1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary.
|
|
|
- Claude Tyler
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
2 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with sphincter muscles in order to A. prevent the backflow of blood. B. expand and recoil with each heart beat. C. divert blood toward areas of increased metabolic activity. D. hold blood in the beds until nutrient and waste exchange is complete. 3. Which of the following best describes a vein? A. Thin-walled, elastic, and equipped with valves. B. Thick-walled, elastic, and equipped with valves. C. Thin-walled, muscular, and supplied with nerves. D. Thick-walled, muscular, and supplied with nerves. 4. The function of an artery is to A. transport blood toward the heart. B. transport blood away from the heart. C. connect the right and left atria directly. D. carry carbon dioxide to the tissue cells. 5. A blood vessel that transports blood out of a capillary bed is a(n) A. vein. B. artery. C. venule. D. arteriole. 6. The most muscular chamber of the heart is the A. left atrium. B. C. left ventricle. D. right ventricle. 7. Based on its function, the heart is often referred to as a double pump. Which of the following would explain this? A. The heart has two sets of valves. B. The heart is controlled by both nerves and hormones. C. The heart moves blood through two circulatory pathways. D. The heart moves blood containing both nutrients and wastes. 8. The structures attached to the atrioventricular valves are called A. atria. B. pulmonary veins. C. semilunar valves. D. chordae tendineae. 9. The main function of the valves in the heart is to A. prevent back-flow of blood. B. divide the heart into four chambers. C. control the volume of blood leaving the heart. D. control the volume of blood entering the heart. 10. Blood leaves the right ventricle via the A. aorta. B. pulmonary trunk. C. coronary arteries. D. anterior vena cava. 11. An irregular heartbeat where contraction of the atria does not always result in contraction of the ventricles, likely indicates a problem with the A. SA node. B. AV node. C. AV valve. D. semi-lunar valve. 12. A condition called tachycardia exists when a person s heartrate is abnormally high. Which of the following explains how tachycardia may arise? A. The Purkinje fibres are over-stimulating the pacemaker. B. The sinoatrial (SA) node is receiving increased stimulation. C. There is increased stimulation by the parasympathetic nervous system. D. Impulses from the sinoatrial (SA) node are not reaching the atrioventricular (AV) node. 13. The atrioventricular (AV) node stimulates the A. aorta. B. Purkinje fibers. C. sinoatrial (SA) node. D. atrioventricular valves. 14. The coordinating structure responsible for an intrinsic heart beat is the A. cerebellum. B. sinoatrial node. C. chordae tendineae. D. sympathetic nervous system. 15. What happens during atrial diastole? A. Atria fill with blood. B. Semi-lunar valves close. C. Ventricles fill with blood. D. Atrioventricular valves open Systole of the ventricles. 2. Opening of the atrio-ventricular valves. 3. Electrical impulse sent from the SA node. 4. Atria fill with blood. The order in which the events above occur during one heartbeat (the cardiac cycle) is A. 2, 1, 3, 4 B. 2, 3, 4, 1 C. 4, 1, 3, 2 D. 4, 3, 2, The blood vessels that carry blood to and from the head are the A. iliac arteries and veins. B. subclavian arteries and veins. C. carotid arteries and jugular veins. D. anterior (superior) and posterior (inferior) vena cavae. 18. The path followed by blood on one circuit through the heart is A. ventricle, atrioventricular valve, semilunar valve, atrium. B. atrium, atrioventricular valve, ventricle, semilunar valve. C. atrium, ventricle, atrioventricular valve, semilunar valve. D. atrium, semilunar valve, ventricle, atrioventricular valve. 19. Which of the following is a characteristic of pulmonary circulation? A. Blood leaves the heart via the aorta. B. Blood in the arteries is deoxygenated. C. Blood in the veins is travelling to the lungs. D. Blood in capillaries absorbs high levels of carbon dioxide. 20. The blood vessel that carries blood from the lungs to the heart is the A. coronary vein. B. coronary artery. C. pulmonary vein. D. pulmonary artery.
3 21. Blood leaves the liver by way of the A. iliac vein. B. renal vein. C. hepatic vein. D. hepatic portal vein. 22. Blood with a high oxygen concentration can be found in both the A. renal artery and the pulmonary artery. B. umbilical vein and the pulmonary vein. C. pulmonary vein and the umbilical artery. D. pulmonary artery and the umbilical artery. 23. Which of the following is a characteristic of systemic circulation? A. Highly oxygenated arterial blood. B. Highly oxygenated venous blood. C. Increased blood pressure in the veins. D. Decreased blood pressure in the arteries. 24. A red blood cell leaves the aorta, makes a circuit through the body and arrives back in the capillaries of the alveoli. The correct sequence of organs through which the cell may have travelled is A. lungs, heart, small intestine, liver. B. small intestine, heart, liver, lungs. C. liver, lungs, small intestine, heart. D. small intestine, liver, heart, lungs. 25. Which of the following would describe the path of the blood in the pulmonary circuit? A. Right ventricle pulmonary trunk pulmonary vein left atrium. B. Left ventricle pulmonary vein pulmonary trunk C. Right ventricle pulmonary vein pulmonary artery left atrium. D. Right atrium pulmonary trunk aorta vena cava 26. The correct path of blood from the heart to the head and back to the heart again is A. right ventricle, vena cava, carotid artery, jugular vein, left atrium. B. left ventricle, aorta, jugular vein, vena cava, carotid artery, C. left ventricle, aorta, carotid artery, jugular vein, vena cava, D. right atrium, carotid artery, aorta, jugular vein, vena cava, left ventricle. 29. Which of the following is a characteristic of systemic circulation? A. Highly oxygenated arterial blood. B. Increased blood pressure in the veins. C. Low carbon dioxide concentration in the veins. D. Increased concentration of reduced hemoglobin (HHb) in the arterial blood. 30. A red blood cell is located in an artery in your right arm. How many capillary beds must this cell pass through before it is returned to the left ventricle? A. one B. two C. three D. four 31. An increase in which of the following would cause hypotension? A. heart rate B. cardiac output C. arteriole dilation D. reabsorption of water by the kidneys 32. Hypertension would be indicated by a blood pressure reading of A. 100 / 80 B. 120 / 50 C. 120 / 80 D. 150 / Which of the following is normal resting systolic blood pressure for an adult? A. 50 mm Hg B. 80 mm Hg C. 120 mm Hg D. 180 mm Hg 34. Blood pressure will be at its highest when A. atria relaxes. B. atria contracts. C. ventricles relax. D. ventricles contract. 35. The highest blood pressure in the aorta occurs when the A. atria contract. B. heart muscle is relaxed. C. blood is pushed to the ventricle. D. blood is pumped from the heart. 36. Capillary beds are equipped with sphincter muscles in order to A. prevent the backflow of blood. B. expand and recoil with each heart beat. C. divert blood toward areas of increased metabolic activity. D. hold blood in the beds until nutrient and waste exchange is complete. 27. The artery that provides oxygen and nutrients to heart tissue is the A. carotid. B. systemic. C. coronary. D. pulmonary. 28. In which of the following vessels would blood contain the highest concentration of carbon dioxide? A. Aorta. B. Carotid artery. C. Pulmonary vein. D. Pulmonary artery.
4 37. Which of the following would occur as a result of the oval opening in the heart remaining open after birth? A. Blood pressure in the lungs would increase. B. Impulses from the sinoatrial (SA) node would stop. C. Blood in the right atrium would mix with blood in the left atrium. D. A greater amount of blood would flow into the pulmonary system. 38. Which of the following structures in fetal circulation functions to deliver blood, which is high in waste, to the placenta? A. Venous duct. B. Umbilical vein. C. Pulmonary veins. D. Umbilical arteries. 39. How do the oxygen and nutrient levels in the adult vena cava compare to those levels in the fetal vena cava? A. The fetal oxygen and nutrient levels are higher. B. The adult oxygen and nutrient levels are higher. C. The fetal nutrient levels are higher, while the oxygen levels are lower. D. The adult nutrient levels are higher, while the oxygen levels are lower. 40. The sequence of structures through which the nerve impulse passes to cause contraction of the heart is A. AV node SA node Purkinje fibres. B. Purkinje fibres AV node SA node. C. Purkinje fibres SA node AV node. D. SA node AV node Purkinje fibres. 41. Thick walls, elastic tissue and smooth muscle are characteristics of A. veins. B. arteries. C. arterioles. D. capillaries. 42. Blockages in which of the following blood vessels reduces blood flow to the heart muscle? A. Aorta. B. Carotid artery. C. Coronary artery. D. Pulmonary artery. 43. A blood vessel which has numerous valves is a(n) A. vein. B. artery. C. arteriole. D. capillary. 44. Which of the following blood vessels provides nutrients to the heart tissue? A. Aorta. B. Carotid artery. C. Coronary artery. D. Inferior vena cava. 45. The SA node (pacemaker) of the heart is located in the wall of the A. left atrium. B. C. left ventricle. D. right ventricle. 46. Which of the following is a function of red blood cells? A. clot blood B. carry oxygen C. fight infection D. regulate osmotic pressure 47. The major component of human blood is A. plasma. B. platelets. C. red cells. D. white cells. 48. transport gases maintain body temperature protect the body against blood loss produce hormones that stimulate metabolism carry digestive enzymes to the small intestine How many of these are functions of the blood? A. two B. three C. four D. five 49. A foreign substance that stimulates an immune response is a(n) A. cancer. B. antigen. C. antibody. D. promoter. 50. Which of the following correctly matches structure with function? A. platelets provide immunity B. plasma proteins carry oxygen C. red blood cells carry carbon dioxide D. white blood cells initiate blood clotting 51. Plasma is composed mostly of A. salt. B. water. C. protein. D. hormones. 52. All of the following are components of plasma except A. salts. B. water. C. proteins. D. platelets.
5 53. Red blood cells originate in the A. liver. B. lymph nodes. C. bone marrow. D. capillary beds. 54. The main function of platelets is to A. fight disease. B. carry oxygen. C. carry nutrients. D. aid in blood clotting. 55. An important function of white blood cells is to A. buffer blood. B. carry oxygen. C. fight infection. D. carry carbon dioxide. 56. Blood proteins are made in the A. liver. B. kidney. C. stomach. D. pancreas. 57. Blood which lacks platelets would not be able to A. clot. B. carry oxygen. C. fight infections. D. transport nutrients Calcium activates an enzyme. 2. Fibrin binds platelets to form a plug. 3. Thrombin converts fibrinogen to fibrin. 4. Platelets and damaged cells release an activator. The correct sequence of events leading to the formation of a blood clot is A. 1, 2, 3, 4. B. 2, 1, 3, 4. C. 3, 4, 1, 2. D. 4, 1, 3, Which of the following is directly involved in the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin? A. Fibrin. B. Carbonic anhydrase. C. Calcium ions (Ca 2+ ) D. Magnesium ions (Mg 2+ ) 60. What occurs when an antigen enters the body? A. There is increased platelet production. B. Red blood cells phagocytize the antigen. C. Antibodies change shape to fit the antigen. D. Specific antibodies are produced and released. 61. The presence of bacteria in the blood will cause the body to produce A. mucus. B. antigens. C. antibodies. D. hydrochloric acid. 62. A foreign substance entering the circulatory system is called a(n) A. platelet. B. antigen. C. antibody. D. hormone. 63. A person with type AB blood has A. A antigens and B antibodies. B. both A and B antigens and A and B antibodies. C. no A or B antigens but both A and B antibodies. D. both A and B antigens but no A or B antibodies. 62. Which of the following blood transfusions is compatible? A. Donor type A and recipient type O. B. Donor type A and recipient type B. C. Donor type O and recipient type B. D. Donor type AB and recipient type O. 63. Hemolytic Disease could occur when a second or third child is born to which of the following couples? A. Rh positive male and Rh positive female. B. Rh negative male and Rh positive female. C. Rh positive male and Rh negative female. D. Rh negative male and Rh negative female. 64. An Rh negative mother is pregnant for the first time with an Rh positive fetus. Just prior to birth some fetal blood cells cross the placenta into the mother. Which of the following will occur? A. The fetus will die before birth. B. The mother will become Rh positive. C. The mother will produce Rh antibodies. D. The fetal red blood cells will become Rh negative. 65. Which chamber of the heart pumps oxygenated blood into the aorta? A. left atrium B. right atrium C. left ventricle D. right ventricle 66. Which of the following organs has a portal system associated with it? A. Skin. B. Lung. C. Liver. D. Heart. 67. The vein carrying the highest concentration of oxygen is the A. iliac. B. renal. C. hepatic. D. pulmonary.
6 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with sphincter muscles in order to A. prevent the backflow of blood. B. expand and recoil with each heart beat. C. divert blood toward areas of increased metabolic activity. D. hold blood in the beds until nutrient and waste exchange is complete. 3. Which of the following best describes a vein? A. Thin-walled, elastic, and equipped with valves. B. Thick-walled, elastic, and equipped with valves. C. Thin-walled, muscular, and supplied with nerves. D. Thick-walled, muscular, and supplied with nerves. 4. The function of an artery is to A. transport blood toward the heart. B. transport blood away from the heart. C. connect the right and left atria directly. D. carry carbon dioxide to the tissue cells. 5. A blood vessel that transports blood out of a capillary bed is a(n) A. vein. B. artery. C. venule. D. arteriole. 6. The most muscular chamber of the heart is the A. left atrium. B. C. left ventricle. D. right ventricle. 7. Based on its function, the heart is often referred to as a double pump. Which of the following would explain this? A. The heart has two sets of valves. B. The heart is controlled by both nerves and hormones. C. The heart moves blood through two circulatory pathways. D. The heart moves blood containing both nutrients and wastes. 8. The structures attached to the atrioventricular valves are called A. atria. B. pulmonary veins. C. semilunar valves. D. chordae tendineae. 9. The main function of the valves in the heart is to A. prevent back-flow of blood. B. divide the heart into four chambers. C. control the volume of blood leaving the heart. D. control the volume of blood entering the heart. 10. Blood leaves the right ventricle via the A. aorta. B. pulmonary trunk. C. coronary arteries. D. anterior vena cava. 11. An irregular heartbeat where contraction of the atria does not always result in contraction of the ventricles, likely indicates a problem with the A. SA node. B. AV node. C. AV valve. D. semi-lunar valve. 12. A condition called tachycardia exists when a person s heartrate is abnormally high. Which of the following explains how tachycardia may arise? A. The Purkinje fibres are over-stimulating the pacemaker. B. The sinoatrial (SA) node is receiving increased stimulation. C. There is increased stimulation by the parasympathetic nervous system. D. Impulses from the sinoatrial (SA) node are not reaching the atrioventricular (AV) node. 13. The atrioventricular (AV) node stimulates the A. aorta. B. Purkinje fibers. C. sinoatrial (SA) node. D. atrioventricular valves. 14. The coordinating structure responsible for an intrinsic heart beat is the A. cerebellum. B. sinoatrial node. C. chordae tendineae. D. sympathetic nervous system. 15. What happens during atrial diastole? A. Atria fill with blood. B. Semi-lunar valves close. C. Ventricles fill with blood. D. Atrioventricular valves open Systole of the ventricles. 2. Opening of the atrio-ventricular valves. 3. Electrical impulse sent from the SA node. 4. Atria fill with blood. The order in which the events above occur during one heartbeat (the cardiac cycle) is A. 2, 1, 3, 4 B. 2, 3, 4, 1 C. 4, 1, 3, 2 D. 4, 3, 2, The blood vessels that carry blood to and from the head are the A. iliac arteries and veins. B. subclavian arteries and veins. C. carotid arteries and jugular veins. D. anterior (superior) and posterior (inferior) vena cavae. 18. The path followed by blood on one circuit through the heart is A. ventricle, atrioventricular valve, semilunar valve, atrium. B. atrium, atrioventricular valve, ventricle, semilunar valve. C. atrium, ventricle, atrioventricular valve, semilunar valve. D. atrium, semilunar valve, ventricle, atrioventricular valve. 19. Which of the following is a characteristic of pulmonary circulation? A. Blood leaves the heart via the aorta. B. Blood in the arteries is deoxygenated. C. Blood in the veins is travelling to the lungs. D. Blood in capillaries absorbs high levels of carbon dioxide. 20. The blood vessel that carries blood from the lungs to the heart is the A. coronary vein. B. coronary artery. C. pulmonary vein. D. pulmonary artery.
7 21. Blood leaves the liver by way of the A. iliac vein. B. renal vein. C. hepatic vein. D. hepatic portal vein. 22. Blood with a high oxygen concentration can be found in both the A. renal artery and the pulmonary artery. B. umbilical vein and the pulmonary vein. C. pulmonary vein and the umbilical artery. D. pulmonary artery and the umbilical artery. 23. Which of the following is a characteristic of systemic circulation? A. Highly oxygenated arterial blood. B. Highly oxygenated venous blood. C. Increased blood pressure in the veins. D. Decreased blood pressure in the arteries. 24. A red blood cell leaves the aorta, makes a circuit through the body and arrives back in the capillaries of the alveoli. The correct sequence of organs through which the cell may have travelled is A. lungs, heart, small intestine, liver. B. small intestine, heart, liver, lungs. C. liver, lungs, small intestine, heart. D. small intestine, liver, heart, lungs. 25. Which of the following would describe the path of the blood in the pulmonary circuit? A. Right ventricle pulmonary trunk pulmonary vein left atrium. B. Left ventricle pulmonary vein pulmonary trunk C. Right ventricle pulmonary vein pulmonary artery left atrium. D. Right atrium pulmonary trunk aorta vena cava 26. The correct path of blood from the heart to the head and back to the heart again is A. right ventricle, vena cava, carotid artery, jugular vein, left atrium. B. left ventricle, aorta, jugular vein, vena cava, carotid artery, C. left ventricle, aorta, carotid artery, jugular vein, vena cava, D. right atrium, carotid artery, aorta, jugular vein, vena cava, left ventricle. 29. Which of the following is a characteristic of systemic circulation? A. Highly oxygenated arterial blood. B. Increased blood pressure in the veins. C. Low carbon dioxide concentration in the veins. D. Increased concentration of reduced hemoglobin (HHb) in the arterial blood. 30. A red blood cell is located in an artery in your right arm. How many capillary beds must this cell pass through before it is returned to the left ventricle? A. one B. two C. three D. four 31. An increase in which of the following would cause hypotension? A. heart rate B. cardiac output C. arteriole dilation D. reabsorption of water by the kidneys 32. Hypertension would be indicated by a blood pressure reading of A. 100 / 80 B. 120 / 50 C. 120 / 80 D. 150 / Which of the following is normal resting systolic blood pressure for an adult? A. 50 mm Hg B. 80 mm Hg C. 120 mm Hg D. 180 mm Hg 34. Blood pressure will be at its highest when A. atria relaxes. B. atria contracts. C. ventricles relax. D. ventricles contract. 35. The highest blood pressure in the aorta occurs when the A. atria contract. B. heart muscle is relaxed. C. blood is pushed to the ventricle. D. blood is pumped from the heart. 36. Capillary beds are equipped with sphincter muscles in order to A. prevent the backflow of blood. B. expand and recoil with each heart beat. C. divert blood toward areas of increased metabolic activity. D. hold blood in the beds until nutrient and waste exchange is complete. 27. The artery that provides oxygen and nutrients to heart tissue is the A. carotid. B. systemic. C. coronary. D. pulmonary. 28. In which of the following vessels would blood contain the highest concentration of carbon dioxide? A. Aorta. B. Carotid artery. C. Pulmonary vein. D. Pulmonary artery.
8 37. Which of the following would occur as a result of the oval opening in the heart remaining open after birth? A. Blood pressure in the lungs would increase. B. Impulses from the sinoatrial (SA) node would stop. C. Blood in the right atrium would mix with blood in the left atrium. D. A greater amount of blood would flow into the pulmonary system. 38. Which of the following structures in fetal circulation functions to deliver blood, which is high in waste, to the placenta? A. Venous duct. B. Umbilical vein. C. Pulmonary veins. D. Umbilical arteries. 39. How do the oxygen and nutrient levels in the adult vena cava compare to those levels in the fetal vena cava? A. The fetal oxygen and nutrient levels are higher. B. The adult oxygen and nutrient levels are higher. C. The fetal nutrient levels are higher, while the oxygen levels are lower. D. The adult nutrient levels are higher, while the oxygen levels are lower. 40. The sequence of structures through which the nerve impulse passes to cause contraction of the heart is A. AV node SA node Purkinje fibres. B. Purkinje fibres AV node SA node. C. Purkinje fibres SA node AV node. D. SA node AV node Purkinje fibres. 41. Thick walls, elastic tissue and smooth muscle are characteristics of A. veins. B. arteries. C. arterioles. D. capillaries. 42. Blockages in which of the following blood vessels reduces blood flow to the heart muscle? A. Aorta. B. Carotid artery. C. Coronary artery. D. Pulmonary artery. 43. A blood vessel which has numerous valves is a(n) A. vein. B. artery. C. arteriole. D. capillary. 44. Which of the following blood vessels provides nutrients to the heart tissue? A. Aorta. B. Carotid artery. C. Coronary artery. D. Inferior vena cava. 45. The SA node (pacemaker) of the heart is located in the wall of the A. left atrium. B. C. left ventricle. D. right ventricle. 46. Which of the following is a function of red blood cells? A. clot blood B. carry oxygen C. fight infection D. regulate osmotic pressure 47. The major component of human blood is A. plasma. B. platelets. C. red cells. D. white cells. 48. transport gases maintain body temperature protect the body against blood loss produce hormones that stimulate metabolism carry digestive enzymes to the small intestine How many of these are functions of the blood? A. two B. three C. four D. five 49. A foreign substance that stimulates an immune response is a(n) A. cancer. B. antigen. C. antibody. D. promoter. 50. Which of the following correctly matches structure with function? A. platelets provide immunity B. plasma proteins carry oxygen C. red blood cells carry carbon dioxide D. white blood cells initiate blood clotting 51. Plasma is composed mostly of A. salt. B. water. C. protein. D. hormones. 52. All of the following are components of plasma except A. salts. B. water. C. proteins. D. platelets.
9 53. Red blood cells originate in the A. liver. B. lymph nodes. C. bone marrow. D. capillary beds. 54. The main function of platelets is to A. fight disease. B. carry oxygen. C. carry nutrients. D. aid in blood clotting. 55. An important function of white blood cells is to A. buffer blood. B. carry oxygen. C. fight infection. D. carry carbon dioxide. 56. Blood proteins are made in the A. liver. B. kidney. C. stomach. D. pancreas. 57. Blood which lacks platelets would not be able to A. clot. B. carry oxygen. C. fight infections. D. transport nutrients Calcium activates an enzyme. 2. Fibrin binds platelets to form a plug. 3. Thrombin converts fibrinogen to fibrin. 4. Platelets and damaged cells release an activator. The correct sequence of events leading to the formation of a blood clot is A. 1, 2, 3, 4. B. 2, 1, 3, 4. C. 3, 4, 1, 2. D. 4, 1, 3, Which of the following is directly involved in the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin? A. Fibrin. B. Carbonic anhydrase. C. Calcium ions (Ca 2+ ) D. Magnesium ions (Mg 2+ ) 60. What occurs when an antigen enters the body? A. There is increased platelet production. B. Red blood cells phagocytize the antigen. C. Antibodies change shape to fit the antigen. D. Specific antibodies are produced and released. 61. The presence of bacteria in the blood will cause the body to produce A. mucus. B. antigens. C. antibodies. D. hydrochloric acid. 62. A foreign substance entering the circulatory system is called a(n) A. platelet. B. antigen. C. antibody. D. hormone. 63. A person with type AB blood has A. A antigens and B antibodies. B. both A and B antigens and A and B antibodies. C. no A or B antigens but both A and B antibodies. D. both A and B antigens but no A or B antibodies. 62. Which of the following blood transfusions is compatible? A. Donor type A and recipient type O. B. Donor type A and recipient type B. C. Donor type O and recipient type B. D. Donor type AB and recipient type O. 63. Hemolytic Disease could occur when a second or third child is born to which of the following couples? A. Rh positive male and Rh positive female. B. Rh negative male and Rh positive female. C. Rh positive male and Rh negative female. D. Rh negative male and Rh negative female. 64. An Rh negative mother is pregnant for the first time with an Rh positive fetus. Just prior to birth some fetal blood cells cross the placenta into the mother. Which of the following will occur? A. The fetus will die before birth. B. The mother will become Rh positive. C. The mother will produce Rh antibodies. D. The fetal red blood cells will become Rh negative. 65. Which chamber of the heart pumps oxygenated blood into the aorta? A. left atrium B. right atrium C. left ventricle D. right ventricle 66. Which of the following organs has a portal system associated with it? A. Skin. B. Lung. C. Liver. D. Heart. 67. The vein carrying the highest concentration of oxygen is the A. iliac. B. renal. C. hepatic. D. pulmonary.
10
11
12
C3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 Worksheet. C3 Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the heart
 Name: Date: C3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 Worksheet C3 Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the heart 1. Label and give the functions of the following: a. left and right atrium: b. left and right ventricle:
Name: Date: C3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 Worksheet C3 Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the heart 1. Label and give the functions of the following: a. left and right atrium: b. left and right ventricle:
Circulatory System Review
 Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
Figure ) The specific chamber of the heart that is indicated by letter A is called the. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 364
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Short Answer Figure 11.1 Using Figure 11.1, identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label.
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Short Answer Figure 11.1 Using Figure 11.1, identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label.
Circulatory System Review ANSWERS
 Circulatory System Review ANSWERS 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? Double membranous sac that surrounds the heart What is myocardium? The muscle tissue
Circulatory System Review ANSWERS 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? Double membranous sac that surrounds the heart What is myocardium? The muscle tissue
Chapter 23. Circulation
 Chapter 23 Circulation Standards CORE: I can describe the components and function of blood. I can describe structure and function of blood vessels. I can compare and contrast systemic and pulmonary systems.
Chapter 23 Circulation Standards CORE: I can describe the components and function of blood. I can describe structure and function of blood vessels. I can compare and contrast systemic and pulmonary systems.
Chapter 12. Capillaries. Circulation. The circulatory system connects with all body tissues
 Chapter 12 Circulation The circulatory system connects with all body s In many animals, microscopic blood vessels called capillaries Form an intricate network among the Red blood cell song Figure 23.1A
Chapter 12 Circulation The circulatory system connects with all body s In many animals, microscopic blood vessels called capillaries Form an intricate network among the Red blood cell song Figure 23.1A
The Mammalian Circulatory System
 The Mammalian Heart The Mammalian Circulatory System Recall: What are the 3 cycles of the mammalian circulatory system? What are their functions? What are the three main vessel types in the mammalian circulatory
The Mammalian Heart The Mammalian Circulatory System Recall: What are the 3 cycles of the mammalian circulatory system? What are their functions? What are the three main vessel types in the mammalian circulatory
Chapter 14. The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Major Function of the Cardiovascular System. Transportation. Structures of the Cardiovascular System. Heart - muscular pump
 Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Blood flows away from the heart in arteries, to the capillaries and back to the heart in the veins
 Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM BLOOD VESSELS
 Name: Block: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms such as
Name: Block: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms such as
10. Thick deposits of lipids on the walls of blood vessels, called, can lead to serious circulatory issues. A. aneurysm B. atherosclerosis C.
 Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet Name: Date: Instructions: Put the answers to each task card in the numbered boxes on the chart. 1 a) left semilunar valve / aortic valve b) blood would backflow
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet Name: Date: Instructions: Put the answers to each task card in the numbered boxes on the chart. 1 a) left semilunar valve / aortic valve b) blood would backflow
Chapter 10 The Circulatory & Lymphatic Systems
 Biology 12 Name: Human Biology Per: Date: Chapter 10 The Circulatory & Lymphatic Systems Complete using BC Biology 12, pages 298 325 10.1 The Blood Vessels pages 298-299 1. Label the blood vessels in this
Biology 12 Name: Human Biology Per: Date: Chapter 10 The Circulatory & Lymphatic Systems Complete using BC Biology 12, pages 298 325 10.1 The Blood Vessels pages 298-299 1. Label the blood vessels in this
d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology
 d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology What can your remember about the heart and blood vessels? What is the Cardiovascular System? The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system,
d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology What can your remember about the heart and blood vessels? What is the Cardiovascular System? The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system,
Cardiovascular System. Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12
 Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
The Cardiovascular System (Heart)
 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System (Heart) A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function
The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System (Heart) A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function
Cardiovascular. Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Nutrients Waste Hormones Immune cells Oxygen
 Cardiovascular The Cardiovascular System - Arteries Arteries Cardiovascular System Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Carry blood away from heart Carotid arteries Deliver
Cardiovascular The Cardiovascular System - Arteries Arteries Cardiovascular System Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Carry blood away from heart Carotid arteries Deliver
The Cardiovascular System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Slides 11.1 11.19 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Cardiovascular System
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Slides 11.1 11.19 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Cardiovascular System
Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels
 Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels 3.2 Learning Objectives 3.2.2 Organisational Complexity of the human 1. Describe the structures and organisation of tissues in the closed circulatory system. 2. Discuss
Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels 3.2 Learning Objectives 3.2.2 Organisational Complexity of the human 1. Describe the structures and organisation of tissues in the closed circulatory system. 2. Discuss
Types of circulatory systems
 Types of circulatory systems Open system Mostly invertebrates Low pressure Haemocoel Suitable for small organisms Closed system Vertebrates High pressure Blood remains in blood vessels Separate tissue
Types of circulatory systems Open system Mostly invertebrates Low pressure Haemocoel Suitable for small organisms Closed system Vertebrates High pressure Blood remains in blood vessels Separate tissue
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY
 TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93)
 Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
Biology 12 - Circulation - Chapter Notes
 Biology 12 - Circulation - Chapter Notes Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms
Biology 12 - Circulation - Chapter Notes Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms
Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Blood o Red blood cells: heamoglobin and oxygen transport o White blood cells: phagocyte phagocytosis (engulf pathogen, vesicles fuse with vacuole,
Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Blood o Red blood cells: heamoglobin and oxygen transport o White blood cells: phagocyte phagocytosis (engulf pathogen, vesicles fuse with vacuole,
The Cardiovascular System home study course
 The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
The Circulatory System. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview The Circulatory System
 33.1 THINK ABOUT IT More than one-third of the 1.2 million Americans who suffer a heart attack each year die. This grim evidence shows that the heart and the circulatory system it powers are vital to life.
33.1 THINK ABOUT IT More than one-third of the 1.2 million Americans who suffer a heart attack each year die. This grim evidence shows that the heart and the circulatory system it powers are vital to life.
Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels
 Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels Most animals have a closed blood system. The blood flows continuously in vessels back to the heart. In an open system the blood is pumped into open ended tubes and
Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels Most animals have a closed blood system. The blood flows continuously in vessels back to the heart. In an open system the blood is pumped into open ended tubes and
Biology Unit 3 The Human Heart P
 Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
Levels of Organization. Chapter 19 6/11/2012. Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body. 4 Primary Tissues
 Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies
 Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
Cardiovascular System. I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart
 Cardiovascular System I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart 1. : Pericardial Cavity serous fluid filled space between the heart and the pericardium B. Heart Wall 1.
Cardiovascular System I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart 1. : Pericardial Cavity serous fluid filled space between the heart and the pericardium B. Heart Wall 1.
Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1 -
 Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1-2. Organs of a closed circulatory system: A. Have valves a. Arteriole B. Regulate blood flow b. Artery C. Lead to heart
Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1-2. Organs of a closed circulatory system: A. Have valves a. Arteriole B. Regulate blood flow b. Artery C. Lead to heart
The Cardiovascular System
 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
A. Incorrect! The left ventricle receives oxygenated blood from the lungs via the left atrium.
 Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Cardiovascular System No. 1 of 10 Instruction: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully (2) Work the problems on paper as needed (3) Pick
Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Cardiovascular System No. 1 of 10 Instruction: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully (2) Work the problems on paper as needed (3) Pick
Unit 10 ~ Learning Guide
 Unit 10 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Unit 10 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Function: Transportation of. Oxygen Nutrients Waste Hormones gases
 Function: Transportation of Oxygen Nutrients Waste Hormones gases Pericardium: double sac of serous membrane filled with fluid (pericardial fluid to be exact) that surrounds the heart. Parietal pericardium:
Function: Transportation of Oxygen Nutrients Waste Hormones gases Pericardium: double sac of serous membrane filled with fluid (pericardial fluid to be exact) that surrounds the heart. Parietal pericardium:
Chapter 16: Circulation
 Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
CIE Biology A-level Topic 8: Transport in mammals
 CIE Biology A-level Topic 8: Transport in mammals Notes Circulatory systems can either be open, for instance in insects, or closed, like in fish and mammals where the blood is confined to blood vessels
CIE Biology A-level Topic 8: Transport in mammals Notes Circulatory systems can either be open, for instance in insects, or closed, like in fish and mammals where the blood is confined to blood vessels
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
The Circulatory System. The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types
 The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
Circulation. Sinoatrial (SA) Node. Atrioventricular (AV) Node. Cardiac Conduction System. Cardiac Conduction System. Linked to the nervous system
 Circulation Cardiac Conduction System AHS A H S Your body resembles a large roadmap. There are routes or arteries that take you downtown to the heart of the city and veins that take you to the outskirts
Circulation Cardiac Conduction System AHS A H S Your body resembles a large roadmap. There are routes or arteries that take you downtown to the heart of the city and veins that take you to the outskirts
CIE Biology GCSE. 9: Transport in animals. Notes.
 CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
The Cardiovascular System
 11 PART A The Cardiovascular System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Cardiovascular
11 PART A The Cardiovascular System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Cardiovascular
1. Label the Diagram using the following terms: artery, arterioles, vein, venules, capillaries, valve, inner wall, middle wall, outer wall
 Bio 20 Ms. Nyboer Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, and the Heart Structure and Function Workbook Use your textbook (Ch. 10) and notes to fill in this workbook Part A: Arteries, Veins, Capillaries 1. Label
Bio 20 Ms. Nyboer Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, and the Heart Structure and Function Workbook Use your textbook (Ch. 10) and notes to fill in this workbook Part A: Arteries, Veins, Capillaries 1. Label
CIRCULATION. Cardiovascular & lymphatic systems Functions. Transport Defense / immunity Homeostasis
 CIRCULATION CIRCULATION Cardiovascular & lymphatic systems Functions Transport Defense / immunity Homeostasis 2 Types of Circulatory Systems Open circulatory system Contains vascular elements Mixing of
CIRCULATION CIRCULATION Cardiovascular & lymphatic systems Functions Transport Defense / immunity Homeostasis 2 Types of Circulatory Systems Open circulatory system Contains vascular elements Mixing of
The Heart. Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet
 The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
Circulatory System 10.1
 1 Circulatory System 10.1 2 ARTERIES Arteries-blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart Thick walls Inner & Outer layers: connective tissue Middle layers are muscle and elastic connective tissue
1 Circulatory System 10.1 2 ARTERIES Arteries-blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart Thick walls Inner & Outer layers: connective tissue Middle layers are muscle and elastic connective tissue
Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes
 Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes Functions of the Circulatory System The circulatory system functions mainly as the body s transport system. It transports: o Oxygen o Nutrients o Cell waste o
Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes Functions of the Circulatory System The circulatory system functions mainly as the body s transport system. It transports: o Oxygen o Nutrients o Cell waste o
c) What is the name of RBC (erythrocyte) formation? Where do blood cells form?
 UNIT 6: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1) List the three general functions of BLOOD. REVIEW QUESTIONS Blood 2) a) What are the three formed elements /cellular elements in blood? b) Describe the composition of the
UNIT 6: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1) List the three general functions of BLOOD. REVIEW QUESTIONS Blood 2) a) What are the three formed elements /cellular elements in blood? b) Describe the composition of the
Summary table: artery capillary vein Blood pressure Hi Low lowest Valves present or Absent Absent Present
 Bi 067: Review of sectn 7-9 - cardiovascular and lymphatic Heart and Blood vessels: 3 Types of blood vessels: 1. Arteries, arterioles -away from heart, O2 rich 2. Capillaries gas and nutrient/waste exchange
Bi 067: Review of sectn 7-9 - cardiovascular and lymphatic Heart and Blood vessels: 3 Types of blood vessels: 1. Arteries, arterioles -away from heart, O2 rich 2. Capillaries gas and nutrient/waste exchange
Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process:
 Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: a. erythrocytes b. leukocytes c. melanocytes d. thrombocytes Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process: a. erythrocytes
Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: a. erythrocytes b. leukocytes c. melanocytes d. thrombocytes Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process: a. erythrocytes
This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia)
 Biology 20 Unit D This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia) requires action of: heart: muscular force to move
Biology 20 Unit D This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia) requires action of: heart: muscular force to move
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM
 IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein THE BLOOD SYSTEM 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein THE BLOOD SYSTEM 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
1. What kind of blood is found in the rt. atrium? (oxygenated or deoxygenated)
 Carl Christennsen, PhD Chap. 19, 20, & 21 - Circulatory System Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy HEART 1. What kind of blood is found in the rt. atrium? (oxygenated or deoxygenated) Where does this blood come from?
Carl Christennsen, PhD Chap. 19, 20, & 21 - Circulatory System Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy HEART 1. What kind of blood is found in the rt. atrium? (oxygenated or deoxygenated) Where does this blood come from?
Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for
 Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for hyperlipidemia! Agenda! - Review objectives for 6.2! - Video of circulatory
Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for hyperlipidemia! Agenda! - Review objectives for 6.2! - Video of circulatory
Chapter 12 Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 12 Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular System Includes Heart and Blood Vessels Transports, nutrients and wastes to and from the tissues 1 The Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Arteries:
Chapter 12 Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular System Includes Heart and Blood Vessels Transports, nutrients and wastes to and from the tissues 1 The Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Arteries:
CIRCULATION & GAS EXCHANGE
 AP BIOLOGY ACTIVITY2.13 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter42 NAME DATE HOUR CIRCULATION & GAS EXCHANGE 1. In general, what is the function of transport systems? 2. What method/structure do most invertebrates use
AP BIOLOGY ACTIVITY2.13 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter42 NAME DATE HOUR CIRCULATION & GAS EXCHANGE 1. In general, what is the function of transport systems? 2. What method/structure do most invertebrates use
The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide.
 Section 1: The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What
Section 1: The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What
The Circulatory System (p )
 The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
Transport in Animals. Gastrovascular cavities. Nutrients and gases can move by processes such as diffusion and active transport.
 Transport in Animals Gastrovascular cavities flatworms and cnidarians Nutrients and gases can move by processes such as diffusion and active transport. Figure 42.1 Internal transport in the cnidarian
Transport in Animals Gastrovascular cavities flatworms and cnidarians Nutrients and gases can move by processes such as diffusion and active transport. Figure 42.1 Internal transport in the cnidarian
Mammalian Transport and The Heart
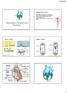 Cardiovascular System AS-G, Chapters 8-9 Blood flows through the body in a closed system (circuit) driven by the pumping power of the heart Closed vs open: does the system have vessels contained the entire
Cardiovascular System AS-G, Chapters 8-9 Blood flows through the body in a closed system (circuit) driven by the pumping power of the heart Closed vs open: does the system have vessels contained the entire
Circulatory System Objective sheet 3
 Circulatory System Objective sheet 3 10. Functions of blood 1) Transport oxygen and nutrients 2) Transport of carbon dioxide and waste 3) Protection against disease causing micro-organisms 4) Clotting
Circulatory System Objective sheet 3 10. Functions of blood 1) Transport oxygen and nutrients 2) Transport of carbon dioxide and waste 3) Protection against disease causing micro-organisms 4) Clotting
Exam 3 Study Guide. 4) The process whereby the binding of antibodies to antigens causes RBCs to clump is called:
 Exam 3 Study Guide 1) Where does hematopoiesis produce new red blood cells: 2) Which of the following is a blood clotting disorder: 3) Treatment of hemophilia often involves: 4) The process whereby the
Exam 3 Study Guide 1) Where does hematopoiesis produce new red blood cells: 2) Which of the following is a blood clotting disorder: 3) Treatment of hemophilia often involves: 4) The process whereby the
2. capillaries - allow exchange of materials between blood and tissue fluid
 Chapter 19 - Vascular System A. categories and general functions: 1. arteries - carry blood away from heart 2. capillaries - allow exchange of materials between blood and tissue fluid 3. veins - return
Chapter 19 - Vascular System A. categories and general functions: 1. arteries - carry blood away from heart 2. capillaries - allow exchange of materials between blood and tissue fluid 3. veins - return
Chapter 05 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 05 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 05 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Date :... Class: A1&2 Time Allowed: 40Minutes Maximum Marks: 25
 1 loomfield Hall School 1 Test (Unit 9) Name :... Paper: iolog y Date :... lass: 1& Time llowed: 40Minutes Maximum Marks: 5 TKheory Section: [Total 16 Marks] Fig. 1.1 shows the changes in blood pressure
1 loomfield Hall School 1 Test (Unit 9) Name :... Paper: iolog y Date :... lass: 1& Time llowed: 40Minutes Maximum Marks: 5 TKheory Section: [Total 16 Marks] Fig. 1.1 shows the changes in blood pressure
Questions on Transport
 Name: Questions on Transport Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topic 6.2 (The Transport System). Answer all questions. This will serve as a study guide for
Name: Questions on Transport Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topic 6.2 (The Transport System). Answer all questions. This will serve as a study guide for
Unit 10 Cardiovascular System
 Unit 10 Cardiovascular System I. Functions Deliver nutrients to cells > O 2, sugars, amino acids, lipids, ions, H 2 O... Remove waste from cells > CO 2, pathogens, toxins, lactic acid... Fight off infection
Unit 10 Cardiovascular System I. Functions Deliver nutrients to cells > O 2, sugars, amino acids, lipids, ions, H 2 O... Remove waste from cells > CO 2, pathogens, toxins, lactic acid... Fight off infection
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
 Biology 30S THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Name: This module adapted from bblearn.merlin.mb.ca 1 Introduction to Circulation The first organ to form, and the last organ to die. The heart is the pump of life. The
Biology 30S THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Name: This module adapted from bblearn.merlin.mb.ca 1 Introduction to Circulation The first organ to form, and the last organ to die. The heart is the pump of life. The
Glossary: The Cardiovascular System
 This glossary includes terms that have been introduced in Lesson 14. Student Resource 14.14 Glossary: The Cardiovascular System Anatomy Terms aorta Large artery that transports blood from the left ventricle
This glossary includes terms that have been introduced in Lesson 14. Student Resource 14.14 Glossary: The Cardiovascular System Anatomy Terms aorta Large artery that transports blood from the left ventricle
b) List the steps that may occur in hemostasis with a brief explanation of what happens in those steps.
 UNIT 6: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1) List the three general functions of BLOOD. REVIEW QUESTIONS Blood 2) a) What are the three formed elements /cellular elements in blood (use anatomy vocabulary)? b) List
UNIT 6: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1) List the three general functions of BLOOD. REVIEW QUESTIONS Blood 2) a) What are the three formed elements /cellular elements in blood (use anatomy vocabulary)? b) List
Unit 11 - The Cardiovascular System 1
 Unit 11 - The Cardiovascular System 1 I. Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System A. The Cardiovascular System 1. A closed system of the heart and blood vessels a) The heart pumps blood b) Blood vessels allow
Unit 11 - The Cardiovascular System 1 I. Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System A. The Cardiovascular System 1. A closed system of the heart and blood vessels a) The heart pumps blood b) Blood vessels allow
CHAPTER 26. Circulation and Gas Exchange
 CHAPTER 26 Circulation and Gas Exchange CO INTRODUCTION Every organism must exchange materials with its environment Exchanges ultimately occur at the cellular level In unicellular organisms, these exchanges
CHAPTER 26 Circulation and Gas Exchange CO INTRODUCTION Every organism must exchange materials with its environment Exchanges ultimately occur at the cellular level In unicellular organisms, these exchanges
37 1 The Circulatory System
 H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
4. The two inferior chambers of the heart are known as the atria. the superior and inferior vena cava, which empty into the left atrium.
 Answer each statement true or false. If the statement is false, change the underlined word to make it true. 1. The heart is located approximately between the second and fifth ribs and posterior to the
Answer each statement true or false. If the statement is false, change the underlined word to make it true. 1. The heart is located approximately between the second and fifth ribs and posterior to the
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions. KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells.
 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
Mr. Epithelium s Anatomy and Physiology Test SSSS
 Mr. Epithelium s Anatomy and Physiology Test SSSS You have 50 minutes to complete this test packet. One 8.5 x 11 cheat sheet is allowed, along with 1 non-programmable calculator dedicated to computation.
Mr. Epithelium s Anatomy and Physiology Test SSSS You have 50 minutes to complete this test packet. One 8.5 x 11 cheat sheet is allowed, along with 1 non-programmable calculator dedicated to computation.
The ancient Babylonians, Egyptians, Indians and Chinese believed the heart was the centre of thinking and emotions
 The Concept of Mind The ancient Babylonians, Egyptians, Indians and Chinese believed the heart was the centre of thinking and emotions Hippocrates 460 BC 370 BC - Thoughts, ideas, and feelings come from
The Concept of Mind The ancient Babylonians, Egyptians, Indians and Chinese believed the heart was the centre of thinking and emotions Hippocrates 460 BC 370 BC - Thoughts, ideas, and feelings come from
Cardiovascular System. Supplementary Information
 Cardiovascular System Supplementary Information THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM - 1 - THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM FUNCTION Transport system carrying nutrient, gases, hormones and waste products to and from the
Cardiovascular System Supplementary Information THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM - 1 - THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM FUNCTION Transport system carrying nutrient, gases, hormones and waste products to and from the
Cardiovascular Physiology
 Cardiovascular Physiology Lecture 1 objectives Explain the basic anatomy of the heart and its arrangement into 4 chambers. Appreciate that blood flows in series through the systemic and pulmonary circulations.
Cardiovascular Physiology Lecture 1 objectives Explain the basic anatomy of the heart and its arrangement into 4 chambers. Appreciate that blood flows in series through the systemic and pulmonary circulations.
The Cardiovascular System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART B The Heart: Cardiac Output Cardiac output (CO) Amount of blood pumped
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART B The Heart: Cardiac Output Cardiac output (CO) Amount of blood pumped
Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system. What are the function of the cardiovascular system? Arteries and arterioles:
 5.1 Overview of the cardiovascular system Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system Includes the heart and blood vessels Brings nutrients to cells and helps get rid of wastes Blood is refreshed in the lung, kidneys,
5.1 Overview of the cardiovascular system Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system Includes the heart and blood vessels Brings nutrients to cells and helps get rid of wastes Blood is refreshed in the lung, kidneys,
Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart
 Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart Interesting Heart Fact Capillaries are so small it takes ten of them to equal the thickness of a human hair. Review What are the 3 parts of the cardiovascular
Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart Interesting Heart Fact Capillaries are so small it takes ten of them to equal the thickness of a human hair. Review What are the 3 parts of the cardiovascular
Lower Secondary Science Blood Circulatory System Notes / Advanced Notes
 Lower Secondary Science Blood Circulatory System Notes / Advanced Notes Double Circulation in Mammals In mammals, there is a double circulation (i.e. blood passes through the heart twice in one complete
Lower Secondary Science Blood Circulatory System Notes / Advanced Notes Double Circulation in Mammals In mammals, there is a double circulation (i.e. blood passes through the heart twice in one complete
Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System
 Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System This color-enhanced image was made with an electron microscope, so the objects it depicts are extremely small. Do you know what they are? This incredible photo shows red
Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System This color-enhanced image was made with an electron microscope, so the objects it depicts are extremely small. Do you know what they are? This incredible photo shows red
THE HEART. Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration
 THE HEART Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration The Circulatory System Also called the Cardiovascular System Circulates blood in the body Transports nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood
THE HEART Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration The Circulatory System Also called the Cardiovascular System Circulates blood in the body Transports nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Vessels Arteries Arteries Arteries
 CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
Chapter 05 Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 05 Cardiovascular System 1 Cardiovascular System: Heart and Blood Vessels 2 Points to ponder What are the functions of the cardiovascular system? What is the anatomy of the heart? Of blood vessels,
Chapter 05 Cardiovascular System 1 Cardiovascular System: Heart and Blood Vessels 2 Points to ponder What are the functions of the cardiovascular system? What is the anatomy of the heart? Of blood vessels,
Open Circulatory System. Closed Circulatory System
 General Types of Circulatory Systems -All circulatory systems exchange gases, nutrients, and wastes at the cellular level -Although all animals need to do this, they do so in a variety of ways: -Two types
General Types of Circulatory Systems -All circulatory systems exchange gases, nutrients, and wastes at the cellular level -Although all animals need to do this, they do so in a variety of ways: -Two types
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System I. Structure of the Heart A. Average adult heart is 14 cm long and 9 cm wide. B. Lies in the mediastinum. C. Enclosed in the pericardium. 1. Fibrous pericardium- Outer, tough connective
Cardiovascular System I. Structure of the Heart A. Average adult heart is 14 cm long and 9 cm wide. B. Lies in the mediastinum. C. Enclosed in the pericardium. 1. Fibrous pericardium- Outer, tough connective
The Cardiovascular System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART A The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART A The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood
Ch. 12 The Circulatory System. The heart. The heart is a double pump. A quick note on arteries vs. veins. = the muscular pump of the CV system
 Ch. 12 The Circulatory System The heart A.k.a. the cardiovascular system Blood was discussed in Ch. 11 Focus of Ch. 12: heart and blood vessels = the muscular pump of the CV system ~ 100,000 heartbeats/day!
Ch. 12 The Circulatory System The heart A.k.a. the cardiovascular system Blood was discussed in Ch. 11 Focus of Ch. 12: heart and blood vessels = the muscular pump of the CV system ~ 100,000 heartbeats/day!
Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems
 34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems section 1 Circulatory System Before You Read Press the tips of two fingers to the inside of your wrist, at a point just below your thumb. Can you feel
34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems section 1 Circulatory System Before You Read Press the tips of two fingers to the inside of your wrist, at a point just below your thumb. Can you feel
Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation
 1 Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Section 9.1 Homeostasis: Life in the Balance Outcomes: I can explain homeostasis I can describe the importance of homeostasis to living things I can explain the
1 Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Section 9.1 Homeostasis: Life in the Balance Outcomes: I can explain homeostasis I can describe the importance of homeostasis to living things I can explain the
Lecture 8. Heart and Circulatory System. Lecture 8
 Lecture 8 Heart and Circulatory System Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Blood 3. Blood Vessels & Blood Pressure 4. The Heart 5. Cardiovascular (Circulatory) System 2 1 Circulatory System Function 1. Transport
Lecture 8 Heart and Circulatory System Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Blood 3. Blood Vessels & Blood Pressure 4. The Heart 5. Cardiovascular (Circulatory) System 2 1 Circulatory System Function 1. Transport
Unit 1: Human Systems. The Circulatory System
 Unit 1: Human Systems The Circulatory System nourish all cells with oxygen, glucose, amino acids and other nutrients and carry away carbon dioxide, urea and other wastes Purposes Transport chemical messengers
Unit 1: Human Systems The Circulatory System nourish all cells with oxygen, glucose, amino acids and other nutrients and carry away carbon dioxide, urea and other wastes Purposes Transport chemical messengers
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Key Questions What are the functions of the circulatory system? How does the heart pump blood through the body? What are three types of blood vessels? Vocabulary myocardium atrium
The Circulatory System Key Questions What are the functions of the circulatory system? How does the heart pump blood through the body? What are three types of blood vessels? Vocabulary myocardium atrium
