Circulatory System Review ANSWERS
|
|
|
- Daniella Day
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Circulatory System Review ANSWERS 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? Double membranous sac that surrounds the heart What is myocardium? The muscle tissue that makes up the heart What is the septum? The tissue that separates the left and right side of the heart b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their function, structure, and location. Right atrium upper right chamber that receives oxygen-poor blood from the vena cava and pumps blood to the right ventricle. Right ventricle (lower right chamber) pumps blood out the pulmonary truck/artery (to the lungs). Left atrium (upper left chamber) receives oxygen-rich blood from the pulmonary veins (from the lungs) and pumps blood to the left ventricle. Left ventricle (lower left chamber) has the thickest myocardium and pumps blood out of the heart via the aorta (to body tissues) c) What are chordae tendinae? Fibrous strands that attached to the AV valves and the ventricles to prevent the ventricle from inverting 2. Know the diagram and table of the blood vessels. a) What is the major (largest) artery of the body? aorta What is the major vein of the body? Vena cava (superior and inferior) b) What is a pulse? The muscular contractions of arteries c) What is Arteriosclerosis? Hardening of the arteries which reduces elasticity of artery wall (associated with aging) Atherosclerosis? Plaque buildup in arteries due to high saturated fats and cholesterol diet. Aneurysm? Weakening of artery wall which can lead to arteries bursting (most common in arteries leading to brain) 3. Know the diagram of ECG and electrical impulses in the heart. a) Explain the electrical cardiac cycle. Medulla oblongata sends message to heart, SA node (pacemaker) in wall of right atrium receives message and causes both atria to contract. AV node at base of right atrium is stimulated by pacemaker and send message along purkinje fibres (nerve fibres within myocardium that surround each ventricle) and cause muscular tissue around ventricles to contract. The entire heart rests. b) Explain how the autonomic nervous system regulates the heartbeat. (parasympathetic and sympathetic) parasympathetic nervous system stimulation decrease heart rate (normally active at rest) whereas the sympathetic nervous system increases heart rate (response to stress) c) What is blood pressure? Pressure of blood against vessel walls created by beating heart What is systolic pressure? Highest arterial pressure What is diastolic pressure? Lowest arterial pressure (ventricle relaxing; atria contracting) 4. Name the functions of the circulatory system. a) Explain how blood pressure changes as the blood moves throughout the body. Highest at aorta, falls through arteries, very, very low in capillaries and remains low in veins b) Explain the factors that affect blood pressure. (hypotension and hypertension) exercise, cholesterol build up, vasoconstriction/vasodilation, increased or decreased blood volume. Hypotension is low BP (below 100). Hypertension is high BP (140/90 or higher) c) Explain the difference between the 5 types of blood vessels.(size, structure, thickness, function, BP, velocity.) arteries thick, muscular layer causing these vessels to be the thickest; take blood away from the heart; highest BP; highest blood velocity; low area (thin inside by structure is thick). Arterioles smaller than arteries and lead to capillaries; decreases in BP and blood velocity but increases in area due to more paths. Capillaires very thin walls and small lumen (only one RBC thick); low BP, low blood velocity, but high area. Venules larger lumen than arterioles; low BP; velocity of blood increases from capillary slightly and area decreases as compared to capillaries. Veins largest lumen; low BP (need valves to assist with blood movement), increase in blood velocity from venules (but not as high as arteries) and low area\
2 d) How is blood pressure affected by vasodilation? Dilation of vessels lowers BP Vasoconstriction? Constriction of vessels increases BP What do these 2 terms mean? Vasodilation means the relaxation of muscle layers in vessels which increases the lumen space inside the vessel whereas vasoconstriction is the contraction of the muscular layer and therefore, decreases the lumen of vessels. 5. Name three different places valves are found in the body. Inside the heart (AV valve and semi-lunar valve), in veins, at the beginning of capillary beds (precapillary sphincters) 6. Explain the 3 different vascular pathways in the body. Pulmonary circuit; systemic circuit & coronary circuit (see notes of schematic diagrams) 7. Explain the hepatic portal system. The nutrients that are absorbed within the capillaries within the villi of the small intestine are directly transferred to the liver capillaries via the hepatic portal vein Distinguish between the hepatic portal vein and the hepatic vein the hepatic portal vein is between the intestine and the liver; whereas the hepatic vein is the from the liver to the heart 8. Explain the process of capillary-tissue fluid exchange. a) What is osmotic pressure? The pressure causes by the water content within the blood and affects the blood volume as well as the exchange that occurs at the capillary level. b) How does it affect the capillaries? OP should be at about 21 mm of Hg in order for efficient exchange to occur between the ECF and the blood capillaries c) How is extra fluid taken up from tissues? Via the lymphatic capillaries d) Label the following diagram for fluid exchange. Include the pressure in mm Hg on the arteriole and venule sides of your diagram. e) What is the pressure in mm Hg in the other blood vessels? Arteriole end Venule end 9. Explain fetal circulation. a) Name 2 ways blood can bypass the lungs. Via arteriole duct or foramen ovalis b) How does the fetal circulatory system change after birth has occurred? Foramen ovalis closes and becomes an indent with the septum and arteriole duct as well as venous duct are closed off, shrink and become ligaments 10. Components of the Blood: a) What is plasma? The yellowish, liquid portion of blood that contains gases, water, proteins, wastes, hormones & salts b) What are erythrocytes? RBC Why are they able to carry such a large protein like hemoglobin? Quaternary protein with iron. c) Explain the structure and function of leukocytes. WBCs that fight infection. Larger than RBC, but fewer in number. Can be granular or agranular
3 d) What are platelets? Enucleated, Cell fragments that function in blood clotting Explain the process of blood clotting. When blood vessel is punctured, platelets congregate and form a plug. Fibrinogen (protein carried in plasma) is enzymatically converted to fibrin which forms a mesh-like network over wound and this network traps RBCs. e) What is the difference between an antigen and antibody? Antigen (a glycoprotein) is on the surface of RBCs and the body s protective response to fight anything foreign is the production of Antibodies. Antibodies attach to foreign material which flags it for destruction by the WBCs. 11. Immunity a) What is immunity? Body s ability to eliminate foreign material Explain the functions of the immune system.defend against pathogens; remove old cells; identifies and destroys abnormal cells; rejects foreign tissue b) Explain the 3 levels of the immune system Physical & chemical barriers such as skin, mucus, acidity of sweat, juices,etc.; WBC response neutrophils enlarge into macrophages which phagocytize material; antibody/antigen response see 10(e) c) Explain the inflammatory response. basophils release histamine (chemical) that causes enlargement (reddening) & increased permeability (swelling) of capillaries to attract macrophages to the area which consume bacteria from site of injury. 12. The Lymphatic System: a) What are the functions of the lymphatic system? What is the main function of it? Main: take up excess fluid from ECF; others: absorb fat from intestinal villi; destruction of foreign material; produce antibodies; b) What is the structure and function of lymph vessels? capillaries and veins with valves to prevent backflow of lymph fluid c) What is extracellular fluid (ECF)? The fluid that exists between the blood capillaries, the cells close to those capillaries and the lymph capillaries d) What are lymph nodes? collection of lymph tissue that forms swellings that produce and store lymphocytes What do they do? Filters debris from lymph fluid e) Explain the function of the different lymph organs. Spleen cleanses blood, produces lymphocytes & macrophages, stores blood. Thymus gland T-cell (a WBC) maturation. Tonsils additional immune defense. Appendix has lymph tissue to fight infection. Bone marrow makes WBCs (and RBCs) 13. Which blood vessels carry blood away from the heart? a) Capillaries b) Venules c) Veins d) Arteries e) Lymph vessels 14. Which statement is NOT a correct association? a) Arteries have muscles linings and are deep in the body b) Capillaries oxygen and nutrient exchange c) Arteries high blood pressure and are deep in the body d) Veins high blood pressure and are deep in the body they are near the surface e) Veins valves return blood to heart 15. Artery and vein are defined by whether they leave or enter the heart. If they were defined by whether they carried oxygenated or deoxygenated blood, we would have to change the name(s) of a) the hepatic portal vein to a hepatic portal artery b) the hepatic and renal systems; they would have to be switched c) the pulmonary artery and vein; they would have to be switched d) the coronary artery and vein; they would have to be switched e) none, since the aorta and vena cavae do not have artery and vein in their names 16. Which blood vessels will have walls only one cell thick? a) Capillaries b) Venules c) Veins d) Arterioles e) Arteries 17. In the fetus, the umbilical cord consists of fetal blood vessels running from the iliac artery and vein to the placenta which functions to diffuse oxygen provided by the mother. What is the nature of an artery and vein in this umbilical cord? a) They would be structurally identical and carry the same levels of hemoglobin b) Just like most arteries and veins, the artery would carry oxygenated blood and the vein would carry deoxygenated blood c) Just like the pulmonary system, the artery would carry deoxygenated blood and the vein would carry oxygenated blood
4 18. There is a condition where a baby is born with an opening (oval opening) in the septum or wall between the right and left sides of the heart. What are reasonable consequences? a) More efficient pumping of blood through the body with pressure from both ventricles b) An equal reading for heartbeat; that is diastole equals systole c) Disability resulting when deoxygenated blood is mixed and sent to the body and partly oxygenated blood is sent to the lungs d) Death due to loss of blood from the circulatory system 19. What is the correct sequence a drop of blood returning from the body encounters in the heart chambers? a) Left atrium-left ventricle-right atrium-right ventricle -left atrium-right ventricle right atrium left ventricle left atrium- right ventricle d) Right atrium- right ventricle-left atrium- left ventricle 20. What is the correct sequence a drop of blood returning from the body encounters in the heart valves? a) Right AV valve aortic semilunar valve - left AV valve pulmonary semilunar valve b) Right AV valve pulmonary semilunar valve left AV valve aortic semilunar valve c) Left AV valve pulmonary semilunar valve right AV valve aortic semilunar valve d) Left AV valve aortic semilunar valve right AV valve pulmonary semilunar valve 21. In the above diagram, a is the a) Inferior/posterior vena cava b) Superior/anterior vena cava 22. In the above diagram, c is the a) Inferior/ posterior vena cava e) AV valve e) Left atrium 23. In the above diagram, d is the a) Inferior/ posterior vena cava 24. In the above diagram, e is the a) Inferior/ posterior vena cava e) aorta e) Aorta 25. Contraction of the right ventricle forces blood initially into the a) Left atrium b) Right atrium d) Pulmonary vein e) Pulmonary artery 26. If you are tracing the path of blood from the right to the left side of the heart, you must mention the a) Lungs d) Superior/anterior vena cava b) Hepatic portal vein e) Inferior/ posterior vena cava 27. In humans, the superior (anterior) vena cava a) Carries blood to the right atrium b) Carries blood away from the right atrium 28. The pacemaker of the heart is termed the a) AV node b) Cardiac centre in the medulla oblongata c) Joins with the aorta d) Has a high blood pressure c) SA node d) Vagus nerve e) Purkinje fibres
5 29. In the above figure, which statement is true concerning blood pressure? a) It always remains the same in all vessels b) It gets progressively lower the further from the heart c) The greater the cross sectional area, the greater the pressure d) The further from the heat, the higher the pressure 30. In the above figure, which type of blood vessel would you expect to be the strongest? a) Arteries c) Capillaries b) Arterioles d) Veins 31. The alternating expansion and recoil of an arterial wall is termed a(n) a) ECG b) EEG c) Pulse 32. Systole occurs when the a) Heart tissue is contracting b) Heart tissue is relaxing d) Hypertension e) Heart murmur 33. Which is NOT a correct association describing aspects of the cardiac cycle? a) Each heartbeat constitutes a cardiac cycle b) Diastole is contraction of the heart and systole is relaxation c) A normal heart rate varies from 60 to 80 beats per minute d) A pulse is the expansion and recoil of artery walls felt near the body surface e) Valves prevent backflow of blood into the heart when the heart relaxes 34. The electrical changes that occur in the heart during contraction are recorded as a) EEGs d) EMGs b) ECGs e) MIGs c) EGGs 35. Which phase of the ECG indicates ventricular excitation and eventual contraction? a) P wave d) U wave b) QRS complex e) I wave c) T wave c) Semilunar valves open and close d) Aortic valves open and close 36. The part of the circulatory system involved with pumping blood to and from the lungs is the a) Systemic circuit d) Pulmonary circuit b) Internal respiration circuit e) ECG circuit c) Microcirculation circuit 37. Which blood vessel has the highest concentration of CO 2? a) Pulmonary artery b) Pulmonary vein 38. Oxygenated blood enters the heart at the a) Left atrium d) Renal vein e) Hepatic portal vein d) Right ventricle
6 39. Which of the following correctly traces the path of blood from the heart to the kidneys and back to the heart again? a) Left ventricle, vena cava, renal vein, kidney, renal artery, aorta, right atrium b) Right atrium, aorta, renal artery, kidney, renal vein, hepatic portal vein, vena cava, left atrium c) Left ventricle, renal artery, kidney, renal vein, vena cava, right atrium d) Left ventricle, aorta, renal artery, kidney, renal vein, vena cava, right atrium 40. Blood travelling from the intestines to the liver is travelling in the a) Pulmonary vein b) Inferior (posterior) vena cava c) Superior (anterior vena cava 41. The blood vessel that provides oxygen to the heart tissue is the a) Pulmonary artery b) Coronary artery c) Left carotid artery 42. The blood that enters the coronary artery comes from the a) Pulmonary artery b) Pulmonary vein d) Coronary vessels e) Hepatic portal vein d) Renal artery e) Left subclavian artery d) Superior (anterior) vena cava e) Inferior (posterior) vena cava 43. Blood flow in the capillaries is a) Slower because there are more capillaries and they represent more flow volume b) Faster because they are smaller and blood must speed up to get through c) The same speed as in the arteries and veins since they are the input and output points d) Highly variable due to different tissues, but must average the same as speeds in arteries and veins 44. If a person has a blood pressure of 120/80, the 120 refers to the a) Diastolic pressure b) Systolic pressure c) Pulse pressure d) Capillary pressure e) Venous pressure 45. Why is it advantageous to have blood move slowly in the capillaries? a) It will not cause damage to the valves b) It maintains the high pressure in the capillaries c) It provides time for substances to be exchanged between blood and tissue fluids d) It creates a greater osmotic pressure for cells 46. Which association is NOT correct? a) Red blood cell transport oxygen b) White blood cells fight infection c) Water maintains blood volume 47. All of the following may be found in the blood except a) Fibrinogen b) Glucose c) Urea 48. Hemoglobin is NOT a) Carried in red blood cells b) An oxygen transporter d) Oxygen cellular respiration e) Platelets fights infection d) Oxygen e) Glycogen 49. The reason red blood cells only live about 120 days is because red blood cells a) Lack a nucleus and therefore cannot defend themselves from pathogen attack b) Lack a nucleus and therefore cannot repair and rebuild cell structures c) Are attacked and eaten by white blood cells d) Are physiologically inferior cells that are not made to last very long 50. Platelets a. Phagocytize bacteria b. Are responsible for blood type c. Initiate clotting d. Transport oxygen e. Are responsible for the buildup of plaques on artery walls c) Made of protein and heme d) Normally found free in the plasma
7 51. In the above diagram, the arrow at number 2 describes the movement of a. Water d. Carbon dioxide b. Glucose e. Water, glucose, and oxygen c. Oxygen 52. In the above diagram, movement of molecules occurs in the direction of arrow 4 due to a. Diffusion d. Blood pressure b. Emulsification c. Osmotic pressure e. Filtration 53. An antibody is a) A compound that reacts with an antigen b) A white blood cell that phagocytizes invading bacteria c) A carbohydrate in the red cell membrane d) A platelet that secretes platelets 54. Which two are needed to fight infection? a) White and red blood cells b) Platelets and proteins 55. The proteins that are found in the blood a) Are formed from amino acids b) Help fight disease c) Aid in blood clotting 56. Blood pressure a) Is the same in all blood vessels b) Is highest in the aorta Label the following diagram: c) Red blood cells and platelets d) White blood cells and proteins d) Help maintain osmotic pressure e) All of the above are true c) Is measured by taking an ECG d) Never rises above normal Pulmonary Trunk/artery Umbilical Artery Aorta Arterial Duct Oval Opening Venous duct Umbilical Vein Umbilical Artery Iliac Artery
Circulatory System Review
 Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary.
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
C3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 Worksheet. C3 Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the heart
 Name: Date: C3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 Worksheet C3 Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the heart 1. Label and give the functions of the following: a. left and right atrium: b. left and right ventricle:
Name: Date: C3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 Worksheet C3 Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the heart 1. Label and give the functions of the following: a. left and right atrium: b. left and right ventricle:
Chapter 23. Circulation
 Chapter 23 Circulation Standards CORE: I can describe the components and function of blood. I can describe structure and function of blood vessels. I can compare and contrast systemic and pulmonary systems.
Chapter 23 Circulation Standards CORE: I can describe the components and function of blood. I can describe structure and function of blood vessels. I can compare and contrast systemic and pulmonary systems.
Cardiovascular System. Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12
 Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia)
 Biology 20 Unit D This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia) requires action of: heart: muscular force to move
Biology 20 Unit D This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia) requires action of: heart: muscular force to move
Chapter 16: Circulation
 Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation
 1 Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Section 9.1 Homeostasis: Life in the Balance Outcomes: I can explain homeostasis I can describe the importance of homeostasis to living things I can explain the
1 Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Section 9.1 Homeostasis: Life in the Balance Outcomes: I can explain homeostasis I can describe the importance of homeostasis to living things I can explain the
Types of circulatory systems
 Types of circulatory systems Open system Mostly invertebrates Low pressure Haemocoel Suitable for small organisms Closed system Vertebrates High pressure Blood remains in blood vessels Separate tissue
Types of circulatory systems Open system Mostly invertebrates Low pressure Haemocoel Suitable for small organisms Closed system Vertebrates High pressure Blood remains in blood vessels Separate tissue
10. Thick deposits of lipids on the walls of blood vessels, called, can lead to serious circulatory issues. A. aneurysm B. atherosclerosis C.
 Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Cardiovascular. Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Nutrients Waste Hormones Immune cells Oxygen
 Cardiovascular The Cardiovascular System - Arteries Arteries Cardiovascular System Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Carry blood away from heart Carotid arteries Deliver
Cardiovascular The Cardiovascular System - Arteries Arteries Cardiovascular System Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Carry blood away from heart Carotid arteries Deliver
Chapter 10 The Circulatory & Lymphatic Systems
 Biology 12 Name: Human Biology Per: Date: Chapter 10 The Circulatory & Lymphatic Systems Complete using BC Biology 12, pages 298 325 10.1 The Blood Vessels pages 298-299 1. Label the blood vessels in this
Biology 12 Name: Human Biology Per: Date: Chapter 10 The Circulatory & Lymphatic Systems Complete using BC Biology 12, pages 298 325 10.1 The Blood Vessels pages 298-299 1. Label the blood vessels in this
Biology 12 - Circulation - Chapter Notes
 Biology 12 - Circulation - Chapter Notes Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms
Biology 12 - Circulation - Chapter Notes Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM BLOOD VESSELS
 Name: Block: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms such as
Name: Block: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms such as
1. Label the Diagram using the following terms: artery, arterioles, vein, venules, capillaries, valve, inner wall, middle wall, outer wall
 Bio 20 Ms. Nyboer Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, and the Heart Structure and Function Workbook Use your textbook (Ch. 10) and notes to fill in this workbook Part A: Arteries, Veins, Capillaries 1. Label
Bio 20 Ms. Nyboer Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, and the Heart Structure and Function Workbook Use your textbook (Ch. 10) and notes to fill in this workbook Part A: Arteries, Veins, Capillaries 1. Label
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
CIE Biology GCSE. 9: Transport in animals. Notes.
 CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Vessels Arteries Arteries Arteries
 CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
The Cardiovascular System home study course
 The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY
 TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
Ch. 12 The Circulatory System. The heart. The heart is a double pump. A quick note on arteries vs. veins. = the muscular pump of the CV system
 Ch. 12 The Circulatory System The heart A.k.a. the cardiovascular system Blood was discussed in Ch. 11 Focus of Ch. 12: heart and blood vessels = the muscular pump of the CV system ~ 100,000 heartbeats/day!
Ch. 12 The Circulatory System The heart A.k.a. the cardiovascular system Blood was discussed in Ch. 11 Focus of Ch. 12: heart and blood vessels = the muscular pump of the CV system ~ 100,000 heartbeats/day!
Levels of Organization. Chapter 19 6/11/2012. Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body. 4 Primary Tissues
 Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
Chapter 12. Capillaries. Circulation. The circulatory system connects with all body tissues
 Chapter 12 Circulation The circulatory system connects with all body s In many animals, microscopic blood vessels called capillaries Form an intricate network among the Red blood cell song Figure 23.1A
Chapter 12 Circulation The circulatory system connects with all body s In many animals, microscopic blood vessels called capillaries Form an intricate network among the Red blood cell song Figure 23.1A
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 12 The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 12 The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans
 Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1 -
 Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1-2. Organs of a closed circulatory system: A. Have valves a. Arteriole B. Regulate blood flow b. Artery C. Lead to heart
Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1-2. Organs of a closed circulatory system: A. Have valves a. Arteriole B. Regulate blood flow b. Artery C. Lead to heart
Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for
 Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for hyperlipidemia! Agenda! - Review objectives for 6.2! - Video of circulatory
Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for hyperlipidemia! Agenda! - Review objectives for 6.2! - Video of circulatory
Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Blood o Red blood cells: heamoglobin and oxygen transport o White blood cells: phagocyte phagocytosis (engulf pathogen, vesicles fuse with vacuole,
Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Blood o Red blood cells: heamoglobin and oxygen transport o White blood cells: phagocyte phagocytosis (engulf pathogen, vesicles fuse with vacuole,
Circulatory System Objective sheet 3
 Circulatory System Objective sheet 3 10. Functions of blood 1) Transport oxygen and nutrients 2) Transport of carbon dioxide and waste 3) Protection against disease causing micro-organisms 4) Clotting
Circulatory System Objective sheet 3 10. Functions of blood 1) Transport oxygen and nutrients 2) Transport of carbon dioxide and waste 3) Protection against disease causing micro-organisms 4) Clotting
Function: Transportation of. Oxygen Nutrients Waste Hormones gases
 Function: Transportation of Oxygen Nutrients Waste Hormones gases Pericardium: double sac of serous membrane filled with fluid (pericardial fluid to be exact) that surrounds the heart. Parietal pericardium:
Function: Transportation of Oxygen Nutrients Waste Hormones gases Pericardium: double sac of serous membrane filled with fluid (pericardial fluid to be exact) that surrounds the heart. Parietal pericardium:
Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels
 Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels Most animals have a closed blood system. The blood flows continuously in vessels back to the heart. In an open system the blood is pumped into open ended tubes and
Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels Most animals have a closed blood system. The blood flows continuously in vessels back to the heart. In an open system the blood is pumped into open ended tubes and
Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes
 Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes Functions of the Circulatory System The circulatory system functions mainly as the body s transport system. It transports: o Oxygen o Nutrients o Cell waste o
Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes Functions of the Circulatory System The circulatory system functions mainly as the body s transport system. It transports: o Oxygen o Nutrients o Cell waste o
Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system. What are the function of the cardiovascular system? Arteries and arterioles:
 5.1 Overview of the cardiovascular system Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system Includes the heart and blood vessels Brings nutrients to cells and helps get rid of wastes Blood is refreshed in the lung, kidneys,
5.1 Overview of the cardiovascular system Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system Includes the heart and blood vessels Brings nutrients to cells and helps get rid of wastes Blood is refreshed in the lung, kidneys,
Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Blood 10/22/2012
 Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System
 Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System This color-enhanced image was made with an electron microscope, so the objects it depicts are extremely small. Do you know what they are? This incredible photo shows red
Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System This color-enhanced image was made with an electron microscope, so the objects it depicts are extremely small. Do you know what they are? This incredible photo shows red
Summary table: artery capillary vein Blood pressure Hi Low lowest Valves present or Absent Absent Present
 Bi 067: Review of sectn 7-9 - cardiovascular and lymphatic Heart and Blood vessels: 3 Types of blood vessels: 1. Arteries, arterioles -away from heart, O2 rich 2. Capillaries gas and nutrient/waste exchange
Bi 067: Review of sectn 7-9 - cardiovascular and lymphatic Heart and Blood vessels: 3 Types of blood vessels: 1. Arteries, arterioles -away from heart, O2 rich 2. Capillaries gas and nutrient/waste exchange
Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93)
 Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
Cardiovascular System. I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart
 Cardiovascular System I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart 1. : Pericardial Cavity serous fluid filled space between the heart and the pericardium B. Heart Wall 1.
Cardiovascular System I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart 1. : Pericardial Cavity serous fluid filled space between the heart and the pericardium B. Heart Wall 1.
d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology
 d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology What can your remember about the heart and blood vessels? What is the Cardiovascular System? The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system,
d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology What can your remember about the heart and blood vessels? What is the Cardiovascular System? The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system,
CIRCULATION Blood and Blood Vessels
 CIRCULATION Blood and Blood Vessels Blood Vessels The 5 Main Types 1. Arteries 2. Arterioles 3. Capillaries 4. Venules 5. Veins http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pgi80ue-amo Arteries: 1) Arteries Function
CIRCULATION Blood and Blood Vessels Blood Vessels The 5 Main Types 1. Arteries 2. Arterioles 3. Capillaries 4. Venules 5. Veins http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pgi80ue-amo Arteries: 1) Arteries Function
The Circulatory System. The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types
 The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
Blood flows away from the heart in arteries, to the capillaries and back to the heart in the veins
 Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
Chapter 12 Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 12 Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular System Includes Heart and Blood Vessels Transports, nutrients and wastes to and from the tissues 1 The Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Arteries:
Chapter 12 Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular System Includes Heart and Blood Vessels Transports, nutrients and wastes to and from the tissues 1 The Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Arteries:
Figure ) The specific chamber of the heart that is indicated by letter A is called the. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 364
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Short Answer Figure 11.1 Using Figure 11.1, identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label.
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Short Answer Figure 11.1 Using Figure 11.1, identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label.
Major Function of the Cardiovascular System. Transportation. Structures of the Cardiovascular System. Heart - muscular pump
 Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Cardiovascular System. Supplementary Information
 Cardiovascular System Supplementary Information THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM - 1 - THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM FUNCTION Transport system carrying nutrient, gases, hormones and waste products to and from the
Cardiovascular System Supplementary Information THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM - 1 - THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM FUNCTION Transport system carrying nutrient, gases, hormones and waste products to and from the
The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide.
 Section 1: The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What
Section 1: The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What
100,000 km of blood vessels!
 Biology 12 - Circulation - Chapter Notes Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms
Biology 12 - Circulation - Chapter Notes Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms
Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels
 Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels 3.2 Learning Objectives 3.2.2 Organisational Complexity of the human 1. Describe the structures and organisation of tissues in the closed circulatory system. 2. Discuss
Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels 3.2 Learning Objectives 3.2.2 Organisational Complexity of the human 1. Describe the structures and organisation of tissues in the closed circulatory system. 2. Discuss
Chapter 14. The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
07 Human transport Biology Notes IGCSE Cambridge #69 Transport in humans - the circulatory system
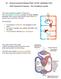 07 Human transport Biology Notes IGCSE Cambridge 2014 #69 Transport in humans - the circulatory system The main transport system of human is the circulatory system, a system of tubes (blood vessels) with
07 Human transport Biology Notes IGCSE Cambridge 2014 #69 Transport in humans - the circulatory system The main transport system of human is the circulatory system, a system of tubes (blood vessels) with
12.1 The Function of Circulation
 12.1 The Function of Circulation The Circulatory System Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) Heart pump beats 100 000 times a day Deliver oxygen and nutrients Function of Circulation Multicellular organisms
12.1 The Function of Circulation The Circulatory System Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) Heart pump beats 100 000 times a day Deliver oxygen and nutrients Function of Circulation Multicellular organisms
Glossary: The Cardiovascular System
 This glossary includes terms that have been introduced in Lesson 14. Student Resource 14.14 Glossary: The Cardiovascular System Anatomy Terms aorta Large artery that transports blood from the left ventricle
This glossary includes terms that have been introduced in Lesson 14. Student Resource 14.14 Glossary: The Cardiovascular System Anatomy Terms aorta Large artery that transports blood from the left ventricle
Cardiovascular System. Chapters 11, 12
 Cardiovascular System Chapters 11, 12 Oxygen enters the cardiovascular system by diffusing from alveoli into blood cells in the capillaries, then binding to hemoglobin in red blood cells. Blood Hematology-
Cardiovascular System Chapters 11, 12 Oxygen enters the cardiovascular system by diffusing from alveoli into blood cells in the capillaries, then binding to hemoglobin in red blood cells. Blood Hematology-
Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process:
 Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: a. erythrocytes b. leukocytes c. melanocytes d. thrombocytes Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process: a. erythrocytes
Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: a. erythrocytes b. leukocytes c. melanocytes d. thrombocytes Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process: a. erythrocytes
1. What kind of blood is found in the rt. atrium? (oxygenated or deoxygenated)
 Carl Christennsen, PhD Chap. 19, 20, & 21 - Circulatory System Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy HEART 1. What kind of blood is found in the rt. atrium? (oxygenated or deoxygenated) Where does this blood come from?
Carl Christennsen, PhD Chap. 19, 20, & 21 - Circulatory System Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy HEART 1. What kind of blood is found in the rt. atrium? (oxygenated or deoxygenated) Where does this blood come from?
The ancient Babylonians, Egyptians, Indians and Chinese believed the heart was the centre of thinking and emotions
 The Concept of Mind The ancient Babylonians, Egyptians, Indians and Chinese believed the heart was the centre of thinking and emotions Hippocrates 460 BC 370 BC - Thoughts, ideas, and feelings come from
The Concept of Mind The ancient Babylonians, Egyptians, Indians and Chinese believed the heart was the centre of thinking and emotions Hippocrates 460 BC 370 BC - Thoughts, ideas, and feelings come from
The Circulatory System (p )
 The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet Name: Date: Instructions: Put the answers to each task card in the numbered boxes on the chart. 1 a) left semilunar valve / aortic valve b) blood would backflow
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet Name: Date: Instructions: Put the answers to each task card in the numbered boxes on the chart. 1 a) left semilunar valve / aortic valve b) blood would backflow
Biology Unit 3 The Human Heart P
 Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
The Mammalian Circulatory System
 The Mammalian Heart The Mammalian Circulatory System Recall: What are the 3 cycles of the mammalian circulatory system? What are their functions? What are the three main vessel types in the mammalian circulatory
The Mammalian Heart The Mammalian Circulatory System Recall: What are the 3 cycles of the mammalian circulatory system? What are their functions? What are the three main vessel types in the mammalian circulatory
Unit 10 Cardiovascular System
 Unit 10 Cardiovascular System I. Functions Deliver nutrients to cells > O 2, sugars, amino acids, lipids, ions, H 2 O... Remove waste from cells > CO 2, pathogens, toxins, lactic acid... Fight off infection
Unit 10 Cardiovascular System I. Functions Deliver nutrients to cells > O 2, sugars, amino acids, lipids, ions, H 2 O... Remove waste from cells > CO 2, pathogens, toxins, lactic acid... Fight off infection
BLOOD VESSELS. Veins and Venules take blood from the to the. Capillaries Venules vein heart Walls are than arterial walls.
 Biology 12 - Circulation - Chapter Notes Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms
Biology 12 - Circulation - Chapter Notes Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY HOMEWORK CHAPTER 11 AND 12
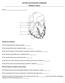 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY HOMEWORK CHAPTER 11 AND 12 Name Identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label. 2) The sinoatrial (SA) node is indicated by letter. 3) The specific chamber
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY HOMEWORK CHAPTER 11 AND 12 Name Identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label. 2) The sinoatrial (SA) node is indicated by letter. 3) The specific chamber
Questions on Transport
 Name: Questions on Transport Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topic 6.2 (The Transport System). Answer all questions. This will serve as a study guide for
Name: Questions on Transport Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topic 6.2 (The Transport System). Answer all questions. This will serve as a study guide for
Mr. Epithelium s Anatomy and Physiology Test SSSS
 Mr. Epithelium s Anatomy and Physiology Test SSSS You have 50 minutes to complete this test packet. One 8.5 x 11 cheat sheet is allowed, along with 1 non-programmable calculator dedicated to computation.
Mr. Epithelium s Anatomy and Physiology Test SSSS You have 50 minutes to complete this test packet. One 8.5 x 11 cheat sheet is allowed, along with 1 non-programmable calculator dedicated to computation.
Test Review Circulatory System Chapters
 Test Review Circulatory System Chapters 13-2010 1. The tissue that forms the tight fitting sac around the heart is the a. parietal pericardium c. myocardium b. visceral pericardium d. endocardium 2. Which
Test Review Circulatory System Chapters 13-2010 1. The tissue that forms the tight fitting sac around the heart is the a. parietal pericardium c. myocardium b. visceral pericardium d. endocardium 2. Which
Lower Secondary Science Blood Circulatory System Notes / Advanced Notes
 Lower Secondary Science Blood Circulatory System Notes / Advanced Notes Double Circulation in Mammals In mammals, there is a double circulation (i.e. blood passes through the heart twice in one complete
Lower Secondary Science Blood Circulatory System Notes / Advanced Notes Double Circulation in Mammals In mammals, there is a double circulation (i.e. blood passes through the heart twice in one complete
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System Blood vessels, heart and blood Functions Transport oxygen, nutrients, waste, hormones White blood cells fighting disease Temperature regulation Blood vessels; Arteries Arteries carry
Cardiovascular System Blood vessels, heart and blood Functions Transport oxygen, nutrients, waste, hormones White blood cells fighting disease Temperature regulation Blood vessels; Arteries Arteries carry
Blood and Heart. Student Learning Objectives:
 Blood and Heart Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major components of the blood. Identify the primary structures associated with the heart Follow the blood through the path of the circulation.
Blood and Heart Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major components of the blood. Identify the primary structures associated with the heart Follow the blood through the path of the circulation.
aliasyraf.wordpress.com
 aliasyraf.wordpress.com 1.1 Understanding the importance of having a transport system in some multicellular organisms 1.1 Understanding the importance of having a transport system in some multicellular
aliasyraf.wordpress.com 1.1 Understanding the importance of having a transport system in some multicellular organisms 1.1 Understanding the importance of having a transport system in some multicellular
Functions of Blood. Blood Vessels. Lymphatic System. Components of the Cardiovascular System. Unit 5 Cardiovascular System: Heart and Blood Vessels
 Unit 5 Cardiovascular System: Heart and Blood Vessels Components of the Cardiovascular System Heart pumps blood Blood vessels the tubes through which the blood flows Functions of Blood Blood removes wastes
Unit 5 Cardiovascular System: Heart and Blood Vessels Components of the Cardiovascular System Heart pumps blood Blood vessels the tubes through which the blood flows Functions of Blood Blood removes wastes
CIRCULATION. Cardiovascular & lymphatic systems Functions. Transport Defense / immunity Homeostasis
 CIRCULATION CIRCULATION Cardiovascular & lymphatic systems Functions Transport Defense / immunity Homeostasis 2 Types of Circulatory Systems Open circulatory system Contains vascular elements Mixing of
CIRCULATION CIRCULATION Cardiovascular & lymphatic systems Functions Transport Defense / immunity Homeostasis 2 Types of Circulatory Systems Open circulatory system Contains vascular elements Mixing of
Unit 1: Human Systems. The Circulatory System
 Unit 1: Human Systems The Circulatory System nourish all cells with oxygen, glucose, amino acids and other nutrients and carry away carbon dioxide, urea and other wastes Purposes Transport chemical messengers
Unit 1: Human Systems The Circulatory System nourish all cells with oxygen, glucose, amino acids and other nutrients and carry away carbon dioxide, urea and other wastes Purposes Transport chemical messengers
Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart
 Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart Interesting Heart Fact Capillaries are so small it takes ten of them to equal the thickness of a human hair. Review What are the 3 parts of the cardiovascular
Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart Interesting Heart Fact Capillaries are so small it takes ten of them to equal the thickness of a human hair. Review What are the 3 parts of the cardiovascular
Blood Functions. Blood and the Cardiovascular System. Blood. Plasma. Erythrocytes (RBCs) Erythrocytes (RBCs) 4/7/2017
 Blood Functions Blood and the Cardiovascular System Distribution Delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all body cells; Transport of wastes to lungs and excretory organs; Transport of hormones Regulation
Blood Functions Blood and the Cardiovascular System Distribution Delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all body cells; Transport of wastes to lungs and excretory organs; Transport of hormones Regulation
The Circulatory System. The circulatory system includes the Heart, Blood Tissue and the Blood Vessels.
 The Circulatory System The circulatory system includes the Heart, Blood Tissue and the Blood Vessels. The Circulatory System-Transport The absorption and circulation of materials throughout an organism
The Circulatory System The circulatory system includes the Heart, Blood Tissue and the Blood Vessels. The Circulatory System-Transport The absorption and circulation of materials throughout an organism
Transport in Animals. Gastrovascular cavities. Nutrients and gases can move by processes such as diffusion and active transport.
 Transport in Animals Gastrovascular cavities flatworms and cnidarians Nutrients and gases can move by processes such as diffusion and active transport. Figure 42.1 Internal transport in the cnidarian
Transport in Animals Gastrovascular cavities flatworms and cnidarians Nutrients and gases can move by processes such as diffusion and active transport. Figure 42.1 Internal transport in the cnidarian
Unit 10 ~ Learning Guide
 Unit 10 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Unit 10 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Structure and organization of blood vessels
 The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
name F septum ; D bicuspid / mitral / atrioventricular, valve ; aorta pulmonary artery K semilunar valve ; right atrium right ventricle ; [6]
![name F septum ; D bicuspid / mitral / atrioventricular, valve ; aorta pulmonary artery K semilunar valve ; right atrium right ventricle ; [6] name F septum ; D bicuspid / mitral / atrioventricular, valve ; aorta pulmonary artery K semilunar valve ; right atrium right ventricle ; [6]](/thumbs/79/79061016.jpg) Question Mark Guidance 1 (a) function letter on Fig. 1.1 name structure that separates oxygenated and deoxygenated blood structure that prevents backflow of blood from ventricle to atrium F septum ; D
Question Mark Guidance 1 (a) function letter on Fig. 1.1 name structure that separates oxygenated and deoxygenated blood structure that prevents backflow of blood from ventricle to atrium F septum ; D
The Cardiovascular System. The Structure of Blood Vessels. The Structure of Blood Vessels. The Blood Vessels. Blood Vessel Review
 The Cardiovascular System The Blood Vessels The Structure of Blood Vessels Blood Vessel Review Arteries carry blood away from the heart Pulmonary trunk to lungs Aorta to everything else Microcirculation
The Cardiovascular System The Blood Vessels The Structure of Blood Vessels Blood Vessel Review Arteries carry blood away from the heart Pulmonary trunk to lungs Aorta to everything else Microcirculation
A. Incorrect! The left ventricle receives oxygenated blood from the lungs via the left atrium.
 Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Cardiovascular System No. 1 of 10 Instruction: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully (2) Work the problems on paper as needed (3) Pick
Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Cardiovascular System No. 1 of 10 Instruction: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully (2) Work the problems on paper as needed (3) Pick
The Cardiovascular System
 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
The Function. To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body.
 The Function To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body. What makes up the circulatory system? 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood vessels Blood travels from the heart to the body
The Function To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body. What makes up the circulatory system? 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood vessels Blood travels from the heart to the body
The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle.
 The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle. From this camber, it passes through the pulmonary semilunar valve
The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle. From this camber, it passes through the pulmonary semilunar valve
Circulatory System 10.1
 1 Circulatory System 10.1 2 ARTERIES Arteries-blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart Thick walls Inner & Outer layers: connective tissue Middle layers are muscle and elastic connective tissue
1 Circulatory System 10.1 2 ARTERIES Arteries-blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart Thick walls Inner & Outer layers: connective tissue Middle layers are muscle and elastic connective tissue
P215 SPRING 2019: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Chaps 13, 14 & 15: pp , , , I. Major Functions of the Circulatory System
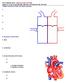 P215 SPRING 2019: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Chaps 13, 14 & 15: pp 360-390, 395-404, 410-428 433-438, 441-445 I. Major Functions of the Circulatory System 1. 2. 3. 4. II. Structure of the Heart 1. atria 2. ventricles
P215 SPRING 2019: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Chaps 13, 14 & 15: pp 360-390, 395-404, 410-428 433-438, 441-445 I. Major Functions of the Circulatory System 1. 2. 3. 4. II. Structure of the Heart 1. atria 2. ventricles
CIE Biology A-level Topic 8: Transport in mammals
 CIE Biology A-level Topic 8: Transport in mammals Notes Circulatory systems can either be open, for instance in insects, or closed, like in fish and mammals where the blood is confined to blood vessels
CIE Biology A-level Topic 8: Transport in mammals Notes Circulatory systems can either be open, for instance in insects, or closed, like in fish and mammals where the blood is confined to blood vessels
37 1 The Circulatory System
 H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
Circulatory System. Circulatory System
 Circulatory System Transportation system of the body There are two types of circulatory systems: 1. Open Circulatory System pumps blood to open ended vessels into the body cavities containing organs, then
Circulatory System Transportation system of the body There are two types of circulatory systems: 1. Open Circulatory System pumps blood to open ended vessels into the body cavities containing organs, then
7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes. Circulation
 1 7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood Vessels Sect. 3: Blood and Lymph Sect. 4: Cardiovascular Health Sect. 1:
1 7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood Vessels Sect. 3: Blood and Lymph Sect. 4: Cardiovascular Health Sect. 1:
Chapter 05 Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 05 Cardiovascular System 1 Cardiovascular System: Heart and Blood Vessels 2 Points to ponder What are the functions of the cardiovascular system? What is the anatomy of the heart? Of blood vessels,
Chapter 05 Cardiovascular System 1 Cardiovascular System: Heart and Blood Vessels 2 Points to ponder What are the functions of the cardiovascular system? What is the anatomy of the heart? Of blood vessels,
Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems
 34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems section 1 Circulatory System Before You Read Press the tips of two fingers to the inside of your wrist, at a point just below your thumb. Can you feel
34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems section 1 Circulatory System Before You Read Press the tips of two fingers to the inside of your wrist, at a point just below your thumb. Can you feel
Circulatory System Notes
 Circulatory System Notes Functions of Circulatory System A. Transports B. Transports C. Transports D. Transports E. of fluids F. G. Regulate temperature H. Blood clotting Characteristics of various blood
Circulatory System Notes Functions of Circulatory System A. Transports B. Transports C. Transports D. Transports E. of fluids F. G. Regulate temperature H. Blood clotting Characteristics of various blood
Circulation and Respiration
 Lesson 10 Circulation and Respiration Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Circulatory System: Features and Functions All circulatory systems have three major parts The heart: a pump that keeps blood
Lesson 10 Circulation and Respiration Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Circulatory System: Features and Functions All circulatory systems have three major parts The heart: a pump that keeps blood
BIOL 4350 Cardiovascular Physiology Dr. Hamilton. Using the figure above, match the following: 1. Purkinje fibers. 2. SA node. 3. AV node.
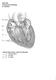 BIOL 4350 Cardiovascular Physiology Dr. Hamilton Using the figure above, match the following: 1. Purkinje fibers. 2. SA node. 3. AV node. 1 Using the figure above, match the following: 4. Atrial depolarization.
BIOL 4350 Cardiovascular Physiology Dr. Hamilton Using the figure above, match the following: 1. Purkinje fibers. 2. SA node. 3. AV node. 1 Using the figure above, match the following: 4. Atrial depolarization.
Chapter 05 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 05 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 05 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease
 Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease Mammals are too large to rely on diffusion. They need a circulatory system to move substances around the body. Blood moves down pressure gradients, from high to
Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease Mammals are too large to rely on diffusion. They need a circulatory system to move substances around the body. Blood moves down pressure gradients, from high to
