Antiarrhythmic Drugs Öner Süzer
|
|
|
- Mervin Parks
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Antiarrhythmic Drugs Öner Süzer Last update: Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı
2 Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı Figure 14 1 Schematic representation of the heart and normal cardiac electrical activity (intracellular recordings from areas indicated and ECG). Sinoatrial node, atrioventricular node, and Purkinje cells display pacemaker activity (phase 4 depolarization). The ECG is the body surface manifestation of the depolarization and repolarization waves of theheart. TheP waveis generated by atrial depolarization, the QRS by ventricular muscle depolarization, and the T wave by ventricular repolarization. Thus, the PR interval is a measure of conduction time from atrium to ventricle, and the QRS duration indicates the time required for all of the ventricular cells to be activated (ie, the intraventricular conduction time). The QT interval reflects the duration of the ventricular action potential. 4 2
3 Katzung & Trevor s Pharmacology Examination & Board Review 7th Edition First choice antiarrhythmic drugs SVT, supraventricular tachycardia; VEB, ventricular ectopic beat; VT, ventricular tachycardia; VF, ventricular fibrillation Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı
4 Sodium Channel-Blocking Drugs (Class 1) Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı No drug 8 4
5 Class 1a effect 9 Class 1b effect 10 5
6 Class 1c effect 11 1a: Quinidine I Cardiac Effects Quinidine has actions similar to those of procainamide: it slows the upstroke of the action potential and conduction, and prolongs the QRS duration of the ECG, by blockade of sodium channels. The drug also prolongs the action potential duration by nonspecific blockade of potassium channels. It has more pronounced cardiac antimuscarinic effects than procainamide. Its toxic cardiac effects include excessive QT interval prolongation and induction of torsade de pointes arrhythmia. Toxic concentrations of quinidine also produce excessive sodium channel blockade with slowed conduction throughout the heart. 12 6
7 1a: Quinidine II Extracardiac Effects Gastrointestinal side effects of diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting are observed in one third to one half of patients. A syndrome of headache, dizziness, and tinnitus (cinchonism) is observed at toxic drug concentrations. Idiosyncratic or immunologic reactions, including thrombocytopenia, hepatitis, angioneurotic edema, and fever, are observed rarely. 13 1a: Quinidine III Pharmacokinetics Quinidine is absorbed readily following oral administration, bound to albumin and α1-acid glycoprotein, and eliminated primarily by hepatic metabolism. The elimination half-life is 6 8 hours. Quinidine is usually administered in a slow release formulation, eg, that of the gluconate salt. 14 7
8 1a: Quinidine IV Therapeutic Use Quinidine is used only occasionally to maintain normal sinus rhythm in patients with atrial flutter/fibrillation. Because of its cardiac and extracardiac side effects, its use is now largely restricted to patients with arrhythmic but othervise normal hearts. In randomized, controlled clinical trials, quinidine-treated patients are twice as likely to remain in normal sinus rhythm compared with controls, but the risk of death is increased two-to threefold. Quinidine is used rarely in patients with ventricular tachycardia. Quinidine is the optical isomer of quinine and is sometimes used intravenously for the treatment of acute, severe malaria. 15 1b: Lidocaine I Cardiac Effects Lidocaine blocks activated and inactivated sodium channels with rapid kinetics; the inactivated state block ensures greater effects on cells with long action potentials such as Purkinje and ventricular cells, compared with atrial cells. The rapid kinetics at normal resting potentials result in recovery from block between action potentials and no effect on conduction. The increased inactivation and slower unbinding kinetics result in the selective depression of conduction in depolarized cells. 16 8
9 1b: Lidocaine II Toxicity CARDIAC Lidocaine is one of the least cardiotoxic of the currently used sodium channel blockers. Proarrhythmic effects, including sinoatrial node arrest, worsening of impaired conduction, and ventricular arrhythmias, are uncommon with lidocaine use. In large doses, especially in patients with preexisting heart failure, lidocaine may cause hypotension partly by depressing myocardial contractility. 17 1b: Lidocaine III Toxicity EXTRACARDIAC Lidocaine's most common adverse effects like those of other local anesthetics are neurologic: paresthesias, tremor, nausea of central origin, lightheadedness, hearing disturbances, slurred speech, and convulsions. These occur most commonly in elderly or otherwise vulnerable patients or when a bolus of the drug is given too rapidly. The effects are dose-related and usually short-lived; seizures respond to intravenous diazepam. In general, if plasma levels above 9 mcg/ml are avoided, lidocaine is well tolerated. 18 9
10 1b: Lidocaine IV Pharmacokinetics & Dosage Because of its extensive first-pass hepatic metabolism lidocaine must be given parenterally. Lidocaine has a half-life of 1 2 hours. In adults, a loading dose of mg administered over about 15 minutes (as a single infusion or as a series of slow boluses) should be followed by a maintenance infusion of 2 4 mg/min to achieve a therapeutic plasma level of 2 6 mcg/ml. Determination of lidocaine plasma levels is of great value in adjusting the infusion rate. Occasional patients with myocardial infarction or other acute illness require (and tolerate) higher concentrations. This may be due to increased plasma α1-acid glycoprotein, an acute phase reactant protein that binds lidocaine, making less free drug available to exert its pharmacologic effects. 19 1b: Lidocaine V Therapeutic Use Lidocaine is the agent of choice for termination of ventricular tachycardia and prevention of ventricular fibrillation after cardioversion in the setting of acute ischemia. However, routine prophylactic use of lidocaine in this setting may actually increase total mortality, possibly by increasing the incidence of asystole, and is not the standard of care. Most physicians administer IV lidocaine only to patients with arrhythmias
11 1c: Propafenone I Propafenone has some structural similarities to propranolol and possesses weak β-blocking activity. Its spectrum of action is very similar to that of quinidine. Its sodium channel blocking kinetics are similar to that of flecainide. 21 1c: Propafenone II Propafenone is metabolized in the liver, with an average half-life of 5 7 hours. The usual daily dosage of propafenone is mg in three doses. The drug is used primarily for supraventricular arrhythmias. The most common adverse effects are a metallic taste and constipation; arrhythmia exacerbation can occur
12 2: β-blockers II Propranolol and similar drugs have antiarrhythmic properties by virtue of their β-receptor blocking action and direct membrane effects. Some of these drugs have selectivity for cardiac β1 receptors, some have intrinsic sympathomimetic activity, some have marked direct membrane effects, and some prolong the cardiac action potential. 23 Katzung & Trevor s Pharmacology Examination & Board Review 7th Edition
13 2: β-blockers II The relative contributions of the β -blocking and direct membrane effects to the antiarrhythmic effects of these drugs are not fully known. Although β blockers are fairly well tolerated, their efficacy for suppression of ventricular ectopic depolarizations is lower than that of sodium channel blockers. However, there is good evidence that these agents can prevent recurrent infarction and sudden death in patients recovering from acute myocardial infarction. 25 2: β-blockers II Esmolol is a short-acting β blocker used primarily as an antiarrhythmic drug for intraoperative and other acute arrhythmias. Sotalol is a nonselective β -blocking drug that prolongs the action potential (class 3 action)
14 Drugs That Prolong Effective Refractory Period by Prolonging Action Potential (Class 3) These drugs prolong action potentials, usually by blocking potassium channels in cardiac muscle or by enhancing inward current, eg, through sodium channels. Action potential prolongation by most of these drugs often exhibits the undesirable property of "reverse use-dependence": action potential prolongation is least marked at fast rates (where it is desirable) and most marked at slow rates, where it can contribute to the risk of torsade de pointes. 27 Drugs That Prolong Effective Refractory Period by Prolonging Action Potential (Class 3) Katzung & Trevor s Pharmacology Examination & Board Review 7th Edition
15 3: Amiodarone I Amiodarone is approved for oral and intravenous use to treat serious ventricular arrhythmias. However, the drug is also highly effective for the treatment of supraventricular arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation. Amiodarone has a broad spectrum of cardiac actions, unusual pharmacokinetics, and important extracardiac adverse effects. 29 3: Amiodarone II Cardiac Effects Amiodarone markedly prolongs the action potential duration (and the QT interval on the ECG) by blockade of IKr (rapid delayed rectifier potassium current). During chronic administration, IKs (slow delayed rectifier potassium current) is also blocked. The action potential duration is prolonged uniformly over a wide range of heart rates; that is, the drug does not have reverse use-dependent action. In spite of its present classification as a class 3 agent, amiodarone also significantly blocks inactivated sodium channels. Its action potential prolonging action reinforces this effect
16 3: Amiodarone III Cardiac Effects (continued) Amiodarone also has weak adrenergic and calcium channel blocking actions. Consequences of these actions include slowing of the heart rate and atrioventricular node conduction. The broad spectrum of actions may account for its relatively high efficacy and low incidence of torsade de pointes despite significant QT interval prolongation. Extracardiac Effects Amiodarone causes peripheral vasodilation. This action is prominent following intravenous administration and may be related to the action of the vehicle. 31 3: Amiodarone IV Toxicity CARDIAC Amiodarone may produce symptomatic bradycardia and heart block in patients with preexisting sinus or atrioventricular node disease. EXTRACARDIAC Amiodarone accumulates in many tissues, including the heart (10 50 times greater than plasma), lung, liver, and skin, and is concentrated in tears. Dose-related pulmonary toxicity is the most important adverse effect. Even on a low dose of 200 mg/d, fatal pulmonary fibrosis may be observed in 1% of patients. Abnormal liver function tests and hepatitis may develop during amiodarone treatment. The skin deposits result in a photodermatitis and a gray-blue skin discoloration in sun-exposed areas, eg, the malar regions. After a few weeks of treatment, asymptomatic corneal microdeposits are present in virtually all patients treated with amiodarone. Halos develop in the peripheral visual fields of some patients. Drug discontinuation is usually not required. Rarely, an optic neuritis may progress to blindness. Amiodarone blocks the peripheral conversion of thyroxine (T4) to triiodothyronine (T3). It is also a potential source of large amounts of inorganic iodine. Amiodarone may result in hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism. Thyroid function should be evaluated prior to initiation of treatment and monitored periodically. Because effects have been described in virtually every organ system, amiodarone treatment should be reevaluated whenever new symptoms develop in a patient, including arrhythmia aggravation
17 3: Amiodarone V Pharmacokinetics Amiodarone is variably absorbed with a bioavailability of 35 65%. It undergoes hepatic metabolism, and the major metabolite, desethylamiodarone, is bioactive. The elimination half-life is complex, with a rapid component of 3 10 days (50% of the drug) and a slower component of several weeks. Following discontinuation of the drug, effects are maintained for 1 3 months. Measurable tissue levels may be observed up to 1 year after discontinuation. A total loading dose of 10 g is usually achieved with g daily doses. The maintenance dose is mg daily. Pharmacologic effects may be achieved rapidly by intravenous loading. QT-prolonging effect is modest with this route of administration, whereas bradycardia and atrioventricular block may be significant. Amiodarone has many important drug interactions and all medications should be reviewed during drug initiation or dose adjustments. Amiodarone is a substrate for the liver cytochrome metabolizing enzyme CYP3A4 and its levels are increased by drugs that inhibit this enzyme, eg, the histamine H2 blocker cimetidine. Drugs that induce CYP3A4, eg, rifampin, decrease amiodarone concentration when coadministered. Amiodarone inhibits the other liver cytochrome metabolizing enzymes and may result in high levels of drugs that are substrates for these enzymes, eg, digoxin and warfarin. 33 3: Amiodarone VI Therapeutic Use Low doses ( mg/d) of amiodarone are effective in maintaining normal sinus rhythm in patients with atrial fibrillation. The drug is effective in the prevention of recurrent ventricular tachycardia. Its use is not associated with an increase in mortality in patients with coronary artery disease or heart failure. In many centers, the implanted cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) has succeeded drug therapy as the primary treatment modality for ventricular tachycardia, but amiodarone may be used for ventricular tachycardia as adjuvant therapy to decrease the frequency of uncomfortable ICD discharges. The drug increases the pacing and defibrillation threshold and these devices require retesting after a maintenance dose has been achieved
18 Calcium Channel Blocking Drugs (Class 4) These drugs, of which verapamil is the prototype, were first introduced as antianginal agents and are discussed in greater detail in that lecture. Verapamil and diltiazem also have antiarrhythmic effects. 35 Calcium Channel Blocking Drugs (Class 4) Katzung & Trevor s Pharmacology Examination & Board Review 7th Edition
19 4: Verapamil I Cardiac Effects Verapamil blocks both activated and inactivated L-type calcium channels. Thus, its effect is more marked in tissues that fire frequently, those that are less completely polarized at rest, and those in which activation depends exclusively on the calcium current, such as the sinoatrial and atrioventricular nodes. Atrioventricular nodal conduction time and effective refractory period are invariably prolonged by therapeutic concentrations. Verapamil usually slows the sinoatrial node by its direct action, but its hypotensive action may occasionally result in a small reflex increase of sinoatrial nodal rate. 37 4: Verapamil II Cardiac Effects (continued) Verapamil can suppress both early and delayed afterdepolarizations and may antagonize slow responses arising in severely depolarized tissue. Extracardiac Effects Verapamil causes peripheral vasodilation, which may be beneficial in hypertension and peripheral vasospastic disorders. Its effects upon smooth muscle produce a number of extracardiac effects
20 4: Verapamil III Toxicity CARDIAC Verapamil's cardiotoxic effects are dose-related and usually avoidable. A common error has been to administer intravenous verapamil to a patient with ventricular tachycardia misdiagnosed as supraventricular tachycardia. In this setting, hypotension and ventricular fibrillation can occur. Verapamil's negative inotropic effects may limit its clinical usefulness in diseased hearts. Verapamil can induce atrioventricular block when used in large doses or in patients with atrioventricular nodal disease. This block can be treated with atropine and β-receptor stimulants. In patients with sinus node disease, verapamil can precipitate sinus arrest. EXTRACARDIAC Adverse effects include constipation, lassitude, nervousness, and peripheral edema. 39 4: Verapamil IV Pharmacokinetics & Dosage The half-life of verapamil is approximately 7 hours. It is extensively metabolized by the liver; after oral administration, its bioavailability is only about 20%. Therefore, verapamil must be administered with caution in patients with hepatic dysfunction. In adult patients without heart failure or sinoatrial or atrioventricular nodal disease, parenteral verapamil can be used to terminate supraventricular tachycardia, although adenosine is the agent of first choice. Verapamil dosage is an initial bolus of 5 mg administered over 2 5 minutes, followed a few minutes later by a second 5 mg bolus if needed. Thereafter, doses of 5 10 mg can be administered every 4 6 hours, or a constant infusion of 0.4 mcg/kg/min may be used. Effective oral dosages are higher than intravenous dosage because of first-pass metabolism and range from 120 to 640 mg daily, divided into three or four doses
21 4: Verapamil V Therapeutic Use Supraventricular tachycardia is the major arrhythmia indication for verapamil. Adenosine or verapamil are preferred over older treatments (propranolol, digoxin, edrophonium, vasoconstrictor agents, and cardioversion) for termination. Verapamil can also reduce the ventricular rate in atrial fibrillation and flutter. It only rarely converts atrial flutter and fibrillation to sinus rhythm. Verapamil is occasionally useful in ventricular arrhythmias. However, the use of intravenous verapamil in a patient with sustained ventricular tachycardia can cause hemodynamic collapse. 41 First choice antiarrhythmic drugs SVT, supraventricular tachycardia; VEB, ventricular ectopic beat; VT, ventricular tachycardia; VF, ventricular fibrillation Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı
22 a Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı
23 Thank you
Antiarrhythmic Drugs Öner Süzer
 Antiarrhythmic Drugs Öner Süzer www.onersuzer.com osuzer@istanbul.edu.tr Last update: 13.01.2009 1 Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı 2005 2 1 Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı 2005 3 Figure 14 1 Schematic representation
Antiarrhythmic Drugs Öner Süzer www.onersuzer.com osuzer@istanbul.edu.tr Last update: 13.01.2009 1 Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı 2005 2 1 Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı 2005 3 Figure 14 1 Schematic representation
PHARMACOLOGY OF ARRHYTHMIAS
 PHARMACOLOGY OF ARRHYTHMIAS Course: Integrated Therapeutics 1 Lecturer: Dr. E. Konorev Date: November 27, 2012 Materials on: Exam #5 Required reading: Katzung, Chapter 14 1 CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Abnormalities
PHARMACOLOGY OF ARRHYTHMIAS Course: Integrated Therapeutics 1 Lecturer: Dr. E. Konorev Date: November 27, 2012 Materials on: Exam #5 Required reading: Katzung, Chapter 14 1 CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Abnormalities
Mr. Eknath Kole M.S. Pharm (NIPER Mohali)
 M.S. Pharm (NIPER Mohali) Drug Class Actions Therapeutic Uses Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effects Other Quinidine IA -Binds to open and inactivated Na+ -Decreases the slope of Phase 4 spontaneous depolarization
M.S. Pharm (NIPER Mohali) Drug Class Actions Therapeutic Uses Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effects Other Quinidine IA -Binds to open and inactivated Na+ -Decreases the slope of Phase 4 spontaneous depolarization
Arrhythmias. Simple-dysfunction cause abnormalities in impulse formation and conduction in the myocardium.
 Arrhythmias Simple-dysfunction cause abnormalities in impulse formation and conduction in the myocardium. However, in clinic it present as a complex family of disorders that show variety of symptoms, for
Arrhythmias Simple-dysfunction cause abnormalities in impulse formation and conduction in the myocardium. However, in clinic it present as a complex family of disorders that show variety of symptoms, for
Antiarrhythmic Drugs 1/31/2018 1
 Antiarrhythmic Drugs 1/31/2018 1 Normal conduction pathway: 1- SA node generates action potential and delivers it to the atria and the AV node 2- The AV node delivers the impulse to purkinje fibers Other
Antiarrhythmic Drugs 1/31/2018 1 Normal conduction pathway: 1- SA node generates action potential and delivers it to the atria and the AV node 2- The AV node delivers the impulse to purkinje fibers Other
Antiarrhythmic Drugs. Munir Gharaibeh MD, PhD, MHPE School of Medicine, The University of Jordan November 2018
 Antiarrhythmic Drugs Munir Gharaibeh MD, PhD, MHPE School of Medicine, The University of Jordan November 2018 2 Ion Permeability Changes Potential Changes Genes and Proteins 3 Cardiac Na+ channels 5 6
Antiarrhythmic Drugs Munir Gharaibeh MD, PhD, MHPE School of Medicine, The University of Jordan November 2018 2 Ion Permeability Changes Potential Changes Genes and Proteins 3 Cardiac Na+ channels 5 6
Antiarrhythmic Drugs
 Antiarrhythmic Drugs DR ATIF ALQUBBANY A S S I S T A N T P R O F E S S O R O F M E D I C I N E / C A R D I O L O G Y C O N S U L T A N T C A R D I O L O G Y & I N T E R V E N T I O N A L E P A C H D /
Antiarrhythmic Drugs DR ATIF ALQUBBANY A S S I S T A N T P R O F E S S O R O F M E D I C I N E / C A R D I O L O G Y C O N S U L T A N T C A R D I O L O G Y & I N T E R V E N T I O N A L E P A C H D /
Chapter 14. Agents used in Cardiac Arrhythmias
 Chapter 14 Agents used in Cardiac Arrhythmias Cardiac arrhythmia Approximately 50% of post-myocardial infarction fatalities result from ventricular tachycarida (VT) or ventricular fibrillation (VF). These
Chapter 14 Agents used in Cardiac Arrhythmias Cardiac arrhythmia Approximately 50% of post-myocardial infarction fatalities result from ventricular tachycarida (VT) or ventricular fibrillation (VF). These
Antiarrhythmic Drugs. Munir Gharaibeh MD, PhD, MHPE School of Medicine, The University of Jordan November 2017
 Antiarrhythmic Drugs Munir Gharaibeh MD, PhD, MHPE School of Medicine, The University of Jordan November 2017 Types of Cardiac Arrhythmias Abnormalities of Impulse Formation: Rate disturbances. Triggered
Antiarrhythmic Drugs Munir Gharaibeh MD, PhD, MHPE School of Medicine, The University of Jordan November 2017 Types of Cardiac Arrhythmias Abnormalities of Impulse Formation: Rate disturbances. Triggered
Chapter 9. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives 9/11/2012. Cardiac Arrhythmias. Define electrical therapy
 Chapter 9 Cardiac Arrhythmias Learning Objectives Define electrical therapy Explain why electrical therapy is preferred initial therapy over drug administration for cardiac arrest and some arrhythmias
Chapter 9 Cardiac Arrhythmias Learning Objectives Define electrical therapy Explain why electrical therapy is preferred initial therapy over drug administration for cardiac arrest and some arrhythmias
Arrhythmias. 1. beat too slowly (sinus bradycardia). Like in heart block
 Arrhythmias It is a simple-dysfunction caused by abnormalities in impulse formation and conduction in the myocardium. The heart is designed in such a way that allows it to generate from the SA node electrical
Arrhythmias It is a simple-dysfunction caused by abnormalities in impulse formation and conduction in the myocardium. The heart is designed in such a way that allows it to generate from the SA node electrical
Chapter 26. Media Directory. Dysrhythmias. Diagnosis/Treatment of Dysrhythmias. Frequency in Population Difficult to Predict
 Chapter 26 Drugs for Dysrythmias Slide 33 Slide 35 Media Directory Propranolol Animation Amiodarone Animation Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Dysrhythmias Abnormalities of electrical
Chapter 26 Drugs for Dysrythmias Slide 33 Slide 35 Media Directory Propranolol Animation Amiodarone Animation Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Dysrhythmias Abnormalities of electrical
Rhythm Control: Is There a Role for the PCP? Blake Norris, MD, FACC BHHI Primary Care Symposium February 28, 2014
 Rhythm Control: Is There a Role for the PCP? Blake Norris, MD, FACC BHHI Primary Care Symposium February 28, 2014 Financial disclosures Consultant Medtronic 3 reasons to evaluate and treat arrhythmias
Rhythm Control: Is There a Role for the PCP? Blake Norris, MD, FACC BHHI Primary Care Symposium February 28, 2014 Financial disclosures Consultant Medtronic 3 reasons to evaluate and treat arrhythmias
Use of Antiarrhythmic Drugs for AF Who, What and How? Dr. Marc Cheng Queen Elizabeth Hospital
 Use of Antiarrhythmic Drugs for AF Who, What and How? Dr. Marc Cheng Queen Elizabeth Hospital Content i. Rhythm versus Rate control ii. Anti-arrhythmic for Rhythm Control iii. Anti-arrhythmic for Rate
Use of Antiarrhythmic Drugs for AF Who, What and How? Dr. Marc Cheng Queen Elizabeth Hospital Content i. Rhythm versus Rate control ii. Anti-arrhythmic for Rhythm Control iii. Anti-arrhythmic for Rate
Amiodarone Prescribing and Monitoring: Back to the Future
 Amiodarone Prescribing and Monitoring: Back to the Future Subha L. Varahan, MD, FHRS, CCDS Electrophysiologist Oklahoma Heart Hospital Oklahoma City, OK Friday, February, 8 th, 2019 Iodinated benzofuran
Amiodarone Prescribing and Monitoring: Back to the Future Subha L. Varahan, MD, FHRS, CCDS Electrophysiologist Oklahoma Heart Hospital Oklahoma City, OK Friday, February, 8 th, 2019 Iodinated benzofuran
ANTI - ARRHYTHMIC DRUGS
 ANTI - ARRHYTHMIC DRUGS CARDIAC ACTION POTENTIAL K Out Balance Ca in/k out Na in K Out GENERATION OF ARRHYTHMIAS Four mechanisms of arrhythmia generation; Increased normal automaticity Abnormal automaticity
ANTI - ARRHYTHMIC DRUGS CARDIAC ACTION POTENTIAL K Out Balance Ca in/k out Na in K Out GENERATION OF ARRHYTHMIAS Four mechanisms of arrhythmia generation; Increased normal automaticity Abnormal automaticity
B. 14 Antidysrhythmic drugs. a. Classify antidysrhythmics by their electrophysiological actions. Vaughan-Williams classification
 B. 14 Antidysrhythmic drugs a. Classify antidysrhythmics by their electrophysiological actions. Vaughan-Williams classification I II III IV membrane stabilizers all ERP, ERP/APD, all except c APD classified
B. 14 Antidysrhythmic drugs a. Classify antidysrhythmics by their electrophysiological actions. Vaughan-Williams classification I II III IV membrane stabilizers all ERP, ERP/APD, all except c APD classified
Atrial Fibrillation 10/2/2018. Depolarization & ECG. Atrial Fibrillation. Hemodynamic Consequences
 Depolarization & ECG Atrial Fibrillation How to make ORDER out of CHAOS Julia Shih, VMD, DACVIM (Cardiology) October 27, 2018 Depolarization & ECG Depolarization & ECG Atrial Fibrillation Hemodynamic Consequences
Depolarization & ECG Atrial Fibrillation How to make ORDER out of CHAOS Julia Shih, VMD, DACVIM (Cardiology) October 27, 2018 Depolarization & ECG Depolarization & ECG Atrial Fibrillation Hemodynamic Consequences
Antidysrhythmics HST-151 1
 HST-151 1 Antidysrhythmics I. Ventricular muscle cell action potential a. Phase 0: Upstroke b. Phase 1: Early-fast repolarization c. Phase 2: Plateau d. Phase 3: Repolarization e. Phase 4: Diastole HST-151
HST-151 1 Antidysrhythmics I. Ventricular muscle cell action potential a. Phase 0: Upstroke b. Phase 1: Early-fast repolarization c. Phase 2: Plateau d. Phase 3: Repolarization e. Phase 4: Diastole HST-151
Instruct patient and caregivers: Need for constant monitoring Potential complications of drug therapy
 Assessment Prior to administration: Assess patient for chest pain, dysrhythmias, and vital signs (initially and throughout therapy) Obtain complete medical history, including allergies, especially heart
Assessment Prior to administration: Assess patient for chest pain, dysrhythmias, and vital signs (initially and throughout therapy) Obtain complete medical history, including allergies, especially heart
DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST. Consultant Sanofi Biosense Webster Honorarium Boehringer Ingelheim St Jude Medical
 DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST Consultant Sanofi Biosense Webster Honorarium Boehringer Ingelheim St Jude Medical ESC Congress Paris, France August 27-31, 2011 Risk & Complications of AADs for Rhythm
DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST Consultant Sanofi Biosense Webster Honorarium Boehringer Ingelheim St Jude Medical ESC Congress Paris, France August 27-31, 2011 Risk & Complications of AADs for Rhythm
ARRHYTHMIA SINUS RHYTHM
 ARRHYTHMIA Dr. Ahmed A. Elberry, MBBCH, MSc, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pharmacy Faculty of pharmacy, KAU 1 SINUS RHYTHM SA node is cardiac pacemaker Normal sinus rhythm 60-100 beats/min Depolarisation
ARRHYTHMIA Dr. Ahmed A. Elberry, MBBCH, MSc, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pharmacy Faculty of pharmacy, KAU 1 SINUS RHYTHM SA node is cardiac pacemaker Normal sinus rhythm 60-100 beats/min Depolarisation
Pediatrics ECG Monitoring. Pediatric Intensive Care Unit Emergency Division
 Pediatrics ECG Monitoring Pediatric Intensive Care Unit Emergency Division 1 Conditions Leading to Pediatric Cardiology Consultation 12.7% of annual consultation Is arrhythmias problems Geggel. Pediatrics.
Pediatrics ECG Monitoring Pediatric Intensive Care Unit Emergency Division 1 Conditions Leading to Pediatric Cardiology Consultation 12.7% of annual consultation Is arrhythmias problems Geggel. Pediatrics.
Intraoperative and Postoperative Arrhythmias: Diagnosis and Treatment
 Intraoperative and Postoperative Arrhythmias: Diagnosis and Treatment Karen L. Booth, MD, Lucile Packard Children s Hospital Arrhythmias are common after congenital heart surgery [1]. Postoperative electrolyte
Intraoperative and Postoperative Arrhythmias: Diagnosis and Treatment Karen L. Booth, MD, Lucile Packard Children s Hospital Arrhythmias are common after congenital heart surgery [1]. Postoperative electrolyte
The pill-in-the-pocket strategy for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation
 The pill-in-the-pocket strategy for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation KONSTANTINOS P. LETSAS, MD, FEHRA LABORATORY OF CARDIAC ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY EVANGELISMOS GENERAL HOSPITAL OF ATHENS ARRHYTHMIAS UPDATE,
The pill-in-the-pocket strategy for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation KONSTANTINOS P. LETSAS, MD, FEHRA LABORATORY OF CARDIAC ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY EVANGELISMOS GENERAL HOSPITAL OF ATHENS ARRHYTHMIAS UPDATE,
a lecture series by SWESEMJR
 Electrolyte disturbances Hypokalaemia Decreased extracellular potassium increases excitability in the myocardial cells and consequently the effect of very severe hypokalaemia is ventricular arrhythmia.
Electrolyte disturbances Hypokalaemia Decreased extracellular potassium increases excitability in the myocardial cells and consequently the effect of very severe hypokalaemia is ventricular arrhythmia.
B-blockers. Effects not related to Beta-Blockade
 B-blockers Effects not related to Beta-Blockade It has been suggested that some intrinsic sympathomimetic activity is desirable to prevent untoward effects such as asthma or excessive bradycardia. Pindolol
B-blockers Effects not related to Beta-Blockade It has been suggested that some intrinsic sympathomimetic activity is desirable to prevent untoward effects such as asthma or excessive bradycardia. Pindolol
Dysrhythmias. Dysrythmias & Anti-Dysrhythmics. EKG Parameters. Dysrhythmias. Components of an ECG Wave. Dysrhythmias
 Dysrhythmias Dysrythmias & Anti-Dysrhythmics Rhythm bad in the heart: Whitewater rafting Electrical impulses coordinate heart Reduction in Cardiac Output PEA Asystole Components of an ECG Wave EKG Parameters
Dysrhythmias Dysrythmias & Anti-Dysrhythmics Rhythm bad in the heart: Whitewater rafting Electrical impulses coordinate heart Reduction in Cardiac Output PEA Asystole Components of an ECG Wave EKG Parameters
ELECTRICAL SIGNALS CONTROL THE CARDIAC ACTIVITY
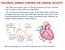 ELECTRICAL SIGNALS CONTROL THE CARDIAC ACTIVITY The heart beat begins when an electrical impulse from the sinoatrial node (SA node or sinus node) moves through it. The normal electrical sequence begins
ELECTRICAL SIGNALS CONTROL THE CARDIAC ACTIVITY The heart beat begins when an electrical impulse from the sinoatrial node (SA node or sinus node) moves through it. The normal electrical sequence begins
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment
 Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
Drugs Controlling Myocyte Excitability and Conduction at the AV node Singh and Vaughan-Williams Classification
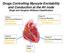 Drugs Controlling Myocyte Excitability and Conduction at the AV node Singh and Vaughan-Williams Classification Class I Na Channel Blockers Flecainide Propafenone Class III K channel Blockers Dofetilide,
Drugs Controlling Myocyte Excitability and Conduction at the AV node Singh and Vaughan-Williams Classification Class I Na Channel Blockers Flecainide Propafenone Class III K channel Blockers Dofetilide,
Chapter (9) Calcium Antagonists
 Chapter (9) Calcium Antagonists (CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS) Classification Mechanism of Anti-ischemic Actions Indications Drug Interaction with Verapamil Contraindications Adverse Effects Treatment of Drug
Chapter (9) Calcium Antagonists (CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS) Classification Mechanism of Anti-ischemic Actions Indications Drug Interaction with Verapamil Contraindications Adverse Effects Treatment of Drug
The most common. hospitalized patients. hypotension due to. filling time Rate control in ICU patients may be difficult as many drugs cause hypotension
 Arrhythmias in the critically ill ICU patients: Approach for rapid recognition & management Objectives Be able to identify and manage: Atrial fibrillation with a rapid ventricular response Atrial flutter
Arrhythmias in the critically ill ICU patients: Approach for rapid recognition & management Objectives Be able to identify and manage: Atrial fibrillation with a rapid ventricular response Atrial flutter
1 Cardiology Acute Care Day 22 April 2013 Arrhythmia Tutorial Course Material
 1 Cardiology Acute Care Day 22 April 2013 Arrhythmia Tutorial Course Material Arrhythmia recognition This tutorial builds on the ECG lecture and provides a framework for approaching any ECG to allow the
1 Cardiology Acute Care Day 22 April 2013 Arrhythmia Tutorial Course Material Arrhythmia recognition This tutorial builds on the ECG lecture and provides a framework for approaching any ECG to allow the
Chapter 16: Arrhythmias and Conduction Disturbances
 Complete the following. Chapter 16: Arrhythmias and Conduction Disturbances 1. Cardiac arrhythmias result from abnormal impulse, abnormal impulse, or both mechanisms together. 2. is the ability of certain
Complete the following. Chapter 16: Arrhythmias and Conduction Disturbances 1. Cardiac arrhythmias result from abnormal impulse, abnormal impulse, or both mechanisms together. 2. is the ability of certain
! YOU NEED TO MONITOR QT INTERVALS IN THESE PATIENTS.
 Antiarrhythmic Pharmacopoeia Powerful drugs, split into 4 major classes, according to the predominant receptor they effect. Some fit into several classes at once, like sotolol. Some don t fit at all, owing
Antiarrhythmic Pharmacopoeia Powerful drugs, split into 4 major classes, according to the predominant receptor they effect. Some fit into several classes at once, like sotolol. Some don t fit at all, owing
CORDARONE Sanofi-Aventis
 CORDARONE Sanofi-Aventis Composition Amiodarone 200 mg; tablets. Also AMPOULES 150 mg/3 ml. Indications Tablets Prevention of recurrence of the following: life-threatening ventricular tachycardias in which
CORDARONE Sanofi-Aventis Composition Amiodarone 200 mg; tablets. Also AMPOULES 150 mg/3 ml. Indications Tablets Prevention of recurrence of the following: life-threatening ventricular tachycardias in which
CSI Skills Lab #5: Arrhythmia Interpretation and Treatment
 CSI 202 - Skills Lab #5: Arrhythmia Interpretation and Treatment Origins of the ACLS Approach: CSI 202 - Skills Lab 5 Notes ACLS training originated in Nebraska in the early 1970 s. Its purpose was to
CSI 202 - Skills Lab #5: Arrhythmia Interpretation and Treatment Origins of the ACLS Approach: CSI 202 - Skills Lab 5 Notes ACLS training originated in Nebraska in the early 1970 s. Its purpose was to
Cardiac arrhythmias. Janusz Witowski. Department of Pathophysiology Poznan University of Medical Sciences. J. Witowski
 Cardiac arrhythmias Janusz Witowski Department of Pathophysiology Poznan University of Medical Sciences A 68-year old man presents to the emergency department late one evening complaining of increasing
Cardiac arrhythmias Janusz Witowski Department of Pathophysiology Poznan University of Medical Sciences A 68-year old man presents to the emergency department late one evening complaining of increasing
CORONARY ARTERIES. LAD Anterior wall of the left vent Lateral wall of left vent Anterior 2/3 of interventricluar septum R & L bundle branches
 CORONARY ARTERIES RCA Right atrium Right ventricle SA node 55% AV node 90% Posterior wall of left ventricle in 90% Posterior third of interventricular septum 90% LAD Anterior wall of the left vent Lateral
CORONARY ARTERIES RCA Right atrium Right ventricle SA node 55% AV node 90% Posterior wall of left ventricle in 90% Posterior third of interventricular septum 90% LAD Anterior wall of the left vent Lateral
ALS MODULE 7 Pharmacology
 ALS MODULE 7 Pharmacology Relates to HLT404C Apply Advanced Resuscitation Techniques Introduction There are no studies that addressed the order of drug administration. There is inadequate evidence to define
ALS MODULE 7 Pharmacology Relates to HLT404C Apply Advanced Resuscitation Techniques Introduction There are no studies that addressed the order of drug administration. There is inadequate evidence to define
CVD: Cardiac Arrhythmias. 1. Final Cardiac Arrhythmias_BMP. 1.1 Cardiovascular Disease. Notes:
 CVD: Cardiac Arrhythmias 1. Final Cardiac Arrhythmias_BMP 1.1 Cardiovascular Disease 1.2 Directions for taking this course 1.3 Content Experts 1.4 Disclosures 1.5 Accreditation Information 1.6 Learning
CVD: Cardiac Arrhythmias 1. Final Cardiac Arrhythmias_BMP 1.1 Cardiovascular Disease 1.2 Directions for taking this course 1.3 Content Experts 1.4 Disclosures 1.5 Accreditation Information 1.6 Learning
Antiarrhythmics 17 I. OVERVIEW II. INTRODUCTION TO THE ARRHYTHMIAS
 Antiarrhythmics 17 I. OVERVIEW In contrast to skeletal muscle, which contracts only when it receives a stimulus, the heart contains specialized cells that exhibit automaticity. This means that they can
Antiarrhythmics 17 I. OVERVIEW In contrast to skeletal muscle, which contracts only when it receives a stimulus, the heart contains specialized cells that exhibit automaticity. This means that they can
Objectives: This presentation will help you to:
 emergency Drugs Objectives: This presentation will help you to: Five rights for medication administration Recognize different cardiac arrhythmias and determine the common drugs used for each one List the
emergency Drugs Objectives: This presentation will help you to: Five rights for medication administration Recognize different cardiac arrhythmias and determine the common drugs used for each one List the
HTEC 91. Performing ECGs: Procedure. Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Topic for Today: Sinus Rhythms. Characteristics of NSR. Conduction Pathway
 HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 3 Performing ECGs: Procedure o ECG protocol: you may NOT do ECG if you have not signed up! If you are signed up and the room is occupied with people who did
HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 3 Performing ECGs: Procedure o ECG protocol: you may NOT do ECG if you have not signed up! If you are signed up and the room is occupied with people who did
Anti arrhythmic drugs. Hilal Al Saffar College of medicine Baghdad University
 Anti arrhythmic drugs Hilal Al Saffar College of medicine Baghdad University Mechanism of Arrhythmia Abnormal heart pulse formation Abnormal heart pulse conduction Classification of Arrhythmia Abnormal
Anti arrhythmic drugs Hilal Al Saffar College of medicine Baghdad University Mechanism of Arrhythmia Abnormal heart pulse formation Abnormal heart pulse conduction Classification of Arrhythmia Abnormal
Review Packet EKG Competency This packet is a review of the information you will need to know for the proctored EKG competency test.
 Review Packet EKG Competency 2015 This packet is a review of the information you will need to know for the proctored EKG competency test. Normal Sinus Rhythm Rhythm: Regular Ventricular Rate: 60-100 bpm
Review Packet EKG Competency 2015 This packet is a review of the information you will need to know for the proctored EKG competency test. Normal Sinus Rhythm Rhythm: Regular Ventricular Rate: 60-100 bpm
Atrial fibrillation in the ICU
 Atrial fibrillation in the ICU Atrial fibrillation Preexisting or incident (new onset) among nearly one in three critically ill patients Formation of arrhythogenic substrate usually fibrosis (CHF, hypertension,
Atrial fibrillation in the ICU Atrial fibrillation Preexisting or incident (new onset) among nearly one in three critically ill patients Formation of arrhythogenic substrate usually fibrosis (CHF, hypertension,
ARRHYTHMIAS IN THE ICU
 ARRHYTHMIAS IN THE ICU Nora Goldschlager, MD MACP, FACC, FAHA, FHRS SFGH Division of Cardiology UCSF IDENTIFIED VARIABLES IN ARRHYTHMOGENESIS Ischemia/infarction (scar) Electrolyte imbalance Proarrhythmia
ARRHYTHMIAS IN THE ICU Nora Goldschlager, MD MACP, FACC, FAHA, FHRS SFGH Division of Cardiology UCSF IDENTIFIED VARIABLES IN ARRHYTHMOGENESIS Ischemia/infarction (scar) Electrolyte imbalance Proarrhythmia
I have nothing to disclose.
 I have nothing to disclose. Antiarrhythmic Therapy in Pregnancy Prof. Ali Oto,MD,FESC,FACC,FHRS Department of Cardiology Hacettepe University,Faculty of Medicine Ankara Arrhythmias in pregnancy An increased
I have nothing to disclose. Antiarrhythmic Therapy in Pregnancy Prof. Ali Oto,MD,FESC,FACC,FHRS Department of Cardiology Hacettepe University,Faculty of Medicine Ankara Arrhythmias in pregnancy An increased
Core Content In Urgent Care Medicine
 Palpitations/Arrhythmias Ebrahim Barkoudah, MD Clinical Instructor in Internal Medicine Harvard Medical School Assistant in Internal Medicine & Pediatrics Massachusetts General Hospital MGH Chelsea Chelsea,
Palpitations/Arrhythmias Ebrahim Barkoudah, MD Clinical Instructor in Internal Medicine Harvard Medical School Assistant in Internal Medicine & Pediatrics Massachusetts General Hospital MGH Chelsea Chelsea,
Arrhythmic Complications of MI. Teferi Mitiku, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California Irvine
 Arrhythmic Complications of MI Teferi Mitiku, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California Irvine Objectives Brief overview -Pathophysiology of Arrhythmia ECG review of typical
Arrhythmic Complications of MI Teferi Mitiku, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California Irvine Objectives Brief overview -Pathophysiology of Arrhythmia ECG review of typical
ARRHYTHMIAS IN THE ICU: DIAGNOSIS AND PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT
 ARRHYTHMIAS IN THE ICU: DIAGNOSIS AND PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT Nora Goldschlager, M.D. MACP, FACC, FAHA, FHRS SFGH Division of Cardiogy UCSF CLINICAL VARIABLES IN ARRHYTHMOGENESIS Ischemia/infarction (scar)
ARRHYTHMIAS IN THE ICU: DIAGNOSIS AND PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT Nora Goldschlager, M.D. MACP, FACC, FAHA, FHRS SFGH Division of Cardiogy UCSF CLINICAL VARIABLES IN ARRHYTHMOGENESIS Ischemia/infarction (scar)
WHAT DO YOU SEE WHEN YOU STIMULATE BETA
 CARDIAC DRUG REVIEW WHAT DO YOU SEE WHEN YOU STIMULATE BETA VASODILATE BRONCHODILATE +CHRONOTROPE +INOTROPE EPI S OTHER NAME? ADRENALIN WHAT DOES EPI DO THAT NOREPI AND DOPAMINE DO NOT DO? BETA 2 BRONCHODILATOR
CARDIAC DRUG REVIEW WHAT DO YOU SEE WHEN YOU STIMULATE BETA VASODILATE BRONCHODILATE +CHRONOTROPE +INOTROPE EPI S OTHER NAME? ADRENALIN WHAT DOES EPI DO THAT NOREPI AND DOPAMINE DO NOT DO? BETA 2 BRONCHODILATOR
Antiarrhythmias. Edward JN Ishac, Ph.D. Smith Building, Room
 Antiarrhythmias Edward JN Ishac, Ph.D. Smith Building, Room 72 eishac@vcu.edu 828-2127 Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology Medical College of Virginia Campus of Virginia Commonwealth University Richmond,
Antiarrhythmias Edward JN Ishac, Ph.D. Smith Building, Room 72 eishac@vcu.edu 828-2127 Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology Medical College of Virginia Campus of Virginia Commonwealth University Richmond,
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: WPW Revised: 11/2013
 Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: WPW Revised: 11/2013 Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW) is a syndrome of pre-excitation of the
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: WPW Revised: 11/2013 Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW) is a syndrome of pre-excitation of the
Rate and Rhythm Control of Atrial Fibrillation
 Rate and Rhythm Control of Atrial Fibrillation April 21, 2017 춘계심혈관통합학술대회 Jaemin Shim, MD, PhD Arrhythmia Center Korea University Anam Hospital Treatment of AF Goal Reducing symptoms Preventing complication
Rate and Rhythm Control of Atrial Fibrillation April 21, 2017 춘계심혈관통합학술대회 Jaemin Shim, MD, PhD Arrhythmia Center Korea University Anam Hospital Treatment of AF Goal Reducing symptoms Preventing complication
PEDIATRIC SVT MANAGEMENT
 PEDIATRIC SVT MANAGEMENT 1 INTRODUCTION Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) can be defined as an abnormally rapid heart rhythm originating above the ventricles, often (but not always) with a narrow QRS
PEDIATRIC SVT MANAGEMENT 1 INTRODUCTION Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) can be defined as an abnormally rapid heart rhythm originating above the ventricles, often (but not always) with a narrow QRS
ΚΟΛΠΙΚΗ ΜΑΡΜΑΡΥΓΗ ΦΑΡΜΑΚΕΥΤΙΚΗ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΙΚΗ ΑΝΑΤΑΞΗ. ΣΠΥΡΟΜΗΤΡΟΣ ΓΕΩΡΓΙΟΣ Καρδιολόγος, Ε/Α, Γ.Ν.Κατερίνης. F.E.S.C
 ΚΟΛΠΙΚΗ ΜΑΡΜΑΡΥΓΗ ΦΑΡΜΑΚΕΥΤΙΚΗ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΙΚΗ ΑΝΑΤΑΞΗ ΣΠΥΡΟΜΗΤΡΟΣ ΓΕΩΡΓΙΟΣ Καρδιολόγος, Ε/Α, Γ.Ν.Κατερίνης. F.E.S.C Definitions of AF: A Simplified Scheme Term Definition Paroxysmal AF AF that terminates
ΚΟΛΠΙΚΗ ΜΑΡΜΑΡΥΓΗ ΦΑΡΜΑΚΕΥΤΙΚΗ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΙΚΗ ΑΝΑΤΑΞΗ ΣΠΥΡΟΜΗΤΡΟΣ ΓΕΩΡΓΙΟΣ Καρδιολόγος, Ε/Α, Γ.Ν.Κατερίνης. F.E.S.C Definitions of AF: A Simplified Scheme Term Definition Paroxysmal AF AF that terminates
Amiodarone. Traffic light classification- Amber 2 Information sheet for Primary Care Prescribers
 Amiodarone Traffic light classification- Amber 2 Information sheet for Primary Care Prescribers Licensed Indications Tachyarrhythmias associated with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome All types of tachyarrhythmias
Amiodarone Traffic light classification- Amber 2 Information sheet for Primary Care Prescribers Licensed Indications Tachyarrhythmias associated with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome All types of tachyarrhythmias
Cardiac Drugs: Chapter 9 Worksheet Cardiac Agents. 1. drugs affect the rate of the heart and can either increase its rate or decrease its rate.
 Complete the following. 1. drugs affect the rate of the heart and can either increase its rate or decrease its rate. 2. drugs affect the force of contraction and can be either positive or negative. 3.
Complete the following. 1. drugs affect the rate of the heart and can either increase its rate or decrease its rate. 2. drugs affect the force of contraction and can be either positive or negative. 3.
4/14/15 HTEC 91. Topics for Today. Guess That Rhythm. Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs) Ventricular Rhythms
 4/14/15 Topics for Today HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 5 Ventricular Rhythms PVCs: Premature Ventricular Contractions VT: Ventricular Tachycardia VF: Ventricular Fibrillation Asystole Study
4/14/15 Topics for Today HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 5 Ventricular Rhythms PVCs: Premature Ventricular Contractions VT: Ventricular Tachycardia VF: Ventricular Fibrillation Asystole Study
Adenosine. poison/drug induced. flushing, chest pain, transient asystole. Precautions: tachycardia. fibrillation, atrial flutter. Indications: or VT
 Adenosine Indications: 1. Narrow complex PSVT 2. Does not convert atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter or VT 1. Side effects include flushing, chest pain, transient asystole 2. May deteriorate widecomplex
Adenosine Indications: 1. Narrow complex PSVT 2. Does not convert atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter or VT 1. Side effects include flushing, chest pain, transient asystole 2. May deteriorate widecomplex
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH. 2% Lidocaine Hydrochloride Injection USP 20 mg/ml
 PRODUCT MONOGRAPH 2% Lidocaine Hydrochloride Injection USP 20 mg/ml 0.4 % Lidocaine Hydrochloride and 5% Dextrose Injection USP Lidocaine Hydrochloride and Dextrose Injection USP Lidocaine Hydrochloride
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH 2% Lidocaine Hydrochloride Injection USP 20 mg/ml 0.4 % Lidocaine Hydrochloride and 5% Dextrose Injection USP Lidocaine Hydrochloride and Dextrose Injection USP Lidocaine Hydrochloride
This document does not consider management of individual arrhythmias look elsewhere, e.g. OHCM.
 Cardiac arrhythmias This document does not consider management of individual arrhythmias look elsewhere, e.g. OHCM. Physiology Automaticity = ability of specialised cardiac conducting tissue to spontaneously
Cardiac arrhythmias This document does not consider management of individual arrhythmias look elsewhere, e.g. OHCM. Physiology Automaticity = ability of specialised cardiac conducting tissue to spontaneously
Pharmacology: Arrhythmias PC PHPP 515 (IT I) Fall JACOBS Wed, Dec. 03 4:00 5:50 PM
 Pharmacology: Arrhythmias PC PHPP 515 (IT I) Fall 2014 JACOBS Wed, Dec. 03 4:00 5:50 PM Required Reading (via Access Pharmacy) Katzung: Chapters 14 Recommended Reading (via Access Pharmacy) Goodman and
Pharmacology: Arrhythmias PC PHPP 515 (IT I) Fall 2014 JACOBS Wed, Dec. 03 4:00 5:50 PM Required Reading (via Access Pharmacy) Katzung: Chapters 14 Recommended Reading (via Access Pharmacy) Goodman and
Antiarrhythmic Pharmacology. The Electronics
 Antiarrhythmic Pharmacology Linking Pharmacological Treatment to the Patient and the Rhythm Presented By: Karen Marzlin BSN, RN,C, CCRN-CMC CNEA 2009 1 The Electronics Action Potential of Cardiac Cells
Antiarrhythmic Pharmacology Linking Pharmacological Treatment to the Patient and the Rhythm Presented By: Karen Marzlin BSN, RN,C, CCRN-CMC CNEA 2009 1 The Electronics Action Potential of Cardiac Cells
TEST BANK FOR ECGS MADE EASY 5TH EDITION BY AEHLERT
 Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-ecgs-made-easy-5thedition-by-aehlert/ TEST BANK FOR ECGS MADE EASY 5TH EDITION BY AEHLERT Chapter 5 TRUE/FALSE 1. The AV junction consists
Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-ecgs-made-easy-5thedition-by-aehlert/ TEST BANK FOR ECGS MADE EASY 5TH EDITION BY AEHLERT Chapter 5 TRUE/FALSE 1. The AV junction consists
Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat
 Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat Diuretic Thiazide diuretics The loop diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics *Hydrochlorothiazide *Chlorthalidone *Furosemide *Torsemide *Bumetanide Aldosterone
Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat Diuretic Thiazide diuretics The loop diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics *Hydrochlorothiazide *Chlorthalidone *Furosemide *Torsemide *Bumetanide Aldosterone
Management of acute Cardiac Arrhythmias
 Management of acute Cardiac Arrhythmias Dr. Zulkeflee Muhammad MBChB (New Zealand), MRCP (United Kingdom) Cardiologist Electrophysiology Unit Istitut Jantung Negara Objectives Review the etiology and recognition
Management of acute Cardiac Arrhythmias Dr. Zulkeflee Muhammad MBChB (New Zealand), MRCP (United Kingdom) Cardiologist Electrophysiology Unit Istitut Jantung Negara Objectives Review the etiology and recognition
The ABCs of EKGs/ECGs for HCPs. Al Heuer, PhD, MBA, RRT, RPFT Professor, Rutgers School of Health Related Professions
 The ABCs of EKGs/ECGs for HCPs Al Heuer, PhD, MBA, RRT, RPFT Professor, Rutgers School of Health Related Professions Learning Objectives Review the basic anatomy of the heart Describe the cardiac conducting
The ABCs of EKGs/ECGs for HCPs Al Heuer, PhD, MBA, RRT, RPFT Professor, Rutgers School of Health Related Professions Learning Objectives Review the basic anatomy of the heart Describe the cardiac conducting
Prehospital Care Monograph
 Prehospital Care Monograph Amiodarone (Cordarone) City of Pittsburgh Bureau of Emergency Medical Services And Medical Direction Committee Center for Emergency Medicine Of Western Pennsylvania 1 This monograph
Prehospital Care Monograph Amiodarone (Cordarone) City of Pittsburgh Bureau of Emergency Medical Services And Medical Direction Committee Center for Emergency Medicine Of Western Pennsylvania 1 This monograph
Cardiac Arrhythmias & Drugs used in Advanced Life Support and Cardiac Emergencies
 Cardiac Arrhythmias & Drugs used in Advanced Life Support and Cardiac Emergencies CNHE Ballarat Health Services Valid from 1 st March 2016 to 31 st June 2018 1 Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) An atrial
Cardiac Arrhythmias & Drugs used in Advanced Life Support and Cardiac Emergencies CNHE Ballarat Health Services Valid from 1 st March 2016 to 31 st June 2018 1 Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) An atrial
Antihypertensive Agents Part-2. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Antihypertensive Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Agents that block production or action of angiotensin Angiotensin-converting
Antihypertensive Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Agents that block production or action of angiotensin Angiotensin-converting
Where are the normal pacemaker and the backup pacemakers of the heart located?
 CASE 9 A 68-year-old woman presents to the emergency center with shortness of breath, light-headedness, and chest pain described as being like an elephant sitting on her chest. She is diagnosed with a
CASE 9 A 68-year-old woman presents to the emergency center with shortness of breath, light-headedness, and chest pain described as being like an elephant sitting on her chest. She is diagnosed with a
Step by step approach to EKG rhythm interpretation:
 Sinus Rhythms Normal sinus arrhythmia Small, slow variation of the R-R interval i.e. variation of the normal sinus heart rate with respiration, etc. Sinus Tachycardia Defined as sinus rhythm with a rate
Sinus Rhythms Normal sinus arrhythmia Small, slow variation of the R-R interval i.e. variation of the normal sinus heart rate with respiration, etc. Sinus Tachycardia Defined as sinus rhythm with a rate
2) Heart Arrhythmias 2 - Dr. Abdullah Sharif
 2) Heart Arrhythmias 2 - Dr. Abdullah Sharif Rhythms from the Sinus Node Sinus Tachycardia: HR > 100 b/m Causes: o Withdrawal of vagal tone & Sympathetic stimulation (exercise, fight or flight) o Fever
2) Heart Arrhythmias 2 - Dr. Abdullah Sharif Rhythms from the Sinus Node Sinus Tachycardia: HR > 100 b/m Causes: o Withdrawal of vagal tone & Sympathetic stimulation (exercise, fight or flight) o Fever
Emergency treatment to SVT Evidence-based Approach. Tran Thao Giang
 Emergency treatment to SVT Evidence-based Approach Tran Thao Giang Description ECG manifestations: HR is extremely rapid and regular (240bpm ± 40) P wave is: usually invisible When visible: anormal P axis,
Emergency treatment to SVT Evidence-based Approach Tran Thao Giang Description ECG manifestations: HR is extremely rapid and regular (240bpm ± 40) P wave is: usually invisible When visible: anormal P axis,
Rytmonorm/Arythmol (propafenone) SR 225 mg, 325 mg, 425 mg Capsules and IR 10 mg, 150 mg, 300 mg Tablets and Intravenous Solution for Injection
 1 CORE SAFETY PROFILE Rytmonorm/Arythmol (propafenone) SR 225 mg, 325 mg, 425 mg Capsules and IR 10 mg, 150 mg, 300 mg Tablets and Intravenous Solution for Injection 4. CLINICAL PARTICULARS 4.2 Posology
1 CORE SAFETY PROFILE Rytmonorm/Arythmol (propafenone) SR 225 mg, 325 mg, 425 mg Capsules and IR 10 mg, 150 mg, 300 mg Tablets and Intravenous Solution for Injection 4. CLINICAL PARTICULARS 4.2 Posology
Pediatrics. Arrhythmias in Children: Bradycardia and Tachycardia Diagnosis and Treatment. Overview
 Pediatrics Arrhythmias in Children: Bradycardia and Tachycardia Diagnosis and Treatment See online here The most common form of cardiac arrhythmia in children is sinus tachycardia which can be caused by
Pediatrics Arrhythmias in Children: Bradycardia and Tachycardia Diagnosis and Treatment See online here The most common form of cardiac arrhythmia in children is sinus tachycardia which can be caused by
Cardiac Arrhythmias. For Pharmacists
 Cardiac Arrhythmias For Pharmacists Agenda Overview of the normal Classification Management Therapy Conclusion Cardiac arrhythmias Overview of the normal Arrhythmia: definition From the Greek a-, loss
Cardiac Arrhythmias For Pharmacists Agenda Overview of the normal Classification Management Therapy Conclusion Cardiac arrhythmias Overview of the normal Arrhythmia: definition From the Greek a-, loss
UNDERSTANDING YOUR ECG: A REVIEW
 UNDERSTANDING YOUR ECG: A REVIEW Health professionals use the electrocardiograph (ECG) rhythm strip to systematically analyse the cardiac rhythm. Before the systematic process of ECG analysis is described
UNDERSTANDING YOUR ECG: A REVIEW Health professionals use the electrocardiograph (ECG) rhythm strip to systematically analyse the cardiac rhythm. Before the systematic process of ECG analysis is described
Ventricular tachycardia Ventricular fibrillation and ICD
 EKG Conference Ventricular tachycardia Ventricular fibrillation and ICD Samsung Medical Center CCU D.I. Hur Ji Won 2006.05.20 Ventricular tachyarrhythmia ventricular tachycardia ventricular fibrillation
EKG Conference Ventricular tachycardia Ventricular fibrillation and ICD Samsung Medical Center CCU D.I. Hur Ji Won 2006.05.20 Ventricular tachyarrhythmia ventricular tachycardia ventricular fibrillation
Nathan Cade, MD Brandon Fainstad, MD Andrew Prouse, MD
 Nathan Cade, MD Brandon Fainstad, MD Andrew Prouse, MD OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the basic electrophysiology of the four causes of wide complex tachycardia. 2. Develop a simple framework for acute management
Nathan Cade, MD Brandon Fainstad, MD Andrew Prouse, MD OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the basic electrophysiology of the four causes of wide complex tachycardia. 2. Develop a simple framework for acute management
Amiodarone Toxicities
 Amiodarone Toxicities Student Rounds Review Ashlie McGuire - Aug. 4, 2016 Amiodarone Use: Antiarrhythmic agent Supraventricular and ventricular tachycardia Favourable for HF patients due to minimal inotropic
Amiodarone Toxicities Student Rounds Review Ashlie McGuire - Aug. 4, 2016 Amiodarone Use: Antiarrhythmic agent Supraventricular and ventricular tachycardia Favourable for HF patients due to minimal inotropic
3. AV Block 1. First-degree AV block 1. Delay in AV node 2. Long PR interval 3. QRS complex follows each P wave 4. Benign, no tx
 1. Rhythms & arrhythmias SA nodal rhythms Sinus rhythm Sinus tachycardia Sinus bradycardia Sinus arrhythmia Sick sinus syndrome SA block Sinus arrest AV blocks First-degree Second-degree Mobitz Type I
1. Rhythms & arrhythmias SA nodal rhythms Sinus rhythm Sinus tachycardia Sinus bradycardia Sinus arrhythmia Sick sinus syndrome SA block Sinus arrest AV blocks First-degree Second-degree Mobitz Type I
EHRA Accreditation Exam - Sample MCQs Cardiac Pacing and ICDs
 EHRA Accreditation Exam - Sample MCQs Cardiac Pacing and ICDs Dear EHRA Member, Dear Colleague, As you know, the EHRA Accreditation Process is becoming increasingly recognised as an important step for
EHRA Accreditation Exam - Sample MCQs Cardiac Pacing and ICDs Dear EHRA Member, Dear Colleague, As you know, the EHRA Accreditation Process is becoming increasingly recognised as an important step for
Lecture outline. Electrical properties of the heart. Automaticity. Excitability. Refractoriness. The ABCs of ECGs Back to Basics Part I
 Lecture outline The ABCs of ECGs Back to Basics Part I Meg Sleeper VMD, DACVIM (cardiology) University of Florida Veterinary School Electrical properties of the heart Action potentials Normal intracardiac
Lecture outline The ABCs of ECGs Back to Basics Part I Meg Sleeper VMD, DACVIM (cardiology) University of Florida Veterinary School Electrical properties of the heart Action potentials Normal intracardiac
ARRHYTHMIAS. REENTERY occurs when propagating impulse fails to die out after normal activation of heart and persist to re excite the heart.
 ARRHYTHMIAS Arrhythmia is defined as loss of cardiac rhythm, especially irregularity of heartbeat. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Ectopic complexes (ectopic beats) 1. By definition, arise from a site other than the sinus
ARRHYTHMIAS Arrhythmia is defined as loss of cardiac rhythm, especially irregularity of heartbeat. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Ectopic complexes (ectopic beats) 1. By definition, arise from a site other than the sinus
Pharmacology. Drugs affecting the Cardiovascular system (Antianginal Drugs)
 Lecture 7 (year3) Dr Noor Al-Hasani Pharmacology University of Baghdad College of dentistry Drugs affecting the Cardiovascular system (Antianginal Drugs) Atherosclerotic disease of the coronary arteries,
Lecture 7 (year3) Dr Noor Al-Hasani Pharmacology University of Baghdad College of dentistry Drugs affecting the Cardiovascular system (Antianginal Drugs) Atherosclerotic disease of the coronary arteries,
Practical Approach to Arrhythmias
 Outline Practical Approach to Arrhythmias Julia Shih, VMD, DACVIM (Cardiology) October 27, 2018 Conduction System ECG Acquisition ECG Interpretation Heart rate Rhythm Arrhythmias Tachyarrhythmias Supraventricular
Outline Practical Approach to Arrhythmias Julia Shih, VMD, DACVIM (Cardiology) October 27, 2018 Conduction System ECG Acquisition ECG Interpretation Heart rate Rhythm Arrhythmias Tachyarrhythmias Supraventricular
Understanding Atrial Fibrillation Management. Roy Lin, MD
 Understanding Atrial Fibrillation Management Roy Lin, MD Disclosure None Definition of atrial fibrillation Atrial fibrillation is a supraventricular tachyarrhythmia characterized by uncoordinated atrial
Understanding Atrial Fibrillation Management Roy Lin, MD Disclosure None Definition of atrial fibrillation Atrial fibrillation is a supraventricular tachyarrhythmia characterized by uncoordinated atrial
APPROACH TO TACHYARRYTHMIAS
 APPROACH TO TACHYARRYTHMIAS PROF.DR.MD.ZAKIR HOSSAIN PROFESSOR AND HEAD DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE SZMCH TACHYARRYTHMIA Cardiac arrythmia is a disturbance of electrical rhythm of heart. Cardac arrythmia with
APPROACH TO TACHYARRYTHMIAS PROF.DR.MD.ZAKIR HOSSAIN PROFESSOR AND HEAD DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE SZMCH TACHYARRYTHMIA Cardiac arrythmia is a disturbance of electrical rhythm of heart. Cardac arrythmia with
Arrhythmias and Heart Failure Dr Chris Lang Consultant Cardiologist and Electrophysiologist Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh
 Arrhythmias and Heart Failure Dr Chris Lang Consultant Cardiologist and Electrophysiologist Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh Arrhythmias and Heart Failure Ventricular Supraventricular VT/VF Primary prevention
Arrhythmias and Heart Failure Dr Chris Lang Consultant Cardiologist and Electrophysiologist Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh Arrhythmias and Heart Failure Ventricular Supraventricular VT/VF Primary prevention
Pharmacotherapy of Antiarrhythmias
 Pharmacotherapy of Antiarrhythmias Edward JN Ishac, Ph.D. Smith Building, Room 72 eishac@vcu.edu 828-2127 Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology Medical College of Virginia Campus of Virginia Commonwealth
Pharmacotherapy of Antiarrhythmias Edward JN Ishac, Ph.D. Smith Building, Room 72 eishac@vcu.edu 828-2127 Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology Medical College of Virginia Campus of Virginia Commonwealth
EKG Rhythm Interpretation Exam
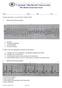 as EKG Rhythm Interpretation Exam Name: Date: ID# Unit Assume each strip is a 6 second strip. Passing is 80%. 1. Identify the following rhythm: a. Asystole b. Ventricular fibrillation c. Atrial fibrillation
as EKG Rhythm Interpretation Exam Name: Date: ID# Unit Assume each strip is a 6 second strip. Passing is 80%. 1. Identify the following rhythm: a. Asystole b. Ventricular fibrillation c. Atrial fibrillation
Manufacturer-prepared NEXTERONE (amiodarone HCl) Ready for you. Ready for the patient.
 AT A MOMENT S NOTICE Manufacturer-prepared NEXTERONE (amiodarone HCl) Ready for you. Ready for the patient. Indications and Usage NEXTERONE (amiodarone HCl) Premixed Injection is indicated for initiation
AT A MOMENT S NOTICE Manufacturer-prepared NEXTERONE (amiodarone HCl) Ready for you. Ready for the patient. Indications and Usage NEXTERONE (amiodarone HCl) Premixed Injection is indicated for initiation
EKG Competency for Agency
 EKG Competency for Agency Name: Date: Agency: 1. The upper chambers of the heart are known as the: a. Atria b. Ventricles c. Mitral Valve d. Aortic Valve 2. The lower chambers of the heart are known as
EKG Competency for Agency Name: Date: Agency: 1. The upper chambers of the heart are known as the: a. Atria b. Ventricles c. Mitral Valve d. Aortic Valve 2. The lower chambers of the heart are known as
Document 3 Summary of Data and Guidance for Medical Professionals
 Document 3 Summary of Data and Guidance for Medical Professionals Anvirzel Anvirzel is a novel antitumor compound extracted from the plant Nerium oleander, which belongs to the family Apocynaceae. Anvirzel
Document 3 Summary of Data and Guidance for Medical Professionals Anvirzel Anvirzel is a novel antitumor compound extracted from the plant Nerium oleander, which belongs to the family Apocynaceae. Anvirzel
Chapter 03: Sinus Mechanisms Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE
 Instant download and all chapters Tesst Bank ECGs Made Easy 5th Edition Barbara J Aehlert https://testbanklab.com/download/tesst-bank-ecgs-made-easy-5th-edition-barbara-jaehlert/ Chapter 03: Sinus Mechanisms
Instant download and all chapters Tesst Bank ECGs Made Easy 5th Edition Barbara J Aehlert https://testbanklab.com/download/tesst-bank-ecgs-made-easy-5th-edition-barbara-jaehlert/ Chapter 03: Sinus Mechanisms
