Direct renin inhibitors: the dawn of a new era, or just a variation on a theme?
|
|
|
- Oswin Harmon
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2007) 22: doi: /ndt/gfm363 Advance Access publication 7 June 2007 Editorial Review Direct renin inhibitors: the dawn of a new era, or just a variation on a theme? Liviu Segall 1, Adrian Covic 1 and David J. A. Goldsmith 2 1 Nephrology, Dialysis and Renal Transplantation Center, C. I. Parhon University Hospital, B-dul Carol I No. 50, Iasi , Romania and 2 Renal Unit, Guy s Hospital, London SE1 9RT, UK Keywords: chronic kidney disease; direct renin inhibitors; renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) inhibitors in chronic kidney disease (CKD): benefits and limitations Numerous studies have demonstrated that the reninangiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) plays an important role in the progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD). Angiotensin (Ang) II generates intrarenal haemodynamic and inflammatory changes that promote proteinuria, growth of glomerular and tubular cells, inhibition of NO synthesis, stimulation of extracellular matrix synthesis and induction of chemokines, reactive oxygen species and apoptosis [1]. In addition, in animal models of renal diseases, aldosterone is also involved in endothelial dysfunction, inflammation, proteinuria and fibrosis [2]. In clinical trials, treatment with angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and Ang II AT1 receptor blockers (ARBs) was proved to slow down the evolution of both diabetic and non-diabetic nephropathies and, therefore, it is currently regarded as the cornerstone of what we call nephroprotection. A controversial issue is whether these agents are superior to other antihypertensive drugs in terms of nephroprotection in other words, do they possess so-called pleiotropic effects? A large meta-analysis [3] suggested that the benefit seen with ACE inhibitors was related to the blood pressure (BP) decrease alone. The truth, as Sarafidis et al. [4] pointed out in a very recent review, is that, indeed, ACE inhibitors exhibit a BP-independent renoprotective effect, but only in patients with proteinuria and advanced CKD (i.e. stage 3 or 4), and also that the higher the baseline Correspondence and offprint requests to: Dr Liviu Segall, MD, Nephrology, Dialysis and Renal Transplantation Center, C. I. Parhon University Hospital, B-dul Carol I No. 50, Iasi , Romania. livsegall@yahoo.com urine protein excretion and its subsequent decrease, the more pronounced the beneficial effect of these drugs is likely to be [4]. However, it is not sufficiently appreciated that, due to the remarkable complexity of the RAAS, neither ACE inhibitors nor ARBs alone can completely suppress its activity (Figure 1). The main limitations of these agents in that regard can be summarized as follows: (i) A substantial proportion of Ang II is generated in the kidneys from Ang I via non-ace pathways, such as chymase [5], which are not susceptible to the actions of ACE inhibitors. (ii) ACE inhibition and ARB, by interrupting negative feedback-loops, result in high plasma (and most likely tissue-) renin concentrations and high plasma renin activity (PRA), which may overcome the drugs effectiveness. The reactivation of Ang II (or Ang II escape ) has been described with both ACE inhibitors and ARBs [6]; however, its clinical significance is not yet fully understood. (iii) Renin can also bind to specific receptors in the mesangium and in the subendothelium of the renal arteries. This binding leads on one hand, to a substantial increase in the catalytic efficiency of conversion of angiotensinogen to Ang I, and, on the other hand, to stimulation of mitogenactivated protein kinases, ERK-1 and ERK-2 [7]. In animal models of nephrotic syndrome, treatment with ACE inhibitors was associated with a reduction in glomerular injury and proteinuria, but also with tubulo-interstitial lesions [8]. These findings support a direct profibrotic role for renin, independent of its Ang-generating effect. (iv) ACE inhibitors induce an acute decrease in plasma aldosterone. This effect, however, is often only transient and followed by a progressive rise in aldosterone levels that ultimately, with long-term ACE inhibition, can reach normal or even elevated concentrations. This aldosterone ß The Author [2007]. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of ERA-EDTA. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please journals.permissions@oxfordjournals.org
2 2436 L. Segall et al. Fig. 1. The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Black arrows show stimulation and gray arrows show inhibition. Dotted lines show alternative pathways mainly documented in experimental studies. aˆ blockers, renin inhibitors, inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) and angiotensin II type-1 receptor blockers (ARB) reduce the activity of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS). AT-R ¼ angiotensin receptor; EP ¼ endopeptidases; EC ¼ endothelial cells. (Reproduced with permission from ref. 21). escape is not well explained, but it might be the result of aldosterone secretion stimulation by high potassium levels induced by ACE inhibition. Aldosterone breakthrough also occurs during long-term ARB treatment, through an AT2-dependent mechanism [9]. (v) The ARBs leave the AT2 receptors unblocked, and some experimental data suggest that these receptors are involved in renal inflammation, by activation of NF-kB in mesangial and endothelial cells and induction of chemokines [6]. Taking all of these mechanisms together, one can see that there is at least the potential for additional benefit from alternative or complementary approaches to RAAS blockade. Combination therapy: more effective, more risks One way in which this last point has been addressed is by dual RAAS blockade with ACE inhibitors and ARBs together. This stratagem is now advocated by many nephrologists, as it has been shown to decrease proteinuria and slow kidney disease progression more effectively than using each of the two drug classes alone [6]. However, such combination therapy carries, undoubtedly, an increased risk of side effects, particularly in certain patients such as the elderly, the saltdepleted, those receiving cyclooxygenase inhibitors, those with renal artery stenosis and during anaesthetic induction [10]. In the CHARM-Added trial, patients with congestive heart failure treated with an ARB and an ACE inhibitor experienced significantly more episodes of hypotension, acute renal failure and hyperkalaemia, compared with those receiving an ACE inhibitor alone [11]. The risk of hyperkalaemia was also increased when the baseline glomerular filtration rate was <35 ml/min [12]. Another useful combination could be the addition of an aldosterone receptor antagonist to patients already receiving an ACE inhibitor or an ARB [13]. In small studies (reviewed by Sarafidis et al. [4]), the use of either spironolactone or eplerenone, on top of ACE inhibitors or ARBs, further decreased proteinuria. However, it is not known whether the addition of an aldosterone antagonist can retard the long-term progression of CKD to end-stage renal failure, but
3 Direct renin inhibitors 2437 promising data have been recently published by Bianchi et al. [14]. On the other hand, such combinations may dangerously increase the serum potassium levels in CKD patients [14]. Direct renin inhibition: an old new strategy of RAAS blockade A new and promising development in RAAS blockade has been initiated with the introduction of the first direct renin inhibitor (DRI), aliskiren, recently approved by the USA Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of hypertension. While this is indeed an exciting progress, it should not be forgotten that beta-blockers (BBs) also induce a significant reduction in plasma renin synthesis, by about one-third. However, as it has been recently discussed at length, their other properties may not make them first-line therapy choices for hypertensive patients [15]. Research on DRIs started over 30 years ago and several agents have been synthesized over this period, but low efficacy, lack of oral availability and high cost prevented their therapeutic application [16]. Aliskiren is the only orally active DRI that progressed to phase- III clinical trials and, is in fact the first new treatment for hypertension since the introduction of ARBs in As there is only one such compound that has undergone significant clinical trial exposure, we are restricted to discussing this to try to understand the potential effects, benefits and safety-concerns of DRIs, but it should be borne in mind that there will most likely be other DRIs in time. Unlike ACE inhibitors and ARBs, DRIs induce a marked and sustained reduction in PRA, and, as a result, the serum levels of Ang I, Ang II and aldosterone dramatically decrease [16]. DRIs do not block other Ang I-releasing enzymes, such as cathepsin D or tonins, but these enzymes appear to be of minor physiological importance [17]. Several studies in animal models by Fisher et al. [18] showed that DRIs cause a significantly higher increase in renal plasma flow than ACE inhibitors, despite similar BP falls, which suggests a more complete inhibition of the renal RAAS. In clinical trials, the addition of aliskiren to PRA-increasing drugs like diuretics, ACE inhibitors and ARBs was shown to prevent the raise or even to lower the PRA [19]. Suppressing the RAAS at the earliest stage with DRIs may be expected to limit the Ang II and the aldosterone escape phenomena, by avoiding the accumulation of their precursors [20]. Although BBs are also capable of reducing the PRA, their influence on Ang I, Ang II and aldosterone is unknown [21]. However, most BBs either decrease (non-selective BBs) or have no influence (b-1-selective BBs) on the renal blood flow and the glomerular filtration rate [22]. Aliskiren s average half-life of 24 h [23] and its 98% trough to peak ratio [24] makes it appropriate for a once daily administration. Since <1% of the drug is excreted by the kidneys [16], there is no need for adjustment of the starting dose in patients with renal insufficiency. Aliskiren concentrations in the kidneys are particularly high and persistent up to 3 weeks after discontinuation of the drug, suggesting that long-term effects could be derived at the tissue level [25]. Aliskiren monotherapy demonstrated significant, dose-dependent antihypertensive effects in several placebo-controlled clinical trials [23]. Compared with other drugs, the BP lowering effect of aliskiren 150 mg/day was similar to that of irbesartan 150 mg/day [26] and hydrochlorothiazide 12.5 mg/day [27], whereas at a dose of 300 mg/day, aliskiren was as potent as hydrochlorothiazide [27], but more effective than ramipril 10 mg/day [28]. Combinations of aliskiren with diuretics [27], calcium-channel blockers [29], ACE inhibitors [28] and ARBs [30] provided greater reductions in BP than any of these drugs alone. Aliskiren is, generally, well tolerated by hypertensive patients. In contrast to ACE inhibitors, it does not induce accumulation of substance P or bradykinin, therefore side effects like cough and angiooedema are implausible [16]. Angiooedema does not occur more often with aliskiren than with placebo, and whereas the incidence of cough is slightly increased with aliskiren, it is still much lower than with ACE inhibitors [23]. Increases in serum potassium >5.5 mmol/l were seldom reported with aliskiren alone; however, when used in combination with an ACE inhibitor in a diabetic population, hyperkalaemia was more frequent [23]. Minor increases in blood urea nitrogen or serum creatinine were observed in <7% of patients treated with aliskiren alone, vs 6% on placebo [23]. Yet, since subjects with significant renal dysfunction, dialysis, nephrotic syndrome or renovascular hypertension were excluded from clinical trials of aliskiren in hypertension, caution is required when prescribing the drug in such patients [23]; clearly, there is an urgent need to investigate DRIs in these special conditions. Better renoprotection with renin inhibitors? From a nephrologist s point of view, renin inhibition seems an interesting new approach for preventing the progression of CKD. Just like ACE inhibitors and ARBs, DRIs were shown to diminish renal vascular resistance and increase renal blood flow. On the other hand, by predominantly dilating the efferent arteriole, the net result is a decrease in the filtration fraction, without a change (or even an increase) in the glomerular filtration rate and the fractional sodium excretion. These effects were seen in animals [31 33], as well as in humans [34,35], and may provide renoprotective benefits, similar to ACE inhibitors and ARBs. Moreover, particular advantages may result from direct renin inhibition, if the Ang-independent profibrotic role of renin (discussed earlier) is considered relevant.
4 2438 L. Segall et al. Direct evidence of favourable effects of renin inhibitors on kidney disease is very scarce; however, a few experimental and clinical trials have yielded notable results. Several researchers studied the renal effects of aliskiren in double transgenic rats, which carry human renin and angiotensinogen genes and spontaneously develop malignant hypertension, leading to multiple organ damage and death, if left untreated. In these animals, aliskiren significantly lowered the BP and albuminuria, in a dose-dependent manner, and normalized the serum creatinine [36]. The antiproteinuric effect of aliskiren persisted even 2 weeks after stopping the treatment [37]. The drug reduced intrarenal inflammation (cell infiltration, C-reactive protein, tumour necrosis factor-a and complement) and fibrosis, to the same extent as losartan did [38]. In six patients with renal dysfunction, a short-acting renin inhibitor, remikiren, reduced proteinuria by 27% (P < 0.01) from a median baseline level of 5.8 g/day [35]. Preliminary data from an ongoing clinical study indicate a more substantial reduction in microalbuminuria with aliskiren ( 61%) compared with ramipril ( 50%) [39]. Conclusion DRIs may have a significant future as renoprotective agents, besides their utility as antihypertensives. The ability to decrease renin concentration and PRA, the more complete inhibition of the RAAS, the expected limitation of Ang II and aldosterone escape phenomena, and the prevention of possible renal-damaging direct effects of renin make DRIs appealing drugs for nephrologists. Certainly though, DRIs have a very long way to go before eventually overtaking the wellestablished ACE inhibitors and ARBs, with their long track record of reducing not just the intermediate endpoint proteinuria, but also the progression of CKD, and conferring cardioprotection and increased survival to many groups of patients with heart failure, diabetes or myocardial infarction. To start with, DRIs may find their place as adjunctive therapies, in combinations with ACE inhibitors or ARBs, or less commonly still, in patients intolerant to these. In the next few years, the results of the first phase III trials with aliskiren in patients with CKD will become available. The ongoing AVOID study (Aliskiren in the Evaluation of Proteinuria in Diabetes) is a 6-month study of aliskiren in addition to losartan in 496 patients with controlled hypertension, type 2 diabetes and proteinuria, with the change in urinary albumin to creatinine ratio as primary endpoint. ALTITUDE (Aliskiren Trial in Type 2 Diabetic Nephropathy) is a type 2 diabetes outcomes study that will be carried out in approximately 6000 subjects, to determine whether aliskiren delays time to diabetic complications in patients with diabetes mellitus and nephropathy [39]. Finally, other DRIs are expected to join aliskiren in clinical use in the years to come, since some of these new agents are currently undergoing animal and pre-clinical investigation [21]. Acknowledgements. The authors wish to address special thanks to Dr Jan A. Staessen, MD, PhD, FESC, FAHA, Laboratory of Hypertension, Leuven, Belgium, for granting them the permission to reproduce the picture The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system [21]. Conflict of interest statement. Dr D.J.A.G. receives honoraria and speaker fees from Novartis, Astellas, Shire, Genzyme, Roche, Amgen and Abbott. Dr A.C. is a member of the speakers bureau for Hoffman La Roche and member of the advisory board of Fresenius Medical Care. Dr L.S. has no conflict of interests to declare. References 1. Ru ster C, Wolf G. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and progression of renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 2006; 17: Nishiyama A, Abe Y. Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies of chronic renal injury: Renoprotective effects of aldosterone blockade. J Pharmacol Sci 2006; 100: Casas JP, Chua W, Loukogeorgakis S et al. Effect of inhibitors of the renin-angiotensin system and other antihypertensive drugs on renal outcomes: systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2005; 366: Sarafidis PA, Khosla N, Bakris GL. Antihypertensive therapy in the presence of proteinuria. Am J Kidney Dis 2007; 49: Hollenberg NK, Fisher NDL. Renal circulation and blockade of the renin-angiotensin system. Hypertension 1995; 26: Wolf G, Ritz E. Combination therapy with ACE inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers to halt progression of chronic renal disease: pathophysiology and indications. Kidney Int 2005; 67: Nguyen G, Delarue F, Burckle C, Bouzhir L, Giller T, Sraer J-D. Pivotal role of the renin/prorenin receptor in angiotensin II production and cellular responses to renin. J Clin Invest 2002; 10: Hamming I, Navis G, Kocks MJ, van Goor H. ACE inhibition has adverse renal effects during dietary sodium restriction in proteinuric and healthy rats. J Pathol 2006; 209: Naruse M, Tanabe A, Sato A et al. Aldosterone breakthrough during angiotensin II receptor antagonist therapy in strokeprone spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertension 2002; 40: Azizi M, Menard J. Combined blockade of the renin-angiotensin system with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonists. Circulation 2004; 109: McMurray JJ, Ostergren J, Swedberg K et al. Effects of candesartan in patients with chronic heart failure and reduced left-ventricular systolic function taking angiotensin-convertingenzyme inhibitors: the CHARM-Added trial. Lancet 2003; 362: Ruilope LM, Aldigier JC, Ponticelli C et al. Safety of the combination of valsartan and benazepril in patients with chronic renal disease: European Group for the Investigation of Valsartan in Chronic Renal Disease. J Hypertens 2000; 18: Covic A, Gusbeth-Tatomir P, Goldsmith DJ. Is it time for spironolactone therapy in dialysis patients? Nephrol Dial Transplant 2006; 21: Bianchi S, Bigazzi R, Campese VM. Long-term effects of spironolactone on proteinuria and kidney function in patients with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 2006; 70:
5 Direct renin inhibitors Lindholm LH, Carlberg B, Samuelsson O. Should beta blockers remain first choice in the treatment of primary hypertension? A meta-analysis. Lancet 2005; 366: Nussberger J, Wuerzner G, Jensen C, Brunner HR. Angiotensin II suppression in humans by the orally active renin inhibitor aliskiren (SPP100). Comparison with enalapril. Hypertension 2002; 39: e1 e8 17. Phillips MI, Speakman EA, Kimura B. Levels of angiotensin and molecular biology of the tissue renin angiotensin systems. Regul Pept 1993; 43: Fisher NDL, Hollenberg NK. Renin inhibition: what are the therapeutic opportunities? J Am Soc Nephrol 2005; 16: O Brien E, Barton J, Nussberger J et al. Aliskiren reduces blood pressure and suppresses plasma renin activity in combination with a thiazide diuretic, an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, or an angiotensin receptor blocker. Hypertension 2007; 49: Athyros VG, Mikhailidis DP, Kakafika AI, Tziomalos K, Karagiannis A. Angiotensin II reactivation and aldosterone escape phenomena in renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system blockade: is oral renin inhibition the solution? Expert Opin Pharmacother 2007; 8: Staessen JA, Li Y, Richart T. Oral renin inhibitors. Lancet 2006; 368: Bakris GL, Hart P, Ritz E. Beta blockers in the management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 2006; 70: Tekturna (aliskiren). Prescribing information ( Mitchell J, Oh B, Herron J et al. Once-daily aliskiren provides effective, smooth 24-hour blood pressure control in patients with hypertension. J Clin Hypertens 2006; 8 [5 Suppl. A]:A93(P-209). Poster presented at ASH Feldman DL, Persohn E, Schutz H et al. Renal localization of the renin inhibitor aliskiren. J Clin Hypertens 2006; 8 [Suppl. A]: A Gradman AH, Schmieder RE, Lins RL et al. Aliskiren, a novel orally effective renin inhibitor, provides dose-dependent antihypertensive efficacy and placebo-like tolerability in hypertensive patients. Circulation 2005; 111: Villamil A, Chrysant S, Calhoun D et al. The novel oral renin inhibitor aliskiren provides effective blood pressure control in patients with hypertension when used alone or in combination with hydrochlorothiazide. J Clin Hypertens 2006; 8 [Suppl. A]: A Uresin Y, Taylor A, Kilo C et al. Aliskiren, a novel rennin inhibitor, has greater BP lowering than ramipril and additional BP lowering when combined with ramipril in patients with diabetes and hypertension. J Hypertens 2006; 24 [Suppl. 4]: S Munger MA, Drummond W, Essop MR et al. Aliskiren as addon to amlodipine provides significant additional blood pressure lowering without increased oedema associated with doubling the amlodipine dose. Abstract presented at WCC/ESC, Barcelona, Spain, 2 6 September, 2006 (P784) 30. Pool JL, Schmieder RE, Azizi M et al. Aliskiren, an orally effective rennin inhibitor, provides antihypertensive efficacy alone and in combination with valsartan. Am J Hypertens 2007; 20: Clozel JP, Veniant MM, Qiu C, Sprecher U, Wolfgang R, Fischli W. Renal vascular and biochemical responses to systemic rennin inhibition in dogs at low renal perfusion pressure. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1999; 34: Verburg KM, Kleinert HD, Chekal MA, Kadam JRC, Young GA. Renal hemodynamic and excretory responses to renin inhibition induced by A J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1990; 252: El Amrani AIK, Me nard J, Gonzales MF, Michel JB. Effects of blocking the angiotensin II receptor, converting enzyme, and rennin activity on the renal hemodynamics of normotensive Guinea pigs. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1993; 22: Fisher NDL, Allan D, Kifor I et al. Responses to converting enzyme and renin inhibition: role of angiotensin II in humans. Hypertension 1994; 23: van Paassen P, de Zeeuw D, Navis G, de Jong PE. Renal and systemic effects of continued treatment with renin inhibitor remikiren in hypertensive patients with normal and impaired renal function. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2000; 15: Pilz B, Shagdarsuren E, Wellner M et al. Aliskiren, a human renin inhibitor, ameliorates cardiac and renal damage in doubletransgenic rats. Hypertension 2005; 46: Feldman D, Jin L, Miserindinomoltini R, Xuan H, Luft F, Muller D. Aliskiren, a human renin inhibitor induces persistent renoprotection comparable to ACE inhibition in double transgenic rats (dtgr). Am J Hypertens 2005; 18: A Shagdarsuren E, Wellner M, Braesen JH et al. Complement activation in angiotensin II-induced organ damage. Circ Res 2005; 97: Chris Jensen J. SPP100 (Aliskiren). The journey from the laboratory bench to market. Received for publication: Accepted in revised form:
Scientific conclusions and detailed explanation of the scientific grounds for the differences from the PRAC recommendation
 Annex I Scientific conclusions, grounds for variation to the terms of the marketing authorisations and detailed explanation of the scientific grounds for the differences from the PRAC recommendation 1
Annex I Scientific conclusions, grounds for variation to the terms of the marketing authorisations and detailed explanation of the scientific grounds for the differences from the PRAC recommendation 1
The CARI Guidelines Caring for Australasians with Renal Impairment. ACE Inhibitor and Angiotensin II Antagonist Combination Treatment GUIDELINES
 ACE Inhibitor and Angiotensin II Antagonist Combination Treatment Date written: September 2004 Final submission: September 2005 Author: Kathy Nicholls GUIDELINES No recommendations possible based on Level
ACE Inhibitor and Angiotensin II Antagonist Combination Treatment Date written: September 2004 Final submission: September 2005 Author: Kathy Nicholls GUIDELINES No recommendations possible based on Level
Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers PROTEINURIA
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers PROTEINURIA
Reducing proteinuria
 Date written: May 2005 Final submission: October 2005 Author: Adrian Gillin Reducing proteinuria GUIDELINES a. The beneficial effect of treatment regimens that include angiotensinconverting enzyme inhibitors
Date written: May 2005 Final submission: October 2005 Author: Adrian Gillin Reducing proteinuria GUIDELINES a. The beneficial effect of treatment regimens that include angiotensinconverting enzyme inhibitors
Aggressive blood pressure reduction and renin angiotensin system blockade in chronic kidney disease: time for re-evaluation?
 http://www.kidney-international.org & 2013 International Society of Nephrology Aggressive blood pressure reduction and renin angiotensin system blockade in chronic kidney disease: time for re-evaluation?
http://www.kidney-international.org & 2013 International Society of Nephrology Aggressive blood pressure reduction and renin angiotensin system blockade in chronic kidney disease: time for re-evaluation?
The Road to Renin System Optimization: Renin Inhibitor
 The Road to Renin System Optimization: Renin Inhibitor A New Perspective on the Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS) Yong-Jin Kim, MD Seoul National University Hospital Human and Economic Costs of Hypertension
The Road to Renin System Optimization: Renin Inhibitor A New Perspective on the Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS) Yong-Jin Kim, MD Seoul National University Hospital Human and Economic Costs of Hypertension
ANGIOTENSIN II RECEPTOR BLOCKERS: MORE THAN THE ALTERNATIVE PRESENTATION BY: PATRICK HO, USC PHARM D. CANDIDATE OF 2017 MENTOR: DR.
 ANGIOTENSIN II RECEPTOR BLOCKERS: MORE THAN THE ALTERNATIVE PRESENTATION BY: PATRICK HO, USC PHARM D. CANDIDATE OF 2017 MENTOR: DR. CRAIG STERN, PHARMD, MBA, RPH, FASCP, FASHP, FICA, FLMI, FAMCP RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN
ANGIOTENSIN II RECEPTOR BLOCKERS: MORE THAN THE ALTERNATIVE PRESENTATION BY: PATRICK HO, USC PHARM D. CANDIDATE OF 2017 MENTOR: DR. CRAIG STERN, PHARMD, MBA, RPH, FASCP, FASHP, FICA, FLMI, FAMCP RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN
HYPERTENSION IN CKD. LEENA ONGAJYOOTH, M.D., Dr.med RENAL UNIT SIRIRAJ HOSPITAL
 HYPERTENSION IN CKD LEENA ONGAJYOOTH, M.D., Dr.med RENAL UNIT SIRIRAJ HOSPITAL Stages in Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease and Therapeutic Strategies Complications Normal Increased risk Damage GFR
HYPERTENSION IN CKD LEENA ONGAJYOOTH, M.D., Dr.med RENAL UNIT SIRIRAJ HOSPITAL Stages in Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease and Therapeutic Strategies Complications Normal Increased risk Damage GFR
Effect of aliskiren on proteinuria in non-diabetic chronic kidney disease: a double-blind, crossover, randomised, controlled trial
 Int Urol Nephrol (2012) 44:1763 1770 DOI 10.1007/s11255-011-0110-z NEPHROLOGY ORIGINAL PAPER Effect of aliskiren on proteinuria in non-diabetic chronic kidney disease: a double-blind, crossover, randomised,
Int Urol Nephrol (2012) 44:1763 1770 DOI 10.1007/s11255-011-0110-z NEPHROLOGY ORIGINAL PAPER Effect of aliskiren on proteinuria in non-diabetic chronic kidney disease: a double-blind, crossover, randomised,
Prof. Armando Torres Nephrology Section Hospital Universitario de Canarias University of La Laguna Tenerife, Canary Islands, Spain.
 Does RAS blockade improve outcomes after kidney transplantation? Armando Torres, La Laguna, Spain Chairs: Hans De Fijter, Leiden, The Netherlands Armando Torres, La Laguna, Spain Prof. Armando Torres Nephrology
Does RAS blockade improve outcomes after kidney transplantation? Armando Torres, La Laguna, Spain Chairs: Hans De Fijter, Leiden, The Netherlands Armando Torres, La Laguna, Spain Prof. Armando Torres Nephrology
Renal protection by inhibition of the renin-angiotensinaldosterone
 Renal protection by inhibition of the renin-angiotensinaldosterone system Tomas Berl Key words: angiotensinconverting enzyme inhibitor, angiotensin receptor blocker, combination therapy, direct renin inhibitor,
Renal protection by inhibition of the renin-angiotensinaldosterone system Tomas Berl Key words: angiotensinconverting enzyme inhibitor, angiotensin receptor blocker, combination therapy, direct renin inhibitor,
Optimal blockade of the Renin- Angiotensin-Aldosterone. in chronic heart failure
 Optimal blockade of the Renin- Angiotensin-Aldosterone Aldosterone- (RAA)-System in chronic heart failure Jan Östergren Department of Medicine Karolinska University Hospital Stockholm, Sweden Key Issues
Optimal blockade of the Renin- Angiotensin-Aldosterone Aldosterone- (RAA)-System in chronic heart failure Jan Östergren Department of Medicine Karolinska University Hospital Stockholm, Sweden Key Issues
Cardiovascular Protection and the RAS
 Cardiovascular Protection and the RAS Katalin Kauser, MD, PhD, DSc Senior Associate Director, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceutical Inc. Micardis Product Pipeline Scientific Support Ridgefield, CT, USA Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular Protection and the RAS Katalin Kauser, MD, PhD, DSc Senior Associate Director, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceutical Inc. Micardis Product Pipeline Scientific Support Ridgefield, CT, USA Cardiovascular
Introduction. Kristina Allikmets REVIEW
 REVIEW Aliskiren an orally active renin inhibitor. Review of pharmacology, pharmacodynamics, kinetics, and clinical potential in the treatment of hypertension Kristina Allikmets Department of Drug Development
REVIEW Aliskiren an orally active renin inhibitor. Review of pharmacology, pharmacodynamics, kinetics, and clinical potential in the treatment of hypertension Kristina Allikmets Department of Drug Development
ACEIs / ARBs NDHP dihydropyridine ( DHP ) ACEIs ARBs ACEIs ARBs NDHP. ( GFR ) 60 ml/min/1.73m ( chronic kidney disease, CKD )
 005 16 175-180 1 1 ( chronic kidney disease, CKD ) 003 ( end-stage renal disease, ESRD ) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors ( ) angiotensin receptor blockers ( ) nondihydropyridine ( NDHP ) / NDHP
005 16 175-180 1 1 ( chronic kidney disease, CKD ) 003 ( end-stage renal disease, ESRD ) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors ( ) angiotensin receptor blockers ( ) nondihydropyridine ( NDHP ) / NDHP
ROLE OF ANGIOTENSIN CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS AND ANGIOTENSIN RECEPTOR BLOCKERS IN TYPE I DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY DR.NASIM MUSA
 ROLE OF ANGIOTENSIN CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS AND ANGIOTENSIN RECEPTOR BLOCKERS IN TYPE I DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY DR.NASIM MUSA Type I IDDM is characterized by The abrupt onset of symptoms Insulinopenia
ROLE OF ANGIOTENSIN CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS AND ANGIOTENSIN RECEPTOR BLOCKERS IN TYPE I DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY DR.NASIM MUSA Type I IDDM is characterized by The abrupt onset of symptoms Insulinopenia
renoprotection therapy goals 208, 209
 Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
Scientific conclusions and detailed explanation of the scientific grounds for the differences from the PRAC recommendation
 Annex I Scientific conclusions, grounds for variation to the terms of the marketing authorisations and detailed explanation of the scientific grounds for the differences from the PRAC recommendation 1
Annex I Scientific conclusions, grounds for variation to the terms of the marketing authorisations and detailed explanation of the scientific grounds for the differences from the PRAC recommendation 1
The renin-angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS) is
 James L. Pool, MD Abstract Background: Despite the availability of many effective, well-tolerated drugs, a significant proportion of treated hypertensive patients still have uncontrolled high blood pressure
James L. Pool, MD Abstract Background: Despite the availability of many effective, well-tolerated drugs, a significant proportion of treated hypertensive patients still have uncontrolled high blood pressure
Antihypertensive Agents Part-2. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Antihypertensive Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Agents that block production or action of angiotensin Angiotensin-converting
Antihypertensive Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Agents that block production or action of angiotensin Angiotensin-converting
The CARI Guidelines Caring for Australasians with Renal Impairment. Blood Pressure Control role of specific antihypertensives
 Blood Pressure Control role of specific antihypertensives Date written: May 2005 Final submission: October 2005 Author: Adrian Gillian GUIDELINES a. Regimens that include angiotensin-converting enzyme
Blood Pressure Control role of specific antihypertensives Date written: May 2005 Final submission: October 2005 Author: Adrian Gillian GUIDELINES a. Regimens that include angiotensin-converting enzyme
SLOWING PROGRESSION OF KIDNEY DISEASE. Mark Rosenberg MD University of Minnesota
 SLOWING PROGRESSION OF KIDNEY DISEASE Mark Rosenberg MD University of Minnesota OUTLINE 1. Epidemiology of progression 2. Therapy to slow progression a. Blood Pressure control b. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone
SLOWING PROGRESSION OF KIDNEY DISEASE Mark Rosenberg MD University of Minnesota OUTLINE 1. Epidemiology of progression 2. Therapy to slow progression a. Blood Pressure control b. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone
Prevention And Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy. MOH Clinical Practice Guidelines 3/2006 Dr Stephen Chew Tec Huan
 Prevention And Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy MOH Clinical Practice Guidelines 3/2006 Dr Stephen Chew Tec Huan Prevention Tight glucose control reduces the development of diabetic nephropathy Progression
Prevention And Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy MOH Clinical Practice Guidelines 3/2006 Dr Stephen Chew Tec Huan Prevention Tight glucose control reduces the development of diabetic nephropathy Progression
Is there a need of new RAAS blockers in diabetic hypertension?
 Is there a need of new RAAS blockers in diabetic hypertension? Dr. Dominik N. Müller First World Congress on Controversies in Obesity, Diabetes and Hypertension Berlin October 2006 Renin-Angiotensin System
Is there a need of new RAAS blockers in diabetic hypertension? Dr. Dominik N. Müller First World Congress on Controversies in Obesity, Diabetes and Hypertension Berlin October 2006 Renin-Angiotensin System
Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
 Early Treatment is the Key Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Stage Description GFR (ml/min/1.73 m 2 ) >90 1 Kidney damage with normal or GFR 2 Mild decrease in GFR 60-89 3 Moderate decrease in GFR
Early Treatment is the Key Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Stage Description GFR (ml/min/1.73 m 2 ) >90 1 Kidney damage with normal or GFR 2 Mild decrease in GFR 60-89 3 Moderate decrease in GFR
The CARI Guidelines Caring for Australians with Renal Impairment. Specific effects of calcium channel blockers in diabetic nephropathy GUIDELINES
 Specific effects of calcium channel blockers in diabetic nephropathy Date written: September 2004 Final submission: September 2005 Author: Kathy Nicholls GUIDELINES a. Non-dihydropyridine calcium channel
Specific effects of calcium channel blockers in diabetic nephropathy Date written: September 2004 Final submission: September 2005 Author: Kathy Nicholls GUIDELINES a. Non-dihydropyridine calcium channel
Keywords albuminuria, hypertension, nephropathy, proteinuria
 Should proteinuria reduction be the criterion for antihypertensive drug selection for patients with kidney disease? Rigas G. Kalaitzidis and George L. Bakris Department of Medicine, Hypertensive Diseases
Should proteinuria reduction be the criterion for antihypertensive drug selection for patients with kidney disease? Rigas G. Kalaitzidis and George L. Bakris Department of Medicine, Hypertensive Diseases
Management of Hypertension
 Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Hypertension Definition and classification of blood pressure levels (mmhg) Category Systolic Diastolic Normal
Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Hypertension Definition and classification of blood pressure levels (mmhg) Category Systolic Diastolic Normal
ACP Brief Fall 2006 prioritization. Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (ARBs) for Proteinuria, Hypertension (HTN) and Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)
 ACP Brief Fall 2006 prioritization Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (ARBs) for Proteinuria, Hypertension (HTN) and Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) Background This topic was submitted by BC PharmaCare during
ACP Brief Fall 2006 prioritization Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (ARBs) for Proteinuria, Hypertension (HTN) and Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) Background This topic was submitted by BC PharmaCare during
Since 1898, when renin was isolated from
 NARRATIVE REVIEW Dual Blockade of the Renin-Angiotensin System for Cardiorenal Protection: An Update Mustafa Arıcı, MD, and Yunus Erdem, MD The renin-angiotensin system (RAS) has an important role in hypertension
NARRATIVE REVIEW Dual Blockade of the Renin-Angiotensin System for Cardiorenal Protection: An Update Mustafa Arıcı, MD, and Yunus Erdem, MD The renin-angiotensin system (RAS) has an important role in hypertension
Amlodipine/olmesartan (Azor ) is indicated for the treatment of hypertension, alone or in combination with other antihypertensive medications.
 Page 1 of 8 Policies Repository Policy Title Policy Number Oral Antihypertensive Agents FS.CLIN.9 Application of Pharmacy Policy is determined by benefits and contracts. Benefits may vary based on product
Page 1 of 8 Policies Repository Policy Title Policy Number Oral Antihypertensive Agents FS.CLIN.9 Application of Pharmacy Policy is determined by benefits and contracts. Benefits may vary based on product
(renoprotective (end-stage renal disease, ESRD) therapies) (JAMA)
 [1], 1., 2. 3. (renoprotective (end-stage renal disease, ESRD) therapies) (JAMA) (multiple risk (renal replacement therapy, RRT) factors intervention treatment MRFIT) [2] ( 1) % (ESRD) ( ) ( 1) 2001 (120
[1], 1., 2. 3. (renoprotective (end-stage renal disease, ESRD) therapies) (JAMA) (multiple risk (renal replacement therapy, RRT) factors intervention treatment MRFIT) [2] ( 1) % (ESRD) ( ) ( 1) 2001 (120
Difficult to Control HTN: It is not all the same. Structured approach to evaluation and treatment
 Difficult to Control HTN: It is not all the same. Structured approach to evaluation and treatment Dmitri Vasin M.D. Nephrologist and ASH certified clinical hypertension specialist Bremerton, WA, USA Johnson
Difficult to Control HTN: It is not all the same. Structured approach to evaluation and treatment Dmitri Vasin M.D. Nephrologist and ASH certified clinical hypertension specialist Bremerton, WA, USA Johnson
Hypertension and diabetic nephropathy
 Hypertension and diabetic nephropathy Elisabeth R. Mathiesen Professor, Chief Physician, Dr sci Dep. Of Endocrinology Rigshospitalet, University of Copenhagen Denmark Hypertension Brain Eye Heart Kidney
Hypertension and diabetic nephropathy Elisabeth R. Mathiesen Professor, Chief Physician, Dr sci Dep. Of Endocrinology Rigshospitalet, University of Copenhagen Denmark Hypertension Brain Eye Heart Kidney
In general, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE)
 AJH 1999;12:195S 203S Are Drugs That Block the Renin-Angiotensin System Effective and Safe in Patients With Renal Insufficiency? Matthew R. Weir Extensive clinical experience with angiotensinconverting
AJH 1999;12:195S 203S Are Drugs That Block the Renin-Angiotensin System Effective and Safe in Patients With Renal Insufficiency? Matthew R. Weir Extensive clinical experience with angiotensinconverting
Management of Hypertensive Chronic Kidney Disease: Role of Calcium Channel Blockers. Robert D. Toto, MD
 R e v i e w P a p e r Management of Hypertensive Chronic Kidney Disease: Role of Calcium Channel Blockers Robert D. Toto, MD Both the prevalence and incidence of end-stage renal disease have been increasing
R e v i e w P a p e r Management of Hypertensive Chronic Kidney Disease: Role of Calcium Channel Blockers Robert D. Toto, MD Both the prevalence and incidence of end-stage renal disease have been increasing
Preventing the cardiovascular complications of hypertension
 European Heart Journal Supplements (2004) 6 (Supplement H), H37 H42 Preventing the cardiovascular complications of hypertension Peter Trenkwalder* Department of Internal Medicine, Starnberg Hospital, Ludwig
European Heart Journal Supplements (2004) 6 (Supplement H), H37 H42 Preventing the cardiovascular complications of hypertension Peter Trenkwalder* Department of Internal Medicine, Starnberg Hospital, Ludwig
New Treatment Options for Diabetic Nephropathy patients. Prof. M. Burnier, Service of Nephrology and Hypertension CHUV, Lausanne, Switzerland
 New Treatment Options for Diabetic Nephropathy patients Prof. M. Burnier, Service of Nephrology and Hypertension CHUV, Lausanne, Switzerland Diabetes and nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy is the most common
New Treatment Options for Diabetic Nephropathy patients Prof. M. Burnier, Service of Nephrology and Hypertension CHUV, Lausanne, Switzerland Diabetes and nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy is the most common
Renal Protection Staying on Target
 Update Staying on Target James Barton, MD, FRCPC As presented at the University of Saskatchewan's Management of Diabetes & Its Complications (May 2004) Gwen s case Gwen, 49, asks you to take on her primary
Update Staying on Target James Barton, MD, FRCPC As presented at the University of Saskatchewan's Management of Diabetes & Its Complications (May 2004) Gwen s case Gwen, 49, asks you to take on her primary
heart failure John McMurray University of Glasgow.
 A to Z of RAAS blockade in heart failure John McMurray BHF Cardiovascular Research Centre University of Glasgow. RAAS inhibition in CHF ACE inhibition in patients with low LVEF CHF CONSENSUS Enalapril
A to Z of RAAS blockade in heart failure John McMurray BHF Cardiovascular Research Centre University of Glasgow. RAAS inhibition in CHF ACE inhibition in patients with low LVEF CHF CONSENSUS Enalapril
Renin inhibition with aliskiren in hypertension: focus on aliskiren/hydrochlorothiazide combination therapy
 REVIEW Renin inhibition with aliskiren in hypertension: focus on aliskiren/hydrochlorothiazide combination therapy Kalathil K Sureshkumar Division of Nephrology and Hypertension, Allegheny General Hospital,
REVIEW Renin inhibition with aliskiren in hypertension: focus on aliskiren/hydrochlorothiazide combination therapy Kalathil K Sureshkumar Division of Nephrology and Hypertension, Allegheny General Hospital,
Amlodipine plus Lisinopril Tablets AMLOPRES-L
 Amlodipine plus Lisinopril Tablets AMLOPRES-L COMPOSITION AMLOPRES-L Each uncoated tablet contains: Amlodipine besylate equivalent to Amlodipine 5 mg and Lisinopril USP equivalent to Lisinopril (anhydrous)
Amlodipine plus Lisinopril Tablets AMLOPRES-L COMPOSITION AMLOPRES-L Each uncoated tablet contains: Amlodipine besylate equivalent to Amlodipine 5 mg and Lisinopril USP equivalent to Lisinopril (anhydrous)
By Prof. Khaled El-Rabat
 What is The Optimum? By Prof. Khaled El-Rabat Professor of Cardiology - Benha Faculty of Medicine HT. Introduction Despite major worldwide efforts over recent decades directed at diagnosing and treating
What is The Optimum? By Prof. Khaled El-Rabat Professor of Cardiology - Benha Faculty of Medicine HT. Introduction Despite major worldwide efforts over recent decades directed at diagnosing and treating
Drugs acting on the reninangiotensin-aldosterone
 Drugs acting on the reninangiotensin-aldosterone system John McMurray Eugene Braunwald Scholar in Cardiovascular Diseases, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Boston & Visiting Professor, Harvard Medical School
Drugs acting on the reninangiotensin-aldosterone system John McMurray Eugene Braunwald Scholar in Cardiovascular Diseases, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Boston & Visiting Professor, Harvard Medical School
Aldosterone synthase inhibitors. John McMurray BHF Cardiovascular Research Centre University of Glasgow
 Aldosterone synthase inhibitors John McMurray BHF Cardiovascular Research Centre University of Glasgow Inhibition of aldosterone synthesis is hypothesized to be of benefit to patients with cardiovascular
Aldosterone synthase inhibitors John McMurray BHF Cardiovascular Research Centre University of Glasgow Inhibition of aldosterone synthesis is hypothesized to be of benefit to patients with cardiovascular
Launch Meeting 3 rd April 2014, Lucas House, Birmingham
 Angiotensin Converting Enzyme inhibitor (ACEi) / Angiotensin Receptor Blocker (ARB) To STOP OR Not in Advanced Renal Disease Launch Meeting 3 rd April 2014, Lucas House, Birmingham Prof Sunil Bhandari
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme inhibitor (ACEi) / Angiotensin Receptor Blocker (ARB) To STOP OR Not in Advanced Renal Disease Launch Meeting 3 rd April 2014, Lucas House, Birmingham Prof Sunil Bhandari
Nephrology. Safety and Tolerability of High-Dose Angiotensin Receptor Blocker Therapy in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Pilot Study
 American Journal of Nephrology Original Report: Patient-Oriented, Translational Research Am J Nephrol 2004;24:340 345 DOI: 10.1159/000078950 Received: March 8, 2004 Accepted: April 5, 2004 Published online:
American Journal of Nephrology Original Report: Patient-Oriented, Translational Research Am J Nephrol 2004;24:340 345 DOI: 10.1159/000078950 Received: March 8, 2004 Accepted: April 5, 2004 Published online:
Entresto Development of sacubitril/valsartan (LCZ696) for the treatment of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction
 Cardio-Metabolic Franchise Entresto Development of sacubitril/valsartan (LCZ696) for the treatment of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction Randy L Webb, PhD Rutgers Workshop October 21, 2016 Heart
Cardio-Metabolic Franchise Entresto Development of sacubitril/valsartan (LCZ696) for the treatment of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction Randy L Webb, PhD Rutgers Workshop October 21, 2016 Heart
6/10/2014. Chronic Kidney Disease - General management and standard of care. Management of CKD according to stage (KDOQI 2002)
 Chronic Kidney Disease - General management and standard of care Dr Nathalie Demoulin, Prof Michel Jadoul Cliniques universitaires Saint-Luc Université Catholique de Louvain What should and can be done
Chronic Kidney Disease - General management and standard of care Dr Nathalie Demoulin, Prof Michel Jadoul Cliniques universitaires Saint-Luc Université Catholique de Louvain What should and can be done
Combination of renin-angiotensinaldosterone. how to choose?
 Combination of renin-angiotensinaldosterone system inhibitors how to choose? Karl Swedberg Professor of Medicine Sahlgrenska Academy University of Gothenburg karl.swedberg@gu.se Disclosures Research grants
Combination of renin-angiotensinaldosterone system inhibitors how to choose? Karl Swedberg Professor of Medicine Sahlgrenska Academy University of Gothenburg karl.swedberg@gu.se Disclosures Research grants
Diuretic uptitration with half dose combined ACEI + ARB better decrease proteinuria than combined ACEI + ARB uptitration
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2010) 25: 22 2224 doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfp776 Advance Access publication 26 January 2010 Diuretic uptitration with half dose combined ACEI + ARB better decrease proteinuria than combined
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2010) 25: 22 2224 doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfp776 Advance Access publication 26 January 2010 Diuretic uptitration with half dose combined ACEI + ARB better decrease proteinuria than combined
0BCore Safety Profile. Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Film-coated tablet 40, 80, 160, 320 mg SE/H/PSUR/0024/003 Date of FAR:
 0BCore Safety Profile Active substance: Valsartan Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Film-coated tablet 40, 80, 160, 320 mg P-RMS: SE/H/PSUR/0024/003 Date of FAR: 28.02.2013 4.2 Posology and method of administration
0BCore Safety Profile Active substance: Valsartan Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Film-coated tablet 40, 80, 160, 320 mg P-RMS: SE/H/PSUR/0024/003 Date of FAR: 28.02.2013 4.2 Posology and method of administration
Review. Rationale for the use of multiple blockers of the renin angiotensin aldosterone system in specific patient populations
 Rationale for the use of multiple blockers of the renin angiotensin aldosterone system in specific patient populations Review Blockers of the renin angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS) have an established
Rationale for the use of multiple blockers of the renin angiotensin aldosterone system in specific patient populations Review Blockers of the renin angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS) have an established
Kerry Cooper M.D. Arizona Kidney Disease and Hypertension Center April 30, 2009
 Kerry Cooper M.D. Arizona Kidney Disease and Hypertension Center April 30, 2009 DR. KERRY COOPER IS ON THE SPEAKER BUREAU OF AMGEN, ABBOTT, GENZYME, SHIRE, AND BMS DR. COOPER IS ALSO INVOLVED IN CLINICAL
Kerry Cooper M.D. Arizona Kidney Disease and Hypertension Center April 30, 2009 DR. KERRY COOPER IS ON THE SPEAKER BUREAU OF AMGEN, ABBOTT, GENZYME, SHIRE, AND BMS DR. COOPER IS ALSO INVOLVED IN CLINICAL
LXIV: DRUGS: 4. RAS BLOCKADE
 LXIV: DRUGS: 4. RAS BLOCKADE ACE Inhibitors Components of RAS Actions of Angiotensin i II Indications for ACEIs Contraindications RAS blockade in hypertension RAS blockade in CAD RAS blockade in HF Limitations
LXIV: DRUGS: 4. RAS BLOCKADE ACE Inhibitors Components of RAS Actions of Angiotensin i II Indications for ACEIs Contraindications RAS blockade in hypertension RAS blockade in CAD RAS blockade in HF Limitations
Where are we with RAS blockade? New Targets.
 Where are we with RAS blockade? New Targets. Pr. M. Burnier Service of Nephrology and Hypertension Consultation Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois Lausanne, Switzerland Introduction of new antihypertensive
Where are we with RAS blockade? New Targets. Pr. M. Burnier Service of Nephrology and Hypertension Consultation Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois Lausanne, Switzerland Introduction of new antihypertensive
Conclusion: Dual blockade of the RAAS is safe. and effective in reducing albuminuria in Asian. type 2 diabetic patients with nephropathy.
 Original Article Singapore Med J 201 0; 51(2) : 1 51 Dual blockade of the renin-angiotensinaldosterone system is safe and effective in reducing albuminuria in Asian type 2 diabetic patients with nephropathy
Original Article Singapore Med J 201 0; 51(2) : 1 51 Dual blockade of the renin-angiotensinaldosterone system is safe and effective in reducing albuminuria in Asian type 2 diabetic patients with nephropathy
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme inhibitor (ACEi) / Angiotensin Receptor Blocker (ARB) To STOP OR Not in Advanced Renal Disease
 Angiotensin Converting Enzyme inhibitor (ACEi) / Angiotensin Receptor Blocker (ARB) To STOP OR Not in Advanced Renal Disease Investigator Meeting 12 th September 2017 - Sheffield Prof Sunil Bhandari Consultant
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme inhibitor (ACEi) / Angiotensin Receptor Blocker (ARB) To STOP OR Not in Advanced Renal Disease Investigator Meeting 12 th September 2017 - Sheffield Prof Sunil Bhandari Consultant
in patients with diabetes, nephropathy and/or chronic kidney disease Summary of recommendations July 2017
 Association of British Clinical Diabetologists (ABCD) and Renal Association clinical guidelines: Hypertension management and reninangiotensin-aldosterone system blockade in patients with diabetes, nephropathy
Association of British Clinical Diabetologists (ABCD) and Renal Association clinical guidelines: Hypertension management and reninangiotensin-aldosterone system blockade in patients with diabetes, nephropathy
THE RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN-ALDOSTERONE SYSTEM
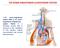 THE RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN-ALDOSTERONE SYSTEM The renin angiotensin system (RAS) or the renin angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS) is a hormone system that is involved in the regulation of the plasma sodium
THE RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN-ALDOSTERONE SYSTEM The renin angiotensin system (RAS) or the renin angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS) is a hormone system that is involved in the regulation of the plasma sodium
Therapeutic Targets and Interventions
 Therapeutic Targets and Interventions Ali Valika, MD, FACC Advanced Heart Failure and Pulmonary Hypertension Advocate Medical Group Midwest Heart Foundation Disclosures: 1. Novartis: Speaker Honorarium
Therapeutic Targets and Interventions Ali Valika, MD, FACC Advanced Heart Failure and Pulmonary Hypertension Advocate Medical Group Midwest Heart Foundation Disclosures: 1. Novartis: Speaker Honorarium
RENAAL, IRMA-2 and IDNT. Three featured trials linking a disease spectrum IDNT RENAAL. Death IRMA 2
 Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy and Proteinuria Background End stage renal disease is a major cause of death and disability among diabetics BP reduction is important to slow the progression of diabetic
Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy and Proteinuria Background End stage renal disease is a major cause of death and disability among diabetics BP reduction is important to slow the progression of diabetic
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEI) and
 Are Two Better Than One? Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors Plus Angiotensin Receptor Blockers for Reducing Blood Pressure and Proteinuria in Kidney Disease Stuart L. Linas Department of Internal
Are Two Better Than One? Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors Plus Angiotensin Receptor Blockers for Reducing Blood Pressure and Proteinuria in Kidney Disease Stuart L. Linas Department of Internal
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Hypertension - Pocket Guide Update 2004 Revision July 2005
 VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Hypertension - Pocket Guide Update 2004 Revision July 2005 1 Any adult in the health care system 2 Obtain blood pressure (BP) (Reliable,
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Hypertension - Pocket Guide Update 2004 Revision July 2005 1 Any adult in the health care system 2 Obtain blood pressure (BP) (Reliable,
ACE Inhibitors and Protection Against Kidney Disease Progression in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: What s the Evidence?
 Reviews ACE Inhibitors and Protection Against Kidney Disease Progression in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: What s the Evidence? George L. Bakris, MD; 1 and Matthew Weir, MD 2 Although angiotensin-converting
Reviews ACE Inhibitors and Protection Against Kidney Disease Progression in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: What s the Evidence? George L. Bakris, MD; 1 and Matthew Weir, MD 2 Although angiotensin-converting
Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat
 Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat Diuretic Thiazide diuretics The loop diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics *Hydrochlorothiazide *Chlorthalidone *Furosemide *Torsemide *Bumetanide Aldosterone
Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat Diuretic Thiazide diuretics The loop diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics *Hydrochlorothiazide *Chlorthalidone *Furosemide *Torsemide *Bumetanide Aldosterone
Tread Carefully Because you Tread on my Nephrons. Prescribing Hints in Renal Disease
 Tread Carefully Because you Tread on my Nephrons Prescribing Hints in Renal Disease David WP Lappin,, MB PhD FRCPI Clinical Lecturer in Medicine and Consultant Nephrologist and General Physician, Merlin
Tread Carefully Because you Tread on my Nephrons Prescribing Hints in Renal Disease David WP Lappin,, MB PhD FRCPI Clinical Lecturer in Medicine and Consultant Nephrologist and General Physician, Merlin
Anastasia Chrysostomou, Eugenia Pedagogos, Lachlan MacGregor, and Gavin J. Becker
 Original Articles Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study on the Effect of the Aldosterone Receptor Antagonist Spironolactone in Patients Who Have Persistent Proteinuria and Are on Long-Term Angiotensin-Converting
Original Articles Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study on the Effect of the Aldosterone Receptor Antagonist Spironolactone in Patients Who Have Persistent Proteinuria and Are on Long-Term Angiotensin-Converting
Since the initial description of angiotensin II mediated
 CLINICAL CARDIOLOGY: PHYSICIAN UPDATE Manipulation of the Renin-Angiotensin System Michael M. Givertz, MD Since the initial description of angiotensin II mediated hypertension 40 years ago, basic and clinical
CLINICAL CARDIOLOGY: PHYSICIAN UPDATE Manipulation of the Renin-Angiotensin System Michael M. Givertz, MD Since the initial description of angiotensin II mediated hypertension 40 years ago, basic and clinical
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in Primary Care (2008) PROVIDER REFERENCE CARDS Chronic Kidney Disease
 VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in Primary Care (2008) PROVIDER REFERECE CARDS Chronic Kidney Disease CKD VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in Primary Care (2008) PROVIDER REFERECE CARDS Chronic Kidney Disease CKD VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management
Younger adults with a family history of premature artherosclerotic disease should have their cardiovascular risk factors measured.
 Appendix 2A - Guidance on Management of Hypertension Measurement of blood pressure All adults from 40 years should have blood pressure measured as part of opportunistic cardiovascular risk assessment.
Appendix 2A - Guidance on Management of Hypertension Measurement of blood pressure All adults from 40 years should have blood pressure measured as part of opportunistic cardiovascular risk assessment.
ABCD and Renal Association Clinical Guidelines for Diabetic Nephropathy-CKD. Management of Dyslipidaemia and Hypertension in Adults Dr Peter Winocour
 ABCD and Renal Association Clinical Guidelines for Diabetic Nephropathy-CKD. Management of Dyslipidaemia and Hypertension in Adults Dr Peter Winocour Dr Indranil Dasgupta Rationale No national practical
ABCD and Renal Association Clinical Guidelines for Diabetic Nephropathy-CKD. Management of Dyslipidaemia and Hypertension in Adults Dr Peter Winocour Dr Indranil Dasgupta Rationale No national practical
Comparison between the efficacy of double blockade and single blockade of RAAS in diabetic kidney disease
 International Journal of Advances in Medicine Gupta A et al. Int J Adv Med. 2018 Aug;5(4):931-935 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20183122
International Journal of Advances in Medicine Gupta A et al. Int J Adv Med. 2018 Aug;5(4):931-935 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20183122
Hypertension Update Clinical Controversies Regarding Age and Race
 Hypertension Update Clinical Controversies Regarding Age and Race Allison Helmer, PharmD, BCACP Assistant Clinical Professor Auburn University Harrison School of Pharmacy July 22, 2017 DISCLOSURE/CONFLICT
Hypertension Update Clinical Controversies Regarding Age and Race Allison Helmer, PharmD, BCACP Assistant Clinical Professor Auburn University Harrison School of Pharmacy July 22, 2017 DISCLOSURE/CONFLICT
The hypertensive kidney and its Management
 The hypertensive kidney and its Management Dr H0 Chung Ping Hypertension Management Seminar 20061124 Hypertensive kidney Kidney damage asymptomatic till late stage Viscous cycle to augment renal damage
The hypertensive kidney and its Management Dr H0 Chung Ping Hypertension Management Seminar 20061124 Hypertensive kidney Kidney damage asymptomatic till late stage Viscous cycle to augment renal damage
SGLT2 inhibition in diabetes: extending from glycaemic control to renal and cardiovascular protection
 SGLT2 inhibition in diabetes: extending from glycaemic control to renal and cardiovascular protection Hiddo Lambers Heerspink Department of Clinical Pharmacy and Pharmacology University Medical Center
SGLT2 inhibition in diabetes: extending from glycaemic control to renal and cardiovascular protection Hiddo Lambers Heerspink Department of Clinical Pharmacy and Pharmacology University Medical Center
Clinical cases with Coversyl 10 mg
 Clinical cases Coversyl 10 mg For upgraded benefits in hypertension A Editorial This brochure, Clinical cases Coversyl 10 mg for upgraded benefits in hypertension, illustrates a variety of hypertensive
Clinical cases Coversyl 10 mg For upgraded benefits in hypertension A Editorial This brochure, Clinical cases Coversyl 10 mg for upgraded benefits in hypertension, illustrates a variety of hypertensive
Review. Renin Inhibitors in Chronic Heart Failure: The Aliskiren Observation of Heart Failure Treatment Study in Context
 Review Renin Inhibitors in Chronic Heart Failure: The Aliskiren Observation of Heart Failure Treatment Study in Context Address for correspondence: HenryKrum,MBBS,PhD,FRACP Centre of Cardiovascular Research
Review Renin Inhibitors in Chronic Heart Failure: The Aliskiren Observation of Heart Failure Treatment Study in Context Address for correspondence: HenryKrum,MBBS,PhD,FRACP Centre of Cardiovascular Research
Clinical Pearls in Renal Medicine
 Clinical Pearls in Renal Medicine Joel A. Gordon MD Professor of Medicine Nephrology Division Staff Physician Kidney Disease and Blood Pressure Clinic Disclosures None of my financial holdings will have
Clinical Pearls in Renal Medicine Joel A. Gordon MD Professor of Medicine Nephrology Division Staff Physician Kidney Disease and Blood Pressure Clinic Disclosures None of my financial holdings will have
Hypertension management and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system blockade in patients with diabetes, nephropathy and/or chronic kidney disease
 Hypertension management and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system blockade in patients with diabetes, nephropathy and/or chronic kidney disease July 2017 Indranil Dasgupta DM FRCP, Debasish Banerjee MD
Hypertension management and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system blockade in patients with diabetes, nephropathy and/or chronic kidney disease July 2017 Indranil Dasgupta DM FRCP, Debasish Banerjee MD
Analysis of Factors Causing Hyperkalemia
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Analysis of Factors Causing Hyperkalemia Kenmei Takaichi 1, Fumi Takemoto 1, Yoshifumi Ubara 1 and Yasumichi Mori 2 Abstract Objective Patients with impaired renal function or diabetes
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Analysis of Factors Causing Hyperkalemia Kenmei Takaichi 1, Fumi Takemoto 1, Yoshifumi Ubara 1 and Yasumichi Mori 2 Abstract Objective Patients with impaired renal function or diabetes
Aliskiren for the Treatment of Hypertension: An Update
 Clinical Medicine: Therapeutics R e v i e w Open Access Full open access to this and thousands of other papers at http://www.la-press.com. Aliskiren for the Treatment of Hypertension: An Update S Lam 1,
Clinical Medicine: Therapeutics R e v i e w Open Access Full open access to this and thousands of other papers at http://www.la-press.com. Aliskiren for the Treatment of Hypertension: An Update S Lam 1,
Combination therapy Giuseppe M.C. Rosano, MD, PhD, MSc, FESC, FHFA St George s Hospitals NHS Trust University of London
 Combination therapy Giuseppe M.C. Rosano, MD, PhD, MSc, FESC, FHFA St George s Hospitals NHS Trust University of London KCS Congress: Impact through collaboration CONTACT: Tel. +254 735 833 803 Email:
Combination therapy Giuseppe M.C. Rosano, MD, PhD, MSc, FESC, FHFA St George s Hospitals NHS Trust University of London KCS Congress: Impact through collaboration CONTACT: Tel. +254 735 833 803 Email:
Protecting the kidneys in lupus nephritis
 Review Protecting the kidneys in lupus nephritis Kidney involvement is common in systemic lupus erythematosus. The inciting event in lupus nephritis is immune complex accumulation in the kidneys. While
Review Protecting the kidneys in lupus nephritis Kidney involvement is common in systemic lupus erythematosus. The inciting event in lupus nephritis is immune complex accumulation in the kidneys. While
Hypertension Update Warwick Jaffe Interventional Cardiologist Ascot Hospital
 Hypertension Update 2008 Warwick Jaffe Interventional Cardiologist Ascot Hospital Definition of Hypertension Continuous variable At some point the risk becomes high enough to justify treatment Treatment
Hypertension Update 2008 Warwick Jaffe Interventional Cardiologist Ascot Hospital Definition of Hypertension Continuous variable At some point the risk becomes high enough to justify treatment Treatment
Hypertension Update 2009
 Hypertension Update 2009 New Drugs, New Goals, New Approaches, New Lessons from Clinical Trials Timothy C Fagan, MD, FACP Professor Emeritus University of Arizona New Drugs Direct Renin Inhibitors Endothelin
Hypertension Update 2009 New Drugs, New Goals, New Approaches, New Lessons from Clinical Trials Timothy C Fagan, MD, FACP Professor Emeritus University of Arizona New Drugs Direct Renin Inhibitors Endothelin
ΑΡΥΙΚΗ ΠΡΟΔΓΓΙΗ ΤΠΔΡΣΑΙΚΟΤ ΑΘΔΝΟΤ. Μ.Β.Παπαβαζιλείοσ Καρδιολόγος FESC - Γιεσθύνηρια ιζμανόγλειον ΓΝΑ Clinical Hypertension Specialist ESH
 ΑΡΥΙΚΗ ΠΡΟΔΓΓΙΗ ΤΠΔΡΣΑΙΚΟΤ ΑΘΔΝΟΤ Μ.Β.Παπαβαζιλείοσ Καρδιολόγος FESC - Γιεσθύνηρια ιζμανόγλειον ΓΝΑ Clinical Hypertension Specialist ESH Hypertension Co-Morbidities HTN Commonly Clusters with Other Risk
ΑΡΥΙΚΗ ΠΡΟΔΓΓΙΗ ΤΠΔΡΣΑΙΚΟΤ ΑΘΔΝΟΤ Μ.Β.Παπαβαζιλείοσ Καρδιολόγος FESC - Γιεσθύνηρια ιζμανόγλειον ΓΝΑ Clinical Hypertension Specialist ESH Hypertension Co-Morbidities HTN Commonly Clusters with Other Risk
Metabolic Syndrome and Chronic Kidney Disease
 Metabolic Syndrome and Chronic Kidney Disease Definition of Metabolic Syndrome National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Adult Treatment Panel (ATP) III Abdominal obesity, defined as a waist circumference
Metabolic Syndrome and Chronic Kidney Disease Definition of Metabolic Syndrome National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Adult Treatment Panel (ATP) III Abdominal obesity, defined as a waist circumference
PP-US-DSE Relypsa, Inc. All rights reserved. Relypsa and the Relypsa logo are trademarks of Relypsa, Inc.
 1 2 There are 4 main objectives that I d like to cover with you today: First, to review the definition, prevalence, and risk of hyperkalemia in certain populations Second, to review why RAASi are recommended
1 2 There are 4 main objectives that I d like to cover with you today: First, to review the definition, prevalence, and risk of hyperkalemia in certain populations Second, to review why RAASi are recommended
Hypertension Management Focus on new RAAS blocker. Disclosure
 Hypertension Management Focus on new RAAS blocker Rameshkumar Raman M.D Endocrine Associates of The Quad Cities Disclosure Speaker bureau Abbott, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Novartis, Takeda, Merck, Solvay
Hypertension Management Focus on new RAAS blocker Rameshkumar Raman M.D Endocrine Associates of The Quad Cities Disclosure Speaker bureau Abbott, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Novartis, Takeda, Merck, Solvay
M2 TEACHING UNDERSTANDING PHARMACOLOGY
 M2 TEACHING UNDERSTANDING PHARMACOLOGY USING CVS SYSTEM AS AN EXAMPLE NIGEL FONG 2 JAN 2014 TODAY S OBJECTIVE Pharmacology often seems like an endless list of mechanisms and side effects to memorize. To
M2 TEACHING UNDERSTANDING PHARMACOLOGY USING CVS SYSTEM AS AN EXAMPLE NIGEL FONG 2 JAN 2014 TODAY S OBJECTIVE Pharmacology often seems like an endless list of mechanisms and side effects to memorize. To
Diabetic Nephropathy 2009
 Diabetic Nephropathy 2009 Michael T McDermott MD Director, Endocrinology and Diabetes Practice University of Colorado Hospital Michael.mcdermott@ucdenver.edu Diabetic Nephropathy Clinical Stages Hyperfunction
Diabetic Nephropathy 2009 Michael T McDermott MD Director, Endocrinology and Diabetes Practice University of Colorado Hospital Michael.mcdermott@ucdenver.edu Diabetic Nephropathy Clinical Stages Hyperfunction
DIRECT RENIN INHIBITOR (DRI) EFFECT ON GFR AND USE IN RENAL ARTERY STENOSIS SCREENING
 DIRECT RENIN INHIBITOR (DRI) EFFECT ON GFR AND USE IN RENAL ARTERY STENOSIS SCREENING Harold Thomas Pretorius, MD, PhD, Nichole Richards, and Michael Harrell Abstract Objective: A new method using a nuclear
DIRECT RENIN INHIBITOR (DRI) EFFECT ON GFR AND USE IN RENAL ARTERY STENOSIS SCREENING Harold Thomas Pretorius, MD, PhD, Nichole Richards, and Michael Harrell Abstract Objective: A new method using a nuclear
DISCLOSURES OUTLINE OUTLINE 9/29/2014 ANTI-HYPERTENSIVE MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE
 ANTI-HYPERTENSIVE MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DISCLOSURES Editor-in-Chief- Nephrology- UpToDate- (Wolters Klewer) Richard J. Glassock, MD, MACP Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA 1 st Annual Internal
ANTI-HYPERTENSIVE MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DISCLOSURES Editor-in-Chief- Nephrology- UpToDate- (Wolters Klewer) Richard J. Glassock, MD, MACP Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA 1 st Annual Internal
Hello, and thank you for joining us for this presentation on novel approaches to understanding risks and treatment of hyperkalemia.
 Hello, and thank you for joining us for this presentation on novel approaches to understanding risks and treatment of hyperkalemia. PP-US-DSE-00032. 2015 Relypsa, Inc. All rights reserved. Relypsa and
Hello, and thank you for joining us for this presentation on novel approaches to understanding risks and treatment of hyperkalemia. PP-US-DSE-00032. 2015 Relypsa, Inc. All rights reserved. Relypsa and
Diabetic Kidney Disease Tripti Singh MD Department of Nephrology University of Wisconsin
 Diabetic Kidney Disease Tripti Singh MD Department of Nephrology University of Wisconsin Disclosures I have no financial relationship with the manufacturers of any commercial product discussed during this
Diabetic Kidney Disease Tripti Singh MD Department of Nephrology University of Wisconsin Disclosures I have no financial relationship with the manufacturers of any commercial product discussed during this
Chronic Kidney Disease Management for Primary Care Physicians. Dr. Allen Liu Consultant Nephrologist KTPH 21 November 2015
 Chronic Kidney Disease Management for Primary Care Physicians Dr. Allen Liu Consultant Nephrologist KTPH 21 November 2015 Singapore Renal Registry 2012 Incidence of Patients on Dialysis by Mode of Dialysis
Chronic Kidney Disease Management for Primary Care Physicians Dr. Allen Liu Consultant Nephrologist KTPH 21 November 2015 Singapore Renal Registry 2012 Incidence of Patients on Dialysis by Mode of Dialysis
Diabetes in Renal Patients. Contents. Understanding Diabetic Nephropathy
 Diabetes in Renal Patients Contents Understanding Diabetic Nephropathy What effect does CKD have on a patient s diabetic control? Diabetic Drugs in CKD and Dialysis Patients Hyper and Hypoglycaemia in
Diabetes in Renal Patients Contents Understanding Diabetic Nephropathy What effect does CKD have on a patient s diabetic control? Diabetic Drugs in CKD and Dialysis Patients Hyper and Hypoglycaemia in
Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Blockade in Diabetic Nephropathy. Present Evidences
 J. Clin. Med. 2015, 4, 1908-1937; doi:10.3390/jcm4111908 Review OPEN ACCESS Journal of Clinical Medicine ISSN 2077-0383 www.mdpi.com/journal/jcm Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Blockade in Diabetic
J. Clin. Med. 2015, 4, 1908-1937; doi:10.3390/jcm4111908 Review OPEN ACCESS Journal of Clinical Medicine ISSN 2077-0383 www.mdpi.com/journal/jcm Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Blockade in Diabetic

 www.usrds.org www.usrds.org 1 1,749 + (2,032) 1,563 to
www.usrds.org www.usrds.org 1 1,749 + (2,032) 1,563 to