The Circulatory System
|
|
|
- Mavis Davidson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Circulatory System
2 Cardiovascular System Facts The average person has nearly 100,000 km of blood vessels running through them. The larger the organism, the slower the heart beats (a woman s heart will beat faster than a man s) A blue whale s heart beats 5 times per minute while a hummingbird s beats closer to 1400 times Blood in your veins is not blue! They look blue due to the way the light is absorbed and reflected in your skin. Your heart produces enough pressure to shoot blood nearly 30 feet.
3 The Heart The heart is the pump in our body which stimulates the movement of the blood. In an adult, it is about the size of a fist. It is located roughly in the middle of the chest between the lungs. It is composed of 4 chambers.
4 The Heart The four chambers of the heart are: Right atrium Right ventricle Left atrium Left ventricle
5 The Heart
6 The Heart The atrium and ventricle on the respective sides are directly linked The left and the right side have no direct link. They are separated by a partition, the septum. For the left and right side, blood flows into the heart through the atrium and is pushed out through the ventricle.
7 The Heart To prevent blood from flowing backwards in the heart, valves are present in the heart These valves are called the atrioventricular valves. Without these, blood would flow backwards through the heart.
8 The Heart There are 5 major blood vessels connected to the heart. Superior and inferior vena cava Pulmonary vein Pulmonary artery Aorta
9 The Heart
10 Function of the Heart The heart pumps blood to the entire body First phase of a heart beat is diastole The heart is at rest and the atriums fill with blood. Next the atriums contract, pushing blood into the ventricles. The final phase is when the ventricles contract, pushing blood out into the arteries. This phase is called systole.
11 The Heart
12 Blood Pressure When you take your blood pressure, you always get 2 numbers The systolic pressure it he higher number and indicate the pressure caused by the contraction of the heart The diastolic pressure is the pressure between beats. It is better to have lower blood pressure, within reason
13 Your Pulse When taking your pulse, the pulse you feel is the systole. An average heart beats around 75 times per minute. This number varies depending on age, gender, physical fitness and physical activity.
14 Types of circulation. The heart is a double pump. There are two circulatory routes which the blood takes. The right side is responsible for the pulmonary circulation. The left side is responsible for the systemic circulation.
15 Circulatory Routes
16 Pulmonary Circulation This circulation brings blood to and away from the lungs. Right side of the heart is responsible for this circulation. Blood is pushed out of the heart by the right ventricle through the pulmonary artery. The blood then passes through the capillaries and then returns to the heart through the pulmonary vein.
17 Systemic Circulation This is the circulation which sends blood out to the body systems (except the lungs). The blood is pushed out the of heart by the left ventricle through the aorta. The aorta splits and sends blood out through different parts of the body. The blood then gives its oxygen, nutrients and other goodies to the body tissues through the capillaries. The blood then returns to the heart through the veins.
18 Blood Vessels Now that we understand how the heart works and we know where the blood goes, let s talk about the pathways it takes. There are three types of blood vessels in our bodies. Arteries Veins Capillaries
19 Arteries Arteries are the largest blood vessels in our bodies They carry blood from the heart to other parts of the body. Their walls are very thick. This helps them withstand high pressures.
20 Arteries
21 Veins Veins carry blood back to the heart from the body systems. They are thinner than arteries. They also have small valves in them to prevent the blood from falling back down. The pressure is lower than in arteries.
22 Veins
23 Veins
24 Capillaries Capillaries are small vessels which are only 1 cell thin. This is the site of gas and nutrient exchange. They are the bridge between the veins and arteries. Where else have we seen capillaries?
25 Capillaries
26 Comparing Blood Vessels
27 Comparing Blood Vessels
28 Diseases of the Heart We are going to discuss 5 diseases of the heart and vessels. Arteriosclerosis Atherosclerosis Angina Heart attack Stroke
29 Arteriosclerosis This is a condition where the arteries thicken and become harder. This causes them to be less flexible. Less flexible means that it puts more pressure on the heart. This is caused by age, smoking, bad diet, drugs and a poor lifestyle There are currently no proven medical treatments for this condition as of yet.
30 Atherosclerosis This conditions is caused by a build up of plaque inside the arteries. These plaques are caused by too much fat and cholesterol in an individuals diet. Treatments are improved diet and exercise. There are some medications which can be taken, but exercise and diet at the first to be tried.
31 Atherosclerosis
32 Angina This is also referred to as angina pectoris. This is a sharp chest pain. This is caused by ischemia to the heart, which means a lack of oxygen to the heart. This is caused by a blockage of the coronary artery, meaning atherosclerosis of the arteries around the heart. Treatments include nitroglycerin, a strong vasodialator.
33 Angina Treatments include nitroglycerin, a strong vasodialator. A vasodilator is something which dilates, opens up, the blood vessels. This allows more blood and thus more oxygen through. Since the cause is blockages of the arteries, taking care of those blockages is the first priority. Again, diet and exercise!
34 Heart Attack This is also called a myocardial infarction. A heart attack is caused by a lack of oxygen to the heart. This causes part of the heart to die. The lack of oxygen is caused by a blockage in the coronary arteries (the vessels which feed the heart).
35 Heart Attack Symptoms of a heart attack are chest pain, numbness in either arms, nausea, shortness of breathe, etc. Nitroglycerin can be administered to help prevent further damage. Without needing to said, heart attacks can be quite deadly. The older you are when you have a heart attack, the more likely you are to survive.
36 Heart Attack
37 Stroke A stroke is caused by a blood vessel in the brain either bursting or becoming blocked. This can lead to loss of brain function, ability to move one or more limbs, loss of speech or many other past abilities. This is due to the lack of oxygen to the brain. The effects could be permanent or temporary and there is no way to know.
38 Stroke Risk factors for a stroke are old age, high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol and smoking. In this case, the smoking can lead to arteriosclerosis which makes the vessels more prone to breaking. Prevention is the best defense against strokes. Once a patient is cleared of the danger of a stroke, the recovery is a long process.
39 Stroke
40 Circulatory System Facts The heart beats around 3 billion times in the averages person's life. About 8 million blood cells die in the human body every second, and the same number are born each second. It takes about 20 seconds for a red blood cell to circle the whole body. Red blood cells make approximately 250,000 round trips of the body. Red blood cells may live for about 4 months circulating throughout the body.
41 Blood Blood is composed of different constituents. It is also the only liquid tissue in the body. A man s body contains approximately 5-6 L of blood and a woman s contains 4-5 L. Although it seems like a homogeneous mixture, blood is a solution of components suspended in a liquid.
42 Blood after centrifugation
43 Plasma The liquid component of the blood. It is 90% water in which has substances dissolved into it such as: Hormones Nutrients Antibodies Waste It is used for transportations of substances.
44 Blood Plasma
45 Blood Constituents Red Blood Cells are red-coloured cells in the form of a biconcave disk. They have no nucleus and very few organelles. There are about 4-6 billion per ml They responsible for carrying oxygen through the use of hemoglobin.
46 Red Blood Cells
47 Blood Constituents White blood cells are transparent cells. There about 4-11 million per ml of blood. Their role in the body is for our immune system. They seek out and attack intruders in our bodies.
48 Types of White Blood Cells
49 Blood Constituents Platelets are irregular cell fragments. There are between million per ml of blood. They help in blood clotting. With a low platelet count, one could bleed to death from a simple paper cut.
50 Platelets
51 Blood Types Humans have 4 different blood types. A B AB O The blood type is determined by surface proteins on the red blood cells. There is also one other substance on their surface The Rh factor
52 Rh Factor The Rh factor is known as the rhesus factor because it was first discovered on the red blood of rhesus monkeys, also known as macaques.
53 Surface Proteins There are proteins on the surface of the red blood cells. The red blood cells are what determine an individuals blood type. There are three different surface proteins A B Rh
54 Surface protein What s your blood type? Blood Type A+ A- B+ B- AB+ AB- O+ O- A X X X X B X X X X Rh X X X X
55 Blood Types in Quebec Distribution of types A, B, AB and O Distribition of Rh Positive and Rh Negative Rh Negati ve 15% O 46% A 42% AB 3% B 9% Rh Positi ve 85%
56 Distribution of the Eight Blood Types in Quebec Distribution of the Eight Blood Types AB+ 3% B+ 7% O- 7% B- 3% A- 6% AB- 1% O+ 39% A+ 36%
57 Blood Transfusions A blood transfusion entails the injection of blood into a person. A donor is defined as the person who gives blood for the purpose of a transfusion A recipient is a person who receives blood from a transfusion
58 Blood Transfusions Before the discovery of blood types in 1902, many transfusions resulted in the death of the recipient. We are well aware of the rules of blood transfusion. What do you think this rule is?
59 The Blood Rule Remember the surface proteins on the red blood cells. Those are the key to safe blood transfusions. To safely receive blood, you must not receive something you don t already have. You cannot receive something which you don t have!
60 Recipient Blood Compatibility Donor O- O+ A- A+ B- B+ AB- AB+ O- X O+ X X A- X X A+ X X X X B- X X B+ X X X X AB- X X X X AB+ X X X X X X X X
61 Blood Compatibility Remember, way for a blood transfusion to work safely the recipient must not receive something which they do not have. If you are blood type A-, you can t receive B or +. This means that O-, which is empty is the universal donor. AB+ is the universal recipient because it already has everything.
How does the Circulatory System maintain
 How does the Circulatory System maintain -It supplies cells throughout the body with oxygen and nutrients while also ridding them of wastes. Transports materials such as: (to cells) (to attack foreign
How does the Circulatory System maintain -It supplies cells throughout the body with oxygen and nutrients while also ridding them of wastes. Transports materials such as: (to cells) (to attack foreign
Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93)
 Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System
 Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System This color-enhanced image was made with an electron microscope, so the objects it depicts are extremely small. Do you know what they are? This incredible photo shows red
Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System This color-enhanced image was made with an electron microscope, so the objects it depicts are extremely small. Do you know what they are? This incredible photo shows red
Heart Facts. The average adult heart beats 72 times a min 100,000 times a day 3,600,000 times a year 2.5 billion times during a lifetime.
 Circulatory System Heart Facts The average adult heart beats 72 times a min 100,000 times a day 3,600,000 times a year 2.5 billion times during a lifetime. Heart Facts Weighs 11 oz A healthy heart pumps
Circulatory System Heart Facts The average adult heart beats 72 times a min 100,000 times a day 3,600,000 times a year 2.5 billion times during a lifetime. Heart Facts Weighs 11 oz A healthy heart pumps
The Function. To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body.
 The Function To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body. What makes up the circulatory system? 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood vessels Blood travels from the heart to the body
The Function To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body. What makes up the circulatory system? 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood vessels Blood travels from the heart to the body
Cardiovascular System
 Component 3-Terminology in Healthcare and Public Health Settings Unit 5-Cardiovascular System This material was developed by The University of Alabama at Birmingham, funded by the Department of Health
Component 3-Terminology in Healthcare and Public Health Settings Unit 5-Cardiovascular System This material was developed by The University of Alabama at Birmingham, funded by the Department of Health
Chapter 16: Circulation
 Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system. What are the function of the cardiovascular system? Arteries and arterioles:
 5.1 Overview of the cardiovascular system Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system Includes the heart and blood vessels Brings nutrients to cells and helps get rid of wastes Blood is refreshed in the lung, kidneys,
5.1 Overview of the cardiovascular system Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system Includes the heart and blood vessels Brings nutrients to cells and helps get rid of wastes Blood is refreshed in the lung, kidneys,
THE HEART. Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration
 THE HEART Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration The Circulatory System Also called the Cardiovascular System Circulates blood in the body Transports nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood
THE HEART Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration The Circulatory System Also called the Cardiovascular System Circulates blood in the body Transports nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood
Terminology in Health Care and Public Health Settings. Cardiovascular System. Cardiovascular System 8/3/2010. Version 1/Fall 2010
 Terminology in Health Care and Public Health Settings Unit 5 1 Also referred to as the Circulatory system Functions Distribute blood to all areas of body Delivery of needed d substances to cells Removal
Terminology in Health Care and Public Health Settings Unit 5 1 Also referred to as the Circulatory system Functions Distribute blood to all areas of body Delivery of needed d substances to cells Removal
Your heart is a muscular pump about the size of your fist, located
 How Your Heart Works Your heart is a muscular pump about the size of your fist, located slightly to the left and behind your breastbone. Its function is to pump blood throughout your body. As your heart
How Your Heart Works Your heart is a muscular pump about the size of your fist, located slightly to the left and behind your breastbone. Its function is to pump blood throughout your body. As your heart
Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Blood 10/22/2012
 Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
Blood Functions. Blood and the Cardiovascular System. Blood. Plasma. Erythrocytes (RBCs) Erythrocytes (RBCs) 4/7/2017
 Blood Functions Blood and the Cardiovascular System Distribution Delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all body cells; Transport of wastes to lungs and excretory organs; Transport of hormones Regulation
Blood Functions Blood and the Cardiovascular System Distribution Delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all body cells; Transport of wastes to lungs and excretory organs; Transport of hormones Regulation
Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation
 1 Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Section 9.1 Homeostasis: Life in the Balance Outcomes: I can explain homeostasis I can describe the importance of homeostasis to living things I can explain the
1 Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Section 9.1 Homeostasis: Life in the Balance Outcomes: I can explain homeostasis I can describe the importance of homeostasis to living things I can explain the
Cells & Systems The Circulatory System
 Cells & Systems The Circulatory System The Circulatory System What does it do? Your body s transportation network Transports Oxygen (O) Transports Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 ) Removes Waste products Delivers
Cells & Systems The Circulatory System The Circulatory System What does it do? Your body s transportation network Transports Oxygen (O) Transports Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 ) Removes Waste products Delivers
2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system
 2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system Essential questions What are the structures of blood? What are the structures of the circulatory system? circulatory system 2 Structures of the circulatory
2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system Essential questions What are the structures of blood? What are the structures of the circulatory system? circulatory system 2 Structures of the circulatory
The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide.
 Section 1: The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What
Section 1: The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What
Circulation.notebook March 07, Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium. Oct 11 3:27 PM. Circulatory System p
 Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Circulatory system The heart Blood Blood Pressure Circulatory Disorders Oct 11 3:27 PM Circulatory System p.304 307 If an organism is small and flat it can transport
Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Circulatory system The heart Blood Blood Pressure Circulatory Disorders Oct 11 3:27 PM Circulatory System p.304 307 If an organism is small and flat it can transport
The Cardiovascular System
 CHAPTER 16 1 SECTION Circulation and Respiration The Cardiovascular System California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.6.j BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these
CHAPTER 16 1 SECTION Circulation and Respiration The Cardiovascular System California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.6.j BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these
2. What makes up the most of your blood? least of your blood? 1. Look like red discs, have a pale center, no nucleus, similar in size
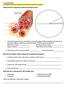 I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System Blood vessels, heart and blood Functions Transport oxygen, nutrients, waste, hormones White blood cells fighting disease Temperature regulation Blood vessels; Arteries Arteries carry
Cardiovascular System Blood vessels, heart and blood Functions Transport oxygen, nutrients, waste, hormones White blood cells fighting disease Temperature regulation Blood vessels; Arteries Arteries carry
Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process:
 Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: a. erythrocytes b. leukocytes c. melanocytes d. thrombocytes Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process: a. erythrocytes
Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: a. erythrocytes b. leukocytes c. melanocytes d. thrombocytes Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process: a. erythrocytes
The Circulatory System (p )
 The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
Learning Objectives; 1. Identify the key features of the cardiovascular system. 2. Describe the function of the cardiovascular system.
 Learning Objectives; 1. Identify the key features of the cardiovascular system. 2. Describe the function of the cardiovascular system. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yaxna8lmoiy The Circulatory System
Learning Objectives; 1. Identify the key features of the cardiovascular system. 2. Describe the function of the cardiovascular system. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yaxna8lmoiy The Circulatory System
Glossary: The Cardiovascular System
 This glossary includes terms that have been introduced in Lesson 14. Student Resource 14.14 Glossary: The Cardiovascular System Anatomy Terms aorta Large artery that transports blood from the left ventricle
This glossary includes terms that have been introduced in Lesson 14. Student Resource 14.14 Glossary: The Cardiovascular System Anatomy Terms aorta Large artery that transports blood from the left ventricle
Circulatory System. Circulatory System
 Circulatory System Transportation system of the body There are two types of circulatory systems: 1. Open Circulatory System pumps blood to open ended vessels into the body cavities containing organs, then
Circulatory System Transportation system of the body There are two types of circulatory systems: 1. Open Circulatory System pumps blood to open ended vessels into the body cavities containing organs, then
Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels
 Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels Most animals have a closed blood system. The blood flows continuously in vessels back to the heart. In an open system the blood is pumped into open ended tubes and
Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels Most animals have a closed blood system. The blood flows continuously in vessels back to the heart. In an open system the blood is pumped into open ended tubes and
Unit 1: Human Systems. The Circulatory System
 Unit 1: Human Systems The Circulatory System nourish all cells with oxygen, glucose, amino acids and other nutrients and carry away carbon dioxide, urea and other wastes Purposes Transport chemical messengers
Unit 1: Human Systems The Circulatory System nourish all cells with oxygen, glucose, amino acids and other nutrients and carry away carbon dioxide, urea and other wastes Purposes Transport chemical messengers
1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary.
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Science Matters Chapter 8 Introduction Living things need a transport system to carry things around the body. In humans its called The Circulatory system. The parts of the system
The Circulatory System Science Matters Chapter 8 Introduction Living things need a transport system to carry things around the body. In humans its called The Circulatory system. The parts of the system
Biology Unit 3 The Human Heart P
 Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions. KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells.
 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
MESA DAY CONTEST RULES
 FOR CENTER DIRECTOR S USE ONLY ANSWERS MODEL SCIENCE THE HEART High School All Grades Students MUST be prepared to answer each question with a complete sentence or sentences. 1. What is the size of the
FOR CENTER DIRECTOR S USE ONLY ANSWERS MODEL SCIENCE THE HEART High School All Grades Students MUST be prepared to answer each question with a complete sentence or sentences. 1. What is the size of the
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels
 Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels 3.2 Learning Objectives 3.2.2 Organisational Complexity of the human 1. Describe the structures and organisation of tissues in the closed circulatory system. 2. Discuss
Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels 3.2 Learning Objectives 3.2.2 Organisational Complexity of the human 1. Describe the structures and organisation of tissues in the closed circulatory system. 2. Discuss
It s Totally Tubular, Dude!
 It s Totally Tubular, Dude! Objective: To learn the structure and function of the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Bell Work: For the following, place the items in order from most simple to most complex:
It s Totally Tubular, Dude! Objective: To learn the structure and function of the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Bell Work: For the following, place the items in order from most simple to most complex:
Section 12.1 Your Cardiovascular System
 Objectives Describe the main functions of the cardiovascular system. Trace the pathway of blood through the heart. Identify three types of blood vessels and the four components of blood. Slide 1 of 31
Objectives Describe the main functions of the cardiovascular system. Trace the pathway of blood through the heart. Identify three types of blood vessels and the four components of blood. Slide 1 of 31
1. Label the Diagram using the following terms: artery, arterioles, vein, venules, capillaries, valve, inner wall, middle wall, outer wall
 Bio 20 Ms. Nyboer Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, and the Heart Structure and Function Workbook Use your textbook (Ch. 10) and notes to fill in this workbook Part A: Arteries, Veins, Capillaries 1. Label
Bio 20 Ms. Nyboer Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, and the Heart Structure and Function Workbook Use your textbook (Ch. 10) and notes to fill in this workbook Part A: Arteries, Veins, Capillaries 1. Label
Types of circulatory systems
 Types of circulatory systems Open system Mostly invertebrates Low pressure Haemocoel Suitable for small organisms Closed system Vertebrates High pressure Blood remains in blood vessels Separate tissue
Types of circulatory systems Open system Mostly invertebrates Low pressure Haemocoel Suitable for small organisms Closed system Vertebrates High pressure Blood remains in blood vessels Separate tissue
The Heart. Made up of 3 different tissue: cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and connective tissue.
 The Heart The Heart Made up of 3 different tissue: cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and connective tissue. Your heart pumps with a regular beat (Heart Rate) Your heart rate can change depending on
The Heart The Heart Made up of 3 different tissue: cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and connective tissue. Your heart pumps with a regular beat (Heart Rate) Your heart rate can change depending on
The Circulatory System. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview The Circulatory System
 33.1 THINK ABOUT IT More than one-third of the 1.2 million Americans who suffer a heart attack each year die. This grim evidence shows that the heart and the circulatory system it powers are vital to life.
33.1 THINK ABOUT IT More than one-third of the 1.2 million Americans who suffer a heart attack each year die. This grim evidence shows that the heart and the circulatory system it powers are vital to life.
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet Name: Date: Instructions: Put the answers to each task card in the numbered boxes on the chart. 1 a) left semilunar valve / aortic valve b) blood would backflow
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet Name: Date: Instructions: Put the answers to each task card in the numbered boxes on the chart. 1 a) left semilunar valve / aortic valve b) blood would backflow
Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems
 34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems section 1 Circulatory System Before You Read Press the tips of two fingers to the inside of your wrist, at a point just below your thumb. Can you feel
34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems section 1 Circulatory System Before You Read Press the tips of two fingers to the inside of your wrist, at a point just below your thumb. Can you feel
HEART DISEASE HEART CONDITIONS, RISKS AND PROTECTION
 Spotlight on Health 2017 HEART DISEASE HEART CONDITIONS, RISKS AND PROTECTION Heart disease is the leading cause of death for both men and women worldwide, accounting for over 17 million deaths per year.
Spotlight on Health 2017 HEART DISEASE HEART CONDITIONS, RISKS AND PROTECTION Heart disease is the leading cause of death for both men and women worldwide, accounting for over 17 million deaths per year.
OB16 Demonstrate the effect of exercise and rest on pulse and breathing rate and appreciate that a balance of each promotes good health
 Biology: 6. The Circulation System Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier Syllabus OB13 Describe the function and composition of blood
Biology: 6. The Circulation System Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier Syllabus OB13 Describe the function and composition of blood
Vocabulary. Heart attack- התקף לב (hetkef lev)
 Vocabulary Cardiovascular (CV) System- מערכת לב וכלי דם (ma arechet lev v klay dahm) Blood- דם (dahm) Blood vessels- כלי דם (klay dahm) Artery/Arteries- עורק/ עורקים (ohrek/ohrakeem) Vein/Veins- וריד/ורידים
Vocabulary Cardiovascular (CV) System- מערכת לב וכלי דם (ma arechet lev v klay dahm) Blood- דם (dahm) Blood vessels- כלי דם (klay dahm) Artery/Arteries- עורק/ עורקים (ohrek/ohrakeem) Vein/Veins- וריד/ורידים
The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle.
 The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle. From this camber, it passes through the pulmonary semilunar valve
The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle. From this camber, it passes through the pulmonary semilunar valve
2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system
 2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system 2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system Essential questions: What are the functions of blood? What are
2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system 2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system Essential questions: What are the functions of blood? What are
TRANSPORT SYSTEM IN LIVING SMPK PENABUR JAKARTA
 TRANSPORT SYSTEM IN LIVING ORGANISM SMPK PENABUR JAKARTA Part 1 PLANT TRANSPORTATION SYSTEM A. PLANT TRANSPORT SYSTEM Transport tissue? Where? A. 1. Water Transport Water liquid matter Affected by environment
TRANSPORT SYSTEM IN LIVING ORGANISM SMPK PENABUR JAKARTA Part 1 PLANT TRANSPORTATION SYSTEM A. PLANT TRANSPORT SYSTEM Transport tissue? Where? A. 1. Water Transport Water liquid matter Affected by environment
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY
 TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for
 Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for hyperlipidemia! Agenda! - Review objectives for 6.2! - Video of circulatory
Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for hyperlipidemia! Agenda! - Review objectives for 6.2! - Video of circulatory
Structure and organization of blood vessels
 The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
2. What makes up the most of your blood? least of your blood? 1. Look like red discs, have a pale center, no nucleus, similar in size
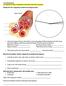 .I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
.I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
7 ANIMALS Blood Vessels.notebook. January 11, Human Blood Vessels
 Human Blood Vessels 1 Arteries All arteries take blood AWAY from the heart, and most arteries carry oxygenated blood. The one exception is the PULMONARY ARTERY which carries de oxygenated blood to the
Human Blood Vessels 1 Arteries All arteries take blood AWAY from the heart, and most arteries carry oxygenated blood. The one exception is the PULMONARY ARTERY which carries de oxygenated blood to the
The Cardiovascular. Parts and Functions
 The Cardiovascular Parts and Functions Parts The cardiovascular system consists of 3 major parts that work together. 1- Heart 2- Lungs 3- Blood Vessels Blood Vessels There are blood vessels that carry
The Cardiovascular Parts and Functions Parts The cardiovascular system consists of 3 major parts that work together. 1- Heart 2- Lungs 3- Blood Vessels Blood Vessels There are blood vessels that carry
The Circulatory System. The circulatory system includes the Heart, Blood Tissue and the Blood Vessels.
 The Circulatory System The circulatory system includes the Heart, Blood Tissue and the Blood Vessels. The Circulatory System-Transport The absorption and circulation of materials throughout an organism
The Circulatory System The circulatory system includes the Heart, Blood Tissue and the Blood Vessels. The Circulatory System-Transport The absorption and circulation of materials throughout an organism
Lecture 8. Heart and Circulatory System. Lecture 8
 Lecture 8 Heart and Circulatory System Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Blood 3. Blood Vessels & Blood Pressure 4. The Heart 5. Cardiovascular (Circulatory) System 2 1 Circulatory System Function 1. Transport
Lecture 8 Heart and Circulatory System Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Blood 3. Blood Vessels & Blood Pressure 4. The Heart 5. Cardiovascular (Circulatory) System 2 1 Circulatory System Function 1. Transport
The circulatory system
 The circulatory system Key words Vessels heart blood plasma platelets haemoglobin To engulf arteries capillaries veins venules lymphocytes Atrium / - a ventricle tricuspid bicuspid cardiac coronary Humans
The circulatory system Key words Vessels heart blood plasma platelets haemoglobin To engulf arteries capillaries veins venules lymphocytes Atrium / - a ventricle tricuspid bicuspid cardiac coronary Humans
Circulation. Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body
 Circulation Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body Heart = muscular organ about the size of your fist which pumps blood.
Circulation Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body Heart = muscular organ about the size of your fist which pumps blood.
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Key Questions What are the functions of the circulatory system? How does the heart pump blood through the body? What are three types of blood vessels? Vocabulary myocardium atrium
The Circulatory System Key Questions What are the functions of the circulatory system? How does the heart pump blood through the body? What are three types of blood vessels? Vocabulary myocardium atrium
7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes. Circulation
 1 7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood Vessels Sect. 3: Blood and Lymph Sect. 4: Cardiovascular Health Sect. 1:
1 7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood Vessels Sect. 3: Blood and Lymph Sect. 4: Cardiovascular Health Sect. 1:
Monday 14 th May The Body Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 10 Cardio-Respiratory System
 Monday 14 th May 2018 The Body Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 10 Cardio-Respiratory System Homework 1. What is the function of the cardiovascular system? 2. List the main components of blood and describe
Monday 14 th May 2018 The Body Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 10 Cardio-Respiratory System Homework 1. What is the function of the cardiovascular system? 2. List the main components of blood and describe
As a courtesy to your fellow classmates please refrain from talking, beating, or snoring. And Now Our Feature Presentation.
 As a courtesy to your fellow classmates please refrain from talking, beating, or snoring. And Now Our Feature Presentation. Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood
As a courtesy to your fellow classmates please refrain from talking, beating, or snoring. And Now Our Feature Presentation. Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood
Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1 -
 Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1-2. Organs of a closed circulatory system: A. Have valves a. Arteriole B. Regulate blood flow b. Artery C. Lead to heart
Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1-2. Organs of a closed circulatory system: A. Have valves a. Arteriole B. Regulate blood flow b. Artery C. Lead to heart
Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes
 Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes Functions of the Circulatory System The circulatory system functions mainly as the body s transport system. It transports: o Oxygen o Nutrients o Cell waste o
Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes Functions of the Circulatory System The circulatory system functions mainly as the body s transport system. It transports: o Oxygen o Nutrients o Cell waste o
The Circulatory System:
 The Circulatory System: The Body s Transport System The Circulatory System! What is the CIRCULATORY SYSTEM? A HIGHWAY NETWORK that LINKS all parts of your body. Consists of the HEART, BLOOD VESSELS, and
The Circulatory System: The Body s Transport System The Circulatory System! What is the CIRCULATORY SYSTEM? A HIGHWAY NETWORK that LINKS all parts of your body. Consists of the HEART, BLOOD VESSELS, and
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System answers to worksheet will either be on the presentation or video By: Lanya King, Geianah Shaw,and Heidi Puerta The Functions of the Circulatory System Respiration- delivers oxygen
The Circulatory System answers to worksheet will either be on the presentation or video By: Lanya King, Geianah Shaw,and Heidi Puerta The Functions of the Circulatory System Respiration- delivers oxygen
Circulatory System. Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. unless otherwise noted. Circulatory System 1
 Circulatory System Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. unless otherwise noted Circulatory System 1 Circulatory System Circulatory system = Cardiovascular system
Circulatory System Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. unless otherwise noted Circulatory System 1 Circulatory System Circulatory system = Cardiovascular system
The Mammalian Circulatory System
 The Mammalian Heart The Mammalian Circulatory System Recall: What are the 3 cycles of the mammalian circulatory system? What are their functions? What are the three main vessel types in the mammalian circulatory
The Mammalian Heart The Mammalian Circulatory System Recall: What are the 3 cycles of the mammalian circulatory system? What are their functions? What are the three main vessel types in the mammalian circulatory
37 1 The Circulatory System
 H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
Chapter 12. Capillaries. Circulation. The circulatory system connects with all body tissues
 Chapter 12 Circulation The circulatory system connects with all body s In many animals, microscopic blood vessels called capillaries Form an intricate network among the Red blood cell song Figure 23.1A
Chapter 12 Circulation The circulatory system connects with all body s In many animals, microscopic blood vessels called capillaries Form an intricate network among the Red blood cell song Figure 23.1A
The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
 The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Lesson 1: What is a Body System? Cells - smallest parts - billions in the body - can have special jobs Tissues - similar cells grouped together - muscle
The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Lesson 1: What is a Body System? Cells - smallest parts - billions in the body - can have special jobs Tissues - similar cells grouped together - muscle
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Some Fun Facts The left side of the heart contains oxygenated blood whereas the right side has de-oxygenated blood. One drop of blood has about 5 million red blood cells and 12 thousand
The Circulatory System Some Fun Facts The left side of the heart contains oxygenated blood whereas the right side has de-oxygenated blood. One drop of blood has about 5 million red blood cells and 12 thousand
Hierarchy of Biological Organization
 Hierarchy of Biological Organization Transport & Exchange (Circulation & Respiration) Cardiovascular System - transports materials What materials? Components of Blood Read about The Components of the Blood
Hierarchy of Biological Organization Transport & Exchange (Circulation & Respiration) Cardiovascular System - transports materials What materials? Components of Blood Read about The Components of the Blood
The Heart. Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet
 The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
Lower Secondary Science Blood Circulatory System Notes / Advanced Notes
 Lower Secondary Science Blood Circulatory System Notes / Advanced Notes Double Circulation in Mammals In mammals, there is a double circulation (i.e. blood passes through the heart twice in one complete
Lower Secondary Science Blood Circulatory System Notes / Advanced Notes Double Circulation in Mammals In mammals, there is a double circulation (i.e. blood passes through the heart twice in one complete
Cardiovascular System- Heart. Miss Wheeler Unit 8
 Cardiovascular System- Heart Miss Wheeler Unit 8 Overview CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM heart vessels Made up of heart, blood vessels, and blood Functions Heart- pump blood Vessels- (veins, arteries, capillaries)
Cardiovascular System- Heart Miss Wheeler Unit 8 Overview CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM heart vessels Made up of heart, blood vessels, and blood Functions Heart- pump blood Vessels- (veins, arteries, capillaries)
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
Level 2 Anatomy and Physiology Bite size revision. Respiratory System. The order of the passage of oxygen into the body (inhalation/inspiration) is: -
 Respiratory System Function of the respiratory system The lungs are located in the chest cavity and their function is to intake oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body. Structure of the respiratory
Respiratory System Function of the respiratory system The lungs are located in the chest cavity and their function is to intake oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body. Structure of the respiratory
Cardiovascular System and Health. Chapter 15
 Cardiovascular System and Health Chapter 15 Cardiovascular Disease Leading cause of death in U.S. Claims 1 life every 43 seconds Often, the first sign is a fatal heart attack Death Rates #1 CVD #2 Cancer
Cardiovascular System and Health Chapter 15 Cardiovascular Disease Leading cause of death in U.S. Claims 1 life every 43 seconds Often, the first sign is a fatal heart attack Death Rates #1 CVD #2 Cancer
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems. Chapter 37: Biology II
 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Chapter 37: Biology II The Circulatory System Larger organisms cannot rely on diffusion to move oxygen, nutrients and wastes through cells The Circulatory System Closed
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Chapter 37: Biology II The Circulatory System Larger organisms cannot rely on diffusion to move oxygen, nutrients and wastes through cells The Circulatory System Closed
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies
 Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart
 Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart Interesting Heart Fact Capillaries are so small it takes ten of them to equal the thickness of a human hair. Review What are the 3 parts of the cardiovascular
Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart Interesting Heart Fact Capillaries are so small it takes ten of them to equal the thickness of a human hair. Review What are the 3 parts of the cardiovascular
CIRCULATION. Cardiovascular & lymphatic systems Functions. Transport Defense / immunity Homeostasis
 CIRCULATION CIRCULATION Cardiovascular & lymphatic systems Functions Transport Defense / immunity Homeostasis 2 Types of Circulatory Systems Open circulatory system Contains vascular elements Mixing of
CIRCULATION CIRCULATION Cardiovascular & lymphatic systems Functions Transport Defense / immunity Homeostasis 2 Types of Circulatory Systems Open circulatory system Contains vascular elements Mixing of
Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages )
 Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages 943 950) Key Concepts What are the structures of the circulatory system? What are the three types of blood vessels
Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages 943 950) Key Concepts What are the structures of the circulatory system? What are the three types of blood vessels
Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages )
 Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages 943 950) What are the structures of the circulatory system? What are the three types of blood vessels in the circulatory
Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages 943 950) What are the structures of the circulatory system? What are the three types of blood vessels in the circulatory
Circulatory Systems. All cells need to take in nutrients and expel metabolic wastes.
 Circulatory Systems All cells need to take in nutrients and expel metabolic wastes. Single celled organisms: nutrients from the environment can diffuse (or be actively transported) directly in to the cell
Circulatory Systems All cells need to take in nutrients and expel metabolic wastes. Single celled organisms: nutrients from the environment can diffuse (or be actively transported) directly in to the cell
Blood flows away from the heart in arteries, to the capillaries and back to the heart in the veins
 Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
Introduction. Every organism must exchange materials and energy with its environment, and this exchange ultimately occurs at the cellular level.
 Introduction Every organism must exchange materials and energy with its environment, and this exchange ultimately occurs at the cellular level. Cells live in aqueous environments. The resources that they
Introduction Every organism must exchange materials and energy with its environment, and this exchange ultimately occurs at the cellular level. Cells live in aqueous environments. The resources that they
AP2 Lab 3 Coronary Vessels, Valves, Sounds, and Dissection
 AP2 Lab 3 Coronary Vessels, Valves, Sounds, and Dissection Project 1 - BLOOD Supply to the Myocardium (Figs. 18.5 &18.10) The myocardium is not nourished by the blood while it is being pumped through the
AP2 Lab 3 Coronary Vessels, Valves, Sounds, and Dissection Project 1 - BLOOD Supply to the Myocardium (Figs. 18.5 &18.10) The myocardium is not nourished by the blood while it is being pumped through the
NHS Training for Physiotherapy Support Workers. Workbook 12 The cardiovascular system
 NHS Training for Physiotherapy Support Workers Workbook 12 The cardiovascular system Contents Workbook 12 The cardiovascular system 1 12.1 Aim 3 12.2 Learning outcomes 3 12.3 The cardiovascular system
NHS Training for Physiotherapy Support Workers Workbook 12 The cardiovascular system Contents Workbook 12 The cardiovascular system 1 12.1 Aim 3 12.2 Learning outcomes 3 12.3 The cardiovascular system
10. Thick deposits of lipids on the walls of blood vessels, called, can lead to serious circulatory issues. A. aneurysm B. atherosclerosis C.
 Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Cardiovascular Disease
 Cardiovascular Disease Chapter 15 Introduction Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death in the U.S. One American dies from CVD every 33 seconds Nearly half of all Americans will die from
Cardiovascular Disease Chapter 15 Introduction Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death in the U.S. One American dies from CVD every 33 seconds Nearly half of all Americans will die from
KS4 Physical Education
 KS4 Physical Education The Circulatory System These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities created
KS4 Physical Education The Circulatory System These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities created
Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders
 Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders Interesting Heart Facts The Electrocardiograph (ECG) was invented in 1902 by Willem Einthoven Dutch Physiologist. This test is still used to evaluate
Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders Interesting Heart Facts The Electrocardiograph (ECG) was invented in 1902 by Willem Einthoven Dutch Physiologist. This test is still used to evaluate
Cardiovascular and Circulatory System The Heart and Blood Vessels
 Cardiovascular and Circulatory System The Heart and Blood Vessels Circulatory Learning Outcomes 1. Identify and explain the functions of the vessels of the Circulatory system. 2. Explain the functions
Cardiovascular and Circulatory System The Heart and Blood Vessels Circulatory Learning Outcomes 1. Identify and explain the functions of the vessels of the Circulatory system. 2. Explain the functions
Summary The Circulatory System Blood and the Lymphatic System. Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall.
 Name Class Date Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Summary 37-1 The Circulatory System The human circulatory system consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. Together with the respiratory
Name Class Date Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Summary 37-1 The Circulatory System The human circulatory system consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. Together with the respiratory
14-1: The Body s Transport System. 7 th Grade Life Science
 7 th Grade Life Science Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system, also called circulatory system, is made of your heart blood vessels, and blood. It is like the network of highways on Earth, where
7 th Grade Life Science Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system, also called circulatory system, is made of your heart blood vessels, and blood. It is like the network of highways on Earth, where
The Circulatory System. The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types
 The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
