From PV loop to Starling curve. S Magder Division of Critical Care, McGill University Health Centre
|
|
|
- Sheila Bryant
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 From PV loop to Starling curve S Magder Division of Critical Care, McGill University Health Centre
2 Otto Frank 1890 s
3 Frank-Starling Relationship ( The Law of the Heart ) The greater the initial stretch of the heart wall the greater the force produced and the greater the output = the Preload - The preload is the force which sets the initial length before the muscle contracts Significance: What goes in will go out
4 The law of the heart Patterson SW, Piper H and Starling EH J Physiol 48: , 1914 the mechanical energy set free on passage from the resting to the contracted state depends on the area of chemically active surfaces, i.e. on the length of the muscle fibers, The Linacre Lecture on the Law of the Heart ( 1915) The energy of contraction, however measured, is a function of the length of the muscle fibre
5 Determinants of Cardiac Function Heart Rate Stroke Volume Preload Afterload Contractility
6 There is no downward portion in Cardiac Muscle (It cannot be stretched beyond L 0 ) Preolad: the tension that sets the initial muscle length Total Tension Active Tension Skeletal Muscle L 0 Passive Stretch Cardiac Muscle L 0 Length Length
7 Otto Frank 1890 s
8 Afterload Load after the onset of shortening has meaning for isotonic contractions (shortening against a constant load Has no meaning for isometric (no shortening) as used for preload studies. Greater afterload --- the less the degree and velocity of muscle shortening Consider lifting 5 Kg above your head versus 40 kg
9 Contractility Defines the velocity and extent of shortening for a given preload and a given afterload ie your heart can change from the equivalent of Fiat to a Ferrari
10 The Ventricular Pressure-Volume Diagram End-systolic Pressure- Volume Curve Passive Filling Curve Volume
11 Holt 1964
12 Duration of Ca 2+ entry and contraction is fixed by HR Ca msec 240 msec ( 80 b/min)
13 Time Varying Elastance -Suga and Sagawa = MAX for the cycle 180 msec Slope is elastance 140 msec 180 msec 100 msec 60 msec Passive Filling Curve Volume
14 Time Varying Elastance ejecting heart 180 msec Slope is elastance 40msec 140 msec 80 msec 100 msec 140 msec 40 msec Volume
15 Pressure-Time Aortic Opening Aortic Closure P ESV & ESP Pressure-Volume Afterload Mitral Closure Mitral Opening EDP & EDV V
16 Problem: PV loop not easy to obtain
17 From Patterson, Piper, Starling: J. Physiol. 1914
18 Output in 10 min Patterson, Piper, Starling: J. Physiol CVP mmh2o CVP (mmh 2 O) Note downward part to the curve Output in 10 min
19 Change in Preload P Pressure-Volume Q Cardiac Function Curve Starling Curve V Filling Pressure (Pra or Pla)
20 Change in Preload (What ever goes in goes out) P Pressure-Volume Q Cardiac Output vs EDV V End-diastolic volume
21 Significance of Starling s Law Consider a situation where the SV of the RV is 101 ml and that of the LV is 100 ml, ie a 1% difference. The heart rate is 70 b/min - In 1.5 hr the total blood volume would be in the lungs What goes in must come out The Starling mechanism provides the fine tuning to match in-flow to out flow
22 Increase in Afterload P Decrease SV New Aortic Opening P Q Cardiac Function Curve Starling Curve Increased ESV V Filling Pressure
23 Decrease in Contractility P Decreased SV Q Cardiac Function Curve Starling Curve ESV Looks like in Afterload V Filling Pressure
24 Decrease in Heart Rate P Q Cardiac Function Curve Starling Curve Looks like: in Contracitility in Afterload V Filling Pressure
25 Decrease in Heart Rate (No effect on SV-filling pressure relationship) P SV SV vs Filling P No Change V Filling Pressure
26 Summary P-V curve gives detailed, specific view of cardiac function but readily obtainable: precise volume measurements are hard to obtain Useful for understanding the potential physiological changes Cardiac function curve is easy to obtain but non-specific: Affected by heart rate, afterload, & contractility
27 P The Pressure Volume Loop Contractility Afterload SV SV Return In the steady state - SV = SV Return V
28 Increase in Afterload P New Aortic Opening P Q Cardiac Function Curve Starling Curve ESV SV SV Return EDV V SV return is maintained No change in Q Filling Pressure
29 Cardiac Function Curve with Increase in Afterload or Decrease Contractility Q But in reality Q is decreased Filling Pressure Predicted no Δ Q Why?
30 The Pressure Volume Loop P ESV & ESP Contractility Afterload EDP & EDV V
Cardiac Output (C.O.) Regulation of Cardiac Output
 Cardiac Output (C.O.) Is the volume of the blood pumped by each ventricle per minute (5 Litre) Stroke volume: Is the volume of the blood pumped by each ventricle per beat. Stroke volume = End diastolic
Cardiac Output (C.O.) Is the volume of the blood pumped by each ventricle per minute (5 Litre) Stroke volume: Is the volume of the blood pumped by each ventricle per beat. Stroke volume = End diastolic
SymBioSys Exercise 2 Cardiac Function Revised and reformatted by C. S. Tritt, Ph.D. Last updated March 20, 2006
 SymBioSys Exercise 2 Cardiac Function Revised and reformatted by C. S. Tritt, Ph.D. Last updated March 20, 2006 The goal of this exercise to explore the behavior of the heart as a mechanical pump. For
SymBioSys Exercise 2 Cardiac Function Revised and reformatted by C. S. Tritt, Ph.D. Last updated March 20, 2006 The goal of this exercise to explore the behavior of the heart as a mechanical pump. For
GIGA - In Silico Medicine, University of Liege, Belgium, 2
 S. Kosta 1,*, A. Pironet 1, J.A. Negroni 2, E.C. Lascano 2, P.C. Dauby 1 1 GIGA - In Silico Medicine, University of Liege, Belgium, 2 Department of Comparative Cellular and Molecular Biology, Favaloro
S. Kosta 1,*, A. Pironet 1, J.A. Negroni 2, E.C. Lascano 2, P.C. Dauby 1 1 GIGA - In Silico Medicine, University of Liege, Belgium, 2 Department of Comparative Cellular and Molecular Biology, Favaloro
LV Systolic Function: Theory and Assessment
 LV Systolic Function: Theory and Assessment February 9, 2007 Joe M. Moody, Jr, MD UTHSCSA and STXVHCS References: Internet, McGraw-Hill E-Books, Milnor, Braunwald Big Picture Cardiovascular system produces
LV Systolic Function: Theory and Assessment February 9, 2007 Joe M. Moody, Jr, MD UTHSCSA and STXVHCS References: Internet, McGraw-Hill E-Books, Milnor, Braunwald Big Picture Cardiovascular system produces
SIKLUS JANTUNG. Rahmatina B. Herman
 SIKLUS JANTUNG Rahmatina B. Herman The Cardiac Cycle Definition: The cardiac events that occur from the beginning of one heartbeat to the beginning of the next The cardiac cycle consists of: - Diastole
SIKLUS JANTUNG Rahmatina B. Herman The Cardiac Cycle Definition: The cardiac events that occur from the beginning of one heartbeat to the beginning of the next The cardiac cycle consists of: - Diastole
Cardiac Cycle MCQ. Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology. Cairo University 2007
 Cardiac Cycle MCQ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim Ahmed, MD Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology Cairo University 2007 1- Regarding the length of systole and diastole: a- At heart rate 75 b/min, the duration of
Cardiac Cycle MCQ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim Ahmed, MD Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology Cairo University 2007 1- Regarding the length of systole and diastole: a- At heart rate 75 b/min, the duration of
Heart Pump and Cardiac Cycle. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD
 Heart Pump and Cardiac Cycle Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Objectives To understand the volume, mechanical, pressure and electrical changes during the cardiac cycle To understand the inter-relationship
Heart Pump and Cardiac Cycle Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Objectives To understand the volume, mechanical, pressure and electrical changes during the cardiac cycle To understand the inter-relationship
DESCRIBE THE FACTORS AFFECTING CARDIAC OUTPUT.
 DESCRIBE THE FACTORS AFFECTING CARDIAC OUTPUT. BY: DISHA PRAKASH I MBBS, ROLL NO: 16M069 OBJECTIVES OF LEARNING Terminology and conceptual understanding of Cardiac Output. Factors regulating Cardiac Output.
DESCRIBE THE FACTORS AFFECTING CARDIAC OUTPUT. BY: DISHA PRAKASH I MBBS, ROLL NO: 16M069 OBJECTIVES OF LEARNING Terminology and conceptual understanding of Cardiac Output. Factors regulating Cardiac Output.
Electrical Conduction
 Sinoatrial (SA) node Electrical Conduction Sets the pace of the heartbeat at 70 bpm AV node (50 bpm) and Purkinje fibers (25 40 bpm) can act as pacemakers under some conditions Internodal pathway from
Sinoatrial (SA) node Electrical Conduction Sets the pace of the heartbeat at 70 bpm AV node (50 bpm) and Purkinje fibers (25 40 bpm) can act as pacemakers under some conditions Internodal pathway from
Principles of Biomedical Systems & Devices. Lecture 8: Cardiovascular Dynamics Dr. Maria Tahamont
 Principles of Biomedical Systems & Devices Lecture 8: Cardiovascular Dynamics Dr. Maria Tahamont Review of Cardiac Anatomy Four chambers Two atria-receive blood from the vena cave and pulmonary veins Two
Principles of Biomedical Systems & Devices Lecture 8: Cardiovascular Dynamics Dr. Maria Tahamont Review of Cardiac Anatomy Four chambers Two atria-receive blood from the vena cave and pulmonary veins Two
Cardiovascular Physiology. Heart Physiology. Introduction. The heart. Electrophysiology of the heart
 Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Physiology Introduction The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and two vascular systems, the systemic and pulmonary circulations. The heart pumps blood through
Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Physiology Introduction The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and two vascular systems, the systemic and pulmonary circulations. The heart pumps blood through
Chapter 9, Part 2. Cardiocirculatory Adjustments to Exercise
 Chapter 9, Part 2 Cardiocirculatory Adjustments to Exercise Electrical Activity of the Heart Contraction of the heart depends on electrical stimulation of the myocardium Impulse is initiated in the right
Chapter 9, Part 2 Cardiocirculatory Adjustments to Exercise Electrical Activity of the Heart Contraction of the heart depends on electrical stimulation of the myocardium Impulse is initiated in the right
2.6 Cardiovascular Computer Simulation
 2.6 Cardiovascular Computer Simulation ROOM 23G22 Contents 1. INTRODUCTION... 4 1.1. GENERAL REMARKS... 4 1.2. LEARNING GOALS... 4 1.3. PHYSIOLOGICAL PARAMETERS... 5 1.4. GLOSSARY... 5 2. USING THE COMPUTER
2.6 Cardiovascular Computer Simulation ROOM 23G22 Contents 1. INTRODUCTION... 4 1.1. GENERAL REMARKS... 4 1.2. LEARNING GOALS... 4 1.3. PHYSIOLOGICAL PARAMETERS... 5 1.4. GLOSSARY... 5 2. USING THE COMPUTER
How does the heart pump? From sarcomere to ejection volume
 How does the heart pump? From sarcomere to ejection volume Piet Claus Cardiovascular Imaging and Dynamics Department of Cardiovascular Diseases University Leuven, Leuven, Belgium Course on deformation
How does the heart pump? From sarcomere to ejection volume Piet Claus Cardiovascular Imaging and Dynamics Department of Cardiovascular Diseases University Leuven, Leuven, Belgium Course on deformation
AS Level OCR Cardiovascular System
 AS Level OCR Cardiovascular System Learning Objectives The link between the Cardiac Cycle and the Conduction system of the heart. The relationship between Stroke volume, Heart rate and Cardiac Output.
AS Level OCR Cardiovascular System Learning Objectives The link between the Cardiac Cycle and the Conduction system of the heart. The relationship between Stroke volume, Heart rate and Cardiac Output.
Cardiac Output MCQ. Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology. Cairo University 2007
 Cardiac Output MCQ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim Ahmed, MD Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology Cairo University 2007 90- Guided by Ohm's law when : a- Cardiac output = 5.6 L/min. b- Systolic and diastolic BP
Cardiac Output MCQ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim Ahmed, MD Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology Cairo University 2007 90- Guided by Ohm's law when : a- Cardiac output = 5.6 L/min. b- Systolic and diastolic BP
During exercise the heart rate is 190 bpm and the stroke volume is 115 ml/beat. What is the cardiac output?
 The Cardiovascular System Part III: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Be able to calculate cardiac output (CO) be able to define heart rate
The Cardiovascular System Part III: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Be able to calculate cardiac output (CO) be able to define heart rate
IP: Regulation of Cardiac Output
 ANP 1105D Winter 2013 Assignment 9: The Heart, part 2: Chap... Assignment 9: The Heart, part 2: Chapter 18 Signed in as Alex Sokolowski Help Close Resources Due: 11:59pm on Monday, March 25, 2013 Note:
ANP 1105D Winter 2013 Assignment 9: The Heart, part 2: Chap... Assignment 9: The Heart, part 2: Chapter 18 Signed in as Alex Sokolowski Help Close Resources Due: 11:59pm on Monday, March 25, 2013 Note:
Chapter 13 The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac Function
 Chapter 13 The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac Function Overview of the Cardiovascular System The Path of Blood Flow through the Heart and Vasculature Anatomy of the Heart Electrical Activity of the Heart
Chapter 13 The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac Function Overview of the Cardiovascular System The Path of Blood Flow through the Heart and Vasculature Anatomy of the Heart Electrical Activity of the Heart
Evaluation of Myocardial Function
 Evaluation of Myocardial Function Kenneth E. Jochim, Ph.D., and Douglas M. Behrendt, M.D. ABSTRACT In assessing myocardial contractility one may examine isolated heart muscle, the isolated whole heart
Evaluation of Myocardial Function Kenneth E. Jochim, Ph.D., and Douglas M. Behrendt, M.D. ABSTRACT In assessing myocardial contractility one may examine isolated heart muscle, the isolated whole heart
Cardiac Physiology an Overview
 Cardiac Physiology an Overview Dr L J Solomon Department of Paediatrics and Child Health School of Medicine Faculty of Health Sciences University of the Free State and PICU Universitas Academic Hospital
Cardiac Physiology an Overview Dr L J Solomon Department of Paediatrics and Child Health School of Medicine Faculty of Health Sciences University of the Free State and PICU Universitas Academic Hospital
RV dysfunction and failure PATHOPHYSIOLOGY. Adam Torbicki MD, Dept Chest Medicine Institute of Tuberculosis and Lung Diseases Warszawa, Poland
 RV dysfunction and failure PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Adam Torbicki MD, Dept Chest Medicine Institute of Tuberculosis and Lung Diseases Warszawa, Poland Normal Right Ventricle (RV) Thinner wall Weaker myocytes Differences
RV dysfunction and failure PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Adam Torbicki MD, Dept Chest Medicine Institute of Tuberculosis and Lung Diseases Warszawa, Poland Normal Right Ventricle (RV) Thinner wall Weaker myocytes Differences
TEACH Lesson Plan Manual for Herlihy s The Human Body in Health and Illness 5 th edition
 TEACH Lesson Plan Manual for Herlihy s The Human Body in Health and Illness 5 th edition Chapter 17 Function of the Heart Lesson 17.1 Function of the Heart 1. Define cardiac cycle with respect to systole
TEACH Lesson Plan Manual for Herlihy s The Human Body in Health and Illness 5 th edition Chapter 17 Function of the Heart Lesson 17.1 Function of the Heart 1. Define cardiac cycle with respect to systole
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Louis D Alecy, D.M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License:
Author(s): Louis D Alecy, D.M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License:
The circulatory system
 Introduction to Physiology (Course # 72336) 1 הלב עקרונות בסיסיים (הכנה למעבדת לב) Adi Mizrahi mizrahia@cc.huji.ac.il Textbook Chapter 12 2 The circulatory system To the heart Away from the heart 3 L 2.5
Introduction to Physiology (Course # 72336) 1 הלב עקרונות בסיסיים (הכנה למעבדת לב) Adi Mizrahi mizrahia@cc.huji.ac.il Textbook Chapter 12 2 The circulatory system To the heart Away from the heart 3 L 2.5
Introduction to Physiology (Course # 72336) 1. Adi Mizrahi Textbook Chapter 12
 Introduction to Physiology (Course # 72336) 1 עקרונות בסיסיים (הכנה למעבדת לב) הלב Adi Mizrahi mizrahia@cc.huji.ac.il Textbook Chapter 12 2 The circulatory system To the heart Away from the heart 3 L 2.5
Introduction to Physiology (Course # 72336) 1 עקרונות בסיסיים (הכנה למעבדת לב) הלב Adi Mizrahi mizrahia@cc.huji.ac.il Textbook Chapter 12 2 The circulatory system To the heart Away from the heart 3 L 2.5
Effect of loading and geometry on functional parameters
 Effect of loading and geometry on functional parameters Piet Claus Cardiovascular Imaging and Dynamics Department of Cardiovascular Diseases Leuven University, Leuven, Belgium 5 th European Echocardiography
Effect of loading and geometry on functional parameters Piet Claus Cardiovascular Imaging and Dynamics Department of Cardiovascular Diseases Leuven University, Leuven, Belgium 5 th European Echocardiography
FUNDAMENTALS OF HEMODYNAMICS, VASOACTIVE DRUGS AND IABP IN THE FAILING HEART
 FUNDAMENTALS OF HEMODYNAMICS, VASOACTIVE DRUGS AND IABP IN THE FAILING HEART CINDY BITHER, MSN, ANP, ANP, AACC, CHFN CHIEF NP, ADV HF PROGRAM MEDSTAR WASHINGTON HOSPITAL CENTER CONFLICTS OF INTEREST NONE
FUNDAMENTALS OF HEMODYNAMICS, VASOACTIVE DRUGS AND IABP IN THE FAILING HEART CINDY BITHER, MSN, ANP, ANP, AACC, CHFN CHIEF NP, ADV HF PROGRAM MEDSTAR WASHINGTON HOSPITAL CENTER CONFLICTS OF INTEREST NONE
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Louis D Alecy, D.M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License:
Author(s): Louis D Alecy, D.M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License:
11/10/2014. Muscular pump Two atria Two ventricles. In mediastinum of thoracic cavity 2/3 of heart's mass lies left of midline of sternum
 It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
Useful Ectopics: Case Study. Effects of vasodilation and the diagnostic value of ectopic heartbeats
 Effects of vasodilation and the diagnostic value of ectopic heartbeats 83 year old man, weight 66 kg, height 177 cm, BSA 1.82m 2. Closure of colostomy. No cardiac history. Screenshot 1 Baseline at start
Effects of vasodilation and the diagnostic value of ectopic heartbeats 83 year old man, weight 66 kg, height 177 cm, BSA 1.82m 2. Closure of colostomy. No cardiac history. Screenshot 1 Baseline at start
Cardiac Output. Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com ( Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (
 Interactive Physiology Cardiac Output Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.aw.com/bc) Page 1. Introduction Cardiac output is
Interactive Physiology Cardiac Output Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.aw.com/bc) Page 1. Introduction Cardiac output is
Eindhoven University of Technology. Exam Modeling Cardiac Function (8W160)
 Eindhoven University of Technology department of Biomedical Engineering group Cardiovascular Biomechanics Exam Modeling Cardiac Function (8W160) January 21, 2011, 14.00 17.00 h This exam consists of 6
Eindhoven University of Technology department of Biomedical Engineering group Cardiovascular Biomechanics Exam Modeling Cardiac Function (8W160) January 21, 2011, 14.00 17.00 h This exam consists of 6
Age-related changes in cardiovascular system. Dr. Rehab Gwada
 Age-related changes in cardiovascular system Dr. Rehab Gwada Objectives explain the main structural and functional changes in cardiovascular system associated with normal aging Introduction aging results
Age-related changes in cardiovascular system Dr. Rehab Gwada Objectives explain the main structural and functional changes in cardiovascular system associated with normal aging Introduction aging results
Fluids: occult effects. S Magder Department of Critical Care, McGill University Health Centre
 Fluids: occult effects S Magder Department of Critical Care, McGill University Health Centre Why is volume important? 1. Water is essential to dissolve substances and allow them to diffuse 2. Necessary
Fluids: occult effects S Magder Department of Critical Care, McGill University Health Centre Why is volume important? 1. Water is essential to dissolve substances and allow them to diffuse 2. Necessary
Topics to be Covered. Cardiac Measurements. Distribution of Blood Volume. Distribution of Pulmonary Ventilation & Blood Flow
 Topics to be Covered MODULE F HEMODYNAMIC MONITORING Cardiac Output Determinants of Stroke Volume Hemodynamic Measurements Pulmonary Artery Catheterization Control of Blood Pressure Heart Failure Cardiac
Topics to be Covered MODULE F HEMODYNAMIC MONITORING Cardiac Output Determinants of Stroke Volume Hemodynamic Measurements Pulmonary Artery Catheterization Control of Blood Pressure Heart Failure Cardiac
Mechanisms of heart failure with normal EF Arterial stiffness and ventricular-arterial coupling. What is the pathophysiology at presentation?
 Mechanisms of heart failure with normal EF Arterial stiffness and ventricular-arterial coupling What is the pathophysiology at presentation? Ventricular-arterial coupling elastance Central arterial pressure
Mechanisms of heart failure with normal EF Arterial stiffness and ventricular-arterial coupling What is the pathophysiology at presentation? Ventricular-arterial coupling elastance Central arterial pressure
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM. Heart 2
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Heart 2 PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Cardiac muscle Striated Short Wide Branched Interconnected Skeletal muscle Striated Long Narrow Cylindrical PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Intercalated
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Heart 2 PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Cardiac muscle Striated Short Wide Branched Interconnected Skeletal muscle Striated Long Narrow Cylindrical PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Intercalated
-12. -Ensherah Mokheemer - ABDULLAH ZREQAT. -Faisal Mohammad. 1 P a g e
 -12 -Ensherah Mokheemer - ABDULLAH ZREQAT -Faisal Mohammad 1 P a g e In the previous lecture we talked about: - cardiac index: we use the cardiac index to compare the cardiac output between different individuals,
-12 -Ensherah Mokheemer - ABDULLAH ZREQAT -Faisal Mohammad 1 P a g e In the previous lecture we talked about: - cardiac index: we use the cardiac index to compare the cardiac output between different individuals,
LV geometric and functional changes in VHD: How to assess? Mi-Seung Shin M.D., Ph.D. Gachon University Gil Hospital
 LV geometric and functional changes in VHD: How to assess? Mi-Seung Shin M.D., Ph.D. Gachon University Gil Hospital LV inflow across MV LV LV outflow across AV LV LV geometric changes Pressure overload
LV geometric and functional changes in VHD: How to assess? Mi-Seung Shin M.D., Ph.D. Gachon University Gil Hospital LV inflow across MV LV LV outflow across AV LV LV geometric changes Pressure overload
BME 5742 Bio-Systems Modeling and Control. Lecture 41 Heart & Blood Circulation Heart Function Basics
 BME 5742 Bio-Systems Modeling and Control Lecture 41 Heart & Blood Circulation Heart Function Basics Dr. Zvi Roth (FAU) 1 Pumps A pump is a device that accepts fluid at a low pressure P 1 and outputs the
BME 5742 Bio-Systems Modeling and Control Lecture 41 Heart & Blood Circulation Heart Function Basics Dr. Zvi Roth (FAU) 1 Pumps A pump is a device that accepts fluid at a low pressure P 1 and outputs the
Mechanical Muscles. Mechanics 1
 Mechanical Muscles Objectives: Physiological optimalization of muscle performance. Length-tension relationship. Force-velocity relationship. Preload and afterload. Effects of muscle fiber characteristics
Mechanical Muscles Objectives: Physiological optimalization of muscle performance. Length-tension relationship. Force-velocity relationship. Preload and afterload. Effects of muscle fiber characteristics
Cardiac Properties MCQ
 Cardiac Properties MCQ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim Ahmed, MD Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology Cairo University 2007 1- Cardiac Valves: a- Prevent backflow of blood from the ventricles to the atria during
Cardiac Properties MCQ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim Ahmed, MD Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology Cairo University 2007 1- Cardiac Valves: a- Prevent backflow of blood from the ventricles to the atria during
The relation between stroke work and end-diastolic volume in the ventricles
 Modelling in Medicine and Biology VI 123 The relation between stroke work and end-diastolic volume in the ventricles R. M. Shoucri Department of Mathematics and Computer Science, Royal Military College
Modelling in Medicine and Biology VI 123 The relation between stroke work and end-diastolic volume in the ventricles R. M. Shoucri Department of Mathematics and Computer Science, Royal Military College
*Generating blood pressure *Routing blood: separates. *Ensuring one-way blood. *Regulating blood supply *Changes in contraction
 *Generating blood pressure *Routing blood: separates pulmonary and systemic circulations *Ensuring one-way blood flow: valves *Regulating blood supply *Changes in contraction rate and force match blood
*Generating blood pressure *Routing blood: separates pulmonary and systemic circulations *Ensuring one-way blood flow: valves *Regulating blood supply *Changes in contraction rate and force match blood
BIOL 219 Spring Chapters 14&15 Cardiovascular System
 1 BIOL 219 Spring 2013 Chapters 14&15 Cardiovascular System Outline: Components of the CV system Heart anatomy Layers of the heart wall Pericardium Heart chambers, valves, blood vessels, septum Atrioventricular
1 BIOL 219 Spring 2013 Chapters 14&15 Cardiovascular System Outline: Components of the CV system Heart anatomy Layers of the heart wall Pericardium Heart chambers, valves, blood vessels, septum Atrioventricular
Pathophysiology: Heart Failure
 Pathophysiology: Heart Failure Mat Maurer, MD Irving Assistant Professor of Medicine Outline Definitions and Classifications Epidemiology Muscle and Chamber Function Pathophysiology Heart Failure: Definitions
Pathophysiology: Heart Failure Mat Maurer, MD Irving Assistant Professor of Medicine Outline Definitions and Classifications Epidemiology Muscle and Chamber Function Pathophysiology Heart Failure: Definitions
Collin County Community College
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 5 The Heart 1 The Heart Beat and the EKG 2 1 The Heart Beat and the EKG P-wave = Atrial depolarization QRS-wave = Ventricular depolarization
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 5 The Heart 1 The Heart Beat and the EKG 2 1 The Heart Beat and the EKG P-wave = Atrial depolarization QRS-wave = Ventricular depolarization
Goal-directed vs Flow-guidedresponsive
 Goal-directed vs Flow-guidedresponsive therapy S Magder Department of Critical Care, McGill University Health Centre Flow-directed vs goal directed strategy for management of hemodynamics S Magder Curr
Goal-directed vs Flow-guidedresponsive therapy S Magder Department of Critical Care, McGill University Health Centre Flow-directed vs goal directed strategy for management of hemodynamics S Magder Curr
Qualitative Physiology: from Qualitative Processes to Virtual Patients 1
 Qualitative Physiology: from Qualitative Processes to Virtual Patients 1 Marc Cavazza 1, Altion Simo 2 1 School of Computing and Mathematics, University of Teesside TS1 3BA Middlesbrough, United Kingdom
Qualitative Physiology: from Qualitative Processes to Virtual Patients 1 Marc Cavazza 1, Altion Simo 2 1 School of Computing and Mathematics, University of Teesside TS1 3BA Middlesbrough, United Kingdom
P215 SPRING 2019: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Chaps 13, 14 & 15: pp , , , I. Major Functions of the Circulatory System
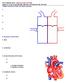 P215 SPRING 2019: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Chaps 13, 14 & 15: pp 360-390, 395-404, 410-428 433-438, 441-445 I. Major Functions of the Circulatory System 1. 2. 3. 4. II. Structure of the Heart 1. atria 2. ventricles
P215 SPRING 2019: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Chaps 13, 14 & 15: pp 360-390, 395-404, 410-428 433-438, 441-445 I. Major Functions of the Circulatory System 1. 2. 3. 4. II. Structure of the Heart 1. atria 2. ventricles
Review of Cardiac Mechanics & Pharmacology 10/23/2016. Brent Dunworth, CRNA, MSN, MBA 1. Learning Objectives
 Brent Dunworth, CRNA, MSN, MBA Associate Director of Advanced Practice Division Chief, Nurse Anesthesia Vanderbilt University Medical Center Nashville, Tennessee Learning Objectives Review the principles
Brent Dunworth, CRNA, MSN, MBA Associate Director of Advanced Practice Division Chief, Nurse Anesthesia Vanderbilt University Medical Center Nashville, Tennessee Learning Objectives Review the principles
Diastology Disclosures: None. Dias2011:1
 Diastology 2011 James D. Thomas, M.D., F.A.C.C. Cardiovascular Imaging Center Department of Cardiology Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland, Ohio, USA Disclosures: None Dias2011:1 Is EVERYBODY a member!?!
Diastology 2011 James D. Thomas, M.D., F.A.C.C. Cardiovascular Imaging Center Department of Cardiology Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland, Ohio, USA Disclosures: None Dias2011:1 Is EVERYBODY a member!?!
Cardiac Output (CO) Definitions. Cardiac Output and venous return. Dr Badri Paudel GMC. Cardiac Output. Venous Return
 Cardiac Output and venous return Dr Badri Paudel GMC Definitions Cardiac Output The quantity of blood pumped into the aorta each minute measured in milliliters (ml) per minute (min) or liters (L) per minute
Cardiac Output and venous return Dr Badri Paudel GMC Definitions Cardiac Output The quantity of blood pumped into the aorta each minute measured in milliliters (ml) per minute (min) or liters (L) per minute
Outline. Pathophysiology: Heart Failure. Heart Failure. Heart Failure: Definitions. Etiologies. Etiologies
 Outline Pathophysiology: Mat Maurer, MD Irving Assistant Professor of Medicine Definitions and Classifications Epidemiology Muscle and Chamber Function Pathophysiology : Definitions An inability of the
Outline Pathophysiology: Mat Maurer, MD Irving Assistant Professor of Medicine Definitions and Classifications Epidemiology Muscle and Chamber Function Pathophysiology : Definitions An inability of the
Echo assessment of the failing heart
 Echo assessment of the failing heart Mark K. Friedberg, MD The Labatt Family Heart Center The Hospital for Sick Children Toronto, Ontario, Canada Cardiac function- definitions Cardiovascular function:
Echo assessment of the failing heart Mark K. Friedberg, MD The Labatt Family Heart Center The Hospital for Sick Children Toronto, Ontario, Canada Cardiac function- definitions Cardiovascular function:
Blood Volume: Vascular and Systemic
 Various examples and supplementary slides that may be used in lecture. These are provided as a resource for M1 students by Dr. HN Mayrovitz Fall 2005. Note that all of the following slides may or may not
Various examples and supplementary slides that may be used in lecture. These are provided as a resource for M1 students by Dr. HN Mayrovitz Fall 2005. Note that all of the following slides may or may not
Circulation: Chapter 25. Cardiac Output. The Mammalian Heart Fig Right side of the heart
 Circulation: Chapter 25 1. Limits of Diffusion A. Small organisms use diffusion B. rapid over small distances 2. Most animals have circulatory systems A. Blood B. Pump (Heart) or propulsive structures
Circulation: Chapter 25 1. Limits of Diffusion A. Small organisms use diffusion B. rapid over small distances 2. Most animals have circulatory systems A. Blood B. Pump (Heart) or propulsive structures
Ventriculo-arterial coupling and diastolic elastance. MasterclassIC Schiermonnikoog 2015
 Ventriculo-arterial coupling and diastolic elastance MasterclassIC Schiermonnikoog 2015 Ventriculo-arterial coupling Dynamic interaction between heart and systemic circulation (modulation of compliance
Ventriculo-arterial coupling and diastolic elastance MasterclassIC Schiermonnikoog 2015 Ventriculo-arterial coupling Dynamic interaction between heart and systemic circulation (modulation of compliance
Ejection across stenotic aortic valve requires a systolic pressure gradient between the LV and aorta. This places a pressure load on the LV.
 Valvular Heart Disease Etiology General Principles Cellular and molecular mechanism of valve damage Structural pathology Functional pathology - stenosis/regurgitation Loading conditions - pressure/volume
Valvular Heart Disease Etiology General Principles Cellular and molecular mechanism of valve damage Structural pathology Functional pathology - stenosis/regurgitation Loading conditions - pressure/volume
Cardiac output and Venous Return. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD
 Cardiac output and Venous Return Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Objectives Define cardiac output and venous return Describe the methods of measurement of CO Outline the factors that regulate cardiac output
Cardiac output and Venous Return Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Objectives Define cardiac output and venous return Describe the methods of measurement of CO Outline the factors that regulate cardiac output
LV Function Cardiac Output EPSS
 LV Function Cardiac Output EPSS Mike Mallin, MD Why is LV function important? Systolic Dysfunction is bad... Is it worse? Is it the cause of my patients dyspnea? Does my patient need a inotrope? Why is
LV Function Cardiac Output EPSS Mike Mallin, MD Why is LV function important? Systolic Dysfunction is bad... Is it worse? Is it the cause of my patients dyspnea? Does my patient need a inotrope? Why is
10/23/2017. Muscular pump Two atria Two ventricles. In mediastinum of thoracic cavity 2/3 of heart's mass lies left of midline of sternum
 It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
Use of an ipad App to simulate pressure-volume loops and cardiovascular physiology
 Adv Physiol Educ 41: 415 424, 2017; doi:10.1152/advan.00204.2016. SOURCEBOOK OF LABORATORY ACTIVITIES IN PHYSIOLOGY Use of an ipad App to simulate pressure-volume loops and cardiovascular physiology Staci
Adv Physiol Educ 41: 415 424, 2017; doi:10.1152/advan.00204.2016. SOURCEBOOK OF LABORATORY ACTIVITIES IN PHYSIOLOGY Use of an ipad App to simulate pressure-volume loops and cardiovascular physiology Staci
TOPIC : Cardiogenic Shock
 University of Ferrara Department of Morphology, Surgery and Experimental Medicine. Section of Anaesthesia and Intensive Care Medicine TOPIC : Cardiogenic Shock What is shock? Shock is a condition of inadequate
University of Ferrara Department of Morphology, Surgery and Experimental Medicine. Section of Anaesthesia and Intensive Care Medicine TOPIC : Cardiogenic Shock What is shock? Shock is a condition of inadequate
Transesophageal Echocardiography
 N. Kolev, G. Huemer, M. Zimpfer Transesophageal Echocardiography A New Monitoring Technique Springer-Verlag Wien New York Nikolai Kolev, MD, FACC Research Cardiologist Associate in Anesthesia and Consultant
N. Kolev, G. Huemer, M. Zimpfer Transesophageal Echocardiography A New Monitoring Technique Springer-Verlag Wien New York Nikolai Kolev, MD, FACC Research Cardiologist Associate in Anesthesia and Consultant
The Cardiac Cycle Clive M. Baumgarten, Ph.D.
 The Cardiac Cycle Clive M. Baumgarten, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe periods comprising cardiac cycle and events within each period 2. Describe the temporal relationships between pressure, blood flow,
The Cardiac Cycle Clive M. Baumgarten, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe periods comprising cardiac cycle and events within each period 2. Describe the temporal relationships between pressure, blood flow,
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF THE HEART I & II
 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF THE HEART I & II Recommended Reading: Guyton, A. Textbook of Medical Physiology, 1 th Edition. Chapters 9, 14, 2. Berne & Levy. Principles of Physiology. 4 th Edition. Chapter
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF THE HEART I & II Recommended Reading: Guyton, A. Textbook of Medical Physiology, 1 th Edition. Chapters 9, 14, 2. Berne & Levy. Principles of Physiology. 4 th Edition. Chapter
NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 September 18 & 20, 2017 Cardiovascular 3 & 4: Mechanical Actions of the Heart and Determinants of Cardiac Output
 NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 September 18 & 20, 2017 Cardiovascular 3 & 4: Mechanical Actions of the Heart and Determinants of Cardiac Output An essential component for the operation of the heart
NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 September 18 & 20, 2017 Cardiovascular 3 & 4: Mechanical Actions of the Heart and Determinants of Cardiac Output An essential component for the operation of the heart
Practice Exercises for the Cardiovascular System
 Practice Exercises for the Cardiovascular System On the diagram below, color the oxygen-rich blood red and the oxygen-poor blood blue. Label the parts: Continued on the next page... Label the parts on
Practice Exercises for the Cardiovascular System On the diagram below, color the oxygen-rich blood red and the oxygen-poor blood blue. Label the parts: Continued on the next page... Label the parts on
Ejection across stenotic aortic valve requires a systolic pressure gradient between the LV and aorta. This places a pressure load on the LV.
 Valvular Heart Disease General Principles Etiology Cellular and molecular mechanism of valve damage Structural pathology Functional pathology - stenosis/regurgitation Loading conditions - pressure/volume
Valvular Heart Disease General Principles Etiology Cellular and molecular mechanism of valve damage Structural pathology Functional pathology - stenosis/regurgitation Loading conditions - pressure/volume
Evolutionary origins of the right ventricle. S Magder Department of Critical Care, McGill University Health Centre
 Evolutionary origins of the right ventricle S Magder Department of Critical Care, McGill University Health Centre Fully separated four chamber heart only evolved in birds and mammals What are the evolutionary
Evolutionary origins of the right ventricle S Magder Department of Critical Care, McGill University Health Centre Fully separated four chamber heart only evolved in birds and mammals What are the evolutionary
BUSINESS. Articles? Grades Midterm Review session
 BUSINESS Articles? Grades Midterm Review session REVIEW Cardiac cells Myogenic cells Properties of contractile cells CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART Conduction pathway SA node (pacemaker) atrial depolarization
BUSINESS Articles? Grades Midterm Review session REVIEW Cardiac cells Myogenic cells Properties of contractile cells CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART Conduction pathway SA node (pacemaker) atrial depolarization
Effect of physiological heart rate changes on left ventricular dimensions and mitral blood flow velocities in the normal fetus
 ELSEVIER Early Human Development 40 (1995) 109-114 Effect of physiological heart rate changes on left ventricular dimensions and mitral blood flow velocities in the normal fetus P.B. Tsyvian a, K.V. Malkin
ELSEVIER Early Human Development 40 (1995) 109-114 Effect of physiological heart rate changes on left ventricular dimensions and mitral blood flow velocities in the normal fetus P.B. Tsyvian a, K.V. Malkin
McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT-B and PHRN Optional Continuing Education 2018 #12 Understanding Preload and Afterload
 McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT-B and PHRN Optional Continuing Education 2018 #12 Understanding Preload and Afterload Cardiac output (CO) represents the volume of blood that is delivered
McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT-B and PHRN Optional Continuing Education 2018 #12 Understanding Preload and Afterload Cardiac output (CO) represents the volume of blood that is delivered
PHYSIOLOGY MeQ'S (Morgan) All the following statements related to blood volume are correct except for: 5 A. Blood volume is about 5 litres. B.
 PHYSIOLOGY MeQ'S (Morgan) Chapter 5 All the following statements related to capillary Starling's forces are correct except for: 1 A. Hydrostatic pressure at arterial end is greater than at venous end.
PHYSIOLOGY MeQ'S (Morgan) Chapter 5 All the following statements related to capillary Starling's forces are correct except for: 1 A. Hydrostatic pressure at arterial end is greater than at venous end.
OT Exam 3, August 19, 2002 Page 1 of 6. Occupational Therapy Physiology, Summer Examination 3. August 19, 2002
 Page 1 of 6 Occupational Therapy Physiology, Summer 2002 Examination 3 August 19, 2002 There are 20 questions and each question is worth 5 points for a total of 100 points. Dr. Heckman's section is questions
Page 1 of 6 Occupational Therapy Physiology, Summer 2002 Examination 3 August 19, 2002 There are 20 questions and each question is worth 5 points for a total of 100 points. Dr. Heckman's section is questions
The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 18 Part A The Cardiovascular System 1/19/16 1 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Similarities of Cardiac and Skeletal Muscle RMP Ion concentration Deploarization Action Potential Repolarization
Chapter 18 Part A The Cardiovascular System 1/19/16 1 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Similarities of Cardiac and Skeletal Muscle RMP Ion concentration Deploarization Action Potential Repolarization
Impedance Cardiography (ICG) Method, Technology and Validity
 Method, Technology and Validity Hemodynamic Basics Cardiovascular System Cardiac Output (CO) Mean arterial pressure (MAP) Variable resistance (SVR) Aortic valve Left ventricle Elastic arteries / Aorta
Method, Technology and Validity Hemodynamic Basics Cardiovascular System Cardiac Output (CO) Mean arterial pressure (MAP) Variable resistance (SVR) Aortic valve Left ventricle Elastic arteries / Aorta
(D) (E) (F) 6. The extrasystolic beat would produce (A) increased pulse pressure because contractility. is increased. increased
 Review Test 1. A 53-year-old woman is found, by arteriography, to have 5% narrowing of her left renal artery. What is the expected change in blood flow through the stenotic artery? Decrease to 1 2 Decrease
Review Test 1. A 53-year-old woman is found, by arteriography, to have 5% narrowing of her left renal artery. What is the expected change in blood flow through the stenotic artery? Decrease to 1 2 Decrease
Why would epidural analgesia cause these symptoms? How would increasing the blood volume change venous pressure (VP)?
 CASE 12 A 25-year-old pregnant woman is in labor at the hospital. She has no medical problems and has had no complications with this pregnancy. She is in the active phase of labor, feeling intense contractions,
CASE 12 A 25-year-old pregnant woman is in labor at the hospital. She has no medical problems and has had no complications with this pregnancy. She is in the active phase of labor, feeling intense contractions,
Chapter 12. Methods for Aerobic Training and Physiologic Responses
 Chapter 12 Methods for Aerobic Training and Physiologic Responses Aerobic Performance Purpose of training Improve performance General principles of physical conditioning Specificity Overload Aerobic Performance
Chapter 12 Methods for Aerobic Training and Physiologic Responses Aerobic Performance Purpose of training Improve performance General principles of physical conditioning Specificity Overload Aerobic Performance
Load and Function - Valvular Heart Disease. Tom Marwick, Cardiovascular Imaging Cleveland Clinic
 Load and Function - Valvular Heart Disease Tom Marwick, Cardiovascular Imaging Cleveland Clinic Indications for surgery in common valve lesions Risks Operative mortality Failed repair - to MVR Operative
Load and Function - Valvular Heart Disease Tom Marwick, Cardiovascular Imaging Cleveland Clinic Indications for surgery in common valve lesions Risks Operative mortality Failed repair - to MVR Operative
instr: Kevin Bonine t.a.: Kristen Potter
 Lecture 17, 18 Oct 2005 Chapter 20-24 Circulation, Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide Transport Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (aka MCB 437, VetSci 437) University of Arizona Fall 2005 instr: Kevin Bonine t.a.:
Lecture 17, 18 Oct 2005 Chapter 20-24 Circulation, Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide Transport Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (aka MCB 437, VetSci 437) University of Arizona Fall 2005 instr: Kevin Bonine t.a.:
Scisense ADV500. Pressure-Volume Measurement System for Cardiac Function Research in All Sizes of Hearts. Pressure-Volume
 Pressure-Volume Scisense ADV500 Pressure-Volume Measurement System for Cardiac Function Research in All Sizes of Hearts True volume in real-time with Admittance technology Variable Segment Length (VSL)
Pressure-Volume Scisense ADV500 Pressure-Volume Measurement System for Cardiac Function Research in All Sizes of Hearts True volume in real-time with Admittance technology Variable Segment Length (VSL)
The Heart. C h a p t e r. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris
 C h a p t e r 20 The Heart PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings Introduction
C h a p t e r 20 The Heart PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings Introduction
THESIS NEW FRANK-STARLING BASED CONTRACTILITY AND VENTRICULAR STIFFNESS INDICES: CLINICALLY APPLICABLE ALTERNATIVE TO EMAX. Submitted by.
 THESIS NEW FRANK-STARLING BASED CONTRACTILITY AND VENTRICULAR STIFFNESS INDICES: CLINICALLY APPLICABLE ALTERNATIVE TO EMAX Submitted by Haiming Tan Graduate Degree Program in Bioengineering In partial
THESIS NEW FRANK-STARLING BASED CONTRACTILITY AND VENTRICULAR STIFFNESS INDICES: CLINICALLY APPLICABLE ALTERNATIVE TO EMAX Submitted by Haiming Tan Graduate Degree Program in Bioengineering In partial
Cardiology. the Sounds: #7 HCM. LV Outflow Obstruction: Aortic Stenosis. (Coming Soon - HCM)
 A Cardiology HCM LV Outflow Obstruction: Aortic Stenosis (Coming Soon - HCM) the Sounds: #7 Howard J. Sachs, MD www.12daysinmarch.com E-mail: Howard@12daysinmarch.com Aortic Valve Disorders Stenosis Regurgitation
A Cardiology HCM LV Outflow Obstruction: Aortic Stenosis (Coming Soon - HCM) the Sounds: #7 Howard J. Sachs, MD www.12daysinmarch.com E-mail: Howard@12daysinmarch.com Aortic Valve Disorders Stenosis Regurgitation
Hemodynamics of Exercise
 Hemodynamics of Exercise Joe M. Moody, Jr, MD UTHSCSA and ALMMVAH, STVAHCS Exercise Physiology - Acute Effects Cardiac Output (Stroke volume, Heart Rate ) Oxygen Extraction (Arteriovenous O 2 difference,
Hemodynamics of Exercise Joe M. Moody, Jr, MD UTHSCSA and ALMMVAH, STVAHCS Exercise Physiology - Acute Effects Cardiac Output (Stroke volume, Heart Rate ) Oxygen Extraction (Arteriovenous O 2 difference,
Fetal gene upregulation by 1-wk TAC is significantly increased in mice lacking RGS2.
 3562-RG-1 Supplementary Figure 1 Fetal gene upregulation by 1-wk is significantly increased in mice lacking RGS2. ANP(Nppa) /BNP(Nppb) A-type and B-type natriuretic peptide; β-mhc (Myh7) beta myosin heavy
3562-RG-1 Supplementary Figure 1 Fetal gene upregulation by 1-wk is significantly increased in mice lacking RGS2. ANP(Nppa) /BNP(Nppb) A-type and B-type natriuretic peptide; β-mhc (Myh7) beta myosin heavy
Heart Failure. Cardiac Anatomy. Functions of the Heart. Cardiac Cycle/Hemodynamics. Determinants of Cardiac Output. Cardiac Output
 Cardiac Anatomy Heart Failure Professor Qing ZHANG Department of Cardiology, West China Hospital www.blaufuss.org Cardiac Cycle/Hemodynamics Functions of the Heart Essential functions of the heart to cover
Cardiac Anatomy Heart Failure Professor Qing ZHANG Department of Cardiology, West China Hospital www.blaufuss.org Cardiac Cycle/Hemodynamics Functions of the Heart Essential functions of the heart to cover
Evaluation of Left Ventricular Function and Hypertrophy Gerard P. Aurigemma MD
 Evaluation of Left Ventricular Function and Hypertrophy Gerard P. Aurigemma MD Board Review Course 2017 43 year old health assistant Severe resistant HTN LT BSA 2 Height 64 1 Here is the M mode echocardiogram
Evaluation of Left Ventricular Function and Hypertrophy Gerard P. Aurigemma MD Board Review Course 2017 43 year old health assistant Severe resistant HTN LT BSA 2 Height 64 1 Here is the M mode echocardiogram
Pathophysiology: Heart Failure. Objectives
 Pathophysiology: Heart Failure Mat Maurer, MD Irving Assistant Professor of Clinical Medicine Objectives At the conclusion of this seminar, learner will be able to: 1. Define heart failure as a clinical
Pathophysiology: Heart Failure Mat Maurer, MD Irving Assistant Professor of Clinical Medicine Objectives At the conclusion of this seminar, learner will be able to: 1. Define heart failure as a clinical
Impedance Cardiography (ICG) Application of ICG for Hypertension Management
 Application of ICG for Hypertension Management 1mA @ 100 khz Impedance Cardiography (ICG) Non-invasive Beat-to-beat Hemodynamic Monitoring Diastole Systole Aortic valve is closed No blood flow in the aorta
Application of ICG for Hypertension Management 1mA @ 100 khz Impedance Cardiography (ICG) Non-invasive Beat-to-beat Hemodynamic Monitoring Diastole Systole Aortic valve is closed No blood flow in the aorta
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM AND RESPONSES TO EXERCISE Mr. S. Kelly PSK 4U North Grenville DHS THE HEART: A REVIEW Cardiac muscle = myocardium Heart divided into two sides, 4 chambers (L & R) RS: pulmonary
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM AND RESPONSES TO EXERCISE Mr. S. Kelly PSK 4U North Grenville DHS THE HEART: A REVIEW Cardiac muscle = myocardium Heart divided into two sides, 4 chambers (L & R) RS: pulmonary
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF THE HEART
 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF THE HEART I. INTRODUCTION The heart is a muscular pump connected to the systemic and pulmonary vascular systems. Working together, the principle job of the heart and vasculature
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF THE HEART I. INTRODUCTION The heart is a muscular pump connected to the systemic and pulmonary vascular systems. Working together, the principle job of the heart and vasculature
Rationale for Prophylactic Support During Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
 Rationale for Prophylactic Support During Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Navin K. Kapur, MD, FACC, FSCAI Assistant Director, Interventional Cardiology Director, Interventional Research Laboratories
Rationale for Prophylactic Support During Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Navin K. Kapur, MD, FACC, FSCAI Assistant Director, Interventional Cardiology Director, Interventional Research Laboratories
