Lower Extremity Arterial Disease
|
|
|
- Maximillian Farmer
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Patient Education Lower Extremity Arterial Disease What you should know This handout explains lower extremity arterial disease and its treatments. It explains: Arterial circulation How the disease affects arteries in the legs Risk factors for developing arterial problems Diagnostic tests Treatment options Surgery Self-care after discharge from the hospital Lower extremity vascular disease affects the blood vessels in your legs. It is also known as: Atherosclerosis Peripheral vascular disease Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) Hardening of the arteries About the Circulatory System The circulatory system (also called the cardiovascular system) is made up of: The heart Large blood vessels called arteries and veins Tiny blood vessels called capillaries When the heart beats, it pumps oxygen-rich blood through the arteries to all parts of the body. The arteries branch out into smaller capillaries, which carry the blood into body tissues and deliver oxygen to the cells. Other capillaries then drain the used blood from the cells and into veins. The veins carry this used blood to the lungs, where it receives new oxygen from the air you inhale. The oxygen-rich blood is then carried to the heart, and the cycle begins again. The illustration on page 2 shows the major arteries and veins in the body.
2 Page 2 Carotid artery Subclavian artery Axillary artery Vena cava Brachia artery Common iliac artery External iliac artery Jugular vein Subclavian vein Cephalic vein Basillic vein Internal iliac arteries Common femoral vein Radial artery Profunda or deep femoral artery Superficial femoral artery Popliteal artery Anterior tibial artery Femoral vein Saphenous vein Peroneal artery Posterior tibial artery Dorsalis pedis artery The major arteries and veins in the body
3 Page 3 What is lower extremity arterial disease? Normally, the lining of an artery is smooth, and blood flows easily through it. In lower extremity arterial disease, the lining of the arteries to the legs become rough and thickened by a buildup of fats called cholesterol and plaque. When this happens, the arteries become narrowed and blood flow is lessened or blocked. If the blockage happens slowly, smaller arteries will form over time. These new arteries will allow some blood to flow around the area that is blocked. This is called collateral circulation, and the new arteries are called collateral blood vessels. What are the symptoms of the disease? When you walk, you may feel pain or cramps in your hips, thighs, or calves, depending on where the blocked arteries are. After walking a short distance, you may find that resting eases the pain. This is called intermittent claudication. The symptoms occur when you walk because the leg muscles need more oxygen-rich blood when you exercise, but they cannot get the oxygen they need because of the arterial narrowing. As the disease progresses, you may feel pain in your toes or your feet. This is called rest pain. It occurs because your body cannot deliver enough blood to your feet when you are resting. Rest pain is usually worse when your legs are elevated, and you may feel less pain when you lower your legs. If the blockage gets very bad, and your legs cannot get the blood they need for growth and repair, the tissue can die. This is called gangrene. Other Signs and Symptoms Some signs of advanced lower extremity arterial disease are: Decreased hair growth on your legs Pale, blue, or red skin color on your leg or foot when it is hanging down Lack of pulses in your foot Numbness, tingling, or pain in your foot, toes, or leg Decreased ability to spread your toes and move your foot Cool temperature of your foot and leg A sore on your foot that does not heal Sometimes, a piece of plaque breaks off inside an artery and travels down the leg until it lodges and blocks blood flow beyond that point. When a blockage occurs suddenly, symptoms come on quickly and are severe because there is not enough time for collateral blood vessels to form.
4 Page 4 Who might get this disease? These health conditions increase your risk for getting lower extremity arterial disease: Smoking High levels of blood cholesterol High blood pressure Diabetes Heart disease Family history of arterial disease Being overweight Your Health Care Team Many health care providers will be involved in diagnosing and treating your disease. They include doctors, nurses, and vascular technologists. They will assess the condition of your blood vessels, explain test results and your surgery options, and help plan your treatment. You are also an important member of your health care team. You play a key role in controlling your disease. To do this, be sure to: Visit your doctor regularly. Change your lifestyle and certain habits to reduce your risk of more problems in your arteries. Can the disease be controlled or prevented? We cannot totally cure or prevent this disease, but you can control certain risk factors by changing your habits and lifestyle. Avoid Tobacco Do not use tobacco in any form. This includes all types of cigarettes, pipes, cigars, and chewing tobacco. Even smoking 1 or 2 cigarettes a day is harmful. The nicotine in tobacco products increases your risk of artherosclerosis. Nicotine causes your blood vessels to constrict (narrow), which prevents the normal amount of blood from reaching your organs and extremities (arms and legs). Smoking also decreases the amount of oxygen in your blood and can cause your blood to clot more easily. Being tobacco-free is the single most important way to help yourself stay healthy. If you smoke, quit. If you do not smoke, never start.
5 Page 5 Change Your Diet Avoid foods that are high in cholesterol and saturated fats to help reduce your risk of artherosclerosis. Cholesterol is found in: Organ and red meats Shellfish Foods that contain whole milk, butter, or cream Saturated fats tend to raise blood cholesterol levels. These fats include: Animal fats Coconut oil Palm oil Cocoa butter (the fat in chocolate) Polyunsaturated fats, such as corn and safflower oils, and monounsaturated fats, such as olive and canola oils, are better for your health. Check nutrition labels and choose foods with these fats. Your doctor may also advise you to limit the salt in your diet to help control high blood pressure or fluid retention. Or, if you are overweight, your doctor may suggest a weight-reduction diet. A dietitian can help you plan a diet that will work for you. Treat High Blood Pressure Untreated high blood pressure (hypertension) makes the heart work harder and puts more stress on the arteries. Have your blood pressure checked regularly, since hypertension often does not have any symptoms. If you have high blood pressure, take your medicines as prescribed by your doctor. Medicine can control high blood pressure, but it does not cure it. You must take your blood pressure medicine for as long as your doctor prescribes it, even if you are feeling good. If your high blood pressure is linked to stress in your life, your doctor or nurse may advise you to take a stress-management class or suggest other ways to help lower your stress. Manage Your Diabetes If you have diabetes, you are more likely to get atherosclerosis. Follow the advice of your diabetes care provider about diet, treatment, and medicines. The effects of diabetes are better controlled if they are treated early and your symptoms are watched closely.
6 Page 6 Exercise Daily exercise helps control atherosclerosis. It does not have to be strenuous. Mild exercise such as walking is helpful and safe for most people with atherosclerosis. But, you must do it regularly to lower the risks of atherosclerosis. If you begin a walking program: Start with short distances, and slowly increase how far you walk. Walk until your leg pain starts, then stop and rest. When your leg pain goes away, begin walking again. If you want to do more strenuous exercise, talk with your doctor before you start. Watch Your Iron Intake Studies show that there may be a link between high levels of iron in the body and a higher risk of atherosclerosis, especially in the arteries that supply blood to the heart. It may be that high levels of iron change how low-density lipoproteins (LDLs) move across the arterial wall, which leads to the fatty streaks that form on the inside the artery. Lower Your Homocysteine Levels Your body produces homocysteine when you digest protein. High levels of homocysteine in the blood can be toxic to the inside of arteries, and this can cause atherosclerosis to develop more rapidly. To lower the levels of homocysteine in your blood, eat foods and take supplements that contain folic acid, vitamin B6, and vitamin B12. Take Care of Your Feet When blood flow to your legs is decreased, small injuries to your feet or toes can result in serious infections, sores, or tissue death (gangrene). Here are some tips for taking good care of your feet: Avoid any situation that might cause foot injury: - Do not expose your feet to very hot or very cold temperatures. - Do not expose your feet to strong chemicals or disinfectants. - Wash your feet thoroughly, but do not soak them. Soaking will remove the natural oils and dry your skin. - Dry your feet well after washing, especially between your toes. Wear shoes that support your feet. - Do not go barefoot, even around the house. - Wear new shoes for only short periods until they are broken in. - Check your shoes before putting them on. Make sure there are no hidden objects inside that might injure your feet.
7 Page 7 Check your feet every day for any injuries or sores. This is even more important if you have diabetes or have reduced feeling in your feet. Use a mirror or ask someone for help if you have trouble seeing your feet and toes. Check for: - Areas of redness - Swelling - Sores - Drainage - Areas that are warm to the touch Use good foot hygiene. - Cut your toenails straight across, no shorter than the length of your toe. - Do not treat corns, calluses, and bunions at home. They should be treated by your doctor or nurse. - Check out special shoes or inserts. They can help keep calluses from forming and make your feet more comfortable. Ask your doctor or nurse to recommend special shoe stores. How is the disease diagnosed? To diagnose lower extremity arterial disease, your doctor will: Ask you questions Examine you Order special tests, which may be noninvasive or invasive Noninvasive Tests Your doctor may send you to the noninvasive vascular laboratory to check the blood flow to your legs. Noninvasive tests: Do not use needles, dyes, or X-rays Are painless Have no known risks or side effects Do not require you to prepare or to receive special care afterward Are done on an outpatient basis, which means you will not need to stay overnight in the hospital These are some of the noninvasive tests your doctor may want you to have: Arterial Blood Pressures, Waveforms, and Exercise Tests These tests use a Doppler (an ultrasound stethoscope) to record the blood flow at different points along your legs. The vascular technologist will place blood pressure cuffs around your arms and
8 Page 8 legs, and then compare the pressure readings from each place. You may be asked to walk on a treadmill, after which your blood pressure will be read and compared again. These tests will show where you have atherosclerosis, and how severe it is. Duplex Scanning This test takes an ultrasound picture of your artery or vein and displays it on a screen. This will show the size of the blood vessel and how well the blood is flowing through it. You will need to lie very still during this test. The vascular technologist will apply gel on your skin over the artery or vein that is being studied. The technician will then place a probe on your skin. The probe emits very short pulses of very high frequency sound, much higher than the ear can hear. The pulses of sound bounce back from your body tissues and are picked up by the probe. Blood moving in your artery or vein creates small echoes, and these show how fast the blood is moving through your blood vessels. Invasive Tests Your doctor may also ask you to have some invasive tests. These tests involve some risks, and you may need to stay overnight in the hospital. Here are some of the invasive tests you may have: Arteriogram An arteriogram is an X-ray of your arteries. For this test, dye will be injected into your artery, either through a needle or a small catheter (a thin, flexible tube). The X-ray image gives your doctor a road map of any blockages in the arteries of your legs. This test may be done on an outpatient basis, or you may need to stay overnight in the hospital. Your doctor will tell you what to expect. An arteriogram is usually done in Radiology. You will be asked to sign a consent form before the procedure is done. You will be awake during the test, but you may be given a medicine to help you relax. You may feel a short warm sensation when the dye is injected. After the test, you will be asked to lie flat in bed for several hours. During this time: Pressure will be applied over your catheter site. The nurse will check your pulses and blood pressure many times. Your doctor will review your test results and talk with you about your treatment options.
9 Page 9 Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) CTA is done to diagnose problems with blood flow. Dye is injected through an IV, and special X-rays of your blood vessels are taken. These X-ray images appear on a screen in the exam room. CTA may be done before an arteriogram. Treatment Your doctor will recommend treatment for your lower extremity arterial disease based on: Your general health Your signs and symptoms The results of your diagnostic tests Mild Atherosclerosis If you have a mild form of the disease, your doctor may advise that you: Stop smoking, if you smoke Start an exercise program to help collateral circulation develop Take medicine to help keep the disease from getting worse Eat a low-fat diet Severe or Progressive Atherosclerosis If your atherosclerosis is severe or progressive (getting worse), your doctor may recommend one or more of these treatments: Balloon Angioplasty: This procedure may be used when there is only a short section of blood vessel that is narrowed or blocked. During an angioplasty, a small catheter with a balloon on one end is placed in your artery where the narrowing is. The balloon is inflated, which flattens on the inner wall of the artery. This makes more room for the blood to flow. The balloon is then deflated, and the catheter is removed. Dye is then injected into the artery to determine if the artery has opened enough. The procedure may be repeated if more opening is needed. Stents or Stent Graft Therapy: This procedure is often done in the blood vessels of your legs, in addition to balloon angioplasty. - A stent is a small wire mesh tube that is placed in a partly blocked artery. It is inflated with a balloon, and holds your artery walls open. This allows blood to flow more freely. - A stent graft is a small wire mesh tube that is woven into a synthetic (man-made) bypass graft material. A stent graft is placed into arteries in your thigh or groin.
10 Page 10 Thrombolytic Therapy: In this procedure, special medicine is given through a catheter in your artery. This medicine breaks up or dissolves blood clots in the blocked blood vessel. This procedure is done only if acute blockage is found within 2 weeks of a blood clot forming. After Treatment for Severe Atherosclerosis You will be in the hospital for a short stay after receiving one of the treatments for severe or progressive atherosclerosis. While you are in the hospital: You will need to lie still. Avoid bending your leg at the hip where the catheters were placed. After the catheter is removed, your nurse will hold pressure over the incision site for 15 to 20 minutes to prevent bleeding. Your blood pressure will be checked often. Your incision site will also be checked to make sure that you are not bleeding. You will receive intravenous (IV) fluids for several hours. When you go home after your procedure: Increase your intake of fluids. This will help your kidneys remove the dye from your body tissues. Call your doctor right away if you: - Have swelling or bleeding from your incision site - Feel lightheaded or dizzy - Have numbness or pain in your leg - Have redness or pain at your incision site Surgery Surgery is one of the treatments for lower extremity vascular disease. Surgery is not a cure, but it may improve symptoms and help you be more independent. If you have severe lower extremity arterial disease, your doctor may advise surgery on certain arteries in your legs. This surgery will help: Improve your circulation Increase how far you can walk Relieve rest pain Heal foot ulcers Prevent amputation
11 Page 11 Your operation will involve either removing the plaque or blood clot from the blocked artery or bypassing the diseased artery. Your doctor will talk with you about your surgery options. Bypass Surgery This operation uses synthetic (man-made) grafts, or one of your own veins, to create a detour around the area where your artery is blocked or narrowed. During the surgery, your doctor will make incisions at certain places on your leg. The two ends of the bypass graft will be sewn to your artery above and below the blockage. Your blood will then flow through the artery, into the bypass graft, then back into the artery and out to the rest of your leg. Preparing for Your Operation Things to Remember Hospital stay: You will be in the hospital for 4 to 10 days after your operation. Going home: You will need to arrange for someone to drive you home when you are ready to leave the hospital. You may also need someone to help you prepare meals and do other household chores for 1 to 2 weeks. 1 Week Before Surgery Aspirin and other medicines: Do not take aspirin or other products that affect blood clotting for 1 week before your operation. Two of these are ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) and naproxen (Aleve, Naprosyn). 48 Hours Before Surgery Shaving: Do not shave any part of your body that you do not already shave every day. If you normally shave near your surgical site, do not shave that area for 2 days (48 hours) before your surgery. 24 Hours Before Surgery Take 2 showers: Take 1 shower the night before and a second shower the morning of your operation. Use the antibacterial soap your nurse gave you to wash your body. Do not use the antibacterial soap on your face and hair. (See directions that came with the soap.) Use your own soap and shampoo on your face and hair. Use clean towels to dry off, and put on clean clothing.
12 Page 12 Arrival time: The pre-surgery nurse will call you by 5 p.m. the night before your operation. If you are having surgery on a Monday, the nurse will call you the Friday before. If you do not hear from the pre-surgery nurse by 5 p.m., please call The pre-surgery nurse will tell you when to come to the hospital and will remind you: - Not to eat or drink after a certain time - Which of your regular medicines to take or not take - To sip only enough water to swallow your pills At the Hospital Heating blanket: To reduce your risk of infection, you will be covered with a heating blanket to warm your body while you wait to go into the operating room. Ask for a heating blanket if you do not receive one. Recovering in the Hospital Waking Up When you wake up after your operation, you will either be in the recovery room or in the intensive care unit (ICU). Monitoring Your Vital Signs Your nurses will check your blood pressure, heart rate, breathing rates, and the pulses in your feet. This will happen many times a day. Coughing and Deep Breathing Your nurse will teach you coughing and deep-breathing exercises. These are important to do after surgery to help prevent pneumonia. Diet Your doctor will talk with you about what you may eat and drink. Activity You should be able to increase your activity every day. Some activities will be limited if you have: A foot ulcer. Until healing begins, you may need to spend more time in bed or in a chair. A bypass graft across a joint. You may not be able to kneel or do other activities that require you to bend your knee or hip joint at a sharp angle.
13 Page 13 Pain The discomfort around your incision will be greatest for 2 to 3 days after surgery. After that, the discomfort should slowly ease. Sutures or Staples You may have sutures or staples to close your incision. These may be removed before you leave the hospital or at your first follow-up visit. Self-care at Home Precautions Medicine given during and after your operation will affect you. For 24 hours after your surgery do not: Drive Travel alone Use machinery Drink alcohol Sign any legal papers or be responsible for the care of another person Incision Care and Showering Avoid using creams or lotions on your incision right after surgery, unless your doctor tells you otherwise. If your sutures or staples were removed before you left the hospital: You may shower when you get home. Gently clean your incisions with soap and water, and pat your skin dry. If your sutures or staples are still in place: Do not get your sutures or staples wet. When your sutures or staples are removed at your follow-up visit, small pieces of tape called Steri-Strips may be placed along your incision. Steri-Strips help support the incision for a few days while it heals. They will usually start to peel away after 5 to 7 days, and can then be pulled off. You may shower with the Steri-Strips in place. Swelling You will have some swelling in your leg for a while after your surgery. To help lessen the swelling: Prop up your legs above the level of your chest when you are sitting or resting.
14 Page 14 Wear the special compression stockings or elastic bandages if your doctor prescribed them. Activity You may feel a little weaker and more tired when you get home. This is normal. It may take several weeks for you to feel like yourself again. As you start to resume your usual activities, be sure to give yourself time to rest. Do not try to do too much. Driving Do not drive if you are taking narcotic pain medicine, and for 24 hours after you stop taking it. Your ability to respond quickly may be impaired. Wait to start driving until your doctor tells you it is OK. Foot Care Your blood flow will improve with surgery, but you must still take good care of your feet and toes: Check your feet every day for areas of irritation. Check the skin between your toes for cracking or sores. Do not soak your feet. Soaking removes natural oils and dries your skin. This may cause your skin to crack. When you wash your feet, use a mild soap and lukewarm water. Dry them well. Apply lanolin cream or lotion to the dry skin on your legs and feet. Trim your toenails to be even with the ends of your toes. File any rough nail edges smooth. - If your vision is impaired, or you cannot reach your feet, ask a family member or friend to help trim your toenails. - If you have diabetes, do not trim your toenails yourself. Ask your diabetes care provider for help. Smoking Do not smoke or use tobacco in any form. Smoking constricts your blood vessels and increases the risk of blood clots. Diet For best healing, your diet must include enough protein, vitamins, and minerals. Your doctor, nurse, or dietitian will talk with you about dietary changes before you leave the hospital.
15 Page 15 Questions? Your questions are important. Call your doctor or health care provider if you have questions or concerns. UWMC clinic staff are also available to help. Weekdays from 8 a.m. to 4 p.m., call the Surgical Specialties Nurse Advice Line at After hours and on weekends and holidays, call and ask for the resident on call for Surgery to be paged. Or, ask for your surgeon to be paged: Dr. Synthetic Grafts If you had a bypass and a synthetic graft material was used, you may need to take antibiotics before having any other surgery, dental work, or invasive procedure in the future. The antibiotics will help prevent infection. Talk with your dentist about whether you will need antibiotics when you have dental work done. Be sure to tell any new doctors or dentists that you have a synthetic bypass graft. Call the Nurse Advice Line or Your Doctor If You Have: Bleeding or drainage that soaks your dressing A fever higher than F (38 C) Shaking and chills Any sign of infection in your incision: - Redness - Increasing pain - Swelling - Tenderness - Foul-smelling drainage - A change in the type or amount of drainage Nausea and/or vomiting Increased pain in your leg A change in the color or temperature of the leg that was operated on Concerns that cannot wait until your follow-up visit Box N.E. Pacific St. Seattle, WA University of Washington Medical Center Published: 08/2003, 05/2011 Clinician Review: 05/2011 Reprints on Health Online:
EDUCATION. Peripheral Artery Disease
 EDUCATION Peripheral Artery Disease Peripheral Artery Disease You may have circulation problems that have to do with your blood vessels. You may feel aches, pains, cramps, numbness or muscle fatigue when
EDUCATION Peripheral Artery Disease Peripheral Artery Disease You may have circulation problems that have to do with your blood vessels. You may feel aches, pains, cramps, numbness or muscle fatigue when
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. What to expect and how to prepare DRAFT. What are liposuction and fat grafting? How do I prepare?
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Liposuction and Fat Grafting for Breast Reconstruction What to expect and how to prepare This handout explains liposuction and fat grafting when used in breast reconstruction.
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Liposuction and Fat Grafting for Breast Reconstruction What to expect and how to prepare This handout explains liposuction and fat grafting when used in breast reconstruction.
Aortic and Iliac Artery Occlusive Disease (Updated 10.08)
 S PATIENT INFORMATION oregon surgical specialists Aortic and Iliac Artery Occlusive Disease (Updated 10.08) Abdominal aortic and iliac artery occlusive disease occurs when the arteries in your abdomen
S PATIENT INFORMATION oregon surgical specialists Aortic and Iliac Artery Occlusive Disease (Updated 10.08) Abdominal aortic and iliac artery occlusive disease occurs when the arteries in your abdomen
Lower Extremity Arterial Disease
 Lower Extremity Arterial Disease Circulating the Facts About Peripheral Disease Brought to you by the Education Committee of the Society for 1 www.svnnet.org Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) Many people
Lower Extremity Arterial Disease Circulating the Facts About Peripheral Disease Brought to you by the Education Committee of the Society for 1 www.svnnet.org Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) Many people
Cardiac Catheterization Lab Procedures
 Patient Education Cardiac Catheterization Lab Procedures This handout describes how cardiac catheterization works. It also explains how to prepare for your procedure and the self-care needed after you
Patient Education Cardiac Catheterization Lab Procedures This handout describes how cardiac catheterization works. It also explains how to prepare for your procedure and the self-care needed after you
PROCEDURES FOR PERIPHERAL ARTERIAL DISEASE
 PROCEDURES FOR PERIPHERAL ARTERIAL DISEASE Improving Blood Flow and Relieving Pain Learning About PAD Your doctor has told you that you have peripheral arterial disease (PAD). This means the arteries in
PROCEDURES FOR PERIPHERAL ARTERIAL DISEASE Improving Blood Flow and Relieving Pain Learning About PAD Your doctor has told you that you have peripheral arterial disease (PAD). This means the arteries in
ANGIOPLASTY AND STENTING
 ANGIOPLASTY AND STENTING What is angioplasty and stenting? During an angioplasty, your vascular surgeon inflates a small balloon inside a narrowed blood vessel. This balloon helps to widen your blood vessel
ANGIOPLASTY AND STENTING What is angioplasty and stenting? During an angioplasty, your vascular surgeon inflates a small balloon inside a narrowed blood vessel. This balloon helps to widen your blood vessel
Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty (PTA) and Stenting For PVS Patients
 Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty (PTA) and Stenting For PVS Patients There are two types of blood vessels in the body arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood rich in oxygen from the heart to all
Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty (PTA) and Stenting For PVS Patients There are two types of blood vessels in the body arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood rich in oxygen from the heart to all
Diabetes - Foot Care
 Diabetes - Foot Care Introduction People with diabetes are more likely than others to have problems with their feet. These problems can lead to dangerous infections of the foot. Recognizing and treating
Diabetes - Foot Care Introduction People with diabetes are more likely than others to have problems with their feet. These problems can lead to dangerous infections of the foot. Recognizing and treating
Before and After Your Surgery
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Before and After Your Surgery Artificial urinary sphincter or male urethral sling surgery This handout explains how to prepare for and what to expect after artificial urinary
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Before and After Your Surgery Artificial urinary sphincter or male urethral sling surgery This handout explains how to prepare for and what to expect after artificial urinary
Abdominal Exam: The examination of the abdomen used by physicians to detect an abdominal aortic aneurysm.
 Glossary of Terms Abdominal Exam: The examination of the abdomen used by physicians to detect an abdominal aortic aneurysm. Angiogram: A diagnostic test requiring the insertion of a catheter into an artery
Glossary of Terms Abdominal Exam: The examination of the abdomen used by physicians to detect an abdominal aortic aneurysm. Angiogram: A diagnostic test requiring the insertion of a catheter into an artery
Coronary angioplasty and stents
 Tests and Procedures Coronary angioplasty and stents By Mayo Clinic Staff Coronary angioplasty (AN-jee-o-plas-tee), also called percutaneous coronary intervention, is a procedure used to open clogged heart
Tests and Procedures Coronary angioplasty and stents By Mayo Clinic Staff Coronary angioplasty (AN-jee-o-plas-tee), also called percutaneous coronary intervention, is a procedure used to open clogged heart
ARTERIAL BYPASS GRAFTS IN THE LEG
 The Christchurch Department of Vascular Surgery is actively involved in research projects aimed at improving treatment for patients with arterial disease. Marilyn Ollett Department of Surgery Christchurch
The Christchurch Department of Vascular Surgery is actively involved in research projects aimed at improving treatment for patients with arterial disease. Marilyn Ollett Department of Surgery Christchurch
GASTRECTOMY. Date of Surgery. Please bring this booklet the day of your surgery. QHC#34
 GASTRECTOMY Date of Surgery Please bring this booklet the day of your surgery. QHC#34 What is a Gastrectomy? A Gastrectomy is the surgical removal of all or part of the stomach. The stomach is the digestion
GASTRECTOMY Date of Surgery Please bring this booklet the day of your surgery. QHC#34 What is a Gastrectomy? A Gastrectomy is the surgical removal of all or part of the stomach. The stomach is the digestion
Cardiac Catheterization Lab Procedures
 Patient Education Cardiac Catheterization Lab Procedures This booklet describes cardiac catheterization. It also details how to prepare for the procedure and the care needed after it is done. Before You
Patient Education Cardiac Catheterization Lab Procedures This booklet describes cardiac catheterization. It also details how to prepare for the procedure and the care needed after it is done. Before You
Advice to patients having an angioplasty
 What is an angioplasty? Advice to patients having an angioplasty An angioplasty is an x ray procedure to open a narrowed or blocked artery in order to improve blood flow. It involves inserting a long tube
What is an angioplasty? Advice to patients having an angioplasty An angioplasty is an x ray procedure to open a narrowed or blocked artery in order to improve blood flow. It involves inserting a long tube
Cardiac Catheterization
 Cardiac Catheterization What is cardiac catheterization? Cardiac catheterization is a procedure used to diagnose and treat cardiovascular conditions. During cardiac catheterization, a long thin tube called
Cardiac Catheterization What is cardiac catheterization? Cardiac catheterization is a procedure used to diagnose and treat cardiovascular conditions. During cardiac catheterization, a long thin tube called
Ileal Conduit Diversion Surgery
 Here are some words and pictures to help you understand this surgery: Bladder: the bladder stores urine that is made by the kidneys Bowels: the bowels are the parts of the body that digest food and fluids.
Here are some words and pictures to help you understand this surgery: Bladder: the bladder stores urine that is made by the kidneys Bowels: the bowels are the parts of the body that digest food and fluids.
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Treatment for blocked heart arteries DRAFT. What are arteries? How do heart arteries become blocked?
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Complex Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) Treatment for blocked heart arteries This handout explains complex percutaneous intervention (PCI) treatment of a coronary
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Complex Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) Treatment for blocked heart arteries This handout explains complex percutaneous intervention (PCI) treatment of a coronary
DIABETES AND FOOTCARE
 DIABETES AND FOOTCARE Self-Care and Treatment for Healthy Feet Don t Take Your Feet for Granted Every day, you depend on your feet to keep you moving. But when you have diabetes, your feet need special
DIABETES AND FOOTCARE Self-Care and Treatment for Healthy Feet Don t Take Your Feet for Granted Every day, you depend on your feet to keep you moving. But when you have diabetes, your feet need special
Introduction What Causes Peripheral Vascular Disease? How Do Doctors Treat Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 9
 Patient Information Table of Contents Introduction... 3 What is Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 5 What Are Some of the Symptoms of Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 7 What Causes Peripheral Vascular Disease?...
Patient Information Table of Contents Introduction... 3 What is Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 5 What Are Some of the Symptoms of Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 7 What Causes Peripheral Vascular Disease?...
Femoro-popliteal bypass surgery. Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England.
 Femoro-popliteal bypass surgery Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained the
Femoro-popliteal bypass surgery Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained the
After Donating Bone Marrow for the NMDP
 Patient Education After Donating Bone Marrow for the NMDP Self-care instructions Thank you for your generous gift of bone marrow, and for all the time and effort you have put in as a donor. Now, it is
Patient Education After Donating Bone Marrow for the NMDP Self-care instructions Thank you for your generous gift of bone marrow, and for all the time and effort you have put in as a donor. Now, it is
Esophagectomy Surgery
 Esophagectomy Surgery What is esophagectomy surgery? Esophagectomy surgery is the removal part, or all, of the esophagus. The esophagus is the tube that your food goes down on the way to your stomach.
Esophagectomy Surgery What is esophagectomy surgery? Esophagectomy surgery is the removal part, or all, of the esophagus. The esophagus is the tube that your food goes down on the way to your stomach.
Angiogram, angioplasty and stenting
 Angiogram, angioplasty and stenting Who is this leaflet for? This leaflet is for people who are having: an angiogram angioplasty (with or without a stent) An angiogram (also called an arteriogram or angiography)
Angiogram, angioplasty and stenting Who is this leaflet for? This leaflet is for people who are having: an angiogram angioplasty (with or without a stent) An angiogram (also called an arteriogram or angiography)
Help Your Body Heal. Clinic Visits. After weight loss surgery
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Follow-up After weight loss surgery This section of the Guide to Your Weight Loss Surgery explains clinic visits and medical and other concerns in the weeks after surgery.
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Follow-up After weight loss surgery This section of the Guide to Your Weight Loss Surgery explains clinic visits and medical and other concerns in the weeks after surgery.
After Donating Bone Marrow for Your Family Member
 Patient Education After Donating Bone Marrow for Your Family Member Self-care instructions Thank you for your generous gift of bone marrow, and for all the time and effort you have put in as a donor. Now,
Patient Education After Donating Bone Marrow for Your Family Member Self-care instructions Thank you for your generous gift of bone marrow, and for all the time and effort you have put in as a donor. Now,
Open Surgery for AAA
 Open Surgery for AAA A Weakened Blood Vessel What does it mean to have an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA)? This is a balloon-like bulge in a major blood vessel, the aorta. The bulge forms at a weak place
Open Surgery for AAA A Weakened Blood Vessel What does it mean to have an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA)? This is a balloon-like bulge in a major blood vessel, the aorta. The bulge forms at a weak place
Dr. Nuelle Knee Replacement: Discharge Care Instructions
 Dr. Nuelle Knee Replacement: Discharge Care Instructions Your Recovery Thank you for allowing us to help you with your knee replacement surgery. We hope that you had a good stay with us. These discharge
Dr. Nuelle Knee Replacement: Discharge Care Instructions Your Recovery Thank you for allowing us to help you with your knee replacement surgery. We hope that you had a good stay with us. These discharge
Angiogram and angioplasty
 Angiogram and angioplasty The femoral arteries run from the groin to the thigh, delivering blood to your legs. When there is a narrowing or blockage in these arteries, the blood supply to the legs is reduced,
Angiogram and angioplasty The femoral arteries run from the groin to the thigh, delivering blood to your legs. When there is a narrowing or blockage in these arteries, the blood supply to the legs is reduced,
Our Vision NADA BoD Strategic Planning Session -
 Who we are NADA is a not-for-profit members-led organization established in 1995 as a result of the rising rates of diabetes among First Nations, Inuit and Métis Peoples in Canada Our Vision - 2016 NADA
Who we are NADA is a not-for-profit members-led organization established in 1995 as a result of the rising rates of diabetes among First Nations, Inuit and Métis Peoples in Canada Our Vision - 2016 NADA
Coronary Angioplasty
 Coronary Angioplasty WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW: Coronary Angioplasty (AN-g-o-plas-tee) is a procedure to open one or more small arteries in your heart. It is also called a "PTI" or "PCI". "PCI" or "PTI" means
Coronary Angioplasty WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW: Coronary Angioplasty (AN-g-o-plas-tee) is a procedure to open one or more small arteries in your heart. It is also called a "PTI" or "PCI". "PCI" or "PTI" means
Coronary Artery Disease
 Coronary Artery Disease This information is at http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/dci/diseases/cad/cad_all.html and is provided by the NHLBI, one of the Institutes of the National Institutes of Health. To
Coronary Artery Disease This information is at http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/dci/diseases/cad/cad_all.html and is provided by the NHLBI, one of the Institutes of the National Institutes of Health. To
Intravascular Ultrasound
 Scan for mobile link. Intravascular Ultrasound Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) uses a transducer or probe to generate sound waves and produce pictures of the coronary arteries. IVUS can show the entire
Scan for mobile link. Intravascular Ultrasound Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) uses a transducer or probe to generate sound waves and produce pictures of the coronary arteries. IVUS can show the entire
Understanding Peripheral
 Patient Information Guide Understanding Peripheral Artery Disease Innova Vascular Self-Expanding Stent System Table of Contents Glossary... 2 What is Peripheral Artery Disease?... 4 Treating Peripheral
Patient Information Guide Understanding Peripheral Artery Disease Innova Vascular Self-Expanding Stent System Table of Contents Glossary... 2 What is Peripheral Artery Disease?... 4 Treating Peripheral
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair
 Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair Endovascular Approach Royal Columbian Hospital Your surgery and recovery at home This booklet belongs to: We also give you Preparing for Your Surgery booklet. Read both
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair Endovascular Approach Royal Columbian Hospital Your surgery and recovery at home This booklet belongs to: We also give you Preparing for Your Surgery booklet. Read both
Care After Your Dental Treatment For Hospital Dentistry patients
 Patient Education Care After Your Dental Treatment For Hospital Dentistry patients Your surgeon today was Dr.. Please carefully follow the instructions in this handout. General Do not disturb the wound
Patient Education Care After Your Dental Treatment For Hospital Dentistry patients Your surgeon today was Dr.. Please carefully follow the instructions in this handout. General Do not disturb the wound
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Hemodialysis. A treatment option for kidney disease. Treatment Options for Kidney Disease
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Hemodialysis A treatment option for kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand the purpose and care of blood access. 2. Understand the purpose and basic principles of hemodialysis.
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Hemodialysis A treatment option for kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand the purpose and care of blood access. 2. Understand the purpose and basic principles of hemodialysis.
DRAFT. Angiography: Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS) What to expect. What is a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt?
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Angiography: Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS) What to expect This handout explains a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt and what to expect when
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Angiography: Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS) What to expect This handout explains a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt and what to expect when
Lung Surgery. Patient Education. What to expect before, during, and after your surgery. Tests Before Surgery. Your Health Care Team
 Patient Education What to expect before, during, and after your surgery This handout explains what will happen before, during, and after your surgery. It also includes information about taking care of
Patient Education What to expect before, during, and after your surgery This handout explains what will happen before, during, and after your surgery. It also includes information about taking care of
Carotid Artery Stenting
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage cardiovascular health. All decisions about the management of Carotid Artery Disease must be made in conjunction with
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage cardiovascular health. All decisions about the management of Carotid Artery Disease must be made in conjunction with
Femoro-femoral bypass surgery. Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England.
 Femoro-femoral bypass surgery Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained the information
Femoro-femoral bypass surgery Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained the information
Discharge Instructions after Carotid Endarterectomy
 after Carotid Endarterectomy Your surgeon was Dr.. When you go home, an adult should stay with you until morning. You should resume your normal activity as tolerated. You may eat a normal diet. Drink plenty
after Carotid Endarterectomy Your surgeon was Dr.. When you go home, an adult should stay with you until morning. You should resume your normal activity as tolerated. You may eat a normal diet. Drink plenty
A Healthy Heart. IN BRIEF: Your Guide to
 IN BRIEF: Your Guide to A Healthy Heart If you re like most people, you may think of heart disease as a problem for other folks. If you re a woman, you may believe that being female protects you from heart
IN BRIEF: Your Guide to A Healthy Heart If you re like most people, you may think of heart disease as a problem for other folks. If you re a woman, you may believe that being female protects you from heart
Transplant Surgery. Patient Education Guide to Your Kidney/Pancreas Transplant Page 9-1. For a kidney/pancreas transplant. Before Your Surgery
 Patient Education Page 9-1 Transplant Surgery For a kidney/pancreas transplant By the time you have your transplant surgery, you may have been waiting for some time. Reading this chapter before surgery
Patient Education Page 9-1 Transplant Surgery For a kidney/pancreas transplant By the time you have your transplant surgery, you may have been waiting for some time. Reading this chapter before surgery
People with diabetes often have trouble with their feet. Read this booklet to learn 7 steps to help keep your feet healthy.
 Form: D-5821 Treat Your Feet: Foot care for people with diabetes People with diabetes often have trouble with their feet. Read this booklet to learn 7 steps to help keep your feet healthy. Diabetes raises
Form: D-5821 Treat Your Feet: Foot care for people with diabetes People with diabetes often have trouble with their feet. Read this booklet to learn 7 steps to help keep your feet healthy. Diabetes raises
Intermittent claudication exercise programme
 Intermittent claudication programme This leaflet explains about an programme that is offered to patients with intermittent claudication. If you have any questions or concerns, please ask a member of staff
Intermittent claudication programme This leaflet explains about an programme that is offered to patients with intermittent claudication. If you have any questions or concerns, please ask a member of staff
Dr. Nuelle Total/Partial Hip Replacement: Discharge Care Instructions
 Dr. Nuelle Total/Partial Hip Replacement: Discharge Care Instructions Your Recovery Thank you for allowing us to help you with your hip replacement surgery. We hope that you had a good stay with us. These
Dr. Nuelle Total/Partial Hip Replacement: Discharge Care Instructions Your Recovery Thank you for allowing us to help you with your hip replacement surgery. We hope that you had a good stay with us. These
Arterial Bypass Grafts to the Legs and Femoral Endarterectomy
 Patient Information Arterial Bypass Grafts to the Legs and Femoral Endarterectomy We expect you to make a rapid recovery after your operation and to experience no serious problems. However, it is important
Patient Information Arterial Bypass Grafts to the Legs and Femoral Endarterectomy We expect you to make a rapid recovery after your operation and to experience no serious problems. However, it is important
Patient & Family Guide. Bowel Surgery.
 Patient & Family Guide 2016 Bowel Surgery www.nshealth.ca Bowel Surgery This pamphlet will answer some of your questions about your stay in hospital and care at home. We hope this information will help
Patient & Family Guide 2016 Bowel Surgery www.nshealth.ca Bowel Surgery This pamphlet will answer some of your questions about your stay in hospital and care at home. We hope this information will help
Atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis happens when the blood vessels
 Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis happens when the blood vessels that carry oxygen and nutrients from your heart to the rest of your body (arteries) become thick and stiff sometimes restricting blood flow
Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis happens when the blood vessels that carry oxygen and nutrients from your heart to the rest of your body (arteries) become thick and stiff sometimes restricting blood flow
CORONARY ARTERY PROCEDURES
 CORONARY ARTERY PROCEDURES Cardiac Catheterization, Stenting, and Bypass Surgery Coronary Artery Disease Your doctor has told you that you may have coronary artery disease (CAD). Having CAD means that
CORONARY ARTERY PROCEDURES Cardiac Catheterization, Stenting, and Bypass Surgery Coronary Artery Disease Your doctor has told you that you may have coronary artery disease (CAD). Having CAD means that
Introduction 3. What is Peripheral Vascular Disease? 5. What Are Some of the Symptoms of Peripheral Vascular Disease? 6
 Patient Information Table of Contents Introduction 3 What is Peripheral Vascular Disease? 5 What Are Some of the Symptoms of Peripheral Vascular Disease? 6 What Causes Peripheral Vascular Disease? 7 How
Patient Information Table of Contents Introduction 3 What is Peripheral Vascular Disease? 5 What Are Some of the Symptoms of Peripheral Vascular Disease? 6 What Causes Peripheral Vascular Disease? 7 How
Intermittent Claudication
 Intermittent Claudication Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Ask 3 Questions Preparation for your Appointments We want you to be active in your healthcare. By telling us what is important to
Intermittent Claudication Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Ask 3 Questions Preparation for your Appointments We want you to be active in your healthcare. By telling us what is important to
PATIENT EDUCATION. Treatments for Coronary Artery Disease
 PATIENT EDUCATION Treatments for Coronary Artery Disease General Information The heart is a powerful muscle that pumps oxygen-rich blood throughout your body. The blood vessels that supply oxygen to your
PATIENT EDUCATION Treatments for Coronary Artery Disease General Information The heart is a powerful muscle that pumps oxygen-rich blood throughout your body. The blood vessels that supply oxygen to your
Peripheral Arterial. Disease
 Peripheral Arterial Disease Peripheral Arterial Disease People take better care of their health when they know what s going on in their bodies. For those with peripheral arterial occlusive disease, this
Peripheral Arterial Disease Peripheral Arterial Disease People take better care of their health when they know what s going on in their bodies. For those with peripheral arterial occlusive disease, this
KNEE ARTHROSCOPY SURGERY
 KNEE ARTHROSCOPY SURGERY SUMMARY OF PROCEDURE Arthroscopy involves looking at the inside of the knee joint with a small telescope and camera (arthroscope). The image is projected onto a television monitor
KNEE ARTHROSCOPY SURGERY SUMMARY OF PROCEDURE Arthroscopy involves looking at the inside of the knee joint with a small telescope and camera (arthroscope). The image is projected onto a television monitor
Deep Vein Thrombosis
 Deep Vein Thrombosis Introduction Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot in a vein. This condition can affect men and women of any age and race. DVT is a potentially serious condition. If not treated,
Deep Vein Thrombosis Introduction Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot in a vein. This condition can affect men and women of any age and race. DVT is a potentially serious condition. If not treated,
DO YOU GET A cramp-like pain. in your leg when you walk that goes away when you rest?
 YOUR HEALTH CARE DECISIONS DO YOU GET A cramp-like pain in your leg when you walk that goes away when you rest? This is one of a series of leaflets based on recent research evidence and guidelines. It
YOUR HEALTH CARE DECISIONS DO YOU GET A cramp-like pain in your leg when you walk that goes away when you rest? This is one of a series of leaflets based on recent research evidence and guidelines. It
Lymphedema. Patient Education. Information for women with breast cancer. What is lymphedema? Surgical Specialties Center
 Patient Education Information for women with breast cancer This handout describes what lymphedema is, the steps you can take to lower your risk, and what signs to look for. Women who have been treated
Patient Education Information for women with breast cancer This handout describes what lymphedema is, the steps you can take to lower your risk, and what signs to look for. Women who have been treated
Learning About. Peripheral Artery Disease
 SM A C P S P E C I A L R E P O R T Learning About Peripheral Artery Disease What Is Peripheral Artery Disease? Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a form of atherosclerosis the hardening and narrowing of
SM A C P S P E C I A L R E P O R T Learning About Peripheral Artery Disease What Is Peripheral Artery Disease? Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a form of atherosclerosis the hardening and narrowing of
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION DRAFT. What is pectus excavatum?
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Modified Ravitch Procedure for Pectus Excavatum What to expect before, during, and after surgery This handout is for patients who are having a modified Ravitch procedure to
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Modified Ravitch Procedure for Pectus Excavatum What to expect before, during, and after surgery This handout is for patients who are having a modified Ravitch procedure to
Spine Surgery Discharge Instructions
 Spine Surgery Discharge Instructions Your sutures or staples need to stay in place for at least 10 days after surgery. To have them removed you can: Call your surgeon s office (the number is on your discharge
Spine Surgery Discharge Instructions Your sutures or staples need to stay in place for at least 10 days after surgery. To have them removed you can: Call your surgeon s office (the number is on your discharge
Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS) About your procedure
 Patient Education Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS) About your procedure This handout explains what a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt is and what to expect when you have
Patient Education Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS) About your procedure This handout explains what a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt is and what to expect when you have
ACL RECONSTRUCTION. Date of Surgery. Please bring this booklet the day of your surgery. QHC#65
 ACL RECONSTRUCTION Date of Surgery Please bring this booklet the day of your surgery. QHC#65 The ACL (Anterior Cruciate Ligament) is the major stabilizing ligament of the knee. The ACL is located in the
ACL RECONSTRUCTION Date of Surgery Please bring this booklet the day of your surgery. QHC#65 The ACL (Anterior Cruciate Ligament) is the major stabilizing ligament of the knee. The ACL is located in the
CARING FOR YOUR CATHETER AT HOME
 CARING FOR YOUR CATHETER AT HOME After surgery (radical prostatectomy) for prostate cancer you will have a urinary catheter for a short period of time and will need to go home with the catheter still in
CARING FOR YOUR CATHETER AT HOME After surgery (radical prostatectomy) for prostate cancer you will have a urinary catheter for a short period of time and will need to go home with the catheter still in
UWMC Clinic Care After Discharge
 Patient Education UWMC Clinic Care After Discharge For a kidney/pancreas transplant Once you are discharged from the hospital, you will enter the next phase of transplant care, outpatient follow-up. You
Patient Education UWMC Clinic Care After Discharge For a kidney/pancreas transplant Once you are discharged from the hospital, you will enter the next phase of transplant care, outpatient follow-up. You
Sores That Will Not Heal
 Sores That Will Not Heal Introduction Some sores have trouble healing on their own. Sores that will not heal are a common problem. Open sores that will not heal are also known as wounds or skin ulcers.
Sores That Will Not Heal Introduction Some sores have trouble healing on their own. Sores that will not heal are a common problem. Open sores that will not heal are also known as wounds or skin ulcers.
Cardiac Catheterization, Coronary Angiogram, and Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI)
 Cardiac Catheterization, Coronary Angiogram, and Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) Cardiac Catheterization, Coronary Angiogram, and Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) Your doctor has recommended
Cardiac Catheterization, Coronary Angiogram, and Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) Cardiac Catheterization, Coronary Angiogram, and Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) Your doctor has recommended
DON T LET LEG PAIN BECOME A REAL THREAT.
 DON T LET LEG PAIN BECOME A REAL THREAT. These three words have the power to change lives. Between 8 to 10 million Americans are estimated to suffer from poor blood flow to the legs and feet potentially
DON T LET LEG PAIN BECOME A REAL THREAT. These three words have the power to change lives. Between 8 to 10 million Americans are estimated to suffer from poor blood flow to the legs and feet potentially
Cardiac Catheterisation and Balloon Coronary Angioplasty
 Cardiac Catheterisation and Balloon Coronary Angioplasty Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Cardiac Catheterisation This process is known as Angiography or Angiogram. It is a test performed under
Cardiac Catheterisation and Balloon Coronary Angioplasty Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Cardiac Catheterisation This process is known as Angiography or Angiogram. It is a test performed under
Femoropopliteal/distal. bypass grafts. Vascular Surgery Patient Information Leaflet
 Femoropopliteal/distal bypass grafts Vascular Surgery Patient Information Leaflet Femoro-popliteal/distal bypass grafts This leaflet tells you about the operation known as a femoropopliteal bypass graft.
Femoropopliteal/distal bypass grafts Vascular Surgery Patient Information Leaflet Femoro-popliteal/distal bypass grafts This leaflet tells you about the operation known as a femoropopliteal bypass graft.
LAPAROSCOPIC HERNIA REPAIR
 LAPAROSCOPIC HERNIA REPAIR Treating Your Hernia with Laparoscopy When You Have a Hernia Anyone can have a hernia. This is a weakness or tear in the wall of the abdomen. It often results from years of wear
LAPAROSCOPIC HERNIA REPAIR Treating Your Hernia with Laparoscopy When You Have a Hernia Anyone can have a hernia. This is a weakness or tear in the wall of the abdomen. It often results from years of wear
Open Radical Prostatectomy Surgery
 To learn about radical prostatectomy surgery, you will need to know these words: The prostate is the sexual gland that makes fluid to help sperm move around. The prostate surrounds the urethra at the neck
To learn about radical prostatectomy surgery, you will need to know these words: The prostate is the sexual gland that makes fluid to help sperm move around. The prostate surrounds the urethra at the neck
Your heart is a muscular pump about the size of your fist, located
 How Your Heart Works Your heart is a muscular pump about the size of your fist, located slightly to the left and behind your breastbone. Its function is to pump blood throughout your body. As your heart
How Your Heart Works Your heart is a muscular pump about the size of your fist, located slightly to the left and behind your breastbone. Its function is to pump blood throughout your body. As your heart
Femoral endarterectomy
 Femoral endarterectomy The femoral arteries run from the groin to the thigh delivering blood to your legs. When there is a narrowing or blockage in these arteries, the blood supply to the legs is reduced,
Femoral endarterectomy The femoral arteries run from the groin to the thigh delivering blood to your legs. When there is a narrowing or blockage in these arteries, the blood supply to the legs is reduced,
Table of Contents. What is Spinal Fusion? Pre-Register for Surgery How Do I Prepare for Surgery?... 3
 www.cpmc.org/learning Spinal Fusion Table of Contents What is Spinal Fusion?... 2 Pre-Register for Surgery... 2 How Do I Prepare for Surgery?... 3 What Can I Expect During My Hospital Stay?... 3 If You
www.cpmc.org/learning Spinal Fusion Table of Contents What is Spinal Fusion?... 2 Pre-Register for Surgery... 2 How Do I Prepare for Surgery?... 3 What Can I Expect During My Hospital Stay?... 3 If You
Leg artery bypass (fem-pop bypass)
 Leg artery bypass (fem-pop bypass) The femoral artery runs down from the groin and into the thigh. This artery delivers blood to your legs. When the femoral artery reaches the back of the knee it becomes
Leg artery bypass (fem-pop bypass) The femoral artery runs down from the groin and into the thigh. This artery delivers blood to your legs. When the femoral artery reaches the back of the knee it becomes
You have been referred to the Hamilton General Hospital to assess if having your mitral heart valve repaired with a mitral clip is right for you.
 Mitral Clip Procedure You have been referred to the Hamilton General Hospital to assess if having your mitral heart valve repaired with a mitral clip is right for you. 2 Mitral Clip Procedure What is mitral
Mitral Clip Procedure You have been referred to the Hamilton General Hospital to assess if having your mitral heart valve repaired with a mitral clip is right for you. 2 Mitral Clip Procedure What is mitral
A Guide for People With Diabetes. Take Care of Your Feet for a
 A Guide for People With Diabetes Take Care of Your Feet for a You can take care of your feet! Do you want to avoid serious foot problems that can lead to a toe, foot, or leg amputation? Take Care of Your
A Guide for People With Diabetes Take Care of Your Feet for a You can take care of your feet! Do you want to avoid serious foot problems that can lead to a toe, foot, or leg amputation? Take Care of Your
Dr. Anant Kumar, M.D. Post-Operative Instructions after Cervical Spine Surgery
 Dr. Anant Kumar, M.D. Post-Operative Instructions after Cervical Spine Surgery We want to make this experience as pleasant as possible for you and your family. If you have any questions before or after
Dr. Anant Kumar, M.D. Post-Operative Instructions after Cervical Spine Surgery We want to make this experience as pleasant as possible for you and your family. If you have any questions before or after
YOUR PATH TO RECOVERY AFTER SHOULDER REPLACEMENT
 YOUR PATH TO RECOVERY AFTER SHOULDER REPLACEMENT Revised 11/2015 Day of Surgery: # 0 After Surgery Day: # 1 Precautions DO NOT actively move your shoulder, lift, carry, reach, bear weight, or reach behind
YOUR PATH TO RECOVERY AFTER SHOULDER REPLACEMENT Revised 11/2015 Day of Surgery: # 0 After Surgery Day: # 1 Precautions DO NOT actively move your shoulder, lift, carry, reach, bear weight, or reach behind
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR)
 Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR) Welcome to the Sanford Health Heart Clinic. It is a privilege to care for you. Your doctor has told you that you may need to have a TAVR procedure. TAVR stands
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR) Welcome to the Sanford Health Heart Clinic. It is a privilege to care for you. Your doctor has told you that you may need to have a TAVR procedure. TAVR stands
Table of Contents. Dialysis Port Care Chemotherapy Port Care G-Tube Care Colostomy Bags Wound Dressings
 Table of Contents Dialysis Port Care Chemotherapy Port Care G-Tube Care Colostomy Bags Wound Dressings Dialysis Port Care Know What Type of Vascular Access You Have. Fistula: An artery in your forearm
Table of Contents Dialysis Port Care Chemotherapy Port Care G-Tube Care Colostomy Bags Wound Dressings Dialysis Port Care Know What Type of Vascular Access You Have. Fistula: An artery in your forearm
Clinic Procedures. After your heart transplant. Lab Tests
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Clinic Procedures After your heart transplant We hope your new heart puts you on the road to a productive, healthy, and happy life. To be sure you and your heart are doing
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Clinic Procedures After your heart transplant We hope your new heart puts you on the road to a productive, healthy, and happy life. To be sure you and your heart are doing
CAST CARE. Helping Broken Bones Heal
 CAST CARE Helping Broken Bones Heal When You Need a Cast Are you injured and in need of a cast? Don t worry, you ll get through it. Wearing a cast will help your injured body part heal. Healing takes time,
CAST CARE Helping Broken Bones Heal When You Need a Cast Are you injured and in need of a cast? Don t worry, you ll get through it. Wearing a cast will help your injured body part heal. Healing takes time,
Department of Vascular Surgery Femoral-Popliteal and Femoral-Distal Bypass Grafts
 Department of Vascular Surgery Femoral-Popliteal and Femoral-Distal Bypass Grafts Why do you need the operation? You need this operation because you have either pain in your legs or a leg ulcer or gangrene
Department of Vascular Surgery Femoral-Popliteal and Femoral-Distal Bypass Grafts Why do you need the operation? You need this operation because you have either pain in your legs or a leg ulcer or gangrene
How to Care for Yourself after Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR)
 How to Care for Yourself after Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR) When do I need to seek emergency care? Call 9-1-1 immediately if you develop: Sudden onset of chest pain Shortness of breath
How to Care for Yourself after Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR) When do I need to seek emergency care? Call 9-1-1 immediately if you develop: Sudden onset of chest pain Shortness of breath
Sorafenib (so-ra-fe-nib) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth.
 For the Patient: Other names: Sorafenib NEXAVAR Sorafenib (so-ra-fe-nib) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. A blood test may be taken before each
For the Patient: Other names: Sorafenib NEXAVAR Sorafenib (so-ra-fe-nib) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. A blood test may be taken before each
Orthotopic Bladder Reconstruction Surgery ~ Neobladder Surgery ~
 Orthotopic Bladder Reconstruction Surgery ~ Neobladder Surgery ~ Here are some words and pictures to help you understand this surgery: Kidney Ureter Bladder Urethra Small bowel An organ in the body that
Orthotopic Bladder Reconstruction Surgery ~ Neobladder Surgery ~ Here are some words and pictures to help you understand this surgery: Kidney Ureter Bladder Urethra Small bowel An organ in the body that
Pre-Op. What to expect on your initial visit. Special instructions before surgery
 Pre-Op What to expect on your initial visit Thorough history and physical. Review of your existing labs, x- rays and other information. Ultrasound of your thyroid and neck if indicated. Fine needle aspiration
Pre-Op What to expect on your initial visit Thorough history and physical. Review of your existing labs, x- rays and other information. Ultrasound of your thyroid and neck if indicated. Fine needle aspiration
LUMBAR MICROSURGERY. Low Back Surgery to Reduce Your Pain
 LUMBAR MICROSURGERY Low Back Surgery to Reduce Your Pain Planning for Low Back Surgery Having a low back (lumbar) problem can be frustrating. You may have pain when you sit, stand, or walk. Even a simple
LUMBAR MICROSURGERY Low Back Surgery to Reduce Your Pain Planning for Low Back Surgery Having a low back (lumbar) problem can be frustrating. You may have pain when you sit, stand, or walk. Even a simple
Dr. Nuelle Fracture Surgery Discharge Care Instructions
 Dr. Nuelle Fracture Surgery Discharge Care Instructions Your Recovery Thank you for allowing us to help you with your injury. We hope that you had a good stay with us. These discharge instructions are
Dr. Nuelle Fracture Surgery Discharge Care Instructions Your Recovery Thank you for allowing us to help you with your injury. We hope that you had a good stay with us. These discharge instructions are
UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS
 UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS ARTERIES Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood to all the organs of the body. Arteries are made up of three important layers:
UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS ARTERIES Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood to all the organs of the body. Arteries are made up of three important layers:
Carotid Angioplasty and Stenting
 Carotid Angioplasty and Stenting Your Carotid Artery Problem The carotid arteries are blood vessels in the neck that carry blood to the brain. One or both of your carotids is narrowed due to a buildup
Carotid Angioplasty and Stenting Your Carotid Artery Problem The carotid arteries are blood vessels in the neck that carry blood to the brain. One or both of your carotids is narrowed due to a buildup
The pillars defining our quality care. We Care!
 The pillars defining our quality care We Care! 1 An umbilical hernia occurs when a tissue bulges out through an opening in time muscles on the abdomen near the navel or belly button (umbilicus). About
The pillars defining our quality care We Care! 1 An umbilical hernia occurs when a tissue bulges out through an opening in time muscles on the abdomen near the navel or belly button (umbilicus). About
Gangrene. Introduction Gangrene is the death of tissues in your body. It happens when a part of your body loses its blood supply.
 Gangrene Introduction Gangrene is the death of tissues in your body. It happens when a part of your body loses its blood supply. Gangrene can happen on the surface of the body, such as on the skin. It
Gangrene Introduction Gangrene is the death of tissues in your body. It happens when a part of your body loses its blood supply. Gangrene can happen on the surface of the body, such as on the skin. It
Patient Education. Ultrasound
 Patient Education Ultrasound What you should know about your Abdominal Ultrasound. An abdominal ultrasound is performed to examine your abdominal organs such as liver, spleen, gall bladder or pancreas.
Patient Education Ultrasound What you should know about your Abdominal Ultrasound. An abdominal ultrasound is performed to examine your abdominal organs such as liver, spleen, gall bladder or pancreas.
Lumbar Epidural Injections. Treatment to Reduce Pain
 Lumbar Epidural Injections Treatment to Reduce Pain What Is a Lumbar Epidural Injection? Your doctor may have suggested you have a lumbar epidural injection. This procedure can help relieve low back and
Lumbar Epidural Injections Treatment to Reduce Pain What Is a Lumbar Epidural Injection? Your doctor may have suggested you have a lumbar epidural injection. This procedure can help relieve low back and
Cardiac Catheterization/Coronary Angiogram Your Procedure and Treatment Options
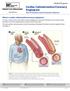 www.hrh.ca Medical Program Cardiac Catheterization/Coronary Angiogram Your Procedure and Treatment Options What is a cardiac catheterization/coronary angiogram? A cardiac catheterization (also called a
www.hrh.ca Medical Program Cardiac Catheterization/Coronary Angiogram Your Procedure and Treatment Options What is a cardiac catheterization/coronary angiogram? A cardiac catheterization (also called a
