Inducibility of Atrial Fibrillation Before and After Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation of Accessory Atrioventricular Connections
|
|
|
- Rosamund Roberts
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 499 Inducibility of Atrial Fibrillation Before and After Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation of Accessory Atrioventricular Connections STEVEN J. KALBFLEISCH, M.D., RAFEL EL-ATASSI, M.D., HUGH CALKI, M.D,, JONATHAN J, LANGBERG, M.D., and FRED MORADY, M.D. Frotn the Division of Cardiology,department of Internal Medicine, University of Michigan Medical Center, Ann Arbor. Michigan f Inducibility of Atrial Fibrillation. Introduction: The purpose of this study was to evaluate the inducihility of atrial fihrillation in patients with an accessory atrioventricular connection (AAVC) and to determine if the inducihility of atrial fihrillation is altered after successful radiofrequency catheter ahlation of the AAVC. Methods and Results: Thirty-seven patients with an AAVC and 36 control patients were prospectively evaluated using a standardized atrial pacing protocol. The high right atrium was paced using a 25-heat drive train, 1.5-second intertrain pause, 10-mA pulse amplitude, and 2- msec pulse duration at cycle lengths of 250 to 100 msec, in 10-msec decrements. Pachig was performed twice at each cycle length. Thirty patients with an AAVC underwent repeat atrial overdrive pacing after successful radiofrequency ahlation of the AAVC. Atrial fihrillation was induced in 26 (70%) patients with an AAVC and 22 (61%) controls (P = ). Atrial flutter was induced In 11 (30%) patients with an AAVC and 13 (36%) controls (P = ). The cumulative percentage of patients with atrial lihrillation/flutter induced at each pacing cycle length wa.s the same in each group. There was no difference in the duration of atrial fihrillatidn/flutler hetween control patients and patients with an AAVC. Among the 30 patients who underwent repeat atrial overdrive pacing after radiofrequency ahlation of an AAVC, there was no difference in the inducihility or duration of atrial fibril la tion/at rial flutter after ablation compared to baseline. Conclusion: These findings indicate that the vulnerability of the atrium to Hhrillate in response to atrial pacing is independent of the presence of an AAVC./J Catdiovasc Electrophysiol, Vol. 4, pp , October 1993) "^ atrial fibrillation, Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, radiofrequency catheter ablation Introduction Long-term follow-up studies after successful surgical or catbeter ablation of accessory atrioventricular connections (AAVC) bave shown tbat tbe incidence of spontaneously occurring atriai fibrillation is significantly reduced.'-^ The expla- Address for correspondence: Fred Morady. M.D., Division of Cardiology. Department of Internal Medicine, University of Michigan Medica! Center, 1500 East Medical Center Drive, Ann Arbor. MI Fax: Manuscript received 22 January 1993; Accepted for publication 24 March nation for this reduction in the incidence of atrial fibrillation after ablation of AAVCs has been unclear. While some studies have suggested that this may t>e due to elimination of atrioventricular reciprocating tachycardia that can degenerate into atrial fibrillation,'-^ another study suggested that the vulnerability of the atrium to atrial fibrillation may be reduced.^ The purpose of this prospective study was to evaluate the inducibility of atrial fibrillation in patients with AAVCs and to determine if tbe inducibility of atrial fibrillation is altered after successful radiofrequency catheter ablation of the AAVC.
2 500 Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology Vot. 4, No. 5, October 1993 Methods Thirty-seven patients with AAVCs and 36 control patients who did not have an AAVC were prospectively evaluated using a standardized atrial pacing protocol. The characteristics of the patients are described in Table 1. Among the patients with ati AAVC, the AAVC was overt in 30 and concealed in 7; the location was left sided in 25 and right sided or posteroseptal in 12. The control group was composed of 19 patients with ventricuiar arrhythmias,. 9 patients with syncope of unknown origin, and 8 patients with palpitations of utiknown etiology. Thirty-six patients with an AAVC did not have structtind heart disease and one had congenital pulmonic stenosis. Twenty patients in the control group did not have hejut disease, 11 had coronary artery disease, 3 had an idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy, and 2 had valvular heart disease. Electrophysiologic Study/Pacing Protocol AH patients provided informed consent and underwent an electrophysiologic test after discontinuation of all antiarrhythmic medications for at least 48 hours. The sinus cycle length, AH interval, HV interval, atrial effective reft-actory period, P wave duration. PA interval at the His jxjsition, atrioventricular block cycle length, and ventriculoatrial block cycle length were determined in each patient. The presence of an AAVC was determined using standard electrophysiologic techniques.'' Atrial overdrive pacing was performed in each patient using a standardized protocol. The high right atrium was paced using a 25-beat drive train. 1.5-second intertrain pause, lo-ma pulse amplitude, and 2-msec pulse duration. Pacing was performed at cycle lengths of 250 to 100 msec in 10- msec decrements. Pacing was performed twice at each pacing cycle length. Pacing was discontinued after the induction of either sustained (> 30 TABLE 1 Palient Characteristics Number of patients Age (years, 37 mean±sd) 35 ± 14 Males/Females 26/11 Heart disease present History of atrial I fibrilhiiiiin 7 Piitients with Control P an AAVC Putients Value 36 AAVC = accessory atrioventricular connection. 53 ±15 < /13 16 < sec) atrial fibrillation or flutter or after three episodes of nonsustained (< 30 sec) atrial fibrillation or flutter. The single longest episode was nscorded in each patient and patients were classified as having either atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter. Atrial fibrillation and flutter were defined using the criteria of Wells et al.*^^ Atrial flutter was defined as a regular atrial tachycardia with an atrial cycle length of 170 to 240 msec, uniform intracardiac atrial electrogram morphology, and an isoelectric interval between atrial complexes. Irregular atrial tachycardias with variable intracardiae electrogram morphology and without isoelectric segments were considered to be atrial fibrillation. A subgroup of 30 patients with an AAVC underwent repeat atrial overdrive pacing after successful radiofrequency ablation of the AAVC. None of these 30 patients had received antiarrhythmic therapy during the course of their procedure. The techniques utilized for radiofrequency ablation of AAVCs have been previously described.^ Results Atrial fibrillation was induced in 26 (70%) patients who had an AAVC, compared to 22 (61%) control patients (P = ). Atrial flutter was induced in 11 (30%) patients with an AAVC compared to 13 (36%) controls (P = ). The induced arrhythmia was sustained in 23 (65%) patients with an AAVC, and 24 (67%) control patients and nonsustained in 14 (38%) patients with an AAVC and II (31%) control patients (P = between the groups). In patients with a sustained arrhythmia, the induced arrhythmia was atrial fibrillation in 16 (70%) and atrial flutter in 7 (30%) patients with an AAVC, and atrial fibrillation in 13 (54%) and atrial flutter in 11 (46%) control patients (P = between the groups). The mean duration of nonsustained atrial flutter was 19 ± 5 seconds and of nonsustained atrial fibrillation was 16 ± 7 seconds. There was no difference between patients with an AAVC and control patients with respect to the baseline sinus cycle length, AH interval, atrial effective refractory period, P wave duration, or PA interval at the His p>osition (Table 2). As expected, the patients with an AAVC had shorter baseline HV intervals, and atrioventricular and ventrieuloatrial block cycle lengths (Table 2). There were no differences in the mean pacing cycle lengths that induced atrial fibrillation or flutter in the patients with an AAVC (198 ±.30 msec) compared to controls (193 ± 25 msec), and there was no difference in the mean pacing cycle length needed to
3 Kalbfleisch, et al. Inducibility of Atrial FibrillatiQn 501 Sinus cycle length {msec) AH interval (msec) HV interval (msec) Atrial ERP (msec) P wave duration (msec) PA interval al His (msec) AVBCL(msec) VABCL(msec) TABLE 2 Baseline Electrophysiologic Data Patients with an AAVC 799 ± ±18 15 ± ± 28 90± ± ± ± 57 Control Patients 792 ± ±32 45 ± ± ± ± ± ± 105 P Value 0, ERP = effective refractory [>eriod: AVBCL = atrioventricular block cycle length: VABCL = ventriculoatria! block cycle length; AAVC = accessory atrioventricular connection. induce atrialfibrillation (194 ± 28 msec) compared to atrial flutter (198 ± 25 msec) when both patient groups were considered together. Both control patients and patients with an AAVC had the same response to atrial pacing at each stage of the pacing protocol (Fig. 1). At each step of the pacing protocol, the cumulative yield of atrial fibrillation/flutter was similar in both groups of patients. Effects of Radiofrequency Ablation Among the 30 patients who underwent radiofrequency ablation of an AAVC, there was no difference in the inducibility or duration of atrial fibrillation or flutter after radiofrequency ahlation of the AAVC compared to baseline (Table 3). The mean pacing cycle length required to induce atrial libtillation/flutter after ablation (195 ± 25 msec) was not difterent than before abiation (199 ± 30 msec). Before and after radiofrequency ablation there was no difference in the response to the atrial pacing protocol (Fig. 2). At each step of the pacing protocol, the cumulative yield of atrial tibrilkitioii/lliitter was similar before and after radiofrequency ablation of the AAVC. Discussion This study demonstrates that a standardized, aggressive atrial pacing protocol results in the induction of atrial fibriiiation or flutter in nearly 100% of patients and that the incidence of alriaj fibrillation or flutter induction in patients with AAVCs is no different than in other patients referred for electrophysiologic evaluation. The cjther major finding of this study is that the incidence of atrial fibrillation induction, its duration, and the pacing cycle length required for induction are not altered after radiofrequency ablation of the AAVC. These findings indicate that the vulnerability of the atria to fibrillate in response to atrial burst pacing is independent of the presence of an AAVC. Previous studies evaluating atrial fibrillation 100%1 5 LU li 80%- 60%- 40%- 20%- AAVC patients. n=37 Conlfol patients. n=35 Uu. 0% PACING CYCLE LENGTH (ms) Figure 1. The cumulative yield of atrial fibrillation and fiutter at each pacing cycle length of the atrial overdrive pacing protocol for patients with accessory atrioventricular connections (AA VC) and control patients. There was no difference between the two groups with respect to the cumulative yield of atrial fibrillation and fiutter at each step in the pacing protocol.
4 502 Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology VoL 4. No. 5, October 1993 TABLE 3 Results of Atrial Pacing Before and After Ablation in 30 Patients with an Accessory Atrioventricular Connection Arrhythrnia Induced Atrial fibrillation Atrial flutter Duration of Arrhythmia Sustained Nonsustained Before Ablalion After Ahlation P =. There was lu) difference before and after ablation in the arrhythmias induced or the duration of the arrhythmias. inducibility before and after surgical or catheter ablation of AAVCs have found a lower incidence of inducibility after successful ablation.'-^ Sharma et al.' studied 38 patients before and after surgical ablation of an AAVC. During the presurgica! electrophysiologic study, atrial pacing at cycle lengths as short as 120 to 150 msec were used and atrial tibrillation was induced in 32 of the 38 patients; during the follow-up electrophysiologjc study, no patient had inducible atrial fibrillation, but atrial pacing was limited to cycle lengths greater than or equal to the atrioventricular block cycle lengths. Haissaguerre et al.- found a lower incidence of atrial fibrillation induction in patients 22 with a history of atriaj fibrillation after successful direct current ablation of AAVCs. In their study, only single or double atrial extrastimuli were used to induce atrial fibrillation and rapid atrial overdrive pacing was not performed. The major difference between our study and these previous studies is the atrial pacing protocols that were utilized. Our study used an aggressive atrial pacing protocol that was operator independent and standardized to be performed the same way in each case. The study of Sharma et al.' used different pacing protocols during the preand postablation electrophysiologic tests. In the study by Haissaguerre et al.,^ the pacing protocol used to induce atrial fibrillation was less aggressive than in our study and it is not clear that the same extrastimulus pacing techniques were used pre- and postablation, since tbe authors did not compare the coupling intervals or the number of extrastimuli used. Although the pacing protocol utilized in this study was aggres.sive and induced atrial fiuttcr or fibrillation in nearly 100% of patients, this does not limit its ability to evaluate the vulnerability of the atria to fibrillate. As Figuies 1 and 2 show, less aggressive protocols that would have limited the pacing cycle lengths to > 150 msec would have simply reduced the total percentage of patients with atrial fibrillation or fiutter induced but would not have produced any difference in inducibility ioo%n Before Ablation, n=30 Atter Ablation, n= _ PACING CYCLE LENGTH {ms) Figure 2. The cumulative yield of atrial fibrillation and fiutter at each pacing cycle length of the atrial overdrive pacing protocol in patients before and after successful radiofrequency catheter ablation of accessory atrioventricular connections. There was no difference in the cutnulative yield of atriat fibrillation or flutter at each step in the pacing protocol before and after successful ablation.
5 Kalbfieisch, etal. Inducibility of Atrial Fibrillation 503 between the different patient groups. There was a small but insignificant difference in the incidence of atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter induction between patients with an AAVC and control patients at pacing cycle lengths > 180 msec. However, as Figure 1 shows, this apparent difference was due to only a 10-msec shift to the right in the curve for the control patients. A limitation of this study is that only one method for assessing the vulnerability of the atrium to fibrillate was used. It is possible that other methods that utilized atrial extrastimulus techniques, different durations of burst pacing, or different pacing-pulse amplitudes may have had different results. The results of this study suggest that it is not a change in the vulnerability of the atrium to tibrillate that accounts for the reduction in the incidence of spontaneous atrial fihrillation after ablation of AAVCs, but instead it is some other factor such as elimination of atrioventricular reciprocating tachycardia or attenuation of ventriculoatrial conduction. Acknowledgment: The authors are grateful to Heidi Williams for her secretarial assistance in the preparation of this manuscript. References 1. Shamia A, Klein G, Guiraudon G, et al: Atrial tibrillation in patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrotne: Incidence after surgical ablation of Ihe accessory pathway. Circulation 1985:1: Haissaguerre M, Fischer B, Labbe T, ct al: Frequency of recurrent atrial fibrillation after catheier ablation of overt accessory pathways. Am J Cardiol 1991 ;69: Roark S, McCarthy E. Lee K. et al: Observations on the occurrence of atrial fibriliation in paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia. Am J Cardiol i986;57: Josepheson ME: Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology: Techniques and Interpretations. Lea & Febiger, Philadelphia, Wells JL, Karp RB, Kouchoukos NT, et al: Characterization of atrial fibrillation in man: Studies following open heart surgery. PACE 1978:1: Wells JL, MacLean WAH, James TN. et al: Characterization of atrial flutter: Studies in man after open heart surgery using fixed alrial electrodes. Circulation 1979:60:3: Calkins H, Langberg J, Sousa J, et al: Radiofrequency catheter ablation of accessory atrioventricular connections in 250 patients: Abbreviated therapeutic approach to Wolff-Parkin son-white syndrome. Circulation I992;85:1337-I346.
6
Double Retrograde Atrial Response After Radiofrequency. ablation of typical AV nodal tieentrant tachycardia
 Double Retrograde Atrial Response After Radiofrequency Ablation of Typical AV Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia STEVEN J. KALBFLEISCH, M.D., S. ADAM STRICKBERGER, M.D.. JOHN D. HUMMEL, M.D., BRIAN D. WILLIAMSON,
Double Retrograde Atrial Response After Radiofrequency Ablation of Typical AV Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia STEVEN J. KALBFLEISCH, M.D., S. ADAM STRICKBERGER, M.D.. JOHN D. HUMMEL, M.D., BRIAN D. WILLIAMSON,
Ventriculoatrial Block During a Narrow-QRS Tachycardia: What Is the Tachycardia Mechanism? IV
 174 ARRHYTHMIA OF THE MONTH Section Editor: Fred Morady, M.D. Ventriculoatrial Block During a Narrow-QRS Tachycardia: What Is the Tachycardia Mechanism? IV FRED MORADY, M.D. From the Cardiology Division,
174 ARRHYTHMIA OF THE MONTH Section Editor: Fred Morady, M.D. Ventriculoatrial Block During a Narrow-QRS Tachycardia: What Is the Tachycardia Mechanism? IV FRED MORADY, M.D. From the Cardiology Division,
H. Oddsson 1, N. Edvardsson and H. Walfridsson. Introduction
 Europace (2002) 4, 201 206 doi:10.1053/eupc.2002.0223, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Episodes of and atrial vulnerability after successful radiofrequency catheter ablation in patients
Europace (2002) 4, 201 206 doi:10.1053/eupc.2002.0223, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Episodes of and atrial vulnerability after successful radiofrequency catheter ablation in patients
Effects of Partial and Complete Ablation of the Slow Pathway on Fast Pathway Properties in Patients with Atrioventricular Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia
 645 Effects of Partial and Complete Ablation of the Slow Pathway on Fast Pathway Properties in Patients with Atrioventricular dal Reentrant Tachycardia S. ADAM STRICKBERGER, M.D., EMILE DAOUD, M.D., MARK
645 Effects of Partial and Complete Ablation of the Slow Pathway on Fast Pathway Properties in Patients with Atrioventricular dal Reentrant Tachycardia S. ADAM STRICKBERGER, M.D., EMILE DAOUD, M.D., MARK
Aortic Leaflet Perforation During Radiofrequency Ablation
 Aortic Leaflet Perforation During Radiofrequency Ablation MARK J. SEIFERT,* FRED MORADY,** HUGH G. CALKINS.** and JONATHAN J. LANGBERG** From the *Division of Internal Medicine and the **Divisian of Cardiology,
Aortic Leaflet Perforation During Radiofrequency Ablation MARK J. SEIFERT,* FRED MORADY,** HUGH G. CALKINS.** and JONATHAN J. LANGBERG** From the *Division of Internal Medicine and the **Divisian of Cardiology,
and fibrillation in pre-excitation (Wolff-Parkinson-
 British Heart Journal, 973, 35, 8ii-8i6. Factors regulating ventricular rates during atrial flutter and fibrillation in pre-excitation (Wolff-Parkinson- White) syndrome Agustin Castellanos, Jr., Robert
British Heart Journal, 973, 35, 8ii-8i6. Factors regulating ventricular rates during atrial flutter and fibrillation in pre-excitation (Wolff-Parkinson- White) syndrome Agustin Castellanos, Jr., Robert
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: WPW Revised: 11/2013
 Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: WPW Revised: 11/2013 Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW) is a syndrome of pre-excitation of the
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: WPW Revised: 11/2013 Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW) is a syndrome of pre-excitation of the
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 33, No. 3, by the American College of Cardiology ISSN /99/$20.
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 33, No. 3, 1999 1999 by the American College of Cardiology ISSN 0735-1097/99/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0735-1097(98)00614-7 A Technique
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 33, No. 3, 1999 1999 by the American College of Cardiology ISSN 0735-1097/99/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0735-1097(98)00614-7 A Technique
A Quantitative Fluoroscopic Comparison of the Coronary Sinus Ostium in Patients With and Without AV Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia
 681 A Quantitative Fluoroscopic Comparison of the Coronary Sinus Ostium in Patients With and Without AV Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia JOHN D. HUMMEL, M.D.. S. ADAM STRICKBERGER. M.D., K. CHING MAN, D.O.,
681 A Quantitative Fluoroscopic Comparison of the Coronary Sinus Ostium in Patients With and Without AV Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia JOHN D. HUMMEL, M.D.. S. ADAM STRICKBERGER. M.D., K. CHING MAN, D.O.,
Incessant Tachycardia Using a Concealed Atrionodal Bypass Tract
 191 Incessant Tachycardia Using a Concealed Atrionodal Bypass Tract ADAM ZIVIN, M.D., atid FRED MORADY, M.D. From the Division of Cardiology. Department of Internal Medicine, University of Michigan Medical
191 Incessant Tachycardia Using a Concealed Atrionodal Bypass Tract ADAM ZIVIN, M.D., atid FRED MORADY, M.D. From the Division of Cardiology. Department of Internal Medicine, University of Michigan Medical
Basic Electrophysiology Protocols
 Indian Journal of Cardiology ISSN-0972-1622 2012 by the Indian Society of Cardiology Vol. 15, (3-4), 27-37 [ 27 Review Article Shomu Bohora Assistant Professor, Deptt. of Cardiology, U.N. Mehta Institute
Indian Journal of Cardiology ISSN-0972-1622 2012 by the Indian Society of Cardiology Vol. 15, (3-4), 27-37 [ 27 Review Article Shomu Bohora Assistant Professor, Deptt. of Cardiology, U.N. Mehta Institute
A Narrow QRS Complex Tachycardia With An Apparently Concentric Retrograde Atrial Activation Sequence
 www.ipej.org 125 Case Report A Narrow QRS Complex Tachycardia With An Apparently Concentric Retrograde Atrial Activation Sequence Miguel A. Arias MD, PhD; Eduardo Castellanos MD, PhD; Alberto Puchol MD;
www.ipej.org 125 Case Report A Narrow QRS Complex Tachycardia With An Apparently Concentric Retrograde Atrial Activation Sequence Miguel A. Arias MD, PhD; Eduardo Castellanos MD, PhD; Alberto Puchol MD;
Atrioventricular (AV) Nodal Reentry Associated with 2:1 Infra-His Conduction Block during Tachycardia in a Patient with AV Nodal Triple Pathways
 Atrioventricular (AV) Nodal Reentry Associated with 2:1 Infra-His Conduction Block during Tachycardia in a Patient with AV Nodal Triple Pathways Haruhiko ABE, M.D., Takashi OHKITA, M.D., Masasuke FUJITA,
Atrioventricular (AV) Nodal Reentry Associated with 2:1 Infra-His Conduction Block during Tachycardia in a Patient with AV Nodal Triple Pathways Haruhiko ABE, M.D., Takashi OHKITA, M.D., Masasuke FUJITA,
480 April 2004 PACE, Vol. 27
 Incremental Value of Isolating the Right Inferior Pulmonary Vein During Pulmonary Vein Isolation Procedures in Patients With Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation HAKAN ORAL, AMAN CHUGH, CHRISTOPH SCHARF, BURR
Incremental Value of Isolating the Right Inferior Pulmonary Vein During Pulmonary Vein Isolation Procedures in Patients With Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation HAKAN ORAL, AMAN CHUGH, CHRISTOPH SCHARF, BURR
Results of Catheter Ablation of Ventricular Tachycardia Using Direct Current Shocks
 Results of Catheter Ablation of Ventricular Tachycardia Using Direct Current Shocks FRED MORADY, MELVIN M. SCHEINMAN, JERRY C. GRIFFIN, JOHN M. HERRE, and WILLIAM H. KOU From the Divisions of Cardiology,
Results of Catheter Ablation of Ventricular Tachycardia Using Direct Current Shocks FRED MORADY, MELVIN M. SCHEINMAN, JERRY C. GRIFFIN, JOHN M. HERRE, and WILLIAM H. KOU From the Divisions of Cardiology,
Bernard Belhassen, MD; Roman Fish, MD; Sami Viskin, MD; Aharon Glick, MD; Michael Glikson, MD; Michael Eldar, MD
 www.ipej.org 3 Original Article Incidence of Dual AV Node Physiology Following Termination of AV Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia by Adenosine-5'-Triphosphate: A Comparison with Drug Administration in Sinus
www.ipej.org 3 Original Article Incidence of Dual AV Node Physiology Following Termination of AV Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia by Adenosine-5'-Triphosphate: A Comparison with Drug Administration in Sinus
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 36, No. 2, by the American College of Cardiology ISSN /00/$20.
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 36, No. 2, 2000 2000 by the American College of Cardiology ISSN 0735-1097/00/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0735-1097(00)00770-1 Diagnostic
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 36, No. 2, 2000 2000 by the American College of Cardiology ISSN 0735-1097/00/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0735-1097(00)00770-1 Diagnostic
CATHETER ABLATION FOR TACHYCARDIAS
 190 CATHETER ABLATION FOR TACHYCARDIAS MASOOD AKHTAR, M.D. T ACHY ARRHYTHMIAS constitute a major cause of mortality and morbidity. The most serious manifestation of cardiac arrhythmia is sudden cardiac
190 CATHETER ABLATION FOR TACHYCARDIAS MASOOD AKHTAR, M.D. T ACHY ARRHYTHMIAS constitute a major cause of mortality and morbidity. The most serious manifestation of cardiac arrhythmia is sudden cardiac
Utility of Atrial and Ventricular Cycle Length Variability in Determining the Mechanism of Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia
 698 Utility of Atrial and Ventricular Cycle Length Variability in Determining the Mechanism of Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia THOMAS C. CRAWFORD, M.D., SIDDHARTH MUKERJI, M.D., ERIC GOOD, D.O.,
698 Utility of Atrial and Ventricular Cycle Length Variability in Determining the Mechanism of Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia THOMAS C. CRAWFORD, M.D., SIDDHARTH MUKERJI, M.D., ERIC GOOD, D.O.,
Case-Based Practical ECG Interpretation for the Generalist
 Case-Based Practical ECG Interpretation for the Generalist Paul D. Varosy, MD, FACC, FAHA, FHRS Director of Cardiac Electrophysiology VA Eastern Colorado Health Care System Associate Professor of Medicine
Case-Based Practical ECG Interpretation for the Generalist Paul D. Varosy, MD, FACC, FAHA, FHRS Director of Cardiac Electrophysiology VA Eastern Colorado Health Care System Associate Professor of Medicine
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT)
 Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) Bruce Stambler, MD Piedmont Heart Atlanta, GA Supraventricular Tachycardia Objectives Types and mechanisms AV nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT) AV reciprocating tachycardia
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) Bruce Stambler, MD Piedmont Heart Atlanta, GA Supraventricular Tachycardia Objectives Types and mechanisms AV nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT) AV reciprocating tachycardia
PARA-HISSIAN CONCEALED ACCESSORY PATHWAY
 PARA-HISSIAN CONCEALED ACCESSORY PATHWAY Anamnestic Findings 41 y.o. man with normal cardiac findings on echocardiography, suffering for paroxysmal supra-ventricular tachycardia since 1982 with rapid onset
PARA-HISSIAN CONCEALED ACCESSORY PATHWAY Anamnestic Findings 41 y.o. man with normal cardiac findings on echocardiography, suffering for paroxysmal supra-ventricular tachycardia since 1982 with rapid onset
Mechanism of Immediate Recurrences of Atrial Fibrillation After Restoration of Sinus Rhythm
 Mechanism of Immediate Recurrences of Atrial Fibrillation After Restoration of Sinus Rhythm AMAN CHUGH, MEHMET OZAYDIN, CHRISTOPH SCHARF, STEVE W.K. LAI, BURR HALL, PETER CHEUNG, FRANK PELOSI, JR, BRADLEY
Mechanism of Immediate Recurrences of Atrial Fibrillation After Restoration of Sinus Rhythm AMAN CHUGH, MEHMET OZAYDIN, CHRISTOPH SCHARF, STEVE W.K. LAI, BURR HALL, PETER CHEUNG, FRANK PELOSI, JR, BRADLEY
Pre-excited tachycardia: Atrial tachycardia with a bystander left lateral accessory pathway
 Pre-excited tachycardia: Atrial tachycardia with a bystander left lateral accessory pathway Jeffrey Munro, DO, Win-Kuang Shen, MD, FHRS, Komandoor Srivathsan, MD From the Department of Cardiovascular Disease,
Pre-excited tachycardia: Atrial tachycardia with a bystander left lateral accessory pathway Jeffrey Munro, DO, Win-Kuang Shen, MD, FHRS, Komandoor Srivathsan, MD From the Department of Cardiovascular Disease,
ARTICLE. Supraventricular Tachycardia in Infancy. Catherine D. DeAngelis, MD. In most infants, SVT is due to an accessory atrioventricular
 Supraventricular Tachycardia in Infancy Evaluation, Management, and Follow-up Susan P. Etheridge, MD; Victoria E. Judd, MD ARTICLE Background: Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) occurs frequently in infancy.
Supraventricular Tachycardia in Infancy Evaluation, Management, and Follow-up Susan P. Etheridge, MD; Victoria E. Judd, MD ARTICLE Background: Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) occurs frequently in infancy.
Differentiating Junctional Tachycardia and Atrioventricular Node Re-Entry Tachycardia Based on Response to Atrial Extrastimulus Pacing
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 52, No. 21, 2008 2008 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/08/$34.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2008.08.030
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 52, No. 21, 2008 2008 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/08/$34.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2008.08.030
Premature Atrial Contractions Managed With Slow Pathway Ablation
 Maced J Med Sci electronic publication ahead of print, published on November 25, 2008 as doi:10.3889/mjms.1857-5773.2008.0018 Trajkov et al. Slow Pathway Ablation Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.
Maced J Med Sci electronic publication ahead of print, published on November 25, 2008 as doi:10.3889/mjms.1857-5773.2008.0018 Trajkov et al. Slow Pathway Ablation Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.
Case 1 Left Atrial Tachycardia
 Case 1 Left Atrial Tachycardia A 16 years old woman was referred to our institution because of recurrent episodes of palpitations and dizziness despite previous ablation procedure( 13 years ago) of postero-septal
Case 1 Left Atrial Tachycardia A 16 years old woman was referred to our institution because of recurrent episodes of palpitations and dizziness despite previous ablation procedure( 13 years ago) of postero-septal
«Aσθενής με ασυμπτωματικό WPW και παροξυσμική κολπική μαρμαρυγή» Χάρης Κοσσυβάκης Επιμελητής A Καρδιολογικό Τμήμα Γ.Ν.Α. «Γ.
 «Aσθενής με ασυμπτωματικό WPW και παροξυσμική κολπική μαρμαρυγή» Χάρης Κοσσυβάκης Επιμελητής A Καρδιολογικό Τμήμα Γ.Ν.Α. «Γ. ΓΕΝΝΗΜΑΤΑΣ» the primary mechanism of SCD in patients with WPW is the rapid conduction
«Aσθενής με ασυμπτωματικό WPW και παροξυσμική κολπική μαρμαρυγή» Χάρης Κοσσυβάκης Επιμελητής A Καρδιολογικό Τμήμα Γ.Ν.Α. «Γ. ΓΕΝΝΗΜΑΤΑΣ» the primary mechanism of SCD in patients with WPW is the rapid conduction
COMPLEX CASE STUDY INNOVATIVE COLLECTIONS. Case presentation
 The Journal of Innovations in Cardiac Rhythm Management, 3 (2012), 939 943 INNOVATIVE COLLECTIONS COMPLEX CASE STUDY Subtle Changes in Electrogram Morphology During Para-Hisian Pacing Performed on IV Adenosine:
The Journal of Innovations in Cardiac Rhythm Management, 3 (2012), 939 943 INNOVATIVE COLLECTIONS COMPLEX CASE STUDY Subtle Changes in Electrogram Morphology During Para-Hisian Pacing Performed on IV Adenosine:
Catheter Ablation of Atypical Atrial Flutter after Cardiac Surgery Using a 3-D Mapping System
 Catheter Ablation of Atypical Atrial Flutter after Cardiac Surgery Using a 3-D Mapping System Myung-Jin Cha Seil Oh ECG & EP CASES Myung-Jin Cha, MD, Seil Oh, MD, PhD, FHRS Department of Internal Medicine,
Catheter Ablation of Atypical Atrial Flutter after Cardiac Surgery Using a 3-D Mapping System Myung-Jin Cha Seil Oh ECG & EP CASES Myung-Jin Cha, MD, Seil Oh, MD, PhD, FHRS Department of Internal Medicine,
Case Report Coexistence of Atrioventricular Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia and Idiopathic Left Ventricular Outflow-Tract Tachycardia
 www.ipej.org 149 Case Report Coexistence of Atrioventricular Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia and Idiopathic Left Ventricular Outflow-Tract Tachycardia Majid Haghjoo, M.D, Arash Arya, M.D, Mohammadreza Dehghani,
www.ipej.org 149 Case Report Coexistence of Atrioventricular Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia and Idiopathic Left Ventricular Outflow-Tract Tachycardia Majid Haghjoo, M.D, Arash Arya, M.D, Mohammadreza Dehghani,
The Effect of Rate on Prolongation of Ventricular Refractoriness by Quinidine in Humans
 The Effect of Rate on Prolongation of Ventricular Refractoriness by Quinidine in Humans SHIMON ROSENHECK, JOAO SOUSA, HUGH CALKINS, ALAN H. KADISH, and FRED MORADY From the Division of Cardiology, Department
The Effect of Rate on Prolongation of Ventricular Refractoriness by Quinidine in Humans SHIMON ROSENHECK, JOAO SOUSA, HUGH CALKINS, ALAN H. KADISH, and FRED MORADY From the Division of Cardiology, Department
A request for a log book extension must be put in writing and sent to BHRS, Unit 6B, Essex House, Cromwell Business Park, Chipping Norton,
 7 7. A request for a log book extension must be put in writing and sent to BHRS, Unit 6B, Essex House, Cromwell Business Park, Chipping Norton, Oxfordshire OX7 5SR. E-mail: admin@bhrs.com. Tel: 01789 867
7 7. A request for a log book extension must be put in writing and sent to BHRS, Unit 6B, Essex House, Cromwell Business Park, Chipping Norton, Oxfordshire OX7 5SR. E-mail: admin@bhrs.com. Tel: 01789 867
WPW syndrome and AVRT
 WPW syndrome and AVRT Myung-Yong Lee, MD, PhD Division of Cardiology Department of Internal Medicine School of Medicine Dankook University, Cheonan, Korea Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) Paroxysmal
WPW syndrome and AVRT Myung-Yong Lee, MD, PhD Division of Cardiology Department of Internal Medicine School of Medicine Dankook University, Cheonan, Korea Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) Paroxysmal
Unusual Tachycardia Association In A patient Without Structural Heart Disease
 www.ipej.org 233 Case Report Unusual Tachycardia Association In A patient Without Structural Heart Disease Eduardo Arana-Rueda, Alonso Pedrote, Lorena Garcia-Riesco, Manuel Frutos-Lopez, Juan A. Sanchez-Brotons
www.ipej.org 233 Case Report Unusual Tachycardia Association In A patient Without Structural Heart Disease Eduardo Arana-Rueda, Alonso Pedrote, Lorena Garcia-Riesco, Manuel Frutos-Lopez, Juan A. Sanchez-Brotons
Asymptomatic WPW Syndrome; Observation or Ablation? 전남대학교병원순환기내과 박형욱
 Asymptomatic WPW Syndrome; Observation or Ablation? 전남대학교병원순환기내과 박형욱 Let It Be? Vs. Just Do It? Natural history of asymptomatic WPW Incidence of sudden cardiac death in natural history studies involving
Asymptomatic WPW Syndrome; Observation or Ablation? 전남대학교병원순환기내과 박형욱 Let It Be? Vs. Just Do It? Natural history of asymptomatic WPW Incidence of sudden cardiac death in natural history studies involving
EHRA Accreditation Exam - Sample MCQs Invasive cardiac electrophysiology
 EHRA Accreditation Exam - Sample MCQs Invasive cardiac electrophysiology Dear EHRA Member, Dear Colleague, As you know, the EHRA Accreditation Process is becoming increasingly recognised as an important
EHRA Accreditation Exam - Sample MCQs Invasive cardiac electrophysiology Dear EHRA Member, Dear Colleague, As you know, the EHRA Accreditation Process is becoming increasingly recognised as an important
Title. CitationJournal of Electrocardiology, 39(4): Issue Date Doc URL. Type. File Information. coronary sinus ostium
 Title Nonreentrant atrioventricular nodal tachycardia due coronary sinus ostium Author(s)Yokoshiki, Hisashi; Sasaki, Koji; Shimokawa, Junichi CitationJournal of Electrocardiology, 39(4): 395-399 Issue
Title Nonreentrant atrioventricular nodal tachycardia due coronary sinus ostium Author(s)Yokoshiki, Hisashi; Sasaki, Koji; Shimokawa, Junichi CitationJournal of Electrocardiology, 39(4): 395-399 Issue
Debate: Asymptomatic Patients with Ventricular Preexcitation Require EP Testing for Risk Stratification. Carlo Pappone, MD, PhD, FACC
 Debate: Asymptomatic Patients with Ventricular Preexcitation Require EP Testing for Risk Stratification Carlo Pappone, MD, PhD, FACC The Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome Demographics Δ waves detectable on
Debate: Asymptomatic Patients with Ventricular Preexcitation Require EP Testing for Risk Stratification Carlo Pappone, MD, PhD, FACC The Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome Demographics Δ waves detectable on
Characteristics of Rapid Rhythms Recorded Within Pulmonary Veins During Atrial Fibrillation
 Characteristics of Rapid Rhythms Recorded Within Pulmonary Veins During Atrial Fibrillation HIROSHI TADA, MEHMET ÖZAYDIN, HAKAN ORAL, BRADLEY P. KNIGHT, AMAN CHUGH, CHRISTOPH SCHARF, FRANK PELOSI, Jr.,
Characteristics of Rapid Rhythms Recorded Within Pulmonary Veins During Atrial Fibrillation HIROSHI TADA, MEHMET ÖZAYDIN, HAKAN ORAL, BRADLEY P. KNIGHT, AMAN CHUGH, CHRISTOPH SCHARF, FRANK PELOSI, Jr.,
Comparison of Endocardial Activation Times at Effective and Ineffective Ablation Sites Within the Pulmonary Veins
 155 Comparison of Endocardial Activation Times at Effective and Ineffective Ablation Sites Within the Pulmonary Veins HUNG-FAT TSE, M.B.B.S.. CHU-PAK LAU, M.D., WILLIAM KOU, M.D.,* FRANK PFLOSI, M.D./^
155 Comparison of Endocardial Activation Times at Effective and Ineffective Ablation Sites Within the Pulmonary Veins HUNG-FAT TSE, M.B.B.S.. CHU-PAK LAU, M.D., WILLIAM KOU, M.D.,* FRANK PFLOSI, M.D./^
Case Report Simultaneous Accessory Pathway and AV Node Mechanical Block
 185 Case Report Simultaneous Accessory Pathway and AV Node Mechanical Block Daniel Garofalo, MD, FRACP, Alfonso Gomez Gallanti, MD, David Filgueiras Rama, MD, Rafael Peinado Peinado, PhD, FESC Unidad de
185 Case Report Simultaneous Accessory Pathway and AV Node Mechanical Block Daniel Garofalo, MD, FRACP, Alfonso Gomez Gallanti, MD, David Filgueiras Rama, MD, Rafael Peinado Peinado, PhD, FESC Unidad de
ACC/AHA Guidelines for Ambulatory Electrocardiography: Executive Summary and Recommendations
 (Circulation. 1999;100:886-893.) 1999 American Heart Association, Inc. ACC/AHA Practice Guidelines ACC/AHA Guidelines for Ambulatory Electrocardiography: Executive Summary and Recommendations A Report
(Circulation. 1999;100:886-893.) 1999 American Heart Association, Inc. ACC/AHA Practice Guidelines ACC/AHA Guidelines for Ambulatory Electrocardiography: Executive Summary and Recommendations A Report
Catheter Ablation of Supraventricular Arrhythmias: State of the Art
 124 NASPE 25TH ANNIVERSARY SERIES Catheter Ablation of Supraventricular Arrhythmias: State of the Art FRED MORADY, M.D. From the Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine, University of Michigan,
124 NASPE 25TH ANNIVERSARY SERIES Catheter Ablation of Supraventricular Arrhythmias: State of the Art FRED MORADY, M.D. From the Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine, University of Michigan,
Electrophysiologic Properties of Pulmonary Veins Assessed Using a Multielectrode Basket Catheter
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 43, No. 12, 2004 2004 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/04/$30.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2004.01.051
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 43, No. 12, 2004 2004 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/04/$30.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2004.01.051
Recent studies have demonstrated
 Hellenic J Cardiol 43: 204-208, 2002 The Predictive Accuracy of the RR Interval Distribution Pattern in the Detection of Dual AV Node Physiology in Patients with Chronic Atrial Fibrillation CONSTANTINE
Hellenic J Cardiol 43: 204-208, 2002 The Predictive Accuracy of the RR Interval Distribution Pattern in the Detection of Dual AV Node Physiology in Patients with Chronic Atrial Fibrillation CONSTANTINE
II V 1 HRA 3 4 HB 5 6 HB 3 4 HB 1 2 CS 7 8 CS 5 6 CS 3 4 CS 1 2 ABL 3 4 ABL 1 2 RVA 3 4. T. Suga et al.
 Table 1. The distance between the positions of the catheter tip Patient Location Before elimination of After elimination of Number of the the accessory pathway the accessory pathway accessory pathway RAO
Table 1. The distance between the positions of the catheter tip Patient Location Before elimination of After elimination of Number of the the accessory pathway the accessory pathway accessory pathway RAO
AF Today: W. For the majority of patients with atrial. are the Options? Chris Case
 AF Today: W hat are the Options? Management strategies for patients with atrial fibrillation should depend on the individual patient. Treatment with medications seems adequate for most patients with atrial
AF Today: W hat are the Options? Management strategies for patients with atrial fibrillation should depend on the individual patient. Treatment with medications seems adequate for most patients with atrial
Reentry in a Pulmonary Vein as a Possible Mechanism of Focal Atrial Fibrillation
 824 Reentry in a Pulmonary Vein as a Possible Mechanism of Focal Atrial Fibrillation BERNARD BELHASSEN, M.D., AHARON GLICK, M.D., and SAMI VISKIN, M.D. From the Department of Cardiology, Tel-Aviv Sourasky
824 Reentry in a Pulmonary Vein as a Possible Mechanism of Focal Atrial Fibrillation BERNARD BELHASSEN, M.D., AHARON GLICK, M.D., and SAMI VISKIN, M.D. From the Department of Cardiology, Tel-Aviv Sourasky
EHRA Accreditation Exam - Sample MCQs Cardiac Pacing and ICDs
 EHRA Accreditation Exam - Sample MCQs Cardiac Pacing and ICDs Dear EHRA Member, Dear Colleague, As you know, the EHRA Accreditation Process is becoming increasingly recognised as an important step for
EHRA Accreditation Exam - Sample MCQs Cardiac Pacing and ICDs Dear EHRA Member, Dear Colleague, As you know, the EHRA Accreditation Process is becoming increasingly recognised as an important step for
Case Report Left Ventricular Dysfunction Caused by Unrecognized Surgical AV block in a Patient with a Manifest Right Free Wall Accessory Pathway
 109 Case Report Left Ventricular Dysfunction Caused by Unrecognized Surgical AV block in a Patient with a Manifest Right Free Wall Accessory Pathway Rakesh Gopinathannair, MD, MA 1, Dwayne N Campbell,
109 Case Report Left Ventricular Dysfunction Caused by Unrecognized Surgical AV block in a Patient with a Manifest Right Free Wall Accessory Pathway Rakesh Gopinathannair, MD, MA 1, Dwayne N Campbell,
Adenosine Mapping for Adenosine-Dependent Accessory Pathway Ablation
 Adenosine Mapping for Adenosine-Dependent Accessory Pathway Ablation MARTIN J. LAPAGE, M.D., M.S.,* MICHAEL J. WALSH, M.D., JOHN H. REED, M.D., M.P.H., and J. PHILIP SAUL, M.D. From the *Department of
Adenosine Mapping for Adenosine-Dependent Accessory Pathway Ablation MARTIN J. LAPAGE, M.D., M.S.,* MICHAEL J. WALSH, M.D., JOHN H. REED, M.D., M.P.H., and J. PHILIP SAUL, M.D. From the *Department of
Impedance Monitoring During Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation in Humans
 Impedance onitoring During Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation in Humans ARK HARVEY, YOON-NYUN KI, JOAO SOUSA, RAEL EL-ATASSI, RED ORADY, HUGH CALKINS, and JONATHAN J. LANGBERG rom the Department of Intemal
Impedance onitoring During Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation in Humans ARK HARVEY, YOON-NYUN KI, JOAO SOUSA, RAEL EL-ATASSI, RED ORADY, HUGH CALKINS, and JONATHAN J. LANGBERG rom the Department of Intemal
Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome
 Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome www.consultant360.com /articles/wolff-parkinson-white-syndrome A 37-year-old woman presented to the office with intermittent dizziness, palpitations, and multiple syncopal
Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome www.consultant360.com /articles/wolff-parkinson-white-syndrome A 37-year-old woman presented to the office with intermittent dizziness, palpitations, and multiple syncopal
'Dual atrioventricular nodal pathways' in patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome*
 Br Heart 7 1980; 43: 7-13 'Dual atrioventricular nodal pathways' in patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome* EDWARD L C PRITCHETT, ERIC N PRYSTOWSKY, DAVID G BENDITT, JOHN J GALLAGHER From the Division
Br Heart 7 1980; 43: 7-13 'Dual atrioventricular nodal pathways' in patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome* EDWARD L C PRITCHETT, ERIC N PRYSTOWSKY, DAVID G BENDITT, JOHN J GALLAGHER From the Division
From the Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan
 Reprinted with permission from JOURNAL OF CARDIOVASCULAR ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY, Volume 13, No. 7, July 2002 Copyright 2002 by Futura Publishing Company, Inc., Armonk, NY 10504-0418 Mechanistic Signi cance
Reprinted with permission from JOURNAL OF CARDIOVASCULAR ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY, Volume 13, No. 7, July 2002 Copyright 2002 by Futura Publishing Company, Inc., Armonk, NY 10504-0418 Mechanistic Signi cance
Self-assessment corner
 Postgrad Med J 1995; 71: 181-185 C) The Fellowship of Postgraduate Medicine, 1995 Self-assessment corner Department of Cardiology, Royal Liverpool University Hospital, Liverpool L7 8XP, UK SS Mushahwar
Postgrad Med J 1995; 71: 181-185 C) The Fellowship of Postgraduate Medicine, 1995 Self-assessment corner Department of Cardiology, Royal Liverpool University Hospital, Liverpool L7 8XP, UK SS Mushahwar
How to ablate typical slow/fast AV nodal reentry tachycardia
 Europace (2000) 2, 15 19 Article No. eupc.1999.0070, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on OW TO... SERIES ow to ablate typical slow/fast AV nodal reentry tachycardia. eidbüchel Department
Europace (2000) 2, 15 19 Article No. eupc.1999.0070, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on OW TO... SERIES ow to ablate typical slow/fast AV nodal reentry tachycardia. eidbüchel Department
Asymptomatic patient with WPW
 Asymptomatic patient with WPW Dimosthenis Avramidis, MD. Arrythmiologist Mitera Children s Hospital Athens Greece Scientific Associate 1st Cardiology Dpt Evangelismos Hospital Athens Greece Preexcitation
Asymptomatic patient with WPW Dimosthenis Avramidis, MD. Arrythmiologist Mitera Children s Hospital Athens Greece Scientific Associate 1st Cardiology Dpt Evangelismos Hospital Athens Greece Preexcitation
Mechanism of Ventricular Tachycardia Termination by Pacing at Left Ventricular Sites in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease
 Journal of Interventional Cardiac Electrophysiology 6, 35 41, 2002 C 2002 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Manufactured in The Netherlands. Mechanism of Ventricular Tachycardia Termination by Pacing at Left
Journal of Interventional Cardiac Electrophysiology 6, 35 41, 2002 C 2002 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Manufactured in The Netherlands. Mechanism of Ventricular Tachycardia Termination by Pacing at Left
PERMANENT PACEMAKERS AND IMPLANTABLE DEFIBRILLATORS Considerations for intensivists
 PERMANENT PACEMAKERS AND IMPLANTABLE DEFIBRILLATORS Considerations for intensivists Craig A. McPherson, MD, FACC Associate Professor of Medicine Constantine Manthous, MD, FACP, FCCP Associate Clinical
PERMANENT PACEMAKERS AND IMPLANTABLE DEFIBRILLATORS Considerations for intensivists Craig A. McPherson, MD, FACC Associate Professor of Medicine Constantine Manthous, MD, FACP, FCCP Associate Clinical
Erdem DiRER,1 MD, Murat OZDEMIR, MD, U. Kemal TEZCAN, MD, Sinan AYDOGDU, MD, Sule KORKMAZ, MD, Yalcim SOZUTEK, MD, and Emine KUTUK, MD
 Can Isolated, Symptomatic, Frequent Ventricular Premature Depolarizations be a Predictor of an Inducible Ventricular Tachycardia? Treatment by Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation Erdem DiRER,1 MD, Murat OZDEMIR,
Can Isolated, Symptomatic, Frequent Ventricular Premature Depolarizations be a Predictor of an Inducible Ventricular Tachycardia? Treatment by Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation Erdem DiRER,1 MD, Murat OZDEMIR,
Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology
 Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills expected of
Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills expected of
Case Report Wide-QRS Tachycardia Inducible by Both Atrial and Ventricular Pacing
 Hellenic J Cardiol 2008; 49: 446-450 Case Report Wide-QRS Tachycardia Inducible by Both Atrial and Ventricular Pacing ELEFTHERIOS GIAZITZOGLOU, DEMOSTHENES G. KATRITSIS Department of Cardiology, Athens
Hellenic J Cardiol 2008; 49: 446-450 Case Report Wide-QRS Tachycardia Inducible by Both Atrial and Ventricular Pacing ELEFTHERIOS GIAZITZOGLOU, DEMOSTHENES G. KATRITSIS Department of Cardiology, Athens
Clinical and Electrocardiographic Characteristics of Patients with Brugada Syndrome: Report of Five Cases of Documented Ventricular Fibrillation
 J Arrhythmia Vol 25 No 1 2009 Original Article Clinical and Electrocardiographic Characteristics of Patients with Brugada Syndrome: Report of Five Cases of Documented Ventricular Fibrillation Seiji Takashio
J Arrhythmia Vol 25 No 1 2009 Original Article Clinical and Electrocardiographic Characteristics of Patients with Brugada Syndrome: Report of Five Cases of Documented Ventricular Fibrillation Seiji Takashio
Case Report. Rajaie Cardiovascular, Medical and Research Center, Iran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. 2
 TEHRAN HEART CENTER Case Report Radiofrequency Ablation of Accessory Pathways in Children with Complex Congenital Cardiac Lesions: A Report of Three Cases Mohammad Dalili, MD *1, Jayakeerthi Y Rao, MD
TEHRAN HEART CENTER Case Report Radiofrequency Ablation of Accessory Pathways in Children with Complex Congenital Cardiac Lesions: A Report of Three Cases Mohammad Dalili, MD *1, Jayakeerthi Y Rao, MD
JIUNN-LEE LIN, MD, SHOEI K. STEPHEN HUANG, MD, FACC, LING-PING LAI, MD, WEN-CHIN KO, MD, YUNG-ZU TSENG, MD, WEN-PIN LIEN, MD, FACC
 JACC Vol. 31, No. 4 March 15, 1998:855 60 855 ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY Clinical and Electrophysiologic Characteristics and Long-Term Efficacy of Slow-Pathway Catheter Ablation in Patients With Spontaneous Supraventricular
JACC Vol. 31, No. 4 March 15, 1998:855 60 855 ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY Clinical and Electrophysiologic Characteristics and Long-Term Efficacy of Slow-Pathway Catheter Ablation in Patients With Spontaneous Supraventricular
file://c:\documents and Settings\admin\My Documents\CV\92.htm
 Page 1 of 5 Amir Farjam Fazelifar, M.D. Assistant Professor of Cardiac Electrophysiology Academic Address: Shaheed Rajaei Cardiovascular, Medical & Research Center, Vali- Asr Avenue Tehran- Iran Tel /
Page 1 of 5 Amir Farjam Fazelifar, M.D. Assistant Professor of Cardiac Electrophysiology Academic Address: Shaheed Rajaei Cardiovascular, Medical & Research Center, Vali- Asr Avenue Tehran- Iran Tel /
Successful treatment of tachycardia-induced cardiomyopathy secondary to dual atrioventricular nodal nonreentrant tachycardia using cryoablation
 Successful treatment of tachycardia-induced cardiomyopathy secondary to dual atrioventricular nodal nonreentrant tachycardia using cryoablation Harold Rivner, MD, * Chris Healy, MD, Raul D. Mitrani, MD,
Successful treatment of tachycardia-induced cardiomyopathy secondary to dual atrioventricular nodal nonreentrant tachycardia using cryoablation Harold Rivner, MD, * Chris Healy, MD, Raul D. Mitrani, MD,
Chapter 16: Arrhythmias and Conduction Disturbances
 Complete the following. Chapter 16: Arrhythmias and Conduction Disturbances 1. Cardiac arrhythmias result from abnormal impulse, abnormal impulse, or both mechanisms together. 2. is the ability of certain
Complete the following. Chapter 16: Arrhythmias and Conduction Disturbances 1. Cardiac arrhythmias result from abnormal impulse, abnormal impulse, or both mechanisms together. 2. is the ability of certain
Original Article Cryoablation of Anteroseptal Accessory Pathways with a His Bundle Electrogram on the Ablation Catheter
 284 Original Article Cryoablation of Anteroseptal Accessory Pathways with a His Bundle Electrogram on the Ablation Catheter Leonardo Liberman, MD,David S. Spar, MD, Mary C. Nash, RN and Eric S. Silver,
284 Original Article Cryoablation of Anteroseptal Accessory Pathways with a His Bundle Electrogram on the Ablation Catheter Leonardo Liberman, MD,David S. Spar, MD, Mary C. Nash, RN and Eric S. Silver,
Catheter Ablation: Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common. Another Option for AF FAQ. Who performs ablation for treatment of AF?
 : Another Option for AF Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a highly common cardiac arrhythmia and a major risk factor for stroke. In this article, Dr. Khan and Dr. Skanes detail how catheter ablation significantly
: Another Option for AF Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a highly common cardiac arrhythmia and a major risk factor for stroke. In this article, Dr. Khan and Dr. Skanes detail how catheter ablation significantly
Pediatrics. Arrhythmias in Children: Bradycardia and Tachycardia Diagnosis and Treatment. Overview
 Pediatrics Arrhythmias in Children: Bradycardia and Tachycardia Diagnosis and Treatment See online here The most common form of cardiac arrhythmia in children is sinus tachycardia which can be caused by
Pediatrics Arrhythmias in Children: Bradycardia and Tachycardia Diagnosis and Treatment See online here The most common form of cardiac arrhythmia in children is sinus tachycardia which can be caused by
Tokyo and Kawasaki, Japan
 JACC Vol. 32, No. 6 November 15, 1998:1731 40 1731 Heterogeneity of Anterograde Fast-Pathway and Retrograde Slow-Pathway Conduction Patterns in Patients With the Fast Slow Form of Atrioventricular Nodal
JACC Vol. 32, No. 6 November 15, 1998:1731 40 1731 Heterogeneity of Anterograde Fast-Pathway and Retrograde Slow-Pathway Conduction Patterns in Patients With the Fast Slow Form of Atrioventricular Nodal
Mission Statement for our Arrhythmia Care
 Mission Statement for our Arrhythmia Care We are dedicated to provide a compassionate and an outstanding care for patients with cardiac arrhythmias. We will be utilizing the cutting edge and the most advanced
Mission Statement for our Arrhythmia Care We are dedicated to provide a compassionate and an outstanding care for patients with cardiac arrhythmias. We will be utilizing the cutting edge and the most advanced
Ji-Eun Ban, MD, Sang-Weon Park, MD, Hyun-Soo Lee, MPH, Jong-Il Choi, MD, and Young-Hoon Kim, MD
 Case Report Print SSN 1738-5520 On-line SSN 1738-5555 Korean Circulation Journal Swallowing-nduced Atrial Tachyarrhythmias Successfully Ablated at the Left Posterior nteratrial Septum in Patient with Wolff-Parkinson-White
Case Report Print SSN 1738-5520 On-line SSN 1738-5555 Korean Circulation Journal Swallowing-nduced Atrial Tachyarrhythmias Successfully Ablated at the Left Posterior nteratrial Septum in Patient with Wolff-Parkinson-White
Declaration of conflict of interest NONE
 Declaration of conflict of interest NONE Transatlantic Electrophysiology Lessons for and from Iberoamerica European Society of Cardiology Mexican Society of Cardiology Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome in
Declaration of conflict of interest NONE Transatlantic Electrophysiology Lessons for and from Iberoamerica European Society of Cardiology Mexican Society of Cardiology Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome in
Characteristics of systolic and diastolic potentials recorded in the left interventricular septum in verapamil-sensitive left ventricular tachycardia
 CASE REPORT Cardiology Journal 2012, Vol. 19, No. 4, pp. 418 423 10.5603/CJ.2012.0075 Copyright 2012 Via Medica ISSN 1897 5593 Characteristics of systolic and diastolic potentials recorded in the left
CASE REPORT Cardiology Journal 2012, Vol. 19, No. 4, pp. 418 423 10.5603/CJ.2012.0075 Copyright 2012 Via Medica ISSN 1897 5593 Characteristics of systolic and diastolic potentials recorded in the left
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 37, No. 6, by the American College of Cardiology ISSN /01/$20.
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 37, No. 6, 2001 2001 by the American College of Cardiology ISSN 0735-1097/01/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0735-1097(01)01206-2 Optimized
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 37, No. 6, 2001 2001 by the American College of Cardiology ISSN 0735-1097/01/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0735-1097(01)01206-2 Optimized
STEVEN J. KALBFLEISCH, MD, RAFAEL EL-ATASSI,, FACC, JONATHAN J. LANGBERG, MD, FACC, FRED MORADY, MD, FACC
 50 JACC vi\! 1- T.--. -., I., I hi:); 8993:80.-1 STEVEN J. KALBFLEISCH, MD, RAFAEL EL-ATASSI,, FACC, JONATHAN J. LANGBERG, MD, FACC, FRED MORADY, MD, FACC Ann Arbor, Michigan Obj&ves. The puqmse of this
50 JACC vi\! 1- T.--. -., I., I hi:); 8993:80.-1 STEVEN J. KALBFLEISCH, MD, RAFAEL EL-ATASSI,, FACC, JONATHAN J. LANGBERG, MD, FACC, FRED MORADY, MD, FACC Ann Arbor, Michigan Obj&ves. The puqmse of this
Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia PSVT.
 Atrial Tachycardia; is the name for an arrhythmia caused by a disorder of the impulse generation in the atrium or the AV node. An area in the atrium sends out rapid signals, which are faster than those
Atrial Tachycardia; is the name for an arrhythmia caused by a disorder of the impulse generation in the atrium or the AV node. An area in the atrium sends out rapid signals, which are faster than those
Analysis During Sinus Rhythm of Critical Sites in Reentry Circuits of Postinfarction Ventricular Tachycardia
 Journal of Interventional Cardiac Electrophysiology 7, 95 103, 2002 C 2002 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Manufactured in The Netherlands. Analysis During Sinus Rhythm of Critical Sites in Reentry Circuits
Journal of Interventional Cardiac Electrophysiology 7, 95 103, 2002 C 2002 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Manufactured in The Netherlands. Analysis During Sinus Rhythm of Critical Sites in Reentry Circuits
Original Article. Tehran Heart Center, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
 TEHRAN HEART CENTER Original Article Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation of Atrioventricular Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia: Success Rates and Complications during 14 Years of Experience Ahmad Yaminisharif,
TEHRAN HEART CENTER Original Article Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation of Atrioventricular Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia: Success Rates and Complications during 14 Years of Experience Ahmad Yaminisharif,
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common sustained
 Chronic Atrial Fibrillation in Patients With Rheumatic Heart Disease Mapping and Radiofrequency Ablation of Flutter Circuits Seen at Initiation After Cardioversion Mohan Nair, MD; Prasad Shah, MD; Ravinder
Chronic Atrial Fibrillation in Patients With Rheumatic Heart Disease Mapping and Radiofrequency Ablation of Flutter Circuits Seen at Initiation After Cardioversion Mohan Nair, MD; Prasad Shah, MD; Ravinder
Arrhythmia Management Joshua M. Cooper, MD, FHRS, FACC
 Arrhythmia Management Joshua M. Cooper, MD, FHRS, FACC Professor of Medicine Director of Cardiac Electrophysiology Temple University Health System Plumbing Electrical System Bradyarrhythmias Sinus Node
Arrhythmia Management Joshua M. Cooper, MD, FHRS, FACC Professor of Medicine Director of Cardiac Electrophysiology Temple University Health System Plumbing Electrical System Bradyarrhythmias Sinus Node
From the Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, University of Michigan Medical Center, Ann Arbor, Michigan
 118 Reprinted with permission from JOURNAL OF CARDIOVASCULAR ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY, Volume 13, No. 2, February 2002 Copyright 2002 by Futura Publishing Company, Inc., Armonk, NY 10504-0418 Differentiation
118 Reprinted with permission from JOURNAL OF CARDIOVASCULAR ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY, Volume 13, No. 2, February 2002 Copyright 2002 by Futura Publishing Company, Inc., Armonk, NY 10504-0418 Differentiation
Repetitive narrow QRS tachycardia in a 61-year-old female patient with recent palpitations
 Journal of Geriatric Cardiology (2018) 15: 193 198 2018 JGC All rights reserved; www.jgc301.com Case Report Open Access Repetitive narrow QRS tachycardia in a 61-year-old female patient with recent palpitations
Journal of Geriatric Cardiology (2018) 15: 193 198 2018 JGC All rights reserved; www.jgc301.com Case Report Open Access Repetitive narrow QRS tachycardia in a 61-year-old female patient with recent palpitations
小児および若年者の特発性心房粗動, 心房細動の頻度と特徴 臨床群と誘発群の比較検討
 原 著 PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY and CARDIAC SURGERY VOL. 26 NO. 4 (332 337) 小児および若年者の特発性心房粗動, 心房細動の頻度と特徴 臨床群と誘発群の比較検討 key words: atrial flutter, atrial fibrillation, electrophysiological study, radiofrequency
原 著 PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY and CARDIAC SURGERY VOL. 26 NO. 4 (332 337) 小児および若年者の特発性心房粗動, 心房細動の頻度と特徴 臨床群と誘発群の比較検討 key words: atrial flutter, atrial fibrillation, electrophysiological study, radiofrequency
Self-Conversion of Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia by Radio-frequency-Triggered Pacemaker
 Self-Conversion of Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia by Radio-frequency-Triggered Pacemaker Parashos Geleris, M.D., Harisios Boudoulas, M.D., Stephen F. Schaal, M.D., and Charles Meckstroth, M.D. ABSTRACT
Self-Conversion of Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia by Radio-frequency-Triggered Pacemaker Parashos Geleris, M.D., Harisios Boudoulas, M.D., Stephen F. Schaal, M.D., and Charles Meckstroth, M.D. ABSTRACT
Uncommon Atrial Flutter Originating in the Left Atrioventricular Groove
 Jpn Circ J 1999; 63: 416 420 Uncommon Atrial Flutter Originating in the Left Atrioventricular Groove Emergence After Successful Catheter Ablation for a Left Concealed Accessory Pathway Yoshinori Kobayashi,
Jpn Circ J 1999; 63: 416 420 Uncommon Atrial Flutter Originating in the Left Atrioventricular Groove Emergence After Successful Catheter Ablation for a Left Concealed Accessory Pathway Yoshinori Kobayashi,
Catheter Ablation of Atrial Tachycardia Originating from the Tip of Right Atrial Appendage
 Case Report Catheter Ablation of Atrial Tachycardia Originating from the Tip of Right Atrial Appendage Masaru Inoue MD, Takao Matsubara MD, Toshihiko Yasuda MD, Kenji Miwa MD, Tadatsugu Gamou MD, Hounin
Case Report Catheter Ablation of Atrial Tachycardia Originating from the Tip of Right Atrial Appendage Masaru Inoue MD, Takao Matsubara MD, Toshihiko Yasuda MD, Kenji Miwa MD, Tadatsugu Gamou MD, Hounin
In certain cases of supraventricular
 Case Report Hellenic J Cardiol 2013; 54: 469-473 A Tachycardia with Varying QRS Morphology and RP Intervals: Differential Diagnosis and Therapy Socrates Korovesis, Eleftherios Giazitzoglou, Demosthenes
Case Report Hellenic J Cardiol 2013; 54: 469-473 A Tachycardia with Varying QRS Morphology and RP Intervals: Differential Diagnosis and Therapy Socrates Korovesis, Eleftherios Giazitzoglou, Demosthenes
BHRS Prep course Pub style Quiz NOT A
 BHRS Prep course Pub style Quiz NOT A Round 1 Quiz questions Common ECG s in CRM Colin Cunnington Over the past 3 months, a 24-yearold man who works as a truck driver has had frequent episodes of pre-syncope
BHRS Prep course Pub style Quiz NOT A Round 1 Quiz questions Common ECG s in CRM Colin Cunnington Over the past 3 months, a 24-yearold man who works as a truck driver has had frequent episodes of pre-syncope
InterQual Care Planning SIM plus Criteria 2014 Clinical Revisions
 InterQual Care Planning SIM plus Criteria 2014 Clinical Revisions The Clinical Revisions provide details of changes to InterQual Clinical Criteria. They do not provide information on changes made to CareEnhance
InterQual Care Planning SIM plus Criteria 2014 Clinical Revisions The Clinical Revisions provide details of changes to InterQual Clinical Criteria. They do not provide information on changes made to CareEnhance
were inserted into the right femoral vein and positioned system and intracardiac recordings were displayed
 CASE REPORTS Termination of Ventricular Tachycardia by Carotid Sinus Massage DAVID S. HESS, M.D., TIMOTHY HANLON, M.D., MELVIN SCHEINMAN, M.D., ROGER BUDGE, M.D., AND JAWAHAR DESAI, M.D. SUMMARY Intracardiac
CASE REPORTS Termination of Ventricular Tachycardia by Carotid Sinus Massage DAVID S. HESS, M.D., TIMOTHY HANLON, M.D., MELVIN SCHEINMAN, M.D., ROGER BUDGE, M.D., AND JAWAHAR DESAI, M.D. SUMMARY Intracardiac
Antifibrotic Therapy Delays Progression from Paroxysmal to Persistent Atrial Fibrillation
 Antifibrotic Therapy Delays Progression from Paroxysmal to Persistent Atrial Fibrillation José Jalife, M.D. Center for Arrhythmia Research University of Michigan No Disclosures The mechanisms that maintain
Antifibrotic Therapy Delays Progression from Paroxysmal to Persistent Atrial Fibrillation José Jalife, M.D. Center for Arrhythmia Research University of Michigan No Disclosures The mechanisms that maintain
A Randomized Study of Prophylactic Catheter Ablation in Asymptomatic Patients with the Wolff Parkinson White Syndrome
 original article A Randomized Study of Prophylactic Catheter Ablation in Asymptomatic Patients with the Wolff Parkinson White Syndrome Carlo Pappone, M.D., Ph.D., Vincenzo Santinelli, M.D., Francesco Manguso,
original article A Randomized Study of Prophylactic Catheter Ablation in Asymptomatic Patients with the Wolff Parkinson White Syndrome Carlo Pappone, M.D., Ph.D., Vincenzo Santinelli, M.D., Francesco Manguso,
CARDIOINSIGHT TM NONINVASIVE 3D MAPPING SYSTEM CLINICAL EVIDENCE SUMMARY
 CARDIOINSIGHT TM NONINVASIVE 3D MAPPING SYSTEM CLINICAL EVIDENCE SUMMARY April 2017 SUPPORTING EVIDENCE RHYTHM AF VT PUBLICATIONS Driver Domains in Persistent Atrial Fibrillation (Haissaiguerre, et al)
CARDIOINSIGHT TM NONINVASIVE 3D MAPPING SYSTEM CLINICAL EVIDENCE SUMMARY April 2017 SUPPORTING EVIDENCE RHYTHM AF VT PUBLICATIONS Driver Domains in Persistent Atrial Fibrillation (Haissaiguerre, et al)
the ECG, 6 mg of intravenous adenosine was administered as a fast bolus through a large bore intravenous cannula in
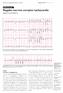 (arrows). Electrocardiography Series Singapore Med.1 2011, 52(3) 146 CME Article Regular narrow complex tachycardia Singh D, Teo S G, Poh K K V Hr JL1 11 VL VF WA, Fig. I ECG shows regular narrow complex
(arrows). Electrocardiography Series Singapore Med.1 2011, 52(3) 146 CME Article Regular narrow complex tachycardia Singh D, Teo S G, Poh K K V Hr JL1 11 VL VF WA, Fig. I ECG shows regular narrow complex
