Review Packet EKG Competency This packet is a review of the information you will need to know for the proctored EKG competency test.
|
|
|
- Mae Baker
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Review Packet EKG Competency 2015 This packet is a review of the information you will need to know for the proctored EKG competency test.
2 Normal Sinus Rhythm Rhythm: Regular Ventricular Rate: bpm P Wave: upright, matching, 1:1 Atrial Rate: bpm PR Interval: seconds QRS Interval: < 0.10 seconds Normal None None
3 Sinus Tachycardia Rhythm: Regular Ventricular Rate: P Wave: upright, matching, 1:1 Atrial Rate: PR Interval: seconds QRS Interval: < 0.10 seconds Increases myocardial oxygen demands, increasing the hearts workload o In an acute MI, this may lead to an increase in myocardial ischemia, angina, or extend the infarct o May also trigger ventricular dysrhythmia o May be a warning sign of right sided heart failure Shortens ventricular filling times which decreases stoke volume which affects cardiac output Exercise Fever Hypoxia Hypovolemic Pulmonary embolism Myocardial ischemia Hypotension Caffeine Alcohol Nicotine Find and treat underlying cause Monitor for signs of decreased coronary perfusion o Diaphoresis o Chest pain o Dyspnea
4 Sinus Bradycardia Rhythm: Regular Ventricular Rate: < 60 bpm P Wave: upright, matching, 1:1 Atrial Rate: < 60 bpm PR Interval: seconds QRS Interval: < 0.10 seconds Normal for trained athletes An MI to the RCA Reperfusion Rhythm Elevated ICP Medications (beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, digitalis) Degenerative diseases, such as sick sinus syndrome Vagal stimulation from vomiting, sleeping, nausea Normal in healthy adults and athletes Can be beneficial in injured hearts to allow increased ventricular filling time and decreased myocardial oxygen demands Some individuals experience a significant decrease in cardiac output (HR x SV = CO) as well as blood pressure Treat only if SYMPTOMATIC: 1. IVP Atropine 2. Pacemaker Temporary transcutaneous or transvenous Chronic bradycardia may require a permanent pacemaker Discontinue any bradycardia inducing medications
5 Sinus Arrhythmia Rhythm: Irregular Ventricular Rate: any rate P Wave: upright, matching, 1:1 Atrial Rate: any rate PR Interval: seconds QRS Interval: <0.10 seconds May be seen in young children and elderly Change in vagal tone due to respirations May also be caused by: Increased ICP Dig toxicity Inferior wall MI None depending on rate If rate is bradycardic, may decrease cardiac output None, unless rate is bradycardic. If patient is symptomatic with bradycardia: o IVP Atropine o Pacemaker
6 Premature Atrial Contraction(PAC) Rhythm: that of underlying rhythm Ventricular Rate: that of underlying P Wave: upright, abnormal in size and shape, p wave may be in T wave Atrial Rate: that of underlying rhythm PR Interval: seconds QRS Interval: <0.10 seconds Can occur in normal hearts o Can be seen with emotional distress Heart disease Ingestion of alcohol, caffeine, or nicotine Hypoxia Myocardial ischemia Chronic lung disease Medications Usually common and do not require treatment Frequent PAC s may warn of or intiate: o PAT o Atrial Fibrillation o Atrial Flutter Usually no treatment Remove underlying cause: o Nicotine o Alcohol o Caffeine
7 Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia (PSVT or SVT) Rhythm: Regular Ventricular Rate: > 150 bpm P Wave: unable to see Atrial Rate: NA PR Interval: NA QRS Interval: <0.10 seconds Stress Caffeine Tobacco Alcohol COPD Digitalis Toxicity Shortens ventricular filling time which can decrease stoke volume which can decrease cardiac output Increases myocardial oxygen requirements and cardiac workload If unstable: o Electrical Cardioversion If stable: 1. Sedation 2. Vagal maneuvers 3. IVP Adenosine 4. Rate controlling medication such as a calcium channel blocker (ex. Diltiazem) or a beta blocker.
8 Atrial Flutter Rhythm: Regular/Irregular Ventricular Rate: varies P Wave: flutter, sawtooth Atrial Rate: bpm PR Interval: NA QRS Interval: <0.10 seconds If ventricular rate is rapid: o Ventricular filling time is shortened which can decrease stoke volume which can decrease cardiac output o Myocardial oxygen requirements and cardiac workload are increased If ventricular rate is slow: Decrease in cardiac output due to slow heart rate Stasis of blood in atria can lead to thrombus formation & possible arterial or pulmonary embolism Valvular heart disease Hypertensive heart disease Cardiomyopathy Heart failure Pulmonary disease Pulmonary emboli Post-cardiac surgery If patient is stable and the rhythm has been present treatment depends on ventricular rate & patient symptoms: Amiodarone, Calcium Channel Blockers, Beta Blockers If unstable: Cardiovert immediately Goal is to restore sinus rhythm!
9 Atrial Fibrillation Rhythm: Irregular Ventricular Rate: varies P Wave: not seen, fibrillatory waves Atrial Rate: >300 bpm PR Interval: NA QRS Interval: < 0.10 seconds Same as atrial flutter. Valvular heart disease Hypertensive disease Coronary heart disease Cardiomyopathy Heart failure Hyperthyroidism Pulmonary disease Cardiac surgery Same as atrial flutter Chronic atrial fibrillation (present for months or years) may not convert to sinus rhythm with any type of therapy. Typically no attempt is made to return chronic atrial fibrillation patients to sinus rhythm.
10 Junctional Rhythm Rhythm: Regular Ventricular Rate: bpm P Wave: inverted, absent, inverted after QRS Atrial Rate: PR Interval: <0.12 seconds QRS Interval: <0.10 seconds AV junction not reliable as pacemaker for long periods The slow rate may cause: o Hypotension o Decrease in Cardiac Output SA node disease Myocardial infarction Dig toxicity Increase in vagal tone Depends on tolerance of slowed heart rate Identify and treat underlying cause If symptomatic: 1. Atropine IVP 2. Transcutaneous or transvenous pacing
11 Accelerated Junctional Rhythm Rhythm: Regular Ventricular Rate: bpm P Wave: inverted, absent, inverted after QRS Atrial Rate: bpm PR Interval: <0.12 seconds QRS Interval: <0.10 seconds Typically well tolerated For some the loss of normal atrial depolarization can cause a decrease in cardiac output. Dig toxicity Damage to AV node secondary to Inferior wall MI Heart failure Acute rheumatic fever Valvular heart disease Open heart surgery Myocarditis should be directed at identifying the underlying cause and correcting it.
12 Junctional Tachycardia Rhythm: Regular Ventricular Rate: >101bpm P Wave: inverted, absent, inverted after QRS Atrial Rate: >101 bpm PR Interval: <0.12 seconds QRS Interval: <0.10 seconds If ventricular rate is rapid: o Ventricular filling time is shortened which can decrease stoke volume which can decrease cardiac output o Myocardial oxygen requirements and cardiac workload are increased Dig Toxicity Damage to AV node (Inferior MI) Heart Failure Myocarditis Rheumatic Fever Identify and treat cause Vagal Maneuvers If there is no apparent cause and the patient is symptomatic: o Diltiazem o Beta blockers o Amiodarone
13 Premature Junctional Contraction Rhythm: Usually regular Ventricular Rate: underlying rhythm P Wave: inverted, absent, or inverted after the QRS Atrial Rate: underlying rhythm PR Interval: <0.12 seconds QRS Interval: <0.10 seconds Alcohol Simulants: o Coffee o Tea o Tobacco Coronary artery disease Digoxin toxicity Inferior wall MI Unusual in healthy adults Early sign of digoxin toxicity May precipitate junctional tachycardia Treat underlying cause
14 Ventricular Fibrillation Rhythm: Chaotic Ventricular Rate: NA P Wave: NA Atrial Rate: NA PR Interval: NA QRS Interval: NA Most common cause of death for people with coronary heart disease Most common cause of sudden cardiac death in patients with an acute MI Other causes: Myocardial Ischemia Cardiomyopathy Hypoxia Cocaine toxicity Electrolyte imbalance No organ perfusion! Check for Pulse! (If there is a pulse, not VF.) If there is no pulse: 1. Defibrillation 2. CPR 3. Drugs: Epinephrine Amiodarone
15 Ventricular Tachycardia Rhythm: Regular Ventricular Rate: >101 bpm P Wave: none Atrial Rate: none PR Interval: NA QRS Interval: 0.12 seconds Seriousness depends on duration, rate, and how well the heart functions Patients may have bursts of VT Sustained VT is a life-threatening arrhythmia Can progress to Ventricular Fibrillation Decrease or absence of Cardiac Output Heart disease Myocardial ischemia or infarction Cardiomyopathy CHF Medications Hypoxia Electrolyte imbalance Assess Patient (pulse, BP, LOC) V. Tach with a pulse and: o Stable 1. Amiodarone 2. Cardioversion o Unstable 1. Cardioversion V. Tach without a pulse: 1. Defibrillation 2. CPR (initiate immediately) 3. Epinephrine 4. Amiodarone
16 Ventricular Standstill Rhythm: Atrial Regular Ventricular Rate: NA P Wave: upright, matching Atrial Rate: varies PR Interval: NA QRS Interval: NA Acidosis Hypoxia Hyperkalemia Hypothermia Drug Overdose
17 Idioventricular Rhythm Rhythm: Regular Ventricular Rate: bpm P Wave: NA Atrial Rate: NA PR Interval: NA QRS Interval: 0.12 seconds Wide and Bizarre Decrease in cardiac output Commonly precedes asystole Sign of a dying heart Disease or injury to the SA node or AV node Medications that can slow or inhibit the SA node or AV node May occur in brief intervals Advanced heart failure CHF Goal is to establish a reliable pacemaker and increase the heart rate Never attempt to obliterate an Idioventricular rhythm with antiarrhythmic drugs Treat with: o Atropine o Transcutaneous or Transvenous pacemaker o Dopamine for hypotension
18 Accelerated Idioventricular Rhythm Rhythm: Regular/Irregular Ventricular Rate: bpm P Wave: NA Atrial Rate: NA PR Interval: NA QRS Interval: 0.12 seconds, Wide and bizarre Typically well tolerated May have decreased cardiac output at lower heart rates Common following thrombolytic therapy Can be a transient rhythm May be a result of dig toxicity No treatment usually necessary Monitor the patient s hemodynamic values (blood pressure)
19 Premature Ventricular Contraction Rhythm: underlying rhythm Ventricular Rate: underlying rhythm P Wave: absent on premature beat Atrial Rate: underlying rhythm PR Interval: none QRS Interval: 0.12 seconds PVC s are very common Become more frequent as we age Can precipitate life-threatening arrhythmias Anxiety Excessive caffeine/alcohol intake Drugs CHF Electrolyte imbalance (Hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia) Heart surgery Reperfusion after thrombolytics Treat the cause Medications Electrolyte replacement Decrease caffeine consumption
20 Asystole Rhythm: NA Ventricular Rate: NA P Wave: NA Atrial Rate: NA PR Interval: NA QRS Interval: NA Most common cause is MI Hypoxia Hypothermia Drug overdose Acidosis Hyper/Hypokalemia No cardiac output!! Poor prognosis despite resuscitative efforts Check for Pulse! Always check another lead to ensure true asystole If no pulse: 1. Initiate CPR 2. Epinephrine or Vasopressin 3. Temporary pacemaker 4. Find and treat underlying cause
21 Sinus Rhythm with First-Degree Heart Block Rhythm: Regular Ventricular Rate: bpm P Wave: upright, matching, 1:1 Atrial Rate: bpm PR Interval: > 0.20 seconds QRS Interval: < 0.10 seconds No specific symptoms Risk for progressing to a more severe AV block Ischemic Injury to AV node or surrounding tissue Medications: Digitalis Beta-blockers Calcium-channel blockers Increased vagal tone Hyperkalemia Inferior wall MI Degeneration due to aging No specific treatment Monitor for development of a more serious AV Block Review and discontinue medications that may cause AV Block
22 Second-Degree Heart Block Type 1 (Wenkebach) Rhythm: Ventricular-Irregular/Regular Atrial-Regular Ventricular Rate: varies P Wave: upright, matching Atrial Rate: varies PR Interval: progressively lengthens QRS Interval: < 0.10 seconds Seldom a serious form of heart block Rarely progresses to higher degree of block Ischemia of the AV due to an inferior MI Same medications as First Degree Acute Infections May be normal in athletes Monitor for development of a more serious AV Block Review and discontinue medications that may cause AV Block If symptomatic due to bradycardia: o Atropine o Pacemaker, not usually necessary
23 Second-Degree Heart Block Type 2 Rhythm: Ventricular-Regular/Irregular Atrial-Regular Ventricular Rate: Vary P Wave: upright, matching, 2:1, 3:1, 4:1 Atrial Rate: varies PR Interval: constant QRS Interval: < 0.10 seconds Can progress suddenly to Third-Degree AV Block or ventricular standstill Associated with anterior or anteroseptal MI Degeneration of electrical conduction system- Usually age related Placement of transvenous pacemaker ASAP (because of possible sudden progression to third-degree block or ventricular standstill) If patient is symptomatic: 1. Transcutaneously pace until transvenous pacemaker can be placed 2. Atropine must be used with cautionmay cause paradoxical slowing of ventricular rate, if ineffective 3. If Atropine or Pacing ineffective treat with Dopamine or Epinephrine infusion
24 Third-Degree Heart Block (Complete) Rhythm: Ventricular-Regular Atrial-Regular Ventricular Rate: varies P Wave: upright, matching Atrial Rate: varies PR Interval: varies QRS Interval: < 0.120seconds Serious and potentially life-threatening arrhythmia May progress to asystole or ventricular standstill with no warning Loss of atrial kick Acute anterior MI Inferior MI Drug toxicity Commonly seen in elderly patients due to degeneration of their conduction system Causes: same as 2 nd degree blocks Placement of transvenous pacemaker ASAP (because of possible sudden progression to ventricular standstill) If patient is symptomatic: 1. Transcutaneously pace until transvenous pacemaker can be placed 2. Atropine should only be used if the QRS is narrow. Will have no effect on complete heart block with a wide QRS 3. If Atropine/Pacing ineffective treat with Dopamine or Epinephrine infusion. Unresolved third-degree heart block will require a permanent pacemaker
25 Ventricular Pacing Chamber Paced: Ventricle Interpretation: Normal V-Pacing Bradycardia Third Degree Heart Block Pauses Overdrive of tachyarrhythmia Prophylactic for heart surgeries Maintains cardiac output and blood pressure Used to treat any of the above etiologies
26 Failure to Capture Chamber Paced: Unknown Interpretation: Failure to capture Bradycardia Third Degree Heart Block Pauses Overdrive of tachyarrythmias Prophylactic for heart surgeries Decreased cardiac output and blood pressure Life threatening emergency! May be fixed by increasing the milli-amps (MA)
27 Undersensing Chamber Paced: Ventricular Interpretation: V-Paced with undersensing Bradycardia Third Degree Heart Block Pauses Overdrive of tachyarrythmias Prophylactic for heart surgeries Decreased cardiac output and blood pressure May cause PVC s or V. Tach if spikes land on t-wave during relative refractory period May be fixed by increasing the milli-volts (MV)
28 Oversensing Distance from spike to spike is too long, the pacer should have fired sooner Pacemaker should have fired here! Chamber Paced: Ventricular Interpretation: V-Paced with oversensing Bradycardia Third Degree Heart Block Pauses Overdrive of tachyarrythmias Prophylactic for heart surgeries Decreased cardiac output and blood pressure May be fixed by decreasing the milli-volts
29 Practice Strips Ventricular Rhythm: Ventricular Rate: P waves: QRS Interval: Atrial Rhythm: Atrial Rate: PR Interval: Interpretation: Ventricular Rhythm: Atrial Rhythm: Ventricular Rate: P waves: QRS Interval: Atrial Rate: PR Interval: Interpretation:
30 Ventricular Rhythm: Atrial Rhythm: Ventricular Rate: P waves: QRS Interval: Atrial Rate: PR Interval: Interpretation: Ventricular Rhythm: Atrial Rhythm: Ventricular Rate: P waves: QRS Interval: Atrial Rate: PR Interval: Interpretation:
31 Ventricular Rhythm: Atrial Rhythm: Ventricular Rate: P waves: QRS Interval: Atrial Rate: PR Interval: Interpretation: Ventricular Rhythm: Atrial Rhythm: Ventricular Rate: P waves: QRS Interval: Atrial Rate: PR Interval: Interpretation:
32 Ventricular Rhythm: Atrial Rhythm: Ventricular Rate: P waves: QRS Interval: Atrial Rate: PR Interval: Interpretation: Ventricular Rhythm: Atrial Rhythm: Ventricular Rate: P waves: QRS Interval: Atrial Rate: PR Interval: Interpretation:
33 Answers to Practice Strips Strip 1: Ventricular Rhythm: Regular Atrial Rhythm: Regular Ventricular Rate: 42 Atrial Rate: 42 P waves: Upright, Matching, 1:1 PR Interval: 0.16 seconds QRS: 0.12 seconds Interpretation: Sinus Bradycardia with IVCD Strip 2: Ventricular Rhythm: Irregular Atrial Rhythm: NA Ventricular Rate: Atrial Rate: NA P waves: Fibrillatory PR Interval: NA QRS: 0.12 seconds Interpretation: Atrial Fibrillation with IVCD Strip 3: Ventricular Rhythm: Regular Atrial Rhythm: NA Ventricular Rate: Atrial Rate: NA P waves: Inverted after QRS complex PR Interval: NA QRS: 0.06 seconds Interpretation: Junctional Rhythm Strip 4: Ventricular Rhythm: NA Atrial Rhythm: NA Ventricular Rate: NA Atrial Rate: NA P waves: NA PR Interval: NA QRS: NA Interpretation: Ventricular Fibrillation
34 Strip 5: Ventricular Rhythm: Regular Atrial Rhythm: NA Ventricular Rate: Atrial Rate: NA P waves: NA PR Interval: NA QRS: seconds Interpretation: AIVR Strip 6: Ventricular Rhythm: Regular Atrial Rhythm: Regular Ventricular Rate: Atrial Rate: 94 P waves: Upright, Matching PR Interval: 0.36, 0.18, 0.50 seconds QRS: 0.24 seconds Interpretation: Third Degree Heart Block or Complete Heart Block Strip 7: Chamber Paced: Ventricle Paced Rate: 60 Interpretation: Venticular paced rhythm with non capture Strip 8: Chamber Paced: Ventricle Paced Rate: 75 Interpretation: V-Paced with Undersensing
Rhythm ECG Characteristics Example. Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR)
 Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Rate: 60-100 per minute Rhythm: R- R = P waves: Upright, similar P-R: 0.12-0.20 second & consistent P:qRs: 1P:1qRs Sinus Tachycardia Exercise Hypovolemia Medications Fever Substances
Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Rate: 60-100 per minute Rhythm: R- R = P waves: Upright, similar P-R: 0.12-0.20 second & consistent P:qRs: 1P:1qRs Sinus Tachycardia Exercise Hypovolemia Medications Fever Substances
CORONARY ARTERIES. LAD Anterior wall of the left vent Lateral wall of left vent Anterior 2/3 of interventricluar septum R & L bundle branches
 CORONARY ARTERIES RCA Right atrium Right ventricle SA node 55% AV node 90% Posterior wall of left ventricle in 90% Posterior third of interventricular septum 90% LAD Anterior wall of the left vent Lateral
CORONARY ARTERIES RCA Right atrium Right ventricle SA node 55% AV node 90% Posterior wall of left ventricle in 90% Posterior third of interventricular septum 90% LAD Anterior wall of the left vent Lateral
Chapter 03: Sinus Mechanisms Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE
 Instant download and all chapters Tesst Bank ECGs Made Easy 5th Edition Barbara J Aehlert https://testbanklab.com/download/tesst-bank-ecgs-made-easy-5th-edition-barbara-jaehlert/ Chapter 03: Sinus Mechanisms
Instant download and all chapters Tesst Bank ECGs Made Easy 5th Edition Barbara J Aehlert https://testbanklab.com/download/tesst-bank-ecgs-made-easy-5th-edition-barbara-jaehlert/ Chapter 03: Sinus Mechanisms
Arrhythmic Complications of MI. Teferi Mitiku, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California Irvine
 Arrhythmic Complications of MI Teferi Mitiku, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California Irvine Objectives Brief overview -Pathophysiology of Arrhythmia ECG review of typical
Arrhythmic Complications of MI Teferi Mitiku, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California Irvine Objectives Brief overview -Pathophysiology of Arrhythmia ECG review of typical
4/14/15 HTEC 91. Topics for Today. Guess That Rhythm. Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs) Ventricular Rhythms
 4/14/15 Topics for Today HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 5 Ventricular Rhythms PVCs: Premature Ventricular Contractions VT: Ventricular Tachycardia VF: Ventricular Fibrillation Asystole Study
4/14/15 Topics for Today HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 5 Ventricular Rhythms PVCs: Premature Ventricular Contractions VT: Ventricular Tachycardia VF: Ventricular Fibrillation Asystole Study
HTEC 91. Performing ECGs: Procedure. Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Topic for Today: Sinus Rhythms. Characteristics of NSR. Conduction Pathway
 HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 3 Performing ECGs: Procedure o ECG protocol: you may NOT do ECG if you have not signed up! If you are signed up and the room is occupied with people who did
HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 3 Performing ECGs: Procedure o ECG protocol: you may NOT do ECG if you have not signed up! If you are signed up and the room is occupied with people who did
CSI Skills Lab #5: Arrhythmia Interpretation and Treatment
 CSI 202 - Skills Lab #5: Arrhythmia Interpretation and Treatment Origins of the ACLS Approach: CSI 202 - Skills Lab 5 Notes ACLS training originated in Nebraska in the early 1970 s. Its purpose was to
CSI 202 - Skills Lab #5: Arrhythmia Interpretation and Treatment Origins of the ACLS Approach: CSI 202 - Skills Lab 5 Notes ACLS training originated in Nebraska in the early 1970 s. Its purpose was to
The ABCs of EKGs/ECGs for HCPs. Al Heuer, PhD, MBA, RRT, RPFT Professor, Rutgers School of Health Related Professions
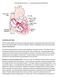
 The ABCs of EKGs/ECGs for HCPs Al Heuer, PhD, MBA, RRT, RPFT Professor, Rutgers School of Health Related Professions Learning Objectives Review the basic anatomy of the heart Describe the cardiac conducting
The ABCs of EKGs/ECGs for HCPs Al Heuer, PhD, MBA, RRT, RPFT Professor, Rutgers School of Health Related Professions Learning Objectives Review the basic anatomy of the heart Describe the cardiac conducting
2) Heart Arrhythmias 2 - Dr. Abdullah Sharif
 2) Heart Arrhythmias 2 - Dr. Abdullah Sharif Rhythms from the Sinus Node Sinus Tachycardia: HR > 100 b/m Causes: o Withdrawal of vagal tone & Sympathetic stimulation (exercise, fight or flight) o Fever
2) Heart Arrhythmias 2 - Dr. Abdullah Sharif Rhythms from the Sinus Node Sinus Tachycardia: HR > 100 b/m Causes: o Withdrawal of vagal tone & Sympathetic stimulation (exercise, fight or flight) o Fever
Chapter 9. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives 9/11/2012. Cardiac Arrhythmias. Define electrical therapy
 Chapter 9 Cardiac Arrhythmias Learning Objectives Define electrical therapy Explain why electrical therapy is preferred initial therapy over drug administration for cardiac arrest and some arrhythmias
Chapter 9 Cardiac Arrhythmias Learning Objectives Define electrical therapy Explain why electrical therapy is preferred initial therapy over drug administration for cardiac arrest and some arrhythmias
Step by step approach to EKG rhythm interpretation:
 Sinus Rhythms Normal sinus arrhythmia Small, slow variation of the R-R interval i.e. variation of the normal sinus heart rate with respiration, etc. Sinus Tachycardia Defined as sinus rhythm with a rate
Sinus Rhythms Normal sinus arrhythmia Small, slow variation of the R-R interval i.e. variation of the normal sinus heart rate with respiration, etc. Sinus Tachycardia Defined as sinus rhythm with a rate
EKG Competency for Agency
 EKG Competency for Agency Name: Date: Agency: 1. The upper chambers of the heart are known as the: a. Atria b. Ventricles c. Mitral Valve d. Aortic Valve 2. The lower chambers of the heart are known as
EKG Competency for Agency Name: Date: Agency: 1. The upper chambers of the heart are known as the: a. Atria b. Ventricles c. Mitral Valve d. Aortic Valve 2. The lower chambers of the heart are known as
MAT vs AFIB. Henry Clemo. Fast & Easy ECGs, 2E 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 MAT vs AFIB Henry Clemo 1 Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia (MAT) > 3 P wave morphologies HR > 100 HR < 100 wandering pacemaker I 2 Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia 3 Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia 4 Multifocal
MAT vs AFIB Henry Clemo 1 Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia (MAT) > 3 P wave morphologies HR > 100 HR < 100 wandering pacemaker I 2 Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia 3 Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia 4 Multifocal
EKG Rhythm Interpretation Exam
 as EKG Rhythm Interpretation Exam Name: Date: ID# Unit Assume each strip is a 6 second strip. Passing is 80%. 1. Identify the following rhythm: a. Asystole b. Ventricular fibrillation c. Atrial fibrillation
as EKG Rhythm Interpretation Exam Name: Date: ID# Unit Assume each strip is a 6 second strip. Passing is 80%. 1. Identify the following rhythm: a. Asystole b. Ventricular fibrillation c. Atrial fibrillation
Northwest Community Healthcare Paramedic Education Program AV Conduction Defects/AV Blocks Connie J. Mattera, M.S., R.N., EMT-P
 Northwest Community Healthcare Paramedic Education Program AV Conduction Defects/ Connie J. Mattera, M.S., R.N., EMT-P Reading assignments: Bledsoe Vol. 3: pp. 88-93; 120-121 (atropine, norepinephrine,
Northwest Community Healthcare Paramedic Education Program AV Conduction Defects/ Connie J. Mattera, M.S., R.N., EMT-P Reading assignments: Bledsoe Vol. 3: pp. 88-93; 120-121 (atropine, norepinephrine,
1. Normal sinus rhythm 2. SINUS BRADYCARDIA
 1. Normal sinus rhythm 2. SINUS BRADYCARDIA No signs and symptoms observe There are severe signs or symptoms o What are the signs and symptom Hypotension
1. Normal sinus rhythm 2. SINUS BRADYCARDIA No signs and symptoms observe There are severe signs or symptoms o What are the signs and symptom Hypotension
Cardiac Arrhythmia How to approach นพ.พ น จ แกวส วรรณะ หน วยโรคห วใจและหลอดเล อด
 Cardiac Arrhythmia How to approach นพ.พ น จ แกวส วรรณะ หน วยโรคห วใจและหลอดเล อด EKG paper is a grid where time is measured along the horizontal axis. Each small square is 1 mm in length and represents
Cardiac Arrhythmia How to approach นพ.พ น จ แกวส วรรณะ หน วยโรคห วใจและหลอดเล อด EKG paper is a grid where time is measured along the horizontal axis. Each small square is 1 mm in length and represents
ACLS Study Guide for Precourse Self-Assessment
 20 rhythm strips on Precourse Self-Assessment with the following matching choices: Agonal Rhythm/Asystole Atrial Fibrillation Flutter Ventricular Fibrillation Monomorphic Ventricular Normal Sinus Rhythm
20 rhythm strips on Precourse Self-Assessment with the following matching choices: Agonal Rhythm/Asystole Atrial Fibrillation Flutter Ventricular Fibrillation Monomorphic Ventricular Normal Sinus Rhythm
-RHYTHM PRACTICE- By Dr.moanes Msc.cardiology Assistant Lecturer of Cardiology Al Azhar University. OBHG Education Subcommittee
 -RHYTHM PRACTICE- By Dr.moanes Msc.cardiology Assistant Lecturer of Cardiology Al Azhar University The Normal Conduction System Sinus Node Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Sinus Bradycardia Sinus Tachycardia
-RHYTHM PRACTICE- By Dr.moanes Msc.cardiology Assistant Lecturer of Cardiology Al Azhar University The Normal Conduction System Sinus Node Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Sinus Bradycardia Sinus Tachycardia
UNDERSTANDING YOUR ECG: A REVIEW
 UNDERSTANDING YOUR ECG: A REVIEW Health professionals use the electrocardiograph (ECG) rhythm strip to systematically analyse the cardiac rhythm. Before the systematic process of ECG analysis is described
UNDERSTANDING YOUR ECG: A REVIEW Health professionals use the electrocardiograph (ECG) rhythm strip to systematically analyse the cardiac rhythm. Before the systematic process of ECG analysis is described
DYSRHYTHMIAS. D. Assess whether or not it is the arrhythmia that is making the patient unstable or symptomatic
 DYSRHYTHMIAS GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS A. The 2015 American Heart Association Guidelines were referred to for this protocol development. Evidence-based science was implemented in those areas where the AHA
DYSRHYTHMIAS GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS A. The 2015 American Heart Association Guidelines were referred to for this protocol development. Evidence-based science was implemented in those areas where the AHA
Course Objectives. Proper Lead Placements. Review the ECG print paper. Review the mechanics of the Myocardium. Review basics of ECG Rhythms
 ECG Interpretations Course Objectives Proper Lead Placements Review the ECG print paper Review the mechanics of the Myocardium Review basics of ECG Rhythms How Leads Work The ECG Leads we use are Bipolar
ECG Interpretations Course Objectives Proper Lead Placements Review the ECG print paper Review the mechanics of the Myocardium Review basics of ECG Rhythms How Leads Work The ECG Leads we use are Bipolar
Anti arrhythmic drugs. Hilal Al Saffar College of medicine Baghdad University
 Anti arrhythmic drugs Hilal Al Saffar College of medicine Baghdad University Mechanism of Arrhythmia Abnormal heart pulse formation Abnormal heart pulse conduction Classification of Arrhythmia Abnormal
Anti arrhythmic drugs Hilal Al Saffar College of medicine Baghdad University Mechanism of Arrhythmia Abnormal heart pulse formation Abnormal heart pulse conduction Classification of Arrhythmia Abnormal
McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Optional CE for EMT-B, Paramedics and PHRN s Bradycardia and Treatments Optional #7 2018
 McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Optional CE for EMT-B, Paramedics and PHRN s Bradycardia and Treatments Optional #7 2018 This month we will be looking at a specific ECG Rhythm and its treatments
McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Optional CE for EMT-B, Paramedics and PHRN s Bradycardia and Treatments Optional #7 2018 This month we will be looking at a specific ECG Rhythm and its treatments
Arrhythmia Study Guide 3 Junctional and Ventricular Rhythms
 Arrhythmia Study Guide 3 Junctional and Ventricular Rhythms JUNCTIONAL RHYTHMS The AV Junction (Bundle of His and surrounding cells) only acts as pacemaker of the heart when the SA Node is not firing normally
Arrhythmia Study Guide 3 Junctional and Ventricular Rhythms JUNCTIONAL RHYTHMS The AV Junction (Bundle of His and surrounding cells) only acts as pacemaker of the heart when the SA Node is not firing normally
The ECG Course. Boone County Fire Protection District EMS Education
 The ECG Course Level I G rated material AV Blocks What Causes AV Block? Long list of bad things that includes ischemia and.. Old age / disease Medications or drugs Electrolyte imbalances Physiologic Blocks
The ECG Course Level I G rated material AV Blocks What Causes AV Block? Long list of bad things that includes ischemia and.. Old age / disease Medications or drugs Electrolyte imbalances Physiologic Blocks
Rate: The atrial and ventricular rates are equal; heart rate is greater than 100 bpm (usually between bpm).
 Sinus Bradycardia Regularity: The R-R intervals are constant; the rhythm is regular. Rate: The atrial and ventricular rates are equal; heart rate is less than 60 bpm. P wave: There is a uniform P wave
Sinus Bradycardia Regularity: The R-R intervals are constant; the rhythm is regular. Rate: The atrial and ventricular rates are equal; heart rate is less than 60 bpm. P wave: There is a uniform P wave
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals
 Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Chapter 7: Junctional Dysrhythmias 2012 The Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Learning Outcomes 7.1 Describe the various junctional dysrhythmias 7.2
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Chapter 7: Junctional Dysrhythmias 2012 The Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Learning Outcomes 7.1 Describe the various junctional dysrhythmias 7.2
8/20/2012. Learning Outcomes (Cont d)
 1 2 3 4 Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Chapter 7: Junctional Dysrhythmias Learning Outcomes 7.1 Describe the various junctional dysrhythmias 7.2 Identify premature junctional complexes
1 2 3 4 Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Chapter 7: Junctional Dysrhythmias Learning Outcomes 7.1 Describe the various junctional dysrhythmias 7.2 Identify premature junctional complexes
Cardiac arrhythmias. Janusz Witowski. Department of Pathophysiology Poznan University of Medical Sciences. J. Witowski
 Cardiac arrhythmias Janusz Witowski Department of Pathophysiology Poznan University of Medical Sciences A 68-year old man presents to the emergency department late one evening complaining of increasing
Cardiac arrhythmias Janusz Witowski Department of Pathophysiology Poznan University of Medical Sciences A 68-year old man presents to the emergency department late one evening complaining of increasing
TEST BANK FOR ECGS MADE EASY 5TH EDITION BY AEHLERT
 Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-ecgs-made-easy-5thedition-by-aehlert/ TEST BANK FOR ECGS MADE EASY 5TH EDITION BY AEHLERT Chapter 5 TRUE/FALSE 1. The AV junction consists
Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-ecgs-made-easy-5thedition-by-aehlert/ TEST BANK FOR ECGS MADE EASY 5TH EDITION BY AEHLERT Chapter 5 TRUE/FALSE 1. The AV junction consists
ECG Interpretation. Introduction to Cardiac Telemetry. Michael Peters, RN, CCRN, CFRN CALSTAR Air Medical Services
 ECG Interpretation Introduction to Cardiac Telemetry Michael Peters, RN, CCRN, CFRN CALSTAR Air Medical Services Disclosures Nothing to disclose Objectives Describe the electrical conduction pathway in
ECG Interpretation Introduction to Cardiac Telemetry Michael Peters, RN, CCRN, CFRN CALSTAR Air Medical Services Disclosures Nothing to disclose Objectives Describe the electrical conduction pathway in
2017 BDKA Review. Regularity Rate P waves PRI QRS Interpretation. Regularity Rate P waves PRI QRS Interpretation 1/1/2017
 1. 2017 BDKA Review 2. 3. 4. Interpretation 5. QT 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. QT 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. QT 19. 20. QT 21. 22. QT 23. 24. Where are pacer spikes? Before the P wave or before the QRS complex?
1. 2017 BDKA Review 2. 3. 4. Interpretation 5. QT 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. QT 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. QT 19. 20. QT 21. 22. QT 23. 24. Where are pacer spikes? Before the P wave or before the QRS complex?
COURSE DESCRIPTION. Rev 2.0 7/2013. Page 1 of 26
 COURSE DESCRIPTION Ventricular dysrhythmias (arrhythmias) are unique and potentially dangerous cardiac rhythms. They are often associated with Code Blue calls, and life and death situations. The only two
COURSE DESCRIPTION Ventricular dysrhythmias (arrhythmias) are unique and potentially dangerous cardiac rhythms. They are often associated with Code Blue calls, and life and death situations. The only two
Objectives: This presentation will help you to:
 emergency Drugs Objectives: This presentation will help you to: Five rights for medication administration Recognize different cardiac arrhythmias and determine the common drugs used for each one List the
emergency Drugs Objectives: This presentation will help you to: Five rights for medication administration Recognize different cardiac arrhythmias and determine the common drugs used for each one List the
PEDIATRIC CARDIAC RHYTHM DISTURBANCES. -Jason Haag, CCEMT-P
 PEDIATRIC CARDIAC RHYTHM DISTURBANCES -Jason Haag, CCEMT-P General: CARDIAC RHYTHM DISTURBANCES - More often the result and not the cause of acute cardiovascular emergencies - Typically the end result
PEDIATRIC CARDIAC RHYTHM DISTURBANCES -Jason Haag, CCEMT-P General: CARDIAC RHYTHM DISTURBANCES - More often the result and not the cause of acute cardiovascular emergencies - Typically the end result
Building Blocks: Deciphering Heart Blocks Visions Symposium AACN 2015
 1 Building Blocks: Deciphering Heart Blocks Visions Symposium AACN 2015 Greta Price MSN-Ed, RN-BC, PCCN Objectives Upon completion of this program, the participate will be able to: Describe the common
1 Building Blocks: Deciphering Heart Blocks Visions Symposium AACN 2015 Greta Price MSN-Ed, RN-BC, PCCN Objectives Upon completion of this program, the participate will be able to: Describe the common
Figure 2. Normal ECG tracing. Table 1.
 Figure 2. Normal ECG tracing that navigates through the left ventricle. Following these bundle branches the impulse finally passes to the terminal points called Purkinje fibers. These Purkinje fibers are
Figure 2. Normal ECG tracing that navigates through the left ventricle. Following these bundle branches the impulse finally passes to the terminal points called Purkinje fibers. These Purkinje fibers are
5AB Dysrhythmia Interpretation tation and Management Review Please complete and return by:
 1 5AB Dysrhythmia Interpretation tation and Management Review 2014 RN Please complete and return by: Overview 2 This review begins with a discussion of the physiology of cardiac conduction, and then covers
1 5AB Dysrhythmia Interpretation tation and Management Review 2014 RN Please complete and return by: Overview 2 This review begins with a discussion of the physiology of cardiac conduction, and then covers
CRC 431 ECG Basics. Bill Pruitt, MBA, RRT, CPFT, AE-C
 CRC 431 ECG Basics Bill Pruitt, MBA, RRT, CPFT, AE-C Resources White s 5 th ed. Ch 6 Electrocardiography Einthoven s Triangle Chest leads and limb leads Egan s 10 th ed. Ch 17 Interpreting the Electrocardiogram
CRC 431 ECG Basics Bill Pruitt, MBA, RRT, CPFT, AE-C Resources White s 5 th ed. Ch 6 Electrocardiography Einthoven s Triangle Chest leads and limb leads Egan s 10 th ed. Ch 17 Interpreting the Electrocardiogram
ABCs of ECGs. Shelby L. Durler
 ABCs of ECGs Shelby L. Durler Objectives Review the A&P of the cardiac conduction system Placement and obtaining 4-lead and 12-lead ECGs Overview of the basics of ECG rhythm interpretation Intrinsic
ABCs of ECGs Shelby L. Durler Objectives Review the A&P of the cardiac conduction system Placement and obtaining 4-lead and 12-lead ECGs Overview of the basics of ECG rhythm interpretation Intrinsic
1 Cardiology Acute Care Day 22 April 2013 Arrhythmia Tutorial Course Material
 1 Cardiology Acute Care Day 22 April 2013 Arrhythmia Tutorial Course Material Arrhythmia recognition This tutorial builds on the ECG lecture and provides a framework for approaching any ECG to allow the
1 Cardiology Acute Care Day 22 April 2013 Arrhythmia Tutorial Course Material Arrhythmia recognition This tutorial builds on the ECG lecture and provides a framework for approaching any ECG to allow the
COUNTY OF SACRAMENTO EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY
 COUNTY OF SACRAMENTO EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY Document # 8024.31 PROGRAM DOCUMENT: Initial Date: 10/26/94 Cardiac Dysrhythmias Last Approval Date: 11/01/16 Effective Date: 11/01/18 Next Review
COUNTY OF SACRAMENTO EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY Document # 8024.31 PROGRAM DOCUMENT: Initial Date: 10/26/94 Cardiac Dysrhythmias Last Approval Date: 11/01/16 Effective Date: 11/01/18 Next Review
Basic Dysrhythmia Interpretation
 Basic Dysrhythmia Interpretation Objectives 2 To understand the Basic ECG To understand the meaning of Dysrhythmia To describe the normal heart conduction system. To describe the normal impulse pathways.
Basic Dysrhythmia Interpretation Objectives 2 To understand the Basic ECG To understand the meaning of Dysrhythmia To describe the normal heart conduction system. To describe the normal impulse pathways.
BEDSIDE ECG INTERPRETATION
 BEDSIDE ECG INTERPRETATION Presented by: Ryan Dean, RN, MSN, CCRN, CCNS, CFRN Flight Nurse 2017 Based on presentations originally by Gennifer DePaoli, RN Objectives Hospital policies Electrical conduction
BEDSIDE ECG INTERPRETATION Presented by: Ryan Dean, RN, MSN, CCRN, CCNS, CFRN Flight Nurse 2017 Based on presentations originally by Gennifer DePaoli, RN Objectives Hospital policies Electrical conduction
ACLS Prep. Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience. Please complete the ACLS Pretest and Please complete this ACLS Prep.
 November, 2013 ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience. Please complete the ACLS Pretest and Please complete this ACLS Prep. ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience.
November, 2013 ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience. Please complete the ACLS Pretest and Please complete this ACLS Prep. ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience.
Dysrhythmias that every Learn how to recognize an abnormal cardiac rhythm and intervene appropriately. By AnneMarie Palatnik, RN, APN-BC, MSN
 Too fast, too slow, too ugly: Dysrhythmias that every Learn how to recognize an abnormal cardiac rhythm and intervene appropriately. By AnneMarie Palatnik, RN, APN-BC, MSN 2.5 ANCC CONTACT HOURS CONTINUOUS
Too fast, too slow, too ugly: Dysrhythmias that every Learn how to recognize an abnormal cardiac rhythm and intervene appropriately. By AnneMarie Palatnik, RN, APN-BC, MSN 2.5 ANCC CONTACT HOURS CONTINUOUS
Atrial fibrillation in the ICU
 Atrial fibrillation in the ICU Atrial fibrillation Preexisting or incident (new onset) among nearly one in three critically ill patients Formation of arrhythogenic substrate usually fibrosis (CHF, hypertension,
Atrial fibrillation in the ICU Atrial fibrillation Preexisting or incident (new onset) among nearly one in three critically ill patients Formation of arrhythogenic substrate usually fibrosis (CHF, hypertension,
Chapter 28, Part 1 Cardiology. Cardiac Physiology. Cardiovascular Anatomy
 Chapter 28, Part 1 Cardiology Part 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy & Physiology, ECG Monitoring, and Dysrhythmia Analysis 1 2 Cardiovascular Anatomy Coronary Circulation Cardiac Physiology The cardiac cycle
Chapter 28, Part 1 Cardiology Part 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy & Physiology, ECG Monitoring, and Dysrhythmia Analysis 1 2 Cardiovascular Anatomy Coronary Circulation Cardiac Physiology The cardiac cycle
ECGs and Arrhythmias: Family Medicine Board Review 2009
 Rate Rhythm Intervals Hypertrophy ECGs and Arrhythmias: Family Medicine Board Review 2009 Axis Jess (Fogler) Waldura, MD University of California, San Francisco walduraj@nccc.ucsf.edu Ischemia Overview
Rate Rhythm Intervals Hypertrophy ECGs and Arrhythmias: Family Medicine Board Review 2009 Axis Jess (Fogler) Waldura, MD University of California, San Francisco walduraj@nccc.ucsf.edu Ischemia Overview
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals
 Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Kathryn A. Booth Thomas O Brien Chapter 5: Rhythm Strip Interpretation and Sinus Rhythms Learning Outcomes 5.1 Explain the process of evaluating ECG tracings
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Kathryn A. Booth Thomas O Brien Chapter 5: Rhythm Strip Interpretation and Sinus Rhythms Learning Outcomes 5.1 Explain the process of evaluating ECG tracings
The most common. hospitalized patients. hypotension due to. filling time Rate control in ICU patients may be difficult as many drugs cause hypotension
 Arrhythmias in the critically ill ICU patients: Approach for rapid recognition & management Objectives Be able to identify and manage: Atrial fibrillation with a rapid ventricular response Atrial flutter
Arrhythmias in the critically ill ICU patients: Approach for rapid recognition & management Objectives Be able to identify and manage: Atrial fibrillation with a rapid ventricular response Atrial flutter
Arrhythmias. Sarah B. Murthi Department of Surgery University of Maryland Medical School R. Adams Cowley Shock Trauma Center
 Arrhythmias Sarah B. Murthi Department of Surgery University of Maryland Medical School R. Adams Cowley Shock Trauma Center 2012 Clinical Congress Presenter Disclosure Slide American College of Surgeons
Arrhythmias Sarah B. Murthi Department of Surgery University of Maryland Medical School R. Adams Cowley Shock Trauma Center 2012 Clinical Congress Presenter Disclosure Slide American College of Surgeons
Practical Approach to Arrhythmias
 Outline Practical Approach to Arrhythmias Julia Shih, VMD, DACVIM (Cardiology) October 27, 2018 Conduction System ECG Acquisition ECG Interpretation Heart rate Rhythm Arrhythmias Tachyarrhythmias Supraventricular
Outline Practical Approach to Arrhythmias Julia Shih, VMD, DACVIM (Cardiology) October 27, 2018 Conduction System ECG Acquisition ECG Interpretation Heart rate Rhythm Arrhythmias Tachyarrhythmias Supraventricular
Contents ECG Study Guide American Heart Association (AHA) Guidelines Highlights Update for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) and
 ECG Study Guide Contents ECG Study Guide... 4 2015 American Heart Association (AHA) Guidelines Highlights Update for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) and Emergency Cardiovascular Care (ECC).... 4 ECG
ECG Study Guide Contents ECG Study Guide... 4 2015 American Heart Association (AHA) Guidelines Highlights Update for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) and Emergency Cardiovascular Care (ECC).... 4 ECG
Junctional Premature Contraction (JPC)
 Where s the PAC? Junctional Premature Contraction (JPC) A junctional premature contraction (JPC) is a beat that originates prematurely in the AV node. It can occur sporadically or in a grouped pattern.
Where s the PAC? Junctional Premature Contraction (JPC) A junctional premature contraction (JPC) is a beat that originates prematurely in the AV node. It can occur sporadically or in a grouped pattern.
Pediatrics. Arrhythmias in Children: Bradycardia and Tachycardia Diagnosis and Treatment. Overview
 Pediatrics Arrhythmias in Children: Bradycardia and Tachycardia Diagnosis and Treatment See online here The most common form of cardiac arrhythmia in children is sinus tachycardia which can be caused by
Pediatrics Arrhythmias in Children: Bradycardia and Tachycardia Diagnosis and Treatment See online here The most common form of cardiac arrhythmia in children is sinus tachycardia which can be caused by
Chad Morsch B.S., ACSM CEP
 What Is Cardiac Stress Testing? Chad Morsch B.S., ACSM CEP A Cardiac Stress Test is a test used to measure the heart's ability to respond to external stress in a controlled clinical environment. Cardiac
What Is Cardiac Stress Testing? Chad Morsch B.S., ACSM CEP A Cardiac Stress Test is a test used to measure the heart's ability to respond to external stress in a controlled clinical environment. Cardiac
Dysrhythmias. Dysrythmias & Anti-Dysrhythmics. EKG Parameters. Dysrhythmias. Components of an ECG Wave. Dysrhythmias
 Dysrhythmias Dysrythmias & Anti-Dysrhythmics Rhythm bad in the heart: Whitewater rafting Electrical impulses coordinate heart Reduction in Cardiac Output PEA Asystole Components of an ECG Wave EKG Parameters
Dysrhythmias Dysrythmias & Anti-Dysrhythmics Rhythm bad in the heart: Whitewater rafting Electrical impulses coordinate heart Reduction in Cardiac Output PEA Asystole Components of an ECG Wave EKG Parameters
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals
 Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Chapter 9: Ventricular Dysrhythmias 2012 The Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Learning Outcomes 9.1 Describe the various ventricular dysrhythmias 9.2
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Chapter 9: Ventricular Dysrhythmias 2012 The Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Learning Outcomes 9.1 Describe the various ventricular dysrhythmias 9.2
Dysrhythmias Chapter
 Dysrhythmias Chapter 36 1.5.17 Copyright 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. Copyright 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. Properties of Cardiac Cells Automaticity Excitability Conductivity
Dysrhythmias Chapter 36 1.5.17 Copyright 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. Copyright 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. Properties of Cardiac Cells Automaticity Excitability Conductivity
Cardiac Arrhythmias. Cathy Percival, RN, FALU, FLMI VP, Medical Director AIG Life and Retirement Company
 Cardiac Arrhythmias Cathy Percival, RN, FALU, FLMI VP, Medical Director AIG Life and Retirement Company The Cardiovascular System Three primary functions Transport of oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to
Cardiac Arrhythmias Cathy Percival, RN, FALU, FLMI VP, Medical Director AIG Life and Retirement Company The Cardiovascular System Three primary functions Transport of oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to
Presented By: Barbara Furry, RN-BC, MS, CCRN, FAHA Director The Center of Excellence in Education Director of HERO
 Presented By: Barbara Furry, RN-BC, MS, CCRN, FAHA Director The Center of Excellence in Education Director of HERO Follow me on Twitter! CEE Med Updates@BarbaraFurryRN Like me on Facebook! What is a
Presented By: Barbara Furry, RN-BC, MS, CCRN, FAHA Director The Center of Excellence in Education Director of HERO Follow me on Twitter! CEE Med Updates@BarbaraFurryRN Like me on Facebook! What is a
MICHIGAN. State Protocols. Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.
 MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.3 Tachycardia PEDIATRIC CARDIAC PEDIATRIC CARDIAC ARREST
MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.3 Tachycardia PEDIATRIC CARDIAC PEDIATRIC CARDIAC ARREST
Cardiology Flash Cards
 Cardiology Flash Cards EKG in a nut shell www.brain101.info Conduction System www.brain101.info 2 Analyzing EKG Step by step Steps in Analyzing ECG'S 1. Rhythm: - Regular _ Sinus, Junctional or Ventricular.
Cardiology Flash Cards EKG in a nut shell www.brain101.info Conduction System www.brain101.info 2 Analyzing EKG Step by step Steps in Analyzing ECG'S 1. Rhythm: - Regular _ Sinus, Junctional or Ventricular.
ACLS Review. Pulse Oximetry to be between 94 99% to avoid hyperoxia (high oxygen tension can lead to tissue death
 ACLS Review BLS CPR BLS CPR changed in 2010. The primary change is from the ABC format to CAB. After establishing unresponsiveness and calling for a code, check for a pulse less than 10 seconds then begin
ACLS Review BLS CPR BLS CPR changed in 2010. The primary change is from the ABC format to CAB. After establishing unresponsiveness and calling for a code, check for a pulse less than 10 seconds then begin
ARRHYTHMIAS IN THE ICU
 ARRHYTHMIAS IN THE ICU Nora Goldschlager, MD MACP, FACC, FAHA, FHRS SFGH Division of Cardiology UCSF IDENTIFIED VARIABLES IN ARRHYTHMOGENESIS Ischemia/infarction (scar) Electrolyte imbalance Proarrhythmia
ARRHYTHMIAS IN THE ICU Nora Goldschlager, MD MACP, FACC, FAHA, FHRS SFGH Division of Cardiology UCSF IDENTIFIED VARIABLES IN ARRHYTHMOGENESIS Ischemia/infarction (scar) Electrolyte imbalance Proarrhythmia
ECG S: A CASE-BASED APPROACH December 6,
 ECG S: A CASE-BASED APPROACH December 6, 2018 1 Faculty Disclosure Faculty: Lorne Gula MD, FRCPC Professor, Western University Cardiologist, Hearth Rhythm Specialist Director, Electrophysiology Laboratory,
ECG S: A CASE-BASED APPROACH December 6, 2018 1 Faculty Disclosure Faculty: Lorne Gula MD, FRCPC Professor, Western University Cardiologist, Hearth Rhythm Specialist Director, Electrophysiology Laboratory,
Dysrhythmias 11/7/2017. Disclosures. 3 reasons to evaluate and treat dysrhythmias. None. Eliminate symptoms and improve hemodynamics
 Dysrhythmias CYDNEY STEWART MD, FACC NOVEMBER 3, 2017 Disclosures None 3 reasons to evaluate and treat dysrhythmias Eliminate symptoms and improve hemodynamics Prevent imminent death/hemodynamic compromise
Dysrhythmias CYDNEY STEWART MD, FACC NOVEMBER 3, 2017 Disclosures None 3 reasons to evaluate and treat dysrhythmias Eliminate symptoms and improve hemodynamics Prevent imminent death/hemodynamic compromise
EKG Abnormalities. Adapted from:
 EKG Abnormalities Adapted from: http://www.bem.fi/book/19/19.htm Some key terms: Arrhythmia-an abnormal rhythm or sequence of events in the EKG Flutter-rapid depolarizations (and therefore contractions)
EKG Abnormalities Adapted from: http://www.bem.fi/book/19/19.htm Some key terms: Arrhythmia-an abnormal rhythm or sequence of events in the EKG Flutter-rapid depolarizations (and therefore contractions)
ECG Interpretation Cat Williams, DVM DACVIM (Cardiology)
 ECG Interpretation Cat Williams, DVM DACVIM (Cardiology) Providing the best quality care and service for the patient, the client, and the referring veterinarian. GOAL: Reduce Anxiety about ECGs Back to
ECG Interpretation Cat Williams, DVM DACVIM (Cardiology) Providing the best quality care and service for the patient, the client, and the referring veterinarian. GOAL: Reduce Anxiety about ECGs Back to
ECG ABNORMALITIES D R. T AM A R A AL Q U D AH
 ECG ABNORMALITIES D R. T AM A R A AL Q U D AH When we interpret an ECG we compare it instantaneously with the normal ECG and normal variants stored in our memory; these memories are stored visually in
ECG ABNORMALITIES D R. T AM A R A AL Q U D AH When we interpret an ECG we compare it instantaneously with the normal ECG and normal variants stored in our memory; these memories are stored visually in
WHAT DO YOU SEE WHEN YOU STIMULATE BETA
 CARDIAC DRUG REVIEW WHAT DO YOU SEE WHEN YOU STIMULATE BETA VASODILATE BRONCHODILATE +CHRONOTROPE +INOTROPE EPI S OTHER NAME? ADRENALIN WHAT DOES EPI DO THAT NOREPI AND DOPAMINE DO NOT DO? BETA 2 BRONCHODILATOR
CARDIAC DRUG REVIEW WHAT DO YOU SEE WHEN YOU STIMULATE BETA VASODILATE BRONCHODILATE +CHRONOTROPE +INOTROPE EPI S OTHER NAME? ADRENALIN WHAT DOES EPI DO THAT NOREPI AND DOPAMINE DO NOT DO? BETA 2 BRONCHODILATOR
physiology 6 Mohammed Jaafer Turquoise team
 15 physiology 6 Mohammed Jaafer 22-3-2016 Turquoise team Cardiac Arrhythmias and Their Electrocardiographic Interpretation Today, we are going to talk about the abnormal excitation. As we said before,
15 physiology 6 Mohammed Jaafer 22-3-2016 Turquoise team Cardiac Arrhythmias and Their Electrocardiographic Interpretation Today, we are going to talk about the abnormal excitation. As we said before,
RN-BC, MS, CCRN, FAHA
 Presented By: Barbara Furry, RN-BC, MS, CCRN, FAHA Director The Center of Excellence in Education Director of HERO Follow me on Twitter! CEE Med Updates@BarbaraFurryRN Like me on Facebook! 1 A. Atropine
Presented By: Barbara Furry, RN-BC, MS, CCRN, FAHA Director The Center of Excellence in Education Director of HERO Follow me on Twitter! CEE Med Updates@BarbaraFurryRN Like me on Facebook! 1 A. Atropine
3. AV Block 1. First-degree AV block 1. Delay in AV node 2. Long PR interval 3. QRS complex follows each P wave 4. Benign, no tx
 1. Rhythms & arrhythmias SA nodal rhythms Sinus rhythm Sinus tachycardia Sinus bradycardia Sinus arrhythmia Sick sinus syndrome SA block Sinus arrest AV blocks First-degree Second-degree Mobitz Type I
1. Rhythms & arrhythmias SA nodal rhythms Sinus rhythm Sinus tachycardia Sinus bradycardia Sinus arrhythmia Sick sinus syndrome SA block Sinus arrest AV blocks First-degree Second-degree Mobitz Type I
ARRHYTHMIAS IN THE ICU: DIAGNOSIS AND PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT
 ARRHYTHMIAS IN THE ICU: DIAGNOSIS AND PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT Nora Goldschlager, M.D. MACP, FACC, FAHA, FHRS SFGH Division of Cardiogy UCSF CLINICAL VARIABLES IN ARRHYTHMOGENESIS Ischemia/infarction (scar)
ARRHYTHMIAS IN THE ICU: DIAGNOSIS AND PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT Nora Goldschlager, M.D. MACP, FACC, FAHA, FHRS SFGH Division of Cardiogy UCSF CLINICAL VARIABLES IN ARRHYTHMOGENESIS Ischemia/infarction (scar)
Rhythm Control: Is There a Role for the PCP? Blake Norris, MD, FACC BHHI Primary Care Symposium February 28, 2014
 Rhythm Control: Is There a Role for the PCP? Blake Norris, MD, FACC BHHI Primary Care Symposium February 28, 2014 Financial disclosures Consultant Medtronic 3 reasons to evaluate and treat arrhythmias
Rhythm Control: Is There a Role for the PCP? Blake Norris, MD, FACC BHHI Primary Care Symposium February 28, 2014 Financial disclosures Consultant Medtronic 3 reasons to evaluate and treat arrhythmias
EKG Intermediate Tips, tricks, tools
 Birmingham Regional Emergency Medical Services System 2018 ALCTE Summer Conference EKG Intermediate Tips, tricks, tools Brian Gober, MAT, ATC, NRP, CSCS Education Services Manager ECC Training Center Coordinator
Birmingham Regional Emergency Medical Services System 2018 ALCTE Summer Conference EKG Intermediate Tips, tricks, tools Brian Gober, MAT, ATC, NRP, CSCS Education Services Manager ECC Training Center Coordinator
national CPR committee Saudi Heart Association (SHA). International Liason Commission Of Resuscitation (ILCOR)
 2 It is our pleasure to present to you this work as a result of team work of the national CPR committee at the Saudi Heart Association (SHA). We adapted the 2010 guidelines as per International Liason
2 It is our pleasure to present to you this work as a result of team work of the national CPR committee at the Saudi Heart Association (SHA). We adapted the 2010 guidelines as per International Liason
Intraoperative and Postoperative Arrhythmias: Diagnosis and Treatment
 Intraoperative and Postoperative Arrhythmias: Diagnosis and Treatment Karen L. Booth, MD, Lucile Packard Children s Hospital Arrhythmias are common after congenital heart surgery [1]. Postoperative electrolyte
Intraoperative and Postoperative Arrhythmias: Diagnosis and Treatment Karen L. Booth, MD, Lucile Packard Children s Hospital Arrhythmias are common after congenital heart surgery [1]. Postoperative electrolyte
Staff. Printed in China. ECGMIQ ISBN-13: ISBN-10:
 Staff Executive Publisher Judith A. Schilling McCann, RN, MSN Clinical Director Joan M. Robinson, RN, MSN Art Director Elaine Kasmer Editors Margaret Eckman, Diane Labus Illustrator Bot Roda Design Assistant
Staff Executive Publisher Judith A. Schilling McCann, RN, MSN Clinical Director Joan M. Robinson, RN, MSN Art Director Elaine Kasmer Editors Margaret Eckman, Diane Labus Illustrator Bot Roda Design Assistant
Please check your answers with correct statements in answer pages after the ECG cases.
 ECG Cases ECG Case 1 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature 2018 S. Okutucu, A. Oto, Interpreting ECGs in Clinical Practice, In Clinical Practice, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-90557-0
ECG Cases ECG Case 1 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature 2018 S. Okutucu, A. Oto, Interpreting ECGs in Clinical Practice, In Clinical Practice, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-90557-0
Cardiovascular Disorders. Heart Disorders. Diagnostic Tests for CV Function. Bio 375. Pathophysiology
 Cardiovascular Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology Heart Disorders Heart disease is ranked as a major cause of death in the U.S. Common heart diseases include: Congenital heart defects Hypertensive heart
Cardiovascular Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology Heart Disorders Heart disease is ranked as a major cause of death in the U.S. Common heart diseases include: Congenital heart defects Hypertensive heart
MEDICATIONS CARDIOVASCULAR URGENCIES & EMERGENCIES 12/29/14. Cardiovascular Emergency Medications. Cardiovascular Emergency Medications
 CARDIOVASCULAR URGENCIES & EMERGENCIES Steven Ganzberg, DMD, MS Director of Anesthesiology, Century City Outpatient Surgery Center Clinical Professor of Anesthesiology, UCLA School of Dentistry sganzberg@ucla.edu
CARDIOVASCULAR URGENCIES & EMERGENCIES Steven Ganzberg, DMD, MS Director of Anesthesiology, Century City Outpatient Surgery Center Clinical Professor of Anesthesiology, UCLA School of Dentistry sganzberg@ucla.edu
12-Lead ECG Interpretation. Kathy Kuznar, RN, ANP
 12-Lead ECG Interpretation Kathy Kuznar, RN, ANP The 12-Lead ECG Objectives Identify the normal morphology and features of the 12- lead ECG. Perform systematic analysis of the 12-lead ECG. Recognize abnormalities
12-Lead ECG Interpretation Kathy Kuznar, RN, ANP The 12-Lead ECG Objectives Identify the normal morphology and features of the 12- lead ECG. Perform systematic analysis of the 12-lead ECG. Recognize abnormalities
Cardiac Arrhythmias & Drugs used in Advanced Life Support and Cardiac Emergencies
 Cardiac Arrhythmias & Drugs used in Advanced Life Support and Cardiac Emergencies CNHE Ballarat Health Services Valid from 1 st March 2016 to 31 st June 2018 1 Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) An atrial
Cardiac Arrhythmias & Drugs used in Advanced Life Support and Cardiac Emergencies CNHE Ballarat Health Services Valid from 1 st March 2016 to 31 st June 2018 1 Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) An atrial
Understanding the 12-lead ECG, part II
 Bundle-branch blocks Understanding the 12-lead ECG, part II Most common electrocardiogram (ECG) abnormality Appears as a wider than normal S complex Occurs when one of the two bundle branches can t conduct
Bundle-branch blocks Understanding the 12-lead ECG, part II Most common electrocardiogram (ECG) abnormality Appears as a wider than normal S complex Occurs when one of the two bundle branches can t conduct
Core Content In Urgent Care Medicine
 Palpitations/Arrhythmias Ebrahim Barkoudah, MD Clinical Instructor in Internal Medicine Harvard Medical School Assistant in Internal Medicine & Pediatrics Massachusetts General Hospital MGH Chelsea Chelsea,
Palpitations/Arrhythmias Ebrahim Barkoudah, MD Clinical Instructor in Internal Medicine Harvard Medical School Assistant in Internal Medicine & Pediatrics Massachusetts General Hospital MGH Chelsea Chelsea,
Ass. Prof. Tomon Thongsri, MD Buddhachinaraj Phitsanuloke Hospital
 Treatment Bradyarrhythmia Ass. Prof. Tomon Thongsri, MD Buddhachinaraj Phitsanuloke Hospital 1 What is the rhythm? Sinus Bradycardia What s rhythm Sinus Bradycardia Treatment Asymptomatic No treatment
Treatment Bradyarrhythmia Ass. Prof. Tomon Thongsri, MD Buddhachinaraj Phitsanuloke Hospital 1 What is the rhythm? Sinus Bradycardia What s rhythm Sinus Bradycardia Treatment Asymptomatic No treatment
Patient Examination. Objectives for Presentation RECOGNITION OF COMMON ARRHYTHMIAS THEIR CAUSES AND TREATMENT OPTIONS 9/8/2016
 RECOGNITION OF COMMON ARRHYTHMIAS THEIR CAUSES AND TREATMENT OPTIONS Ryan Fries, DVM, DACVIM (Cardiology) Clinical Assistant Professor University of Illinois Department of Clinical Veterinary Medicine
RECOGNITION OF COMMON ARRHYTHMIAS THEIR CAUSES AND TREATMENT OPTIONS Ryan Fries, DVM, DACVIM (Cardiology) Clinical Assistant Professor University of Illinois Department of Clinical Veterinary Medicine
Basic ECG Interpretation Module Notebook
 Basic ECG Interpretation Module Notebook ECG_Notebook_04.27.05 Page 1 of 142 Basic ECG Interpretation Table of Contents Module Objectives... 3 Module Outline... 6 Lesson I... 6 Lesson II... 8 Lesson III...
Basic ECG Interpretation Module Notebook ECG_Notebook_04.27.05 Page 1 of 142 Basic ECG Interpretation Table of Contents Module Objectives... 3 Module Outline... 6 Lesson I... 6 Lesson II... 8 Lesson III...
Puzzling Pacemakers Cheryl Herrmann, APN, CCRN, CCNS-CSC-CMC
 Puzzling Pacemakers Cheryl Herrmann, APN, CCRN, CCNS-CSC-CMC Pacemaker: An electric device implanted in the body to regulate the heart beat. Delivers electrical stimuli over leads with electrodes in contact
Puzzling Pacemakers Cheryl Herrmann, APN, CCRN, CCNS-CSC-CMC Pacemaker: An electric device implanted in the body to regulate the heart beat. Delivers electrical stimuli over leads with electrodes in contact
ECGs and Arrhythmias: Family Medicine Board Review 2012
 Overview ECGs and Arrhythmias: Family Medicine Board Review 2012 Jess Waldura, MD University of California, San Francisco walduraj@nccc.ucsf.edu Bundle branch blocks Quick review of ischemia Arrhythmias
Overview ECGs and Arrhythmias: Family Medicine Board Review 2012 Jess Waldura, MD University of California, San Francisco walduraj@nccc.ucsf.edu Bundle branch blocks Quick review of ischemia Arrhythmias
ARRHYTHMIAS IN THE INTENSIVE CARE UNIT
 ARRHYTHMIAS IN THE INTENSIVE CARE UNIT Nicole Van Israël, DVM, CESOpht, CertSAM, CertVC, DECVIM-CA (Cardiology), MSc, MRCVS European Specialist in Veterinary Cardiology Animal CardioPulmonary Consultancy
ARRHYTHMIAS IN THE INTENSIVE CARE UNIT Nicole Van Israël, DVM, CESOpht, CertSAM, CertVC, DECVIM-CA (Cardiology), MSc, MRCVS European Specialist in Veterinary Cardiology Animal CardioPulmonary Consultancy
INDEX. Kingston General Hospital May Introduction Page 2. Cardiac Conduction System Page 3. Introduction to Cardiac Monitoring Page 5
 Kingston General Hospital May 2008 INDEX Introduction Page 2 Cardiac Conduction System Page 3 Introduction to Cardiac Monitoring Page 5 Recording Electrical Events Page 9 Waves of the ECG Complex Page
Kingston General Hospital May 2008 INDEX Introduction Page 2 Cardiac Conduction System Page 3 Introduction to Cardiac Monitoring Page 5 Recording Electrical Events Page 9 Waves of the ECG Complex Page
APPROACH TO TACHYARRYTHMIAS
 APPROACH TO TACHYARRYTHMIAS PROF.DR.MD.ZAKIR HOSSAIN PROFESSOR AND HEAD DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE SZMCH TACHYARRYTHMIA Cardiac arrythmia is a disturbance of electrical rhythm of heart. Cardac arrythmia with
APPROACH TO TACHYARRYTHMIAS PROF.DR.MD.ZAKIR HOSSAIN PROFESSOR AND HEAD DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE SZMCH TACHYARRYTHMIA Cardiac arrythmia is a disturbance of electrical rhythm of heart. Cardac arrythmia with
Adenosine. poison/drug induced. flushing, chest pain, transient asystole. Precautions: tachycardia. fibrillation, atrial flutter. Indications: or VT
 Adenosine Indications: 1. Narrow complex PSVT 2. Does not convert atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter or VT 1. Side effects include flushing, chest pain, transient asystole 2. May deteriorate widecomplex
Adenosine Indications: 1. Narrow complex PSVT 2. Does not convert atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter or VT 1. Side effects include flushing, chest pain, transient asystole 2. May deteriorate widecomplex
European Resuscitation Council
 European Resuscitation Council Objectives To know basic elements to evaluate patients with rythm disturbance To know advanced treatment of paediatric cardiac arrest To know emergency treatment of most
European Resuscitation Council Objectives To know basic elements to evaluate patients with rythm disturbance To know advanced treatment of paediatric cardiac arrest To know emergency treatment of most
ECG Interpretation and Clinical Significance
 Confirming Pages ECG Interpretation and Clinical Significance Chapter Outline 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 5.8 5.9 5.10 Learning Outcomes Key Terms Introduction (p. 114) Identifying the Components of the
Confirming Pages ECG Interpretation and Clinical Significance Chapter Outline 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 5.8 5.9 5.10 Learning Outcomes Key Terms Introduction (p. 114) Identifying the Components of the
