Medical Terminology. 1 P a g e
|
|
|
- George Wilson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Medical Terminology 1 P a g e
2 2 P a g e
3 Medical Terminology Assignment Guidelines When terms are assigned, primarily the Latin or Greek word parts will be given; however, combined forms of the word parts as well as specific specialized terms that are not Latin based will be tested on. Each student will use a section of your 3-ring binder as a place to define your medterms. Format guidelines: A. Use a 3 - column format when defining Latin or Greek word parts. Use a format similar to what you see below. Word Part (also identify if it s a root, suffix, or prefix) Definition of Word Part Example of combined use of word with definition (This must be an actual word that exists in the Englsih language. It cannot be a made up word) Rhino (Root) Nose Rhinoceros: mammalian species of ungulates native to Africa and Asia, known prominently for their horns. Use some form of color-coding system to aid studying. For example you may want to use different colors to represent a root, prefix, or suffix B. Use Cornell-Note format when defining specialized terms presented to you. The definitions for these specialized terms can be found embedded within the assigned reading in your Medical Terminology textbook. For example Specialized Term Diagnosis Definition Identification of Disease *** Important note: it is your job to comb through the chapter as you define these terms. Any additional terms or combined use of the Latin and Greek word parts presented in the chapter are also still your responsibility to know. The terms given to you on your list to define are only the highlights. Med Terms are Accumulative 3 P a g e
4 Chapter 1 Med Term List Roots Prefixes Suffixes Specialized Terms Abdomin/o Ab- -algia Diagnosis Arteri/o Ad- -centisis Hypertension Arthr/o Dys- -dynia Hypotension Ather/o Endo- -ectomy Ileum Cardi/o Eu- -gram Ilium Cyan/o Hyper- -graphy Infection Enter/o Hypo- -itis Inflammation Erythr/o Inter- -malacia Ligation Gastr/o Intra- -megaly Mucous Hem/o Peri- -necrosis Mucus Hepat/o Sub- -ology Palpation Laryng/o Supra- -oma Palpitation Leuk/o -osis ( ism esis ia) Prognosis Melan/o -ostomy Prostate Myc/o -otomy Prostrate Myel/o -pathy Pyrosis My/o -plasty Supination Neur/o -rrhage Suppuration Ot/o -rrhaphy Symptom Poli/o -rrhea Syndrome Py/o -rrhexis Trauma Pyr/o -sclerosis Triage Rhin/o -scopy Viral -stenosis Virile 4 P a g e
5 Building Medical Termin/o logy My word part and definition My partner s word part and definition Another partner s word part and definition Our Word Parts Combined Translation 5 P a g e
6 6 P a g e
7 7 P a g e
8 8 P a g e
9 9 P a g e
10 10 P a g e
11 11 P a g e
12 12 P a g e
13 13 P a g e
14 14 P a g e
15 15 P a g e
16 Chapter 2 Med Term Focus: Human Body and Orientation and Genetic Diseases Note all Med Terms exams are cumulative! Terms marked with (*) you are expected to know these, but you do not need to define. Roots Prefixes Suffixes Specialized Terms Aden/o Bi- -crine Abdominopelvic * Adip/o Dia- -plasia Ascites Anter/o Epi- -plasm Anatomic position * Caud/o Gen- -stasis Anatomy * Cephal/o Exo- Anomaly Chondr/o Eti- Body Cavity * Chrom/o A- Cerebral Palsy Col/o Ante- Cystic Fibrosis Coron/o De- Deoxyribonucleic acid Crani/o Retro- Diaphragm Cyt/o Down Syndrome/Trisomy 21 Dist/o Dors/o or Dors/i Hepat/o Hist/o Home/o Hyster/o Infer/o Lapar/o Later/o Lumb/o Medi/o Nephr/o Oste/o Endothelium Epithelium Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Gametes Hemophilia Huntington s Disease/chorea Hypochondriac Iatrogenic idiopathic Inguinal Mesentery Muscular Dystrophy Nosocomial Path/o Nucleus * Poster/o Proxim/o Somat/o or Soma Parietal Peritoneum Phenylketonuria Spin/o Physiology * 16 P a g e
17 Roots Prefixes Suffixes Specialized Terms Super/o Sagittal * Thora/o or Thorac/o Sickle Cell Anemia Ventr/o Stem cells Tay-Sachs Disease Transverse * Umbilical * Visceral 17 P a g e
18 18 P a g e
19 19 P a g e
20 20 P a g e
21 21 P a g e
22 22 P a g e
23 23 P a g e
24 24 P a g e
25 25 P a g e
26 26 P a g e
27 27 P a g e
28 Chapter 5 Med Term Focus: Cardiovascular System - Structures Roots Specialized Terms Specialized Terms Cardi/o Pericardium Pulse Vascul/o Pericardial fluid Blood Pressure Arteri/o Epicardium Systolic Pressure Phag/o Myocardium Diastolic Pressure Hemat/o or hem/o Endocardium Plasma (blood plasma) Ven/o Coronary artery and veins Fibrinogen Angi/o Atrium Prothrombin Aort/o Interatrial septum Serum Phleb/o Interventricular septum Erythrocytes Thromb/o Tricuspid valve Hemoglobin Pulmonary semilunar valve Reticulocytes Prefixes Mitral valve or bicuspid valve Leukocytes End- Aortic semilunar valve Neutrophils Sinoatrial node (natural Tachy- pacemaker) Phagocytosis Atrioventricular node Basophils Suffixes Bundle of His Eosinophils -emia Purkinje fibers Lymphocytes Aorta Coronary artery Arterioles Capillaries Venules Superior Vena Cava Inferior Vena Cava Monocytes Thrombocytes (platelets) 28 P a g e
29 29 P a g e
30 30 P a g e
31 31 P a g e
32 32 P a g e
33 33 P a g e
34 34 P a g e
Chapter 1: Introduction to Medical Terminology
 Chapter 1: Introduction to Medical Terminology MATCHING Match each definition with the correct word part. a. abnormal condition b. deficient c. excessive d. pain e. surgical removal 1. -algia 2. -ectomy
Chapter 1: Introduction to Medical Terminology MATCHING Match each definition with the correct word part. a. abnormal condition b. deficient c. excessive d. pain e. surgical removal 1. -algia 2. -ectomy
Biomedical Terminology. Cardiovascular and Lymphatic System
 Biomedical Terminology Cardiovascular and Lymphatic System Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular system is composed of the Heart (cardi/o) Blood vessels (angi/o) Arteries (arteri/o) blood vessels which
Biomedical Terminology Cardiovascular and Lymphatic System Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular system is composed of the Heart (cardi/o) Blood vessels (angi/o) Arteries (arteri/o) blood vessels which
The Heart. Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet
 The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
Chapter 14. The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Biology 105 Human Biology QZM CVS. Cardiovascular System. Name these Vessels, Valves and Chambers
 Cardiovascular System Name these Vessels, Valves and Chambers 1. The heart and pericardium are located within the and medial to the A) pleural cavities B) peritoneal cavity C) cardiac skeleton D) mediastinum
Cardiovascular System Name these Vessels, Valves and Chambers 1. The heart and pericardium are located within the and medial to the A) pleural cavities B) peritoneal cavity C) cardiac skeleton D) mediastinum
Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process:
 Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: a. erythrocytes b. leukocytes c. melanocytes d. thrombocytes Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process: a. erythrocytes
Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: a. erythrocytes b. leukocytes c. melanocytes d. thrombocytes Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process: a. erythrocytes
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Overview Heart and Vessels 2 Major Divisions Pulmonary Circuit Systemic Circuit Closed and Continuous Loop Location Aorta Superior vena cava Right lung Pulmonary trunk Base of heart
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Overview Heart and Vessels 2 Major Divisions Pulmonary Circuit Systemic Circuit Closed and Continuous Loop Location Aorta Superior vena cava Right lung Pulmonary trunk Base of heart
Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al
 ACTIVITY 9: BLOOD AND HEART OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection instructions BEFORE YOU
ACTIVITY 9: BLOOD AND HEART OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection instructions BEFORE YOU
2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system
 2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system Essential questions What are the structures of blood? What are the structures of the circulatory system? circulatory system 2 Structures of the circulatory
2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system Essential questions What are the structures of blood? What are the structures of the circulatory system? circulatory system 2 Structures of the circulatory
ACTIVITY 9: BLOOD AND HEART BLOOD
 ACTIVITY 9: BLOOD AND HEART OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection instructions BEFORE YOU
ACTIVITY 9: BLOOD AND HEART OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection instructions BEFORE YOU
Major Function of the Cardiovascular System. Transportation. Structures of the Cardiovascular System. Heart - muscular pump
 Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
BLOOD I. Composition and Function of Blood
 BLOOD I. Composition and Function of Blood A. Components 1. Blood is the only fluid tissue 2. Has living blood cells and nonliving fluid matrix 3. Breakdown of blood sample a. Formed elements b. Plasma
BLOOD I. Composition and Function of Blood A. Components 1. Blood is the only fluid tissue 2. Has living blood cells and nonliving fluid matrix 3. Breakdown of blood sample a. Formed elements b. Plasma
List as many as you can think of Go To --Student Worksheet Med Terms I am going to start you off
 Medical Terminology You may fear learning medical terminology thinking of it as a whole new language. Actually it is just a combination of terms many of which you are familiar with. Each student needs
Medical Terminology You may fear learning medical terminology thinking of it as a whole new language. Actually it is just a combination of terms many of which you are familiar with. Each student needs
Medical Terminology The Fun in Deciphering Words. Julie A. Shay, RHIA Santa Fe HIT Program Director AAPC Conference September 29, 2012
 Julie A. Shay, RHIA Santa Fe HIT Program Director AAPC Conference September 29, 2012 Back to the Basics Pieces, Parts, Whole Body Systems Musculoskeletal Cardiovascular Solve the Puzzle 1. Word roots
Julie A. Shay, RHIA Santa Fe HIT Program Director AAPC Conference September 29, 2012 Back to the Basics Pieces, Parts, Whole Body Systems Musculoskeletal Cardiovascular Solve the Puzzle 1. Word roots
CIRCULATION & GAS EXCHANGE
 AP BIOLOGY ACTIVITY2.13 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter42 NAME DATE HOUR CIRCULATION & GAS EXCHANGE 1. In general, what is the function of transport systems? 2. What method/structure do most invertebrates use
AP BIOLOGY ACTIVITY2.13 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter42 NAME DATE HOUR CIRCULATION & GAS EXCHANGE 1. In general, what is the function of transport systems? 2. What method/structure do most invertebrates use
The Body as a Whole. Instructor Resource Material for
 5 Instructor Resource Material for The Body as a Whole HANDOUT 5.1 Listing Basic to Complex List the terms in order from most basic (1) to most complex (6): organs, organism, cells, chemicals, tissues,
5 Instructor Resource Material for The Body as a Whole HANDOUT 5.1 Listing Basic to Complex List the terms in order from most basic (1) to most complex (6): organs, organism, cells, chemicals, tissues,
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. All answers to questions asking for a combining form must be written in the combining form style,
Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. All answers to questions asking for a combining form must be written in the combining form style,
TEACHING TOOLS FOR CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
 TEACHING TOOLS FOR CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY CHAPTER 1 The Instructor Resources teaching tools for this chapter include: The answer key for the Learning Exercises for the chapter, located
TEACHING TOOLS FOR CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY CHAPTER 1 The Instructor Resources teaching tools for this chapter include: The answer key for the Learning Exercises for the chapter, located
CHAPTER 1 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY BUILDING BLOCKS
 CHAPTER 1 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY BUILDING BLOCKS COMPLETION 1. An enlarged stomach is known as. gastromegaly 2. Inflammation of the joints is known as. arthritis 3. Pertaining to the stomach is known as.
CHAPTER 1 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY BUILDING BLOCKS COMPLETION 1. An enlarged stomach is known as. gastromegaly 2. Inflammation of the joints is known as. arthritis 3. Pertaining to the stomach is known as.
Cardiovascular System. I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart
 Cardiovascular System I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart 1. : Pericardial Cavity serous fluid filled space between the heart and the pericardium B. Heart Wall 1.
Cardiovascular System I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart 1. : Pericardial Cavity serous fluid filled space between the heart and the pericardium B. Heart Wall 1.
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet Name: Date: Instructions: Put the answers to each task card in the numbered boxes on the chart. 1 a) left semilunar valve / aortic valve b) blood would backflow
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet Name: Date: Instructions: Put the answers to each task card in the numbered boxes on the chart. 1 a) left semilunar valve / aortic valve b) blood would backflow
Unit 8: Blood / Lymph / Cardiovascular System
 Name: Period: Unit 8: Blood / Lymph / Cardiovascular System Test Review 1. Identify the general formed elements of the blood and their general functions. a. Erythrocytes: b. Leukocytes: c. Thrombocytes:
Name: Period: Unit 8: Blood / Lymph / Cardiovascular System Test Review 1. Identify the general formed elements of the blood and their general functions. a. Erythrocytes: b. Leukocytes: c. Thrombocytes:
A DAYS CARDIOVASCULAR UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 4/12
 A DAYS CARDIOVASCULAR UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 4/12 MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY 3/20 - B 3/21 - A 3/22 - B 3/23 - A 3/24 - B 3/27 - A Dissection Ethics Debate 3/28 - B 3/29 - A Intro to Cardiovascular
A DAYS CARDIOVASCULAR UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 4/12 MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY 3/20 - B 3/21 - A 3/22 - B 3/23 - A 3/24 - B 3/27 - A Dissection Ethics Debate 3/28 - B 3/29 - A Intro to Cardiovascular
the Cardiovascular System I
 the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
The Cardiovascular System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Slides 11.1 11.19 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Cardiovascular System
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Slides 11.1 11.19 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Cardiovascular System
AP2 Lab 1 - Blood & Heart
 AP2 Lab 1 - Blood & Heart Project 1 - Formed Elements Identification & Recognition See fig. 17.10 and Table 17.2. Instructor may also provide other images. Note: See Fig. 17.11 All formed elements are
AP2 Lab 1 - Blood & Heart Project 1 - Formed Elements Identification & Recognition See fig. 17.10 and Table 17.2. Instructor may also provide other images. Note: See Fig. 17.11 All formed elements are
Appendix B English Terms
 Appendix B English Terms English Word Abnormal condition Abnormal condition (produced by something specified) above, upon above adrenal glands after, behind against air air, lung anterior, front anus,
Appendix B English Terms English Word Abnormal condition Abnormal condition (produced by something specified) above, upon above adrenal glands after, behind against air air, lung anterior, front anus,
STRUCTURES OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 STRUCTURES OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Also called the circulatory system Consists of the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries Main function is to pump/circulate oxygenated blood
STRUCTURES OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Also called the circulatory system Consists of the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries Main function is to pump/circulate oxygenated blood
CV Anatomy Quiz. Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green
 CV Anatomy Quiz Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green Q1 The location of the heart is correctly described as A) lateral to the lungs. B) medial to the sternum. C) superior to the diaphragm. D) posterior to the spinal
CV Anatomy Quiz Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green Q1 The location of the heart is correctly described as A) lateral to the lungs. B) medial to the sternum. C) superior to the diaphragm. D) posterior to the spinal
UNIT 8 - BLOOD / LYMPHATIC / CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEMS TERMINOLOGY
 UNIT 8 - BLOOD / LYMPHATIC / CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEMS TERMINOLOGY Prefixes, Suffixes, and Root Words an anti -apheresis -blast -crit -cyte cyt/o -emia erythr/o ferr fibr/o -gen hemat/o hem/o -ic -in -is
UNIT 8 - BLOOD / LYMPHATIC / CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEMS TERMINOLOGY Prefixes, Suffixes, and Root Words an anti -apheresis -blast -crit -cyte cyt/o -emia erythr/o ferr fibr/o -gen hemat/o hem/o -ic -in -is
MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY. Complete! Second Edition CHAPTER. The Human Body in Health and Disease Content Review Slides
 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY Complete! Second Edition CHAPTER 4 The Human Body in Health and Disease Content Review Slides Learning Objectives Define and spell the word parts used to create terms for the human
MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY Complete! Second Edition CHAPTER 4 The Human Body in Health and Disease Content Review Slides Learning Objectives Define and spell the word parts used to create terms for the human
Blood and Heart. Student Learning Objectives:
 Blood and Heart Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major components of the blood. Identify the primary structures associated with the heart Follow the blood through the path of the circulation.
Blood and Heart Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major components of the blood. Identify the primary structures associated with the heart Follow the blood through the path of the circulation.
The Cardiovascular System
 11 PART A The Cardiovascular System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Cardiovascular
11 PART A The Cardiovascular System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart
 Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart Interesting Heart Fact Capillaries are so small it takes ten of them to equal the thickness of a human hair. Review What are the 3 parts of the cardiovascular
Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart Interesting Heart Fact Capillaries are so small it takes ten of them to equal the thickness of a human hair. Review What are the 3 parts of the cardiovascular
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System The Heart Cardiovascular System The Heart Overview What does the heart do? By timed muscular contractions creates pressure gradients blood moves then from high pressure to low pressure
Cardiovascular System The Heart Cardiovascular System The Heart Overview What does the heart do? By timed muscular contractions creates pressure gradients blood moves then from high pressure to low pressure
Cardiovascular System
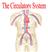 Cardiovascular System BELLWORK: Define using technology angio hemo/hema cardio brady as in bradycardia tachy as in tachycardia Standards 8) Outline basic concepts of normal structure and function of all
Cardiovascular System BELLWORK: Define using technology angio hemo/hema cardio brady as in bradycardia tachy as in tachycardia Standards 8) Outline basic concepts of normal structure and function of all
Clinical Cardiovascular System Quiz
 Quiz Description Clinical Cardiovascular System Quiz Q.1) Q.2) Q.3) Q.4) Q.5) Q.6) Q.7) Q.8) The prefix angio refers to. artery blood heart cavity ves sel The prefix cardio refers to. veins heart blood
Quiz Description Clinical Cardiovascular System Quiz Q.1) Q.2) Q.3) Q.4) Q.5) Q.6) Q.7) Q.8) The prefix angio refers to. artery blood heart cavity ves sel The prefix cardio refers to. veins heart blood
This system consists of the heart (cardi/o) and blood vessels (vascular). It is this system
 SECTION 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM This system consists of the heart (cardi/o) and blood vessels (vascular). It is this system that allows blood to travel through the body. The heart works as a pump to keep
SECTION 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM This system consists of the heart (cardi/o) and blood vessels (vascular). It is this system that allows blood to travel through the body. The heart works as a pump to keep
Sample Exam Biology 2050 Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems
 Sample Exam Biology 2050 Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems Note: Not all of the lymphatic system will be on the actual exam next Monday so disregard any questions that deal with something that wasn t covered
Sample Exam Biology 2050 Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems Note: Not all of the lymphatic system will be on the actual exam next Monday so disregard any questions that deal with something that wasn t covered
The Cardiovascular System
 The Cardiovascular System The Manila Times College of Subic Prepared by: Stevens B. Badar, RN, MANc THE HEART Anatomy of the Heart Location and Size approx. the size of a person s fist, hollow and cone-shaped,
The Cardiovascular System The Manila Times College of Subic Prepared by: Stevens B. Badar, RN, MANc THE HEART Anatomy of the Heart Location and Size approx. the size of a person s fist, hollow and cone-shaped,
Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 19 Worksheet 1- The Heart
 Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 19 Worksheet 1- The Heart Name Date Period 1. The "double pump" function of the heart includes the right side, which serves as the circuit pump, while the left side
Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 19 Worksheet 1- The Heart Name Date Period 1. The "double pump" function of the heart includes the right side, which serves as the circuit pump, while the left side
Unit 10 Cardiovascular System
 Unit 10 Cardiovascular System I. Functions Deliver nutrients to cells > O 2, sugars, amino acids, lipids, ions, H 2 O... Remove waste from cells > CO 2, pathogens, toxins, lactic acid... Fight off infection
Unit 10 Cardiovascular System I. Functions Deliver nutrients to cells > O 2, sugars, amino acids, lipids, ions, H 2 O... Remove waste from cells > CO 2, pathogens, toxins, lactic acid... Fight off infection
2. right heart = pulmonary pump takes blood to lungs to pick up oxygen and get rid of carbon dioxide
 A. location in thorax, in inferior mediastinum posterior to sternum medial to lungs superior to diaphragm anterior to vertebrae orientation - oblique apex points down and to the left 2/3 of mass on left
A. location in thorax, in inferior mediastinum posterior to sternum medial to lungs superior to diaphragm anterior to vertebrae orientation - oblique apex points down and to the left 2/3 of mass on left
THE HEART. A. The Pericardium - a double sac of serous membrane surrounding the heart
 THE HEART I. Size and Location: A. Fist-size weighing less than a pound (250 to 350 grams). B. Located in the mediastinum between the 2 nd rib and the 5 th intercostal space. 1. Tipped to the left, resting
THE HEART I. Size and Location: A. Fist-size weighing less than a pound (250 to 350 grams). B. Located in the mediastinum between the 2 nd rib and the 5 th intercostal space. 1. Tipped to the left, resting
The Circulatory System. The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types
 The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system
 2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system 2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system Essential questions: What are the functions of blood? What are
2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system 2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system Essential questions: What are the functions of blood? What are
Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart -
 Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart - Give a detailed description of the superficial and internal anatomy of the heart, including the pericardium, the myocardium, and the cardiac muscle. Trace the
Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart - Give a detailed description of the superficial and internal anatomy of the heart, including the pericardium, the myocardium, and the cardiac muscle. Trace the
KEY - Sample Exam Biology 2050 Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems - KEY
 KEY - Sample Exam Biology 2050 Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems - KEY Note: Not all of the lymphatic system will be on the actual exam next Monday so disregard any questions that deal with something that
KEY - Sample Exam Biology 2050 Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems - KEY Note: Not all of the lymphatic system will be on the actual exam next Monday so disregard any questions that deal with something that
Transport in Animals. Gastrovascular cavities. Nutrients and gases can move by processes such as diffusion and active transport.
 Transport in Animals Gastrovascular cavities flatworms and cnidarians Nutrients and gases can move by processes such as diffusion and active transport. Figure 42.1 Internal transport in the cnidarian
Transport in Animals Gastrovascular cavities flatworms and cnidarians Nutrients and gases can move by processes such as diffusion and active transport. Figure 42.1 Internal transport in the cnidarian
THE HEART OBJECTIVES: LOCATION OF THE HEART IN THE THORACIC CAVITY CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY II CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR THE HEART OBJECTIVES: Describe the anatomy of the heart and identify and give the functions of all parts. (pp. 356 363) Trace the flow of blood
BIOLOGY II CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR THE HEART OBJECTIVES: Describe the anatomy of the heart and identify and give the functions of all parts. (pp. 356 363) Trace the flow of blood
Upon completion of this continuing education course, the professional should be able to:
 COURSE DESCRIPTION This course is designed for individuals working in medical support services (e.g., billing, insurance, transcription, records, medical assisting, etc.) to review, refine, and expand
COURSE DESCRIPTION This course is designed for individuals working in medical support services (e.g., billing, insurance, transcription, records, medical assisting, etc.) to review, refine, and expand
Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders
 Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders Interesting Heart Facts The Electrocardiograph (ECG) was invented in 1902 by Willem Einthoven Dutch Physiologist. This test is still used to evaluate
Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders Interesting Heart Facts The Electrocardiograph (ECG) was invented in 1902 by Willem Einthoven Dutch Physiologist. This test is still used to evaluate
Anatomy of the Heart. Figure 20 2c
 Anatomy of the Heart Figure 20 2c Pericardium & Myocardium Remember, the heart sits in it s own cavity, known as the mediastinum. The heart is surrounded by the Pericardium, a double lining of the pericardial
Anatomy of the Heart Figure 20 2c Pericardium & Myocardium Remember, the heart sits in it s own cavity, known as the mediastinum. The heart is surrounded by the Pericardium, a double lining of the pericardial
The Cardiovascular System
 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
4. The two inferior chambers of the heart are known as the atria. the superior and inferior vena cava, which empty into the left atrium.
 Answer each statement true or false. If the statement is false, change the underlined word to make it true. 1. The heart is located approximately between the second and fifth ribs and posterior to the
Answer each statement true or false. If the statement is false, change the underlined word to make it true. 1. The heart is located approximately between the second and fifth ribs and posterior to the
PRINTABLE FLASHCARD DIRECTIONS:
 PRINTABLE FLASHCARD DIRECTIONS: Use Avery 8471 Business Cards. 10 cards per sheet x 220 cards = 22 sheets. (You can also reformat to fit other size cards). Just be careful to align word parts with definitions
PRINTABLE FLASHCARD DIRECTIONS: Use Avery 8471 Business Cards. 10 cards per sheet x 220 cards = 22 sheets. (You can also reformat to fit other size cards). Just be careful to align word parts with definitions
The Heart. The Heart A muscular double pump. The Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits
 C H A P T E R 19 The Heart The Heart A muscular double pump circuit takes blood to and from the lungs Systemic circuit vessels transport blood to and from body tissues Atria receive blood from the pulmonary
C H A P T E R 19 The Heart The Heart A muscular double pump circuit takes blood to and from the lungs Systemic circuit vessels transport blood to and from body tissues Atria receive blood from the pulmonary
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System Heart: hollow muscular organ, pumps blood full of nutrients throughout the body Arteries: carry blood away from the heart Capillaries: smaller vessels, microscopic, exchange of nutrients
Cardiovascular System Heart: hollow muscular organ, pumps blood full of nutrients throughout the body Arteries: carry blood away from the heart Capillaries: smaller vessels, microscopic, exchange of nutrients
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System angio BELLWORK Day One: Define using technology hemo/hema cardio Medical Therapeutics Standards 11) Outline the gross normal structure and function of all body systems and summarize
Cardiovascular System angio BELLWORK Day One: Define using technology hemo/hema cardio Medical Therapeutics Standards 11) Outline the gross normal structure and function of all body systems and summarize
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM. Part 1
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Part 1 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Blood Heart Blood vessels What is the function of this system? What other systems does it affect? CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Functions Transport gases,
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Part 1 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Blood Heart Blood vessels What is the function of this system? What other systems does it affect? CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Functions Transport gases,
Figure ) The specific chamber of the heart that is indicated by letter A is called the. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 364
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Short Answer Figure 11.1 Using Figure 11.1, identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label.
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Short Answer Figure 11.1 Using Figure 11.1, identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label.
Chapter 20 (1) The Heart
 Chapter 20 (1) The Heart Learning Objectives Describe the location and structure of the heart Describe the path of a drop of blood from the superior vena cava or inferior vena cava through the heart out
Chapter 20 (1) The Heart Learning Objectives Describe the location and structure of the heart Describe the path of a drop of blood from the superior vena cava or inferior vena cava through the heart out
The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle.
 The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle. From this camber, it passes through the pulmonary semilunar valve
The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle. From this camber, it passes through the pulmonary semilunar valve
Test Review Circulatory System Chapters
 Test Review Circulatory System Chapters 13-2010 1. The tissue that forms the tight fitting sac around the heart is the a. parietal pericardium c. myocardium b. visceral pericardium d. endocardium 2. Which
Test Review Circulatory System Chapters 13-2010 1. The tissue that forms the tight fitting sac around the heart is the a. parietal pericardium c. myocardium b. visceral pericardium d. endocardium 2. Which
MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY. Complete! Second Edition CHAPTER. Understanding Suffixes. Content Review Slides
 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY Complete! Second Edition CHAPTER 2 Understanding Suffixes Content Review Slides Learning Objectives Define and spell the suffixes often used in medical terminology. Identify suffixes
MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY Complete! Second Edition CHAPTER 2 Understanding Suffixes Content Review Slides Learning Objectives Define and spell the suffixes often used in medical terminology. Identify suffixes
Chapter 18 - Heart. I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity)
 Chapter 18 - Heart I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity) A. Coverings: heart enclosed in double walled sac called the pericardium 1. Fibrous pericardium: dense connective
Chapter 18 - Heart I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity) A. Coverings: heart enclosed in double walled sac called the pericardium 1. Fibrous pericardium: dense connective
2. What makes up the most of your blood? least of your blood? 1. Look like red discs, have a pale center, no nucleus, similar in size
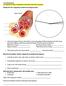 .I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
.I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
2/28/18. Cardiovascular System. Introduction. Anatomy. Chapter 26. Body is 60% to 80% fluid (by volume) Systems responsible for fluid movement are:
 Cardiovascular System Chapter 26 1 Introduction Body is 60% to 80% fluid (by volume) Systems responsible for fluid movement are: - Cardiovascular helps move fluid - Lymphatic Both called pick-up and delivery
Cardiovascular System Chapter 26 1 Introduction Body is 60% to 80% fluid (by volume) Systems responsible for fluid movement are: - Cardiovascular helps move fluid - Lymphatic Both called pick-up and delivery
9 Review. Labeling Exercise. Blood high in oxygen. Blood low in oxygen. Chapter 9 Circulation: The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 195
 Chapter 9 Circulation: The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 195 Chapter 9 Review Labeling Exercise THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Write the name of each numbered part on the corresponding line of the answer
Chapter 9 Circulation: The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 195 Chapter 9 Review Labeling Exercise THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Write the name of each numbered part on the corresponding line of the answer
Bio 104 Cardiovascular System
 29 Blood: Introduction (Chapter 14) A. Characteristics of Blood 1. Blood Volume Lecture Outline: Cardiovascular System Hole s HAP [Chapters 14, 15, 16] 2. Blood Composition a. Blood Cells Red blood cells
29 Blood: Introduction (Chapter 14) A. Characteristics of Blood 1. Blood Volume Lecture Outline: Cardiovascular System Hole s HAP [Chapters 14, 15, 16] 2. Blood Composition a. Blood Cells Red blood cells
The Cardiovascular System (Heart)
 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System (Heart) A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function
The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System (Heart) A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences College of Agriculture & Veterinary Medicine RMTU San Marcelino Introduction The cardiovascular system
The Circulatory System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences College of Agriculture & Veterinary Medicine RMTU San Marcelino Introduction The cardiovascular system
The Cardiovascular System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Slides 11.1 11.19 Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Functions of the Cardiovascular system Function of the heart: to pump blood
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Slides 11.1 11.19 Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Functions of the Cardiovascular system Function of the heart: to pump blood
Chapter 12 Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 12 Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular System Includes Heart and Blood Vessels Transports, nutrients and wastes to and from the tissues 1 The Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Arteries:
Chapter 12 Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular System Includes Heart and Blood Vessels Transports, nutrients and wastes to and from the tissues 1 The Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Arteries:
Lab 1 Blood Composition and formed elements
 Lab 1 Blood Composition and formed elements Plasma 55% of whole blood 90% water 8% proteins from liver 2% misc. Nutrients: AA, glucose, lipids vitamins, minerals Wastes: urea, uric acid, creatine, ammonium
Lab 1 Blood Composition and formed elements Plasma 55% of whole blood 90% water 8% proteins from liver 2% misc. Nutrients: AA, glucose, lipids vitamins, minerals Wastes: urea, uric acid, creatine, ammonium
C3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 Worksheet. C3 Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the heart
 Name: Date: C3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 Worksheet C3 Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the heart 1. Label and give the functions of the following: a. left and right atrium: b. left and right ventricle:
Name: Date: C3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 Worksheet C3 Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the heart 1. Label and give the functions of the following: a. left and right atrium: b. left and right ventricle:
HUMAN HEART. Learn the following structures on the heart models.
 HUMAN HEART Learn the following structures on the heart models. The human heart has four chambers that consist of the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The atria are smaller
HUMAN HEART Learn the following structures on the heart models. The human heart has four chambers that consist of the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The atria are smaller
Large Arteries of Heart
 Cardiovascular System (Part A-2) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Arteries Capillaries Veins Heart Anatomy Conduction System Blood pressure Fetal circulation Susie Turner, M.D. 1/5/13 Large Arteries of Heart
Cardiovascular System (Part A-2) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Arteries Capillaries Veins Heart Anatomy Conduction System Blood pressure Fetal circulation Susie Turner, M.D. 1/5/13 Large Arteries of Heart
The Cardiovascular System. Chapter 15. Cardiovascular System FYI. Cardiology Closed systemof the heart & blood vessels. Functions
 Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
The cardiovascular system is composed of the heart and blood vessels that carry blood to and from the body s organs. There are 2 major circuits:
 1 The cardiovascular system is composed of the heart and blood vessels that carry blood to and from the body s organs. There are 2 major circuits: pulmonary and systemic. The pulmonary goes out to the
1 The cardiovascular system is composed of the heart and blood vessels that carry blood to and from the body s organs. There are 2 major circuits: pulmonary and systemic. The pulmonary goes out to the
Circulatory System: Introduction. Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt. San Antonio College
 Circulatory System: Introduction Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt. San Antonio College Components Cardiovascular system Lymphatic system Cardiovascular system Heart, blood vessels, blood Functions: transport
Circulatory System: Introduction Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt. San Antonio College Components Cardiovascular system Lymphatic system Cardiovascular system Heart, blood vessels, blood Functions: transport
10. Thick deposits of lipids on the walls of blood vessels, called, can lead to serious circulatory issues. A. aneurysm B. atherosclerosis C.
 Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Heart Anatomy. 7/5/02 Stephen G Davenport 1
 Heart Anatomy Copyright 1999, Stephen G. Davenport, No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form without prior written permission. 7/5/02 Stephen
Heart Anatomy Copyright 1999, Stephen G. Davenport, No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form without prior written permission. 7/5/02 Stephen
Human Anatomy, First Edition
 Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 22 : Heart 1 Functions of the Heart Center of the cardiovascular system, the heart. Connects to blood vessels that transport blood between the
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 22 : Heart 1 Functions of the Heart Center of the cardiovascular system, the heart. Connects to blood vessels that transport blood between the
Middle mediastinum---- heart & pericardium. Dep. of Human Anatomy Zhou Hongying
 Middle mediastinum---- heart & pericardium Dep. of Human Anatomy Zhou Hongying eaglezhyxzy@163.com Subdivisions of the mediastinum Contents of Middle mediastinum Heart Pericardium: a serous sac enclosing
Middle mediastinum---- heart & pericardium Dep. of Human Anatomy Zhou Hongying eaglezhyxzy@163.com Subdivisions of the mediastinum Contents of Middle mediastinum Heart Pericardium: a serous sac enclosing
Bellwork Define: hemostasis anticoagulation hemophilia (Then write the underline portion of the two state standards in your notes).
 Bellwork Define: hemostasis anticoagulation hemophilia (Then write the underline portion of the two state standards in your notes). A&P Standards 31) Identify the liquid and cellular components of blood
Bellwork Define: hemostasis anticoagulation hemophilia (Then write the underline portion of the two state standards in your notes). A&P Standards 31) Identify the liquid and cellular components of blood
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
Lab Activity 23. Cardiac Anatomy. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 23 Cardiac Anatomy Portland Community College BI 232 Cardiac Muscle Histology Branching cells Intercalated disc: contains many gap junctions connecting the adjacent cell cytoplasm, creates
Lab Activity 23 Cardiac Anatomy Portland Community College BI 232 Cardiac Muscle Histology Branching cells Intercalated disc: contains many gap junctions connecting the adjacent cell cytoplasm, creates
NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY
 NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY Testing Services and School of Allied Health & Communicative Disorders HSCI 318 Proficiency Examination Medical Terminology COURSE DESCRIPTION: A study of the basic language
NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY Testing Services and School of Allied Health & Communicative Disorders HSCI 318 Proficiency Examination Medical Terminology COURSE DESCRIPTION: A study of the basic language
Cardiovascular System- Heart. Miss Wheeler Unit 8
 Cardiovascular System- Heart Miss Wheeler Unit 8 Overview CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM heart vessels Made up of heart, blood vessels, and blood Functions Heart- pump blood Vessels- (veins, arteries, capillaries)
Cardiovascular System- Heart Miss Wheeler Unit 8 Overview CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM heart vessels Made up of heart, blood vessels, and blood Functions Heart- pump blood Vessels- (veins, arteries, capillaries)
AN ATOMY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 Student Name CHAPTER 18 AN ATOMY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM T he heart is actually two pumps one moves blood to the lungs, the other pushes it out into the body. These two functions seem rather elementary
Student Name CHAPTER 18 AN ATOMY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM T he heart is actually two pumps one moves blood to the lungs, the other pushes it out into the body. These two functions seem rather elementary
Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation
 1 Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Section 9.1 Homeostasis: Life in the Balance Outcomes: I can explain homeostasis I can describe the importance of homeostasis to living things I can explain the
1 Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Section 9.1 Homeostasis: Life in the Balance Outcomes: I can explain homeostasis I can describe the importance of homeostasis to living things I can explain the
Chapter 12. Capillaries. Circulation. The circulatory system connects with all body tissues
 Chapter 12 Circulation The circulatory system connects with all body s In many animals, microscopic blood vessels called capillaries Form an intricate network among the Red blood cell song Figure 23.1A
Chapter 12 Circulation The circulatory system connects with all body s In many animals, microscopic blood vessels called capillaries Form an intricate network among the Red blood cell song Figure 23.1A
Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1 -
 Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1-2. Organs of a closed circulatory system: A. Have valves a. Arteriole B. Regulate blood flow b. Artery C. Lead to heart
Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1-2. Organs of a closed circulatory system: A. Have valves a. Arteriole B. Regulate blood flow b. Artery C. Lead to heart
Class XI Chapter 18 Body Fluids and Circulation Biology
 Question 1: Name the components of the formed elements in the blood and mention one major function of each of them. The component elements in the blood are: (1) Erythrocytes: They are the most abundant
Question 1: Name the components of the formed elements in the blood and mention one major function of each of them. The component elements in the blood are: (1) Erythrocytes: They are the most abundant
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies
 Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
Lab 6: Blood. BIO104 Laboratory Handouts 147. Unit 12: Blood and Lymphatics. 1. Blood Characteristics Volume Functions Composition -
 147 Lab 6: Blood Unit 12: Blood and Lymphatics Ex. 12-1: Formed Elements (Cells) of Blood, p. 313-316 1. Blood Characteristics Volume Functions Composition - 2. Leukocytes (WBCs) a. WBC count normal b.
147 Lab 6: Blood Unit 12: Blood and Lymphatics Ex. 12-1: Formed Elements (Cells) of Blood, p. 313-316 1. Blood Characteristics Volume Functions Composition - 2. Leukocytes (WBCs) a. WBC count normal b.
Blood Functions. Blood and the Cardiovascular System. Blood. Plasma. Erythrocytes (RBCs) Erythrocytes (RBCs) 4/7/2017
 Blood Functions Blood and the Cardiovascular System Distribution Delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all body cells; Transport of wastes to lungs and excretory organs; Transport of hormones Regulation
Blood Functions Blood and the Cardiovascular System Distribution Delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all body cells; Transport of wastes to lungs and excretory organs; Transport of hormones Regulation
THE HEART. Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration
 THE HEART Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration The Circulatory System Also called the Cardiovascular System Circulates blood in the body Transports nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood
THE HEART Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration The Circulatory System Also called the Cardiovascular System Circulates blood in the body Transports nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood
The HEART. What is it???? Pericardium. Heart Facts. This muscle never stops working It works when you are asleep
 This muscle never stops working It works when you are asleep The HEART It works when you eat It really works when you exercise. What is it???? Located between the lungs in the mid thoracic region Apex
This muscle never stops working It works when you are asleep The HEART It works when you eat It really works when you exercise. What is it???? Located between the lungs in the mid thoracic region Apex
