Traumatic Cardiac Arrest Protocol
|
|
|
- Sydney Harmon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Traumatic Cardiac Arrest Protocol Background: Major Trauma continues to be the leading worldwide cause of death in young adults. Mortality remains high but there are reports of good neurological outcomes from traumatic cardiac arrest following introduction of treatment algorithms and use of clamshell thoracotomy. Rapid, effective intervention is required to address potential reversible causes of traumatic cardiac arrest. The aim was to develop a simple algorithm to manage the major trauma patient in actual or imminent cardiac arrest that could be utilised by services in the North East of England. Current ILCOR guidelines do not contain a standard algorithm for management of traumatic cardiac arrest. It was decided to split the algorithm into 2 sections; penetrating and blunt trauma. Methods: A review of recent literature on traumatic cardiac arrest protocols. Traumatic cardiac arrest algorithms were reviewed from Lockey et al (1) and Sherren et al (2) and adaptations made to fit our current practice and geographical constraints. The protocol was designed to be used in a Major Trauma Centre and Trauma Unit Emergency Department. Results: The algorithm developed addresses the need for potential reversible causes of traumatic cardiac arrest. This includes immediate control of external haemorrhage, IV/IO access and blood transfusion, optimising oxygenation, bilateral chest decompression to exclude tension pneumothorax and resuscitative thoracotomy to treat cardiac tamponade and its cause. The algorithm also stipulates time guidelines and the introduction that these interventions need to be undertaken simultaneously with optional external cardiac compressions. Conclusion: The suggested algorithm is designed for a highly trained senior physician-led hospital Emergency Department Trauma Team. It aims to identify the early recognition of patients who fit these criteria and maximise the number of neurologically intact survivors in out-of-hospital TCA.
2 1. Introduction Survival rates following traumatic cardiac arrest (TCA) are known to be poor but resuscitation is not universally futile. (2) There are distinct differences in the pathophysiology between medical cardiac arrests and TCA. Traumatic pathologies associated with an improved chance of successful resuscitation include hypoxia, tension pneumothorax and cardiac tamponade. (1) Lockey et al (1) recently published an algorithm for traumatic cardiac arrest in Resuscitation, June It suggests incorporating resuscitative on-scene thoracotomy into our algorithms for traumatic cardiac arrest. It is a consequence of the very same group s previously published data on prehospital clamshell thoracotomies in patients with cardiac arrest due to penetrating chest injuries. (3) In the emergency department it has been demonstrated that if blunt trauma patients have had more than 5 min of CPR or penetrating trauma patients have had mote than 15 min, resuscitative thoracotomy is likely to be futile. (4) Peri-arrest is imminent cardiac arrest in these patients. These patients should too be entered into the algorithm for targeted interventions. Often after intubation, and therefore planning and preparation pre intubation are vital. Clinical care of patients suffering medical cardiac arrest follow national guidelines. A definitive evidence-base for many interventions does not exist, and this is unlikely to change due to practical difficulties in devising ethically sound randomised, controlled and blinded studies. Current guidelines apply irrespective of the presumed cause of cardiac arrest: emphasis is on immediate and minimally interrupted cardiac compressions, and once effective CPR and monitoring is established, the final bullet point in the during CPR box is correct reversible causes. There is some evidence that this process improves outcomes in some cases of cardiac arrest, for example Ventricular Fibrillation due to myocardial infarction. The pathophysiology of traumatic cardiac arrest is different and the Resuscitation Council guidelines address this in the 4 H s and 4 T s. It is reasonable to assume the following H s and T s apply to traumatic cardiac arrest: Hypovolaemia, Hypoxia, Tension Pneumothorax and Cardiac Tamponade. Massive head injury is not listed as if this is the cause of cardiac arrest it is generally accepted to be incompatible with successful resuscitation.
3 2. Explanation of Algorithm: The aim of the algorithm is to rapidly identify and correct reversible causes of TCA. Transport of TCA patients with ongoing CPR is futile and either they need to have key interventions done at scene in a pre-hospital setting or transported rapidly to definitive in hospital Emergency Department Trauma Team for surgical intervention. Identify/Rule out Medical Causes of Cardiac Arrest History from bystanders/paramedics Clinical evidence Penetrating: (a) Diagnosis of traumatic cardiac arrest Rapid clinical assessment identified over 10 seconds. Agonal or absent respiration and absence of a central pulse should immediately follow the algorithm if deemed to be traumatic in nature. (b) Identify penetrating injury to Trunk or Limbs Rapid examination to above areas to identify potential penetrating wounds. Ensure examination of patients back. (c) Identify if any Evidence of Futility Are there and conditions unequivocally associated with death: Massive cranial and cerebral destruction Hemicorporectomy or similar massive injury Decomposition putrefaction Incineration Hypostasis Rigor mortis Foetal maceration (d) Optional external cardiac compressions to be performed and BLS/ALS algorithms to be commenced whilst reversible causes are treated. Given the high incidence of hypovolaemia, hypoxia and obstructive shock prior to TCA, the role of adrenaline and chest compressions are limited. The current guidelines have the emphasis on early chest compressions: in the case of hypovolaemia this will lead to compression of an empty heart and is not expected to deliver effective circulation. Tamponade and tension pneumothorax will prevent effective cardiac compression. When resources allow, simultaneous
4 CPR should be delivered, however there is no role for isolated CPR this will not reverse the underlying condition. (e) Simultaneous Interventions to be performed as reversible causes are ruled out using HOTT pneumonic. Hypovolaemia should be managed with control of active external haemorrhage. Direct pressure to bleeding wounds, use of haemostatic agents, application of tourniquets and splintage of pelvis/limb fractures. IV access or IO access should be obtained expeditiously to allow rapid transfusion of blood products for volume resuscitation. Oxygenation with endotracheal intubation and positive pressure ventilation should be achieved as early as possible to correct airway obstruction and hypoxia and prevent traumatic asphyxia. It is key to ensure etco2 is attached and monitor. It has been shown that an etco2 <= 1.3kPa has limited survival and cessation of resuscitation should be considered. Tension pneumothorax should be excluded by rapid bilateral chest decompression. Ideally by simple thoracostomy which is routinely used in a pre hospital setting. This has shown to be more effective than cannula decompression which are more prone to kinking or blockage. Cardiac Tamponade should be excluded when ROSC is not successful and the algorithm indicates moving onto Immediate Clamshell Thoracotomy. Where release of cardiac tamponade does not result in ROSC patients may benefit from internal cardiac massage. (f) ROSC If ROSC achieved then ensure Code Red Activation/Major Haemorrhage and the presence of a Cardiothoracic Surgeon. Theatre staff activation and transfer to theatre for definitive surgery. If ROSC is not achieved with Simultaneous Interventions then an Immediate Clamshell Thoracotomy should be considered and performed. The current Timeline guidance for this is within 15 minutes for Penetrating Trauma and within 10 minutes for Blunt Trauma.
5 If successful, then ensure Code Red Activation/Major Haemorrhage and the presence of a Cardiothoracic Surgeon. Theatre staff activation and transfer to theatre for definitive surgery. If unsuccessful consider stopping resuscitation. Blunt: (g) Proceed with above simultaneous intervention (h) Additional interventions Follow ALS algorithm to include CPR and adrenaline administration. Depending on the cause of traumatic cardiac arrest chest compressions may provide some blood flow during cardiac arrest and should be continued whilst the history and mechanism of injury are established. These are indicated in blunt trauma which may be partially effective while reversible pathology is addressed. (8) ECG monitoring and appropriate defibrillation used as indicated. Defibrillation pads to be placed in the normal chest position, which will aid rhythm monitoring. They can be used as defibrillation pads whilst chest open or closed. Ultrasound can be used to help establish whether a pericardial effusion is present. In blunt trauma it is a helpful tool to accumulate evidence before moving onto a clamshell thoracotomy. (i) Continue with algorithm
6 3. Discussion The use of algorithms provides emergency medical services both in an MTC and a Trauma Unit Emergency Department with a protocol/guidance and a standard of care. It also ensures delivery of care in a rapid, succinct format which is beneficial for patients and easier to utilise for staff. Education and training can be delivered to all key personnel via the protocol driven algorithm. Pre-hospital and Emergency Department thoracotomy has been associated with a significant survival rate in patients with cardiac tamponade but needs to be performed in systems with clear governance processes in place. (9) 4. Conclusion: The algorithm presents a standardised simple approach to traumatic cardiac arrest which can be used in a hospital setting. This has specifically been adapted for Major Trauma Centres and Trauma Units.
7 References: (1)Resuscitation Jun;84(6): Development of a simple algorithm to guide the effective management of traumatic cardiac arrest. Lockey DJ, Lyon RM, Davies GE. (2) Critical Care 2013, 17(Suppl 2):P281. Algorithm for the resuscitation of traumatic cardiac arrest patients in a physician-staffed helicopter emergency medical service. PB Sherren, C Reid, K Habig, B Burns (3) J Trauma 2011 May;70(5):E75-8. Thirteen survivors of prehospital thoracotomy for penetrating trauma: a prehospital physician-performed resuscitation procedure that can yield good results. (4) J Am Coll Surg 2004;199:211 5.Powell DW,Moore EE, Cothren CC, et al. Is emergency department resuscitative thoracotomy futile care for the critically injured patient requiring prehospital cardiopulmonary resuscitation? (5). Emerg Med J 2005;22:8 16. Leigh-Smith S. Tension pneumothorax time for a re-think? (6). Prehosp Emerg Care 2009;13:18 27Holcomb JB, McManus JG, Kerr ST, et al. Needle versus tube thoracostomy in a swine model of traumatic tension hemopneumothorax. (7) Ann Emerg Med, 2006 Sep; 48(3): Traumatic Cardiac arrest: who are the survivors? (8) J Trauma 1989;29: Luna GK, Pavlin EG, Kirkman T, et al. Hemodynamic effects of external cardiac massage in trauma shock. (9) J Trauma Acute Care Surg 2012;73: Mattox KL. Editorial critique.
Traumatic Cardiac Arrest
 HELICOPTER OPERATING PROCEDURE Traumatic Cardiac Arrest HOP No: C/06 Issued: April 2013 Page: 1 of 5 Revision No: 2 TRIM No: 09/300 Document No: D13/5679 Distribution: Sydney X Illawarra X Orange X Helicopter
HELICOPTER OPERATING PROCEDURE Traumatic Cardiac Arrest HOP No: C/06 Issued: April 2013 Page: 1 of 5 Revision No: 2 TRIM No: 09/300 Document No: D13/5679 Distribution: Sydney X Illawarra X Orange X Helicopter
Lecture. ALS Algorithm
 Lecture ALS Algorithm 1 Learning outcomes The ALS algorithm Treatment of shockable and non-shockable rhythms Potentially reversible causes of cardiac arrest 2 Adult ALS Algorithm 3 To confirm cardiac arrest
Lecture ALS Algorithm 1 Learning outcomes The ALS algorithm Treatment of shockable and non-shockable rhythms Potentially reversible causes of cardiac arrest 2 Adult ALS Algorithm 3 To confirm cardiac arrest
Cardiac Arrest due to Trauma
 Cardiac Arrest due to Trauma Colonel Michael Reade MBBS MPH DPhil DMedSc DIMCRCSEd AFRACMA FANZCA FCICM ADF Professor of Military Medicine & Surgery University of Queensland & ADF Joint Health Command
Cardiac Arrest due to Trauma Colonel Michael Reade MBBS MPH DPhil DMedSc DIMCRCSEd AFRACMA FANZCA FCICM ADF Professor of Military Medicine & Surgery University of Queensland & ADF Joint Health Command
Resuscitation Checklist
 Resuscitation Checklist Actions if multiple responders are on scene Is resuscitation appropriate? Conditions incompatible with life Advanced decision in place Based on the information available, the senior
Resuscitation Checklist Actions if multiple responders are on scene Is resuscitation appropriate? Conditions incompatible with life Advanced decision in place Based on the information available, the senior
Advanced Life Support
 Standard Operating Procedure 2.1 Advanced Life Support Position Responsible: Head of Operations CGC Approved: October 2017 Related Documents Further Information 1.0 Background Magpas Resuscitation Policy
Standard Operating Procedure 2.1 Advanced Life Support Position Responsible: Head of Operations CGC Approved: October 2017 Related Documents Further Information 1.0 Background Magpas Resuscitation Policy
Do chest compressions have a role in the early treatment of haemorrhage - induced traumatic cardiac arrest
 15 th National Resuscitation Congress 4 th April 2018 Do chest compressions have a role in the early treatment of haemorrhage - induced traumatic cardiac arrest Dr Sarah Watts 1, Surg Capt Jason Smith
15 th National Resuscitation Congress 4 th April 2018 Do chest compressions have a role in the early treatment of haemorrhage - induced traumatic cardiac arrest Dr Sarah Watts 1, Surg Capt Jason Smith
Advanced Resuscitation - Adult
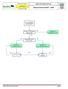 C02A Resuscitation 2017-03-23 17 years & older Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adult Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
C02A Resuscitation 2017-03-23 17 years & older Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adult Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
Advanced Resuscitation - Child
 C02C Resuscitation 2017-03-23 1 up to 10 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Child Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
C02C Resuscitation 2017-03-23 1 up to 10 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Child Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
Cardiac Arrest Guidelines Trauma Resuscitation Guidelines Prehospital Resuscitation Guidelines
 Resuscitation Guidelines Chapter 49 Resuscitation Guidelines NICHOLAS T. Tarmey, FRCA,* and R. Scott Frazer, FFARCSI INTRODUCTION EXISTING GUIDELINES Cardiac Arrest Guidelines Trauma Resuscitation Guidelines
Resuscitation Guidelines Chapter 49 Resuscitation Guidelines NICHOLAS T. Tarmey, FRCA,* and R. Scott Frazer, FFARCSI INTRODUCTION EXISTING GUIDELINES Cardiac Arrest Guidelines Trauma Resuscitation Guidelines
Advanced Resuscitation - Adolescent
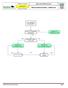 C02B Resuscitation 2017-03-23 10 up to 17 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adolescent Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia
C02B Resuscitation 2017-03-23 10 up to 17 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adolescent Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia
Department of Paediatrics Clinical Guideline. Advanced Paediatric Life Support. Sequence of actions. 1. Establish basic life support
 Advanced Paediatric Life Support Sequence of actions 1. Establish basic life support 2. Oxygenate, ventilate, and start chest compression: - Provide positive-pressure ventilation with high-concentration
Advanced Paediatric Life Support Sequence of actions 1. Establish basic life support 2. Oxygenate, ventilate, and start chest compression: - Provide positive-pressure ventilation with high-concentration
Post Resuscitation (ROSC) Care
 Standard Operating Procedure 2.10 Post Resuscitation (ROSC) Care Position Responsible: Medical Director Approved: Clinical Governance Committee Related Documents: This document is the intellectual property
Standard Operating Procedure 2.10 Post Resuscitation (ROSC) Care Position Responsible: Medical Director Approved: Clinical Governance Committee Related Documents: This document is the intellectual property
The ALS Algorithm and Post Resuscitation Care
 The ALS Algorithm and Post Resuscitation Care CET - Ballarat Health Services Valid from 1 st July 2018 to 30 th June 2020 2 Defibrillation Produces simultaneous mass depolarisation of myocardial cells
The ALS Algorithm and Post Resuscitation Care CET - Ballarat Health Services Valid from 1 st July 2018 to 30 th June 2020 2 Defibrillation Produces simultaneous mass depolarisation of myocardial cells
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation in Adults
 Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation in Adults Fatma Özdemir, MD Emergency Deparment of Uludag University Faculty of Medicine OVERVIEW Introduction Pathophysiology BLS algorithm ALS algorithm Post resuscitation
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation in Adults Fatma Özdemir, MD Emergency Deparment of Uludag University Faculty of Medicine OVERVIEW Introduction Pathophysiology BLS algorithm ALS algorithm Post resuscitation
Purpose This Operating Procedure provides guidance on the management of blunt thoracic traumatic injury
 Blunt Thoracic Trauma HELI.CLI.09 Purpose This Operating Procedure provides guidance on the management of blunt thoracic traumatic injury Procedure Management of Blunt Thoracic Traumatic Injury For Review
Blunt Thoracic Trauma HELI.CLI.09 Purpose This Operating Procedure provides guidance on the management of blunt thoracic traumatic injury Procedure Management of Blunt Thoracic Traumatic Injury For Review
Johnson County Emergency Medical Services Page 23
 Non-resuscitation Situations: Resuscitation should not be initiated in the following situations: Prolonged arrest as evidenced by lividity in dependent parts, rigor mortis, tissue decomposition, or generalized
Non-resuscitation Situations: Resuscitation should not be initiated in the following situations: Prolonged arrest as evidenced by lividity in dependent parts, rigor mortis, tissue decomposition, or generalized
Consider Treatable Underlying Causes Early
 Page 1 of 8 Cardiac Arrest Timeout Checklist Assign roles for Pit Crew CPR o Compressors x 2 o Airway o Lead responsible for coordinating team, making decisions o Medications Continuous compressions at
Page 1 of 8 Cardiac Arrest Timeout Checklist Assign roles for Pit Crew CPR o Compressors x 2 o Airway o Lead responsible for coordinating team, making decisions o Medications Continuous compressions at
The Primary Survey. C. Clay Cothren, MD FACS. Attending Surgeon, Denver Health Medical Center Assistant Professor of Surgery, University of Colorado
 The Primary Survey C. Clay Cothren, MD FACS Attending Surgeon, Denver Health Medical Center Assistant Professor of Surgery, University of Colorado Outlining the ABCs Why do we need such an approach? The
The Primary Survey C. Clay Cothren, MD FACS Attending Surgeon, Denver Health Medical Center Assistant Professor of Surgery, University of Colorado Outlining the ABCs Why do we need such an approach? The
Adult Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support 2015 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular
 Adult Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support 2015 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care 1 DR. Alireza Abootalebi Assistant Professor Of
Adult Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support 2015 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care 1 DR. Alireza Abootalebi Assistant Professor Of
Management of Cardiac Arrest Based on : 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines
 Management of Cardiac Arrest Based on : 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines www.circ.ahajournals.org Elham Pishbin. M.D Assistant Professor of Emergency Medicine MUMS C H E S Advanced Life Support
Management of Cardiac Arrest Based on : 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines www.circ.ahajournals.org Elham Pishbin. M.D Assistant Professor of Emergency Medicine MUMS C H E S Advanced Life Support
Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 5 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General This protocol should be followed for all pediatric cardiac arrests. If an arrest is of a known traumatic origin refer to the Dead on
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 5 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General This protocol should be followed for all pediatric cardiac arrests. If an arrest is of a known traumatic origin refer to the Dead on
Chapter 29 - Chest_and_Abdominal_Trauma
 Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 29.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 11, 15, 18, 27 29.2 Describe mechanisms of injury commonly associated with chest injuries. Slides
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 29.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 11, 15, 18, 27 29.2 Describe mechanisms of injury commonly associated with chest injuries. Slides
Don t let your patients turn blue! Isn t it about time you used etco 2?
 Don t let your patients turn blue! Isn t it about time you used etco 2? American Association of Critical Care Nurses National Teaching Institute Expo Ed 2013 Susan Thibeault MS, CRNA, APRN, CCRN, EMT-P
Don t let your patients turn blue! Isn t it about time you used etco 2? American Association of Critical Care Nurses National Teaching Institute Expo Ed 2013 Susan Thibeault MS, CRNA, APRN, CCRN, EMT-P
Michigan Pediatric Cardiac Protocols. Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Advanced Life Support. Algorithm. Learning outcomes. Shockable rhythms (VF/VT) Introduction. Treatment of shockable rhythms (VF/VT) CHAPTER
 CHAPTER Advanced Life Support 6 Algorithm Learning outcomes To understand: The function of the advanced life support (ALS) algorithm The importance of minimally interrupted high quality chest compressions
CHAPTER Advanced Life Support 6 Algorithm Learning outcomes To understand: The function of the advanced life support (ALS) algorithm The importance of minimally interrupted high quality chest compressions
THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS RELATE TO THE RESUSCITATION COUNCIL (UK) RESUSCITATION GUIDELINES 2005
 THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS RELATE TO THE RESUSCITATION COUNCIL (UK) RESUSCITATION GUIDELINES 2005 1. The guidelines suggest that in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests, attended but unwitnessed by health care
THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS RELATE TO THE RESUSCITATION COUNCIL (UK) RESUSCITATION GUIDELINES 2005 1. The guidelines suggest that in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests, attended but unwitnessed by health care
The Primary Survey. Clay Cothren Burlew, MD FACS
 The Primary Survey Clay Cothren Burlew, MD FACS Director, Surgical Intensive Care Unit Attending Surgeon, Denver Health Medical Center Associate Professor of Surgery, University of Colorado Outlining the
The Primary Survey Clay Cothren Burlew, MD FACS Director, Surgical Intensive Care Unit Attending Surgeon, Denver Health Medical Center Associate Professor of Surgery, University of Colorado Outlining the
In-hospital Resuscitation
 In-hospital Resuscitation Introduction This new section in the guidelines describes the sequence of actions for starting in-hospital resuscitation. Hospital staff are often trained in basic life support
In-hospital Resuscitation Introduction This new section in the guidelines describes the sequence of actions for starting in-hospital resuscitation. Hospital staff are often trained in basic life support
Michigan Pediatric Cardiac Protocols. Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Medical NREMT-PTE. NREMT Paramedic Trauma Exam.
 Medical NREMT-PTE NREMT Paramedic Trauma Exam https://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/nremt-pte Question: 41 Which of the following most accurately describes the finding of jugular venous distension
Medical NREMT-PTE NREMT Paramedic Trauma Exam https://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/nremt-pte Question: 41 Which of the following most accurately describes the finding of jugular venous distension
MICHIGAN. State Protocols. Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.
 MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.3 Tachycardia PEDIATRIC CARDIAC PEDIATRIC CARDIAC ARREST
MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.3 Tachycardia PEDIATRIC CARDIAC PEDIATRIC CARDIAC ARREST
RCH Trauma Guideline. Management of Traumatic Pneumothorax & Haemothorax. Trauma Service, Division of Surgery
 RCH Trauma Guideline Management of Traumatic Pneumothorax & Haemothorax Trauma Service, Division of Surgery Aim To describe safe and competent management of traumatic pneumothorax and haemothorax at RCH.
RCH Trauma Guideline Management of Traumatic Pneumothorax & Haemothorax Trauma Service, Division of Surgery Aim To describe safe and competent management of traumatic pneumothorax and haemothorax at RCH.
ADVANCED LIFE SUPPORT
 ANSWERS IN ITALICS WITH REFERENCES 1. The guidelines suggest that in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests, attended but unwitnessed by health care professionals equipped with a manual defibrillator, the providers
ANSWERS IN ITALICS WITH REFERENCES 1. The guidelines suggest that in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests, attended but unwitnessed by health care professionals equipped with a manual defibrillator, the providers
3. D Objective: Chapter 4, Objective 4 Page: 79 Rationale: A carbon dioxide level below 35 mmhg indicates hyperventilation.
 1. A Objective: Chapter 1, Objective 3 Page: 14 Rationale: The sudden increase in acceleration produces posterior displacement of the occupants and possible hyperextension of the cervical spine if the
1. A Objective: Chapter 1, Objective 3 Page: 14 Rationale: The sudden increase in acceleration produces posterior displacement of the occupants and possible hyperextension of the cervical spine if the
Routine Patient Care Guidelines - Adult
 Routine Patient Care Guidelines - Adult All levels of provider will complete an initial & focused assessment on every patient, and as standing order, use necessary and appropriate skills and procedures
Routine Patient Care Guidelines - Adult All levels of provider will complete an initial & focused assessment on every patient, and as standing order, use necessary and appropriate skills and procedures
The Importance of CPR in Sudden Cardiac Arrest
 The Importance of CPR in Sudden Cardiac Arrest By Adrian Waller, Public Safety Manager, ZOLL Medical. Feb 2011 The Importance of CPR in Sudden Cardiac Arrest By Adrian Waller, Public Safety Manager, ZOLL
The Importance of CPR in Sudden Cardiac Arrest By Adrian Waller, Public Safety Manager, ZOLL Medical. Feb 2011 The Importance of CPR in Sudden Cardiac Arrest By Adrian Waller, Public Safety Manager, ZOLL
Manual Defibrillation. CPR AGE: 18 years LOA: Altered HR: N/A RR: N/A SBP: N/A Other: N/A
 ROC AMIODARONE, LIDOCAINE OR PLACEBO FOR OUT OF HOSPITAL CARDIAC ARREST DUE TO VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION OR TACHYCARDIA (ALPS) STUDY: MEDICAL CARDIAC ARREST MEDICAL DIRECTIVE An Advanced Care Paramedic
ROC AMIODARONE, LIDOCAINE OR PLACEBO FOR OUT OF HOSPITAL CARDIAC ARREST DUE TO VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION OR TACHYCARDIA (ALPS) STUDY: MEDICAL CARDIAC ARREST MEDICAL DIRECTIVE An Advanced Care Paramedic
Title of Guideline (must include the word Guideline (not. Guidelines. Contact Name and Job Title (author)
 Title of Guideline (must include the word Guideline (not protocol, policy, procedure etc) Contact Name and Job Title (author) Directorate & Speciality Date of submission Date on which guideline must be
Title of Guideline (must include the word Guideline (not protocol, policy, procedure etc) Contact Name and Job Title (author) Directorate & Speciality Date of submission Date on which guideline must be
ACUTE CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF TRAUMA Tina Gaarder, MD, PhD
 ACUTE CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF TRAUMA Tina Gaarder, MD, PhD Trauma represents a leading cause of disability and preventable death and is mainly affecting people between 15 and 40 years of age, accounting
ACUTE CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF TRAUMA Tina Gaarder, MD, PhD Trauma represents a leading cause of disability and preventable death and is mainly affecting people between 15 and 40 years of age, accounting
Pre-Hospital and Emergency Department Resuscitative Thoracotomy
 Pre-Hospital and Emergency Department Programme Directors: Mr Jim Connolly Consultant A&E Surgeon Accident and Emergency Department, Royal Victoria Infirmary Dr Paul Wallman Consultant in Emergency Medicine
Pre-Hospital and Emergency Department Programme Directors: Mr Jim Connolly Consultant A&E Surgeon Accident and Emergency Department, Royal Victoria Infirmary Dr Paul Wallman Consultant in Emergency Medicine
Portage County EMS Patient Care Guidelines. Cardiac Arrest
 Portage County EMS Patient Care Guidelines Cardiac Arrest Note: These guidelines are based on (or adapted from) the current American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency
Portage County EMS Patient Care Guidelines Cardiac Arrest Note: These guidelines are based on (or adapted from) the current American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency
Science Behind Resuscitation. Vic Parwani, MD ED Medical Director CarolinaEast Health System August 6 th, 2013
 Science Behind Resuscitation Vic Parwani, MD ED Medical Director CarolinaEast Health System August 6 th, 2013 Conflict of Interest No Financial or Industrial Conflicts Slides: Drs. Nelson, Cole and Larabee
Science Behind Resuscitation Vic Parwani, MD ED Medical Director CarolinaEast Health System August 6 th, 2013 Conflict of Interest No Financial or Industrial Conflicts Slides: Drs. Nelson, Cole and Larabee
Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) Science Update 2015
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) Science Update 2015 What s New in ACLS for 2015? Adult CPR CPR remains (Compressions, Airway, Breathing Chest compressions has priority over all other
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) Science Update 2015 What s New in ACLS for 2015? Adult CPR CPR remains (Compressions, Airway, Breathing Chest compressions has priority over all other
ILCOR, ARC & NZRC PAEDIATRIC RESUSCITATION RECOMMENDATIONS 2010
 ILCOR, ARC & NZRC PAEDIATRIC RESUSCITATION RECOMMENDATIONS 2010 Jim Tibballs Officer, RCH Convenor, Paediatric Sub-Committee, (ARC) ARC Paediatric Representative International Liaison Committee on (ILCOR)
ILCOR, ARC & NZRC PAEDIATRIC RESUSCITATION RECOMMENDATIONS 2010 Jim Tibballs Officer, RCH Convenor, Paediatric Sub-Committee, (ARC) ARC Paediatric Representative International Liaison Committee on (ILCOR)
CONSENSUS STATEMENT 2018 MANAGEMENT OF TRAUMATIC CARDIAC ARREST
 CONSENSUS STATEMENT 2018 MANAGEMENT OF TRAUMATIC CARDIAC ARREST 1. Introduction 1.1. Traumatic cardiac arrest (TCA) is a rare event typically associated with a poor outcome. Recent epidemiological data
CONSENSUS STATEMENT 2018 MANAGEMENT OF TRAUMATIC CARDIAC ARREST 1. Introduction 1.1. Traumatic cardiac arrest (TCA) is a rare event typically associated with a poor outcome. Recent epidemiological data
Prehospital Resuscitation for the 21 st Century Simulation Case. VF/Asystole
 Prehospital Resuscitation for the 21 st Century Simulation Case VF/Asystole Case History 1 (hypovolemic cardiac arrest secondary to massive upper GI bleed) 56 year-old male patient who fainted in the presence
Prehospital Resuscitation for the 21 st Century Simulation Case VF/Asystole Case History 1 (hypovolemic cardiac arrest secondary to massive upper GI bleed) 56 year-old male patient who fainted in the presence
WORKSHEET for Evidence-Based Review of Science for Veterinary CPCR
 RECOVER 2011 1 of 7 WORKSHEET for Evidence-Based Review of Science for Veterinary CPCR 1. Basic Demographics Worksheet author(s) Ann Peruski Date Submitted for review: 18 Apr 2011 Mailing address: 6995
RECOVER 2011 1 of 7 WORKSHEET for Evidence-Based Review of Science for Veterinary CPCR 1. Basic Demographics Worksheet author(s) Ann Peruski Date Submitted for review: 18 Apr 2011 Mailing address: 6995
2015 Interim Training Materials
 2015 Interim Training Materials ACLS Manual and ACLS EP Manual Comparison Chart Assessment sequence Manual, Part 2: The Systematic Approach, and Part BLS Changes The HCP should check for response while
2015 Interim Training Materials ACLS Manual and ACLS EP Manual Comparison Chart Assessment sequence Manual, Part 2: The Systematic Approach, and Part BLS Changes The HCP should check for response while
Developments in Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Guidelines
 Developments in Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Guidelines Bernd W. Böttiger Seite 1 To preserve human life by making high quality resuscitation available to all Outcome after CPR in Germany ROSC ( Return
Developments in Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Guidelines Bernd W. Böttiger Seite 1 To preserve human life by making high quality resuscitation available to all Outcome after CPR in Germany ROSC ( Return
Acute Pericardial Tamponade
 Acute Pericardial Tamponade Marx: Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice, 5th ed. Epidemiology The reported incidence of acute pericardial tamponade is approximately 2% in patients
Acute Pericardial Tamponade Marx: Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice, 5th ed. Epidemiology The reported incidence of acute pericardial tamponade is approximately 2% in patients
In ESH we usually see blunt chest trauma but penetrating injuries also treated here (usually as single injuries, like stab wound)
 Chest Trauma Dr Csaba Dioszeghy MD PhD FRCEM FFICM FERC East Surrey Hospital Emergency Department Scope Thoracic injuries are common and can be life threatening In ESH we usually see blunt chest trauma
Chest Trauma Dr Csaba Dioszeghy MD PhD FRCEM FFICM FERC East Surrey Hospital Emergency Department Scope Thoracic injuries are common and can be life threatening In ESH we usually see blunt chest trauma
Lesson 4-3: Cardiac Emergencies. CARDIAC EMERGENCIES Angina, AMI, CHF and AED
 Lesson 4-3: Cardiac Emergencies CARDIAC EMERGENCIES Angina, AMI, CHF and AED THREE FAMILIAR CARDIAC CONDITIONS Angina Pectoris Acute Myocardial Infarction Congestive Heart Failure ANGINA PECTORIS Chest
Lesson 4-3: Cardiac Emergencies CARDIAC EMERGENCIES Angina, AMI, CHF and AED THREE FAMILIAR CARDIAC CONDITIONS Angina Pectoris Acute Myocardial Infarction Congestive Heart Failure ANGINA PECTORIS Chest
Disclosures. Extra-Corporeal Membrane Oxygenation During Cardio- Pulmonary Resuscitation ECPR April 22, 2016 ECG. Case. Case. Case Summary 4/22/2016
 Extra-Corporeal Membrane Oxygenation During Cardio- Pulmonary Resuscitation ECPR April 22, 2016 Nothing to disclose. Disclosures Ivan J Chavez MD Case ECG History 60 y/o male No prior history of CAD In
Extra-Corporeal Membrane Oxygenation During Cardio- Pulmonary Resuscitation ECPR April 22, 2016 Nothing to disclose. Disclosures Ivan J Chavez MD Case ECG History 60 y/o male No prior history of CAD In
Update on Sudden Cardiac Death and Resuscitation
 Update on Sudden Cardiac Death and Resuscitation Ashish R. Panchal, MD, PhD Medical Director Center for Emergency Medical Services Assistant Professor Clinical Department of Emergency Medicine The Ohio
Update on Sudden Cardiac Death and Resuscitation Ashish R. Panchal, MD, PhD Medical Director Center for Emergency Medical Services Assistant Professor Clinical Department of Emergency Medicine The Ohio
CARDIAC ARREST IN SPECIAL CIRCUMSTANCES 2
 CARDIAC ARREST IN SPECIAL CIRCUMSTANCES 2 M1 Objectives To understand how resuscitation techniques should be modified in the special circumstances of: Hypothermia Immersion and submersion Poisoning Pregnancy
CARDIAC ARREST IN SPECIAL CIRCUMSTANCES 2 M1 Objectives To understand how resuscitation techniques should be modified in the special circumstances of: Hypothermia Immersion and submersion Poisoning Pregnancy
European Resuscitation Council
 European Resuscitation Council Objectives To know basic elements to evaluate patients with rythm disturbance To know advanced treatment of paediatric cardiac arrest To know emergency treatment of most
European Resuscitation Council Objectives To know basic elements to evaluate patients with rythm disturbance To know advanced treatment of paediatric cardiac arrest To know emergency treatment of most
Pediatric Trauma Practice. Guideline for Management of the Child in Shock. Background
 Pediatric Trauma Practice Guideline for Management of the Child in Shock Background Guideline for Management Trauma is the leading cause of death in children and adolescents in the United States. Although
Pediatric Trauma Practice Guideline for Management of the Child in Shock Background Guideline for Management Trauma is the leading cause of death in children and adolescents in the United States. Although
1. In a rear-impact motor vehicle crash, which area of the spine is most susceptible to injury? A. Cervical B. Thoracic C. Lumbar D.
 1. In a rear-impact motor vehicle crash, which area of the spine is most susceptible to injury? A. Cervical B. Thoracic C. Lumbar D. Sacral-coccygeal 2. A 36-year-old male sustains blunt force thoracic
1. In a rear-impact motor vehicle crash, which area of the spine is most susceptible to injury? A. Cervical B. Thoracic C. Lumbar D. Sacral-coccygeal 2. A 36-year-old male sustains blunt force thoracic
New and Future Trends in EMS. Ron Brown, MD, FACEP Paramedic Lecture Series 2018
 New and Future Trends in EMS Ron Brown, MD, FACEP Paramedic Lecture Series 2018 New technologies and protocols DSD Mechanical Compression ITD BiPAP Ultrasound Double Sequential Defibrillation Two defibrillators
New and Future Trends in EMS Ron Brown, MD, FACEP Paramedic Lecture Series 2018 New technologies and protocols DSD Mechanical Compression ITD BiPAP Ultrasound Double Sequential Defibrillation Two defibrillators
HealthCare Training Service
 HealthCare Training Service Advanced Life Support Exam Time: Perusal Time: 20 minutes 5 minutes Total Marks: 25 Instructions: Read each question carefully. Using a pencil, record your response to each
HealthCare Training Service Advanced Life Support Exam Time: Perusal Time: 20 minutes 5 minutes Total Marks: 25 Instructions: Read each question carefully. Using a pencil, record your response to each
San Benito County EMS Agency Section 700: Patient Care Procedures
 Purpose: To outline the steps EMTs & paramedics will take to manage possible life threats in any child or adult patient they encounter. This policy is in effect for all treatment protocols & is to be referred
Purpose: To outline the steps EMTs & paramedics will take to manage possible life threats in any child or adult patient they encounter. This policy is in effect for all treatment protocols & is to be referred
Head injuries. Severity of head injuries
 Head injuries ED Teaching day 23 rd October Severity of head injuries Minor GCS 14-15 Must not have any of the following: Amnesia 10min Neurological sign or symptom Skull fracture (clinically or radiologically)
Head injuries ED Teaching day 23 rd October Severity of head injuries Minor GCS 14-15 Must not have any of the following: Amnesia 10min Neurological sign or symptom Skull fracture (clinically or radiologically)
Chapter 29 - Chest Injuries
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 National EMS Education Standard Competencies (1 of 5) Trauma Applies fundamental knowledge to provide basic emergency care and transportation based on assessment findings for an acutely
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 National EMS Education Standard Competencies (1 of 5) Trauma Applies fundamental knowledge to provide basic emergency care and transportation based on assessment findings for an acutely
PROTOCOL 1 Endotracheal Intubation (Adult and Pediatric) REQUEST EMT-P RESPONSE DO NOT DELAY TRANSPORT
 PROTOCOL 1 Endotracheal Intubation (Adult and Pediatric) 1. Basic Life Support airway management procedures are initiated. 2. Endotracheal Intubation is indicated under any of the following conditions:
PROTOCOL 1 Endotracheal Intubation (Adult and Pediatric) 1. Basic Life Support airway management procedures are initiated. 2. Endotracheal Intubation is indicated under any of the following conditions:
1 Pediatric Advanced Life Support Science Update What s New for 2010? 3 CPR. 4 4 Steps of BLS Survey 5 CPR 6 CPR.
 1 Pediatric Advanced Life Support Science Update 2010 2 What s New for 2010? 3 CPR Take no longer than seconds for pulse check Rate at least on per minute (instead of around 100 per minute ) Depth change:
1 Pediatric Advanced Life Support Science Update 2010 2 What s New for 2010? 3 CPR Take no longer than seconds for pulse check Rate at least on per minute (instead of around 100 per minute ) Depth change:
Cardiac arrest Cardiac arrest (CA) occurs when the heart ceases to produce an effective pulse and circulate blood It includes four conditions:
 Basic Life Support: Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR). 2017 Lecture prepared by, Amer A. Hasanien RN, CNS, PhD Cardiac arrest Cardiac arrest (CA) occurs when the heart ceases to produce an effective
Basic Life Support: Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR). 2017 Lecture prepared by, Amer A. Hasanien RN, CNS, PhD Cardiac arrest Cardiac arrest (CA) occurs when the heart ceases to produce an effective
Science Behind CPR Update from Darrell Nelson, MD, FACEP Emergency Medicine Wake Forest University Health Sciences
 Science Behind CPR Update from 2010 Darrell Nelson, MD, FACEP Emergency Medicine Wake Forest University Health Sciences FRAMING THE DISCUSSION NO ONE SURVIVES CARDIAC ARREST, EXCEPT ON TV Conflicts of
Science Behind CPR Update from 2010 Darrell Nelson, MD, FACEP Emergency Medicine Wake Forest University Health Sciences FRAMING THE DISCUSSION NO ONE SURVIVES CARDIAC ARREST, EXCEPT ON TV Conflicts of
18% Survival from In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Ways we can do better! National Teaching Institute Denver, CO Class Code: 149 A
 18% Survival from In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Ways we can do better! National Teaching Institute Denver, CO Class Code: 149 A Nicole Kupchik RN, MN, CCNS, CCRN, PCCN Independent CNS/Staff Nurse Objectives
18% Survival from In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Ways we can do better! National Teaching Institute Denver, CO Class Code: 149 A Nicole Kupchik RN, MN, CCNS, CCRN, PCCN Independent CNS/Staff Nurse Objectives
Maternal Collapse Guideline
 Maternal Collapse Guideline Guideline Number: 664 Supersedes: Classification Clinical Version No: Date of EqIA: Approved by: Date Approved: Date made active: Review Date: 1 Obstetric Written Documentation
Maternal Collapse Guideline Guideline Number: 664 Supersedes: Classification Clinical Version No: Date of EqIA: Approved by: Date Approved: Date made active: Review Date: 1 Obstetric Written Documentation
Outcome from paediatric cardiac arrest associated with trauma
 Resuscitation (2007) 75, 29 34 CLINICAL PAPER Outcome from paediatric cardiac arrest associated with trauma K. Crewdson, D. Lockey, G. Davies London Helicopter Emergency Medical Service, Royal London Hospital,
Resuscitation (2007) 75, 29 34 CLINICAL PAPER Outcome from paediatric cardiac arrest associated with trauma K. Crewdson, D. Lockey, G. Davies London Helicopter Emergency Medical Service, Royal London Hospital,
Wake County EMS System Peer Review/Clinical Data/System Performance
 P a g e 1 Wake County EMS System Peer Review/Clinical Data/System Performance Explanations and Definitions for Reports Wake County EMS engages in regular external review. The System makes quarterly reports
P a g e 1 Wake County EMS System Peer Review/Clinical Data/System Performance Explanations and Definitions for Reports Wake County EMS engages in regular external review. The System makes quarterly reports
Cardiac arrest simulation teaching (CASTeach) session
 Cardiac arrest simulation teaching (CASTeach) session Instructor guidance Key learning outcomes Overall aim: Scenarios should be facilitated by the Instructor in such a way that they are performed correctly.
Cardiac arrest simulation teaching (CASTeach) session Instructor guidance Key learning outcomes Overall aim: Scenarios should be facilitated by the Instructor in such a way that they are performed correctly.
PALS Case Scenario Testing Checklist Respiratory Case Scenario 1 Upper Airway Obstruction
 Respiratory Case Scenario 1 Upper Airway Obstruction Directs administration of 100% oxygen or supplementary oxygen as needed to support oxygenation Identifies signs and symptoms of upper airway obstruction
Respiratory Case Scenario 1 Upper Airway Obstruction Directs administration of 100% oxygen or supplementary oxygen as needed to support oxygenation Identifies signs and symptoms of upper airway obstruction
MICHIGAN. State Protocols
 MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 Protocol Name Adult Cardiac Table of Contents General Cardiac Arrest Bradycardia Tachycardia Pulmonary Edema/CHF Chest Pain/Acute Coronary Syndrome
MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 Protocol Name Adult Cardiac Table of Contents General Cardiac Arrest Bradycardia Tachycardia Pulmonary Edema/CHF Chest Pain/Acute Coronary Syndrome
Introduction To ACLS,1 18 April 2011 INTRODUCTION TO ACLS
 Introduction To ACLS,1 INTRODUCTION TO ACLS EPIDEMIOLOGY In Singapore, every year about 2,400 people suffer from an acute myocardial infarction. Of these about 900 die as a result of sudden cardiac arrest,
Introduction To ACLS,1 INTRODUCTION TO ACLS EPIDEMIOLOGY In Singapore, every year about 2,400 people suffer from an acute myocardial infarction. Of these about 900 die as a result of sudden cardiac arrest,
But unfortunately, the first sign of cardiovascular disease is often the last. Chest-Compression-Only Resuscitation Gordon A.
 THE UNIVERSITY OF ARIZONA Sarver Heart Center 1 THE UNIVERSITY OF ARIZONA Sarver Heart Center 2 But unfortunately, the first sign of cardiovascular disease is often the last 3 4 1 5 6 7 8 2 Risk of Cardiac
THE UNIVERSITY OF ARIZONA Sarver Heart Center 1 THE UNIVERSITY OF ARIZONA Sarver Heart Center 2 But unfortunately, the first sign of cardiovascular disease is often the last 3 4 1 5 6 7 8 2 Risk of Cardiac
TEACHING BASIC LIFE SUPPORT (& ALS)
 TEACHING BASIC LIFE SUPPORT (& ALS) Anton Koželj, R.N., B. Sc., lecturer Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Maribor Žitna ulica 15, 2000 Maribor, Slovenia Fact s To know-how to perform basic life
TEACHING BASIC LIFE SUPPORT (& ALS) Anton Koželj, R.N., B. Sc., lecturer Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Maribor Žitna ulica 15, 2000 Maribor, Slovenia Fact s To know-how to perform basic life
Checklist 3: Transporting a Patient in Cardiac Arrest
 Checklist 3: Transporting a Patient in Cardiac Arrest The procedures surrounding the transport of a patient in cardiac arrest are complex and it is important for Paramedics to understand the impact on
Checklist 3: Transporting a Patient in Cardiac Arrest The procedures surrounding the transport of a patient in cardiac arrest are complex and it is important for Paramedics to understand the impact on
Resuscitation Guidelines update. Dr. Luis García-Castrillo Riesgo EuSEM Vice president
 Resuscitation Guidelines update Dr. Luis García-Castrillo Riesgo EuSEM Vice president There are no COIs to disclose in this presentation. CPR Mile Stones 1958 -William Kouwenhoven, cardiac massage. 1967
Resuscitation Guidelines update Dr. Luis García-Castrillo Riesgo EuSEM Vice president There are no COIs to disclose in this presentation. CPR Mile Stones 1958 -William Kouwenhoven, cardiac massage. 1967
Adult Basic Life Support
 Adult Basic Life Support UNRESPONSIVE? Shout for help Open airway NOT BREATHING NORMALLY? Call 112* 30 chest compressions 2 rescue breaths 30 compressions *or national emergency number Fig 1.2_Adult BLS
Adult Basic Life Support UNRESPONSIVE? Shout for help Open airway NOT BREATHING NORMALLY? Call 112* 30 chest compressions 2 rescue breaths 30 compressions *or national emergency number Fig 1.2_Adult BLS
Update on Sudden Cardiac Death and Resuscitation
 Update on Sudden Cardiac Death and Resuscitation Ashish R. Panchal, MD, PhD Medical Director Center for Emergency Medical Services Assistant Professor Clinical Department of Emergency Medicine The Ohio
Update on Sudden Cardiac Death and Resuscitation Ashish R. Panchal, MD, PhD Medical Director Center for Emergency Medical Services Assistant Professor Clinical Department of Emergency Medicine The Ohio
ITLS Advanced Pre-Test Annotated Key 8 th Edition
 1. A Objective: Chapter 1, Objective 3 Page: 14 Rationale: The sudden increase in acceleration produces posterior displacement of the occupants and possible hyperextension of the cervical spine if the
1. A Objective: Chapter 1, Objective 3 Page: 14 Rationale: The sudden increase in acceleration produces posterior displacement of the occupants and possible hyperextension of the cervical spine if the
Portage County EMS Annual Skills Labs
 Portage County EMS Annual Skills Labs Scope: Provide skills labs for all Emergency Medical Responders and First Response EMTs to assure proficiency of skills and satisfy the Wisconsin State approved Operational
Portage County EMS Annual Skills Labs Scope: Provide skills labs for all Emergency Medical Responders and First Response EMTs to assure proficiency of skills and satisfy the Wisconsin State approved Operational
ROC PRIMED Questions and Answers
 ROC PRIMED Questions and Answers 1) What is the ROC PRIMED study? ROC PRIMED stands for the Resuscitation Outcomes Consortium Prehospital Resuscitation using an IMpedance valve and Early versus Delayed
ROC PRIMED Questions and Answers 1) What is the ROC PRIMED study? ROC PRIMED stands for the Resuscitation Outcomes Consortium Prehospital Resuscitation using an IMpedance valve and Early versus Delayed
HOW TO SURVIVE ELECTRICAL STORM
 HOW TO SURVIVE ELECTRICAL STORM DR. LAURA CHAHOUD, DO EMERGENCY MEDICINE PGY-4 ST MARY MERCY HOSPITAL OUTLINE What is electrical storm? Case intro ACLS Approaches to management Dual axis defibrillation
HOW TO SURVIVE ELECTRICAL STORM DR. LAURA CHAHOUD, DO EMERGENCY MEDICINE PGY-4 ST MARY MERCY HOSPITAL OUTLINE What is electrical storm? Case intro ACLS Approaches to management Dual axis defibrillation
Putting it all together: 1. The arrested patient 2. The shocked patient 3. The breathless patient
 Putting it all together: 1. The arrested patient 2. The shocked patient 3. The breathless patient 1 The Arrested Patient Adapted from Lichtenstein's SESAME protocol, with permission 2 Summary 1. (Ongoing
Putting it all together: 1. The arrested patient 2. The shocked patient 3. The breathless patient 1 The Arrested Patient Adapted from Lichtenstein's SESAME protocol, with permission 2 Summary 1. (Ongoing
CHEST INJURY PULMONARY CONTUSION
 CHEST INJURY PULMONARY CONTUSION Introduction Pulmonary contusion refers to blunt traumatic lung parenchymal injury which results in oedema and haemorrhaging into alveolar spaces. It may also result in
CHEST INJURY PULMONARY CONTUSION Introduction Pulmonary contusion refers to blunt traumatic lung parenchymal injury which results in oedema and haemorrhaging into alveolar spaces. It may also result in
Adult Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support. Emergency Procedures in PT
 Adult Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support Emergency Procedures in PT BLS Can be learned & practiced by the general public Includes: CPR First Aid (e.g. choking relief) Use of AED ACLS Used by healthcare
Adult Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support Emergency Procedures in PT BLS Can be learned & practiced by the general public Includes: CPR First Aid (e.g. choking relief) Use of AED ACLS Used by healthcare
ITLS Pediatric Provider Course Basic Pre-Test
 ITLS Pediatric Provider Course Basic Pre-Test 1. You arrive at the scene of a motor vehicle collision and are directed to evaluate a child who was in one of the vehicles. The patient appears to be a child
ITLS Pediatric Provider Course Basic Pre-Test 1. You arrive at the scene of a motor vehicle collision and are directed to evaluate a child who was in one of the vehicles. The patient appears to be a child
ACLS/ACS Updates 2015
 ACLS/ACS Updates 2015 Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support by: Fareed Al Nozha, JBIM, ABIM, FKFSH&RC(Cardiology) Consultant Cardiologist Faculty, National CPR Committee, ACLS Program Head, SHA Dr Abdulhalim
ACLS/ACS Updates 2015 Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support by: Fareed Al Nozha, JBIM, ABIM, FKFSH&RC(Cardiology) Consultant Cardiologist Faculty, National CPR Committee, ACLS Program Head, SHA Dr Abdulhalim
The Management of Chest Trauma. Tom Scaletta, MD FAAEM Immediate Past President, AAEM
 The Management of Chest Trauma Tom Scaletta, MD FAAEM Immediate Past President, AAEM Trichotomizing Rib Fractures Upper 1-3 vascular injuries Middle 4-9 Lower 10-12 12 liver/spleen injuries Management
The Management of Chest Trauma Tom Scaletta, MD FAAEM Immediate Past President, AAEM Trichotomizing Rib Fractures Upper 1-3 vascular injuries Middle 4-9 Lower 10-12 12 liver/spleen injuries Management
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Hasegawa K, Hiraide A, Chang Y, Brown DFM. Association of prehospital advancied airway management with neurologic outcome and survival in patients with out-of-hospital cardiac
Supplementary Online Content Hasegawa K, Hiraide A, Chang Y, Brown DFM. Association of prehospital advancied airway management with neurologic outcome and survival in patients with out-of-hospital cardiac
Appropriate Use of Emergency Department Thoracotomy: Implications for the Thoracic Surgeon
 Appropriate Use of Emergency Department Thoracotomy: Implications for the Thoracic Surgeon Nathan M. Mollberg, DO, Cavin Glenn, MD, Jobin John, MD, Stephen R. Wise, MD, Ryan Sullivan, MD, Amir Vafa, MD,
Appropriate Use of Emergency Department Thoracotomy: Implications for the Thoracic Surgeon Nathan M. Mollberg, DO, Cavin Glenn, MD, Jobin John, MD, Stephen R. Wise, MD, Ryan Sullivan, MD, Amir Vafa, MD,
Pediatric CPR. Mustafa SERİNKEN MD Professor of Emergency Medicine, Pamukkale University, TURKEY
 Pediatric CPR Mustafa SERİNKEN MD Professor of Emergency Medicine, Pamukkale University, TURKEY What are the differences? Normal limits ADULT CARDIOPULMONARY ARREST CAUSES INFANTS AND CHILDREN İschemic
Pediatric CPR Mustafa SERİNKEN MD Professor of Emergency Medicine, Pamukkale University, TURKEY What are the differences? Normal limits ADULT CARDIOPULMONARY ARREST CAUSES INFANTS AND CHILDREN İschemic
Future of Cardiac Arrest Management for Paramedics
 Future of Cardiac Arrest Management for Paramedics EMS TODAY 2013 Mark Whitbread Consultant Paramedic London Ambulance Service London Ambulance Service NHS Trust 620 sq miles 8.2 million population 2011/12
Future of Cardiac Arrest Management for Paramedics EMS TODAY 2013 Mark Whitbread Consultant Paramedic London Ambulance Service London Ambulance Service NHS Trust 620 sq miles 8.2 million population 2011/12
After this review our system decided to implement guidelines which allowed EMS personnel to
 How far is too far? A review of the evidence for Prehospital Termination of Resuscitation after Cardiac Arrest Shalu S. Patel, MD Christine Van Dillen MD University of Florida-Gainesville Out-of-hospital
How far is too far? A review of the evidence for Prehospital Termination of Resuscitation after Cardiac Arrest Shalu S. Patel, MD Christine Van Dillen MD University of Florida-Gainesville Out-of-hospital
Icu-cpr PICTURE QUIZ march 2014
 Department of surgery Icu-cpr PICTURE QUIZ march 2014 Prepared by Dr. Karam Kamal Younis Assistant professor and consultant surgeon Convener of the Department of Surgery College of Medicine University
Department of surgery Icu-cpr PICTURE QUIZ march 2014 Prepared by Dr. Karam Kamal Younis Assistant professor and consultant surgeon Convener of the Department of Surgery College of Medicine University
Tissue Plasminogen Activator in In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest with Pulseless Electrical Activity
 Tissue Plasminogen Activator in In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest with Pulseless Electrical Activity Hannah Jordan A. Study Purpose and Rationale Pulseless electrical activity during cardiac arrest carries a
Tissue Plasminogen Activator in In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest with Pulseless Electrical Activity Hannah Jordan A. Study Purpose and Rationale Pulseless electrical activity during cardiac arrest carries a
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdomen, and aorta, as causes of shock, point-of-care ultrasonography in assessment of, 915 917 Abdominal compartment syndrome, trauma patient
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdomen, and aorta, as causes of shock, point-of-care ultrasonography in assessment of, 915 917 Abdominal compartment syndrome, trauma patient
Key statistics from the National Cardiac Arrest Audit: Paediatric arrests April 2012 to March 2017
 Key statistics from the National Cardiac Arrest Audit: Paediatric arrests April 12 to March 17 Supported by Resuscitation Council (UK) and Intensive Care National Audit & Research Centre (ICNARC) Data
Key statistics from the National Cardiac Arrest Audit: Paediatric arrests April 12 to March 17 Supported by Resuscitation Council (UK) and Intensive Care National Audit & Research Centre (ICNARC) Data
