effects of angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor to cardiovascular and renal disease. Because of the detrimental effects associated
|
|
|
- William Rose
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Olmesartan Medoxomil for Hypertension: A Clinical Review Daryl Norwood, PharmD, Evans Branch III, PharmD, Bridget Smith, MD, and Marlon Honeywell, PharmD ABSTRACT Olmesartan medoxomil is the latest angiotensin II receptor blocker approved for use in the U.S. Potential advantages of this drug include once-daily dosing, an absence of significant adverse reactions, a well-tolerated side-effect profile, and a cost-effective average wholesale price. Olmesartan medoxomil is currently being used as an alternative therapeutic antihypertensive agent for patients intolerant of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Future studies are needed to determine whether this agent might prove useful in the treatment of cardiovascular and renal disease as well. OVERVIEW In April 2002, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved olmesartan medoxomil (Benicar, Sankyo Pharma), for the treatment of hypertension. The latest in a growing class of agents known as the angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), the drug works by inhibiting the Dr. Norwood is Clinical Assistant Professor in the Division of Pharmacy Practice, College of Pharmacy, at Florida A&M University in Miami, Florida, and a Clinical Pharmacy Specialist in ambulatory care in Fort Lauderdale, Florida. Dr. Branch is Clinical Assistant Professor in the Division of Pharmacy Practice, College of Pharmacy, at Florida A&M University in Miami, Florida. Dr. Smith is an Internal Medicine Resident at Jackson Memorial Hospital in Miami, Florida. Dr. Honeywell is Clinical Assistant Professor in the Division of Pharmacy Practice, College of Pharmacy, at Florida A & M University in Tallahassee, Florida, and a Clinical Pharmacy Specialist in ambulatory care in Tallahassee. Drug Forecast is a regular department coordinated by Alan Caspi, PhD, PharmD, MBA, President of Caspi & Associates in New York. effects of angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor and one of the key contributors to cardiovascular and renal disease. Because of the detrimental effects associated with elevated levels of angiotensin II, retarding its actions has been a major focus in the treatment of chronic disease states such as hypertension, heart failure, and proteinuria. The angiotensinconverting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors remain the first-line therapy for these disease states; however, by virtue of their mechanism, olmesartan medoxomil and other ARBs appear to offer an effective and a better-tolerated alternative. To date, the FDA has approved seven ARBs for use in the U.S. Of these, losartan (Cozaar, Merck) was the first to be marketed, followed by valsartan (Diovan, Novartis), irbesartan (Avapro, Bristol-Myers Squibb), candesartan (Atacand, AstraZeneca), telmisartan (Micardis, Boehringer Ingelheim), eprosartan (Teveten, Solvay), and, more recently, olmesartan medoxomil. Currently, all of the available ARBs have been approved only for the treatment of hypertension; however, this class of agents has also demonstrated effectiveness in preventing atheromas, 1 3 improving survival in patients with heart failure caused by systolic dysfunction, 4,5 decreasing endothelial dysfunction, 6,7 increasing fibrinolysis, 8 reducing proteinuria, and preserving kidney function in diabetic patients. 9 This article summarizes the pharmacology, pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, adverse effects, and clinical efficacy of olmesartan medoxomil. PHARMACOLOGY Angiotensin II is the primary vasoactive hormone of the renin angiotensin system and plays an important role in the pathophysiology of several chronic disease states. It is found in a variety of tissues and formed primarily from the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, a reaction catalyzed by ACE. To a lesser degree, human chymase and other non-ace pathways also generate angiotensin II. Once synthesized, angiotensin II produces its biological effects by binding to either the angiotensin II AT 1 or AT 2 receptor subtype. The AT 1 receptor is found in brain, renal, myocardial, vascular, and adrenal tissue. Angiotensin II AT 2 receptors are located in the adrenal medullary tissue, uterus, and brain. AT 1 receptors mediate the majority of responses crucial to cardiovascular and renal function (Figure 1). Less is known about the role of AT 2 receptors; however, when these receptors are stimulated, they can cause vasodilation and can decrease endothelium proliferation. 10 Like all ARBs, olmesartan medoxomil exerts its pharmacological actions by selectively blocking angiotensin II AT 1 receptor sites in the vascular smooth muscle, thus inhibiting the vasoconstrictor effects of angiotensin II. Although the ARBs have some structural and pharmacokinetic differences, few pharmacological differences separate these agents from one another. One notable variation is the degree of binding to the AT 1 receptor compared with the AT 2 receptor; olmesartan medoxomil exhibits more than a 12,500-fold greater affinity for the AT 1 receptor than for the AT 2 receptor, making it theoretically the second most potent agent. The order of binding affinity to the AT 1 receptor, compared with the AT 2 receptor, for the ARBs appears to be as follows: valsartan > olmesartan medoxomil > candesartan > irbesartan > telmisartan > losartan > eprosartan Because of a lack of head-to-head clinical trials, it is uncertain whether this order in- Vol. 27 No. 12 December 2002 P&T 611
2 Renin Angiotensin System Renin ACE AT 1 receptor stimulation Vasoconstriction Arginine vasopressin Aldosterone production Efferent constriction Vessel hypertrophy Myocardial hypertrophy Norepinephrine release Na+ retention Mesangial contraction Angiotensinogen Angiotensin I Angiotensin II dicates differences in clinical efficacy. One binding characteristic that is more likely to influence therapeutic efficacy is the ability of different agents in this class to bind competitively or noncompetitively to the AT 1 receptor. Levels of circulating angiotensin II can increase over time with a continuous blockade of angiotensin II receptors by the ARBs. The pharmacological effect of competitive antagonists (i.e., the active metabolite of eprosartan and losartan) can be overcome by elevated levels of angiotensin II, resulting in a shorter duration of action for these agents. As a result, twice-daily administration seems necessary for optimal 24- hour blood pressure (BP) control with eprosartan and losartan. The therapeutic actions of noncompetitive antagonists (i.e., olmesartan, valsartan, irbesartan, telmisartan, and candesartan) are unaffected by increased amounts of angiotensin II, thus leading to longer terminal half-lives for these ARBs. With the noncompetitive antagonists, 24-hour BP control with once-daily dosing appears possible. 14 AT 2 receptor stimulation Vasodilation? Endothelium proliferation? Figure 1 The renin angiotensin system and the effects of angiotensin II. ACE = angiotensin-converting enzyme; AT, angiotensin; Na = sodium. PHARMACOKINETICS Olmesartan medoxomil, which is administered as a prodrug, is rapidly and completely de-esterified to the active metabolite olmesartan (RNH-6270) during absorption from the gastrointestinal tract. Following the conversion of olmesartan medoxomil to olmesartan, virtually no further metabolism occurs. The bioavailability of olmesartan is approximately 26%, similar to that of losartan and valsartan. Following oral administration, the peak plasma concentration (C max ) of olmesartan is reached after one to two hours. The bioavailability of olmesartan is not affected by food. 15,16 Olmesartan is eliminated in a biphasic manner, with a terminal elimination half-life of approximately 13 hours. It is highly bound to plasma proteins (99%) and does not penetrate red blood cells. Olmesartan takes approximately three to five days to reach a steady state, and there is no accumulation in plasma with once-daily dosing. The pharmacokinetics of olmesartan medoxomil was studied in adults age 65 years and older. A modest accumulation was observed in these patients with repeated dosing; overall, however, maximum plasma concentrations were no different in the older patients than in those younger than 65. The pharmacokinetic profiles of the various ARBs are presented in Table 1. ADVERSE EFFECTS The safety and tolerability of olmesartan medoxomil have been evaluated in several clinical trials. Data were pooled from seven randomized trials involving a total of 3,095 patients with hypertension who received olmesartan medoxomil (2.5 to 80 mg/day) for six to 12 weeks. Overall, patients tolerated the drug well, and the incidence of adverse events was similar to that for placebo (42.2% and 42.7%, respectively) The most commonly reported side effects were headache, upper respiratory tract infections, and influenza-like symptoms. Dizziness was also frequently noted, with the incidence greater in these patients than in those receiving placebo (2.8% vs. 0.9%, P =.01). Six patients receiving olmesartan medoxomil discontinued therapy because of dizziness. The total discontinuation rates were 1.6% in the treatment group and 0.7% in the placebo group. Oparil et al. 21 found that the rate of dizziness associated with olmesartan medoxomil (1.4%) was similar to the rates for losartan (0.7%), valsartan (1.4%), and irbesartan (3.4%). Angioedema and a dry, persistent cough are two important class-related adverse events that may limit the use of ACE inhibitors. Levels of circulating ACE and, subsequently, substance P and bradykinin are unaffected by the ARBs, thereby reducing the potential for ACE inhibitor induced cough or angioedema. In clinical trials, the incidence of cough was similar 612 P&T December 2002 Vol. 27 No. 12
3 for olmesartan medoxomil (0.9%) and placebo (0.7%). 22 This rate is much lower than that reported in users of the ACE inhibitors; in those patients, cough has been noted to occur in up to 39% of cases. 23 Angioedema has rarely occurred with ARB therapy, although facial edema has been reported in five patients receiving olmesartan medoxomil. 22 During the first trimester of pregnancy, olmesartan medoxomil may be used with caution; it is considered a pregnancy category C drug during this time. Because of its potential to cause fetal and neonatal injury, however, it is considered a pregnancy category D drug during the last six months of therapy and should not be used unless the benefits outweigh the potential risks. Nonetheless, once a patient becomes pregnant, efforts should be made to discontinue therapy. 22 No studies evaluating the excretion of olmesartan in breast milk have been conducted; however, low concentrations of the drug have been detected in the milk of lactating rats. Therefore, it is possible that olmesartan might be excreted in human breast milk as well, and a decision to discontinue breast-feeding or the drug itself should be made. DOSING Olmesartan medoxomil is supplied as 5-, 20-, and 40-mg film-coated tablets. The usual recommended starting dose is 20 mg once daily (range, from 10 to 80 mg daily). Twice-daily dosing offers no advantage over the same total dose given once daily and is not recommended. After two weeks of therapy, the daily dose may be increased to 40 mg in patients needing further reduction of BP. Doses above 40 mg do not appear to have any greater effect. If BP is not controlled by olmesartan medoxomil alone, a diuretic may be added. Dosing adjustments do not appear necessary for elderly patients or for patients with moderate to marked renal dysfunction (creatinine clearance less than 40 ml/minute) or with hepatic dysfunction. 22 DRUG INTERACTIONS Olmesartan medoxomil does not appear to have any clinically relevant drug interactions. The co-administration of antacids does not significantly alter its bioavailability, 24 and no clinically significant drug interactions have been reported with the co-administration of digoxin or warfarin. 25 Because olmesartan medoxomil is not metabolized by the cytochrome P-450 system, drugs that in- Table 1 Pharmacokinetic Properties of the Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers Olmesartan 22 Losartan 30 Valsartan 31 Irbesartan 32 Candesartan 33 Telmisartan 34 Eprosartan 35 Brand name Benicar Cozaar Diovan Avapro Atacand Micardis Teveten Manufacturer Sankyo Pharma Merck Novartis Bristol-Myers AstraZeneca Boehringer Solvay Squibb Ingelheim F (%) Active Yes Yes No No Yes No No metabolite T max (hr) (metabolite, No ) t 1/2 (hr) (metabolite, Only 11% 5 9 (metabolite, 6 9) (metabolite, biotransformed 8 13) 3 11) Metabolism De-esterification CYP-2C9 Unknown CYP 2C9 O-demethylation Conjugation Glucoronide (primary and 3A4 conjugation pathway) Elimination (%) 8 12 renal, 35 renal, 10 renal, 20 renal, 33 renal, >97 biliary 7 renal, biliary 60 biliary >80 biliary 80 biliary 67 biliary 90 biliary Food No 10% decrease ~50% decrease No No 6% 20% decrease Delayed interactions in bioavailability in AUC (NS) in bioavailability absorption (NS) Drug None Rifampin, None None None Digoxin None interactions fluconazole (significant) Dose in hepatic No change Initial dosage No change No change No change Use with No change impairment in dose in dose* in dose* in dose* caution in dose Dose in renal No change No change No change No change No change No change No change impairment in dose in dose in dose in dose in dose in dose in dose * No change in dosage for mild to moderate hepatic dysfunction; exercise care in severe disease (no data available). No dosage adjustment necessary unless the patient is volume-depleted. No change in dosage for mild to moderate renal dysfunction; exercise care in severe disease (no data available). AUC = area under the curve; CYP = cytochrome P-450; F = bioavailability; t1/2 = elimination half-life; T max = time of maximum plasma concentration. Vol. 27 No. 12 December 2002 P&T 613
4 Table 2 Recommended Daily Dosage and Average Wholesale Price* of the Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers Olmesartan medoxomil Losartan Valsartan Irbesartan Candesartan Telmisartan Eprosartan Brand name Benicar Cozaar Diovan Avapro Atacand Micardis Teveten Manufacturer Sankyo Pharma Merck Novartis Bristol-Myers AstraZeneca Boehringer Solvay Squibb Ingelheim Approved Hypertension Hypertension Hypertension Hypertension Hypertension Hypertension Hypertension indications and nephropathy and heart failure and nephropathy in type 2 diabetic (NYHA classes II in type 2 diabetic patients with to IV) patients with hypertension hypertension Dosage form 5-, 20-, and 25-, 50-, and 80- and 160-mg 75-, 150-, and 4-, 8-, 16-, and 20-, 40- and 400- and 800-mg 40-mg tablets 100-mg tablets capsules 300-mg tablets 32-mg tablets 80-mg tablets tablets Dosage range 5 80 mg daily mg daily mg daily mg daily 4 32 mg daily mg daily mg and frequency (may divide (may divide daily (may doses) doses) divide doses) AWP*/ tablet 5 mg/$ mg/$ mg/$ mg/$ mg/$ mg $ mg/$1.03 or capsule 20 mg/$ mg/$ mg/$ mg/$ mg/$ mg/$ mg/$ mg/$ mg/$ mg/$ mg/$ mg/$ mg/$1.96 * The average wholesale price (AWP) is a published price list and does not represent the actual prescription-filling fee for the patient; this may be higher. The AWP cost (rounded to the nearest dollar) is based on the Red Book Update. Montvale, NJ: Medical Economics Company, Inc.; NYHA = New York Heart Association. duce, inhibit, or are metabolized by this enzyme do not appear to interact with it. CLINICAL EFFICACY Seven placebo-controlled studies involved 2,693 patients with essential hypertension; 2,145 patients received olmesartan medoxomil, and 548 patients received placebo. Doses ranged from 2.5 to 80 mg once daily for six to12 weeks. Patient responses to olmesartan medoxomil were dose-related; doses of 20 mg daily produced an overall reduction of sitting trough BP (the lowest measured BP with the patient sitting) of about 10/6 mm Hg over placebo, and doses of 40 mg daily produced an overall sitting trough BP reduction of about 12/7 mm Hg over placebo. Doses greater than 40 mg did not offer any additional effects. 20 Various published and unpublished comparative studies have also reported on the antihypertensive efficacy of olmesartan medoxomil Olmesartan Medoxomil versus Atenolol The Van Mieghem Study In a double-blind study, patients were randomly assigned to receive either olmesartan medoxomil 10 mg once daily (n = 165) or atenolol 50 mg once daily (n = 161) for 12 weeks. If the desired response was not attained after four weeks of treatment, the dosage of either medication could be doubled. After only two weeks of therapy, a decrease in the mean sitting diastolic BP at trough was seen in both treatment groups and became more pronounced during the next two weeks. The mean change from the baseline value in diastolic BP at 12 weeks was mm Hg for the olmesartan medoxomil group and mm Hg for the atenolol group. There was a small but significantly greater reduction in systolic BP from the baseline with olmesartan medoxomil ( ) than with atenolol ( ). The Püchler Study In another double-blind study, patients with moderate to severe hypertension (mean sitting diastolic BP of 100 to 120 mm Hg receiving 25 mg of hydrochlorothiazide [HCTZ] daily) were randomly assigned to receive either olmesartan medoxomil (10 mg) once daily plus HCTZ or atenolol (50 mg) once daily plus HCTZ for 12 weeks. If the diastolic BP remained at or greater than 90 mm Hg and/or had decreased by less than 10 mm Hg from the baseline after four weeks of therapy, the dosage of either drug could be doubled. Mean reductions in systolic BP and diastolic BP from the baseline were similar for the olmesartan medoxomil group ( / mm Hg) and the atenolo1 group ( / mm Hg). Olmesartan Medoxomil versus Captopril The Williams Study In a multicenter, double-blind study, patients with mild to moderate hypertension (mean sitting diastolic BP of 95 to 114 mm Hg) were randomly assigned to receive either olmesartan medoxomil (5 mg) once daily or captopril (25 mg) twice daily for up to 12 weeks. The doses of either drug could be doubled after four weeks of therapy if the diastolic BP was at or above 90 mm Hg or had decreased less than 10 mm Hg from baseline values. The dosage of either drug could be doubled again after eight weeks if the diastolic BP remained uncontrolled. The reduction in the seated trough diastolic BP from the baseline was greater in the olmesartan medoxomil group ( P&T December 2002 Vol. 27 No. 12
5 0.6 mm Hg) than in the captopril group ( mm Hg; mean difference 3.1 mm Hg, 95% confidence interval [CI] of 4.8, 1.5). In addition, reductions in mean systolic BP were greater in the olmesartan medoxomil group ( mm Hg) than in the captopril group ( mm Hg; mean difference 7.6 mm Hg, 95% CI of 10.4, 4.7). Olmesartan Medoxomil versus Other Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers The Ball Study In a multicenter, double-blind study, 28 patients with mild to moderate hypertension (mean sitting diastolic BP of 95 to 114 mm Hg) were randomly assigned to receive either olmesartan medoxomil 10 mg once daily (n = 158) or losartan 50 mg once daily (n = 152) for 12 weeks. After four weeks of treatment, if the diastolic BP was greater than 90 mm Hg or had decreased less than 10 mm Hg from the baseline, the dose of either drug could be doubled. If the diastolic BP remained uncontrolled, HCTZ (12.5 mg) once daily could be added to the treatment regimen after 12 weeks and could be doubled after 16 weeks. After 12 weeks, the mean reduction in seated trough diastolic BP in the olmesartan medoxomil group ( mm Hg) was significantly greater than in the losartan group ( mm Hg; mean difference 2.1 mm Hg, 95% CI of 3.6, 0.5). Further, the reduction in mean the seated systolic BP was greater in the olmesartan group than in the losartan group ( vs mm Hg; mean difference 3.3 mm Hg, 95% CI of 6.0, 0.6). The Oparil Study In another multicenter, double-blind study, patients with hypertension (mean sitting diastolic BP of 100 to 115 mm Hg) were randomly assigned to receive one of four AII-receptor antagonists (olmesartan medoxomil 20 mg once daily, losartan 50 mg once daily, valsartan 80 mg once daily, or irbesartan 150 mg once daily) for eight weeks. After eight weeks, the mean reduction in the seated cuff diastolic BP from the baseline value was significantly greater in the patients receiving olmesartan medoxomil ( 11 mm Hg) than in patients receiving losartan ( 8.2 mm Hg, P = <.0002), valsartan ( 7.9 mm Hg; P <.0001), or irbesartan ( 9.9 mm Hg, P =.0412). Although the reduction in the mean seated systolic BP was not significant, it was also greater in patients receiving olmesartan medoxomil than in those receiving losartan ( 9.5 mm Hg), valsartan ( 8.4 mm Hg), and irbesartan ( 11.0 mm Hg). At week eight, the mean 24-hour ambulatory systolic BP was reduced significantly more with olmesartan medoxomil ( 12.5 mm Hg) than with losartan and valsartan ( 9.0 and 8.1 mm Hg; P <.05) but not more than with irbesartan ( 11.3 mm Hg). Conclusion Results from these trials suggest that olmesartan medoxomil can be as effective as atenolol and more effective than captopril, losartan, valsartan, and irbesartan in reducing systolic or diastolic BP. COST AND FORMULARY RECOMMENDATIONS The average wholesale prices (AWPs) of olmesartan medoxomil and the other ARBs are listed in Table 2. The AWP does not directly reflect the price paid by the institution or group purchasing organization; at a cost of $1.31/day, however, olmesartan medoxomil appears to be one of the more affordable agents in its class. Along with other potential advantages (i.e., once-daily dosing, no significant drug interactions, and a well-tolerated sideeffect profile) olmesartan medoxomil is thus an antihypertensive agent worth considering as an addition to any formulary. Ultimately, the decision to add olmesartan medoxomil to the formulary depends on whether (1) the AWP is reflective of the purchasing contract for institutions and (2) olmesartan medoxomil is granted FDA approval for the treatment of other disease states. In addition to the treatment of hypertension, some ARBs (losartan, valsartan, and irbesartan) have other FDA-approved indications, perhaps making them more attractive formulary products. SUMMARY Olmesartan medoxomil is the newest angiotensin II receptor blocker approved in the U.S. for the treatment of hypertension. It is well tolerated, with an adverseeffect profile similar to that of placebo, except for the incidence of dizziness (which is greater with olmesartan medoxomil), and is devoid of any significant drug interactions. The drug provides smooth 24-hour BP control with oncedaily dosing, and comparative studies suggest that it might have a greater efficacy than captopril, losartan, valsartan, and irbesartan. Currently, olmesartan medoxomil has a place in therapy as an alternative antihypertensive agent for patients intolerant of ACE inhibitors. However, because the ACE inhibitors as well as some ARBs are also indicated for the treatment of heart failure, left ventricular dysfunction after myocardial infarction, and/or proteinuria, further studies are warranted to establish olmesartan medoxomil as a cardiovascular or renal protective agent. REFERENCES 1. Strawn WB, Chappell MC, Dean RH, et al. Inhibition of early atherogenesis by losartan in monkeys with diet-induced hypercholesterolemia. Circulation 2000; 101: Johnstone MT, Perez A, Stewart R, et al. The angiotensin receptor blocker: Candesartan reduces atherosclerosis in a dose-dependent manner [Abstract]. J Am Coll Cardiol 2000; Vaughn DE. AT 1 receptor blockade atherosclerosis: Hopeful insights into vascular protection. Circulation 2000; 101: Pitt B, Segal R, Martinez FA, et al. Randomized trial of losartan versus captopril in patients over 65 with heart failure. Lancet 1997;349: Pitt B, Poole-Wilson PA, Segal R, et al. Effect of losartan compared with captopril on mortality in patients with symptomatic heart failure: Randomized trial the Losartan Heart Failure Survival Study Elite II. Lancet 2000;355: Watanabe H, Kakihara M. Losartan improves endothelium dependent vasodilation in patients with non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus [Abstract]. J Am Coll Cardiol 2000; de las Heras N, Aragoncillo P, Maese R, et al. AT 1 receptor antagonism reduces endothelial dysfunction and intimal thickening in atherosclerotic rabbits. Am J Hypertens 1999;34(Pt 2): Erdem Y, Usalan C, Haznedaroglu IC, et al. Effects of angiotensin-converting enzyme and angiotensin II receptor inhibition on impaired fibrinolysis in systemic hypertension. Am J Hypertens 1999;12(11, Pt 1): Chung O, Unger T. Angiotensin II receptor blockade and end organ protection. Am J Hypertens 1999;12(Suppl 12) (1 2):150S. Vol. 27 No. 12 December 2002 P&T 617
6 10. Greenbert BH: Role of angiotensin receptor blockers in heart failure not yet resolved. Circulation 1999;100: Herbert J-M, Delisée C, Dol F, et al. Effect of SR 47436, a novel angiotensin II AT 1 receptor antagonist, on human vascular smooth muscle cells in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol 1994;251: de Gasparo M, Whitebread S. Binding of valsartan to mammalian angiotensin AT 1 receptors. Regul Pept 1995;59: Edwards RM, Aiyar N, Ohlstein EH, et al. Pharmacological characterization of the nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonist, SK&F J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1992;260(1): McConnaughey MM, McConnaughey JS, Ingenito AJ. Practical considerations of the pharmacology of angiotensin receptor blockers. J Clin Pharmacol 1999; 39: Neutel JM. Clinical studies of CS-866, the newest angiotensin II receptor antagonist. Am J Cardiol 2001;87(Suppl):37C 43C. 16. Schwocho LR, Masonson HN. Pharmacokinetics of CS-866, a new angiotensin II receptor blocker, in healthy subjects. J Clin Pharmacol 2001;41: Püchler K, Laeis P, Gunther A, et al. Safety, tolerability and efficacy of the new oral angiotensin II (AT 1 )-receptor antagonist CS-866 in patients with mild to moderate hypertension [Abstract No. P.11]. J Hum Hypertens 1999;13(Suppl 3): Masonson HN, Punzi HA, Neutel JM, et al. CS-866 (angiotensin II receptor antagonist): A double-blind study using ambulatory blood pressure monitoring in hypertensive patients [Abstract No. D035]. Am J Hypertens 1998;11(4 Pt 2): Püchler K, Laeis P, Stumpe KO. A comparison of the efficacy and safety of the oral angiotensin II antagonist olmesartan medoxomil with those of atenolol in patients with moderate to severe hypertension under continuous treatment with hydrochlorothiazide [Abstract No. P2.175]. J Hypertens 2001;19(Suppl 2): Neutel JM. Clinical studies of CS-866, the newest angiotensin II receptor antagonist. Am J Cardiol 2001;87(8A): Oparil S, Williams D, Chrysant SG, et al. Comparative efficacy of olmesartan, losartan, valsartan, and irbesartan in the control of essential hypertension. J Clin Hypertens 2001;3: Benicar package insert. Sankyo Pharma, Inc, New York. 23. Israili ZH, Hall WD. Cough and angioneurotic edema associated with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor therapy: A review of the literature and pathophysiology. Ann Intern Med 1992;117: Kawaratani T, Laeis P, Püchler K, et al. The effect of an antacid (aluminum magnesium hydroxide) on the pharmacokinetics and safety of the oral angiotensin II antagonist CS-866 in healthy male subjects [Abstract No. 145]. J Hypertens 1999;17(Suppl 3):S Püchler K, Laeis P, Kawaratani T, et al. The effect of the combination of the oral angiotensin II antagonist CS-866 and warfarin on pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics and safety in healthy male subjects [Abstract No. 271]. J Hypertens 1999;17(Suppl 3): Van Mieghem W. A multicentre, double-blind, efficacy, tolerability and safety study of the oral angiotensin II antagonist olmesartan medoxomil versus atenolol in patients with mild to moderate essential hypertension [Abstract No. P2.174]. J Hypertens 2001;19 (Suppl 2): Williams PA. A multicentre, double-blind, efficacy, tolerability and safety study of the oral angiotensin II antagonist olmesartan medoxomil versus captopril in patients with mild to moderate essential hypertension. J Hypertens 2001;19(Suppl 2): Ball K. A multicentre, double-blind, efficacy, tolerability and safety study of the oral angiotensin II antagonist olmesartan medoxomil versus losartan in patients with mild to moderate essential hypertension [Abstract No. P2.176]. J Hypertens 2001;19(Suppl 2): Oparil S, Williams D, Chrysant SG, et al. Comparative efficacy of olmesartan, losartan, valsartan and irbesartan in the control of essential hypertension. J Clin Hypertens 2001;3: Cozaar package insert. Merck, West Point, PA, Diovan package insert. Novartis, East Hanover, NJ, Avapro package insert. Bristol-Myers Squibb, Princeton, NJ, Atacand package insert. Astra Pharmaceuticals, Wayne, PA, Micardis package insert. Boehringer Ingelheim, Ridgefield, CT, Teveten package insert. Solvay, Buffalo Grove, IL, P&T December 2002 Vol. 27 No. 12
Amlodipine/olmesartan (Azor ) is indicated for the treatment of hypertension, alone or in combination with other antihypertensive medications.
 Page 1 of 8 Policies Repository Policy Title Policy Number Oral Antihypertensive Agents FS.CLIN.9 Application of Pharmacy Policy is determined by benefits and contracts. Benefits may vary based on product
Page 1 of 8 Policies Repository Policy Title Policy Number Oral Antihypertensive Agents FS.CLIN.9 Application of Pharmacy Policy is determined by benefits and contracts. Benefits may vary based on product
Antihypertensive efficacy of olmesartan compared with other antihypertensive drugs
 (2002) 16 (Suppl 2), S24 S28 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/jhh compared with other antihypertensive drugs University Clinic Bonn, Department of Internal
(2002) 16 (Suppl 2), S24 S28 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/jhh compared with other antihypertensive drugs University Clinic Bonn, Department of Internal
HTN: 80 mg once daily 23,f 80 mg once daily 23,f Hypertension 40, 80 mg $82.66 (80 mg once daily) HTN: 8-32 mg daily in one or two divided doses 1
 Detail-Document #260301 This Detail-Document accompanies the related article published in PHARMACIST S LETTER / PRESCRIBER S LETTER March 2010 ~ Volume 26 ~ Number 260301 Comparison of Angiotensin Receptor
Detail-Document #260301 This Detail-Document accompanies the related article published in PHARMACIST S LETTER / PRESCRIBER S LETTER March 2010 ~ Volume 26 ~ Number 260301 Comparison of Angiotensin Receptor
PHARMACEUTICAL INFORMATION AZILSARTAN
 AZEARLY Tablets Each Tablet Contains Azilsartan 20/40/80 mg PHARMACEUTICAL INFORMATION AZILSARTAN Generic name: Azilsartan Chemical name: 2-Ethoxy-1-{[2'-(5-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)-4-biphenylyl]methyl}-
AZEARLY Tablets Each Tablet Contains Azilsartan 20/40/80 mg PHARMACEUTICAL INFORMATION AZILSARTAN Generic name: Azilsartan Chemical name: 2-Ethoxy-1-{[2'-(5-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)-4-biphenylyl]methyl}-
COMPOSITION. A film coated tablet contains. Active ingredient: irbesartan 75 mg, 150 mg or 300 mg. Rotazar (Film coated tablets) Irbesartan
 Rotazar (Film coated tablets) Irbesartan Rotazar 75 mg, 150 mg, 300 mg COMPOSITION A film coated tablet contains Active ingredient: irbesartan 75 mg, 150 mg or 300 mg. Rotazar 75 mg, 150 mg, 300 mg PHARMACOLOGICAL
Rotazar (Film coated tablets) Irbesartan Rotazar 75 mg, 150 mg, 300 mg COMPOSITION A film coated tablet contains Active ingredient: irbesartan 75 mg, 150 mg or 300 mg. Rotazar 75 mg, 150 mg, 300 mg PHARMACOLOGICAL
Indication as per product monograph: Indicated for the treatment of mild to moderate essential hypertension.
 Report on New Patented Drugs Olmetec Under its transparency initiative, the PMPRB publishes the results of the reviews of new patented drug products conducted by Board Staff for purposes of applying the
Report on New Patented Drugs Olmetec Under its transparency initiative, the PMPRB publishes the results of the reviews of new patented drug products conducted by Board Staff for purposes of applying the
Azilsartan Medoxomil (Edarbi) The Eighth Angiotensin II Receptor Blocker
 Medoxomil (Edarbi) The Eighth Angiotensin II Receptor Blocker Jocelyn D. Jones, PharmD, BCPS; Sylvia H. Jackson, PharmD, MEd, CDE; Carmen Agboton, PharmD; and Tonya S. Martin, PharmD, CGP, MAEd INTRODUCTION
Medoxomil (Edarbi) The Eighth Angiotensin II Receptor Blocker Jocelyn D. Jones, PharmD, BCPS; Sylvia H. Jackson, PharmD, MEd, CDE; Carmen Agboton, PharmD; and Tonya S. Martin, PharmD, CGP, MAEd INTRODUCTION
ANGIOTENSIN II RECEPTOR BLOCKERS: MORE THAN THE ALTERNATIVE PRESENTATION BY: PATRICK HO, USC PHARM D. CANDIDATE OF 2017 MENTOR: DR.
 ANGIOTENSIN II RECEPTOR BLOCKERS: MORE THAN THE ALTERNATIVE PRESENTATION BY: PATRICK HO, USC PHARM D. CANDIDATE OF 2017 MENTOR: DR. CRAIG STERN, PHARMD, MBA, RPH, FASCP, FASHP, FICA, FLMI, FAMCP RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN
ANGIOTENSIN II RECEPTOR BLOCKERS: MORE THAN THE ALTERNATIVE PRESENTATION BY: PATRICK HO, USC PHARM D. CANDIDATE OF 2017 MENTOR: DR. CRAIG STERN, PHARMD, MBA, RPH, FASCP, FASHP, FICA, FLMI, FAMCP RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN
Hypertension: Focus on Olmesartan Medoxomil
 REVIEW Hypertension: Focus on Olmesartan Medoxomil Allison M. Bell 1 and Diane Nykamp 2 1 Mercer University College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences, Atlanta, Georgia U.S.A. 2 Department of Pharmacy Practice,
REVIEW Hypertension: Focus on Olmesartan Medoxomil Allison M. Bell 1 and Diane Nykamp 2 1 Mercer University College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences, Atlanta, Georgia U.S.A. 2 Department of Pharmacy Practice,
II. Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs) Drug Class Review
 DOD PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS COMMITTEE RECOMMENDATIONS INFORMATION FOR THE DOD BENEFICIARY ADVISORY PANEL I. Uniform Formulary Review Process Under 10 U.S.C. 1074g, as implemented by 32 C.F.R. 199.21,
DOD PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS COMMITTEE RECOMMENDATIONS INFORMATION FOR THE DOD BENEFICIARY ADVISORY PANEL I. Uniform Formulary Review Process Under 10 U.S.C. 1074g, as implemented by 32 C.F.R. 199.21,
Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers Dosage in hypertensive patients as well as patients with left ventricular hypertrophy
 Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers [Developed, August 1996; Revised, December 1996; July 1997; June 1998; July 1999; September 2000; July 2001; September 2001; July 2002; July 2003; April 2008; March 2011;
Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers [Developed, August 1996; Revised, December 1996; July 1997; June 1998; July 1999; September 2000; July 2001; September 2001; July 2002; July 2003; April 2008; March 2011;
Efficacy and safety of Olmesartan,Losartan, Valsartan, and Irbesartan in the Control of Essential Hypertension
 Efficacy and safety of Olmesartan,Losartan, Valsartan, and Irbesartan in the Control of Essential Hypertension Done by :Meznah zaid Al-mutairi Pharm.D Candidate Princess Nora Bint Abdul Rahman University
Efficacy and safety of Olmesartan,Losartan, Valsartan, and Irbesartan in the Control of Essential Hypertension Done by :Meznah zaid Al-mutairi Pharm.D Candidate Princess Nora Bint Abdul Rahman University
Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonists (ARBs), Renin Inhibitors, and Combinations Step Therapy Program Summary
 OBJECTIVE The intent of the Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonists (ARBs), Renin Inhibitors, and Combinations Step Therapy (ST) program is to encourage use of cost-effective generic products - ACEIs, ACEI
OBJECTIVE The intent of the Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonists (ARBs), Renin Inhibitors, and Combinations Step Therapy (ST) program is to encourage use of cost-effective generic products - ACEIs, ACEI
See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information.
 Clinical Policy: (Diovan, Diovan HCT, Exforge, Exforge HCT, Teveten) Reference Number: CP.HNMC.16 Effective Date: 11.16.16 Last Review Date: 11.17 Line of Business: Medicaid Medi-Cal Revision Log See Important
Clinical Policy: (Diovan, Diovan HCT, Exforge, Exforge HCT, Teveten) Reference Number: CP.HNMC.16 Effective Date: 11.16.16 Last Review Date: 11.17 Line of Business: Medicaid Medi-Cal Revision Log See Important
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Antihypertensive Medications Page 1 of 10 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Antihypertensive Medications Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization
Antihypertensive Medications Page 1 of 10 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Antihypertensive Medications Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization
Antihypertensive Agents Part-2. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Antihypertensive Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Agents that block production or action of angiotensin Angiotensin-converting
Antihypertensive Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Agents that block production or action of angiotensin Angiotensin-converting
Optimal blockade of the Renin- Angiotensin-Aldosterone. in chronic heart failure
 Optimal blockade of the Renin- Angiotensin-Aldosterone Aldosterone- (RAA)-System in chronic heart failure Jan Östergren Department of Medicine Karolinska University Hospital Stockholm, Sweden Key Issues
Optimal blockade of the Renin- Angiotensin-Aldosterone Aldosterone- (RAA)-System in chronic heart failure Jan Östergren Department of Medicine Karolinska University Hospital Stockholm, Sweden Key Issues
Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat
 Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat Diuretic Thiazide diuretics The loop diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics *Hydrochlorothiazide *Chlorthalidone *Furosemide *Torsemide *Bumetanide Aldosterone
Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat Diuretic Thiazide diuretics The loop diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics *Hydrochlorothiazide *Chlorthalidone *Furosemide *Torsemide *Bumetanide Aldosterone
PRODUCT CIRCULAR. Tablets COZAAR (losartan potassium) I. THERAPEUTIC CLASS II. INDICATIONS III. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION PAK-CZR-T
 PRODUCT CIRCULAR Tablets I. THERAPEUTIC CLASS, the first of a new class of agents for the treatment of hypertension, is an angiotensin II receptor (type AT 1 ) antagonist. also provides a reduction in
PRODUCT CIRCULAR Tablets I. THERAPEUTIC CLASS, the first of a new class of agents for the treatment of hypertension, is an angiotensin II receptor (type AT 1 ) antagonist. also provides a reduction in
See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information.
 Clinical Policy: Olmesartan/Amlodipine (Azor), Olmesartan/Amlodipine/ HCTZ (Tribenzor) Reference Number: CP.CPA.XX Effective Date: 11.16.16 Last Review Date: 08.18 Line of Business: Commercial See Important
Clinical Policy: Olmesartan/Amlodipine (Azor), Olmesartan/Amlodipine/ HCTZ (Tribenzor) Reference Number: CP.CPA.XX Effective Date: 11.16.16 Last Review Date: 08.18 Line of Business: Commercial See Important
Angiotensin receptors: their pharmacological aspects and side effects vis-à-vis receptor blocker drugs
 Int. Jr. Bioinformatic and Biological Sci. : v.2 n.3 and 4, p. 145-152. Dec. 2014 DOI No. 10.5958/2321-7111.2014.00012.2 3 Angiotensin receptors: their pharmacological aspects and side effects vis-à-vis
Int. Jr. Bioinformatic and Biological Sci. : v.2 n.3 and 4, p. 145-152. Dec. 2014 DOI No. 10.5958/2321-7111.2014.00012.2 3 Angiotensin receptors: their pharmacological aspects and side effects vis-à-vis
Clinical Policy: Angiotesin II Receptor Blockers and Renin Inhibitors Reference Number: CP.HNMC.15 Effective Date: Last Review Date: 08.
 Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.HNMC.15 Effective Date: 11.16.16 Last Review Date: 08.17 Revision Log Line of Business: Medicaid Medi-Cal See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important
Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.HNMC.15 Effective Date: 11.16.16 Last Review Date: 08.17 Revision Log Line of Business: Medicaid Medi-Cal See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important
MICARDIS Composition Pharmacological properties Pharmacokinetics
 MICARDIS Boehringer (Tablet) Composition 1 tablet contains 40 or 80 mg [1,1 -biphenyl]-2-carboxylic acid, 4 -[(1,4 dime-thyl- 2 -propyl[2,6-bi-1h-benzimidazole]-1 -yl)methyl] (= telmisartan) Excipients:
MICARDIS Boehringer (Tablet) Composition 1 tablet contains 40 or 80 mg [1,1 -biphenyl]-2-carboxylic acid, 4 -[(1,4 dime-thyl- 2 -propyl[2,6-bi-1h-benzimidazole]-1 -yl)methyl] (= telmisartan) Excipients:
Lisinopril 20 converting to losartan
 Search Lisinopril 20 converting to losartan Stop wasting your time with unanswered searches. lisinopril 40 mg to losartan conversion,cannot Find low price Best. Winds SSW at 10 to 20. Lisinopril 20 to
Search Lisinopril 20 converting to losartan Stop wasting your time with unanswered searches. lisinopril 40 mg to losartan conversion,cannot Find low price Best. Winds SSW at 10 to 20. Lisinopril 20 to
Amlodipine plus Lisinopril Tablets AMLOPRES-L
 Amlodipine plus Lisinopril Tablets AMLOPRES-L COMPOSITION AMLOPRES-L Each uncoated tablet contains: Amlodipine besylate equivalent to Amlodipine 5 mg and Lisinopril USP equivalent to Lisinopril (anhydrous)
Amlodipine plus Lisinopril Tablets AMLOPRES-L COMPOSITION AMLOPRES-L Each uncoated tablet contains: Amlodipine besylate equivalent to Amlodipine 5 mg and Lisinopril USP equivalent to Lisinopril (anhydrous)
azilsartan medoxomil
 azilsartan medoxomil edarbi 40mg Tablet 80mg Tablet ANTIHYPERTENSIVE Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonist FORMULATION: Each tablet contains 40mg Azilsartan medoxomil (as potassium) Each tablet contains 80mg
azilsartan medoxomil edarbi 40mg Tablet 80mg Tablet ANTIHYPERTENSIVE Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonist FORMULATION: Each tablet contains 40mg Azilsartan medoxomil (as potassium) Each tablet contains 80mg
Combination of renin-angiotensinaldosterone. how to choose?
 Combination of renin-angiotensinaldosterone system inhibitors how to choose? Karl Swedberg Professor of Medicine Sahlgrenska Academy University of Gothenburg karl.swedberg@gu.se Disclosures Research grants
Combination of renin-angiotensinaldosterone system inhibitors how to choose? Karl Swedberg Professor of Medicine Sahlgrenska Academy University of Gothenburg karl.swedberg@gu.se Disclosures Research grants
EPLERENONE (INSPRA ) THE FIRST SELECTIVE ALDOSTERONE RECEPTOR ANTAGONIST FOR THE TREATMENT OF HYPERTENSION
 Volume 18, Issue 6 March 2003 EPLERENONE (INSPRA ) THE FIRST SELECTIVE ALDOSTERONE RECEPTOR ANTAGONIST FOR THE TREATMENT OF HYPERTENSION Eun-Jeong Kim, Pharm.D. Candidate Introduction Approximately 50
Volume 18, Issue 6 March 2003 EPLERENONE (INSPRA ) THE FIRST SELECTIVE ALDOSTERONE RECEPTOR ANTAGONIST FOR THE TREATMENT OF HYPERTENSION Eun-Jeong Kim, Pharm.D. Candidate Introduction Approximately 50
LACIPIL QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
 LACIPIL lacidipine QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Lacidipine, 2 mg - round shaped white engraved on one face. Lacidipine, 4 mg - oval white with break line on both faces. Lacidipine, 6 mg - oval
LACIPIL lacidipine QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Lacidipine, 2 mg - round shaped white engraved on one face. Lacidipine, 4 mg - oval white with break line on both faces. Lacidipine, 6 mg - oval
State of the art treatment of hypertension: established and new drugs. Prof. M. Burnier Service of Nephrology and Hypertension Lausanne, Switzerland
 State of the art treatment of hypertension: established and new drugs Prof. M. Burnier Service of Nephrology and Hypertension Lausanne, Switzerland First line therapies in hypertension ACE inhibitors AT
State of the art treatment of hypertension: established and new drugs Prof. M. Burnier Service of Nephrology and Hypertension Lausanne, Switzerland First line therapies in hypertension ACE inhibitors AT
AT 1 -receptor blockers: differences that matter
 (2002) 16, S9 S16 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/jhh AT 1 -receptor blockers: differences that matter Division of Cardiovascular Diseases, The Western
(2002) 16, S9 S16 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/jhh AT 1 -receptor blockers: differences that matter Division of Cardiovascular Diseases, The Western
Mayo Clin Proc, March 2003, Vol 78 Role of ARBs in Treatment of Heart Failure 335 system, tissue-based RAS has long-term effects that can modify cardi
 334 Concise Review for Clinicians Therapeutic Role of Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers in the Treatment of Heart Failure Concise Review for Clinicians PRERANA MANOHAR, MD, AND ILEANA L. PIÑA, MD Angiotensin
334 Concise Review for Clinicians Therapeutic Role of Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers in the Treatment of Heart Failure Concise Review for Clinicians PRERANA MANOHAR, MD, AND ILEANA L. PIÑA, MD Angiotensin
LOZAR. Composition Each tablet contains Losartan potassium 50 mg.
 LOZAR Composition Each tablet contains Losartan potassium 50 mg. Tablets Action Angiotensin II [formed from angiotensin I in a reaction catalyzed by angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE, kininase II)], is
LOZAR Composition Each tablet contains Losartan potassium 50 mg. Tablets Action Angiotensin II [formed from angiotensin I in a reaction catalyzed by angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE, kininase II)], is
ACP Brief Fall 2006 prioritization. Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (ARBs) for Proteinuria, Hypertension (HTN) and Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)
 ACP Brief Fall 2006 prioritization Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (ARBs) for Proteinuria, Hypertension (HTN) and Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) Background This topic was submitted by BC PharmaCare during
ACP Brief Fall 2006 prioritization Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (ARBs) for Proteinuria, Hypertension (HTN) and Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) Background This topic was submitted by BC PharmaCare during
Parameters Candesartan Eprosartan Irbesartan Losartan Olmesartan Telmirsartan Valsartan Food effect No effect <25% No effect 10% No effect 6% 40%
 Statewide Pharmacy and Therapeutics 7/30/04 Formulary Class Review Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonists (AIIRAs) Candesartan (Atacand, AstraZeneca) Eprosartan (Teveten, Biovail) Irbesartan (Avapro, BMS/S-S)
Statewide Pharmacy and Therapeutics 7/30/04 Formulary Class Review Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonists (AIIRAs) Candesartan (Atacand, AstraZeneca) Eprosartan (Teveten, Biovail) Irbesartan (Avapro, BMS/S-S)
By Prof. Khaled El-Rabat
 What is The Optimum? By Prof. Khaled El-Rabat Professor of Cardiology - Benha Faculty of Medicine HT. Introduction Despite major worldwide efforts over recent decades directed at diagnosing and treating
What is The Optimum? By Prof. Khaled El-Rabat Professor of Cardiology - Benha Faculty of Medicine HT. Introduction Despite major worldwide efforts over recent decades directed at diagnosing and treating
The hypertensive effects of the renin-angiotensin
 Comparison of Telmisartan vs. Valsartan in the Treatment of Mild to Moderate Hypertension Using Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring George Bakris, MD A prospective, randomized, open-label, blinded end-point
Comparison of Telmisartan vs. Valsartan in the Treatment of Mild to Moderate Hypertension Using Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring George Bakris, MD A prospective, randomized, open-label, blinded end-point
HYPERTENSION IN CKD. LEENA ONGAJYOOTH, M.D., Dr.med RENAL UNIT SIRIRAJ HOSPITAL
 HYPERTENSION IN CKD LEENA ONGAJYOOTH, M.D., Dr.med RENAL UNIT SIRIRAJ HOSPITAL Stages in Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease and Therapeutic Strategies Complications Normal Increased risk Damage GFR
HYPERTENSION IN CKD LEENA ONGAJYOOTH, M.D., Dr.med RENAL UNIT SIRIRAJ HOSPITAL Stages in Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease and Therapeutic Strategies Complications Normal Increased risk Damage GFR
Since the initial description of angiotensin II mediated
 CLINICAL CARDIOLOGY: PHYSICIAN UPDATE Manipulation of the Renin-Angiotensin System Michael M. Givertz, MD Since the initial description of angiotensin II mediated hypertension 40 years ago, basic and clinical
CLINICAL CARDIOLOGY: PHYSICIAN UPDATE Manipulation of the Renin-Angiotensin System Michael M. Givertz, MD Since the initial description of angiotensin II mediated hypertension 40 years ago, basic and clinical
Volume 6; Number 1 January 2012 NICE CLINICAL GUIDELINE 127: HYPERTENSION CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF PRIMARY HYPERTENSION IN ADULTS (AUGUST 2011)
 Volume 6; Number 1 January 2012 NICE CLINICAL GUIDELINE 127: HYPERTENSION CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF PRIMARY HYPERTENSION IN ADULTS (AUGUST 2011) What s new in hypertension? NICE has issued an updated Clinical
Volume 6; Number 1 January 2012 NICE CLINICAL GUIDELINE 127: HYPERTENSION CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF PRIMARY HYPERTENSION IN ADULTS (AUGUST 2011) What s new in hypertension? NICE has issued an updated Clinical
Clinical Policy: ACEI and ARB Duplicate Therapy Reference Number: CP.PMN.61 Effective Date: Last Review Date: 05.18
 Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.PMN.61 Effective Date: 08.01.14 Last Review Date: 05.18 Line of Business: Medicaid Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory
Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.PMN.61 Effective Date: 08.01.14 Last Review Date: 05.18 Line of Business: Medicaid Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory
The P&T Committee Lisinopril (Qbrelis )
 Situation Background Assessment The P&T Committee Lisinopril (Qbrelis ) Qbrelis, 1 mg/ml lisinopril oral solution, has recently become an FDA- approved formulation. Current practice at UK Chandler Medical
Situation Background Assessment The P&T Committee Lisinopril (Qbrelis ) Qbrelis, 1 mg/ml lisinopril oral solution, has recently become an FDA- approved formulation. Current practice at UK Chandler Medical
THE RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN-ALDOSTERONE SYSTEM
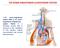 THE RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN-ALDOSTERONE SYSTEM The renin angiotensin system (RAS) or the renin angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS) is a hormone system that is involved in the regulation of the plasma sodium
THE RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN-ALDOSTERONE SYSTEM The renin angiotensin system (RAS) or the renin angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS) is a hormone system that is involved in the regulation of the plasma sodium
Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs
 Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs Blood Pressure Normal = sys
Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs Blood Pressure Normal = sys
Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) are the
 Comparative Efficacy of Olmesartan, Losartan, Valsartan, and Irbesartan in the Control of Essential Hypertension Suzanne Oparil, MD; 1 David Williams, MD; 2 Steven G. Chrysant, MD, PhD; 3 Thomas C. Marbury,
Comparative Efficacy of Olmesartan, Losartan, Valsartan, and Irbesartan in the Control of Essential Hypertension Suzanne Oparil, MD; 1 David Williams, MD; 2 Steven G. Chrysant, MD, PhD; 3 Thomas C. Marbury,
0BCore Safety Profile. Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Film-coated tablet 40, 80, 160, 320 mg SE/H/PSUR/0024/003 Date of FAR:
 0BCore Safety Profile Active substance: Valsartan Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Film-coated tablet 40, 80, 160, 320 mg P-RMS: SE/H/PSUR/0024/003 Date of FAR: 28.02.2013 4.2 Posology and method of administration
0BCore Safety Profile Active substance: Valsartan Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Film-coated tablet 40, 80, 160, 320 mg P-RMS: SE/H/PSUR/0024/003 Date of FAR: 28.02.2013 4.2 Posology and method of administration
INSPRA 25 & 50 mg TABLETS
 INSPRA 25 & 50 mg TABLETS SCHEDULING STATUS: Schedule 4 PROPRIETARY NAMES (and dosage forms): INSPRA 25 (Tablets) INSPRA 50 (Tablets) COMPOSITION: INSPRA 25: INSPRA 50: Each tablet contains 25 mg eplerenone
INSPRA 25 & 50 mg TABLETS SCHEDULING STATUS: Schedule 4 PROPRIETARY NAMES (and dosage forms): INSPRA 25 (Tablets) INSPRA 50 (Tablets) COMPOSITION: INSPRA 25: INSPRA 50: Each tablet contains 25 mg eplerenone
Cardiovascular Protection and the RAS
 Cardiovascular Protection and the RAS Katalin Kauser, MD, PhD, DSc Senior Associate Director, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceutical Inc. Micardis Product Pipeline Scientific Support Ridgefield, CT, USA Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular Protection and the RAS Katalin Kauser, MD, PhD, DSc Senior Associate Director, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceutical Inc. Micardis Product Pipeline Scientific Support Ridgefield, CT, USA Cardiovascular
Scientific conclusions and detailed explanation of the scientific grounds for the differences from the PRAC recommendation
 Annex I Scientific conclusions, grounds for variation to the terms of the marketing authorisations and detailed explanation of the scientific grounds for the differences from the PRAC recommendation 1
Annex I Scientific conclusions, grounds for variation to the terms of the marketing authorisations and detailed explanation of the scientific grounds for the differences from the PRAC recommendation 1
1/4/18. Heart Failure Guideline Review and Update. Disclosure. Pharmacist Objectives. Pharmacy Technician Objectives. What is Heart Failure?
 Disclosure Heart Failure Guideline Review and Update I have had no financial relationship over the past 12 months with any commercial sponsor with a vested interest in this presentation. Natalie Beiter,
Disclosure Heart Failure Guideline Review and Update I have had no financial relationship over the past 12 months with any commercial sponsor with a vested interest in this presentation. Natalie Beiter,
ABSTRACT ORIGINAL RESEARCH. Joel Neutel Ali Shojaee Jen-Fue Maa. Adv Ther (2012) 29(6): DOI /s z
 Adv Ther (212) 29(6):58 523. DOI 1.17/s12325-12-3-z ORIGINAL RESEARCH Efficacy of Amlodipine/Olmesartan ± Hydrochlorothiazide in Patients Uncontrolled on Prior Calcium Channel Blocker or Angiotensin II
Adv Ther (212) 29(6):58 523. DOI 1.17/s12325-12-3-z ORIGINAL RESEARCH Efficacy of Amlodipine/Olmesartan ± Hydrochlorothiazide in Patients Uncontrolled on Prior Calcium Channel Blocker or Angiotensin II
ARxCH. Annual Review of Changes in Healthcare. Entresto: An Overview for Pharmacists
 Entresto: An Overview for Pharmacists David Comshaw, PharmD Candidate 2019 1 Gyen Musgrave, PharmD Candidate 2019 1 Suzanne Surowiec, PharmD, BCACP 1 Jason Guy, PharmD 1 1 University of Findlay College
Entresto: An Overview for Pharmacists David Comshaw, PharmD Candidate 2019 1 Gyen Musgrave, PharmD Candidate 2019 1 Suzanne Surowiec, PharmD, BCACP 1 Jason Guy, PharmD 1 1 University of Findlay College
Neprilysin Inhibitor (Entresto ) Prior Authorization and Quantity Limit Program Summary
 Neprilysin Inhibitor (Entresto ) Prior Authorization and Quantity Limit Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS DOSAGE 1 Indication Entresto Reduce the risk of cardiovascular (sacubitril/valsartan) death
Neprilysin Inhibitor (Entresto ) Prior Authorization and Quantity Limit Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS DOSAGE 1 Indication Entresto Reduce the risk of cardiovascular (sacubitril/valsartan) death
Byvalson. (nebivolol, valsartan) New Product Slideshow
 Byvalson (nebivolol, valsartan) New Product Slideshow Introduction Brand name: Byvalson Generic name: Nebivolol, valsartan Pharmacological class: Beta-blocker + angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) Strength
Byvalson (nebivolol, valsartan) New Product Slideshow Introduction Brand name: Byvalson Generic name: Nebivolol, valsartan Pharmacological class: Beta-blocker + angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) Strength
Hypertension and diabetic nephropathy
 Hypertension and diabetic nephropathy Elisabeth R. Mathiesen Professor, Chief Physician, Dr sci Dep. Of Endocrinology Rigshospitalet, University of Copenhagen Denmark Hypertension Brain Eye Heart Kidney
Hypertension and diabetic nephropathy Elisabeth R. Mathiesen Professor, Chief Physician, Dr sci Dep. Of Endocrinology Rigshospitalet, University of Copenhagen Denmark Hypertension Brain Eye Heart Kidney
Original Paper. ID: 7805
 Original Paper The Efficacy and Safety of Initial Use of Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide Fixed-Dose Combination in Hypertensive Patients With and Without High Cardiovascular Risk Matthew R. Weir, MD; 1
Original Paper The Efficacy and Safety of Initial Use of Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide Fixed-Dose Combination in Hypertensive Patients With and Without High Cardiovascular Risk Matthew R. Weir, MD; 1
Guidelines for the Prescribing of Sacubitril / Valsartan
 Hull & East Riding Prescribing Committee Guidelines for the Prescribing of Sacubitril / Valsartan 1. BACKGROUND Sacubitril valsartan is an angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitor, including both a neprilysin
Hull & East Riding Prescribing Committee Guidelines for the Prescribing of Sacubitril / Valsartan 1. BACKGROUND Sacubitril valsartan is an angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitor, including both a neprilysin
LXIV: DRUGS: 4. RAS BLOCKADE
 LXIV: DRUGS: 4. RAS BLOCKADE ACE Inhibitors Components of RAS Actions of Angiotensin i II Indications for ACEIs Contraindications RAS blockade in hypertension RAS blockade in CAD RAS blockade in HF Limitations
LXIV: DRUGS: 4. RAS BLOCKADE ACE Inhibitors Components of RAS Actions of Angiotensin i II Indications for ACEIs Contraindications RAS blockade in hypertension RAS blockade in CAD RAS blockade in HF Limitations
Entresto Development of sacubitril/valsartan (LCZ696) for the treatment of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction
 Cardio-Metabolic Franchise Entresto Development of sacubitril/valsartan (LCZ696) for the treatment of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction Randy L Webb, PhD Rutgers Workshop October 21, 2016 Heart
Cardio-Metabolic Franchise Entresto Development of sacubitril/valsartan (LCZ696) for the treatment of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction Randy L Webb, PhD Rutgers Workshop October 21, 2016 Heart
heart failure John McMurray University of Glasgow.
 A to Z of RAAS blockade in heart failure John McMurray BHF Cardiovascular Research Centre University of Glasgow. RAAS inhibition in CHF ACE inhibition in patients with low LVEF CHF CONSENSUS Enalapril
A to Z of RAAS blockade in heart failure John McMurray BHF Cardiovascular Research Centre University of Glasgow. RAAS inhibition in CHF ACE inhibition in patients with low LVEF CHF CONSENSUS Enalapril
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 27 May 2009
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 27 May 2009 RASILEZ HCT 150 mg/12.5 mg, film-coated tablets B/30 (CIP code: 392 151-6) RASILEZ HCT 150 mg/25 mg, film-coated
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 27 May 2009 RASILEZ HCT 150 mg/12.5 mg, film-coated tablets B/30 (CIP code: 392 151-6) RASILEZ HCT 150 mg/25 mg, film-coated
Pharmacy Medical Policy Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonists
 Pharmacy Medical Policy Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonists Table of Contents Policy: Commercial Information Pertaining to All Policies Endnotes Policy: Medicare References Forms Policy History Policy
Pharmacy Medical Policy Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonists Table of Contents Policy: Commercial Information Pertaining to All Policies Endnotes Policy: Medicare References Forms Policy History Policy
Drugs acting on the reninangiotensin-aldosterone
 Drugs acting on the reninangiotensin-aldosterone system John McMurray Eugene Braunwald Scholar in Cardiovascular Diseases, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Boston & Visiting Professor, Harvard Medical School
Drugs acting on the reninangiotensin-aldosterone system John McMurray Eugene Braunwald Scholar in Cardiovascular Diseases, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Boston & Visiting Professor, Harvard Medical School
Hypertension Update Warwick Jaffe Interventional Cardiologist Ascot Hospital
 Hypertension Update 2008 Warwick Jaffe Interventional Cardiologist Ascot Hospital Definition of Hypertension Continuous variable At some point the risk becomes high enough to justify treatment Treatment
Hypertension Update 2008 Warwick Jaffe Interventional Cardiologist Ascot Hospital Definition of Hypertension Continuous variable At some point the risk becomes high enough to justify treatment Treatment
ACE inhibitors vs ARBs: Is one class better for heart failure?
 HEART FAILURE UPDATE MARK E. DUNLAP, MD * Associate Professor of Medicine, Physiology, and Biophysics, Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, and Louis B. Stokes Cleveland VA Medical Center,
HEART FAILURE UPDATE MARK E. DUNLAP, MD * Associate Professor of Medicine, Physiology, and Biophysics, Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, and Louis B. Stokes Cleveland VA Medical Center,
COZAAR Merck Sharp & Dhome
 COZAAR Merck Sharp & Dhome 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Cozaar 50 and Cozaar 100 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each tablet of Cozaar contains 50 mg or 100 mg of losartan potassium. For
COZAAR Merck Sharp & Dhome 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Cozaar 50 and Cozaar 100 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each tablet of Cozaar contains 50 mg or 100 mg of losartan potassium. For
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in Primary Care (2008) PROVIDER REFERENCE CARDS Chronic Kidney Disease
 VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in Primary Care (2008) PROVIDER REFERECE CARDS Chronic Kidney Disease CKD VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in Primary Care (2008) PROVIDER REFERECE CARDS Chronic Kidney Disease CKD VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management
A Fresh Look at ARBs : Focus on HF survival data
 A Fresh Look at ARBs : Focus on HF survival data Seok-Min Kang, MD, Ph D. Division of Cardiology, Severance Cardiovascular Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea HF specialists ARBs,
A Fresh Look at ARBs : Focus on HF survival data Seok-Min Kang, MD, Ph D. Division of Cardiology, Severance Cardiovascular Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea HF specialists ARBs,
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 7 January 2009
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 7 January 2009 LERCAPRESS 10 mg/10 mg, film-coated tablets Pack of 30 (CIP code: 385 953-3) Pack of 90 (CIP code:
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 7 January 2009 LERCAPRESS 10 mg/10 mg, film-coated tablets Pack of 30 (CIP code: 385 953-3) Pack of 90 (CIP code:
Elements for a public summary
 VI.2 Elements for a public summary VI.2.1Overview of disease epidemiology 1 Losartan is indicated for: Treatment of essential hypertension in adults and in children and adolescent 6 18 years of age. Treatment
VI.2 Elements for a public summary VI.2.1Overview of disease epidemiology 1 Losartan is indicated for: Treatment of essential hypertension in adults and in children and adolescent 6 18 years of age. Treatment
SCIENTIFIC DISCUSSION
 SCIENTIFIC DISCUSSION This module reflects the initial scientific discussion and scientific discussion on procedures which have been finalised before 1 September 2004. For scientific information on procedures
SCIENTIFIC DISCUSSION This module reflects the initial scientific discussion and scientific discussion on procedures which have been finalised before 1 September 2004. For scientific information on procedures
VALUE OF ACEI IN THE MANAGEMENT OF HYPERTENSION
 VALUE OF ACEI IN THE MANAGEMENT OF HYPERTENSION Dr Catherine BESEME Paris 6 th December 2005 6 th International Congress of Bangladesh Society of Medicine Hypertension is a risk factor at the source, with
VALUE OF ACEI IN THE MANAGEMENT OF HYPERTENSION Dr Catherine BESEME Paris 6 th December 2005 6 th International Congress of Bangladesh Society of Medicine Hypertension is a risk factor at the source, with
The control of hypertension in the. Reaching for Aggressive Blood Pressure Goals: Role of Angiotensin Receptor Blockade in Combination Therapy REPORTS
 REPORTS Reaching for Aggressive Blood Pressure Goals: Role of Angiotensin Receptor Blockade in Combination Therapy By Richard V. Milani, MD Abstract Elevated blood pressure, particularly systolic blood
REPORTS Reaching for Aggressive Blood Pressure Goals: Role of Angiotensin Receptor Blockade in Combination Therapy By Richard V. Milani, MD Abstract Elevated blood pressure, particularly systolic blood
Combination therapy Giuseppe M.C. Rosano, MD, PhD, MSc, FESC, FHFA St George s Hospitals NHS Trust University of London
 Combination therapy Giuseppe M.C. Rosano, MD, PhD, MSc, FESC, FHFA St George s Hospitals NHS Trust University of London KCS Congress: Impact through collaboration CONTACT: Tel. +254 735 833 803 Email:
Combination therapy Giuseppe M.C. Rosano, MD, PhD, MSc, FESC, FHFA St George s Hospitals NHS Trust University of London KCS Congress: Impact through collaboration CONTACT: Tel. +254 735 833 803 Email:
Class Update: Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors (ACEIs), Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (ARBs), and Direct Renin Inhibitors (DRIs)
 Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35, Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-945-5220 Fax 503-947-1119 Class Update: Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors
Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35, Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-945-5220 Fax 503-947-1119 Class Update: Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors
Clinical Updates in the Treatment of Hypertension JNC 7 vs. JNC 8. Lauren Thomas, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Practice Resident South Pointe Hospital
 Clinical Updates in the Treatment of Hypertension JNC 7 vs. JNC 8 Lauren Thomas, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Practice Resident South Pointe Hospital Objectives Review the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC
Clinical Updates in the Treatment of Hypertension JNC 7 vs. JNC 8 Lauren Thomas, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Practice Resident South Pointe Hospital Objectives Review the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC
Don t let the pressure get to you:
 Balanced information for better care Don t let the pressure get to you: Current evidence-based goals for treating hypertension A cornerstone of primary care: Lowering high blood pressure prevents cardiovascular
Balanced information for better care Don t let the pressure get to you: Current evidence-based goals for treating hypertension A cornerstone of primary care: Lowering high blood pressure prevents cardiovascular
Losartan lisinopril equivalent dose 新着 news 2018 年 3 月 6 日高等部 3 年生 大阪リゾート & スポーツ専門学校に合格! 2018 年 3 月 2 日茨木市立山手台小学校との交流.
 P ford residence southampton, ny Losartan lisinopril equivalent dose 新着 news 2018 年 3 月 6 日高等部 3 年生 大阪リゾート & スポーツ専門学校に合格! 2018 年 3 月 2 日茨木市立山手台小学校との交流. Losartan is classified as FDA pregnancy risk category
P ford residence southampton, ny Losartan lisinopril equivalent dose 新着 news 2018 年 3 月 6 日高等部 3 年生 大阪リゾート & スポーツ専門学校に合格! 2018 年 3 月 2 日茨木市立山手台小学校との交流. Losartan is classified as FDA pregnancy risk category
Page 1 of DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS Tablets: 75 mg, 150 mg, 300 mg (3)
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use IRBESARTAN TABLETS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for IRBESARTAN TABLETS.
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use IRBESARTAN TABLETS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for IRBESARTAN TABLETS.
Phase 3 investigation of aprocitentan for resistant hypertension management. Investor Webcast June 2018
 Phase 3 investigation of aprocitentan for resistant hypertension management Investor Webcast June 2018 The following information contains certain forward-looking statements, relating to the company s business,
Phase 3 investigation of aprocitentan for resistant hypertension management Investor Webcast June 2018 The following information contains certain forward-looking statements, relating to the company s business,
The CARI Guidelines Caring for Australasians with Renal Impairment. ACE Inhibitor and Angiotensin II Antagonist Combination Treatment GUIDELINES
 ACE Inhibitor and Angiotensin II Antagonist Combination Treatment Date written: September 2004 Final submission: September 2005 Author: Kathy Nicholls GUIDELINES No recommendations possible based on Level
ACE Inhibitor and Angiotensin II Antagonist Combination Treatment Date written: September 2004 Final submission: September 2005 Author: Kathy Nicholls GUIDELINES No recommendations possible based on Level
Healthcare Implications of Achieving JNC 7 Blood Pressure Goals in Clinical Practice
 CONTINUING EDUCATION Healthcare Implications of Achieving JNC 7 Blood Pressure Goals in Clinical Practice GOAL To provide participants with current information about current blood pressure goals and effective
CONTINUING EDUCATION Healthcare Implications of Achieving JNC 7 Blood Pressure Goals in Clinical Practice GOAL To provide participants with current information about current blood pressure goals and effective
Beta 1 Beta blockers A - Propranolol,
 Pharma Lecture 3 Beta blockers that we are most interested in are the ones that target Beta 1 receptors. Beta blockers A - Propranolol, it s a non-selective competitive antagonist of beta 1 and beta 2
Pharma Lecture 3 Beta blockers that we are most interested in are the ones that target Beta 1 receptors. Beta blockers A - Propranolol, it s a non-selective competitive antagonist of beta 1 and beta 2
AZMARDA Tablets (Sacubitril/Valsartan)
 Published on: 20 Mar 2017 AZMARDA Tablets (Sacubitril/Valsartan) Composition AZMARDA 50 Each film-coated tablet contains: 24 mg sacubitril and 26 mg valsartan as sodium salt complex AZMARDA 100 Each film-coated
Published on: 20 Mar 2017 AZMARDA Tablets (Sacubitril/Valsartan) Composition AZMARDA 50 Each film-coated tablet contains: 24 mg sacubitril and 26 mg valsartan as sodium salt complex AZMARDA 100 Each film-coated
Modern Management of Hypertension
 Modern Management of Hypertension Robert B. Baron MD Professor of Medicine Associate Dean for GME and CME Declaration of full disclosure: No conflict of interest Current Status of Hypertension Prevalence
Modern Management of Hypertension Robert B. Baron MD Professor of Medicine Associate Dean for GME and CME Declaration of full disclosure: No conflict of interest Current Status of Hypertension Prevalence
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Valsartan Sandoz 40 mg film-coated tablets Valsartan Sandoz 80 mg film-coated tablets Valsartan Sandoz 160 mg film-coated tablets Valsartan
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Valsartan Sandoz 40 mg film-coated tablets Valsartan Sandoz 80 mg film-coated tablets Valsartan Sandoz 160 mg film-coated tablets Valsartan
1.1. Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonists and Taste Disorders
 1.1. Angiotensin II Receptor and Taste Disorders Introduction The angiotensin II receptor antagonists (ARBs) and angiotensin II receptor antagonist combination with hydrocholorothiazide available on the
1.1. Angiotensin II Receptor and Taste Disorders Introduction The angiotensin II receptor antagonists (ARBs) and angiotensin II receptor antagonist combination with hydrocholorothiazide available on the
ADVANCES IN MANAGEMENT OF HYPERTENSION
 Advances in Management of Robert B. Baron MD Professor of Medicine Associate Dean for GME and CME Declaration of full disclosure: No conflict of interest Current Status of Prevalence 29%; Blacks 33.5%
Advances in Management of Robert B. Baron MD Professor of Medicine Associate Dean for GME and CME Declaration of full disclosure: No conflict of interest Current Status of Prevalence 29%; Blacks 33.5%
Lisinopril losartan conversion dose
 P ford residence southampton, ny Lisinopril losartan conversion dose Deep in-house technology, streaming expertise, and partnerships with the widest range of digital platforms secures our position as the
P ford residence southampton, ny Lisinopril losartan conversion dose Deep in-house technology, streaming expertise, and partnerships with the widest range of digital platforms secures our position as the
Preventing and Treating High Blood Pressure
 Preventing and Treating High Blood Pressure: Finding the Right Balance of Integrative and Pharmacologic Approaches Robert B. Baron MD Professor of Medicine Associate Dean for GME and CME Blood Pressure
Preventing and Treating High Blood Pressure: Finding the Right Balance of Integrative and Pharmacologic Approaches Robert B. Baron MD Professor of Medicine Associate Dean for GME and CME Blood Pressure
High-dose monotherapy vs low-dose combination therapy of calcium channel blockers and angiotensin receptor blockers in mild to moderate hypertension
 (2005) 19, 491 496 & 2005 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/05 $30.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE High-dose monotherapy vs low-dose combination therapy of calcium channel blockers
(2005) 19, 491 496 & 2005 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/05 $30.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE High-dose monotherapy vs low-dose combination therapy of calcium channel blockers
Cardiac Protection across the cardiac continuum. Dong-Ju Choi, MD, PhD College of Medicine Seoul National University
 Cardiac Protection across the cardiac continuum Dong-Ju Choi, MD, PhD College of Medicine Seoul National University Renin Angiotensin Cascade Nitric oxide (NO) Bradykinin Degradation products ACE ACEI
Cardiac Protection across the cardiac continuum Dong-Ju Choi, MD, PhD College of Medicine Seoul National University Renin Angiotensin Cascade Nitric oxide (NO) Bradykinin Degradation products ACE ACEI
Managing Hypertension in Diabetes Sean Stewart, PharmD, BCPS, BCACP, CLS Internal Medicine Park Nicollet Clinic St Louis Park.
 Managing Hypertension in Diabetes 2015 Sean Stewart, PharmD, BCPS, BCACP, CLS Internal Medicine Park Nicollet Clinic St Louis Park Case Scenario Mike M is a 59 year old man with type 2 diabetes managed
Managing Hypertension in Diabetes 2015 Sean Stewart, PharmD, BCPS, BCACP, CLS Internal Medicine Park Nicollet Clinic St Louis Park Case Scenario Mike M is a 59 year old man with type 2 diabetes managed
Managing Hypertension in 2016
 Managing Hypertension in 2016: Where Do We Draw the Line? Disclosure No relevant financial relationships Robert B. Baron MD MS Professor and Associate Dean UCSF School of Medicine baron@medicine.ucsf.edu
Managing Hypertension in 2016: Where Do We Draw the Line? Disclosure No relevant financial relationships Robert B. Baron MD MS Professor and Associate Dean UCSF School of Medicine baron@medicine.ucsf.edu
Anti-hypertensive agents
 Anti-hypertensive agents Dr. Pran Kishore Deb Assistant Professor, Pharmaceutical Medicinal Chemistry Faculty of Pharmacy, Philadelphia University-Jordan Email: pdeb@philadelphia.edu.jo Anti-hypertensive
Anti-hypertensive agents Dr. Pran Kishore Deb Assistant Professor, Pharmaceutical Medicinal Chemistry Faculty of Pharmacy, Philadelphia University-Jordan Email: pdeb@philadelphia.edu.jo Anti-hypertensive
Eplerenon Medical Valley + Eplerenon Stada
 VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Heart failure is a complex syndrome, clinically characterized by signs and symptoms secondary to abnormal cardiac function. It
VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Heart failure is a complex syndrome, clinically characterized by signs and symptoms secondary to abnormal cardiac function. It
Each tablet contains:
 Composition: Each tablet contains: Tolvaptan 15/30mg Pharmacokinetic properties: In healthy subjects the pharmacokinetics of tolvaptan after single doses of up to 480 mg and multiple doses up to 300 mg
Composition: Each tablet contains: Tolvaptan 15/30mg Pharmacokinetic properties: In healthy subjects the pharmacokinetics of tolvaptan after single doses of up to 480 mg and multiple doses up to 300 mg
Losartan lisinopril equivalent dose
 新着 news 2018 年 2 月 28 日 jica 国際協力中学生 高校生エッセイコンテスト 2017 表彰式 2018 年 2 月 19 日 2017 年度第 8 回卒業式を挙行. CHFpatients.com - Ace inhibitors explained in plain English - the primary drug treatment for heart failure
新着 news 2018 年 2 月 28 日 jica 国際協力中学生 高校生エッセイコンテスト 2017 表彰式 2018 年 2 月 19 日 2017 年度第 8 回卒業式を挙行. CHFpatients.com - Ace inhibitors explained in plain English - the primary drug treatment for heart failure
ANNEX I SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS. Medicinal product no longer authorised
 ANNEX I SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Sprimeo 150 mg film-coated tablets 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each film-coated tablet contains 150 mg aliskiren
ANNEX I SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Sprimeo 150 mg film-coated tablets 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each film-coated tablet contains 150 mg aliskiren
ACE Inhibitors and ARBs To Protect Your Heart? A Guide for Patients Being Treated for Stable Coronary Heart Disease
 ACE Inhibitors and ARBs To Protect Your Heart? A Guide for Patients Being Treated for Stable Coronary Heart Disease Is This Guide Right for Me? This Guide Is for You If: You have coronary heart disease,
ACE Inhibitors and ARBs To Protect Your Heart? A Guide for Patients Being Treated for Stable Coronary Heart Disease Is This Guide Right for Me? This Guide Is for You If: You have coronary heart disease,
