Original Article. Intima-Media thickness at the Origin of the Right Subclavian Artery as an Early Marker of Cardiovascular Risk
|
|
|
- Magdalene Allen
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Subclavian Artery as an Early Marker of Cardiovascular Risk Carlos Alberto Engelhorn, Ana Luiza Engelhorn, Maria Fernanda Cassou, Cassiana Casagrande Zanoni, Carlos José Gosalan, Emerson Ribas, Adriana Pacholok, Marcela de Fátima Koehler Pontifícia Universidade Católica do Paraná e Angiolab, Curitiba, PR, Brazil Objective: Common carotid artery intima-media thickness (IMT) is considered a factor of cardiovascular risk and an early marker of coronary artery disease. This study aimed to investigate the existence of a correlation between IMT in the carotid arteries and at the origin of the right subclavian artery, as well as to evaluate IMT in the subclavian artery as an earlier marker of cardiovascular risk. Methods: One hundred and six consecutive patients, 52 males and 54 females, average age 51 years, underwent color Doppler ultrasonography to evaluate carotid and right subclavian arteries. The relationship between carotid IMT and right subclavian IMT was assessed using the Pearson s correlation coefficient analysis and a 95% confidence interval. Reliability of right subclavian artery IMT measurement for the diagnosis of early thickening (considering a > 0.8 mm carotid thickness as reference) was described as to sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value, and accuracy. Cutoff values for the right subclavian IMT were indicated by the ROC curve, and p values 0.05 were considered statistically significant. Results: Out of the 41 patients whose carotid arteries were IMT-free, 30 (73%) had right subclavian artery IMT values > 0.8 mm. The mean IMT value for the carotid artery was 0.87 mm (SD = 0.23) and for the subclavian artery, 1.17 mm (SD = 0.46), with a 0.31 correlation coefficient (95% CI: 0.12; 0.47). The ROC curve analysis indicated a cut-off value of 0.7 mm for the right subclavian artery IMT, using as reference a 0.8 mm cut-off value for the carotid artery (91% sensitivity, 27% specificity, 66% PPV, 65% NPV, and 66% accuracy). Conclusion: Our study showed that carotid artery IMT correlates well with right subclavian artery IMT. With a 0.7 mm cut-off value, it is possible to detect IMT in the right subclavian artery earlier than in the carotid arteries. The IMT at the origin of the right subclavian artery can be considered an earlier marker for the assessment of cardiovascular risk. Key words: Media-intima thickening, coronary arteriosclerosis, myocardial infarction, early diagnosis. Atherosclerosis is a generalized disease of the artery wall that may progress, recede, or stabilize depending on several factors 1. This dynamic process is characterized by artery wall remodeling, which may go unnoticed for a long time or may be clinically observable as an acute vascular event. The detection of cardiovascular disease markers enables early intervention on modifiable factors for atherosclerosis, such as lifestyle changes, strict management of arterial hypertension, hyperlipidemia and diabetes mellitus 2. Carotid artery intima-media thickness (IMT), as measured by high-resolution vascular ultrasonography, is currently considered a marker of generalized atherosclerotic disease, mainly of early coronary artery disease 2-8. Enlargement of the carotid intima-media complex is associated with most cardiovascular risk factors: male gender, familial history of cerebrovascular accident or acute myocardial infarction, smoking, diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, left ventricular hypertrophy, hyperhomocysteinemia, and age Carotid artery IMT helps to determine more accurately the cardiovascular risks of hypertensive patients with no injury to the target organ as evidenced by routine tests, such as the electrocardiogram As a marker of cardiovascular risk, IMT can be detected in the distal common carotid artery, at carotid bifurcation, in the internal carotid and, more recently, in the common femoral artery 21,22. Nevertheless, studies have shown that the measurement of the IMT in the internal carotid shows a better correlation with risk factors for coronary artery disease 23. In routine studies of the brachiocephalic branch and the origin of the right subclavian artery in patients referred to our laboratory for cardiovascular risk assessment [by measurement of the carotid artery IMT, we observed that some patients with no carotid intima-media thickness showed IMT at the origin of the right subclavian artery. For this reason, the objective of this study was to investigate the existence of an association between carotid artery IMT and at the origin of the right subclavian artery, and also evaluate if IMT measured in the right subclavian artery could be considered an earlier marker for cardiovascular disease. Mailing Address: Carlos Alberto Engelhorn Rua Dep. Heitor Alencar Furtado, 1720 ap Curitiba, PR, Brazil carlos.engelhorn@pucpr.br Received on 06/02/05; revised manuscript received August 20, 2005; accepted on 10/17/05 556
2 Methods One hundred and six consecutive patients underwent highresolution vascular ultrasonography to have their carotid and subclavian arteries evaluated. Inclusion criteria for the study were asymptomatic subjects with risk factors for coronary artery disease, such as: male patients over 55 years of age and female patients over 65 years of age; systemic arterial hypertension; diabetes mellitus; smoking; hyperlipidemia; obesity; sedentarism and familial history of early coronary artery disease. Criteria for exclusion were subjects with no risk factors for cardiovascular disease, and the presence of atherosclerotic plaque in the carotid arteries, as shown by color Doppler vascular ultrasonography. Measurement of IMT was taken at the common distal carotid (1-2 cm proximal to carotid bifurcation), and bilaterally in the internal carotid, as well as at the origin of the right subclavian artery. During the analysis, the greatest right and left carotid IMT values were considered, as well as the value measured at the origin of the right subclavian artery. The right subclavian artery was easily evaluated since it is more superficial than the contra-lateral subclavian artery; however, this does not denote advantages or technical limitations relative to the carotid arteries. The left subclavian artery was not included in the study due to its deeper location that limits assessment of the origin of this vessel. The measurement of the intima-media complex was performed with the help of Siemens Sonoline Elegra vascular ultrasonography equipment. A 7.5 mhz linear transducer was used, with a frequency range of 7-9 mhz, longitudinal section and B-mode images. Thickness measurement was performed at the anterior or posterior artery wall, as the distance between two echogenic lines corresponding to the lumen-intima and media-adventitia interfaces of the artery wall 17, The relationship between carotid artery IMT and right subclavian artery was assessed using Pearson s correlation coefficient and a 95% confidence interval. Taking into consideration the carotid classification as a reference standard for the diagnosis of early thickening (values 0.8 indicated early thickening), a ROC curve was adjusted for subclavian ITM values and the cut-off value was determined for this same classification. To evaluate the result obtained, sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value, and accuracy were calculated for the subclavian IMT in identifying early thickening. In order to evaluate the reproducibility of the method, two independent observers measured the carotid IMT of thirteen patients. Variance components and a 95% confidence interval were used throughout the analysis. Results Fifty-two men (49%) and 54 women (51%), between 23 and 83 years of age (average age years) were evaluated. Table 1 shows the prevalence of the risk factors studied for coronary artery disease. Correlation between carotid artery IMT and right subclavian artery IMT - Taking into consideration a > 0.8 mm value for the right subclavian artery IMT, 41 carotid arteries were IMT-free, whereas 30 (73%) right subclavian arteries showed IMT > 0.8 mm. Out of the 65 carotid arteries with early thickening, 59 (91%) subclavian arteries showed IMT > 0.8 mm. The average IMT value obtained in the carotid artery (Chart 1) was 0.87 mm (0.5 mm minimum, 1.3 mm maximum, 0.9 mm median, and standard deviation 0.23). The mean IMT value obtained in the right subclavian artery (Chart 2) was 1.7 mm (0.4 mm minimum, 2.8 mm maximum, 1.1 mm median, and 0.46 standard deviation). The analysis of reproducibility of the method indicated a 10.2% error between the [two] investigators. The correlation coefficient between the carotid artery IMT and the right subclavian artery IMT was 0.31%, with a 95% confidence interval ranging from 0.12 to Subclavian artery IMT as an indicator of early thickening - A 0.8 mm carotid thickening was established as the standard cutoff value for the diagnosis of early IMT. Therefore, carotid IMT values under 0.8 mm were considered normal, whereas values over 0.8 mm were considered as early thickening. According to the ROC curve (Chart 3), 0.7 mm was the cut-off value for the IMT at the origin of the right subclavian artery that best characterizes the thickening. The 0.7 mm cut-off value at the origin of the right subclavian artery, when compared to the 0.8 mm IMT reference value in the carotid arteries, showed sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV, and accuracy values of 91%, 27%, 66%, 65%, and 66%, respectively. Table 2 displays sensitivity levels for other IMT cut-off values in the right subclavian artery. Discussion The identification of artery wall changes in asymptomatic subjects indicates the need for a more strict control of cardiovascular risk factors, seeking to prevent future coronary events. Population and hospital-based studies used non-invasive techniques to evaluate early changes in the structure and function of the artery wall, such as the measurement of the intima-media complex, investigation of endothelial dysfunction, and coronary artery calcification 25,27,28. Carotid artery IMT measurement is a safe, low-cost, and easily reproducible method suitable for identifying those patients with subclinical atherosclerotic disease and higher risks for coronary artery disease 7,25,29,30. Studies determined 0.8 mm as the reference value for early thickening of the intima-media complex associated with an increase in cardiovascular risks 4,18, Groot et al conducted a study with 315 patients with familial hypercholesterolemia compared to 118 controls, and showed that an intima-media thickening of up to 0.8 mm would be considered normal. The familial hypercholesterolemia patients reached a 0.8 mm IMT value at the age of 40 years, whereas control group patients reached such a value only at 76 years of age, when their cardiovascular risk would be greater due to age 4. Asymptomatic individuals with a low to intermediate pretest probability of coronary artery disease, and a carotid IMT value over 1 mm, are at a higher risk of developing coronary 557
3 Risk factors for CAD Systemic arterial hypertension Diabetes mellitus Smoking Hyperlipidemia Obesity Sedentarism Family history of CAD Number of patients 36 34% 4 4% 28 26% 39 37% 19 18% 30 28% 42 40% Table 1 - Prevalence of risk factors for coronary artery disease (CAD) events in the future 8,25,29,30,34. Multicentric studies showed that patients with an IMT greater than 1 mm have a higher risk of acute myocardial infarction within four years 7,29,30. Since the objective of our study was to determine an earlier marker of cardiovascular risk, we used a 0.8 mm cut-off value. In this study, the correlation coefficient between the carotid artery IMT and the right subclavian artery IMT was 0.31, with a 95% confidence interval ranging from 0.12 to The fact that zero is not included in this interval indicates the significance of this correlation. However, considering the limits of the 95% confidence interval, it is clear that despite the low value of the lower limit, the upper limit indicates a good correlation between the carotid artery IMT and the right subclavian artery IMT. In this study, considering a 91% sensitivity value, a 0.7 mm IMT was determined for the right subclavian artery (lower than the 0.8 mm reference value used for the carotid artery). This suggests that the measurement of the thickening at the origin of the subclavian artery can be an earlier marker of cardiovascular risk. The IMT, measured by B-mode ultrasound image, consists of the distance between two echogenic lines corresponding to the lumen-intima and media-adventitia interfaces of the artery wall. Since even high-resolution vascular ultrasonography is incapable of distinguishing the intima layer from the media layer of the artery wall, the intima-media complex measurement is routinely used. An increase in the thickness of the intima-media complex may be due to thickening of the media layer or the intima layer. It is known that the atherosclerotic disease affects primarily the intima layer of the artery wall. Carotid and subclavian arteries are elastic arteries, consisting mainly of the intima layer and a very small muscle component. By contrast, in peripheral arteries such as the femoral artery, medial muscle layer prevails. Therefore, carotid and subclavian IMT represents mainly thickening of the intima layer, which is associated with the presence of atherosclerotic disease 3,26,35,36. A carotid artery IMT value over 1.3 mm is considered an atherosclerotic plaque 37. One possible explanation for the earlier intima-media thickening in the right subclavian artery would be the presence of greater vessel angulation at its origin as compared to the carotid artery bifurcation. Higher speeds in the inner curvature border, as observed at the origin of the right subclavian artery, are responsible for the increase in endothelial surface stress and shear forces at the site 38. The artery wall stress CAROTID ARTERY Number of cases Sensibilidade Especificidade Thickening Chart 1 - Distribution of the highest IMT values observed in the carotid arteries 558
4 SUBCLAVIAN ARTERY Number of cases Thickening Chart 2 - Distribution of the highest IMT values observed in the right subclavian artery. Indexes < 0.8; 0.8 < 0.9; 0.9 < 1; 1 < 1.1; 1.1 < 1.2; 1.2 Sensitivity 90.8% 81.5% 81.5% 67.7% 56.9% Specificity 26.8% 31.7% 36.6% 51.2% 75.6% PV+ 66.% 65.4% 67.1% 68.8% 78.7% PV- 64.7% 52.0% 55.6% 50.0% 52.5% Efficiency 66.0% 62.3% 64.2% 61.3% 64.2% * The reference standard was the 0.8 mm cut-off value for the carotid artery IMT (<0.8 mm normal; > 0.8 early IMT). Table 2 - Indexes of right subclavian artery thickening according to different cut-off values and the resulting greater shear force would contribute to the development of the intima-media thickening and a posterior atherosclerotic plaque at the site. Back in 1963, Texon proposed that lower inner wall pressures would favor atheroma deposition in the curvatures 39. However, there are no studies in medical literature associating right subclavian artery IMT and cardiovascular risk factors. This study observed that out of the 41 patients whose carotid arteries were IMT-free, thirty (73%) had right subclavian artery IMT values > 0.8mm. This finding shows that, even when the carotid artery is normal, the subclavian artery may show thickening of the intima-media complex. Consequently, the presence of IMT may be detected earlier in the subclavian artery rather than in the carotid artery, enabling an earlier prescription of aggressive management of cardiovascular risk factors in order to prevent future coronary events. The authors conclude that there is an association between carotid artery IMT and the IMT at the origin of the right subclavian artery. With a 0.7 mm cut-off value, it is possible to detect IMT earlier in the subclavian artery than in the carotid arteries. The IMT at the origin of the right subclavian artery may be considered an earlier marker for the evaluation of cardiovascular risks. Potential Conflict of Interest No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported. 559
5 Sensitivity Sensibility 1, , , , , , ,4 0.4 SUBCLAV.ROC, Area = SE = , , , , , , , , , , , , , , ,0 1.0 Specificity Especificidade Chart 3 - ROC curve data used for the definition of the cut-off value that best characterizes thickening for the right subclavian artery. References 1. Badimon JJ, Fuster V, Chesebro JH, Badimon L. Coronary atherosclerosis: a multifactorial disease. Circulation 1993; 87 (suppl): II3-II Wittes J, Lakatos J, Probstfield J. Surrogate endpoints in clinical trials. Stat Med 1989; 8: Grobbee DE, Bots ML. Carotid artery intima-media thickness as an indicator of generalized atheroclerosis. J Int Med 1994; 236: Groot E, Hovingh GK, Wiegman A, et al. Measurement of arterial wal thickness as a surrogate marker for atherosclerosis. Circulation 2004; 109 (suppl III): III-33 III Van Bortel LM. What does intima-media thickness tell us? J Hypertens 2005; 23: Bots ML, Grobbee DE, Hofman A, Witteman JCM. Common carotid intimamedia thickness and risk of acute myocardial infaction. Stroke 2005; 36: O Leary DH, Polak JF, Kronmal RA, Manolio TA, Burke GL, Wolfson SK Jr. Carotid-artery intima and media thickness as a risk factor for myocardial infarction and stroke in older adults. Cardiovascular Health Study Collaborative Research Group. N Engl J Med 1999; 340: Simon A, Gariepy J, Chironi G, Mengnien JL, Levenson J. Intima-media thickness: a new tool for diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular risk. J Hypertens 2002; 20: Crouse JR, Tang R, Espeland MA, Terry JG, Morgan T, Mercuri M. Association of extra-cranial carotid atheroclerosis progression with coronary status and risk factors in patients with and without coronary artery disease. Circulation 2002; 106: Luedemann J, Schminke U, Berger K, et al. Association between behaviordependent cardiovascular risk factors and asyntomatic carotid atheroclerosis in a general population. Stroke 2002; 33: Stein JH, Douglas PS, Srinivasan SR, et al. Distribution and cross-sectional age-related increases of carotid artery intima-media thickness in young adults. The Bogalusa Heart Study. Stroke 2004; 35: Jerrard-Dunne P, Markus HS, Steckel Da, Buehler A, von Kegler S, Stizer M. Early carotid atherosclerosis and family history of vascular disease. Specific effects on arterial sites have implications for genetic studies. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2003; 23: Weber F. Risk factors for subclinical carotid atherosclerosis in healthy men. Neurology 2002; 59: Tropeano AI, Boutouyrie P, Katsahian S, Laloux B, Laurent S. Glucose level is a major determinant of carotid intima-media thickness in patients with hypertension and hyperglycemia. J Hipertens 2004; 22: Liu ML, Yilitalo K, Salonen R, Salonen JT, Taskinen MR. Circulating oxidized low-density lipoprotein and its association with carotid intima-media thickness in asyntomatic members of familial combined hiperlipidemia families. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2004; 24: Wang TJ, Nam BH, D Agostinho RB, et al. Carotid intima-media thickness is associated with premature parental coronary heart disease. The Framinghan Heart Study. Circulation 2003; 108: Vaudo G, Schillaci G, Evangelista F, Pasqualini L, Verdecchia P, Mannarino E. Arterial wall thickening at different sites and its association with left ventricular hypertrophy in newly diagnosed essential hypertension. Am J Hypertens 2000; 13: Cuspidi C, Ambrosioni E, Mancia G, Pessina AC, Trimarco B, Znachetti A. Role o echocardiography and carotid ultrasonography in stratifying risk in patients with essential hypertension: the Assesment of Prognostic Risk Observational Survey. J Hypertens 2002; 20: Zakopoulos NA, Tsivgoulis G, Barlas G, et al. Time rate of bood pressure variation is associated with increased common carotid artery intima-media thickness. Hypertension 2005; 45: Guidelines committee European Society of Hypertension European Society of Cardiology guidelines for manegement of arterial hypertension. J Hypertens 2003; 21: Held C, Hjemdahl P, Eriksson SV, Björkander I, Forslund L, Rehnquivist N. Prognostic implications of intima-media thickness and plaques in the carotid and femoral arteries in patiens with stable angina. Eur Heart J 2001; 22:
6 22. Lelakis JP, Papamichael CM, Cimponeriu AT, et al. Atherosclerotic changes of extra-coronary arteries are associated with the extent of coronary atheroclerosis. Am J Cardiol 2000; 85: Mackinnon AD, Jerrard-Dunne P, Tizer M, Buehler A, von Kegler S, Markus HS. Rates and determinants of site-specific progression of carotid artery intima-media thickness. The carotid atheroclerosis progression study. Stroke 2004; 35: Pignoli P, Tremoli E, Poli A, Oreste P, Paoletti R. Intimal plus medial thickness of the arterial wall: a directed mesurement with ultrasound imaging. Circulation 1986; 74: Bots ML, Dijk JM, Oren A, Grobbee DE. Carotid intima-media thickness, arterial wall stiffness and risk of cardiovascular disease: current evidence. J Hipertens 2002; Sinha AK, Eigenbrodt M, Mehta JL. Does carotid intima media thickness indicate coronary atheroclerosis? Curr Opin Cardiol 2002; 17: Simon A, Megnien JL, Levenson J. Coronary risk estimation and treatment of hypercholesterolemia. Circulation 1997; 96: Hollander M, Hak AE, Koudstaal PJ, et al. Comparison between measures of atheroclerosis and risk of stroke. Stroke 2003; 34: Chambless LE, Heiss G, Folson AR, Szklo M, Sharrett AR, Cleg LX. Association of coronary heart disease incidence with carotid arterial wall thickness and major risk factors: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study. Am J Epidemiol 1997; 146: Bots ML, Hoes AW, Koudstaal PJ, Hofman A, Grobbee DE. Common carotid intima-media thickness and risk of stroke and miocardial infaction: the Rotterdan Study. Circulation 1997; 96: Jadkav UM, Kaddam NN. Carotid intima-media thickness as an independent predictor of coronary artery disease. Indian Heart J 2001; 53 (4): Rohani M, Jogestrand T, Ekberg M, et al. Interrelation between the extent of atherosclerosis in the thoracic aorta, carotid intima-media thickness and the extent of coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis 2005; 179 (2): Hodis HN, Mack WJ, Selzer RH, Liu C, Azen SP. The role of carotid arterial intima-media thickness in predicting clinical coronary events. Ann Intern Med 1998; 128: Aminbakhsh A, Mancini GB. Carotid intima-media thickness mesurements: waht defines an abnormality? A systematic review. Clin Invest Med 1999; 4: Slonen JT, Salonen R. Ultrasound B-mode imaging in observational studies of atherosclerotic progression. Circulation 1997; 87 (3 Suppl): II Montenegro MRG. Estrutura da parede vascular. In Maffei FHA, Lastória S, Yoshida WB, Rollo HA. (ed.). Doenças Vasculares Periféricas. 3 ed. Rio de Janeiro: Medsi; 2002, v.1, Zanchetti A, Bond MJ, Henning M, et al. On behalf of the ELSA investigators. Risk factors associated with alterations in carotid intima-media thickness in hypertension: baseline data from the European Lacidipine Studty on Atherosclerosis. J Hyperten 1998; 16: Lopes OU. Estudo das doenças vasculares periféricas a partir da dinâmica dos fluidos. In: Maffei FHA, Lastória S, Yoshida WB, Rollo HA. (ed.). Doenças vasculares periféricas. 3 ed., Rio de Janeiro: Medsi; 2002, v.1, Texon M. The role of vascular dynamics in the development of atherosclerosis. In Sandler M, Bourne GH (ed.). Atherosclerosis and Its Origiti. New York: Academic Press, 1963:
Asian J. Exp. Sci., Vol. 27, No. 1, 2013; 67-72
 Carotid Intima-media Thickness as a Surrogate Marker of Atherosclerosis and its Correlation with Coronary Risk Factors and Angiographic Severity of Coronary Artery Disease. 1 2 Rajeev Gupta and Rajendra
Carotid Intima-media Thickness as a Surrogate Marker of Atherosclerosis and its Correlation with Coronary Risk Factors and Angiographic Severity of Coronary Artery Disease. 1 2 Rajeev Gupta and Rajendra
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: carotid_intimal_medial_thickness 12/2006 10/2016 10/2018 10/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Ultrasonographic
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: carotid_intimal_medial_thickness 12/2006 10/2016 10/2018 10/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Ultrasonographic
Rates and Determinants of Site-Specific Progression of Carotid Artery Intima-Media Thickness. The Carotid Atherosclerosis Progression Study
 Rates and Determinants of Site-Specific Progression of Carotid Artery Intima-Media Thickness The Carotid Atherosclerosis Progression Study Andrew D. Mackinnon, MRCP; Paula Jerrard-Dunne, MRCPI; Matthias
Rates and Determinants of Site-Specific Progression of Carotid Artery Intima-Media Thickness The Carotid Atherosclerosis Progression Study Andrew D. Mackinnon, MRCP; Paula Jerrard-Dunne, MRCPI; Matthias
The clinical significance of carotid intima-media thickness in cardiovascular diseases: a survey in Beijing
 (2008) 22, 259 265 & 2008 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/08 $30.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE The clinical significance of carotid intima-media thickness in cardiovascular
(2008) 22, 259 265 & 2008 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/08 $30.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE The clinical significance of carotid intima-media thickness in cardiovascular
Individuals of African and African Caribbean descent living
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.D. Mackinnon P. Jerrard-Dunne L. Porteous H.S. Markus Carotid Intima-Media Thickness is Greater but Carotid Plaque Prevalence is Lower in Black Compared with White Subjects BACKGROUND
ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.D. Mackinnon P. Jerrard-Dunne L. Porteous H.S. Markus Carotid Intima-Media Thickness is Greater but Carotid Plaque Prevalence is Lower in Black Compared with White Subjects BACKGROUND
Clinical Investigation and Reports. Predictive Value of Noninvasive Measures of Atherosclerosis for Incident Myocardial Infarction
 Clinical Investigation and Reports Predictive Value of Noninvasive Measures of Atherosclerosis for Incident Myocardial Infarction The Rotterdam Study Irene M. van der Meer, MD, PhD; Michiel L. Bots, MD,
Clinical Investigation and Reports Predictive Value of Noninvasive Measures of Atherosclerosis for Incident Myocardial Infarction The Rotterdam Study Irene M. van der Meer, MD, PhD; Michiel L. Bots, MD,
Is the Ankle-Brachial Index a Useful Screening Test for Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Asymptomatic, Middle-Aged Adults?
 Is the Ankle-Brachial Index a Useful Screening Test for Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Asymptomatic, Middle-Aged Adults? Rachael A. Wyman, MD; Jon G. Keevil, MD; Kjersten L. Busse, RN, MSN; Susan E. Aeschlimann,
Is the Ankle-Brachial Index a Useful Screening Test for Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Asymptomatic, Middle-Aged Adults? Rachael A. Wyman, MD; Jon G. Keevil, MD; Kjersten L. Busse, RN, MSN; Susan E. Aeschlimann,
JMSCR Vol 4 Issue 06 Page June 2016
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 5.88 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i6.69 Role of Aging, Hypertension and Dyslipidaemia
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 5.88 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i6.69 Role of Aging, Hypertension and Dyslipidaemia
C oronary artery disease (CAD) remains the main cause
 1286 CARDIOVASCULAR MEDICINE Association of increased carotid intima-media thickness with the extent of coronary artery disease A Kablak-Ziembicka, W Tracz, T Przewlocki, P Pieniazek, A Sokolowski, M Konieczynska...
1286 CARDIOVASCULAR MEDICINE Association of increased carotid intima-media thickness with the extent of coronary artery disease A Kablak-Ziembicka, W Tracz, T Przewlocki, P Pieniazek, A Sokolowski, M Konieczynska...
JMSCR Vol 04 Issue 10 Page October 2016
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i10.82 Carotid Intima Media Thickness and Can
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i10.82 Carotid Intima Media Thickness and Can
Citation for published version (APA): Terpstra, W. F. (2003). Beyond blood pressure monitoring Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Beyond blood pressure monitoring Terpstra, Willem Fopke IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
University of Groningen Beyond blood pressure monitoring Terpstra, Willem Fopke IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
Is Carotid Intima-Media Thickness Useful in Cardiovascular Disease Risk Assessment? The Rotterdam Study
 Is Carotid Intima-Media Thickness Useful in Cardiovascular Disease Risk Assessment? The Rotterdam Study Antonio Iglesias del Sol, MD; Karel G.M. Moons, MD, PhD; Monika Hollander, MD; Albert Hofman, MD,
Is Carotid Intima-Media Thickness Useful in Cardiovascular Disease Risk Assessment? The Rotterdam Study Antonio Iglesias del Sol, MD; Karel G.M. Moons, MD, PhD; Monika Hollander, MD; Albert Hofman, MD,
Diagnostic Accuracy of Carotid Ultrasonography in Screening for Coronary Artery Disease
 J Cardiol 2000 ; 36: 295 302 Diagnostic Accuracy of Carotid Ultrasonography in Screening for Coronary Artery Disease Tomohiro Nobuhiko Yutaka Yoshihiko Katsuhiro Takayoshi Tsuyoshi Toshinori Shigeyasu
J Cardiol 2000 ; 36: 295 302 Diagnostic Accuracy of Carotid Ultrasonography in Screening for Coronary Artery Disease Tomohiro Nobuhiko Yutaka Yoshihiko Katsuhiro Takayoshi Tsuyoshi Toshinori Shigeyasu
Intima-Media Thickness
 European Society of Cardiology Stockholm, 30th August 2010 Intima-Media Thickness Integration of arterial assessment into clinical practice Prof Arno Schmidt-Trucksäss, MD Institute of Exercise and Health
European Society of Cardiology Stockholm, 30th August 2010 Intima-Media Thickness Integration of arterial assessment into clinical practice Prof Arno Schmidt-Trucksäss, MD Institute of Exercise and Health
Imaging Biomarkers: utilisation for the purposes of registration. EMEA-EFPIA Workshop on Biomarkers 15 December 2006
 Imaging Biomarkers: utilisation for the purposes of registration EMEA-EFPIA Workshop on Biomarkers 15 December 2006 Vascular Imaging Technologies Carotid Ultrasound-IMT IVUS-PAV QCA-% stenosis 2 ICH E
Imaging Biomarkers: utilisation for the purposes of registration EMEA-EFPIA Workshop on Biomarkers 15 December 2006 Vascular Imaging Technologies Carotid Ultrasound-IMT IVUS-PAV QCA-% stenosis 2 ICH E
Objective Calcium score carotid IMT hs-crp
 P3952 Role of coronary calcium score, carotid intima-media thickness and C-reactive protein in predicting extent of coronary artery disease in young patients. Bedside Poster P3952 Role of coronary calcium
P3952 Role of coronary calcium score, carotid intima-media thickness and C-reactive protein in predicting extent of coronary artery disease in young patients. Bedside Poster P3952 Role of coronary calcium
ASSOCIATION BETWEEN COMMON CAROTID INTIMA-MEDIA THICKNESS (CAROTID IMT) AND CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE Srinivasa Rao Malladi 1
 ASSOCIATION BETWEEN COMMON CAROTID INTIMA-MEDIA THICKNESS (CAROTID IMT) AND CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE Srinivasa Rao Malladi 1 HOWTOCITETHISARTICLE: Srinivasa Rao Malladi. Association between Common Carotid
ASSOCIATION BETWEEN COMMON CAROTID INTIMA-MEDIA THICKNESS (CAROTID IMT) AND CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE Srinivasa Rao Malladi 1 HOWTOCITETHISARTICLE: Srinivasa Rao Malladi. Association between Common Carotid
Correlation Between the Intima Media Thickness of the Proximal and Distal Common Carotids
 Correlation Between the Intima Media Thickness of the Proximal and Distal Common Carotids Leonard Hermann Roelke 1, Sergio Lamego Rodrigues 1, Paulo Andrade Lotufo 2, Jose Geraldo Mill 1 Universidade Federal
Correlation Between the Intima Media Thickness of the Proximal and Distal Common Carotids Leonard Hermann Roelke 1, Sergio Lamego Rodrigues 1, Paulo Andrade Lotufo 2, Jose Geraldo Mill 1 Universidade Federal
ARIC Manuscript Proposal # 1036r. PC Reviewed: _07/26/05 Status: D Priority: SC Reviewed: Status: Priority:
 ARIC Manuscript Proposal # 1036r PC Reviewed: _07/26/05 Status: D Priority: SC Reviewed: Status: Priority: 1.a. Full Title: The Association between Isolated vs Combined Large and Small Artery Disease with
ARIC Manuscript Proposal # 1036r PC Reviewed: _07/26/05 Status: D Priority: SC Reviewed: Status: Priority: 1.a. Full Title: The Association between Isolated vs Combined Large and Small Artery Disease with
Carotid artery intima-media thickness is a marker for coronary artery disease
 Scientific Journal of Medical Science (2013) 2(8) 145-150 ISSN 2322-5025 doi: 10.14196/sjms.v2.i8.894 Contents lists available at Sjournals Journal homepage: www.sjournals.com Original article Carotid
Scientific Journal of Medical Science (2013) 2(8) 145-150 ISSN 2322-5025 doi: 10.14196/sjms.v2.i8.894 Contents lists available at Sjournals Journal homepage: www.sjournals.com Original article Carotid
Original article: Evaluation of association between serum gamma glutamyltransferase activity and carotid intima media thickness
 Original article: Evaluation of association between serum gamma glutamyltransferase activity and carotid intima media thickness *Dr. Madhulika Mahashabde, **Dr. Suryaprakash Rajesh Kothe *Associate Professor,
Original article: Evaluation of association between serum gamma glutamyltransferase activity and carotid intima media thickness *Dr. Madhulika Mahashabde, **Dr. Suryaprakash Rajesh Kothe *Associate Professor,
Coronary artery disease (CAD) risk factors
 Background Coronary artery disease (CAD) risk factors CAD Risk factors Hypertension Insulin resistance /diabetes Dyslipidemia Smoking /Obesity Male gender/ Old age Atherosclerosis Arterial stiffness precedes
Background Coronary artery disease (CAD) risk factors CAD Risk factors Hypertension Insulin resistance /diabetes Dyslipidemia Smoking /Obesity Male gender/ Old age Atherosclerosis Arterial stiffness precedes
Carotid-Wall Intima Media Thickness and Cardiovascular Events
 original article Carotid-Wall Intima Media Thickness and Cardiovascular Events Joseph F. Polak, M.D., M.P.H., Michael J. Pencina, Ph.D., Karol M. Pencina, Ph.D., Christopher J. O Donnell, M.D., M.P.H.,
original article Carotid-Wall Intima Media Thickness and Cardiovascular Events Joseph F. Polak, M.D., M.P.H., Michael J. Pencina, Ph.D., Karol M. Pencina, Ph.D., Christopher J. O Donnell, M.D., M.P.H.,
Night time blood pressure and cardiovascular structure in a middle-aged general population in northern Italy: the Vobarno Study
 (2001) 15, 879 885 2001 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/01 $15.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Night time blood pressure and cardiovascular structure in a middle-aged general
(2001) 15, 879 885 2001 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/01 $15.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Night time blood pressure and cardiovascular structure in a middle-aged general
COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP)
 European Medicines Agency Pre-Authorisation Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 30 May 2008 Doc. Ref. EMEA/CHMP/EWP/255210/2008 COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) CONCEPT PAPER
European Medicines Agency Pre-Authorisation Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 30 May 2008 Doc. Ref. EMEA/CHMP/EWP/255210/2008 COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) CONCEPT PAPER
Prevalence and Significance of Carotid Plaques in Patients With Coronary Atherosclerosis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2009.39.8.317 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2009 The Korean Society of Cardiology Prevalence and Significance of Carotid Plaques in Patients
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2009.39.8.317 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2009 The Korean Society of Cardiology Prevalence and Significance of Carotid Plaques in Patients
Correlations between measures of atherosclerosis change using carotid ultrasonography and coronary angiography
 Atherosclerosis 150 (2000) 371 379 www.elsevier.com/locate/atherosclerosis Correlations between measures of atherosclerosis change using carotid ultrasonography and coronary angiography Wendy J. Mack a,b,
Atherosclerosis 150 (2000) 371 379 www.elsevier.com/locate/atherosclerosis Correlations between measures of atherosclerosis change using carotid ultrasonography and coronary angiography Wendy J. Mack a,b,
Intima Media Thickness Variability (IMTV) and its association with cerebrovascular events: a novel marker of carotid therosclerosis?
 Original Article Intima Media Thickness Variability (IMTV) and its association with cerebrovascular events: a novel marker of carotid therosclerosis? Luca Saba 1, Giorgio Mallarini 1, Roberto Sanfilippo
Original Article Intima Media Thickness Variability (IMTV) and its association with cerebrovascular events: a novel marker of carotid therosclerosis? Luca Saba 1, Giorgio Mallarini 1, Roberto Sanfilippo
Sonographic Assessment of Intima Media Thickness of Common Carotid Artery in Normotensive and Hypertensive Individuals
 Sonographic Assessment of Intima Media Thickness of Common Carotid Artery in Normotensive and Hypertensive Individuals Rana Muhammad Athar Azeem Shams, Ahmed Naeem, Muhammad Yousaf, Hasham Hafeez Hanjra,
Sonographic Assessment of Intima Media Thickness of Common Carotid Artery in Normotensive and Hypertensive Individuals Rana Muhammad Athar Azeem Shams, Ahmed Naeem, Muhammad Yousaf, Hasham Hafeez Hanjra,
Associations between cardiovascular risk factors and
 Predictors of Carotid Intima-Media Thickness Progression in Young Adults The Bogalusa Heart Study Heather M. Johnson, MD; Pamela S. Douglas, MD; Sathanur R. Srinivasan, PhD; M. Gene Bond, PhD; Rong Tang,
Predictors of Carotid Intima-Media Thickness Progression in Young Adults The Bogalusa Heart Study Heather M. Johnson, MD; Pamela S. Douglas, MD; Sathanur R. Srinivasan, PhD; M. Gene Bond, PhD; Rong Tang,
ABSTRACT ORIGINAL ARTICLE INTRODUCTION. e-issn: p-issn: doi: /apjhs G. Vikas Naik 1 *, K. P.
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE e-issn: 2349-0659 p-issn: 2350-0964 doi: 10.21276/apjhs.2018.5.1.21 Carotid intima-media thickness as a predictor of atherosclerosis in diabetic and non-diabetic subjects - A study from
ORIGINAL ARTICLE e-issn: 2349-0659 p-issn: 2350-0964 doi: 10.21276/apjhs.2018.5.1.21 Carotid intima-media thickness as a predictor of atherosclerosis in diabetic and non-diabetic subjects - A study from
Role of imaging in risk assessment models: the example of CIMT
 Role of imaging in risk assessment models: the example of CIMT Diederick E. Grobbee, MD, PhD, FESC Professor of Clinical Epidemiology Julius Center for Health Sciences and Primary Care, University Medical
Role of imaging in risk assessment models: the example of CIMT Diederick E. Grobbee, MD, PhD, FESC Professor of Clinical Epidemiology Julius Center for Health Sciences and Primary Care, University Medical
Combined Measurement of Carotid Stiffness and Intima-Media Thickness Improves Prediction of Complex Aortic Plaques in Patients With Ischemic Stroke
 Combined Measurement of Carotid Stiffness and Intima-Media Thickness Improves Prediction of Complex Aortic Plaques in Patients With Ischemic Stroke Andreas Harloff, MD; Christoph Strecker; Matthias Reinhard,
Combined Measurement of Carotid Stiffness and Intima-Media Thickness Improves Prediction of Complex Aortic Plaques in Patients With Ischemic Stroke Andreas Harloff, MD; Christoph Strecker; Matthias Reinhard,
Non-invasive assessment of atherosclerosis
 Uday M Jadhav*, MD; Amit Saraf, MD; Snehal Tanna * Department of Cardiology, MGM New Bombay Hospital, Vashi, India Department of Medicine, Jupiter Hospital & Kaushalya Hospital, Thane, India Diabetology
Uday M Jadhav*, MD; Amit Saraf, MD; Snehal Tanna * Department of Cardiology, MGM New Bombay Hospital, Vashi, India Department of Medicine, Jupiter Hospital & Kaushalya Hospital, Thane, India Diabetology
Cross-sectional Study of Abnormal Intima Medial Thickness of Common Carotid Artery in Acute Cerebral Infarct Patients
 Original Article Cross-sectional Study of Abnormal Intima Medial Thickness of Common Carotid Artery in Acute Cerebral Infarct Patients DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2018/35156:2374 Radiology Section vishwanath T
Original Article Cross-sectional Study of Abnormal Intima Medial Thickness of Common Carotid Artery in Acute Cerebral Infarct Patients DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2018/35156:2374 Radiology Section vishwanath T
Key words: coronary artery disease; intima-media thickness; occult atherosclerosis; peripheral arterial disease; ultrasonic biopsy
 Association of Subclinical Wall Changes of Carotid, Femoral, and Popliteal Arteries With Obstructive Coronary Artery Disease in Patients Undergoing Coronary Angiography* Alexandros Kafetzakis, MD; George
Association of Subclinical Wall Changes of Carotid, Femoral, and Popliteal Arteries With Obstructive Coronary Artery Disease in Patients Undergoing Coronary Angiography* Alexandros Kafetzakis, MD; George
The New England Journal of Medicine CAROTID-ARTERY INTIMA AND MEDIA THICKNESS AS A RISK FACTOR FOR MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION AND STROKE IN OLDER ADULTS
 CAROTID-ARTERY INTIMA AND MEDIA THICKNESS AS A RISK FACTOR FOR MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION AND STROKE IN OLDER ADULTS DANIEL H. O LEARY, M.D., JOSEPH F. POLAK, M.D., M.P.H., RICHARD A. KRONMAL, PH.D., TERI A.
CAROTID-ARTERY INTIMA AND MEDIA THICKNESS AS A RISK FACTOR FOR MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION AND STROKE IN OLDER ADULTS DANIEL H. O LEARY, M.D., JOSEPH F. POLAK, M.D., M.P.H., RICHARD A. KRONMAL, PH.D., TERI A.
ARIC Manuscript Proposal #1233. PC Reviewed: 4_/_10/07 Status: _A Priority: 2_ SC Reviewed: Status: Priority:
 ARIC Manuscript Proposal #1233 PC Reviewed: 4_/_10/07 Status: _A Priority: 2_ SC Reviewed: Status: Priority: 1.a. Full Title: Subclinical atherosclerosis precedes type 2 diabetes in the ARIC study cohort
ARIC Manuscript Proposal #1233 PC Reviewed: 4_/_10/07 Status: _A Priority: 2_ SC Reviewed: Status: Priority: 1.a. Full Title: Subclinical atherosclerosis precedes type 2 diabetes in the ARIC study cohort
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 39, No. 7, by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN /02/$22.
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 39, No. 7, 2002 2002 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/02/$22.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0735-1097(02)01748-5
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 39, No. 7, 2002 2002 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/02/$22.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0735-1097(02)01748-5
Data Alert. Vascular Biology Working Group. Blunting the atherosclerotic process in patients with coronary artery disease.
 1994--4 Vascular Biology Working Group www.vbwg.org c/o Medical Education Consultants, LLC 25 Sylvan Road South, Westport, CT 688 Chairman: Carl J. Pepine, MD Eminent Scholar American Heart Association
1994--4 Vascular Biology Working Group www.vbwg.org c/o Medical Education Consultants, LLC 25 Sylvan Road South, Westport, CT 688 Chairman: Carl J. Pepine, MD Eminent Scholar American Heart Association
Which CVS risk reduction strategy fits better to carotid US findings?
 Which CVS risk reduction strategy fits better to carotid US findings? Dougalis A, Soulaidopoulos S, Cholongitas E, Chalevas P, Vettas Ch, Doumtsis P, Vaitsi K, Diavasti M, Mandala E, Garyfallos A 4th Department
Which CVS risk reduction strategy fits better to carotid US findings? Dougalis A, Soulaidopoulos S, Cholongitas E, Chalevas P, Vettas Ch, Doumtsis P, Vaitsi K, Diavasti M, Mandala E, Garyfallos A 4th Department
Correlation of Common Carotid Artery Intima Media Thickness, Intracranial Arterial Stenosis and Post-stroke Cognitive Impairment
 207 Correlation of Common Carotid Artery Intima Media Thickness, Intracranial Arterial Stenosis and Post-stroke Cognitive Impairment Yong-Hui Lee and Shoou-Jeng Yeh Abstract- Background and Purpose: Atherosclerosis
207 Correlation of Common Carotid Artery Intima Media Thickness, Intracranial Arterial Stenosis and Post-stroke Cognitive Impairment Yong-Hui Lee and Shoou-Jeng Yeh Abstract- Background and Purpose: Atherosclerosis
The development of atherosclerosis is now considered to
 C-Reactive Protein Is an Independent Predictor of the Rate of Increase in Early Carotid Atherosclerosis Hiroyuki Hashimoto, MD; Kazuo Kitagawa, MD, PhD; Hidetaka Hougaku, MD, PhD; Yoshiomi Shimizu, MD;
C-Reactive Protein Is an Independent Predictor of the Rate of Increase in Early Carotid Atherosclerosis Hiroyuki Hashimoto, MD; Kazuo Kitagawa, MD, PhD; Hidetaka Hougaku, MD, PhD; Yoshiomi Shimizu, MD;
Association between pulse pressure, carotid intima media thickness and carotid and/or iliofemoral plaque in hypertensive patients
 (2004) 18, 325 331 & 2004 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/04 $25.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Association between pulse pressure, carotid intima media thickness and carotid
(2004) 18, 325 331 & 2004 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/04 $25.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Association between pulse pressure, carotid intima media thickness and carotid
Chapter 01. General introduction and outline
 Chapter 01 General introduction and outline General introduction and outline Introduction Cardiovascular disease is the main cause of death in patients with hypertension and in patients with type-1 diabetes
Chapter 01 General introduction and outline General introduction and outline Introduction Cardiovascular disease is the main cause of death in patients with hypertension and in patients with type-1 diabetes
JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 12 Page December 2018
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i12.115 Evaluation of Carotid Intima
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i12.115 Evaluation of Carotid Intima
Relations of Intimal-Medial Thickness Among Sites Within the Carotid Artery as Evaluated by B-Mode Ultrasound
 1581 Relations of Intimal-Medial Thickness Among Sites Within the Carotid Artery as Evaluated by B-Mode Ultrasound George Howard, DrPH; Gregory L. Burke, MD; Gregory W. Evans, MS; John R. Crouse III, MD;
1581 Relations of Intimal-Medial Thickness Among Sites Within the Carotid Artery as Evaluated by B-Mode Ultrasound George Howard, DrPH; Gregory L. Burke, MD; Gregory W. Evans, MS; John R. Crouse III, MD;
Prognostic Value of Brachial Artery Endothelial Function and Wall Thickness
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 46, No. 6, 2005 2005 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/05/$30.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2005.05.070
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 46, No. 6, 2005 2005 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/05/$30.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2005.05.070
Hypertension. Clinical Perspective on p 1090
 Hypertension Baseline Values but Not Treatment-Induced Changes in Carotid Intima-Media Thickness Predict Incident Cardiovascular Events in Treated Hypertensive Patients Findings in the European Lacidipine
Hypertension Baseline Values but Not Treatment-Induced Changes in Carotid Intima-Media Thickness Predict Incident Cardiovascular Events in Treated Hypertensive Patients Findings in the European Lacidipine
Carotid ecodoppler and transesophageal echocardiography: complementary methods for evaluation of atherosclerosis?
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CLINICAL NEUROSCIENCES AND MENTAL HEALTH ORIGINAL RESEARCH Carotid ecodoppler and transesophageal echocardiography: complementary methods for evaluation of atherosclerosis? Joana
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CLINICAL NEUROSCIENCES AND MENTAL HEALTH ORIGINAL RESEARCH Carotid ecodoppler and transesophageal echocardiography: complementary methods for evaluation of atherosclerosis? Joana
Carotid Intima Media Thickness and Carotid Plaques Improves Prediction of Obstructive Angiographic Coronary Artery Disease in Women
 Carotid Artery Disease Carotid Intima Media Thickness and Carotid Plaques Improves Prediction of Obstructive Angiographic Coronary Artery Disease in Women Angiology 64(1) 57-63 ª The Author(s) 2013 Reprints
Carotid Artery Disease Carotid Intima Media Thickness and Carotid Plaques Improves Prediction of Obstructive Angiographic Coronary Artery Disease in Women Angiology 64(1) 57-63 ª The Author(s) 2013 Reprints
An evaluation of the reproducibility of the measurement of the intima-media thickness of carotid arteries
 O R I G I N A L ARTICLE Folia Morphol. Vol. 62, No. 1, pp. 25 31 Copyright 2003 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl An evaluation of the reproducibility of the measurement of the intima-media
O R I G I N A L ARTICLE Folia Morphol. Vol. 62, No. 1, pp. 25 31 Copyright 2003 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl An evaluation of the reproducibility of the measurement of the intima-media
Received: March 2008; in final form May 2008.
 RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN BRACHIAL ARTERY FLOW- MEDIATED DILATION AND CAROTID ARTERY INTIMA MEDIA THICKNESS IN THE MIDDLE-AGED SUBJECTS WITH LOW CARDIOVASCULAR RISK GERMAINE SĂVOIU*, LAVINIA NOVEANU**, O. FIRA-MLADINESCU*,
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN BRACHIAL ARTERY FLOW- MEDIATED DILATION AND CAROTID ARTERY INTIMA MEDIA THICKNESS IN THE MIDDLE-AGED SUBJECTS WITH LOW CARDIOVASCULAR RISK GERMAINE SĂVOIU*, LAVINIA NOVEANU**, O. FIRA-MLADINESCU*,
Carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) and carotid plaques in young Nepalese patients with angiographically documented coronary artery disease
 Original Article Carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) and carotid plaques in young Nepalese patients with angiographically documented coronary artery disease Yuba Raj Limbu, Rajib Rajbhandari, Ranjit
Original Article Carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) and carotid plaques in young Nepalese patients with angiographically documented coronary artery disease Yuba Raj Limbu, Rajib Rajbhandari, Ranjit
Measurements of carotid intima media thickness in non-invasive high-frequency ultrasound images: the effect of dynamic range setting
 Gaarder and Seierstad Cardiovascular Ultrasound 2015, 13:5 CARDIOVASCULAR ULTRASOUND RESEARCH Open Access Measurements of carotid intima media thickness in non-invasive high-frequency ultrasound images:
Gaarder and Seierstad Cardiovascular Ultrasound 2015, 13:5 CARDIOVASCULAR ULTRASOUND RESEARCH Open Access Measurements of carotid intima media thickness in non-invasive high-frequency ultrasound images:
Carotid intima media thickness as an usefull tool in predicting cerebrovaskular events
 Carotid intima media thickness as an usefull tool in predicting cerebrovaskular events Poster No.: C-0005 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit A. Rahimic - Catic; Sarajevo/BA
Carotid intima media thickness as an usefull tool in predicting cerebrovaskular events Poster No.: C-0005 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit A. Rahimic - Catic; Sarajevo/BA
Carotid Artery Plaque Burden, Stiffness, and Mortality Risk in Elderly Men. A Prospective, Population-Based Cohort Study
 Carotid Artery Plaque Burden, Stiffness, and Risk in Elderly Men A Prospective, Population-Based Cohort Study Stefan Störk, MD; Annewieke W. van den Beld, MD; Clemens von Schacky, MD; Christiane E. Angermann,
Carotid Artery Plaque Burden, Stiffness, and Risk in Elderly Men A Prospective, Population-Based Cohort Study Stefan Störk, MD; Annewieke W. van den Beld, MD; Clemens von Schacky, MD; Christiane E. Angermann,
Cardiac Computed Tomography (CT) and Coronary CT Angiography Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) - Assessment of Emerging Risk Factors
 2.02.16 Ultrasonographic Measurement of Carotid Intima- Medial Thickness as an Assessment of Subclinical Atherosclerosis Section 2.0 Medicine Subsection 2.02 Cardiology Effective Date January 1, 2015 Original
2.02.16 Ultrasonographic Measurement of Carotid Intima- Medial Thickness as an Assessment of Subclinical Atherosclerosis Section 2.0 Medicine Subsection 2.02 Cardiology Effective Date January 1, 2015 Original
The presenter does not have any potential conflicts of interest to disclose
 Carotid intima-media thickness as a predictor of multi territory atherosclerotic occlusive disease in patients with symptomatic subclavian artery obstruction Leszek Wrotniak 1, Anna Kabłak Ziembicka 1,
Carotid intima-media thickness as a predictor of multi territory atherosclerotic occlusive disease in patients with symptomatic subclavian artery obstruction Leszek Wrotniak 1, Anna Kabłak Ziembicka 1,
Preintrusive thickening of artery walls is detectable in
 Differential Effects of Nifedipine and Co-Amilozide on the Progression of Early Carotid Wall Changes Alain Simon, MD; Jérome Gariépy, MD; Dominique Moyse, PhD; Jaime Levenson, MD Background Common carotid
Differential Effects of Nifedipine and Co-Amilozide on the Progression of Early Carotid Wall Changes Alain Simon, MD; Jérome Gariépy, MD; Dominique Moyse, PhD; Jaime Levenson, MD Background Common carotid
Normal blood vessels A= artery V= vein
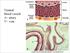 Normal blood vessels A= artery V= vein Artery (A) versus vein (V) ARTERIOSCLEROSIS Arteriosclerosis ="hardening of the arteries" arterial wall thickening and loss of elasticity. Three patterns are recognized,
Normal blood vessels A= artery V= vein Artery (A) versus vein (V) ARTERIOSCLEROSIS Arteriosclerosis ="hardening of the arteries" arterial wall thickening and loss of elasticity. Three patterns are recognized,
CLINICAL STUDY. Yasser Khalil, MD; Bertrand Mukete, MD; Michael J. Durkin, MD; June Coccia, MS, RVT; Martin E. Matsumura, MD
 117 CLINICAL STUDY A Comparison of Assessment of Coronary Calcium vs Carotid Intima Media Thickness for Determination of Vascular Age and Adjustment of the Framingham Risk Score Yasser Khalil, MD; Bertrand
117 CLINICAL STUDY A Comparison of Assessment of Coronary Calcium vs Carotid Intima Media Thickness for Determination of Vascular Age and Adjustment of the Framingham Risk Score Yasser Khalil, MD; Bertrand
Culprit Lesion Remodeling and Long-term (> 5years) Prognosis in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome
 Culprit Lesion Remodeling and Long-term (> 5years) Prognosis in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome Hiroyuki Okura*, MD; Nobuya Matsushita**,MD Kenji Shimeno**, MD; Hiroyuki Yamaghishi**, MD Iku Toda**,
Culprit Lesion Remodeling and Long-term (> 5years) Prognosis in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome Hiroyuki Okura*, MD; Nobuya Matsushita**,MD Kenji Shimeno**, MD; Hiroyuki Yamaghishi**, MD Iku Toda**,
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. Materials and Methods. Study design
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Materials and Methods Study design The ELSA-Brasil design and concepts have been detailed elsewhere 1. The ELSA-Brasil is a cohort study of active or retired 15,105 civil servants,
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Materials and Methods Study design The ELSA-Brasil design and concepts have been detailed elsewhere 1. The ELSA-Brasil is a cohort study of active or retired 15,105 civil servants,
Omics and coronary atherosclerosis
 Omics and coronary atherosclerosis Dr.ssa Rosalinda Madonna Centro Scienze dell Invecchiamento e Medicina Traslazionale CESI-Met Università G. d Annunzio Chieti Geographic Distribution of Relative Mortality
Omics and coronary atherosclerosis Dr.ssa Rosalinda Madonna Centro Scienze dell Invecchiamento e Medicina Traslazionale CESI-Met Università G. d Annunzio Chieti Geographic Distribution of Relative Mortality
PATIENTS AND METHODS:
 BACKGROUND: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic systemic inflammatory disease characterized by erosive synovitis that involves peripheral joints and implicates an important influence in the quality
BACKGROUND: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic systemic inflammatory disease characterized by erosive synovitis that involves peripheral joints and implicates an important influence in the quality
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Am J Cardiol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2008 January 24.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Am J Cardiol. 2008 January 15; 101(2): 186 192. Coronary Artery Calcium, Carotid Artery Wall Thickness and Cardiovascular Disease
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Am J Cardiol. 2008 January 15; 101(2): 186 192. Coronary Artery Calcium, Carotid Artery Wall Thickness and Cardiovascular Disease
Summary. Cyprian Wolski, Arkadiusz Rotkiewicz, Piotr Grzelak, Marcin Elgalal, Ludomir Stefańczyk. Background
 Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2011; 76(4): 15-20 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Received: 2010.11.24 Accepted: 2011.08.16 Comparison of tomographic coronary artery calcification index (calcium score) and ultrasonographic
Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2011; 76(4): 15-20 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Received: 2010.11.24 Accepted: 2011.08.16 Comparison of tomographic coronary artery calcification index (calcium score) and ultrasonographic
Atherosclerosis is a complex cardiovascular disorder that
 Genetic Basis of Variation in Carotid Artery Plaque in the San Antonio Family Heart Study Kelly J. Hunt, PhD; Ravindranath Duggirala, PhD; Harald H.H. Göring, PhD; Jeff T. Williams, PhD; Laura Almasy,
Genetic Basis of Variation in Carotid Artery Plaque in the San Antonio Family Heart Study Kelly J. Hunt, PhD; Ravindranath Duggirala, PhD; Harald H.H. Göring, PhD; Jeff T. Williams, PhD; Laura Almasy,
Name of Policy: Ultrasonographic Measurement of Carotid Intimal-Medial Thickness as an Assessment of Subclinical Atherosclerosis
 Name of Policy: Ultrasonographic Measurement of Carotid Intimal-Medial Thickness as an Assessment of Subclinical Atherosclerosis Policy #: 245 Latest Review Date: July 2014 Category: Medicine Policy Grade:
Name of Policy: Ultrasonographic Measurement of Carotid Intimal-Medial Thickness as an Assessment of Subclinical Atherosclerosis Policy #: 245 Latest Review Date: July 2014 Category: Medicine Policy Grade:
Association of Isolated Systolic, Isolated Diastolic, and Systolic-Diastolic Masked Hypertension With Carotid Artery Intima-Media Thickness
 ORIGINAL PAPER Association of Isolated Systolic, Isolated Diastolic, and Systolic-Diastolic Masked Hypertension With Carotid Artery Intima-Media Thickness Efstathios Manios, MD; 1 Fotios Michas, MD; 1
ORIGINAL PAPER Association of Isolated Systolic, Isolated Diastolic, and Systolic-Diastolic Masked Hypertension With Carotid Artery Intima-Media Thickness Efstathios Manios, MD; 1 Fotios Michas, MD; 1
Η σημασία της αρτηριακής σκληρίας στην εκτίμηση της διαστολικής δυσλειτουργίας στην υπέρταση. Θεραπευτικές παρεμβάσεις
 Η σημασία της αρτηριακής σκληρίας στην εκτίμηση της διαστολικής δυσλειτουργίας στην υπέρταση. Θεραπευτικές παρεμβάσεις Ελένη Τριανταφυλλίδη Επιμελήτρια Α Β Πανεπιστημιακή Καρδιολογική Κλινική Αττικό Νοσοκομείο
Η σημασία της αρτηριακής σκληρίας στην εκτίμηση της διαστολικής δυσλειτουργίας στην υπέρταση. Θεραπευτικές παρεμβάσεις Ελένη Τριανταφυλλίδη Επιμελήτρια Α Β Πανεπιστημιακή Καρδιολογική Κλινική Αττικό Νοσοκομείο
Carotid Artery Plaque Burden, Stiffness, and Mortality Risk in Elderly Men. A Prospective, Population-Based Cohort Study.
 Carotid Plaque and Mortality risk in Elderly Men. Störk et al. In press at Circulation 2004 Carotid Artery Plaque Burden, Stiffness, and Mortality Risk in Elderly Men. A Prospective, Population-Based Cohort
Carotid Plaque and Mortality risk in Elderly Men. Störk et al. In press at Circulation 2004 Carotid Artery Plaque Burden, Stiffness, and Mortality Risk in Elderly Men. A Prospective, Population-Based Cohort
The Role of Carotid Ultrasound for Cardiovascular Risk Stratification beyond Traditional Risk Factors
 Review Article http://dx.doi.org/.9/ymj... pissn: -9, eissn: 9- Yonsei Med J ():-, The Role of Carotid Ultrasound for Cardiovascular Risk Stratification beyond Traditional Risk Factors Chan Joo Lee and
Review Article http://dx.doi.org/.9/ymj... pissn: -9, eissn: 9- Yonsei Med J ():-, The Role of Carotid Ultrasound for Cardiovascular Risk Stratification beyond Traditional Risk Factors Chan Joo Lee and
Is Carotid Artery Ultrasound Still Useful Method for Evaluation of Atherosclerosis?
 Review Article Print ISSN 1738-5520 On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Korean Circulation Journal Is Carotid Artery Ultrasound Still Useful Method for Evaluation of Atherosclerosis? Gee-Hee Kim, MD 1, and Ho-Joong
Review Article Print ISSN 1738-5520 On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Korean Circulation Journal Is Carotid Artery Ultrasound Still Useful Method for Evaluation of Atherosclerosis? Gee-Hee Kim, MD 1, and Ho-Joong
Screening for Cardiovascular Risk (2/6/09)
 Screening for Cardiovascular Risk (2/6/09) Andrew Nicolaides MS, FRCS, FRCSE, PhD (Hon) Emeritus Professor of Vascular Surgery, Imperial College, London, UK Chairman, Cardiovascular Disease Educational
Screening for Cardiovascular Risk (2/6/09) Andrew Nicolaides MS, FRCS, FRCSE, PhD (Hon) Emeritus Professor of Vascular Surgery, Imperial College, London, UK Chairman, Cardiovascular Disease Educational
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Ultrasonographic Measurement of Carotid Intimal-Medial Thickness Page 1 of 11 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Ultrasonographic Measurement of Carotid
Ultrasonographic Measurement of Carotid Intimal-Medial Thickness Page 1 of 11 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Ultrasonographic Measurement of Carotid
Vascular disease. Structural evaluation of vascular disease. Goo-Yeong Cho, MD, PhD Seoul National University Bundang Hospital
 Vascular disease. Structural evaluation of vascular disease Goo-Yeong Cho, MD, PhD Seoul National University Bundang Hospital resistance vessels : arteries
Vascular disease. Structural evaluation of vascular disease Goo-Yeong Cho, MD, PhD Seoul National University Bundang Hospital resistance vessels : arteries
Stroke. 2012;43: ; originally published online May 1, 2012; doi: /STROKEAHA
 Risk Factors for Progression of Carotid Intima-Media Thickness and Total Plaque Area : A 13-Year Follow-Up Study: The Tromsø Study Marit Herder, Stein Harald Johnsen, Kjell Arne Arntzen and Ellisiv B.
Risk Factors for Progression of Carotid Intima-Media Thickness and Total Plaque Area : A 13-Year Follow-Up Study: The Tromsø Study Marit Herder, Stein Harald Johnsen, Kjell Arne Arntzen and Ellisiv B.
Carotid intima-media thickness is not related with clinical outcomes in young hypertensives
 Yu et al. Clinical Hypertension (2015) 21:15 DOI 10.1186/s40885-015-0021-x RESEARCH Open Access Carotid intima-media thickness is not related with clinical outcomes in young hypertensives Jin-Sok Yu, Yun-Seok
Yu et al. Clinical Hypertension (2015) 21:15 DOI 10.1186/s40885-015-0021-x RESEARCH Open Access Carotid intima-media thickness is not related with clinical outcomes in young hypertensives Jin-Sok Yu, Yun-Seok
Journal of American Science 2014;10(8)
 Role of Doppler Ultrasound and Peripheral Angiography (as a Diagnostic Modality of Atherosclerosis) in Combination with Conventional Atherosclerosis Risk Factors in Coronary Artery Disease Prediction Hussein
Role of Doppler Ultrasound and Peripheral Angiography (as a Diagnostic Modality of Atherosclerosis) in Combination with Conventional Atherosclerosis Risk Factors in Coronary Artery Disease Prediction Hussein
CAROTID INTIMA-MEDIA THICKNESS. Dimitrios N. Nikas, MD, PhD, FESC Interventional Cardiologist Ioannina University Hospital
 CAROTID INTIMA-MEDIA THICKNESS Dimitrios N. Nikas, MD, PhD, FESC Interventional Cardiologist Ioannina University Hospital I, DIMITRIOS N. NIKAS, MD, PHD, FESC, HAVE NO CONFLICT OF INTEREST TO DECLARE RELATED
CAROTID INTIMA-MEDIA THICKNESS Dimitrios N. Nikas, MD, PhD, FESC Interventional Cardiologist Ioannina University Hospital I, DIMITRIOS N. NIKAS, MD, PHD, FESC, HAVE NO CONFLICT OF INTEREST TO DECLARE RELATED
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 39, No. 4, by the American College of Cardiology ISSN /02/$22.
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 39, No. 4, 2002 2002 by the American College of Cardiology ISSN 0735-1097/02/$22.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0735-1097(01)01783-1 Effects
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 39, No. 4, 2002 2002 by the American College of Cardiology ISSN 0735-1097/02/$22.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0735-1097(01)01783-1 Effects
Arterial blood pressure may be divided into 2 components:
 Cross-Sectional and 4-Year Longitudinal Associations Between Brachial Pulse Pressure and Common Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in a General Population The EVA Study Mahmoud Zureik, MD, PhD; Pierre-Jean
Cross-Sectional and 4-Year Longitudinal Associations Between Brachial Pulse Pressure and Common Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in a General Population The EVA Study Mahmoud Zureik, MD, PhD; Pierre-Jean
The relationship between mechanical properties of carotid artery and coronary artery disease
 European Heart Journal Cardiovascular Imaging (2012) 13, 568 573 doi:10.1093/ejechocard/jer259 The relationship between mechanical properties of carotid artery and coronary artery disease Su-A Kim, Seong-Mi
European Heart Journal Cardiovascular Imaging (2012) 13, 568 573 doi:10.1093/ejechocard/jer259 The relationship between mechanical properties of carotid artery and coronary artery disease Su-A Kim, Seong-Mi
Preclinical Detection of CAD: Is it worth the effort? Michael H. Crawford, MD
 Preclinical Detection of CAD: Is it worth the effort? Michael H. Crawford, MD 1 Preclinical? No symptoms No physical findings No diagnostic ECG findings No chest X-ray X findings No diagnostic events 2
Preclinical Detection of CAD: Is it worth the effort? Michael H. Crawford, MD 1 Preclinical? No symptoms No physical findings No diagnostic ECG findings No chest X-ray X findings No diagnostic events 2
Hypertension is a major risk factor for morbidity
 O r i g i n a l P a p e r Long-Term Effects of a Losartan- Compared With an Atenolol-Based Treatment Regimen on Carotid Artery Plaque Development in Hypertensive Patients With Left Ventricular Hypertrophy:
O r i g i n a l P a p e r Long-Term Effects of a Losartan- Compared With an Atenolol-Based Treatment Regimen on Carotid Artery Plaque Development in Hypertensive Patients With Left Ventricular Hypertrophy:
Morphological duplex ultrasound criteria how to assess and report echolucency, inhomogeneity and ulceration
 Morphological duplex ultrasound criteria how to assess and report echolucency, inhomogeneity and ulceration Prof. Daniel Staub, Angiology, University Hospital Basel, Switzerland daniel.staub@usb.ch Disclosure
Morphological duplex ultrasound criteria how to assess and report echolucency, inhomogeneity and ulceration Prof. Daniel Staub, Angiology, University Hospital Basel, Switzerland daniel.staub@usb.ch Disclosure
Atherosclerosis Regression An Overview of Recent Findings & Issues
 Atherosclerosis Regression An Overview of Recent Findings & Issues 13th Angioplasty Summit 2008 Cheol Whan Lee, MD University of Ulsan, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea CardioVascular Research Foundation
Atherosclerosis Regression An Overview of Recent Findings & Issues 13th Angioplasty Summit 2008 Cheol Whan Lee, MD University of Ulsan, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea CardioVascular Research Foundation
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis
 Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
Abstract nr AHA, Chicago November European Heart Journal Cardiovascular Imaging, in press. Nr Peter Blomstrand
 Left Ventricular Diastolic Function Assessed by Echocardiography and Tissue Doppler Imaging is a strong Predictor of Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Peter Blomstrand, Martin
Left Ventricular Diastolic Function Assessed by Echocardiography and Tissue Doppler Imaging is a strong Predictor of Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Peter Blomstrand, Martin
Subclinical atherosclerosis in CVD: Risk stratification & management Raul Santos, MD
 Subclinical atherosclerosis in CVD: Risk stratification & management Raul Santos, MD Sao Paulo Medical School Sao Paolo, Brazil Subclinical atherosclerosis in CVD risk: Stratification & management Prof.
Subclinical atherosclerosis in CVD: Risk stratification & management Raul Santos, MD Sao Paulo Medical School Sao Paolo, Brazil Subclinical atherosclerosis in CVD risk: Stratification & management Prof.
Atherosclerotic disease regression with statins: studies using vascular markers
 International Journal of Cardiology 96 (2004) 447 459 www.elsevier.com/locate/ijcard Atherosclerotic disease regression with statins: studies using vascular markers Diederick E. Grobbee*, Michiel L. Bots
International Journal of Cardiology 96 (2004) 447 459 www.elsevier.com/locate/ijcard Atherosclerotic disease regression with statins: studies using vascular markers Diederick E. Grobbee*, Michiel L. Bots
Evaluation of carotid intima-medial thickness as a marker of atherosclerosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
 43 Research Article Evaluation of carotid intima-medial thickness as a marker of atherosclerosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Authors : Dr. G.S Kejriwal MD 1, Dr. M. Jyothirmayee
43 Research Article Evaluation of carotid intima-medial thickness as a marker of atherosclerosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Authors : Dr. G.S Kejriwal MD 1, Dr. M. Jyothirmayee
Theoretical and practical questions in the evaluation of arterial function Miklós Illyés MD. Ph.D.
 Theoretical and practical questions in the evaluation of arterial function Miklós Illyés MD. Ph.D. TensioMed Arterial Stiffness Centre, Budapest Heart Institute, Faculty of Medicine, University of Pécs
Theoretical and practical questions in the evaluation of arterial function Miklós Illyés MD. Ph.D. TensioMed Arterial Stiffness Centre, Budapest Heart Institute, Faculty of Medicine, University of Pécs
Association between Plasma Homocysteine Concentrations and Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease
 Association between Plasma Homocysteine Concentrations and Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease ROXANA BUZAŞ, CORINA ŞERBAN, IOANA SUCEAVA, DANIEL LIGHEZAN University
Association between Plasma Homocysteine Concentrations and Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease ROXANA BUZAŞ, CORINA ŞERBAN, IOANA SUCEAVA, DANIEL LIGHEZAN University
Autonomic nervous system, inflammation and preclinical carotid atherosclerosis in depressed subjects with coronary risk factors
 Autonomic nervous system, inflammation and preclinical carotid atherosclerosis in depressed subjects with coronary risk factors Carmine Pizzi 1 ; Lamberto Manzoli 2, Stefano Mancini 3 ; Gigliola Bedetti
Autonomic nervous system, inflammation and preclinical carotid atherosclerosis in depressed subjects with coronary risk factors Carmine Pizzi 1 ; Lamberto Manzoli 2, Stefano Mancini 3 ; Gigliola Bedetti
The clinical trial information provided in this public disclosure synopsis is supplied for informational purposes only.
 The clinical trial information provided in this public disclosure synopsis is supplied for informational purposes only. Please note that the results reported in any single trial may not reflect the overall
The clinical trial information provided in this public disclosure synopsis is supplied for informational purposes only. Please note that the results reported in any single trial may not reflect the overall
