Vein of Galen aneurysm: Aneurysmal characteristics and clinical features as predictive factors April 2010 2 Pronzini F, Fontijn J, Fauchère JC, Bucher HU, Clinic of Neonatology,
CASE REPORT. Hannah Lively-Endicott, BA, 1 Angelina M. Dixon, MD, 2 Joyce Varghese, DO 3
 CASE REPORT Ochsner Journal 18:417 422, 2018 Academic Division of Ochsner Clinic Foundation DOI: 10.31486/toj.18.0051 Severe Acute Kidney Injury With Significant Uremia in an Infant Found to Have Inferior
CASE REPORT Ochsner Journal 18:417 422, 2018 Academic Division of Ochsner Clinic Foundation DOI: 10.31486/toj.18.0051 Severe Acute Kidney Injury With Significant Uremia in an Infant Found to Have Inferior
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis in a preterm infant
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis in a preterm infant February 2014 2 Georgi R, Berger M, Schnyder I, Berger S, McDougall J, Division of Neonatology (GR, BM, McDJ), Department
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis in a preterm infant February 2014 2 Georgi R, Berger M, Schnyder I, Berger S, McDougall J, Division of Neonatology (GR, BM, McDJ), Department
How I treat venous thrombosis in children
 How I treat How I treat venous thrombosis in children Marilyn J. Manco-Johnson Introduction Evidence-based medicine for pediatric thrombosis is in its infancy. As recently as 10 years ago, antithrombotic
How I treat How I treat venous thrombosis in children Marilyn J. Manco-Johnson Introduction Evidence-based medicine for pediatric thrombosis is in its infancy. As recently as 10 years ago, antithrombotic
Patients with cancer are at a greater risk of developing venous thromboembolism than non-cancer patients, partly due to the 1
 CANCER ASSOCIATED THROMBOSIS TREATMENT Patients with cancer are at a greater risk of developing venous thromboembolism than non-cancer patients, partly due to the 1 ability of tumour cells to activate
CANCER ASSOCIATED THROMBOSIS TREATMENT Patients with cancer are at a greater risk of developing venous thromboembolism than non-cancer patients, partly due to the 1 ability of tumour cells to activate
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Prolonged arterial hypotension due to propofol used for endotracheal intubation in a newborn infant
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Prolonged arterial hypotension due to propofol used for endotracheal intubation in a newborn infant July 2001 2 Wagner B, Intensive Care Unit, University Children s Hospital
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Prolonged arterial hypotension due to propofol used for endotracheal intubation in a newborn infant July 2001 2 Wagner B, Intensive Care Unit, University Children s Hospital
P-RMS: LT/H/PSUR/0004/001
 Core Safety Profile Active substance: Dalteparine Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Solution for injection, 2500 I.U./0.2ml, 2500 I.U./ml, 5000 I.U./0.2ml, 7500 I.U./0.3ml, 7500 I.U./0.75ml, 10000 I.U./0.4ml,
Core Safety Profile Active substance: Dalteparine Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Solution for injection, 2500 I.U./0.2ml, 2500 I.U./ml, 5000 I.U./0.2ml, 7500 I.U./0.3ml, 7500 I.U./0.75ml, 10000 I.U./0.4ml,
This chapter will describe the effectiveness of antithrombotic
 Antithrombotic Therapy for Venous Thromboembolic Disease The Seventh ACCP Conference on Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic Therapy Harry R. Büller, MD, Chair; Giancarlo Agnelli, MD; Russel D. Hull, MBBS,
Antithrombotic Therapy for Venous Thromboembolic Disease The Seventh ACCP Conference on Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic Therapy Harry R. Büller, MD, Chair; Giancarlo Agnelli, MD; Russel D. Hull, MBBS,
The control patients had at least the combination of cardiovascular failure necessitating vasoactive
 ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Material and methods Patients The control patients had at least the combination of cardiovascular failure necessitating vasoactive medication, respiratory failure necessitating
ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Material and methods Patients The control patients had at least the combination of cardiovascular failure necessitating vasoactive medication, respiratory failure necessitating
incidence of cancer-associated thrombosis (CAT) is further increased by additional risk factors such as chemotherapeutic 2
 CANCER ASSOCIATED THROMBOSIS TREATMENT Patients with cancer are at a greater risk of developing venous thromboembolism than non-cancer patients, partly due to the ability of tumour cells to activate the
CANCER ASSOCIATED THROMBOSIS TREATMENT Patients with cancer are at a greater risk of developing venous thromboembolism than non-cancer patients, partly due to the ability of tumour cells to activate the
Diagnosis and Treatment of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism
 Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Evidence Report/Technology Assessment Diagnosis and Treatment of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Summary Number 68 Overview Venous thromboembolism
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Evidence Report/Technology Assessment Diagnosis and Treatment of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Summary Number 68 Overview Venous thromboembolism
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominal tumors, in children, 530 531 Alkalinization, in tumor lysis syndrome, 516 Allopurinol, in tumor lysis syndrome, 515 Anaphylaxis, drug
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominal tumors, in children, 530 531 Alkalinization, in tumor lysis syndrome, 516 Allopurinol, in tumor lysis syndrome, 515 Anaphylaxis, drug
Risk Factor Evaluation for Thrombosis and Bleeding in Pediatric Patients with Heart Disease
 Risk Factor Evaluation for Thrombosis and Bleeding in Pediatric Patients with Heart Disease Kristen Nelson, MD Johns Hopkins University Director, Pediatric Cardiac Critical Care Why Does it Matter? Pediatric
Risk Factor Evaluation for Thrombosis and Bleeding in Pediatric Patients with Heart Disease Kristen Nelson, MD Johns Hopkins University Director, Pediatric Cardiac Critical Care Why Does it Matter? Pediatric
Should infants with perinatal thrombosis be screened for thrombophilia and treated by anticoagulants?
 Should infants with perinatal thrombosis be screened for thrombophilia and treated by anticoagulants? Shoshana Revel-Vilk, MD MSc Pediatric Hematology Center, Pediatric Hematology/Oncology Department,
Should infants with perinatal thrombosis be screened for thrombophilia and treated by anticoagulants? Shoshana Revel-Vilk, MD MSc Pediatric Hematology Center, Pediatric Hematology/Oncology Department,
Extensive cystic periventricular leukomalacia following early-onset group B streptococcal sepsis in a very low birth weight infant
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Extensive cystic periventricular leukomalacia following early-onset group B streptococcal sepsis in a very low birth weight infant July 2012 2 Berger TM, Caduff JC, Neonatal
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Extensive cystic periventricular leukomalacia following early-onset group B streptococcal sepsis in a very low birth weight infant July 2012 2 Berger TM, Caduff JC, Neonatal
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Diagnostic evaluation of a symptomatic cerebrovascular accident in a neonate with focal convulsions
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Diagnostic evaluation of a symptomatic cerebrovascular accident in a neonate with focal convulsions July 2013 2 Anderson S, Rimensberger P, Service de Néonatologie et des Soins
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Diagnostic evaluation of a symptomatic cerebrovascular accident in a neonate with focal convulsions July 2013 2 Anderson S, Rimensberger P, Service de Néonatologie et des Soins
Successful Treatment of Bilateral Renal Vein Thrombosis in a Patient with Nephrotic Syndrome: A Case Report Z Li,J Li, F Liu ABSTRACT
 Successful Treatment of Bilateral Renal Vein Thrombosis in a Patient with Nephrotic Syndrome: A Case Report Z Li,J Li, F Liu ABSTRACT Renal vein thrombosis is a well-known complication of nephrotic syndrome,
Successful Treatment of Bilateral Renal Vein Thrombosis in a Patient with Nephrotic Syndrome: A Case Report Z Li,J Li, F Liu ABSTRACT Renal vein thrombosis is a well-known complication of nephrotic syndrome,
Jessica Bryan, Natalia Evans, Karlyn Henderson, & Whitney Parks
 Jessica Bryan, Natalia Evans, Karlyn Henderson, & Whitney Parks 1. What is the most common cause of death in hospitalized patients? 1. Hospital-acquired infection 2. Pulmonary embolism 3. Myocardial infarction
Jessica Bryan, Natalia Evans, Karlyn Henderson, & Whitney Parks 1. What is the most common cause of death in hospitalized patients? 1. Hospital-acquired infection 2. Pulmonary embolism 3. Myocardial infarction
Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis
 Approved by: Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis Vice President and Chief Medical Officer; and Vice President and Chief Operating Officer Corporate Policy & Procedures Manual Number: Date Approved January
Approved by: Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis Vice President and Chief Medical Officer; and Vice President and Chief Operating Officer Corporate Policy & Procedures Manual Number: Date Approved January
UNIVERSITA DI PADOVA. Un tema particolare (II): Le trombosi venose in pediatria
 UNIVERSITA DI PADOVA Un tema particolare (II): Le trombosi venose in pediatria Elena Campello Dipartimento di Medicina Università di Padova Bologna, 6 Novembre 2015 Introduction Pediatric thrombosis: -
UNIVERSITA DI PADOVA Un tema particolare (II): Le trombosi venose in pediatria Elena Campello Dipartimento di Medicina Università di Padova Bologna, 6 Novembre 2015 Introduction Pediatric thrombosis: -
Epidemiology of venous thrombosis in children with cancer
 Review Article 1015 Epidemiology of venous thrombosis in children with cancer Dana Piovesan 1 ; Chantal Attard 1,2 ; Paul Monagle 1,2,3 ; Vera Ignjatovic 1,2 1 Murdoch Childrens Research Institute, Royal
Review Article 1015 Epidemiology of venous thrombosis in children with cancer Dana Piovesan 1 ; Chantal Attard 1,2 ; Paul Monagle 1,2,3 ; Vera Ignjatovic 1,2 1 Murdoch Childrens Research Institute, Royal
Pediatric thrombosis: Diagnosis and Management
 Pediatric thrombosis: Diagnosis and Management Vilmarie Rodriguez, MD Professor Pediatric and Adolescent Medicine Department of Pediatric and Adolescent Medicine Division Pediatric Hematology-Oncology
Pediatric thrombosis: Diagnosis and Management Vilmarie Rodriguez, MD Professor Pediatric and Adolescent Medicine Department of Pediatric and Adolescent Medicine Division Pediatric Hematology-Oncology
A pregnant patient with a prosthetic valve Giacomo Boccuzzi, MD, FESC
 A pregnant patient with a prosthetic valve Giacomo Boccuzzi, MD, FESC Department of Invasive Cardiology, Ospedale San Giovanni Bosco, Turin, Italy *C.V. was born the 24th May 1980 Rheumatic fever during
A pregnant patient with a prosthetic valve Giacomo Boccuzzi, MD, FESC Department of Invasive Cardiology, Ospedale San Giovanni Bosco, Turin, Italy *C.V. was born the 24th May 1980 Rheumatic fever during
Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia. Steven Baroletti, PharmD., M.B.A., BCPS Brigham and Women s Hospital
 Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia Steven Baroletti, PharmD., M.B.A., BCPS Brigham and Women s Hospital Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) A serious concern associated with thrombosis development following
Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia Steven Baroletti, PharmD., M.B.A., BCPS Brigham and Women s Hospital Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) A serious concern associated with thrombosis development following
DVT Pathophysiology and Prophylaxis in Medically Hospitalized Patients. David Liff MD Oklahoma Heart Institute Vascular Center
 DVT Pathophysiology and Prophylaxis in Medically Hospitalized Patients David Liff MD Oklahoma Heart Institute Vascular Center Overview Pathophysiology of DVT Epidemiology and risk factors for DVT in the
DVT Pathophysiology and Prophylaxis in Medically Hospitalized Patients David Liff MD Oklahoma Heart Institute Vascular Center Overview Pathophysiology of DVT Epidemiology and risk factors for DVT in the
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Pulmonary complications of congenital listeriosis in a preterm infant
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Pulmonary complications of congenital listeriosis in a preterm infant April 2009 2 Mészàros A, el Helou S, Zimmermann U, Berger TM, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Pulmonary complications of congenital listeriosis in a preterm infant April 2009 2 Mészàros A, el Helou S, Zimmermann U, Berger TM, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit
Management of Neonatal Thrombosis
 Management of Neonatal Thrombosis Matthew A. Saxonhouse, MD KEYWORDS Neonatal thrombosis Thromboembolism Vasospasm Venous thrombosis Arterial thrombosis Prothrombotic disorder THE NEONATAL HEMOSTATIC SYSTEM
Management of Neonatal Thrombosis Matthew A. Saxonhouse, MD KEYWORDS Neonatal thrombosis Thromboembolism Vasospasm Venous thrombosis Arterial thrombosis Prothrombotic disorder THE NEONATAL HEMOSTATIC SYSTEM
CARDIAC PROBLEMS IN PREGNANCY
 CARDIAC PROBLEMS IN PREGNANCY LAS VEGAS, NEVADA, USA 27 February 1 March 2016 SUCCESSFUL TREATMENT WITH RECOMBINANT TISSUE PLASMINOGEN ACTIVATOR OF MASSIVE PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN THE 16 TH WEEK OF PREGNANCY
CARDIAC PROBLEMS IN PREGNANCY LAS VEGAS, NEVADA, USA 27 February 1 March 2016 SUCCESSFUL TREATMENT WITH RECOMBINANT TISSUE PLASMINOGEN ACTIVATOR OF MASSIVE PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN THE 16 TH WEEK OF PREGNANCY
Welcome! Copyright (C) 2018 by ASPHO
 Welcome! To join the call dial (303) 248-0285, code 8055841#. All participants are placed on mute for the duration of the webinar. Type questions in the chat box at the bottom left hand side of your screen.
Welcome! To join the call dial (303) 248-0285, code 8055841#. All participants are placed on mute for the duration of the webinar. Type questions in the chat box at the bottom left hand side of your screen.
Thrombophilia. Diagnosis and Management. Kevin P. Hubbard, DO, FACOI
 Thrombophilia Diagnosis and Management Kevin P. Hubbard, DO, FACOI Clinical Professor of Medicine Kansas City University of Medicine and Biosciences-College of Osteopathic Medicine Kansas City, Missouri
Thrombophilia Diagnosis and Management Kevin P. Hubbard, DO, FACOI Clinical Professor of Medicine Kansas City University of Medicine and Biosciences-College of Osteopathic Medicine Kansas City, Missouri
Appendix IV - Prescribing Guidance for Apixaban
 Appendix IV - Prescribing Guidance for Apixaban Patient Factors Dose of Apixaban If your patient has any of the following MAJOR risk factors: Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients
Appendix IV - Prescribing Guidance for Apixaban Patient Factors Dose of Apixaban If your patient has any of the following MAJOR risk factors: Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients
Atlantic Provinces Pediatric Hematology/Oncology Network Réseau d Oncologie et Hématologie Pédiatrique des Provinces Atlantiques
 Atlantic Provinces Pediatric Hematology/Oncology Network Réseau d Oncologie et Hématologie Pédiatrique des Provinces Atlantiques 5850/5980 University Avenue, PO Box 9700, Halifax, NS, B3K 6R8 (902) 470-8888
Atlantic Provinces Pediatric Hematology/Oncology Network Réseau d Oncologie et Hématologie Pédiatrique des Provinces Atlantiques 5850/5980 University Avenue, PO Box 9700, Halifax, NS, B3K 6R8 (902) 470-8888
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Neonatal gastric perforation
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Neonatal gastric perforation September 2002 2 Zankl A, Stähelin J, Roth K, Boudny P and Zeilinger G, Children s Hospital of Aarau (ZA, SJ, RK, ZG) and Institute of Pathology
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Neonatal gastric perforation September 2002 2 Zankl A, Stähelin J, Roth K, Boudny P and Zeilinger G, Children s Hospital of Aarau (ZA, SJ, RK, ZG) and Institute of Pathology
WARFARIN: PERI OPERATIVE MANAGEMENT
 WARFARIN: PERI OPERATIVE MANAGEMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide an approach to the perioperative management of warfarin treated patients who require an elective or urgent surgery/procedure. To provide an approach
WARFARIN: PERI OPERATIVE MANAGEMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide an approach to the perioperative management of warfarin treated patients who require an elective or urgent surgery/procedure. To provide an approach
Paediatric Anticoagulant Guidelines. Bhavee Patel, Gareth Thomas
 Paediatric Anticoagulant Guidelines Author: Bhavee Patel, Gareth Thomas Specialty: Paediatrics Date Approved: 18 th July 2012 Approved by: W&CH Quality & Safety Group Date for Review: June 2015 PAEDIATRIC
Paediatric Anticoagulant Guidelines Author: Bhavee Patel, Gareth Thomas Specialty: Paediatrics Date Approved: 18 th July 2012 Approved by: W&CH Quality & Safety Group Date for Review: June 2015 PAEDIATRIC
DVT - initial management NSCCG
 Background information Information resources for patients and carers Updates to this care map Synonyms Below knee DVT and bleeding risks Patient with confirmed DVT Scan confirms superficial thrombophlebitis
Background information Information resources for patients and carers Updates to this care map Synonyms Below knee DVT and bleeding risks Patient with confirmed DVT Scan confirms superficial thrombophlebitis
Keep catheter. Anticoagulate. Yes. Symptoms resolved? Yes. No Catheter needed? Other access sites available? Yes. Anticoagulate. Place new catheter
 Chief Anticoagulation and Thrombosis Service UCSF, SF VA MED CTR Thromboembolism Q&A Management of the Hospitalized Patient, SF, CA October 2012 CASES & ANSWERS 1. A 55 year old woman being treated for
Chief Anticoagulation and Thrombosis Service UCSF, SF VA MED CTR Thromboembolism Q&A Management of the Hospitalized Patient, SF, CA October 2012 CASES & ANSWERS 1. A 55 year old woman being treated for
A 50-year-old woman with syncope
 Hira Shahzad 1, Ali Bin Sarwar Zubairi 2 1 Medical College, Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi 2 Department of Medicine, Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi, Pakistan Ali Bin Sarwar Zubairi Associate
Hira Shahzad 1, Ali Bin Sarwar Zubairi 2 1 Medical College, Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi 2 Department of Medicine, Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi, Pakistan Ali Bin Sarwar Zubairi Associate
PULMONARY EMBOLISM -CASE REPORT-
 University Goce Delcev, Faculty of Medical sciences, Stip University Clinic of Cardiology, Skopje R. Of Macedonia PULMONARY EMBOLISM -CASE REPORT- Gordana Kamceva MD mr.sci Acknowledgment Marija Vavlukis
University Goce Delcev, Faculty of Medical sciences, Stip University Clinic of Cardiology, Skopje R. Of Macedonia PULMONARY EMBOLISM -CASE REPORT- Gordana Kamceva MD mr.sci Acknowledgment Marija Vavlukis
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Prenatal closure of the ductus arteriosus
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Prenatal closure of the ductus arteriosus March 2007 Leone A, Fasnacht M, Beinder E, Arlettaz R, Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (LA, AR), University Hospital Zurich, Cardiology
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Prenatal closure of the ductus arteriosus March 2007 Leone A, Fasnacht M, Beinder E, Arlettaz R, Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (LA, AR), University Hospital Zurich, Cardiology
Antithrombotic Therapy in Neonates and Children
 CHEST Supplement ANTITHROMBOTIC THERAPY AND PREVENTION OF THROMBOSIS, 9TH ED: ACCP GUIDELINES Antithrombotic Therapy in Neonates and Children Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed:
CHEST Supplement ANTITHROMBOTIC THERAPY AND PREVENTION OF THROMBOSIS, 9TH ED: ACCP GUIDELINES Antithrombotic Therapy in Neonates and Children Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed:
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Preterm infant with. pulmonary hypertension and hypopituitarism
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Preterm infant with pulmonary hypertension and hypopituitarism November 2007 2 Pilgrim S, Stocker M, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensiv Care Unit, Children s Hospital of Lucerne,
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Preterm infant with pulmonary hypertension and hypopituitarism November 2007 2 Pilgrim S, Stocker M, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensiv Care Unit, Children s Hospital of Lucerne,
HEPARIN-INDUCED THROMBOCYTOPENIA (HIT)
 HEPARIN-INDUCED THROMBOCYTOPENIA (HIT) OBJECTIVE: To assist clinicians with the investigation and management of suspected and documented heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT). BACKGROUND: HIT is a transient,
HEPARIN-INDUCED THROMBOCYTOPENIA (HIT) OBJECTIVE: To assist clinicians with the investigation and management of suspected and documented heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT). BACKGROUND: HIT is a transient,
Thrombosis and emboli. Peter Nagy
 Thrombosis and emboli Peter Nagy A thrombus is any solid object developing from the blood in vivo within the vascular system or heart. Thrombosis is hemostasis in the wrong place. Major components, forms:
Thrombosis and emboli Peter Nagy A thrombus is any solid object developing from the blood in vivo within the vascular system or heart. Thrombosis is hemostasis in the wrong place. Major components, forms:
Coagulation, Haemostasis and interpretation of Coagulation tests
 Coagulation, Haemostasis and interpretation of Coagulation tests Learning Outcomes Indicate the normal ranges for routine clotting screen and explain what each measurement means Recognise how to detect
Coagulation, Haemostasis and interpretation of Coagulation tests Learning Outcomes Indicate the normal ranges for routine clotting screen and explain what each measurement means Recognise how to detect
Pulmonary Embolism Is it the Greatest Danger in Deep Vein Thrombosis?
 Difficult issues in Deep Vein Thrombosis: Pulmonary Embolism Is it the Greatest Danger in Deep Vein Thrombosis? Raluca Dulgheru; C Gherghinescu; B Dorobat; H Muresan; R Darabont; M Cinteza; D Vinereanu
Difficult issues in Deep Vein Thrombosis: Pulmonary Embolism Is it the Greatest Danger in Deep Vein Thrombosis? Raluca Dulgheru; C Gherghinescu; B Dorobat; H Muresan; R Darabont; M Cinteza; D Vinereanu
Renal Vein Thrombosis secondary to pyelonephritis: Case presentation
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Renal Vein Thrombosis secondary to pyelonephritis: Case presentation Anusha Skandini Ganeshan*, Angel Alberto Calderon Chongo Internal Medicine Department, Seychelles Hospital, Seychelles
RESEARCH ARTICLE Renal Vein Thrombosis secondary to pyelonephritis: Case presentation Anusha Skandini Ganeshan*, Angel Alberto Calderon Chongo Internal Medicine Department, Seychelles Hospital, Seychelles
DEEP VENOUS THROMBOSIS (DVT), SUSPECTED ACUTE, INVOLVING A PROXIMAL LIMB
 DEEP VENOUS THROMBOSIS (DVT), SUSPECTED ACUTE, INVOLVING A PROXIMAL LIMB Step 1. Evaluate Signs of limb ischemia (reduced pulses or perfusion)? If YES, then Consult Surgeon STAT. (Consult Hematologist
DEEP VENOUS THROMBOSIS (DVT), SUSPECTED ACUTE, INVOLVING A PROXIMAL LIMB Step 1. Evaluate Signs of limb ischemia (reduced pulses or perfusion)? If YES, then Consult Surgeon STAT. (Consult Hematologist
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Duration of Anticoagulant Therapy. Linda R. Kelly PharmD, PhC, CACP September 17, 2016
 Duration of Anticoagulant Therapy Linda R. Kelly PharmD, PhC, CACP September 17, 2016 Conflicts of Interest No conflicts of interest to report Objectives At the end of the program participants will be
Duration of Anticoagulant Therapy Linda R. Kelly PharmD, PhC, CACP September 17, 2016 Conflicts of Interest No conflicts of interest to report Objectives At the end of the program participants will be
VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM: DURATION OF TREATMENT
 VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM: DURATION OF TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide guidance on the recommended duration of anticoagulant therapy for venous thromboembolism (VTE). BACKGROUND: Recurrent episodes of VTE
VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM: DURATION OF TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide guidance on the recommended duration of anticoagulant therapy for venous thromboembolism (VTE). BACKGROUND: Recurrent episodes of VTE
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Multiple infantile hemangiomas in a preterm infant
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Multiple infantile hemangiomas in a preterm infant November 2017 Heschl K, Romaine Arlettaz R, Department of Neonatology (HK, AR), University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland Title
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Multiple infantile hemangiomas in a preterm infant November 2017 Heschl K, Romaine Arlettaz R, Department of Neonatology (HK, AR), University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland Title
Prevention and treatment of venous thromboembolic disease
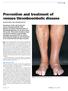 REVIEW Prevention and treatment of venous thromboembolic disease SUSAN McNEILL AND CATHERINE BAGOT Awareness of the risk factors for venous thromboembolic (VTE) disease and timely administration of thromboprophylaxis
REVIEW Prevention and treatment of venous thromboembolic disease SUSAN McNEILL AND CATHERINE BAGOT Awareness of the risk factors for venous thromboembolic (VTE) disease and timely administration of thromboprophylaxis
Acute Pulmonary Embolism and Deep Vein Thrombosis. Barbara LeVarge MD Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Pulmonary Hypertension Center COPYRIGHT
 Acute Pulmonary Embolism and Deep Vein Thrombosis Barbara LeVarge MD Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Pulmonary Hypertension Center Acute PE and DVT No disclosures. Acute PE and DVT Learning objectives
Acute Pulmonary Embolism and Deep Vein Thrombosis Barbara LeVarge MD Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Pulmonary Hypertension Center Acute PE and DVT No disclosures. Acute PE and DVT Learning objectives
Are there still any valid indications for thrombophilia screening in DVT?
 Carotid artery stenosis and risk of stroke Are there still any valid indications for thrombophilia screening in DVT? Armando Mansilha MD, PhD, FEBVS Faculty of Medicine of University of Porto Munich, 2016
Carotid artery stenosis and risk of stroke Are there still any valid indications for thrombophilia screening in DVT? Armando Mansilha MD, PhD, FEBVS Faculty of Medicine of University of Porto Munich, 2016
MANAGEMENT OF BLEEDING AND EXCESSIVE ANTICOAGULATION IN ADULTS RECEIVING ANTI-COAGULANTS
 Hairmyres Hospital MANAGEMENT OF BLEEDING AND EXCESSIVE ANTICOAGULATION IN ADULTS RECEIVING ANTI-COAGULANTS Bleeding in patients on anticoagulants, even in the absence of over-anticoagulation, can be life-threatening
Hairmyres Hospital MANAGEMENT OF BLEEDING AND EXCESSIVE ANTICOAGULATION IN ADULTS RECEIVING ANTI-COAGULANTS Bleeding in patients on anticoagulants, even in the absence of over-anticoagulation, can be life-threatening
Anticoagulant Therapy During Pregnancy
 Anticoagulant Therapy During Pregnancy AIM - June 2007 Russell K. Laros, Jr., MD Thromboembolism and Pregnancy Leading Non-Obstetrical Cause of Maternal Mortality Early recognition and proper treatment
Anticoagulant Therapy During Pregnancy AIM - June 2007 Russell K. Laros, Jr., MD Thromboembolism and Pregnancy Leading Non-Obstetrical Cause of Maternal Mortality Early recognition and proper treatment
Disclosures. DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment. Questions To Ask. Dr. Susanna Shin - DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment. Acute Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) None
 Disclosures DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment None Susanna Shin, MD, FACS Assistant Professor University of Washington Acute Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT) Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
Disclosures DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment None Susanna Shin, MD, FACS Assistant Professor University of Washington Acute Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT) Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
Successful Pulmonary Embolectomy of a Saddle Pulmonary Thromboembolism in a Preterm Neonate
 Successful Pulmonary Embolectomy of a Saddle Pulmonary Thromboembolism in a Preterm Neonate Kaarthigeyan Kalaniti, MBBS, MD a, Mauro Lo Rito, MD b, Edward J. Hickey, MD b,c, V. Ben Sivarajan, MD, MS c,d,e
Successful Pulmonary Embolectomy of a Saddle Pulmonary Thromboembolism in a Preterm Neonate Kaarthigeyan Kalaniti, MBBS, MD a, Mauro Lo Rito, MD b, Edward J. Hickey, MD b,c, V. Ben Sivarajan, MD, MS c,d,e
Treatment Options and How They Work
 Treatment Options and How They Work Robin Offord Director of Clinical Pharmacy UCL Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust robin.offord@uclh.nhs.uk Introducing the term anticoagulant... What they do Inhibit the
Treatment Options and How They Work Robin Offord Director of Clinical Pharmacy UCL Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust robin.offord@uclh.nhs.uk Introducing the term anticoagulant... What they do Inhibit the
PE Pathway. The charts are listed as follows:
 PE Pathway This document comprises 6 simple flow charts to assist clinicians in the investigation and treatment of suspected or confirmed Acute Pulmonary Emboli. The pathway has been put together using
PE Pathway This document comprises 6 simple flow charts to assist clinicians in the investigation and treatment of suspected or confirmed Acute Pulmonary Emboli. The pathway has been put together using
Present-on-Admission (POA) Coding
 1 Present-on-Admission (POA) Coding Michael Pine, MD, MBA Michael Pine and Associates, Inc 2 POA and Coding Guidelines (1) Unless otherwise specified, a POA modifier must be assigned to each principal
1 Present-on-Admission (POA) Coding Michael Pine, MD, MBA Michael Pine and Associates, Inc 2 POA and Coding Guidelines (1) Unless otherwise specified, a POA modifier must be assigned to each principal
Blood Thinner Agent. Done by: Meznah Al-mutairi Pharm.D Candidate PNU Collage of Pharmacy
 Blood Thinner Agent Done by: Meznah Al-mutairi Pharm.D Candidate PNU Collage of Pharmacy Outline: Blood thinner agent definition. anticoagulants drugs. Thrombolytics. Blood thinner agent Therapeutic interference
Blood Thinner Agent Done by: Meznah Al-mutairi Pharm.D Candidate PNU Collage of Pharmacy Outline: Blood thinner agent definition. anticoagulants drugs. Thrombolytics. Blood thinner agent Therapeutic interference
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Peripartal management of a prenatally diagnosed large oral cyst
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Peripartal management of a prenatally diagnosed large oral cyst May 2007 2 Fontana M, Berger TM, Winiker H, Jöhr M, Nagel H, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (FM,
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Peripartal management of a prenatally diagnosed large oral cyst May 2007 2 Fontana M, Berger TM, Winiker H, Jöhr M, Nagel H, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (FM,
Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin
 Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.04.019 10/15/2007 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 05/01/2016 Section: Prescription Drugs
Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.04.019 10/15/2007 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 05/01/2016 Section: Prescription Drugs
Handbook for Venous Thromboembolism
 Handbook for Venous Thromboembolism Gregory Piazza Benjamin Hohlfelder Samuel Z. Goldhaber Handbook for Venous Thromboembolism Gregory Piazza Cardiovascular Division Harvard Medical School Brigham and
Handbook for Venous Thromboembolism Gregory Piazza Benjamin Hohlfelder Samuel Z. Goldhaber Handbook for Venous Thromboembolism Gregory Piazza Cardiovascular Division Harvard Medical School Brigham and
WARFARIN: PERI-OPERATIVE MANAGEMENT
 WARFARIN: PERI-OPERATIVE MANAGEMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide an approach to the perioperative management of warfarin-treated patients who require an elective or urgent surgery/procedure. To provide an approach
WARFARIN: PERI-OPERATIVE MANAGEMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide an approach to the perioperative management of warfarin-treated patients who require an elective or urgent surgery/procedure. To provide an approach
Guidance for management of bleeding in patients taking the new oral anticoagulant drugs: rivaroxaban, dabigatran or apixaban
 Guidance for management of bleeding in patients taking the new oral anticoagulant drugs: rivaroxaban, dabigatran or apixaban Purpose The aim of this guidance is to outline the management of patients presenting
Guidance for management of bleeding in patients taking the new oral anticoagulant drugs: rivaroxaban, dabigatran or apixaban Purpose The aim of this guidance is to outline the management of patients presenting
ADMINISTRATIVE CLINICAL Page 1 of 6
 ADMINISTRATIVE CLINICAL Page 1 of 6 Anticoagulant Guidelines #2: REVERSAL OF OR MANAGEMENT OF BLEEDING WITH ANTICOAGULANTS Origination Date: Revision Date: Reviewed Date: 09/12 09/12, 01/13, 11/13, 11/15
ADMINISTRATIVE CLINICAL Page 1 of 6 Anticoagulant Guidelines #2: REVERSAL OF OR MANAGEMENT OF BLEEDING WITH ANTICOAGULANTS Origination Date: Revision Date: Reviewed Date: 09/12 09/12, 01/13, 11/13, 11/15
THROMBOPHILIA SCREENING
 THROMBOPHILIA SCREENING Introduction The regulation of haemostasis Normally, when a clot occurs, it exactly occurs where it has to be and does not grow more than necessary due to the action of the haemostasis
THROMBOPHILIA SCREENING Introduction The regulation of haemostasis Normally, when a clot occurs, it exactly occurs where it has to be and does not grow more than necessary due to the action of the haemostasis
Changing the Ambulatory Training Paradigm: The Design and Implementation of an Outpatient Pulmonology Fellowship Curriculum
 Online Data Supplement Changing the Ambulatory Training Paradigm: The Design and Implementation of an Outpatient Pulmonology Fellowship Curriculum Stacey M. Kassutto, C. Jessica Dine, Maryl Kreider, Rupal
Online Data Supplement Changing the Ambulatory Training Paradigm: The Design and Implementation of an Outpatient Pulmonology Fellowship Curriculum Stacey M. Kassutto, C. Jessica Dine, Maryl Kreider, Rupal
Thromboprophylaxis in Patients with Congenital Heart Disease. Rachel Keashen, MSN, CRNP 10/19/2018
 Thromboprophylaxis in Patients with Congenital Heart Disease Rachel Keashen, MSN, CRNP 10/19/2018 No disclosures/conflicts of interest COI Objectives Be able to name 2 thromboprophylaxis agents used to
Thromboprophylaxis in Patients with Congenital Heart Disease Rachel Keashen, MSN, CRNP 10/19/2018 No disclosures/conflicts of interest COI Objectives Be able to name 2 thromboprophylaxis agents used to
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Mismetti P, Laporte S, Pellerin O, Ennezat P-V, Couturaud F, Elias A, et al. Effect of a retrievable inferior vena cava filter plus anticoagulation vs anticoagulation alone
Supplementary Online Content Mismetti P, Laporte S, Pellerin O, Ennezat P-V, Couturaud F, Elias A, et al. Effect of a retrievable inferior vena cava filter plus anticoagulation vs anticoagulation alone
Objectives. Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis. Case VTE WHY DO IT? Question: Who Is At Risk?
 Objectives Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis Rishi Garg, MD Department of Medicine Identify patients at risk for VTE Options for VTE prophylaxis Current Recommendations (based on The Seventh ACCP
Objectives Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis Rishi Garg, MD Department of Medicine Identify patients at risk for VTE Options for VTE prophylaxis Current Recommendations (based on The Seventh ACCP
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a pervasive LOW-MOLECULAR-WEIGHT HEPARIN IN THE TREATMENT OF ACUTE DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS AND PULMONARY EMBOLISM *
 LOW-MOLECULAR-WEIGHT HEPARIN IN THE TREATMENT OF ACUTE DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS AND PULMONARY EMBOLISM * Geno J. Merli, MD ABSTRACT There are more than 170 000 hospital admissions each year for deep vein thrombosis
LOW-MOLECULAR-WEIGHT HEPARIN IN THE TREATMENT OF ACUTE DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS AND PULMONARY EMBOLISM * Geno J. Merli, MD ABSTRACT There are more than 170 000 hospital admissions each year for deep vein thrombosis
