ASSESSMENT OF SELF-CARE IN HEART FAILURE PATIENTS
|
|
|
- Alaina Conley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original article Cogitare Enferm. (22)3: e51082, 2017 ASSESSMENT OF SELF-CARE IN HEART FAILURE PATIENTS Juliana Medeiros 1, Carolina de Araújo Medeiros 2 ABSTRACT: The objective in this study was to characterize the clinical and sociodemographic profile of heart failure patients and to describe the self-care behavior. Descriptive and cross-sectional study with a non-probabilistic sample of 57 cardiology nursing patients at a public hospital in Recife, Brazil, between May and September The self-care was assessed by means of the Self-Care of Heart Failure Index version 6.2, Brazilian version. The participants mean age was 62.9 years; 31 (54.4%) men; 36 (63.2%) literate; 26 (45.6%) suffering from hypertensive etiology and 30 (52.6%) in functional class III. The mean scores for the subscales indicated inappropriate self-care (self-care maintenance: 43.3; self-care management: 37.5 and confidence in self-care: 54.3). Higher scores were associated with education, with literate participants obtaining a mean score of 61 points (p=0.002). Investments are needed to improve self-care and nursing can play a relevant role in this improvement. DESCRIPTORS: Self-care; Heart failure; Cardiovascular nursing; Quality of life: Chronic illness. AVALIAÇÃO DO AUTOCUIDADO NOS PORTADORES DE INSUFICIÊNCIA CARDÍACA RESUMO: O objetivo deste estudo foi caracterizar o perfil clínico e sociodemográfico dos portadores de Insuficiência Cardíaca e descrever o comportamento de autocuidado. Estudo transversal descritivo, com amostra não probabilística de 57 pacientes da enfermaria cardiológica de hospital público do Recife, Brasil, entre maio e setembro de O autocuidado foi avaliado pela Self- Care of Heart Failure Index versão 6.2, versão brasileira. A idade média dos participantes foi de 62,9 anos; 31 (54,4%) homens; 36 (63,2%) alfabetizados; 26 (45,6%) de etiologia hipertensiva e 30 (52,6%) em classe funcional III. As médias dos escores nas subescalas indicaram autocuidado inadequado (manutenção do autocuidado: 43,3; manejo do autocuidado: 37,5 e confiança do autocuidado: 54,3). Escores mais elevados foram associados com escolaridade, os alfabetizados obtiveram média de 61 pontos (p=0,002). São necessários investimentos para melhorar o autocuidado e a enfermagem pode ter papel relevante nessa melhora. DESCRITORES: Autocuidado; Insuficiência cardíaca; Enfermagem cardiovascular; Qualidade de vida; Doença crônica. EVALUACIÓN DEL AUTOCUIDADO EN LOS PORTADORES DE INSUFICIENCIA CARDÍACA RESUMEN: El objetivo de este estudio fue caracterizar el perfil clínico y sociodemográfico de los portadores de Insuficiencia Cardíaca y describir el comportamiento de autocuidado. Estudio transversal descriptivo, con muestra no probabilística de 57 pacientes de la enfermaría cardiológica de hospital público de Recife, Brasil, entre mayo y septiembre de El autocuidado fue evaluado por la Self-Care of Heart Failure Index versión 6.2, versión brasileña. El promedio de edad de los participantes fue de 62,9 años; 31 (54,4%) hombres; 36 (63,2%) alfabetizados; 26 (45,6%) de etiología hipertensiva y 30 (52,6%) en clase funcional III. Los promedios de los scores en las subescalas indicaron autocuidado inadecuado (mantenimiento del autocuidado: 43,3; gestión del autocuidado: 37,5 y confianza en el autocuidado: 54,3). Puntuaciones superiores fueron asociadas con escolaridad, los alfabetizados alcanzaron promedio de 61 puntos (p=0,002). Son necesarias inversiones para mejorar el autocuidado y la enfermería puede ter papel relevante en esa mejora. DESCRIPTORES: Autocuidado; Insuficiencia cardíaca; Enfermería cardiovascular; Calidad de vida; Enfermedad crónica. 1 RN. Specialist in Cardiology. Nursing Resident in Cardiology at Hospital Dom Helder Câmara. Cabo de Santo Agostinho, PE, Brazil. 2 RN. M.Sc. in Health Sciences. Clinical Nurse at Pernambuco Health Department. Recife, PE, Brazil. Corresponding author: Received: 06/03/2017 Juliana Medeiros Finalized: 22/08/2017 Hospital Dom Helder Câmara R. Minas Novas, Natal, RN, Brasil julianamedeiros@outlook.com
2 INTRODUCTION Cogitare Enferm. (22)3: e51082, 2017 Heart Failure (HF) is a chronic and progressive syndrome, associated with hospital readmissions, low quality of life, risk of early mortality, and causing high costs for the health system. It is a systemic disease, defined as a cardiac dysfunction that causes inadequate blood supply to meet the metabolic needs of tissue in case of normal venous return, or does so only under high filling pressure. Evidenced by a set of signs and symptoms of pulmonary and systemic congestion, it is characterized as the final stage of all cardiovascular diseases (1). In Brazil, it is estimated that 6.4 million Brazilians suffer from HF. This disease is responsible for high hospital costs, for a large number of emergency care cases, it causes loss of quality of life and, often, early retirements with high costs for the country (2). The treatment of HF involves the association of pharmacological and non-pharmacological therapy. Pharmacological treatment consists of the optimization of drugs with proven impact on morbidity and mortality. Associated with pharmacological treatment, measures related to adherence to medications and lifestyle changes related to self-care offer proven benefits (3). The success of treatment depends on patients compliance, who need to modify behaviors and lifestyles. Therefore, proper knowledge about the disease, signs and symptoms of decompensation and its treatment is necessary to avoid hospitalization and improve the quality of life (3). In HF, self-care refers to people s behaviors to maintain their health and the decisions they make about the worsening of symptoms when they occur. Self-care maintenance involves compliance with pharmacological recommendations, consumption of low-salt diet, cessation of tobacco use, limited alcohol consumption, daily monitoring of weight, and signs or symptoms of HF decompensation. In this perspective, self-care is a decision-making process that patients use in choosing behaviors that maintain physiological stability, and how they respond to symptoms when they occur (4). Studies show that self-care in HF is inadequate and that individuals who participated in a selfmanagement educational program showed better self-care behavior. Sociodemographic characteristics, cultural aspects, level of education and clinical characteristic of HF are described in the literature as variables that influence the self-care of HF patients (4). The little knowledge about HF and its treatment, as well as self-care measures, has been considered a predictor of clinical instability and consequent hospital readmission. Studies show that hospital readmissions could be avoided in approximately 40-59% of HF patients, through discharge planning, adequate rehabilitation, identification of problems regarding correct medication use, and patient and family orientation for the early recognition of signs and symptoms of HF (5). Lack of knowledge contributes to the worsening of patients quality of life, social isolation, increased comorbidities, absence of self-care, lack of knowledge about signs and symptoms, and non-compliance with the treatment. These factors are inherent to increasing health spending, since patients knowledge about their condition is determinant for the treatment compliance and success (6). Little research has been done in Brazil on self-care behavior, which justifies this study. Knowing the habit of Brazilians with HF contributes to the nurses recognition of behaviors that need to be modified or included to control the disease and, consequently, achieve a better quality of life. The objective of this study was to characterize the clinical and sociodemographic profile of patients with HF and to describe the self-care behavior of adult patients with HF, using the Brazilian version of the Self-Care of Heart Failure Index (SCHFI). METHOD A cross-sectional, observational study was carried out with data obtained through a face-to-face interview, involving a non-probabilistic sample of 57 adult patients with a background diagnosis of HF, admitted to the cardiology ward of a public hospital specialized in cardiology in the metropolitan
3 region of Recife, Brazil. The study took place from May to September For recruitment, the researchers previously checked the medical records of potentially eligible patients. The following inclusion criteria were applied: patients aged 18 years; of both sexes, diagnosed with HF; second or other hospitalization; cause of hospitalization decompensated HF; the patient is stable. Patients with first hospitalization, in a compromised or severe condition or without a confirmed diagnosis of HF were excluded. Self-care behavior was evaluated using the Brazilian version of the Self-Care of Heart Failure Index (SCHFI) (7). The SCHFI is a self-care measure composed of 22 items, divided into three scales: self-care maintenance (10 items) related to behaviors to maintain physiological stability; self-care management (6 items) related to patients behavior when symptoms occur and confidence in self-care (6 items). The scores for each domain range from points, calculated by transforming the pure scores (each scale item ranges from 1 to 4). Higher scores reflect higher self-care and scores 70 points for each subscale indicate adequate self-care (7). Regarding the sociodemographic variables, we considered age, sex, education, race, marital life and family income. The clinical variables studied were: functional class of HF (according to the researchers evaluation at the time of data collection, according to the New York Heart Association (NYHA) guidelines)(6) and etiology of HF (as recorded in the patient s chart). The data were analyzed in IBM SPSS v for Microsoft Windows. Descriptive statistics were applied to the sociodemographic variables. The variables of the Self-Care Heart Failure Index were presented as means, standard deviations and 95% confidence intervals. Finally, the difference of means was analyzed between the Self-Care Heart Failure Index scores and the variables gender, education, functional class and etiology of heart failure. Education was dichotomized into literate and illiterate. The functional class was analyzed in four categories and the etiology was analyzed in six categories, which were included in the research. The dichotomous variables (gender and education) were analyzed using Student s t-test for independent samples. Functional class was analyzed by means of ANOVA and etiology using the Kruskal-Wallis test. For all tests, statistical significance was set at p <0.05. The study received approval from the Research Ethics Committee of the Instituto de Medicina Integral Professor Fernando Figueira - IMIP / PE under opinion RESULTS Fifty-seven patients were evaluated, with an average age of 62 years, ranging from 29 to 89 years, predominantly male, with hypertension as the cause of HF and in functional class III. In Table 1, the participants sociodemographic and clinical characteristics are presented. Table 1 Sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of participants (N=57). Metropolitan Region of Recife, PE, Brazil, 2016 (continues) Variables Mean SD N % Age (years) 62,9 12,2 Gender Male Female Ethnic origin White Afro-American Mulatto Education
4 Illiterate Literate Marital Status Single Married Divorced Widowed Family income < 1 minimum wage minimum wage > 1 minimum wage Etiology Hypertensive Chagas disease Ischemic Idiopathic Valvar Alcoholic Functional class I II III IV In Table 2, the descriptive statistics are presented for the scales: self-care maintenance (maintenance), self-care management (management) and trust in self-care (trust). The proportions of patients with appropriate self-care (score 70 points) were: maintenance = two patients (3.5%), management = eight patients (14%) and trust = 15 (26.3%). Table 2 Descriptive statistics of Self-Care Heart Failure Index, Brazilian version (N=57). Metropolitan Region of Recife, PE, Brazil, 2016 (continues) Self-care maintenance Mean Standard Deviation 95% CI 1. Do you weigh yourself? Do you check if your ankles are swollen? Do you try to avoid getting sick (for example: be vaccinated against flu, avoiding contact with sick people)? Do you practice any physical activity? Are you assiduous in the consultations with the doctor or nurse? Do you ingest a low-salt diet? Do you exercise for 30 minutes? Do you forget or fail to take any of your medicines? Do you request foods with little salt when eating out or visiting someone? Do you use a system (pillbox or reminders) to remind you about your medicines? Total score Self-care maintenance
5 Self-care management Cogitare Enferm. (22)3: e51082, How quickly did you recognize them as symptoms of heart failure? Reduce the salt in your diet Reduce fluid intake Take a further diuretic Contact your doctor or nurse for guidance Think of one of the above features you tried the last time when you had trouble to breathe or swollen ankles. Are you sure this feature helped you? Total score Self-care management Trust in self-care 17. Be free of the heart failure symptoms Follow the recommended treatment Assess the importance of your symptoms Recognize changes in health if they occur Do something that can relieve your symptoms Assess whether a drug works Total score Trust in self-care Tables 3, 4 and 5 present the results of the association tests among selected variables and the SCHFI. In the subscale trust in self-care, the variable education (p=0.002) was significant for better self-care (Table 5). Table 3 Analysis of difference of means between selected variables and Self-Care Heart Failure Index, subscale self-care maintenance, Brazilian version (N=57). Metropolitan Region of Recife, PE, Brazil, 2016 Variables Mean SD p-value Gender 0,46 Male 45 20,7 Female 41,3 16 Education 0,12 Illiterate 38,2 19,2 Literate 46,2 17,9 Functional class 0,466 I 37,8 13,9 II 47,5 16,2 III 40,9 21 IV 50,7 14,8 Etiology 0,513 Hypertensive 43,3 15,8 Chagas disease Ischemic 42,8 22,2 Idiopathic 43,8 19,9 Valvar 40 18,6 Alcoholic 27,8 1,9
6 Table 4 Analysis of difference of means between selected variables and Self-Care Heart Failure Index, subscale self-care management, Brazilian version (N=57). Metropolitan Region of Recife, PE, Brazil, 2016 Variables Mean SD p-value Gender Male Female Education Illiterate Literate Functional class I II III IV Etiology Hypertensive Chagas disease Ischemic Idiopathic Valvar Alcoholic Table 5 Analysis of difference of means between selected variables and Self-Care Heart Failure Index, subscale trust in self-care, Brazilian version (N=57). Metropolitan Region of Recife, PE, Brazil, 2016 Variables Mean SD p-value Gender Male Female Education Illiterate Literate Functional class I II III IV Etiology Hypertensive Chagas disease Ischemic Idiopathic Valvar Alcoholic DISCUSSION
7 In this study, the mean scores obtained on the maintenance, management and trust in self-care scales of the SCHFI, version 6.2, were all inferior to 70 points (Table 2), which is the minimum limit for scores indicating adequate self-care. These results are similar to the study conducted in the state of Rio Grande do Sul, where scores for self-care maintenance (47; standard deviation-sd = 28.3) and confidence in self-care (58; sd = 25.5) (8) were similar to the scores in this study (43.3; sd = 2.5 and 54.3; sd = 2.8, respectively, according to Table 2). This was not the case for self-care management though, which in the study mentioned had a mean score of 57 (sd = 14.3), against 37.5 in this study (sd = 3.1, Table 2). The content of the self-care maintenance scale deals with behaviors to maintain physiological stability (4). The proportion of adequate self-care (3.5%) in the self-care maintenance scale was relatively similar to the result of an evaluation performed in the city of São Paulo, which was 6.9% (4). In another study conducted in Italy, however, the observed value was higher (55.26%) than the result of this study, even though it was inferior to the scale classified as adequate, showing a significant difference (9). This can be explained by patients lack of knowledge about the disease and adequate care. Participation in multidisciplinary programs aimed at symptom control is a common strategy in other realities, different from the reality of the study population, which could explain the results regarding maintenance of self-care (4). Among the items in the self-care maintenance subscale, the lowest mean scores were for behaviors: Do you practice any physical activity?, Do you exercise for 30 minutes? (Table 2). These findings are similar to those of other studies, showing that low level of physical activity is common among patients with heart failure, despite possible cultural differences (4,9-10). The low level of physical activity may be related to activity intolerance and exacerbation of symptoms in case of exertion, common in patients with HF, and to the lack of programs to promote the practice of physical activities by HF patients in Brazil (4). Evidence on the benefits of physical activity turns physical exercise into an important form of disease control and treatment. Guidance on the exercise to be performed should be individualized according to the degree of HF and the age of the patient. A home walking program is one of the best options to prevent the negative consequences, both physiologically and psychologically, of inactivity. Patients should be instructed to identify if there is absence or presence of fatigue and shortness of breath to perform daily activities and, thereafter, gradually begin physical exercise if there is no medical restriction (11). The subscale self-care management is related to the behavior of patients when symptoms occur. The proportion of patients with adequate self-care (14%) was equal to the result found in a study conducted in the city of São Paulo (14.7%), higher than that found in a study with a Thai population (5.0%) (12), but lower than that found in samples of Italians (24.4%) (9) and Chinese (34.9%) (10). The item ingesting an additional diuretic had one of the lowest scores in the self-care management scale (Table 2), which may have contributed to the fact that the mean score on this scale was far below adequate, as observed in other studies (4,9-10). In the hospital where this research was conducted, recommending the use of an extra diuretic is not a routine practice. The proportion of patients with confidence in adequate self-care (26.3%) was higher than in the study conducted in São Paulo (19.0%) (4) and in developed countries such as Italy (21.2%) (9). It is believed that confidence in self-care has a moderating effect on self-care in different outcomes, such as compliance. The implementation of multidisciplinary programs with home visits and telephone follow-up, so that the patient properly recognizes and manages his symptoms, is a combination whose effectiveness for self-care can strengthen the patient s confidence in the dominion of his health condition. Another important consideration is that the scale of confidence in self-care may be influenced by social desirability, which requires caution in the interpretation of results related to this scale (4). Male patients scored higher than women on the self-care maintenance and management subscales, but the score was not significant (p = and p = 0.391, respectively). This result is different from another study carried out in Italy, in which women s self-care was greater than men s (9). This can be explained by the fact that the number of men interviewed has been higher than the number of female
8 participants. Men and women with HF may have different experiences and thus use distinct strategies to confront the disease. Women can have a better perception of health and construct more effective coping strategies than men (13). The literate patients had better self-care compared to the illiterate in the three subscales, but only the self-care confidence scale was significant (p = 0.002). The result supports a survey conducted in Rio Grande do Sul, in which patients with higher education levels presented higher self-care scores (14). As in our study, the greater the patient s level of education, the greater his/her ability to understand the disease, signs/symptoms and the easier the decision making for health promotion, recovery and protection. Patients with functional class IV had better self-care in the subscales self-care maintenance and management, but without significance. This result differs from the study conducted in Italy (9), in which patients with functional class IV obtained worse self-care in the three subscales. In the confidence subscale, the patient with functional class I had good self-care while, in a Chinese study, patients with functional class II had better self-care in the confidence subscale (10). Regarding the etiology, there was no significance in the results of the three subscales. No studies were found in the literature that related the etiology to the self-care of patients with heart failure. The study showed that participating patients have poor self-management. This result suggests the need for urgent interventions to promote self-care in the population. Nurses have a fundamental role in promoting the health of these patients, promoting actions so that they can be trained for self-care, and thus possess autonomy to maintain their health condition and, hence, a better quality of life. The evaluation of self-care behavior in HF is fundamental in the approach of HF clients, so that nurses can contribute effectively to the development of cognitive and instrumental skills that facilitate the adoption of adaptive strategies that contribute to the maintenance of independence in self-care, in a process of empowerment and autonomy. The actions aim to promote improvements in patients quality of life, making them more active in decision making about the way of life, taking responsibility for the behaviors that lead to the improvement of their health (11). This study was limited by the patients lack of knowledge about the disease, which made it difficult to understand some of the questions in the questionnaire. FINAL CONSIDERATIONS The study showed that self-care in this group of Brazilian is improper, but similar to other countries. Further studies are needed to get to know the self-care models in cases of HF and identify relevant variables in the self-care response. These research results will be useful to develop nursing interventions that can promote and improve this population s self-care. Studies that produce and summarize evidence about the interventions to maintain and manage selfcare in HF patients are needed to guide the team s therapeutic decisions, with a view to offering the best possible quality of life to these patients. REFERENCES 1. Galvão PC da C, Gomes ET, Figueirêdo TR, Bezerra SMMS. Diagnósticos de enfermagem aplicados a pacientes com insuficiência cardíaca descompensada. Cogitare Enferm. [Internet] 2016;21(2) [acesso em 6 fev 2017]. Disponível: 2. de Freitas MTS, Puschel VAA. Insuficiência Cardíaca: expressões do conhecimento das pessoas sobre a doença. Rev. esc. enferm. USP. [Internet] 2013;47(4) [acesso em 8 fev 2017]. Disponível: S
9 3. Bertuzzi D, de Souza EN, Moraes MA, Mussi C, Rabelo ER. The knowledge of patients with heart failure in the homecare context: an experimental study. Online Brazilian J. Nurs. [Internet] 2012;11(3) [acesso em 6 fev 2017]. Disponível: 4. da Conceição AP, dos Santos MA, dos Santos B, da Cruz DALM. Self-care in heart failure patients. Rev. Latino- Americana Enfermagem. [Internet] 2015;23(4) [acesso em 25 jan 2017]. Disponível: 5. Azzolin KO, Lemos DM, Lucena AF, Rabelo-Silva ER. Home-based nursing interventions improve knowledge of disease and management in patients with heart failure. Rev. Latino-Am. Enfermagem. [Internet] 2015;23(1) [acesso em 8 fev 2017]. Disponível: 6. Bocchi EA, Braga FGM, Ferreira SMA, Rohde LEP, de Oliveira WA, de Almeida DR, et al. III Diretriz brasileira de insuficiência cardíaca crônica. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2009;93(Suppl. 1): Ávila CW. Adaptação transcultural e Validação da Self-Care of heart failure index Versão 6.2 para o uso no Brasil [dissertação]. Porto Alegre: Universidade Federal do Rio Grade do Sul; Ávila CW, Riegel B, Pokorski SC, Camey S, Silveira LCJ, Rabelo-Silva ER. Cross-Cultural Adaptation and Psychometric Testing of the Brazilian Version of the Self-Care of Heart Failure Index Version 6.2. Nurs. Res. Pract. [Internet] 2013;(178976) [acesso em 10 fev 2010]. Disponível: 9. Cocchieri A, Riegel B, D Agostino F, Rocco G, Fida R, Alvaro R, et al. Describing self-care in Italian adults with heart failure and identifying determinants of poor self-care. Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs. [Internet] 2015;14(2) [acesso em 6 fev 2017]. Disponível: Tung HH, Chen SC, Yin WH, Cheng CH, Wang TJ, Wu SF. Self care behavior in patients with heart failure in Taiwan. Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs. [Internet] 2012;11(2) [acesso em 6 fev 2017]. Disponível: ejcnurse Pereira FAC. O Autocuidado na Insuficiência Cardíaca: tradução, adaptação e validação da european heart failure self-care behaviour scale para o contexto português [dissertação]. Porto: Instituto de Ciências Biomédicas Abel Salazar da Universidade do Porto em Ciências de Enfermagem; Lee CS, Suwanno J, Riegel B. The relationship between self-care and health status domains in Thai patients with heart failure. Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs. [Internet] 2009;8(4) [acesso 10 fev 2017]. Disponível: org/ /j.ejcnurse Ferreira VMP, Silva LN, Furuya RK, Schmidt A, Rossi LA, Dantas RAS. Self-care, sense of coherence and depression in patients hospitalized for descompensated heart failure. Rev. esc. enferm. USP. [Internet] 2015;49(3) [acesso em 17 jan 2017]. Disponível: Linn AC, Azzolin K, de Souza EN. Association between self-care and hospital readmissions of patients with heart failure. Rev. bras. enferm. [Internet] 2016;69(3) [acesso em 17 jan 2017]. Disponível: org/ / i.
Clinical Study Predictors of Better Self-Care in Patients with Heart Failure after Six Months of Follow-Up Home Visits
 Nursing Research and Practice Volume 2013, Article ID 254352, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/254352 Clinical Study Predictors of Better Self-Care in Patients with Heart Failure after Six Months
Nursing Research and Practice Volume 2013, Article ID 254352, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/254352 Clinical Study Predictors of Better Self-Care in Patients with Heart Failure after Six Months
PHYSICAL AND PSYCHOSOCIAL EFFECTS OF HEART FAILURE IN PERCEIVED QUALITY OF LIFE*
 Original article Cogitare Enferm. (22)2: e49783, 2017 PHYSICAL AND PSYCHOSOCIAL EFFECTS OF HEART FAILURE IN PERCEIVED QUALITY OF LIFE* Mailson Marques de Sousa 1, Jacira dos Santos Oliveira 2, Maria Julia
Original article Cogitare Enferm. (22)2: e49783, 2017 PHYSICAL AND PSYCHOSOCIAL EFFECTS OF HEART FAILURE IN PERCEIVED QUALITY OF LIFE* Mailson Marques de Sousa 1, Jacira dos Santos Oliveira 2, Maria Julia
THE PREVALENCE OF PROSTATE CANCER DIAGNOSTIC TESTS IN A RURAL COMMUNITY
 91 THE PREVALENCE OF PROSTATE CANCER DIAGNOSTIC TESTS IN A RURAL COMMUNITY Rosana Amora Ascari¹, Scheila Pelissari², Márcia Danieli Schmitt³, Olvani Martins da Silva 1, Eliana Buss 1, Tania Maria Ascari
91 THE PREVALENCE OF PROSTATE CANCER DIAGNOSTIC TESTS IN A RURAL COMMUNITY Rosana Amora Ascari¹, Scheila Pelissari², Márcia Danieli Schmitt³, Olvani Martins da Silva 1, Eliana Buss 1, Tania Maria Ascari
Adaptation and Applicability of a Diuretic Algorithm for Patients with Heart Failure
 Adaptation and Applicability of a Diuretic Algorithm for Patients with Heart Failure Maria Karolina Echer Ferreira Feijó 1,2, Andreia Biolo 2, Eneida Rejane Rabelo-Silva 1,2 Universidade Federal do Rio
Adaptation and Applicability of a Diuretic Algorithm for Patients with Heart Failure Maria Karolina Echer Ferreira Feijó 1,2, Andreia Biolo 2, Eneida Rejane Rabelo-Silva 1,2 Universidade Federal do Rio
Research Article Cross-Cultural Adaptation and Psychometric Testing of the Brazilian Version of the Self-Care of Heart Failure Index Version 6.
 Nursing Research and Practice Volume 2013, Article ID 178976, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/178976 Research Article Cross-Cultural Adaptation and Psychometric Testing of the Brazilian Version
Nursing Research and Practice Volume 2013, Article ID 178976, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/178976 Research Article Cross-Cultural Adaptation and Psychometric Testing of the Brazilian Version
Who discovers the cutaneous melanoma * Quem descobre o melanoma cutâneo *
 244 Clinical, Epidemiological, Laboratory and Therapeutic Investigation Who discovers the cutaneous melanoma * Quem descobre o melanoma cutâneo * Marcus Maia 1 Marianne Basso 2 Abstract: BACKGROUND - In
244 Clinical, Epidemiological, Laboratory and Therapeutic Investigation Who discovers the cutaneous melanoma * Quem descobre o melanoma cutâneo * Marcus Maia 1 Marianne Basso 2 Abstract: BACKGROUND - In
HEALTH LITERACY AMONG DIALYSIS PATIENTS
 HEALTH LITERACY AMONG DIALYSIS PATIENTS Conceicao Martins mcamartinsp@gmail.com Sofia Campos sofiamargaridacampos@gmail.com Joao Duarte duarte.johnny@gmail.com Rosa Martins rmartins.viseu@gmail.com Daniel
HEALTH LITERACY AMONG DIALYSIS PATIENTS Conceicao Martins mcamartinsp@gmail.com Sofia Campos sofiamargaridacampos@gmail.com Joao Duarte duarte.johnny@gmail.com Rosa Martins rmartins.viseu@gmail.com Daniel
Assessment of hope in patients with chronic illness and their family or caregivers*
 Original Article Assessment of hope in patients with chronic illness and their family or caregivers* Avaliação da esperança em pacientes com doença crônica e em familiares ou cuidadores Evaluación de la
Original Article Assessment of hope in patients with chronic illness and their family or caregivers* Avaliação da esperança em pacientes com doença crônica e em familiares ou cuidadores Evaluación de la
Revista da Escola de Enfermagem da USP ISSN: Universidade de São Paulo Brasil
 Revista da Escola de Enfermagem da USP ISSN: 0080-6234 reeusp@usp.br Universidade de São Paulo Brasil Lumertz Saffi, Marco Aurélio; Jacques de Macedo Junior, Luis Joeci; Trojahn, Melina Maria; Polanczyk,
Revista da Escola de Enfermagem da USP ISSN: 0080-6234 reeusp@usp.br Universidade de São Paulo Brasil Lumertz Saffi, Marco Aurélio; Jacques de Macedo Junior, Luis Joeci; Trojahn, Melina Maria; Polanczyk,
CHAPTER - III METHODOLOGY
 74 CHAPTER - III METHODOLOGY This study was designed to determine the effectiveness of nurse-led cardiac rehabilitation on adherence and quality of life among patients with heart failure. 3.1. RESEARCH
74 CHAPTER - III METHODOLOGY This study was designed to determine the effectiveness of nurse-led cardiac rehabilitation on adherence and quality of life among patients with heart failure. 3.1. RESEARCH
How does depression affect self-care?
 How does depression affect self-care? I. Lesman-Leegte, Department of Cardiology University Medical Centre Groningen The Netherlands g.a.t.lesman-leegte@thorax.umcg.nl The University Medical Centre Groningen
How does depression affect self-care? I. Lesman-Leegte, Department of Cardiology University Medical Centre Groningen The Netherlands g.a.t.lesman-leegte@thorax.umcg.nl The University Medical Centre Groningen
Relationship between self-care and depression and anxiety symptoms in individuals undergoing hemodialysis
 DOI: 10.15253/2175-6783.2017000200006 www.revistarene.ufc.br Original Article Relationship between self-care and depression and anxiety symptoms in individuals undergoing hemodialysis Relação entre autocuidado
DOI: 10.15253/2175-6783.2017000200006 www.revistarene.ufc.br Original Article Relationship between self-care and depression and anxiety symptoms in individuals undergoing hemodialysis Relação entre autocuidado
CULTURAL ADAPTATION AND VALIDATION OF THE HERTH HOPE INDEX FOR PORTUGUESE LANGUAGE: STUDY IN PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC ILLNESS
 - 754 - Artigo Original CULTURAL ADAPTATION AND VALIDATION OF THE HERTH HOPE INDEX FOR PORTUGUESE LANGUAGE: STUDY IN PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC ILLNESS Alessandra Cristina Sartore Balsanelli 1, Sonia Aurora
- 754 - Artigo Original CULTURAL ADAPTATION AND VALIDATION OF THE HERTH HOPE INDEX FOR PORTUGUESE LANGUAGE: STUDY IN PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC ILLNESS Alessandra Cristina Sartore Balsanelli 1, Sonia Aurora
HEALTH-RELATED QUALITY OF LIFE OF PEOPLE WITH DIABETES MELLITUS
 Research HEALTH-RELATED QUALITY OF LIFE OF PEOPLE WITH DIABETES MELLITUS QUALIDADE DE VIDA RELACIONADA À SAÚDE DE PESSOAS COM DIABETES MELLITUS CALIDAD DE VIDA RELACIONADA A LA SALUD DE PERSONAS CON DIABETES
Research HEALTH-RELATED QUALITY OF LIFE OF PEOPLE WITH DIABETES MELLITUS QUALIDADE DE VIDA RELACIONADA À SAÚDE DE PESSOAS COM DIABETES MELLITUS CALIDAD DE VIDA RELACIONADA A LA SALUD DE PERSONAS CON DIABETES
The sign of the Cross of Andreas in the iris and Diabetes Mellitus: a longitudinal study
 Salles LF, Silva MJP Original Article DOI: 10.1590/S0080-623420150000400013 The sign of the Cross of Andreas in the iris and Diabetes Mellitus: a longitudinal study O sinal da Cruz de Andréas na íris e
Salles LF, Silva MJP Original Article DOI: 10.1590/S0080-623420150000400013 The sign of the Cross of Andreas in the iris and Diabetes Mellitus: a longitudinal study O sinal da Cruz de Andréas na íris e
Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 171 ( 2015 ) ICEEPSY 2014
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 171 ( 2015 ) 289 293 ICEEPSY 2014 Empowerment and adherence to the therapeutic regimen in people with diabetes
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 171 ( 2015 ) 289 293 ICEEPSY 2014 Empowerment and adherence to the therapeutic regimen in people with diabetes
Author s response to reviews
 Author s response to reviews Title: Effectiveness of an educational intervention for sodium restriction in patients with hypertension: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial Authors: Marcela
Author s response to reviews Title: Effectiveness of an educational intervention for sodium restriction in patients with hypertension: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial Authors: Marcela
14ª Conferência Internacional de Investigação em Enfermagem 14 th International Conference of Nursing Research
 14ª Conferência Internacional de Investigação em Enfermagem 14 th International Conference of Nursing Research A translação do conhecimento de enfermagem: Uma força para a mudança na prática clínica! Translational
14ª Conferência Internacional de Investigação em Enfermagem 14 th International Conference of Nursing Research A translação do conhecimento de enfermagem: Uma força para a mudança na prática clínica! Translational
Disease Management Program Heart Failure
 Insuficiência Cardíaca HCor - 2015 Disease Management Program Heart Failure Felix Ramires Professor Livre-Docente FMUSP Coordenador do Programa de IC HCor felix.ramires@incor.usp.br Heart Failure - Epidemiology
Insuficiência Cardíaca HCor - 2015 Disease Management Program Heart Failure Felix Ramires Professor Livre-Docente FMUSP Coordenador do Programa de IC HCor felix.ramires@incor.usp.br Heart Failure - Epidemiology
Heart Failure Mortality Trend in Salvador, Bahia, Brazil CONCLUSION KEY WORDS
 Article Original Article Heart Failure Mortality Trend in Salvador, Bahia, Brazil Adriana Lopes Latado, Luiz Carlos Santana Passos, Rodrigo Guedes, Alessandra B. Santos, Marianna Andrade, Simone Moura
Article Original Article Heart Failure Mortality Trend in Salvador, Bahia, Brazil Adriana Lopes Latado, Luiz Carlos Santana Passos, Rodrigo Guedes, Alessandra B. Santos, Marianna Andrade, Simone Moura
Factors Affecting Adherence to Self-care Behaviors among Outpatients with Heart Failure in Korea. Ok, Jong Sun 1 Choi, Heejung 2
 Korean Journal of Adult Nursing (Korean J Adult Nurs) Vol. 27 No. 2, 242-250, April 2015 ISSN 1225-4886 (Print) / ISSN 2288-338X (Online) http://dx.doi.org/10.7475/kjan.2015.27.2.242 Factors Affecting
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing (Korean J Adult Nurs) Vol. 27 No. 2, 242-250, April 2015 ISSN 1225-4886 (Print) / ISSN 2288-338X (Online) http://dx.doi.org/10.7475/kjan.2015.27.2.242 Factors Affecting
Freire EAM *,**,***, Bruscato A ***,****, Leite DRC *, Sousa TTS *, Ciconelli RM **,*** Abstract. Introduction
 ARTIGO ORIGINAL TRANSLATION INTO BRAZILIAN PORTUGUESE, CULTURAL ADAPTATION AND VALIDATATION OF THE SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS QUALITY OF LIFE QUESTIONNAIRE ( SLEQOL) Freire EAM *,**,***, Bruscato A ***,****,
ARTIGO ORIGINAL TRANSLATION INTO BRAZILIAN PORTUGUESE, CULTURAL ADAPTATION AND VALIDATATION OF THE SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS QUALITY OF LIFE QUESTIONNAIRE ( SLEQOL) Freire EAM *,**,***, Bruscato A ***,****,
Descritpive study of risk factors to arterial hypertension among victims of cerebrovascular accident
 Descritpive study of risk factors to arterial hypertension among victims of cerebrovascular accident Larissa Bento de Araújo Mendonça¹, Francisca Elisangela Teixeira Lima², Islene Victor Barbosa³, Maria
Descritpive study of risk factors to arterial hypertension among victims of cerebrovascular accident Larissa Bento de Araújo Mendonça¹, Francisca Elisangela Teixeira Lima², Islene Victor Barbosa³, Maria
Socio-demographic profile of patients in a clinical Peritoneal Dialysis of Sergipe, Brazil
 SCIENTIA PLENA VOL. 8, NUM. 3 2012 www.scientiaplena.org.br Socio-demographic profile of patients in a clinical Peritoneal Dialysis of Sergipe, Brazil V. S. Santos 1 ; A. C. F. Abud 2 ; J. A. B. Alves
SCIENTIA PLENA VOL. 8, NUM. 3 2012 www.scientiaplena.org.br Socio-demographic profile of patients in a clinical Peritoneal Dialysis of Sergipe, Brazil V. S. Santos 1 ; A. C. F. Abud 2 ; J. A. B. Alves
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem ISSN: Universidade de São Paulo Brasil
 Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem ISSN: 0104-1169 rlae@eerp.usp.br Universidade de São Paulo Brasil Ottaviani, Ana Carolina; Nestor Souza, Érica; de Camargo Drago, Natália; Zazzetta de Mendiondo,
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem ISSN: 0104-1169 rlae@eerp.usp.br Universidade de São Paulo Brasil Ottaviani, Ana Carolina; Nestor Souza, Érica; de Camargo Drago, Natália; Zazzetta de Mendiondo,
Self-care, sense of coherence and depression in patients hospitalized for decompensated heart failure
 Original ARTICLE DOI: 10.1590/S0080-623420150000300005 Self-care, sense of coherence and depression in patients hospitalized for decompensated heart failure Autocuidado, senso de coerência e depressão
Original ARTICLE DOI: 10.1590/S0080-623420150000300005 Self-care, sense of coherence and depression in patients hospitalized for decompensated heart failure Autocuidado, senso de coerência e depressão
DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST
 DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST Socio-cultural influences of heart failure self-care among an ethnic minority population Victoria Vaughan Dickson, PhD, CRNP Assistant Professor Brookdale Fellow 2010
DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST Socio-cultural influences of heart failure self-care among an ethnic minority population Victoria Vaughan Dickson, PhD, CRNP Assistant Professor Brookdale Fellow 2010
Validation of the Portuguese Version of the Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Questionnaire
 Validation of the Portuguese Version of the Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Questionnaire Vitor Oliveira Carvalho, Guilherme Veiga Guimarães, Dirceu Carrara, Fernando Bacal, Edimar Alcides Bocchi Laboratório
Validation of the Portuguese Version of the Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Questionnaire Vitor Oliveira Carvalho, Guilherme Veiga Guimarães, Dirceu Carrara, Fernando Bacal, Edimar Alcides Bocchi Laboratório
Reference Guide for Group Education
 A p l a n o f a c t i o n f o r l i f e Reference Guide for Group Education Session 5 Plan of Action: Part I Overview of the Plan of Action and Management of Respiratory Infections Plan of Action: Objectives
A p l a n o f a c t i o n f o r l i f e Reference Guide for Group Education Session 5 Plan of Action: Part I Overview of the Plan of Action and Management of Respiratory Infections Plan of Action: Objectives
Evaluation of arterial pressure measurements comparing traditional and gold standard methods
 Original Article Evaluation of arterial pressure comparing traditional and gold standard methods Avaliação das medidas de pressão arterial comparando o método tradicional e o padrão-ouro Luciano Elias
Original Article Evaluation of arterial pressure comparing traditional and gold standard methods Avaliação das medidas de pressão arterial comparando o método tradicional e o padrão-ouro Luciano Elias
Quality of life of chronic renal patients on hemodialysis in Marília, SP, Brazil
 Original Article Artigo Original Quality of life of chronic renal patients on hemodialysis in Marília, SP, Brazil A qualidade de vida dos pacientes renais crônicos em hemodiálise na região de Marília,
Original Article Artigo Original Quality of life of chronic renal patients on hemodialysis in Marília, SP, Brazil A qualidade de vida dos pacientes renais crônicos em hemodiálise na região de Marília,
Tuberculosis surveillance and health information system in Brazil,
 Rev Saúde Pública 7;41(Supl. 1) José Ueleres Braga Tuberculosis surveillance and health information system in Brazil, 1-3 ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE: To assess the quality of tuberculosis surveillance in Brazil.
Rev Saúde Pública 7;41(Supl. 1) José Ueleres Braga Tuberculosis surveillance and health information system in Brazil, 1-3 ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE: To assess the quality of tuberculosis surveillance in Brazil.
Locus of control and contraceptive knowledge, attitude and practice among university students
 Rev Saúde Pública 2010;44(1):39-44 Aline Salheb Alves I Maria Helena Baena de Moraes Lopes II Locus of control and contraceptive knowledge, attitude and practice among university students Lócus de controle
Rev Saúde Pública 2010;44(1):39-44 Aline Salheb Alves I Maria Helena Baena de Moraes Lopes II Locus of control and contraceptive knowledge, attitude and practice among university students Lócus de controle
Revista da Escola de Enfermagem da USP ISSN: Universidade de São Paulo Brasil
 Revista da Escola de Enfermagem da USP ISSN: 0080-6234 reeusp@usp.br Universidade de São Paulo Brasil Donida Silvério, Camila; Spadoti Dantas, Rosana Aparecida; Rodrigues Silva Carvalho, Ariana Avaliação
Revista da Escola de Enfermagem da USP ISSN: 0080-6234 reeusp@usp.br Universidade de São Paulo Brasil Donida Silvério, Camila; Spadoti Dantas, Rosana Aparecida; Rodrigues Silva Carvalho, Ariana Avaliação
ILLNESS PERCEPTIONS IN BRAZILIAN WOMEN WITH CERVICAL CAN- CER, WOMEN WITH PRECURSORY LESIONS AND HEALTHY WOMEN
 PSICOONCOLOGÍA. Vol. 10, Núm. 2-3, 2013, pp. 417-423 ISSN: 1696-7240 DOI: 10.5209/rev_PSIC.2013.v10.n2-3.43459 ILLNESS PERCEPTIONS IN BRAZILIAN WOMEN WITH CERVICAL CAN- CER, WOMEN WITH PRECURSORY LESIONS
PSICOONCOLOGÍA. Vol. 10, Núm. 2-3, 2013, pp. 417-423 ISSN: 1696-7240 DOI: 10.5209/rev_PSIC.2013.v10.n2-3.43459 ILLNESS PERCEPTIONS IN BRAZILIAN WOMEN WITH CERVICAL CAN- CER, WOMEN WITH PRECURSORY LESIONS
Age and gender differences in heart failure symptom cluster profiles Kristen A. Sethares, PhD, RN, CNE College of Nursing University of Massachusetts
 Age and gender differences in heart failure symptom cluster profiles Kristen A. Sethares, PhD, RN, CNE College of Nursing University of Massachusetts Dartmouth, No. Dartmouth, Ma. Heart Failure Affects
Age and gender differences in heart failure symptom cluster profiles Kristen A. Sethares, PhD, RN, CNE College of Nursing University of Massachusetts Dartmouth, No. Dartmouth, Ma. Heart Failure Affects
QUALITY OF LIFE IN PATIENTS WITH DIABETES USING THE DIABETES 39 (D-39) INSTRUMENT
 138 instrument. Rev Gaúcha Enferm. 2013, 34 (3):138-146. ORIGINAL ARTICLE QUALITY OF LIFE IN PATIENTS WITH DIABETES USING THE DIABETES 39 (D-39) INSTRUMENT Luana Rosas ZULIAN a, Manoel Antônio dos SANTOS
138 instrument. Rev Gaúcha Enferm. 2013, 34 (3):138-146. ORIGINAL ARTICLE QUALITY OF LIFE IN PATIENTS WITH DIABETES USING THE DIABETES 39 (D-39) INSTRUMENT Luana Rosas ZULIAN a, Manoel Antônio dos SANTOS
Patients in Sudan. Department of Medical Nursing, Faculty of Nursing Al Neelain University, Khartoum, Sudan
 Factors affecting treatment Compliance of Heart Failure a,b*, Imad Fadl-Elmula c a Department of Medical Nursing, Faculty of Nursing Al Neelain University, Khartoum, Sudan b Department of Nursing, Faculty
Factors affecting treatment Compliance of Heart Failure a,b*, Imad Fadl-Elmula c a Department of Medical Nursing, Faculty of Nursing Al Neelain University, Khartoum, Sudan b Department of Nursing, Faculty
Chronic low back pain: pain intensity, disability and quality of life
 Original Article Chronic low back pain: pain intensity, disability and quality of life Dor lombar crônica: intensidade de dor, incapacidade e qualidade de vida Thais Stefane 1 Amanda Munari dos Santos
Original Article Chronic low back pain: pain intensity, disability and quality of life Dor lombar crônica: intensidade de dor, incapacidade e qualidade de vida Thais Stefane 1 Amanda Munari dos Santos
Step 1: Help your patients come prepared to their appointment. Step 2: Important communication reminders for the first follow-up visit
 Making the Most of the Follow-Up Visit It s not enough for a patient to keep their follow-up appointment the appointment must also be a good one. Here are important reminders for a clinician, particularly
Making the Most of the Follow-Up Visit It s not enough for a patient to keep their follow-up appointment the appointment must also be a good one. Here are important reminders for a clinician, particularly
DESCRITORES Neoplasias colorretais. Fadiga. Depressão. Assistência paliativa.
 depression in patients with colorectal cancer * CO-MORBIDADE FADIGA E DEPRESSÃO EM PACIENTES COM CÂNCER COLO-RETAL ORIGINAL ARTICLE ENFERMEDAD CONCOMITANTE: FATIGA Y DEPRESIÓN EN PACIENTES CON CÁNCER COLON-RECTAL
depression in patients with colorectal cancer * CO-MORBIDADE FADIGA E DEPRESSÃO EM PACIENTES COM CÂNCER COLO-RETAL ORIGINAL ARTICLE ENFERMEDAD CONCOMITANTE: FATIGA Y DEPRESIÓN EN PACIENTES CON CÁNCER COLON-RECTAL
Mapping cancer, cardiovascular and malaria research in Brazil
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2) 33: 853-867 Mapping cancer, cardiovascular and malaria research ISSN 1-879X Overview 853 Mapping cancer, cardiovascular and malaria research in
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2) 33: 853-867 Mapping cancer, cardiovascular and malaria research ISSN 1-879X Overview 853 Mapping cancer, cardiovascular and malaria research in
Quality of life of people with diabetic foot
 DOI: 10.15253/2175-6783.2016000200006 www.revistarene.ufc.br Original Article Quality of life of people with diabetic foot Qualidade de vida de pessoas com pé diabético Pedro Martins Lima Neto 1, Paulo
DOI: 10.15253/2175-6783.2016000200006 www.revistarene.ufc.br Original Article Quality of life of people with diabetic foot Qualidade de vida de pessoas com pé diabético Pedro Martins Lima Neto 1, Paulo
Self-Efficacy When Multiple Comorbid Conditions Challenge Heart Failure Self-Care
 Self-Efficacy When Multiple Comorbid Conditions Challenge Heart Failure Self-Care Victoria Vaughan Dickson, PhD, CRNP New York University, College of Nursing Harleah G. Buck, PhD, CHNP The Pennsylvania
Self-Efficacy When Multiple Comorbid Conditions Challenge Heart Failure Self-Care Victoria Vaughan Dickson, PhD, CRNP New York University, College of Nursing Harleah G. Buck, PhD, CHNP The Pennsylvania
Quality of life and people living with AIDS: relationship with sociodemographic and health aspects 1
 Rev. Latino-Am. Enfermagem 2014 July-Aug.;22(4):582-90 DOI: 10.1590/0104-1169.3350.2455 Original Article Quality of life and people living with AIDS: relationship with sociodemographic and health aspects
Rev. Latino-Am. Enfermagem 2014 July-Aug.;22(4):582-90 DOI: 10.1590/0104-1169.3350.2455 Original Article Quality of life and people living with AIDS: relationship with sociodemographic and health aspects
Empowering Older Adults On Drug Adherence A Collaborative Service Model. Cheng Po-po, Peggy Nurse Consultant (Gerontology) Yan Chai Hospital, KWC, HA
 Empowering Older Adults On Drug Adherence A Collaborative Service Model Cheng Po-po, Peggy Nurse Consultant (Gerontology) Yan Chai Hospital, KWC, HA Introduction Older adults have multiple pathologies
Empowering Older Adults On Drug Adherence A Collaborative Service Model Cheng Po-po, Peggy Nurse Consultant (Gerontology) Yan Chai Hospital, KWC, HA Introduction Older adults have multiple pathologies
NOT FOR REPRODUCTION. Feelings of powerlessness in patients with venous leg ulcers. research
 Feelings of powerlessness in patients with venous leg ulcers G.M. Salomé, 1 RN, PhD; D.G. Openheimer, 1 Masters student; S.A. de Almeida, 1 RN M.L.G.B. Bueno, 1 Masters student; R.A.A. Dutra, 1 Masters
Feelings of powerlessness in patients with venous leg ulcers G.M. Salomé, 1 RN, PhD; D.G. Openheimer, 1 Masters student; S.A. de Almeida, 1 RN M.L.G.B. Bueno, 1 Masters student; R.A.A. Dutra, 1 Masters
Validity of four indirect methods to measure adherence in primary care hypertensives
 (2007) 21, 579 584 & 2007 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/07 $30.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Validity of four indirect methods to measure adherence in primary care hypertensives
(2007) 21, 579 584 & 2007 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/07 $30.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Validity of four indirect methods to measure adherence in primary care hypertensives
Quality of life of HIV seropositive women
 Original Article Quality of life of HIV seropositive women Qualidade de vida de mulheres portadoras do HIV Jéssica Monique Bellini 1 Renata Karina Reis 1 Lilian Andreia Fleck Reinato 1 Rosilane de Lima
Original Article Quality of life of HIV seropositive women Qualidade de vida de mulheres portadoras do HIV Jéssica Monique Bellini 1 Renata Karina Reis 1 Lilian Andreia Fleck Reinato 1 Rosilane de Lima
Living with Congestive Heart Failure
 Living with Congestive Heart Failure Introduction Congestive heart failure, also known as chronic heart failure, is a common condition that affects millions of people every year. It is possible to control
Living with Congestive Heart Failure Introduction Congestive heart failure, also known as chronic heart failure, is a common condition that affects millions of people every year. It is possible to control
Adherence to health behaviour advice in heart failure
 Adherence to health behaviour advice in heart failure Prof. Nana Pogosova National Research Center for Preventive Medicine Moscow, Russian Federation Heart Failure (HF) As the final point for many cardiac
Adherence to health behaviour advice in heart failure Prof. Nana Pogosova National Research Center for Preventive Medicine Moscow, Russian Federation Heart Failure (HF) As the final point for many cardiac
Chapter 3 - Does Low Well-being Modify the Effects of
 Chapter 3 - Does Low Well-being Modify the Effects of PRISMA (Dutch DESMOND), a Structured Selfmanagement-education Program for People with Type 2 Diabetes? Published as: van Vugt M, de Wit M, Bader S,
Chapter 3 - Does Low Well-being Modify the Effects of PRISMA (Dutch DESMOND), a Structured Selfmanagement-education Program for People with Type 2 Diabetes? Published as: van Vugt M, de Wit M, Bader S,
Knowledge and risk perception on HIV/AIDS by Brazilian population: 1998 and 2005
 Rev Saúde Pública 2008;42(Supl. 1) Maria Paula Ferreira Grupo de Estudos de População, Sexualidade e Aids* Knowledge and risk perception on HIV/AIDS by Brazilian population: 1998 and 2005 ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE:
Rev Saúde Pública 2008;42(Supl. 1) Maria Paula Ferreira Grupo de Estudos de População, Sexualidade e Aids* Knowledge and risk perception on HIV/AIDS by Brazilian population: 1998 and 2005 ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE:
Hospitalization and Mortality Rates for Heart Failure in Public Hospitals in São Paulo
 Hospitalization and Mortality Rates for Heart Failure in Public Hospitals in São Paulo Henrique L. Godoy, José A. Silveira, Eduardo Segalla, Dirceu R. Almeida Universidade Federal de São Paulo, SP, Brazil
Hospitalization and Mortality Rates for Heart Failure in Public Hospitals in São Paulo Henrique L. Godoy, José A. Silveira, Eduardo Segalla, Dirceu R. Almeida Universidade Federal de São Paulo, SP, Brazil
Cultural adaptation and validation of the Freiburg Life Quality Assessment Wound Module to Brazilian Portuguese 1
 Rev. Latino-Am. Enfermagem 2016;24:e2684 DOI: 10.1590/1518-8345.0289.2684 Original Article Cultural adaptation and validation of the Freiburg Life Quality Assessment Wound Module to Brazilian Portuguese
Rev. Latino-Am. Enfermagem 2016;24:e2684 DOI: 10.1590/1518-8345.0289.2684 Original Article Cultural adaptation and validation of the Freiburg Life Quality Assessment Wound Module to Brazilian Portuguese
Health-related quality of life in patients admitted after a first episode of acute coronary syndrome
 Universidade de São Paulo Biblioteca Digital da Produção Intelectual - BDPI Departamento Enfermagem Geral e Especializada - EERP/ERG Artigos e Materiais de Revistas Científicas - EERP/ERG 2011 Health-related
Universidade de São Paulo Biblioteca Digital da Produção Intelectual - BDPI Departamento Enfermagem Geral e Especializada - EERP/ERG Artigos e Materiais de Revistas Científicas - EERP/ERG 2011 Health-related
Translation and cultural adaptation of the stroke impact scale 2.0 (SIS): a quality-of-life scale for stroke
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI: 10.1590/1516-3180.2017.0114281017 Translation and cultural adaptation of the stroke impact scale 2.0 (SIS): a quality-of-life scale for stroke Aline Dias Brandão I, Natasha Bertocco
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI: 10.1590/1516-3180.2017.0114281017 Translation and cultural adaptation of the stroke impact scale 2.0 (SIS): a quality-of-life scale for stroke Aline Dias Brandão I, Natasha Bertocco
994 Rev. Latino-Am. Enfermagem 2014 Nov.-Dec.;22(6):
 994 Rev. Latino-Am. Enfermagem 2014 Nov.-Dec.;22(6):994-1000 DOI: 10.1590/0104-1169.3534.2508 Original Article Quality of life, clinical characteristics and treatment adherence of people living with HIV/AIDS
994 Rev. Latino-Am. Enfermagem 2014 Nov.-Dec.;22(6):994-1000 DOI: 10.1590/0104-1169.3534.2508 Original Article Quality of life, clinical characteristics and treatment adherence of people living with HIV/AIDS
Flávia de Lima Osório, 1 José Alexandre S Crippa, 1 Sonia Regina Loureiro 1
 BRIEF REPORT Cross-cultural validation of the Brazilian Portuguese version of the Social Phobia Inventory (SPIN): study of the items and internal consistency Validação transcultural da versão para o português
BRIEF REPORT Cross-cultural validation of the Brazilian Portuguese version of the Social Phobia Inventory (SPIN): study of the items and internal consistency Validação transcultural da versão para o português
Worries about memory loss and knowledge on Alzheimer s disease in community-dwelling elderly from Brazil
 DOI: 10.1590/S1980-57642011DN05020009 Dement Neuropsychol 2011 June;5(2):108-113 Original Article Worries about memory loss and knowledge on Alzheimer s disease in community-dwelling elderly from Brazil
DOI: 10.1590/S1980-57642011DN05020009 Dement Neuropsychol 2011 June;5(2):108-113 Original Article Worries about memory loss and knowledge on Alzheimer s disease in community-dwelling elderly from Brazil
Difficulties concerning Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 in children and adolescents
 DOI: 10.15253/2175-6783.2016000500010 www.revistarene.ufc.br Original Article Difficulties concerning Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 in children and adolescents Dificuldades de crianças e adolescentes com Diabetes
DOI: 10.15253/2175-6783.2016000500010 www.revistarene.ufc.br Original Article Difficulties concerning Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 in children and adolescents Dificuldades de crianças e adolescentes com Diabetes
Cardiovascular Risk Estimation by the ASCVD Risk Estimator Application in a University Hospital
 492 International Journal of Cardiovascular Sciences. 2018;31(5)492-498 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cardiovascular Risk Estimation by the ASCVD Risk Estimator Application in a University Hospital Thalita dos Anjos
492 International Journal of Cardiovascular Sciences. 2018;31(5)492-498 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cardiovascular Risk Estimation by the ASCVD Risk Estimator Application in a University Hospital Thalita dos Anjos
Innovation and quality in managing cardiovascular patients: Role of the BPC in Brazil. Fábio P. Taniguchi, MD, MBA, PhD Principal Investigador
 Innovation and quality in managing cardiovascular patients: Role of the BPC in Brazil Fábio P. Taniguchi, MD, MBA, PhD Principal Investigador BPC - Brazil Heart Failure Coronary Artery Disease Atrial
Innovation and quality in managing cardiovascular patients: Role of the BPC in Brazil Fábio P. Taniguchi, MD, MBA, PhD Principal Investigador BPC - Brazil Heart Failure Coronary Artery Disease Atrial
Acute asthma management in children: knowledge of the topic among health professionals at teaching hospitals in the city of Recife, Brazil*
 Original Article Acute asthma management in children: knowledge of the topic among health professionals at teaching hospitals in the city of Recife, Brazil* Manejo de crises asmáticas em crianças: conhecimento
Original Article Acute asthma management in children: knowledge of the topic among health professionals at teaching hospitals in the city of Recife, Brazil* Manejo de crises asmáticas em crianças: conhecimento
Analysis Treatment Guideline versus Clinical Practice Protocol in Patients Hospitalized due to Heart Failure
 Analysis Treatment Guideline versus Clinical Practice Protocol in Patients Hospitalized due to Heart Failure Alessandra da Graça Corrêa 1, Marcia Makdisse 1, Marcelo Katz 1, Thamires Campos Santana 1,
Analysis Treatment Guideline versus Clinical Practice Protocol in Patients Hospitalized due to Heart Failure Alessandra da Graça Corrêa 1, Marcia Makdisse 1, Marcelo Katz 1, Thamires Campos Santana 1,
Heart Failure Guidelines For your Daily Practice
 Heart Failure Guidelines For your Daily Practice Juan M. Aranda, Jr., MD, FACC, FHFSA Professor of Medicine Director of Heart Failure and Cardiac Transplantation University of Florida College of Medicine
Heart Failure Guidelines For your Daily Practice Juan M. Aranda, Jr., MD, FACC, FHFSA Professor of Medicine Director of Heart Failure and Cardiac Transplantation University of Florida College of Medicine
Depression in the elderly: are doctors investigating it?
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Depression in the elderly: are doctors investigating it? Rev Bras Pisquiatr 2004;26(3):145-9 Fernando Kratz Gazalle, a Pedro Curi Hallal b and Maurício Silva de Lima c Original version
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Depression in the elderly: are doctors investigating it? Rev Bras Pisquiatr 2004;26(3):145-9 Fernando Kratz Gazalle, a Pedro Curi Hallal b and Maurício Silva de Lima c Original version
Adherence to immunosuppressive treatment in post-renal transplant patients: a descriptiveexploratory
 Adherence to immunosuppressive treatment in post-renal transplant patients: a descriptiveexploratory study Greisse da Silveira Maissiat 1, Sandra Mara Marin 2, Carla Rafaela Delagnolli Fuzinatto 2 1 Santa
Adherence to immunosuppressive treatment in post-renal transplant patients: a descriptiveexploratory study Greisse da Silveira Maissiat 1, Sandra Mara Marin 2, Carla Rafaela Delagnolli Fuzinatto 2 1 Santa
Clinical Usefulness of Coronary Angiography in Patients with Left Ventricular Dysfunction
 Clinical Usefulness of Coronary Angiography in Patients with Left Ventricular Dysfunction Rodrigo Morel Vieira de Melo, Eduardo França Pessoa de Melo, Bruno Biselli, Germano Emilio Conceição Souza, Edimar
Clinical Usefulness of Coronary Angiography in Patients with Left Ventricular Dysfunction Rodrigo Morel Vieira de Melo, Eduardo França Pessoa de Melo, Bruno Biselli, Germano Emilio Conceição Souza, Edimar
Heart Failure (HF) - Primary Care Flow Charts. Pre diagnosis Symptoms or signs suggestive of HF
 Heart Failure (HF) - Primary Care Flow Charts Pre diagnosis Symptoms or signs suggestive of HF 12 lead ECG Normal examination and 12 lead ECG HF highly unlikely Abnormal 12 lead ECG HF Possible Arrange
Heart Failure (HF) - Primary Care Flow Charts Pre diagnosis Symptoms or signs suggestive of HF 12 lead ECG Normal examination and 12 lead ECG HF highly unlikely Abnormal 12 lead ECG HF Possible Arrange
Heart Failure (HF) - Primary Care Flow Charts. Symptoms or signs suggestive of HF. Pre diagnosis. Refer to the Heart Failure Clinic at VHK for
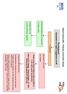 Heart Failure (HF) - Primary Care Flow Charts Pre diagnosis Symptoms or signs suggestive of HF 12 lead ECG Normal examination and 12 lead ECG HF highly unlikely Abnormal 12 lead ECG HF Possible Arrange
Heart Failure (HF) - Primary Care Flow Charts Pre diagnosis Symptoms or signs suggestive of HF 12 lead ECG Normal examination and 12 lead ECG HF highly unlikely Abnormal 12 lead ECG HF Possible Arrange
Walking improves sleep quality and mood status of women with fibromyalgia syndrome*
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Walking improves sleep quality and mood status of women with fibromyalgia syndrome* Praticar caminhada melhora a qualidade do sono e os estados de humor em mulheres com síndrome da fibromialgia
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Walking improves sleep quality and mood status of women with fibromyalgia syndrome* Praticar caminhada melhora a qualidade do sono e os estados de humor em mulheres com síndrome da fibromialgia
HEALTHY AND FULFILLING LIFESTYLE
 Reference Guide for Individual Patient Education Keeping a Healthy and Fulfilling Lifestyle Educational topics: 1. Healthy and Fulfilling Lifestyle Health and COPD Healthy Life Habits o No smoking o Medication
Reference Guide for Individual Patient Education Keeping a Healthy and Fulfilling Lifestyle Educational topics: 1. Healthy and Fulfilling Lifestyle Health and COPD Healthy Life Habits o No smoking o Medication
Reducing 30-day Rehospitalization for Heart Failure: An Attainable Goal?
 Reducing 30-day Rehospitalization for Heart Failure: An Attainable Goal? Ileana L. Piña, MD, MPH Professor of Medicine, Epi/Biostats Case Western Reserve University Graduate VA Quality Scholar Cleveland
Reducing 30-day Rehospitalization for Heart Failure: An Attainable Goal? Ileana L. Piña, MD, MPH Professor of Medicine, Epi/Biostats Case Western Reserve University Graduate VA Quality Scholar Cleveland
Non-Profit Academic Project, developed under the Open Acces Initiative
 Red de Revistas Científicas de América Latina, el Caribe, España y Portugal Sistema de Información Científica English version Pedrolo, Edivane; Reichembach Danski, Mitzy Tannia; Adami Vayego, Stela; Rodrigues
Red de Revistas Científicas de América Latina, el Caribe, España y Portugal Sistema de Información Científica English version Pedrolo, Edivane; Reichembach Danski, Mitzy Tannia; Adami Vayego, Stela; Rodrigues
Mattis Dementia Rating Scale (DRS) Normative data for the Brazilian middle-age and elderly populations
 Original Articles Mattis Dementia Rating Scale (DRS) Normative data for the Brazilian middle-age and elderly populations Maria Paula Foss 1, Viviane Amaral de Carvalho 2, Thais Helena Machado 3, Geraldo
Original Articles Mattis Dementia Rating Scale (DRS) Normative data for the Brazilian middle-age and elderly populations Maria Paula Foss 1, Viviane Amaral de Carvalho 2, Thais Helena Machado 3, Geraldo
International Journal of Research in Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapeutics
 International Journal of Research in Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapeutics ISSN Print: 2278-2648 IJRPP Vol.4 Issue 3 Jul Sep - 2015 ISSN Online: 2278-2656 Journal Home page: Research article Open Access
International Journal of Research in Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapeutics ISSN Print: 2278-2648 IJRPP Vol.4 Issue 3 Jul Sep - 2015 ISSN Online: 2278-2656 Journal Home page: Research article Open Access
SOCIODEMOGRAPHIC AND EPIDEMIOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF PROSTATECTOMIZED PATIENTS AT THE HOSPITAL AMARAL CARVALHO OF JAÚ
 Vol.8,n.1,pp.05-09 (Sep - Nov 2014) Brazilian Journal of Surgery and Clinical Research- SOCIODEMOGRAPHIC AND EPIDEMIOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF PROSTATECTOMIZED PATIENTS AT THE HOSPITAL AMARAL CARVALHO
Vol.8,n.1,pp.05-09 (Sep - Nov 2014) Brazilian Journal of Surgery and Clinical Research- SOCIODEMOGRAPHIC AND EPIDEMIOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF PROSTATECTOMIZED PATIENTS AT THE HOSPITAL AMARAL CARVALHO
Dementia & Neuropsychologia ISSN: Associação Neurologia Cognitiva e do Comportamento. Brasil
 Dementia & Neuropsychologia ISSN: 1980-5764 demneuropsy@uol.com.br Associação Neurologia Cognitiva e do Comportamento Brasil Martins de Oliveira, Glaucia; Cachioni, Meire; Falcão, Deusivania; Batistoni,
Dementia & Neuropsychologia ISSN: 1980-5764 demneuropsy@uol.com.br Associação Neurologia Cognitiva e do Comportamento Brasil Martins de Oliveira, Glaucia; Cachioni, Meire; Falcão, Deusivania; Batistoni,
Central obesity is a major clinical and public health
 original article Prevalence of central obesity in a large sample of adolescents from public schools in Recife, Brazil Prevalência de obesidade central em grande amostra de adolescentes de escolas públicas
original article Prevalence of central obesity in a large sample of adolescents from public schools in Recife, Brazil Prevalência de obesidade central em grande amostra de adolescentes de escolas públicas
Quality of Life of Hypertensive Patients and Comparison of two Instruments of HRQOL Measure
 Quality of Life of Hypertensive Patients and Comparison of two Instruments of HRQOL Measure Michelle Adler Normando Carvalho, Isabela Bispo Santos Silva, Sarah Brito Pinheiro Ramos, Laura Fernandes Coelho,
Quality of Life of Hypertensive Patients and Comparison of two Instruments of HRQOL Measure Michelle Adler Normando Carvalho, Isabela Bispo Santos Silva, Sarah Brito Pinheiro Ramos, Laura Fernandes Coelho,
Objectives. Systolic Heart Failure: Definitions. Heart Failure: Historical Perspective 2/7/2009
 Objectives Diastolic Heart Failure and Indications for Echocardiography in the Asian Population Damon M. Kwan, MD UCSF Asian Heart & Vascular Symposium 02.07.09 Define diastolic heart failure and differentiate
Objectives Diastolic Heart Failure and Indications for Echocardiography in the Asian Population Damon M. Kwan, MD UCSF Asian Heart & Vascular Symposium 02.07.09 Define diastolic heart failure and differentiate
Patient Details Hidden. Clinical Enrollment. Quality of Life. EuroQOL (EQ-5D) Enroll Patient. Not Started. Not Started
 Patient Details Hidden Show Patient Clinical Enrollment t Started Quality of Life t Started EuroQOL (EQ-5D) Did the patient complete a EuroQOL form? Please select a reason why the EuroQOL was not completed:
Patient Details Hidden Show Patient Clinical Enrollment t Started Quality of Life t Started EuroQOL (EQ-5D) Did the patient complete a EuroQOL form? Please select a reason why the EuroQOL was not completed:
Aim: To describe self-medication habits of patients with
 Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol 2006;72(1):83-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Self-medication profile of ENT patients Alexandre Barbosa Servidoni 1, Liliane Coelho 1, Marcos de Lima Navarro 2, Fernanda Gobbi de Ávila 2,
Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol 2006;72(1):83-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Self-medication profile of ENT patients Alexandre Barbosa Servidoni 1, Liliane Coelho 1, Marcos de Lima Navarro 2, Fernanda Gobbi de Ávila 2,
Rocha 1, Gabriela Guimaraes Oliveira 1, Jessika Cefrin 1, Vanessa Cuentro 1, Claudine Lamanna Schirmer 1 and Maria Marina Serrao Cabral 1
 Diabetes Management Comparing the Prevalence and Drug Treatment Rates of Diabetes, Hypertension and Dyslipidemia between Japan and Brazil, using 2013 National Health Surveys Rocha 1, Gabriela Guimaraes
Diabetes Management Comparing the Prevalence and Drug Treatment Rates of Diabetes, Hypertension and Dyslipidemia between Japan and Brazil, using 2013 National Health Surveys Rocha 1, Gabriela Guimaraes
The life after myocardial infarction: a long quiet river?
 The life after myocardial infarction: a long quiet river? Cardiac rehabilitation: for whom and how? Dr. Barnabas GELLEN MD, PhD, FESC Poitiers JESFC 2018 - Paris Conflicts of interest Speaker honoraria
The life after myocardial infarction: a long quiet river? Cardiac rehabilitation: for whom and how? Dr. Barnabas GELLEN MD, PhD, FESC Poitiers JESFC 2018 - Paris Conflicts of interest Speaker honoraria
maintaining gains and relapse prevention
 maintaining gains and relapse prevention Tips for preventing a future increase in symptoms 3 If you do experience an increase in symptoms 8 What to do if you become pregnant again 9 2013 BC Reproductive
maintaining gains and relapse prevention Tips for preventing a future increase in symptoms 3 If you do experience an increase in symptoms 8 What to do if you become pregnant again 9 2013 BC Reproductive
The Failing Heart in Primary Care
 The Failing Heart in Primary Care Hamid Ikram How fares the Heart Failure Epidemic? 4357 patients, 57% women, mean age 74 years HFSA 2010 Practice Guideline (3.1) Heart Failure Prevention A careful and
The Failing Heart in Primary Care Hamid Ikram How fares the Heart Failure Epidemic? 4357 patients, 57% women, mean age 74 years HFSA 2010 Practice Guideline (3.1) Heart Failure Prevention A careful and
Quality of life and medication adherence in hypertensive patients
 Original Article Quality of life and medication adherence in hypertensive patients Qualidade de vida e adesão medicamentosa para pessoas hipertensas Ana Paula Ferreira Maciel 1 Henderson Barbosa Pimenta
Original Article Quality of life and medication adherence in hypertensive patients Qualidade de vida e adesão medicamentosa para pessoas hipertensas Ana Paula Ferreira Maciel 1 Henderson Barbosa Pimenta
Frailty assessment of institutionalized elderly
 Original Article Frailty assessment of institutionalized elderly Avaliação da fragilidade de idosos institucionalizados Cíntia Lira Borges 1 Maria Josefina da Silva 2 Jorge Wilker Bezerra Clares 1 Maria
Original Article Frailty assessment of institutionalized elderly Avaliação da fragilidade de idosos institucionalizados Cíntia Lira Borges 1 Maria Josefina da Silva 2 Jorge Wilker Bezerra Clares 1 Maria
Brazilian version of the Breast Evaluation Questionnaire: cultural adaptation and validation
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vendramin Ferreira Franco LF T FS et et al. et al. al. Brazilian version of the Breast Evaluation Questionnaire: cultural adaptation and validation Tradução para a língua portuguesa, adaptação
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vendramin Ferreira Franco LF T FS et et al. et al. al. Brazilian version of the Breast Evaluation Questionnaire: cultural adaptation and validation Tradução para a língua portuguesa, adaptação
Heart failure (HF) is a complex clinical syndrome that results in the. impairment of the heart s ability to fill or to pump out blood.
 Introduction: Heart failure (HF) is a complex clinical syndrome that results in the impairment of the heart s ability to fill or to pump out blood. As of 2013, an estimated 5.8 million people in the United
Introduction: Heart failure (HF) is a complex clinical syndrome that results in the impairment of the heart s ability to fill or to pump out blood. As of 2013, an estimated 5.8 million people in the United
Quality of life of people with non communicable diseases
 Original Article NUJHS Vol. 5, No.3, September 015, ISSN 49-7110 Quality of life of people with non communicable diseases 1 3 Anju Rose, Shashidhara Y.N. & Manjula 1 3 MSc Nursing Student, Associate Professor
Original Article NUJHS Vol. 5, No.3, September 015, ISSN 49-7110 Quality of life of people with non communicable diseases 1 3 Anju Rose, Shashidhara Y.N. & Manjula 1 3 MSc Nursing Student, Associate Professor
Self-Care Behaviors among women with Hypertension in Saudi Arabia
 IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science (IOSR-JNHS) e-issn: 2320 1959.p- ISSN: 2320 1940 Volume 5, Issue 3 Ver. III (May. - Jun. 2016), PP 52-56 www.iosrjournals.org Self-Care Behaviors among women
IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science (IOSR-JNHS) e-issn: 2320 1959.p- ISSN: 2320 1940 Volume 5, Issue 3 Ver. III (May. - Jun. 2016), PP 52-56 www.iosrjournals.org Self-Care Behaviors among women
Reduction of pain in clients with autoimmune bullous dermatoses: evaluation by fuzzy logic
 ISSN: 1676-4285 Reduction of pain in clients with autoimmune bullous dermatoses: evaluation by fuzzy logic Euzeli da Silva Brandão 1, Iraci dos Santos 2, Regina Serrão Lanzillotti 2 1 Federal University
ISSN: 1676-4285 Reduction of pain in clients with autoimmune bullous dermatoses: evaluation by fuzzy logic Euzeli da Silva Brandão 1, Iraci dos Santos 2, Regina Serrão Lanzillotti 2 1 Federal University
Hospitalization due to complications of arterial hypertension in primary care patients
 Original Article Hospitalization due to complications of arterial hypertension in primary care patients Hospitalização por agravos da hipertensão arterial em pacientes da atenção primária Mayckel da Silva
Original Article Hospitalization due to complications of arterial hypertension in primary care patients Hospitalização por agravos da hipertensão arterial em pacientes da atenção primária Mayckel da Silva
Does quality of life predict morbidity or mortality in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF)?
 Does quality of life predict morbidity or mortality in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF)? Erika Friedmann a, Eleanor Schron, b Sue A. Thomas a a University of Maryland School of Nursing; b NEI, National
Does quality of life predict morbidity or mortality in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF)? Erika Friedmann a, Eleanor Schron, b Sue A. Thomas a a University of Maryland School of Nursing; b NEI, National
Clear and Easy #11. Skypark Publishing. Molina Healthcare 24 Hour Nurse Advice Line (888)
 Clear and Easy #11 Molina Healthcare 24 Hour Nurse Advice Line (888) 275-8750 TTY: (866) 735-2929 Molina Healthcare Línea de TeleSalud Disponible las 24 Horas (866) 648-3537 TTY: (866) 833-4703 Skypark
Clear and Easy #11 Molina Healthcare 24 Hour Nurse Advice Line (888) 275-8750 TTY: (866) 735-2929 Molina Healthcare Línea de TeleSalud Disponible las 24 Horas (866) 648-3537 TTY: (866) 833-4703 Skypark
Keynote Address II Managing Acute Heart Failure: What Can We Do to Improve Outcomes?
 Keynote Address II Managing Acute Heart Failure: What Can We Do to Improve Outcomes? 24 th Annual San Diego Heart Failure Symposium June 1-2, 2018 La Jolla, CA Barry Greenberg, MD Distinguished Professor
Keynote Address II Managing Acute Heart Failure: What Can We Do to Improve Outcomes? 24 th Annual San Diego Heart Failure Symposium June 1-2, 2018 La Jolla, CA Barry Greenberg, MD Distinguished Professor
