Jennifer Hsieh 1, Amar Thosani 1, Matthew Grunwald 2, Satish Nagula 1, Juan Carlos Bucobo 1, Jonathan M. Buscaglia 1. Introduction
|
|
|
- Tyler Douglas
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 How We Do It Serial insertion of bilateral uncovered metal stents for malignant hilar obstruction using an 8 Fr biliary system: a case series of 17 consecutive patients Jennifer Hsieh 1, Amar Thosani 1, Matthew Grunwald 2, Satish Nagula 1, Juan Carlos Bucobo 1, Jonathan M. Buscaglia 1 1 Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Stony Brook University Hospital, Stony Brook, N, USA; 2 Stony Brook School of Medicine, Stony Brook, New ork, USA Correspondence to: Jennifer Hsieh, MD. 303 East 60th St, Apt. 32e, N 10022, USA. chacopye@yahoo.com. Abstract: Controversy exists over the need for unilateral versus bilateral stent placement in patients with malignant obstruction at the biliary hilum. Placement of bilateral uncovered self-expanding metal stent (UCSEMS) at this location is technically challenging, and generally associated with lower rates of procedural success. Serial insertion of side-by-side UCSEMS may be especially difficult when simultaneous deployment is not possible using larger stent delivery catheters. In this single-center, retrospective case series of all patients who underwent bilateral placement of uncovered Wallflex TM biliary stents between July 2008 and July 2014, we evaluate the feasibility, technical success, and safety of patients undergoing serial insertion of bilateral UCSEMS using the 8 Fr Wallflex TM biliary system for malignant hilar obstruction. A total of 17 patients were included. Primary cholangiocarcinoma, Bismuth IV, was the most common diagnosis. Mean procedure time was 54.4 minutes. Overall procedural technical success was achieved in 17/17 patients. Stricture dilation was necessary prior to Wallflex TM insertion in 8/17 patients (47.1%). Transpapillary extension of two stents was performed in all patients. There were no cases of stent deployment malfunction, or inability to insert or deploy the 2 nd stent. Nine of 17 patients (52.9%) required inpatient hospitalization following ERCP; the most common indications were abdominal pain and need for IV antibiotics. There was one case of ERCP-related cholangitis otherwise; there were no other major complications. Bilateral, serial insertion of UCSEMS using the 8 Fr Wallflex TM biliary system in malignant hilar obstruction is feasible with an excellent technical success profile. Using this device for side-by-side deployment of UCSEMS appears to be safe in the majority of patients. Keywords: Biliary obstruction; hilar obstruction; biliary stricture; Wallflex TM stent Submitted Mar 02, Accepted for publication May 26, doi: /j.issn View this article at: Introduction There remains considerable debate over the need for unilateral versus bilateral stent placement in patients with malignant obstruction of the biliary hilum. Unilateral insertion of uncovered self-expanding metal stents (UCSEMS) for unresectable cholangiocarcinoma involving the hilum has been shown to be safe, feasible, and effective for the majority of patients (1,2). Placement of bilateral UCSEMS is technically challenging, and generally associated with lower rates of procedural success. Furthermore, metal stent insertion into both the right and left ductal systems appears to be comparable to unilateral insertion with regards to overall patency and complicationfree survival, while increasing infectious complication rates (1-3). Despite these potential advantages to unilateral UCSEMS, the goal of palliative stent placement in malignant biliary obstruction is to drain at least 50% of the liver volume
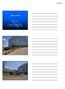
2 HepatoBiliary Surgery and Nutrition, Vol 4, No 5 October 2015 (4,5). Drainage of more than half the liver volume often requires placement of more than one stent, resulting in bilateral or multi-segmental UCSEMS insertion. Previous studies examining the optimal technique in bilateral UCSEMS placement have reported significant technical limitations when stents are deployed in standard side-byside fashion (6-8). Passing the second UCSEMS alongside the first stent is often impossible due to the radial expansive force from the previously deployed stent. However, with the development of thinner 6 Fr delivery catheters, two stents can be inserted through the working channel of the duodenoscope for bilateral, simultaneous deployment (6,9). Alternatively, the second stent may be deployed through the large interstices of the first stent using stent-in-stent technique (9), particularly when utilizing laser-cut (as opposed to woven) metal stents. The Wallflex TM uncovered biliary stent (Boston Scientific Inc., Marlborough, MA, USA) is a woven UCSEMS that utilizes an 8 Fr delivery catheter. The larger catheter size prevents simultaneous insertion of two stents down the endoscope channel. Also, the braided (woven) design of the stent creates smaller interstices, thus virtually preventing stent-in-stent deployment technique when placing bilateral stents. There are limited data, if any, on the technical success profile of this particular UCSEMS when used for bilateral palliation of malignant hilar obstruction. In the following report, we describe the feasibility and technical success, as well as procedural safety, in a series of 17 patients undergoing bilateral UCSEMS for malignant obstruction at the biliary hilum utilizing this 8 Fr delivery system. Study design and endoscopic technique This study was approved by the Stony Brook University Institutional Review Board (IRB). A retrospective review of our hospital s endoscopy procedure software was performed between July 2008 and July Only ERCP cases in which bilateral UCSEMS were deployed for malignant hilar obstruction using the Wallflex TM biliary stent were selected. The total number of attempted cases using the Wallflex TM biliary stent was not included in this series, as this information is not routinely recorded in our electronic endoscopy records. Additional clinical data were gathered from the patients electronic medical record, including demographic characteristics, laboratory values, cancer treatment plans, and overall clinical course and hospitalizations. ERCP procedures were performed as clinically indicated after obtaining informed consent. 349 All procedures were performed by one of three endoscopists (JMB, SN, JCB) with anesthesia support. A standard therapeutic-channel video duodenoscope (models TJF-160 and TJF-180, Olympus America Inc., Center Valley, PA, USA) was used in each case. Biliary sphincterotomy was performed in all patients, or had been previously performed, before stent placement. Stricture dilation was utilized as needed for easier passage of the stent delivery catheter. Prophylactic intravenous antibiotics were given at the time of each procedure. Routine use of post-procedure antibiotics was not performed, unless the endoscopist noted inadequate drainage from a segment of liver that was filled with contrast. Following a diagnostic cholangiogram, two guidewires (0.035-inch HydraJagwire or Jagwire, Boston Scientific Inc., Marlborough, MA, USA) were placed through the working channel of the duodenoscope and directed into the both the right and left ductal systems. These wires were positioned in side-by-side configuration. The hepatic duct with the more severe stenosis, or the more acute angle in take-off from the hilum, was chosen first for stent deployment. A preloaded 8 Fr delivery system was passed over this guidewire, alongside the second guidewire, and pushed up into the appropriate duct. The goal in choosing the proper stent size was to allow for at least 1 cm of patent stent above the stricture, while the distal end cross the ampullary orifice into the duodenum. The first stent was deployed completely alongside the existing, adjacent guidewire. After complete deployment of the first UCSEMS, the delivery catheter was removed leaving its guidewire in place. The second 8 Fr UCSEMS delivery system was then inserted over the second guidewire. This stent was gently pushed up into the other ductal system alongside the previously deployed stent. Some degree of endoscope position alteration was usually required to allow for complete advancement of the stent catheter across stricture while the first stent was already in place. Once the second UCSEMS was in the appropriate position, this stent was fully deployed with the aim of allowing the distal end to cross the ampullary orifice as seen in Figure 1. After fully deployed, the stent delivery catheter and both guidewires were removed. Statistics Descriptive statistics were reported as a mean value with standard deviation, or a median value with range, for all continuous variables. No additional statistical analyses were
3 350 Hsieh et al. Wallflex TM stent in hilar biliary obstruction Figure 1 Fluoroscopic image of bilateral Wallflex TM UCSEMS at the hilum. performed for this series. Results and discussion A total of 17 patients with malignant hilar obstruction were identified in which bilateral UCSEMS were inserted. The clinical characteristics of these 17 patients are listed in Table 1. Thirteen of 17 patients were male (76.5%). The median age was 63 years old (range, years). Most patients had primary cholangiocarcinoma, Bismuth classification IV, as the cause of their biliary obstruction. Metastatic cancers due to non-biliary malignancies were the causes of obstruction in the remaining 8/17 patients. All patients who were stented were at the initial phases of their chemotherapy regimens. All patients presented with obstructive jaundice and pruritus. The mean total bilirubin level prior to undergoing any biliary intervention was 13.4±13.7 mg/dl (Table 1). The mean length of the longest segment of biliary stricture was 1.5±0.8 cm. Three patients (17.6%) had multi-focal disease, with additional strictures either above or below the hilum. Eleven of 17 patients (64.7%) had an initial ERCP with plastic stent placement prior to UCSEMS insertion; median number of stents placed was 2 (range, 1-3). Procedure characteristics are shown in Table 2. The average procedure time was 54.4 minutes (range, minutes). In 8/17 patients (47.1%), balloon dilation of the stricture was performed prior to UCSEMS placement. In all but two patients, both biliary stents were successfully deployed with their distal ends crossing the ampullary orifice within the duodenum. In both of these patients, a 3 rd uncovered 40 mm 8 mm UCSEMS was inserted over the 2 nd guidewire to allow for adequate transpapillary drainage. All procedures were technically successful. There were no episodes of stent deployment malfunction in these 17 cases. One patient required initial placement of a percutaneous transhepatic biliary drain prior to successful ERCP because of failed retrograde biliary cannulation. The drain was removed at the time of the 2 nd ERCP in which bilateral UCSEMS were inserted. Nine of 17 patients (52.9%) required inpatient hospitalization following their elective outpatient procedure. The reasons for admission were post-procedure abdominal pain and the need for intravenous antibiotics to prevent cholangitis (due inadequate drainage of contrast from one segment of liver). There was only one case of post-procedure cholangitis treated successfully with antibiotics. This patient also required subsequent percutaneous transhepatic biliary drain placement due to persistent hyperbilirubinemia. There were no episodes of post-procedure stent obstruction, pancreatitis, perforation, bleeding, or other infections aside from cholangitis in this series. There were no deaths directly related to the ERCP procedure. Post-procedure bilirubin levels 2 weeks after stent insertion were not universally available. However, at least 10/17 patients (58.8%) were seeing an oncologist for palliative chemotherapy after stent placement, suggesting adequate biliary drainage. The remaining seven patients elected for hospice care only, or were lost to follow-up. Biliary drainage for unresectable malignant hilar obstruction is challenging and frequently performed by the insertion of UCSEMS, in an attempt to reduce hyperbilirubinemia so that patients may undergo palliative chemotherapy. Though controversy exists over unilateral versus bilateral stenting, the placement of bilateral stents is often necessary to drain more than half the liver volume and provide the best opportunity for improvement in hepatic function. With the advent of new and improved biliary endoprostheses, the technical feasibility of bilateral stenting has become somewhat less challenging for the biliary endoscopist. Following the recent introduction of the Wallflex TM biliary UCSEMS into clinical practice, there have been limited data describing the use of this particular stent for bilateral palliation of malignant hilar obstruction. In 2012, Luigiano and colleagues (10) were the first to specifically compare the Wallflex TM UCSEMS with its predecessor UCSEMS, the biliary Wallstent. Although late adverse events appeared to be lower in the Wallflex TM group
4 HepatoBiliary Surgery and Nutrition, Vol 4, No 5 October Table 1 Patient characteristics Patient Age Gender Etiology T.bil (mg/dl) Location Length (cm) Prior plastic stents 1 75 M Metastatic small cell lung cancer 30.5 Bismuth IV M Primary cholangiocarcinoma 33.9 Bismuth IV M Metastatic lymphoma 9.8 Bismuth II M Metastatic pancreatic cancer 3.1 Bismuth II M Primary cholangiocarcinoma 3.5 Bismuth IV F Metastatic pancreatic cancer 7.1 Bismuth IV* 2, M Primary cholangiocarcinoma 4.5 Bismuth IV M Primary cholangiocarcinoma 9.5 Bismuth IV F Metastatic gallbladder cancer 2.6 Bismuth IV M Metastatic appendiceal cancer 4.5 Bismuth IV F Metastatic pancreatic cancer 2.6 Bismuth IV M Metastatic colon cancer 12.4 Bismuth IV F Primary cholangiocarcinoma 8.6 Bismuth IV M Primary cholangiocarcinoma 0.4 Bismuth IV* 4, M Primary cholangiocarcinoma 48.3 Bismuth IV* 2.5, M Primary cholangiocarcinoma 19.5 Bismuth IV M Primary cholangiocarcinoma 27 Bismuth IV Pre-procedure characteristics of all 17 patients undergoing bilateral Wallflex biliary stent placement. Length refers to longest segment of bile duct stenosis; 2 nd value in type IV* patients for length of multi-focal stenosis; *, type IV obstruction with additional multi-focal disease. (10.3% vs. 27.8%), only a small proportion of patients in this study had hilar obstruction (12% Wallflex TM and 4% Wallstent ), and there was no report of bilateral Wallflex TM insertion (10). Almadi and colleagues recently performed a thorough meta-analysis examining the use of covered and uncovered SEMS for biliary obstruction, many of which utilized the Wallflex TM stent (11). However, this study was designed to focus on distal biliary obstruction, and bilateral placement across the hilum was not addressed. Earlier studies that examined the feasibility of bilateral biliary stenting specifically in hilar malignancies focused mainly on biliary stents with smaller delivery systems, such as the 6 Fr Zilver 635 UCSEMS (Cook Medical Inc., Winston Salem, NC, USA), or the 7 Fr Fusion Zilver UCSEMS (Cook Medical Inc., Winston Salem, NC, USA). In 2009, Kim et al. (12) reported a technical success rate of 85.3% (29/34) using the stent-in-stent technique with the 7 Fr Zilver delivery system in conjunction with the Niti-S Biliary stent (Taewoong Medical Co., South Korea). It was suggested that the Zilver s slimmer 7 Fr delivery system is what allowed for this UCSEMS to be inserted through the central portion of the stent into the contralateral hepatic duct. Chennat et al. (6) conducted a small case series of 16 patients examining side-by-side simultaneous deployment of the 6 Fr delivery system Zilver biliary stent with a success rate of 62.5% (10/16). However, the bilateral hilar stents did not bridge the ampullary region, and so all of these patients required additional stent placement to achieve transpapillary drainage. In this brief report, we demonstrate our initial results regarding the feasibility, technical success, and early procedural safety of bilateral uncovered Wallflex TM insertion for malignant hilar strictures. Bilateral stenting was successfully achieved in less than 1 hour (average time 54 minutes) in all 17 patients; keeping in mind that the total number of attempted cases was not reported. Though the rate of inpatient hospitalization is somewhat higher compared to the early complication rates reported in prior studies [53% vs % (3,9)], the majority of postprocedure admissions were due to transient abdominal pain rather than procedure-related complications (i.e., pancreatitis, hemobilia, liver abscess, stent obstruction, etc.). Only one patient developed procedural-induced
5 352 Hsieh et al. Wallflex TM stent in hilar biliary obstruction Table 2 Procedure characteristics related specifics Patient Procedure Stent type Balloon Technical time (mins) (mm) type (/N) success (/N) , 80 8 N , 80 8 N , N , N , , 80 8 N , , , , 80 8 N , 80 8 N , 80 8, 40 8* , 80 8 N , 80 8 N , 40 8, 40 8* , , 40 8 *3 rd, overlapping stent to allow for extension out the ampullary orifice. cholangitis; but this patient was treated successfully with IV antibiotics and no further clinical consequences. Although the Wallflex TM UCSEMS utilizes a larger 8 Fr delivery catheter with smaller interstices than other available stents, the inability to perform traditional side-by-side or stentin-stent techniques (9) did not prevent successful insertion or cause deployment malfunction. Serial or subsequent stent placement was not limited by the radial force of the first stent deployed. The reason for this is likely related to the flexible nature of the completely deployed first stent. Furthermore, although not unique to this stent, its looped and flared ends may limit to some degree the amount of stent migration that occurs when pushing the second stent catheter into position before deployment. Lastly, many of our patients had previous plastic stents (64.7%) or balloon dilation (47.1%) prior to UCSEMS insertion. Some or all of these factors may account for the high degree of technical success observed in this series. There are clearly limitations and inherent biases with this retrospective case series that warrant mention. As noted above, many of the patients had prior plastic stents inserted, and this may have facilitated the ease of insertion of either the first or the second 8 Fr delivery catheter. Furthermore, balloon dilation of the stricture was not uniformly performed in each patient, and pre-dilation of a stricture also affects the ease of subsequent stent insertion. In addition, there was lack of standardization in the diameter sizes of each stent inserted, as well as heterogeneity in the different types of malignant hilar obstruction intervened upon. Each of these factors may affect the technical success rate, and therefore the safety profile, of bilateral UCSEMS placement. Finally, long-term clinical outcomes were not addressed as many of the patients were discharged after their procedures with follow-up at outside institutions. In conclusion, there are limited data describing the use of the 8 Fr delivery Wallflex TM stent for the treatment of hilar biliary obstruction, and no prior reports that specifically examine the bilateral insertion of this endoprosthesis. This case series illustrates that decompression of malignant hilar biliary obstruction can be reasonably achieved by means of bilateral insertion of UCSEMS using these biliary stents. Serial placement of this device into the right and left systems can be performed with good technical feasibility and safety profiles. Despite its larger delivery size, the unique design of this stent appears to enable the biliary endoscopist to overcome the difficulties traditionally encountered in deploying bilateral stents within anatomically complex locations. Acknowledgements None. Footnote Conflicts of Interest: Juan Carlos Bucobo and Jonathan M. Buscaglia are consultants and speakers for Boston Scientific, Inc. Ethical Statement: This study was approved by the Stony Brook University Institutional Review Board. ERCP procedures were performed as clinically indicated after obtaining informed consent. References 1. De Palma GD, Galloro G, Siciliano S, et al. Unilateral
6 HepatoBiliary Surgery and Nutrition, Vol 4, No 5 October versus bilateral endoscopic hepatic duct drainage in patients with malignant hilar biliary obstruction: results of a prospective, randomized, and controlled study. Gastrointest Endosc 2001;53: De Palma GD, Pezzullo A, Rega M, et al. Unilateral placement of metallic stents for malignant hilar obstruction: a prospective study. Gastrointest Endosc 2003;58: Iwano H, Ryozawa S, Ishigaki N, et al. Unilateral versus bilateral drainage using self-expandable metallic stent for unresectable hilar biliary obstruction. Dig Endosc 2011;23: Rerknimitr R, Angsuwatcharakon P, Ratanachu-ek T, et al. Asia-Pacific consensus recommendations for endoscopic and interventional management of hilar cholangiocarcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2013;28: Lee TH. Technical tips and issues of biliary stenting, focusing on malignant hilar obstruction. Clin Endosc 2013;46: Chennat J, Waxman I. Initial performance profile of a new 6F self-expanding metal stent for palliation of malignant hilar biliary obstruction. Gastrointest Endosc 2010;72: Dumas R, Demuth N, Buckley M, et al. Endoscopic bilateral metal stent placement for malignant hilar stenoses: identification of optimal technique. Gastrointest Endosc 2000;51: Cheng JL, Bruno MJ, Bergman JJ, et al. Endoscopic palliation of patients with biliary obstruction caused by nonresectable hilar cholangiocarcinoma: efficacy of selfexpandable metallic Wallstents. Gastrointest Endosc 2002;56: Law R, Baron TH. Bilateral metal stents for hilar biliary obstruction using a 6Fr delivery system: outcomes following bilateral and side-by-side stent deployment. Dig Dis Sci 2013;58: Luigiano C, Ferrara F, Cennamo V, et al. A comparison of uncovered metal stents for the palliation of patients with malignant biliary obstruction: nitinol vs. stainless steel. Dig Liver Dis 2012;44: Almadi MA, Barkun AN, Martel M. No benefit of covered vs uncovered self-expandable metal stents in patients with malignant distal biliary obstruction: a meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2013;11: Kim J, Kang DH, Kim HW, et al. Usefulness of slimmer and open-cell-design stents for endoscopic bilateral stenting and endoscopic revision in patients with hilar cholangiocarcinoma (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 2009;70: Cite this article as: Hsieh J, Thosani A, Grunwald M, Nagula S, Bucobo JC, Buscaglia JM. Serial insertion of bilateral uncovered metal stents for malignant hilar obstruction using an 8 Fr biliary system: a case series of 17 consecutive patients. HepatoBiliary Surg Nutr 2015;4(5): doi: / j.issn
Expandable stents in digestive pathology present use in an emergency hospital
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Article received on November30, 2015 and accepted for publishing on December15, 2015. Expandable stents in digestive pathology present use in an emergency hospital Mădălina Ilie 1, Vasile
ORIGINAL ARTICLES Article received on November30, 2015 and accepted for publishing on December15, 2015. Expandable stents in digestive pathology present use in an emergency hospital Mădălina Ilie 1, Vasile
ACUTE CHOLANGITIS AS a result of an occluded
 Digestive Endoscopy 2017; 29 (Suppl. 2): 88 93 doi: 10.1111/den.12836 Current status of biliary drainage strategy for acute cholangitis Endoscopic treatment for acute cholangitis with common bile duct
Digestive Endoscopy 2017; 29 (Suppl. 2): 88 93 doi: 10.1111/den.12836 Current status of biliary drainage strategy for acute cholangitis Endoscopic treatment for acute cholangitis with common bile duct
Approach to the Biliary Stricture
 Approach to the Biliary Stricture ACG Eastern Postgraduate Course Washington DC June 8, 2014 Steven A. Edmundowicz MD FASGE Chief of Endoscopy Division of Gastroenterology Professor of Medicine Disclosures
Approach to the Biliary Stricture ACG Eastern Postgraduate Course Washington DC June 8, 2014 Steven A. Edmundowicz MD FASGE Chief of Endoscopy Division of Gastroenterology Professor of Medicine Disclosures
Maximize Control. Minimize Migration.
 Maximize Control. Minimize Migration. New SHORT WIRE Delivery System SHORT W IRE BILIARY ENDOPROSTHESIS Improved treatment of biliary strictures The self-expanding, fully covered metal stent is intended
Maximize Control. Minimize Migration. New SHORT WIRE Delivery System SHORT W IRE BILIARY ENDOPROSTHESIS Improved treatment of biliary strictures The self-expanding, fully covered metal stent is intended
Endoscopic Management of Biliary Strictures. Sammy Ho, MD Director of Pancreaticobiliary Services and Endoscopic Ultrasound Montefiore Medical Center
 Endoscopic Management of Biliary Strictures Sammy Ho, MD Director of Pancreaticobiliary Services and Endoscopic Ultrasound Montefiore Medical Center Malignant Biliary Strictures Etiologies: Pancreatic
Endoscopic Management of Biliary Strictures Sammy Ho, MD Director of Pancreaticobiliary Services and Endoscopic Ultrasound Montefiore Medical Center Malignant Biliary Strictures Etiologies: Pancreatic
Стенты «Ella-cs» Уважаемые коллеги! Высылаем очередной выпуск «Issue of ELLA Abstracts»
 Уважаемые коллеги! Высылаем очередной выпуск «Issue of ELLA Abstracts» A. Esophageal Stenting and related topics 1 AMJG 2009; 104:1329 1330 Letters to Editor Early Tracheal Stenosis Post Esophageal Stent
Уважаемые коллеги! Высылаем очередной выпуск «Issue of ELLA Abstracts» A. Esophageal Stenting and related topics 1 AMJG 2009; 104:1329 1330 Letters to Editor Early Tracheal Stenosis Post Esophageal Stent
Manuel José Antunes Liberato * and Jorge Manuel Tavares Canena
 Liberato and Canena BMC Gastroenterology 2012, 12:103 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Endoscopic stenting for hilar cholangiocarcinoma: efficacy of unilateral and bilateral placement of plastic and metal
Liberato and Canena BMC Gastroenterology 2012, 12:103 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Endoscopic stenting for hilar cholangiocarcinoma: efficacy of unilateral and bilateral placement of plastic and metal
Clinical Study Covered Metal Stenting for Malignant Lower Biliary Stricture with Pancreatic Duct Obstruction: Is Endoscopic Sphincterotomy Needed?
 Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2013, Article ID 375613, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/375613 Clinical Study Covered Metal Stenting for Malignant Lower Biliary Stricture with Pancreatic
Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2013, Article ID 375613, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/375613 Clinical Study Covered Metal Stenting for Malignant Lower Biliary Stricture with Pancreatic
Evaluation of a 12-mm diameter covered self-expandable end bare metal stent for malignant biliary obstruction
 Evaluation of a 12-mm diameter covered self-expandable end bare metal stent for malignant biliary obstruction Authors Kazunori Nakaoka, Senju Hashimoto, Naoto Kawabe, Takuji Nakano, Toshiki Kan, Masashi
Evaluation of a 12-mm diameter covered self-expandable end bare metal stent for malignant biliary obstruction Authors Kazunori Nakaoka, Senju Hashimoto, Naoto Kawabe, Takuji Nakano, Toshiki Kan, Masashi
Bilateral stenting methods for hilar biliary obstructions
 RAPID COMMUNICATION Bilateral stenting methods for hilar biliary obstructions Wandong Hong, I Shanxi Chen, II Qihuai Zhu, I Huichun Chen, III Jingye Pan, IV Qingke Huang I* I First Affiliated Hospital
RAPID COMMUNICATION Bilateral stenting methods for hilar biliary obstructions Wandong Hong, I Shanxi Chen, II Qihuai Zhu, I Huichun Chen, III Jingye Pan, IV Qingke Huang I* I First Affiliated Hospital
Endoscopic stenting in bile duct cancer increases liver volume
 Endoscopic stenting in bile duct cancer increases liver volume Chang Hun Lee 1,3, Seung Young Seo 1,3, Seong Hun Kim 1,3, In Hee Kim 1,3, Sang Wook Kim 1,3, Soo Teik Lee 1,3, Dae Ghon Kim 1,3, Jae Do Yang
Endoscopic stenting in bile duct cancer increases liver volume Chang Hun Lee 1,3, Seung Young Seo 1,3, Seong Hun Kim 1,3, In Hee Kim 1,3, Sang Wook Kim 1,3, Soo Teik Lee 1,3, Dae Ghon Kim 1,3, Jae Do Yang
Making ERCP Easy: Tips From A Master
 Making ERCP Easy: Tips From A Master Raj J. Shah, M.D., FASGE Associate Professor of Medicine University of Colorado School of Medicine Co-Director, Endoscopy Director, Pancreaticobiliary Endoscopy Services
Making ERCP Easy: Tips From A Master Raj J. Shah, M.D., FASGE Associate Professor of Medicine University of Colorado School of Medicine Co-Director, Endoscopy Director, Pancreaticobiliary Endoscopy Services
Endoscopic Management of the Iatrogenic CBD Injury
 The Liver Week 2014, Jeju, Korea Endoscopic Management of the Iatrogenic CBD Injury Jong Ho Moon, MD, PhD Department of Internal Medicine Soon Chun Hyang University School of Medicine Bucheon/Seoul, KOREA
The Liver Week 2014, Jeju, Korea Endoscopic Management of the Iatrogenic CBD Injury Jong Ho Moon, MD, PhD Department of Internal Medicine Soon Chun Hyang University School of Medicine Bucheon/Seoul, KOREA
Early Infectious Complications of Percutaneous Metallic Stent Insertion for Malignant Biliary Obstruction
 Vascular and Interventional Radiology Original Research Sol et al. Stent Insertion in Biliary Obstruction Vascular and Interventional Radiology Original Research Yu Li Sol 1 Chang Won Kim 1 Ung Bae Jeon
Vascular and Interventional Radiology Original Research Sol et al. Stent Insertion in Biliary Obstruction Vascular and Interventional Radiology Original Research Yu Li Sol 1 Chang Won Kim 1 Ung Bae Jeon
Partially Covered Metal Stents May Not Prolong Stent Patency Compared to Uncovered Stents in Unresectable Malignant Distal Biliary Obstruction
 Gut and Liver, Vol. 11, No. 3, May 217, pp. 44-446 ORiginal Article Partially Covered Metal Stents May Not Prolong Stent Patency Compared to Uncovered Stents in Unresectable Malignant Distal Biliary Obstruction
Gut and Liver, Vol. 11, No. 3, May 217, pp. 44-446 ORiginal Article Partially Covered Metal Stents May Not Prolong Stent Patency Compared to Uncovered Stents in Unresectable Malignant Distal Biliary Obstruction
Biliary Metal Stents MAKING A DIFFERENCE TO HEALTH
 Biliary Metal Stents In a fast paced and maturing market, Diagmed Healthcare s Hanarostent has managed to continue to innovate and add unique and clinically superior features to its already premium range.
Biliary Metal Stents In a fast paced and maturing market, Diagmed Healthcare s Hanarostent has managed to continue to innovate and add unique and clinically superior features to its already premium range.
WallFlex Stents Technique Spotlights
 WallFlex Stents Technique Spotlights OPEN TO THE POSSIBILITIES SEAN E. McGarr, do Kennebec Gastrointestinal Associates Maine General Medical Center, Augusta, ME 04330, United States Director of Gastrointestinal
WallFlex Stents Technique Spotlights OPEN TO THE POSSIBILITIES SEAN E. McGarr, do Kennebec Gastrointestinal Associates Maine General Medical Center, Augusta, ME 04330, United States Director of Gastrointestinal
Principles of ERCP: papilla cannulation, indications/contraindications and risks. Dr. med. Henrik Csaba Horváth PhD
 Principles of ERCP: papilla cannulation, indications/contraindications and risks Dr. med. Henrik Csaba Horváth PhD Evolution of ERCP 1968. 1970s ECPG Endoscopic CholangioPancreatoGraphy Japan 1974 Biliary
Principles of ERCP: papilla cannulation, indications/contraindications and risks Dr. med. Henrik Csaba Horváth PhD Evolution of ERCP 1968. 1970s ECPG Endoscopic CholangioPancreatoGraphy Japan 1974 Biliary
Interventional Endoscopy in PB Malignancy
 Interventional Endoscopy in PB Malignancy 7 th Annual Symposium on GI Cancers St Louis, Missouri Sept 20 th, 2008 David L Carr-Locke MA, MB BChir, DRCOG, FRCP, FACG, FASGE Director, Endoscopy Institute,
Interventional Endoscopy in PB Malignancy 7 th Annual Symposium on GI Cancers St Louis, Missouri Sept 20 th, 2008 David L Carr-Locke MA, MB BChir, DRCOG, FRCP, FACG, FASGE Director, Endoscopy Institute,
The first stents designed for use in the biliary tree and
 Imaging and Advanced Technology Michael B. Wallace, Section Editor Expandable Gastrointestinal Stents TODD H. BARON Department of Medicine, Division of Gastroenterology & Hepatology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester,
Imaging and Advanced Technology Michael B. Wallace, Section Editor Expandable Gastrointestinal Stents TODD H. BARON Department of Medicine, Division of Gastroenterology & Hepatology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester,
STRICTURES OF THE BILE DUCTS Session No.: 5. Andrea Tringali Digestive Endoscopy Unit Catholic University Rome - Italy
 STRICTURES OF THE BILE DUCTS Session No.: 5 Andrea Tringali Digestive Endoscopy Unit Catholic University Rome - Italy Drainage of biliary strictures. The history before 1980 Surgical bypass Percutaneous
STRICTURES OF THE BILE DUCTS Session No.: 5 Andrea Tringali Digestive Endoscopy Unit Catholic University Rome - Italy Drainage of biliary strictures. The history before 1980 Surgical bypass Percutaneous
Air cholangiography in endoscopic bilateral stent-in-stent placement of metallic stents for malignant hilar biliary obstruction
 618132TAG0010.1177/1756283X15618132Therapeutic Advances in GastroenterologyJM Lee, SH Lee research-article2015 Therapeutic Advances in Gastroenterology Original Research Air cholangiography in endoscopic
618132TAG0010.1177/1756283X15618132Therapeutic Advances in GastroenterologyJM Lee, SH Lee research-article2015 Therapeutic Advances in Gastroenterology Original Research Air cholangiography in endoscopic
Paola Figueroa-Barojas, Mihir R. Bakhru, Nagy A. Habib, Kristi Ellen, Jennifer Millman, Armeen Jamal-Kabani, Monica Gaidhane, and Michel Kahaleh
 Oncology Volume 2013, Article ID 910897, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/910897 Clinical Study Safety and Efficacy of Radiofrequency Ablation in the Management of Unresectable Bile Duct and Pancreatic
Oncology Volume 2013, Article ID 910897, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/910897 Clinical Study Safety and Efficacy of Radiofrequency Ablation in the Management of Unresectable Bile Duct and Pancreatic
Biliary Strictures: the Long and the Short of It. Willis Parsons, M.D. Medical Director of GI Lab Northwest Community Hospital Arlington Heights, IL
 Biliary Strictures: the Long and the Short of It Willis Parsons, M.D. Medical Director of GI Lab Northwest Community Hospital Arlington Heights, IL Consultant to Cook Medical Disclosure Objectives 1) Understand
Biliary Strictures: the Long and the Short of It Willis Parsons, M.D. Medical Director of GI Lab Northwest Community Hospital Arlington Heights, IL Consultant to Cook Medical Disclosure Objectives 1) Understand
Endoscopic Stent Placement in the Palliation of Malignant Biliary Obstruction
 REVIEW Clin Endosc 2011;44:76-86 Print ISSN 2234-2400 / On-line ISSN 2234-2443 http://dx.doi.org/10.5946/ce.2011.44.2.76 Open Access Endoscopic Stent Placement in the Palliation of Malignant Biliary Obstruction
REVIEW Clin Endosc 2011;44:76-86 Print ISSN 2234-2400 / On-line ISSN 2234-2443 http://dx.doi.org/10.5946/ce.2011.44.2.76 Open Access Endoscopic Stent Placement in the Palliation of Malignant Biliary Obstruction
A tale of two LAMS: a report of benign tissue ingrowth resulting in recurrent gastric outlet obstruction
 A tale of two LAMS: a report of benign tissue ingrowth resulting in recurrent gastric outlet obstruction Authors Parth J. Parekh, Mohammad H. Shakhatreh, Paul Yeaton Institution Department of Internal
A tale of two LAMS: a report of benign tissue ingrowth resulting in recurrent gastric outlet obstruction Authors Parth J. Parekh, Mohammad H. Shakhatreh, Paul Yeaton Institution Department of Internal
Percutaneous Metallic Stent Placement for Palliative Management of Malignant Biliary Hilar Obstruction
 Original Article Intervention https://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2018.19.4.597 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2018;19(4):597-605 Percutaneous Metallic Stent Placement for Palliative Management
Original Article Intervention https://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2018.19.4.597 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2018;19(4):597-605 Percutaneous Metallic Stent Placement for Palliative Management
WallFlex Biliary RX Fully Covered Stent System Prescriptive Information
 Caution/Rx Only: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. Warning Contents supplied STERILE using an ethylene oxide (EO) process. Do not use if sterile barrier
Caution/Rx Only: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. Warning Contents supplied STERILE using an ethylene oxide (EO) process. Do not use if sterile barrier
Allium Trans-hepatic Biliary Stent (BIS)
 Allium Trans-hepatic Biliary (BIS) Instructions for Use Manufactured by Allium Ltd. DEVICE NAME Allium Trans-hepatic Biliary (BIS) DEVICE DESCRIPTION The Trans-hepatic BIS is a flexible, self-expanding
Allium Trans-hepatic Biliary (BIS) Instructions for Use Manufactured by Allium Ltd. DEVICE NAME Allium Trans-hepatic Biliary (BIS) DEVICE DESCRIPTION The Trans-hepatic BIS is a flexible, self-expanding
WallFlex Biliary Metal Stents
 WallFlex Biliary Metal Stents Please Note: These steps are intended to be for general guidance only. For complete instructions for use, indications, contraindications and warnings, please refer to the
WallFlex Biliary Metal Stents Please Note: These steps are intended to be for general guidance only. For complete instructions for use, indications, contraindications and warnings, please refer to the
Colorectal stenting. Alessandro Repici, MD Digestive Endoscopy Unit IRCCS Istituto Clinico Humanitas Milano, Italy
 Colorectal stenting Alessandro Repici, MD Digestive Endoscopy Unit IRCCS Istituto Clinico Humanitas Milano, Italy Metal Stents for Obstructing Colorectal Cancer Dohomoto was credited as the first to report
Colorectal stenting Alessandro Repici, MD Digestive Endoscopy Unit IRCCS Istituto Clinico Humanitas Milano, Italy Metal Stents for Obstructing Colorectal Cancer Dohomoto was credited as the first to report
Intraluminal Brachytherapy after Metallic Stent Placement in Primary Bile Duct Carcinoma 1
 Intraluminal Brachytherapy after Metallic Stent Placement in Primary Bile Duct Carcinoma 1 Kyu-Hong Park, M.D., Soon Gu Cho, M.D., Sung-Gwon Kang, M.D. 1,2, Don Haeng Lee, M.D. 3, Woo Cheol Kim, M.D. 4,
Intraluminal Brachytherapy after Metallic Stent Placement in Primary Bile Duct Carcinoma 1 Kyu-Hong Park, M.D., Soon Gu Cho, M.D., Sung-Gwon Kang, M.D. 1,2, Don Haeng Lee, M.D. 3, Woo Cheol Kim, M.D. 4,
INTRODUCTION. Key Words: Cholestasis, extrahepatic; Stents; Cholangiography; Endoscopic retrograde. ORiginal Article
 Gut and Liver, Vol. 7, No. 6, November 2013, pp. 725-730 ORiginal Article A Novel, Fully Covered Laser-Cut Nitinol Stent with Antimigration Properties for Nonresectable Distal Malignant Biliary Obstruction:
Gut and Liver, Vol. 7, No. 6, November 2013, pp. 725-730 ORiginal Article A Novel, Fully Covered Laser-Cut Nitinol Stent with Antimigration Properties for Nonresectable Distal Malignant Biliary Obstruction:
Covered biliary stents with proximal bare stent extension for the palliation of malignant biliary disease: can we reduce tumour overgrowth rate?
 Original Article Covered biliary stents with proximal bare stent extension for the palliation of malignant biliary disease: can we reduce tumour overgrowth rate? Miltiadis Krokidis 1, Adam Hatzidakis 2
Original Article Covered biliary stents with proximal bare stent extension for the palliation of malignant biliary disease: can we reduce tumour overgrowth rate? Miltiadis Krokidis 1, Adam Hatzidakis 2
Percutaneous biliary drainage: complications and efficiency at short and mean terms: about 50 cases
 Percutaneous biliary drainage: complications and efficiency at short and mean terms: about 50 cases Poster No.: C-1497 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Matri, L. Ben Farhat, I. Marzouk
Percutaneous biliary drainage: complications and efficiency at short and mean terms: about 50 cases Poster No.: C-1497 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Matri, L. Ben Farhat, I. Marzouk
RX Biliary System. Start
 Start We re in! When you control the wire, efficiency comes along for the ride. The of Physician-Controlled Wireguided Cannulation Physician-controlled wireguided cannulation (WGC) facilitates deep biliary
Start We re in! When you control the wire, efficiency comes along for the ride. The of Physician-Controlled Wireguided Cannulation Physician-controlled wireguided cannulation (WGC) facilitates deep biliary
Lumen Apposing Metal Stents: Expanding the Role of the Interventional Endoscopist. Alireza Sedarat, MD UCLA Division of Digestive Diseases
 Lumen Apposing Metal Stents: Expanding the Role of the Interventional Endoscopist Alireza Sedarat, MD UCLA Division of Digestive Diseases Disclosures Consultant for Boston Scientific and Olympus Corporation
Lumen Apposing Metal Stents: Expanding the Role of the Interventional Endoscopist Alireza Sedarat, MD UCLA Division of Digestive Diseases Disclosures Consultant for Boston Scientific and Olympus Corporation
Placement of self-expanding metal stents is a safe and effective palliative
 Diagn Interv Radiol 2012; 18:360 364 Turkish Society of Radiology 2012 ABDOMINAL IMAGING ORIGINAL ARTICLE Placement of duodenal stents across the duodenal papilla may predispose to acute pancreatitis:
Diagn Interv Radiol 2012; 18:360 364 Turkish Society of Radiology 2012 ABDOMINAL IMAGING ORIGINAL ARTICLE Placement of duodenal stents across the duodenal papilla may predispose to acute pancreatitis:
Biliary stenting: Indications, choice of stents and results: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) clinical guideline
 Guideline 277 Biliary stenting: Indications, choice of stents and results: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) clinical guideline Authors J.-M. Dumonceau 1, A. Tringali 2, D. Blero 3,
Guideline 277 Biliary stenting: Indications, choice of stents and results: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) clinical guideline Authors J.-M. Dumonceau 1, A. Tringali 2, D. Blero 3,
Evaluation and Management of Refractory Biliary Stricture. J. David Horwhat, MD, FACG Director of Endoscopy Lancaster Gastroenterology, Inc.
 Evaluation and Management of Refractory Biliary Stricture J. David Horwhat, MD, FACG Director of Endoscopy Lancaster Gastroenterology, Inc Outline What defines a refractory biliary stricture Endoscopic
Evaluation and Management of Refractory Biliary Stricture J. David Horwhat, MD, FACG Director of Endoscopy Lancaster Gastroenterology, Inc Outline What defines a refractory biliary stricture Endoscopic
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Clinical Efficacy of Endoscopic Pancreatic Drainage for Pain Relief with Malignant Pancreatic Duct Obstruction
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2014.15.16.6823 RESEARCH ARTICLE Clinical Efficacy of Endoscopic Pancreatic Drainage for Pain Relief with Malignant Pancreatic Duct Obstruction Fei Gao 1 *, Shuren Ma
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2014.15.16.6823 RESEARCH ARTICLE Clinical Efficacy of Endoscopic Pancreatic Drainage for Pain Relief with Malignant Pancreatic Duct Obstruction Fei Gao 1 *, Shuren Ma
A Guide for Patients Living with a Biliary Metal Stent
 A Guide for Patients Living with a Biliary Metal Stent What is a biliary metal stent? A biliary metal stent (also known as a bile duct stent ) is a flexible metallic tube specially designed to hold your
A Guide for Patients Living with a Biliary Metal Stent What is a biliary metal stent? A biliary metal stent (also known as a bile duct stent ) is a flexible metallic tube specially designed to hold your
Self Expandable Metallic Stents in Malignant Biliary Obstruction: Safety and Efficacy
 METALLIC THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE STENTS IN MALIGNANT MEDICAL JOURNAL BILIARY OBSTRUCTION Self Expandable Metallic Stents in Malignant Biliary Obstruction: Safety and Efficacy Rabah Hiab Asreah*,Qasim Lefta
METALLIC THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE STENTS IN MALIGNANT MEDICAL JOURNAL BILIARY OBSTRUCTION Self Expandable Metallic Stents in Malignant Biliary Obstruction: Safety and Efficacy Rabah Hiab Asreah*,Qasim Lefta
Practical applications and learning curve for EUS-guided hepaticoenterostomy: results of a large single-center US retrospective analysis
 Original article Practical applications and learning curve for EUS-guided hepaticoenterostomy: results of a large single-center US retrospective analysis Authors Theodore W. James, Todd H. Baron Institution
Original article Practical applications and learning curve for EUS-guided hepaticoenterostomy: results of a large single-center US retrospective analysis Authors Theodore W. James, Todd H. Baron Institution
Review Article Fully Covered Self-Expandable Metal Stents for Treatment of Both Benign and Malignant Biliary Disorders
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy Volume 2012, Article ID 498617, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/498617 Review Article Fully Covered Self-Expandable Metal Stents for Treatment
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy Volume 2012, Article ID 498617, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/498617 Review Article Fully Covered Self-Expandable Metal Stents for Treatment
Colangitis Esclerosante Primaria: Manejo Clínico y Endoscópico
 Colangitis Esclerosante Primaria: Manejo Clínico y Endoscópico Andrés Cárdenas, MD, MMSc, PhD, AGAF, FAASLD GI / Liver Unit, Hospital Clinic Institut de Malalties Digestives i Metaboliques Associate Professor
Colangitis Esclerosante Primaria: Manejo Clínico y Endoscópico Andrés Cárdenas, MD, MMSc, PhD, AGAF, FAASLD GI / Liver Unit, Hospital Clinic Institut de Malalties Digestives i Metaboliques Associate Professor
ORIGINAL PAPERS. R. Insertion of fully covered self-expanding metal stents in benign biliary diseases. ABSTRACT MATERIALS AND METHODS INTRODUCTION
 ORIGINAL PAPERS Insertion of fully covered self-expanding metal stents in benign biliary diseases Mariana Omodeo, Ignacio Málaga, Dante Manazzoni, Cecilia Curvale, Julio de María, Martín Guidi and Raúl
ORIGINAL PAPERS Insertion of fully covered self-expanding metal stents in benign biliary diseases Mariana Omodeo, Ignacio Málaga, Dante Manazzoni, Cecilia Curvale, Julio de María, Martín Guidi and Raúl
Stenting of the Cystic Duct in Benign Disease: A Definitive Treatment for the Elderly and Unwell
 Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol (2015) 38:964 970 DOI 10.1007/s00270-014-1014-y CLINICAL INVESTIGATION NON-VASCULAR INTERVENTIONS Stenting of the Cystic Duct in Benign Disease: A Definitive Treatment for the
Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol (2015) 38:964 970 DOI 10.1007/s00270-014-1014-y CLINICAL INVESTIGATION NON-VASCULAR INTERVENTIONS Stenting of the Cystic Duct in Benign Disease: A Definitive Treatment for the
Title: Insertion of fully covered self-expanding. metal stents in benign biliary diseases. Rev
 Title: Insertion of fully covered self-expanding metal stents in benign biliary diseases Authors: Mariana Omodeo, Ignacio Malaga, Dante Manazzoni, Cecilia Curvale, Julio de Maria, Martín Alejandro Guidi,
Title: Insertion of fully covered self-expanding metal stents in benign biliary diseases Authors: Mariana Omodeo, Ignacio Malaga, Dante Manazzoni, Cecilia Curvale, Julio de Maria, Martín Alejandro Guidi,
Clinical Study Multicenter Randomized Trial of 10-French versus 11.5-French Plastic Stents for Malignant Biliary Obstruction
 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy Volume 2013, Article ID 891915, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/891915 Clinical Study Multicenter Randomized Trial of 10-French versus 11.5-French Plastic Stents
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy Volume 2013, Article ID 891915, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/891915 Clinical Study Multicenter Randomized Trial of 10-French versus 11.5-French Plastic Stents
Management of the Mucin Filled Bile Duct. A Complication of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Tumor of the Pancreas
 CASE REPORT Management of the Mucin Filled Bile Duct. A Complication of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Tumor of the Pancreas Anand Patel, Louis Lambiase, Antonio Decarli, Ali Fazel Division of Gastroenterology
CASE REPORT Management of the Mucin Filled Bile Duct. A Complication of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Tumor of the Pancreas Anand Patel, Louis Lambiase, Antonio Decarli, Ali Fazel Division of Gastroenterology
6/17/2016. ERCP in June 26, Kenneth M. Sigman, M.D. Birmingham Gastroenterology Associates
 ERCP in 2016 June 26, 2016 Kenneth M. Sigman, M.D. Birmingham Gastroenterology Associates 1 2 3 Diagnostic/Therapeutic ERCP Biliary Obstruction Benign stricture Malignant Stones Ductal injuries Cholangitis
ERCP in 2016 June 26, 2016 Kenneth M. Sigman, M.D. Birmingham Gastroenterology Associates 1 2 3 Diagnostic/Therapeutic ERCP Biliary Obstruction Benign stricture Malignant Stones Ductal injuries Cholangitis
Effectiveness and safety of metallic stent for ileocecal obstructive colon cancer: a report of 4 cases
 Effectiveness and safety of metallic stent for ileocecal obstructive colon cancer: a report of 4 cases Authors Tatsuya Ishii 1,KosukeMinaga 2, Satoshi Ogawa 3, Maiko Ikenouchi 1, Tomoe Yoshikawa 1,TakujiAkamatsu
Effectiveness and safety of metallic stent for ileocecal obstructive colon cancer: a report of 4 cases Authors Tatsuya Ishii 1,KosukeMinaga 2, Satoshi Ogawa 3, Maiko Ikenouchi 1, Tomoe Yoshikawa 1,TakujiAkamatsu
Percutaneous Biliary Drainage Using Open Cell Stents for Malignant Biliary Hilar Obstruction
 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2012.13.6.795 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2012;13(6):795-802 Percutaneous Biliary Drainage Using Open Cell Stents for Malignant Biliary
Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2012.13.6.795 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2012;13(6):795-802 Percutaneous Biliary Drainage Using Open Cell Stents for Malignant Biliary
Endoscopic Deployment of Multiple JOSTENT SelfX Is Effective and Safe in Treatment of Malignant Hilar Biliary Strictures
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2008;6:401 408 ENDOSCOPY CORNER Endoscopic Deployment of Multiple JOSTENT SelfX Is Effective and Safe in Treatment of Malignant Hilar Biliary Strictures HIROFUMI
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2008;6:401 408 ENDOSCOPY CORNER Endoscopic Deployment of Multiple JOSTENT SelfX Is Effective and Safe in Treatment of Malignant Hilar Biliary Strictures HIROFUMI
Correspondence should be addressed to Roberto Di Mitri;
 e Scientific World Journal, Article ID 651765, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/651765 Clinical Study The New Nitinol Conformable Self-Expandable Metal Stents for Malignant Colonic Obstruction: A
e Scientific World Journal, Article ID 651765, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/651765 Clinical Study The New Nitinol Conformable Self-Expandable Metal Stents for Malignant Colonic Obstruction: A
Owen Dickinson. Consultant in Endoscopy & Interventional Radiology. Upper GI Stenting. Rotherham Foundation Trust
 Owen Dickinson Consultant in Endoscopy & Interventional Radiology Upper GI Stenting Rotherham Foundation Trust Owen Dickinson Consultant in Endoscopy & Interventional Radiology Rotherham Foundation Trust
Owen Dickinson Consultant in Endoscopy & Interventional Radiology Upper GI Stenting Rotherham Foundation Trust Owen Dickinson Consultant in Endoscopy & Interventional Radiology Rotherham Foundation Trust
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
 Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Medical Imaging and Treatment of the Bile and Pancreatic Ducts CIE-02718 Understanding ERCP Brochure Update_F.indd 1 7/11/18 9:51 A Minimally Invasive
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Medical Imaging and Treatment of the Bile and Pancreatic Ducts CIE-02718 Understanding ERCP Brochure Update_F.indd 1 7/11/18 9:51 A Minimally Invasive
Diagnosis of tumor extension in biliary carcinoma has. Differential Diagnosis and Treatment of Biliary Strictures
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2009;7:S79 S83 Differential Diagnosis and Treatment of Biliary Strictures KAZUO INUI, JUNJI YOSHINO, and HIRONAO MIYOSHI Department of Internal Medicine, Second
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2009;7:S79 S83 Differential Diagnosis and Treatment of Biliary Strictures KAZUO INUI, JUNJI YOSHINO, and HIRONAO MIYOSHI Department of Internal Medicine, Second
North Medical Endoscopic Biliary Stent (BilS)
 North Medical Endoscopic Biliary Stent (BilS) Instructions for Use Manufactured by North Medical DEVICE NAME North Medical Endoscopic Biliary Stent (BilS) DEVICE DESCRIPTION North Medical's BilS stent
North Medical Endoscopic Biliary Stent (BilS) Instructions for Use Manufactured by North Medical DEVICE NAME North Medical Endoscopic Biliary Stent (BilS) DEVICE DESCRIPTION North Medical's BilS stent
Naoyuki Toyota, Tadahiro Takada, Hodaka Amano, Masahiro Yoshida, Fumihiko Miura, and Keita Wada
 J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg (2006) 13:80 85 DOI 10.1007/s00534-005-1062-4 Endoscopic naso-gallbladder drainage in the treatment of acute cholecystitis: alleviates inflammation and fixes operator s aim
J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg (2006) 13:80 85 DOI 10.1007/s00534-005-1062-4 Endoscopic naso-gallbladder drainage in the treatment of acute cholecystitis: alleviates inflammation and fixes operator s aim
7/11/2017. We re gonna help a lot of people today. Biliary/Pancreatic Endoscopy. AGS July 1-2, Kenneth M. Sigman, MD
 Biliary/Pancreatic Endoscopy AGS July 1-2, 2017 Kenneth M. Sigman, MD We re gonna help a lot of people today 1 2 3 4 Cannulation It all starts with cannulation Double Wire Cannulation Difficult cannulations
Biliary/Pancreatic Endoscopy AGS July 1-2, 2017 Kenneth M. Sigman, MD We re gonna help a lot of people today 1 2 3 4 Cannulation It all starts with cannulation Double Wire Cannulation Difficult cannulations
Endoscopic biliary self-expandable metallic stent in malignant biliary obstruction with or without sphincterotomy: systematic review and meta-analysis
 Review Endoscopic biliary self-expandable metallic in malignant biliary obstruction with or without sphincterotomy: systematic review and meta-analysis Authors Benedetto Mangiavillano 1, 2, Amedeo Montale
Review Endoscopic biliary self-expandable metallic in malignant biliary obstruction with or without sphincterotomy: systematic review and meta-analysis Authors Benedetto Mangiavillano 1, 2, Amedeo Montale
Follow this and additional works at:
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2016 A comparison between endoscopic ultrasoundguided rendezvous and percutaneous biliary drainage after failed
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2016 A comparison between endoscopic ultrasoundguided rendezvous and percutaneous biliary drainage after failed
The management of malignant tumours involving the main
 REVIEW Hilar tumours Guido Costamagna MD FACG, Andrea Tringali MD, Lucio Petruzziello MD, Cristiano Spada MD G Costamagna, A Tringali, L Petruzziello, C Spada. Hilar tumours. Can J Gastroenterol 2004;18(7):451-454.
REVIEW Hilar tumours Guido Costamagna MD FACG, Andrea Tringali MD, Lucio Petruzziello MD, Cristiano Spada MD G Costamagna, A Tringali, L Petruzziello, C Spada. Hilar tumours. Can J Gastroenterol 2004;18(7):451-454.
Enteral stenting for gastric outlet obstruction and afferent limb syndrome following pancreaticoduodenectomy
 CASE SERIES Annals of Gastroenterology (2014) 27, 1-5 Enteral stenting for gastric outlet obstruction and afferent limb syndrome following pancreaticoduodenectomy Wilson T. Kwong a, Syed M. Fehmi a, Andrew
CASE SERIES Annals of Gastroenterology (2014) 27, 1-5 Enteral stenting for gastric outlet obstruction and afferent limb syndrome following pancreaticoduodenectomy Wilson T. Kwong a, Syed M. Fehmi a, Andrew
Tratamiento endoscópico de la CEP. En quien como y cuando?
 Tratamiento endoscópico de la CEP. En quien como y cuando? Andrés Cárdenas, MD, MMSc, PhD, AGAF, FAASLD GI / Liver Unit, Hospital Clinic Institut de Malalties Digestives i Metaboliques University of Barcelona
Tratamiento endoscópico de la CEP. En quien como y cuando? Andrés Cárdenas, MD, MMSc, PhD, AGAF, FAASLD GI / Liver Unit, Hospital Clinic Institut de Malalties Digestives i Metaboliques University of Barcelona
Abstract Background Stent blockage is a multifactorial process in which stent design and materials, bacteria, proteins, and bile viscosity
 Gut 2000;46:395 400 395 Radiology, South Manchester University Hospitals NHS Trust, Withington, Nell Lane, Manchester M20 2LR, UK R E England D F Martin Medical Statistics, South Manchester University
Gut 2000;46:395 400 395 Radiology, South Manchester University Hospitals NHS Trust, Withington, Nell Lane, Manchester M20 2LR, UK R E England D F Martin Medical Statistics, South Manchester University
Percutaneous biliary drainage catheter insertion in patients with extensive hepatic metastatic tumor burden
 Original Article Percutaneous biliary drainage catheter insertion in patients with extensive hepatic metastatic tumor burden Eun L. Langman 1, Paul V. Suhocki 1, Herbert I. Hurwitz 2, Michael A. Morse
Original Article Percutaneous biliary drainage catheter insertion in patients with extensive hepatic metastatic tumor burden Eun L. Langman 1, Paul V. Suhocki 1, Herbert I. Hurwitz 2, Michael A. Morse
Title: The endoscopic ultrasound-assisted Rendez-Vous technique for treatment of recurrent pancreatitis due to pancreas divisum and ansa pancreatica
 Title: The endoscopic ultrasound-assisted Rendez-Vous technique for treatment of recurrent pancreatitis due to pancreas divisum and ansa pancreatica Authors: Sergio López-Durán, Celia Zaera, Juan Ángel
Title: The endoscopic ultrasound-assisted Rendez-Vous technique for treatment of recurrent pancreatitis due to pancreas divisum and ansa pancreatica Authors: Sergio López-Durán, Celia Zaera, Juan Ángel
Case Scenario 1. Discharge Summary
 Case Scenario 1 Discharge Summary A 69-year-old woman was on vacation and noted that she was becoming jaundiced. Two months prior to leaving on that trip, she had had a workup that included an abdominal
Case Scenario 1 Discharge Summary A 69-year-old woman was on vacation and noted that she was becoming jaundiced. Two months prior to leaving on that trip, she had had a workup that included an abdominal
Research Article Risk Factors for Migration, Fracture, and Dislocation of Pancreatic Stents
 Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2015, Article ID 365457, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/365457 Research Article Risk Factors for Migration, Fracture, and Dislocation of Pancreatic
Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2015, Article ID 365457, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/365457 Research Article Risk Factors for Migration, Fracture, and Dislocation of Pancreatic
The Endoscopic Management of PSC
 The Endoscopic Management of PSC Raj J. Shah, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Director, Pancreaticobiliary Endoscopy Services University of Colorado at Denver and the Health Sciences Center Why did
The Endoscopic Management of PSC Raj J. Shah, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Director, Pancreaticobiliary Endoscopy Services University of Colorado at Denver and the Health Sciences Center Why did
Trimming of a Broken Migrated Biliary Metal Stent with the Nd:YAG Laser
 16 Trimming of a Broken Migrated Biliary Metal Stent with the Nd:YAG Laser I. Zuber-Jerger F. Kullmann Department of Internal Medicine I, University of Regensburg, Regensburg, Germany Key Words Broken
16 Trimming of a Broken Migrated Biliary Metal Stent with the Nd:YAG Laser I. Zuber-Jerger F. Kullmann Department of Internal Medicine I, University of Regensburg, Regensburg, Germany Key Words Broken
Metal versus plastic stents for malignant biliary obstruction: An update meta-analysis
 Clinics and Research in Hepatology and Gastroenterology (2013) xxx, xxx xxx Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Metal versus plastic stents for malignant biliary obstruction: An
Clinics and Research in Hepatology and Gastroenterology (2013) xxx, xxx xxx Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Metal versus plastic stents for malignant biliary obstruction: An
A Novel Partially Covered Self-Expandable Metallic Stent with Proximal Flare in Patients with Malignant Gastric Outlet Obstruction
 Gut and Liver, Vol. 11, No. 4, July 2017, pp. 481-488 ORiginal Article A Novel Partially Covered Self-Expandable Metallic Stent with Proximal Flare in Patients with Malignant Gastric Outlet Obstruction
Gut and Liver, Vol. 11, No. 4, July 2017, pp. 481-488 ORiginal Article A Novel Partially Covered Self-Expandable Metallic Stent with Proximal Flare in Patients with Malignant Gastric Outlet Obstruction
ERCP complications and challenges in their diagnosis and management.
 ERCP complications and challenges in their diagnosis and management. Sandie R Thomson Chair of the Division of Gastroenterology, University of Cape Town ERCP Do I have a good Indication? . Algorithm for
ERCP complications and challenges in their diagnosis and management. Sandie R Thomson Chair of the Division of Gastroenterology, University of Cape Town ERCP Do I have a good Indication? . Algorithm for
Lumen-apposing covered self-expanding metal stent for management of benign gastrointestinal strictures
 E96 THIEME Lumen-apposing covered self-expanding metal stent for management of benign gastrointestinal strictures Authors Institution Shounak Majumder, Navtej S. Buttar, Christopher Gostout, Michael J.
E96 THIEME Lumen-apposing covered self-expanding metal stent for management of benign gastrointestinal strictures Authors Institution Shounak Majumder, Navtej S. Buttar, Christopher Gostout, Michael J.
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of endoscopic bipolar radiofrequency ablation for treating biliary obstructions caused
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of endoscopic bipolar radiofrequency ablation for treating biliary obstructions caused
LIVER, PANCREAS, AND BILIARY TRACT
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2012;10:1157 1161 LIVER, PANCREAS, AND BILIARY TRACT Delayed and Unsuccessful Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography Are Associated With Worse Outcomes
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2012;10:1157 1161 LIVER, PANCREAS, AND BILIARY TRACT Delayed and Unsuccessful Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography Are Associated With Worse Outcomes
Clinical features of gallstone impaction at the ampulla of Vater and the effectiveness of endoscopic biliary drainage without papillotomy
 E806 THIEME Clinical features of gallstone impaction at the ampulla of Vater and the effectiveness of endoscopic biliary drainage without Authors Yuichi Takano 1, Masatsugu Nagahama 1, Naotaka Maruoka
E806 THIEME Clinical features of gallstone impaction at the ampulla of Vater and the effectiveness of endoscopic biliary drainage without Authors Yuichi Takano 1, Masatsugu Nagahama 1, Naotaka Maruoka
ERCP and EUS: What s New and What Should We Do?
 ERCP and EUS: What s New and What Should We Do? Rajesh N. Keswani, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine EUS/ERCP in 2015 THE
ERCP and EUS: What s New and What Should We Do? Rajesh N. Keswani, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine EUS/ERCP in 2015 THE
Original Article INTRODUCTION
 Original Article A retrospective study evaluating endoscopic ultrasound guided drainage of pancreatic fluid collections using a novel lumen apposing metal stent on an electrocautery enhanced delivery system
Original Article A retrospective study evaluating endoscopic ultrasound guided drainage of pancreatic fluid collections using a novel lumen apposing metal stent on an electrocautery enhanced delivery system
Clinical Performance of GORE VIABIL Biliary Endoprosthesis in the Treatment of Malignant Strictures
 Clinical Performance of GORE VIABIL Biliary Endoprosthesis in the Treatment of Malignant Strictures Scientific Literature Summary (n = 663 patients) * GORE VIABIL Biliary Endoprosthesis Advancing Biliary
Clinical Performance of GORE VIABIL Biliary Endoprosthesis in the Treatment of Malignant Strictures Scientific Literature Summary (n = 663 patients) * GORE VIABIL Biliary Endoprosthesis Advancing Biliary
The role of ERCP in chronic pancreatitis
 The role of ERCP in chronic pancreatitis Marianna Arvanitakis Erasme University Hospital, ULB, Brussels, Belgium 10 th Nottingham Endoscopy Masterclass SPEAKER DECLARATIONS This presenter has the following
The role of ERCP in chronic pancreatitis Marianna Arvanitakis Erasme University Hospital, ULB, Brussels, Belgium 10 th Nottingham Endoscopy Masterclass SPEAKER DECLARATIONS This presenter has the following
Endoscopic stent placement throughout the gastrointestinal tract van den Berg, M.W.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Endoscopic stent placement throughout the gastrointestinal tract van den Berg, M.W. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van den Berg, M. W.
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Endoscopic stent placement throughout the gastrointestinal tract van den Berg, M.W. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van den Berg, M. W.
Endoscopic ultrasound guided gastrojejunostomy
 Review Article Endoscopic ultrasound guided gastrojejunostomy Enad Dawod 1, Jose M. Nieto 2 1 Weill Cornell Medicine, Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, New York, NY, USA; 2 Borland Groover
Review Article Endoscopic ultrasound guided gastrojejunostomy Enad Dawod 1, Jose M. Nieto 2 1 Weill Cornell Medicine, Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, New York, NY, USA; 2 Borland Groover
Advanced Cannulation Techniques
 Advanced Cannulation Techniques Priya A. Jamidar, M.D., FASGE Professor of Medicine, Director of Endoscopy Yale School Disclosures Consultant to Boston Scientific and Olympus America Cannulation at ERCP
Advanced Cannulation Techniques Priya A. Jamidar, M.D., FASGE Professor of Medicine, Director of Endoscopy Yale School Disclosures Consultant to Boston Scientific and Olympus America Cannulation at ERCP
EUS-Guided Transduodenal Biliary Drainage in Unresectable Pancreatic Cancer with Obstructive Jaundice
 CASE REPORT EUS-Guided Transduodenal Biliary Drainage in Unresectable Pancreatic Cancer with Obstructive Jaundice Tiing Leong Ang, Eng Kiong Teo, Kwong Ming Fock Division of Gastroenterology, Department
CASE REPORT EUS-Guided Transduodenal Biliary Drainage in Unresectable Pancreatic Cancer with Obstructive Jaundice Tiing Leong Ang, Eng Kiong Teo, Kwong Ming Fock Division of Gastroenterology, Department
Double endoscopic bypass for gastric outlet obstruction and biliary obstruction
 Double endoscopic bypass for gastric outlet obstruction and biliary obstruction Authors Olaya I. Brewer Gutierrez 1,JoseNieto 2, Shayan Irani 3, Theodore James 4,RenataPierattiBueno 1, Yen-I Chen 1, Majidah
Double endoscopic bypass for gastric outlet obstruction and biliary obstruction Authors Olaya I. Brewer Gutierrez 1,JoseNieto 2, Shayan Irani 3, Theodore James 4,RenataPierattiBueno 1, Yen-I Chen 1, Majidah
Research Article Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Biliary Drainage Using Self-Expandable Metal Stent for Malignant Biliary Obstruction
 Hindawi Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2017, Article ID 6284094, 10 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6284094 Research Article Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Biliary Drainage Using Self-Expandable
Hindawi Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2017, Article ID 6284094, 10 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6284094 Research Article Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Biliary Drainage Using Self-Expandable
PANCREATIC PSEUDOCYST DRAINAGE: ENDOSCOPIC APPROACHES & THE NURSING ROLE. PRESENTED BY: Susan DePasquale, CGRN, MSN
 PANCREATIC PSEUDOCYST DRAINAGE: ENDOSCOPIC APPROACHES & THE NURSING ROLE PRESENTED BY: Susan DePasquale, CGRN, MSN Pancreatic Fluid Collection (PFC) A result of pancreatic duct (PD) and side branch disruption,
PANCREATIC PSEUDOCYST DRAINAGE: ENDOSCOPIC APPROACHES & THE NURSING ROLE PRESENTED BY: Susan DePasquale, CGRN, MSN Pancreatic Fluid Collection (PFC) A result of pancreatic duct (PD) and side branch disruption,
Review Article Covered Stents versus Uncovered Stents for Unresectable Malignant Biliary Strictures: A Meta-Analysis
 BioMed Research International Volume 6, Article ID 6867, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/./6/6867 Review Article Covered Stents versus Uncovered Stents for Unresectable Malignant Biliary Strictures: A Meta-Analysis
BioMed Research International Volume 6, Article ID 6867, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/./6/6867 Review Article Covered Stents versus Uncovered Stents for Unresectable Malignant Biliary Strictures: A Meta-Analysis
Is a Metallic Stent Useful for Non Resectable Esophageal Cancer?
 Original Article Is a Metallic Stent Useful for Non Resectable Esophageal Cancer? Shinsuke Wada, MD, 1 Tsuyoshi Noguchi, MD, 1 Shinsuke Takeno, MD, 1 Hatsuo Moriyama, MD, 1 Tsuyoshi Hashimoto, MD, 1 Yuzo
Original Article Is a Metallic Stent Useful for Non Resectable Esophageal Cancer? Shinsuke Wada, MD, 1 Tsuyoshi Noguchi, MD, 1 Shinsuke Takeno, MD, 1 Hatsuo Moriyama, MD, 1 Tsuyoshi Hashimoto, MD, 1 Yuzo
Double-Stent System with Long Duodenal Extension for Palliative Treatment of Malignant Extrahepatic Biliary Obstructions: A Prospective Study
 Original Article Intervention https://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2018.19.2.230 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2018;19(2):230-236 Double-Stent System with Long Duodenal Extension for Palliative
Original Article Intervention https://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2018.19.2.230 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2018;19(2):230-236 Double-Stent System with Long Duodenal Extension for Palliative
Jintao Guo, Siyu Sun, Xiang Liu, Sheng Wang, Nan Ge, and Guoxin Wang. 1. Introduction. 2. Patients and Methods
 Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2016, Article ID 9469472, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9469472 Clinical Study Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Biliary Drainage Using a Fully Covered
Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2016, Article ID 9469472, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9469472 Clinical Study Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Biliary Drainage Using a Fully Covered
ORIGINAL ARTICLE: Clinical Endoscopy
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE: Clinical Endoscopy Anchoring flap versus flared end, fully covered self-expandable metal stents to prevent migration in patients with benign biliary strictures: a multicenter, prospective,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE: Clinical Endoscopy Anchoring flap versus flared end, fully covered self-expandable metal stents to prevent migration in patients with benign biliary strictures: a multicenter, prospective,
What can you expect after your ERCP?
 ERCP Explained and respond to bed rest, pain relief and fasting to rest the gut with the patient needing to stay in hospital for only a few days. Some patients develop severe pancreatitis and may require
ERCP Explained and respond to bed rest, pain relief and fasting to rest the gut with the patient needing to stay in hospital for only a few days. Some patients develop severe pancreatitis and may require
Endoscopic treatment of primary sclerosing cholangitis: Is there something new?
 Endoscopic treatment of primary sclerosing cholangitis: Is there something new? Arnaud Lemmers, MD, PhD Gastroenterology Department, Erasme Hospital, ULB, Brussels BASL December 1st 2017 AGENDA Introduction
Endoscopic treatment of primary sclerosing cholangitis: Is there something new? Arnaud Lemmers, MD, PhD Gastroenterology Department, Erasme Hospital, ULB, Brussels BASL December 1st 2017 AGENDA Introduction
Colonic stenting anno 2014
 Jeanin E. van Hooft, MD, PhD Gastroenterologist Academic Medical Centre Dept. of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Amsterdam, Netherlands Annual meeting of Colonic Stent Safe Procedure Research Group May
Jeanin E. van Hooft, MD, PhD Gastroenterologist Academic Medical Centre Dept. of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Amsterdam, Netherlands Annual meeting of Colonic Stent Safe Procedure Research Group May
