X-Plain Atrial Fibrillation Reference Summary
|
|
|
- Alan Logan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 X-Plain Atrial Fibrillation Reference Summary Introduction Atrial fibrillation is a common heart condition that affects approximately 2.5 million Americans every year. Atrial fibrillation requires immediate medical attention. If not treated it can lead to life-threatening strokes. The treatment of atrial fibrillation may require long-term medication and possibly electroshock to the heart. This reference summary will discuss the symptoms and treatment options for atrial fibrillation. Anatomy The heart is the most important muscle in the body. It is formed by 2 sides, the right side and the left side. Each side has 2 chambers, an atrium and a larger ventricle. Blood comes from the body to the right atrium. From there it is pumped to the right ventricle. The right ventricle pumps the blood to the lungs. In the lungs, oxygen is delivered to the blood. From the lungs blood goes to the left atrium and then to the left ventricle. From there it is pumped to the rest of the body. Atrium Ventricle Atrium Ventricle Heart contractions are synchronized. A normal heart rate varies between 60 and 100 beats per minute while a person is at rest. The muscles of the heart contract and pump blood because, they are stimulated by a small electric current. The electric current in the heart starts in an area of the atria known as the sinus node. 1
2 It causes the atria to contract and pump blood to the ventricles. From the sinus node, the electric current travels through fibers similar to electric cables, to another area of the ventricles known as the atrio-ventricular node or AV node. From the AV node the electric current goes to the ventricles and causes them to contract and pump blood. Atrial Fibrillation Atrial fibrillation occurs when the electric current in the heart is generated from all over the atria at a very high speed, between 300 and 500 impulses a minute. This does not allow the atria to contract in a synchronized fashion. Because of the high number of impulses generated by the heart, and their location, the atria begin to quiver. This is known in medical terms as fibrillation. When this happens the ventricles contract independently from the atria. This causes a fast, irregular heart rate between 80 and 160 beats per minute. Such a rapid and irregular heart rate causes some blood to remain in the heart after every contraction. This results in blood pooling in the heart chambers, which increases the risk of blood clot formation. These blood clots can get dislodged and travel to the brain and lungs where they could block the flow of blood. When the flow of blood is interrupted a fatal or disabling stroke could occur. Causes Coronary artery disease and heart failure are the two main causes of atrial fibrillation. Rheumatic heart disease, which affects the valves of the heart, also increases the chance of atrial fibrillation. Hypertension and diabetes can also play a role in damaging the atria of the heart and can cause atrial fibrillation. An over-active thyroid gland, chronic lung diseases such as COPD and inflammation of the lining of the heart can also cause the atria to fibrillate. 2
3 Rarely atrial fibrillation occurs in otherwise healthy people without an underlying disease. Symptoms Atrial fibrillation may not have any symptoms. Most patients do feel chest palpitations and possibly skipped heartbeats. If the heart rate becomes very high or if the heart becomes unable to pump blood adequately, patients may feel chest pain known as angina. They may also feel lightheadedness and may even faint. Diagnosis Atrial fibrillation is diagnosed by an electro-cardiogram, also known as an EKG. This test takes only a few minutes. During this test, electrodes are placed on the chest and body to record the heart s electrical impulses. Because atrial fibrillation comes and goes, and may not happen during an EKG, you may be asked to wear a portable EKG. This portable EKG test, known as a Holter monitor, lasts for 24 hours. Your physician will also want to determine what is causing atrial fibrillation. He or she will check your heart, blood pressure, blood sugar, and levels of thyroid hormone. Treatment Some cases of atrial fibrillation may improve on their own. If this happens, your physician will still perform tests to make sure you do not have any of the diseases that can cause atrial fibrillation. If it persists, your physician can treat it in one of several ways. The underlying cause of atrial fibrillation will have to be treated. This sometimes causes the heart rate to become normal again. For example, if atrial fibrillation is caused by an over-active thyroid gland, the thyroid gland may need to be surgically removed. If a heart valve disease causes atrial fibrillation, a valve replacement surgery may be necessary. Controlling high blood pressure and your blood sugar level, as well as preventing any further heart problems, may also help in some cases. If atrial fibrillation does not improve, other procedures may be tried. Your physician may attempt to revert your heart rate to normal. This is known as cardioversion. 3
4 If cardioversion is not recommended or is not successful, blood thinners are given to prevent blood clots from forming in the heart. Cardioversion Cardioversion, or reverting the heart rate to normal, can be done with various medications or using an electric shock to the chest area. Depending on the patient s condition, another procedure called catheter radiofrequency ablation may be attempted. During this procedure, parts of the electrical pathways of the heart are destroyed using a small electric current. This current is delivered to the heart using a catheter that is threaded through the blood vessels into the heart. After this procedure a pacemaker may need to be placed because the heart loses its ability to generate and regulate the heart beat. Patients may also be placed on long-term medications to prevent the atrial fibrillation from recurring. Anticoagulation or Blood Thinning If cardioversion is not successful, the risk of blood clots forming inside the heart becomes very high. Blood thinners are then administered to help decrease the chance of blood clots forming. The most common blood thinner used is warfarin (Coumadin ). Warfarin is a very helpful medication that has potentially significant side effects. Your physician will need to check your blood regularly to prescribe the correct dosage. Regular follow up visits with your physician are essential in preventing complications due to atrial fibrillation or warfarin. Prevention The best way to prevent atrial fibrillation from occurring is to take steps toward keeping your heart healthy. These steps include: 1. Not smoking 2. Eating a low-fat diet 3. Controlling your blood pressure and blood sugar levels 4. Exercising regularly under your physician s supervision Unfortunately, atrial fibrillation may not be totally preventable, and long-term treatment of this condition may be needed. 4
5 Summary Atrial fibrillation is an abnormal, irregular heart rhythm. It typically causes a rapid heartbeat. Atrial fibrillation is a serious disease because it can cause blood clots that can travel from the heart to the brain, resulting in a stroke. Thanks to advances in medicine, several treatment options are available. Most patients can still live a very healthy and productive life after treatment. It is important to follow-up with a physician regularly. 5
Arrhythmias. Pulmonary Artery
 Arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmia is an irregularity of the heart beat that causes the heart to beat too slowly, too fast, or irregularly. There are different types of arrhythmias. Most arrhythmias
Arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmia is an irregularity of the heart beat that causes the heart to beat too slowly, too fast, or irregularly. There are different types of arrhythmias. Most arrhythmias
Atrial Fibrillation & Arrhythmias
 Atrial Fibrillation & Arrhythmias Symptoms and Treatments FloridaHospital.com Atrial Fibrillation According to the American Heart Association, Atrial fibrillation (AF) affects an estimated 2.7 million
Atrial Fibrillation & Arrhythmias Symptoms and Treatments FloridaHospital.com Atrial Fibrillation According to the American Heart Association, Atrial fibrillation (AF) affects an estimated 2.7 million
About atrial fibrillation (AFib) Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) What is AFib? What s the danger? Who gets AFib?
 Understanding AFib Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) About AFib 3 How Your Heart Works 4 Types of AFib 5 Symptoms 5 Risk Factors 5 How is AFib Diagnosed? 6 Treatment 6 What to Ask Your Doctor 7 A normal heartbeat
Understanding AFib Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) About AFib 3 How Your Heart Works 4 Types of AFib 5 Symptoms 5 Risk Factors 5 How is AFib Diagnosed? 6 Treatment 6 What to Ask Your Doctor 7 A normal heartbeat
Understanding Atrial Fibrillation A guide for patients
 Understanding Atrial Fibrillation A guide for patients Your doctor has determined that you have atrial fibrillation (AF), a common disturbance of the heart s rhythm. This pamphlet will answer many of your
Understanding Atrial Fibrillation A guide for patients Your doctor has determined that you have atrial fibrillation (AF), a common disturbance of the heart s rhythm. This pamphlet will answer many of your
Management strategies for atrial fibrillation Thursday, 20 October :27
 ALTHOUGH anyone who has had to run up a flight of steps or has had a frightening experience is quite familiar with a racing heartbeat, for the more than 2 million Americans who suffer from atrial fibrillation
ALTHOUGH anyone who has had to run up a flight of steps or has had a frightening experience is quite familiar with a racing heartbeat, for the more than 2 million Americans who suffer from atrial fibrillation
Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology
 Definition of atrial fibrillation Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology Atrial Fibrillation Ablation Atrial fibrillation is a heart rhythm disturbance that causes an irregular (and often
Definition of atrial fibrillation Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology Atrial Fibrillation Ablation Atrial fibrillation is a heart rhythm disturbance that causes an irregular (and often
Patient Resources: Arrhythmias and Congenital Heart Disease
 Patient Resources: Arrhythmias and Congenital Heart Disease Overview Arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms) can develop in patients with congenital heart disease (CHD) due to thickening/weakening of their
Patient Resources: Arrhythmias and Congenital Heart Disease Overview Arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms) can develop in patients with congenital heart disease (CHD) due to thickening/weakening of their
INFORMATION. Atrial Fibrillation. Summary. Information from the
 1. Information from the For more information contact Heartline 1300 362 787 or www.heartfoundation.com.au Atrial Fibrillation INFORMATION Summary What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation (AF) is
1. Information from the For more information contact Heartline 1300 362 787 or www.heartfoundation.com.au Atrial Fibrillation INFORMATION Summary What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation (AF) is
Atrial Fibrillation. Damage to your heart caused by a heart attack or rheumatic heart disease
 Atrial Fibrillation GENERAL INFORMATION: What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation is a condition that causes the atria (top chambers of the heart) to shake or quiver. Normally, there is 1 contraction
Atrial Fibrillation GENERAL INFORMATION: What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation is a condition that causes the atria (top chambers of the heart) to shake or quiver. Normally, there is 1 contraction
Special health. guide. Hugh Calkins, M.D., and Ronald Berger, M.D., Ph.D. Guide to Understanding. Atrial Fibrillation WITH
 Hugh Calkins, M.D., and Ronald Berger, M.D., Ph.D. Guide to Understanding Atrial Fibrillation WITH Table of Contents Atrial Fibrillation: An Introduction... 1 How AF Affects the Heart... 2 Who Gets AF?...
Hugh Calkins, M.D., and Ronald Berger, M.D., Ph.D. Guide to Understanding Atrial Fibrillation WITH Table of Contents Atrial Fibrillation: An Introduction... 1 How AF Affects the Heart... 2 Who Gets AF?...
Introduction. What atrial fibrillation (AF) is Warning signs & symptoms, and risk factors for developing AFrelated
 Got FIB? Introduction FAST, IRREGULAR heartbeats = FIB FIB is short for fibrillation fibrillation, or quivering of the top two chambers of the heart (the atria) Important that you understand: What atrial
Got FIB? Introduction FAST, IRREGULAR heartbeats = FIB FIB is short for fibrillation fibrillation, or quivering of the top two chambers of the heart (the atria) Important that you understand: What atrial
GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Atrial Flutter (AFL) Rate and Rhythm Control Stroke Prevention This document is endorsed by: A Comprehensive Resource from the
PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Atrial Flutter (AFL) Rate and Rhythm Control Stroke Prevention This document is endorsed by: A Comprehensive Resource from the
Catheter Ablation. Patient Education
 Catheter Ablation Patient Education Allina Health System Your heart has four chambers. Two upper chambers (atria) pump blood to the two lower chambers (ventricles). In order for the heart to pump, it requires
Catheter Ablation Patient Education Allina Health System Your heart has four chambers. Two upper chambers (atria) pump blood to the two lower chambers (ventricles). In order for the heart to pump, it requires
Atrial Fibrillation Your quick guide
 Atrial Fibrillation Your quick guide Coronary heart disease is the UK s single biggest killer. For over 50 years we ve pioneered research that s transformed the lives of people living with heart and circulatory
Atrial Fibrillation Your quick guide Coronary heart disease is the UK s single biggest killer. For over 50 years we ve pioneered research that s transformed the lives of people living with heart and circulatory
Pacemaker and AV Node Ablation Patient Information
 Melbourne Heart Rhythm Pacemaker and AV Node Ablation Patient Information The Heart The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two upper chambers
Melbourne Heart Rhythm Pacemaker and AV Node Ablation Patient Information The Heart The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two upper chambers
Understanding. Atrial Fibrillation. For more information, visit. CardioSmart.org/AFib
 Understanding Atrial Fibrillation For more information, visit CardioSmart.org/AFib Understanding Atrial Fibrillation What is ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (AFib)? When it s operating normally, your heart pumps to
Understanding Atrial Fibrillation For more information, visit CardioSmart.org/AFib Understanding Atrial Fibrillation What is ATRIAL FIBRILLATION (AFib)? When it s operating normally, your heart pumps to
How does the heart work? The heart is muscle whose main function is a pump; to push blood the rest of your body.
 1 You have a condition called atrial fibrillation. I would like you to learn more about this condition. You should read about it below, and can also watch an Internet program about it. After reading about
1 You have a condition called atrial fibrillation. I would like you to learn more about this condition. You should read about it below, and can also watch an Internet program about it. After reading about
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION ANSWERS. A Patient Education Handbook on Electrophysiology
 ATRIAL FIBRILLATION ANSWERS A Patient Education Handbook on Electrophysiology MY LIFE HAS TAKEN A TURN FOR THE BETTER. -Emie Bishop ARRHYTHMIAANSWERS.COM AF ANSWERS. A PATIENT EDUCATION HANDBOOK ON ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION ANSWERS A Patient Education Handbook on Electrophysiology MY LIFE HAS TAKEN A TURN FOR THE BETTER. -Emie Bishop ARRHYTHMIAANSWERS.COM AF ANSWERS. A PATIENT EDUCATION HANDBOOK ON ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY
Atrial Fibrillation. Why It s Important. Updated on 2007 / 11 / 23. Microlife Corp ww.microlife.com. Page 1
 Atrial Fibrillation Why It s Important Microlife Corp ww.microlife.com Updated on 2007 / 11 / 23 Page 1 CONTENT ORIGINAL PRESENTATION P3 ~ P13 UPDATED ASH ABSTRACT SUBMISSION INFORMATION INTERESTING LINK
Atrial Fibrillation Why It s Important Microlife Corp ww.microlife.com Updated on 2007 / 11 / 23 Page 1 CONTENT ORIGINAL PRESENTATION P3 ~ P13 UPDATED ASH ABSTRACT SUBMISSION INFORMATION INTERESTING LINK
THE HEART THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
 THE HEART THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM There are three primary closed cycles: 1) Cardiac circulation pathway of blood within the heart 2) Pulmonary circulation blood from the heart to lungs and back 3) Systemic
THE HEART THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM There are three primary closed cycles: 1) Cardiac circulation pathway of blood within the heart 2) Pulmonary circulation blood from the heart to lungs and back 3) Systemic
All About the Heart. Structures of the heart. Layers. Chambers
 All About the Heart Your heart is a muscle. It is slightly larger than your fist and weighs less than a pound. It is located to the left of the middle of your chest. Your heart pumps blood to the lungs
All About the Heart Your heart is a muscle. It is slightly larger than your fist and weighs less than a pound. It is located to the left of the middle of your chest. Your heart pumps blood to the lungs
Fibrillation. Living. withatrial. Further information
 Further information Anticoagulation UK is committed to the prevention of thrombosis and to providing information and support to help people maintain their quality of life whilst on anticoagulant or antiplatelet
Further information Anticoagulation UK is committed to the prevention of thrombosis and to providing information and support to help people maintain their quality of life whilst on anticoagulant or antiplatelet
X-Plain Pacemaker Reference Summary
 X-Plain Pacemaker Reference Summary Introduction A pacemaker is a device that regulates the heart beat. More than half a million Americans use a pacemaker. If your doctor recommends that you have a pacemaker,
X-Plain Pacemaker Reference Summary Introduction A pacemaker is a device that regulates the heart beat. More than half a million Americans use a pacemaker. If your doctor recommends that you have a pacemaker,
Understanding Atrial Fibrillation
 Understanding Atrial Fibrillation Todd J. Florin, M.D. Table of Contents The Normal Heart...1 What is Atrial Fibrillation...3 Risks of Afib: Stroke...5 Treatment Options...7 Radiofrequency Ablation...9
Understanding Atrial Fibrillation Todd J. Florin, M.D. Table of Contents The Normal Heart...1 What is Atrial Fibrillation...3 Risks of Afib: Stroke...5 Treatment Options...7 Radiofrequency Ablation...9
Diseases. Cardiovascular System
 Diseases Cardiovascular System Angina Pectoris A condition marked by severe pain in the chest, often spreading to the shoulder or neck. Caused by inadequate blood supply to the heart. Cardiomyopathy Refers
Diseases Cardiovascular System Angina Pectoris A condition marked by severe pain in the chest, often spreading to the shoulder or neck. Caused by inadequate blood supply to the heart. Cardiomyopathy Refers
PhD FRCP MESC MEAPCI. Consultant Cardiologist SVT - Supra Ventricular Tachycardia. Coronary Arteries
 SVT - Supra Ventricular Tachycardia Coronary Arteries Overview LMS Supraventricular tachycardia is defined as an abnormally fast heartbeat. It's a describes a group of arrhythmias which all originate from
SVT - Supra Ventricular Tachycardia Coronary Arteries Overview LMS Supraventricular tachycardia is defined as an abnormally fast heartbeat. It's a describes a group of arrhythmias which all originate from
BIOTRONIK Clinical Studies IMPACT Clinical Study Patient Information. IMPACT Clinical Study: Patient Information Guide
 BIOTRONIK Clinical Studies IMPACT Clinical Study Patient Information IMPACT Clinical Study: Patient Information Guide Introduction and Objectives IMPACT is a clinical research study. Approximately 2,700
BIOTRONIK Clinical Studies IMPACT Clinical Study Patient Information IMPACT Clinical Study: Patient Information Guide Introduction and Objectives IMPACT is a clinical research study. Approximately 2,700
Direct Current (DC) Cardioversion
 Page 1 of 10 Direct Current (DC) Cardioversion Introduction This leaflet is to inform you about your planned Direct Current (DC) electrical cardioversion. A cardioversion is an electrical treatment which
Page 1 of 10 Direct Current (DC) Cardioversion Introduction This leaflet is to inform you about your planned Direct Current (DC) electrical cardioversion. A cardioversion is an electrical treatment which
Atrial Flutter Patient Information
 AF A Atrial Flutter Patient Information Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary Anti-arrhythmic
AF A Atrial Flutter Patient Information Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary Anti-arrhythmic
Atrial Fibrillation: What Should You Know? I (888)
 Atrial Fibrillation: What Should You Know? I was exhausted doing simple tasks because of my AFib. I couldn t walk from the store to my car in the parking lot. Then, I had a MAZE procedure. It was a very
Atrial Fibrillation: What Should You Know? I was exhausted doing simple tasks because of my AFib. I couldn t walk from the store to my car in the parking lot. Then, I had a MAZE procedure. It was a very
RESTORE YOUR RHYTHM. Atrial Fibrillation Information and Treatment Options. To make an appointment, call
 RESTORE YOUR RHYTHM Atrial Fibrillation Information and Treatment Options To make an appointment, call 1-866-847-7194. Managing your AFib? We can help you. Atrial fibrillation is the most common abnormal
RESTORE YOUR RHYTHM Atrial Fibrillation Information and Treatment Options To make an appointment, call 1-866-847-7194. Managing your AFib? We can help you. Atrial fibrillation is the most common abnormal
Atrial Fibrillaton. Key: RA: right atrium RV: right ventricle PA: pulmonic artery LA: left atrium LV: left ventricle AO: aorta
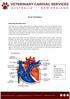 Atrial Fibrillaton How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right
Atrial Fibrillaton How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right
Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Patient Information
 Australia www.atrialfibrillation-au.org www.afa-international.org Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Fibrillation (AF)
Australia www.atrialfibrillation-au.org www.afa-international.org Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Fibrillation (AF)
Cardiac Cycle. Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. First the two atria contract at the same time.
 The Heartbeat Cardiac Cycle Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. First the two atria contract at the same time. Next the two ventricles contract at the same time. Then all the chambers relax. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=frd3k6lkhws
The Heartbeat Cardiac Cycle Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. First the two atria contract at the same time. Next the two ventricles contract at the same time. Then all the chambers relax. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=frd3k6lkhws
Atrial fibrillation and you. Atrial fibrillation and your treatment options
 Atrial fibrillation and you Atrial fibrillation and your treatment options What you need to know about Atrial Fibrillation The Normal Heart Rhythm Electrical System of the Heart The heart pumps blood to
Atrial fibrillation and you Atrial fibrillation and your treatment options What you need to know about Atrial Fibrillation The Normal Heart Rhythm Electrical System of the Heart The heart pumps blood to
Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels
 Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels 3.2 Learning Objectives 3.2.2 Organisational Complexity of the human 1. Describe the structures and organisation of tissues in the closed circulatory system. 2. Discuss
Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels 3.2 Learning Objectives 3.2.2 Organisational Complexity of the human 1. Describe the structures and organisation of tissues in the closed circulatory system. 2. Discuss
Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology
 Definition of electrophysiology study and ablation Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology Electrophysiology Study and Ablation An electrophysiology, or EP, study is a test of the heart
Definition of electrophysiology study and ablation Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology Electrophysiology Study and Ablation An electrophysiology, or EP, study is a test of the heart
ICD Implantation Patient Information
 Melbourne Heart Rhythm ICD Implantation Patient Information The Heart The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two upper chambers (the right atrium
Melbourne Heart Rhythm ICD Implantation Patient Information The Heart The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two upper chambers (the right atrium
Atrial Fibrillation Information for patients
 be informed about... Atrial Fibrillation Information for patients Atrial fibrillation (AF) is an abnormal heart rhythm. This pamphlet answers some questions you may have about AF, and gives an overview
be informed about... Atrial Fibrillation Information for patients Atrial fibrillation (AF) is an abnormal heart rhythm. This pamphlet answers some questions you may have about AF, and gives an overview
The Mammalian Circulatory System
 The Mammalian Heart The Mammalian Circulatory System Recall: What are the 3 cycles of the mammalian circulatory system? What are their functions? What are the three main vessel types in the mammalian circulatory
The Mammalian Heart The Mammalian Circulatory System Recall: What are the 3 cycles of the mammalian circulatory system? What are their functions? What are the three main vessel types in the mammalian circulatory
UNDERSTANDING ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES
 UNDERSTANDING ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES Testing and Treating Your Heart s Electrical System A Problem with Your Heart Rhythm The speed and pattern of a heartbeat is called the heart rhythm. The rhythm
UNDERSTANDING ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES Testing and Treating Your Heart s Electrical System A Problem with Your Heart Rhythm The speed and pattern of a heartbeat is called the heart rhythm. The rhythm
Heart Disease. Signs and Symptoms
 Heart Disease The term "heart disease" refers to several types of heart conditions. The most common type is coronary artery disease, which can cause heart attack, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
Heart Disease The term "heart disease" refers to several types of heart conditions. The most common type is coronary artery disease, which can cause heart attack, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
Radiofrequency ablation for atrial fibrillation in association with other cardiac surgery
 Issue date: May 2005 Radiofrequency ablation for atrial fibrillation in association with other cardiac surgery Understanding NICE guidance information for people considering the procedure, and for the
Issue date: May 2005 Radiofrequency ablation for atrial fibrillation in association with other cardiac surgery Understanding NICE guidance information for people considering the procedure, and for the
Objectives of the Heart
 Objectives of the Heart Electrical activity of the heart Action potential EKG Cardiac cycle Heart sounds Heart Rate The heart s beat separated into 2 phases Relaxed phase diastole (filling of the chambers)
Objectives of the Heart Electrical activity of the heart Action potential EKG Cardiac cycle Heart sounds Heart Rate The heart s beat separated into 2 phases Relaxed phase diastole (filling of the chambers)
Atrial Fibrillation (Afib) Patient Guide. Guide contents: 2 What Is Atrial Fibrillation (Afib)? 3 What Happens During Afib?
 Guide contents: 2 What Is Atrial Fibrillation (Afib)? 3 What Happens During Afib? 4 For Your Appointment 5 For Your Future 6 Symptom Tracker Form 7 Your Team at Orlando Health Atrial Fibrillation (Afib)
Guide contents: 2 What Is Atrial Fibrillation (Afib)? 3 What Happens During Afib? 4 For Your Appointment 5 For Your Future 6 Symptom Tracker Form 7 Your Team at Orlando Health Atrial Fibrillation (Afib)
CATHETER ABLATION for ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 CATHETER ABLATION for ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Atrial Fibrillation Clinic Dr. Richard Leather, Dr. Larry Sterns, Dr Paul Novak, Dr. Chris Lane and Dr. Sikkel Royal Jubilee Hospital Block 3 rd floor, Rm 343
CATHETER ABLATION for ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Atrial Fibrillation Clinic Dr. Richard Leather, Dr. Larry Sterns, Dr Paul Novak, Dr. Chris Lane and Dr. Sikkel Royal Jubilee Hospital Block 3 rd floor, Rm 343
Abnormal Heart Rhythms (Arrhythmias)
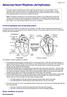 Abnormal Heart Rhythms (Arrhythmias) Page 1 of 5 The heart needs a small electrical current to pass through the heart in a very set pattern. This is called the heart's conduction system. This leaflet explains
Abnormal Heart Rhythms (Arrhythmias) Page 1 of 5 The heart needs a small electrical current to pass through the heart in a very set pattern. This is called the heart's conduction system. This leaflet explains
Unit 1: Human Systems. The Circulatory System
 Unit 1: Human Systems The Circulatory System nourish all cells with oxygen, glucose, amino acids and other nutrients and carry away carbon dioxide, urea and other wastes Purposes Transport chemical messengers
Unit 1: Human Systems The Circulatory System nourish all cells with oxygen, glucose, amino acids and other nutrients and carry away carbon dioxide, urea and other wastes Purposes Transport chemical messengers
AF AND YOU AN INFORMATION BOOKLET FOR PEOPLE LIVING WITH ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 www.irishheart.ie AF AND YOU AN INFORMATION BOOKLET FOR PEOPLE LIVING WITH ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Registered charity number CHY 5507 Produced by the Irish Heart Foundation This booklet is one of the publications
www.irishheart.ie AF AND YOU AN INFORMATION BOOKLET FOR PEOPLE LIVING WITH ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Registered charity number CHY 5507 Produced by the Irish Heart Foundation This booklet is one of the publications
37 1 The Circulatory System
 H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
Sample. Analyzing the Heart with EKG. Computer
 Analyzing the Heart with EKG Computer An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in
Analyzing the Heart with EKG Computer An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in
Newer pacemakers also can monitor your blood temperature, breathing, and other factors and adjust your heart rate to changes in your activity.
 Pacemakers & Defibrillators A pacemaker system consists of a battery, a computerized generator and wires with sensors called electrodes on one end. The battery powers the generator, and both are surrounded
Pacemakers & Defibrillators A pacemaker system consists of a battery, a computerized generator and wires with sensors called electrodes on one end. The battery powers the generator, and both are surrounded
The Cardiovascular System
 CHAPTER 16 1 SECTION Circulation and Respiration The Cardiovascular System California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.6.j BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these
CHAPTER 16 1 SECTION Circulation and Respiration The Cardiovascular System California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.6.j BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these
Unit 6: Circulatory System. 6.2 Heart
 Unit 6: Circulatory System 6.2 Heart Functions of Circulatory System 1. The heart is the pump necessary to circulate blood to all parts of the body 2. Arteries, veins and capillaries are the structures
Unit 6: Circulatory System 6.2 Heart Functions of Circulatory System 1. The heart is the pump necessary to circulate blood to all parts of the body 2. Arteries, veins and capillaries are the structures
The Circulatory System. The circulatory system includes the Heart, Blood Tissue and the Blood Vessels.
 The Circulatory System The circulatory system includes the Heart, Blood Tissue and the Blood Vessels. The Circulatory System-Transport The absorption and circulation of materials throughout an organism
The Circulatory System The circulatory system includes the Heart, Blood Tissue and the Blood Vessels. The Circulatory System-Transport The absorption and circulation of materials throughout an organism
HEART SERIES H9 UNDERSTANDING ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 HEART SERIES H9 UNDERSTANDING ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Chest Heart & Stroke Scotland improves the quality of life for people in Scotland affected by chest, heart and stroke illness, through medical research,
HEART SERIES H9 UNDERSTANDING ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Chest Heart & Stroke Scotland improves the quality of life for people in Scotland affected by chest, heart and stroke illness, through medical research,
Cryoablation for atrial fibrillation in association with other cardiac surgery. Issue date: May 2005
 Issue date: May 2005 Cryoablation for atrial fibrillation in association with other cardiac surgery Understanding NICE guidance information for people considering the procedure, and for the public Information
Issue date: May 2005 Cryoablation for atrial fibrillation in association with other cardiac surgery Understanding NICE guidance information for people considering the procedure, and for the public Information
Information for patients, parents and guardians. Your child s doctor has recommended that your child has a procedure called an ablation.
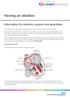 Having an ablation Information for patients, parents and guardians Your child s doctor has recommended that your child has a procedure called an ablation. An ablation is a treatment for an abnormal heartbeat.
Having an ablation Information for patients, parents and guardians Your child s doctor has recommended that your child has a procedure called an ablation. An ablation is a treatment for an abnormal heartbeat.
Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders
 Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders Interesting Heart Facts The Electrocardiograph (ECG) was invented in 1902 by Willem Einthoven Dutch Physiologist. This test is still used to evaluate
Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders Interesting Heart Facts The Electrocardiograph (ECG) was invented in 1902 by Willem Einthoven Dutch Physiologist. This test is still used to evaluate
Mission Statement for our Arrhythmia Care
 Mission Statement for our Arrhythmia Care We are dedicated to provide a compassionate and an outstanding care for patients with cardiac arrhythmias. We will be utilizing the cutting edge and the most advanced
Mission Statement for our Arrhythmia Care We are dedicated to provide a compassionate and an outstanding care for patients with cardiac arrhythmias. We will be utilizing the cutting edge and the most advanced
Cardiac Arrhythmias. Cathy Percival, RN, FALU, FLMI VP, Medical Director AIG Life and Retirement Company
 Cardiac Arrhythmias Cathy Percival, RN, FALU, FLMI VP, Medical Director AIG Life and Retirement Company The Cardiovascular System Three primary functions Transport of oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to
Cardiac Arrhythmias Cathy Percival, RN, FALU, FLMI VP, Medical Director AIG Life and Retirement Company The Cardiovascular System Three primary functions Transport of oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to
Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy Patient Information
 Melbourne Heart Rhythm Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy Patient Information Normal Heart Function The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two
Melbourne Heart Rhythm Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy Patient Information Normal Heart Function The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two
Heart Valve Replacement
 Heart Valve Replacement Introduction Sometimes people have serious problems with the valves in their hearts. A heart valve repair or replacement surgery restores or replaces a defective heart valve. If
Heart Valve Replacement Introduction Sometimes people have serious problems with the valves in their hearts. A heart valve repair or replacement surgery restores or replaces a defective heart valve. If
Blood Thinning in Atrial Fibrillation (AF)
 AF A Blood Thinning in Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary Antiarrhythmic
AF A Blood Thinning in Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary Antiarrhythmic
The Heart. Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet
 The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia PSVT.
 Atrial Tachycardia; is the name for an arrhythmia caused by a disorder of the impulse generation in the atrium or the AV node. An area in the atrium sends out rapid signals, which are faster than those
Atrial Tachycardia; is the name for an arrhythmia caused by a disorder of the impulse generation in the atrium or the AV node. An area in the atrium sends out rapid signals, which are faster than those
Circulatory system of mammals
 Circulatory system of mammals Explain the cardiac cycle and its initiation Discuss the internal factors that control heart action Blood flows through the heart as a result of pressure differences Blood
Circulatory system of mammals Explain the cardiac cycle and its initiation Discuss the internal factors that control heart action Blood flows through the heart as a result of pressure differences Blood
12 Lead EKG. Brigham and Women's Hospital
 12 Lead EKG What is the heart? The heart is the organ that is responsible for pumping blood rich in oxygen to all parts of the body It is located in the center of the chest and is approximately the size
12 Lead EKG What is the heart? The heart is the organ that is responsible for pumping blood rich in oxygen to all parts of the body It is located in the center of the chest and is approximately the size
Heart Failure. Symptoms and Treatments. FloridaHospital.com
 Heart Failure Symptoms and Treatments FloridaHospital.com Understanding Heart Failure According to the American Heart Association, one in five people over age 40 will develop heart failure. Right now,
Heart Failure Symptoms and Treatments FloridaHospital.com Understanding Heart Failure According to the American Heart Association, one in five people over age 40 will develop heart failure. Right now,
2
 1 2 Although the term "cardiomyopathy" could theoretically apply to almost any disease affecting the heart, it is usually reserved for "severe myocardial disease leading to heart failure".cardiomyopathy
1 2 Although the term "cardiomyopathy" could theoretically apply to almost any disease affecting the heart, it is usually reserved for "severe myocardial disease leading to heart failure".cardiomyopathy
Heart Problems and Treatments
 Heart Problems and Treatments A healthy heart Your heart s main functions are to receive used blood from your body and pump fresh oxygen rich blood to nourish your body. To do this well: The heart muscle
Heart Problems and Treatments A healthy heart Your heart s main functions are to receive used blood from your body and pump fresh oxygen rich blood to nourish your body. To do this well: The heart muscle
Healthy Blood Pressure Healthy Heart Beat. Initiated by the World Hypertension League
 Healthy Blood Pressure Healthy Heart Beat Initiated by the World Hypertension League MAY 17, 2013 What is Hypertension? Hypertension Is A Global Epidemic! Hypertension is most commonly known as High Blood
Healthy Blood Pressure Healthy Heart Beat Initiated by the World Hypertension League MAY 17, 2013 What is Hypertension? Hypertension Is A Global Epidemic! Hypertension is most commonly known as High Blood
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System Blood vessels, heart and blood Functions Transport oxygen, nutrients, waste, hormones White blood cells fighting disease Temperature regulation Blood vessels; Arteries Arteries carry
Cardiovascular System Blood vessels, heart and blood Functions Transport oxygen, nutrients, waste, hormones White blood cells fighting disease Temperature regulation Blood vessels; Arteries Arteries carry
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
Biology Unit 3 The Human Heart P
 Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology WATCHMAN Left Atrial Appendage Closure Device
 Patient Information Guide Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology WATCHMAN Left Atrial Appendage Closure Device Your doctor has recommended that you consider undergoing a procedure to
Patient Information Guide Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology WATCHMAN Left Atrial Appendage Closure Device Your doctor has recommended that you consider undergoing a procedure to
d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology
 d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology What can your remember about the heart and blood vessels? What is the Cardiovascular System? The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system,
d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology What can your remember about the heart and blood vessels? What is the Cardiovascular System? The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system,
Guide to Cardiology Care at Scripps
 Guide to Cardiology Care at Scripps Cardiology is the word in health care associated with heart, but the body s vascular system is also an important part of heart care. Your body has more than 60,000 miles
Guide to Cardiology Care at Scripps Cardiology is the word in health care associated with heart, but the body s vascular system is also an important part of heart care. Your body has more than 60,000 miles
Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system. What are the function of the cardiovascular system? Arteries and arterioles:
 5.1 Overview of the cardiovascular system Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system Includes the heart and blood vessels Brings nutrients to cells and helps get rid of wastes Blood is refreshed in the lung, kidneys,
5.1 Overview of the cardiovascular system Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system Includes the heart and blood vessels Brings nutrients to cells and helps get rid of wastes Blood is refreshed in the lung, kidneys,
Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels
 Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels Most animals have a closed blood system. The blood flows continuously in vessels back to the heart. In an open system the blood is pumped into open ended tubes and
Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels Most animals have a closed blood system. The blood flows continuously in vessels back to the heart. In an open system the blood is pumped into open ended tubes and
VT Ablation in Structural Heart Disease Patient Information
 Melbourne Heart Rhythm VT Ablation in Structural Heart Disease Patient Information Ventricular Tachycardia in Structural Heart Disease (VT-SHD) Ventricular tachycardia (VT) is an abnormal rapid heart rhythm
Melbourne Heart Rhythm VT Ablation in Structural Heart Disease Patient Information Ventricular Tachycardia in Structural Heart Disease (VT-SHD) Ventricular tachycardia (VT) is an abnormal rapid heart rhythm
1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary.
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
Electrocardiography Abnormalities (Arrhythmias) 7. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD
 Electrocardiography Abnormalities (Arrhythmias) 7 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Causes of Cardiac Arrythmias Abnormal rhythmicity of the pacemaker Shift of pacemaker from sinus node Blocks at different
Electrocardiography Abnormalities (Arrhythmias) 7 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Causes of Cardiac Arrythmias Abnormal rhythmicity of the pacemaker Shift of pacemaker from sinus node Blocks at different
Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease
 Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease Mammals are too large to rely on diffusion. They need a circulatory system to move substances around the body. Blood moves down pressure gradients, from high to
Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease Mammals are too large to rely on diffusion. They need a circulatory system to move substances around the body. Blood moves down pressure gradients, from high to
Cardiac Conduction System
 Cardiac Conduction System What causes the Heart to Beat? Heart contracts by electrical signals! Cardiac muscle tissue contracts on its own an electrical signal is sent out by the heart so that all cells
Cardiac Conduction System What causes the Heart to Beat? Heart contracts by electrical signals! Cardiac muscle tissue contracts on its own an electrical signal is sent out by the heart so that all cells
Catheter Ablation for Supraventricular Tachycardias
 Catheter Ablation for Supraventricular Tachycardias - A Patient's Guide - Westby G. Fisher, MD, FACC Director, Cardiac Electrophysiology Evanston Northwesten Healthcare Evanston, IL, USA (Last Updated
Catheter Ablation for Supraventricular Tachycardias - A Patient's Guide - Westby G. Fisher, MD, FACC Director, Cardiac Electrophysiology Evanston Northwesten Healthcare Evanston, IL, USA (Last Updated
OVERVIEW OF ARRHYTHMIA
 ARRHYTHMIA ABLATION ARRHYTHMIA ABLATION OVERVIEW OF ARRHYTHMIA WHAT IS AN ARRHYTHMIA? There are some people who experience abnormal heart rhythms. The heart rate may be too fast or frequently irregular.
ARRHYTHMIA ABLATION ARRHYTHMIA ABLATION OVERVIEW OF ARRHYTHMIA WHAT IS AN ARRHYTHMIA? There are some people who experience abnormal heart rhythms. The heart rate may be too fast or frequently irregular.
Arrhythmia 341. Ahmad Hersi Professor of Cardiology KSU
 Arrhythmia 341 Ahmad Hersi Professor of Cardiology KSU Objectives Epidemiology and Mechanisms of AF Evaluation of AF patients Classification of AF Treatment and Risk stratification of AF Identify other
Arrhythmia 341 Ahmad Hersi Professor of Cardiology KSU Objectives Epidemiology and Mechanisms of AF Evaluation of AF patients Classification of AF Treatment and Risk stratification of AF Identify other
Heart. Heart 2-Tunica media: middle layer (media ='middle') muscle fibers (smooth or cardiac).
 t. innermost lumenal General Circulatory system heart and blood vessels walls have 3 layers (inside to outside) 1-Tunica interna: aka tunica intima layer--lumenal layer epithelium--endothelium simple squamous
t. innermost lumenal General Circulatory system heart and blood vessels walls have 3 layers (inside to outside) 1-Tunica interna: aka tunica intima layer--lumenal layer epithelium--endothelium simple squamous
Information about TIA
 Information about TIA Transient Ischemic Attack (mini-stroke) Did I have a TIA? Did you have stroke-like symptoms such as slurred speech or weakness in one arm that seemed to go away after a few minutes
Information about TIA Transient Ischemic Attack (mini-stroke) Did I have a TIA? Did you have stroke-like symptoms such as slurred speech or weakness in one arm that seemed to go away after a few minutes
Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation
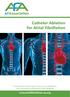 AF A Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary Anti-arrhythmic
AF A Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary Anti-arrhythmic
PATIENT WITH ARRHYTHMIA IN DENTIST S OFFICE. Małgorzata Kurpesa, MD., PhD. Chair&Department of Cardiology
 PATIENT WITH ARRHYTHMIA IN DENTIST S OFFICE Małgorzata Kurpesa, MD., PhD. Chair&Department of Cardiology Medical University of Łódź The heart is made up of four chambers Left Atrium Right Atrium Left Ventricle
PATIENT WITH ARRHYTHMIA IN DENTIST S OFFICE Małgorzata Kurpesa, MD., PhD. Chair&Department of Cardiology Medical University of Łódź The heart is made up of four chambers Left Atrium Right Atrium Left Ventricle
2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system
 2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system 2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system Essential questions: What are the functions of blood? What are
2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system 2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system Essential questions: What are the functions of blood? What are
10/8/2018. Lecture 9. Cardiovascular Health. Lecture Heart 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factor
 Lecture 9 Cardiovascular Health 1 Lecture 9 1. Heart 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factor 1 The Heart Muscular Pump The Heart Receives blood low pressure then increases the pressure
Lecture 9 Cardiovascular Health 1 Lecture 9 1. Heart 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factor 1 The Heart Muscular Pump The Heart Receives blood low pressure then increases the pressure
Types of circulatory systems
 Types of circulatory systems Open system Mostly invertebrates Low pressure Haemocoel Suitable for small organisms Closed system Vertebrates High pressure Blood remains in blood vessels Separate tissue
Types of circulatory systems Open system Mostly invertebrates Low pressure Haemocoel Suitable for small organisms Closed system Vertebrates High pressure Blood remains in blood vessels Separate tissue
Patient & Primary Care Checklist
 www.afa-us.org established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation Patient & Primary Care Checklist www.afa-us.org Tel: (843) 785 4101 Non-profit organization 501(C)(3) AFA 2011 AFA - US
www.afa-us.org established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation Patient & Primary Care Checklist www.afa-us.org Tel: (843) 785 4101 Non-profit organization 501(C)(3) AFA 2011 AFA - US
Get the Facts on Atrial Fibrillation
 Get the Facts on Atrial Fibrillation The content provided here is for informational purposes only. It is not intended to diagnose or treat a health problem or disease, or to replace professional medical
Get the Facts on Atrial Fibrillation The content provided here is for informational purposes only. It is not intended to diagnose or treat a health problem or disease, or to replace professional medical
Ventricular Tachycardia in Structurally Normal Hearts (Idiopathic VT) Patient Information
 Melbourne Heart Rhythm Ventricular Tachycardia in Structurally Normal Hearts (Idiopathic VT) Patient Information What is Ventricular Tachycardia? Ventricular tachycardia (VT) is an abnormal rapid heart
Melbourne Heart Rhythm Ventricular Tachycardia in Structurally Normal Hearts (Idiopathic VT) Patient Information What is Ventricular Tachycardia? Ventricular tachycardia (VT) is an abnormal rapid heart
The Circulatory System. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview The Circulatory System
 33.1 THINK ABOUT IT More than one-third of the 1.2 million Americans who suffer a heart attack each year die. This grim evidence shows that the heart and the circulatory system it powers are vital to life.
33.1 THINK ABOUT IT More than one-third of the 1.2 million Americans who suffer a heart attack each year die. This grim evidence shows that the heart and the circulatory system it powers are vital to life.
