Measure and correlate cardiovascular metrics for both resting and aerobic conditions.
|
|
|
- Agnes Williams
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Student ID # Team Name: Fine Winer Student Names: Razzle Dazzle and Twitter Glitter Lab Assignment: Lab #6 Date: March 15, 2012 Lab Title: Comparison of Cardiovascular Stress Response to Heart Rate, Blood pressure and Respiratory Rate Purpose / Objective: Measure and correlate cardiovascular metrics for both resting and aerobic conditions. Hypotheses: A body at rest will increase in heart rate, blood pressure, and respiratory rate when physical activity / stress are prompted for a variable period of time. There is a direct correlation between aerobic activity and increased metrics. Within an individual heart rate, blood pressure, and respiratory rate will respond differently to varied conditions of stress. Physical health, age and BMI will show direct correlations Heart rate, blood pressure and respiratory rate will overall respond differently to varied conditions of stress. Metrics will decrease from peak to 10 minute post exertion resting phase for all cases. Female vs. Male data is expected to show a difference in blood pressure, heart rate and respiratory rate. Males in all cases of stress are expected to show higher metrics than woman. My personal data is expected to be consistently higher than other females in my class. Having a categorized obese BMI, my metrics will show a direct correlation to expectably high cardiovascular metrics. Materials / Subjects / Specimens: Three specimens were measured One male and two females A personal iphone was used to accurately time heart rate beats per minute for each subject Respiratory rate was measured in breaths per minute Blood pressure was measured using a Stethoscope and a Sphygmomanometer (blood pressure cuff) Methods / Tools / Instrumentation / Procedures: Stethoscope, Sphygmomanometer (blood pressure cuff) and personal iphone were used to make all measurements Measured resting heart rate, respiratory rate and blood pressure while sitting
2 Measured resting heart rate, respiratory rate and blood pressure while standing Measured resting heart rate, respiratory rate and blood pressure while in supine position Specimens heart rate, respiratory rate and blood pressure were measured after an elevated 5 minute walk Specimens heart rate, respiratory rate and blood pressure were measured at 3 minute recovery, 6 minute recovery and 10 minute recovery With the blood pressure cuff deflated and the air valve closed, the cuff was wrapped around each specimens arm. The end of the Stethoscope was placed under the blood pressure cuff. The blood pressure cuff was inflated to a little above 180 mm Hg. (This collapses the major arteries in the arm) Air was then slowly released by gently turning the air valve, and the drop in pressure was watched. Results: Table #1 and figure #1 summarize blood pressure statistics for all sample populations by gender. For all subjects, average blood pressure dramatically rises from resting to an increased peak at the time of exercise. The most prominent observation to be made is that from the time of peak elevation to the 10 minute resting recovery mark there is a significant decrease in blood pressure. See attachments Graph #1 & #2 Table 1 Figure 1 Table #2 summarizes my personal respiratory rate and the average respiratory rates for the females in my Biology 105 class pre 5 minute aerobic exercise. With a BMI (shown in figure #2) that is established as obese there is a direct correlation between my height/weight/age(shown in figure#4) and my resting respiratory rates. The most prominent observation is that when in supine position my respiratory rate decreases dramatically compared to my siting and standing resting respiratory rates. See Graph #3 in Attachments
3 Table #2 Height Weight Age BMI Respiratory Respiratory Respiratory Rate Rest Rate Rest Rate Rest Sit Stand Sup Me (SMD) F Means Figure #2 Figure#3 Table #3 summarizes metrics for female and male means. Table #3 shows the direct correlation between average heart rates for females and average heart rates for males in varied conditions of stress. The table indicates males have a higher resting heart rate in sitting, standing, and supine position but females have a higher metrics like heart rate at peak elevation and all recovery phases. Also see in figure #4 where the only phase that is higher for females is recovery. Table #3
4 Varible Points of Blood Pressure Figure #4 Female Means Male Means Table #4 shows how individual woman at various ages differ in metrics. The table below (table 4) shows direct correlations between age and both respiratory rate and also heart rate from resting through recovery post exercise phases. The table shows that individuals within a controlled group do vary in metrics. The most prominent observation is that subject F4 whom is the oldest female subject has the lowest resting heart rate but is perfectly average with the other female subjects when it comes to respiratory rate. Figure #5 shows an example of target heart ranges for adults based on age courtesy of the American Heart Association. Table #4 Ht Rate Rest Sit Resp Rate Rest Sit Ht Rate Rest Sup Respiratory Rate Rset Sup Resp Rate Elev Ht Rate Rec 3 Resp Rate Rec 3 Ht Rate Rec 10 Resp Rate Rec 10 Code Notes Age Ht Rate Elev F1 SMD F2 KAH F3 PMD F4 LAS
5 Figure #5 Analysis / Discussion: Our hypothesis that men would have higher metrics in all aspects of varied stresses was disproven. Even though our data collected in class showed the average males heart rate was higher in resting phases as soon as the aerobic exercise peaked the heart rate for the woman it remained higher than the men s throughout the recovery phases. The fact the correlation does not hold true in the peak and post aerobic phases might possibly indicate an error in our mechanism or in the data we speculated. In fact we learned that heart rate of men is lower than women because size of the heart in men is 25% larger than in women. Larger heart can pump more blood than smaller heart in one beat. Another reason of low heart rate in men than women is capacity of lungs in men is 25-30% higher than women. Men are generally larger with a larger muscular structure allowing the heart to pump blood harder throughout the body generating and spreading oxygen which causes dilation of blood vessels. Men were more likely to have
6 engaged in moderate to-vigorous PA [Physical activity] 3 times per week than women (60.3% versus 53.1%, respectively) according to the American Heart Association, which can contribute to better heart health and the steady line of decrease in heart rate on Graph #4 in attachments. Our hypothesis that an individual heart rate, blood pressure, and respiratory rate will respond differently to varied conditions of stress was validated. There is a direct correlation associated with the increase in metrics associated with the stress of exercise. Results demonstrate that as you grow older, you may not be able to tolerate as much exercise as you once did. It takes longer for the pulse to increase when exercising, and longer to slow back down after exercise. The maximum heart rate reached with exercise is lowered as age increases. There are a lot of variables that affect an individual s metrics, such as environmental factors, health and overall fitness levels. Heart rate can vary as the body s need to absorb oxygen and excrete carbon dioxide changes, such as during exercise. Our bodies naturally regulate metrics, with built in mechanisms like perspiring to control body temperature. Aging decreases one's ability to sweat. Some older adults find it more difficult to tell when they are becoming overheated. In proving our hypothesis we concluded that upright exercise caused systolic blood pressure to gradually increase while diastolic blood pressure remains about the same when being compared to resting blood pressure (Refer to Graph #1 in Attachments). Diastolic pressure when the pressure is weakest, may even decrease due to vasodilation which is the slight dilation of blood vessels caused by the heart pumping harder to spread more oxygen throughout the body. The systolic number shows pressure at peak times when heartbeats force blood through the veins. During exercise systolic pressure is effected the most (also shown in Graph #1) since it is directly connected to how the heart operates. Contracting muscles and the narrowing of blood vessels is a contributing factor in increased blood pressure. There was a significant increase in our data for all subject means with systole blood pressure and just as our research has shown the diastole blood pressure remained about the same, only varying 3-4 units between resting and peak elevated metrics. Our hypothesis that metrics will decrease from peak to 10 minute post exertion resting phase for all cases was validated. There is a direct correlation between the decreases from peak to 10 minute post exertion resting phase for all cases due to the decrease in activity level. (Refer to Graph #2 in Attachments) As activity level decreases, vasopressor agents that increase heart rate are decreased in a reverse feedback loop of blood pressure homeostasis.
7 With the more volume of blood entering the heart, the more will be pumped out. With a lower blood return after exercise, the heart will respond by beating slower and less force per beat. The adult heart at rest normally beats at a rate of 60 to 100 bpm (beats per minute). According to the Mayo Clinic trained athletes normally have a resting heart rate as low as 40 to 60 bpm-. Children below the age of 10 usually have higher resting heart rates than adults. Our hypothesis that my obese BMI directly correlated to a higher respiratory rate along with other metrics such as my heart rate. Correlation between various cardiac parameters and BMI in obese, showed that there was a statistically significant positive correlation between various cardiac parameters and BMI. There must be a tradeoff between getting more oxygen to the muscles and hyperventilating. The diaphragm can only contract and relax at a certain maximum rate; this limits the breathing rate and at the same time avoids CO2 buildup. Athletes or highly fit individuals have a higher tolerance to the higher rate of breathing during aerobic exercise, allowing them to maintain lower pulse and blood pressure while transporting sufficient oxygen to needy cells. The correlation between BMI and resting breathing rate follows the proportionality that exists between body weight and rate of oxygen consumption. The fact I am larger than average females in our case study showed our hypothesis that there is a direct correlation between BMI and respiratory rates because of the amount of oxygen needed to supply my tissues compared to the smaller amount needed for someone 2/3 my weight. Figure B in attachments shows another analysis table of examples of how obese BMI and Higher cardiac parameters are positively correlated to subjects with lower/healthier BMIs. Conclusions / Further Considerations: In summary I have come to the conclusion that factors such as age, bmi, gender, and overall physical health will greatly impact cardiovascular metrics pre, during and post aerobic excersise phases.
8 Attachments: Graph #1 Blood Pressure Metrics for All Mean Subjects during Resting and Peak Elevation As hypothesized graph #1 shows in all cases from resting to the peak point after a 5 minute aerobic exercise an obvious increase in blood pressure, indicated by the top trend line showing Systolic blood pressure. The bottom trend line compared diastolic blood pressure at both resting and peak showing only a slight variance making diastolic pressure steady from the resting phase to the peak phase. BP Systole Sit BP Diastole Sit BP Systole Elevation BP Diastole Elevation Graph #2 Heart Rate of All Subject Averages from Peak Elevation Post 5 Minute Aerobic Activity to Recovery 10 Minutes Post Activity
9 Graph #2 shows as hypothesized metrics will decrease from peak to 10 minute post exertion resting phase for all cases. The Male Mean had the lowest decrease in Heart rate from Peak to 10 Minute Recovery and the Sample Mean had the greatest decrease with a drop of approx. 19 BPM Me Male Mean Female Mean Sample Mean 65 Ht Rate Elev Ht Rate Rec 10 Graph #3 Personal Respiratory Metrics for Resting Phases Pre Elevation and Recovery Graph #3 shows a clearer view of as hypothesized my personal respiratory rates pre elevation exercise were greater than those of the average female which was shown in Table #2. Again we also can see that in correlation with my obese BMI my supine respiratory rate drops dramatically from my sitting and standing rest metrics. Effects on Obese BMI and Normal are visible on Figure B.
10 Breaths Per Minute Personal (SMD) Respiratory Rates Resp Rate Rest Sit Resp Rate Rest Stand Respiratory Rate Rset Sup Respiratory Rates Pre 5 Minute Elevation Phase Figure B Graph #4 Female vs. Male data Graph #4 shows as hypothesized heart rate metrics for males is higher than females for resting conditions including sitting, standing and supine. This graph shows that our hypothesis that males would have higher metrics in all conditions was disproven by the facts of graph #4 that females actually have higher heart rate metrics at elevation from aerobic exercise, and the 3,6, and 10 minute recovery phases post exercise.
11 Female Mean Male Mean Sample Mean Me Ht Rate Rest Sit Ht Rate Rest Ht Rate Rest Stand Sup Ht Rate Elev Ht Rate Rec 3 Ht Rate Rec 6 Ht Rate Rec 10 Graph #5 and #6 show individual female heart rates and respiratory rates from resting to recovery post exercise. Graph #5 shows female subjects 1,2,3 and 4 that range in ages from 24 to 32 and how their individual heart rates very when tested at resting, peak elevation and revovery post excersice. As Hypothesized, metrics for individuals in a controlled group (females) is veried as the chart shows in the slopes of the trend lines which helps to make observations about individual rates of recovery and even rates of incline from resting to peak heart rate. Graph #6 shows how respiratory rates for women of different ages varies within an individual. The rate at which the markers are droping varies from individual to individual, no two females in this subject group have the same rate incline or decline at any points of stress, resting or recovery. Figure C
12 shows heart rates for various excersize zones of body stress and how they correlate to age.
13 Figure C
14 References Observations: Mayo Clinic Staff, 2011, Jonathan L Gelfand, MD, 2010, M. H. Laughlin, Dept. of Biomedical Sciences, Univ. of Missouri & Columbia, MO, Suzanne Mendjiwa, 2010, Raw Data: American Heart Association, 2010, Skarphedinsson JO, Elam M, Jungersten L & Wallin BG (1997). Sympathetic nerve traffic correlates with the release of nitric oxide in humans: implications for blood pressure control. J Physiol501, Commission on Social Determinants of Health. Closing the gap in a generation: health equity through action on the social determinants of health. Geneva, World Health Organization, 2008, Drawings/ Diagrams/illustrations: Kanavi Roopa Shekharappa et al. / Int J Biol Med Res. 2011; 2(2): , ndex_and_cardiovascular_parameters_in_obese_and_non_obese_in_different_age_groups.pdf
15 Blair M. Rowitz, MD FACS, 2001, Cardiovascular risk factors, and coronary mortality: 15 year follow-up of middle-aged men and women in castern Finland. Circulation. 1996; 93: Nieman, D. C. The Exercise-Health Connection. 2001, Exercise Zones, Minute Ventilation During Moderate Exercise (15-Fold Metabolism), Detailed Analysis: Anna Burkhead, Suzy Borgschulte,
LAB 9: Metabolic Rates
 LAB 9: Metabolic Rates Introduction: The cardiovascular (circulatory) system functions to deliver oxygen and nutrients to tissues for growth and metabolism, and to remove metabolic wastes. The heart pumps
LAB 9: Metabolic Rates Introduction: The cardiovascular (circulatory) system functions to deliver oxygen and nutrients to tissues for growth and metabolism, and to remove metabolic wastes. The heart pumps
Identify and describe the circulation system that is missing from the organizer above.
 Lesson 15.1 NOTES: The Circulatory System (Unlock) Essential Question: -What are the structures and functions of the circulatory system? Learning Target(s): -I can identify structures and explain functions
Lesson 15.1 NOTES: The Circulatory System (Unlock) Essential Question: -What are the structures and functions of the circulatory system? Learning Target(s): -I can identify structures and explain functions
#6 - Cardiovascular III Heart Sounds, Pulse Rate, Hemoglobin Saturation, and Blood Pressure
 #6 - Cardiovascular III Heart Sounds, Pulse Rate, Hemoglobin Saturation, and Blood Pressure Objectives: Observe slide of artery and vein cross-section Auscultate heart sounds using a stethoscope Measure
#6 - Cardiovascular III Heart Sounds, Pulse Rate, Hemoglobin Saturation, and Blood Pressure Objectives: Observe slide of artery and vein cross-section Auscultate heart sounds using a stethoscope Measure
Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 2
 Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 2 65 minutes 65 marks Page of 23 Q. A person did five different activities in turn. These activities needed increasing amounts of energy. For each activity two
Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 2 65 minutes 65 marks Page of 23 Q. A person did five different activities in turn. These activities needed increasing amounts of energy. For each activity two
AP Biology Lab 10 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
 AP Biology Laboratory Date: Name and Period: AP Biology Lab 10 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM OVERVIEW In this lab you will: 1. in Exercise 10A you will learn how to measure blood pressure. 2. in
AP Biology Laboratory Date: Name and Period: AP Biology Lab 10 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM OVERVIEW In this lab you will: 1. in Exercise 10A you will learn how to measure blood pressure. 2. in
LAB: Blood Pressure Measurable Indicator of the Health of the Circulatory System!
 LAB: Blood Measurable Indicator of the Health of the Circulatory System! Lab Objectives. At the completion of the lab, you should be able to: measure pulse or heart rate (HR) and respiratory rate (RR);
LAB: Blood Measurable Indicator of the Health of the Circulatory System! Lab Objectives. At the completion of the lab, you should be able to: measure pulse or heart rate (HR) and respiratory rate (RR);
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM
 IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein THE BLOOD SYSTEM 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein THE BLOOD SYSTEM 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
Chapter 15: Measuring Height, Weight, and Vital Signs. Copyright 2012 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
 Chapter 15: Measuring Height, Weight, and Vital Signs Height and Weight Weight Baseline measurement at patient s first visit Measured in kg or lbs Common types of scales Balance beam Dial Digital Height
Chapter 15: Measuring Height, Weight, and Vital Signs Height and Weight Weight Baseline measurement at patient s first visit Measured in kg or lbs Common types of scales Balance beam Dial Digital Height
Female Populations. By: Kelsey Joyce. Group Members: Sooriya Jhanagan, Nelson Ferreira, Lindsay Hummell. TA: Jingjie Hu. Biology 240W Section 002
 The Influence of Exercise on Pulse and Blood to the Male and Female Populations By: Kelsey Joyce Group Members: Sooriya Jhanagan, Nelson Ferreira, Lindsay Hummell TA: Jingjie Hu Biology 240W Section 002
The Influence of Exercise on Pulse and Blood to the Male and Female Populations By: Kelsey Joyce Group Members: Sooriya Jhanagan, Nelson Ferreira, Lindsay Hummell TA: Jingjie Hu Biology 240W Section 002
Physiology of the Circulatory System modified from
 Physiology of the Circulatory System modified from http://www.ekcsk12.org/science/aplabreview/aplab10.htm Introduction The circulatory system functions to deliver oxygen and nutrients to tissues for growth
Physiology of the Circulatory System modified from http://www.ekcsk12.org/science/aplabreview/aplab10.htm Introduction The circulatory system functions to deliver oxygen and nutrients to tissues for growth
science-u.org What affects blood Blood Pressure Directions You Will Need BEST FOR GRADES 5-8 ESTIMATED TIME Minutes
 What affects blood pressure? BEST FOR GRADES 5-8 ESTIMATED TIME 25-60 Minutes You Will Need Sphygmomanometer (blood pressure cuff) Stethoscope Blood pressure cuffs and stethoscopes can be found online
What affects blood pressure? BEST FOR GRADES 5-8 ESTIMATED TIME 25-60 Minutes You Will Need Sphygmomanometer (blood pressure cuff) Stethoscope Blood pressure cuffs and stethoscopes can be found online
Lab #10 Physiology of the Circulatory System
 Lab #10 Physiology of the Circulatory System Introduction The circulatory system functions to deliver oxygen an nutrients to tissues for growth and metabolism, and to remove metabolic wastes. The heart
Lab #10 Physiology of the Circulatory System Introduction The circulatory system functions to deliver oxygen an nutrients to tissues for growth and metabolism, and to remove metabolic wastes. The heart
Student Name: Pre-Lab: Homeostasis Notes, Body Temperature Activity + Video; Introduction in this Lab.
 Anatomy and Physiology Homeostasis: Lab Student Name: Pre-Lab: Homeostasis Notes, Body Temperature Activity + Video; Introduction in this Lab. Homeostasis: The Link with Health The word homeostasis literally
Anatomy and Physiology Homeostasis: Lab Student Name: Pre-Lab: Homeostasis Notes, Body Temperature Activity + Video; Introduction in this Lab. Homeostasis: The Link with Health The word homeostasis literally
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM
 IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Key Questions What are the functions of the circulatory system? How does the heart pump blood through the body? What are three types of blood vessels? Vocabulary myocardium atrium
The Circulatory System Key Questions What are the functions of the circulatory system? How does the heart pump blood through the body? What are three types of blood vessels? Vocabulary myocardium atrium
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiol I (Kristan) Lecture 14 Cardiovascular control mechanisms p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiol I (Kristan) Lecture 14 Cardiovascular control mechanisms p. 1 Terms you should understand: hemorrhage, intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms, anoxia, myocardial contractility, residual
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiol I (Kristan) Lecture 14 Cardiovascular control mechanisms p. 1 Terms you should understand: hemorrhage, intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms, anoxia, myocardial contractility, residual
Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 1
 Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 57 minutes 57 marks Page of 23 Q. An athlete did a 6-month training programme. The graph shows the effect of the same amount of exercise on his heart rate before
Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 57 minutes 57 marks Page of 23 Q. An athlete did a 6-month training programme. The graph shows the effect of the same amount of exercise on his heart rate before
The Circulatory System. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview The Circulatory System
 33.1 THINK ABOUT IT More than one-third of the 1.2 million Americans who suffer a heart attack each year die. This grim evidence shows that the heart and the circulatory system it powers are vital to life.
33.1 THINK ABOUT IT More than one-third of the 1.2 million Americans who suffer a heart attack each year die. This grim evidence shows that the heart and the circulatory system it powers are vital to life.
Making Connections Practice Mrs. Fornaro
 Making Connections Practice Mrs. Fornaro Name Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the information below and on your knowledge of biology. Progressive Resistance Exercise Progressive resistance exercise
Making Connections Practice Mrs. Fornaro Name Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the information below and on your knowledge of biology. Progressive Resistance Exercise Progressive resistance exercise
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG)
 Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
Warm Up- Monday -AND- Setup Cornell Notes.
 Warm Up- Monday Brainstorm in your notebook: If the heart sends blood to all organs, how and where does the heart get blood to provide oxygen for its muscles? -AND- Setup Cornell Notes. Announcements Unit
Warm Up- Monday Brainstorm in your notebook: If the heart sends blood to all organs, how and where does the heart get blood to provide oxygen for its muscles? -AND- Setup Cornell Notes. Announcements Unit
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY NAME Detection of heart sounds. Clean the ear pieces of the stethoscope before using. The ear pieces should be pointing slightly forward when inserted into the ears because
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY NAME Detection of heart sounds. Clean the ear pieces of the stethoscope before using. The ear pieces should be pointing slightly forward when inserted into the ears because
CAMOSUN COLLEGE BIOLOGY 144 (2010) LABS
 LAB 8: CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY PART 1. HEART SOUNDS AND PULSE DETERMINATIONS Introduction Two distinct sounds can be heard during each cardiac cycle. These sounds are commonly described as lub and dup
LAB 8: CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY PART 1. HEART SOUNDS AND PULSE DETERMINATIONS Introduction Two distinct sounds can be heard during each cardiac cycle. These sounds are commonly described as lub and dup
Control of Heart Rate
 Control of Heart Rate Control of Heart Rate The beating of your heart is an involuntary movement one that is beyond your direct control. The nerve impulse that causes the heart to beat originates within
Control of Heart Rate Control of Heart Rate The beating of your heart is an involuntary movement one that is beyond your direct control. The nerve impulse that causes the heart to beat originates within
PART I: HEART ANATOMY
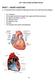 Lab 7: Heart Sounds and Blood Pressure PART I: HEART ANATOMY a) You should be able to identify the following structures on an adult human heart diagram. the 4 chambers the bicuspid (mitral) and tricuspid
Lab 7: Heart Sounds and Blood Pressure PART I: HEART ANATOMY a) You should be able to identify the following structures on an adult human heart diagram. the 4 chambers the bicuspid (mitral) and tricuspid
Vital Signs. Vital Signs. Vital Signs
 Vital Signs Vital Signs Why do vital signs? Determine relative status of vital organs Establish baseline Monitor response to Rx, meds Observe trends Determine need for further evaluation, Rx, intervention
Vital Signs Vital Signs Why do vital signs? Determine relative status of vital organs Establish baseline Monitor response to Rx, meds Observe trends Determine need for further evaluation, Rx, intervention
KS4 Physical Education
 KS4 Physical Education The Effects of Exercise These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities
KS4 Physical Education The Effects of Exercise These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities
Ambulatory Services Orientation & Skill Review Skill Performance Checklist: Vital Signs. Name: Date:
 Evaluation Levels Behavior Level 3 Met Performed all skills competently. No behaviors omitted. Level 2 Satisfactory Omitted no more than three (3) non-critical behaviors. Level 1 Unsatisfactory Omitted
Evaluation Levels Behavior Level 3 Met Performed all skills competently. No behaviors omitted. Level 2 Satisfactory Omitted no more than three (3) non-critical behaviors. Level 1 Unsatisfactory Omitted
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE. MEASURING BLOOD PRESSURE - MANUAL (equ04)
 SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE: ISSUED FOR: MEASURING BLOOD PRESSURE - MANUAL Nursing DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: 2/80 7/17 1 of 5 RESPONSIBILITY: RN, LPN, Patient Care Technician Multi-skilled
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE: ISSUED FOR: MEASURING BLOOD PRESSURE - MANUAL Nursing DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: 2/80 7/17 1 of 5 RESPONSIBILITY: RN, LPN, Patient Care Technician Multi-skilled
d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology
 d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology What can your remember about the heart and blood vessels? What is the Cardiovascular System? The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system,
d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology What can your remember about the heart and blood vessels? What is the Cardiovascular System? The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system,
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Circulatory System Learning Outcomes State the type of tissue the heart is made of State the function of the heart State the number of chambers in the heart Know how the blood flows
The Circulatory System Circulatory System Learning Outcomes State the type of tissue the heart is made of State the function of the heart State the number of chambers in the heart Know how the blood flows
Unit 1: Human Systems. The Circulatory System
 Unit 1: Human Systems The Circulatory System nourish all cells with oxygen, glucose, amino acids and other nutrients and carry away carbon dioxide, urea and other wastes Purposes Transport chemical messengers
Unit 1: Human Systems The Circulatory System nourish all cells with oxygen, glucose, amino acids and other nutrients and carry away carbon dioxide, urea and other wastes Purposes Transport chemical messengers
Taking and recording blood pressure and pulse. City Gate Training Centre all rights reserved
 Taking and recording blood pressure and pulse City Gate Training Centre all rights reserved Course Content: Definition of Blood Pressure Normal Blood Pressure Readings Systolic and Diastolic Blood Pressure
Taking and recording blood pressure and pulse City Gate Training Centre all rights reserved Course Content: Definition of Blood Pressure Normal Blood Pressure Readings Systolic and Diastolic Blood Pressure
12.2 Monitoring the Human Circulatory System
 12.2 Monitoring the Human Circulatory System Video 1: 3D Animation of Heart Pumping Blood blood flow through the heart... Video 2: Hank Reviews Everything on the Heart https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x9zz6tcxari
12.2 Monitoring the Human Circulatory System Video 1: 3D Animation of Heart Pumping Blood blood flow through the heart... Video 2: Hank Reviews Everything on the Heart https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x9zz6tcxari
Biology 105 Human Biology. Session: Section: Class Location: Days / Time: Instructor:
 Student ID#: 1 2 3 4 5 6 Student Name MS Universe s Lab Assignment #: Lab #4 Team Name: Body Builders Lab Title: Muscle Date: 2014-04-01 Purpose / Objective(s): Take measurements in the lab of effects
Student ID#: 1 2 3 4 5 6 Student Name MS Universe s Lab Assignment #: Lab #4 Team Name: Body Builders Lab Title: Muscle Date: 2014-04-01 Purpose / Objective(s): Take measurements in the lab of effects
Biology Unit 3 The Human Heart P
 Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
Biology 236 Spring 2002 Campos/Wurdak/Fahey Laboratory 4. Cardiovascular and Respiratory Adjustments to Stationary Bicycle Exercise.
 BACKGROUND: Cardiovascular and Respiratory Adjustments to Stationary Bicycle Exercise. The integration of cardiovascular and respiratory adjustments occurring in response to varying levels of metabolic
BACKGROUND: Cardiovascular and Respiratory Adjustments to Stationary Bicycle Exercise. The integration of cardiovascular and respiratory adjustments occurring in response to varying levels of metabolic
AS OCR PHYSICAL EDUCATION The Vascular System
 AS OCR PHYSICAL EDUCATION The Vascular System Learning Objectives: - Distribution of Cardiac output at rest and during exercise - Role of the Vasomotor centre, arterioles and pre-capillary sphincters -
AS OCR PHYSICAL EDUCATION The Vascular System Learning Objectives: - Distribution of Cardiac output at rest and during exercise - Role of the Vasomotor centre, arterioles and pre-capillary sphincters -
Heart Rate and Blood Pressure as Vital Signs
 Heart Rate and Blood Pressure as Vital Signs Computer 10 Since the earliest days of medicine heart rate has been recognized as a vital sign an indicator of health, disease, excitement, and stress. Medical
Heart Rate and Blood Pressure as Vital Signs Computer 10 Since the earliest days of medicine heart rate has been recognized as a vital sign an indicator of health, disease, excitement, and stress. Medical
Science 8 Chapter 12 Section 1
 Science 8 Chapter 12 Section 1 How Body Systems are Connected (pp. 436-445) System Coordination Cellular Respiration There are 4 different body systems that all play a part in the process of cellular respiration:
Science 8 Chapter 12 Section 1 How Body Systems are Connected (pp. 436-445) System Coordination Cellular Respiration There are 4 different body systems that all play a part in the process of cellular respiration:
AMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF SLEEP TECHNOLOGISTS TECHNICAL GUIDELINE FOR PATIENT ASSESSMENT AND VITAL SIGNS MEASUREMENT AND DOCUMENTATION
 AMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF SLEEP TECHNOLOGISTS TECHNICAL GUIDELINE FOR PATIENT ASSESSMENT AND VITAL SIGNS MEASUREMENT AND DOCUMENTATION SUMMARY: Sleep technologists observe and monitor physical signs and
AMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF SLEEP TECHNOLOGISTS TECHNICAL GUIDELINE FOR PATIENT ASSESSMENT AND VITAL SIGNS MEASUREMENT AND DOCUMENTATION SUMMARY: Sleep technologists observe and monitor physical signs and
Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems
 34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems section 1 Circulatory System Before You Read Press the tips of two fingers to the inside of your wrist, at a point just below your thumb. Can you feel
34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems section 1 Circulatory System Before You Read Press the tips of two fingers to the inside of your wrist, at a point just below your thumb. Can you feel
Human Cardiovascular Physiology: Blood Pressure and Pulse Determinations
 ighapmlre33apg269_274 5/12/04 3:10 PM Page 269 impos03 302:bjighapmL:ighapmLrevshts:layouts: NAME Human Cardiovascular Physiology: Blood Pressure and Pulse Determinations LAB TIME/DATE REVIEW SHEET exercise
ighapmlre33apg269_274 5/12/04 3:10 PM Page 269 impos03 302:bjighapmL:ighapmLrevshts:layouts: NAME Human Cardiovascular Physiology: Blood Pressure and Pulse Determinations LAB TIME/DATE REVIEW SHEET exercise
How To Measure Vital Signs
 How To Measure Vital Signs How to Use This Tutorial This tutorial is intended for healthcare providers or students to teach basic vital signs skills Use the navigation buttons below to move through the
How To Measure Vital Signs How to Use This Tutorial This tutorial is intended for healthcare providers or students to teach basic vital signs skills Use the navigation buttons below to move through the
Performance Enhancement. Cardiovascular/Respiratory Systems and Athletic Performance
 Performance Enhancement Cardiovascular/Respiratory Systems and Athletic Performance Functions of the Cardiovascular System Deliver oxygen & nutrients to body tissues Carry wastes from the cells Anatomy
Performance Enhancement Cardiovascular/Respiratory Systems and Athletic Performance Functions of the Cardiovascular System Deliver oxygen & nutrients to body tissues Carry wastes from the cells Anatomy
Blood Pressure Laboratory
 Introduction The blood that circulates throughout the body maintains a flow and pressure. The nervous system can change the flow and pressure based on the particular needs at a given time. For example,
Introduction The blood that circulates throughout the body maintains a flow and pressure. The nervous system can change the flow and pressure based on the particular needs at a given time. For example,
Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93)
 Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
Hypertension and Heart Disease. Weldon James, MD, Mercy Clinic Family Medicine, Union
 Hypertension and Heart Disease Weldon James, MD, Mercy Clinic Family Medicine, Union The Silent Killer High blood pressure, also known as HBP or hypertension, is a widely misunderstood medical condition
Hypertension and Heart Disease Weldon James, MD, Mercy Clinic Family Medicine, Union The Silent Killer High blood pressure, also known as HBP or hypertension, is a widely misunderstood medical condition
The Heart 1 of 34 Boardworks Ltd 2012
 The Heart 1 of 34 Boardworks Ltd 2012 2 of 34 Boardworks Ltd 2012 What does the heart do? 3 of 34 Boardworks Ltd 2012 The heart is a muscular organ located in the thorax. It pumps blood continuously around
The Heart 1 of 34 Boardworks Ltd 2012 2 of 34 Boardworks Ltd 2012 What does the heart do? 3 of 34 Boardworks Ltd 2012 The heart is a muscular organ located in the thorax. It pumps blood continuously around
Lab Period: Name: Physiology Chapter 14 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure, Plus Fun Review Study Guide
 Lab Period: Name: Physiology Chapter 14 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure, Plus Fun Review Study Guide Main Idea: The function of the circulatory system is to maintain adequate blood flow to all tissues. Clinical
Lab Period: Name: Physiology Chapter 14 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure, Plus Fun Review Study Guide Main Idea: The function of the circulatory system is to maintain adequate blood flow to all tissues. Clinical
Name Class Date. Bell Diaphragm. Chest piece. Stethoscope
 Name Class Date Sensing Circulation Exploring the Effects of Exercise on Heart Rate Investigative Lab 30 8 Questions How do the sounds you hear through a stethoscope relate to the stages of a heartbeat?
Name Class Date Sensing Circulation Exploring the Effects of Exercise on Heart Rate Investigative Lab 30 8 Questions How do the sounds you hear through a stethoscope relate to the stages of a heartbeat?
Heart Rate, Blood Pressure, and Exercise. Evaluation copy
 Heart Rate, Blood Pressure, and Exercise Computer 11 The adaptability of the heart can be observed during exercise, when the metabolic activity of skeletal muscles increases. The cardiovascular system,
Heart Rate, Blood Pressure, and Exercise Computer 11 The adaptability of the heart can be observed during exercise, when the metabolic activity of skeletal muscles increases. The cardiovascular system,
Clinical Research Coordinator Skills Program
 Clinical Research Coordinator Skills Program Vital Signs This Skill Requires Provider direction Standard Precautions Using purell before and after contact with the patient or the patient s environment
Clinical Research Coordinator Skills Program Vital Signs This Skill Requires Provider direction Standard Precautions Using purell before and after contact with the patient or the patient s environment
Biomedical Instrumentation E. Blood Pressure
 Biomedical Instrumentation E. Blood Pressure Dr Gari Clifford Adapted from slides by Prof. Lionel Tarassenko Blood pressure Blood is pumped around the body by the heart. It makes its way around the body
Biomedical Instrumentation E. Blood Pressure Dr Gari Clifford Adapted from slides by Prof. Lionel Tarassenko Blood pressure Blood is pumped around the body by the heart. It makes its way around the body
AGENDA for 04/04/14 AGENDA: HOMEWORK: Due Tues, Online Quiz: OBJECTIVES:
 AGENDA for 04/04/14 AGENDA: 1. Pump Your Blood Performances 2. 4.2.2: Blood Pressure Experimental Design and Writing a Formal Lab Report OBJECTIVES: 1. Measure blood pressure and use the reading to indicate
AGENDA for 04/04/14 AGENDA: 1. Pump Your Blood Performances 2. 4.2.2: Blood Pressure Experimental Design and Writing a Formal Lab Report OBJECTIVES: 1. Measure blood pressure and use the reading to indicate
BLOOD PRESSURE. Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration
 BLOOD PRESSURE Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration Blood Pressure The force of your blood pushing on the walls of your arteries. How is Blood Pressure Measured? Measured at an artery in the arm and
BLOOD PRESSURE Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration Blood Pressure The force of your blood pushing on the walls of your arteries. How is Blood Pressure Measured? Measured at an artery in the arm and
Crucial Signs כל הזכויות שמורות למד"א מרחב ירושלים
 Crucial Signs Dan Drory, MDA Paramedic and Instructor, 2011 What are Signs? Sign Objective, measurable Symptom Subjective, evaluated by the patient ( Chest Pain, Difficulties Breathing, Headache ) Signs
Crucial Signs Dan Drory, MDA Paramedic and Instructor, 2011 What are Signs? Sign Objective, measurable Symptom Subjective, evaluated by the patient ( Chest Pain, Difficulties Breathing, Headache ) Signs
Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart
 Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart Interesting Heart Fact Capillaries are so small it takes ten of them to equal the thickness of a human hair. Review What are the 3 parts of the cardiovascular
Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart Interesting Heart Fact Capillaries are so small it takes ten of them to equal the thickness of a human hair. Review What are the 3 parts of the cardiovascular
Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels
 Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels 3.2 Learning Objectives 3.2.2 Organisational Complexity of the human 1. Describe the structures and organisation of tissues in the closed circulatory system. 2. Discuss
Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels 3.2 Learning Objectives 3.2.2 Organisational Complexity of the human 1. Describe the structures and organisation of tissues in the closed circulatory system. 2. Discuss
Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels
 Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels Most animals have a closed blood system. The blood flows continuously in vessels back to the heart. In an open system the blood is pumped into open ended tubes and
Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels Most animals have a closed blood system. The blood flows continuously in vessels back to the heart. In an open system the blood is pumped into open ended tubes and
MANUAL BLOOD PRESSURE MONITOR BPM 168B Contents Blood Pressure Monitor Intended Use What is blood pressure?
 MANUAL BLOOD PRESSURE MONITOR BPM 168B Contents 01... Blood Pressure Monitor Intended Use 02... 1. What is blood pressure? 02... 2. Why is it useful measure blood pressure at home?... A. WHO blood pressure
MANUAL BLOOD PRESSURE MONITOR BPM 168B Contents 01... Blood Pressure Monitor Intended Use 02... 1. What is blood pressure? 02... 2. Why is it useful measure blood pressure at home?... A. WHO blood pressure
Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The list gives some structures in the blood and circulatory system.
 Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The list gives some structures in the blood and circulatory system. heart artery red blood cell ventricle capillary plasma vein white blood cell platelets Which of
Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The list gives some structures in the blood and circulatory system. heart artery red blood cell ventricle capillary plasma vein white blood cell platelets Which of
iworx Sample Lab Experiment HC-5: Body Position, Exercise, and Cardiac Output
 Experiment HC-5: Body Position, Exercise, and Cardiac Output Exercise 1: Cardiac Output While Reclining Aim: To determine the cardiac output of a subject through the measurement of blood pressures and
Experiment HC-5: Body Position, Exercise, and Cardiac Output Exercise 1: Cardiac Output While Reclining Aim: To determine the cardiac output of a subject through the measurement of blood pressures and
Pancreas: digestive enzymes Liver: bile-helps to digest fat, stored in gallblader; breaks down toxins, makes some parts of blood
 1 2 3 Pancreas: digestive enzymes Liver: bile-helps to digest fat, stored in gallblader; breaks down toxins, makes some parts of blood 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Highlights: - A pulse consists of two phases: contraction
1 2 3 Pancreas: digestive enzymes Liver: bile-helps to digest fat, stored in gallblader; breaks down toxins, makes some parts of blood 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Highlights: - A pulse consists of two phases: contraction
Objectives of the Heart
 Objectives of the Heart Electrical activity of the heart Action potential EKG Cardiac cycle Heart sounds Heart Rate The heart s beat separated into 2 phases Relaxed phase diastole (filling of the chambers)
Objectives of the Heart Electrical activity of the heart Action potential EKG Cardiac cycle Heart sounds Heart Rate The heart s beat separated into 2 phases Relaxed phase diastole (filling of the chambers)
Chapter 29 1/8/2018. Vital Signs. Measuring and Reporting Vital Signs. Key Terms
 Chapter 29 Vital Signs Key Terms Blood pressure Body temperature Diastolic pressure Hypertension Hypotension Pulse Pulse rate Respiration Sphygmomanometer Stethoscope Systolic pressure Vital signs Measuring
Chapter 29 Vital Signs Key Terms Blood pressure Body temperature Diastolic pressure Hypertension Hypotension Pulse Pulse rate Respiration Sphygmomanometer Stethoscope Systolic pressure Vital signs Measuring
37 1 The Circulatory System
 H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
Physiological Measurements Training for Care/Nursing & LD Small Group Home Staff
 Physiological Measurements Training for Care/Nursing & LD Small Group Home Staff CONTENTS 1. The National Early Warning Score 2. Respiratory Rate 3. Oxygen Saturations 4. Temperature 5. Blood Pressure
Physiological Measurements Training for Care/Nursing & LD Small Group Home Staff CONTENTS 1. The National Early Warning Score 2. Respiratory Rate 3. Oxygen Saturations 4. Temperature 5. Blood Pressure
Human Circulation and Respiration Chapter 38
 Human Circulation and Respiration Chapter 38 Goals: 1. Compare closed and open circulatory systems. 2. Label the parts of the human heart. 3. Explain how blood travels through the heart; identify chambers
Human Circulation and Respiration Chapter 38 Goals: 1. Compare closed and open circulatory systems. 2. Label the parts of the human heart. 3. Explain how blood travels through the heart; identify chambers
name F septum ; D bicuspid / mitral / atrioventricular, valve ; aorta pulmonary artery K semilunar valve ; right atrium right ventricle ; [6]
![name F septum ; D bicuspid / mitral / atrioventricular, valve ; aorta pulmonary artery K semilunar valve ; right atrium right ventricle ; [6] name F septum ; D bicuspid / mitral / atrioventricular, valve ; aorta pulmonary artery K semilunar valve ; right atrium right ventricle ; [6]](/thumbs/79/79061016.jpg) Question Mark Guidance 1 (a) function letter on Fig. 1.1 name structure that separates oxygenated and deoxygenated blood structure that prevents backflow of blood from ventricle to atrium F septum ; D
Question Mark Guidance 1 (a) function letter on Fig. 1.1 name structure that separates oxygenated and deoxygenated blood structure that prevents backflow of blood from ventricle to atrium F septum ; D
14-1: The Body s Transport System. 7 th Grade Life Science
 7 th Grade Life Science Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system, also called circulatory system, is made of your heart blood vessels, and blood. It is like the network of highways on Earth, where
7 th Grade Life Science Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system, also called circulatory system, is made of your heart blood vessels, and blood. It is like the network of highways on Earth, where
The cardiovascular and respiratory system
 The cardiovascular and respiratory system For this unit you need to be able to... Learning Outcomes: Covered? Confident? Understand and be able to give sporting examples of when each respiratory system
The cardiovascular and respiratory system For this unit you need to be able to... Learning Outcomes: Covered? Confident? Understand and be able to give sporting examples of when each respiratory system
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM : (circulatory system) Lab-4
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM : (circulatory system) Lab-4 The Circulatory System: The circulatory system (cardiovascular system) has 3 basic components:- *A muscular pump: heart *Interconnecting tubes: blood
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM : (circulatory system) Lab-4 The Circulatory System: The circulatory system (cardiovascular system) has 3 basic components:- *A muscular pump: heart *Interconnecting tubes: blood
VCERT PE Final Test Revision
 VCERT PE Final Test Revision Skeletal System This one is known as the Condyloid Joint Definition: The point at which two or more bones meet to produce movement. Slightly Moveable Joints- spine Fix Joints-
VCERT PE Final Test Revision Skeletal System This one is known as the Condyloid Joint Definition: The point at which two or more bones meet to produce movement. Slightly Moveable Joints- spine Fix Joints-
The Body s Transport System (pp )
 The Body s Transport System (pp. 538 547) This section describes how the heart, blood vessels, and blood work together to carry materials throughout the body. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, complete
The Body s Transport System (pp. 538 547) This section describes how the heart, blood vessels, and blood work together to carry materials throughout the body. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, complete
Chapter 15: The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 15: The Cardiovascular System McArdle, W. D., Katch, F. I., & Katch, V. L. (2010). Exercise Physiology: Nutrition, Energy, and Human Performance (7 ed.). Baltimore, MD.: Lippincott Williams and
Chapter 15: The Cardiovascular System McArdle, W. D., Katch, F. I., & Katch, V. L. (2010). Exercise Physiology: Nutrition, Energy, and Human Performance (7 ed.). Baltimore, MD.: Lippincott Williams and
LEARNING OUTCOME The students will be able to elicit vital signs correctly on human volunteers/patients
 Vital signs (pulse, blood pressure, temperature, respiratory rate, pain) are physiological parameters that a healthcare professional requires when dealing with patients. Accurate measurement of vital signs
Vital signs (pulse, blood pressure, temperature, respiratory rate, pain) are physiological parameters that a healthcare professional requires when dealing with patients. Accurate measurement of vital signs
Cardiovascular Responses to Exercise
 CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY 69 Case 13 Cardiovascular Responses to Exercise Cassandra Farias is a 34-year-old dietician at an academic medical center. She believes in the importance of a healthy lifestyle
CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY 69 Case 13 Cardiovascular Responses to Exercise Cassandra Farias is a 34-year-old dietician at an academic medical center. She believes in the importance of a healthy lifestyle
Cardiovascular System. Supplementary Information
 Cardiovascular System Supplementary Information THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM - 1 - THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM FUNCTION Transport system carrying nutrient, gases, hormones and waste products to and from the
Cardiovascular System Supplementary Information THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM - 1 - THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM FUNCTION Transport system carrying nutrient, gases, hormones and waste products to and from the
Blood Flow and Blood Pressure Regulation *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44806 1 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure Regulation * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By the end of this
OpenStax-CNX module: m44806 1 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure Regulation * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By the end of this
BLOOD PRESSURE ASSESSMENT
 BLOOD PRESSURE ASSESSMENT Course Principles of Health Science Unit X Vital Signs Course Health Science Unit VI CPR / AED & First Aid Essential Question How do health care skills help to promote health
BLOOD PRESSURE ASSESSMENT Course Principles of Health Science Unit X Vital Signs Course Health Science Unit VI CPR / AED & First Aid Essential Question How do health care skills help to promote health
Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems
 Chapter Test A Part A: Multiple Choice CHAPTER 34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems In the space at the left, write the letter of the phrase that best answers each question. 1. Which is the
Chapter Test A Part A: Multiple Choice CHAPTER 34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems In the space at the left, write the letter of the phrase that best answers each question. 1. Which is the
In this activity, you will learn and practice many of the techniques used in the health/ medical profession for assessing a patient's cardiac health.
 Cardiac Vital Measurement Lab In this activity, you will learn and practice many of the techniques used in the health/ medical profession for assessing a patient's cardiac health. 1 By now you should know
Cardiac Vital Measurement Lab In this activity, you will learn and practice many of the techniques used in the health/ medical profession for assessing a patient's cardiac health. 1 By now you should know
The Heart. Made up of 3 different tissue: cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and connective tissue.
 The Heart The Heart Made up of 3 different tissue: cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and connective tissue. Your heart pumps with a regular beat (Heart Rate) Your heart rate can change depending on
The Heart The Heart Made up of 3 different tissue: cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and connective tissue. Your heart pumps with a regular beat (Heart Rate) Your heart rate can change depending on
AP Biology Lab 10 Physiology of the Circulatory System Lab Activity Student Study Guide
 TM AP Biology Lab 10 Physiology of the Circulatory System Lab Activity Student Study Guide BACKGROUND Some of your arteries and veins are as big around as your thumb, and some are almost too small to see.
TM AP Biology Lab 10 Physiology of the Circulatory System Lab Activity Student Study Guide BACKGROUND Some of your arteries and veins are as big around as your thumb, and some are almost too small to see.
2. Measure a subject's blood pressure and heart rate both at rest and during exercise.
 Lab Activity 11 The Cardiovascular System Student Learning Objectives After completing this lab, you should be able to: 1. Define, explain and correctly use the key terms. 2. Measure a subject's blood
Lab Activity 11 The Cardiovascular System Student Learning Objectives After completing this lab, you should be able to: 1. Define, explain and correctly use the key terms. 2. Measure a subject's blood
Structure and organization of blood vessels
 The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
Introduction. Every organism must exchange materials and energy with its environment, and this exchange ultimately occurs at the cellular level.
 Introduction Every organism must exchange materials and energy with its environment, and this exchange ultimately occurs at the cellular level. Cells live in aqueous environments. The resources that they
Introduction Every organism must exchange materials and energy with its environment, and this exchange ultimately occurs at the cellular level. Cells live in aqueous environments. The resources that they
This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia)
 Biology 20 Unit D This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia) requires action of: heart: muscular force to move
Biology 20 Unit D This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia) requires action of: heart: muscular force to move
Large Arteries of Heart
 Cardiovascular System (Part A-2) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Arteries Capillaries Veins Heart Anatomy Conduction System Blood pressure Fetal circulation Susie Turner, M.D. 1/5/13 Large Arteries of Heart
Cardiovascular System (Part A-2) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Arteries Capillaries Veins Heart Anatomy Conduction System Blood pressure Fetal circulation Susie Turner, M.D. 1/5/13 Large Arteries of Heart
Cardiovascular Learners MUST KNOW R A G. Know the double- circulatory system (systemic and pulmonary)
 Please do the following 1. Read the Learners must know section (see below) 2. Watch the GCSE POD video 3. Attempt Exam Questions 4. Mark your answers 5. Reflect and repeat until you are successful and
Please do the following 1. Read the Learners must know section (see below) 2. Watch the GCSE POD video 3. Attempt Exam Questions 4. Mark your answers 5. Reflect and repeat until you are successful and
Cardiovascular Physiology
 Cardiovascular Physiology The mammalian heart is a pump that pushes blood around the body and is made of four chambers: right and left atria and right and left ventricles. The two atria act as collecting
Cardiovascular Physiology The mammalian heart is a pump that pushes blood around the body and is made of four chambers: right and left atria and right and left ventricles. The two atria act as collecting
Unit 10 ~ Learning Guide
 Unit 10 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Unit 10 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
(D) (E) (F) 6. The extrasystolic beat would produce (A) increased pulse pressure because contractility. is increased. increased
 Review Test 1. A 53-year-old woman is found, by arteriography, to have 5% narrowing of her left renal artery. What is the expected change in blood flow through the stenotic artery? Decrease to 1 2 Decrease
Review Test 1. A 53-year-old woman is found, by arteriography, to have 5% narrowing of her left renal artery. What is the expected change in blood flow through the stenotic artery? Decrease to 1 2 Decrease
Physiology of Circulation
 Physiology of Circulation Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Blood vessels Arteries: Blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to the lungs and tissues. Arterioles are small arteries that deliver blood to the
Physiology of Circulation Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Blood vessels Arteries: Blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to the lungs and tissues. Arterioles are small arteries that deliver blood to the
Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation. Biology 2201
 Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Biology 2201 Homeostasis The steady state of conditions inside a living organism that allows it to function properly Homeostasis is the dynamic equilibrium of the
Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Biology 2201 Homeostasis The steady state of conditions inside a living organism that allows it to function properly Homeostasis is the dynamic equilibrium of the
HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 13a Station Lab Activity
 HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 13a Station Lab Activity Name(s): Period: Date: The Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is made up of the heart, blood, and blood vessels. It functions as
HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 13a Station Lab Activity Name(s): Period: Date: The Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is made up of the heart, blood, and blood vessels. It functions as
Learner resource 1b Heart Rate Investigation
 Worksheet B AIMS OF THIS SESSION: 1. Learn how to take your own and someone else s radial pulse. 2. Investigate the short-term effects of exercise on heart rate. What is your pulse? The radial pulse is
Worksheet B AIMS OF THIS SESSION: 1. Learn how to take your own and someone else s radial pulse. 2. Investigate the short-term effects of exercise on heart rate. What is your pulse? The radial pulse is
The Cardiovascular System
 CHAPTER 16 1 SECTION Circulation and Respiration The Cardiovascular System California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.6.j BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these
CHAPTER 16 1 SECTION Circulation and Respiration The Cardiovascular System California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.6.j BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these
