Blood Vessels. veins. valve. to the heart. capillaries from the heart. arteries. Visual 25-1
|
|
|
- Elfrieda Merritt
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Blood Vessels veins valve to the heart capillaries from the heart arteries Visual 25-1
2 Human Heart pulmonary arteries superior vena cava aorta pulmonary veins semilunar valves right atrium pulmonary arteries pulmonary veins right AV valve left atrium left AV valve left ventricle right ventricle pericardium inferior vena cava septum aorta Visual 25-2a
3 Human Heart Visual 25-2b
4 Path of Blood in the Heart oxygenated blood deoxygenated blood Visual 25-3a
5 Path of Blood in the Heart oxygenated blood deoxygenated blood Visual 25-3b
6 Path of Blood in the Body body organs superior vena cava pulmonary artery pulmonary artery lung aorta lung pulmonary vein inferior vena cava pulmonary vein left side of heart right side of heart body organs Visual 25-5
7 Exchange of Gases in Capillaries oxygenated blood oxygenated blood CO 2 CO 2 CO 2 O 2 O 2 lung erythrocytes CO 2 organs of the body O 2 O 2 deoxygenated blood deoxygenated blood Visual 25-6
8 Blood Clotting Platelets rupture, releasing a chemical into the blood. The chemical triggers the formation of protein fibers. The protein fibers trap blood cells, forming a clot. Visual 25-7
9 Blood Pressure normal blood pressure arteries decreasing in diameter increases blood pressure heart s pumping more blood increases blood pressure heart s pumping more blood and arteries decreasing in diameter increases blood pressure Visual 25-8
10 Mucous Membrane with Cilia mucous membrane trapped organism cilia mucus Visual 25-9
11 Splinter Wound Bacteria (green) enter the body on the end of a splinter. Macrophages (purple) squeeze through the capillary walls. As the wound heals, the macrophages finish destroying the bacteria. Visual 25-10
12 Human Immune System macrophage B cells B2 plasma cells T cells B1 bacteria B3 antibodies B5 A1 killer T cells B4 A2 memory B cell A4 A3 infected cell memory T cell The immune response: When macrophages identify a foreign substance (bacteria), two series of events begin to happen simultaneously. T cells activate killer T cells (A1) as well as B cells (B1). Some killer T cells attack the bacteria (A2), and others attack infected cells (A3). Meanwhile, the activated B cells produce plasma cells (B2), which in turn produce antibodies (B3). The antibodies attack the invading bacteria (B4). After the bacteria have been destroyed, some T cells (A4) and some B cells (B5) become memory cells to guard against future infections. Leftover antibodies also remain in the bloodstream, enhancing the body s immunity. Visual 25-11
13 Nephron artery vein fluid leaves blood vessel and enters the nephron tube kidney fluid returns to blood vessel, leaving wastes in nephron fluid waste (urine) passes out of the nephron nephron Visual 25-12a
14 Nephron kidney nephron Visual 25-12b
15 Human Excretory System blood flow kidney aorta inferior vena cava ureters urethra urinary bladder Visual 25-13a
16 Human Excretory System Visual 25-13b
17 Circulatory System left side of the heart pulmonary veins aorta arteries capillaries in the lungs capillaries in the body organs veins pulmonary arteries vena cavae right side of the heart Visual 25-14a
18 Circulatory System left side of the heart veins aorta the lungs in in the body organs arteries right side of the heart Visual 25-14b
19 Circulatory System pulmonary veins inferior and superior vena cavae right atrium left atrium veins capillaries in the lungs right AV valve right ventricle left AV valve left ventricle capillaries in the body organs pulmonary semilunar valve aortic semilunar valve arteries pulmonary arteries aorta Visual 25-15a
20 Circulatory System pulmonary inferior and superior right atrium capillaries in the left AV valve capillaries in the pulmonary aortic semilunar valve arteries pulmonary Visual 25-15b
Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93)
 Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
THE HEART. Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration
 THE HEART Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration The Circulatory System Also called the Cardiovascular System Circulates blood in the body Transports nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood
THE HEART Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration The Circulatory System Also called the Cardiovascular System Circulates blood in the body Transports nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood
The Function. To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body.
 The Function To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body. What makes up the circulatory system? 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood vessels Blood travels from the heart to the body
The Function To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body. What makes up the circulatory system? 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood vessels Blood travels from the heart to the body
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY CAPTAINS TRYOUT TEST- WAUBONSIE VALLEY HIGH SCHOOL
 1 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY CAPTAINS TRYOUT TEST- WAUBONSIE VALLEY HIGH SCHOOL NAMES: Multiple choice (1 pt per question) 1. What percentage of blood plasma is not reabsorbed by the blood capillaries? a.
1 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY CAPTAINS TRYOUT TEST- WAUBONSIE VALLEY HIGH SCHOOL NAMES: Multiple choice (1 pt per question) 1. What percentage of blood plasma is not reabsorbed by the blood capillaries? a.
The Cardiovascular. Parts and Functions
 The Cardiovascular Parts and Functions Parts The cardiovascular system consists of 3 major parts that work together. 1- Heart 2- Lungs 3- Blood Vessels Blood Vessels There are blood vessels that carry
The Cardiovascular Parts and Functions Parts The cardiovascular system consists of 3 major parts that work together. 1- Heart 2- Lungs 3- Blood Vessels Blood Vessels There are blood vessels that carry
It s Totally Tubular, Dude!
 It s Totally Tubular, Dude! Objective: To learn the structure and function of the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Bell Work: For the following, place the items in order from most simple to most complex:
It s Totally Tubular, Dude! Objective: To learn the structure and function of the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Bell Work: For the following, place the items in order from most simple to most complex:
Glossary: The Cardiovascular System
 This glossary includes terms that have been introduced in Lesson 14. Student Resource 14.14 Glossary: The Cardiovascular System Anatomy Terms aorta Large artery that transports blood from the left ventricle
This glossary includes terms that have been introduced in Lesson 14. Student Resource 14.14 Glossary: The Cardiovascular System Anatomy Terms aorta Large artery that transports blood from the left ventricle
12.1 The Function of Circulation
 12.1 The Function of Circulation The Circulatory System Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) Heart pump beats 100 000 times a day Deliver oxygen and nutrients Function of Circulation Multicellular organisms
12.1 The Function of Circulation The Circulatory System Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) Heart pump beats 100 000 times a day Deliver oxygen and nutrients Function of Circulation Multicellular organisms
Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes
 Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes Functions of the Circulatory System The circulatory system functions mainly as the body s transport system. It transports: o Oxygen o Nutrients o Cell waste o
Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes Functions of the Circulatory System The circulatory system functions mainly as the body s transport system. It transports: o Oxygen o Nutrients o Cell waste o
ACTIVITY: The Heart Cycle
 ACTIVITY: The Heart Cycle In this activity, you will follow the flow of blood through the heart. Your heart has two jobs to do, and its two sides have separate responsibilities: The left side pumps oxygen-enriched
ACTIVITY: The Heart Cycle In this activity, you will follow the flow of blood through the heart. Your heart has two jobs to do, and its two sides have separate responsibilities: The left side pumps oxygen-enriched
Chapter 16: Circulation
 Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
HEALTH FITNESS AND SPORT
 BOOK 4 HEALTH FITNESS AND SPORT SECTION 3 EXERCISE AND FITNESS IN HUMANS THE STRUCTURE OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The human nervous system consists of: the central nervous system (CNS) the brain and spinal
BOOK 4 HEALTH FITNESS AND SPORT SECTION 3 EXERCISE AND FITNESS IN HUMANS THE STRUCTURE OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The human nervous system consists of: the central nervous system (CNS) the brain and spinal
Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Blood o Red blood cells: heamoglobin and oxygen transport o White blood cells: phagocyte phagocytosis (engulf pathogen, vesicles fuse with vacuole,
Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Blood o Red blood cells: heamoglobin and oxygen transport o White blood cells: phagocyte phagocytosis (engulf pathogen, vesicles fuse with vacuole,
2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system
 2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system Essential questions What are the structures of blood? What are the structures of the circulatory system? circulatory system 2 Structures of the circulatory
2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system Essential questions What are the structures of blood? What are the structures of the circulatory system? circulatory system 2 Structures of the circulatory
Lecture 8. Heart and Circulatory System. Lecture 8
 Lecture 8 Heart and Circulatory System Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Blood 3. Blood Vessels & Blood Pressure 4. The Heart 5. Cardiovascular (Circulatory) System 2 1 Circulatory System Function 1. Transport
Lecture 8 Heart and Circulatory System Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Blood 3. Blood Vessels & Blood Pressure 4. The Heart 5. Cardiovascular (Circulatory) System 2 1 Circulatory System Function 1. Transport
Cardiovascular System- Heart. Miss Wheeler Unit 8
 Cardiovascular System- Heart Miss Wheeler Unit 8 Overview CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM heart vessels Made up of heart, blood vessels, and blood Functions Heart- pump blood Vessels- (veins, arteries, capillaries)
Cardiovascular System- Heart Miss Wheeler Unit 8 Overview CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM heart vessels Made up of heart, blood vessels, and blood Functions Heart- pump blood Vessels- (veins, arteries, capillaries)
The circulatory system is a complex series of tubes that transports nutrient-rich blood and waste products throughout the entire body.
 Circulatory System The circulatory system is a complex series of tubes that transports nutrient-rich blood and waste products throughout the entire body. What does blood consist of? The blood consists
Circulatory System The circulatory system is a complex series of tubes that transports nutrient-rich blood and waste products throughout the entire body. What does blood consist of? The blood consists
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
5 th Primary. Science
 Final revision sheet A-Complete the following: 1. two lungs. 2. Kidney 3. Soil 4. friction. 5. cancelled 6. silt soil, clay soil,sand soil. 7. avoid mixing of the blood. 8. Silt - yellow. 9. Clay - sand.
Final revision sheet A-Complete the following: 1. two lungs. 2. Kidney 3. Soil 4. friction. 5. cancelled 6. silt soil, clay soil,sand soil. 7. avoid mixing of the blood. 8. Silt - yellow. 9. Clay - sand.
CIRCULATION & GAS EXCHANGE
 AP BIOLOGY ACTIVITY2.13 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter42 NAME DATE HOUR CIRCULATION & GAS EXCHANGE 1. In general, what is the function of transport systems? 2. What method/structure do most invertebrates use
AP BIOLOGY ACTIVITY2.13 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter42 NAME DATE HOUR CIRCULATION & GAS EXCHANGE 1. In general, what is the function of transport systems? 2. What method/structure do most invertebrates use
C3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 Worksheet. C3 Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the heart
 Name: Date: C3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 Worksheet C3 Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the heart 1. Label and give the functions of the following: a. left and right atrium: b. left and right ventricle:
Name: Date: C3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 Worksheet C3 Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the heart 1. Label and give the functions of the following: a. left and right atrium: b. left and right ventricle:
Chapter 14. The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Biology Unit 3 The Human Heart P
 Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary.
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
(2) (1) (3) (4) BLOOD PATHWAY ASSESSMENT RUBRIC
 BLOODPATHWAYASSESSMENT(4) BLOOD%PATHWAY%ASSESSMENT%(3)% BLOODPATHWAYASSESSMENT(3) (4) (3) (2) (1) Using a completely blank diagram of the heart, all valves, chambers, great vessels, and direction of blood
BLOODPATHWAYASSESSMENT(4) BLOOD%PATHWAY%ASSESSMENT%(3)% BLOODPATHWAYASSESSMENT(3) (4) (3) (2) (1) Using a completely blank diagram of the heart, all valves, chambers, great vessels, and direction of blood
Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation
 1 Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Section 9.1 Homeostasis: Life in the Balance Outcomes: I can explain homeostasis I can describe the importance of homeostasis to living things I can explain the
1 Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Section 9.1 Homeostasis: Life in the Balance Outcomes: I can explain homeostasis I can describe the importance of homeostasis to living things I can explain the
Circulatory System Review
 Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
The Human Body Systems Chapter 19, 20 & 21
 The Human Body Systems Chapter 19, 20 & 21 I. Chapter 19 - Circulatory System A. A closed system consisting of the 4 chambered heart, a network of arteries, veins, capillaries, blood and the lymph system
The Human Body Systems Chapter 19, 20 & 21 I. Chapter 19 - Circulatory System A. A closed system consisting of the 4 chambered heart, a network of arteries, veins, capillaries, blood and the lymph system
The Heart. Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet
 The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
The Cardiovascular System (Heart)
 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System (Heart) A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function
The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System (Heart) A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function
The circulatory system
 The circulatory system Key words Vessels heart blood plasma platelets haemoglobin To engulf arteries capillaries veins venules lymphocytes Atrium / - a ventricle tricuspid bicuspid cardiac coronary Humans
The circulatory system Key words Vessels heart blood plasma platelets haemoglobin To engulf arteries capillaries veins venules lymphocytes Atrium / - a ventricle tricuspid bicuspid cardiac coronary Humans
Circulatory Systems. All cells need to take in nutrients and expel metabolic wastes.
 Circulatory Systems All cells need to take in nutrients and expel metabolic wastes. Single celled organisms: nutrients from the environment can diffuse (or be actively transported) directly in to the cell
Circulatory Systems All cells need to take in nutrients and expel metabolic wastes. Single celled organisms: nutrients from the environment can diffuse (or be actively transported) directly in to the cell
Levels of Organization. Chapter 19 6/11/2012. Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body. 4 Primary Tissues
 Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM BLOOD VESSELS
 Name: Block: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms such as
Name: Block: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms such as
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY
 TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
Book Second Term Test Model Answers. Page 84 to 87
 1. Write the scientific term: a. Red blood cells b. Aorta c. Ball bearings d. Air resistance e. silt soil f. sand soil 2. Write a brief account: Book Second Term Test Model Answers Page 84 to 87 a. friction:
1. Write the scientific term: a. Red blood cells b. Aorta c. Ball bearings d. Air resistance e. silt soil f. sand soil 2. Write a brief account: Book Second Term Test Model Answers Page 84 to 87 a. friction:
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Science Matters Chapter 8 Introduction Living things need a transport system to carry things around the body. In humans its called The Circulatory system. The parts of the system
The Circulatory System Science Matters Chapter 8 Introduction Living things need a transport system to carry things around the body. In humans its called The Circulatory system. The parts of the system
Blood and Heart. Student Learning Objectives:
 Blood and Heart Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major components of the blood. Identify the primary structures associated with the heart Follow the blood through the path of the circulation.
Blood and Heart Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major components of the blood. Identify the primary structures associated with the heart Follow the blood through the path of the circulation.
Human Body Systems. Long narrow tube mixes enzymes with food Small nutrient molecules diffuse into blood
 Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process:
 Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: a. erythrocytes b. leukocytes c. melanocytes d. thrombocytes Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process: a. erythrocytes
Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: a. erythrocytes b. leukocytes c. melanocytes d. thrombocytes Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process: a. erythrocytes
Circulation and Respiration
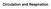 Circulation and Respiration Miller, Geoffrey. 2009. Spent: Sex, Evolution, and Consumer Behavior. Miller, Geoffrey. 2009. Spent: Sex, Evolution, and Consumer Behavior. Respiratory system moves O 2 into,
Circulation and Respiration Miller, Geoffrey. 2009. Spent: Sex, Evolution, and Consumer Behavior. Miller, Geoffrey. 2009. Spent: Sex, Evolution, and Consumer Behavior. Respiratory system moves O 2 into,
Cardiovascular System. Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12
 Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans
 Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
A. Incorrect! The left ventricle receives oxygenated blood from the lungs via the left atrium.
 DAT Biology - Problem Drill 10: The Circulatory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. What is the flow of deoxygenated blood through the heart as it returns from the body? Question #01 (A) Vena cava; right ventricle;
DAT Biology - Problem Drill 10: The Circulatory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. What is the flow of deoxygenated blood through the heart as it returns from the body? Question #01 (A) Vena cava; right ventricle;
Types of circulatory systems
 Types of circulatory systems Open system Mostly invertebrates Low pressure Haemocoel Suitable for small organisms Closed system Vertebrates High pressure Blood remains in blood vessels Separate tissue
Types of circulatory systems Open system Mostly invertebrates Low pressure Haemocoel Suitable for small organisms Closed system Vertebrates High pressure Blood remains in blood vessels Separate tissue
Cardiovascular System
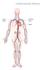 Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular System - Function The cardiovascular system transports, from one part of the body to another: nutrients, oxygen, ions, proteins, hormones and other signaling molecules,
Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular System - Function The cardiovascular system transports, from one part of the body to another: nutrients, oxygen, ions, proteins, hormones and other signaling molecules,
Circulatory System Objective sheet 3
 Circulatory System Objective sheet 3 10. Functions of blood 1) Transport oxygen and nutrients 2) Transport of carbon dioxide and waste 3) Protection against disease causing micro-organisms 4) Clotting
Circulatory System Objective sheet 3 10. Functions of blood 1) Transport oxygen and nutrients 2) Transport of carbon dioxide and waste 3) Protection against disease causing micro-organisms 4) Clotting
Level 2 Anatomy and Physiology Bite size revision. Respiratory System. The order of the passage of oxygen into the body (inhalation/inspiration) is: -
 Respiratory System Function of the respiratory system The lungs are located in the chest cavity and their function is to intake oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body. Structure of the respiratory
Respiratory System Function of the respiratory system The lungs are located in the chest cavity and their function is to intake oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body. Structure of the respiratory
Biology. A Guide to the Natural World. Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath. Fifth Edition.
 Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
How does the Circulatory System maintain
 How does the Circulatory System maintain -It supplies cells throughout the body with oxygen and nutrients while also ridding them of wastes. Transports materials such as: (to cells) (to attack foreign
How does the Circulatory System maintain -It supplies cells throughout the body with oxygen and nutrients while also ridding them of wastes. Transports materials such as: (to cells) (to attack foreign
Circulation.notebook March 07, Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium. Oct 11 3:27 PM. Circulatory System p
 Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Circulatory system The heart Blood Blood Pressure Circulatory Disorders Oct 11 3:27 PM Circulatory System p.304 307 If an organism is small and flat it can transport
Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Circulatory system The heart Blood Blood Pressure Circulatory Disorders Oct 11 3:27 PM Circulatory System p.304 307 If an organism is small and flat it can transport
The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle.
 The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle. From this camber, it passes through the pulmonary semilunar valve
The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle. From this camber, it passes through the pulmonary semilunar valve
 Caledonia Science the system that circulates blood and lymph through the body, consisting of the heart, blood vessels, The is the muscle that moves the blood throughout the highway system of vessles. The
Caledonia Science the system that circulates blood and lymph through the body, consisting of the heart, blood vessels, The is the muscle that moves the blood throughout the highway system of vessles. The
Functions of the Circulatory System
 Functions of the Circulatory System Carry oxygen from lungs to tissues Carry carbon dioxide from tissues to lungs thereby aiding in the exchange of gases Helps carry nutrients to cells Helps to fight against
Functions of the Circulatory System Carry oxygen from lungs to tissues Carry carbon dioxide from tissues to lungs thereby aiding in the exchange of gases Helps carry nutrients to cells Helps to fight against
Table of Contents: #41: Comparative Circulatory System Assignment Page: #41: Monday January 9, 2017: Comparative Circulatory System
 NOTEBOOK Table of Contents: #41: Comparative Circulatory System Assignment Page: #41: Monday January 9, 2017: Comparative Circulatory System Agenda: 1. Comparative Circulatory System (Notes with Handout)
NOTEBOOK Table of Contents: #41: Comparative Circulatory System Assignment Page: #41: Monday January 9, 2017: Comparative Circulatory System Agenda: 1. Comparative Circulatory System (Notes with Handout)
The Heart. Made up of 3 different tissue: cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and connective tissue.
 The Heart The Heart Made up of 3 different tissue: cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and connective tissue. Your heart pumps with a regular beat (Heart Rate) Your heart rate can change depending on
The Heart The Heart Made up of 3 different tissue: cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and connective tissue. Your heart pumps with a regular beat (Heart Rate) Your heart rate can change depending on
CIE Biology GCSE. 9: Transport in animals. Notes.
 CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT
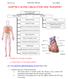 CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
Mr. Epithelium s Anatomy and Physiology Test SSSS
 Mr. Epithelium s Anatomy and Physiology Test SSSS You have 50 minutes to complete this test packet. One 8.5 x 11 cheat sheet is allowed, along with 1 non-programmable calculator dedicated to computation.
Mr. Epithelium s Anatomy and Physiology Test SSSS You have 50 minutes to complete this test packet. One 8.5 x 11 cheat sheet is allowed, along with 1 non-programmable calculator dedicated to computation.
Cardiovascular System Notes
 Cardiovascular System Notes Cardiovascular System a transportation system that carries needed substances to cells and waste products away from cells. Functions Transports nutrients to cells Transports
Cardiovascular System Notes Cardiovascular System a transportation system that carries needed substances to cells and waste products away from cells. Functions Transports nutrients to cells Transports
STRUCTURES OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 STRUCTURES OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Also called the circulatory system Consists of the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries Main function is to pump/circulate oxygenated blood
STRUCTURES OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Also called the circulatory system Consists of the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries Main function is to pump/circulate oxygenated blood
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System answers to worksheet will either be on the presentation or video By: Lanya King, Geianah Shaw,and Heidi Puerta The Functions of the Circulatory System Respiration- delivers oxygen
The Circulatory System answers to worksheet will either be on the presentation or video By: Lanya King, Geianah Shaw,and Heidi Puerta The Functions of the Circulatory System Respiration- delivers oxygen
Organ Systems (ch21-26) Practice Questions. Name:
 1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
Cardiovascular. Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Nutrients Waste Hormones Immune cells Oxygen
 Cardiovascular The Cardiovascular System - Arteries Arteries Cardiovascular System Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Carry blood away from heart Carotid arteries Deliver
Cardiovascular The Cardiovascular System - Arteries Arteries Cardiovascular System Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Carry blood away from heart Carotid arteries Deliver
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet Name: Date: Instructions: Put the answers to each task card in the numbered boxes on the chart. 1 a) left semilunar valve / aortic valve b) blood would backflow
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet Name: Date: Instructions: Put the answers to each task card in the numbered boxes on the chart. 1 a) left semilunar valve / aortic valve b) blood would backflow
Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System
 Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System This color-enhanced image was made with an electron microscope, so the objects it depicts are extremely small. Do you know what they are? This incredible photo shows red
Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System This color-enhanced image was made with an electron microscope, so the objects it depicts are extremely small. Do you know what they are? This incredible photo shows red
Lower Secondary Science Blood Circulatory System Notes / Advanced Notes
 Lower Secondary Science Blood Circulatory System Notes / Advanced Notes Double Circulation in Mammals In mammals, there is a double circulation (i.e. blood passes through the heart twice in one complete
Lower Secondary Science Blood Circulatory System Notes / Advanced Notes Double Circulation in Mammals In mammals, there is a double circulation (i.e. blood passes through the heart twice in one complete
2. What makes up the most of your blood? least of your blood? 1. Look like red discs, have a pale center, no nucleus, similar in size
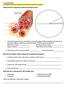 I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for
 Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for hyperlipidemia! Agenda! - Review objectives for 6.2! - Video of circulatory
Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for hyperlipidemia! Agenda! - Review objectives for 6.2! - Video of circulatory
Transportation and Excretion 7 th Biology
 Page1 Transportation and Excretion 7 th Biology William Harvey was an English physician was the first to give the details of blood circulation, the properties of blood and the pumping of blood by the heart.
Page1 Transportation and Excretion 7 th Biology William Harvey was an English physician was the first to give the details of blood circulation, the properties of blood and the pumping of blood by the heart.
The Cardiovascular System home study course
 The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
Blood Functions. Blood and the Cardiovascular System. Blood. Plasma. Erythrocytes (RBCs) Erythrocytes (RBCs) 4/7/2017
 Blood Functions Blood and the Cardiovascular System Distribution Delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all body cells; Transport of wastes to lungs and excretory organs; Transport of hormones Regulation
Blood Functions Blood and the Cardiovascular System Distribution Delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all body cells; Transport of wastes to lungs and excretory organs; Transport of hormones Regulation
TRANSPORTATION IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS
 TRANSPORTATION IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS Circulatory system: organ system for the circulation of materials inside the body Materials transported in the body: Water, Oxygen, Carbon dioxide, Nutrients, Hormones
TRANSPORTATION IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS Circulatory system: organ system for the circulation of materials inside the body Materials transported in the body: Water, Oxygen, Carbon dioxide, Nutrients, Hormones
1 Which substances are dissolved in human blood plasma? carbon dioxide, haemoglobin and glucose. carbon dioxide, oxygen and haemoglobin
 1 Which substances are dissolved in human blood plasma? carbon dioxide, haemoglobin and glucose carbon dioxide, oxygen and haemoglobin glucose, hormones and urea oxygen, urea and starch 2 Which chamber
1 Which substances are dissolved in human blood plasma? carbon dioxide, haemoglobin and glucose carbon dioxide, oxygen and haemoglobin glucose, hormones and urea oxygen, urea and starch 2 Which chamber
Multicellular Organisms. Sub-Topic 2.6 Transport Systems in Animals
 Multicellular Organisms Sub-Topic 2.6 Transport Systems in Animals On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to state that: In mammals a transport system is required to deliver essential substances
Multicellular Organisms Sub-Topic 2.6 Transport Systems in Animals On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to state that: In mammals a transport system is required to deliver essential substances
Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart
 Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart Interesting Heart Fact Capillaries are so small it takes ten of them to equal the thickness of a human hair. Review What are the 3 parts of the cardiovascular
Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart Interesting Heart Fact Capillaries are so small it takes ten of them to equal the thickness of a human hair. Review What are the 3 parts of the cardiovascular
Circulatory System. and. Respiratory System. Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song THE HEART LUNGS. Monday, May 23, 2011
 Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels
 Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels 3.2 Learning Objectives 3.2.2 Organisational Complexity of the human 1. Describe the structures and organisation of tissues in the closed circulatory system. 2. Discuss
Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels 3.2 Learning Objectives 3.2.2 Organisational Complexity of the human 1. Describe the structures and organisation of tissues in the closed circulatory system. 2. Discuss
Circulatory System Review ANSWERS
 Circulatory System Review ANSWERS 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? Double membranous sac that surrounds the heart What is myocardium? The muscle tissue
Circulatory System Review ANSWERS 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? Double membranous sac that surrounds the heart What is myocardium? The muscle tissue
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Worksheet
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Worksheet NAME Section A: Blood Basics http://www.psbc.org/hematology/01_index.htm Although blood appears to be red liquid it is actually composed of yellowish liquid called plasma
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Worksheet NAME Section A: Blood Basics http://www.psbc.org/hematology/01_index.htm Although blood appears to be red liquid it is actually composed of yellowish liquid called plasma
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM AND BLOOD
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM AND BLOOD The circulatory system is a group of organs which carry food and oxygen to and remove waste from every cel l in the body. Arteries-Lead away from the heart Plasma - -+-- 55%
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM AND BLOOD The circulatory system is a group of organs which carry food and oxygen to and remove waste from every cel l in the body. Arteries-Lead away from the heart Plasma - -+-- 55%
The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide.
 Section 1: The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What
Section 1: The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY HOMEWORK CHAPTER 11 AND 12
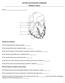 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY HOMEWORK CHAPTER 11 AND 12 Name Identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label. 2) The sinoatrial (SA) node is indicated by letter. 3) The specific chamber
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY HOMEWORK CHAPTER 11 AND 12 Name Identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label. 2) The sinoatrial (SA) node is indicated by letter. 3) The specific chamber
Cardiovascular System. I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart
 Cardiovascular System I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart 1. : Pericardial Cavity serous fluid filled space between the heart and the pericardium B. Heart Wall 1.
Cardiovascular System I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart 1. : Pericardial Cavity serous fluid filled space between the heart and the pericardium B. Heart Wall 1.
OVARIES URETER FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS
 URETER OVARIES FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS REPRODUCTIVE PRODUCE FEMALE HORMONES EXCRETORY FROM KIDNEY TO BLADDER EXCRETORY STORES URINE REPRODUCTIVE TRANSPORTS
URETER OVARIES FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS REPRODUCTIVE PRODUCE FEMALE HORMONES EXCRETORY FROM KIDNEY TO BLADDER EXCRETORY STORES URINE REPRODUCTIVE TRANSPORTS
DAY ONE BLOOD. What do you know about blood? What does it do? What is it made of? Where is it made?
 BLOOD AND THE HEART DAY ONE BLOOD What do you know about blood? What does it do? What is it made of? Where is it made? BLOOD Transports gases Brings in oxygen Removes carbon dioxide MAIN FUNCTIONS OF
BLOOD AND THE HEART DAY ONE BLOOD What do you know about blood? What does it do? What is it made of? Where is it made? BLOOD Transports gases Brings in oxygen Removes carbon dioxide MAIN FUNCTIONS OF
Circulatory System 10.1
 1 Circulatory System 10.1 2 ARTERIES Arteries-blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart Thick walls Inner & Outer layers: connective tissue Middle layers are muscle and elastic connective tissue
1 Circulatory System 10.1 2 ARTERIES Arteries-blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart Thick walls Inner & Outer layers: connective tissue Middle layers are muscle and elastic connective tissue
Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1 -
 Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1-2. Organs of a closed circulatory system: A. Have valves a. Arteriole B. Regulate blood flow b. Artery C. Lead to heart
Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1-2. Organs of a closed circulatory system: A. Have valves a. Arteriole B. Regulate blood flow b. Artery C. Lead to heart
Circulatory System. Chapter 32
 Circulatory System Chapter 32 Invertebrates w/o a Circulatory System If an organism has a sac body plan, circulatory systems are not necessary. Sac body plans mean cells are capable of gas and nutrient
Circulatory System Chapter 32 Invertebrates w/o a Circulatory System If an organism has a sac body plan, circulatory systems are not necessary. Sac body plans mean cells are capable of gas and nutrient
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System
 Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
Circulatory System. 3. Blood. 1. Heart. 1. Veins A blood vessel that returns blood to the heart
 Day 1. Circulatory System uman Body Transport The Circulatory System 2. ARTERIES 1. eart & VEINS 3. Blood Process: Transport Circulatory System The process where substances move (distributed) into and
Day 1. Circulatory System uman Body Transport The Circulatory System 2. ARTERIES 1. eart & VEINS 3. Blood Process: Transport Circulatory System The process where substances move (distributed) into and
Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The list gives some structures in the blood and circulatory system.
 Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The list gives some structures in the blood and circulatory system. heart artery red blood cell ventricle capillary plasma vein white blood cell platelets Which of
Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The list gives some structures in the blood and circulatory system. heart artery red blood cell ventricle capillary plasma vein white blood cell platelets Which of
Unit 10 Cardiovascular System
 Unit 10 Cardiovascular System I. Functions Deliver nutrients to cells > O 2, sugars, amino acids, lipids, ions, H 2 O... Remove waste from cells > CO 2, pathogens, toxins, lactic acid... Fight off infection
Unit 10 Cardiovascular System I. Functions Deliver nutrients to cells > O 2, sugars, amino acids, lipids, ions, H 2 O... Remove waste from cells > CO 2, pathogens, toxins, lactic acid... Fight off infection
Summary table: artery capillary vein Blood pressure Hi Low lowest Valves present or Absent Absent Present
 Bi 067: Review of sectn 7-9 - cardiovascular and lymphatic Heart and Blood vessels: 3 Types of blood vessels: 1. Arteries, arterioles -away from heart, O2 rich 2. Capillaries gas and nutrient/waste exchange
Bi 067: Review of sectn 7-9 - cardiovascular and lymphatic Heart and Blood vessels: 3 Types of blood vessels: 1. Arteries, arterioles -away from heart, O2 rich 2. Capillaries gas and nutrient/waste exchange
Learning Objectives; 1. Identify the key features of the cardiovascular system. 2. Describe the function of the cardiovascular system.
 Learning Objectives; 1. Identify the key features of the cardiovascular system. 2. Describe the function of the cardiovascular system. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yaxna8lmoiy The Circulatory System
Learning Objectives; 1. Identify the key features of the cardiovascular system. 2. Describe the function of the cardiovascular system. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yaxna8lmoiy The Circulatory System
Chapter 17. Clearing the Air: Respiratory, Cardiovascular, and Excretory Systems. Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System
 17.1 Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Chapter 17 Clearing the Air: Respiratory, Cardiovascular, and Excretory Systems Exhaled smoke + smoke directly from cigarette tip = (ETS) Affects and (non-smoker
17.1 Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Chapter 17 Clearing the Air: Respiratory, Cardiovascular, and Excretory Systems Exhaled smoke + smoke directly from cigarette tip = (ETS) Affects and (non-smoker
Monday 14 th May The Body Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 10 Cardio-Respiratory System
 Monday 14 th May 2018 The Body Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 10 Cardio-Respiratory System Homework 1. What is the function of the cardiovascular system? 2. List the main components of blood and describe
Monday 14 th May 2018 The Body Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 10 Cardio-Respiratory System Homework 1. What is the function of the cardiovascular system? 2. List the main components of blood and describe
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies
 Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions. KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells.
 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems
 34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems section 1 Circulatory System Before You Read Press the tips of two fingers to the inside of your wrist, at a point just below your thumb. Can you feel
34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems section 1 Circulatory System Before You Read Press the tips of two fingers to the inside of your wrist, at a point just below your thumb. Can you feel
