Lecture outline. Electrical properties of the heart. Automaticity. Excitability. Refractoriness. The ABCs of ECGs Back to Basics Part I
|
|
|
- Luke Goodman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture outline The ABCs of ECGs Back to Basics Part I Meg Sleeper VMD, DACVIM (cardiology) University of Florida Veterinary School Electrical properties of the heart Action potentials Normal intracardiac conduction ECG interpretation (cases) Electrical properties of the heart Automaticity Excitability Refractoriness Conductivity Automaticity Only pacemaker cells are normally capable of beating spontaneously Gradual diastolic reduction in action potential (becoming less negative) toward the cell s threshold potential. Excitability Refractoriness All resting myocytes are capable of responding to an effective stimulus by generating an action potential. Period of recovery following excitation when cells cannot respond to stimuli. Excitability is gradually restored. 1
2 Conductivity Intercalated discs in the ends of muscle fibers give the atria and ventricles the property of a syncytium. Therefore, if propagation is blocked along the preferential conducting pathway, depolarization can still spread directly from one cell to the next (a slower process). Conduction speed is dependent on cell size (slower in smaller cells), and is normally slowest at the AV node. Contractility Peak tension developed by myocardial cells at a specific resting fiber length. ECG gives no information regarding contractility or pump function Cardiac cell action potential Pacemaker cell action potential QRS ECG P T 4 I Ca Ventricular cell action potential Na+ In Ca++ In 3 K+ Out mv I k inward current inactivated -90 mv 4 Resting 4 Resting Pacemaker Cells Analysis of Cardiac Arrhythmias Site of impulse origin Supraventricular: SA node, atria, AV node Ventricular Rate: atrial and ventricular Sinus node AV node Purkinje Fiber Timing Premature beats: occur early in the sequence of normal beats Escape beats: occur after a pause in the sequence of beats 2
3 Normal wave morphology - + Supraventricular vs. ventricular beats In lead II, the RA is negative and the LL is positive. Therefore, normally in lead II, the P wave is positive and the QRS is predominantly positive (R wave). APC VPC VPC and APC Pauses Premature vs. escape ectopics APC: Non- Compensatory Pause Premature beats occur earlier than the next expected beat VPC: Compensatory Pause Escape beats occur after a pause Basic ECG classification Arrhythmias Supraventricular origin Normal (sinus) Bradycardias Tachycardias Ventricular origin Aberrant conduction AV block (may also be bradycardia) Bundle branch block Sinus arrhythmia in a dog; HR 74 bpm QRS Sinus rhythm in a cat; HR 220 bpm QRS P P T 3
4 ECG #1 7 year old mc Jack Russell terrier 50 mm/sec; 1mV=1cm ECG #1 7 year old mc Jack Russell terrier 50 mm/sec; 1mV=1cm HR@ 90 bpm R waves regularly irregular ECG #1 7 year old mc Jack Russell terrier 50 mm/sec; 1mV=1cm HR@ 90 bpm ECG #1 7 year old mc Jack Russell terrier 50 mm/sec; 1mV=1cm HR@ 90 bpm Normal QRS morphology and the same in all complexes P waves present for every QRS with consistent PR P waves have variable amplitude ECG #2 3 year old mc MIXB; automobile accident 25 mm/sec; 1mV=1cm Normal heart rate Supraventricular (normal morphology) Variable P wave with normal and consistent PR intervals Wandering pacemaker/sinus arrhythmia Treatment: None necessary 4
5 ECG #2 3 year old mc MIXB; automobile accident 25 mm/sec; 1mV=1cm HR@150 bpm ECG #2 3 year old mc MIXB; automobile accident 25 mm/sec; 1mV=1cm HR@150 bpm RR regularity: slight irregularity vs. regular QRS morphology: normal and wide (two different morphologies) Fusion beat ECG #2 3 year old mc MIXB; automobile accident 25 mm/sec; 1mV=1cm HR@150 bpm P waves: present for some of the QRSs (narrow QRSs) ECG #3 3 year old Labrador retriever; presenting for an episode of weakness Normal heart rate Episode of ventricular rhythm with a normal heart rate Diagnosis: Accelerated idioventricular rhythm with underlying sinus arrhythmia Treatment: Ventricular antiarrhythmic only if rate is fast enough to negatively impact blood pressure; generally self limiting 5
6 ECG #3 3 year old Labrador retriever; presenting for an episode of weakness HR@ 300/150 bpm ECG #3 3 year old Labrador retriever; presenting for an episode of weakness HR@ 300/150 bpm RR regularity: regular with abrupt transitions QRS morphology: narrow/normal ECG #3 3 year old Labrador retriever; presenting for an episode of weakness HR@ 300/150 bpm P waves: not always visible; transition begins with premature P wave Tachycardia with normal QRS morphology >>supraventricular Paroxysmal transitions >>not sinus Diagnosis: Supraventricular tachycardia or paroxysmal atrial tachycardia Treatment for supraventricular tachycardia Diltiazem mg/kg q 8 hours (oral) mg/kg IV bolus, then 2-6 mcg/kg/min CRI Digoxin mg/kg q 12 hours (oral) Beta blocker Atenolol: mg/kg q hours (oral) Esmolol: mcg/kg IV bolus every 5 min up to 500 mcg/kg maximum; mcg/kg/min CRI ECG #4 5 year old great Dane, no clinical signs 6
7 ECG #4 5 year old great Dane, no clinical signs HR- 160 bpm ECG #4 5 year old great Dane, no clinical signs HR- 160 bpm RR regularity: irregular QRS morphology: normal width to increased with variable morphology ( ) P waves present for most complexes but not all Normal to mildly increased heart rate with irregular rhythm Occasional premature, wide morphology complexes Rhythm diagnosis: Ventricular premature complexes; multiform Treatment ventricular ectopy In asymptomatic dogs, there is no evidence that starting anti-arrhythmic therapy will reduce the risk of a fatal arrhythmia The arrhythmia may be a sign of structural myocardial disease, particularly in breed predisposed to acquired heart disease. Recommend further evaluation: Echocardiogram Holter monitor CAST Cardiac Arrhythmia Supression Trial (N Engl J Med. 1989;321: } ECG example #5 5 year old Boxer, an episode of syncope There was an increased mortality in post-myocardial infarction patients given Class 1c antiarrhythmic agents. 7
8 ECG example #5 5 year old Boxer, an episode of syncope HR- 160 bpm; brief period of 300 bpm ECG example #5 5 year old Boxer, an episode of syncope HR- 160 bpm; brief period of 300 bpm RR regularity: irregular QRS morphology: normal width and increased width complexes P waves present for most complexes but not all Normal to mildly increased heart rate with periods of rapid heart rate Some premature, wide morphology complexes Rhythm diagnosis: Ventricular premature complexes and nonsustained ventricular tachycardia Treatment ventricular ectopy In symptomatic dogs, while there is no evidence that starting anti-arrhythmic therapy will reduce the risk of a fatal arrhythmia, effective therapy will reduce clinical signs Ventricular anti-arrhythmics to consider for non-sustained ventricular tachycardia: Mexilitine: 5-8 mg/kg three times daily (oral) Sotalol: 1-2 mg/kg twice daily (oral) The arrhythmia may be a sign of structural myocardial disease, particularly in breed predisposed to acquired heart disease. Recommend further evaluation: Echocardiogram Holter monitor ECG # 6 3 year old MIXB; normal 25 mm/sec; 1 mv=1cm ECG # 6 3 year old MIXB; normal 25 mm/sec; 1 mv=1cm HR@ 100bpm RR regularity: irregular QRS morphology: narrow/normal 8
9 ECG # 6 3 year old MIXB; normal 25 mm/sec; 1 mv=1cm HR@ 100bpm ECG # 6 3 year old MIXB; normal 25 mm/sec; 1 mv=1cm HR@ 100bpm P waves: occasional un-conducted P waves ( ) PR interval progressively lengthens prior to blocked P wave Pattern mirrors sinus arrhythmia RR variation ECG # 7 9 year old toy poodle with degenerative valve disease; currently on furosemide, enalapril and pimobendan 25 mm/sec; 1 mv=1 cm Normal heart rate with irregular rhythm Occasional blocked P waves QRS morphology normal Rhythm diagnosis: asymptomatic Second degree and athletic AV block dogs type 1 (Wenchebach) Treatment: Generally none necessary; usually ECG # 7 9 year old toy poodle with degenerative valve disease; currently on furosemide, enalapril and pimobendan 25 mm/sec; 1 mv=1 cm HR@ 160 bpm Rhythm: irregularly irregular QRS morphology: normal/narrow No P waves Irregularly, irregular rhythm Lack of P waves Normal QRS morphology Rhythm diagnosis: Atrial fibrillation Treatment: in a small breed dog with underlying heart disease, control heart rate with digoxin and/or diltiazem 9
10 ECG example #8 9 year old cocker spaniel; no clinical signs ECG example #8 9 year old cocker spaniel; no clinical signs HR-50 bpm RR regularity: irregular; predominantly long RR cycles (some longer than 2 seconds), occasional short cycles QRS morphology: narrow/normal ECG example #8 9 year old cocker spaniel; no clinical signs HR-50 bpm Bradycardia (sinus bradycardia) Negative P waves correspond to long RR cycles>>junctional escape beats Occasional premature beats P waves: intermittent; morphology variable Diagnosis: Sick sinus syndrome Differentiate from high vagal tone>> Atropine response test (0.04 mg/kg IV or IM) Treatment If atropine response test is normal, look for underlying disease that is causing elevated vagal tone (respiratory, GI, ocular or neurologic) If abnormal atropine response test, gold standard therapy would be pacemaker. If not possible consider medical management with: Propantheline bromide: mg/kg q 8-12 hour (oral) Terbutaline: mg/dog PO q 8-12 hour (oral) Theophylline: 10 mg/kg q 12 hour (extended release; oral) ECG #9 12 year old DSH; no clinical signs 25 mm/sec; 1 mv= 1 cm 10
11 ECG #9 12 year old DSH; no clinical signs 25 mm/sec; 1 mv= 1 cm HR@100 bpm ECG #9 12 year old DSH; no clinical signs 25 mm/sec; 1 mv= 1 cm HR@100 bpm RR regularity: regular QRS morphology: normal width to slightly increased with right axis deviation P waves: regular and asynchronous with QRSs Bradycardia Regular RR and PP, but asynchronous PR intervals variable Diagnosis: Complete heart block or third degree AV block Treatment complete heart block Depends on symptoms If asymptomatic: No treatment, monitoring for secondary heart disease If symptomatic: Pacemaker vs medical management Terbutaline 0.1 mg/kg q 8 hours (oral) Theophylline 4 mg/kg q 12 hours (oral) 19 mg/kg q 24 hours (extended release; oral) ECG #10 Paper speed 50 mm/sec; 1mV=1cm 7 year old Newfoundland; no clinical signs ECG #10 Paper speed 50 mm/sec; 1mV=1cm 7 year old Newfoundland; no clinical signs HR@ 150 bpm I II III avr avl RR regularity: irregular 11
12 ECG #10 Paper speed 50 mm/sec; 1mV=1cm 7 year old Newfoundland; no clinical signs HR@ 150 bpm ECG #10 Paper speed 50 mm/sec; 1mV=1cm 7 year old Newfoundland; no clinical signs HR@ 150 bpm Wide QRSs QRS= 4.5 mm or 4.5 X 0.02 seconds= 0.90 sec; Normal < 0.60 sec (canine) No P waves Differentials for wide complex QRS Ventricular in origin Electrolyte disturbance- most often hyperkalemia Aberrant conduction- bundle branch block Irregular RR No P waves QRS prolongation most likely due to right bundle branch block (ventricular rhythm should be regular) Rhythm diagnosis: atrial fibrillation with RBBB Diagnostics and treatment Any questions? margaretmsleeper@ufl.edu Bundle branch blocks No treatment Lone atrial fibrillation vs. rapid atrial fibrillation Echocardiogram to evaluate heart structure Rate control if necessary Digoxin: mg/kg q 12 hours (oral) Diltiazem: mg/kg q 8 hours (oral) Cardioversion 12
Electrocardiography. How to obtain an ECG. The Cardiac Conduction System. The Cardiac Conduction System 10/14/2015
 Electrocardiography Sarah Lehman, VMD Resident in Cardiology, CVCA The Veterinary Forum presented by The LifeCentre October 18, 2015 The Cardiac Conduction System The Cardiac Conduction System How to obtain
Electrocardiography Sarah Lehman, VMD Resident in Cardiology, CVCA The Veterinary Forum presented by The LifeCentre October 18, 2015 The Cardiac Conduction System The Cardiac Conduction System How to obtain
ECG Interpretation Cat Williams, DVM DACVIM (Cardiology)
 ECG Interpretation Cat Williams, DVM DACVIM (Cardiology) Providing the best quality care and service for the patient, the client, and the referring veterinarian. GOAL: Reduce Anxiety about ECGs Back to
ECG Interpretation Cat Williams, DVM DACVIM (Cardiology) Providing the best quality care and service for the patient, the client, and the referring veterinarian. GOAL: Reduce Anxiety about ECGs Back to
Practical Approach to Arrhythmias
 Outline Practical Approach to Arrhythmias Julia Shih, VMD, DACVIM (Cardiology) October 27, 2018 Conduction System ECG Acquisition ECG Interpretation Heart rate Rhythm Arrhythmias Tachyarrhythmias Supraventricular
Outline Practical Approach to Arrhythmias Julia Shih, VMD, DACVIM (Cardiology) October 27, 2018 Conduction System ECG Acquisition ECG Interpretation Heart rate Rhythm Arrhythmias Tachyarrhythmias Supraventricular
Step by step approach to EKG rhythm interpretation:
 Sinus Rhythms Normal sinus arrhythmia Small, slow variation of the R-R interval i.e. variation of the normal sinus heart rate with respiration, etc. Sinus Tachycardia Defined as sinus rhythm with a rate
Sinus Rhythms Normal sinus arrhythmia Small, slow variation of the R-R interval i.e. variation of the normal sinus heart rate with respiration, etc. Sinus Tachycardia Defined as sinus rhythm with a rate
Patient Examination. Objectives for Presentation RECOGNITION OF COMMON ARRHYTHMIAS THEIR CAUSES AND TREATMENT OPTIONS 9/8/2016
 RECOGNITION OF COMMON ARRHYTHMIAS THEIR CAUSES AND TREATMENT OPTIONS Ryan Fries, DVM, DACVIM (Cardiology) Clinical Assistant Professor University of Illinois Department of Clinical Veterinary Medicine
RECOGNITION OF COMMON ARRHYTHMIAS THEIR CAUSES AND TREATMENT OPTIONS Ryan Fries, DVM, DACVIM (Cardiology) Clinical Assistant Professor University of Illinois Department of Clinical Veterinary Medicine
UNDERSTANDING YOUR ECG: A REVIEW
 UNDERSTANDING YOUR ECG: A REVIEW Health professionals use the electrocardiograph (ECG) rhythm strip to systematically analyse the cardiac rhythm. Before the systematic process of ECG analysis is described
UNDERSTANDING YOUR ECG: A REVIEW Health professionals use the electrocardiograph (ECG) rhythm strip to systematically analyse the cardiac rhythm. Before the systematic process of ECG analysis is described
ECG interpretation basics
 ECG interpretation basics Michał Walczewski, MD Krzysztof Ozierański, MD 21.03.18 Electrical conduction system of the heart Limb leads Precordial leads 21.03.18 Precordial leads Precordial leads 21.03.18
ECG interpretation basics Michał Walczewski, MD Krzysztof Ozierański, MD 21.03.18 Electrical conduction system of the heart Limb leads Precordial leads 21.03.18 Precordial leads Precordial leads 21.03.18
6/14/17. Recognizing and Treating LifeThreatening Arrhythmias. Overview. Why do an ECG?
 6/14/17 Recognizing and Treating LifeThreatening Arrhythmias Sandy Tou, DVM DACVIM (Cardiology & Internal Medicine) Raleigh, NC Overview Brief overview of basic ECG principles ECG diagnosis & treatment
6/14/17 Recognizing and Treating LifeThreatening Arrhythmias Sandy Tou, DVM DACVIM (Cardiology & Internal Medicine) Raleigh, NC Overview Brief overview of basic ECG principles ECG diagnosis & treatment
Minding your P s and Q s Understanding ECG s. Samantha Knell, RVT
 Minding your P s and Q s Understanding ECG s Samantha Knell, RVT In Veterinary field for 20 years RVT since 7/2015 Team Leader at Rockville CVCA since 8/2016 Vice President of Maryland Veterinary Technician
Minding your P s and Q s Understanding ECG s Samantha Knell, RVT In Veterinary field for 20 years RVT since 7/2015 Team Leader at Rockville CVCA since 8/2016 Vice President of Maryland Veterinary Technician
ARRHYTHMIAS IN THE INTENSIVE CARE UNIT
 ARRHYTHMIAS IN THE INTENSIVE CARE UNIT Nicole Van Israël, DVM, CESOpht, CertSAM, CertVC, DECVIM-CA (Cardiology), MSc, MRCVS European Specialist in Veterinary Cardiology Animal CardioPulmonary Consultancy
ARRHYTHMIAS IN THE INTENSIVE CARE UNIT Nicole Van Israël, DVM, CESOpht, CertSAM, CertVC, DECVIM-CA (Cardiology), MSc, MRCVS European Specialist in Veterinary Cardiology Animal CardioPulmonary Consultancy
ECG ABNORMALITIES D R. T AM A R A AL Q U D AH
 ECG ABNORMALITIES D R. T AM A R A AL Q U D AH When we interpret an ECG we compare it instantaneously with the normal ECG and normal variants stored in our memory; these memories are stored visually in
ECG ABNORMALITIES D R. T AM A R A AL Q U D AH When we interpret an ECG we compare it instantaneously with the normal ECG and normal variants stored in our memory; these memories are stored visually in
Atrial Fibrillation 10/2/2018. Depolarization & ECG. Atrial Fibrillation. Hemodynamic Consequences
 Depolarization & ECG Atrial Fibrillation How to make ORDER out of CHAOS Julia Shih, VMD, DACVIM (Cardiology) October 27, 2018 Depolarization & ECG Depolarization & ECG Atrial Fibrillation Hemodynamic Consequences
Depolarization & ECG Atrial Fibrillation How to make ORDER out of CHAOS Julia Shih, VMD, DACVIM (Cardiology) October 27, 2018 Depolarization & ECG Depolarization & ECG Atrial Fibrillation Hemodynamic Consequences
Dr.Binoy Skaria 13/07/15
 Dr.Binoy Skaria binoyskaria@hotmail.com binoy.skaria@heartofengland.nhs.uk 13/07/15 Acknowledgement Medtronic, Google images & Elsevier for slides Natalie Ryan, Events Manager, HEFT- for organising the
Dr.Binoy Skaria binoyskaria@hotmail.com binoy.skaria@heartofengland.nhs.uk 13/07/15 Acknowledgement Medtronic, Google images & Elsevier for slides Natalie Ryan, Events Manager, HEFT- for organising the
CRC 431 ECG Basics. Bill Pruitt, MBA, RRT, CPFT, AE-C
 CRC 431 ECG Basics Bill Pruitt, MBA, RRT, CPFT, AE-C Resources White s 5 th ed. Ch 6 Electrocardiography Einthoven s Triangle Chest leads and limb leads Egan s 10 th ed. Ch 17 Interpreting the Electrocardiogram
CRC 431 ECG Basics Bill Pruitt, MBA, RRT, CPFT, AE-C Resources White s 5 th ed. Ch 6 Electrocardiography Einthoven s Triangle Chest leads and limb leads Egan s 10 th ed. Ch 17 Interpreting the Electrocardiogram
TEST BANK FOR ECGS MADE EASY 5TH EDITION BY AEHLERT
 Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-ecgs-made-easy-5thedition-by-aehlert/ TEST BANK FOR ECGS MADE EASY 5TH EDITION BY AEHLERT Chapter 5 TRUE/FALSE 1. The AV junction consists
Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-ecgs-made-easy-5thedition-by-aehlert/ TEST BANK FOR ECGS MADE EASY 5TH EDITION BY AEHLERT Chapter 5 TRUE/FALSE 1. The AV junction consists
Cardiac arrhythmias. Janusz Witowski. Department of Pathophysiology Poznan University of Medical Sciences. J. Witowski
 Cardiac arrhythmias Janusz Witowski Department of Pathophysiology Poznan University of Medical Sciences A 68-year old man presents to the emergency department late one evening complaining of increasing
Cardiac arrhythmias Janusz Witowski Department of Pathophysiology Poznan University of Medical Sciences A 68-year old man presents to the emergency department late one evening complaining of increasing
Electrocardiography Abnormalities (Arrhythmias) 7. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD
 Electrocardiography Abnormalities (Arrhythmias) 7 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Causes of Cardiac Arrythmias Abnormal rhythmicity of the pacemaker Shift of pacemaker from sinus node Blocks at different
Electrocardiography Abnormalities (Arrhythmias) 7 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Causes of Cardiac Arrythmias Abnormal rhythmicity of the pacemaker Shift of pacemaker from sinus node Blocks at different
HTEC 91. Performing ECGs: Procedure. Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Topic for Today: Sinus Rhythms. Characteristics of NSR. Conduction Pathway
 HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 3 Performing ECGs: Procedure o ECG protocol: you may NOT do ECG if you have not signed up! If you are signed up and the room is occupied with people who did
HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 3 Performing ECGs: Procedure o ECG protocol: you may NOT do ECG if you have not signed up! If you are signed up and the room is occupied with people who did
ABCs of ECGs. Shelby L. Durler
 ABCs of ECGs Shelby L. Durler Objectives Review the A&P of the cardiac conduction system Placement and obtaining 4-lead and 12-lead ECGs Overview of the basics of ECG rhythm interpretation Intrinsic
ABCs of ECGs Shelby L. Durler Objectives Review the A&P of the cardiac conduction system Placement and obtaining 4-lead and 12-lead ECGs Overview of the basics of ECG rhythm interpretation Intrinsic
CORONARY ARTERIES. LAD Anterior wall of the left vent Lateral wall of left vent Anterior 2/3 of interventricluar septum R & L bundle branches
 CORONARY ARTERIES RCA Right atrium Right ventricle SA node 55% AV node 90% Posterior wall of left ventricle in 90% Posterior third of interventricular septum 90% LAD Anterior wall of the left vent Lateral
CORONARY ARTERIES RCA Right atrium Right ventricle SA node 55% AV node 90% Posterior wall of left ventricle in 90% Posterior third of interventricular septum 90% LAD Anterior wall of the left vent Lateral
Arrhythmic Complications of MI. Teferi Mitiku, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California Irvine
 Arrhythmic Complications of MI Teferi Mitiku, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California Irvine Objectives Brief overview -Pathophysiology of Arrhythmia ECG review of typical
Arrhythmic Complications of MI Teferi Mitiku, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California Irvine Objectives Brief overview -Pathophysiology of Arrhythmia ECG review of typical
EKG Competency for Agency
 EKG Competency for Agency Name: Date: Agency: 1. The upper chambers of the heart are known as the: a. Atria b. Ventricles c. Mitral Valve d. Aortic Valve 2. The lower chambers of the heart are known as
EKG Competency for Agency Name: Date: Agency: 1. The upper chambers of the heart are known as the: a. Atria b. Ventricles c. Mitral Valve d. Aortic Valve 2. The lower chambers of the heart are known as
Chapter 9. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives 9/11/2012. Cardiac Arrhythmias. Define electrical therapy
 Chapter 9 Cardiac Arrhythmias Learning Objectives Define electrical therapy Explain why electrical therapy is preferred initial therapy over drug administration for cardiac arrest and some arrhythmias
Chapter 9 Cardiac Arrhythmias Learning Objectives Define electrical therapy Explain why electrical therapy is preferred initial therapy over drug administration for cardiac arrest and some arrhythmias
ECGs and Arrhythmias: Family Medicine Board Review 2009
 Rate Rhythm Intervals Hypertrophy ECGs and Arrhythmias: Family Medicine Board Review 2009 Axis Jess (Fogler) Waldura, MD University of California, San Francisco walduraj@nccc.ucsf.edu Ischemia Overview
Rate Rhythm Intervals Hypertrophy ECGs and Arrhythmias: Family Medicine Board Review 2009 Axis Jess (Fogler) Waldura, MD University of California, San Francisco walduraj@nccc.ucsf.edu Ischemia Overview
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals
 Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Chapter 7: Junctional Dysrhythmias 2012 The Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Learning Outcomes 7.1 Describe the various junctional dysrhythmias 7.2
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Chapter 7: Junctional Dysrhythmias 2012 The Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Learning Outcomes 7.1 Describe the various junctional dysrhythmias 7.2
8/20/2012. Learning Outcomes (Cont d)
 1 2 3 4 Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Chapter 7: Junctional Dysrhythmias Learning Outcomes 7.1 Describe the various junctional dysrhythmias 7.2 Identify premature junctional complexes
1 2 3 4 Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Chapter 7: Junctional Dysrhythmias Learning Outcomes 7.1 Describe the various junctional dysrhythmias 7.2 Identify premature junctional complexes
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals
 Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Kathryn A. Booth Thomas O Brien Chapter 5: Rhythm Strip Interpretation and Sinus Rhythms Learning Outcomes 5.1 Explain the process of evaluating ECG tracings
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Kathryn A. Booth Thomas O Brien Chapter 5: Rhythm Strip Interpretation and Sinus Rhythms Learning Outcomes 5.1 Explain the process of evaluating ECG tracings
Cardiology Flash Cards
 Cardiology Flash Cards EKG in a nut shell www.brain101.info Conduction System www.brain101.info 2 Analyzing EKG Step by step Steps in Analyzing ECG'S 1. Rhythm: - Regular _ Sinus, Junctional or Ventricular.
Cardiology Flash Cards EKG in a nut shell www.brain101.info Conduction System www.brain101.info 2 Analyzing EKG Step by step Steps in Analyzing ECG'S 1. Rhythm: - Regular _ Sinus, Junctional or Ventricular.
The Electrocardiogram part II. Dr. Adelina Vlad, MD PhD
 The Electrocardiogram part II Dr. Adelina Vlad, MD PhD Basic Interpretation of the ECG 1) Evaluate calibration 2) Calculate rate 3) Determine rhythm 4) Determine QRS axis 5) Measure intervals 6) Analyze
The Electrocardiogram part II Dr. Adelina Vlad, MD PhD Basic Interpretation of the ECG 1) Evaluate calibration 2) Calculate rate 3) Determine rhythm 4) Determine QRS axis 5) Measure intervals 6) Analyze
Where are the normal pacemaker and the backup pacemakers of the heart located?
 CASE 9 A 68-year-old woman presents to the emergency center with shortness of breath, light-headedness, and chest pain described as being like an elephant sitting on her chest. She is diagnosed with a
CASE 9 A 68-year-old woman presents to the emergency center with shortness of breath, light-headedness, and chest pain described as being like an elephant sitting on her chest. She is diagnosed with a
Full file at
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What electrical event must occur for atrial kick to occur? 1) A) Atrial repolarization B) Ventricular
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What electrical event must occur for atrial kick to occur? 1) A) Atrial repolarization B) Ventricular
SIMPLY ECGs. Dr William Dooley
 SIMPLY ECGs Dr William Dooley Content Basic ECG interpretation pattern Some common (examined) abnormalities Presenting ECGs in context Setting up an ECG Setting up an ECG 1 V1-4 th Right intercostal space
SIMPLY ECGs Dr William Dooley Content Basic ECG interpretation pattern Some common (examined) abnormalities Presenting ECGs in context Setting up an ECG Setting up an ECG 1 V1-4 th Right intercostal space
Core Content In Urgent Care Medicine
 Palpitations/Arrhythmias Ebrahim Barkoudah, MD Clinical Instructor in Internal Medicine Harvard Medical School Assistant in Internal Medicine & Pediatrics Massachusetts General Hospital MGH Chelsea Chelsea,
Palpitations/Arrhythmias Ebrahim Barkoudah, MD Clinical Instructor in Internal Medicine Harvard Medical School Assistant in Internal Medicine & Pediatrics Massachusetts General Hospital MGH Chelsea Chelsea,
Case-Based Practical ECG Interpretation for the Generalist
 Case-Based Practical ECG Interpretation for the Generalist Paul D. Varosy, MD, FACC, FAHA, FHRS Director of Cardiac Electrophysiology VA Eastern Colorado Health Care System Associate Professor of Medicine
Case-Based Practical ECG Interpretation for the Generalist Paul D. Varosy, MD, FACC, FAHA, FHRS Director of Cardiac Electrophysiology VA Eastern Colorado Health Care System Associate Professor of Medicine
WHAT S THAT RHYTHM I AM HEARING? GUIDE TO AUSCULTATION OF ARRHYTHMIAS IN HORSES
 WHAT S THAT RHYTHM I AM HEARING? GUIDE TO AUSCULTATION OF ARRHYTHMIAS IN HORSES Michelle Henry Barton DVM, PhD, DACVIM University of Georgia, Athens, GA INTRODUCTION The purpose of this talk is to review
WHAT S THAT RHYTHM I AM HEARING? GUIDE TO AUSCULTATION OF ARRHYTHMIAS IN HORSES Michelle Henry Barton DVM, PhD, DACVIM University of Georgia, Athens, GA INTRODUCTION The purpose of this talk is to review
Intraoperative and Postoperative Arrhythmias: Diagnosis and Treatment
 Intraoperative and Postoperative Arrhythmias: Diagnosis and Treatment Karen L. Booth, MD, Lucile Packard Children s Hospital Arrhythmias are common after congenital heart surgery [1]. Postoperative electrolyte
Intraoperative and Postoperative Arrhythmias: Diagnosis and Treatment Karen L. Booth, MD, Lucile Packard Children s Hospital Arrhythmias are common after congenital heart surgery [1]. Postoperative electrolyte
Northwest Community Healthcare Paramedic Education Program AV Conduction Defects/AV Blocks Connie J. Mattera, M.S., R.N., EMT-P
 Northwest Community Healthcare Paramedic Education Program AV Conduction Defects/ Connie J. Mattera, M.S., R.N., EMT-P Reading assignments: Bledsoe Vol. 3: pp. 88-93; 120-121 (atropine, norepinephrine,
Northwest Community Healthcare Paramedic Education Program AV Conduction Defects/ Connie J. Mattera, M.S., R.N., EMT-P Reading assignments: Bledsoe Vol. 3: pp. 88-93; 120-121 (atropine, norepinephrine,
Course Objectives. Proper Lead Placements. Review the ECG print paper. Review the mechanics of the Myocardium. Review basics of ECG Rhythms
 ECG Interpretations Course Objectives Proper Lead Placements Review the ECG print paper Review the mechanics of the Myocardium Review basics of ECG Rhythms How Leads Work The ECG Leads we use are Bipolar
ECG Interpretations Course Objectives Proper Lead Placements Review the ECG print paper Review the mechanics of the Myocardium Review basics of ECG Rhythms How Leads Work The ECG Leads we use are Bipolar
EKG Abnormalities. Adapted from:
 EKG Abnormalities Adapted from: http://www.bem.fi/book/19/19.htm Some key terms: Arrhythmia-an abnormal rhythm or sequence of events in the EKG Flutter-rapid depolarizations (and therefore contractions)
EKG Abnormalities Adapted from: http://www.bem.fi/book/19/19.htm Some key terms: Arrhythmia-an abnormal rhythm or sequence of events in the EKG Flutter-rapid depolarizations (and therefore contractions)
The ABCs of EKGs/ECGs for HCPs. Al Heuer, PhD, MBA, RRT, RPFT Professor, Rutgers School of Health Related Professions
 The ABCs of EKGs/ECGs for HCPs Al Heuer, PhD, MBA, RRT, RPFT Professor, Rutgers School of Health Related Professions Learning Objectives Review the basic anatomy of the heart Describe the cardiac conducting
The ABCs of EKGs/ECGs for HCPs Al Heuer, PhD, MBA, RRT, RPFT Professor, Rutgers School of Health Related Professions Learning Objectives Review the basic anatomy of the heart Describe the cardiac conducting
2) Heart Arrhythmias 2 - Dr. Abdullah Sharif
 2) Heart Arrhythmias 2 - Dr. Abdullah Sharif Rhythms from the Sinus Node Sinus Tachycardia: HR > 100 b/m Causes: o Withdrawal of vagal tone & Sympathetic stimulation (exercise, fight or flight) o Fever
2) Heart Arrhythmias 2 - Dr. Abdullah Sharif Rhythms from the Sinus Node Sinus Tachycardia: HR > 100 b/m Causes: o Withdrawal of vagal tone & Sympathetic stimulation (exercise, fight or flight) o Fever
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007
 Proceedings of the World Small Animal Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Next WSAVA Congress ECG INTERPRETATION Adrian Boswood MA VetMB DVC DECVIM-CA(Cardiology) MRCVS The Royal Veterinary College, Hawkshead
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Next WSAVA Congress ECG INTERPRETATION Adrian Boswood MA VetMB DVC DECVIM-CA(Cardiology) MRCVS The Royal Veterinary College, Hawkshead
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT)
 Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) Daniel Frisch, MD Cardiology Division, Electrophysiology Section Thomas Jefferson University Hospital daniel.frisch@jefferson.edu Short RP Are these the Mid same RP tachycardias?
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) Daniel Frisch, MD Cardiology Division, Electrophysiology Section Thomas Jefferson University Hospital daniel.frisch@jefferson.edu Short RP Are these the Mid same RP tachycardias?
10 ECGs No Practitioner Can Afford to Miss. Objectives
 10 ECGs No Practitioner Can Afford to Miss Mary L. Dohrmann, MD Professor of Clinical Medicine Division of Cardiovascular Medicine University of Missouri School of Medicine No disclosures Objectives 1.
10 ECGs No Practitioner Can Afford to Miss Mary L. Dohrmann, MD Professor of Clinical Medicine Division of Cardiovascular Medicine University of Missouri School of Medicine No disclosures Objectives 1.
FLB s What Are Those Funny-Looking Beats?
 FLB s What Are Those Funny-Looking Beats? Reading Assignment (pages 27-45 in Outline ) The 5-Step Method ECG #: Mearurements: Rhythm (s): Conduction: Waveform: Interpretation: A= V= PR= QRS= QT= Axis=
FLB s What Are Those Funny-Looking Beats? Reading Assignment (pages 27-45 in Outline ) The 5-Step Method ECG #: Mearurements: Rhythm (s): Conduction: Waveform: Interpretation: A= V= PR= QRS= QT= Axis=
Pathologic ECG. Adelina Vlad, MD PhD
 Pathologic ECG Adelina Vlad, MD PhD Basic Interpretation of the ECG 1) Evaluate calibration 2) Calculate rate 3) Determine rhythm 4) Determine QRS axis 5) Measure intervals 6) Analyze the morphology and
Pathologic ECG Adelina Vlad, MD PhD Basic Interpretation of the ECG 1) Evaluate calibration 2) Calculate rate 3) Determine rhythm 4) Determine QRS axis 5) Measure intervals 6) Analyze the morphology and
ECG QUIZ Luc DE ROY Brussels Belgium Disclosure in relation to this topic: none
 ECG QUIZ Luc DE ROY Brussels Belgium Disclosure in relation to this topic: none TEST EXAMPLE What is the colour of this rectangle? 1. Blue? 2. Red? 3. Purple? 4. Green? 5. Yellow? 6. 1 and 3? 7. Any of
ECG QUIZ Luc DE ROY Brussels Belgium Disclosure in relation to this topic: none TEST EXAMPLE What is the colour of this rectangle? 1. Blue? 2. Red? 3. Purple? 4. Green? 5. Yellow? 6. 1 and 3? 7. Any of
Chapter 12: Cardiovascular Physiology System Overview
 Chapter 12: Cardiovascular Physiology System Overview Components of the cardiovascular system: Heart Vascular system Blood Figure 12-1 Plasma includes water, ions, proteins, nutrients, hormones, wastes,
Chapter 12: Cardiovascular Physiology System Overview Components of the cardiovascular system: Heart Vascular system Blood Figure 12-1 Plasma includes water, ions, proteins, nutrients, hormones, wastes,
SIMPLY ECGs. Dr William Dooley
 SIMPLY ECGs Dr William Dooley 1 No anatomy just interpretation 2 Setting up an ECG 3 Setting up an ECG 1 V1-4 th Right intercostal space at sternal border 2 V2-4 th Left intercostal space at sternal border
SIMPLY ECGs Dr William Dooley 1 No anatomy just interpretation 2 Setting up an ECG 3 Setting up an ECG 1 V1-4 th Right intercostal space at sternal border 2 V2-4 th Left intercostal space at sternal border
CRITICAL CARE OF THE CARDIAC PATIENT WEBINAR VET 2017
 CRITICAL CARE OF THE CARDIAC PATIENT WEBINAR VET 2017 The Heart The heart is undoubtedly the most important organ in the body. Unfortunately, when it is not functioning properly, it can have dire consequences.
CRITICAL CARE OF THE CARDIAC PATIENT WEBINAR VET 2017 The Heart The heart is undoubtedly the most important organ in the body. Unfortunately, when it is not functioning properly, it can have dire consequences.
Ventricular Tachycardia Basics
 Ventricular Tachycardia Basics OVERVIEW Ventricular refers to the ventricles of the heart; tachycardia is the medical term for rapid heart rate The heart of the dog or cat is composed of four chambers;
Ventricular Tachycardia Basics OVERVIEW Ventricular refers to the ventricles of the heart; tachycardia is the medical term for rapid heart rate The heart of the dog or cat is composed of four chambers;
Arrhythmia Study Guide 3 Junctional and Ventricular Rhythms
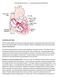 Arrhythmia Study Guide 3 Junctional and Ventricular Rhythms JUNCTIONAL RHYTHMS The AV Junction (Bundle of His and surrounding cells) only acts as pacemaker of the heart when the SA Node is not firing normally
Arrhythmia Study Guide 3 Junctional and Ventricular Rhythms JUNCTIONAL RHYTHMS The AV Junction (Bundle of His and surrounding cells) only acts as pacemaker of the heart when the SA Node is not firing normally
physiology 6 Mohammed Jaafer Turquoise team
 15 physiology 6 Mohammed Jaafer 22-3-2016 Turquoise team Cardiac Arrhythmias and Their Electrocardiographic Interpretation Today, we are going to talk about the abnormal excitation. As we said before,
15 physiology 6 Mohammed Jaafer 22-3-2016 Turquoise team Cardiac Arrhythmias and Their Electrocardiographic Interpretation Today, we are going to talk about the abnormal excitation. As we said before,
The ECG Course. Boone County Fire Protection District EMS Education
 The ECG Course Level I G rated material AV Blocks What Causes AV Block? Long list of bad things that includes ischemia and.. Old age / disease Medications or drugs Electrolyte imbalances Physiologic Blocks
The ECG Course Level I G rated material AV Blocks What Causes AV Block? Long list of bad things that includes ischemia and.. Old age / disease Medications or drugs Electrolyte imbalances Physiologic Blocks
Diploma in Electrocardiography
 The Society for Cardiological Science and Technology Diploma in Electrocardiography The Society makes this award to candidates who can demonstrate the ability to accurately record a resting 12-lead electrocardiogram
The Society for Cardiological Science and Technology Diploma in Electrocardiography The Society makes this award to candidates who can demonstrate the ability to accurately record a resting 12-lead electrocardiogram
Arrhythmias. 1. beat too slowly (sinus bradycardia). Like in heart block
 Arrhythmias It is a simple-dysfunction caused by abnormalities in impulse formation and conduction in the myocardium. The heart is designed in such a way that allows it to generate from the SA node electrical
Arrhythmias It is a simple-dysfunction caused by abnormalities in impulse formation and conduction in the myocardium. The heart is designed in such a way that allows it to generate from the SA node electrical
2017 BDKA Review. Regularity Rate P waves PRI QRS Interpretation. Regularity Rate P waves PRI QRS Interpretation 1/1/2017
 1. 2017 BDKA Review 2. 3. 4. Interpretation 5. QT 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. QT 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. QT 19. 20. QT 21. 22. QT 23. 24. Where are pacer spikes? Before the P wave or before the QRS complex?
1. 2017 BDKA Review 2. 3. 4. Interpretation 5. QT 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. QT 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. QT 19. 20. QT 21. 22. QT 23. 24. Where are pacer spikes? Before the P wave or before the QRS complex?
ECG CONVENTIONS AND INTERVALS
 1 ECG Waveforms and Intervals ECG waveforms labeled alphabetically P wave== represents atrial depolarization QRS complex=ventricular depolarization ST-T-U complex (ST segment, T wave, and U wave)== V repolarization.
1 ECG Waveforms and Intervals ECG waveforms labeled alphabetically P wave== represents atrial depolarization QRS complex=ventricular depolarization ST-T-U complex (ST segment, T wave, and U wave)== V repolarization.
If the P wave > 0.12 sec( 3 mm) usually in any lead. Notched P wave usually in lead I,aVl may be lead II Negative terminal portion of P wave in V1, 1
 If the P wave > 0.12 sec( 3 mm) usually in any lead. Notched P wave usually in lead I,aVl may be lead II Negative terminal portion of P wave in V1, 1 mm depth and 3 mm width( most specific) Since Mitral
If the P wave > 0.12 sec( 3 mm) usually in any lead. Notched P wave usually in lead I,aVl may be lead II Negative terminal portion of P wave in V1, 1 mm depth and 3 mm width( most specific) Since Mitral
Blocks classification by their constancy or steadiness
 Blocks classification by their constancy or steadiness By their constance the blocks can be: 1. Permanent 2. Temporary, transient or transitory 3. Intermittent (Okajima 1980): 3a) Dependent on heart rate:
Blocks classification by their constancy or steadiness By their constance the blocks can be: 1. Permanent 2. Temporary, transient or transitory 3. Intermittent (Okajima 1980): 3a) Dependent on heart rate:
Introduction. Circulation
 Introduction Circulation 1- Systemic (general) circulation 2- Pulmonary circulation carries oxygenated blood to all parts of the body carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs From Lt. ventricle aorta From
Introduction Circulation 1- Systemic (general) circulation 2- Pulmonary circulation carries oxygenated blood to all parts of the body carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs From Lt. ventricle aorta From
Cardiac Arrhythmia How to approach นพ.พ น จ แกวส วรรณะ หน วยโรคห วใจและหลอดเล อด
 Cardiac Arrhythmia How to approach นพ.พ น จ แกวส วรรณะ หน วยโรคห วใจและหลอดเล อด EKG paper is a grid where time is measured along the horizontal axis. Each small square is 1 mm in length and represents
Cardiac Arrhythmia How to approach นพ.พ น จ แกวส วรรณะ หน วยโรคห วใจและหลอดเล อด EKG paper is a grid where time is measured along the horizontal axis. Each small square is 1 mm in length and represents
a lecture series by SWESEMJR
 Electrolyte disturbances Hypokalaemia Decreased extracellular potassium increases excitability in the myocardial cells and consequently the effect of very severe hypokalaemia is ventricular arrhythmia.
Electrolyte disturbances Hypokalaemia Decreased extracellular potassium increases excitability in the myocardial cells and consequently the effect of very severe hypokalaemia is ventricular arrhythmia.
Family Medicine for English language students of Medical University of Lodz ECG. Jakub Dorożyński
 Family Medicine for English language students of Medical University of Lodz ECG Jakub Dorożyński Parts of an ECG The standard ECG has 12 leads: six of them are considered limb leads because they are placed
Family Medicine for English language students of Medical University of Lodz ECG Jakub Dorożyński Parts of an ECG The standard ECG has 12 leads: six of them are considered limb leads because they are placed
-RHYTHM PRACTICE- By Dr.moanes Msc.cardiology Assistant Lecturer of Cardiology Al Azhar University. OBHG Education Subcommittee
 -RHYTHM PRACTICE- By Dr.moanes Msc.cardiology Assistant Lecturer of Cardiology Al Azhar University The Normal Conduction System Sinus Node Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Sinus Bradycardia Sinus Tachycardia
-RHYTHM PRACTICE- By Dr.moanes Msc.cardiology Assistant Lecturer of Cardiology Al Azhar University The Normal Conduction System Sinus Node Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Sinus Bradycardia Sinus Tachycardia
Module 1: Introduction to ECG & Normal ECG
 Module 1: Introduction to ECG & Normal ECG Importance of Correct anatomical positions Measurements & Morphologies ONLY accurate if Precise anatomical positions adhered to Standardised techniques are used
Module 1: Introduction to ECG & Normal ECG Importance of Correct anatomical positions Measurements & Morphologies ONLY accurate if Precise anatomical positions adhered to Standardised techniques are used
1 Cardiology Acute Care Day 22 April 2013 Arrhythmia Tutorial Course Material
 1 Cardiology Acute Care Day 22 April 2013 Arrhythmia Tutorial Course Material Arrhythmia recognition This tutorial builds on the ECG lecture and provides a framework for approaching any ECG to allow the
1 Cardiology Acute Care Day 22 April 2013 Arrhythmia Tutorial Course Material Arrhythmia recognition This tutorial builds on the ECG lecture and provides a framework for approaching any ECG to allow the
Review Packet EKG Competency This packet is a review of the information you will need to know for the proctored EKG competency test.
 Review Packet EKG Competency 2015 This packet is a review of the information you will need to know for the proctored EKG competency test. Normal Sinus Rhythm Rhythm: Regular Ventricular Rate: 60-100 bpm
Review Packet EKG Competency 2015 This packet is a review of the information you will need to know for the proctored EKG competency test. Normal Sinus Rhythm Rhythm: Regular Ventricular Rate: 60-100 bpm
The Electrocardiogram
 The Electrocardiogram Chapters 11 and 13 AUTUMN WEDAN AND NATASHA MCDOUGAL The Normal Electrocardiogram P-wave Generated when the atria depolarizes QRS-Complex Ventricles depolarizing before a contraction
The Electrocardiogram Chapters 11 and 13 AUTUMN WEDAN AND NATASHA MCDOUGAL The Normal Electrocardiogram P-wave Generated when the atria depolarizes QRS-Complex Ventricles depolarizing before a contraction
Antiarrhythmic Drugs
 Antiarrhythmic Drugs DR ATIF ALQUBBANY A S S I S T A N T P R O F E S S O R O F M E D I C I N E / C A R D I O L O G Y C O N S U L T A N T C A R D I O L O G Y & I N T E R V E N T I O N A L E P A C H D /
Antiarrhythmic Drugs DR ATIF ALQUBBANY A S S I S T A N T P R O F E S S O R O F M E D I C I N E / C A R D I O L O G Y C O N S U L T A N T C A R D I O L O G Y & I N T E R V E N T I O N A L E P A C H D /
Chapter 16: Arrhythmias and Conduction Disturbances
 Complete the following. Chapter 16: Arrhythmias and Conduction Disturbances 1. Cardiac arrhythmias result from abnormal impulse, abnormal impulse, or both mechanisms together. 2. is the ability of certain
Complete the following. Chapter 16: Arrhythmias and Conduction Disturbances 1. Cardiac arrhythmias result from abnormal impulse, abnormal impulse, or both mechanisms together. 2. is the ability of certain
Please check your answers with correct statements in answer pages after the ECG cases.
 ECG Cases ECG Case 1 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature 2018 S. Okutucu, A. Oto, Interpreting ECGs in Clinical Practice, In Clinical Practice, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-90557-0
ECG Cases ECG Case 1 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature 2018 S. Okutucu, A. Oto, Interpreting ECGs in Clinical Practice, In Clinical Practice, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-90557-0
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM. Heart 2
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Heart 2 PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Cardiac muscle Striated Short Wide Branched Interconnected Skeletal muscle Striated Long Narrow Cylindrical PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Intercalated
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Heart 2 PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Cardiac muscle Striated Short Wide Branched Interconnected Skeletal muscle Striated Long Narrow Cylindrical PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Intercalated
ECG Interpretation Made Easy
 ECG Interpretation Made Easy Dr. A Tageldien Abdellah, MSc MD EBSC Lecturer of Cardiology- Hull University Hull York Medical School 2007-2008 ECG Interpretation Made Easy Synopsis Benefits Objectives Process
ECG Interpretation Made Easy Dr. A Tageldien Abdellah, MSc MD EBSC Lecturer of Cardiology- Hull University Hull York Medical School 2007-2008 ECG Interpretation Made Easy Synopsis Benefits Objectives Process
Bradydysrhythmias and Atrioventricular Conduction Blocks
 Emerg Med Clin N Am 24 (2006) 1 9 Bradydysrhythmias and Atrioventricular Conduction Blocks Jacob W. Ufberg, MD*, Jennifer S. Clark, MD Department of Emergency Medicine, Temple University School of Medicine,
Emerg Med Clin N Am 24 (2006) 1 9 Bradydysrhythmias and Atrioventricular Conduction Blocks Jacob W. Ufberg, MD*, Jennifer S. Clark, MD Department of Emergency Medicine, Temple University School of Medicine,
Basic Dysrhythmia Interpretation
 Basic Dysrhythmia Interpretation Objectives 2 To understand the Basic ECG To understand the meaning of Dysrhythmia To describe the normal heart conduction system. To describe the normal impulse pathways.
Basic Dysrhythmia Interpretation Objectives 2 To understand the Basic ECG To understand the meaning of Dysrhythmia To describe the normal heart conduction system. To describe the normal impulse pathways.
Reading Assignment (p1-91 in Outline ) Objectives What s in an ECG?
 Reading Assignment (p1-91 in Outline ) Objectives What s in an ECG? The 5-Step Method ECG #: Mearurements: Rhythm (s): Conduction: Waveform: Interpretation: A= V= PR= QRS= QT= Axis= 1. Compute the 5 basic
Reading Assignment (p1-91 in Outline ) Objectives What s in an ECG? The 5-Step Method ECG #: Mearurements: Rhythm (s): Conduction: Waveform: Interpretation: A= V= PR= QRS= QT= Axis= 1. Compute the 5 basic
The pill-in-the-pocket strategy for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation
 The pill-in-the-pocket strategy for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation KONSTANTINOS P. LETSAS, MD, FEHRA LABORATORY OF CARDIAC ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY EVANGELISMOS GENERAL HOSPITAL OF ATHENS ARRHYTHMIAS UPDATE,
The pill-in-the-pocket strategy for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation KONSTANTINOS P. LETSAS, MD, FEHRA LABORATORY OF CARDIAC ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY EVANGELISMOS GENERAL HOSPITAL OF ATHENS ARRHYTHMIAS UPDATE,
Miscellaneous Stuff Keep reading the Outline
 Miscellaneous Stuff Keep reading the Outline Welcome to the 5-Step Method ECG #: Mearurements: Rhythm (s): Conduction: Waveform: Interpretation: A= V= PR= QRS= QT= Axis= 1. Compute the 5 basic measurements:
Miscellaneous Stuff Keep reading the Outline Welcome to the 5-Step Method ECG #: Mearurements: Rhythm (s): Conduction: Waveform: Interpretation: A= V= PR= QRS= QT= Axis= 1. Compute the 5 basic measurements:
National Coverage Determination (NCD) for Cardiac Pacemakers (20.8)
 Page 1 of 12 Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services National Coverage Determination (NCD) for Cardiac Pacemakers (20.8) Tracking Information Publication Number 100-3 Manual Section Number 20.8 Manual
Page 1 of 12 Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services National Coverage Determination (NCD) for Cardiac Pacemakers (20.8) Tracking Information Publication Number 100-3 Manual Section Number 20.8 Manual
Rhythm ECG Characteristics Example. Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR)
 Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Rate: 60-100 per minute Rhythm: R- R = P waves: Upright, similar P-R: 0.12-0.20 second & consistent P:qRs: 1P:1qRs Sinus Tachycardia Exercise Hypovolemia Medications Fever Substances
Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Rate: 60-100 per minute Rhythm: R- R = P waves: Upright, similar P-R: 0.12-0.20 second & consistent P:qRs: 1P:1qRs Sinus Tachycardia Exercise Hypovolemia Medications Fever Substances
CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS IN NEONATE
 Introduction: CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS IN NEONATE DR. PANKAJ SAKHUJA Neonatologist Average heart rate in a healthy newborn is 120-160 beats/min and the range is from 80-230 beats/min. A normal (sinus) rhythm
Introduction: CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS IN NEONATE DR. PANKAJ SAKHUJA Neonatologist Average heart rate in a healthy newborn is 120-160 beats/min and the range is from 80-230 beats/min. A normal (sinus) rhythm
Cardiac Cycle. Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. First the two atria contract at the same time.
 The Heartbeat Cardiac Cycle Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. First the two atria contract at the same time. Next the two ventricles contract at the same time. Then all the chambers relax. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=frd3k6lkhws
The Heartbeat Cardiac Cycle Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. First the two atria contract at the same time. Next the two ventricles contract at the same time. Then all the chambers relax. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=frd3k6lkhws
HR: 50 bpm (Sinus) PR: 280 ms QRS: 120 ms QT: 490 ms Axis: -70. Sinus bradycardia with one ventricular escape (*)
 1? HR: 50 bpm (Sinus) PR: 280 ms QRS: 120 ms QT: 490 ms Axis: -70 1 Sinus P waves? 2 sinus cycles The pause (2 sinus cycles) suggests that the sinus fired (?) but did not conduct to the atria (i.e., missing
1? HR: 50 bpm (Sinus) PR: 280 ms QRS: 120 ms QT: 490 ms Axis: -70 1 Sinus P waves? 2 sinus cycles The pause (2 sinus cycles) suggests that the sinus fired (?) but did not conduct to the atria (i.e., missing
Understanding the 12-lead ECG, part II
 Bundle-branch blocks Understanding the 12-lead ECG, part II Most common electrocardiogram (ECG) abnormality Appears as a wider than normal S complex Occurs when one of the two bundle branches can t conduct
Bundle-branch blocks Understanding the 12-lead ECG, part II Most common electrocardiogram (ECG) abnormality Appears as a wider than normal S complex Occurs when one of the two bundle branches can t conduct
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: WPW Revised: 11/2013
 Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: WPW Revised: 11/2013 Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW) is a syndrome of pre-excitation of the
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: WPW Revised: 11/2013 Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW) is a syndrome of pre-excitation of the
General Introduction to ECG. Reading Assignment (p2-16 in PDF Outline )
 General Introduction to ECG Reading Assignment (p2-16 in PDF Outline ) Objectives 1. Practice the 5-step Method 2. Differential Diagnosis: R & L axis deviation 3. Differential Diagnosis: Poor R-wave progression
General Introduction to ECG Reading Assignment (p2-16 in PDF Outline ) Objectives 1. Practice the 5-step Method 2. Differential Diagnosis: R & L axis deviation 3. Differential Diagnosis: Poor R-wave progression
PART I. Disorders of the Heart Rhythm: Basic Principles
 PART I Disorders of the Heart Rhythm: Basic Principles FET01.indd 1 1/11/06 9:53:05 AM FET01.indd 2 1/11/06 9:53:06 AM CHAPTER 1 The Cardiac Electrical System The heart spontaneously generates electrical
PART I Disorders of the Heart Rhythm: Basic Principles FET01.indd 1 1/11/06 9:53:05 AM FET01.indd 2 1/11/06 9:53:06 AM CHAPTER 1 The Cardiac Electrical System The heart spontaneously generates electrical
Bundle Branch & Fascicular Blocks. Reading Assignment (p53-58 in Outline )
 Bundle Branch & Fascicular Blocks Reading Assignment (p53-58 in Outline ) Objectives 1. QRS analysis of Right and Left BBB 2. Uncomplicated vs complicated BBB 3. Diagnosis of RBBB with LAFB and LPFB 4.
Bundle Branch & Fascicular Blocks Reading Assignment (p53-58 in Outline ) Objectives 1. QRS analysis of Right and Left BBB 2. Uncomplicated vs complicated BBB 3. Diagnosis of RBBB with LAFB and LPFB 4.
Dr. Schroeder has no financial relationships to disclose
 Valerie A Schroeder MD MS Assistant Professor University of Kansas Medical Center READING THE WAVES- THE HEART S ELECTRICAL MESSAGE FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE Dr. Schroeder has no financial relationships to
Valerie A Schroeder MD MS Assistant Professor University of Kansas Medical Center READING THE WAVES- THE HEART S ELECTRICAL MESSAGE FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE Dr. Schroeder has no financial relationships to
ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY KEVIN REBECK PA-C. For more presentations
 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY KEVIN REBECK PA-C For more presentations www.medicalppt.blogspot.com Objectives ECG History Pathophysiology Basics Case Historys Electrical activation of the heart In the heart
ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY KEVIN REBECK PA-C For more presentations www.medicalppt.blogspot.com Objectives ECG History Pathophysiology Basics Case Historys Electrical activation of the heart In the heart
24 Hour Holter Report
 Mass Veterinary Cardiology Services Inc 35 Suffield St Agawam, MA 11 413-372-5127/413-734-1292 413-372-5127 Exam Date: OCT 2 13-8:19am Record No: 7581 Provider: NANCY MORRIS DVM, DACVIM-C Medical Record
Mass Veterinary Cardiology Services Inc 35 Suffield St Agawam, MA 11 413-372-5127/413-734-1292 413-372-5127 Exam Date: OCT 2 13-8:19am Record No: 7581 Provider: NANCY MORRIS DVM, DACVIM-C Medical Record
4/14/15 HTEC 91. Topics for Today. Guess That Rhythm. Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs) Ventricular Rhythms
 4/14/15 Topics for Today HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 5 Ventricular Rhythms PVCs: Premature Ventricular Contractions VT: Ventricular Tachycardia VF: Ventricular Fibrillation Asystole Study
4/14/15 Topics for Today HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 5 Ventricular Rhythms PVCs: Premature Ventricular Contractions VT: Ventricular Tachycardia VF: Ventricular Fibrillation Asystole Study
The most common. hospitalized patients. hypotension due to. filling time Rate control in ICU patients may be difficult as many drugs cause hypotension
 Arrhythmias in the critically ill ICU patients: Approach for rapid recognition & management Objectives Be able to identify and manage: Atrial fibrillation with a rapid ventricular response Atrial flutter
Arrhythmias in the critically ill ICU patients: Approach for rapid recognition & management Objectives Be able to identify and manage: Atrial fibrillation with a rapid ventricular response Atrial flutter
Electrical Conduction
 Sinoatrial (SA) node Electrical Conduction Sets the pace of the heartbeat at 70 bpm AV node (50 bpm) and Purkinje fibers (25 40 bpm) can act as pacemakers under some conditions Internodal pathway from
Sinoatrial (SA) node Electrical Conduction Sets the pace of the heartbeat at 70 bpm AV node (50 bpm) and Purkinje fibers (25 40 bpm) can act as pacemakers under some conditions Internodal pathway from
V. TACHYCARDIAS Rapid rhythm abnormalities
 V. TACHYCARDIAS Rapid rhythm abnormalities Tachyarrhythmias currently account for up to 350,000 deaths annually in the US. In addition to these clearly dangerous rhythm disturbances, other forms of more
V. TACHYCARDIAS Rapid rhythm abnormalities Tachyarrhythmias currently account for up to 350,000 deaths annually in the US. In addition to these clearly dangerous rhythm disturbances, other forms of more
Study methodology for screening candidates to athletes risk
 1. Periodical Evaluations: each 2 years. Study methodology for screening candidates to athletes risk 2. Personal history: Personal history of murmur in childhood; dizziness, syncope, palpitations, intolerance
1. Periodical Evaluations: each 2 years. Study methodology for screening candidates to athletes risk 2. Personal history: Personal history of murmur in childhood; dizziness, syncope, palpitations, intolerance
EKG Rhythm Interpretation Exam
 as EKG Rhythm Interpretation Exam Name: Date: ID# Unit Assume each strip is a 6 second strip. Passing is 80%. 1. Identify the following rhythm: a. Asystole b. Ventricular fibrillation c. Atrial fibrillation
as EKG Rhythm Interpretation Exam Name: Date: ID# Unit Assume each strip is a 6 second strip. Passing is 80%. 1. Identify the following rhythm: a. Asystole b. Ventricular fibrillation c. Atrial fibrillation
Appendix D Output Code and Interpretation of Analysis
 Appendix D Output Code and Interpretation of Analysis 8 Arrhythmia Code No. Description 8002 Marked rhythm irregularity 8110 Sinus rhythm 8102 Sinus arrhythmia 8108 Marked sinus arrhythmia 8120 Sinus tachycardia
Appendix D Output Code and Interpretation of Analysis 8 Arrhythmia Code No. Description 8002 Marked rhythm irregularity 8110 Sinus rhythm 8102 Sinus arrhythmia 8108 Marked sinus arrhythmia 8120 Sinus tachycardia
Ventricular arrhythmias
 Ventricular arrhythmias Assoc.Prof. Lucie Riedlbauchová, MD, PhD Department of Cardiology University HospitalMotol and2nd FacultyofMedicine, Charles University in Prague Definition and classification Ventricular
Ventricular arrhythmias Assoc.Prof. Lucie Riedlbauchová, MD, PhD Department of Cardiology University HospitalMotol and2nd FacultyofMedicine, Charles University in Prague Definition and classification Ventricular
